- 1School of Materials, Guangdong Industry Polytechnic University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 3Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Zakho, Zakho, Iraq
- 4Department of Biological and Biomedical Sciences, Glasgow Caledonian University, Glasgow, United Kingdom
- 5Pu Ai Medical School, Shaoyang University, Shaoyang, Hunan, China
Background: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common retinal disorder, causing blindness in aged individuals. One of the traditional Chinese medicines, modified Zhujing pill (MZP), has been widely used to treat various ocular disorders, including AMD; however, its protective mechanisms remain elusive. In this study, we explored the functional role of MZP in high-fat-diet-fed mice, a commonly used model for AMD.
Methods: Compounds of MZP water extract were identified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/mass spectrometry (MS)/MS. The mice were divided into three groups: group 1 mice fed with control diet (CD), group 2 mice fed with high-fat diet (HFD), and group 3 mice fed with HFD for 12 weeks; groups 1 and 2 were then treated with physiological saline, while group 3 was treated with MZP for 4 weeks. The cholesterol level and expression of cholesterol homeostasis-associated genes, antioxidant genes, and proinflammatory cytokines in mouse tissues were measured using biochemical approaches. Mouse cecum microbiota compositions and metabolic functions were analyzed using 16rRNA sequencing and bioinformatics approach.
Results: HFD-fed mice had high levels of cholesterol in the retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells, liver, and serum, a decreased expression of cholesterol homeostasis-associated genes and antioxidant genes in the RPE and liver, and an increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines. MZP treatment counteracted HFD-induced pathologic effects. Additionally, HFD altered cecum bacterial compositions and diversities associated with individual metabolic pathways. These metabolic pathways are involved in the biosynthesis of bacterial metabolites, mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and inflammation. MZP reversed most of the changes back to control characteristics.
Conclusion: We postulate that the beneficial effects of MZP against AMD are possibly related to lowering the cholesterol level, suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation, and modulating gut microbiota and associated functions.
1 Introduction
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a severe retinal disorder, affecting over 200 million patients over 50 years old globally (Wong et al., 2014). The major clinical feature of AMD is abnormal focal and diffuse extracellular deposits underneath the retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) layer, which are thought to cause dysfunction and later atrophy of RPE, followed by loss of photoreceptors (Jiang et al., 2025). The retinal pathology of AMD patients demonstrates that cholesterol is enriched in these deposits, suggesting that dysregulation of cholesterol homeostasis may contribute to AMD pathogenesis (Curcio et al., 2005; Pang et al., 2015). Genome-wide association studies have demonstrated that some cholesterol metabolism/transport genes are associated with AMD (Fritsche et al., 2016). Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statin treatment, confer a reduced risk in developing AMD (McGwin et al., 2005); conversely, a cholesterol-enriched diet is thought to increase the risk of developing AMD (Cao et al., 2022b). A high-cholesterol diet can also induce AMD-like features in rabbits (Dasari et al., 2011). This data further supports the hypothesis that cholesterol is involved in the formation and progression of AMD.
The RPE layer is a polarized single cell layer that predominantly functions in providing nutrients for photoreceptors and renewing photoreceptor outer segments. The RPE also plays a critical role in retinal cholesterol homeostasis. The RPE can perform de novo cholesterol synthesis as cholesterol synthesis pathway genes, such as HMGCR, DHCR24, and SQLE, are expressed in human and mouse RPE (Zheng et al., 2012, 2015; Louer et al., 2020); similarly, genes involved in cholesterol metabolism and trafficking—for example, CYP27A1, CYP46A1, NR1H3 (encoding LXRα), ABCA1, and ABCG1—are also expressed in human and mouse RPE (Zheng et al., 2012; Biswas et al., 2017, 2021). RPE-specific knockout of mouse Abca1 caused impaired cholesterol efflux and accumulation of cholesterol-ester-enriched lipid droplets in the RPE (Storti et al., 2019). The translocator protein (TSPO), a mitochondrial outer membrane protein, mediates cholesterol metabolism and trafficking in the RPE. Loss of TSPO in human RPE (ARPE-19) cells results in defective cholesterol efflux and an increased intracellular level of cholesterol (Biswas et al., 2017). Global knockout of Tspo in mice causes an increase in the levels of cholesterol, triglyceride, and phospholipids, downregulates the expression of cholesterol metabolism and trafficking genes, and increases inflammation in the RPE (Farhan et al., 2021). The RPE takes up LDL-bound cholesterol mainly from choroidal capillary vessels via LDLR-mediated endocytosis. Excess cholesterol in the RPE is returned to the liver via cholesterol reverse transport for storage as cholesterol esters or for excretion in the bile (Zhang et al., 2021).
As a complex retinal disorder, AMD is associated with complicated pathological mechanisms. It is putative that oxidative stress, inflammation, dysregulation of lipid metabolism, and angiogenesis are major contributors to the pathogenesis of AMD (Jiang et al., 2025). Consolidated data also suggests that gut dysbiosis is associated with AMD (Xiao et al., 2023). A comparison of gut microbiota between AMD patients and healthy controls has shown changes in microbiota composition—for example, Zhang et al. demonstrate that fecal samples of AMD patients have high levels of Bacteroidota and Proteobacteria and a low level of Firmicutes compared to that of the controls (Zhang et al., 2023). Evidence from AMD rodent models is consistent with the findings of clinical studies. High-fat-diet (HFD) -induced gut dysbiosis in mice exacerbates the formation of choroid neovascularization and microglia activation, both of which are key features of AMD (Andriessen et al., 2016). Studies from germ-free (GF) and specific pathogen-free (SPF) models provide direct evidence of gut microbiota associated with AMD. GF mice display reduced lesion size and microglia activation in laser-induced choroidal neovascularization compared to that of SPF mice; gut microbiota possibly is involved in the regulation of gene expression in the RPE, as over 660 genes are differentially expressed between GF and SPF mice in the RPE. Most of these genes function in inflammatory response, immune regulation, and angiogenesis (Zhang et al., 2022).
Current treatments for AMD include anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) therapy (for neovascular AMD) and anti-complement therapy (for nonexudative AMD) via intravitreal injections (Boopathiraj et al., 2024). These treatments can cause adverse events and complications—for example, intraocular inflammation, retinal detachment, ocular hemorrhage, and cataract. Therefore, alternative effective treatments for AMD are required. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used in the treatment of AMD patients for thousands of years in China, and 101 formulas have been reported, containing 167 Chinese medicines (Li et al., 2022). However, TCM has not been accepted for the treatment of AMD in Western countries, perhaps due to unelucidated complicated mechanisms. Zhujing pill (ZP) is one of the TCM formulas that is firstly described in the medicine book Taiping Holy Prescriptions for Universal Relief, edited by Huaiyin Wang in Song dynasty, and initially composed of three Chinese herbs: Tusizi (Cuscuta chinensis Lam), Dihuang (Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata), and Cheqianzi (Plantago asiatical) (Wang, 1958). Dr Da-Fu Chen, a famous ophthalmologist, modified the formula in his TCM ophthalmological book in 1978, removing one medicinal herb and adding seven others (Chen, 1978). Based on the theory of TCM, the therapeutic effects of ZP or modified ZP (MZP) on various disorders are through balancing Yin and Yang and tonifying the liver and kidney. ZP or MZP has shown protective effects against retinal disorders including retinitis pigmentosa (Fan and Zhang, 2018), diabetic retinopathy (Lei et al., 2018; Cui et al., 2023), and age-related macular degeneration (Feng et al., 2024). However, the underlying therapeutic mechanisms remain elusive.
In this study, we aimed to investigate the protective role of MZP against AMD in the regulation of cholesterol metabolism, suppression of both oxidative stress and inflammation, and modulation of gut microbiota. The HFD-fed mouse model, although utilizing young mice, recapitulates the major pathological features of AMD (Andriessen et al., 2016; Biswas et al., 2021; Sterling et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2023). We therefore treated HFD-fed mice with MZP, measured the cholesterol level in the RPE, liver, and serum, quantified the expression of cholesterol-metabolism-associated genes in the RPE and liver, and examined the microbiota. We found that MZP modulated RPE cholesterol metabolism and gut microbiota. Our study can improve the understanding of the therapeutic effects of TCM and promote the recognition of TCM in treating AMD in Western countries.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Preparation of MZP water extract
MZP, purchased from the First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, included Chushizi (Broussonetia papyrifera (L.), Vent Morus papyrifera L., dried fruit) 15 g, Gouqizi (Lycium chinense Mill, dried fruit) 12 g, Tusizi (Cuscuta chinensis Lam, dried seeds) 15 g, Wuweizi (Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill, dried fruit) 12 g, Chongweizi (Leonurus japonicus Houtt, dried fruit) 10 g, Cheqianzi (Plantago asiatical, dried seeds) 12 g, Mugua (Chaenomeles sinensis, dried fruit) 12 g, Sanqi (Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen, dried roots) 3 g, and Hanshuishi (Gypsum rubrum) 10 g. MZP was initially soaked with 50 mL distilled water (dH2O) for 20 min, then boiled, and simmered for 30 min. The first batch of decoction was obtained by filtering through a cheesecloth. The herbal mixture was again soaked in 50 mL dH2O for 20 min and then boiled for 30 min at a low simmer. The second batch of decoction was strained. Both batches were mixed, concentrated to 1.10 g/mL, aliquoted, and stored in a freezer.
2.2 Compound identification in water-extracted MZP
Water extract of MZP (from Section 2.1) was concentrated and dried to form powder in a glass evaporating dish within a vacuum oven. Then, 2 mg of powder was initially dissolved in 1 mL ultrapure water and further diluted with acetonitrile to a final concentration of 2 µg/mL. The samples were run in duplicate and in both positive and negative ionization modes at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a gradient elution scheme (Supplementary Figure S1) on a reverse-phase column (HALO 90 A RP-AMIDE 2 UM 2.1 X150M) and Thermo Scientific Q-exactive orbitrap mass spectrometer as the high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (HPLC/MS)/MS setup. MZMINE 4.5.0 was used to process the data and identify the components with MASSBANK (https://massbank.eu/MassBank) and global natural products social molecular networking (GNPS) libraries (https://gnps.ucsd.edu) with the standard MZ Wizard settings for HPLC-Orbitrap-DDA.
2.3 Animal experiments
All animal work was approved by the Animal Welfare Committee of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (license number: SYXK (Xiang) 2019-0009). C57BL/6 male mice (4 weeks old) were randomly divided into three groups (10 mice in each group), with one group (group 1) fed with chow diet and the other two groups (group 2 and group 3) fed with HFD containing 78.75% chow diet, 10% lard, 10% corn oil, 1% cholesterol, and 0.25% sodium cholate. After 12 weeks of feeding, groups 1 and 2 had daily intra-gastric administration of physiological saline for 4 weeks, while group 3 had daily intra-gastric administration of MZP water extract (14.69 g/kg body weight) for 4 weeks. The dose of MZP treatment was calculated based on the clinical dose in treating AMD patients using the formula: mouse dose (g/kg) = human dose (g/kg) × Km ratio, guided by a previous publication (Nair and Jacob, 2016). During the treatment period, animals in group 1 were fed with a chow diet, and animals in group 2 and group 3 were fed with HFD. The body weight of all animals was monitored every 2 weeks. After the treatment, the animals were euthanized by exposure to CO2 for 10 min (5 min of induction time with CO2 flowrate at 20% of the chamber volume per minute and 5 min of dwell time), and tissues were collected for further studies.
2.4 Quantification of gene expression
Total RNAs were extracted from mouse RPE and liver using TRIzol™ reagent (cat. no. 15596026, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Paisley, Scotland), following the manufacturer’s guidance. cDNA was synthesized, and the mRNA level of individual targeted genes was measured using a SuperScript III reverse transcription kit (cat. no. 18080093, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Paisley, Scotland) and the Syber Green kit (cat. no. 4309155, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Paisley, Scotland), respectively. The cycle threshold (CT) values of targeted genes were normalized to the housekeeping gene, Gapdh, and then analyzed using the 2-ΔΔCt formula. Primer sequences are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
2.5 Biochemical assays
Total cholesterol in mouse RPE, liver, and serum was measured using a commercial cholesterol assay kit (cat. no. A12216, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Paisley, Scotland) based on the manufacturer’s protocol. Proinflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) were detected using the Mini ABTS ELISA Development Kits (cat. no. 900-K47 for IL-1β; cat. no. 900-K50 for IL-6; cat. no. 900-K54 for TNFα; purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Paisley, Scotland), following the manufacturer’s guidance.
