- 1Department of Veterinary Diagnostic and Production Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, United States
- 2National Laboratory for Veterinary Quality Control on Poultry Production, Animal Health Research Institute, Agriculture Research Center, Giza, Egypt
- 3Exotic and Emerging Avian Viral Disease Research Unit, Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory, United States National Poultry Research Center, Athens, GA, United States
- 4Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences, Animal Health Diagnostic Center, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, United States
- 5Department of Avian and Rabbit Diseases, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
- 6Texas A&M Veterinary Medical Diagnostic Laboratory, College Station, TX, United States
- 7Department of Avian and Rabbit Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt
- 8Department of Population Health, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, United States
Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) stands at the forefront of third-generation sequencing, utilizing a nanopore sequencing approach to achieve high-throughput DNA and RNA sequencing. This technology offers several key advantages, including real-time data generation, portability, and long-read capabilities, making it an increasingly valuable tool for a wide range of applications. This review will focus on the use of ONT in veterinary diagnostics exploring the evolving applications of ONT in veterinary medicine and its use in detecting viral and bacterial pathogens, antimicrobial resistance profiling, foodborne disease surveillance, and metagenomic analysis. We provide an overview of the diverse sequencing workflows available, from sample preparation to bioinformatics analysis, and highlight their advantages over traditional sequencing methods. While powerful, nanopore sequencing does present challenges such as error rates, barcode crosstalk, and workflow complexities. This review will address these issues and discuss potential future developments, as well as the long-term impact of ONT on the field of genomics. As nanopore sequencing technology continues to advance, its role in veterinary diagnostics is expected to expand significantly, leading to improvements in disease surveillance, outbreak response, and contributions to crucial One Health initiatives.
1 Introduction
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized genomic research in the 21st century, enabling high-throughput, cost-effective, and comprehensive analysis of nucleic acids (van Dijk et al., 2014; McCombie et al., 2019). By generating high-depth sequencing data, NGS technologies allow the detection of minor variants, accelerate the development of novel computational approaches for sequence analysis, and overcome the selective biases of traditional Sanger sequencing, enabling impartial insights into population sequence diversity (Mardis, 2011; Koboldt et al., 2013). Key moments in the evolution of NGS include massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) in 2000 by Lynx Therapeutics, followed by 454 Life Sciences’ pyrosequencing technology in 2004, which introduced the Roche GS20 as the first NGS platform on the market (Reinartz et al., 2002; Wheeler et al., 2008; Koboldt et al., 2013). This platform could produce up to 20 million base pairs, revolutionizing DNA sequencing. By 2008, the first study utilizing NGS to sequence a human genome was published, demonstrating the feasibility of large-scale sequencing projects (Levy et al., 2007). The following years saw continuous advancements, such as Illumina’s HiSeq X Ten sequencer in 2014, which achieved the milestone of a $1, 000 genome (Mardis, 2011; Goodwin et al., 2016). In 2022, Ultima Genomics announced the $100 genome, signaling the rapid trajectory of innovation in NGS technologies (Ultima_Genomics, 2022).
NGS overcame the primary drawbacks of first-generation sequencing (low throughput, time-consuming, high cost per base) (Heather and Chain, 2016) by allowing the simultaneous sequencing of millions of fragments, drastically reducing both time and cost (Shendure and Ji, 2008). This enabled complex genomic studies, such as whole-genome sequencing (WGS), transcriptomics, and metagenomics. Although NGS represented a significant advancement in sequencing technology, it also has certain limitations, including high upfront costs and short read length. Furthermore, analyzing data after sequencing requires the use of complex bioinformatic tools and techniques (Ari and Arikan, 2016). In response to these limitations, third-generation sequencing (TGS) emerged in 2011 with the launch of the PacBio system (Athanasopoulou et al., 2021), which can generate an average of 10 kb reads and a maximum length of 80 kb (Goodwin et al., 2016; Van Dijk et al., 2018), enabling it to cover repetitive regions in complicated genomes. In less than a decade of TGS development, many sequencing platforms have emerged, each contributing uniquely to the field. However, Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) stands out as a representative of TGS (Pugh, 2023; Warburton and Sebra, 2023), that offers unique advantages, such as real-time sequencing, portability, and long-read capabilities (Lu et al., 2016) supporting a wide range of veterinary applications. Since ONT remains a commercially dominant provider of nanopore-based sequencing (Wang et al., 2021; Maimaiti et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024), this review will focus exclusively on platforms provided by ONT.
In the field of animal health, ONT uses are not limited to infectious diseases. As one example of its diverse applications in animal health, ONT has been pivotal in decoding the genomes of livestock and companion animals. This information is crucial for understanding genetic traits related to disease resistance, productivity, and behavior, ultimately contributing to breeding programs and welfare improvements (Lamb et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2024). However, veterinary infectious diseases remain one of the most impactful aspects of animal health, with effects far reaching into many facets of our life including zoonotic threats, public health, food safety, and global trade (Arefiev et al., 2020; Thomas et al., 2023; Biggel et al., 2024; Hong et al., 2024; Oh et al., 2024). Therefore, this review focuses on ONT applications in veterinary infectious diseases. In addition to the introductory section, this review is organized into seven additional sections. Section two outlines the historical development of ONT, including its evolving methodology, sequencing platforms, and chemistries. Sections three and four explore key components of ONT workflows, focusing on wet lab procedures and dry lab analyses, respectively, to highlight best practices and commonly used tools. The core of the review is presented in section five, which offers an in-depth overview of ONT applications in veterinary medicine, encompassing viral, bacterial, and metagenomic investigations. Lastly, the review concludes with a discussion of current challenges and future perspectives for ONT in this field.
2 Historical background and evolution of ONT
The concept of sequencing molecules through a pore originated in the 1980s, marking a revolutionary advancement in the field of sequencing (Deamer et al., 2016). This approach has vastly broadened the range of sequencing applications, enabling the sequencing of not only DNA but also the native forms of RNA, proteins, ions, and other biomolecules, effectively moving beyond the limitations of traditional sequencing-by-synthesis methods. In nanopore sequencing, molecules are identified as they pass through the pore based on changes in electrical current, which are detected and translated into sequencing information (Dekker, 2007; Branton et al., 2008; Maitra et al., 2012; Deamer et al., 2016). Since the first successful demonstration of DNA sequencing through a pore was achieved in 1996 (Kasianowicz et al., 1996), the field has reached significant milestones that have advanced nanopore sequencing technology. These included the capability to process single DNA strands with precision at the single-base level and control the sequencing speed to achieve good signal-to-noise ratio and basecall accuracy.
The core functionality of nanopore sequencing lies in a nanopore molecule (normally biological nanopores) inserted in an electrical resistance membrane. Biological nanopores offer particular advantages due to their high reproducibility and the ease with which they can be modified using modern molecular biology technologies, such as protein sequence manipulation (Feng et al., 2015). When voltage is applied to the system, DNA moves from the cis to a trans compartment. As the molecule passes through the pore, each nucleotide causes distinct current changes, allowing base modification capture (Jain et al., 2016). Motor proteins (component of the sequencing adapters (Heron, 2019)) are an essential component of nanopore sequencing, as they unwind double-stranded nucleic acids and regulate the translocation of molecules through the pore (Branton et al., 2008; Deamer et al., 2016; Van Dijk et al., 2018; Noakes et al., 2019). This control minimizes fluctuations in translocation kinetics and enhances signal acquisition, ultimately improving data accuracy. A detailed description of DNA motor proteins utilized in ONT platforms is provided in (Byrd and Raney, 2019).
ONT licensed its nanopore sequencing patent in 2007 and publicly introduced its technology during the Advances in Genome Biology and Technology (AGBT) conference in 2012. However, access to the technology was initially limited to selected users through the MinION Access Program (MAP) (Deamer et al., 2016) launched in 2014. Also, to support the technology evaluation and optimization, a group of MAP participants established the MinION Analysis and Reference Consortium (MARC) with the goal of assessing ONT sequencing platforms performance and developing standardized protocols and reference datasets for the ONT user community (Ip et al., 2015; Jain et al., 2017).
Since its release, ONT has focused on continuously optimizing multiple aspects of the technology, including the refinement of nanopores and motor protein, molecular translocation speed (balancing between yield and accuracy), buffer compositions, and sequencing modalities. Since 2014, numerous versions of the nanopore and motor protein system were released, beginning with R6 (June 2014), followed by R7 (July 2014), R7.3 (October 2014), R9 (May 2016), R9.4 (October 2016), R9.5 (May 2017), R10 (March 2019), R10.3 (January 2020), R10.4 (September 2021), and the most recent R10.4.1 (June 2022) (Wang et al., 2021). Each version brought incremental read accuracy, signal resolution, and durability improvements. In addition to sequencing chemistry, the sequencing modalities have also changed over time. Early protocols incorporated 2D and 1D2 library preparations to improve read accuracy by sequencing both strands of a DNA molecule. In the 2D library format, the template strand is sequenced first, followed by a hairpin adapter and the complement strand. With the 1D2 method (released in 2017, compatible with R9.5), each strand is ligated with a special adapter such that there is a high probability (60%) that one strand will immediately be captured by the same nanopore following the sequencing of the other strand of dsDNA. However, most recent library preparation protocols have shifted to the 1D approach, in which single strands of DNA are ligated to adaptors in both ends and are sequenced individually (Ip et al., 2015; Jain et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2021).
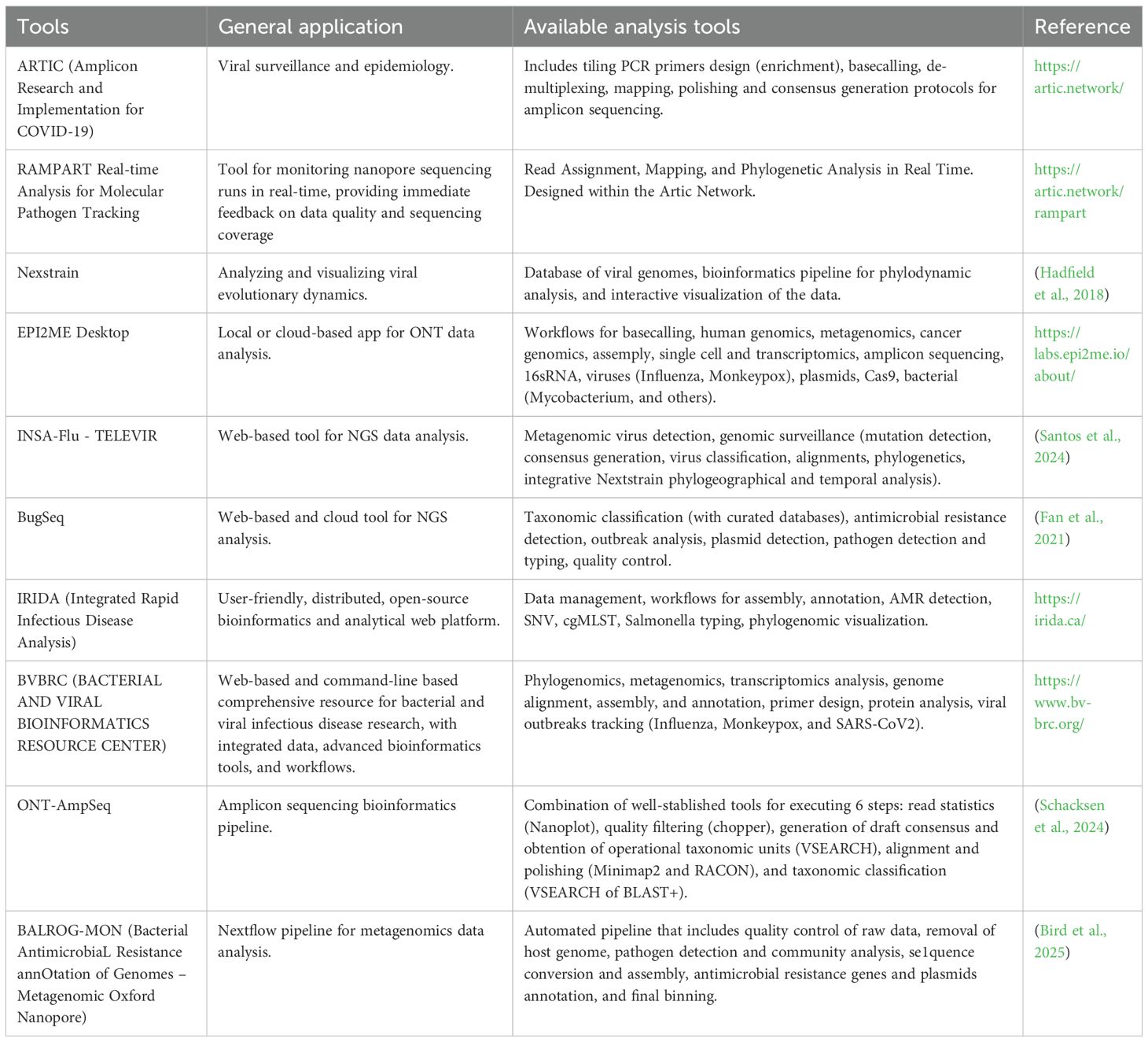
ONT provides sequencing devices that meet a wide range of user needs, from compact, portable options to high-throughput instruments (Figure 1). The first device, the MinION, became available in 2014 as an early access product, and in 2015 its second version, MinION Mk1, was released. Later, in 2016, the next version, Mk1B, was launched, and it remains available to customers up to date. In February 2025, ONT released a new iteration of Mk1B, the Mk1D, which incorporates significant advancements in design, temperature control, and simplified laptop connection through USB-C cable. Another MinION model is the Mk1C, which was introduced in 2020 as an all-in-one device with integrated GPU for running sequencing experiments, real-time base-calling, and downstream analysis. However, the Mk1C was discontinued in March 2024, with hardware support available until June 2025 and software support until June 2026. MinION devices operate with the same flow cell type (Clarke, 2019), with 512 channels and 4 pores in each channel.
Figure 1. Timeline for ONT major releases from 2014 to 2025, including flow cells, chemistries, and devices. Figure was created in https://BioRender.com.
For users requiring increased throughput, ONT introduced the GridION in 2017, a device capable of operating up to five MinION flow cells concurrently and equipped with a high-power computer within the unit that will handle live base-calling. In 2019, there was a transition from GridION X5 to the matured GridION Mk1. The PromethION 48 (P48) was released to further enhance sequencing capacities in 2018. This system utilizes a different flow cell (PromethION flow cells) than previous devices, with a higher pore count (2, 675 channels, with 4 pores in each channel), allowing for higher data output generation. The P48 can run up to 48 independent flow cells simultaneously, presenting the highest throughput ONT option. In 2019, ONT released the PromethION 24 (P24), which uses the same flow cell type as the PromethION 48 but supports up to 24 flow cells. The most recent addition to the ONT portfolio, the PromethION 2 (P2), provides higher throughput than the MinION while catering to smaller-scale projects than the PromethION 48. This device is available as a standalone unit or in an integrated configuration with an attached computer. For applications requiring lower input and smaller sample numbers, ONT launched the Flongle flow cell in 2019. The Flongle contains 128 nanopores and can be used in either the MinION or GridION devices through the use of an adapter (Wang et al., 2021).
Finally, following the tendencies of end-to-end automated sequencing workflows, ONT released ElysION in 2025 (Technologies, O.N, 2025). This workstation includes different positions for plates, samples, and reagents, and robotic liquid handlers, that can perform from extraction of samples to library loading, minimizing human interaction and streamlining the process. Currently version allows for running up to 3 Mk1D devices with library prepared with the Rapid Barcoding Kit.
In addition to the versatility of sequencing equipment, a great differential of ONT is the lower startup costs compared to other NGS platforms, making sequencing accessible for different size laboratories. As reference, a starter pack can be purchased with less than $5, 000 and gives the user the necessary to start sequencing (a sequencing device - MinION Mk1D, a flow cell, and sequencing kit).
3 Oxford nanopore technologies workflow
Alongside the diversity of equipment available, there is also a variety of wet lab workflows for ONT, which are highly customizable and vary based on the specific objectives of the experiment. These differences are critical to optimize the sequencing process and ensure the accuracy and relevance of the results for each application. However, key steps are consistent across various experiments, including nucleic acid extraction, library preparation, loading, sequencing, data generation, and analysis. Additionally, optional steps, such as nucleic acid fragmentation, size selection, and microbial nucleic acid enrichment step, may be incorporated depending on the researcher’s objectives and the specific goals of the experiment (Wang et al., 2021).
Although this section highlights available tools and validated workflows developed by ONT internal teams, the authors strongly recommend that laboratories perform independent optimization when implementing this technology in their routine diagnostics or research. Multiple studies have emphasized the importance of evaluating the performance of different protocols, as comparative assessments enable the selection of the most suitable approach for specific laboratory conditions and objectives (Esnault et al., 2021; Maghini et al., 2021; Eagle et al., 2023; Ip et al., 2023; Chaves et al., 2024; Goraichuk et al., 2024a; Goraichuk and Suarez, 2025; Perlas et al., 2025; Weigl et al., 2025). In this section we will describe technical details of each of the steps with practical expertise gained from using ONT in different setups. We aim for this section to be a useful guide and a practical introduction to basic laboratory procedures involved in using ONT. Information in this section is foundational for further discussion in the following sections.
3.1 Sample preparation
3.1.1 Nucleic acid extraction
Nucleic acid extraction is a critical first step in ONT sequencing, ensuring high quality and enough input material for successful sequencing outcomes. Numerous extraction protocols are available (Table 1), and selecting the most suitable method is a complex process that depends on the sample type and the specific objectives of the experiment. Notably, the ability to generate long reads primarily depends on the input sample, extraction of high-molecular-weight nucleic acid and library preparation rather than limitations inherent to the sequencing process (Quick and Loman, 2018). While numerous extraction protocols have been described in the literature, they generally share key steps, including cell lysis, purification, and elution/precipitation (Quick and Loman, 2018). These steps are achieved through various methods, such as liquid-phase separation (e.g., phenol-chloroform extraction), solid-phase extraction (e.g., spin-column kits, gravity flow columns, and magnetic beads), and enzymatic methods (Shin, 2013; Quick and Loman, 2018; Chaves et al., 2024).
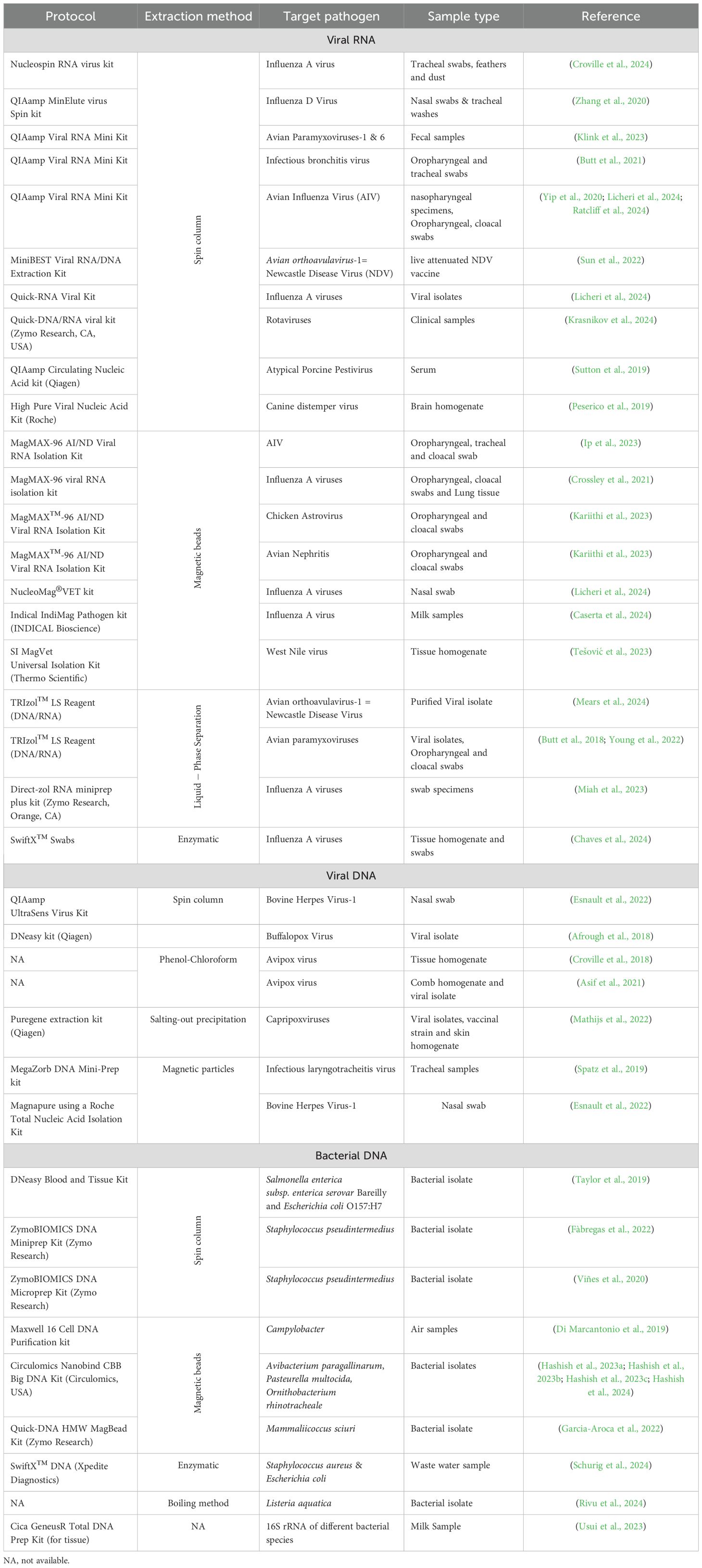
Table 1. List of different nucleic acid extraction protocols used before Nanopore sequencing of various pathogens.
No universally ideal nucleic extraction method exists, as the aim of the sequencing run, individual preferences and prior experience often influence the protocol choice. The extraction methods can vary substantially depending on the extracted sample (such as tissue, blood, urine, or soil) and the type of genomic input (RNA, bacterial or eukaryotic genomic DNA, plasmid DNA, etc.). Alternatively, in-house methods without using a commercial kit or modifying kit protocols to increase yields are also popular. Some examples of RNA extraction kits were compared, including their utilization in well-equipped laboratories (Chaves et al., 2024), or towards field application (Chaves et al., 2024). For DNA extraction, some studies have been published evaluating extraction kits’ impact on the quality, accuracy, and efficiency of subsequent nanopore sequencing experiments (Framst et al., 2022; Trigodet et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022; Eagle et al., 2023; Gand et al., 2023).
