- Department of Emergency, Xinqiao Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
The prevalence of fungal infections has been increasing consistently in recent years, particularly among immunocompromised individuals, resulting in increased mortality. The World Health Organization (WHO) now lists “super fungi”, such as Candida auris as global public health threats, highlighting the urgent requirement for new antifungal therapies. Although conventional agents such as azoles and polyenes remain prevalent in medical treatment, challenges including drug resistance, limited selectivity, and high toxicity limit their value, prompting the need for the development of more effective therapeutic strategies. Current research trends are shifting towards multi-mechanistic combination therapies and biotechnology-driven approaches, which demonstrate significant potential. This review summarizes recent advances and outlines directions for future antifungal drug development and new therapies.
1 Introduction
In recent years, the incidence of fungal infections has risen alarmingly, driven by immunosuppression from organ transplantation and chemotherapy for cancer treatment (Burki, 2023; Zhang et al., 2023; Ikuta et al., 2024). This population is significantly more likely to face severe infections and has high mortality rates (Pagano et al., 2017; Wiederhold and Gibas, 2018; Oberoi et al., 2023). Among the fungi of concern, Candida auris and Aspergillus have posed significant threats to patient safety and public health worldwide (Lamoth et al., 2017; Janniger and Kapila, 2021; Horton et al., 2023; Iliev et al., 2024; Proctor et al., 2025). The emergence of these resistant strains is exacerbated by the widespread use of antifungal medications, inadvertently contributing to the development of drug resistance (Fisher et al., 2022; Lockhart et al., 2023). This phenomenon poses a serious challenge to the management of fungal infections, and urgent and innovative therapeutic strategies are needed to address this growing public health crisis (Brown et al., 2012). Furthermore, fungal infections of the central nervous system (CNS), such as cryptococcal meningitis, represent a particularly devastating manifestation associated with high mortality rates (Ashley, 2019; Lino et al., 2024). Their management is compounded by the formidable challenge of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which severely restricts the access of most antifungal drugs to the site of infection, necessitating prolonged treatment courses and highlighting an urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies (Nau et al., 2010; Schwartz et al., 2018).
Traditional antifungal therapies, including azoles, echinocandins, and polyenes, have been the keystone of treatment for these infections (Patterson, 2006; Saini et al., 2025). However, the limitations of these agents are becoming increasingly apparent, especially in the context of rapidly emerging resistance. For example, Candida glabrata and C. auris have developed significant resistance to multiple antifungal classes, complicating treatment regimens and leading to treatment failures. The challenge is further exacerbated by the poor bioavailability and pharmacokinetic profiles of many antifungal drugs, limiting their effectiveness in treating systemic infections (Lass-Florl, 2011; Lewis, 2011). Consequently, there is an urgent need for novel antifungal drugs with new mechanisms of action that are effective in targeting drug-resistant strains while minimizing toxicity to patients (Donlin and Meyers, 2022; Hoenigl et al., 2024).
In addition to the development of new antifungals, innovative strategies such as combination therapy and the use of nanotechnology for drug delivery are being explored to enhance the efficacy of existing treatments. Combination therapy, which involves using multiple antifungal agents concurrently, has shown promise in improving treatment outcomes and reducing the likelihood of resistance development (Toepfer et al., 2024; Wake et al., 2024). Furthermore, the integration of nanotechnology in antifungal drug delivery systems has the potential to enhance the bioavailability and targeted action of antifungal agents, thereby improving therapeutic outcomes. These advancements are crucial since they not only provide alternative treatment options but also open the way for a more personalized approach to the management of fungal infections in susceptible populations.
As the landscape of fungal infections is changing, the medical community must remain alert to monitor trends in antifungal resistance and adjust treatment strategies accordingly. Continued research into the mechanisms of drug resistance, the development of rapid diagnostic tools, and the exploration of novel therapeutic avenues are essential to address the challenges posed by invasive fungal infections. In face of this growing public health threat, the integration of multidisciplinary approaches, including microbiology, pharmacology, and immunology, will be crucial in developing effective interventions to safeguard patient health and improve outcomes.
2 Epidemiological status of fungal infections
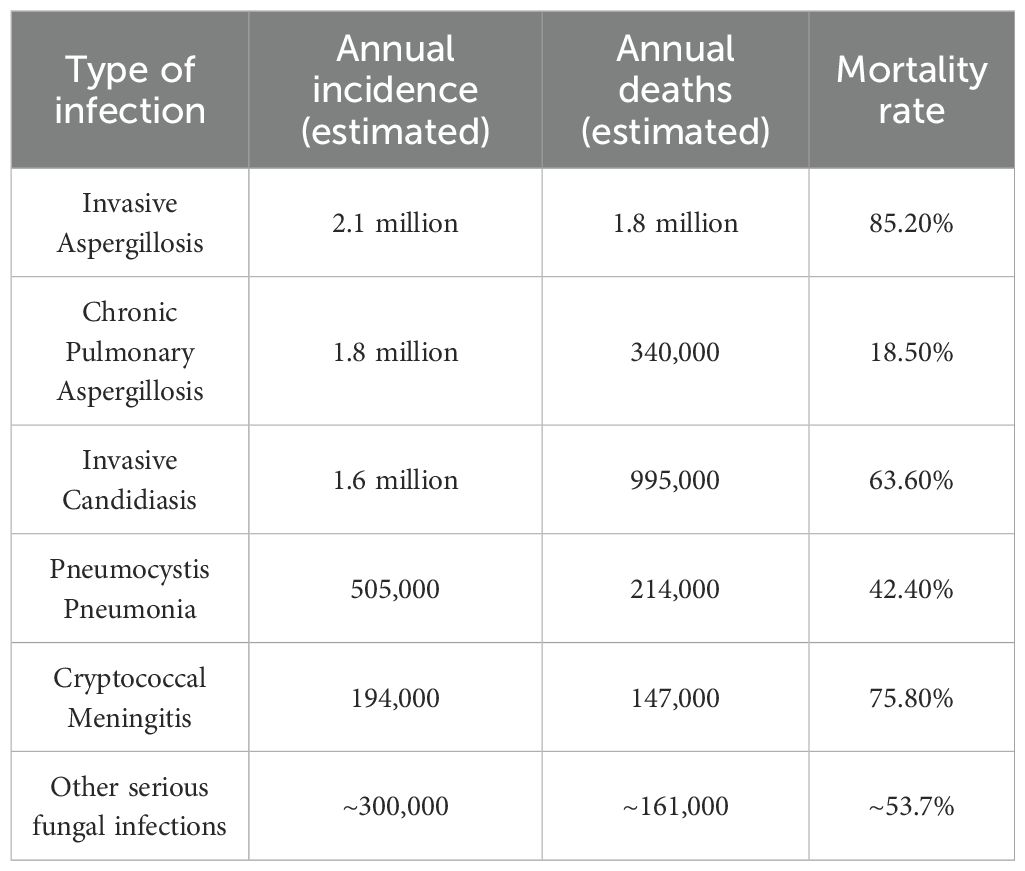
The global burden of fungal infections is substantial, with millions of cases reported annually (Denning, 2024; Iliev et al., 2024). Recent estimates indicate that invasive fungal infections result in an annual incidence of 65 million invasive fungal infections and 3.8 million deaths (Denning, 2024) (Table 1). On October 25, 2022, WHO released its first fungal priority pathogen list, ranking 19 invasive fungi as critical, high, or medium priority based on incidence, mortality, resistance, and therapeutic options (Burki, 2023). The incidence of cryptococcal meningitis in HIV-positive individuals remains alarmingly high, with an estimated 223,000 cases and 181,000 deaths annually (Rajasingham et al., 2017). Additionally, the rise in antifungal resistance complicates treatment paradigms, with studies showing that an increasing number of Candida albicans isolates are resistant to commonly used antifungal drugs (Fisher et al., 2022; Sobel, 2023). These data underscore the urgent need for improved diagnostic, preventive, and therapeutic strategies to address the growing threat of fungal infections globally.
Fungal infections represent a significant public health challenge globally, characterized by complex epidemiological features influenced by various factors. Skin and nail infections are particularly common, and dermatophyte infections, caused primarily by Trichophyton spp., are the primary pathogens of skin, hair, and nail infections worldwide (Thakur, 2015; Chanyachailert et al., 2023). The epidemiology of these infections varies across different geographic regions and specific populations, and their prevalence patterns have changed over recent years (Havlickova et al., 2008; Coulibaly et al., 2018; Chanyachailert et al., 2023). Filamentous fungi also cause high mortality and pose a serious public-health threat. Aspergillus, Mucorales and Fusarium drive the high mortality of invasive fungal infections, especially in immunocompromised hosts, including patients with hematological malignancies, transplant recipients, and individuals with severe COVID-19 or liver disease (Barros et al., 2023; Harris, 2023; Hlaing et al., 2023; Oberoi et al., 2023).
The epidemiology of fungal infections is significantly influenced by the host’s immune status, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. Immunocompromise reduces the ability to generate an effective immune response, making these individuals more susceptible to opportunistic pathogens (Dobes et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2023). A multi-center study of 234 adult HSCT (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation) recipients found that invasive candidiasis comprised 24.8% of all invasive fungal infections (Neofytos et al., 2009). The use of immunosuppressive therapies further exacerbates this risk by impairing both innate and adaptive immune responses (Schleimer, 2005; Gregory et al., 2023).
Despite advances in antifungal therapy, mortality rates from cryptococcal meningitis remain unacceptably high, particularly in resource-limited settings and immunocompromised populations, underscoring its significance as a global health threat (Pyrgos et al., 2013). Cryptococcosis and aspergillosis are among the most common fungal infections affecting the CNS, often leading to severe morbidity and high mortality rates (Vu et al., 2014). The difficulty in treating these infections is compounded by the inefficiency of most antifungal drugs in penetrating the BBB, which significantly limits their therapeutic efficacy (Nau et al., 2010). Understanding the epidemiological trends and risk factors associated with fungal CNS infections is also crucial for developing targeted prevention and treatment strategies.
3 Classification, mechanism of action and limitations of traditional antifungal drugs
Invasive fungal infections caused by Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus are now major public health concerns. The mainstay of therapy remains three drug classes-azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins (Figure 1), but the effectiveness of these drugs is declining due to their toxicity, drug-drug interactions and rapidly expanding resistance (Berman and Krysan, 2020).