2.6 Sequencing and bioinformatic analysis of 16S rRNA genes
Animal cecum samples were collected, and total DNA was extracted using a QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, UK) based on the manufacturer’s guidance. The V3+V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using upstream and downstream primers 338F 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′ and 806R 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′. The amplified products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and purified using a gel extraction kit. The library was constructed by a second PCR with Illumina adapters attached to the originally amplified products. High-throughput sequencing of the library was then conducted using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform.
Raw data were initially filtered using Trimmomatic v0.33, followed by primer sequence removal with Cutadapt v1.9.1. Sequence assembly and chimera removal were performed using USEARCH v10, and reads were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at a 97.0% similarity threshold. Alpha diversity was compared using the Simpson and Shannon indices with the R v3.1.1 software. Beta diversity differences between groups were compared using PCoA analysis based on Bray–Curtis and weighted UniFrac distances, performed with QIIME2 software. The relative abundance means of the phyla was visualized by Stacked plots chart, with the cluster of these phyla represented by a heatmap using the SRplot tool (https://www.bioinformatics.com.cn). The differences of the taxa relative abundance between groups were assessed using Wilcoxon tests. Predicated functional profile of the gut microbiome was performed using the Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt2). The differences of the relative abundance of MetaCyc pathways among groups were determined using Wilcoxon tests. In addition, the predicated abundance of functional genes was analyzed based on Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) orthologs (KOs) using 16S rRNA gene sequence database identifiers by KEGG. The relative abundance of KOs across the three experimental groups was assessed using the online iDEP (https://bioinformatics.sdstate.edu/idep/). Differences in KO profiles among the three groups were presented through cluster heatmap, dendrograms, and volcano plot to highlight statistically significant variations compared by log2 FC and adjusted p-value.
2.7 Data analysis
Data from the quantification of gene expression and biochemical assays was presented as mean ± SE and analyzed with the GraphPad Prism software (version 10, www.graphpad.com). P-value <0.05 was considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 Identification of main compounds in water-extracted MZP
HPLC–MS/MS was used to identify the main compounds in water-extracted MZP, and both positive and negative ion modes were analyzed in the total ion current chromatograms (Figure 1). Based on the MZmine software, 63 compounds were identified in positive ion mode (Supplementary Table S2), and 81 compounds were identified in negative ion mode (Supplementary Table S3), when aligning to the two available databases (MASSBANK and GNPS). When the duplicated compounds in both positive and negative ion modes were excluded, 115 compounds remained, of which 23% were flavonoids, 11% were terpenes, 11% were phospholipids, 11% were carboxylic acids, 7% were cinnamic acids, 7% were phenolic, 5% coumarins, 3% pyridines, 3% sesquiterpenes, 3% fatty acids, and 16% were other compounds.
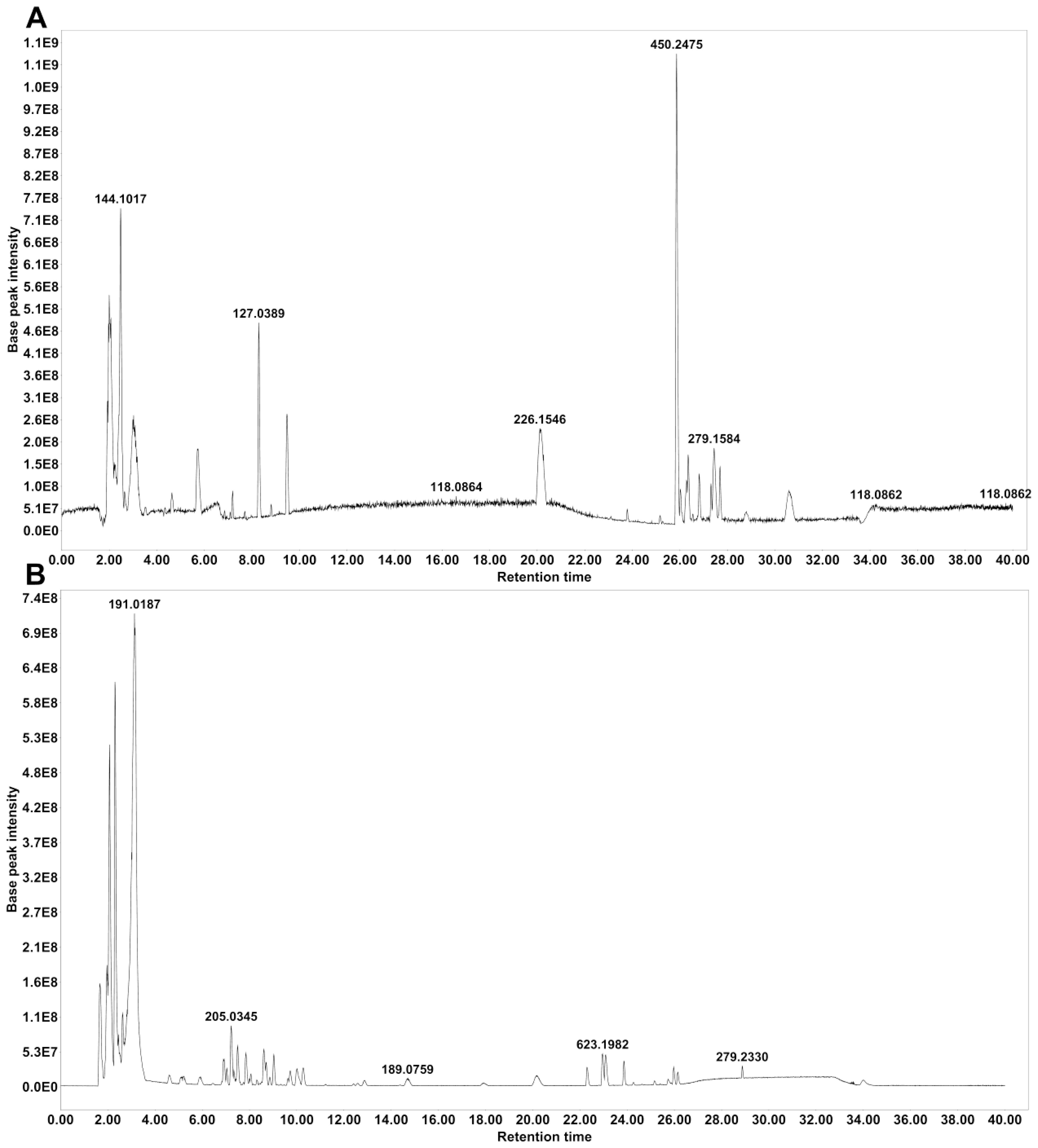
Figure 1. Base peak chromatograms of modified Zhujing pill (MZP) water extract obtained in positive (A) and negative (B) ionization modes.
3.2 MZP treatment decreased the cholesterol level in the RPE, liver, and serum of HFD-fed mice
The HFD-fed mouse model has been widely used to study the pathogenesis of AMD (Biswas et al., 2021; Keeling et al., 2022). We monitored the body weight of all animals in the three groups during the experimental period and noticed that, from week 2, HFD-fed animals (groups 2 and 3) gained significantly more body weight than that of animals fed with chow diet (group 1). After MZP treatment, the body weight of MZP-treated animals was not significantly different to that of HFD-fed animals, indicating that MZP had no effect on mouse body weight (Supplementary Figure S2).
When we examined the cholesterol level in the RPE, liver, and serum in all animals, we found that HFD-fed animals had significantly higher levels of cholesterol in the examined tissues, when compared to that of animals fed with chow diet, and that MZP administration counteracted HFD-induced effects (Figure 2A). We also measured the expression of cholesterol homeostasis-associated genes in the RPE and liver. The expression of cholesterol metabolism genes (Cyp27a1 and Cyp46a1), cholesterol metabolism regulator gene (Nr1h3, encoding LXRα), and cholesterol trafficking genes (Abca1 and Abcg1) was significantly downregulated in the RPE and liver of HFD-fed mice compared to that of mice fed with chow diet; MZP reversed the HFD-induced effects by upregulating the expression of these genes (Figures 2B, C).
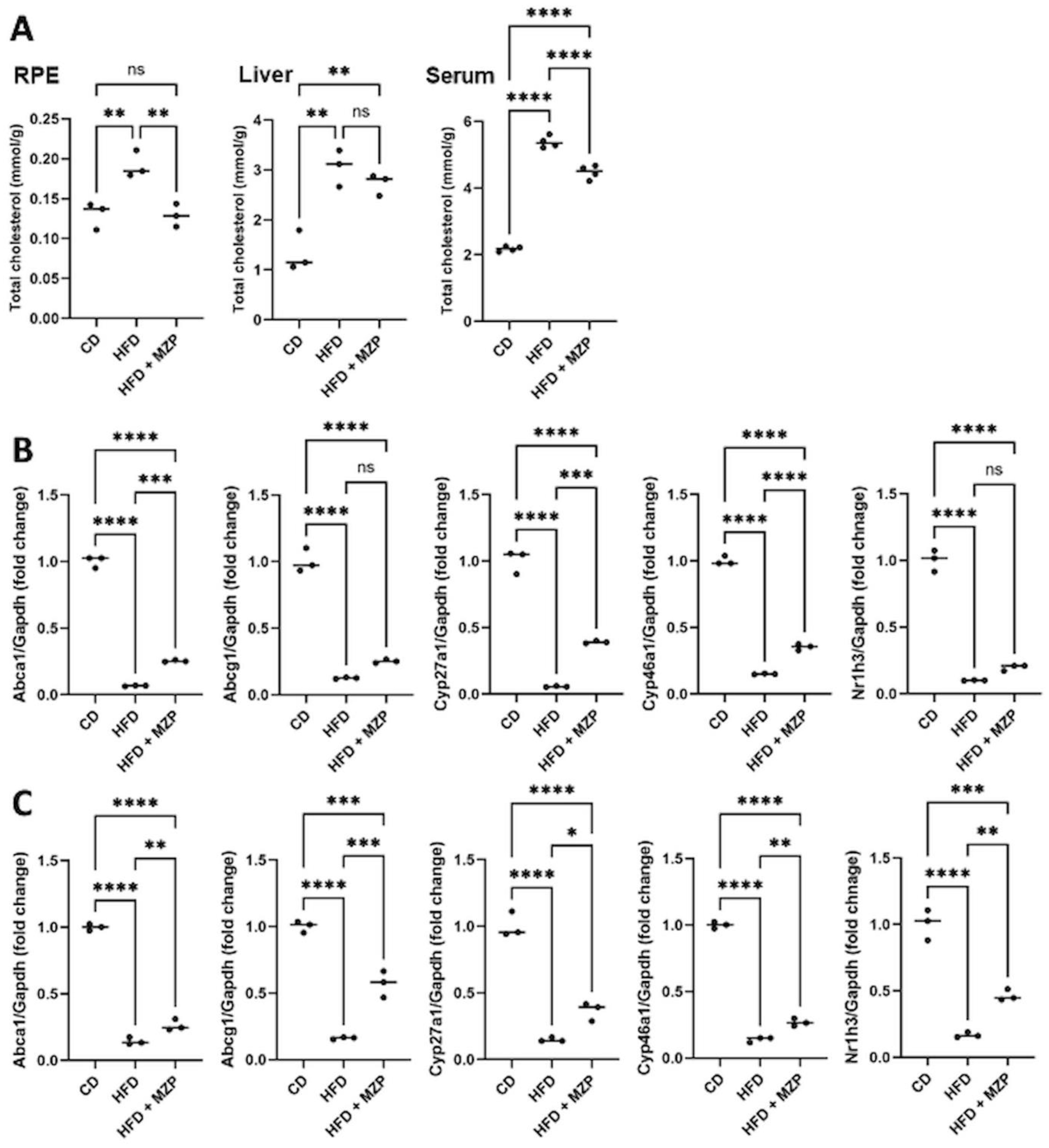
Figure 2. MZP regulated cholesterol metabolism in HFD-fed mice. (A) Cholesterol level in the RPE, liver, and serum of three animal groups. Samples from six animals of each group were pooled and subjected to cholesterol measurement. (B) mRNA levels of cholesterol trafficking and metabolism genes in the RPE of CD, HFD, and HFD+MZP animals. Samples from six animals of each group were pooled; total RNAs were extracted and subjected to qRT-PCR detection. (C) mRNA levels of cholesterol trafficking and metabolism genes in the liver of CD, HFD, and HFD+MZP animals. Samples from six animals of each group were pooled; total RNAs were extracted and subjected to qRT-PCR detection. CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP); RPE, retinal pigment epithelial cells. Ns, no significance; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
3.3 MZP treatment modulated the expression of antioxidant and inflammation genes in the tissues of HFD-fed mice
It is well documented that HFD can induce oxidative stress and inflammation, which contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic disorders, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases (27). We found that the expression of antioxidant genes catalase, superoxide dismutase (Sod1), and glutathione peroxidase 1 (Gpx1) was significantly decreased in the RPE and liver of HFD-fed mice compared to that of mice fed with chow diet. MZP treatment led to an increase in the expression of these genes, though the expressional levels of the three genes were still less than that of mice fed with chow diet (Figures 3A, B). We further examined the expression of proinflammatory cytokine genes IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα in the RPE and liver of the three groups. HFD-fed mice had a marked increase in the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα in the RPE and liver when compared to that of mice fed with chow diet; however, MZP administration significantly decreased the expression of the three genes in both RPE and liver compared to that of HFD-fed animals (Figures 3C, D).
