- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine of Puyang Oilfield General Hospital, Puyang, China
- 3State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Diseases, China-Singapore Belt and Road Joint Laboratory on Infection Research and Drug Development, National Medical Center for Infectious Diseases, Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
Background: Raoultella ornithinolytica is an infrequent opportunistic pathogen capable of causing multi-site infections and frequently harboring a broad array of resistance determinants, thereby complicating antimicrobial therapy. Here we report the genomic characterization of the extensively drug-resistant strain FAHZZU6693, which concurrently harbors blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10 genes and tmexCD2-toprJ2 resistance cluster.
Methods: Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) and average nucleotide identity (ANI) were employed to confirm the species identity as R. ornithinolytica. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) delineated the corresponding antimicrobial phenotypes. S1 nuclease pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (S1-PFGE), Southern blotting and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) elucidated the isolate’s complete molecular architecture.
Results: Globally, R. ornithinolytica strains harboring related resistance genes exhibit diverse geographical distribution. Strain FAHZZU6693 is resistant to most antibiotics, except amikacin and chloramphenicol. The blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10 genes and the tmexCD2-toprJ2 cluster in this strain are plasmid-borne. These occur in conserved genetic contexts: xerC-mcr-10-ISEc36-ISEc27-ISEcl1 and umuC-IS881-tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2-umuC. Further analysis indicates that the insertion sequence ISEc27 and the gene element umuC play a crucial role in the dissemination of the mcr-10 gene and the tmexCD2-toprJ2 gene cluster.
Conclusions: This study combines database analysis to comprehensively describe the distribution of R. ornithinolytica strains carrying the target genes and characterizes the genomic features of a clinically Multi-drug resistant strain, providing a theoretical foundation for preventing the spread of such bacteria.
1 Introduction
Raoultella ornithinolytica is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacillus possessing a capsule (De Coster et al., 2024). Molecular phylogeny based on rpoB sequencing led to its reclassification from the genus Klebsiella to Raoultella in 2001 (Etani et al., 2023). The organism is routinely recovered from water, soil and plants, and seafood has been identified as a potential reservoir of infection (Mader et al., 2013). Human isolates are documented sporadically, and clinical cases have been reported spanning the central nervous system, abdomen, eye, urinary tract, joints, biliary tract and bloodstream (Giran et al., 2025; Jones et al., 2024; Assadi et al., 2025).
In 2009, the first case of R. ornithinolytica carrying KPC-type carbapenemase causing an infection was reported in New Jersey, USA. The patient succumbed to the infection after failing to respond to anti-infective therapy. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed that the strain was resistant to both imipenem and meropenem. Genomic sequencing demonstrated that the blaKPC gene was located on a plasmid and was associated with the transposon Tn4401c (Castanheira et al., 2009). Four years later, the first case of R. ornithinolytica carrying NDM-1-type carbapenemase was reported in India. The strain caused a surgical site infection and exhibited resistance to imipenem and meropenem, as indicated by antimicrobial susceptibility testing. The patient recovered following treatment with tigecycline (Khajuria et al., 2013). Regrettably, no further investigation into the blaNDM-1 gene of this strain was conducted. Subsequently, in a R. ornithinolytica strain reported in China, the blaNDM gene was found to be located within a Tn125-like element (ISAba125-blaNDM-1-bleMBL-trpF-ISSen4-Tn5403) and was situated on a transferable IncN-type incompatibility plasmid (Sun et al., 2015). In 2020, the first case of an R. ornithinolytica strain isolated from the environment that harbored both blaNDM-1 and blaKPC-2 was reported (Dang et al., 2020), indicating that different types of carbapenemase genes are continuously accumulating in R. ornithinolytica.
It was not until 2019 that the mcr-8 gene was first reported in R. ornithinolytica from a poultry farm in China, with the strain harboring resistance to colistin (Wang et al., 2019). Additionally, in 2021, a R. ornithinolytica strain harboring the tigecycline resistance gene tmexCD2-toprJ2 was first isolated from a sputum sample of a patient with a pulmonary infection. This strain was also positive for blaNDM-1 and blaKPC-2, exhibiting resistance to most antibiotics, including tigecycline, imipenem, and meropenem. Genomic studies revealed that the tmexCD2-toprJ2 gene cluster is present on both the chromosome and an IncFI plasmid, and exists within a transposable unit (xerD-like-int3-like-thf2-ybjD-umuD-ΔumuC1-int1-like-int2-like-hp1-hp2-tnfxB2-ISBvi2-tmexCD2-toprJ2-ΔumuC1), confirming that this gene can be acquired through horizontal transfer (Wang et al., 2021).
Globally, the dissemination of tigecycline resistant tmexCD-toprJ and colistin resistant mcr genes among carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales has precipitated extensively drug-resistant pathogens, prompting urgent clinical concern. Here we report the first isolation, from a blood culture, of R. ornithinolytica simultaneously harboring blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10 and tmexCD2-toprJ2 genes, all encoded on plasmids, conferring resistance to carbapenems, polymyxin B and tigecycline and posing a new challenge for antimicrobial therapy.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing
In this study, bacterial species identification was performed using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). PCR assays were conducted to detect the colistin resistance genes mcr-1 to mcr-10 and the tigecycline resistance gene cluster tmexCD-toprJ. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) was performed by broth microdilution for polymyxin B and tigecycline, and by agar dilution for all other agents. Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 was included for quality control. The breakpoints for tigecycline were interpreted according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) guidelines, while the other breakpoints were interpreted according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines (Humphries et al., 2021).
2.2 Plasmid characterization
The number and approximate size of plasmids in the isolate were determined by S1 nuclease–pulsed-field gel electrophoresis; Southern blotting confirmed that blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10 and tmexCD2-toprJ2 are plasmid-borne. The available recipient strains in the laboratory include rifampicin-resistant Escherichia coli EC600 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAORI, colistin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAOCO, and azide-resistant Escherichia coli J53. However, due to the isolate’s resistance to rifampicin and colistin, as well as the intensified regulation on hazardous chemicals in China making sodium azide unavailable for laboratory verification, it’s impossible to use the existing recipient strains to confirm plasmid conjugation. Consequently, the experiment could only rely on oriTfinder for prediction.
2.3 Whole-genome sequencing and analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted using the SteadyPure Bacterial DNA Kit and sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies (Oxford, UK) platforms. Sequencing reads were assembled with Unicycler. Genome annotation was performed with Prokka. ResFinder was queried to identify acquired resistance determinants; plasmid types were assigned with PlasmidFinder. Insertion sequences and transposons were detected using ISFinder. Multiple plasmid sequences were compared with BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG), and genetic contexts of resistance genes were visualized in Easyfig. A phylogeny was constructed with Gubbins (Genealogies Unbiased By recomBinations In Nucleotide Sequences).
3 Results
3.1 Identification and resistance characterization of R. ornithinolytica FAHZZU6693
Strain FAHZZU6693 was isolated from a patient in the hematology department who was admitted for fever and mild pulmonary infection, later diagnosed with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Despite etoposide (VP-16) treatment, the initial anti-infection regimen (biapenem) was ineffective, and the patient remained febrile. The antibiotic regimen was adjusted multiple times: piperacillin/tazobactam + voriconazole, piperacillin/tazobactam + voriconazole + imipenem, vancomycin + biapenem, tigecycline + piperacillin, and tigecycline + piperacillin + colistin. However, the therapeutic outcomes remained unsatisfactory, and the patient’s condition continued to deteriorate.