To obtain the highest quality nucleic acid samples, the extract should undergo evaluation for concentration, purity, and fragment length to maximize the output of each sequencing experiment. Accurate quantification of nucleic acid concentration is typically performed using fluorometric methods, such as the Qubit assay(2024). Maximizing the purity of extracted nucleic acids ensures improved ONT yields, as chemical and biological impurities can compromise nanopores, potentially reducing the lifespan of flow cells (Maghini et al., 2021; Wick et al., 2023). NanoDrop™ Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) is one of the suggested methods to confirm extract purity, by assessing the OD 260/280 (1.8 for DNA and 2.0 for RNA) and OD 260/230 (from 2-2.0). Those ratios can be an indicative of protein and extraction reagents contamination in the final eluted nucleic acid. Various analytical tools can be employed to assess nucleic acid fragment length, including gel electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis-based systems such as the Bioanalyzer, Fragment Analyzer, or TapeStation (Bogner and Killeen, 2005; 2015; Dong et al., 2019). Specifically for RNA, avoiding RNase contamination and damage by freeze/thaw cycles and improper storage is crucial. RNA quality should be evaluated using the RNA integrity number (eRIN) calculation (Schroeder et al., 2006), and for the situations when ribosomal RNA is not present (e.g., viral RNA), the overall length of the fragments can be assessed from the generated electropherogram from the output of the Bioanalyzer and TapeStation. When possible, samples showing degraded RNA should be re-extracted so that only high-quality RNA is used for sequencing to reduce sequencing bias (Prawer et al., 2023). For a simple overview of DNA/RNA quality check before sequencing, there is an available guide provided by ONT (Technologies, O.N, a).
3.1.2 Sample enrichment or depletion
Direct nanopore sequencing from clinical samples is often challenged by excessive host DNA/RNA contamination, which significantly reduces microbial read sensitivity. To overcome this, pathogen(s) enrichment or host nucleic acid depletion strategies are essential (Marchukov et al., 2023). Several enrichment and depletion strategies are available, including wet lab-based methods applied before or during library preparation and in silico approaches implemented during data analysis. Wet lab methods include enzymatic methods, probe hybridization-based methods, DNA-intercalating dyes, size selection, or target enrichment (Goraichuk et al., 2024b). For direct RNA sequencing or cDNA sequencing, polyadenylated RNA can be positively selected using poly(A) + enrichment such as Oligo d(T) beads (Wang et al., 2009). ONT also offers several PCR-based methods for the positive selection of a target through amplification. There is extensive work being done in the field of avian viruses towards improving sequencing results via host-depletion and targeted sample enrichment mechanisms (Bakre et al., 2023; Narvaez et al., 2023; Noh et al., 2023; Goraichuk et al., 2024b; Kuchinski et al., 2024). For the in-silico enrichment, Nanopore Adaptive Sampling (NAS) stands out as a unique feature of ONT, and more details are described in section 5.3.1.
3.2 Library preparation
Library preparation is necessary for a successful ONT experiment, ensuring that DNA or RNA is properly prepared after sequencing adapters – which integrate leader strands, enzyme motors, and tethering elements (Heron, 2019), and barcodes are attached (multiplexed samples) (Heron, 2019). Key considerations during this stage include accurate quantification and normalization of input material to maintain even sequencing coverage and strict sterile conditions to prevent contamination. Proper library preparation allows for high sequencing efficiency, minimizes biases, and improves data quality. Even though ONT still offers the possibility of purchasing older versions of the library preparation kits for selected customers, the kits displayed for public purchase are only for the latest chemistry (kits 14). Therefore, in this section, we will focus on kit 14.
3.2.1 Library preparation for DNA sequencing
ONT has developed 8 different kits that can be used for sequencing DNA. These kits range in their template inputs and can produce the full spectrum of read length from as short as 20 nucleotides (targeted gene motifs of interest) to ultra-long reads up to 4+ million base pairs (Mbp) (van Dijk et al., 2023). Each kit varies in library preparation steps and input sample requirements.
ONT provides the Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit (SQK-ULK114) for the longest read length, specifically designed for ultra-high molecular weight DNA, such as eukaryotic genomes. This kit employs tagmentation with a transposome complex, facilitating rapid adapter addition. A similar transposome cleavage mechanism is used in the Rapid Sequencing Kit (SQK-RAD114). The Rapid Sequencing Kit is ONT’s simplest and fastest library preparation method, requiring only a single step that takes approximately 10 minutes. For native adapter addition, ONT offers Ligation Sequencing Kits (SQK-LSK114), which support various template inputs, including total genomic DNA, PCR amplicons, whole genome amplification products, and cDNA. Unlike rapid kits, these require DNA repair and end preparation before adapter ligation.
Several ONT kits also support multiplexing, reducing per-sample sequencing costs. Among the transposome-based chemistries, multiplexing is enabled by the Rapid PCR Barcoding Kit (SQK-RPB114) and the Rapid Barcoding Kits (SQK-RBK114.24 and SQK-RBK114.96), allowing up to 24 or 96 samples per run. For native barcoding, ONT provides the Native Barcoding Kit (SQK-NBD114), which also accommodates 24 or 96 unique barcodes in a single sequencing run. Finally, the dual barcoding option is available and increases the multiplexing capability up to 2, 304 samples (Technologies, O.N, b). Additionally, ONT offers a specific kit for bacterial 16S sequencing that is based on a PCR with specific 16S primers followed by rapid sequencing adapters attachment.
A summary of ONT’s available library preparation methods is illustrated in Figure 2.
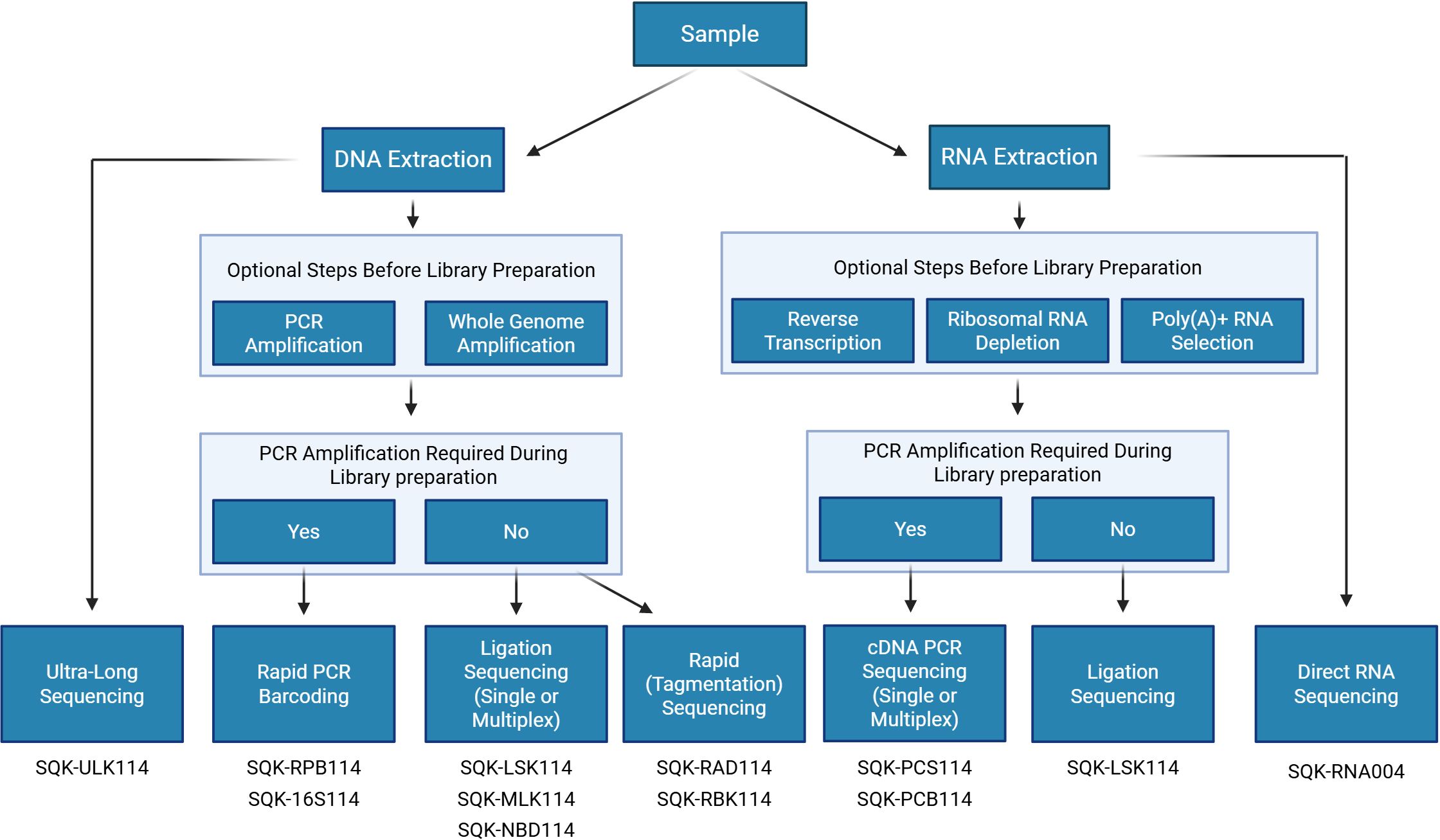
Figure 2. Workflow for selecting the appropriate ONT sequencing kit. Figure was created in https://BioRender.com.
3.2.2 Library preparation for RNA sequencing
ONT offers two different methods for sequencing RNA: direct RNA sequencing (SQK-RNA004) or cDNA sequencing, which can be performed with selection for full-length transcripts by PCR (SQK-PCS114- for individual samples and SQK-PCB114- for multiple samples, using barcodes) or direct cDNA sequencing with the Ligation kit (SQK-LSK114). Both methods can begin with either total RNA from a sample or a modified subset of total RNA that has either been enriched, depleted, or reverse transcribed. With Direct RNA Sequencing (DRS), total RNA can be used directly, offering the shortest library preparation time slightly more than 2 hours. Currently, there are no multiplexing options for DRS, but ONT’s recent updates suggest early access to barcoded DRS later in 2025 (London Calling, 2025), offering a more cost-effective alternative to sequencing single samples individually. cDNA sequencing can be used for a single sample or multiplexed with up to 24 samples in a single run to reduce the cost per sample significantly.
Direct RNA sequencing can be used in either an untargeted or targeted manner to evaluate the complete transcriptome of a sample or for the detection of a specific RNA, respectively. Direct RNA sequencing enables direct sequencing of positive or negative sense RNAs depending on the adapter used. Viral genome sequences have been obtained using DRS from viruses in the Arteriviridae (Zhang et al., 2021), Coronaviridae (Viehweger et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2023), Flaviviridae (Keller et al., 2018), Orthomyxoviridae (Keller et al., 2018), Peribunyaviridae (Wongsurawat et al., 2019), Picornaviridae (Keller et al., 2018), Reoviridae (Xu et al., 2024), Retroviridae (Baek et al., 2024), Rhabdoviridae (Wongsurawat et al., 2019), and Togaviridae (Wongsurawat et al., 2019; Baquero-Perez et al., 2024; Tan et al., 2024) families, and recently the important poultry pathogen Newcastle Disease virus in the Paramyxoviridae family (Mears et al., 2024).
3.3 Flow cell priming and loading
Flow cells serve as the core hardware component for ONT sequencing. Through one of the available sequencing devices (MinION, GridION or PromethION), they are connected to ONT’s MinKNOW software, which controls the initiation, monitoring, and termination of the sequencing run (Technologies, M.O.N, a). DNA- or RNA-specific nanopores within the flow cell are embedded in electrically resistant polymer membranes arranged across an array connected to a sensor chip. As nucleic acid molecules pass through the nanopore, the disruption in electric current produces characteristic electrical signals, known as “squiggle, “ which are then decoded using different base-calling algorithms to generate nucleotide sequences. Although the sequencing process is similar for both RNA and DNA, the flow cells differ based on the type of nucleotide-specific nanopore proteins embedded within the membrane, which are optimized for the respective molecule type (Jain et al., 2016).
Flow cells are shipped and stored with a protective storage buffer covering the nanopore array. This buffer preserves pore stability during storage and contains a dilute solution composed of ssDNA that allows an initial quality control check to assess the number of available pores (Clarke, 2019). Before starting a sequencing run, checking the flow cell’s active pore count using MinKNOW is essential to ensure enough pores for a successful run. The minimum warranty pore counts vary between the different flow cell types, 50 pores for the Flongle, 800 for the MinION, and 5, 000 for PromethION flow cells. Flow cells falling below these thresholds are typically considered unsuitable for optimal performance under ONT’s warranty guidelines (Technologies, C.T.D.O.N). Additionally, proper flow cell storage and maintenance are crucial for optimal performance. Flow cell must be stored at 4°C (never frozen) and used within 3 months if closed or one month if opened (Payne et al., 2021). Considering laboratories with low throughput, this short lifespan can be an issue, since ordering flow cells in batch is more cost-efficient and storing them for long periods of time is not recommended. One solution in this case is to set up separate scheduled deliveries and not receive multiple flow cells at once, still taking advantage of the better deals when ordering them in batches.
Before loading a library, the storage buffer must be carefully removed and the pores primed with a dedicated priming solution to prepare the system for sequencing. During priming and loading the flow cell, it is critical to prevent the introduction of air bubbles, as they will damage the nanopores and compromise sequencing performance. After flow cell priming, the prepared sequencing library is diluted in ONT’s sequencing buffer and library solution before loading onto the nanopore array. Each flow cell is supplied with a light shield to protect the array from light damage and should be placed after loading the samples before initiating the sequencing run (guide, G.s; Technologies, C.T.D.O.N).
3.4 Sequencing process and data acquisition
All ONT sequencing devices are controlled through the ONT software MinKNOW (Technologies, M.O.N, a). This software provides a graphic user interface for setting up, starting, and monitoring each sequencing run. MinKNOW manages the sequencing workflow, from flow cell quality control to data acquisition and storage. The “squiggle” data is recorded in POD5 or FAST5 file formats during each run with some tools available to facilitate conversion between these two formats (Technologies, O.N, c). These raw data files can be processed within MinKNOW or exported to external software tools for downstream analysis to interpret the signal and perform base-calling of the data. Basecalled reads can be stored in FASTQ or BAM formats for downstream analysis.
MinKNOW offers flexible run configuration options for the sequencing run, including stopping sequencing at a set time or if a data threshold has been reached. Integrated within MinKNOW, Dorado (https://github.com/nanoporetech/dorado, 2025), ONT’s latest base-calling software, enables real-time base-calling during sequencing using the base-calling model of your choice (fast, high accuracy (HAC), or super high accuracy modes (SUP)), balancing speed and accuracy depending on computational resources. While real-time base-calling accelerates time-to-result, HAC and SUP modes are more computationally demanding and require high computing power to keep up with real-time data generation and base calling. Dorado is also able to perform demultiplexing when multiple barcodes are selected in a single run (Technologies, M.O.N, b; https://github.com/nanoporetech/dorado, 2025).
When real-time base calling is enabled, MinKNOW can also conduct Nanopore adaptive sampling (NAS), a selective sequencing feature that maps reads to provided sequences to enrich or deplete sequencing reads from the data set. This in silico targeted approach increases the target depth of coverage during the sequencing run without additional laboratory preparation steps (Martin et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024). In addition to NAS, a beta feature in MinKNOW named “barcode balancing” uses a similar adaptive feedback principle as NAS and is intended to keep the reads count homogeneously distributed across barcoded samples. However, as this feature remains under development, its use may reduce the overall sequencing output due to the increased computational demands of pores in active feedback, reducing sequencing efficiency and rejecting reads over time.
Continuous monitoring of sequencing runs in MinKNOW is not only possible but highly recommended, as performance can fluctuate due to many factors, such as pore occupancy and viability, temperature, translocation speed, and system memory usage. Any unexpected changes can be quickly identified through the graphic output from MinNKOW, allowing users to decide whether to continue or stop the run. Several key parameters can influence run performance, including 1) temperature, which directly affects both read accuracy and output generation; 2) translocation speed, set at 400 b/s for DNA and 70b/s for RNA for current R10.4.1 flow cells; 3) pore occupancy (Heron, 2019) (percentage of pores in sequencing state compared to total number of pores available for sequencing), which should be higher than 95% especially at the start of a run to maximize output generation and maintain pore health over time.
4 Bioinformatics and data analysis tools
Bioinformatics plays a critical role in transforming raw sequencing data into meaningful biological insights. For ONT experiments targeting infectious diseases data, bioinformatics workflows typically include basecalling, pre-processing, alignment, assembly, variant calling, and downstream analyses such as taxonomic classification or gene annotation. These steps are essential for ensuring data accuracy, interpretation, and applicability in research and diagnostics.
4.1 Pre-processing Reads
As a primary data analysis step, pre-processing sequencing reads is essential for improving data quality and computational efficiency for further analysis. This step includes quality control, read filtering, adapter/primer trimming, and host read depletion.
Trimming adapters and primers (e.g., in amplicon-based sequencing) and filtering out short and low-quality reads are essential in data pre-processing. Tools such as Chopper (De Coster and Rademakers, 2023), Porechop (2025), and Cutadapt (Martin, 2011) are valuable for adapter trimming. Chopper’s integration into various bioinformatics workflows provides enhanced functionality when paired with tools like NanoFilt for further quality filtering. Additional tools such as FastQ-screen (Wingett and Andrews, 2018), VirusHunter (Zhao et al., 2013), and RINS (Bhaduri et al., 2012) help identify specific sequences of interest in NGS datasets. For long-read quality assessment tools like longQC (Fukasawa et al., 2020), MinionQC (Lanfear et al., 2019), SequelQC (Hufnagel et al., 2019), Nanoplot (De Coster et al., 2018), and pycoQC (Leger and Leonardi, 2019) provide comprehensive quality metrics and generate informative quality plots. Together, these bioinformatics solutions form comprehensive pre-processing pipelines, enabling high-quality data extraction for clinical, epidemiological, and research applications (Delahaye and Nicolas, 2021).
Beyond quality control, another crucial step involves host genome removal, which reduces non-targeted sequences and optimizes computing time and data storage. For ONT’s long-read data, Nanolyse (2025) is a recommended tool for efficient host genome removal. For metagenomic sequencing, addressing issues such as short read lengths, low quality, adapters, and untargeted host sequences typically involves two key stages: (1) host sequence removal and (2) classification and quality control. Read mappers such as BWA (Li and Durbin, 2009), Bowtie (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012), and Minimap2 (Li, 2018) are commonly used to align sequencing reads to known contaminant databases, enabling the filtering of untargeted sequences. In addition, specialized tools such as Decontam (Davis et al., 2018) and Recentrifuge (Martinez, 2018) help with contaminant identification based on statistical correlations of sequence concentration or frequency, respectively. These tools require validation for automated contaminant removal.
4.2 Taxonomic characterization and abundance profiling
Whole-genome shotgun metagenomics relies on comparing sequencing reads to comprehensive databases, such as IMG/M (Hadjithomas et al., 2017), MG-RAST (Keegan et al., 2016), and NCBI RefSeq (Sayers et al., 2022) for taxonomic identification. Tools like MEGAN-LR (Huson et al., 2018) assign reads to taxonomic groups using the lowest common ancestor (LCA) algorithm. MEGAN-LR is compatible with alignments generated by tools like Minimap2 (Li, 2018), NGMLR4, NGMLR4, or translated protein sequence alignments from DIAMOND (Buchfink et al., 2015). A recent benchmark study of taxonomic classifiers (Marić et al., 2024) demonstrated that long-read sequencing improves classification precision, whereas short-read classification methods applied to long-read data result in elevated false-positive rates, particularly with tools like Kraken2 (Wood et al., 2019) and Centrifuge (Kim et al., 2016). Among the best-performing tools for long-read taxonomic classification were Sourmash (Irber et al., 2024), BugSeq (Fan et al., 2021), and MEGAN-LR (Huson et al., 2018) when using Minimap2 or DIAMOND for alignments (Marić et al., 2024).
Unlike traditional classifiers such as Kraken2 and Centrifuge, which primarily operate on nucleotide sequences, Kaiju utilizes a reference database of annotated protein-coding genes. This approach enables Kaiju to overcome the limitations associated with the redundancy of the genetic code, making it particularly effective for classifying divergent organisms, including viruses that may not have closely related counterparts in existing databases (Menzel et al., 2016). Kaiju has been effectively used in studies to classify viral sequences derived from complex metagenomic samples, demonstrating its utility in understanding viral diversity and ecology (Wu et al., 2024).
In addition to Kaiju, several other tools adopt a similar protein-based classification approach. vConTACT is designed for the classification of double-stranded DNA viruses, utilizing protein sequences to infer phylogenetic relationships among viral genomes (Bolduc et al., 2017). VPF-Class assigns taxonomic labels and host prediction of uncultivated viruses based on viral protein families (Pons et al., 2021). Additionally, VirTAXA enhances RNA virus taxonomic classification by incorporating remote homology searches and tree-based validation, further exemplifying the advantages of protein-based classification in virology (Zhu et al., 2024).
For species abundance estimation, Bracken (Lu et al., 2017) is a widely used bioinformatics tool designed to refine taxonomic classifications provided by Kraken (Lu et al., 2017). Bracken employs a Bayesian reestimation approach to improve species and genus-level abundance predictions, particularly in datasets containing closely related viral species. Given the high genetic similarity among viral genomes, Bracken enhances resolution by adjusting abundance estimates based on the distribution of reads across taxonomic ranks (Wood et al., 2019). The KrakenTools suite (Davis et al., 2013), which includes both Kraken and Bracken, further enhances the efficiency and accuracy of metagenomic classification workflows by combining rapid taxonomic assignments with refined abundance profiling (Lu and Salzberg, 2020). However, Bracken does not account for genome size bias, meaning species with larger genomes may be underrepresented. In contrast, organisms with small, highly abundant genomes may appear overrepresented in metagenomic datasets.
To address these biases, alternative approaches such as coverage-based normalization can be applied, where relative abundance is estimated based on sequencing depth (reads per kilobase per million mapped reads, RPKM) rather than absolute read counts. Other methods include the Genome Relative Abundance using Mixture Model (GRAMMy), which corrects genome size discrepancies when estimating taxonomic abundances. These normalization strategies help improve the accuracy of microbial and viral population profiling in metagenomic studies.
Together, these taxonomic classification and abundance estimation strategies enable ONT users to obtain high-resolution microbial and viral community profiles, balancing computational efficiency with classification accuracy.