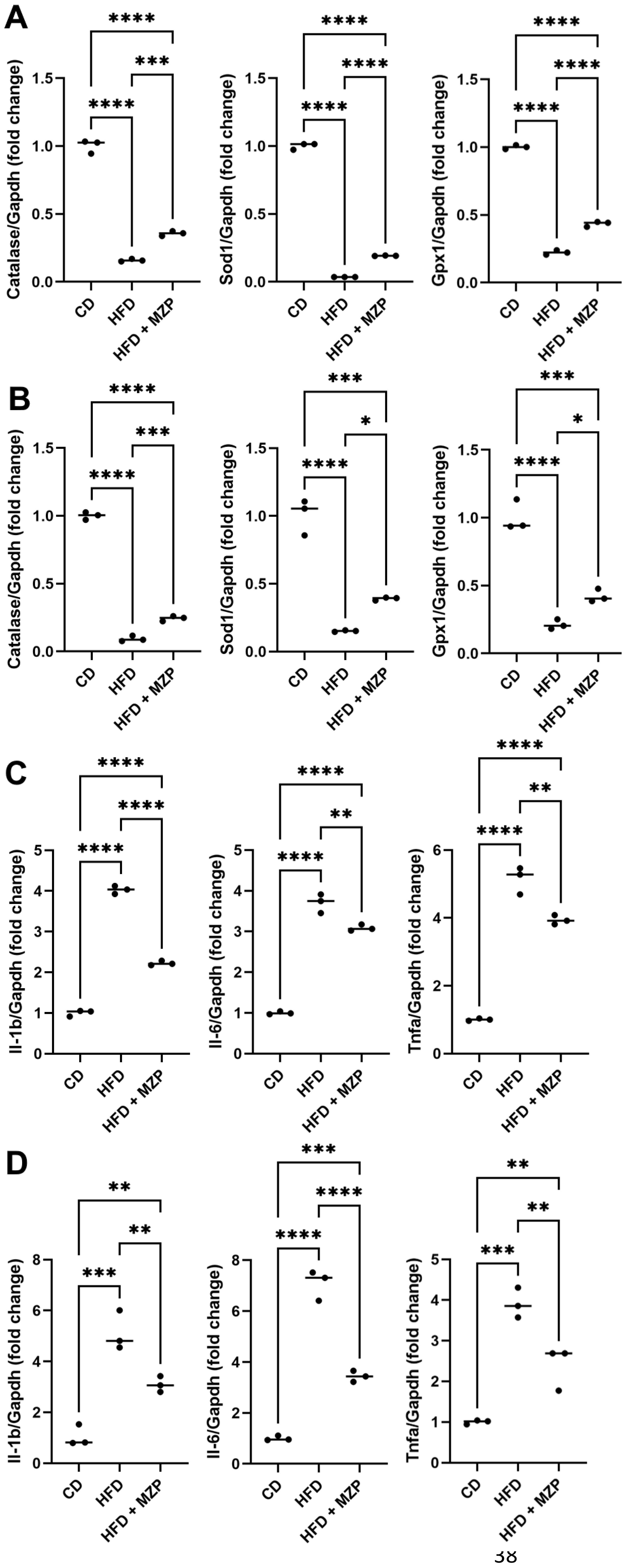
Figure 3. MZP regulated oxidative stress and inflammation in the RPE and the liver. (A) mRNA levels of antioxidant genes in the RPE. (B) mRNA levels of antioxidant genes in the liver. (C) mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokine genes in the RPE. (D) mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokine genes in the liver. Samples from six animals of each group were pooled; total RNAs were extracted and subjected to qRT-PCR detection. CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP); RPE, retinal pigment epithelial cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
We also measured the IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα protein levels in the liver and serum and found that HFD-fed mice had significantly higher levels of the three cytokines than that of mice fed with chow diet. The MZP treatment resulted in a marked decrease in the levels of these cytokines compared to that of HFD-fed mice (Figure 4).
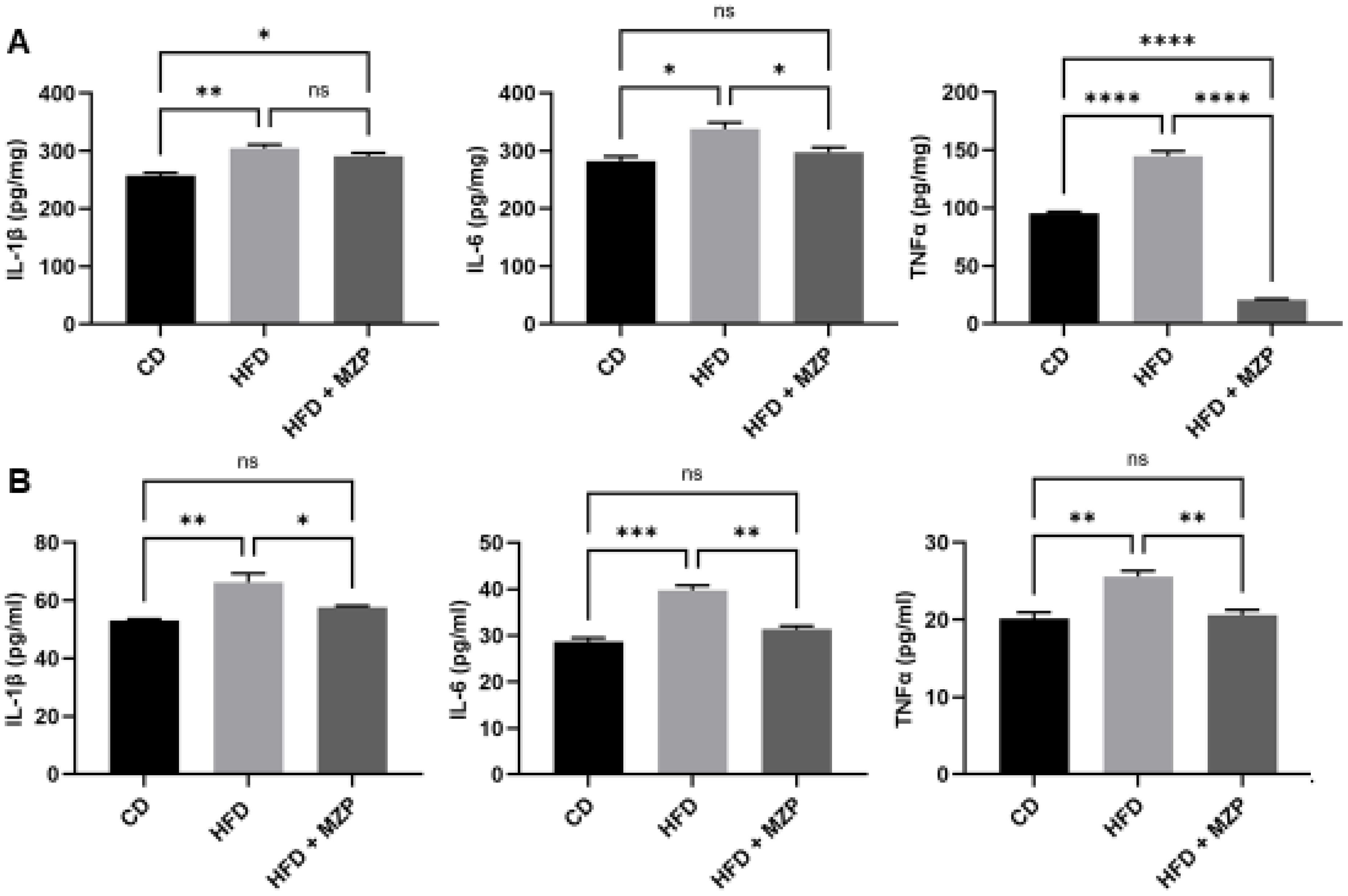
Figure 4. MZP decreased the levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the liver (A) and the serum (B). Samples from six animals of each group were pooled and subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP). Ns, no significance; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
3.4 MZP administration modulated the diversity and composition of gut microbiota
Numerous studies have reported that HFD induces dysbiosis, which plays an important role in the formation and progression of chronic diseases (Chen et al., 2023). We analyzed the microbiota in the cecum of six animals of each group using QIIME 2 Software. In total, 1,474,934 sequence reads was obtained from all samples. Following quality control filtering, overlapping and merging paired-end reads for each individual sample, removing reads that failed to merge, and chimera filtering, 1,161,226 high-quality non-chimeric merged reads were used for bacterial taxonomic and diversity analysis (Supplementary Table S4).
Alpha (α) diversity measures the diversity of microbial communities in individual samples, while beta (β) diversity refers to the difference in composition of microbial communities between samples. We applied α- and β-diversities to analyze the diversity and composition of the cecum bacterial communities in the three groups. A general reduction in the α-diversity metrics was observed in the HFD group compared to the CD group, though there was no significant difference (Figure 5A); on the other hand, the metrics in the MZP-treated group were significantly increased when compared to the HFD group, nearly returning to the level of the CD group. PCoA of β diversity analysis based on the unweighted UniFrac distance matrix (PCo1 contribution 60.45%, PCo2 contribution 19.15%) and the Bray–Curtis distance matrix (PCo1 contribution 49.09%, PCo2 contribution 18.06%) revealed that samples from the CD and HFD + MZP groups were closely clustered, while samples from the HFD group were more dispersed (Figure 5B). This suggests a higher similarity in microbiota composition within the CD and HFD + MZP groups and greater variability within the HFD group. These findings indicated that MZP has a potential regulatory effect on the gut microbiota structure altered by a high-fat diet.
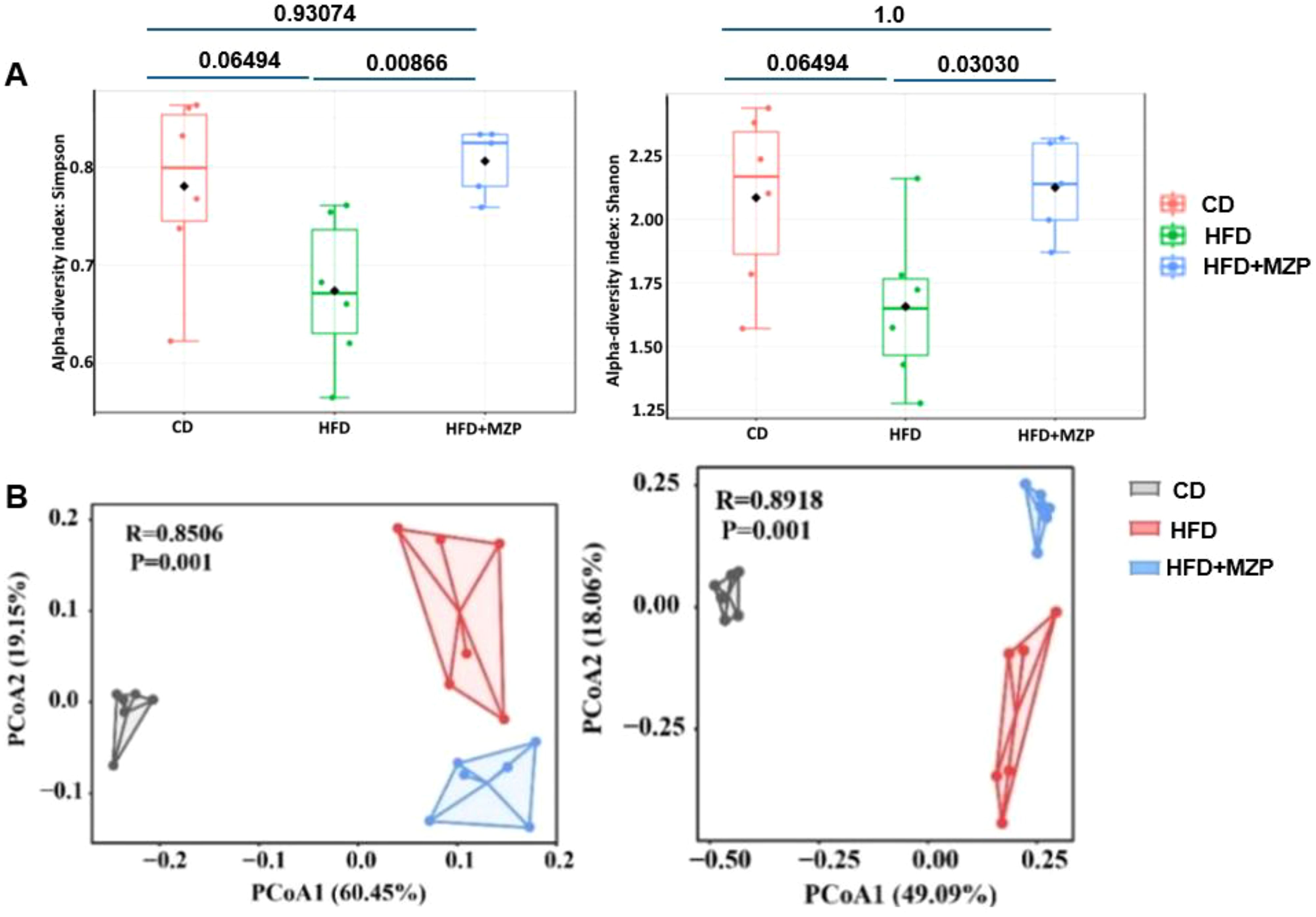
Figure 5. (A) α-diversity pf bacterial communities among the three animal groups using the Simpson and Shannon index. (B) β-diversity of bacterial communities among the three animal groups using Bray–Curtis (left panel) and weighted unifrac (right panel) index. CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP).
