- Centre for Nanobiotechnology, Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India
Phenylketonuria is an unusual inherited metabolic disease induced by mutations of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene, resulting in phenylalanine accumulation. The current treatments only focus on restricting lifelong dietary intake of phenylalanine, posing a significant challenge to concordance and living standards. Emerging evidence on phenylketonuria disorders underscores the gut microbiome involving probiotics as a key mediator of host metabolic processes. This review encompasses the insights into the pathophysiology of phenylketonuria, gut probiotics, the amino acid metabolism of phenylalanine, the mechanism of action of probiotics, and the therapeutic potential of the treatments available.
1 Introduction
Phenylketonuria, otherwise known as a deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. It is often distinguished by the inability to metabolize the phenylalanine amino acid (AA) resulting from PAH inadequacy. PAH is crucial for the conversion of tyrosine from phenylalanine, an important essential AA for various functions in humans. The deficiency or absence of PAH leads to the aggregation of phenylalanine in the blood and brain, inducing various neurological and metabolic disorders. Whereas higher concentrations of phenylalanine induce brain dysfunction. In the absence of treatment, the dysfunction leads to acute intellectual impairment, epilepsy, and behavioral complications (van Spronsen et al., 2021; Russo et al., 2025).
The prevalence of Phenylketonuria is identified worldwide in many countries, and its variation is larger when compared to its prevalence. In the United States, the overall incidence of Phenylketonuria was about 1/15,000. It was even greater for Caucasians and native Americans. Whereas it was lower for African American, Asian, and Hispanic populations. In countries such as Turkey, it was found to be as high as 1/4000 live births (Phenylketonuria, 2023). The prevalence of Phenylketonuria in the newborn screening coverage done in Brazil was identified with an annual incidence of 4–8 per/100,000 live births. Further, a record of 7615 patients was registered in their health systems (Vargas et al., 2025). Based on the reports of a French database on January 1, 2018, 3549 patients were reported with Phenylketonuria (Arnoux et al., 2024).
Probiotics or “live micro-organisms”, when consumed in an appropriate dose, have an impact on their host. Important functions like metabolic, barrier effects, and trophic functions rely on these bacterial communities. Dysbiosis in them has a negative impact on human health as well. The interactions between the human gut system, nutrients, microbes, and host cells significantly contribute to the gut homeostasis and development of the host. So, the application of probiotics has gained importance in disease treatment (Butel, 2014). Gut microbes play a pivotal part in metabolic processing in humans, and their alteration may lead to various metabolic disorders. In recent times, novel treatments using engineered probiotics for handling various metabolic disorders are being developed (Barati et al., 2024).
The primary treatment for phenylketonuria disease is the restriction of Phenylalanine from the patient’s diet, augmented with L-AA. Trillions of gut-associated bacteria or gut microbiota are present in healthy humans. The gut microbiota constitution can be modulated by various environmental and external factors, including diets and antibiotic exposure. The nutrition in the food of Phenylketonuria patients affects the host physiology as well as the gut microbiome environment. A study was conducted to characterize the gut microbiota of Phenylketonuria patients and healthy individuals using next-generation sequencing. It revealed the reduction of certain bacterial species from healthy individuals, indicating the significant differences in the metabolism of glucose and amino acids (De Oliveira et al., 2016).
This review comprises the pathophysiology of Phenylketonuria, its treatment methods, the exclusive role of probiotics, and their role in disease management. Further, the mechanism of action of probiotics, the limitations, and challenges in treating this metabolic disorder are discussed in detail, including an update on the probiotics and Phenylketonuria.
2 Pathophysiology of phenylketonuria
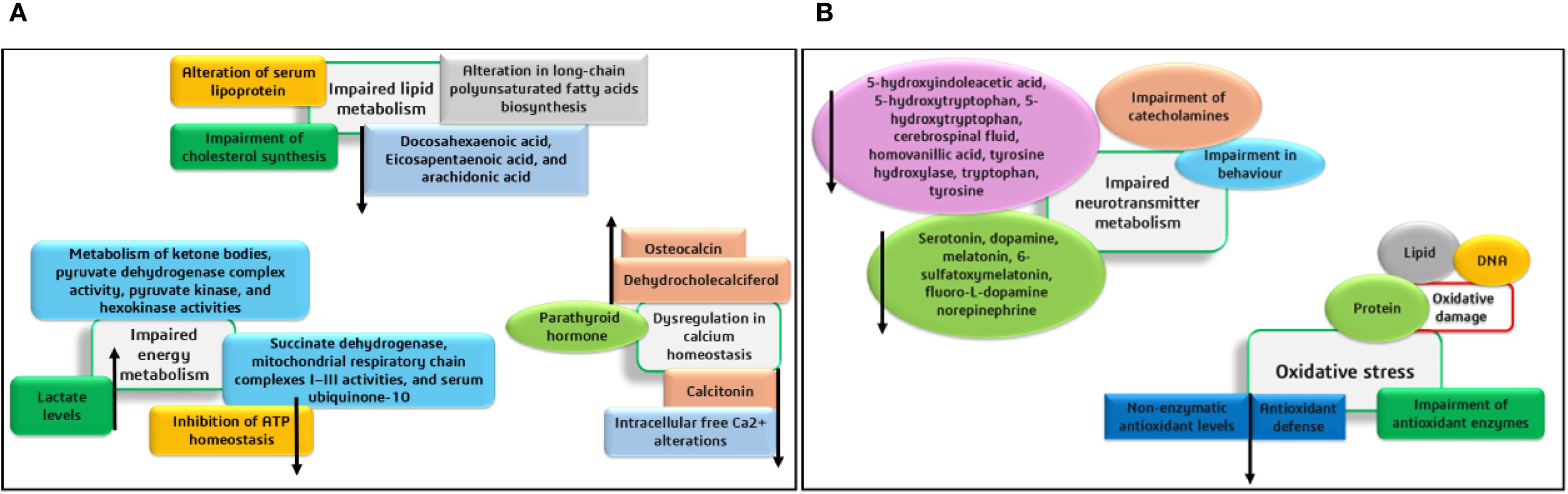