4.3 Reference-based genome assembly
Reference-based genome assembly relies on the availability and completeness of reference genomes to guide sequence alignment and variant detection. While this approach is highly effective for well-characterized organisms, it often faces challenges with novel variants, structural variations, or incomplete reference genomes. Long-read sequencing has shown advantages over short-read methods by resolving ambiguities in repetitive, homologous, or structurally complex regions that are often misassembled or ambiguous short-read datasets (Croville et al., 2018).
Commonly used long-read aligners for reference-based assembly include Minimap2 (Li, 2018) and NGMLR4 (Sedlazeck et al., 2018), which are optimized for mapping high-error-rate reads while maintaining sensitivity to structural variations. GraphMap (Sović et al., 2016) is another long-read mapper specifically designed for ONT sequencing data, offering high sensitivity and accuracy in detecting structural variations and mapping highly diverged sequences. Additionally, the Winnowmap (Jain et al., 2020) tool improves mapping in repetitive genomic regions by incorporating repeat-aware mapping strategies, making it particularly useful for genomes with high repeat content or complex structural rearrangements. These mappers are essential for achieving high-confidence genome alignments and enhancing downstream analyses.
For variant calling and haplotype phasing, tools like Clair3 (Su et al., 2022), NanoVar (Tham et al., 2020) and NanoCaller (Ahsan et al., 2021) utilize deep learning models and statistical frameworks to enhance the accuracy of single nucleotide variant (SNV) detection leveraging long-read data. Additionally, Medaka (https://github.com/nanoporetech/medaka) incorporates neural networks to estimate allele frequencies and refine variant predictions, which is particularly useful in uneven sequencing coverage or to distinguish between heterozygous and homozygous variants.
4.4 De novo genome assembly
De novo genome assembly presents unique challenges, particularly in resolving repetitive regions and intergenomic repeats, which can hinder assembly tools, especially when repeats exceed the overlap length of reads or contigs (Wenger et al., 2019; Kazantseva et al., 2023). Traditionally, hybrid assemblies combining long and short reads have been widely used to address these issues. However, advancements in reducing long-read error rates are gradually making hybrid assemblies obsolete (Bickhart et al., 2017). For metagenomic assembly, several tools like Hifiasm-meta (Feng et al., 2022), Canu (Koren et al., 2017), and MetaFlye (Kolmogorov et al., 2020) are among the most widely used assemblers. Benchmarks have reported that Canu produces more complete assemblies (Kiguchi et al., 2021), though MetaFlye has shown slight advantages in other contexts, such as handling large genomes or complex microbial communities (Zhang et al., 2023). Despite these advances, error correction methods for long reads can reduce errors but may inadvertently remove low-frequency variations and strains, impacting strain detection (Zhang et al., 2023). These limitations highlight the need for further optimization in metagenomic pipelines, particularly for highly diverse microbial communities.
For bacterial genome assembly, several long-read assemblers are widely used, including Canu (Koren et al., 2017), Flye (Kolmogorov et al., 2019), Raven (Vaser and Šikić, 2021), and Redbean (Ruan and Li, 2020). Trycycler (Wick et al., 2021) is a consensus-based approach that integrates multiple assemblers such as Flye (Kolmogorov et al., 2019), Raven (Vaser and Šikić, 2021), and Miniasm (Li, 2016) to improve assembly accuracy and completeness. However, even with high-coverage long-read sequencing, regardless of the assembler used, most bacterial genome assemblies still contain errors that could be avoided with improved assembly algorithms. Different assemblers applied to the same read set are likely to produce distinct assembly errors (Wick and Holt, 2021). A comparison of different long-read assemblers revealed that Flye and Trycycler produced higher-quality assemblies with a complete, closed genome (Kumar et al., 2024). Flye has proven to be the most efficient tool for de novo genetic assembly (Boostrom et al., 2022). As a result, it has been widely employed for complete bacterial genome assemblies, followed by polishing with short-read data (e.g., Illumina reads) using Pilon to correct residual errors and improve consensus accuracy (Chen et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2021; Eman Gadu et al., 2025). For assembly polishing, tools like PEPPER (Shafin et al., 2021), in combination with Medaka, are recommended for improving assembly accuracy in diverse samples (Lee et al., 2021).
The rapid expansion of viral diversity through metagenomic sequencing has outpaced the development of comprehensive reference databases. The identification of genomes from metagenomic data is crucial for expanding our understanding of viral diversity, yet many of these genomes remain uncatalogued (Garretto et al., 2019). The annotation of novel viruses absent from reference databases poses significant challenges due to the diversity and complexity of viral genomes. Tools like Prokka (Seemann, 2014), which are primarily designed for prokaryotic genome annotation, may not be fully equipped to handle the unique characteristics of viral sequences, particularly those newly discovered or poorly characterized. This is where specialized tools such as VIBRANT (Kieft et al., 2019) come into play. VIBRANT is specifically designed to automate viral genome recovery, annotation, and curation from genomic sequences, making it particularly suitable for handling the vast array of viral diversity encountered in metagenomic studies (Kieft et al., 2020). However, database limitations, such as contaminants or biases, remain persistent challenges in viral genome assembly and annotation, highlighting the need for curated reference databases and improved classification frameworks (Breitwieser et al., 2019).
4.5 Variant annotation
Widely used tools for variant annotation include SNPEff (Cingolani et al., 2012), ANNOVAR (Wang et al., 2010), and Ensembl-VEP (Thormann et al., 2019). They facilitate variant annotation by mapping detected variants to known genomic features such as coding regions, regulatory elements, and disease-associated mutations. Despite advancements in annotation tools, metagenomic classification continues to face challenges, particularly in resolving sub-strain variations and addressing cross-species mapping ambiguities, which remain significant hurdles in bacterial and viral genomics (Wilm et al., 2012; Agustinho et al., 2024).
The ability to accurately identify low-frequency variants is crucial for nanopore sequencing, especially in applications such as intra-host viral population studies and evolution analysis. LoFreq (Wilm et al., 2012) is one of the most effective tools for identifying low-frequency variants, as it applies a probabilistic framework that helps distinguish true variants from sequencing errors. This is particularly valuable in nanopore sequencing, where higher error rates can obscure biologically relevant mutations. However, while LoFreq improves sensitivity, its raw output often requires further refinement to enhance the accuracy of variant calls. This is where Variabel (Liu et al., 2022) comes into play. Variabel is designed as a complementary tool that polishes LoFreq’s results by applying additional filtering and correction algorithms, thereby reducing false positives and improving precision. This refinement step can improve the precision of variant calling, particularly in datasets with high error rates.
As long-read sequencing technologies continue to improve, integrating robust variant annotation pipelines that combine error-aware variant calling (LoFreq) with post-correction filtering (Variabel) will be essential for achieving accurate and high-confidence genomic insights, particularly in microbial and viral genomics. Additional custom available tools that can perform different available analyses are described in Table 2.
4.6 Point-and-click tools and workflows
Even though the backend of sequencing analysis relies on huge efforts from bioinformaticians and computer scientists, the end goal of extracting valuable information from the data is accessible for people with different computational expertise. This is possible due to the large availability of user-friendly tools that can be used online or upon local installation.
From the ONT efforts, EPI2ME Desktop comes as a great resource to the community helping in the analysis of a variety of data with end-to-end workflows. Some examples of general workflows (that can be applied for different types of data and pathogens) include post-run basecalling, alignment, metagenomics, amplicon analysis, bacterial genomes assembly, single cell, transcriptomics and telomeric sequences. Additionally, specific pathogen workflows are also available, such as for Influenza A and B viruses, Monkeypox virus, and the ARTIC SARS-CoV-2 sequencing analysis. In addition to the ONT platform, there are other free-access online platforms such as BACTERIAL AND VIRAL BIOINFORMATICS RESOURCE CENTER (BV-BRC) (Olson et al., 2023), and INSA-Flu – TELEVIR (Santos et al., 2024) that allow for different analysis, such as alignment, assembly, and phylogenetics from different pathogens. Finaly, Galaxy is an open-source, web-based platform that enables users to perform complex computational analyses through an intuitive graphical interface, eliminating the need for programming expertise. It integrates a broad suite of tools for sequence analysis, data processing, visualization, and workflow automation, promoting reproducibility and transparency in research (Afgan et al., 2018).
5 Applications for veterinary infectious diseases diagnostics
ONT sequencing platforms enhanced the detection of emerging pathogens and co-infections, decreasing the time to results, which can be critical in outbreak situations. Its ability to generate real-time sequencing data has transformed veterinary diagnostics by enabling on-site sequencing in diverse laboratory settings, including field and remote environments. Additionally, ONT-based metagenomic sequencing allows for the agnostic detection of multiple pathogens within a single sample, offering a comprehensive understanding of complex infections and microbial communities. In this section, we will discuss the application of nanopore sequencing in veterinary infectious diseases diagnostics, with a particular focus on viral and bacterial diseases and metagenomic approaches.
5.1 Viral diseases
This section will provide a summary of the current knowledge of ONT use for detecting and characterizing veterinary viral pathogens. Additionally, a complete description of viral pathogens characterized by ONT is described in Table 3.
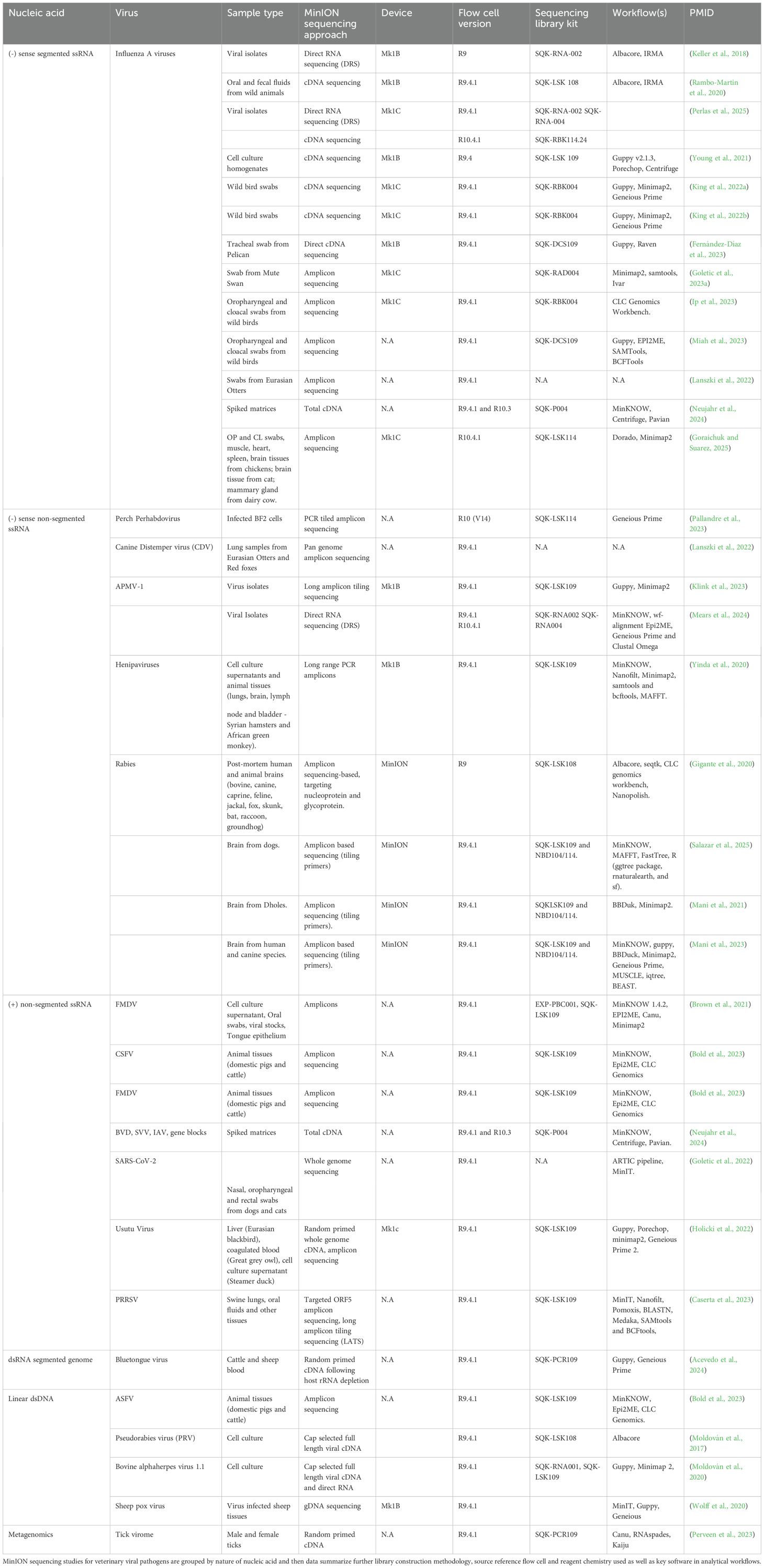
Table 3. Tabular summary of MinION sequencing data for various veterinary viral pathogens of interest.
5.1.1 RNA viruses
5.1.1.1 Negative-sense RNA viruses
Diagnosis of Influenza viruses in the clinic and the field relies on both serology and molecular tests, and genotype characterization is based on viral sequencing. While Sanger and Illumina sequencing have traditionally been the primary methods for viral sequencing, nanopore sequencing has recently been adapted. Influenza has become a key focus for ongoing real-time surveillance using ONT, and there are many available literature (King et al., 2022a; King et al., 2022b; Fernández-Díaz et al., 2023; Goletic et al., 2023a; Ip et al., 2023; Miah et al., 2023). One notable example of the application of Oxford ONT for detecting a highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) outbreak in dairy cattle was recently documented (Caserta et al., 2024).
Current ONT workflows for influenza sequencing can use either viral RNA directly or viral cDNA generated via reverse transcription (John et al., 2025). Keller et al. (Keller et al., 2018) demonstrated that an adapter-based approach targeting the universally conserved 12 nucleotides at the 3’ end of each influenza genome segment could successfully capture all 8 influenza genome segments from a common laboratory strain rA/Puerto Rico/8/1934 as well as three circulating human strains (A/Florida/20/2018(H1N1pdm09), A/Texas/50/2012(H3N2), A/British Columbia/1/2015), and an avian strain (A/chicken Ghana/20/2015 (H5N1)). In a follow-up study, the authors implemented a cDNA-based sequencing workflow to rapidly sequence 13 full-length influenza genomes during an active influenza outbreak at a swine exhibition. The study identified a cluster of influenza viruses that were rapidly differentiating from current pre-pandemic candidate vaccine viruses, highlighting ONT’s potential for real-time outbreak monitoring (Rambo-Martin et al., 2020). Another study presented how nanopore sequencing outperformed traditional virus isolation and Illumina-based influenza A detection from infected tissue samples, further supporting its diagnostic utility (Hosokawa-Muto et al., 2022). Additionally, magnetic hydrogel particles were also demonstrated to improve the percentage of sequenced reads mapping to viral references of influenza A virus, respiratory syncytial virus, and SARS-CoV2 from spiked viral transport media samples (Andersen et al., 2023).
Beyond influenza, Newcastle disease virus (NDV), a member of the Paramyxoviridae family, is another economically important negative-sense single-stranded RNA (-ssRNA) virus causing significant losses in the poultry industry. A recent study proposed the long amplicon tiling sequencing (LATS) approach for nanopore sequencing of NDV on the MinION platform (Klink et al., 2023). Total RNA from fecal samples was used to generate overlapping tiling amplicons across the ~15.2kb NDV genome, allowing for rapid whole-genome sequencing (Klink et al., 2023). In addition, another study successfully employed full-length direct RNA sequencing of the NDV genome using the MinION device, highlighting ONT’s versatility in direct RNA virus detection (Mears et al., 2024).
Canine distemper virus (CDV), another highly contagious paramyxovirus, was recently identified in Eurasian otter retrospective lung tissue samples spanning a 21-year retrospective period (2000-2021) using nanopore sequencing (Lanszki et al., 2022). This study amplified and sequenced full-length CDV genomes, demonstrating ONT’s applicability in wildlife pathogen surveillance and retrospective genomic epidemiology. Other notable -ssRNA viruses sequenced using ONT platforms include henipaviruses (Hendra, Nipah, and Cedar viruses) (Yinda et al., 2020) and perhabdoviruses, which are negative-sense non-segmented ssRNA viruses that infect fish, supporting ONT’s expanding role in aquatic veterinary virology (Pallandre et al., 2023).
In the context of important viral zoonotic diseases, rabies stands out as a cause of fatal encephalitis in different animal species, including humans. Intensive work has been applied ONT towards better diagnosis of this disease in different countries (Gigante et al., 2020; Mani et al., 2021; Bautista et al., 2023; Capin et al., 2023; Mani et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024; Salazar et al., 2025). Nanopore sequencing was utilized as a tool for a rapid and affordable characterization of the virus, with the intention of establishing effective viral surveillance in developing countries.
5.1.1.2 Positive-sense RNA viruses
Food-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) is a highly contagious positive-sense ssRNA virus that causes disease in cloven-hoofed animals and domestic livestock. FMDV is classified as a select agent due to its severe economic impact on livestock industries worldwide. The current diagnostic approach is based on sequencing the variable protein 1 (VP1) region of the 8.4 kb FMDV genome that classifies it into seven distinct serotypes. However, FMDV detection and sequencing are typically performed in specialized BSL-3 facilities, which can delay outbreak control decisions.
Recent studies have demonstrated the advantages of ONT sequencing for FMDV diagnostics (Shaw et al., 2025). Brown et al. amplified the P1 gene of FMDV from cell culture-derived and field samples and successfully sequenced them within 30 minutes and 2.5 hours, respectively, using the MinION platform (Brown et al., 2021). Similarly, Bold et al. utilized nanopore sequencing to identify the African swine fever virus, classical swine fever virus, and FMDV segments in infected animals in Mongolia, achieving 91-100% sequence identity to reference strains (Bold et al., 2023). Xu et al. demonstrated direct RNA sequencing of FMDV without the need for reverse transcription, enabling full-genome sequencing within 50 minutes (Xu et al., 2024). This approach provided a fast, low-cost alternative to traditional amplicon-based sequencing or PCR-based genotyping, both time- and resource-intensive. Additionally, Neujahr et al. evaluated nanopore sequencing using cell culture supernatants spiked with bovine viral diarrhea, bovine herpesvirus 1, porcine Seneca Valley virus, and influenza A viruses, demonstrating that total cDNA sequencing could accurately identify viral genomes from mixed samples (Neujahr et al., 2024).
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are another important group of positive-sense RNA viruses recently involved in several human and veterinary outbreaks. WGS has played a critical role in identifying novel variants and understanding viral evolution. A six-hour nanopore sequencing protocol for Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) coronavirus was recently demonstrated (Kim et al., 2021), using a two-step RT-PCR-sequencing strategy. In this approach, first-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using random hexamers, followed by targeted amplified to generate 2.5-3.0 kb amplicons spanning the entire MERS genome using universal primers. Beyond MERS, nanopore sequencing has also been used to demonstrate human-to-dog SARS-CoV-2 transmission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (Goletic et al., 2022). This study confirmed that viral sequences from domestic pet dogs and cats’ nasal, oropharyngeal, and rectal swabs were genetically identical to those obtained from their human companions. In addition to human-origin coronaviruses, nanopore sequencing was successfully applied for animal coronaviruses diagnosis, including major pathogens such as infectious bronchitis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, which cause significant economic losses in poultry and swine industries (Butt et al., 2018; Butt et al., 2021; Butt et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2022; Olarte-Castillo Ximena et al., 2024).
Another major positive-sense RNA virus affecting swine is the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Nanopore sequencing has been used to characterize PRRSV genomes from clinical samples, including tissues and oral fluids, using a combination of targeted amplicon sequencing of ORF5 and long amplicon tiling sequencing (LATS) approach, successfully identifying multiple PRRSV lineages from infected swine populations (Caserta et al., 2023). In addition, Misu et al. optimized PRRVS whole-genome sequencing to obtain critical information from the 5’ and 3’ ends of the viral genomes, regions that typically remain poorly represented in NGS sequencing datasets (Misu et al., 2023). This method involved micrococcal nuclease treatment to degrade extra-viral nucleic acids and sequencing using an amplicon-based strategy, facilitating the full-length genome reconstruction for ssRNA, dsRNA, and DNA viruses.
Beyond livestock pathogens, nanopore sequencing has also been used to sequence other positive-sense RNA viruses, such as the Usutu virus, a mosquito-borne zoonotic virus that causes encephalitis in birds and humans. MinION sequencing has enabled rapid identification and characterization of USUV genomic diversity, aiding in avian disease surveillance and zoonotic risk assessment (Holicki et al., 2022).
5.1.2 DNA viruses
Nanopore sequencing has facilitated WGS, transcriptome profiling, and metagenomic analysis of DNA viruses, providing valuable insights into viral evolution, pathogenesis, and host-virus interactions. One key example is the pseudorabies virus (PRV), a 142 kb double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) virus from the Herpesvirus family. PRV is a major animal herpesvirus that causes Aujeszky’s disease, primarily affecting pigs but also capable of infecting other mammals. Nanopore transcriptome sequencing was carried out on poly(A)+ and cap containing full-length transcripts using the direct RNA sequencing strategy (Moldován et al., 2017).
Similarly, ONT sequencing has been employed to study bovine alphaherpesvirus 1.1 (BoHV-1.1), the causative agent of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Moldovan et al. used nanopore sequencing to characterize the BoHV-1.1 transcriptome at multiple time points post-infection, enabling a dynamic analysis of viral gene expression throughout the course of infection (Moldován et al., 2020). ONT has also been utilized for poxvirus genome sequencing. Wolff et al. characterized full-length genomes of sheep pox virus directly from infected animal tissues using the MinION platform (Wolff et al., 2020).
Beyond specific viral pathogens, ONT has also contributed to virome studies in arthropod vectors. Pallandre et al. characterized and compared viromes of male and female ticks by sequencing the random-primed cDNA using ONT chemistry (Perveen et al., 2023). This study demonstrated ONT’s utility for high-throughput viral metagenomics, helping to identify novel tick-associated viruses that could have veterinary or zoonotic relevance. Herpesviruses have also been recently characterized in guinea pigs, with nanopore sequencing revealing genomic variations and strain diversity among guinea pig herpesvirus isolates (Doukoure et al., 2024). This highlights ONT’s potential for veterinary virology research beyond livestock and companion animals, extending into wildlife and experimental animal models.