To analyze the phylogenetic structure and relative abundance of gut microbiota, a total of 205 taxa were identified from 14 phyla, including Acidobacteriota, Actinobacteriota, Armatimonadota, Bacteroidota, Campilobacterota, Cyanobacteria, Deferribacterota, Desulfobacterota, Firmicutes, Fusobacteriota, Patescibacteria, Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, and Verrucomicrobiota, containing 63 classified families and 103 classified genera (Supplementary Table S5). Notably, the structure and relative abundance of the gut bacteria were significantly varied among the three experimental groups. Figure 6A illustrates the relative abundance of gut bacteria at the phylum level. In the CD group, Bacteroidota and Firmicutes were the predominant phyla, followed by Patescibacteria and Desulfobacterota; in the HFD group, Firmicutes was the predominant phylum, followed by Desulfobacterota and Actinobacteriota. By contrast, in the MZP-treated group, Desulfobacterota was the predominant phylum, followed by Firmicutes. Heatmap analysis also demonstrated distinct clustering patterns among the three groups, indicating a clear separation of the gut bacterial profiles of the HFD group from the same cluster within the branch for both CD and MZP-treated groups (Figure 6B). Firmicutes and Bacteroidota are the two major bacterial phyla in the gut and play a critical role in maintaining gut health. HFD can dysregulate the gut microbiota, mainly the abundance of Firmicutes and Bacterodota (Chen et al., 2023). We also found that Firmicutes in the HFD group was significantly more abundant in the HFD group compared to both the CD and HFD+MZP groups, while the abundance of Firmicutes in the CD group was not significantly different to that of the HFD+MZP group. However, the abundance of Bacteroidetes was marked lower in the HFD group compared to that of the CD group, while the abundance of Bacteroidetes was significantly increased in the HFD+MZP group compared to that of the HFD group. The ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes, a biomarker for dysbiosis, was significantly higher than that of both the CD and HFD+MZP groups (Figure 6C). In addition, HFD induced a significant elevation of the abundance in both Actinobacteriota and Proteobacteria phyla, and MZP reversed the HFD-induced effect (data not shown).
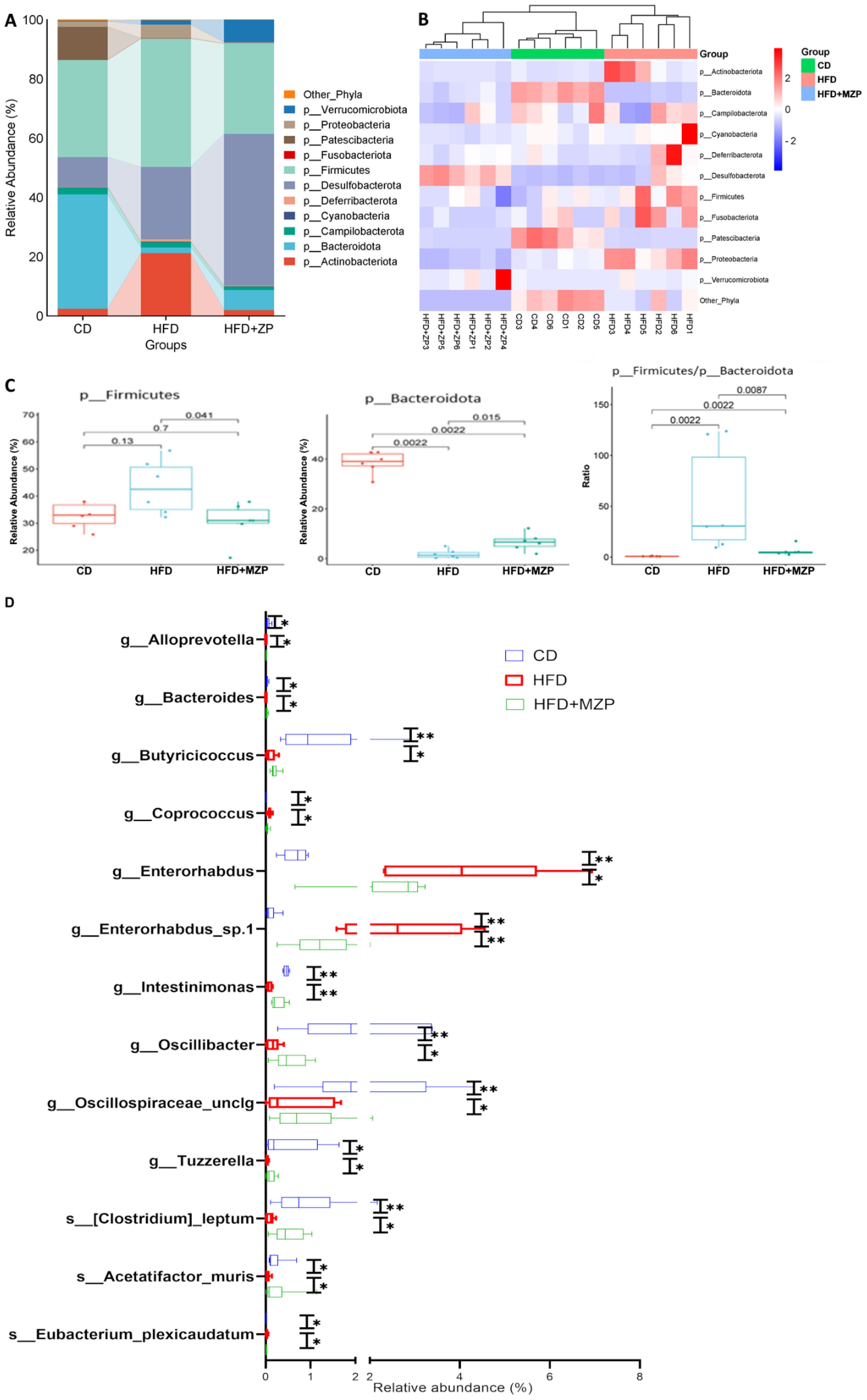
Figure 6. MZP modulated cecum microbiota. (A) Different abundance of the phyla among the three experimental groups. (B) Heatmap representation of phyla abundance from individual samples of three experiment groups. (C) Comparison of the abundance of Firmicutes and Bacteroidota among the three experimental groups and the ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidota. (D) Genera and species with significantly increased or decreased abundance in the HFD group, when compared to both the CD and HFD+MZP groups. CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Several taxa were markedly increased in the HFD group, but these taxa were significantly reduced in the HFD+MZP group, with levels partially restoring toward those observed in the CD group. These taxa were g_Alloprevotella, g_Coprococcus, g_Enterorhabdus, g_Enterorhabdus_sp.1, and s_Eubacterium_plexicaudatum. By contrast, some taxa that were reduced in the HFD group showed an increased abundance in the HFD+MZP group, resembling more closely the CD group. These included g_Bacteroides, g_Butyricicoccus, g_Intestinimonas, g_Oscillospiraceae_unclg, g_Tuzzerella, s_Acetatifactor_muris, and s:[Clostridium]_leptum (Figure 6D). In addition, various other taxa exhibited differential abundance patterns among the three groups, indicating broader microbial shifts influenced by dietary intervention and MZP treatment (data not shown).
3.5 MZP moderated the metabolic pathways of bacterial communities
PICRUSt2 was carried out to determine the MetaCyc metabolic pathways to explore the roles of gut microbiome across the three experimental groups. Out of the 393 predicted MetaCyc pathways, 235 were significantly different among the three experimental groups (Supplementary Table S6) after excluding those pathways with a mean relative abundance less than 0.001 in all groups. When comparing the HFD group to the CD group, the abundance of 55 metabolic pathways was significantly increased and 18 pathways decreased; when comparing the HFD group to the HFD+MZP group, the abundance of 93 pathways was significantly increased and 51 pathways decreased; when comparing the HFD+MZP group to the CD group, the abundance of 75 pathways was significantly increased and 100 pathways decreased (Supplementary Table S6). Notably, the abundance of 16 pathways—for example, flavin biosynthesis I, acetyl-CoA fermentation to butanoate II, and biotin biosynthesis II—in the HFD group was significantly lower than that of both the CD and HFD+MZP groups; 29 pathways—e.g., enterobacterial common antigen biosynthesis and superpathway of (Kdo)2-lipid A biosynthesis—were significantly enriched in HFD when compared to both the CD and HFD+ZP groups (Figure 7). The data indicated a strong functional shift induced by a high-fat diet alone and restoration in the MZP-treated group to the CD group.
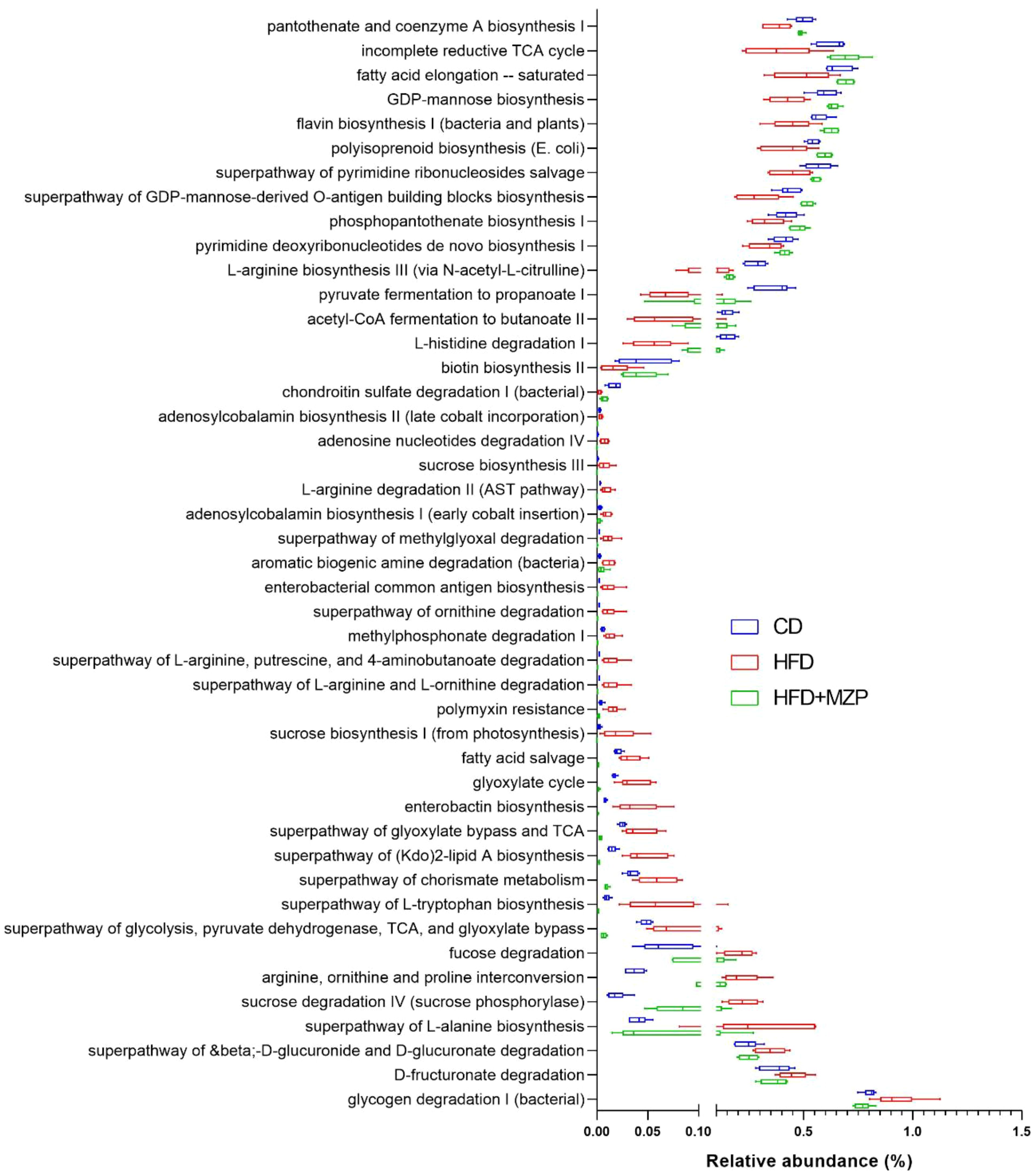
Figure 7. MetaCyc pathways with significantly decreased or increased relative abundance in the HFD group when compared to both the CD and HFD+MZP groups. CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP).