The organs and body fluids of Phenylketonuria patients are affected by the phenylalanine accumulation and its metabolites due to PAH deficiency. In the kidney and liver, the major phenylalanine metabolic pathway requires the hydroxylation of PAH by Tyrosine, and other alternative metabolic pathways are more trivial. The Phenylketonuria patients show intense neurological damage in the regions of the corpus callosum and striatum. Alterations in cortical regions and hypomyelination further lead to intellectual shortfall and neurodegeneration. In animal and human systems, metabolic changes, including oxidative stress, defective protein and neurotransmitter synthesis, and mitochondrial disorders were identified. The impacts of various metabolic alterations are depicted in Figures 1A, B. Further, the mechanisms involved in the disordered cerebral metabolisms and cognitive functional developments have not been completely unraveled (Schuck et al., 2015; de Groot et al., 2010).
Studies also state that hypothetically, the main factor behind the pathophysiological mechanism of cognitive disorders is the reduction of cerebral neurotransmitters (like dopamine and serotonin) caused by reduced availability of the AAs (Tyrosine and tryptophan). Additionally, in the presence of higher phenylalanine levels, the decrease in protein synthesis occurs due to the irregular uptake of non-phenylalanine large neutral AAs by the brain. The findings of researchers suggest that the major symptoms of this disease are mostly found in the brain, and the exact mechanism of pathophysiology is yet to be explored for a detailed understanding (Schuck et al., 2015; de Groot et al., 2010). Recent findings suggest that PAH is crucial for catalyzing the hydroxylation of phenylalanine to tyrosine, and this process includes the cofactor BH4 (rate-limiting step). During this process, BH4 is converted to quinonoid dihydrobiopterin (qBH2- oxidized form). The PAH enzyme facilitates the irreversible conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine. The Cofactor BH4 is synthesized from guanosine triphosphate in different tissues, including the liver, and is also recycled after the hydroxylation of phenylalanine through enzyme-based catalytic reduction. The deficiency of PAH leads to phenylalanine accumulation in all tissues and also causes relative tyrosine deficiency (Elhawary et al., 2022).
From a genetic perspective, Phenylketonuria is an inborn defect of phenylalanine metabolism due to pathogenic variants in the PAH gene. Further, genetic studies reveal that an individual with PKU receives a defective gene from their parents (both), and the gene located on chromosome 12q23.2 (90 kb) plays a role in numerous mutations in the PAH gene (autosomal recessive pattern). These mutations induce a reduction in PAH activity or a complete deficiency of the PAH enzyme. More than 1000 PAH gene variants have been reported, and their effects vary with the residual range of PAH activity in Phenylketonuria patients (Blau, 2016; van Spronsen et al., 2021; Russo et al., 2025; Elhawary et al., 2022).
3 Role of gut microbiota in amino acid metabolism – phenylalanine
Phenylketonuria is a metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of the hepatic enzyme PAH, resulting in high levels of the AA phenylalanine in the blood and brain. This leads to severe cognitive and psychological deficits, which can be partially prevented by dietary treatment. The behavioral pattern of Phenylketonuria patients can be linked to the gut-microbiome-brain axis, as diet plays a crucial role in modulating gut microbiome composition (van der Goot et al., 2022). The Gut microbiota and the central nervous system are related through major pathways such as the intestinal-mucosal barrier way, immune system route, gut-microbiome metabolic pathway, neuroanatomical pathway, the neuroendocrine-hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis pathway, and the blood-brain barrier. In consideration of Phenylketonuria, the diet plays a significant role in the gut-brain axis, as it affects the key intermediaries involved in the communication pathway. The microbes that produce metabolites like short-chain fatty acids, Gamma-aminobutyric acid, threonine, serotonin, glutamate, carnosine, Phenylalanine, aspartic acid, alanine, lysine, tyrosine, glycine, gut hormones/incretins, and ammonia may influence brain function or vice versa. Furthermore, gut microbiota might regulate the integrity of both the gut and the blood-brain barrier. This might lead to improper nutrient absorption (Mucosal surface) (Verduci et al., 2020).