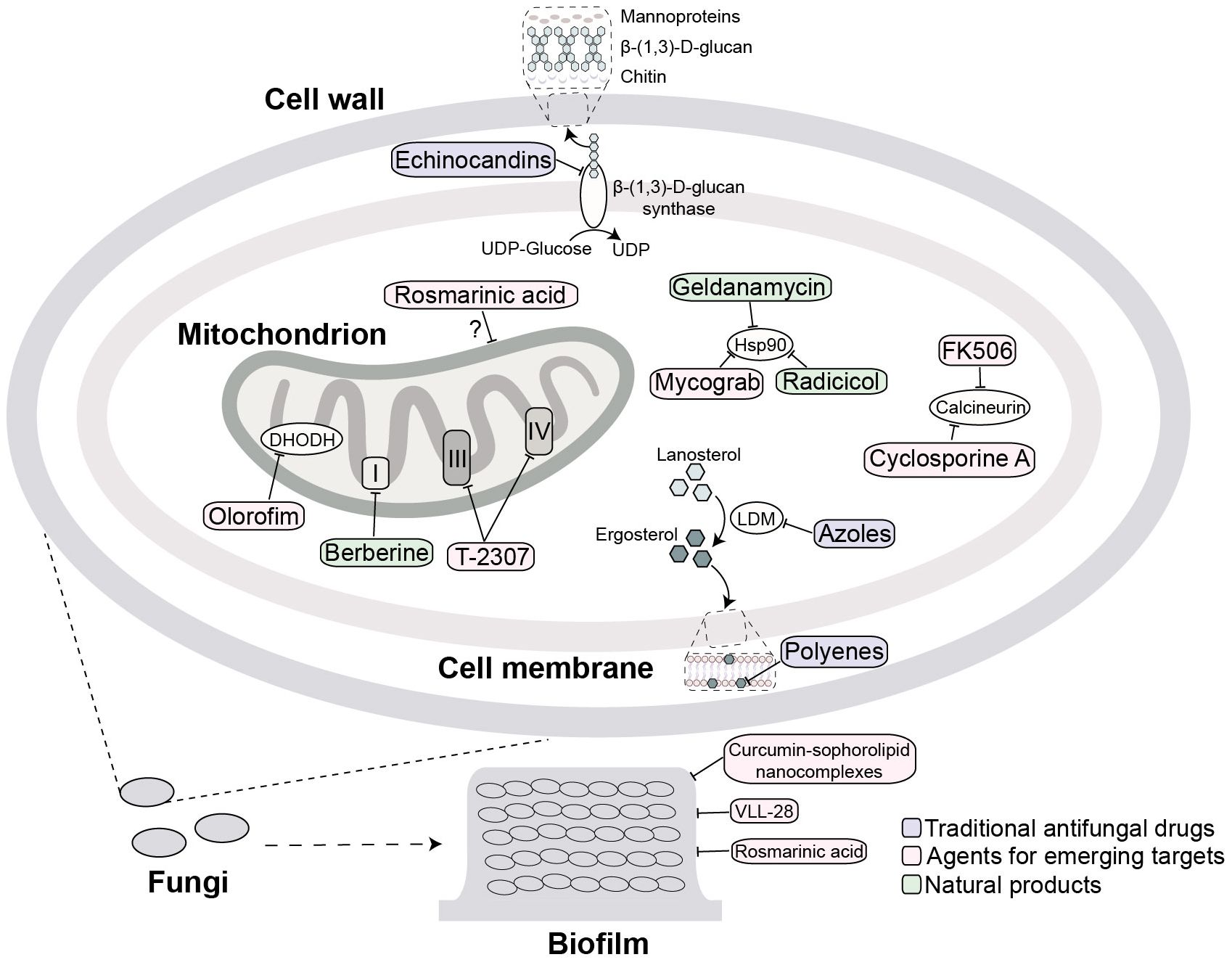
Figure 1. Antifungal agents targets and their mechanism of action. Traditional key targets include: surface β-(1,3)-D-glucan synthase (inhibited by echinocandins); ergosterol (its biosynthesis inhibited at lanosterol demethylase (LDM) by azoles or directly bound by polyenes). Emerging targets include: mitochondria (target by rosmarinic acid, berberine, T2307 and olorofim); calcineurin (targeted by cyclosporine A and FK506); and Hsp90 (targeted by geldanamycin, radicicol and Mycograb). Extracellular biofilm disruption is targeted by agents such as curcumin-sophorolipid nanocomplexes, VLL-28, and rosmarinic acid. The purple, pink and green squares mark traditional antifungal drugs, agents for emerging targets and natural products, respectively.
3.1 Azole antifungal agent
Azoles represent a widely utilized class of antifungal agents, with numerous compounds developed over the years and ongoing efforts to introduce new derivatives (Kim et al., 2022). Their mechanism of action involves the inhibition of lanosterol 14-α-demethylase (LDM), a key enzyme contributing to the 14-α-demethylation of lanosterol, thereby blocking the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway. This inhibition disrupts the integrity of the fungal cell membrane by preventing ergosterol production and promoting the accumulation of toxic sterol intermediates, ultimately impairing fungal growth and leading to cell death (Maertens, 2004).
Azole antifungals, such as fluconazole and itraconazole, are now widely used for the treatment of various fungal infections due to their efficacy and oral bioavailability. However, their clinical utility has been hampered by several challenges. One of the most significant issues is the emergence of drug resistance in fungal pathogens, particularly C. albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Resistance mechanisms include alterations in drug target, overexpression of efflux pumps, and biofilm formation, which significantly reduce the efficacy of azole therapy (Kaur and Nobile, 2023; van de Veerdonk et al., 2025). Besides resistance, dose-limiting toxicity is another major obstacle to prolonged azole use. The most common is dose-dependent hepatotoxicity, which can range from asymptomatic transaminase elevation to acute liver injury (Song and Deresinski, 2005; David and Hamilton, 2010; Buhler et al., 2019). Moreover, certain azoles like voriconazole and fluconazole can increase the risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias (Gueta et al., 2017; Berger et al., 2018; Kitaya et al., 2024). Another pivotal toxicity is endocrine disruption, most pronounced with ketoconazole, which potently inhibits steroidogenesis and may precipitate adrenal insufficiency and gynecomastia (Benitez and Carver, 2019). Additionally, azole drugs have significant drug-drug interactions, especially in immunocompromised patients who are often on multiple medications. These interactions can lead to increased toxicity or reduced efficacy of either the azole or the co-administered drugs (Patterson et al., 2016). Furthermore, the pharmacokinetics of azoles can vary among individuals due to factors such as genetic polymorphisms in drug-metabolizing enzymes, which complicate treatment regimens (Weiss et al., 2009; Lee et al., 2012).
3.2 Polyene drugs
Amphotericin B (AmB), discovered in 1956, remains the gold standard for systemic antifungal therapy because of its broad spectrum and low resistance rate (Sundriyal et al., 2006). Among polyenes, AmB, nystatin, and natamycin are the most widely utilized (Carolus et al., 2020; Carmo et al., 2023). AmB exerts its antifungal effect by binding to ergosterol, an essential component of the fungal cell membrane, thereby forming transmembrane pores that disrupt membrane integrity and induce intracellular damage (Carolus et al., 2020). Given its poor oral bioavailability, AmB is administered intravenously and often used in combination with other antifungal agents, such as flucytosine or fluconazole for the treatment of severe Cryptococcus and Candida infections (Boutin and Luong, 2024), or with echinocandins or azoles for aspergillosis and mucormycosis (Carmo et al., 2023). Nephrotoxicity is the principal limitation and can lead to renal failure, especially in vulnerable patients (Gursoy et al., 2021). The high intrinsic toxicity of AmB has prompted the development of lipid formulations aimed at reducing side effects while maintaining antifungal efficacy (Wingard et al., 2000), yet adverse effects and the need for renal monitoring still restrict use. Moreover, the emergence of resistant fungal strains further complicates the therapeutic landscape, as some species exhibit reduced susceptibility to polyenes (Young et al., 2003; Vandeputte et al., 2007, 2008; Purkait et al., 2012; Ponte-Sucre et al., 2017). The development of resistance mechanisms, including alterations in ergosterol biosynthesis, poses a significant challenge to the effective use of polyene antifungals (Vandeputte et al., 2008).
3.3 Echinocandins
Echinocandins comprise important antifungal agents, such as caspofungin, micafungin, and anidulafungin, which are approved for clinical use and exert their antifungal effects by inhibiting the synthesis of β-(1,3)-D-glucan in the fungal cell wall (Misiek and Hoffmeister, 2007; Szymanski et al., 2022). Given the high abundance of glucans in the fungal cell wall and their absence in mammalian cells, this mechanism of action confers strong antifungal efficacy with minimal host toxicity. Clinically, echinocandins serve as first-line therapy for candidiasis and are combined with other antifungals for aspergillosis (Mroczynska and Brillowska-Dabrowska, 2020). Echinocandins exhibit water solubility and are formulated as lyophilized powders that must be administered intravenously due to their low oral bioavailability and poor gastrointestinal absorption (Szymanski et al., 2022). Adverse events are less common than with older agents but can include edema, bronchospasm, dyspnea, and hypotension (Szymanski et al., 2022). However, the emergence of resistance to echinocandins poses a significant challenge in clinical practice. The primary mechanism of echinocandin resistance involves mutations in the FKS genes, which encode the catalytic subunit of β-(1,3)-D-glucan synthase, the target of echinocandins. These mutations occur in specific “hot spot” regions and reduce the enzyme’s sensitivity to the drug, leading to higher minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) (Wiederhold, 2016; Hori and Shibuya, 2018).
The historical development of fungal infection treatment has been a complex and lengthy process, involving drug research and development, advances in diagnostic technology, and continuous optimization of clinical practice. Early research on fungal diseases began in the late 19th century, including the discovery of histoplasmosis and other conditions. During this period, medical understanding of fungal diseases remained in its exploratory phase, lacking systematic treatment protocols (Espinel-Ingroff, 1996). In 1979, studies demonstrated that AmB combined with flucytosine, a drug which inhibits the synthesis of DNA, was more effective than monotherapy in treating cryptococcal meningitis (Bennett et al., 1979). In 1992, fluconazole proved superior to AmB in preventing recurrence of cryptococcal meningitis. In 2004, the treatment of systemic fungal infections involved the use of multiple antifungal agents, such as polyenes, imidazole, and triazoles (Wu et al., 2004). However, the treatment of fungal infections continues to face challenges, such as resistance to antifungal drugs, the complexity of drug development, and limitations in diagnostic technologies.
3.4 Natural products
Natural products have long been recognized for their therapeutic potential, and their application in antifungal therapy is gaining fresh interest due to the increasing incidence of drug-resistant fungal infections (Soares et al., 2013; Dong et al., 2023). These compounds, derived from various sources such as plants, fungi, and marine organisms, exhibit a wide range of bioactivity that can be harnessed for antifungal applications.
Essential oils are volatile blends dominated by mono- and sesquiterpenes that preserve food but are seldom used as antifungals (Bakkali et al., 2008). They permeabilize membranes, vacuolate cytoplasm, and disorganize hyphae, primarily acting fungistatically but causing lysis at high dose (Basak and Guha, 2018). Eugenol, a phenol that reduced ergosterol synthesis, and its derivatives can inhibit the growth of C. albicans and Candida parapsilosis with MIC ranging from 50 to 100 μg mL-1, and showed a similar binding pattern of fluconazole and posaconazole at the LDM binding site (Dutra et al., 2023). Additionally, the hydroalcoholic plant extract of fresh leaves of Aloe vera is effective in inhibiting the mycelial growth of multiple pathogenic fungi, such as Botrytis gladiolorum and Fusarium oxysporum (Rosca-Casian et al., 2007). Black pepper oil, a natural preservative with antioxidant, hepatoprotective and antifungal activities, can alter the membrane permeability in Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus ochraceus, Fusarium graminearum and Penicillium viridans, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. The composition of this oil is complex, rich in mono- and sesquiterpenes, as well as phenols, flavonoids, and proanthocyanidins, and the nature of the bioactive molecules involved in the antifungal action is not known (Zhang et al., 2021). Propolis, a resinous hive product abundant in polyphenolic flavonoids and caffeic acid derivatives, has emerged as a promising adjuvant in anti-cryptococcal therapy. Propolis from the stingless bee significantly reduces cell wall-associated melanin in Cryptococcus neoformans, thereby enhancing macrophage-mediated fungal clearance without detectable cytotoxicity (Mamoon et al., 2020). Moreover, Argüelles et al. showed that a 1:4 combination of propolis and carnosic acid exhibited a synergistic fungicidal effect on C. neoformans without causing detectable changes in cellular morphology. Furthermore, exposure of mature biofilms to various carnosic acid–propolis formulations diminished the metabolic activity of the sessile cells forming biofilms (Arguelles et al., 2021).