In addition, bacterial functional gene content based on the KEGG orthologs (KOs) was predicted using PICRUSt2 to highlight the key roles of the gut microbiome across three experimental groups. From a total of 6,433 predicted KOs, the top 4,300 most abundant KOs were selected for further analysis. Heatmaps and hierarchical clustering visualization of those KOs across the 18 samples revealed a distinct separation between the HFD group and both the CD and HFD+MZP groups, using absolute Pearson distance with complete linkage clustering (Figure 8A). Additional analysis using volcano plots was conducted to assess differential KO abundance based on log2 fold changes and adjusted p-value (-log10). Figure 8B illustrates that the abundance of 843 KOs was significantly reduced and that of 1,924 was increased in the HFD group compared to the CD group; similarly, when comparing the HFD group to the HFD+MZP group, the activity of 1,050 KOs was significantly reduced and that of 2,940 was elevated. Conversely, the abundance of 2,916 KOs was downregulated and that of 1,075 upregulated when the HFD+MZP group was compared to the CD group. Supplementary Figure S3 highlights the top 50 significantly altered KOs (25 upregulated and 25 downregulated) in the HFD group compared to the HFD+MZP group. These KOs were also used for comparison among the other experimental groups, indicating consistent functional shifts by MZP treatment. Among the significantly changed KOs, functions associated with citrate cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle), butanoate metabolism, and riboflavin metabolism were significantly decreased in the HFD group compared to both the CD and HFD+MZP groups. By contrast, entries associated with the invasion signaling pathway were markedly abundant in the HFD group compared to both the CD and HFD+MZP groups (Figure 9).
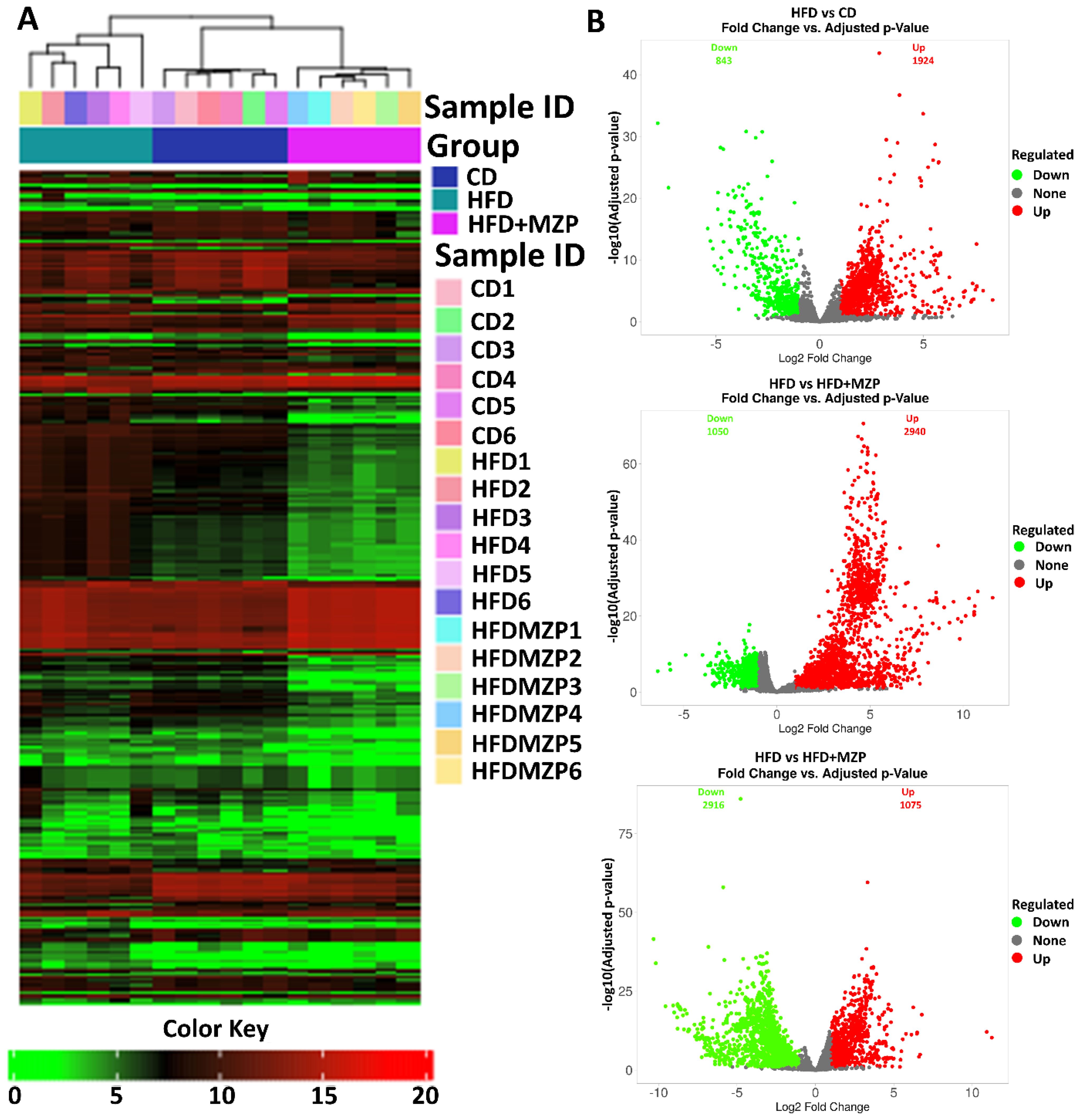
Figure 8. MZP regulated the abundance of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes orthologs (KOs). (A) Heatmap representation of KOs in individual samples of the three experimental groups. (B) Volcano plots showing upregulated (labeled in red) and downregulated (labeled in green) KOs, compared between two groups. CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP).
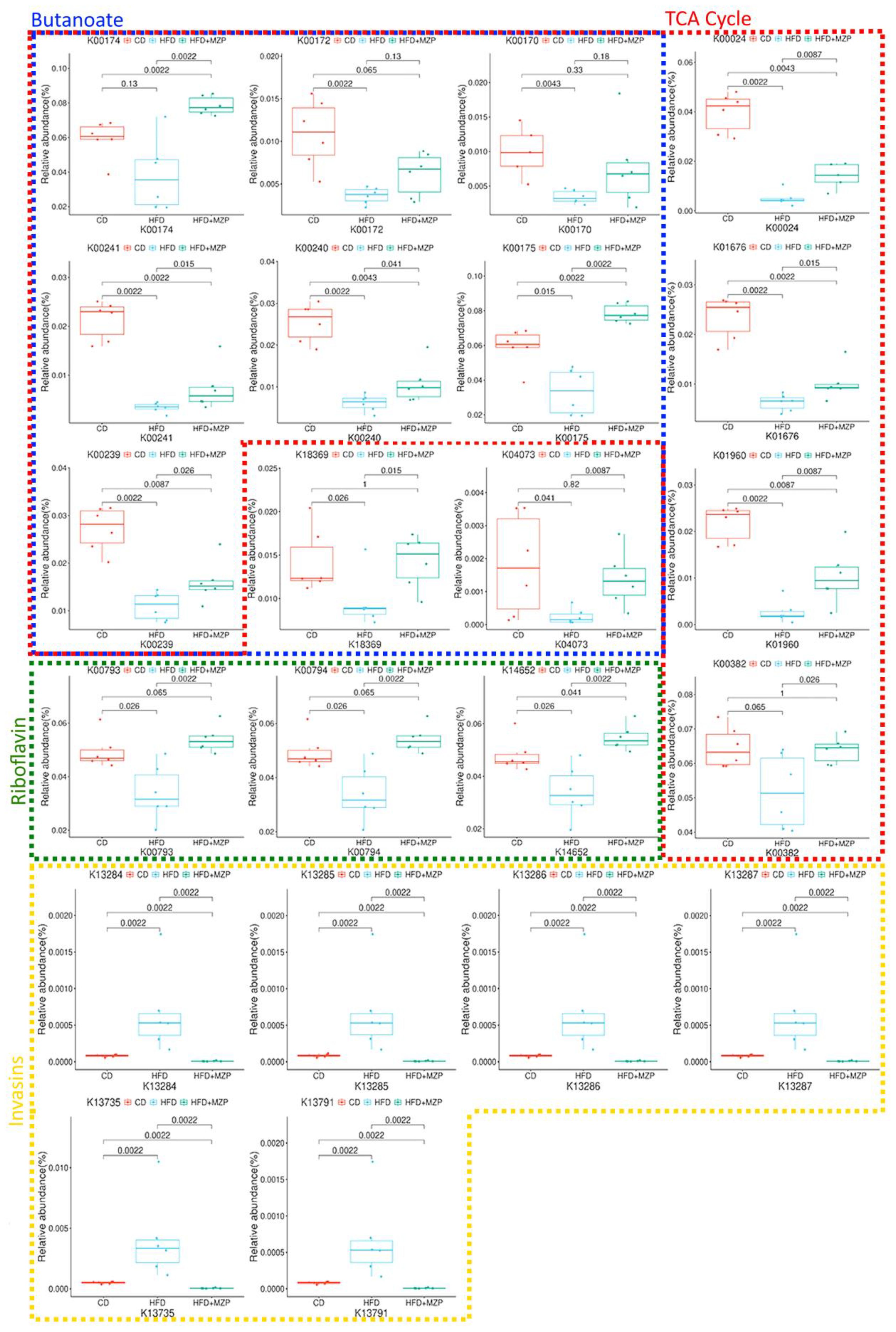
Figure 9. Selected KOs involved in citrate cycle, butanoate metabolism, riboflavin metabolism, and invasion signaling. CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP).
3.6 Cecum bacteria were correlated with proinflammatory cytokines
The results of the correlation analysis between cecum bacterial and proinflammatory cytokines are presented in Figure 10. The data indicated that the relative abundance of the characteristic bacterial genera uncultured bacterium f Muribaculaceae and Candidatus Saccharimonas in the CD group showed a significant negative correlation with liver IL-6 level (p < 0.05). Additionally, the relative abundance of uncultured bacterium f Muribaculaceae, Alloprevotella, and Alistipes was significantly negatively correlated with the serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α (p < 0.05).