A phenylalanine-restricted diet provided with additional L-AAs is the core treatment for this disease, and in a study conducted by De Oliveira et al., 2016, the gut microbiota of 8 Phenylketonuria patients with a phenylalanine-restricted diet and 10 healthy individuals were compared. The result indicated that Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes sp., were the most dominant phyla in both groups. Phenylketonuria patients showed reduced abundance of Odoribacter Sp., Coprococcus Sp., Ruminococcus Sp., Erysipelotrichaceae, Lachnospiraceae families, Clostridiaceae, and Clostridiales class, Dorea, Lachnospira, and Veillonella genera, and enrichment of Peptostreptococcaceae, Prevotella, and Akkermansia (De Oliveira et al., 2016).
Recent studies have shown that dietary phenylalanine, upon reaching the colon, is metabolized by specific gut microbes through enzymatic pathways involving phenylpyruvate decarboxylase and phenylpyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase. These microbial actions lead to the production of phenylacetic acid, which is subsequently conjugated in the liver with glutamine to form phenylacetyl glutamine (PAGln). PAGln is not just a metabolic byproduct—it also functions as a bioactive compound linked to thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, and neuroinflammation. Elevated levels of PAGln have been linked to gut dysbiosis and chronic diseases involving the heart, kidney, and brain. This highlights that the microbial transformation of AAs can extend beyond the gut, influencing systemic health (Krishnamoorthy et al., 2024).
Phenylalanine is a significant aromatic AA in Phenylketonuria disease. Tyrosine is synthesized from phenylalanine hydroxylation, and tyrosine hydroxylase is the critical enzyme responsible for converting tyrosine into catecholamines like norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine. Phenylalanine and tyrosine are mediated via the fermentation process by gut microbes into phenolic compounds. The two phenolic derivatives, p-cresol sulfate and p-cresol, are absent in germ-free mice, indicating the impact of the gut microbes in the production of both compounds. Bacterial species like Proteus vulgaris, Lactobacillaceae, Clostridium difficile, and C. scatalogenes are engaged in the formation of p-cresol from tyrosine. Furthermore, the relative abundance of the two bacterial metabolites p-cresol and phenylacetylglutamate, which originated from AAs (phenylalanine and tyrosine) metabolism, is greater in persons with multiple sclerosis compared to controls (Rebeaud et al., 2022). These studies correlate the role of gut microbes in altering the metabolic processes in humans.
4 Mechanism of action of probiotics
Probiotics have been used as food and feed for humans and animals over the years, which has helped to keep the gut healthy and balanced (Sakandar and Zhang, 2021; Xavier-Santos et al., 2022). Probiotics play a prominent role in gut microbiota, metabolic processes, and immune responses (Pires et al., 2024). It has been shown that the correlation between probiotics and gut microbiota is closely related to systemic inflammation and metabolic homeostasis (Chandrasekaran et al., 2024). Although the benefits of probiotics have been understood, the mechanism through which they function is still under investigation (Gul and Durante-Mangoni, 2024).
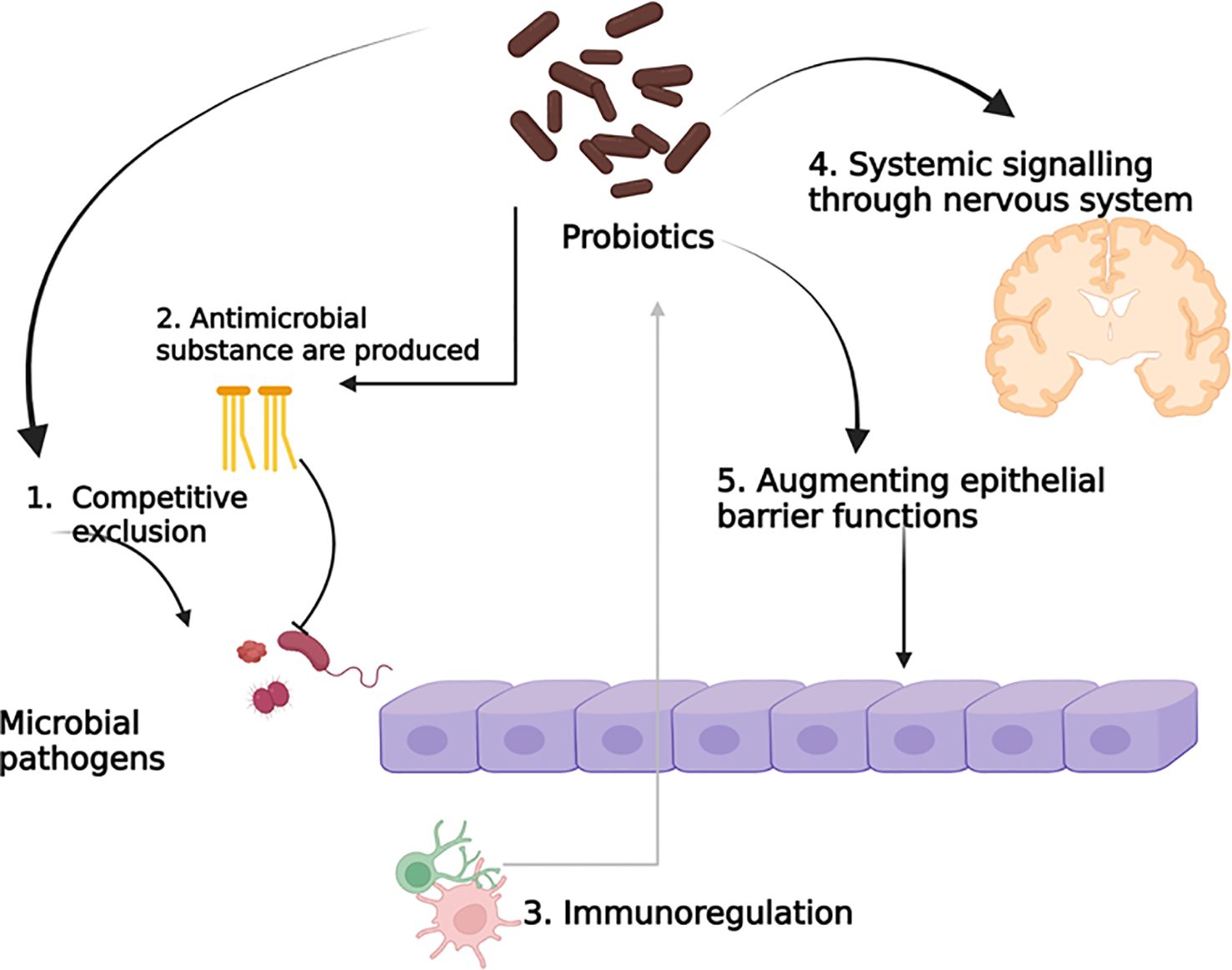
The mode of action of probiotics mainly focuses on metabolite production, such as vitamins, 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphtoic acid, short-chain fatty acids, a bifidogenic and anti-inflammatory product (Le Barz et al., 2015). However, the probiotic can change the gut microbiota directly, or the gut microbiota randomly changes with probiotic treatment, as the changes can happen in both directions, and as a result, they are connected to each other. However, it remains unclear whether the two-way mechanism and interactions are dependent or independent. Probiotics are associated with cell components such as peptidoglycans, polysaccharides, teichoic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid, cell-surface-bound and secretory proteins, bacteriocins, polyphosphate, and fatty acids, which can obstruct interactions. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase has a potential therapeutic effect, which was obtained from bacteria in Phenylketonuria when administered orally through Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 and Lactobacillus reuteri (Durrer et al., 2017; Isabella et al., 2018; Puurunen et al., 2021). The potential probiotic mechanism of action is depicted in Figure 2.