Recent research has identified numerous natural products with significant antifungal properties, which have shown efficacy against common fungal pathogens like Candida, Aspergillus, or Cryptococcus spp (Dong et al., 2023). The mechanisms of action of these natural antifungals often involve disrupting fungal cell membranes and inhibiting cell wall synthesis (Curto et al., 2021; Kowalczyk, 2024), making them valuable candidates for drug development. Studies have shown that potent antifungal natural products in the structural classes such as flavonoids, terpenoids, and alkaloids have significant efficacy against C. albicans and Aspergillus spp. Their mechanisms involve targeted disruption of fungal membrane integrity via ergosterol complexation, inhibition of β-glucan synthase, or interference with essential metabolic pathways like chitin biosynthesis (Sultan and Ali, 2011; Wijnants et al., 2022; Jayaweera et al., 2025).
The integration of natural products into antifungal therapy not only provides a sustainable alternative to synthetic drugs, but also opens the way for the discovery of novel compounds that can be used in combination therapies to combat drug-resistant infections effectively. Substantial evidence confirms synergistic interactions between clinical antifungals and natural products, including essential botanical oils (Mentha, Pelargonium, Allium, Origanum, and Thymus spp.) (Bhattacharya et al., 2021) and purified phytochemicals (berberine, curcumin, cinnamyl alcohol, eugenol, magnolol, allicin) (Herman and Herman, 2023). Berberine chloride, found in many plants and acting on several enzymatic activities, can enhance the fungistatic activity of fluconazole against fluconazole-resistant clinical isolates of C. albicans (Quan et al., 2006). Augostine et al. screened 800 natural-product pairs and identified 34 synergistic combinations containing eugenol, β-escin, curcumin, or berberine; three of these combinations inhibited growth of human and plant pathogens, including C. albicans, A. fumigatus, Zymoseptoria tritici and Botrytis cinerea, and overcame azole resistance and biofilms (Augostine and Avery, 2022). Moreover, although carnosic acid and propolis polyphenols alone display modest antifungal potency (Ota et al., 2001; Birtic et al., 2015), their combination can act synergistically against C. neoformans (Arguelles et al., 2021) and C. albicans (Arguelles et al., 2020).
However, the effectiveness of these traditional antifungal drugs in treating CNS infections is significantly hindered by their poor penetration of the BBB. The BBB is a protective structure that regulates the movement of particles into and out of the brain, making it difficult for many drugs to reach therapeutic concentrations in the CNS (Reguera-Gomez et al., 2023). Based on published physicochemical and pharmacokinetic data, Wirth et al. systematically summarized the ability of antifungal drugs to penetrate the CNS. Although AmB achieves low concentration in cerebrospinal fluid, it remains the most effective drug for treating fungal CNS infections (Wirth and Ishida, 2020). Studies have investigated whether there is a correlation between the MICs of AmB and treatment efficacy (Andes, 2006; Park et al., 2006). However, current evidence indicates that the relationship between AmB concentration in cerebrospinal fluid and the therapeutic outcome of CNS fungal infections is not obviously significant (Kethireddy and Andes, 2007). The concentrations of AmB in cerebrospinal fluid during meningitis progression in both animals and humans remain below 1% (Wirth and Ishida, 2020). This may be attributed to the presence of CNS lesions causing BBB disruption, thereby enhancing the permeability of antifungal agents (Pyrgos et al., 2010). Additionally, evidence suggests that fungal cell wall components such as Cryptococcus glucuronoxylomannan (GXM) can weaken the BBB by modulating the RhoA pathway in brain microvascular endothelial cells (Lee et al., 2023; Reguera-Gomez et al., 2023). Therefore, the combination of drugs targeting this pathway with traditional antifungal agents may enhance the efficacy of treating CNS infections.
4 The development strategies of antifungal agents and medical therapy
4.1 Discovery and validation of emerging targets
Traditional antifungal agents used for the treatment of systemic infections primarily target three key fungal structures: ergosterol synthesis (azoles), ergosterol directly (polyenes), or cell wall synthesis (echinocandins). Recent advances have substantially expanded our understanding of structural and functional components of fungal pathogens, clarifying how these pathogens establish infection (Odds et al., 2003; Perfect, 2017). Developing new antifungal agents and strategies is crucial, especially for CNS infections where the BBB limits drug penetration (Reguera-Gomez et al., 2023). Current research focuses on identifying new antifungal targets, combining antifungal drugs with complementary mechanisms of action, and developing advanced delivery systems, such as nanoparticles and liposomes, thereby enhancing drug bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy at fungal infection sites. This section reviews emerging antifungal targets and the mechanism-based compounds moving through preclinical development (Figure 1).
4.1.1 Calcineurin
The calcineurin signaling complex represents an established therapeutic target for novel antifungal development, given its validated regulatory functions in fungal growth, stress adaptation, and virulence expression across diverse pathogenic species (Rusnak and Mertz, 2000; Park et al., 2016; Juvvadi et al., 2017). Calcineurin constitutes a dimeric serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase complex, composed of a regulatory B subunit [calcineurin B (CnB)] and catalytic subunit [calcineurin A (CnA) (Rusnak and Mertz, 2000), activated by Ca²+-calmodulin signaling and exhibiting high structural and functional conservation across eukaryotic organisms. Calcineurin orchestrates distinct regulatory functions across biological systems: in mammalian T cells, it modulates transcription factors such as nuclear factor of activated T cells to control interleukin-2-mediated immune activation (Steinbach et al., 2007). Conversely, in pathogenic fungi, this phosphatase serves as a central node for stress response pathways governing growth, antifungal resistance, and virulence (Rusnak and Mertz, 2000; Steinbach et al., 2007; Park et al., 2016). Therapeutically, calcineurin is inhibited by immunosuppressants tacrolimus FK506 and cyclosporine A (CsA), which exhibit broad-spectrum activity against C. neoformans, Candida spp., and A. fumigatus (Odom et al., 1997b; Blankenship et al., 2003; Steinbach et al., 2006). However, their utility as antifungal agents is precluded due to concurrent host immunosuppression. Current strategy to circumvent this limitation is the development of FK506 analogues that selectively penetrate fungal membranes while inert in mammalian systems (Nambu et al., 2017). However, the translational potential of FK506 and CsA for antifungal drug development remains constrained by dose-limiting immunosuppressive effect. Analogues of FK506 by biosynthesis or pharmacological modification exhibited reduced immunosuppressive activity but maintained significant antifungal activity (Odom et al., 1997a; Beom et al., 2019; Gobeil et al., 2021; Hoy et al., 2022). Recent elucidation of the crystallographic structures of CnA and CnB subunits in complex with FK506 and its cognate binding protein FKBP12 in A. fumigatus, C. albicans, and C. neoformans provides a structural foundation for rational design of novel FK506 analogs with enhanced antifungal specificity (Juvvadi et al., 2019; Rivera et al., 2023).
4.1.2 Hsp90
Hsp90 represents an evolutionarily conserved heat shock protein that couples the free energy derived from ATP hydrolysis to facilitate the folding and conformational stabilization of conformationally labile client proteins, including kinases, transcription factors, and signal transduction regulators (Richter et al., 2010). The therapeutic appeal of targeting Hsp90 arises from its role as a central signaling hub that regulates growth, stress adaptation, antifungal resistance, and virulence across diverse fungal pathogens (Cowen and Lindquist, 2005; Shapiro et al., 2009; Singh et al., 2009; Taipale et al., 2010; Leach et al., 2012; Robbins et al., 2012; Lamoth et al., 2016).
Natural products geldanamycin and radicicol are inhibitors of Hsp90, replacing ATP and blocking the function of Hsp90 (DeBoer et al., 1970; Schulte et al., 1998). Hsp90 inhibitors potentiate fluconazole efficacy against C. albicans infection in a Galleria mellonella model (Cowen et al., 2009). However, the high conserved characteristic of Hsp90 results in toxicity when inhibited, thus limiting the utility of contemporary Hsp90 inhibitors in mammalian fungal infection models (Taipale et al., 2010). A recombinant 28kDa monoclonal antibody that binds to fungal Hsp90, Mycograb (efungumab [Mycograb; NeuTec Pharma/Novartis]) was developed. Both in vitro and animal studies revealed that Mycograb in combination with AmB has a synergistic effect on a variety of pathogenic Candida spp (Matthews et al., 2003). In addition, better clinical validation was shown in patients with invasive candidiasis who were given Mycograb antibody in combination with AmB (Pachl et al., 2006). Notably, marketing authorization for Mycograb was withheld by regulatory authorities in November 2006 owing to quality concerns. Subsequently, a modified variant designated Mycograb C28Y underwent development; however, this reformulated therapeutic formulation demonstrated reduced efficacy compared to the original antibody formulation (Bugli et al., 2013).
4.1.3 Mitochondria
Mitochondria serve as the primary ATP-generating organelles in eukaryotes, driving oxidative phosphorylation and tricarboxylic acid cycle to produce cellular ATP. Beyond energy metabolism, fungal mitochondria regulate amino acid synthesis, phospholipid biogenesis, virulence, and antifungal resistance through respiration-coupled processes (Chatre and Ricchetti, 2014; Chang and Doering, 2018; Malina et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020), thus it has emerged as an antifungal target.
Rosmarinic acid significantly directly inhibited C. albicans mitochondrial function, with MTT assay data indicating over 50% reduction in metabolic activity (Ivanov et al., 2022). Berberine accumulates in fungal mitochondria, impairing membrane potential and inhibiting Complex I activity. This compound also disrupts Mdr1p-mediated efflux in C. albicans, reversing multidrug resistance. In vivo studies confirm the efficacy of this compound by prolonging survival in murine models of disseminated Mdr1p-overexpressing candidiasis (Tong et al., 2021).
The arylamidine compound T-2307 demonstrates broad-spectrum fungicidal activity against Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus spp. in vitro and prevents disseminated murine infections (Nishikawa et al., 2017; Wiederhold et al., 2020; Gerlach et al., 2021). Notably, polyamine transporters are minimally expressed in mammalian cells such as rat hepatocytes (Nishikawa et al., 2010, 2016), and targeted inhibition of mitochondrial Complex III and IV through selective uptake of fungal polyamine transporters can lead to membrane potential collapse of fungal mitochondria (Shibata et al., 2012; Yamashita et al., 2019). The negligible effect on rat mitochondria highlights its therapeutic selectivity (Shibata et al., 2012). ATI-2307 is currently in advanced preclinical development (licensed to Appili Therapeutics in 2019) and has demonstrated a favorable safety profile in Phase I clinical trials.
Olorofim (F901318) is a first-in-class orotomide antifungal that selectively inhibits fungal dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), a mitochondrial enzyme critical for de novo pyrimidine synthesis, with a selectivity 2,000-fold greater than that of the human enzyme (Oliver et al., 2016). It effectively disrupts DNA/RNA synthesis and virulence in molds and dimorphic fungi but is inactive against yeasts like Candida and Cryptococcus (Buil et al., 2017). In murine models of invasive aspergillosis, Olorofim improved survival by inhibiting fungal growth (Oliver et al., 2016; du Pre et al., 2018). Olorofim is currently in the global Phase III clinical trial (OASIS study, NCT05101187), aiming to evaluate its efficacy and safety in patients with invasive aspergillosis.
4.1.4 Biofilms
Fungal biofilms, structured communities embedded in extracellular matrix, are emerging therapeutic targets. Their dense sterol-rich layers, persister cells, up-regulated efflux pumps, and drug-restricting polysaccharide-protein matrix enable immune evasion and multifactorial resistance (Kernien et al., 2017; Pierce et al., 2017; Silva et al., 2017). Innovative anti-biofilm strategies are exemplified by: (1) curcumin-sophorolipid nanocomplexes disrupting C. albicans biofilm structure through downregulation of hyphal regulators (SAP4, HWP1, HYR1) and resistance genes (ERG11) (Rajasekar et al., 2021); (2) archaeal-derived antimicrobial peptide VLL-28 damaging cell wall integrity (Roscetto et al., 2018); (3) rosmarinic acid suppressing exopolysaccharide production and biofilm maturation (Ivanov et al., 2022) and (4) photodynamic therapy eradicating C. auris biofilms via photosensitizer-activated reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Bapat and Nobile, 2021). These approaches target previously inaccessible resistance mechanisms, such as matrix disruption, morphogenetic interference, and physical ablation, while highlighting the urgent need for agents with both biofilm disruption and immunomodulatory effects to overcome therapeutic barriers.