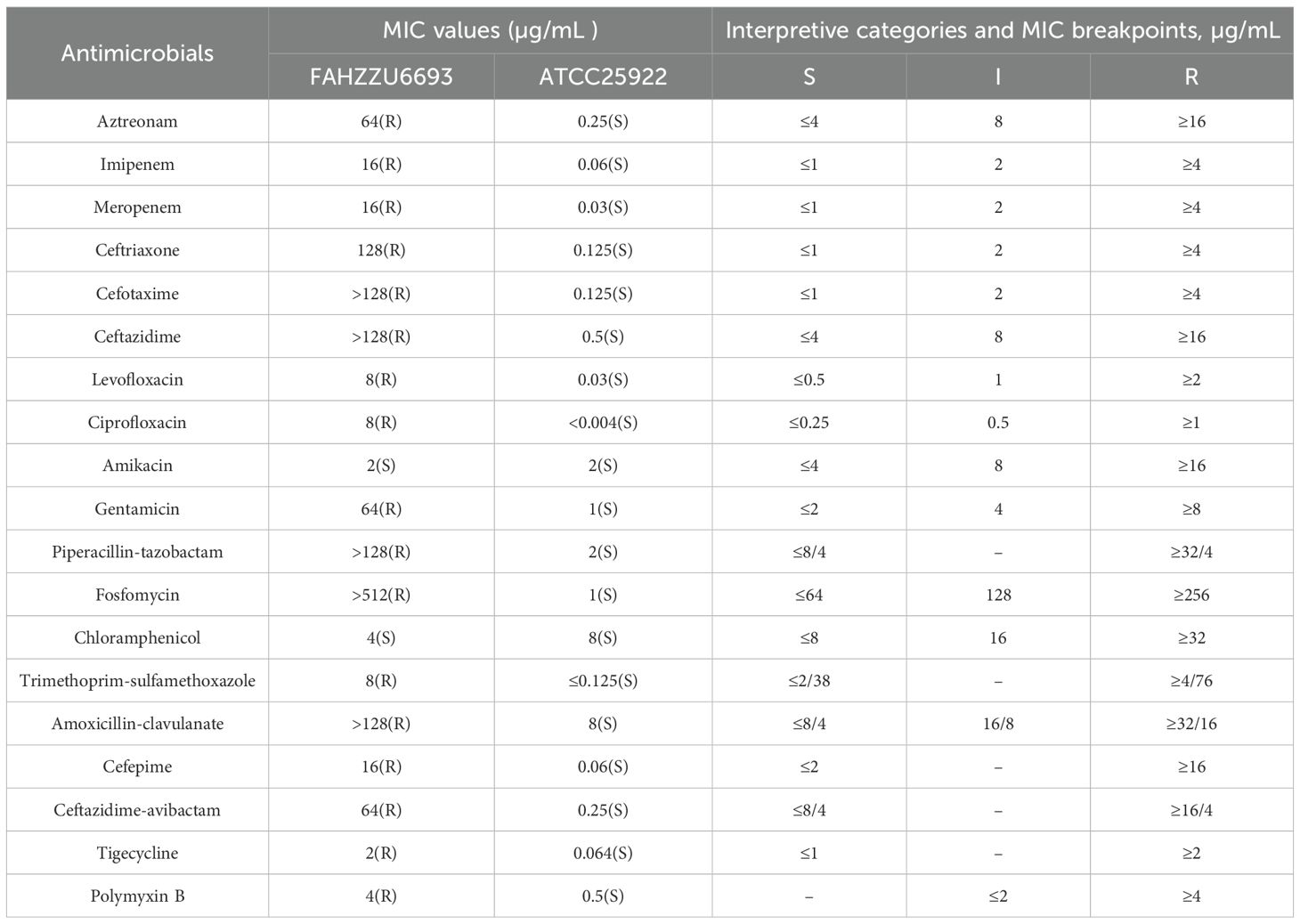
Strain FAHZZU6693 was identified as R. ornithinolytica by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS). Its antimicrobial susceptibility profile is summarized in Table 1: the isolate was resistant to aztreonam, imipenem, meropenem, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, piperacillin-tazobactam, fosfomycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefepime, ceftazidime-avibactam, tigecycline and polymyxin B, but remained susceptible to amikacin and chloramphenicol.
3.2 Genomic characterization of R. ornithinolytica FAHZZU6693
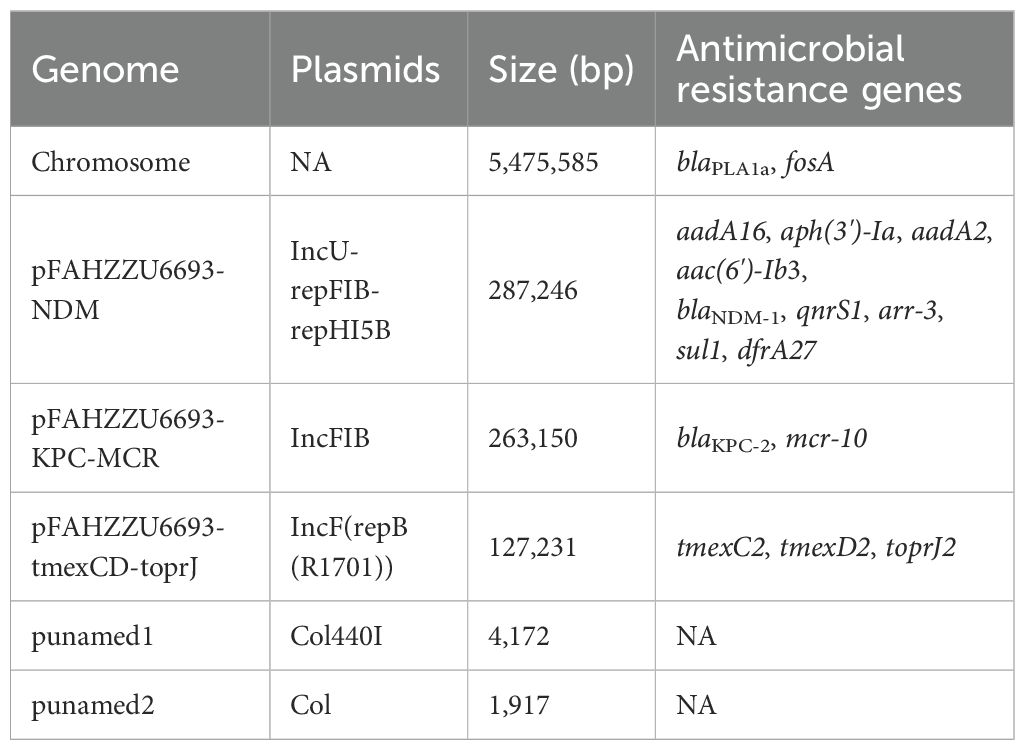
R. ornithinolytica FAHZZU6693 contains a chromosome (5,475,585 bp) with an average GC content of 55.75%, two plasmids (1,917 bp and 4,172 bp), and three megaplasmids (127,231 bp, 263,150 bp, and 287,246 bp). PlasmidFinder assigned these to the incompatibility groups Col, Col440I, repB(R1701), IncFIB and IncU-repFIB-repHI5B, respectively. ResFinder identified 17 acquired resistance genes, located predominantly on the IncU-repFIB-repHI5B, IncFIB and repB(R1701) plasmids as well as on the chromosome; details are given in Table 2. OriTfinder results revealed that pFAHZZU6693-KPC-MCR and pFAHZZU6693-tmexCD-toprJ plasmids carry complete conjugal transfer modules that are capable of facilitating horizontal dissemination. These modules include the origin of transfer site (oriT), relaxase gene, genes encoding type IV coupling protein (T4CP), and genes encoding the bacterial type IV secretion system (T4SS). By contrast, pFAHZZU6693-NDM lacks the origin of transfer site (oriT).