5 Phenylalanine metabolic mechanisms in phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria is one of the genetic disorders that is seen in approximately 1 in 23,930 newborns (Hillert et al., 2020). It is an autosomal recessive condition, which in turn means both parents should carry and pass the recessive gene (Bobrova et al., 2025). In chromosome 12q23.2, the PAH gene is located, which codes for the PAH enzyme involved in the metabolic pathway of phenylketonuria (Blau et al., 2010). The catalysis of L-phenylalanine to L-tyrosine by para-hydroxylation of the aromatic side chains was done by PAH (Flydal and Martinez, 2013). PAH is associated with the family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid, whereas tyrosine can be synthesized by the hydroxylation of phenylalanine. When PAH is low in the body, it results in the excess formation of phenylalanine, leading to hyperphenylalaninemia and Phenylketonuria (Williams et al., 2008). Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) can bind to the domain for catalysis of PAH, and it acts as the cofactor for the reaction. The exact mechanism of phenylalanine on brain damage is still unclear, but the impact on the central nervous system depends on the presence of phenylalanine in the brain, with younger, developing brains being more vulnerable (van Spronsen et al., 2009; Hawks et al., 2019; Romani et al., 2017).
Over the last decades, new treatments have been introduced to modify microbiota. Probiotic integration is also highlighted in this treatment process. The microbiota changes the microbial population, alters their composition, and affects the functionality of the microbes. Therefore, studies show that therapies can help treat metabolic disorders (de Groot et al., 2017; Le Barz et al., 2015). Isabella et al. (2018) formulated a synthetic strain of E. coli that can produce some enzymes that can break down the amino acid phenylalanine, which can even work in low oxygen conditions (Isabella et al., 2018). Recent research has examined how the Phenylketonuria treatment diet and phenylalanine affect children, showing a significant difference in their gut microbiota between Phenylketonuria individuals and non-Phenylketonuria individuals (Bassanini et al., 2019; De Oliveira et al., 2016).
Genetically modified probiotics, which are developed as live biotherapeutic agents, represent advanced and targeted alternative treatment methods for treating Phenylketonuria (de Oliveira Filho et al., 2022). Clinical development of therapeutics will have to adhere to strict regulatory controls and cannot be scaled in the same way as other products (Charbonneau et al., 2020). In Phenylketonuria patients, microbial community diversity is lowered, causing an imbalanced gut microbiome (dysbiosis) (Mosca et al., 2016), which means that some beneficial bacterial species are missing or reduced partially (Verduci et al., 2018; Mancilla et al., 2021; Pinheiro de Oliveira et al., 2016). The gut microbiota imbalance of Phenylketonuria patients is influenced by the nutrient intake in their diet. They consume higher glycemic index and glycemic load foods when compared to patients with mild hyperphenylalaninemia (Verduci et al., 2020, 2018). In vitro experiments show that in Phenylketonuria, some chemicals are formed from the breakdown of Phenylalanine and form phenylpropionic acid, phenyllactic acid, and phenylacetic acid, which interfere with the antioxidant enzymes. The accumulated substance affects the function and activity of these cells, which protects the body from oxidative damage. Phenyllactic acid and phenylacetic acid increased the activity of superoxide dismutase in animals, while phenylpropionic acid decreased the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in brain tissues (Moraes et al., 2013; Rosa et al., 2012).