Target-driven antifungal drug development is a promising strategy to address the growing burden of fungal infections and the rise of antifungal resistance. By focusing on specific molecular targets, this approach offers the potential for more precise, effective, and safer therapies. However, overcoming the existing challenges will require sustained investment, innovation, and collaboration across the scientific community.
4.2 Combination therapy
Multi-mechanism combination therapy addresses core limitations of conventional antifungals, particularly drug resistance and pharmacokinetic constraint, by harnessing synergistic interactions between agents targeting distinct pathogenic pathways. This approach, validated through quantitative frameworks like the fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI<0.5 defining synergy), builds upon antibacterial combination principles now adapted to medical mycology (Ganesan et al., 2004; Shaban et al., 2020; Carnero et al., 2025).
Cryptococcal infections, particularly cryptococcal meningitis, remain a significant global health challenge, especially among immunocompromised individuals. The limited antifungal drugs and the emergence of resistance have necessitated the development of multi-mechanism combination therapies to improve treatment outcomes. Combination therapy targets cryptococcal infections through multiple mechanisms: AmB: Disrupts fungal cell membranes by binding to ergosterol, leading to cell lysis. Flucytosine: Inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis by converting to 5-fluorouracil within fungal cells. Fluconazole: Inhibits ergosterol synthesis, weakening the fungal cell wall and enhancing the effects of other antifungals. This multi-mechanism approach not only improves fungal clearance but also reduces the likelihood of resistance development (Day et al., 2013).
The combination of AmB and flucytosine is considered the gold standard for treating cryptococcal meningitis. In clinical studies, this combination was effective against around 37% of isolates (Bandalizadeh et al., 2020). Another effective combination is AmB with fluconazole. Fluconazole inhibits ergosterol synthesis, complementing the membrane-disrupting action of AmB. This combination has shown synergistic effects in 31% of cases, making it a viable alternative, especially in regions where flucytosine is unavailable. Additionally, the combination of fluconazole plus flucytosine has demonstrated synergy in 12.5% of isolates, providing another therapeutic option (Bandalizadeh et al., 2020). The combination of fluconazole and terbinafine is also effective. Terbinafine inhibits squalene epoxidase and this combination has demonstrated significant correlations in minimum inhibitory concentrations for both species (Taha et al., 2024). Recent studies have demonstrated that One-week AmB combined with flucytosine, and two-week fluconazole combined with flucytosine regimens are effective as induction therapy for cryptococcal meningitis in resource-poor areas. Meanwhile, side effects (e.g., severe anemia) are more likely to occur with the two-week regimen than with the one-week AmB (Molloy et al., 2018). Additionally, single high-dose liposomal AmB combined with flucytosine and fluconazole has shown promise, with efficacy comparable to standard therapy while reducing adverse events (Jarvis et al., 2022).
Clinical drugs available for the treatment of candidiasis are confined to four mechanistic classes: polyenes, azoles, allylamines, and echinocandins. Compounds such as azoles and echinocandins inhibit essential C. albicans pathways, resulting in the rapid development of drug-resistant mutants; in contrast, AmB retains a lower incidence of resistance. Zhu et al. found that Artemisinin (ART), antimalarial active molecules, can act as a potentiator of AmB, effectively inhibiting C. albicans colonization and oral candidiasis (Zhu et al., 2021). ART upregulates ergosterol biosynthesis genes (ERG1, ERG3, ERG9, ERG11) and raises membrane ergosterol in C. albicans, thereby enhancing AmB binding and sensitivity (Zhu et al., 2021). Besifloxacin, an FDA-approved antibacterial, also shows antifungal activity. Combined with fluconazole, it reduced the MIC of fluconazole from 2 to 0.5 mg L-1 and, at 100 mg/kg/day, lowered renal fungal burden by 83% in a murine systemic candidiasis model (Chakraborty et al., 2025).
Panobinostat, an FDA-approved pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor, synergizes with fluconazole against azole-resistant C. albicans, reducing the MIC from 128 to 0.5–2 μg mL-1 and that of fluconazole from >512 to 0.25–0.5 μg mL-1. Panobinostat combined with fluconazole is synergistic against both planktonic C. albicans and its biofilms and markedly improves survival in Galleria mellonella infection model (Su et al., 2020). Chai et al. showed that quinoline-chalcone derivatives combined with fluconazole suppress azole-resistant C. albicans growth and biofilm formation, trigger ROS accumulation, compromise mitochondrial integrity, and deplete intracellular ATP (Chai et al., 2023).
Combination therapy represents a promising approach to overcoming the challenges posed by antifungal resistance and drug toxicity. By utilizing the synergistic effects of multiple agents, this strategy not only improves treatment efficacy but also reduces the risk of resistance and adverse effects. As fungal infections rise, combination therapy will become essential for better patient outcomes and for advancing antifungal strategies.
4.3 Biotech-driven antifungal drug development
Biotechnology-driven approaches are important for drug target discovery and identification and optimization of novel antifungal compounds with unique mechanisms of action. For example, the application of CRISPR-Cas9 technology has facilitated the exploration of fungal genetics, allowing researchers to create targeted mutations that can reveal potential drug targets and pathways involved in antifungal resistance (Hassane et al., 2025). Scientists have developed CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system for many filamentous fungi, including Trichoderma reesei, Neurospora crassa and Aspergillus nidulans (Matsu-Ura et al., 2015; Nodvig et al., 2015; Al Abdallah et al., 2017). Prior to CRISPR-Cas9, fungal genome editing relied on homologous recombination and ZFNs (Zinc Finger Nucleases), which were labor-intensive and inefficient, but CRISPR-Cas9 overcame these limitations, permitting simultaneous, high-efficiency multiplex gene editing (Arnau et al., 1991; Zhang et al., 2024). CRISPR-Cas9-mediated fungal mutagenesis, as exemplified by FKS1 editing in C. glabrata for echinocandin target validation, has been employed to identify resistance mechanisms (Hou et al., 2019). In addition, CRISPR-Cas9 has been used in Fusarium graminearum, the wheat scab pathogen, to inactivate mycotoxin biosynthetic genes, thereby attenuating virulence (Luo et al., 2023). Targeted genome editing can also attenuate fungal virulence, enabling the construction of avirulent strains (Song et al., 2019).
Moreover, nanotechnology-based formulations improve the solubility, delivery, and efficacy of both existing and new antifungal agents, addressing issues related to solubility and bioavailability and making optimized dosing feasible. Using an in vitro fungal-infected epithelial model, Lestner et al. characterized the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of different AmB formulations, indicating the importance of optimizing drug absorption for disease treatment (Lestner et al., 2010). Lipid nanocapsules (LNCs) have emerged as a multifunctional and efficient drug delivery platform, particularly for hydrophobic and challenging drugs like AmB. LNCs are prepared using solvent-free, low-energy methods such as the phase inversion temperature process, which is scalable and energy-efficient. This makes the production of AmB-loaded LNCs feasible for industrial applications (Aparicio-Blanco et al., 2019; Urimi et al., 2021). LNCs reconstituting AmB (Nano-LAmB) enhance cerebral spinal fluid penetration by 8-fold in cryptococcal meningitis models (Gazzoni et al., 2012; Alvarez-Uria et al., 2018).
Improvement and optimization of currently available antifungals also play a crucial role in the treatment of pathogenic fungi. AmB, a natural bacterial polyene, serves as the ultimate therapeutic option for systemic mycoses. Its potent fungicidal activity is counterbalanced by dose-limiting nephrotoxicity, confining its use to refractory infections. Maji et al. have elucidated the structural basis of the membrane activity of AmB using a modular synthetic platform guided by crystallographic, functional and in silico analyses. Rationalization of its ergosterol- and cholesterol-binding structural domains yielded an analog that selectively extracts fungal ergosterol while retaining mammalian cholesterol, thereby preserving glomerular integrity. This improvement is expected to enhance the efficacy and safety of treating life-threatening fungal diseases (Maji et al., 2023). In another recent study, Deng et al. utilized a phylogenetically-guided discovery strategy to target polyene macrolides containing an aminodeoxyglucose mycosamine and identified a promising antifungal candidate drug mandimycin, which exhibits potent, broad-spectrum fungicidal activity in vitro and in vivo against multidrug-resistant isolates (Deng et al., 2025). Rather than binding ergosterol, mandimycin disrupts membrane phospholipids and triggers ion efflux. Therefore, it remains effective against drug-resistant strains that target ergosterol, while being more soluble and less nephrotoxic (Deng et al., 2025).
Biotechnology has enabled the efficient production of antifungal peptides (AMPs). AMPs have emerged as promising candidates due to their broad-spectrum activity and low propensity for resistance development. Recent studies have highlighted the efficacy of antifungal peptides and lipopeptides, which exhibit potent activity against various fungal pathogens, including drug-resistant strains (Neubauer et al., 2020; Dos Reis et al., 2023; Helmy and Parang, 2023; Zhou et al., 2024). PAF102 peptide, designed for enhanced antifungal activity, has been successfully produced in Pichia pastoris using oleosin fusion technology. This method allows high yields of up to 180 mg L-1 of yeast culture, with the peptide accumulating in lipid droplets for easy extraction (Popa et al., 2019). Proteus mirabilis urease β subunit (PmUreβ) has demonstrated significant antifungal activity against Candida spp., reducing viability by over 50% at low concentrations, with potency varying by species and incubation temperature. PmUreβ further reduced C. albicans biofilm formation and its antifungal activity arises from disruption of cell-wall integrity without damaging the cell membrane, making it a potential alternative to conventional antifungals (Perin et al., 2025). The antifungal protein, naturally secreted by the filamentous ascomycete Aspergillus giganteus, exhibits potent activity against human and phytopathogenic fungi without affecting the viability of bacteria, yeast, plant and mammalian cells (Meyer, 2008).
Biotechnology is reshaping antifungal drug development by offering new tools to overcome the shortcomings of current therapies. Nanomaterials, genetic engineering, and the improvement of drug structures are already expanding treatment options. However, current biotechnology-driven approaches face multiple risks in clinical applications. Primary concerns regarding gene editing technologies include off-target effects, which may lead to genotoxicity and disruption of essential cellular processes; the largely unexplored long-term ecological implications of releasing genetically modified organisms; and the technical difficulty of achieving efficient and safe in vivo delivery of editing machinery to specific fungal cells (Krappmann, 2017). AMPs face limitations such as proteolytic degradation, unfavorable pharmacokinetics, and potential nephrotoxicity at higher doses. A critical safety concern is their propensity to induce hemolysis and cytotoxicity in host cells (Biswaro et al., 2018). Moreover, despite their initial high efficacy, the long-term use of AMPs may ultimately drive resistance development (Pimienta et al., 2022). For nanoparticle-based delivery systems, the intrinsic toxicity profiles of the carriers require thorough investigation (Biswaro et al., 2018). Therefore, further studies are needed to optimize the effectiveness, safety and scalability of these technologies.
