- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 2Institute of Antibiotics, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Joint Laboratory of Hospital & Enterprise for Pathogen Diagnosis of Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections and Innovative Drug R&D, Shanghai, China
- 4Medical Laboratory Center, JiLin Provincial People’s Hospital, Changchun, China
- 5Key Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacology of Antibiotics, Ministry of Health, Shanghai, China
Objectives: To investigate the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms and intra-hospital clonal dissemination of carbapenem-resistant ST477 Klebsiella michiganensis.
Methods: Between 14 December 2019 and 23 August 2020, six K. michiganensis isolates producing NDM-type carbapenemases were recovered from Jilin Provincial People’s Hospital in China. Antimicrobial susceptibility was determined using the broth microdilution method. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) was performed for all isolates. Sequence typing (ST), resistance genes, and plasmid types were identified using the PubMLST, ResFinder, and PlasmidFinder databases, respectively. Conjugation experiments were conducted to assess plasmid transferability. Additionally, 344 publicly available K. michiganensis genomes were retrieved and used to construct a phylogenetic tree based on core-genome single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Results: WGS revealed that all six isolates belonged to ST477 and harbored blaNDM-1, blaSFO-1, and blaVEB-3. The maximum pairwise difference among the six isolates was only 8 SNPs, indicating clonal transmission. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed high-level resistance to imipenem, meropenem, and ceftazidime-avibactam, while susceptibility was retained to amikacin, aztreonam-avibactam, eravacycline, tigecycline, and colistin. Conjugation assays confirmed that the blaNDM-1-carrying plasmid was self-transmissible. Clinical data showed that four of the six patients had a history of transfer to the intensive care unit (ICU). Phylogenetic analysis combined with resistance gene profiling based on publicly available genomes revealed that 50% (175/350) of K. michiganensis isolates from human hosts carried carbapenem resistance genes. Notably, Isolates from China exhibited a higher carriage rate of carbapenemase genes (76.1%, 51/67). No ST477-related genomes were identified in current public datasets.
Conclusions: This study is the first to report the clonal dissemination of ST477 K. michiganensis harboring blaNDM-1 in a Chinese hospital.
1 Introduction
Klebsiella oxytoca is an opportunistic pathogen that can be detected in the feces of approximately 8–10% of healthy adults (Savino et al., 2009). With the advancement of genomics, researchers have discovered that K. oxytoca is not a single species, but rather a complex comprising at least six distinct species (Yang et al., 2022), including Klebsiella grimontii, Klebsiella huaxiensis, Klebsiella michiganensis, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pasteurii, and Klebsiella spallanzanii. Among them, K. michiganensis is a newly recognized species, initially isolated from a domestic toothbrush holder (Saha et al., 2013). K. michiganensis shares typical phenotypic characteristics of the Klebsiella genus, and phylogenomic analysis has shown that it is most closely related to K. oxytoca (Wyres et al., 2020). As a result, it is often misidentified as K. oxytoca in routine clinical diagnostics. Although clinical reports of K. michiganensis remain limited, genomic studies of the K. oxytoca complex have revealed that K. michiganensis represents a significant proportion of isolates within this group (Gómez et al., 2021; Wan et al., 2023), suggesting its pathogenic potential may be underestimated.
The greatest clinical threat posed by K. michiganensis lies in its multidrug resistance, particularly the emergence of carbapenem-resistant strains (Zhang et al., 2021; Luo et al., 2023). Carbapenems are often regarded as the last line of defense for treating severe infections (Li et al., 2023b). Once K. michiganensis acquires resistance to carbapenems, conventional antibiotic therapies often fail, substantially increasing the difficulty of clinical treatment and the mortality rate of affected patients. The production of carbapenemases is the primary mechanism of carbapenem resistance in bacteria. In particular, strains producing metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) can hydrolyse almost all β-lactam antibiotics except aztreonam. Among MBLs, New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM) is the most prevalent. Since its first identification in India in 2008 (Yong et al., 2009), NDM genes have been detected in a wide range of pathogens, including members of the Enterobacterales, Acinetobacter, and Pseudomonas genera (Johnson and Woodford, 2013). In addition, the horizontal transfer of plasmids carrying resistance genes further facilitates the dissemination of resistance among bacteria (Frankel et al., 2023). Mobile genetic elements (MGEs), such as insertion sequences, integrons, and transposons, frequently found in bacterial genomes, contribute to the interspecies spread of resistance genes through horizontal gene transfer (Mann et al., 2022; Macesic et al., 2023). Previous studies have shown that K. michiganensis also harbors diverse MGEs and possesses the ability to acquire and disseminate resistance genes through transposition and recombination (Campos-Madueno et al., 2021; Luo et al., 2022).
In this study, we characterized the molecular features of six clinical ST477 K. michiganensis isolates carrying blaNDM-1 and performed a comparative genomic analysis with publicly available K. michiganensis genomes from human hosts worldwide. A phylogenetic tree was constructed to investigate the evolutionary characteristics of this species.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial isolates
Between 14 December 2019 and 23 August 2020, six non-duplicate pathogenic strains were isolated from clinical specimens of six hospitalized patients at Jilin Provincial People’s Hospital (only the first isolate per patient was included).Initial identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) indicated that all isolates belonged to the Klebsiella oxytoca complex. Specifically, strains KO24–256 and KO24–259 were isolated from pus, KO24–260 from a throat swab, KO24–263 from whole blood, KO24–297 from pleural fluid, and KO24–298 from urine. Final species identification by whole-genome sequencing confirmed all isolates as K. michiganensis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed to screen for carbapenemase genes, including blaKPC, blaNDM, blaIMP, blaOXA-48, and blaVIM. Quality control strains for antimicrobial susceptibility testing included Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853.
2.2 Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of antimicrobial agents were determined using the broth microdilution method according to the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). The antibiotics tested included imipenem, meropenem, meropenem-vaborbactam, aztreonam-avibactam, ceftazidime-avibactam, piperacillin-tazobactam, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, cefepime, aztreonam, amikacin, ciprofloxacin, sitafloxacin, colistin, tigecycline, and eravacycline. Interpretation of MIC results was performed as follows: colistin and aztreonam-avibactam were interpreted according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) breakpoints (The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 2024); tigecycline and eravacycline were interpreted based on the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) breakpoints for Enterobacterales (U.S. Food and Drug Administration., 2023); breakpoints for the remaining agents were interpreted according to the CLSI 2024 guidelines (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute., 2024).