5.2 Bacterial diseases
Bacterial infections in poultry and livestock represent a major threat to animal and human health, with significant implications for the economic and food safety concerns (Salyer et al., 2017). In the poultry industry, bacterial diseases account for approximately half of the non–outbreak-related mortality among broiler breeders and commercial layers (Stokholm et al., 2010; Naundrup Thøfner et al., 2019). When bacterial outbreaks occur, mortality rates can increase dramatically, sometimes almost eradicating entire flocks (Thøfner and Christensen, 2021). To meet the needs of the food industry, various molecular-based methods have been developed, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and enzyme-linked fluorescence assays (ELFA). However, the most used methods are those based on nucleic acid amplification, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), real-time PCR (qPCR), and more recently, digital PCR (dPCR) (Saiki et al., 1985; Kralik and Ricchi, 2017; Lei et al., 2021; Saravanan et al., 2021). In addition to these methods, other technologies have been reported that offer advantages over PCR, such as nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) (Compton, 1991), recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) (Piepenburg et al., 2006), and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) (Notomi et al., 2000). However, all these technologies share a common limitation: they are designed to detect a single specific microbe, which presents a clear challenge, as food products and animal infections may include various potential pathogens. As a result, scientists have turned to NGS using platforms for massive parallel sequencing.
This section will discuss the application of nanopore sequencing in veterinary bacterial disease diagnostics, focusing on pathogen detection, antimicrobial resistance profiling, and foodborne pathogen surveillance.
5.2.1 Generation of complete bacterial genomes
Creating fully annotated and complete genomes is crucial for understanding microorganisms’ true diversity and biology. An ideal bacterial genome assembly is one in which the assembled sequence perfectly matches the organism’s genome, with each replicon sequence being complete and free of errors (Wick et al., 2023). Generally, there are two broad goals to consider in genome assembly: accuracy and completeness. Accuracy pertains to the number of errors in the assembled sequences (contigs), which can range from small mistakes (e.g., incorrect base pairs) to larger issues (e.g., additions, deletions, or inversions of hundreds of bases). Completeness, on the other hand, refers to the length of the contigs compared to the corresponding full genomic sequence, indicating how fragmented the assembly is. Longer contigs are preferable, ideally with each contig representing a whole replicon in the genome (Foster-Nyarko et al., 2023).
There are two main methods for generating complete bacterial genomes: hybrid assembly using a combination of long-reads and short-reads, and assembly using only long-reads generated by PacBio or ONT, followed by polishing of the genome with short reads to improve sequence quality (De Maio et al., 2019; Wick and Holt, 2021). Hybrid approaches combine long reads, which provide information regarding the structure of the genome, and short reads, which facilitate detailed assembly at local scales and help to correct errors in long reads (Heron, 2019; Noakes et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2024). Various studies have demonstrated the ability to generate complete genomes by hybrid assembly workflows (Eman Gadu et al., 2025; Shelkamy et al., 2025).
The hybrid assembly tool Unicycler has demonstrated superior performance compared to other hybrid assemblers in generating fully closed genomes (Liu et al., 2024). Short-read sequencing is typically used to obtain incomplete draft genomes. While short-read sequencing technologies, like Illumina and MGI NGS, offer high base-calling accuracy, they can only provide data about fragmented draft genomes. As research progresses, scientists generally prefer to obtain accurate, complete genomes instead (Cohen et al., 2019; Kathirvel et al., 2021).
The ability of ONT to generate near-complete bacterial genomes has been demonstrated in multiple studies. Sereika et al. (Sereika et al., 2022) successfully produced near-finished microbial genomes using ONT R9.4.1 and R10.4 data by sequencing the ZymoBIOMICS HMW (high molecular weight) DNA Standard D6322 (Zymo mock), which includes seven bacterial species and one fungus. This nanopore method offers significant advantages for producing complete genome assemblies from microorganisms.
5.2.2 Detection of antimicrobial resistance genes
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in bacteria is a significant challenge in production animals and highlights concerns about the possible transmission of resistance genes or resistant organisms from animals to humans through the food chain (Cox et al., 2021). AMR can lead to antibiotic failure in high-risk individuals and those with invasive infections (Kollef, 2008). The real-time nature of nanopore sequencing allows for dynamic AMR profiling enabling early detection of resistance genes as sequencing data are generated, which can guide timely intervention strategies, disease management, infection control, and policy development (Cao et al., 2016; Břinda et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2020).
Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of combining ONT long reads with short-read sequencing to obtain complete, high-resolution AMR profiles. In a Canadian study (Cox et al., 2021), researchers employed the hybrid assembler Unicycler (Wick et al., 2017), which integrates Illumina short reads and ONT long reads, to analyze 25 Salmonella isolates from humans and four from chickens. The long-read data enabled the closure of numerous plasmids, revealing the presence of gentamicin resistance genes and highlighting the potential for transmission of resistant Salmonella strains between poultry and humans (Cox et al., 2021). Similarly, Maguire et al. (Maguire et al., 2022a) utilized GridION long-read sequencing combined with MiSeq short reads for hybrid assembly to close eight Salmonella enterica genomes isolated from broiler farms and processing plants in Trinidad and Tobago. This hybrid approach identified multi-drug resistance genes, including those conferring resistance to quinolone and extended-spectrum β-lactams, emphasizing ONT’s utility in AMR surveillance in the poultry industry.
Chen et al. (Chen et al., 2020) sequenced 25 phenotypically multidrug-resistant Salmonella isolates, including S. Indiana, S. Typhimurium, and S. Enteritidis, using either ONT MinION long reads, Illumina MiSeq short reads, or a combination of both, and assembled them using Unicycler (Wick et al., 2017). They observed that relying solely on MinION long reads resulted in false-negative identification of tetracycline resistance genes in 11 out of 19 assemblies compared to MiSeq and hybrid approaches (Chen et al., 2020). However MinION outperformed MiSeq in plasmid identification (Chen et al., 2020). The study found that MinION was superior in identifying quinolone resistance, parC mutations, which strongly indicate quinolone resistance, but performed poorly in detecting plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes. This study also highlights the discrepancy between MiSeq short reads and MinION long reads in identifying aminoglycoside, ampicillin, amikacin, kanamycin, gentamicin, sulfonamide, and trimethoprim resistance genes (Chen et al., 2020). Despite these discrepancies, the ability of ONT to generate complete bacterial genomes has enabled deeper investigations into AMR mechanisms, including correlations between AMR genes, CRISPR-Cas elements, and mobile genetic elements.
Plasmids play a critical role in the horizontal gene transfer of AMR genes, facilitating the spread of resistance across bacterial species. Several studies have leveraged ONT sequencing to characterize AMR-associated plasmids in veterinary pathogens. In one study, a large (>200 kb) plasmid was identified as harboring the colistin resistance mcr-1 gene in avian pathogenic E. coli from diseased broiler chickens in Germany (Hornsey et al., 2019). They utilized both MinION long reads and Illumina short reads through the plasmidSPAdes assembler in hybrid mode. Although they were unable to achieve a closed assembly of the plasmid, which they attributed to the presence of repeat sequences and possibly other related plasmids, they successfully identified the mcr-1 gene (Hornsey et al., 2019). However, Chalmers et al. (Chalmers et al., 2021), obtained a closed assembly of 14 plasmids ranging from 87, 018 bp to 163, 767 bp using MinION long read sequencing only (SQK-LSK109 and native barcoding kits) through Flye assembler (Kolmogorov et al., 2019). These plasmids had extended cephalosporin resistance genes (Chalmers et al., 2021) extracted from E. coli isolates as well. Chalmers et al. (Chalmers et al., 2021), reported the presence of multiple MLST and pMLST types; however, accurately identifying these types was often challenging due to the error-prone nature associated with MinION sequencing. The authors also mentioned that single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis of the sequenced plasmids was not feasible because of the same reason. Conversely, Lamb et al. (2020), fine-tuned genotype-calling parameters, successfully identifying over 85% of SNPs with accuracy. This provides preliminary evidence supporting the application of ONT for real-time SNPs identification in bacterial genomes.
Beyond detecting AMR genes, ONT sequencing enables the characterization of the genetic environment surrounding resistance determinants, providing insights into how resistance genes spread within microbial populations. Yang et al. (Yang et al., 2022) used MinION long-read sequencing to identify the genetic environment of florfenicol and oxazolidinone resistance genes in chicken and pig fecal samples, focusing on the role of mobile genetic elements, particularly transposons, in their horizontal transfer.
ONT sequencing has emerged as a valuable tool for AMR surveillance, offering real-time insights into resistance gene transmission, plasmid dynamics, and bacterial adaptation. While hybrid sequencing approaches combining ONT and short-read data remain the most accurate method for AMR detection, ONT alone provides advantages for plasmid reconstruction, rapid SNP genotyping, and mobile genetic element characterization. Future improvements in base-calling accuracy, SNP resolution, and automated AMR annotation pipelines will further enhance ONT’s utility for antimicrobial resistance monitoring in veterinary and public health settings.
5.2.3 Investigation of bacterial foodborne diseases
Food contamination with microbial pathogens, causing foodborne illness, is a substantial public health issue, resulting in millions of cases and thousands of deaths annually in the US alone (Stevens et al., 2022). In 2015, the World Health Organization released a report estimating the global impact of foodborne diseases, which significantly contribute to morbidity and mortality. The report identified 31 hazards, primarily various types of microorganisms, and estimated that these were responsible for 600 million illnesses (Organization, W.H, 2021). Salmonella, Campylobacter spp., pathogenic Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Yersinia enterocolitica, and Staphylococcus aureus are among the most common foodborne pathogens, affecting millions of people annually (Kadariya et al., 2014; Ehuwa et al., 2021). To address this global challenge, rapid detection of foodborne pathogens is crucial for ensuring food safety. NGS can overcome challenges faced by traditional bacterial culture methods in today’s large-scale production systems (Azinheiro et al., 2022).
ONT sequencing has demonstrated strong potential for foodborne pathogen surveillance. Azinheiro et al. (Azinheiro et al., 2022) developed an easy-to-implement method that enables the simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens using long-read NGS with MinION. They employed a semi-targeted approach by combining a non-targeted detection method, NGS, with selective media to help reduce interference from non-pathogenic bacteria. An enrichment step was also used to recover various pathogens, including Salmonella Enteritidis and Typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli O157:H7. They utilized Flongle to lower costs. The results obtained through nanopore sequencing showed strong consistency with those from qPCR and culture.
Among bacterial foodborne pathogens, Salmonella remains one of the most common causes of foodborne illness in humans, with most infections linked to contaminated poultry products. Reducing Salmonella carriage in chickens is a critical strategy for minimizing the risk of transmission to humans (Shaji et al., 2023). Using ONT to help reduce the carrier state of pathogens in poultry is a very promising application. By enabling comprehensive detection of multiple pathogens, ONT has the potential to improve food safety monitoring and intervention strategies, reduce the risk of large-scale outbreaks, and support public health efforts to prevent foodborne disease transmission.
5.3 Metagenomic nanopore sequencing in veterinary medicine
ONT has emerged as a powerful tool for sequencing microorganisms, and it has been extensively applied in animal metagenomic NGS (mNGS) studies with a wide range of goals. Metagenomic can be defined as the analysis of microbial communities from specific environments in a culture-independent and agnostic approach to capture the existing diversity (Handelsman, 2004). Metagenomic studies may be categorized into functional analyses, which focus on identifying bioactive compounds and functional genes, or investigative objectives, such as characterizing microbial ecosystems, detecting emerging pathogens, and studying host-microbe interactions (Handelsman, 2004; Bibby, 2013; Kaszab et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021).
In veterinary medicine, ONT metagenomics has been particularly useful for microbial diversity and taxonomic studies (Cuscó et al., 2019; Kulikov et al., 2020; Cuscó et al., 2021; Cuscó et al., 2022; Huggins et al., 2024a; Opitz-Ríos et al., 2024), pathogen screening and surveillance (Vibin et al., 2020; Kipp et al., 2023; Ergunay et al., 2024; Huggins et al., 2024b), monitoring of zoonotic agents (Jahan et al., 2021; Issae et al., 2023; Lee et al., 2024; Opitz-Ríos et al., 2024), dietary analysis (Freed et al., 2023; Kruasuwan et al., 2023; Pawar et al., 2023), and diagnostics of challenging cases including multifactorial diseases, and mixed infections where co-infections with vaccine and field strains complicate disease diagnosis (Theuns et al., 2018; Butt et al., 2022; Huggins et al., 2022; Ergunay et al., 2023; Lamb et al., 2023; Huggins et al., 2024b). ONT’s ability to provide rapid pathogen detection has also been demonstrated in veterinary diagnostic settings (Esnault et al., 2022), successfully utilizing nanopore sequencing with different sample types, including urine, skin, and environmental samples surrounding veterinary hospitals (Kamathewatta et al., 2019; Ring et al., 2023).
Metagenomic sequencing using ONT sequencing platforms has significantly contributed to livestock health management. For instance, rapid sequencing diagnostics enable pre-movement screening of animals, preventing the introduction of pathogens into disease-free herds, and the quick identification of emerging pathogens mitigates the risk of potential large-scale outbreaks (Lamb et al., 2020). Also, metagenomics analysis based on nanopore sequencing technology has demonstrated outstanding performance in detecting foodborne pathogens (Buytaers et al., 2021). Salmonella and Listeria are among the many microbial communities that have been identified in a variety of food products thanks to this technology (Afonso and Afonso, 2023). Research has also shown that it may be used to evaluate the microbiomes of food processing settings, providing information about the sources of contamination and supporting the creation of intervention plans. This method has enhanced disease surveillance in chicken farms by identifying microbiological pollutants like Campylobacter and Escherichia coli. Furthermore, its capacity to examine genes linked to antibiotic resistance facilitates more focused intervention tactics, improving food safety (Leonard et al., 2018).
One of the most significant advantages of ONT sequencing is its adaptability across different laboratory and field settings. Different studies presented the feasibility of nanopore sequencing for on-site pathogen diagnostics, made possible by the MinION portable sequencer and ease of library preparation protocols (Edwards et al., 2016; Krehenwinkel et al., 2019; Marin et al., 2022; Bloemen et al., 2023; Fomsgaard et al., 2023). Marin et al. (Marin et al., 2022), proposed a sequencing workflow that uses MinION and mobile DNA barcoding with Bento Lab (Chang et al., 2020), which successfully identified Campylobacter jejuni from cecal content within 5 hours, from sample collection to sequence analysis, using Nanopore 16S Barcoding Kit (SQK-RAB204). In a recent study, a portable MinION-based sequencing kit was developed to rapidly sequence avian influenza virus hemagglutinin segments from both wild bird and poultry feces using an offline bioinformatics pipeline (de Vries et al., 2022). This portable field-deployable sequencing approach demonstrates the potential for ONT MinION sequencing to be used for rapid pathotyping directly in the field, reducing the time required for disease detection and response.
Metagenomic sequencing offers a significant advantage in veterinary pathogen discovery compared to targeted NGS because it does not require a priori hypothesis. Therefore it can detect novel species and highly variable viruses without needing a specific primer design (Gauthier et al., 2023). Several studies have leveraged nanopore sequencing for novel pathogen discovery, with researchers successfully identifying a new Rickettsia species in European ticks, Lloviu virus in bats, and porcine kobuvirus in diarrheic feces in Belgium (Theuns et al., 2018; Goletic et al., 2023b; Nelson et al., 2024). Another study demonstrated how nanopore sequencing enabled the resolution of complex viral genomes, such as avipoxviruses, which contain highly repetitive regions and genetic insertions and deletions acquired after long-term recombination events. These findings highlight ONT’s ability to overcome challenges associated with short-read sequencing, which often fails to resolve highly repetitive or structurally complex genomes (Croville et al., 2018).
Integrating ONT sequencing into veterinary metagenomics has transformed pathogen surveillance, disease diagnostics, and microbiome research. Its portability, real-time sequencing capabilities, and ability to detect novel and diverse microbial species make it an essential tool in modern veterinary medicine.
5.3.1 Enrichment approaches coupled with ONT metagenomics
One of the key limitations of metagenomic sequencing is its dependence on the initial pathogen load in clinical or environmental samples, which can significantly compromise sensitivity and sequencing depth. To mitigate this issue, several wet lab and bioinformatics enrichment strategies have been developed to improve sensitivity, including untargeted amplification techniques (Young et al., 2021; Claro et al., 2022; Han and Xia, 2023) and depletion of non-target sequences, predominantly host-derived DNA or RNA (Esnault et al., 2021; Goraichuk et al., 2024b; Herman et al., 2024).
One of the most widely used enrichment techniques in metagenomic sequencing is Sequence-Independent Single Primer Amplification (SISPA), an approach that dates back to the 1990s (Reyes and Kim, 1991; Peserico et al., 2019; Schuele et al., 2020; Sarchese et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2022; Palombieri et al., 2022; Schulz et al., 2022; Toh et al., 2022; Vanmechelen et al., 2022; Alkie et al., 2023; Chauhan et al., 2023; Di Profio et al., 2023; Horemans et al., 2023; Acevedo et al., 2024; Caserta et al., 2024; Gondard et al., 2024). SISPA has been extensively applied for the recovery of RNA and DNA viruses from clinical samples, as well as for bacterial pathogens. For example, the Bluetongue virus was recently identified in infected cattle and sheep in Cuba using the SISPA method combined with nanopore sequencing, demonstrating its utility for rapid viral pathogen detection in veterinary settings (Acevedo et al., 2024).
SISPA-based sequencing has also been adapted for multiplexed, random amplification to facilitate untargeted sequencing of co-infections in veterinary samples. Butt et al. (Butt et al., 2022) developed a multiplexed, random amplification-based for untargeted nanopore sequencing and compared it to Illumina MiSeq for detecting viral and bacterial co-infections in poultry. Although the ONT MinION sequencer produced fewer total reads than the Illumina MiSeq platform, it offered significant cost and turnaround time advantages, making it an attractive option for pathogen identification in clinical and field settings. Similarly, Young et al. (Young et al., 2021) used a random primer-based strand-switching strategy to sequence influenza A and other RNA and DNA viruses on the MinION platform achieving 20X coverage per virus. This pipeline demonstrated the ability to distinguish mixed infections and detect novel viruses, even when reference genomes were unavailable. Another successful untargeted amplification method, the SMART-9N approach, was combined with ONT sequencing to identify the first case of the Monkeypox virus in Brazil in 2022, emphasizing its diagnostic potential in emerging infectious disease surveillance (Claro et al., 2022).
Instead of relying on multiplex PCR assays that target only a specific pathogen or a limited set of microorganisms, computational approaches have been developed to design primers targeting conserved regions across multiple microbial species (Collatz et al., 2022). This strategy, often coupled with degenerate primers, enables broad-spectrum pathogen detection directly from complex clinical or environmental samples (Ghezzi et al., 2024). By integrating massive amplification techniques with nanopore sequencing, the sensitivity of pathogens detection can be increased even in samples with low microbial loads.
In addition to wet lab enrichment strategies, computational strategies have also been developed to filter out non-target sequences and improve sequencing efficiency. For instance, Yang et al. (Yang et al., 2022) utilized BLASR (https://anaconda.org/bioconda/blasr) software to eliminate host DNA from chicken and pig fecal samples, reducing background contamination and enhancing microbial detection. Another promising approach, described earlier, is Nanopore adaptive sampling (NAS), a real-time, targeted sequencing method that can enrich specific DNA sequences while depleting unwanted reads (Martin et al., 2022; Ong et al., 2022; Kipp et al., 2023). NAS is particularly useful in metagenomics because it allows for preferential sequencing of rare species or less abundant microbial species, making it a powerful tool for studying complex microbial communities and rare pathogens.
A recent study developed a metagenomic sequencing (mNGS) workflow (Cheng et al., 2022) utilizing ONT adaptive sequencing to deplete the human host genome while enabling simultaneously real-time identification of AMR genes directly from clinical respiratory samples within six hours (Cheng et al., 2022). While NAS offers significant advantages in metagenomic studies, it is important to consider the challenges and limitations associated with this technology. For instance, the efficiency of NAS can be affected by the length of DNA molecules and the abundance of target species, which may require careful optimization of experimental conditions. Additionally, while NAS enhances the detection of target sequences, it may reduce the overall sequencing output due to the rejection of non-target molecules. Despite these challenges, NAS remains a promising tool for advancing metagenomic research in animal populations, offering new insights into biodiversity, pathogen dynamics, and antimicrobial resistance. However, recent software updates have enhanced NAS precision, allowing for a more accurate selection of target sequences and increasing its utility in veterinary pathogen surveillance and microbiome research (Ulrich et al., 2022). Overall, enrichment strategies coupled with ONT sequencing have significantly expanded the scope of veterinary metagenomics, enabling high-resolution pathogen detection, real-time diagnostics, and enhanced characterization of complex microbial ecosystems.
6 Challenges and limitations
Nanopore sequencing, like other NGS technologies, has its strengths and limitations. While it is highly effective for detecting structural variants and real-time analysis, its accuracy can be lower than that of traditional short-read methods (Norris et al., 2016). This section, therefore, highlights the specific challenges of ONT and some general limitations of NGS.
6.1 Common challenges among NGS platforms
First, regarding mNGS, even though it offers a broad range of applications, it poses many challenges and limitations to veterinary diagnostics. In clinical samples, the presence of host nucleic acids can further complicate the sequencing process, leading to low genome coverage and potential misinterpretation of the viral sequences (Quick et al., 2017). For instance, studies have shown that when viral titters are low, the depth of sequencing may not be adequate to characterize the viral genome effectively (Kilianski et al., 2016). Biased DNA extraction and sequencing can hinder the comprehensive characterization of microbial communities, potentially leading to the omission of low-abundance microorganisms that may be clinically significant. Additionally, the absence of a universally accepted “gold standard” analysis tool introduces variability in data interpretation and reproducibility. Imperfections in reference databases, including missing sequencing data, further limit the accuracy of pathogen identification. Moreover, the clinical importance of findings often requires additional confirmation, as the presence of genetic material does not always correlate with active infection. These limitations underscore the need for continuous optimization of workflows and analytical methods, not only for ONT but all NGS platforms in their use in the metagenomic approach (Zhang et al., 2021; Gauthier et al., 2023). In this context, Afonso et al. elucidated key aspects of sampling collection when the main objective is non-targeted sequencing in active surveillance scenarios (Afonso and Afonso, 2023).
Chimeric and artifact reads also pose significant challenges in data interpretation. These issues can be mitigated by employing bioinformatics tools that distinguish true biological signals from artifacts and applying stringent filtering criteria during data analysis (Razook et al., 2020). Several bioinformatic tools have been developed to address chimeric reads, but their success has been moderate, emphasizing the need for further improvements in base-calling and filtering algorithms.