5 Conclusion
Fungal infections by WHO-critical priority pathogens impose significant mortality burdens globally. While traditional antifungals possess well-defined mechanisms, their clinical application remains hampered by increasing drug resistance. Therefore, the development of new therapeutic approaches is particularly important. Beyond calcineurin, Hsp90, and mitochondrial pathways, fundamental research must uncover new targets to sustain antifungal drug discovery. Drug combinations offer possibilities for the treatment of fungal diseases, including combinations of classical antibiotics with other natural products such as ART. Meanwhile, biotechnology is accelerating antifungal innovation: CRISPR-Cas9 rapidly identifies essential genes related to pathogenicity and drug-resistance; LNCs enhance the delivery and uptake of drug; structure-guided redesign of existing agents lowers toxicity and delays resistance; and the discovery of natural antimicrobial peptides extend the selectivity of antifungal drugs. The application of currently available resources and the development of technology will be important in our fight against future fungal infections and increasing drug resistance.
Author contributions
DL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. RZ: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. XG: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Funds for this research were supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82302549 to XG), Chongqing Talent Program (CQYC20220303710 to RZ), Young Doctoral Talent Incubation Program of Xinqiao Hospital of Army Medical University (2023YQB017 to XG, 2024YQB016 to DL) and the Municipal Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTB2024NSCQ-MSX1230 to XG).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al Abdallah, Q., Ge, W., and Fortwendel, J. R. (2017). A simple and universal system for gene manipulation in aspergillus fumigatus: in vitro-assembled cas9-guide RNA ribonucleoproteins coupled with microhomology repair templates. mSphere 2, e00446-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00446-17
Alvarez-Uria, G., Midde, M., Battula, J., and Pujari, H. N. B. (2018). Safety and tolerability of intrathecal liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) for cryptococcal meningitis: a retrospective study in HIV-infected patients. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 5, 77–81. doi: 10.1177/2049936118782846
Andes, D. (2006). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antifungals. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 20, 679–697. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2006.06.007
Aparicio-Blanco, J., Sebastian, V., Rodriguez-Amaro, M., Garcia-Diaz, H. C., and Torres-Suarez, A. I. (2019). Size-tailored design of highly monodisperse lipid nanocapsules for drug delivery. J. BioMed. Nanotechnol 15, 1149–1161. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2019.2765
Arguelles, A., Sanchez-Fresneda, R., Guirao-Abad, J. P., Belda, C., Lozano, J. A., Solano, F., et al. (2020). Novel Bi-Factorial Strategy against Candida albicans Viability Using Carnosic Acid and Propolis: Synergistic Antifungal Action. Microorganisms 8, 749. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8050749
Arguelles, A., Sanchez-Fresneda, R., Martinez-Marmol, E., Lozano, J. A., Solano, F., and Arguelles, J. C. (2021). A Specific Mixture of Propolis and Carnosic Acid Triggers a Strong Fungicidal Action against Cryptococcus neoformans. Antibiotics (Basel) 10, 1395. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111395
Arnau, J., Jepsen, L. P., and Stroman, P. (1991). Integrative transformation by homologous recombination in the zygomycete Mucor circinelloides. Mol. Gen. Genet. 225, 193–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00269847
Ashley, E. D. (2019). Antifungal drugs: special problems treating central nervous system infections. J. Fungi (Basel) 5, 97. doi: 10.3390/jof5040097
Augostine, C. R. and Avery, S. V. (2022). Discovery of natural products with antifungal potential through combinatorial synergy. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.866840
Bakkali, F., Averbeck, S., Averbeck, D., and Idaomar, M. (2008). Biological effects of essential oils–a review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 46, 446–475. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.09.106
Bandalizadeh, Z., Shokohi, T., Badali, H., Abastabar, M., Babamahmoudi, F., Davoodi, L., et al. (2020). Molecular epidemiology and antifungal susceptibility profiles of clinical Cryptococcus neoformans/Cryptococcus gattii species complex. J. Med. Microbiol. 69, 72–81. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001101
Bapat, P. S. and Nobile, C. J. (2021). Photodynamic therapy is effective against candida auris biofilms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.713092
Barros, N., Rosenblatt, R. E., Phipps, M. M., Fomin, V., and Mansour, M. K. (2023). Invasive fungal infections in liver diseases. Hepatol. Commun. 7, e0216. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000216
Basak, S. and Guha, P. (2018). A review on antifungal activity and mode of action of essential oils and their delivery as nano-sized oil droplets in food system. J. Food Sci. Technol. 55, 4701–4710. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3394-5
Benitez, L. L. and Carver, P. L. (2019). Adverse effects associated with long-term administration of azole antifungal agents. Drugs 79, 833–853. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01127-8
Bennett, J. E., Dismukes, W. E., Duma, R. J., Medoff, G., Sande, M. A., Gallis, H., et al. (1979). A comparison of amphotericin B alone and combined with flucytosine in the treatment of cryptoccal meningitis. N Engl. J. Med. 301, 126–131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907193010303
Beom, J. Y., Jung, J. A., Lee, K. T., Hwangbo, A., Song, M. C., Lee, Y., et al. (2019). Biosynthesis of nonimmunosuppressive FK506 analogues with antifungal activity. J. Nat. Prod 82, 2078–2086. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00144
Berger, F. A., Monadian, N., de Groot, N. M. S., Santbergen, B., van der Sijs, H., Becker, M. L., et al. (2018). QTc prolongation during ciprofloxacin and fluconazole combination therapy: prevalence and associated risk factors. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 84, 369–378. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13457
Berman, J. and Krysan, D. J. (2020). Drug resistance and tolerance in fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 18, 319–331. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0322-2
Bhattacharya, R., Rolta, R., Dev, K., and Sourirajan, A. (2021). Synergistic potential of essential oils with antibiotics to combat fungal pathogens: Present status and future perspectives. Phytother. Res. 35, 6089–6100. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7218
Birtic, S., Dussort, P., Pierre, F. X., Bily, A. C., and Roller, M. (2015). Carnosic acid. Phytochemistry 115, 9–19. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.12.026
Biswaro, L. S., da Costa Sousa, M. G., Rezende, T. M. B., Dias, S. C., and Franco, O. L. (2018). Antimicrobial peptides and nanotechnology, recent advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00855
Blankenship, J. R., Wormley, F. L., Boyce, M. K., Schell, W. A., Filler, S. G., Perfect, J. R., et al. (2003). Calcineurin is essential for Candida albicans survival in serum and virulence. Eukaryot Cell 2, 422–430. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.3.422-430.2003
Boutin, C. A. and Luong, M. L. (2024). Update on therapeutic approaches for invasive fungal infections in adults. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 11, 20499361231224980. doi: 10.1177/20499361231224980
Brown, G. D., Denning, D. W., Gow, N. A., Levitz, S. M., Netea, M. G., and White, T. C. (2012). Hidden killers: human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 4, 165rv113. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004404
Bugli, F., Cacaci, M., Martini, C., Torelli, R., Posteraro, B., Sanguinetti, M., et al. (2013). Human monoclonal antibody-based therapy in the treatment of invasive candidiasis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 403121. doi: 10.1155/2013/403121
Buhler, T., Medinger, M., Bouitbir, J., Krahenbuhl, S., and Leuppi-Taegtmeyer, A. (2019). Hepatotoxicity due to azole antimycotic agents in a HLA B*35:02-positive patient. Front. Pharmacol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00645
Buil, J. B., Rijs, A., Meis, J. F., Birch, M., Law, D., Melchers, W. J. G., et al. (2017). In vitro activity of the novel antifungal compound F901318 against difficult-to-treat Aspergillus isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 72, 2548–2552. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx177
Burki, T. (2023). WHO publish fungal priority pathogens list. Lancet Microbe 4, e74. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00003-4
Carmo, A., Rocha, M., Pereirinha, P., Tome, R., and Costa, E. (2023). Antifungals: from pharmacokinetics to clinical practice. Antibiotics (Basel) 12, 884. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12050884
Carnero, L. G., Li, X., de Castro, P. A., Pinzan, C. F., Campanella, J. E. M., Malavazi, I., et al. (2025). Colistin enhances caspofungin antifungal efficacy against Aspergillus fumigatus by modulating calcium homeostasis and stress responses. Nat. Commun. 16, 5967. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60991-z
Carolus, H., Pierson, S., Lagrou, K., and Van Dijck, P. (2020). Amphotericin B and other polyenes-discovery, clinical use, mode of action and drug resistance. J. Fungi (Basel) 6, 321. doi: 10.3390/jof6040321
Chai, N., Sun, A., Zhu, X., Li, Y., Wang, R., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Antifungal evaluation of quinoline-chalcone derivatives combined with FLC against drug-resistant Candida albicans. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 86, 129242. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129242
Chakraborty, S., Pawaskar, A., Metkari, S., Madan, T., and Idicula-Thomas, S. (2025). Identification and evaluation of besifloxacin as repurposed antifungal drug in combination with fluconazole against candida albicans. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 105, e70138. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.70138
Chang, A. L. and Doering, T. L. (2018). Maintenance of mitochondrial morphology in cryptococcus neoformans is critical for stress resistance and virulence. mBio 9, e01375-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01375-18
Chanyachailert, P., Leeyaphan, C., and Bunyaratavej, S. (2023). Cutaneous fungal infections caused by dermatophytes and non-dermatophytes: an updated comprehensive review of epidemiology, clinical presentations, and diagnostic testing. J. Fungi (Basel) 9, 669. doi: 10.3390/jof9060669
Chatre, L. and Ricchetti, M. (2014). Are mitochondria the Achilles’ heel of the Kingdom Fungi? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 20, 49–54. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.05.001
Chen, J., Shao, J., Dai, M., Fang, W., and Yang, Y. L. (2023). Adaptive immunology of Cryptococcus neoformans infections-an update. Front. Immunol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1174967
Coulibaly, O., L’Ollivier, C., Piarroux, R., and Ranque, S. (2018). Epidemiology of human dermatophytoses in Africa. Med. Mycol 56, 145–161. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myx048
Cowen, L. E. and Lindquist, S. (2005). Hsp90 potentiates the rapid evolution of new traits: drug resistance in diverse fungi. Science 309, 2185–2189. doi: 10.1126/science.1118370
Cowen, L. E., Singh, S. D., Kohler, J. R., Collins, C., Zaas, A. K., Schell, W. A., et al. (2009). Harnessing Hsp90 function as a powerful, broadly effective therapeutic strategy for fungal infectious disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 2818–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813394106
Curto, M. A., Butassi, E., Ribas, J. C., Svetaz, L. A., and Cortes, J. C. G. (2021). Natural products targeting the synthesis of beta(1,3)-D-glucan and chitin of the fungal cell wall. Existing drugs and recent findings. Phytomedicine 88, 153556. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153556
David, S. and Hamilton, J. P. (2010). Drug-induced liver injury. US Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Rev. 6, 73–80.