3.3 Phylogenetic analysis and multilocus sequence typing of R. ornithinolytica
A search of the NCBI database identified 586 R. ornithinolytica isolates. Resistance gene analysis revealed a detection rate of 11.3% for the blaKPC gene, 8.2% for the blaNDM gene, and 2.4% for isolates carrying both carbapenemase genes simultaneously. Additionally, the mcr gene, conferring colistin resistance, was detected in 1.0% of isolates, while the resistance-nodulation-division family (RND) efflux pump gene cluster tmexCD-toprJ, associated with tigecycline resistance, was identified in 2.2% of isolates. Notably, among tmexCD-toprJ-positive isolates, 46.1% co-harbored the blaNDM gene, and 30.0% co-harbored colistin resistance genes (mcr-10 or mcr-8). Further analysis showed that 106 of the 586 isolates carried at least one resistance determinant, including blaKPC, blaNDM, tmexCD-toprJ, or mcr. Of these, 1 isolate originated from animals, 60 from humans, and 45 from the environment. Strains carrying KPC or NDM-type carbapenemases were documented worldwide, with the majority recovered from China and the United States. In contrast, the tmexCD-toprJ gene cluster was only detected in isolates from China and Vietnam, indicating that Asia is the principal continental reservoir for tmexCD-toprJ-positive R. ornithinolytica (Figure 1).
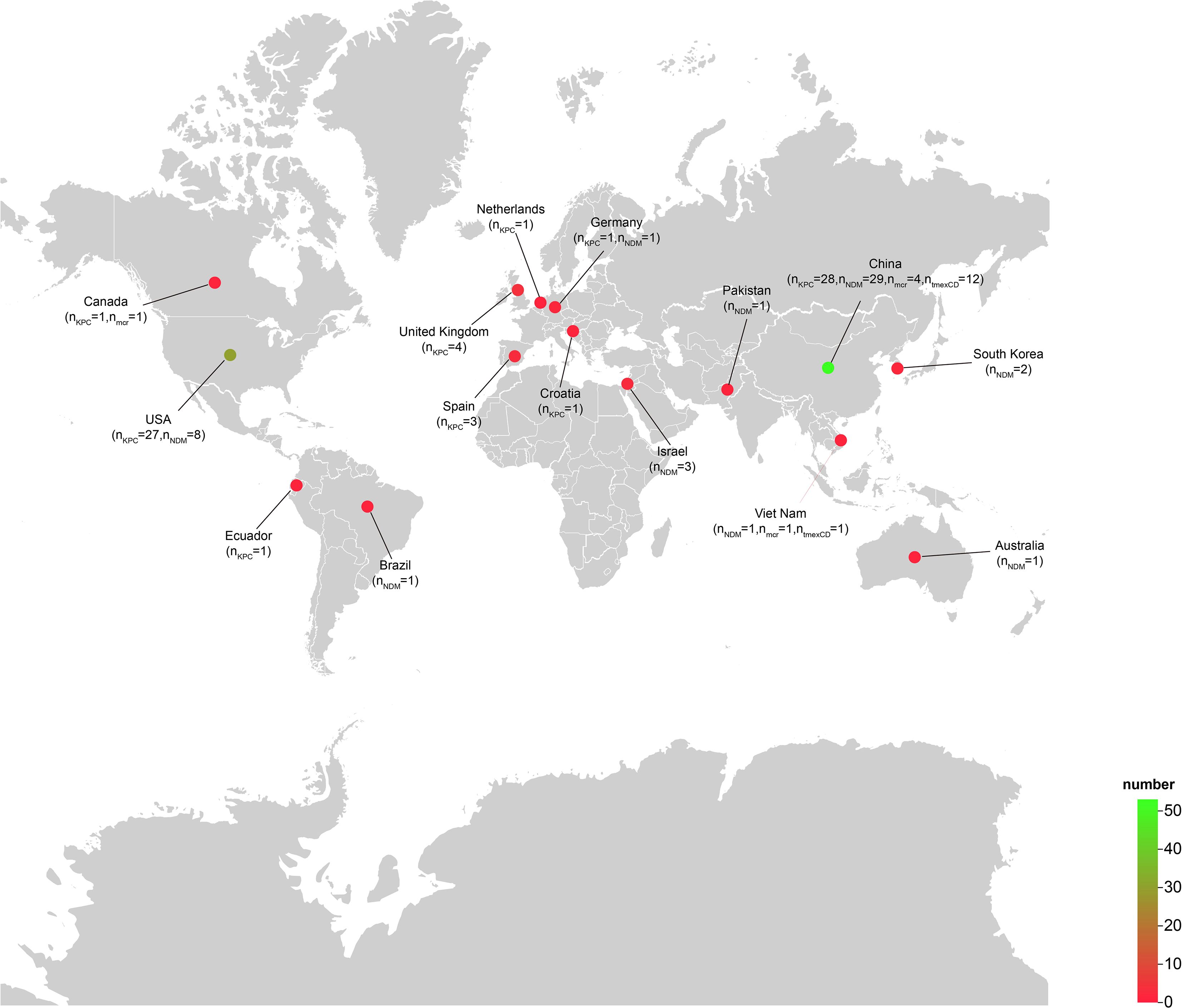
Figure 1. Geographical distribution of Raoultella ornithinolytica isolates harboring blaNDM, blaKPC, mcr-10 or tmexCD-toprJ. A total of 106 Raoultella ornithinolytica genomes carrying at least one of the four resistance determinants were retrieved from NCBI; 105 of these had associated geographical metadata. The color gradient from red to green indicates an increasing number of isolates per country. The map was generated with the web platform ChiPlot (https://www.chiplot.online) (Xie et al., 2023).
Concurrently, we reconstructed a phylogeny that incorporated the 106 publicly available isolates together with strain FAHZZU6693 (Figure 2). The analysis identified GCA_025376845.1 as the closest evolutionary relative of FAHZZU6693; this isolate was recovered in 2019 from hospital sewage at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, China. Compared with FAHZZU6693, it carries an additional IncX3 plasmid but lacks the resistance determinants blaKPC-2 and mcr-10. Across the entire collection, IncFII replicons were the most prevalent incompatibility group, followed by IncFIB. All strains harbored the β-lactamase gene blaPLA, and 99% additionally carried fosA, oqxA and oqxB. The blaKPC was the dominant carbapenemase. Only a minority of isolates possessed the tigecycline-resistance determinant tmexCD–toprJ or the colistin resistance genes mcr-10 and mcr-8.