The concentration of RNA/DNA in sequencing libraries also plays a critical role in sequencing success. High concentrations can overload the flow cell, whereas low concentrations may lead to inadequate sequencing depth, limiting the detection of low-abundance pathogens. Normalization strategies, such as accurate sample quantification and dilution to optimal input levels, are essential to achieve balanced sequencing performance (Maguire et al., 2023). From ONT platforms, while PCR-free protocols such as the Native Barcoding protocol eliminate amplification biases, they may result in lower overall sequencing yields, requiring high-quality input material for successful sequencing (Gilpatrick et al., 2019).
Another limitation is the potential for cross-contamination during wet lab preparation when multiple samples are batched together. This issue can lead to erroneous results, particularly in samples with varying viral loads, where high-titer samples may contaminate the sequencing reads of low-titer samples (Lewandowski et al., 2019). Moreover, the need for stringent demultiplexing criteria to mitigate this risk often results in a significant reduction in the total data available for analysis, typically by about 50% (Lewandowski et al., 2019). Barcode crosstalk is an additional challenge in NGS when multiplexing samples. Some studies have attempted to develop classifiers to correct barcode crosstalk, improving sequencing accuracy (Xu et al., 2018; Gauthier et al., 2021). However, this remains an active area of research, as crosstalk correction is often dependent on sample composition and sequencing depth. The lower accuracy of ONT compared to Illumina and PacBio sequencing further exacerbates barcode misclassification issues, requiring robust bioinformatics tools to address the problem (Schuele et al., 2020; Maguire et al., 2022b).
6.2 Nanopore sequencing-specific challenges
Nanopore sequencing, as a long-read technology, depends on the integrity of nucleic acid and fragmentation significantly influences the sequencing outputs. Excessive fragmentation can reduce read lengths and coverage, ultimately impacting overall data quality. Strategies to minimize fragmentation include optimizing extraction protocols to preserve high molecular-weight DNA (Maguire et al., 2021; Zeng et al., 2024) and employing gentle lysis methods to enhance DNA recovery while minimizing shearing (Maguire et al., 2021). Additionally, the dominance of short reads complicates genomic assembly and analysis of nanopore data. Optimizing library preparation protocols to favor longer fragments and employing computational tools to filter short reads can help address this issue (Lin et al., 2023). Variability in read lengths further necessitates the development of statistical methods, such as length normalization and mixed models, to integrate this variability into quantitative analyses (Lin et al., 2023).
There are also limitations and challenges regarding ONT flow cells. First, even though flow cells are claimed to be washable and re-usable by the manufacturer, this advantage should be utilized carefully, because proper washing cannot completely remove previous libraries, and carryover is a common issue. One suggestion to minimize this limitation is to use different barcodes across different libraries loaded, or even different chemistries (e.g., Rapid Barcodes or Native Barcodes), minimizing the wrong assignment of reads to used barcodes Additionally, flow cells are a big source of variation across sequencing experiments, because they do not perform the same (even flow cells from the same batch) in terms of pore durability and data generation. This is a challenge in terms of protocols optimization and validation, since inter-experiment reproducibility can be hindered by flow cell performance. Finally, while the Flongle is designed for lower sample numbers and offers a more affordable option for sequencing, it is limited in the volume of data it can generate and sequencing error rate, as studies have indicated that the Flongle may exhibit higher error rates, potentially due to differences in the squiggle space and base calling algorithms (John et al., 2024). The reported raw read accuracy for Flongle flow cells has been around 85%, while improved, still falls short of the accuracy levels achieved by competing technologies (Lee et al., 2022). This discrepancy can lead to challenges in achieving high single-base accuracy, which is crucial for reliable genomic analyses (Lee et al., 2024).
Although the rapid evolution of ONT in terms of hardware, software, library preparation chemistries, and flow cells has driven major improvements, it has also created challenges for diagnostic laboratories. The frequent updates complicate workflow optimization and validation, processes that are essential before diagnostic use. Continuous changes in flow cell chemistry and sequencing kits can hinder reproducibility and comparability of results over time, as data generated with different versions may not be directly comparable. Moreover, each update often requires new optimization, retraining of personnel, and re-validation of bioinformatics pipelines, increasing the time and cost burden for implementation in regulated diagnostic settings. From a regulatory standpoint, these frequent modifications pose difficulties for standardization and accreditation, since validated workflows can quickly become outdated. In addition, software updates and changes in basecalling models may introduce variability in data formats and performance metrics, affecting interoperability with existing databases and analytical tools.
7 Future perspectives
Despite these challenges and limitations, nanopore sequencing continues to evolve rapidly, with ongoing improvements in base-calling algorithms, error correction tools, and library preparation techniques. Overcoming these challenges will require a combination of wet lab optimizations, computational advancements, and standardization of analytical workflows, ultimately enhancing the reliability and applicability of nanopore sequencing in veterinary medicine. Additionally, to better educate the scientific community about the performance of this technology in different scenarios, standardized minimum reporting requirements for ONT data should be established. Reporting standardized sequencing and quality parameters would enable more meaningful comparisons among studies and facilitate method reproducibility. For example, having in mind the variable performance of the flow cells, statistics such as starting and ending number of pores, as well as pore degradation overtime can be a good piece of information to be disclosed. Furthermore, sequencing output metrics, including total number of reads generated (pass and fail, classified or unclassified), total number of bases, read length statistics, and read quality distributions are important assessments of performance of the experiment. Finally, for data processing and final analysis results, alignment rates, target coverage (depth and breadth, uniformity and dropout regions), read identity and accuracy should also be disclosed when appropriate.
One of the most notable improvements in ONT sequencing has been the introduction of the new Q20+ (V14) chemistry and its associated R10 flow cell, which have significantly improved read accuracy. The R10 flow cell features a dual reader head design, which enhances the resolution of homopolymeric regions and reduces the error rates associated with indels, a persistent challenge in previous versions (Johansson et al., 2021; Cuber et al., 2022). Studies have demonstrated that the R10 chemistry can achieve a median alignment identity exceeding 99.7%, a marked improvement from earlier iterations (Bogaerts et al., 2024). Additionally, advances in base-calling algorithms have also improved homopolymeric region identification accuracy. Continuous improvements in computational tools are necessary to address these issues effectively and further enhance ONT’s reliability in clinical and research applications (Cornelis et al., 2017). Additionally, recent advancements in real-time base-calling have significantly enhanced both the speed and accuracy of nanopore sequencing by the integration of deep learning algorithms, enabling more efficient data processing (Ahmed et al., 2021). These improvements are particularly valuable for applications requiring highly accurate data and rapid turnaround, such as clinical diagnostics, vaccine efficacy monitoring, variant detection, and outbreak surveillance (Greninger et al., 2015). As machine learning and AI-based bioinformatics pipelines evolve, their incorporation into real-time base-calling workflows will help further reduce sequencing errors and improve variant detection and genome assembly.
Another notable trend in recent years has been the automation of laboratory workflows, including NGS steps, which enhances reproducibility, reduces hands-on time, and increases throughput (Hess et al., 2020; Socea et al., 2023). Different companies currently provide solutions for automation, including liquid-handling automation platforms of various sizes and costs. Commonly used systems include the Hamilton NGS STAR/STARlet, Tecan DreamPrep NGS, Beckman Coulter Biomek i-7, Opentrons OT-2, Agilent Bravo, Eppendorf epMotion 5073t/5075t, and Revvity Sciclone G3 NGSx. These vendors have stablished partnership with ONT and available automated library preparation protocols (including Ligation Sequencing Kit, Native Barcoding ki, and Rapid Barcoding kit) are available (Technologies, O.N, d).Nanopore sequencing has helped democratize sequencing by making it more accessible, affordable, and versatile, bringing various advancements in genomics. This accessibility has empowered researchers and institutions in low- and middle-income countries, allowing them to participate in global initiatives and contribute to scientific discovery and innovation. The application of long-read sequencing has enabled groundbreaking projects such as telomere-to-telomere (T2T) genome assemblies in animal and plant species (Belser et al., 2021; Sholes et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2023; Schmidt et al., 2024). Additionally, ONT has been utilized for the Functional Annotation of Animal Genome (FAANG) project (Project, F.A.o.A.G.F), a global collaboration that generates comprehensive genomic datasets for animal species such as chicken, swine, bovine, and fish. As described previously in this review, one of ONT’s most transformative aspects has been its portability, first realized with the MinION sequencer, which has allowed on-site sequencing in extreme environments, including Arctic, rainforests, remote wildlife habitats, and even space (McIntyre et al., 2016; Castro-Wallace et al., 2017; Johnson et al., 2017; Parker et al., 2017; Pomerantz et al., 2018; Gowers et al., 2019; Carr et al., 2020).
While ONT’s impact on human medicine has been well-established, particularly in infectious disease research, genetic disorders, and oncology, its growing applications in animal medicine will likely expand in the coming years, further integrating real-time sequencing into veterinary and environmental health research. Some ONT applications from human medicine have already been adopted in veterinary medicine and will continue to be integrated. For example, outbreak tracing (Bosmeny et al., 2023; Campos et al., 2023; Buenestado-Serrano et al., 2024; Croville et al., 2024; Lohde et al., 2024) and vaccine monitoring (Campos et al., 2023; Girgis et al., 2023) are key areas of interest in this context. One example of this application in veterinary medicine was tracing an avian influenza outbreak between 2020–2022 in flocks in France and utilizing an amplicon-based sequencing (Croville et al., 2024). Using this methodology, sequencing directly from clinical field samples was achieved rather than examining samples following a viral isolation step on cell culture or embryonated eggs. This experience emphasized the importance of NGS, as PCR could not handle the detection of minority variants in HPAI strains that could be relevant to viral surveillance.
In the last decade, the refinement in bioinformatics and chemistry has allowed the ONT platform to successfully sequence native DNA, RNA, and, more recently, peptides, positioning it as the pioneer in direct polypeptide sequencin. The multiomics concept–including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and epigenomics - centered in one platform is possible with ONT. Unlike conventional sequencing approaches, native DNA sequencing with ONT eliminates amplification bias, preserving the original molecular modifications and allowing for direct detection of DNA methylation. The epigenetic insights have been linked to disease prediction in humans and livestock performance traits (Hayes et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). The recent demonstration of peptide sequencing using ONT further expands its multiomic capabilities, offering new possibilities for studying host-pathogen interactions, immune responses, and molecular mechanisms of disease (Motone et al., 2024).
While independently studying DNA, RNA transcripts, and proteomics provides valuable insights, an integrated analysis yields a more nuanced understanding of microbiome-host interactions. By integrating these approaches, ONT facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of molecular biology and how microbial population, host DNA coding information, transcripts, and translated proteins collectively impact phenotypes and disease/non-disease state.
8 Conclusion
In the genomic era, ONT established itself as a cornerstone technology offering unique sequencing platforms that transcend traditional barriers in sequencing applications for diagnostics, surveillance, and genomic research. Its long-read, real-time sequencing capabilities have significantly advanced veterinary medicine, enabling rapid pathogen detection, antimicrobial resistance profiling, outbreak tracing, and comprehensive metagenomic studies. Moreover, ONT is pivotal in One Health initiatives, integrating human, animal, and environmental health to enhance global disease monitoring and prevention. As the technology evolves and improves accuracy, cost-efficiency, and accessibility, its applications in veterinary diagnostics and research will further expand, driving precision medicine, epidemiological surveillance, and genomic innovation. Its impact on veterinary medicine remains boundless with ongoing advancements, offering transformative solutions to enhance animal health, food safety, and global public health.
Author contributions
MC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AH: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IG: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SN: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ME: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Mention of trade names or commercial products does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA). Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. All opinions expressed in this paper are the authors’ and do not necessarily reflect the policies and views of USDA, ARS. The USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Acevedo, A.M., Postic, L., Curiel, M., Gondard, M., Bréard, E., Zientara, S., et al. (2024). Detection, characterization and sequencing of BTV serotypes circulating in Cuba in 2022. Viruses 16, 164. doi: 10.3390/v16010164
Afgan, E., Baker, D., Batut, B., Van Den Beek, M., Bouvier, D., Čech, M., et al. (2018). The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, W537–W544. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky379
Afonso, C. L. and Afonso, A. M. (2023). Next-generation sequencing for the detection of microbial agents in avian clinical samples. Veterinary Sci. 10, 690. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10120690
Afrough, B., Zafar, A., Hasan, R., and Hewson, R. (2018). Complete genome sequence of buffalopox virus. Genome Announcements 6. doi: 10.1128/genomea.00444-18
Agustinho, D. P., Fu, Y., Menon, V. K., Metcalf, G. A., Treangen, T. J., Sedlazeck, F. J., et al. (2024). Unveiling microbial diversity: harnessing long-read sequencing technology. Nat. Methods 21, 954–966. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02262-1
Ahmed, O., Rossi, M., Kovaka, S., Schatz, M. C., Gagie, T., Boucher, C., et al. (2021). Pan-genomic matching statistics for targeted nanopore sequencing. Iscience 24, 102696. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102696
Ahsan, M. U., Liu, Q., Fang, L., and Wang, K. (2021). NanoCaller for accurate detection of SNPs and indels in difficult-to-map regions from long-read sequencing by haplotype-aware deep neural networks. Genome Biol. 22, 1–33. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02472-2
Alkie, T. N., Cox, S., Embury-Hyatt, C., Stevens, B., Pople, N., Pybus, M. J., et al. (2023). Characterization of neurotropic HPAI H5N1 viruses with novel genome constellations and mammalian adaptive mutations in free-living mesocarnivores in Canada. Emerging Microbes infections 12, 2186608. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2186608
Andersen, P., Barksdale, S., Barclay, R. A., Smith, N., Fernandes, J., Besse, K., et al. (2023). Magnetic hydrogel particles improve nanopore sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory viruses. Sci. Rep. 13, 2163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29206-7
Arefiev, V., Kovalenko, G., Frant, M., Chumachenko, T., Polyvianna, Y., Pivnenko, S., et al. (2020). Complete Genome Sequence of Salmonella enterica subsp. Microbiol. Resour Announc 9. doi: 10.1128/mra.01171-20
Ari, Ş. and Arikan, M. (2016). Next-Generation Sequencing: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Future, in Plant Omics: Trends and Applications. Eds. Hakeem, K. R., Tombuloğlu, H., and Tombuloğlu, G. (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 109–135.
Asif, K., O’Rourke, D., Legione, A. R., Shil, P., Marenda, M. S., Noormohammadi, A. H., et al. (2021). Whole-genome based strain identification of fowlpox virus directly from cutaneous tissue and propagated virus. PloS One 16, e0261122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261122
Athanasopoulou, K., Boti, M. A., Adamopoulos, P. G., Skourou, P. C., and Scorilas, A. (2021). Third-generation sequencing: the spearhead towards the radical transformation of modern genomics. Life 12, 30. doi: 10.3390/life12010030
(2024). Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/document/input-dna-rna-qc.
manual., A.T.s.u. (2015). Available online at: https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/usermanuals/public/G2964-90000_TapeStation_USR_ENU.pdf.
(2025).Nanolyse. Available online at: https://github.com/wdecoster/nanolyse (Accessed April 14, 2025).
Azinheiro, S., Roumani, F., Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L., Carvalho, J., Prado, M., and Garrido-Maestu, A. (2022). Combination of Recombinase Polymerase Amplification with SYBR Green I for naked-eye, same-day detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in ground meat. Food Control 132, 108494. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108494
Baek, A., Lee, G. E., Golconda, S., Rayhan, A., Manganaris, A. A., Chen, S., et al. (2024). Single-molecule epitranscriptomic analysis of full-length HIV-1 RNAs reveals functional roles of site-specific m(6)As. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 1340–1355. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01638-5
Bakre, A., Kariithi, H. M., and Suarez, D. L. (2023). Alternative probe hybridization buffers for target RNA depletion and viral sequence recovery in NGS for poultry samples. J. Virol. Methods 321, 114793. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2023.114793
Baquero-Perez, B., Yonchev, I. D., Delgado-Tejedor, A., Medina, R., Puig-Torrents, M., Sudbery, I., et al. (2024). N(6)-methyladenosine modification is not a general trait of viral RNA genomes. Nat. Commun. 15, 1964. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46278-9
Bautista, C., Jaswant, G., French, H., Campbell, K., Durrant, R., Gifford, R., et al. (2023). Whole genome sequencing for rapid characterization of rabies virus using nanopore technology. J. Vis. Exp. 198), e65414. doi: 10.3791/65414
Belser, C., Baurens, F. C., Noel, B., Martin, G., Cruaud, C., Istace, B., et al. (2021). Telomere-to-telomere gapless chromosomes of banana using nanopore sequencing. Commun. Biol. 4, 1047. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02559-3
Bhaduri, A., Qu, K., Lee, C. S., Ungewickell, A., and Khavari, P. A (2012). Rapid identification of non-human sequences in high-throughput sequencing datasets. Bioinformatics 28, 1174–1175. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts100
Bibby, K. (2013). Metagenomic identification of viral pathogens. Trends Biotechnol. 31, 275–279. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.01.016
Bickhart, D. M., Rosen, B. D., Koren, S., Sayre, B. L., Hastie, A. R., Chan, S., et al. (2017). Single-molecule sequencing and chromatin conformation capture enable de novo reference assembly of the domestic goat genome. Nat. Genet. 49, 643–650. doi: 10.1038/ng.3802
Biggel, M., Cernela, N., Horlbog, J. A., and Stephan, R. (2024). Oxford Nanopore’s 2024 sequencing technology for. J. Clin. Microbiol. 62, e0108324. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01083-24
Bird, E., Pickens, V., Molik, D., Silver, K., and Nayduch, D. (2025). BALROG-MON: a high-throughput pipeline for Bacterial AntimicrobiaL Resistance annOtation of Genomes-Metagenomic Oxford Nanopore. Micropublication Biol. 2025, 10–17912. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001427
Bloemen, B., Gand, M., Vanneste, K., Marchal, K., Roosens, N. H. C., and De Keersmaecker, S. C. J. (2023). Development of a portable on-site applicable metagenomic data generation workflow for enhanced pathogen and antimicrobial resistance surveillance. Sci. Rep. 13, 19656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46771-z
Bogaerts, B., Van den Bossche, A., Verhaegen, B., Delbrassinne, L., Mattheus, W., Nouws, S., et al. (2024). Closing the gap: Oxford Nanopore Technologies R10 sequencing allows comparable results to Illumina sequencing for SNP-based outbreak investigation of bacterial pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 62, e01576–e01523. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01576-23
Bogner, P. N. and Killeen, A. A. (2005). Extraction of Nucleic Acids, in Molecular Diagnostics: For the Clinical Laboratorian. Eds. Coleman, W. B. and Tsongalis, G. J. (Totowa, NJ: Humana Press), 25–30.
Bold, D., Souza-Neto, J. A., Gombo-Ochir, D., Gaudreault, N. N., Meekins, D. A., McDowell, C. D., et al. (2023). Rapid identification of ASFV, CSFV and FMDV from Mongolian outbreaks with minION short amplicon sequencing. Pathogens 12, 533. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12040533
Bolduc, B., Jang, H. B., Doulcier, G., You, Z. Q., Roux, S., and Sullivan, M. B. (2017). vConTACT: an iVirus tool to classify double-stranded DNA viruses that infect Archaea and Bacteria. PeerJ 5, e3243. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3243
Boostrom, I., Portal, E. A. R., Spiller, O. B., Walsh, T. R., and Sands, K. (2022). Comparing long-read assemblers to explore the potential of a sustainable low-cost, low-infrastructure approach to sequence antimicrobial resistant bacteria with oxford nanopore sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 13, 796465. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.796465
Bosmeny, M. S., White, A. A., Pater, A. A., Crew, J., Geltz, J., and Gagnon, K. T. (2023). Global mpox lineage discovery and rapid outbreak tracking with nanopore sequencing. Virol. J. 20, 90. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02059-2
Branton, D., Deamer, D. W., Marziali, A., Bayley, H., Benner, S. A., Butler, T., et al. (2008). The potential and challenges of nanopore sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 1146–1153. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1495
Breitwieser, F. P., Lu, J., and Salzberg, S. L. (2019). A review of methods and databases for metagenomic classification and assembly. Briefings Bioinf. 20, 1125–1136. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx120
Břinda, K., Callendrello, A., Cowley, L., Charalampous, T., Lee, R. S., MacFadden, D. R., et al. (2018). Lineage calling can identify antibiotic resistant clones within minutes. bioRxiv 403204, 455–464. doi: 10.1101/403204
Brown, E., Freimanis, G., Shaw, A. E., Horton, D. L., Gubbins, S., and King, D. (2021). Characterising foot-and-mouth disease virus in clinical samples using nanopore sequencing. Front. Vet. Sci. 8, 656256. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.656256
Buchfink, B., Xie, C., and Huson, D. H. (2015). Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 12, 59–60. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3176
Buenestado-Serrano, S., Herranz, M., Otero-Sobrino, A., Molero-Salinas, A., Rodríguez-Grande, C., Sanz-Pérez, A., et al. (2024). Accelerating SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance in a routine clinical setting with nanopore sequencing. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 314, 151599. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2024.151599
Butt, S. L., Taylor, T. L., Volkening, J. D., Dimitrov, K. M., and Williams-Coplin, D. (2018). Rapid virulence prediction and identification of Newcastle disease virus genotypes using third-generation sequencing. Virol. J. 15, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-1077-5
Butt, S. L., Erwood, E. C., Zhang, J., Sellers, H. S., Young, K., Lahmers, K. K., et al. (2021). Real-time, MinION-based, amplicon sequencing for lineage typing of infectious bronchitis virus from upper respiratory samples. J. Veterinary Diagn. Invest. 33, 179–190. doi: 10.1177/1040638720910107
Butt, S. L., Kariithi, H. M., Volkening, J. D., Taylor, T. L., Leyson, C., Pantin-Jackwood, M., et al. (2022). Comparable outcomes from long and short read random sequencing of total RNA for detection of pathogens in chicken respiratory samples. Front. Veterinary Sci. 9, 1073919. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1073919
Buytaers, F. E., Saltykova, A., Denayer, S., Verhaegen, B., Vanneste, K., Roosens, N. H. C., et al. (2021). Towards real-time and affordable strain-level metagenomics-based foodborne outbreak investigations using Oxford nanopore sequencing technologies. Front. Microbiol. 12, 738284. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.738284
Byrd, A. K. and Raney, K. D. (2019). “Helicases and DNA motor proteins,” in Nanopore Sequencing: An Introduction (World Scientific), 59–74.