2.3 Whole-genome sequencing and bioinformatic analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from all isolates using a commercial DNA extraction kit following the manufacturer’s instructions. WGS was performed on all six clinical isolates using the Illumina short-read sequencing platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). In addition, isolate KO24–256 underwent long-read sequencing using the Nanopore platform (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK) for further analysis. Raw reads were quality filtered and trimmed using Sickle (https://github.com/najoshi/sickle), and hybrid assembly was carried out with SPAdes v3.12.0 to generate high-quality draft genomes. The assembled genomes were analyzed using BLAST against several databases: sequence typing was performed with PubMLST; plasmid replicon types were identified with PlasmidFinder and PMLST; and acquired antimicrobial resistance genes were identified with ResFinder. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) distances among isolates were calculated using Snippy v4.6.0 (https://github.com/tseemann/snippy). For KO24-256, open reading frames (ORFs) on the resistance plasmid were predicted and annotated using RAST v2.0 (https://rast.nmpdr.org) and BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
2.4 Conjugation assay
To assess the transferability of the resistance plasmid, a conjugation assay was performed using isolate KO24–256 as the donor strain and Escherichia coli J53 as the recipient strain. The experiment was conducted using a standard liquid mating method. Donor and recipient strains were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and co-cultured in LB broth pre-warmed to 37 °C.Transconjugants were selected on Mueller–Hinton (MH) agar plates containing dual antibiotics: ampicillin (100 mg/L) and sodium azide (100 mg/L). Positive colonies growing on the selective medium were identified using MALDI-TOF MS. The presence of the blaNDM-1 gene in transconjugants was confirmed by PCR followed by Sanger sequencing. Plasmid DNA was extracted from transconjugants using the Qiagen Plasmid Midi Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and further validated by short-read sequencing on the Illumina platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.5 Phylogenetic analysis
To further investigate the evolutionary relationship of clinical ST477 K. michiganensis isolates, we downloaded all available K. michiganensis genomes sequenced between 2012 and 2024 from the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center (PATRIC). After filtering out low-quality assemblies and non-human host isolates, a total of 344 genomes were retained for analysis. These were combined with the six isolates from this study to construct a core genome-based phylogenetic tree. In total, 350 K. michiganensis genomes were included, representing isolates from 31 countries worldwide. Pairwise single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) distances between genomes were calculated using Snippy v4.6.0 under default parameters. The phylogenetic tree was visualized and refined using FastTree and ChiPlot (Xie et al., 2023).
3 Results
3.1 Patient characteristics and epidemiological investigation
The six hospitalized patients had a mean age of 63.5 years (range: 31–89 years). Five patients (all except Patient 4) underwent invasive procedures, including tracheal intubation, surgery, or puncture. The patients were admitted to five different hospital wards, and four (excluding Patient 5 and Patient 6) had a history of ICU admission. Notably, Patients 3 and 4 were hospitalized in the ICU during overlapping periods. Of particular interest, Patient 1 was transferred from a local hospital to the Department of Burns and Plastic Surgery at Jilin Provincial People’s Hospital on 14 December 2019 due to extensive burns. A pathogen was first isolated from wound pus on hospital day 27 (9 January 2020). Subsequently, the same organism was detected in the following specimens from other patients: sputum from Patient 4 (26 February 2020), throat swab from Patient 3 (6 March 2020), pus from Patient 2 (28 March 2020), and urine from Patient 5 (4 May 2020). The final isolate was obtained from the urine of Patient 6 on 5 August 2020. Among the six patients, three recovered and were discharged, while the other three were discharged after electing to discontinue treatment due to clinical deterioration. Detailed hospitalization histories and antibiotic usage for each patient are shown in (Figure 1).
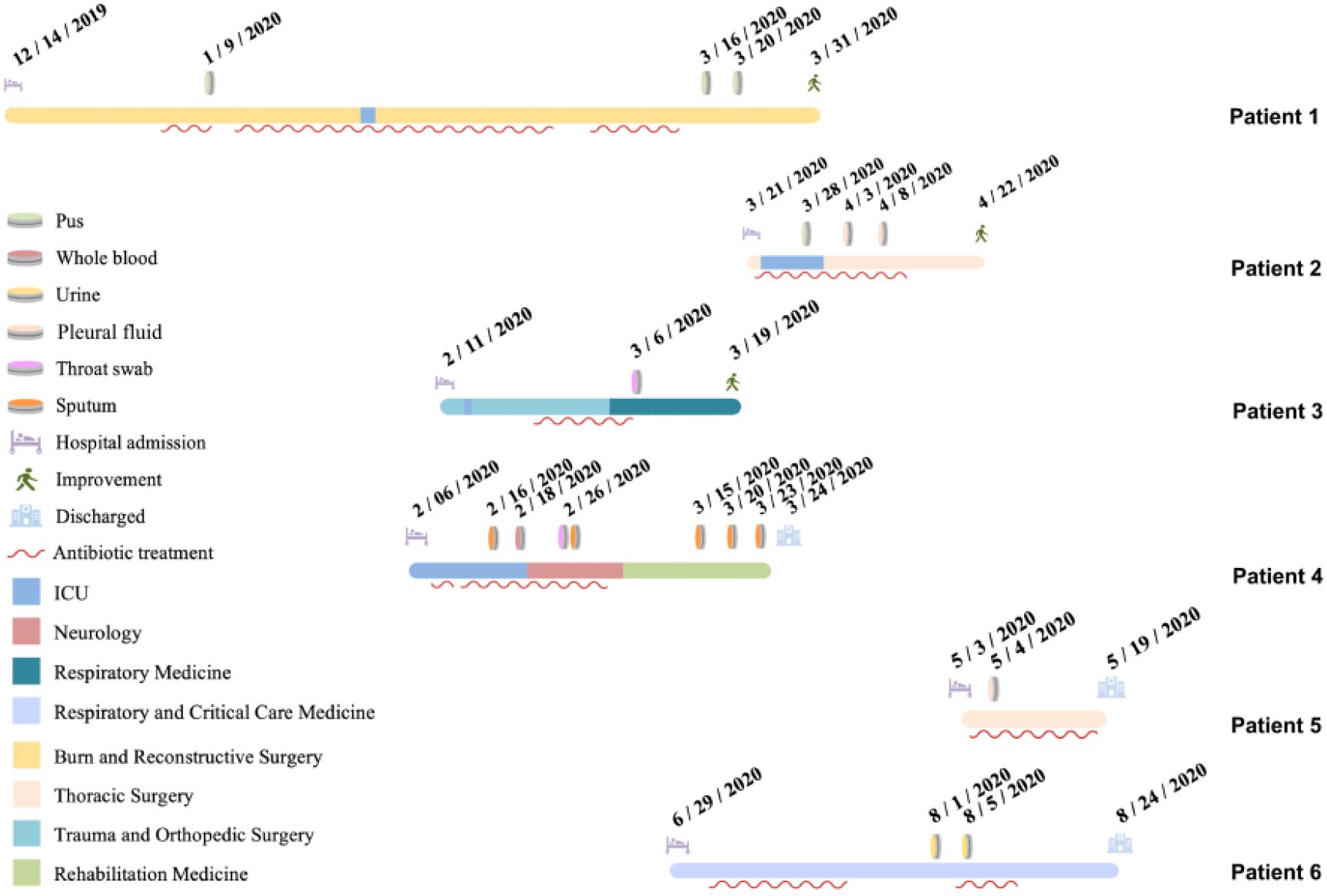
Figure 1. Epidemiological overview of the six patients included in this study. Each horizontal bar represents the hospitalization timeline of one patient(the timeline for Patient 6 is displayed separately), with different colors indicating different hospital wards. Red wavy lines denote periods of antibiotic treatment. Admission and discharge dates, as well as the dates of pathogen isolation (with colors indicating different specimen types), are marked numerically on the timeline. Different symbols at the end of each timeline indicate the discharge outcome of each patient.