Day, J. N., Chau, T. T. H., Wolbers, M., Mai, P. P., Dung, N. T., Mai, N. H., et al. (2013). Combination antifungal therapy for cryptococcal meningitis. N Engl. J. Med. 368, 1291–1302. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110404
DeBoer, C., Meulman, P. A., Wnuk, R. J., and Peterson, D. H. (1970). Geldanamycin, a new antibiotic. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 23, 442–447. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.442
Deng, Q., Li, Y., He, W., Chen, T., Liu, N., Ma, L., et al. (2025). A polyene macrolide targeting phospholipids in the fungal cell membrane. Nature 640, 743–751. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08678-9
Denning, D. W. (2024). Global incidence and mortality of severe fungal disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 24, e428–e438. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00692-8
Dobes, J., Ben-Nun, O., Binyamin, A., Stoler-Barak, L., Oftedal, B. E., Goldfarb, Y., et al. (2022). Extrathymic expression of Aire controls the induction of effective T(H)17 cell-mediated immune response to Candida albicans. Nat. Immunol. 23, 1098–1108. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01247-6
Dong, F. R., Gao, L., Wang, L., Jiang, Y. Y., and Jin, Y. S. (2023). Natural products as antifungal agents against invasive fungi. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 23, 1859–1917. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666230417105227
Donlin, M. J. and Meyers, M. J. (2022). Repurposing and optimization of drugs for discovery of novel antifungals. Drug Discov. Today 27, 2008–2014. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.04.021
Dos Reis, T. F., de Castro, P. A., Bastos, R. W., Pinzan, C. F., Souza, P. F. N., Ackloo, S., et al. (2023). A host defense peptide mimetic, brilacidin, potentiates caspofungin antifungal activity against human pathogenic fungi. Nat. Commun. 14, 2052. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37573-y
du Pre, S., Beckmann, N., Almeida, M. C., Sibley, G. E. M., Law, D., Brand, A. C., et al. (2018). Effect of the novel antifungal drug F901318 (Olorofim) on growth and viability of aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, e00231-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00231-18
Dutra, J. A. P., Maximino, S. C., Goncalves, R. C. R., Morais, P. A. B., de Lima Silva, W. C., Rodrigues, R. P., et al. (2023). Anti-Candida, docking studies, and in vitro metabolism-mediated cytotoxicity evaluation of Eugenol derivatives. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 101, 350–363. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14131
Espinel-Ingroff, A. (1996). History of medical mycology in the United States. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 9, 235–272. doi: 10.1128/CMR.9.2.235
Fisher, M. C., Alastruey-Izquierdo, A., Berman, J., Bicanic, T., Bignell, E. M., Bowyer, P., et al. (2022). Tackling the emerging threat of antifungal resistance to human health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 557–571. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00720-1
Ganesan, L. T., Manavathu, E. K., Cutright, J. L., Alangaden, G. J., and Chandrasekar, P. H. (2004). In-vitro activity of nikkomycin Z alone and in combination with polyenes, triazoles or echinocandins against Aspergillus fumigatus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 10, 961–966. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.00996.x
Gazzoni, A. F., Capilla, J., Mayayo, E., and Guarro, J. (2012). Efficacy of intrathecal administration of liposomal amphotericin B combined with voriconazole in a murine model of cryptococcal meningitis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 39, 223–227. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.10.014
Gerlach, E. S., Altamirano, S., Yoder, J. M., Luggya, T. S., Akampurira, A., Meya, D. B., et al. (2021). ATI-2307 exhibits equivalent antifungal activity in cryptococcus neoformans clinical isolates with high and low fluconazole IC(50). Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.695240
Gobeil, S. M., Bobay, B. G., Juvvadi, P. R., Cole, D. C., Heitman, J., Steinbach, W. J., et al. (2021). Leveraging fungal and human calcineurin-inhibitor structures, biophysical data, and dynamics to design selective and nonimmunosuppressive FK506 analogs. mBio 12, e0300021. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03000-21
Gregory, M. H., Spec, A., Stwalley, D., Gremida, A., Mejia-Chew, C., Nickel, K. B., et al. (2023). Corticosteroids increase the risk of invasive fungal infections more than tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Crohns Colitis 360 5, otad010. doi: 10.1093/crocol/otad010
Gueta, I., Loebstein, R., Markovits, N., Kamari, Y., Halkin, H., Livni, G., et al. (2017). Voriconazole-induced QT prolongation among hemato-oncologic patients: clinical characteristics and risk factors. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 73, 1181–1185. doi: 10.1007/s00228-017-2284-5
Gursoy, V., Ozkalemkas, F., Ozkocaman, V., Serenli Yegen, Z., Ethem Pinar, I., Ener, B., et al. (2021). Conventional amphotericin B associated nephrotoxicity in patients with hematologic Malignancies. Cureus 13, e16445. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16445
Harris, E. (2023). Patients with COVID-19 and fungal infections had high mortality rates. JAMA 330, 210–211. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.11957
Hassane, A. M. A., Obiedallah, M., Karimi, J., Khattab, S. M. R., Hussein, H. R., Abo-Dahab, Y., et al. (2025). Unravelling fungal genome editing revolution: pathological and biotechnological application aspects. Arch. Microbiol. 207, 150. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04360-w
Havlickova, B., Czaika, V. A., and Friedrich, M. (2008). Epidemiological trends in skin mycoses worldwide. Mycoses 51 Suppl 4, 2–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01606.x
Helmy, N. M. and Parang, K. (2023). Cyclic peptides with antifungal properties derived from bacteria, fungi, plants, and synthetic sources. Pharm. (Basel) 16, 892. doi: 10.3390/ph16060892
Herman, A. and Herman, A. P. (2023). Herbal products and their active constituents for diabetic wound healing-preclinical and clinical studies: A systematic review. Pharmaceutics 15, 281. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010281
Hlaing, K. M., Monday, L. M., Nucci, M., Nouer, S. A., and Revankar, S. G. (2023). Invasive fungal infections associated with COVID-19. J. Fungi (Basel) 9, 667. doi: 10.3390/jof9060667
Hoenigl, M., Arastehfar, A., Arendrup, M. C., Bruggemann, R., Carvalho, A., Chiller, T., et al. (2024). Novel antifungals and treatment approaches to tackle resistance and improve outcomes of invasive fungal disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 37, e0007423. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00074-23
Hori, Y. and Shibuya, K. (2018). Role of FKS gene in the susceptibility of pathogenic fungi to echinocandins. Med. Mycol J. 59, E31–E40. doi: 10.3314/mmj.18.004
Horton, M. V., Holt, A. M., and Nett, J. E. (2023). Mechanisms of pathogenicity for the emerging fungus Candida auris. PloS Pathog. 19, e1011843. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011843
Hou, X., Healey, K. R., Shor, E., Kordalewska, M., Ortigosa, C. J., Paderu, P., et al. (2019). Novel FKS1 and FKS2 modifications in a high-level echinocandin resistant clinical isolate of Candida glabrata. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 8, 1619–1625. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1684209
Hoy, M. J., Park, E., Lee, H., Lim, W. Y., Cole, D. C., DeBouver, N. D., et al. (2022). Structure-guided synthesis of FK506 and FK520 analogs with increased selectivity exhibit in vivo therapeutic efficacy against cryptococcus. mBio 13, e0104922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01049-22
Ikuta, K. S., Mestrovic, T., and Naghavi, M. (2024). Global incidence and mortality of severe fungal disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 24, e268. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00102-6
Iliev, I. D., Brown, G. D., Bacher, P., Gaffen, S. L., Heitman, J., Klein, B. S., et al. (2024). Focus on fungi. Cell 187, 5121–5127. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.016
Ivanov, M., Kostić, M., Stojković, D., and Soković, M. (2022). Rosmarinic acid–Modes of antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of a common plant polyphenol. South Afr. J. Bot. 146, 521–527. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2021.11.050
Janniger, E. J. and Kapila, R. (2021). Public health issues with Candida auris in COVID-19 patients. World Med. Health Policy 13, 766–772. doi: 10.1002/wmh3.472
Jarvis, J. N., Lawrence, D. S., Meya, D. B., Kagimu, E., Kasibante, J., Mpoza, E., et al. (2022). Single-dose liposomal amphotericin B treatment for cryptococcal meningitis. N Engl. J. Med. 386, 1109–1120. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2111904
Jayaweera, S. L. D., Van, T. T. H., and Dias, D. A. (2025). Antifungal natural products originating from endophytic and rhizospheric microbes isolated from coastal vegetation. J. Xenobiot 15, 32. doi: 10.3390/jox15010032
Juvvadi, P. R., Fox, D., 3rd, Bobay, B. G., Hoy, M. J., Gobeil, S. M. C., Venters, R. A., et al. (2019). Harnessing calcineurin-FK506-FKBP12 crystal structures from invasive fungal pathogens to develop antifungal agents. Nat. Commun. 10, 4275. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12199-1
Juvvadi, P. R., Lee, S. C., Heitman, J., and Steinbach, W. J. (2017). Calcineurin in fungal virulence and drug resistance: Prospects for harnessing targeted inhibition of calcineurin for an antifungal therapeutic approach. Virulence 8, 186–197. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1201250
Kaur, J. and Nobile, C. J. (2023). Antifungal drug-resistance mechanisms in Candida biofilms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 71, 102237. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2022.102237
Kernien, J. F., Snarr, B. D., Sheppard, D. C., and Nett, J. E. (2017). The interface between fungal biofilms and innate immunity. Front. Immunol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01968
Kethireddy, S. and Andes, D. (2007). CNS pharmacokinetics of antifungal agents. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 3, 573–581. doi: 10.1517/17425225.3.4.573
Kim, J. H., Cheng, L. W., and Land, K. M. (2022). Advances in antifungal development: discovery of new drugs and drug repurposing. Pharm. (Basel) 15, 787. doi: 10.3390/ph15070787
Kitaya, S., Nakano, M., Katori, Y., Yasuda, S., and Kanamori, H. (2024). QTc interval prolongation as an adverse event of azole antifungal drugs: case report and literature review. Microorganisms 12, 1619. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081619
Kowalczyk, A. (2024). Essential Oils against Candida auris-A Promising Approach for Antifungal Activity. Antibiotics (Basel) 13, 568. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060568
Krappmann, S. (2017). CRISPR-Cas9, the new kid on the block of fungal molecular biology. Med. Mycol 55, 16–23. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myw097
Lamoth, F., Chung, S. J., Damonti, L., and Alexander, B. D. (2017). Changing epidemiology of invasive mold infections in patients receiving azole prophylaxis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 64, 1619–1621. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix130
Lamoth, F., Juvvadi, P. R., and Steinbach, W. J. (2016). Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90): A novel antifungal target against Aspergillus fumigatus. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 42, 310–321. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2014.947239
Lass-Florl, C. (2011). Triazole antifungal agents in invasive fungal infections: a comparative review. Drugs 71, 2405–2419. doi: 10.2165/11596540-000000000-00000
Leach, M. D., Budge, S., Walker, L., Munro, C., Cowen, L. E., and Brown, A. J. (2012). Hsp90 orchestrates transcriptional regulation by Hsf1 and cell wall remodelling by MAPK signalling during thermal adaptation in a pathogenic yeast. PloS Pathog. 8, e1003069. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003069
Lee, H. H., Carmichael, D. J., Ribeiro, V., Parisi, D. N., Munzen, M. E., Charles-Nino, C. L., et al. (2023). Glucuronoxylomannan intranasal challenge prior to Cryptococcus neoformans pulmonary infection enhances cerebral cryptococcosis in rodents. PloS Pathog. 19, e1010941. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010941
Lee, S., Kim, B. H., Nam, W. S., Yoon, S. H., Cho, J. Y., Shin, S. G., et al. (2012). Effect of CYP2C19 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of voriconazole after single and multiple doses in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 52, 195–203. doi: 10.1177/0091270010395510
Lestner, J. M., Howard, S. J., Goodwin, J., Gregson, L., Majithiya, J., Walsh, T. J., et al. (2010). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of amphotericin B deoxycholate, liposomal amphotericin B, and amphotericin B lipid complex in an in vitro model of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 3432–3441. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01586-09
Lewis, R. E. (2011). Current concepts in antifungal pharmacology. Mayo Clin. Proc. 86, 805–817. doi: 10.4065/mcp.2011.0247
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, H., Wei, X., Chen, P., et al. (2020). Mitochondrial dysfunctions trigger the calcium signaling-dependent fungal multidrug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 1711–1721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911560116
Lino, R., Guimaraes, A. R., Sousa, E., Azevedo, M., and Santos, L. (2024). Emerging fungal infections of the central nervous system in the past decade: A literature review. Infect. Dis. Rep. 16, 952–976. doi: 10.3390/idr16050076
Lockhart, S. R., Chowdhary, A., and Gold, J. A. W. (2023). The rapid emergence of antifungal-resistant human-pathogenic fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 818–832. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00960-9
Luo, K., Guo, J., He, D., Li, G., and Ouellet, T. (2023). Deoxynivalenol accumulation and detoxification in cereals and its potential role in wheat-Fusarium graminearum interactions. aBIOTECH 4, 155–171. doi: 10.1007/s42994-023-00096-7
Maertens, J. A. (2004). History of the development of azole derivatives. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 10 Suppl 1, 1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1470-9465.2004.00841.x
Maji, A., Soutar, C. P., Zhang, J., Lewandowska, A., Uno, B. E., Yan, S., et al. (2023). Tuning sterol extraction kinetics yields a renal-sparing polyene antifungal. Nature 623, 1079–1085. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06710-4
Malina, C., Larsson, C., and Nielsen, J. (2018). Yeast mitochondria: an overview of mitochondrial biology and the potential of mitochondrial systems biology. FEMS Yeast Res. 18, 10.1093. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foy040
Mamoon, K., Thammasit, P., Iadnut, A., Kitidee, K., Anukool, U., Tragoolpua, Y., et al. (2020). Unveiling the properties of thai stingless bee propolis via diminishing cell wall-associated cryptococcal melanin and enhancing the fungicidal activity of macrophages. Antibiotics (Basel) 9, 420. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9070420