Campos, G. S., Giovanetti, M., Moraes, L., Hora, H. S. D., Bandeira, A. C. A., Alcantara, K., et al. (2023). Genomic monitoring unveils a high prevalence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant in vaccine breakthrough cases in Bahia, Brazil. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1992) 69, 257–261. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20220955
Cao, M. D., Ganesamoorthy, D., Elliott, A. G., Zhang, H., Cooper, M. A., and Coin, L. J. M. (2016). Streaming algorithms for identification pathogens and antibiotic resistance potential from real-time MinION™ sequencing. Gigascience 5, s13742–016-0137-2. doi: 10.1186/s13742-016-0137-2
Capin, J. B. G., Sanque, A. J. C., Eng, M. N. J., Lagare, A., Sepulveda, M. C. B., and Murao, L. A. E. (2023). Emerging genomic trends on rabies virus in Davao Region, Philippines, 2018–2021. Viruses 15, 1658. doi: 10.3390/v15081658
Carr, C. E., Bryan, N. C., Saboda, K. N., Bhattaru, S. A., Ruvkun, G., and Zuber, M. T. (2020). Nanopore sequencing at Mars, Europa, and microgravity conditions. NPJ Microgravity 6, 24. doi: 10.1038/s41526-020-00113-9
Caserta, L. C., Zhang, J., Piñeyro, P., and Diel, D. G. (2023). Rapid genotyping of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) using MinION nanopore sequencing. PloS One 18, e0282767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282767
Caserta, L. C., Frye, E. A., Butt, S. L., Laverack, M., Nooruzzaman, M., Covaleda, L. M., et al. (2024). Spillover of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus to dairy cattle. Nature p, 1–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07849-4
Castro-Wallace, S. L., Chiu, C. Y., John, K. K., Stahl, S. E., Rubins, K. H., McIntyre, A. B. R., et al. (2017). Nanopore DNA sequencing and genome assembly on the international space station. Sci. Rep. 7, 18022. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18364-0
Chalmers, G., Cobean, J., Snyder, R. P., Barta, J. R., and Boerlin, P. (2021). Extended-spectrum cephalosporin resistance in Escherichia coli from broiler chickens raised with or without antibiotics in Ontario, Canada. Veterinary Microbiol. 258, 109116. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109116
Chang, J. J. M., Ip, Y. C. A., Ng, C. S. L., and Huang, D. (2020). Takeaways from mobile DNA barcoding with BentoLab and MinION. Genes 11, 1121. doi: 10.3390/genes11101121
Chauhan, R. P., Fogel, R., and Limson, J. (2023). Nanopore minION sequencing generates a white spot syndrome virus genome from a pooled cloacal swab sample of domestic chickens in South Africa. Microorganisms 11, 2802. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112802
Chaves, M., Hashish, A., Osemeke, O., Sato, Y., Suarez, D. L., and El-Gazzar, M. (2024). Evaluation of commercial RNA extraction protocols for avian influenza virus using nanopore metagenomic sequencing. Viruses 16, 1429. doi: 10.3390/v16091429
Chaves, M., Shelkamy, M., Gadu, E., Nadendla, S., Aminu, O. S., Sato, Y., et al. (2024). Portable Nanopore Sequencing Technology: Optimization of Extraction Protocols Towards On-site Applications (Nashville - TN: American Association of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosticians). A.H.
Chen, Z., Erickson, D. L., and Meng, J. (2021). Polishing the Oxford Nanopore long-read assemblies of bacterial pathogens with Illumina short reads to improve genomic analyses. Genomics 113, 1366–1377. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.03.018
Chen, Z., Kuang, D., Xu, X., Gonzalez-Escalona, N., Erickson, D. L., Brown, E., et al. (2020). Genomic analyses of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Indiana, Typhimurium, and Enteritidis isolates using MinION and MiSeq sequencing technologies. PloS One 15, e0235641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235641
Chen, L., Gao, X., Xue, W., Yuan, S., Liu, M., and Sun, Z. (2022). Rapid metagenomic identification of two major swine pathogens with real-time nanopore sequencing. J. Virological Methods 306, 114545. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2022.114545
Chen, J., Wang, Z., Tan, K., Huang, W., Shi, J., Li, T., et al. (2023). A complete telomere-to-telomere assembly of the maize genome. Nat. Genet. 55, 1221–1231. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01419-6
Cheng, H., Sun, Y., Yang, Q., Deng, M., Yu, Z., Zhu, G., et al. (2022). A rapid bacterial pathogen and antimicrobial resistance diagnosis workflow using Oxford nanopore adaptive sequencing method. Briefings Bioinf. 23, bbac453. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac453
Cingolani, P., Platts, A., Wang, L. L., Coon, M., Nguyen, T., Wang, L., et al. (2012). A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. fly 6, 80–92. doi: 10.4161/fly.19695
Clarke, J. (2019). Development of multipore sequencing instruments, in Nanopore Sequencing: An Introduction (World Scientific), 75–89.
Claro, I. M., Romano, C. M., da Silva Candido, D., de, Lima E. L., Lindoso, J. A. L., Ramundo, M. S., et al. (2022). Shotgun metagenomic sequencing of the first case of monkeypox virus in Brazil, 2022. Rev. do Instituto Med. Trop. São Paulo 64, e48. doi: 10.1590/s1678-9946202264048
Cohen, K. A., Manson, A. L., Desjardins, C. A., Abeel, T., and Earl, A. M. (2019). Deciphering drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using whole-genome sequencing: progress, promise, and challenges. Genome Med. 11, 45. doi: 10.1186/s13073-019-0660-8
Collatz, M., Braun, S. D., Monecke, S., and Ehricht, R. (2022). ConsensusPrime—A bioinformatic pipeline for ideal consensus primer design. BioMedInformatics 2, 637–642. doi: 10.3390/biomedinformatics2040041
Compton, J. (1991). Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Nature 350, 91–92. doi: 10.1038/350091a0
Cornelis, S., Gansemans, Y., Deleye, L., Deforce, D., and Van Nieuwerburgh, F. (2017). Forensic SNP genotyping using nanopore MinION sequencing. Sci. Rep. 7, 41759. doi: 10.1038/srep41759
Cox, G. W., Parmley, E. J., Avery, B. P., Irwin, R. J., Reid-Smith, R. J., Deckert, A. E, et al. (2021). A One-Health genomic investigation of gentamicin resistance in Salmonella from human and chicken sources in Canada, 2014 to 2017. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 65. doi: 10.1128/aac.00966-21
Crossley, B. M., Rejmanek, D., Baroch, J., Stanton, J. B., Young, K. T., Killian, M. L., et al. (2021). Nanopore sequencing as a rapid tool for identification and pathotyping of avian influenza A viruses. J. Veterinary Diagn. Invest. 33, 253–260. doi: 10.1177/1040638720984114
Croville, G., Loc’h, G. L., Zanchetta, C., Manno, M., Camus-Bouclainville, C., Klopp, C., et al. (2018). Rapid whole-genome based typing and surveillance of avipoxviruses using nanopore sequencing. J. virological Methods 261, 34–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.08.003
Croville, G., Walch, M., Sécula, A., Lèbre, L., Silva, S., Filaire, F., et al. (2024). An amplicon-based nanopore sequencing workflow for rapid tracking of avian influenza outbreaks, France, 2020-2022. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14, 1257586. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1257586
Cuber, P., Chooneea, D., Geeves, C., Salatino, S., Creedy, T. J., Griffin, C., et al. (2022). Comparing the accuracy and efficiency of third generation DNA barcode sequencing: Oxford Nanopore Technologies versus Pacific Biosciences. BioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/2022.07.13.499863
Cuscó, A., Salas, A., Torre, C., and Francino, O. (2019). Shallow metagenomics with Nanopore sequencing in canine fecal microbiota improved bacterial taxonomy and identified an uncultured CrAssphage. bioRxiv, 585067. doi: 10.1101/585067
Cuscó, A., Pérez, D., Viñes, J., Fàbregas, N., and Francino, O. (2021). Long-read metagenomics retrieves complete single-contig bacterial genomes from canine feces. BMC Genomics 22, 330. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07607-0
Cuscó, A., Pérez, D., Viñes, J., Fàbregas1, N., and Francino, O. (2022). Novel canine high-quality metagenome-assembled genomes, prophages and host-associated plasmids provided by long-read metagenomics together with Hi-C proximity ligation. Microbial Genomics 8, 000802. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000802
Davis, M. P. A., van Dongen, S., Abreu-Goodger, C., Bartonicek, N., and Enright, A. J. (2013). Kraken: a set of tools for quality control and analysis of high-throughput sequence data. Methods 63, 41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.06.027
Davis, N. M., Proctor, D. M., Holmes, S. P., Relman, D. A., and Callahan, B. J. (2018). Simple statistical identification and removal of contaminant sequences in marker-gene and metagenomics data. Microbiome 6, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0605-2
Deamer, D., Akeson, M., and Branton, D. (2016). Three decades of nanopore sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 518–524. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3423
De Coster, W., D’hert, S., Schultz, D. T., Cruts, M., and Van Broeckhoven, C. (2018). NanoPack: visualizing and processing long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 34, 2666–2669. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty149
De Coster, W. and Rademakers, R. (2023). NanoPack2: population-scale evaluation of long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 39, btad311. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad311
Dekker, C. (2007). Solid-state nanopores. Nat. nanotechnology 2, 209–215. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.27
Delahaye, C. and Nicolas, J. (2021). Sequencing DNA with nanopores: Troubles and biases. PloS One 16, e0257521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257521
De Maio, N., Shaw, L. P., Hubbard, A., George, S., Sanderson, N. D., Swann, J., et al. (2019). Comparison of long-read sequencing technologies in the hybrid assembly of complex bacterial genomes. Microbial Genomics 5, e000294. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000294
de Vries, E. M., Cogan, N. O. I., Gubala, A. J., Mee, P. T., O'Riley, K. J., Rodoni, B. C., et al. (2022). Rapid, in-field deployable, avian influenza virus haemagglutinin characterisation tool using MinION technology. Sci. Rep. 12, 11886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16048-y
Di Marcantonio, L., Curini, V., Marotta, F., Di Serafino, G., Di Giannatale, E., Neri, D., et al. (2019). “Metagenomic minION sequencing for campylobacter surveillance on air samples in Italian poultry farms,” in 29th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (Amsterdam, Netherlands). D.D.M.
Di Profio, F., Sarchese, V., Fruci, P., Aste, G., Martella, V., Palombieri, A., et al. (2023). Exploring the enteric virome of cats with acute gastroenteritis. Veterinary Sci. 10, 362. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10050362
Dong, L., Yoshizawa, J., and Li, X. (2019). “Nucleic acid isolation and quality control,” in Biobanking: Methods and Protocols. Ed. Yong, W. H. (Springer New York, New York, NY), 325–343.
Doukoure, B., Le, Pennec Y., Troupin, C., Grayo, S., Eiden, M., Groschup, M. H., et al. (2024). Seroprevalence and phylogenetic characterization of hepatitis E virus (Paslahepevirus balayani) in Guinean pig population. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 24, 540–545. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2023.0104
Eagle, S. H. C., Robertson, J., Bastedo, D. P., Liu, K., and Nash, J. H. E. (2023). Evaluation of five commercial DNA extraction kits using Salmonella as a model for implementation of rapid Nanopore sequencing in routine diagnostic laboratories. Access Microbiol. 5, 000468. v3. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000468.v3
Edwards, A., Debbonaire, A. R., Sattler, B., Mur, L. A., and Hodson, A. J. (2016). Extreme metagenomics using nanopore DNA sequencing: a field report from Svalbard, 78 N. BioRxiv 10, 073965. doi: 10.1101/073965
Ehuwa, O., Jaiswal, A. K., and Jaiswal, S. (2021). Salmonella, food safety and food handling practices. Foods 10, 907. doi: 10.3390/foods10050907
Eman Gadu, A. H., Shelkamy, M. M. S., Chaves, M., Srednik, M. E., Sato, Y., and El-Gazzar, M. (2025). Complete Genome Sequences of two Campylobacter bilis Isolates from Layer Chickens with Spotty Liver Disease. Microbiol. Resource Announcements. 14, e01305–24. doi: 10.1128/mra.01305-24
Ergunay, K., Dincer, E., Justi, S. A., Bourke, B. P., Nelson, S. P., Liao, H. M., et al. (2023). Impact of nanopore-based metagenome sequencing on tick-borne virus detection. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1177651. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1177651
Ergunay, K., Boldbaatar, B., Bourke, B. P., Caicedo-Quiroga, L., Tucker, C. L., Letizia, A. G., et al. (2024). Metagenomic nanopore sequencing of tickborne pathogens, Mongolia. Emerging Infect. Dis. 30, S105. doi: 10.3201/eid3014.240128
Esnault, G., Earley, B., Cormican, P., Waters, S. M., Lemon, K., Barry, T., et al. (2021). Optimisation of rapid untargeted nanopore DNA virus metagenomics using cell cultures and calves experimentally infected with bovine herpes virus-1. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-783575/v1
Esnault, G., Earley, B., Cormican, P., Waters, S. M., Lemon, K., Cosby, S. L., et al. (2022). Assessment of rapid MinION Nanopore DNA virus meta-genomics using calves experimentally infected with bovine herpes virus-1. Viruses 14, 1859. doi: 10.3390/v14091859
Fàbregas, N., Pérez, D., Viñes, J., Fonticoba, R., Cuscó, A., Migura-García, L., et al. (2022). Whole-genome sequencing and de novo assembly of 67 Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strains isolated from the skin of healthy dogs. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 11, e00039–e00022. doi: 10.1128/mra.00039-22
Fan, J., Huang, S., and Chorlton, S. D. (2021). BugSeq: a highly accurate cloud platform for long-read metagenomic analyses. BMC Bioinf. 22, 160. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04089-5
Feng, Y., Zhang, Y., Ying, C., Wang, D., and Du, C. (2015). Nanopore-based fourth-generation DNA sequencing technology. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. 13, 4–16. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.01.009
Feng, X., Cheng, H., Portik, D., and Li, H. (2022). Metagenome assembly of high-fidelity long reads with hifiasm-meta. Nat. Methods 19, 671–674. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01478-3
Fernández-Díaz, M., Villanueva-Pérez, D., Tataje-Lavanda, L., Montalvan-Avalos, A., Isasi-Rivas, G., Lulo-Vargas, M., et al. (2023). Detection and genomic characterization of an avian influenza virus subtype H5N1 (Clade 2.3.4.4b) strain isolated from a pelican in Peru. Microbiol. Resour Announc 12, e0019923. doi: 10.1128/mra.00199-23
Fomsgaard, A. S., Tahas, S. A., Spiess, K., Polacek, C., Fonager, J., and Belsham, G. J. (2023). Unbiased virus detection in a Danish zoo using a portable metagenomic sequencing system. Viruses 15, 1399. doi: 10.3390/v15061399
Foster-Nyarko, E., Cottingham, H., Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Lam, M. M. C., Wyres, K. L., et al. (2023). Nanopore-only assemblies for genomic surveillance of the global priority drug-resistant pathogen, Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbial Genomics 9, 000936. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000936
Framst, I., Andrea, C. D., Baquero, M., and Maboni, G. (2022). Development of a long-read next generation sequencing workflow for improved characterization of fastidious respiratory mycoplasmas. Microbiology 168, 001249. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001249
Freed, N. E., Smith, A. N. H., Breckell, G., Dale, J., and Silander, O. K. (2023). Nanopore sequencing of metagenomic DNA from rat stomach contents to infer diet. New Z. J. Ecol. 47. doi: 10.20417/nzjecol.47.3554
Fukasawa, Y., Ermini, L., Wang, H., Carty, K., and Cheung, M. S. (2020). LongQC: a quality control tool for third generation sequencing long read data. G3: Genes Genomes Genet. 10, 1193–1196. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400864
Gand, M., Bloemen, B., Vanneste, K., Roosens, N. H. C., and De Keersmaecker, S. C. J. (2023). Comparison of 6 DNA extraction methods for isolation of high yield of high molecular weight DNA suitable for shotgun metagenomics Nanopore sequencing to detect bacteria. BMC Genomics 24, 438. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09537-5
Garcia-Aroca, T., Souza, S. S. R., Ikhimiukor, O. O., Marcovici, M. M., Smith, J. T., Amador, S., et al. (2022). Genome sequencing of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Mammaliicoccus sciuri from diseased animals. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 11, e00714–e00722. doi: 10.1128/mra.00714-22
Garretto, A., Hatzopoulos, T., and Putonti, C. (2019). virMine: automated detection of viral sequences from complex metagenomic samples. PeerJ 7, e6695. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6695
Gauthier, N. P., Nelson, C., Bonsall, M. B., Locher, K., Charles, M., MacDonald, C., et al. (2021). Nanopore metagenomic sequencing for detection and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. PloS One 16, e0259712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259712
Gauthier, N. P., Chorlton, S. D., Krajden, M., and Manges, A. R. (2023). Agnostic sequencing for detection of viral pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 36, e00119–e00122. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00119-22
Ghezzi, H., Fan, Y. M., Ng, K. M., Burckhardt, J. C., Pepin, D. M., Lin, X., et al. (2024). PUPpy: a primer design pipeline for substrain-level microbial detection and absolute quantification. mSphere 9, e00360–e00324. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00360-24
Gigante, C. M., Yale, G., Condori, R. E., Costa, N. C., Van Long, N., Minh, P. Q., et al. (2020). Portable rabies virus sequencing in canine rabies endemic countries using the Oxford Nanopore MinION. Viruses 12, 1255. doi: 10.3390/v12111255
Gilpatrick, T., Lee, I., Graham, J. E., Raimondeau, E., Bowen, R., Heron, A., et al. (2019). Targeted nanopore sequencing with Cas9 for studies of methylation, structural variants, and mutations. BioRxiv, 604173. doi: 10.1101/604173
Girgis, S. T., Adika, E., Nenyewodey, F. E., Senoo, D. K. Jr., Ngoi, J. M., Bandoh, K., et al. (2023). Drug resistance and vaccine target surveillance of Plasmodium falciparum using nanopore sequencing in Ghana. Nat. Microbiol. 8, 2365–2377. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01516-6
Goletic, S., Goletic, T., Softic, A., Zahirovic, A., Rukavina, D., Kavazovic, A., et al. (2022). The evidence of SARS-CoV-2 human-to-pets transmission in household settings in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Front. Genet. 13, 839205. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.839205
Goletic, S., Softic, A., Omeragic, J., Koro-Spahic, A., Kapo, N., Sabic, E., et al. (2023a). Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of highly pathogenic H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Front. Vet. Sci. 10, 1255213. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1255213
Goletic, S., Goletic, T., Omeragic, J., Supic, J., Kapo, N., Nicevic, M., et al. (2023b). Metagenomic sequencing of lloviu virus from dead Schreiber’s bats in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Microorganisms 11, 2892. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11122892
Gondard, M., Postic, L., Garin, E., Turpaud, M., Vorimore, F., Ngwa-Mbot, D., et al. (2024). Exceptional bluetongue virus (BTV) and epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV) circulation in France in 2023. Virus Res. 350, 199489. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199489
Goodwin, S., McPherson, J. D., and McCombie, W. R. (2016). Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 17, 333–351. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.49
Goraichuk, I. V., Harden, M., Spackman, E., and Suarez, D. L. (2024a). Improved influenza A whole-genome sequencing protocol. Front. Cell. Infection Microbiol. 14, 1497278. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1497278
Goraichuk, I. V., Risalvato, J., Pantin-Jackwood, M., and Suarez, D. L. (2024b). The 28S rRNA RT-qPCR assay for host depletion evaluation to enhance avian virus detection in Illumina and Nanopore sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1328987. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1328987
Goraichuk, I. V. and Suarez, D. L. (2025). Custom barcoded primers for influenza A nanopore sequencing: enhanced performance with reduced preparation time. Front. Cell. Infection Microbiol. 15, 1545032. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1545032
Gowers, G. F., Vince, O., Charles, J. H., Klarenberg, I., Ellis, T., and Edwards, A. (2019). Entirely off-grid and solar-powered DNA sequencing of microbial communities during an ice cap traverse expedition. Genes (Basel) 10, 902. doi: 10.3390/genes10110902
Greninger, A. L., Naccache, S. N., Federman, S., Yu, G., Mbala, P., Bres, V., et al. (2015). Rapid metagenomic identification of viral pathogens in clinical samples by real-time nanopore sequencing analysis. Genome Med. 7, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13073-015-0220-9
guide, G.s. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/document/guides/getting-started-guide-rapid-114?utm_source=chatgpt.com (Accessed April 14, 2025).
Hadfield, J., Megill, C., Bell, S. M., Huddleston, J., Potter, B., Callender, C., et al. (2018). Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 34, 4121–4123. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty407
Hadjithomas, M., Chen, I. A., Chu, K., Huang, J., Ratner, A., Palaniappan, K., et al. (2017). IMG-ABC: new features for bacterial secondary metabolism analysis and targeted biosynthetic gene cluster discovery in thousands of microbial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, D560–D565. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1103
Han, X. and Xia, Z. (2023). Application of host-depleted nanopore metagenomic sequencing in the clinical detection of pathogens in pigs and cats. Animals 13, 3838. doi: 10.3390/ani13243838
Handelsman, J. (2004). Metagenomics: application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68, 669–685. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.4.669-685.2004
Hashish, A., Chaves, M., Macedo, N. R., Sato, Y., Schmitz-Esser, S., Wilson, D., et al. (2023a). Complete genome sequences generated using hybrid Nanopore-Illumina assembly of two non-typical Avibacterium paragallinarum strains isolated from clinically normal chicken flocks. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 12, e00128–e00123. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00128-23
Hashish, A., Johnson, T. J., Chundru, D., Williams, M. L., Sato, Y., Macedo, N. R., et al. (2023b). Complete genome sequences of three Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale strains from avian sources, using hybrid nanopore-illumina assembly. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 12, e01059–e01022. doi: 10.1128/mra.01059-22
Hashish, A., Johnson, T. J., Smith, E., Chundru, D., Williams, M. L., Macedo, N. R., et al. (2023c). Complete genome sequences of two Pasteurella multocida isolates from seabirds. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 12, e01365–e01322. doi: 10.1128/mra.01365-22
Hashish, A., Johnson, T. J., Ghanem, M., Sato, Y., Macedo, N. R., LeCount, K. J., et al. (2024). Complete genome sequences of eight Pasteurella multocida isolates representing all lipopolysaccharide outer core loci. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 13, e00604–e00624. doi: 10.1128/mra.00604-24
Hayes, B. J., Nguyen, L. T., Forutan, M., Engle, B. N., Lamb, H. J., Copley, J. P., et al. (2021). An epigenetic aging clock for cattle using portable sequencing technology. Front. Genet. 12, 760450. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.760450
Heather, J. M. and Chain, B. (2016). The sequence of sequencers: The history of sequencing DNA. Genomics 107, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2015.11.003
Herman, E. K., Lacoste, S. R., Freeman, C. N., Otto, S. J., McCarthy, E. L., Links, M. G., et al. (2024). Bacterial enrichment prior to third-generation metagenomic sequencing improves detection of BRD pathogens and genetic determinants of antimicrobial resistance in feedlot cattle. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1386319. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1386319
Heron, A. J. (2019). “Molecular engineering DNA and RNA for nanopore sequencing,” in Nanopore Sequencing: An Introduction (World Scientific, Singapore), 107–146.