3.2 Antimicrobial susceptibility and conjugation assays
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed that all six K. michiganensis isolates were resistant to imipenem (MIC range: 4 - 32 μg/mL), meropenem (MIC range: 8 - >32 μg/mL), and ceftazidime-avibactam (MIC>64 μg/mL). Isolate KO24–298 exhibited intermediate susceptibility to meropenem-vaborbactam, while the other five isolates were resistant. Among the antibiotics tested, only amikacin, aztreonam-avibactam, eravacycline, tigecycline, and colistin demonstrated good in vitro activity (Table 1).Conjugation assays confirmed that the blaNDM-1-carrying plasmid in KO24–256 could be successfully transferred to the recipient strain E. coli J53. The resulting transconjugant exhibited resistance to imipenem (MIC = 16 μg/mL), meropenem (MIC = 16 μg/mL), meropenem-vaborbactam (MIC=32 μg/mL), and ceftazidime-avibactam (MIC>64 μg/mL). Compared with the recipient strain, the MICs of imipenem, meropenem, meropenem-vaborbactam, and ceftazidime-avibactam in the transconjugant increased by at least 128-, 512-, 1024-, and 256-fold, respectively (Table 1).
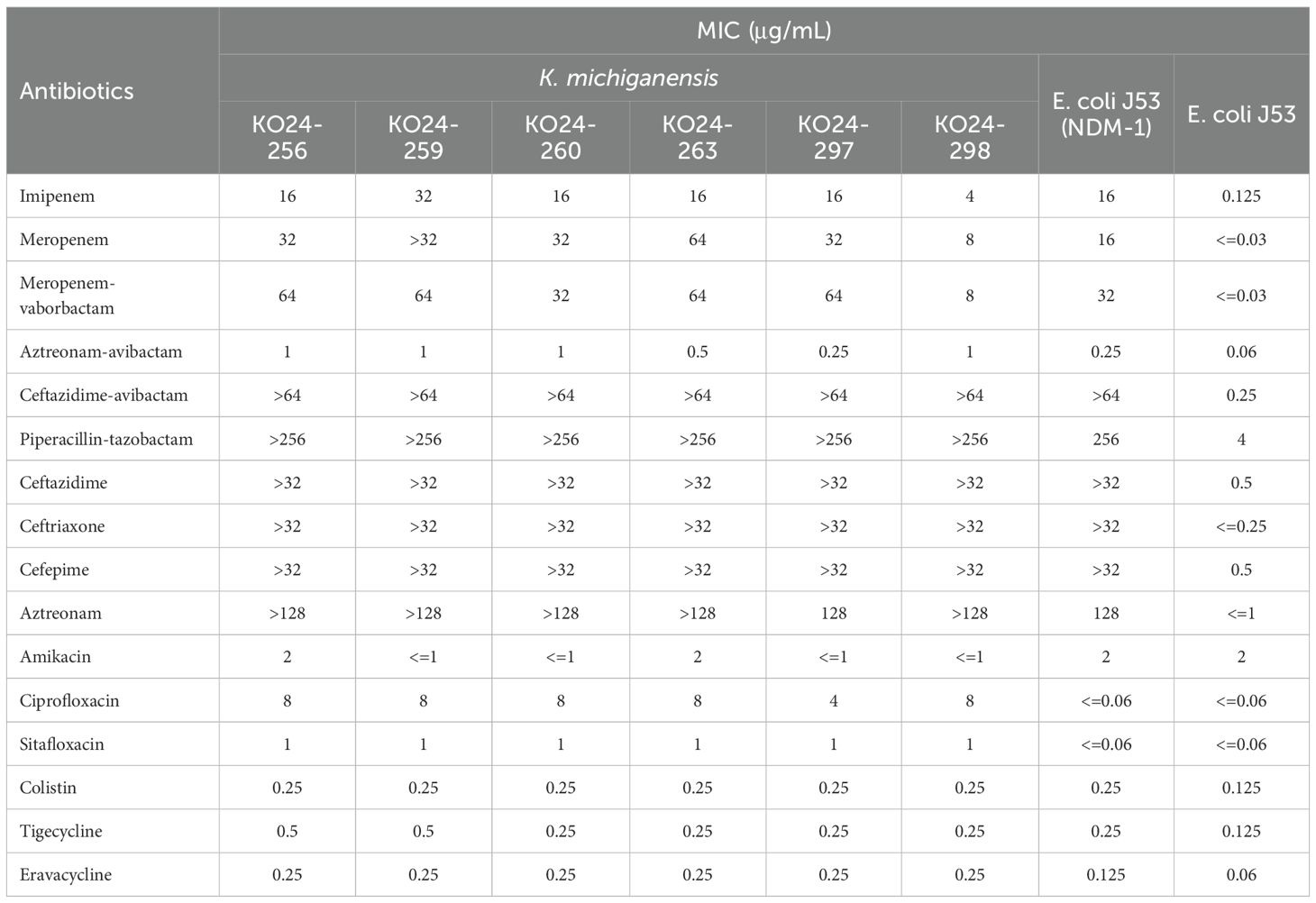
Table 1. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of clinical isolates, the transconjugant, and the recipient strain.