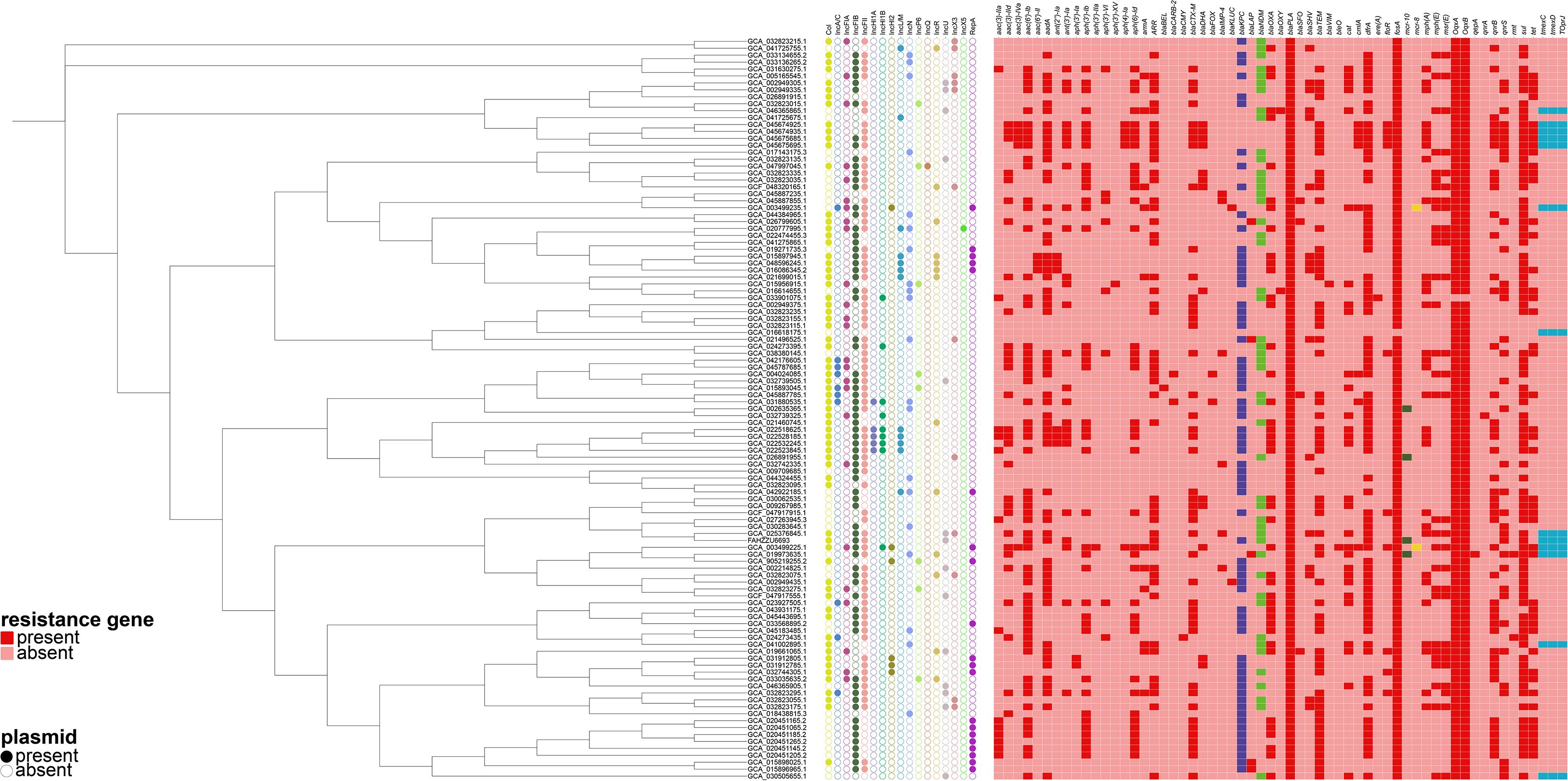
Figure 2. A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the core genome sequences of the strain FAHZZU6693 used in this study and 106 Raoultella ornithinolytica strains selected from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database. A heatmap was then generated in conjunction with the plasmid types and antibiotic resistance genes carried by these strains.
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) of strain FAHZZU6693 revealed a previously unassigned sequence type, defined by the allelic profile gapA29, infB28, mdh63, pgi37, phoE47, rpoB28 and tonB40. Similarly, MLST of 106 selected R. ornithinolytica isolates showed that 105 represented unassigned sequence types, with infB28, mdh63, pgi37, phoE7, rpoB43 and tonB40 being the most prevalent alleles.
3.4 Structural characterization of the blaNDM-1-bearing plasmid
The carbapenem-resistance gene blaNDM-1 is harbored on the 287,246 bp IncU-repFIB-repHI5B plasmid pFAHZZU6693-NDM (47.7% GC). BLASTN searches of the NCBI nucleotide database revealed 100% query coverage and 100% nucleotide identity with pJHKP172-298k (CP180680.1) and pJHKP139-296k (CP180659.1) from Klebsiella pneumoniae, and 100% query coverage with 99.97% nucleotide identity to pCRKP353-NDM1 (CP141633.1) from Klebsiella variicola (Figure 3).This study demonstrates that pFAHZZU6693-NDM harbors two multidrug resistance (MDR) regions, designated MDR1 and MDR2. MDR1 spans 11,972 bp (coordinates 248,293–260,265 bp), is flanked by xerC and IS26, and encompasses a class 1 integron (248,293–250,700 bp) carrying the resistance gene sul1; within the integron are the aminoglycoside-resistance gene ant(3´)-Ila and the disinfectant-resistance gene qacE. MDR2 (coordinates 274,661–285,316; 10,655 bp) also contains a class 1 integron (280,812–285,316 bp) that harbors five resistance determinants. The carbapenemase gene blaNDM-1 is situated immediately upstream of this integron and confers resistance to carbapenems.
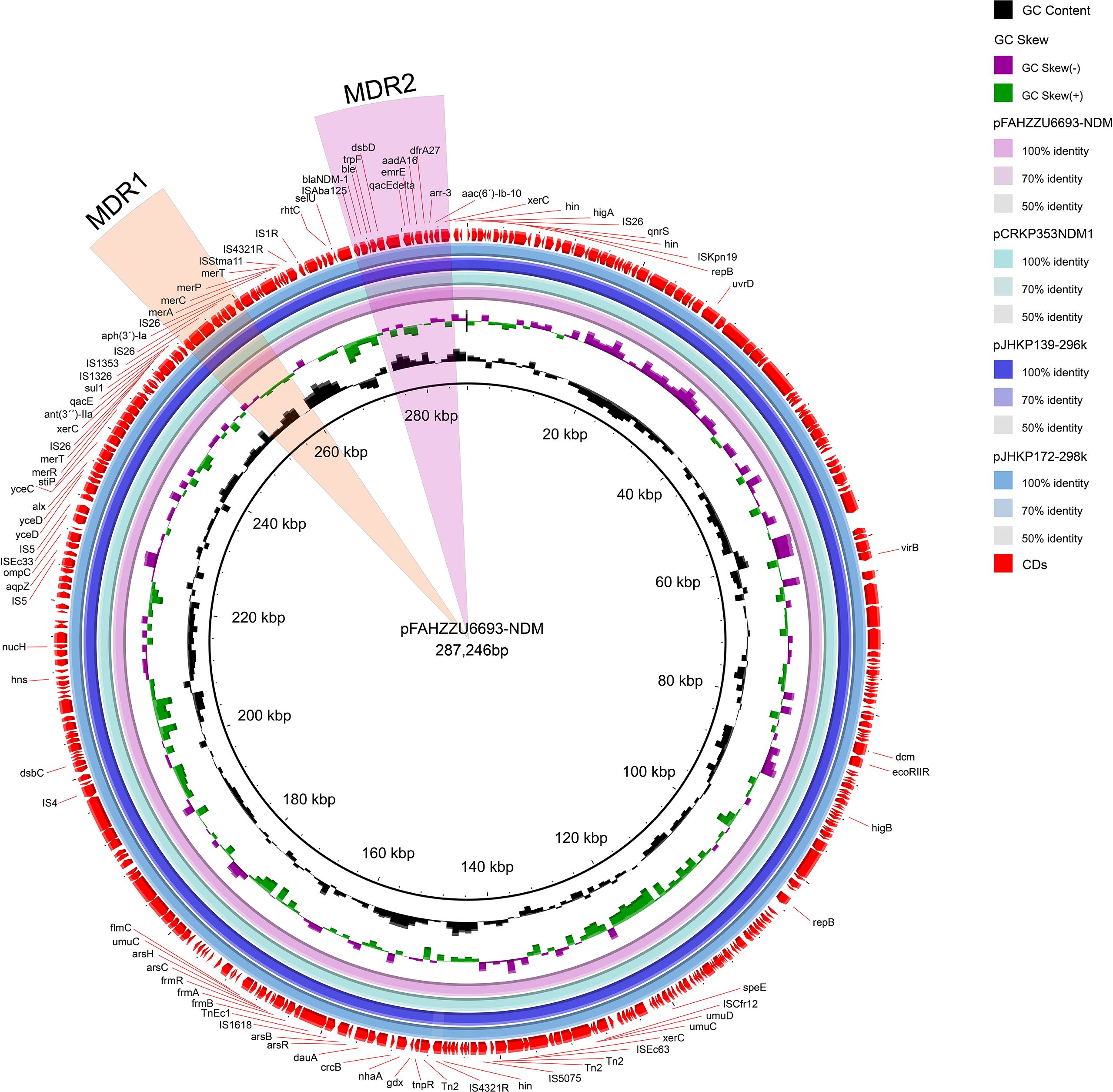
Figure 3. Circular map comparison of the pFAHZZU6693-NDM plasmid with the genomes of pCRKP353-NDM1, pJHKP139-296k, and pJHKP172-298k. The MDR1 and MDR2 regions are highlighted in orange and pink, respectively.