Matsu-Ura, T., Baek, M., Kwon, J., and Hong, C. (2015). Efficient gene editing in Neurospora crassa with CRISPR technology. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2, 4. doi: 10.1186/s40694-015-0015-1
Matthews, R. C., Rigg, G., Hodgetts, S., Carter, T., Chapman, C., Gregory, C., et al. (2003). Preclinical assessment of the efficacy of mycograb, a human recombinant antibody against fungal HSP90. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 2208–2216. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2208-2216.2003
Meyer, V. (2008). A small protein that fights fungi: AFP as a new promising antifungal agent of biotechnological value. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 78, 17–28. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1291-3
Misiek, M. and Hoffmeister, D. (2007). Fungal genetics, genomics, and secondary metabolites in pharmaceutical sciences. Planta Med. 73, 103–115. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-967104
Molloy, S. F., Kanyama, C., Heyderman, R. S., Loyse, A., Kouanfack, C., Chanda, D., et al. (2018). Antifungal combinations for treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in africa. N Engl. J. Med. 378, 1004–1017. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1710922
Mroczynska, M. and Brillowska-Dabrowska, A. (2020). Review on current status of echinocandins use. Antibiotics (Basel) 9, 227. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9050227
Nambu, M., Covel, J. A., Kapoor, M., Li, X., Moloney, M. K., Numa, M. M., et al. (2017). A calcineurin antifungal strategy with analogs of FK506. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 27, 2465–2471. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.04.004
Nau, R., Sorgel, F., and Eiffert, H. (2010). Penetration of drugs through the blood-cerebrospinal fluid/blood-brain barrier for treatment of central nervous system infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 23, 858–883. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00007-10
Neofytos, D., Horn, D., Anaissie, E., Steinbach, W., Olyaei, A., Fishman, J., et al. (2009). Epidemiology and outcome of invasive fungal infection in adult hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: analysis of Multicenter Prospective Antifungal Therapy (PATH) Alliance registry. Clin. Infect. Dis. 48, 265–273. doi: 10.1086/595846
Neubauer, D., Jaskiewicz, M., Bauer, M., Golacki, K., and Kamysz, W. (2020). Ultrashort cationic lipopeptides-effect of N-terminal amino acid and fatty acid type on antimicrobial activity and hemolysis. Molecules 25, 257. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020257
Nishikawa, H., Fukuda, Y., Mitsuyama, J., Tashiro, M., Tanaka, A., Takazono, T., et al. (2017). In vitro and in vivo antifungal activities of T-2307, a novel arylamidine, against Cryptococcus gattii: an emerging fungal pathogen. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 72, 1709–1713. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx020
Nishikawa, H., Sakagami, T., Yamada, E., Fukuda, Y., Hayakawa, H., Nomura, N., et al. (2016). T-2307, a novel arylamidine, is transported into Candida albicans by a high-affinity spermine and spermidine carrier regulated by Agp2. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 71, 1845–1855. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw095
Nishikawa, H., Yamada, E., Shibata, T., Uchihashi, S., Fan, H., Hayakawa, H., et al. (2010). Uptake of T-2307, a novel arylamidine, in Candida albicans. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65, 1681–1687. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq177
Nodvig, C. S., Nielsen, J. B., Kogle, M. E., and Mortensen, U. H. (2015). A CRISPR-cas9 system for genetic engineering of filamentous fungi. PloS One 10, e0133085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133085
Oberoi, J. K., Sheoran, L., Sagar, T., and Saxena, S. (2023). Invasive fungal infections in hemato-oncology. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 44, 100353. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmmb.2023.01.011
Odds, F. C., Brown, A. J., and Gow, N. A. (2003). Antifungal agents: mechanisms of action. Trends Microbiol. 11, 272–279. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(03)00117-3
Odom, A., Del Poeta, M., Perfect, J., and Heitman, J. (1997a). The immunosuppressant FK506 and its nonimmunosuppressive analog L-685,818 are toxic to Cryptococcus neoformans by inhibition of a common target protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41, 156–161. doi: 10.1128/AAC.41.1.156
Odom, A., Muir, S., Lim, E., Toffaletti, D. L., Perfect, J., and Heitman, J. (1997b). Calcineurin is required for virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans. EMBO J. 16, 2576–2589. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.10.2576
Oliver, J. D., Sibley, G. E. M., Beckmann, N., Dobb, K. S., Slater, M. J., McEntee, L., et al. (2016). F901318 represents a novel class of antifungal drug that inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 12809–12814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608304113
Ota, C., Unterkircher, C., Fantinato, V., and Shimizu, M. T. (2001). Antifungal activity of propolis on different species of Candida. Mycoses 44, 375–378. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0507.2001.00671.x
Pachl, J., Svoboda, P., Jacobs, F., Vandewoude, K., van der Hoven, B., Spronk, P., et al. (2006). A randomized, blinded, multicenter trial of lipid-associated amphotericin B alone versus in combination with an antibody-based inhibitor of heat shock protein 90 in patients with invasive candidiasis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 42, 1404–1413. doi: 10.1086/503428
Pagano, L., Busca, A., Candoni, A., Cattaneo, C., Cesaro, S., Fanci, R., et al. (2017). Risk stratification for invasive fungal infections in patients with hematological Malignancies: SEIFEM recommendations. Blood Rev. 31, 17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2016.09.002
Park, B. J., Arthington-Skaggs, B. A., Hajjeh, R. A., Iqbal, N., Ciblak, M. A., Lee-Yang, W., et al. (2006). Evaluation of amphotericin B interpretive breakpoints for Candida bloodstream isolates by correlation with therapeutic outcome. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 1287–1292. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1287-1292.2006
Park, H. S., Chow, E. W., Fu, C., Soderblom, E. J., Moseley, M. A., Heitman, J., et al. (2016). Calcineurin targets involved in stress survival and fungal virulence. PloS Pathog. 12, e1005873. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005873
Patterson, T. F. (2006). Treatment of invasive aspergillosis: Polyenes, echinocandins, or azoles? Med. Mycol 44, S357–S362. doi: 10.1080/13693780600826715
Patterson, T. F., Thompson, G. R., Denning, D. W., Fishman, J. A., Hadley, S., Herbrecht, R., et al. (2016). Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the infectious diseases society of america. Clin. Infect. Dis. 63, e1–e60. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw326
Perfect, J. R. (2017). The antifungal pipeline: a reality check. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 16, 603–616. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.46
Perin, A. P. A., Reuwsaat, J. C. V., Motta, H., Lopes, F. C., Grahl, M. V. C., Tavanti, A. G., et al. (2025). A cell wall-targeting urease-derived peptide as a potential antifungal agent against Candida species. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 8, 100399. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2025.100399
Pierce, C. G., Vila, T., Romo, J. A., Montelongo-Jauregui, D., Wall, G., Ramasubramanian, A., et al. (2017). The candida albicans biofilm matrix: composition, structure and function. J. Fungi (Basel) 3, 14. doi: 10.3390/jof3010014
Pimienta, D. A., Cruz Mosquera, F. E., Palacios Velasco, I., Giraldo Rodas, M., Onate-Garzon, J., and Liscano, Y. (2022). Specific Focus on Antifungal Peptides against Azole Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. J. Fungi (Basel) 9, 42. doi: 10.3390/jof9010042
Ponte-Sucre, A., Gamarro, F., Dujardin, J. C., Barrett, M. P., Lopez-Velez, R., Garcia-Hernandez, R., et al. (2017). Drug resistance and treatment failure in leishmaniasis: A 21st century challenge. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 11, e0006052. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006052
Popa, C., Shi, X., Ruiz, T., Ferrer, P., and Coca, M. (2019). Biotechnological production of the cell penetrating antifungal PAF102 peptide in pichia pastoris. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01472
Proctor, D. M., Sansom, S. E., Deming, C., Conlan, S., Blaustein, R. A., Atkins, T. K., et al. (2025). Clonal Candida auris and ESKAPE pathogens on the skin of residents of nursing homes. Nature 639, 1016–1023. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08608-9
Purkait, B., Kumar, A., Nandi, N., Sardar, A. H., Das, S., Kumar, S., et al. (2012). Mechanism of amphotericin B resistance in clinical isolates of Leishmania donovani. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56, 1031–1041. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00030-11
Pyrgos, V., Mickiene, D., Sein, T., Cotton, M., Fransesconi, A., Mizrahi, I., et al. (2010). Effects of immunomodulatory and organism-associated molecules on the permeability of an in vitro blood-brain barrier model to amphotericin B and fluconazole. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 1305–1310. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01263-09
Pyrgos, V., Seitz, A. E., Steiner, C. A., Prevots, D. R., and Williamson, P. R. (2013). Epidemiology of cryptococcal meningitis in the US: 1997-2009. PloS One 8, e56269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056269
Quan, H., Cao, Y. Y., Xu, Z., Zhao, J. X., Gao, P. H., Qin, X. F., et al. (2006). Potent in vitro synergism of fluconazole and berberine chloride against clinical isolates of Candida albicans resistant to fluconazole. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 1096–1099. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.3.1096-1099.2006
Rajasekar, V., Darne, P., Prabhune, A., Kao, R. Y. T., Solomon, A. P., Ramage, G., et al. (2021). A curcumin-sophorolipid nanocomplex inhibits Candida albicans filamentation and biofilm development. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 200, 111617. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111617
Rajasingham, R., Smith, R. M., Park, B. J., Jarvis, J. N., Govender, N. P., Chiller, T. M., et al. (2017). Global burden of disease of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: an updated analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 17, 873–881. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30243-8
Reguera-Gomez, M., Dores, M. R., and Martinez, L. R. (2023). Innovative and potential treatments for fungal central nervous system infections. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 76, 102397. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102397
Richter, K., Haslbeck, M., and Buchner, J. (2010). The heat shock response: life on the verge of death. Mol. Cell 40, 253–266. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.006
Rivera, A., Young Lim, W., Park, E., Dome, P. A., Hoy, M. J., Spasojevic, I., et al. (2023). Enhanced fungal specificity and in vivo therapeutic efficacy of a C-22-modified FK520 analog against C. neoformans. mBio 14, e0181023. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01810-23
Robbins, N., Leach, M. D., and Cowen, L. E. (2012). Lysine deacetylases Hda1 and Rpd3 regulate Hsp90 function thereby governing fungal drug resistance. Cell Rep. 2, 878–888. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.035
Rosca-Casian, O., Parvu, M., Vlase, L., and Tamas, M. (2007). Antifungal activity of Aloe vera leaves. Fitoterapia 78, 219–222. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2006.11.008
Roscetto, E., Contursi, P., Vollaro, A., Fusco, S., Notomista, E., and Catania, M. R. (2018). Antifungal and anti-biofilm activity of the first cryptic antimicrobial peptide from an archaeal protein against Candida spp. clinical isolates. Sci. Rep. 8, 17570. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35530-0
Rusnak, F. and Mertz, P. (2000). Calcineurin: form and function. Physiol. Rev. 80, 1483–1521. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2000.80.4.1483
Saini, V., Safwan, S. M., Mehta, D., Das, E. E., and Bajaj, A. (2025). Recent advances in the development of antifungal agents: beyond azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins. ACS Infect. Dis. 11, 1271–1295. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00828
Schleimer, R. P. (2005). Innate immune responses and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: “Terminator” or “Terminator 2”? Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2, 342–346. doi: 10.1513/pats.200504-030SR
Schulte, T. W., Akinaga, S., Soga, S., Sullivan, W., Stensgard, B., Toft, D., et al. (1998). Antibiotic radicicol binds to the N-terminal domain of Hsp90 and shares important biologic activities with geldanamycin. Cell Stress Chaperones 3, 100–108. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(1998)003<0100:arbttn>2.3.co;2
Schwartz, S., Kontoyiannis, D. P., Harrison, T., and Ruhnke, M. (2018). Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of fungal infections of the CNS. Lancet Neurol. 17, 362–372. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30030-9
Shaban, S., Patel, M., and Ahmad, A. (2020). Improved efficacy of antifungal drugs in combination with monoterpene phenols against Candida auris. Sci. Rep. 10, 1162. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58203-3
Shapiro, R. S., Uppuluri, P., Zaas, A. K., Collins, C., Senn, H., Perfect, J. R., et al. (2009). Hsp90 orchestrates temperature-dependent Candida albicans morphogenesis via Ras1-PKA signaling. Curr. Biol. 19, 621–629. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.03.017
Shibata, T., Takahashi, T., Yamada, E., Kimura, A., Nishikawa, H., Hayakawa, H., et al. (2012). T-2307 causes collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential in yeast. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56, 5892–5897. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05954-11
Silva, S., Rodrigues, C. F., Araujo, D., Rodrigues, M. E., and Henriques, M. (2017). Candida species biofilms’ Antifungal resistance. J. Fungi (Basel) 3, 8. doi: 10.3390/jof3010008
Singh, S. D., Robbins, N., Zaas, A. K., Schell, W. A., Perfect, J. R., and Cowen, L. E. (2009). Hsp90 governs echinocandin resistance in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans via calcineurin. PloS Pathog. 5, e1000532. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000532
Soares, L. A., de Cassia Orlandi Sardi, J., Gullo, F. P., de Souza Pitangui, N., Scorzoni, L., Leite, F. S., et al. (2013). Anti dermatophytic therapy–prospects for the discovery of new drugs from natural products. Braz. J. Microbiol. 44, 1035–1041. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822014005000011
Sobel, J. D. (2023). Resistance to fluconazole of candida albicans in vaginal isolates: a 10-year study in a clinical referral center. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 67, e0018123. doi: 10.1128/aac.00181-23
Song, J. C. and Deresinski, S. (2005). Hepatotoxicity of antifungal agents. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 6, 170–177.