3.3 Whole-genome sequencing and plasmid characterization of K. michiganensis KO24-256
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) analysis revealed that all six K. michiganensis isolates belonged to ST477 (allelic profile: gapA 3; infB 41; mdh 20; pgi 21; phoE 20; rpoB 6; tonB 25). All isolates harbored multiple resistance genes, including the carbapenemase gene (blaNDM-1), β-lactamase genes (blaVEB-3, blaSFO-1, blaTEM-1B, blaOXY-1-1), and genes conferring resistance to quinolones (qnrS1), sulfonamides (sul1, sul2), chloramphenicol (floR), tetracyclines (tet(A)), trimethoprim (dfrA12, dfrA27), macrolides (mph(A)), and rifampicin (ARR-3). Among the six isolates, aminoglycoside resistance genes varied slightly. Isolates KO24-256, KO24-260, KO24-263, and KO24–298 carried aph(3’)-Ia, aph(6)-Id, aph(3’’)-Ib, aadA2, and aac(3)-IId, whereas isolates KO24–259 and KO24–297 only carried aph(3’)-Ia, aadA2, and aac(3)-IId. Pairwise SNP analysis revealed a maximum of only 8 SNP differences among the six isolates, indicating clonal dissemination.
To obtain a more complete genomic profile, long-read sequencing of K. michiganensis KO24–256 was performed using the Nanopore platform. The assembled genome had a total length of 6413616 bp, comprising a 5982250 bp circular chromosome and two circular plasmids, designated KO24-256p1 (356849 bp) and KO24-256p2 (74517 bp). The chromosome harbored the aph(3’)-Ia and blaOXY-1–1 genes, conferring resistance to aminoglycosides and β-lactams, respectively. Plasmid KO24-256p1 carried multiple resistance genes, including blaNDM-1, blaVEB-3, blaSFO-1, blaTEM-1B, aac(3)-IId, mph(A), dfrA27, ARR-3, and two copies of sul1 (Figure 2A), mediating resistance to carbapenems, β-lactams, aminoglycosides, macrolides, trimethoprim, rifampin, and sulphonamides. This plasmid could not be assigned to any known replicon type in the PlasmidFinder database (using thresholds of ≥50% identity and ≥20% coverage). However, annotation using the RAST platform suggested the presence of four putative plasmid replicons. Comparative genomic analysis revealed that KO24-256p1 shared 100% query coverage and 99.99% identity with plasmid pC39-334kb (accession no. CP061701) from Klebsiella pneumoniae strain C39, isolated in Zhengzhou, China, in 2019. Gene structure comparison showed that resistance genes in both plasmids were clustered in an approximately 5 kb multidrug resistance (MDR) island, flanked by multiple mobile genetic elements. In comparison, pC39-334kb harbored two additional resistance genes, qnrA7 and an extra copy of sul1 (Figure 2B). The second plasmid, KO24-256p2, was identified as an IncR-type plasmid and carried several resistance genes, including aph(6)-Id, aph(3’’)-Ib, aadA2, floR, qnrS1, sul1, sul2, tet(A), and dfrA12.

Figure 2. (A) Circular comparison of plasmid KO24-256p1 with plasmid pC39-334kb (CP061701), K. pneumoniae plasmid unnamed1 (CP053670), and pKP-16-57-NDM-1 (MZ836809). Different colored rings represent different plasmids. (B) Comparative genetic context of plasmid KO24-256p1 and pC39-334kb. Genes are indicated by arrows and colored based on their predicted functional categories.
3.4 Phylogenetic analysis
A total of 344 publicly available K. michiganensis genomes isolated from human hosts across the globe were retrieved from public databases and analyzed alongside the six clinical isolates from this study, resulting in a phylogenetic tree comprising 350 strains in total. These isolates originated from 31 countries, with the majority collected from the United States (n = 67), China (n = 67), Switzerland (n = 61), Japan (n = 31), Australia (n = 28), Germany (n = 25), Poland (n = 11), the United Kingdom (n = 8), the Czech Republic (n = 5), and Mexico (n = 5); the remaining 42 isolates came from other countries. The phylogenetic tree revealed a high degree of genomic homology among the isolates, with most clustering into a single evolutionary branch, indicating close relatedness. MLST typing showed genetic diversity, with the predominant sequence types being ST29 (n = 36), ST43 (n = 18), ST27 (n = 16), ST85 (n = 15), ST50 (n = 12), ST84 (n = 10), and ST180 (n = 10). Analysis of carbapenem resistance gene distribution showed that 50% (175/350) of isolates carried at least one carbapenem resistance gene, while 3.7% (13/350) harbored two or more such genes. The distribution of resistance genes varied across country: isolates from the United States predominantly carried blaKPC-3 and blaKPC-4; those from China carried blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, and blaIMP-4; from Japan, blaIMP-1; from Australia, blaNDM-1 and blaIMP-4; from Germany, blaVIM-1; from Poland, blaVIM variants; and from the United Kingdom, blaKPC-2 and blaGES-5. Notably, although Swiss isolates accounted for a substantial proportion (17.4%, 61/350), only two were found to carry carbapenem resistance genes. Interestingly, none of the K. michiganensis isolates available in public databases shared the same sequence type (ST477) as those identified in this study. The most closely related strains phylogenetically were one ST381 isolate from China and one ST417 isolate from Switzerland, neither of which harbored carbapenem resistance genes (Figure 3).