3.5 Structural characterization of co-harboring blaKPC-2 and mcr-10 plasmid
S1-PFGE and Southern blotting, combined with whole-genome sequencing, revealed that the colistin resistance determinant mcr-10 and the carbapenemase gene blaKPC-2 are co-located on the 52.19% GC IncFIB plasmid pFAHZZU6693-KPC-MCR (Figures 4A, B). To investigate the genetic context of mcr-10 in R. ornithinolytica, we surveyed the NCBI repository and found three isolates carrying this colistin resistance determinant; whole-genome sequences were available for two. Comparative genomic analysis revealed that the mcr-10 gene exhibits a conserved genetic structure of xerC-mcr-10-ISEc36-ISEc27. The mcr-10 gene in punamed1, isolated from humans, and in FAHZZU6693-KPC-MCR shares an identical genetic context of xerC-mcr-10-ISEc36-ISEc27-ISEcl1. In contrast, in the environmental plasmid pNUITM-VR1_2 DNA, the genetic environment of mcr-10 is distinguished by ISEhe3 occupying the position of ISEcl1 (Figure 5). Additionally, PlasmidFinder assigned both punamed1 and pNUITM-VR1_2 DNA to the IncFIB–IncFII incompatibility group.
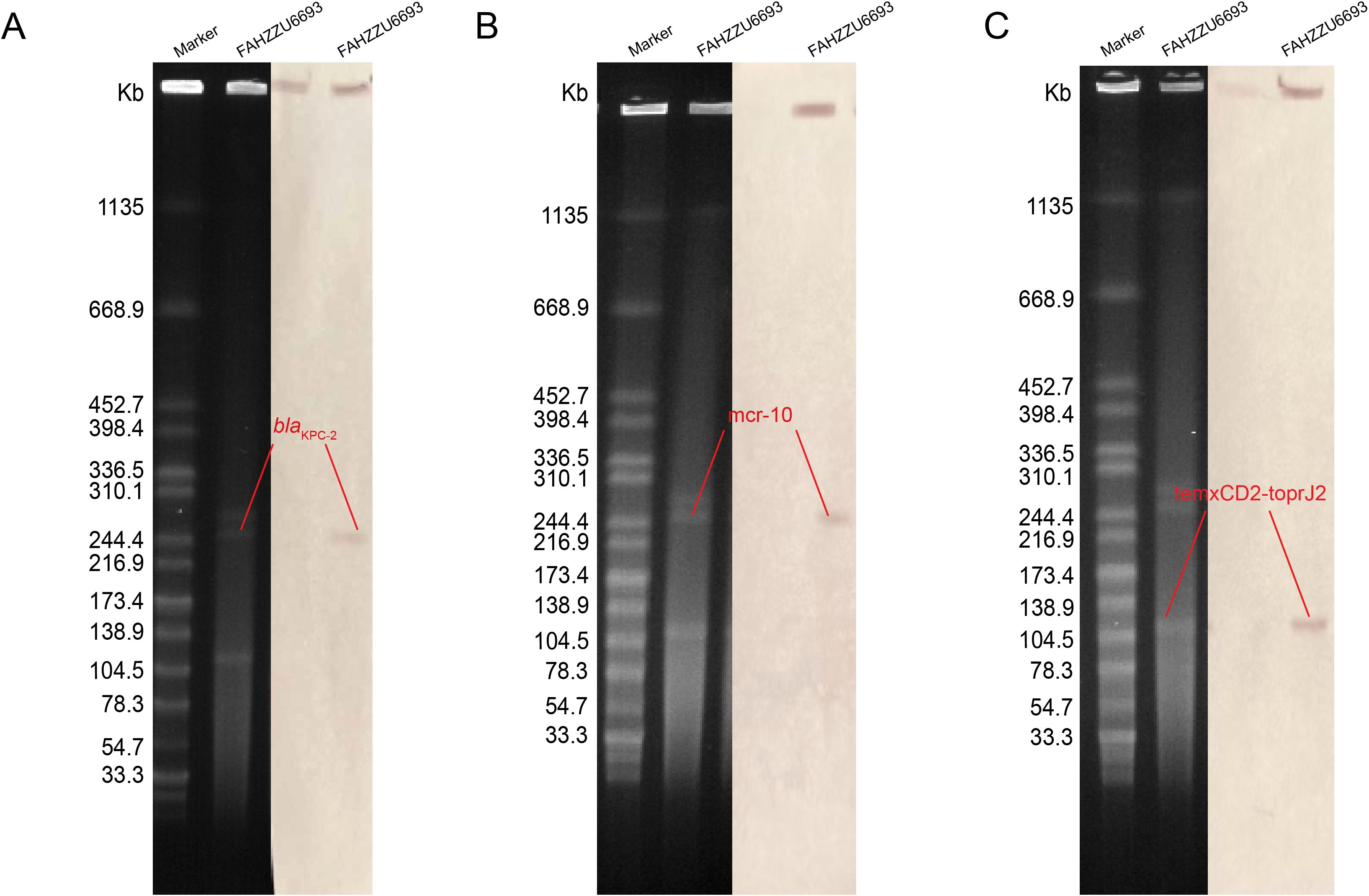
Figure 4. The S1 nuclease pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (S1-PFGE) profiles and Southern blot analysis results of strain FAHZZU6693 are shown. (A–C) illustrate the localization of the resistance genes blaKPC-2, mcr-10, and tmcxCD2-toprJ2 to plasmids, respectively. The molecular weight marker used is Salmonella enterica serovar Braenderup H9812.