Hess, J. F., Kohl, T. A., Kotrová, M., Rönsch, K., Paprotka, T., Mohr, V., et al. (2020). Library preparation for next generation sequencing: A review of automation strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 41, 107537. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107537
Holicki, C. M., Bergmann, F., Stoek, F., Schulz, A., Groschup, M. H., Ziegler, U., et al. (2022). Expedited retrieval of high-quality Usutu virus genomes via Nanopore sequencing with and without target enrichment. Front. Microbiol. 13, 1044316. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1044316
Hong, Y. P., Chen, B. H., Wang, Y. W., Teng, R. H., Wei, H. L., and Chiou, C. S. (2024). The usefulness of nanopore sequencing in whole-genome sequencing-based genotyping of. Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e0050924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00509-24
Horemans, M., Van Bets, J., Maes, T. J., Maes, P., and Vanmechelen, B. (2023). Discovery and genome characterization of six new orthoparamyxoviruses in small Belgian mammals. Virus Evol. 9, vead065. doi: 10.1093/ve/vead065
Hornsey, M., Betts, J. W., Mehat, J. W., Wareham, D. W., van Vliet, A. H., Woodward, M. J., et al. (2019). Characterization of a colistin-resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli ST69 isolate recovered from a broiler chicken in Germany. J. Med. Microbiol. 68, 111–114. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000882
Hosokawa-Muto, J., Sassa-O'Brien, Y., Fujinami, Y., and Nakahara, H. (2022). Analysis comparison for rapid identification of pathogenic virus from infected tissue samples. Diagnostics (Basel) 12, 196. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12010196
https://github.com/nanoporetech/dorado (2025). Available online at: https://github.com/nanoporetech/dorado (Accessed April 14, 2025).
https://github.com/nanoporetech/medaka. Available online at: https://github.com/nanoporetech/medaka (Accessed April 13, 2025).
Hufnagel, D. E., Hufford, M. B., and Seetharam, A. S. (2019). SequelQC: analyzing pacBio sequel raw sequence quality. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/611814
Huggins, L. G., Namgyel, U., Wangchuk, P., Atapattu, U., Traub, R., and Colella, V. (2022). Nanopore sequencing using the full-length 16S rRNA gene for detection of blood-borne bacteria in dogs reveals a novel species of hemotropic mycoplasma. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e03088–e03022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03088-22
Huggins, L. G., Colella, V., Atapattu, U., Koehler, A. V., and Traub, R. J. (2024a). Metabarcoding using nanopore long-read sequencing for the unbiased characterization of apicomplexan haemoparasites. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 24, e13878. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13878
Huggins, L. G., Colella, V., Young, N. D., and Traub, R. J. (2024b). Metabarcoding using nanopore sequencing enables identification of diverse and zoonotic vector-borne pathogens from neglected regions: A case study investigating dogs from Bhutan. One Health 19, 100839. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2024.100839
Huson, D. H., Albrecht, B., Bağcı, C., Bessarab, I., Gorska, A., Jolic, D., et al. (2018). MEGAN-LR: new algorithms allow accurate binning and easy interactive exploration of metagenomic long reads and contigs. Biol. direct 13, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/s13062-018-0208-7
Ip, C. L. C., Loose, M., Tyson, J. R., de Cesare, M., Brown, B. L., Jain, M., et al. (2015). MinION Analysis and Reference Consortium: Phase 1 data release and analysis. F1000Research 4, 1075. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.7201.1
Ip, H. S., Uhm, S., Killian, M. L., and Torchetti, M. K. (2023). An evaluation of avian influenza virus whole-genome sequencing approaches using nanopore technology. Microorganisms 11, 529. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020529
Irber, L., Pierce-Ward, N. T., Abuelanin, M., Alexander, H., Anant, A., Barve, K., et al. (2024). sourmash v4: A multitool to quickly search, compare, and analyze genomic and metagenomic data sets. J. Open Source Software 9, 6830. doi: 10.21105/joss.06830
Issae, A. R., Katakweba, A. S., Kicheleri, R. P., Chengula, A. A., Van Zwetselaar, M., and Kasanga, C. J. (2023). Exploring pathogenic and zoonotic bacteria from wild rodents, dogs, and humans of the Ngorongoro district in Tanzania using metagenomics next-generation sequencing. Zoonotic Dis. 3, 226–242. doi: 10.3390/zoonoticdis3030019
Jahan, N. A., Lindsey, L. L., Kipp, E. J., Reinschmidt, A., Heins, B. J., Runck, A. M., et al. (2021). Nanopore-based surveillance of zoonotic bacterial pathogens in farm-dwelling peridomestic rodents. Pathogens 10, 1183. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091183
Jain, M., Olsen, H. E., Paten, B., and Akeson, M. (2016). The Oxford Nanopore MinION: delivery of nanopore sequencing to the genomics community. Genome Biol. 17, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1103-0
Jain, M., Tyson, J. R., Loose, M., Eccles, D. A., Ip, C. L. C., and O’Grady, J. (2017). MinION analysis and reference consortium: phase 2 data release and analysis of R9. 0 chemistry. F1000Res 6, 760. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11354.1
Jain, C., Rhie, A., Zhang, H., Chu, C., Walenz, B. P., Koren, S., et al. (2020). Weighted minimizer sampling improves long read mapping. Bioinformatics 36, i111–i118. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa435
Johansson, T., Koskela, S., Yohannes, D. A., Partanen, J., and Saavalainen, P. (2021). Targeted RNA-based Oxford nanopore sequencing for typing 12 classical HLA genes. Front. Genet. 12, 635601. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.635601
John, A., Dreifuss, D., Kang, S., Bratus-Neuenschwander, A., Zajac, N., Topolsky, I., et al. (2024). Assessing different next-generation sequencing technologies for wastewater-based epidemiology. medRxiv. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2024.122465
John, A., Kang, S., Fuhrmann, L., Topolsky, I., Kent, C., Quick, J., et al. (2025). Characterizing influenza A virus lineages and clinically relevant mutations through high-coverage wastewater sequencing. Water Res. 287, 124453. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2025.124453
Johnson, S. S., Zaikova, E., Goerlitz, D. S., Bai, Y., and Tighe, S. W. (2017). Real-time DNA sequencing in the antarctic dry valleys using the oxford nanopore sequencer. J. Biomol Tech 28, 2–7. doi: 10.7171/jbt.17-2801-009
Kadariya, J., Smith, T. C., and Thapaliya, D. (2014). Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal food-borne disease: an ongoing challenge in public health. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 827965. doi: 10.1155/2014/827965
Kamathewatta, K. I., Bushell, R. N., Young, N. D., Stevenson, M. A., Billman-Jacobe, H., Browning, G. F., et al. (2019). Exploration of antibiotic resistance risks in a veterinary teaching hospital with Oxford Nanopore long read sequencing. PloS One 14, e0217600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217600
Kariithi, H. M., Volkening, J. D., Chiwanga, G. H., Pantin-Jackwood, M. J., Msoffe, P. L. M., and Suarez, D. L. (2023). Genome sequences and characterization of chicken Astrovirus and avian nephritis virus from Tanzanian live bird markets. Viruses 15, 1247. doi: 10.3390/v15061247
Kasianowicz, J. J., Brandin, E., Branton, D., and Deamer, D. W. (1996). Characterization of individual polynucleotide molecules using a membrane channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 93, 13770–13773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.24.13770
Kaszab, E., Doszpoly, A., Lanave, G., Verma, A., Bányai, K., Malik, Y. S., et al. (2020). “Metagenomics revealing new virus species in farm and pet animals and aquaculture,” in Genomics and Biotechnological Advances in Veterinary, Poultry, and Fisheries (Elsevier), 29–73.
Kathirvel, K., Rudhra, O., Rajapandian, S. G. K., Prajna, N. V., Lalitha, P., and Devarajan, B. (2021). Characterization of antibiotic resistance and virulence genes of ocular methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains through complete genome analysis. Exp. Eye Res. 212, 108764. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108764
Kazantseva, E., Donmez, A., Pop, M., and Kolmogorov, M. (2023). stRainy: assembly-based metagenomic strain phasing using long reads. preprint. Bioinformatics.
Keegan, K. P., Glass, E. M., and Meyer, F. (2016). MG-RAST, a metagenomics service for analysis of microbial community structure and function. Microbial Environ. Genomics (MEG). 1399, 207–233. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3369-3_13
Keller, M. W., Rambo-Martin, B. L., Wilson, M. M., Ridenour, C. A., Shepard, S. S., Stark, T. J., et al. (2018). Direct RNA sequencing of the coding complete influenza A virus genome. Sci. Rep. 8, 14408. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32615-8
Kieft, K., Zhou, Z., and Anantharaman, K. (2019). VIBRANT: Automated recovery, annotation and curation of microbial viruses, and evaluation of virome function from genomic sequences. BioRXiv, 855387. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00867-0
Kieft, K., Zhou, Z., and Anantharaman, K. (2020). VIBRANT: automated recovery, annotation and curation of microbial viruses, and evaluation of viral community function from genomic sequences. Microbiome 8, 1–23. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00867-0
Kiguchi, Y., Nishijima, S., Kumar, N., Hattori, M., and Suda, W. (2021). Long-read metagenomics of multiple displacement amplified DNA of low-biomass human gut phageomes by SACRA pre-processing chimeric reads. DNA Res. 28, dsab019. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsab019
Kilianski, A., Roth, P. A., Liem, A. T., Hill, J. M., Willis, K. L., Rossmaier, R. D., et al. (2016). Use of unamplified RNA/cDNA–hybrid nanopore sequencing for rapid detection and characterization of RNA viruses. Emerging Infect. Dis. 22, 1448. doi: 10.3201/eid2208.160270
Kim, D., Song, L., Breitwieser, F. P., and Salzberg, S. L. (2016). Centrifuge: rapid and sensitive classification of metagenomic sequences. Genome Res. 26, 1721–1729. doi: 10.1101/gr.210641.116
Kim, K. W., Choi, S., Shin, S. K., Lee, I., Ku, K. B., Kim, S. J., et al. (2021). A half-day genome sequencing protocol for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Front. Microbiol. 12, 602754. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.602754
King, J., Harder, T., Globig, A., Stacker, L., Günther, A., Grund, C., et al. (2022a). Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus incursions of subtype H5N8, H5N5, H5N1, H5N4, and H5N3 in Germany during 2020-21. Virus Evol. 8, veac035. doi: 10.1093/ve/veac035
King, J., Staubach, C., Lüder, C., Koethe, S., Günther, A., Stacker, L., et al. (2022b). Connect to protect: dynamics and genetic connections of highly pathogenic avian influenza outbreaks in poultry from 2016 to 2021 in Germany. Viruses 14, 1849. doi: 10.20944/preprints202208.0024.v1
Kipp, E. J., Lindsey, L. L., Khoo, B., Faulk, C., Oliver, J. D., and Larsen, P. A. (2023). Metagenomic surveillance for bacterial tick-borne pathogens using nanopore adaptive sampling. Sci. Rep. 13, 10991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37134-9
Klink, A. C., Rula, O., Sushko, M., Bezymennyi, M., Mezinov, O., Gaidash, O., et al. (2023). Discovery of avian paramyxoviruses APMV-1 and APMV-6 in shorebirds and waterfowl in southern Ukraine. Viruses 15, 699. doi: 10.3390/v15030699
Koboldt, D. C., Steinberg, K. M., Larson, D. E., Wilson, R. K., and Mardis, E. R. (2013). The next-generation sequencing revolution and its impact on genomics. Cell 155, 27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.006
Kollef, M. H. (2008). Broad-spectrum antimicrobials and the treatment of serious bacterial infections: getting it right up front. Clin. Infect. Dis. 47, S3–S13. doi: 10.1086/590061
Kolmogorov, M., Yuan, J., Lin, Y., and Pevzner, P. A. (2019). Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 540–546. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0072-8
Kolmogorov, M., Bickhart, D. M., Behsaz, B., Gurevich, A., Rayko, M., Shin, S. B., et al. (2020). metaFlye: scalable long-read metagenome assembly using repeat graphs. Nat. Methods 17, 1103–1110. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-00971-x
Koren, S., Walenz, B. P., Berlin, K., Miller, J. R., Bergman, N. H., and Phillippy, A. M. (2017). Canu: scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 27, 722–736. doi: 10.1101/gr.215087.116
Kralik, P. and Ricchi, M. (2017). A basic guide to real time PCR in microbial diagnostics: definitions, parameters, and everything. Front. Microbiol. 8, 108. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00108
Krasnikov, N., Gulyukin, A., Aliper, T., and Yuzhakov, A. (2024). Complete genome characterization by nanopore sequencing of rotaviruses A, B, and C circulating on large-scale pig farms in Russia. Virol. J. 21, 289. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02567-9
Krehenwinkel, H., Pomerantz, A., Henderson, J. B., Kennedy, S. R., Lim, J. Y., Swamy, V., et al. (2019). Nanopore sequencing of long ribosomal DNA amplicons enables portable and simple biodiversity assessments with high phylogenetic resolution across broad taxonomic scale. GigaScience 8, giz006. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz006
Kruasuwan, W., Jenjaroenpun, P., Arigul, T., Chokesajjawatee, N., Leekitcharoenphon, P., Foongladda, S., et al. (2023). Nanopore sequencing discloses compositional quality of commercial probiotic feed supplements. Sci. Rep. 13, 4540. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31626-4
Kuchinski, K. S., Coombe, M., Mansour, S. C., Cortez, G. A. P., Kalhor, M., Himsworth, C. G., et al. (2024). Targeted genomic sequencing of avian influenza viruses in wetland sediment from wild bird habitats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 90, e0084223. doi: 10.1128/aem.00842-23
Kulikov, E. E., Golomidova, A. K., Babenko, V. V., and Letarov, A. V. (2020). A simple method for extraction of the horse feces virome DNA, suitable for oxford nanopore sequencing. Microbiology 89, 246–249. doi: 10.1134/S002626172002006X
Kumar, A., Häggblom, M. M., and Kerkhof, L. J. (2024). “A step-by-step guide to sequencing and assembly of complete bacterial genomes using the oxford nanopore minION,” in High Throughput Gene Screening: Methods and Protocols (Springer), 31–43.
Lamb, H. J., Hayes, B. J., Nguyen, L. T., and Ross, E. M. (2020). The future of livestock management: a review of real-time portable sequencing applied to livestock. Genes 11, 1478. doi: 10.3390/genes11121478
Lamb, H. J., Nguyen, L. T., Briody, T. E., Ambrose, R. K., Hayes, B. J., Mahony, T. J., et al. (2023). Skim-Nanopore sequencing for routine genomic evaluation and bacterial pathogen detection in cattle. Anim. Production Sci. 63, 1074–1085. doi: 10.1071/AN22451
Lanfear, R., Schalamun, M., Kainer, D., Wang, W., and Schwessinger, B. (2019). MinIONQC: fast and simple quality control for MinION sequencing data. Bioinformatics 35, 523–525. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty654
Langmead, B. and Salzberg, S. L. (2012). Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
Lanszki, Z., Lanszki, J., Tóth, G. E., Zeghbib, S., Jakab, F., and Kemenesi, G. (2022). Retrospective Detection and Complete Genomic Sequencing of Canine morbillivirus in Eurasian Otter (Lutra lutra) Using Nanopore Technology. Viruses 14, 1433. doi: 10.3390/v14071433
Lee, H.-J., Cho, I.-S., and Jeong, R.-D. (2022). Nanopore metagenomics sequencing for rapid diagnosis and characterization of lily viruses. Plant Pathol. J. 38, 503. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.06.2022.0084
Lee, J. Y., Kong, M., Oh, J., Lim, J. S., Chung, S. H., Kim, J.-M., et al. (2021). Comparative evaluation of Nanopore polishing tools for microbial genome assembly and polishing strategies for downstream analysis. Sci. Rep. 11, 20740. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00178-w
Lee, H.-J., Kim, H.-J., Cho, I.-S., and Jeong, R.-D. (2024). Comprehensive identification of pathogenic microbes and antimicrobial resistance genes in food products using nanopore sequencing-based metagenomics. Food Microbiol. 121, 104493. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2024.104493
Lee, A. W.-T., Ng, I. C.-F., Wong, E. Y.-K., Wong, I. T.-F., Sze, R. P.-P., Chan, K.-Y., et al. (2024). Identification of viruses infecting phalaenopsis orchids using nanopore sequencing and development of an RT-RPA-CRISPR/cas12a for rapid visual detection of nerine latent virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 2666. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052666
Leger, A. and Leonardi, T. (2019). pycoQC, interactive quality control for Oxford Nanopore Sequencing. J. Open Source Software 4, 1236. doi: 10.21105/joss.01236
Lei, S., Chen, S., and Zhong, Q. (2021). Digital PCR for accurate quantification of pathogens: Principles, applications, challenges and future prospects. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 184, 750–759. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.132
Leonard, H., Colodner, R., Halachmi, S., and Segal, E. (2018). Recent advances in the race to design a rapid diagnostic test for antimicrobial resistance. ACS Sensors 3, 2202–2217. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.8b00900
Levy, S., Sutton, G., Ng, P. C., Feuk, L., Halpern, A. L., Walenz, B. P., et al. (2007). The diploid genome sequence of an individual human. PloS Biol. 5, e254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050254
Lewandowski, K., Xu, Y., Pullan, S. T., Lumley, S. F., Foster, D., Sanderson, N., et al. (2019). Metagenomic nanopore sequencing of influenza virus direct from clinical respiratory samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 58. doi: 10.1128/jcm.00963-19
Li, H. (2016). Minimap and miniasm: fast mapping and de novo assembly for noisy long sequences. Bioinformatics 32, 2103–2110. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw152
Li, H. (2018). Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 34, 3094–3100. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191
Li, H. and Durbin, R. (2009). Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. bioinformatics 25, 1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Licheri, M., Licheri, M. F., Mwanga, M., Graaf-Rau, A., Sägesser, C., Bittel, P., et al. (2024). Optimized workflow for high-throughput whole genome surveillance of Influenza A virus. BMC Genome Medicine. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5216720/v1
Lin, C. H., Chen, B., Chao, D. Y., Hsieh, F. C., Yang, C. C., Hsu, H. W., et al. (2023). Unveiling the biology of defective viral genomes in vitro and in vivo: implications for gene expression and pathogenesis of coronavirus. Virol. J. 20, 225. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02189-7
Lin, Y., Dai, Y., Zhang, S., Guo, H., Yang, L., Li, J., et al. (2023). Application of nanopore adaptive sequencing in pathogen detection of a patient with Chlamydia psittaci infection. Front. Cell. Infection Microbiol. 13, 1064317. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1064317
Liu, Y., Kearney, J., Mahmoud, M., Kille, B., Sedlazeck, F. J., and Treangen, T. J. (2022). Rescuing low frequency variants within intra-host viral populations directly from Oxford Nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Commun. 13, 1321. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28852-1
Liu, X., Wu, J., Li, M., Zuo, F., and Zhang, G. (2024). A comparative full-length transcriptome analysis using oxford nanopore technologies (ONT) in four tissues of bovine origin. Anim. (Basel) 14. doi: 10.3390/ani14111646
Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Li, J., Yan, X., Xu, W., Yi, L., et al. (2024). Rapid diagnosis of a fox’s death case using nanopore sequencing reveals the infection with an Artic-like rabies virus. Virologica Sin. 39, 840. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2024.08.010
Lohde, M., Wagner, G. E., Dabernig-Heinz, J., Viehweger, A., Braun, S. D., Monecke, S., et al. (2024). Accurate bacterial outbreak tracing with Oxford Nanopore sequencing and reduction of methylation-induced errors. Genome Res. 34, 2039–2047. doi: 10.1101/gr.278848.123
Lu, J., Breitwieser, F. P., Thielen, P., and Salzberg, S. L. (2017). Bracken: estimating species abundance in metagenomics data. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 3, e104. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.104
Lu, H., Giordano, F., and Ning, Z. (2016). Oxford nanopore minION sequencing and genome assembly. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. 14, 265–279. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.004
Lu, J. and Salzberg, S. L. (2020). Ultrafast and accurate 16S rRNA microbial community analysis using Kraken 2 and Bracken. Microbiome.
Maghini, D. G., Moss, E. L., Vance, S. E., and Bhatt, A. S. (2021). Improved high-molecular-weight DNA extraction, nanopore sequencing and metagenomic assembly from the human gut microbiome. Nat. Protoc. 16, 458–471. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-00424-x
Maguire, M., Kase, J. A., Roberson, D., Muruvanda, T., Brown, E. W., Allard, M., et al. (2021). Precision long-read metagenomics sequencing for food safety by detection and assembly of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in irrigation water. PloS One 16, e0245172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245172
Maguire, M., Kase, J. A., Brown, E. W., Allard, M. W., Musser, S. M., and González-Escalona, N. (2022a). Genomic comparison of eight closed genomes of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica strains isolated from broiler farms and processing plants in Trinidad and Tobago. Front. Microbiol. 13, 863104. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.863104
Maguire, M., Khan, A. S., Adesiyun, A. A., Georges, K., and Gonzalez-Escalona, N. (2022b). Metagenomic survey of agricultural water using long read sequencing: considerations for a successful analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 830300. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.830300
Maguire, M., Ramachandran, P., Tallent, S., Mammel, M. K., Brown, E. W., Allard, M. W., et al. (2023). Precision metagenomics sequencing for food safety: hybrid assembly of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in enriched agricultural water. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1221668. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1221668
Maimaiti, M., Kong, L., Yu, Q., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Yang, C., et al. (2024). Analytical performance of a novel nanopore sequencing for SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance. J. Med. Virol. 96, e70108. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70108
Maitra, R. D., Kim, J., and Dunbar, W. B. (2012). Recent advances in nanopore sequencing. Electrophoresis 33, 3418–3428. doi: 10.1002/elps.201200272
Mani, R. S., Harsha, P. K., Pattabiraman, C., Prasad, P., Sujatha, A., Abraham, S. S., et al. (2021). Rabies in the endangered Asiatic wild dog (Cuon alpinus) in India. Transboundary Emerging Dis. 68, 3012–3014. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14333
Mani, R., Harsha, P., Prasad, P., Pattabiraman, C., Ansil, B. R., Yale, G., et al. (2023). Whole genome sequencing of rabies virus from archived human and canine brain tissues from southern India using Nanopore technology. Authorea Preprints. doi: 10.22541/au.167767386.66616245/v1
Marchukov, D., Li, J., Juillerat, P., Misselwitz, B., and Yilmaz, B. (2023). Benchmarking microbial DNA enrichment protocols from human intestinal biopsies. Front. Genet. 14, 1184473. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1184473
Mardis, E. R. (2011). A decade’s perspective on DNA sequencing technology. Nature 470, 198–203. doi: 10.1038/nature09796
Marić, J., Križanović, K., Riondet, S., Nagarajan, N., and Šikić, M. (2024). Comparative analysis of metagenomic classifiers for long-read sequencing datasets. BMC Bioinf. 25, 15. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05634-8
Marin, C., Marco-Jiménez, F., Martínez-Priego, L., De Marco-Romero, G., Soriano-Chirona, V., Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L., et al. (2022). Rapid oxford nanopore technologies MinION sequencing workflow for Campylobacter jejuni identification in broilers on site—a proof-of-concept study. Animals 12, 2065. doi: 10.3390/ani12162065
Martin, M. (2011). Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 17, 10–12. doi: 10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Martin, S., Heavens, D., Lan, Y., Horsfield, S., Clark, M. D., and Leggett, R. M. (2022). Nanopore adaptive sampling: a tool for enrichment of low abundance species in metagenomic samples. Genome Biol. 23, 11. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02582-x
Martinez, J. M. M. (2018). “Longitudinal metagenomics,” in Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology (Portal de Produccio Cientifica Universitat de València).