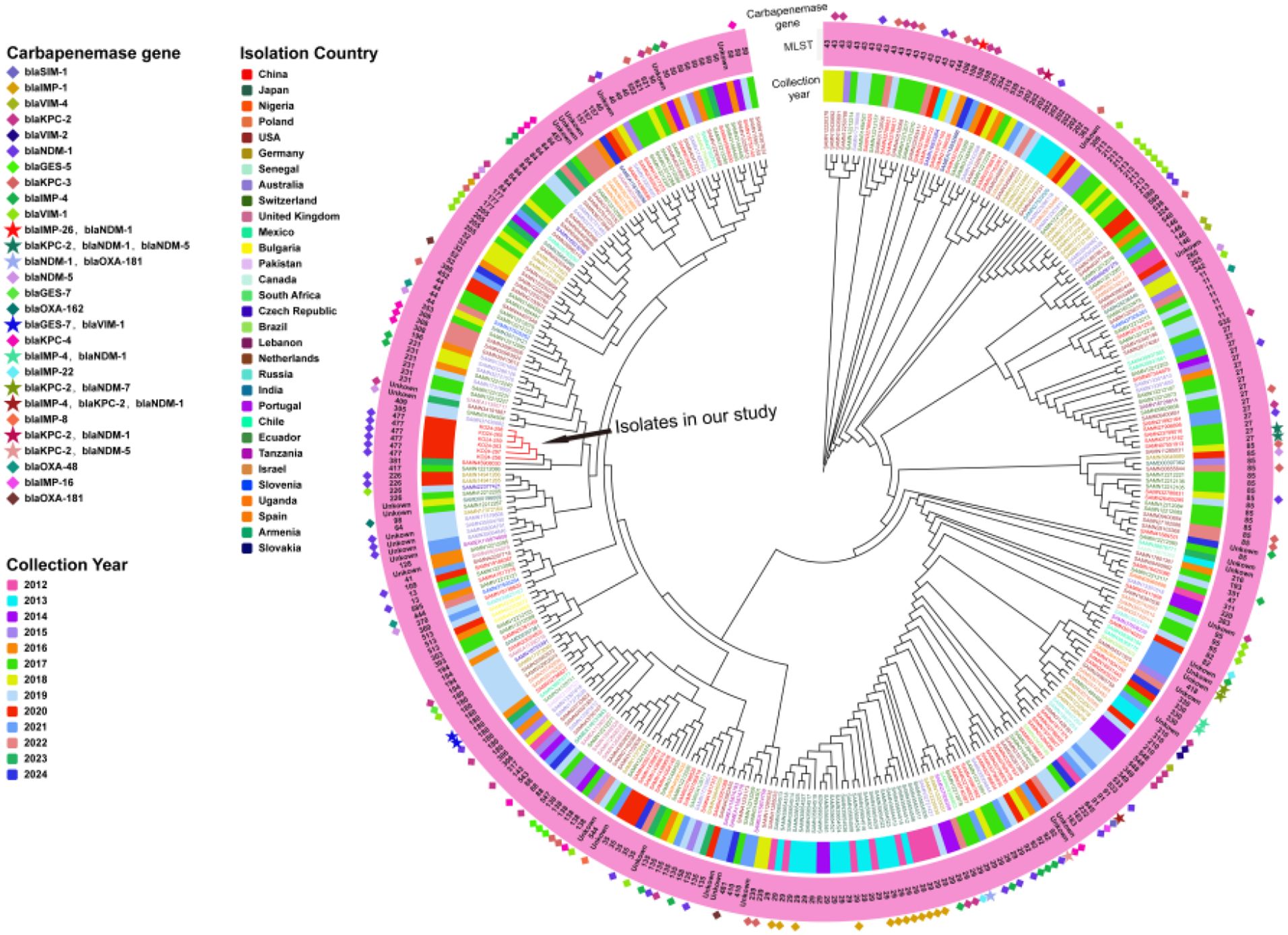
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of 344 K. michiganensis genomes retrieved from the PATRIC and six ST477 K. michiganensis clinical isolates from this study. Starting from the outermost circle, carbapenem resistance genes are represented using distinct symbols and color combinations. The second circle shows the MLST of each strain in text format. The third circle indicates the collection year of the strains using different color bars. The inner circle uses different colors to represent the countries from which the strains were isolated.
4 Discussion
Although K. michiganensis is less commonly encountered than K. pneumoniae, it has increasingly been recognized as an emerging pathogen associated with human infections (Chen et al., 2020). In 2020, an outbreak of ESBL-producing K. michiganensis was reported in a neonatal unit in an Australian hospital, in which contaminated detergent was suspected to be a potential source of infection (Chapman et al., 2020). In addition, in 2021, three ST92 K. michiganensis strains carrying tet(X4) and tmexCD2-toprJ2 were isolated from pork samples in Jiangsu Province, China. Genomic comparisons revealed only a few SNP differences between these isolates and those of human origin, suggesting possible cross-host clonal transmission (Li et al., 2023a).In the present study, we report six carbapenem-resistant ST477 K. michiganensis strains isolated from a hospital in Jilin Province, China. Whole-genome sequencing showed that these strains differed by no more than 8 SNPs, indicating a high level of clonal relatedness. However, retrospective analysis of publicly available K. michiganensis genomes globally did not identify any strains with the same sequence type, suggesting that ST477 is a rare type and may represent a regionally circulating clone or a recently emerged lineage.
K. michiganensis is often classified within K. oxytoca complex in clinical settings, and large-scale studies specifically focusing on this species remain limited. In a recent multicenter study conducted by Li et al (Li et al., 2024)in 2024, 103 K. oxytoca complex isolates collected from 69 hospitals across China between January 2020 and November 2021 were analyzed, revealing that K. michiganensis accounted for a substantial proportion (46.60%, 48/103) of the isolates—a finding consistent with previous reports (Gómez et al., 2021; Wan et al., 2023). This study further demonstrated that K. michiganensis exhibited significantly higher in vitro resistance rates to commonly used antibiotics than other members of the K. oxytoca complex, including an 8.7% resistance rate to carbapenems. Of particular concern is a 2018 clinical isolate reported in Zhejiang Province, China, which co-harbored blaKPC-2, blaNDM-1, and blaNDM-5, and showed susceptibility only to tigecycline and colistin in vitro (Zheng et al., 2018). In the present study, the six K. michiganensis isolates harbored blaNDM-1, along with the uncommon resistance genes blaVEB-3 and blaSFO-1. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing indicated that these strains were only susceptible to amikacin, aztreonam-avibactam, eravacycline, tigecycline, and colistin. However, previous studies have reported K. michiganensis strains carrying the tmexCD-toprJ gene cluster, which confers resistance to tetracyclines via efflux mechanisms, as well as the mcr gene, associated with colistin resistance (Wang et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022a). These findings underscore the need for continued surveillance of emerging resistance mechanisms in this species.