6 Therapeutic potential
Initially, the most widely used therapy for Phenylketonuria patients was a blend of protein and Phenylalanine-restricted nutritional food. In 2007, the Food and Drug Administration approved sapropterin dihydrochloride, the first pharmacological agent for phenylketonuria, which is a synthetic version of the naturally occurring cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). BH4 is essential for PAH activity, and any defects in its synthetic pathway can result in PAH deficiency and elevated Phenylalanine concentrations. Pegvaliase, endorsed in 2018, was a medical intervention for Phenylketonuria patients. It is a novel substitutive enzyme therapy containing pegylated phenylalanine ammonia lyase, especially for patients unresponsive to sapropterin. Administered through subcutaneous injection daily, it converts Phenylalanine into ammonia and trans-cinnamic acid. Phenylketonuria patients aged 18 and older in the United States were approved for its usage. Clinical trials showed that individuals administered pegvaliase showed a much greater reduction of phenylalanine levels when compared to those who followed diet-based treatments or a blend of diet and sapropterin. After a treatment of 2 years, 61% and 51% of treated people reached phenylalanine levels of ≤360 and ≤120 μmol/L (blood), respectively. However, pegvaliase is associated with adverse effects ranging from benign reactions in injection regions to anaphylaxis. Consequently, all patients, pharmacies, and practitioners are obliged to enroll in a risk analysis and mitigation framework program before formerly initiating the therapy (Shrestha et al., 2025).
In a study conducted by Williams et al. (2025), Sepiapterin, a natural precursor of BH4, was developed as a treatment for children and adults with Phenylketonuria. Sepiapterin is safe and effective in lowering the blood phenylalanine levels in responsive individuals. The phase III APHENITY trial demonstrated that sepiapterin significantly lowered elevated phenylalanine levels in responsive children and adults with Phenylketonuria. Ongoing long-term studies aim to assess its effects on neurocognitive function, overall health status, nutritional outcomes, and quality of life in treated individuals. Table 1 describes the different therapies available for phenylketonuria, their efficacy mechanism, and side effects.
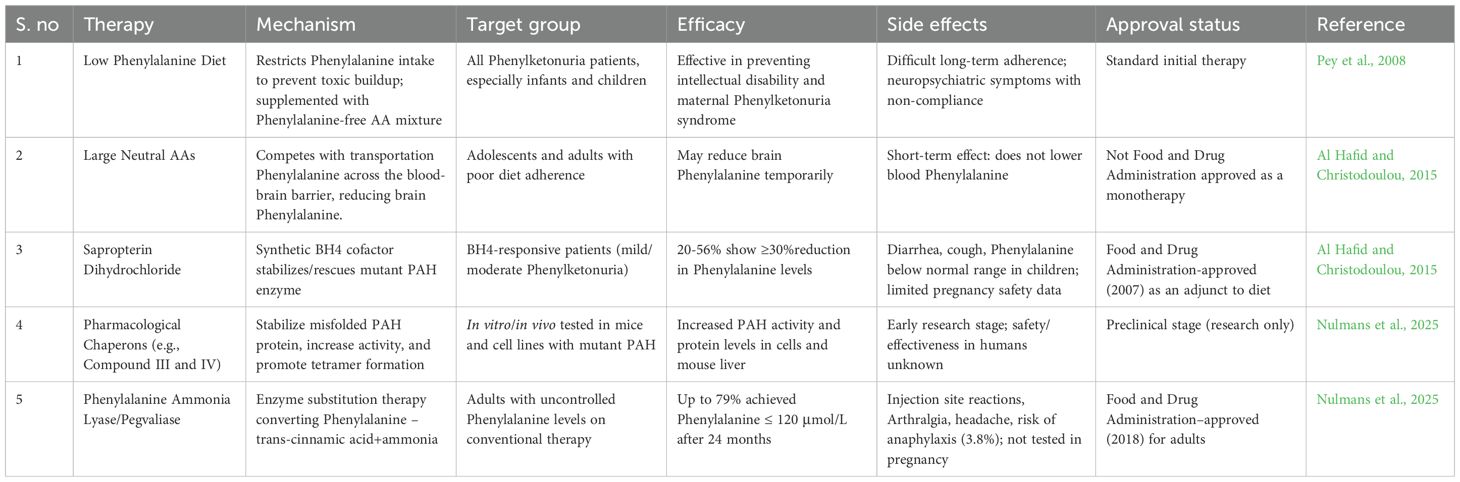
Table 1. Different therapies available for phenylketonuria, their efficacy mechanism, and side effects.