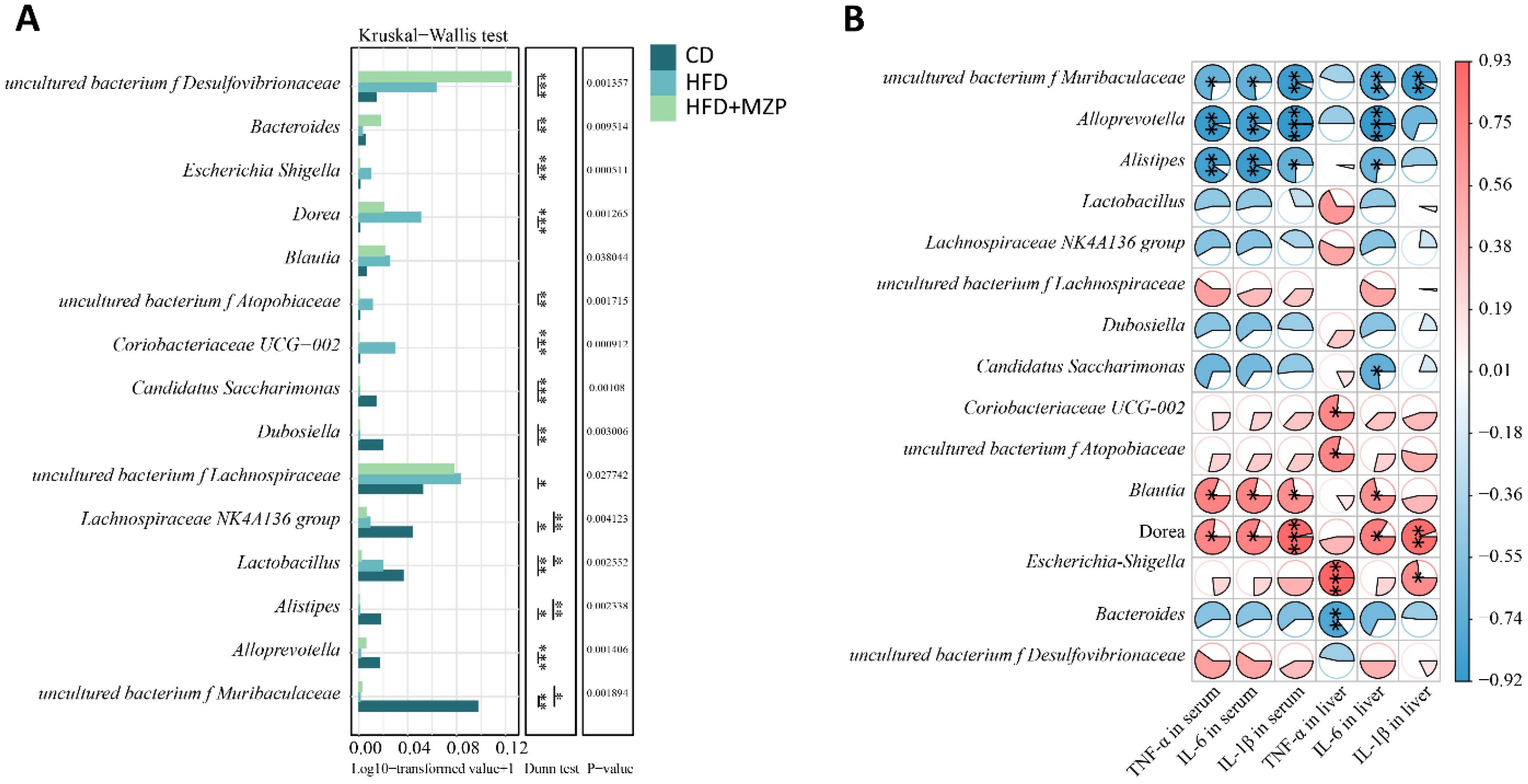
Figure 10. Correlation analysis between cecum characteristic genera and proinflammatory cytokines. (A) Multifunctional differential analysis of characteristic genera. (B) Heatmap showing the correlation between liver and serum proinflammatory cytokines and bacteria. Mann–Kruskal–Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple-comparisons test was used to estimate the significant differences. The t-test based on the Pearson correlation coefficient was used to test the significance of the correlation coefficient. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (n = 6). CD, control diet; HFD, high-fat diet; HFD+MZP, high-fat diet (HFD) + modified Zhujing pill (MZP).
The relative abundance of the characteristic bacterial genera Coriobacteriaceae UCG-002, uncultured bacterium f Atopobiaceae, and Escherichia Shigella in the HFD group exhibited a significant positive correlation with the liver TNF-α level (p < 0.05). Additionally, the relative abundance of Blautia and Dorea was significantly positively correlated with the liver IL-6 levels as well as serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α (p < 0.05).
The relative abundance of the characteristic bacterial genus Bacteroides in the HFD+MZP group was negatively correlated with the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in both the liver and serum, while the relative abundance of uncultured bacterium f Desulfovibrionaceae was positively correlated with the levels of those cytokines. Notably, the liver TNF-α level showed a significant negative correlation with the relative abundance of Bacteroides (p < 0.01).
4 Discussion
Although MZP is widely used to treat AMD patients and has shown therapeutic benefits, the protective mechanisms are poorly understood. Here we treated HFD-fed mice, a commonly used AMD model, with MZP for 4 weeks and found that MZP counteracted the HFD-induced effects via decreasing the cholesterol accumulation, upregulating the expression of cholesterol metabolism and trafficking genes, and suppressing the oxidative stress and inflammation in mouse RPE and liver as well as modulating the composition, diversity, and metabolic pathways of gut microbiota.
Cholesterol is a versatile lipid with multiple functional roles, such as maintaining cell membrane structure, producing hormones, assisting digestion, and regulating cell signaling pathways. Cholesterol biosynthesis, metabolism, and excretion are tightly controlled, and dysregulation of cholesterol homeostasis is associated with various disorders, e.g., cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases (Duan et al., 2022). Abnormal deposits of cholesterol and its metabolites (e.g., 7-ketocholesterol) are enriched in the drusen of AMD patients, suggesting that cholesterol plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AMD (Zhang et al., 2021). The RPE has a high-level expression of cholesterol homeostasis-associated genes, including HMGCR, SCREBP2, SCAP, NR1H3, CYP27A1, CYP46A1, ABCA1, and ABCG1 (Zheng et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2021). Global loss of mouse cholesterol metabolism enzyme CYP27A1 or CYP46A1 results in dysregulated retinal cholesterol homeostasis, sub-RPE deposits of cholesterol, and abnormal vascularization in the retina (Omarova et al., 2012; Saadane et al., 2019). Conditional loss of both cholesterol transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1 in the RPE causes intracellular abnormal lipid accumulation composed predominantly of cholesteryl esters in the RPE, RPE atrophy, and progressive photoreceptor degeneration (Storti et al., 2019). Here we found that HFD, which is associated with an increased risk of developing AMD in humans, induced the elevated level of cholesterol in the RPE and downregulated the expression of genes related to cholesterol metabolism and transport. The downregulated expression of these genes can lower cholesterol metabolism and trafficking, resulting in the accumulation of cholesterol in the RPE. MZP treatment lowered the cholesterol level in HFD-fed mouse RPE, possibly via promoting cholesterol metabolism and trafficking. Excess cholesterol in the RPE returns via reverse transport to the liver, where cholesterol can be stored as cholesteryl esters or excreted by forming bile acids. HFD also increased the cholesterol level in the liver; one possible explanation is a deficit in bile acid biosynthesis, as the expression of Cyp27a1, one of the bile acid synthesizing enzymes, was downregulated, and MZP counteracted the effect. Therefore, it would be worth exploring the bile-acid-synthesis-associated enzymes in the liver of experimental animals.
HFD, known as “Western diet”, can induce oxidative stress and inflammation and is associated with an increased risk of developing AMD (Biswas et al., 2021; Sterling et al., 2022). Rodents fed with HFD demonstrate the pathological features of AMD; for example, HFD intake potentiates laser-induced choroidal neovascularization, a major pathological feature of neovascular AMD (Andriessen et al., 2016; Xiao et al., 2023). A previous work has demonstrated that HFD induces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), lowers the expression of antioxidant genes, and upregulates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the RPE (Biswas et al., 2021). Here we also found that HFD downregulated the expression of antioxidant genes and upregulated the expression of proinflammatory cytokine genes in the RPE and liver, and MZP treatment reversed the HFD-induced effects. This data is consistent with an earlier report on the antioxidant capacity of MZP in human RPE cells treated with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Yang et al., 2025). The molecular mechanisms of HFD-induced oxidative stress and inflammation are complicated, involving mitochondrial dysfunction, ROS production, activation of proinflammatory signaling, and damages to cells and tissues. One of the possibilities is associated with cholesterol, as accumulated cholesterol in the RPE can be autoxidized to form toxic oxysterols, such as 7-ketocholesterol, which are enriched in the drusen and can induce oxidative stress, inflammation, and damage to the RPE and photoreceptor cells (Zhang et al., 2021). Additionally, a recent work has shown that HFD causes damage to RPE cells via IL-1β-regulated expression of iron importers and exporters, iron accumulation, and oxidative damage (Sterling et al., 2022). Therefore, it is reasonable to investigate further whether MZP treatment decreases the production of toxic oxysterols and regulates the expression of iron importers/exporters in the RPE of HFD-fed mice.
Accumulated data have demonstrated that abnormal alteration of the gut microbiota is associated with AMD. A previous report by Zinkernagel et al. showed that AMD patients had abundant genera Anaerotruncus and Oscillibacter together with species Ruminococcus torques and Eubacterium ventriosum and low abundance of species Bacteroides eggerthii when compared to that of healthy controls. Metabolic functional analysis predicted that the abundance of glutamate degradation, L-alanine fermentation, and arginine biosynthesis was higher in AMD patients (Zinkernagel et al., 2017). Another study reported that AMD patients had a greater abundance of genera Lactobacillus and Veillonella and a decreased abundance of genera Anaerobutyricum, Anaerosipes, Blautia, Desulfovibrio, Eggerthella, Faecalibacterium, Massilistercora, and Megamonas. The authors also identified increased activities in 15 metabolic pathways and decreased activities in 45 metabolic pathways in AMD patients compared to that of the controls (Xue et al., 2023). The composition of the gut microbiota is predominantly influenced by diet. HFD can induce dysbiosis in the hosts and contribute to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders, including AMD (Cao et al., 2022b; Chen et al., 2023). A previous study showed that HFD resulted in a decreased abundance of Bacteroidetes and an increased abundance of Firmicutes as well as an elevated ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes compared to that of chow diet; HFD also induced high levels of gut permeability, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) production, and systemic inflammation, which possibly exacerbated laser-induced choroidal neovascularization, a key pathological feature of neovascular AMD (Andriessen et al., 2016). In the current study, we also found significant changes in the composition of microbiota in the three experimental groups. HFD-fed animals had an increased abundance of Firmicutes and a decreased abundance of Bacteroidota with a higher ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidota as well as abundance changes for some genera and species; MZP treatment partially reversed those changes back to similar levels of the CD group.
Gut microbiota has been reported to play an important role in cholesterol metabolism via cholesterol conversion. Some gut bacteria can directly convert cholesterol to coprostanol, which is poorly absorbed by the intestine and leads to an increase in cholesterol excretion into the feces and a reduction of cholesterol absorption into the bloodstream (Kenny et al., 2020). Kenny et al. identified the bacterial cholesterol-metabolizing enzymes, encoded by the intestinal sterol metabolism A (ismA) genes in Clostridium cluster IV-related bacteria, and found that individuals with high levels of IsmA-encoding bacteria are associated with low levels of fecal and serum cholesterol (Kenny et al., 2020). Li et al. further demonstrated that the abundance of Oscillibacter clusters was associated with low levels of fecal and serum cholesterol and identified genes encoding cholesterol-α-glucosyltransferase (CgT), IsmA, and TSPO. CgT is known to metabolize cholesterol to cholesteryl glucosides, IsmA converts cholesterol to coprostanol, and TSPO transports cholesterol from the mitochondrial outer membrane to the inner membrane (Li et al., 2024). In the current study, we found that the abundance of Oscillibacter genus and Clostridium leptum was significantly lower in the HFD group than that of both CD and HFD+MZP groups. This possibly leads to decreased cholesterol metabolism in the gut and increased uptake of cholesterol into the bloodstream. Our results showed that the HFD group had higher levels of cholesterol in the serum, liver, and RPE compared to that of both the CD and HFD+MZP groups. Oscillibacter-encoded TSPO may also play a role in the increased levels of cholesterol in HFD-fed mouse tissues, as our previous studies have shown that the loss of TSPO in mice results in higher levels of cholesterol in the serum, liver, and RPE (Farhan et al., 2021, 2025).