Since the first discovery of NDM in India, it has rapidly disseminated worldwide. In China, the blaNDM-1 gene was first detected in Acinetobacter baumannii in 2011 (Chen et al., 2011). As of 15 April 2025, a total of 78 NDM variants have been recorded in the Beta-Lactamase DataBase (BLDB; http://bldb.eu/) (Naas et al., 2017). To date, blaNDM-positive K. michiganensis isolates have been reported in China, Japan, South Africa and other countries, where the gene is typically located on IncFIB or IncX3 plasmids (Yamada et al., 2024). In this study, we identified a blaNDM-1 gene located on a novel plasmid that harbored sequence fragments related to both IncF and IncH1 replicon types, suggesting that the plasmid may have arisen from the recombination of multiple plasmid backbones. In K. michiganensis, blaNDM is commonly associated with the classical Tn125 composite transposon structure, flanked by two copies of ISAba125 and frequently accompanied downstream by the bleMBL and trpF genes. This configuration has been reported not only on IncX3 plasmids but also on IncFIB(K)-type plasmids (Prah et al., 2022; Jiang et al., 2023). However, in our isolate, the genetic context of blaNDM-1 differed from these classical structures: an IS26 insertion was found upstream of a truncated ISAba125 element, a configuration previously observed in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, and Citrobacter freundii isolates (Weber et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2021). Previous studies have demonstrated that insertion sequences (ISs) can mediate plasmid recombination and horizontal gene transfer of resistance genes, with IS26 in particular recognized as a key driver of the rapid dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria (Harmer et al., 2014; He et al., 2015; Partridge et al., 2018). Our findings support this view, as multiple IS26 elements were identified in the multidrug resistance island of KO24-256p1, potentially facilitating the integration of multiple resistance genes.
blaSFO is a relatively rare ESBL gene that was first identified in 1999 on a plasmid from Enterobacter cloacae isolated in Japan (Matsumoto and Inoue, 1999). It was designated SFO-1 due to its highest homology with a β-lactamase from Serratia fonticola. Although blaSFO-1 remains uncommon in clinical isolates, it has been increasingly reported worldwide in recent years (Fernández et al., 2011; Chen et al., 2024; Skwor et al., 2024). Similarly, VEB (Vietnamese extended-spectrum β-lactamase) is also an infrequent ESBL that has been detected in raw meat and animals in China (A Wohlfahrtiimonas chitiniclastica with a novel type of blaVEB-1-carrying plasmid isolated from a zebra in China, 2023; Mao et al., 2024). Notably, a blaVEB-3-harboring Enterobacter cloacae strain was previously linked to a nosocomial outbreak in Shanghai, China (Jiang et al., 2005). Despite limited data on the genetic context of blaVEB-3, some studies suggest it is commonly associated with intI1 (Jiang et al., 2005), while blaSFO-1 is often embedded in integron gene cassettes within transposon Tn5393 (Zhou et al., 2017). These findings are consistent with our observations in plasmid KO24-256p1. It is likely that horizontal gene transfer and homologous recombination mediated by various mobile genetic elements contributed to the formation of the multidrug resistance island in KO24-256p1. Although most ESBLs lack the ability to hydrolyze carbapenems, resistance may still occur in the presence of porin loss or mutations, or overexpression of efflux pumps (Li et al., 2022b; Roy et al., 2022).
Through genomic analysis of K. michiganensis isolates derived from human hosts in public databases, we found that 50% (175/350) of the strains harbored carbapenem resistance genes, suggesting that K. michiganensis may serve as an important reservoir for carbapenemase genes. The global distribution of MLST types among K. michiganensis strains was relatively scattered, with ST29, ST43, ST27, and ST85 being the most common. Notably, ST29 strains were primarily identified in Japan, with the majority carrying the blaIMP-1 gene. ST43 and ST27 showed no clear geographic clustering and exhibited diverse carbapenem resistance gene profiles. ST85 was predominantly detected in Switzerland; however, none of these isolates carried carbapenemase genes. ST477 strains have only been identified in Jilin Province, China. Furthermore, the blaNDM-1, blaVEB-3, and blaSFO-1 resistance genes may have integrated into the K. michiganensis genome through mobile genetic elements. The localized clonal dissemination of these strains could be likely associated with multiple factors, including the regional prevalence of the strain, the presence of specific resistance genes, and the unique transmission dynamics in the hospital environment. Although K. michiganensis is less frequently isolated in clinical settings compared to K. pneumoniae or E. coli, the high prevalence of carbapenemase genes among its isolates is a concerning trend. With the rapid advancement of high-throughput sequencing technologies, the clinical relevance of K. michiganensis is gaining increasing attention. Our findings highlight the importance of improving the identification and surveillance of this species in clinical microbiology laboratories, particularly molecular epidemiological investigations of carbapenem-resistant strains, to enable early detection of potential outbreaks and the implementation of effective infection control strategies to mitigate its transmission risk within healthcare settings.
5 Conclusion
In summary, this study is the first to report the nosocomial clonal dissemination of carbapenem-resistant ST477 K. michiganensis. Genomic analysis revealed that resistance genes including blaNDM-1, blaVEB-3, and blaSFO-1 co-localize within a multidrug resistance region on a self-transmissible plasmid. Comparative genomics indicated that horizontal gene transfer and homologous recombination mediated by mobile genetic elements such as insertion sequences, transposons, and integrons likely play a critical role in the formation of the multidrug resistance island.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author contributions
HL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. CY: Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. MJ: Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JJ: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SW: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Resources, Writing – original draft. FH: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. XX: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Jilin Provincial Department of Science and Technology (YDZJ202402064CXJD), the China Antimicrobial Surveillance Network (independent medical grants from Pfizer, 2018QD100), and the Shanghai Antimicrobial Surveillance Network (grant 3030231003). The funding was provided for the research only. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or manuscript preparation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Liu, M, Ji, X, Sun, Y, Zhu, L, and Guo, X. (2023). A Wohlfahrtiimonas chitiniclastica with a novel type of blaVEB-1-carrying plasmid isolated from a zebra in China. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1276314. J, G., W, Z., J, G., L, Z., G, L., F, H., et al.