7 Limitations and challenges
Reduction in PAH activity leads to various changes in the synthesis of cerebral myelin and proteins. Additionally, the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline in the brain are significantly reduced. If left untreated, the development of the brain is extremely affected, causing significant intellectual disability and behavioral interference. Currently, only a few methods are involved in overcoming the challenges faced by Phenylketonuria. The use of the neonatal heel prick diagnostic method during birth can be used to analyze diseases at an earlier stage. The inclusion of a proper phenylalanine-confined diet (dietary treatment) has led to the maintenance of adequate neurodevelopment until adulthood. Studies state that the dietary method notably improved cognitive and psychiatric levels of the Phenylketonuria-affected individuals. Nevertheless, few individuals who maintain their nutritional habits persistently with proper control also have an increasing risk of mood, anxiety, or attentional disorders throughout their lives. On the other hand, the resulting effects of prolonged protein-limited foods on the functioning of the brain remain unexplored. Further, a concentration of 120–360 μmol/L blood phenylalanine should be maintained throughout the lifespan. The availability of limited data for clinicians makes it challenging to treat adult Phenylketonuria patients with psychiatric disorders. Further, advancements in 3D food printing are emerging for personally curated, high-nutrient-optimized, and sensory-appetizing foods, providing a novel dietary therapy for Phenylketonuria patients. In addition, a novel treatment like enzyme therapy holds promising results without limited dietary practices for better cognitive processing and mental health. For instance, regular subcutaneous injection of pegylated Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase or pegvaliase (PALYNZIQ®) serves as a propitious genetic therapy in the clinical trials done recently. Casein glycomacropeptide improves immunological processes and enhances large neutral amino acids for the prevention of plasma Phe transportation to the brain. Sapropterin hydrochloride or Kuvan®, an analog of BH4, aids as a potential therapy for activating residual PAH, which in turn decreases the blood phenylalanine level. Though these therapies help in managing the disease, the identification of new Phenylketonuria modifiers is necessary in the future. Other options, like cost-effective next-generation sequencing, can be used to rapidly analyze the genes and genomes to provide personalized diagnostics in the future (Russo et al., 2025; Ashe et al., 2019; Elhawary et al., 2022).
8 Future perspectives
Emerging research on the gut microbiota’s role in phenylalanine metabolism opens new avenues for microbiome-targeted therapies in Phenylketonuria management. Future strategies may include personalized probiotics or engineered gut microbes to modulate Phenylalanine levels and reduce toxic metabolites like PAGln. Further studies on microbial pathways could aid in discovering novel bioactive compounds impacting systemic health. Advances in precision nutrition and microbiota editing may improve cognitive outcomes in Phenylketonuria patients. Long-term clinical trials are essential to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and sustainability of these innovative microbiome-based interventions.
Author contributions
AK: Validation, Writing – original draft. SV: Investigation, Writing – original draft. HJ: Validation, Writing – original draft. JT: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the research work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al Hafid, N. and Christodoulou, J. (2015). Phenylketonuria: a review of current and future treatments. Trans. Pediatr. 4, 304–317. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2224-4336.2015.10.07
Arnoux, J.-B., Douillard, C., Maillot, F., Bouée, S., Jacob, C., Schneider, K. M., et al. (2024). Health economic impact of patients with phenylketonuria (PKU) in France – A nationwide study of health insurance claims data. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 41, 101134. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2024.101134
Ashe, K., Kelso, W., Farrand, S., Panetta, J., Fazio, T., De Jong, G., et al. (2019). Psychiatric and cognitive aspects of phenylketonuria: the limitations of diet and promise of new treatments. Front. Psychiatry 10. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00561
Barati, M., Mosharkesh, E., Tahmassian, A. H., Khodaei, M., Jabbari, M., Kalhori, A., et al. (2024). Engineered probiotics for the management of congenital metabolic diseases: A systematic review. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 29, 1–7. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2024.29.1.1
Bassanini, G., Ceccarani, C., Borgo, F., Severgnini, M., Rovelli, V., Morace, G., et al. (2019). Phenylketonuria diet promotes shifts in firmicutes populations. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00101
Blau, N. (2016). Genetics of phenylketonuria: then and now. Hum. Mutat. 37, 508–515. doi: 10.1002/humu.22980
Blau, N., van Spronsen, F. J., and Levy, H. L. (2010). Phenylketonuria. Lancet 376, 1417–1427. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60961-0
Bobrova, N. A., Lyubimova, D. I., Mishina, D. M., Lobanova, V. S., Valieva, S. I., Mityaeva, O. N., et al. (2025). Experimental animal models of phenylketonuria: pros and cons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 5262. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115262
Butel, M.-J. (2014). Probiotics, gut microbiota and health. Med. Mal Infect. 44, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2013.10.002