Song, R., Zhai, Q., Sun, L., Huang, E., Zhang, Y., Zhu, Y., et al. (2019). CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technology in filamentous fungi: progress and perspective. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 103, 6919–6932. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10007-w
Steinbach, W. J., Cramer, R. A., Jr., Perfect, B. Z., Asfaw, Y. G., Sauer, T. C., Najvar, L. K., et al. (2006). Calcineurin controls growth, morphology, and pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot Cell 5, 1091–1103. doi: 10.1128/EC.00139-06
Steinbach, W. J., Reedy, J. L., Cramer, R. A., Jr., Perfect, J. R., and Heitman, J. (2007). Harnessing calcineurin as a novel anti-infective agent against invasive fungal infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5, 418–430. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1680
Su, S., Shi, X., Xu, W., Li, Y., Chen, X., Jia, S., et al. (2020). Antifungal activity and potential mechanism of panobinostat in combination with fluconazole against candida albicans. Front. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01584
Sultan, T. and Ali, S. A. (2011). Psoralea corylifolia extracts stimulate cholinergic-like psoralen receptors of tadpole-tail melanophores, leading to skin darkening. J. Recept Signal Transduct Res. 31, 39–44. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2010.508164
Sundriyal, S., Sharma, R. K., and Jain, R. (2006). Current advances in antifungal targets and drug development. Curr. Med. Chem. 13, 1321–1335. doi: 10.2174/092986706776873023
Szymanski, M., Chmielewska, S., Czyzewska, U., Malinowska, M., and Tylicki, A. (2022). Echinocandins - structure, mechanism of action and use in antifungal therapy. J. Enzyme Inhib Med. Chem. 37, 876–894. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2050224
Taha, M., Tartor, Y. H., Elaziz, R. M. A., and Elsohaby, I. (2024). Genetic diversity and antifungal susceptibilities of environmental Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii species complexes. IMA Fungus 15, 21. doi: 10.1186/s43008-024-00153-w
Taipale, M., Jarosz, D. F., and Lindquist, S. (2010). HSP90 at the hub of protein homeostasis: emerging mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 515–528. doi: 10.1038/nrm2918
Thakur, R. (2015). Spectrum of dermatophyte infections in Botswana. Clin. Cosmet Investig. Dermatol. 8, 127–133. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S78237
Toepfer, S., Keniya, M. V., Lackner, M., and Monk, B. C. (2024). Azole combinations and multi-targeting drugs that synergistically inhibit candidozyma auris. J. Fungi (Basel) 10, 698. doi: 10.3390/jof10100698
Tong, Y., Zhang, J., Sun, N., Wang, X. M., Wei, Q., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Berberine reverses multidrug resistance in Candida albicans by hijacking the drug efflux pump Mdr1p. Sci. Bull. (Beijing) 66, 1895–1905. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2020.12.035
Urimi, D., Widenbring, R., Perez Garcia, R. O., Gedda, L., Edwards, K., Loftsson, T., et al. (2021). Formulation development and upscaling of lipid nanocapsules as a drug delivery system for a novel cyclic GMP analogue intended for retinal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 602, 120640. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120640
Vandeputte, P., Tronchin, G., Berges, T., Hennequin, C., Chabasse, D., and Bouchara, J. P. (2007). Reduced susceptibility to polyenes associated with a missense mutation in the ERG6 gene in a clinical isolate of Candida glabrata with pseudohyphal growth. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 982–990. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01510-06
Vandeputte, P., Tronchin, G., Larcher, G., Ernoult, E., Berges, T., Chabasse, D., et al. (2008). A nonsense mutation in the ERG6 gene leads to reduced susceptibility to polyenes in a clinical isolate of Candida glabrata. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 3701–3709. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00423-08
van de Veerdonk, F. L., Carvalho, A., Wauters, J., Chamilos, G., and Verweij, P. E. (2025). Aspergillus fumigatus biology, immunopathogenicity and drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 23, 652–666. doi: 10.1038/s41579-025-01180-z
Vu, K., Tham, R., Uhrig, J. P., Thompson, G. R., Na Pombejra, S., Jamklang, M., et al. (2014). Invasion of the central nervous system by Cryptococcus neoformans requires a secreted fungal metalloprotease. mBio 5, e01101–e01114. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01101-14
Wake, R. M., Allebone-Salt, P. E., John, L. L. H., Caswall, B. A., Govender, N. P., Ben-Ami, R., et al. (2024). Optimizing the treatment of invasive candidiasis-A case for combination therapy. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 11, ofae072. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae072
Weiss, J., Ten Hoevel, M. M., Burhenne, J., Walter-Sack, I., Hoffmann, M. M., Rengelshausen, J., et al. (2009). CYP2C19 genotype is a major factor contributing to the highly variable pharmacokinetics of voriconazole. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 49, 196–204. doi: 10.1177/0091270008327537
Wiederhold, N. P. (2016). Echinocandin resistance in candida species: a review of recent developments. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 18, 42. doi: 10.1007/s11908-016-0549-2
Wiederhold, N. P. and Gibas, C. F. C. (2018). From the clinical mycology laboratory: new species and changes in fungal taxonomy and nomenclature. J. Fungi (Basel) 4, 138. doi: 10.3390/jof4040138
Wiederhold, N. P., Najvar, L. K., Jaramillo, R., Olivo, M., Patterson, H., Connell, A., et al. (2020). The Novel Arylamidine T-2307 Demonstrates In Vitro and In Vivo Activity against Candida auris. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64, e02198-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02198-19
Wijnants, S., Vreys, J., and Van Dijck, P. (2022). Interesting antifungal drug targets in the central metabolism of Candida albicans. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 43, 69–79. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.10.003
Wingard, J. R., White, M. H., Anaissie, E., Raffalli, J., Goodman, J., Arrieta, A., et al. (2000). A randomized, double-blind comparative trial evaluating the safety of liposomal amphotericin B versus amphotericin B lipid complex in the empirical treatment of febrile neutropenia. L Amph/ABLC Collaborative Study Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 31, 1155–1163. doi: 10.1086/317451
Wirth, F. and Ishida, K. (2020). Antifungal drugs: An updated review of central nervous system pharmacokinetics. Mycoses 63, 1047–1059. doi: 10.1111/myc.13157
Wu, J. J., Pang, K. R., Huang, D. B., and Tyring, S. K. (2004). Therapy of systemic fungal infections. Dermatol. Ther. 17, 532–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1396-0296.2004.04057.x
Yamashita, K., Miyazaki, T., Fukuda, Y., Mitsuyama, J., Saijo, T., Shimamura, S., et al. (2019). The novel arylamidine T-2307 selectively disrupts yeast mitochondrial function by inhibiting respiratory chain complexes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63, e00374-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00374-19
Young, L. Y., Hull, C. M., and Heitman, J. (2003). Disruption of ergosterol biosynthesis confers resistance to amphotericin B in Candida lusitaniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 2717–2724. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.9.2717-2724.2003
Zhang, Z., Bills, G. F., and An, Z. (2023). Advances in the treatment of invasive fungal disease. PloS Pathog. 19, e1011322. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011322
Zhang, J., Li, K., Sun, Y., Yao, C., Liu, W., Liu, H., et al. (2024). An efficient CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system based on a multiple sgRNA processing platform in Trichoderma reesei for strain improvement and enzyme production. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod 17, 22. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02468-7
Zhang, C., Zhao, J., Famous, E., Pan, S., Peng, X., and Tian, J. (2021). Antioxidant, hepatoprotective and antifungal activities of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) essential oil. Food Chem. 346, 128845. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128845
Zhou, M., Liu, L., Cong, Z., Jiang, W., Xiao, X., Xie, J., et al. (2024). A dual-targeting antifungal is effective against multidrug-resistant human fungal pathogens. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 1325–1339. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01662-5
Keywords: fungal infections, antifungal drugs, combination therapy, biotechnology-driven approaches, drug development
Citation: Liu D, Zhou R and Gao X (2025) Recent innovations and challenges in the treatment of fungal infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1676009. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1676009
Received: 29 July 2025; Accepted: 18 September 2025;
Published: 01 October 2025.
Edited by:
Yuanwei Zhang, Nanjing Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Marta Reguera-Gomez, University of Florida, United StatesRidho Asra, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom
Cássia Milena De Souza, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (Fiocruz), Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Zhou and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xindi Gao, Z2FveGluZGkxOTkzQHRtbXUuZWR1LmNu; Renjie Zhou, emhvdXJlbmppZUB0bW11LmVkdS5jbg==
 Di Liu
Di Liu Renjie Zhou*
Renjie Zhou* Xindi Gao
Xindi Gao