Campos-Madueno, E. I., Sigrist, T., Flückiger, U. M., Risch, L., Bodmer, T., and Endimiani, A. (2021). First report of a blaVIM-1 metallo-β-lactamase-possessing Klebsiella michiganensis. J. Glob Antimicrob. Resist. 25, 310–314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2021.03.027
Chapman, P., Forde, B. M., Roberts, L. W., Bergh, H., Vesey, D., Jennison, A. V., et al. (2020). Genomic Investigation Reveals Contaminated Detergent as the Source of an Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella michiganensis Outbreak in a Neonatal Unit. J. Clin. Microbiol. 58, e01980–e01919. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01980-19
Chen, Y., Brook, T. C., Soe, C. Z., O’Neill, I., Alcon-Giner, C., Leelastwattanagul, O., et al. (2020). Preterm infants harbour diverse Klebsiella populations, including atypical species that encode and produce an array of antimicrobial resistance- and virulence-associated factors. Microb. Genom 6, e000377. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000377
Chen, H., Xue, H., Liu, R., Shen, J., Zheng, B., and Li., L. (2024). Coexistence of blaIMP-4 and blaSFO-1 in an IncHI5B plasmid harbored by tigecycline-non-susceptible Klebsiella variicola strain. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. antimicrobials 23:24. doi: 10.1186/s12941-024-00680-9
Chen, Y., Zhou, Z., Jiang, Y., and Yu, Y. (2011). Emergence of NDM-1-producing acinetobacter baumannii in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 66, 1255–1259. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr082
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2024). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 34th ed (Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI supplement M100).
Fernández, A., Pereira, M. J., Suárez, J. M., Poza, M., Treviño, M., Villalón, P., et al. (2011). Emergence in Spain of a multidrug-resistant Enterobacter cloacae clinical isolate producing SFO-1 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49, 822–828. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01872-10
Frankel, G., David, S., Low, W. W., Seddon, C., Wong, J. L. C., and Beis, K. (2023). Plasmids pick a bacterial partner before committing to conjugation. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, 8925–8933. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad678
Gómez, M., Valverde, A., Del Campo, R., Rodríguez, J. M., and Maldonado-Barragán, A. (2021). Phenotypic and molecular characterization of commensal, community-acquired and nosocomial klebsiella spp. Microorganisms 9, 2344. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112344
Harmer, C. J., Moran, R. A., and Hall, R. M. (2014). Movement of IS26-associated antibiotic resistance genes occurs via a translocatable unit that includes a single IS26 and preferentially inserts adjacent to another IS26. mBio 5, e01801–e01814. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01801-14
He, S., Hickman, A. B., Varani, A. M., Siguier, P., Chandler, M., Dekker, J. P., et al. (2015). Insertion sequence IS26 reorganizes plasmids in clinically isolated multidrug-resistant bacteria by replicative transposition. mBio 6, e00762. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00762-15
Jiang, T., Li, G., Huang, L., Ding, D., Ruan, Z., and Yan, J. (2023). Genomic and Phylogenetic Analysis of a Multidrug-Resistant blaNDM-carrying Klebsiella michiganensis in China. Infect. Drug Resist. 16, 3109–3116. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S409544
Jiang, X., Ni, Y., Jiang, Y., Yuan, F., Han, L., Li, M., et al. (2005). Outbreak of infection caused by Enterobacter cloacae producing the novel VEB-3 beta-lactamase in China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 826–831. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.826-831.2005
Johnson, A. P. and Woodford, N. (2013). Global spread of antibiotic resistance: the example of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM)-mediated carbapenem resistance. J. Med. Microbiol. 62, 499–513. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.052555-0
Li, S., Jiang, X., Li, C., Ju, Y., Yue, L., Chen, F., et al. (2022a). A bla SIM-1 and mcr-9.2 harboring Klebsiella michiganensis strain reported and genomic characteristics of Klebsiella michiganensis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.973901
Li, S., Shen, S., Ding, L., Han, R., Guo, Y., Yin, D., et al. (2022b). First Report of bla CTX-M-167, bla SHV-1, and bla TEM-1B Carrying Klebsiella pneumonia Showing High-Level Resistance to Carbapenems. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.916304
Li, Y., Wu, Y., Li, D., Du, L., Zhao, L., Wang, R., et al. (2024). Multicenter comparative genomic study of Klebsiella oxytoca complex reveals a highly antibiotic-resistant subspecies of Klebsiellamichiganensis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 57, 138–147. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2023.10.014
Li, Y., Xu, L., Li, Y., Wang, M., He, T., Bai, L., et al. (2023a). Genomic and functional analysis of high-level tigecycline resistant Klebsiella michiganensis co-carrying tet(X4) and tmexCD2-toprJ2 from pork. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 391, 391–393. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110138
Li, Y., Zhang, X., Ji, B., Wulamu, W., Yushan, N., Guo, X., et al. (2023b). One-stage revision using intra-articular carbapenem infusion effectively treats chronic periprosthetic joint infection caused by Gram-negative organisms. Bone Joint J. 105-B, 284–293. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.105B3.BJJ-2022-0926.R1
Luo, X., Dong, F., Dai, P., Xu, M., Yu, L., Hu, D., et al. (2023). Coexistence of blaKPC-2 and blaNDM-1 in one IncHI5 plasmid confers transferable carbapenem resistance from a clinical isolate of Klebsiella michiganensis in China. J. Glob Antimicrob. Resist. 35, 104–109. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2023.09.006
Luo, X., Zhang, J., Yuan, M., Mou, S., Xu, M., Hu, D., et al. (2022). Epidemiology of klebsiella michiganensis carrying multidrug-resistant incHI5 plasmids in the southeast coastal area of China. Infect. Drug Resist. 15, 1831–1843. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S358839
Macesic, N., Hawkey, J., Vezina, B., Wisniewski, J. A., Cottingham, H., Blakeway, L. V., et al. (2023). Genomic dissection of endemic carbapenem resistance reveals metallo-beta-lactamase dissemination through clonal, plasmid and integron transfer. Nat. Commun. 14, 4764. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39915-2
Mann, R., Rafei, R., Gunawan, C., Harmer, C. J., and Hamidian, M. (2022). Variants of Tn6924, a Novel Tn7 Family Transposon Carrying the blaNDM Metallo-β-Lactamase and 14 Copies of the aphA6 Amikacin Resistance Genes Found in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0174521. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01745-21