Chandrasekaran, P., Weiskirchen, S., and Weiskirchen, R. (2024). Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: an overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 6022. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116022
Charbonneau, M. R., Isabella, V. M., Li, N., and Kurtz, C. B. (2020). Developing a new class of engineered live bacterial therapeutics to treat human diseases. Nat. Commun. 11, 1738. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15508-1
de Groot, M. J., Hoeksma, M., Blau, N., Reijngoud, D. J., and van Spronsen, F. J. (2010). Pathogenesis of cognitive dysfunction in phenylketonuria: Review of hypotheses☆. Mol. Genet. Metab. 99, S86–S89. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.10.016
de Groot, P. F., Frissen, M. N., de Clercq, N. C., and Nieuwdorp, M. (2017). Fecal microbiota transplantation in metabolic syndrome: History, present and future. Gut Microbes 8, 253–267. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1293224
De Oliveira, F. P., Mendes, R. H., Dobbler, P. T., Mai, V., Pylro, V. S., Waugh, S. G., et al. (2016). Phenylketonuria and gut microbiota: A controlled study based on next-generation sequencing. PLoS One 11, 1–15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157513
de Oliveira Filho, J. G., Carvalho, A. S. E. S., Alves, J. D. S., and Egea, M. B. (2022). Next-generation probiotics as a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of phenylketonuria: a review. Nutr. Rev. 80, 2100–2112. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuac024
Durrer, A., Gumiere, T., Taketani, R. G., da Costa, D. P., Pereira e Silva, M. D. C., and Andreote, F. D. (2017). The drivers underlying biogeographical patterns of bacterial communities in soils under sugarcane cultivation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 110, 12–20. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.11.005
Elhawary, N. A., AlJahdali, I. A., Abumansour, I. S., Elhawary, E. N., Gaboon, N., Dandini, M., et al. (2022). Genetic etiology and clinical challenges of phenylketonuria. Hum. Genomics 16, 22. doi: 10.1186/s40246-022-00398-9
Flydal, M. I. and Martinez, A. (2013). Phenylalanine hydroxylase: Function, structure, and regulation. IUBMB Life 65, 341–349. doi: 10.1002/iub.1150
Gul, S. and Durante-Mangoni, E. (2024). Unraveling the puzzle: health benefits of probiotics—A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Med. 13, 1436. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051436
Hawks, Z., Hood, A. M., Lerman-Sinkoff, D. B., Shimony, J. S., Rutlin, J., Lagoni, D., et al. (2019). White and gray matter brain development in children and young adults with phenylketonuria. NeuroImage Clin. 23, 101916. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101916
Hillert, A., Anikster, Y., Belanger-Quintana, A., Burlina, A., Burton, B. K., Carducci, C., et al. (2020). The genetic landscape and epidemiology of phenylketonuria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 107, 234–250. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.06.006
Isabella, V. M., Ha, B. N., Castillo, M. J., Lubkowicz, D. J., Rowe, S. E., Millet, Y. A., et al. (2018). Development of a synthetic live bacterial therapeutic for the human metabolic disease phenylketonuria. Nat. Biotechnol. 36, 857–864. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4222
Krishnamoorthy, N. K., Kalyan, M., Hediyal, T. A., Anand, N., Kendaganna, P. H., Pendyala, G., et al. (2024). Role of the gut bacteria-derived metabolite phenylacetylglutamine in health and diseases. ACS Omega. 9 (3), 3164–3172. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08184
Le Barz, M., Anhê, F. F., Varin, T. V., Desjardins, Y., Levy, E., Roy, D., et al. (2015). Probiotics as complementary treatment for metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metab. J. 39, 291. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.291
Mancilla, V. J., Mann, A. E., Zhang, Y., and Allen, M. S. (2021). The adult phenylketonuria (PKU) gut microbiome. Microorganisms 9, 530. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030530
Moraes, T. B., Jacques, C. E. D., Rosa, A. P., Dalazen, G. R., Terra, M., Coelho, J. G., et al. (2013). Role of catalase and superoxide dismutase activities on oxidative stress in the brain of a phenylketonuria animal model and the effect of lipoic acid. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 33, 253–260. doi: 10.1007/s10571-012-9892-5
Mosca, A., Leclerc, M., and Hugot, J. P. (2016). Gut microbiota diversity and human diseases: should we reintroduce key predators in our ecosystem? Front. Microbiol. 7. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00455
Nulmans, I., Lequeue, S., Desmet, L., Neuckermans, J., and De Kock, J. (2025). Current state of the treatment landscape of phenylketonuria. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 20, 281. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03840-y
Pey, A. L., Ying, M., Cremades, N., Velazquez-Campoy, A., Scherer, T., Thöny, B., et al. (2008). Identification of pharmacological chaperones as potential therapeutic agents to treat phenylketonuria. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 2858–2867. doi: 10.1172/JCI34355
Pinheiro de Oliveira, F., Mendes, R. H., Dobbler, P. T., Mai, V., Pylro, V. S., Waugh, S. G., et al. (2016). Phenylketonuria and gut microbiota: A controlled study based on next-generation sequencing. PLoS One 11, e0157513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157513
Pires, L., González-Paramás, A. M., Heleno, S. A., and Calhelha, R. C. (2024). The role of gut microbiota in the etiopathogenesis of multiple chronic diseases. Antibiotics 13, 392. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050392