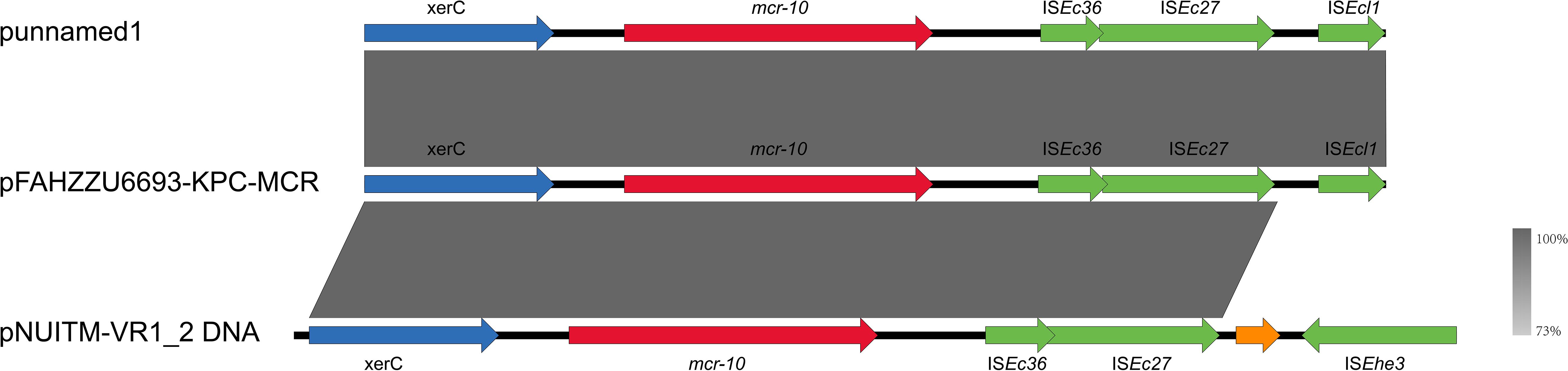
Figure 5. Genetic environment of the mcr-10 gene in the pFAHZZU6693-KPC-MCR plasmid. Genes are represented in different colors: functional genes are shown in blue, the resistance gene mcr-10 is highlighted in red, insertion elements are indicated in green, and hypothetical proteins are depicted in orange. The transcriptional direction of each gene is indicated by arrows.
3.6 Structural characterization of the tmexCD2-toprJ2-harboring plasmid
The tigecycline resistance gene cluster tmexCD2-toprJ2 is located on the IncF (repB(R1701)) plasmid pFAHZZU6693-tmexCD-toprJ (Figure 4C), which has a GC content of 53.83%. BLASTN searches in the NCBI nucleotide database revealed that pFAHZZU6693-tmexCD-toprJ shares 89% query coverage and over 99% nucleotide identity with plasmids from R. ornithinolytica pKP20-425-1-1 (accession number: CP109615.1) and K. pneumoniae pKP19-3088-159k and pKP20-558-3 (Figure 6A). To investigate the core genomic context of tmexCD2-toprJ2 in R. ornithinolytica, we identified five R. ornithinolytica strains carrying tmexCD2-toprJ2 through the NCBI database, of which three strains had whole-genome sequences. Among these, two strains harbored tmexCD2-toprJ2 on the chromosome, while one strain carried it on a plasmid. The conserved genomic context of tmexCD2-toprJ2 in R. ornithinolytica is umuC-IS881-tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2-umuC (Figure 6B). The presence of the insertion element IS881 and flanking umuC genes endows these strains with the ability to acquire and mobilize the tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2 cassette, thereby facilitating its dissemination among R. ornithinolytica strains.
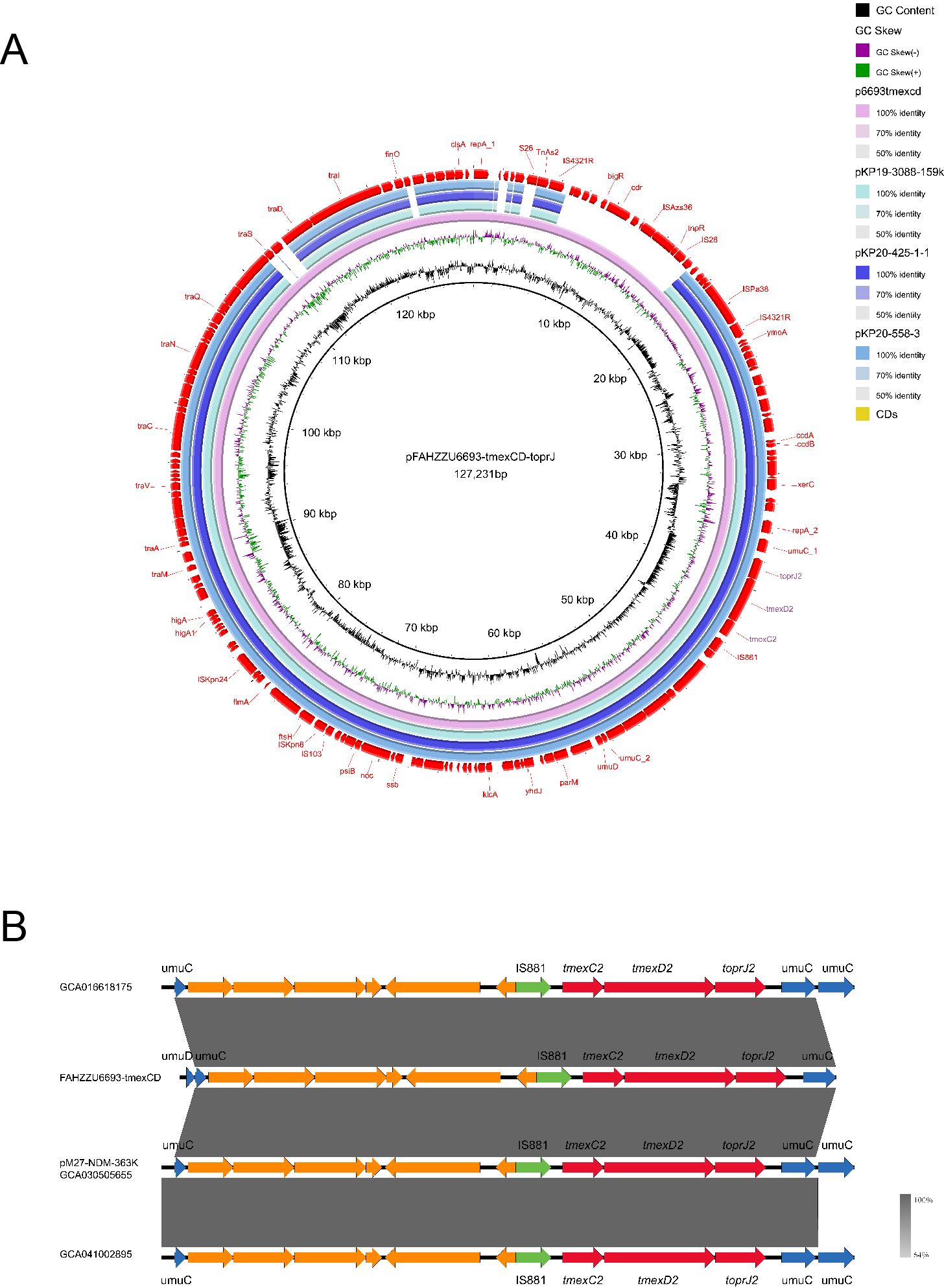
Figure 6. Genomic characteristics of the pFAHZZU6693-tmexCD-toprJ plasmid and the genetic environment of the tmexCD2-toprJ2 gene cluster. (A) Circular map comparison of the pFAHZZU6693-tmexCD-toprJ plasmid with the genomes of pKP19-3088-159k, pKP20-425-1-1, and pKP20-558–3 plasmids. (B) Genetic environment of the tmexCD2-toprJ2 gene cluster in Raoultella ornithinolytica. Genes are depicted in different colors: functional genes are shown in blue, the resistance gene tmexCD2-toprJ2 is highlighted in red, insertion elements are indicated in green, and hypothetical proteins are shown in orange. The transcriptional direction of each gene is indicated by arrows.