Mao, L.-Y., Wang, Q., Lin, H., Wang, H.-N., and Lei, C.-W. (2024). Novel multidrug resistance genomic islands and transposon carrying blaVEB-1 identified in mcr-positive Aeromonas strains from raw meat in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 79, 678–682. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkae031
Matsumoto, Y. and Inoue, M. (1999). Characterization of SFO-1, a plasmid-mediated inducible class A beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43, 307–313. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.2.307
Naas, T., Oueslati, S., Bonnin, R. A., Dabos, M. L., Zavala, A., Dortet, L., et al. (2017). Beta-lactamase database (BLDB) - structure and function. J. Enzyme Inhib Med. Chem. 32, 917–919. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1344235
Partridge, S. R., Kwong, S. M., Firth, N., and Jensen, S. O. (2018). Mobile genetic elements associated with antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 31, e00088–e00017. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00088-17
Prah, I., Nukui, Y., Yamaoka, S., and Saito, R. (2022). Emergence of a high-risk klebsiella michiganensis clone disseminating carbapenemase genes. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.880248
Roy, S., Junghare, V., Dutta, S., Hazra, S., and Basu, S. (2022). Differential Binding of Carbapenems with the AdeABC Efflux Pump and Modulation of the Expression of AdeB Linked to Novel Mutations within Two-Component System AdeRS in Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. mSystems 7, e0021722. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00217-22
Saha, R., Farrance, C. E., Verghese, B., Hong, S., and Donofrio, R. S. (2013). Klebsiella michiganensis sp. nov., a new bacterium isolated from a tooth brush holder. Curr. Microbiol. 66, 72–78. doi: 10.1007/s00284-012-0245-x
Savino, F., Cordisco, L., Tarasco, V., Calabrese, R., Palumeri, E., and Matteuzzi, D. (2009). Molecular identification of coliform bacteria from colicky breastfed infants. Acta Paediatr. 98, 1582–1588. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2009.01419.x
Skwor, T., Jones, D. C., Cahak, C., and Newton, R. J. (2024). First Report and Characterization of a Plasmid-Encoded blaSFO-1 in a Multi-Drug-Resistant Aeromonas hydrophila Clinical Isolate. Microorganisms 12, 494. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030494
The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (2024). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 14.0. Available online at: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (Accessed October 10, 2025).
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2023). Tigecycline Injection products. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-resources/tigecycline-injection-products (Accessed October 10, 2025).
Wan, W., Yang, X., Yu, H., Wang, M., Jia, W., Huang, B., et al. (2023). Genomic characterization of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella oxytoca complex in China: a multi-center study. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1153781
Wang, Y., Zhu, B., Liu, M., Dong, X., Ma, J., Li, X., et al. (2021). Characterization of IncHI1B Plasmids Encoding Efflux Pump TmexCD2-ToprJ2 in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella variicola, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae, and Klebsiella michiganensis Strains. Front. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.759208
Weber, R. E., Pietsch, M., Frühauf, A., Pfeifer, Y., Martin, M., Luft, D., et al. (2019). IS26-mediated transfer of bla NDM-1 as the main route of resistance transmission during a polyclonal, multispecies outbreak in a german hospital. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02817
Wyres, K. L., Lam, M. M. C., and Holt, K. E. (2020). Population genomics of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 18, 344–359. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0315-1
Xie, J., Chen, Y., Cai, G., Cai, R., Hu, Z., and Wang, H. (2023). Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, W587–W592. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad359
Yamada, A. Y., Souza, A. R. D., Bertani, A. M. D. J., Campos, K. R., Sacchi, C. T., Assis, D. B. D., et al. (2024). Genomic characterization of a clinical NDM-1-producing klebsiella michiganensis from Brazil. Microorganisms 12, 1408. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071408
Yang, J., Long, H., Hu, Y., Feng, Y., McNally, A., and Zong, Z. (2022). Klebsiella oxytoca complex: update on taxonomy, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 35, e00006–e00021. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00006-21
Yong, D., Toleman, M. A., Giske, C. G., Cho, H. S., Sundman, K., Lee, K., et al. (2009). Characterization of a new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla(NDM-1), and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53, 5046–5054. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00774-09
Zhang, Y., Gu, D., Yang, X., Wu, Y., Liu, C., Shen, Z., et al. (2021). Emergence and genomic characterization of a KPC-2-, NDM-1-, and IMP-4-producing klebsiella michiganensis isolate. Front. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.762509
Zhao, Q.-Y., Zhu, J.-H., Cai, R.-M., Zheng, X.-R., Zhang, L.-J., Chang, M.-X., et al. (2021). IS26 Is Responsible for the Evolution and Transmission of blaNDM-Harboring Plasmids in Escherichia coli of Poultry Origin in China. mSystems 6, e0064621. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00646-21
Zheng, B., Xu, H., Yu, X., Lv, T., Jiang, X., Cheng, H., et al. (2018). Identification and genomic characterization of a KPC-2-, NDM-1- and NDM-5-producing Klebsiella michiganensis isolate. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 73, 536–538. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx415
Keywords: Klebsiella michiganensis, carbapenem resistance, clonal dissemination, blaNDM-1, whole-genome sequencing
Citation: Liu H, Yan C, Jiao M, Jiang J, Wang S, Wei Z, Hu F and Xu X (2025) Clonal dissemination of carbapenem-resistant ST477 Klebsiella michiganensis co-producing NDM-1, SFO-1, and VEB-3 in a Chinese hospital. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1679043. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1679043
Received: 04 August 2025; Accepted: 06 October 2025;
Published: 22 October 2025.
Edited by:
Jinxin Zhao, Nursing & Health Sciences, Monash University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Xi Li, People’s Hospital of Hangzhou Medical College, ChinaBinghuai Lu, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, China
Siqiang Niu, First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yan, Jiao, Jiang, Wang, Wei, Hu and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fupin Hu, aHVmdXBpbkBmdWRhbi5lZHUuY24=; Xuesong Xu, eHV4c0BqbHUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hao Liu
Hao Liu Chao Yan1†
Chao Yan1† Fupin Hu
Fupin Hu Xuesong Xu
Xuesong Xu