MetaCyc pathway analysis showed significant changes in many metabolic pathways among the experimental groups, of which activities in 16 pathways were significantly decreased and in 29 pathways were significantly increased compared to the CD group. MZP treatment reversed these changes. Some of those pathways—such as the biosynthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) and flavin, acetyl-CoA fermentation to butanoate II (significantly decreased in the HFD group), and superpathway of (kdo)2-lipid A biosynthesis (significantly increased in the HFD group)—are possibly associated with AMD pathogenesis as their functions are related to oxidative stress and inflammation. CoA functions in multiple metabolic pathways, such as citrate cycle, fatty acid oxidation, and synthesis of amino acids. CoA can also play a protective role against oxidative stress through protein CoAlation, which protects cysteine residues being irreversibly oxidized by ROS (Filonenko and Gout, 2023). Furthermore, CoA plays a crucial role in anti-inflammation by modulating immune cell activation and function (Miallot et al., 2023). Flavin is a co-factor for various enzymes, such as glutathione reductase that restores intracellular glutathione; flavin functions in various metabolic pathways, and the deficiency of flavin homeostasis is associated with retina aging and degeneration (Sinha et al., 2018). Butanoate is synthesized by gut bacteria and plays a crucial role in regulating host metabolic pathways and inhibiting inflammation. Previous studies have demonstrated that butanoate can enhance retinal function, suppress retinal inflammation, and mitigate retinal pathology in models of retinal degeneration (Nguyen et al., 2024). Conversely, enterobacterial common antigen, enterobactin, (kdo)2-lipid A, and polymixin are proinflammation-generating factors that can induce inflammation and damage to the host (Holst, 2007; Wang et al., 2015; Saha et al., 2020; Kagi et al., 2022). (kdo)2-lipid A is the core component of LPS, which can activate inflammation via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway in the RPE and exacerbate laser-induced neovascularization in mice (Tsioti et al., 2024). Therefore, it would be worthwhile examining these beneficial and toxic bacterial metabolites in host tissues, e.g., the gut, the liver, and the RPE. Further analysis of KOs demonstrated that many pathways were upregulated or downregulated when a comparison was made between the two experimental groups. Some upregulated or downregulated pathways induced by HFD were fully or partially reversed by MZP treatment. Of particular interest is the fact that functions associated with TCA cycle, metabolism of butanoate, and riboflavin were less abundant in the HFD group compared to both the CD and HFD+MZP groups. These pathways are associated with cellular energy production in the mitochondria (Donohoe et al., 2011; Jackson and Theiss, 2020; Vezza et al., 2020), suggesting that there is a crosstalk between gut microbiota and host mitochondrial function and that MZP can possibly enhance the mitochondrial function via modulating the gut microbiota. On the other hand, functions related to the invasin signaling pathway were more abundant in the HFD group compared to the CD and HFD+MZP groups. The invasin signaling pathway can facilitate pathogenic bacterial infection and induce inflammation (Dhar and Virdi, 2014). Therefore, MZP may inactivate the invasion signaling pathway and suppress bacterial infection and associated inflammation.
Analyses of gut microbiota and proinflammatory cytokines showed that some bacterial genera/families were positive or negatively associated with serum and/or liver proinflammatory cytokines. It should be noted that Dora was positively associated with serum IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα and liver IL-1β and IL-6. The abundance of Dora was also significantly higher in the HFD group compared to that of the CD and HFD+MZP groups. Genus Dorea has been reported to be associated with an increased risk of developing early AMD (Wei et al., 2025). Dorea plays an important role in the formation of gut barrier and demonstrates proinflammatory capacities including the induction of IFNγ, metabolism of sialic acids, and degradation of mucin; patients with inflammatory disorders also have a high abundance of Dorea (Shahi et al., 2017). On the other hand, Alistipes, Alloprevotella, and uncultured bacterium f Muribaculaceae were negatively associated with serum IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα and liver Il-6. The abundance of Alistipes, Alloprevotella, and uncultured bacterium f Muribaculaceae was significantly lower in the HFD group compared to the CD group, and MZP treatment slightly increased the abundance of Alloprevotella and uncultured bacterium f Muribaculaceae in the HFD-MZP group compared to that of the HFD. The data suggests that Alistipes, Alloprevotella, and uncultured bacterium f Muribaculaceae possibly are associated with anti-proinflammatory effects, consistent with some previous reports (Li et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2024; Lin et al., 2025).
MZP contains eight medicinal herbs, of which we identified 115 compounds. Most of the identified compounds are polyphenols, including flavonoids (23%), phenolics (7%), and coumarins (5%). Polyphenols have been demonstrated to have beneficial effects against oxidative stress and inflammation in AMD models (Pawlowska et al., 2019). Individual or a combination of polyphenols (luteolin, naringenin, and quercetin, also identified in MZP in the present study) has been shown to suppress H2O2-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in human RPE cells (Cao et al., 2022a). Previous studies have shown that MZP treatment increased the SOD activity and GSSH-Px level and lowered the levels of proinflammatory effectors in the serum and the retina of diabetic rats (Lei et al., 2018). Here we also found that MZP upregulated the expression of antioxidant genes and downregulated the expression of proinflammatory cytokine genes. In addition, our preliminary data demonstrated that MZP decreased ROS production, increased the expression of antioxidant genes, and alleviated the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in H2O2-challenged human RPE cells (data not shown). Polyphenol-enriched diet extracts or individual polyphenols have been shown to regulate cholesterol metabolism, modulate the gut microbiota, and provide protective effects in treating cholesterol-associated disorders (Cheng et al., 2023). Future studies will validate the beneficial effects of individual or a combination of identified polyphenols against AMD in in vitro and in vivo models.
5 Conclusion
The purpose of this study was to unravel the protective mechanisms of MZP against AMD in HFD-fed animals. This study demonstrated that HFD increased the cholesterol level in the RPE, liver, and serum and was associated with oxidative stress and inflammation. HFD also caused gut microbiota dysbiosis. MZP treatment reversed the HFD-induced effects. It is possible that dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism and elevated oxidative stress and inflammation are associated with abnormal changes in gut bacterial composition and metabolic pathways. Polyphenols, as predominantly identified compounds in MZP, are suggested to play a critical role in counteracting HFD-induced toxic effects via regulation of cholesterol metabolism, inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation, and modulation of gut microbiota (Figure 11).
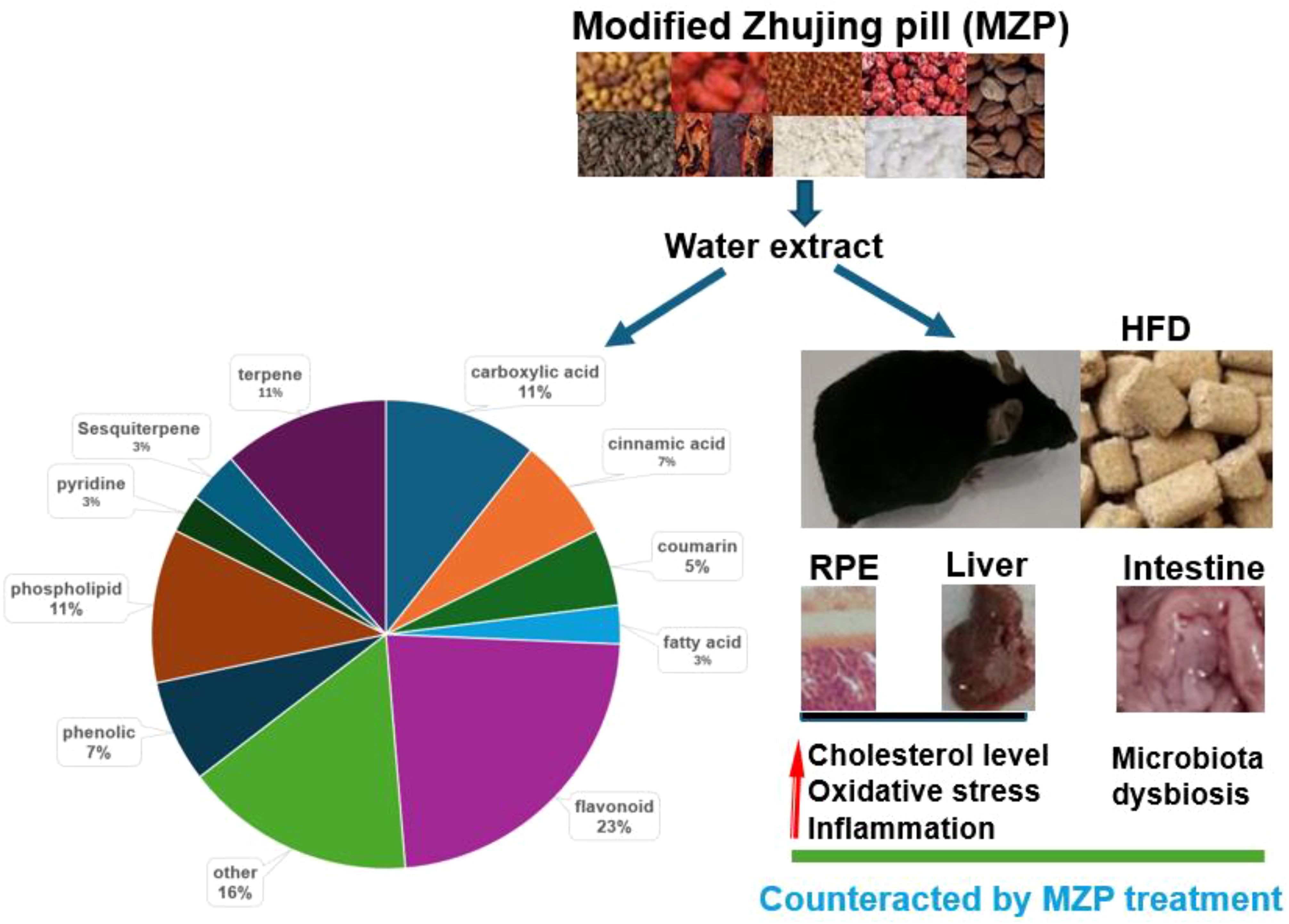
Figure 11. Protective mechanisms of MZP against AMD. HFD can induce cholesterol accumulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and gut microbiota dysbiosis. MZP can counteract HFD-induced toxic effects mainly via polyphenols. AMD, age-related macular degeneration; HFD, high-fat diet; MZP, modified Zhujing pill; RPE, retinal pigment epithelial cells.
Data availability statement
The data presented in this study are deposited in the NCBI Bioproject database with Accession Number PRJNA1347468.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Hunan University of Chinese Medicine. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SC: Investigation, Writing – original draft. SX: Investigation, Writing – original draft. KI: Writing – original draft, Investigation. MB: Writing – original draft, Investigation. XL: Writing – original draft, Investigation. JR: Writing – review & editing. ZT: Project administration, Writing – original draft. ZH: Writing – original draft, Project administration. XS: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was partially supported by the Locus Scholarship Program of Hunan Province, China (No. 2019–23 to XS), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong province, Guangdong, China (No. 2022A1515110258 to SC) and Guangdong Provincial Department of Education Key Project (No. 2022ZDZX3049 to SC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1691360/full#supplementary-material
References
Andriessen, E. M., Wilson, A. M., Mawambo, G., Dejda, A., Miloudi, K., Sennlaub, F., et al. (2016). Gut microbiota influences pathological angiogenesis in obesity-driven choroidal neovascularization. EMBO Mol. Med. 8, 1366–1379. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606531
Biswas, L., Ibrahim, K. S., Li, X., Zhou, X., Zeng, Z., Craft, J., et al. (2021). Effect of a TSPO ligand on retinal pigment epithelial cholesterol homeostasis in high-fat fed mice, implication for age-related macular degeneration. Exp. Eye. Res. 208, 108625. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108625
Biswas, L., Zhou, X., Dhillon, B., Graham, A., and Shu, X. (2017). Retinal pigment epithelium cholesterol efflux mediated by the 18 kDa translocator protein, TSPO, a potential target for treating age-related macular degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26, 4327–4339. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx319
Boopathiraj, N., Wagner, I. V., Dorairaj, S. K., Miller, D. D., and Stewart, M. W. (2024). Recent updates on the diagnosis and management of age-related macular degeneration. Mayo. Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes. 8, 364–374. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.003
Cao, Y., Li, Y., Gkerdi, A., Reilly, J., Tan, Z., and Shu, X. (2022b). Association of nutrients, specific dietary patterns, and probiotics with age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Med. Chem. 29, 6141–6158. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220511142817
Cao, Y., Li, X. Y., Tchivelekete, G. M., Li, X., Zhou, X., He, Z., et al. (2022a). Bioinformatical and biochemical analyses on the protective role of traditional Chinese medicine against age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Eye. Res. 47, 1450–1462. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2022.2108456
Chen, D. F. (1978). Essentials of six meridians in ophthalmology of traditional Chinese medicine (Chengdu: Sichuan People’s Publishing House), 62–71.
Chen, J., Xiao, Y., Li, D., Zhang, S., Wu, Y., Zhang, Q., et al. (2023). New insights into the mechanisms of high-fat diet mediated gut microbiota in chronic diseases. Imeta 2, e69. doi: 10.1002/imt2.69
Cheng, H., Zhang, D., Wu, J., Liu, J., Zhou, Y., Tan, Y., et al. (2023). Interactions between gut microbiota and polyphenols: A mechanistic and metabolomic review. Phytomedicine 119, 154979. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023
Cui, J., Shi, E., Wang, Y., and Liu, T. (2023). Network pharmacology study of the mechanism under lying the therapeutic effect of Zhujing pill and its main component oleanolic acid against diabetic retinopathy. Biosci. Rep. 43, BSR20220893. doi: 10.1042/BSR20220893
Curcio, C. A., Presley, J. B., Malek, G., Medeiros, N. E., Avery, D. V., and Kruth, H. S. (2005). Esterified and unesterified cholesterol in drusen and basal deposits of eyes with age-related maculopathy. Exp. Eye. Res. 81, 731–741. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.04.012
Dasari, B., Prasanthi, J. R., Marwarha, G., Singh, B. B., and Ghribi, O. (2011). Cholesterol-enriched diet causes age-related macular degeneration-like pathology in rabbit retina. BMC Ophthalmol. 11, 22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-11-22
Dhar, M. S. and Virdi, J. S. (2014). Strategies used by Yersinia enterocolitica to evade killing by the host: thinking beyond Yops. Microbes Infect. 16, 87–95. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2013.11.002
Donohoe, D. R., Garge, N., Zhang, X., Sun, W., O’Connell, T. M., Bunger, M. K., et al. (2011). The microbiome and butyrate regulate energy metabolism and autophagy in the mammalian colon. Cell Metab. 13, 517–526. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.018
Duan, Y., Gong, K., Xu, S., Zhang, F., Meng, X., and Han, J. (2022). Regulation of cholesterol homeostasis in health and diseases: from mechanisms to targeted therapeutics. Signal Transduction Targeting Ther. 7, 265. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01125-5
Fan, M. F. and Zhang, X. Y. (2018). The clinical effective rate of modified Zhujing pills prescription in the treatment of primary retinitis pigmentosa and its effect on visual acuity of patients. Elec. J. Clin. Med. Lit. 5, 164–165.