4 Discussion
The coexistence of blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10, and tmexCD2-toprJ2 genes in R. ornithinolytica is reported for the first time, with no prior reports documented. The strain was identified as Multi-drug resistant with an unknown sequence type (ST). Data analysis revealed that 99% of R. ornithinolytica strains lack defined ST, indicating that further research is needed for molecular typing of this species, which is of great significance for subsequent studies. Notably, 18.3% of R. ornithinolytica isolates were found to carry at least one carbapenemase, colistin, or tigecycline resistance gene, suggesting that this species has become a reservoir of multidrug resistance genes. More critically, the co-occurrence of blaKPC and blaNDM carbapenemase genes in the same strain may render most β-lactam antibiotics ineffective. Additionally, the high coexistence frequency of colistin and tigecycline resistance genes with carbapenemase genes may drive the emergence of “super-drug resistant” plasmids, thereby accelerating the spread of multidrug resistance. Sample sources indicate that R. ornithinolytica is not only widely present in human samples globally but has also been isolated from livestock and hospital wastewater, suggesting transmission pathways involving the environment, food, and healthcare settings. This underscores the importance of implementing integrated surveillance that encompasses human, animal, and environmental health within the framework of the “One Health” concept.
The whole-genome sequencing results of the FAHZZU6693 strain revealed that the blaPLA and fosA genes are located on the chromosome, while all other resistance genes are harbored on plasmids. Analysis of the complete whole-genome sequences from the selected strains showed that all R. ornithinolytica strains carry the blaPLA gene, which is located on the chromosome. This provides a genetic basis for the intrinsic resistance of R. ornithinolytica to amoxicillin, ampicillin, and ticarcillin. The study by Yang Lang et al. demonstrated that strains harboring two copies of the blaNDM-1 gene exhibit significantly enhanced resistance to carbapenems (Yang et al., 2021). The antimicrobial susceptibility profile of strain FAHZZU6693, which shows high resistance to imipenem and meropenem, is likely closely related to its co-carriage of both blaNDM-1 and blaKPC-2 genes. As previously reported, K. pneumoniae strains co-harboring blaNDM and blaKPC genes typically acquire a blaNDM-carrying plasmid in KPC-producing K. pneumoniae (Li et al., 2025). Similarly, considering the chronological order of reports on strains carrying different enzyme types, R. ornithinolytica strains harboring both blaNDM-1 and blaKPC-2 likely follow a similar acquisition pathway. Previous studies have confirmed that the blaNDM gene can spread resistance gene among different bacterial species via plasmid-mediated horizontal transfer. In this study, analysis using OriTfinder revealed that the pFAHZZU6693-NDM plasmid carries a relaxase gene, a gene encoding a type IV coupling protein (T4CP), and a gene cluster for a bacterial type IV secretion system (T4SS); however, no origin of transfer site (oriT) was identified. Theoretically, the absence of oriT may limit the horizontal transfer capacity of this plasmid. However, prior research has indicated that most conjugative and mobilizable plasmids lack recognizable oriT sequences (Ares-Arroyo et al., 2024). The conjugal transfer ability of this plasmid has not yet been verified in this study, which represents one of its limitations. In future research, if sodium azide becomes available, we plan to further validate the transferability of pFAHZZU6693-NDM using the recipient strain J53.
To date, ten different mcr genes, including mcr-1 to mcr-10, have been reported globally (Partridge et al., 2018). The mcr-1 gene is the most common and widely distributed colistin resistance gene (Abdullah et al., 2024). Interestingly, the results of this study indicate that mcr-10 has emerged as the most prevalent colistin resistance gene in R. ornithinolytica, followed by mcr-8. No other mcr gene variants have been reported in this species. This suggests that mcr-10 may have acquired an adaptive advantage within R. ornithinolytica, potentially attributable to the conserved genetic structure of xerC-mcr-10-ISEc36-ISEc27. In this study, we observed that genetic sequence differences between environmental and human-derived strains are confined solely to the insertion sequence region downstream of ISEc27. Furthermore, this study is the first to report the co-localization of mcr-10 and blaKPC-2 on the same plasmid. Considering the large prevalence of carbapenem-resistant strains producing KPC-type carbapenemases in the region and the predominance of IncFIB-type plasmids (Mohamed et al., 2019), we hypothesize that in R. ornithinolytica, ISEc27 may mediate the horizontal transfer of the mcr-10 gene on blaKPC-carrying IncFIB plasmids. Given that plasmids are capable of autonomous replication and horizontal transfer (Liu et al., 2024), this significantly increases the potential risk of the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains. Previous research has established a certain degree of biological relatedness between R. ornithinolytica and K. pneumoniae, with their genes exhibiting robust horizontal transfer capabilities (Zhai et al., 2025). Thus, the extensive drug resistance background already present in K. pneumoniae will further exacerbate the clinical infection risk associated with this pathogen.
Most concerning is the coexistence of the tigecycline resistance gene cluster tmexCD2-toprJ2 and the colistin resistance gene mcr-10 within the same strain, effectively breaching the last two lines of defense available in antibiotic selection (Cheng et al., 2020). A strain of K. pneumoniae isolated from a patient with pulmonary infection in China was found to harbor the tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2 gene cluster on both the chromosome and a plasmid (Wang et al., 2021). This suggests that the tmexCD2-toprJ2 gene cluster is capable of horizontal transfer between the chromosome and plasmid. The tmexCD2-toprJ2 gene cluster exists in the structure of umuC-IS881-tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2-umuC, with 100% nucleotide identity, regardless of its location on the chromosome or plasmid. Previous studies have demonstrated that umuC has the capacity for DNA cleavage and repair (Murison et al., 2017), and it is widely distributed in genetic material. Thus, the umuC gene is likely to facilitate the horizontal transfer of the tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2 structure. Given this, it is essential to further investigate the potential mechanisms of umuC-mediated gene transfer in order to curb the accumulation and dissemination of resistance genes among strains. Experimental research by Hong Yao et al. has demonstrated that IncF [repB(R1701)] has conjugative transfer capabilities. In terms of genetic structure, it contains both IncFII and IncFI replicons (Yao et al., 2024). Investigations into the plasmid types carried by R. ornithinolytica have shown that IncFII and IncFI plasmids are the two most common types. This provides a dual advantage for the dissemination of the tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2 structure.