Puurunen, M. K., Vockley, J., Searle, S. L., Sacharow, S. J., Phillips, J. A., Denney, W. S., et al. (2021). Safety and pharmacodynamics of an engineered E. coli Nissle for the treatment of phenylketonuria: a first-in-human phase 1/2a study. Nat. Metab. 3, 1125–1132. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00430-7
Rebeaud, J., Peter, B., and Pot, C. (2022). How microbiota-derived metabolites link the gut to the brain during neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 10128. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710128
Romani, C., Palermo, L., MacDonald, A., Limback, E., Hall, S. K., and Geberhiwot, T. (2017). The impact of phenylalanine levels on cognitive outcomes in adults with phenylketonuria: Effects across tasks and developmental stages. Neuropsychology 31, 242–254. doi: 10.1037/neu0000336
Rosa, A. P., Jacques, C. E. D., Moraes, T. B., Wannmacher, C. M. D., de Mattos Dutra, Â., and Dutra-Filho, C. S. (2012). Phenylpyruvic acid decreases glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in rat brain. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 32, 1113–1118. doi: 10.1007/s10571-012-9834-2
Russo, G. L., Puleo, S., Cavella, S., Scala, I., Fidaleo, M., and Di Monaco, R. (2025). Advancements in food science for Phenylketonuria (PKU) management: a comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 65, 3208–3222. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2360075
Sakandar, H. A. and Zhang, H. (2021). Trends in Probiotic(s)-Fermented milks and their in vivo functionality: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 110, 55–65. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.054
Schuck, P. F., Malgarin, F., Cararo, J. H., Cardoso, F., Streck, E. L., and Ferreira, G. C. (2015). Phenylketonuria pathophysiology: on the role of metabolic alterations. Aging Dis. 6, 390–399. doi: 10.14336/AD.2015.0827
Shrestha, S., Zagel, A. L., Pillai, N. R., Ahmed, A., Jacobson, J., Ranasinghe, A., et al. (2025). Pegvaliase therapy for phenylketonuria: Real-world safety, efficacy, and medication access outcomes in a pharmacist-led pegvaliase program. Genet. Med. 27, 101405. doi: 10.1016/j.gim.2025.101405
Stone, W. L., Basit, H., and Los, E.. (2023). Phenylketonuria (StatPearls Publishing LLC: StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK535378.
van der Goot, E., Vink, S. N., van Vliet, D., van Spronsen, F. J., Falcao Salles, J., and van der Zee, E. A. (2022). Gut-microbiome composition in response to phenylketonuria depends on dietary phenylalanine in BTBR pahenu2 mice. Front. Nutr. 8. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.735366
van Spronsen, F. J., Blau, N., Harding, C., Burlina, A., Longo, N., and Bosch, A. M. (2021). Phenylketonuria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 7, 36. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00267-0
van Spronsen, F. J., Hoeksma, M., and Reijngoud, D. (2009). Brain dysfunction in phenylketonuria: Is phenylalanine toxicity the only possible cause? J. Inherit Metab. Dis. 32, 46–51. doi: 10.1007/s10545-008-0946-2
Vargas, P. R., Poubel, M., Martins, B., Velez, P., Vilela, D., Mesojedovas, D., et al. (2025). Patient journey and disease burden characterization of the population with phenylketonuria (PKU) in Brazil: a retrospective analysis through data reported in the public health system administrative database (DATASUS). Lancet Regional Health - A. 47, 101134. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2025.101134
Verduci, E., Carbone, M. T., Borghi, E., Ottaviano, E., Burlina, A., and Biasucci, G. (2020). Nutrition, microbiota and role of gut-brain axis in subjects with phenylketonuria (PKU): A review. Nutrients 12, 3319. doi: 10.3390/nu12113319
Verduci, E., Moretti, F., Bassanini, G., Banderali, G., Rovelli, V., Casiraghi, M. C., et al. (2018). Phenylketonuric diet negatively impacts on butyrate production. Nutrition Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 28, 385–392. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2018.01.004
Williams, R. A., Bell, D. A., Hooper, A. J., and Burnett, J. R. (2025). Sepiapterin for the treatment of phenylketonuria. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 26, 933–938. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2025.2498477
Williams, R. A., Mamotte, C. D., and Burnett, J. R. (2008). Phenylketonuria: an inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 29, 31–41. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2423317/
Xavier-Santos, D., Padilha, M., Fabiano, G. A., Vinderola, G., Gomes Cruz, A., Sivieri, K., et al. (2022). Evidences and perspectives of the use of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics as adjuvants for prevention and treatment of COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 120, 174–192. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.12.033
Keywords: phenylketonuria, metabolic disorders, human, gut probiotics, amino acids, phenylalanine, mechanism, tyrosine
Citation: Kalla Veedu A, Vijayakumar S, Joseph HA and Thomas J (2025) Impact of gut probiotic metabolites on phenylketonuria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1682110. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1682110
Received: 08 August 2025; Accepted: 22 September 2025;
Published: 13 October 2025.
Edited by:
Senbagam Duraisamy, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, IndiaReviewed by:
Sneeha Veerakumar, PP Savani University, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Kalla Veedu, Vijayakumar, Joseph and Thomas. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: John Thomas, am9obi50aG9tYXNAdml0LmFjLmlu; dGhfam9objI4QHlhaG9vLmNvLmlu
 Anjana Kalla Veedu
Anjana Kalla Veedu Sujithra Vijayakumar
Sujithra Vijayakumar Hannah A. Joseph
Hannah A. Joseph John Thomas
John Thomas