Farhan, F., Almarhoun, M., Wong, A., Findlay, A. S., Bartholomew, C., Williams, M. T., et al. (2021). Deletion of TSPO causes dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism in mouse retina. Cells 10, 3066. doi: 10.3390/cells10113066
Farhan, F., Raghupathy, R. K., Baran, M. R., Wong, A., Biswas, L., Jiang, H. R., et al. (2025). Dysregulation of lipid metabolism in the liver of Tspo knockout mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1870, 159566. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2024.159566
Feng, S., Zhou, X., Zhang, Y., Yang, N., Zhou, S., Xiong, C., et al. (2024). Clinical study on the treatment of dry age-related macular degeneration of liver and kidney insufficiency type with modified zhujing pills. J. Nanjing. Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 40, 521–526.
Filonenko, V. and Gout, I. (2023). Discovery and functional characterisation of protein CoAlation and the antioxidant function of coenzyme A. BBA. Adv. 3, 100075. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2023.100075
Fritsche, L. G., Igl, W., Bailey, J. N. C., Grassmann, F., Sengupta, S., Bragg-Gresham, J. L., et al. (2016). A large genome-wide association study of age-related macular degeneration highlights contributions of rare and common variants. Nat. Genet. 48, 134–143. doi: 10.1038/ng.3448
Holst, O. (2007). The structures of core regions from enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides–an update. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 271, 3–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00708.x
Jackson, D. N. and Theiss, A. L. (2020). Gut bacteria signaling to mitochondria in intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gut. Microbes 11, 285–304. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2019.1592421
Jiang, F., Ma, J., Lei, C., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, M. (2025). Age-related macular degeneration: cellular and molecular signaling mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 6174. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136174
Kagi, T., Naganuma, R., Inoue, A., Noguchi, T., Hamano, S., Sekiguchi, Y., et al. (2022). The polypeptide antibiotic polymyxin B acts as a pro-inflammatory irritant by preferentially targeting macrophages. J. Antibiot. 75, 29–39. doi: 10.1038/s41429-021-00490-7
Keeling, E., Lynn, S. A., Koh, Y. M., Scott, J. A., Kendall, A., Gatherer, M., et al. (2022). A high fat “Western-style” Diet induces AMD-like features in wildtype mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 66, 2100823. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202100823
Kenny, D. J., Plichta, D. R., Shungin, D., Koppel, N., Hall, A. B., Fu, B., et al. (2020). Cholesterol metabolism by uncultured human gut bacteria influences host cholesterol level. Cell Host Microbe 28, 245–257. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.013
Lei, J., He, J., Ren, C., Zhou, Y., Chen, X., and Dou, J. (2018). Protective effects of the Chinese herbal medicine prescription Zhujing pill on retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 98, 643–650. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.071
Li, Y., Li, X., Li, X., Zeng, Z., Strang, N., Shu, X., et al. (2022). Non-neglectable therapeutic options for age-related macular degeneration: A promising perspective from traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 282, 114531. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114531
Li, A. L., Ni, W. W., Zhang, Q. M., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, H. Y., et al. (2020). Effect of cinnamon essential oil on gut microbiota in the mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Microbiol. Immunol. 64, 23–32. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12749
Li, C., Stražar, M., Mohamed, A. M., Pacheco, J. A., Walker, R. L., Lebar, T., et al. (2024). Gut microbiome and metabolome profiling in Framingham heart study reveals cholesterol-metabolizing bacteria. Cell 187, 1834–1852. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.014
Lin, X., Xu, M., Lan, R., Hu, D., Zhang, S., Zhang, S., et al. (2025). Gut commensal Alistipes shahii improves experimental colitis in mice with reduced intestinal epithelial damage and cytokine secretion. MSystems 10, e0160724. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01607-24
Louer, E. M., Yi, G., Carmone, C., Robben, J., Stunnenberg, H. G., den Hollander, A. I., et al. (2020). Genes involved in energy metabolism are differentially expressed during the day–night cycle in murine retinal pigment epithelium. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 61, 49–49. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.5.49
McGwin, G., Jr., Xie, A., and Owsley, C. (2005). The use of cholesterol-lowering medications and age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 112, 488–494. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.10.027
Miallot, R., Millet, V., Galland, F., and Naquet, P. (2023). The vitamin B5/coenzyme A axis: A target for immunomodulation? Eur. J. Immunol. 53, 2350435. doi: 10.1002/eji.202350435
Nair, A. B. and Jacob, S. (2016). A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic. Clin. Pharm. 7, 27–31. doi: 10.4103/0976-0105.177703
Nguyen, Y., Rudd Zhong Manis, J., Ronczkowski, N. M., Bui, T., Oxenrider, A., Jadeja, R. N., et al. (2024). Unveiling the gut-eye axis: how microbial metabolites influence ocular health and disease. Front. Med. 11, 1377186. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1377186
Omarova, S., Charvet, C. D., Reem, R. E., Mast, N., Zheng, W., Huang, S., et al. (2012). Abnormal vascularization in mouse retina with dysregulated retinal cholesterol homeostasis. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 3012–3023. doi: 10.1172/JCI63816
Pang, C. E., Messinger, J. D., Zanzottera, E. C., Freund, K. B., and Curcio, C. A. (2015). The onion sign in neovascular age-related macular degeneration represents cholesterol crystals. Ophthalmology 122, 2316–2326. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.07.008
Pawlowska, E., Szczepanska, J., Koskela, A., Kaarniranta, K., and Blasiak, J. (2019). Dietary polyphenols in age-related macular degeneration: protection against oxidative stress and beyond. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 9682318. doi: 10.1155/2019/9682318
Saadane, A., Mast, N., Trichonas, G., Chakraborty, D., Hammer, S., Busik, J. V., et al. (2019). Retinal vascular abnormalities and microglia activation in mice with deficiency in cytochrome P450 46A1–mediated cholesterol removal. Am. J. Pathol. 189, 405–425. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.10.013
Saha, P., Yeoh, B. S., Xiao, X., Golonka, R. M., Abokor, A. A., Wenceslau, C. F., et al. (2020). Enterobactin induces the chemokine, interleukin-8, from intestinal epithelia by chelating intracellular iron. Gut. Microbes 12, 1841548. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1841548
Shahi, S. K., Freedman, S. N., and Mangalam, A. K. (2017). Gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis: The players involved and the roles they play. Gut. Microbes 8, 607–615. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1349041
Sinha, T., Makia, M., Du, J., Naash, M. I., and Al-Ubaidi, M. R. (2018). Flavin homeostasis in the mouse retina during aging and degeneration. J. Nutr. Biochem. 62, 123–133. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.09.003
Sterling, J. K., Baumann, B., Foshe, S., Voigt, A., Guttha, S., Alnemri, A., et al. (2022). Inflammatory adipose activates a nutritional immunity pathway leading to retinal dysfunction. Cell Res. 39, 110942. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110942
Storti, F., Klee, K., Todorova, V., Steiner, R., Othman, A., van der Velde-Visser, S., et al. (2019). Impaired ABCA1/ABCG1-mediated lipid efflux in the mouse retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) leads to retinal degeneration. Elife 8, e45100. doi: 10.7554/eLife.45100
Tsioti, I., Steiner, B. L., Escher, P., Zinkernagel, M. S., Benz, P. M., and Kokona, D. (2024). Systemic lipopolysaccharide exposure exacerbates choroidal neovascularization in mice. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 32, 19–30. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2022.2147547
Vezza, T., Abad-Jiménez, Z., Marti-Cabrera, M., Rocha, M., and Víctor, V. M. (2020). Microbiota-mitochondria inter-talk: a potential therapeutic strategy in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Antioxidants 9, 848. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090848
Wang, H. (1958). Taiping holy prescriptions for universal relief (Beijing: the People’s Medical Publishing House), 983.
Wang, X., Quinn, P. J., and Yan, A. (2015). Kdo2-lipid A: structural diversity and impact on immunopharmacology. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc 90, 408–427. doi: 10.1111/brv.12114
Wei, P., Gao, S., and Han, G. (2025). Evidence for genetic causal association between the gut microbiome, derived metabolites, and age-related macular degeneration: A mediation mendelian randomization analysis. Biomedicines 13, 639. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030639
Wong, W. L., Su, X., Li, X., Cheung, C. M. G., Klein, R., Cheng, C. Y., et al. (2014). Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2, e106–e116. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70145-1
Xiao, J., Zhang, J. Y., Luo, W., He, P. C., and Skondra, D. (2023). The emerging role of gut microbiota in age-related macular degeneration. Am. J. Pathol. 193, 1627–1637. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.04.006
Xue, W., Peng, P., Wen, X., Meng, H., Qin, Y., Deng, T., et al. (2023). Metagenomic sequencing analysis identifies cross-cohort gut microbial signatures associated with age-related macular degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 64, 11. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.5.11
Yang, N., Xiong, C., Feng, S., Gao, M., Zhou, S., Hui, Q., et al. (2025). Modified ZhuJing pill protects retinal pigment epithelium against oxidative stress-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition through Nrf2-mediated Akt/GSK3β pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1545731. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545731
Zhang, X., Alhasani, R. H., Zhou, X., Reilly, J., Zeng, Z., Strang, N., et al. (2021). Oxysterols and retinal degeneration. Br. J. Pharmacol. 178. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545731
Zhang, Y., Wang, T., Wan, Z., Bai, J., Xue, Y., Dai, R., et al. (2023). Alterations of the intestinal microbiota in age-related macular degeneration. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1069325
Zhang, J. Y., Xie, B., Barba, H., Nadeem, U., Movahedan, A., Deng, N., et al. (2022). Absence of gut microbiota is associated with RPE/choroid transcriptomic changes related to age-related macular degeneration pathobiology and decreased choroidal neovascularization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 9676. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179676
Zheng, W., Mast, N., Saadane, A., and Pikuleva, I. A. (2015). Pathways of cholesterol homeostasis in mouse retina responsive to dietary and pharmacologic treatments. J. Lipid Res. 56, 81–97. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M053439
Zheng, W., Reem, R. E., Omarova, S., Huang, S., DiPatre, P. L., Charvet, C. D., et al. (2012). Spatial distribution of the pathways of cholesterol homeostasis in human retina. PloS One 7, e37926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037926
Zhu, Y., Chen, B., Zhang, X., Akbar, M. T., Wu, T., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Exploration of the Muribaculaceae family in the gut microbiota: diversity, metabolism, and function. Nutrients 16, 2660. doi: 10.3390/nu16162660
Keywords: age related macular degeneration, cholesterol, oxidative stress, inflammation, gut microbiota, modified Zhujing pill
Citation: Cen S, Xie S, Ibrahim KS, Baran MR, Li X, Reilly J, Tan Z, He Z and Shu X (2025) Modified Zhujing pill regulates RPE cholesterol metabolism and gut microbiota in an age-related macular degeneration mouse model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1691360. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1691360
Received: 23 August 2025; Accepted: 13 October 2025;
Published: 31 October 2025.
Edited by:
Feifei Shi, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, ChinaReviewed by:
Mohd Aizuddin Mohd Lazaldin, University Technology Malaysia, MalaysiaLiu Dongbo, Hunan Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Cen, Xie, Ibrahim, Baran, Li, Reilly, Tan, He and Shu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinhua Shu, eGluaHVhLnNodUBnY3UuYWMudWs=; Zhiming He, NDAwMDNAaG5zeXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors share first authorship
 Shuibin Cen1†
Shuibin Cen1† Shiqin Xie
Shiqin Xie Khalid S. Ibrahim
Khalid S. Ibrahim Michal R. Baran
Michal R. Baran Xing Li
Xing Li Xinhua Shu
Xinhua Shu