5 Conclusion
In this study, for the first time, the coexistence of blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10, and the tmexC2-tmexD2-toprJ2 gene cluster was identified in a clinical isolate of R. ornithinolytica, with these genetic elements residing on plasmids. Comprehensive analysis of R. ornithinolytica strains from the NCBI database revealed distinct geographical distribution patterns for these resistance genes. The conserved genetic contexts of these elements, coupled with the presence of abundant plasmid-associated mobile genetic elements, suggest the enhanced acquisition and recombination of these resistance genes. R. ornithinolytica, as a reservoir of multidrug resistance genes, introduces a severe potential risk to public health. Thus, enhanced surveillance of this pathogen, particularly those strains harboring multiple resistance genes and genetic clusters, is of critical importance.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA1267968.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (No. 2024-KY-0318). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YY: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources. YR: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. LF: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Resources. HY: Data curation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RC: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft. CL: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. YS: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. YJ: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. XG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Joint Construction Project of Henan Province Medical Science and Technology Research Program (Grant No. LHGJ20230920) and the Henan Province Science and Technology Research Program (Grant No. 232102310176).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1675929/full#supplementary-material
References
Abdullah, S., Mushtaq, M. A., Ullah, K., Hassan, B., Azam, M., Zahoor, M. A., et al. (2024). Dissemination of clinical Escherichia coli harboring the mcr-1 gene in Pakistan. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1502528. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1502528
Ares-Arroyo, M., Nucci, A., and Rocha, E. P. C. (2024). Expanding the diversity of origin of transfer-containing sequences in mobilizable plasmids. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 3240–3253. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01844-1
Assadi, R. A., AlAwadhi, H. A., Hasson, N. H. A., and Assadi, R. A. (2025). Fatal case of sepsis caused by Raoultella ornithinolytica: A rare opportunistic pathogen. IDCases. 39, e02156. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2025.e02156
Castanheira, M., Deshpande, L. M., DiPersio, J. R., Kang, J., Weinstein, M. P., and Jones, R. N. (2009). First descriptions of blaKPC in Raoultella spp. (R. planticola and R. ornithinolytica): report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program. J. Clin. Microbiol. 47, 4129–4130. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01502-09
Cheng, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Guo, Y., Zhou, Y., Xiao, T., et al. (2020). Identification of novel tetracycline resistance gene tet(X14) and its co-occurrence with tet(X2) in a tigecycline-resistant and colistin-resistant Empedobacter stercoris. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 9, 1843–1852. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1803769
Dang, B., Zhang, H., Li, Z., Ma, S., and Xu, Z. (2020). Coexistence of the blaNDM-1-carrying plasmid pWLK-NDM and the blaKPC-2-carrying plasmid pWLK-KPC in a Raoultella ornithinolytica isolate. Sci. Rep. 10, 2360. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59341-4
De Coster, D. A., Carroll, M., Lavender, J., and Gibson, R. (2024). A case of raoultella ornithinolytica cholangitis in A liver transplant recipient. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 11, 004758. doi: 10.12890/2024_004758
Etani, T., Kondo, S., Yanase, T., Morikawa, T., Aoki, M., Gonda, M., et al. (2023). Clinical characteristics of Raoultella ornithinolytica bacteremia and antimicrobial susceptibility of Raoultella ornithinolytica. J. Infect. Chemother. 29, 554–557. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2023.01.023
Giran, M., Behera, H. S., Nanda, R., and Padhy, S. K. First report of Raoultella ornithinolytica endophthalmitis. Retin Cases Brief Rep. (2025). doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000001758
Humphries, R., Bobenchik, A. M., Hindler, J. A., and Schuetz, A. N. (2021). Overview of changes to the clinical and laboratory standards institute performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, M100, 31st edition. J. Clin. Microbiol. 59, e0021321. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00213-21
Jones, D. T., Srinivasmurthy, R., Pandit, M., Tovar, R., Ho, L., and Wairimu, K. (2024). Raoultella ornithinolytica urinary tract infection in a patient with triple-negative breast cancer. Cureus. 16, e64742. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64742
Khajuria, A., Praharaj, A. K., Grover, N., and Kumar, M. (2013). First report of blaNDM-1 in Raoultella ornithinolytica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57, 1092–1093. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02147-12
Li, J., Wu, W., Wu, H., Huang, J., Li, Z., Wang, J., et al. (2025). Rapid emergence, transmission, and evolution of KPC and NDM coproducing carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Res. 293, 128049. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2025.128049
Liu, R., Chen, Y., Xu, H., Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Liu, X., et al. (2024). Fusion event mediated by IS903B between chromosome and plasmid in two MCR-9- and KPC-2-co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Drug Resist. Updat. 77, 101139. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2024.101139
Mader, D. A., Kerrigan, D., and Pai, J. (2013). Acute encephalopathy in a patient with raoultella ornithinolytica infection: A challenging presentation. R I Med. J. 107, 7–9.
Mohamed, E. R., Ali, M. Y., Waly, N., Halby, H. M., and El-Baky, R. M. A. (2019). The Inc FII Plasmid and its Contribution in the Transmission of blaNDM-1 and blaKPC-2 in Klebsiella pneumoniae in Egypt. Antibiotics (Basel). 8, 266. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8040266
Murison, D. A., Timson, R. C., Koleva, B. N., Ordazzo, M., and Beuning, P. J. (2017). Identification of the dimer exchange interface of the bacterial DNA damage response protein umud. Biochemistry. 56, 4773–4785. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00560
Partridge, S. R., Kwong, S. M., Firth, N., and Jensen, S. O. (2018). Mobile genetic elements associated with antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 31, e00088–e00017. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00088-17
Sun, F., Yin, Z., Feng, J., Qiu, Y., Zhang, D., Luo, W., et al. (2015). Production of plasmid-encoding NDM-1 in clinical Raoultella ornithinolytica and Leclercia adecarboxylata from China. Front. Microbiol. 6, 458. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00458
Wang, C. Z., Gao, X., Yang, Q. W., Lv, L. C., Wan, M., Yang, J., et al. (2021). A Novel Transferable Resistance-Nodulation-Division Pump Gene Cluster, tmexCD2-toprJ2, Confers Tigecycline Resistance in Raoultella ornithinolytica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65, e02229–e02220. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02229-20
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2019). Emergence of Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-8 and Its Variant in Raoultella ornithinolytica. Front. Microbiol. 10, 228. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00228
Xie, J., Chen, Y., Cai, G., Cai, R., Hu, Z., and Wang, H. (2023). Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, W587–Ww92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad359
Yang, L., He, H., Chen, Q., Wang, K., Lin, Y., Li, P., et al. (2021). Nosocomial Outbreak of Carbapenemase-Producing Proteus mirabilis With Two Novel Salmonella Genomic Island 1 Variants Carrying Different blaNDM-1 Gene Copies in China. Front. Microbiol. 12, 800938.
Yao, H., Zhang, T., Peng, K., Peng, J., Liu, X., Xia, Z., et al. (2024). Conjugative plasmids facilitate the transmission of tmexCD2-toprJ2 among carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Total Environ. 906, 167373. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167373
Keywords: Raoultella ornithinolytica, blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10, tmexCD2-toprJ2
Citation: Ye Y, Rao Y, Fang L, Ye H, Chen R, Li C, Shen Y, Jia Y and Guo X (2025) The emergence and spread of blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, mcr-10 genes, and the tmexCD2-toprJ2 gene cluster in extensively drug-resistant clinical Raoultella ornithinolytica. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1675929. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1675929
Received: 29 July 2025; Accepted: 24 October 2025;
Published: 05 November 2025.
Edited by:
Dimosthenis Chochlakis, University of Crete, GreeceReviewed by:
Ariadnna Cruz-Córdova, Federico Gómez Children’s Hospital, MexicoWeishuai Zhai, China Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Ye, Rao, Fang, Ye, Chen, Li, Shen, Jia and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaobing Guo, Z3hiaW5nOTI4QHp6dS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yafei Ye1†
Yafei Ye1† Yuting Rao
Yuting Rao Lei Fang
Lei Fang Ruyan Chen
Ruyan Chen Chenyu Li
Chenyu Li Yuanyuan Jia
Yuanyuan Jia Xiaobing Guo
Xiaobing Guo