Mathijs, E., Haegeman, A., De Clercq, K., Van Borm, S., and Vandenbussche, F. (2022). A robust, cost-effective and widely applicable whole-genome sequencing protocol for capripoxviruses. J. Virological Methods 301, 114464. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2022.114464
McCombie, W. R., McPherson, J. D., and Mardis, E. R. (2019). Next-generation sequencing technologies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 9, p.a036798. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036798
McIntyre, A. B. R., Rizzardi, L., Yu, A. M., Alexander, N., Rosen, G. L., Botkin, D. J., et al. (2016). Nanopore sequencing in microgravity. NPJ Microgravity 2, 16035. doi: 10.1038/npjmgrav.2016.35
Mears, M. C., Read, Q. D., and Bakre, A. (2024). Comparison of direct RNA sequencing of Orthoavulavirus javaense using two different chemistries on the MinION platform. J. Virol. Methods 333, 115103. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2024.115103
Menzel, P., Ng, K. L., and Krogh, A. (2016). Fast and sensitive taxonomic classification for metagenomics with Kaiju. Nat. Commun. 7, 11257. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11257
Miah, M., Hossain, M. E., Hasan, R., Alam, M. S., Puspo, J. A., Hasan, M. M., et al. (2023). Culture-independent workflow for nanopore minION-based sequencing of influenza A virus. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e0494622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04946-22
Misu, M., Yoshikawa, T., Sugimoto, S., Takamatsu, Y., Kurosu, T., Ouji, Y., et al. (2023). Rapid whole genome sequencing methods for RNA viruses. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1137086. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1137086
Moldován, N., Tombácz, D., Szűcs, A., Csabai, Z., Snyder, M., and Boldogkői, Z. (2017). Multi-platform sequencing approach reveals a novel transcriptome profile in pseudorabies virus. Front. Microbiol. 8, 2708. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02708
Moldován, N., Torma, G., Gulyás, G., Hornyák, Á., Zádori, Z., Jefferson, V. A., et al. (2020). Time-course profiling of bovine alphaherpesvirus 1.1 transcriptome using multiplatform sequencing. Sci. Rep. 10, 20496.
Motone, Keisuke, Kontogiorgos-Heintz, Daphne, Wee, Jasmine, Kurihara, Kyoko, Yang, Sangbeom, Roote, Gwendolin, et al. (2024). Multi-pass, single-molecule nanopore reading of long protein strands. Nature 633, 662–669. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07935-7
Narvaez, S. A., Harrell, T. L., Oluwayinka, O., Sellers, H. S., Khalid, Z., Hauck, R., et al. (2023). Optimizing the conditions for whole-genome sequencing of avian reoviruses. Viruses 15, 1938. doi: 10.3390/v15091938
Naundrup Thøfner, I. C., Ladefoged Poulsen, L., Bisgaard, M., Christensen, H., Heidemann Olsen, R., and Christensen, J. P. (2019). Longitudinal study on causes of mortality in Danish broiler breeders. Avian Dis. 63, 400–410. doi: 10.1637/12006-113018-Reg.1
Nelson, S. P., Ergunay, K., Bourke, B. P., Reinbold-Wasson, D. D., Caicedo-Quiroga, L., Kirkitadze, G., et al. (2024). Nanopore-based metagenomics reveal a new Rickettsia in Europe. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. 15, 102305. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2023.102305
Neujahr, A. C., Loy, D. S., Loy, J. D., Brodersen, B. W., Fernando, S. C., et al. (2024). Rapid detection of high consequence and emerging viral pathogens in pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 11, 1341783. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1341783
Noakes, M. T., Brinkerhoff, H., Laszlo, A. H., Derrington, I. M., Langford, K. W., Mount, J. W., et al. (2019). Increasing the accuracy of nanopore DNA sequencing using a time-varying cross membrane voltage. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 651–656. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0096-0
Noh, E. B., Heo, G. B., Lee, K. N., Kang, Y. M., An, S. H., Kim, N., et al. (2023). Subtype specific virus enrichment with immunomagnetic separation method followed by NGS unravels the mixture of H5 and H9 avian influenza virus. J. Virol. Methods 320, 114773. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2023.114773
Norris, A. L., Workman, R. E., Fan, Y., Eshleman, J. R., and Timp, W. (2016). Nanopore sequencing detects structural variants in cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 17, 246–253. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139236
Notomi, T., Okayama, H., Masubuchi, H., Yonekawa, T., Watanabe, K., Amino, N., et al. (2000). Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, e63–e63. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.12.e63
Oh, J. Y., Do, K. H., Jeong, J. H., Kwak, S., Choe, S., An, D., et al. (2024). Whole genome sequencing analysis of enteropathogenic. J. Vet. Sci. 26, p.e1. doi: 10.4142/jvs.24225
Olarte-Castillo Ximena, A., Goodman Laura, B., and Whittaker Gary, R. (2024). Molecular detection using hybridization capture and next-generation sequencing reveals cross-species transmission of feline coronavirus type-1 between a domestic cat and a captive wild felid. Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e00061–e00024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00061-24
Olson, R. D., Assaf, R., Brettin, T., Conrad, N., Cucinell, C., Davis, J. J., et al. (2023). Introducing the bacterial and viral bioinformatics resource center (BV-BRC): a resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D678–D689. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1003
Ong, C. T., Ross, E. M., Boe-Hansen, G., Turni, C., Hayes, B. J., Fordyce, G., et al. (2022). Adaptive sampling during sequencing reveals the origins of the bovine reproductive tract microbiome across reproductive stages and sexes. Sci. Rep. 12, 15075. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19022-w
Opitz-Ríos, C., Burgos-Pacheco, A., Paredes-Cárcamo, F., Campanini-Salinas, J., and Medina, D. A. (2024). Metagenomics insight into veterinary and zoonotic pathogens identified in urban wetlands of Los Lagos, Chile. Pathogens 13, 788. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090788
Organization, W.H (2021). Estimating the burden of foodborne diseases: a practical handbook for countries: a guide for planning, implementing and reporting country-level burden of foodborne disease (World Health Organization).
Pallandre, L., Flores, D., Pozet, F., and Bigarré, L. (2023). Nearly complete genome sequence of a Perhabdovirus isolated on European perch (Perca fluviatilis). Microbiol. Resour Announc 12, e0044223. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00442-23
Palombieri, A., Sarchese, V., Giordano, M. V., Fruci, P., Crisi, P. E., Aste, G., et al. (2022). Detection and characterization of feline Calicivirus associated with paw and mouth disease. Animals 13, 65. doi: 10.3390/ani13010065
Parker, J., Helmstetter, A. J., Devey, D., Wilkinson, T., and Papadopulos, A. S. T. (2017). Field-based species identification of closely-related plants using real-time nanopore sequencing. Sci. Rep. 7, 8345. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08461-5
Pawar, S. S., Mohanapure, P. A., Brahmane, M. P., Bhendarkar, M. P., Nirmale, A. V., and Kurade, N. P. (2023). Metagenomics: A novel tool for livestock and poultry improvement: A review. Agric. Rev. 44, 264–268.
Payne, A., Holmes, N., Clarke, T., Munro, R., Debebe, B. J., and Loose, M. (2021). Readfish enables targeted nanopore sequencing of gigabase-sized genomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 39, 442–450. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-00746-x
Perlas, A., Reska, T., Croville, G., Tarrés-Freixas, F., Guérin, J.-L., Majó, N., et al. (2025). Improvements in RNA and DNA nanopore sequencing allow for rapid genetic characterization of avian influenza. Virus Evol. 11, veaf010. doi: 10.1093/ve/veaf010
Perveen, N., Kundu, B., Sudalaimuthuasari, N., Al-Maskari, R. S., Muzaffar, S. B., and Al-Deeb, M. A. (2023). Virome diversity of Hyalomma dromedarii ticks collected from camels in the United Arab Emirates. Vet. World 16, 439–448. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2023.439-448
Peserico, A., Marcacci, M., Malatesta, D., Di Domenico, M., Pratelli, A., Mangone, I., et al. (2019). Diagnosis and characterization of canine distemper virus through sequencing by MinION nanopore technology. Sci. Rep. 9, 1714. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37497-4
Piepenburg, O., Williams, C. H., Stemple, D. L., and Armes, N. A. (2006). DNA detection using recombination proteins. PloS Biol. 4, e204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040204
Pomerantz, A., Peñafiel, N., Arteaga, A., Bustamante, L., Pichardo, F., Coloma, L. A., et al. (2018). Real-time DNA barcoding in a rainforest using nanopore sequencing: opportunities for rapid biodiversity assessments and local capacity building. Gigascience 7, p.giy033. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giy033
Pons, J. C., Paez-Espino, D., Riera, G., Ivanova, N., Kyrpides, N. C., and Llabrés, M. (2021). VPF-Class: taxonomic assignment and host prediction of uncultivated viruses based on viral protein families. Bioinformatics 37, 1805–1813. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab026
Porechop (2025). Available online at: https://github.com/rrwick/Porechop (Accessed April 14, 2025).
Prawer, Y. D. J., Gleeson, J., De Paoli-Iseppi, R., and Clark, M. B. (2023). Pervasive effects of RNA degradation on Nanopore direct RNA sequencing. NAR Genom Bioinform. 5, lqad060. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad060
Project, F.A.o.A.G.F. Available online at: https://www.animalgenome.org/community/FAANG/proj.php (Accessed April 15, 2025).
Pugh, J. (2023). The current state of nanopore sequencing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2632, 3–14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2996-3_1
Quick, J., Grubaugh, N. D., Pullan, S. T., Claro, I. M., Smith, A. D., Gangavarapu, K., et al. (2017). Multiplex PCR method for MinION and Illumina sequencing of Zika and other virus genomes directly from clinical samples. Nat. Protoc. 12, 1261–1276. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2017.066
Quick, J. and Loman, N. (2018). Nanopore sequencing book: DNA extraction and purification methods. Nanopore Sequencing: Introduction p, 1–27.
Rambo-Martin, B. L., Keller, M. W., Wilson, M. M., Nolting, J. M., Anderson, T. K., Vincent, A. L., et al. (2020). Influenza A virus field surveillance at a swine-human interface. mSphere 5, 10–1128. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00822-19
Ratcliff, J. D., Merritt, B., Gooden, H., Siegers, J. Y., Srikanth, A., Yann, S., et al. (2024). Improved resolution of avian influenza virus using Oxford Nanopore R10 sequencing chemistry. Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e01880–e01824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01880-24
Razook, Z., Mehra, S., Gilchrist, B., Utama, D., Lautu-Gumal, D., Fola, A., et al. (2020). Real time, field-deployable whole genome sequencing of malaria parasites using nanopore technology. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/2020.12.17.423341
Reinartz, J., Bruyns, E., Lin, J. Z., Burcham, T., Brenner, S., Bowen, B., et al. (2002). Massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) as a tool for in-depth quantitative gene expression profiling in all organisms. Brief Funct. Genomic Proteomic 1, 95–104. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/1.1.95
Reyes, G. R. and Kim, J. P. (1991). Sequence-independent, single-primer amplification (SISPA) of complex DNA populations. Mol. Cell. Probes 5, 473–481. doi: 10.1016/S0890-8508(05)80020-9
Ring, N., Low, A. S., Wee, B., Paterson, G. K., Nuttall, T., Gally, D., et al. (2023). Rapid metagenomic sequencing for diagnosis and antimicrobial sensitivity prediction of canine bacterial infections. Microbial Genomics 9, 001066. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001066
Rivu, S., Smith, E., Stafford, G., and Ahmed, S. (2024). Draft genome sequence of Listeria aquatica strain SG_BD1, isolated from a cow dung sample in Bangladesh. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 13, e00729–e00724. doi: 10.1128/mra.00729-24
Ruan, J. and Li, H. (2020). Fast and accurate long-read assembly with wtdbg2. Nat. Methods 17, 155–158. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0669-3
Saiki, R. K., Scharf, S., Faloona, F., Mullis, K. B., Horn, G. T., Erlich, H. A., et al. (1985). Enzymatic amplification of β-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230, 1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980
Salazar, R., Brunker, K., Díaz, E. W., Zegarra, E., Monroy, Y., Baldarrago, G. N., et al. (2025). Genomic characterization of a dog-mediated rabies outbreak in El Pedregal, Arequipa, Peru. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 19, e0012396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012396
Salyer, S. J., Silver, R., Simone, K., and Barton Behravesh, C. (2017). Prioritizing zoonoses for global health capacity building—themes from One Health zoonotic disease workshops in 7 countries, 2014–2016. Emerging Infect. Dis. 23, S55. doi: 10.3201/eid2313.170418
Santos, J. D., Sobral, D., Pinheiro, M., Isidro, J., Bogaardt, C., Pinto, M., et al. (2024). INSaFLU-TELEVIR: an open web-based bioinformatics suite for viral metagenomic detection and routine genomic surveillance. Genome Med. 16, 61. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01334-3
Saravanan, A., Senthil Kumar, P., Hemavathy, R. V., Jeevanantham, S., Kamalesh, R., Sneha, S., et al. (2021). Methods of detection of food-borne pathogens: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 189–207. doi: 10.1007/s10311-020-01072-z
Sarchese, V., Fruci, P., Palombieri, A., Di Profio, F., Robetto, S., Ercolini, C., et al. (2021). Molecular identification and characterization of a genotype 3 hepatitis E virus (HEV) strain detected in a wolf faecal sample, Italy. Animals 11, 3465. doi: 10.3390/ani11123465
Sayers, E. W., Bolton, E. E., Brister, J. R., Canese, K., Chan, J., Comeau, D. C., et al. (2022). Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, D20–D26. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1112
Schacksen, P. S., Østergaard, S. K., Eskildsen, M. H., and Nielsen, J. L. (2024). Complete pipeline for Oxford Nanopore Technology amplicon sequencing (ONT-AmpSeq): from pre-processing to creating an operational taxonomic unit table. FEBS Open Bio 14, 1779–1787. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13868
Schmidt, T. T., Tyer, C., Rughani, P., Haggblom, C., Jones, J. R., Dai, X., et al. (2024). High resolution long-read telomere sequencing reveals dynamic mechanisms in aging and cancer. Nat. Commun. 15, 5149. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48917-7
Schroeder, A., Mueller, O., Stocker, S., Salowsky, R., Leiber, M., Gassmann, M., et al. (2006). The RIN: an RNA integrity number for assigning integrity values to RNA measurements. BMC Mol. Biol. 7, 3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-7-3
Schuele, L., Cassidy, H., Lizarazo, E., Strutzberg-Minder, K., Schuetze, S., Loebert, S., et al. (2020). Assessment of viral targeted sequence capture using nanopore sequencing directly from clinical samples. Viruses 12, 1358. doi: 10.3390/v12121358
Schulz, A., Sadeghi, B., Stoek, F., King, J., Fischer, K., Pohlmann, A., et al. (2022). Whole-genome sequencing of six neglected arboviruses circulating in Africa using sequence-independent single primer amplification (SISPA) and MinION Nanopore technologies. Pathogens 11, 1502. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11121502
Schurig, S., Ceruti, A., Wende, A., Lübcke, P., Eger, E., Schaufler, K., et al. (2024). Rapid identification of bacterial composition in wastewater by combining reverse purification nucleic acid extraction and nanopore sequencing. ACS ES&T Water 4, 1808–1818. doi: 10.1021/acsestwater.3c00794
Sedlazeck, F. J., Rescheneder, P., Smolka, M., Fang, H., Nattestad, M., Von Haeseler, A., et al. (2018). Accurate detection of complex structural variations using single-molecule sequencing. Nat. Methods 15, 461–468. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0001-7
Seemann, T. (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30, 2068–2069. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Sereika, M., Kirkegaard, R. H., Karst, S. M., Michaelsen, T. Y., Sørensen, E. A., Wollenberg, R. D., et al. (2022). Oxford Nanopore R10. 4 long-read sequencing enables the generation of near-finished bacterial genomes from pure cultures and metagenomes without short-read or reference polishing. Nat. Methods 19, 823–826. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01539-7
Shafin, K., Pesout, T., Chang, P.-C., Nattestad, M., Kolesnikov, A., Goel, S., et al. (2021). Haplotype-aware variant calling with PEPPER-Margin-DeepVariant enables high accuracy in nanopore long-reads. Nat. Methods 18, 1322–1332. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01299-w
Shaji, S., Selvaraj, R., and Shanmugasundaram, R. (2023). Salmonella infection in poultry: a review on the pathogen and control strategies. Microorganisms 11, 2814. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112814
Shaw, A. E., Lebani, K., González Gordon, L., Ihearahu, U. E., Wadsworth, J., Hicks, H. M., et al. (2025). Universal amplification and sequencing of foot-and-mouth disease virus complete genomes using nanopore technology. BMC Genomics 26, 770. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11938-7
Shelkamy, M. M. S., Hashish, A., Srednik, M. E., Gadu, E., Chaves, M., Macedo, N., et al. (2025). Eight complete and four draft genome sequences of nonpathogenic Avibacterium paragallinarum isolates from naive, healthy layer chickens in the USA. Microbiol. Resource Announcements. 14, e01334–e01324. doi: 10.1128/mra.01334-24
Shendure, J. and Ji, H. (2008). Next-generation DNA sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 1135–1145. doi: 10.1038/nbt1486
Shin, J. H. (2013). Nucleic acid extraction techniques. Advanced Techniques Diagn. Microbiol., 209–225. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-3970-7_11
Sholes, S. L., Karimian, K., Gershman, A., Kelly, T. J., Timp, W., Greider, C. W., et al. (2022). Chromosome-specific telomere lengths and the minimal functional telomere revealed by nanopore sequencing. Genome Res. 32, 616–628. doi: 10.1101/gr.275868.121
Socea, J. N., Stone, V. N., Qian, X., Gibbs, P. L., and Levinson, K. J. (2023). Implementing laboratory automation for next-generation sequencing: benefits and challenges for library preparation. Front. Public Health 11, 1195581. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1195581
Sović, I., Śikić, M., Wilm, A., Fenlon, S. N., Chen, S., and Nagarajan, N. (2016). Fast and sensitive mapping of nanopore sequencing reads with GraphMap. Nat. Commun. 7, 11307. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11307
Spatz, S. J., Garcia, M., Riblet, S., Ross, T. A., Volkening, J. D., Taylor, T. L., et al. (2019). MinION sequencing to genotype US strains of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Avian Pathol. 48, 255–269. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2019.1579298
Stevens, E. L., Carleton, H. A., Beal, J., Tillman, G. E., Lindsey, R. L., Lauer, A. C., et al. (2022). Use of whole genome sequencing by the federal interagency collaboration for genomics for food and feed safety in the United States. J. Food Prot. 85, 755–772. doi: 10.4315/JFP-21-437
Stokholm, N. M., Permin, A., Bisgaard, M., and Christensen, J. P. (2010). Causes of mortality in commercial organic layers in Denmark. Avian Dis. 54, 1241–1250. doi: 10.1637/9375-041910-Reg.1
Su, J., Zheng, Z., Ahmed, S. S., Lam, T.-W., and Luo, R. (2022). Clair3-trio: high-performance Nanopore long-read variant calling in family trios with trio-to-trio deep neural networks. Briefings Bioinf. 23, bbac301. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac301
Sun, K., Tian, C., Cao, M., Yu, X., Yin, C., and Ye, Z. (2022). Nanopore sequencing approach for variation detection of a live attenuated Newcastle disease virus vaccine. BioTechniques 72, 201–206. doi: 10.2144/btn-2022-0014
Sutton, K. M., Lahmers, K. K., Harris, S. P., Wijesena, H. R., Mote, B. E., Kachman, S. D., et al. (2019). Detection of atypical porcine pestivirus genome in newborn piglets affected by congenital tremor and high preweaning mortality. J. Anim. Sci. 97, 4093–4100. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz267
Tan, L., Guo, Z., Wang, X., Kim, D. Y., and Li, R. (2024). Utilization of nanopore direct RNA sequencing to analyze viral RNA modifications. mSystems 9, e0116323. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01163-23
Taylor, T. L., Volkening, J. D., DeJesus, E., Simmons, M., Dimitrov, K. M., Tillman, G. E., et al. (2019). Rapid, multiplexed, whole genome and plasmid sequencing of foodborne pathogens using long-read nanopore technology. Sci. Rep. 9, 16350. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52424-x
Technologies, C.T.D.O.N. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/document/chemistry-technical-document (Accessed April 14, 2025).
Technologies, M.O.N. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/document/minknow-tech-doc (Accessed April 14, 2025).
Technologies, M.O.N. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/document/experiment-companion-minknow (Accessed April 14, 2025).
Technologies, O.N Input DNA/RNA QC. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/document/input-dna-rna-qc (Accessed October 23, 2025).
Technologies, O.N Dual-barcoding. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/document/ligation-sequencing-dual-barcoding-v14 (Accessed April 13, 2025).
Technologies, O.N Convert FAST5 files to POD5. Available online at: https://pod5.nanoporetech.com/ (Accessed June 17, 2025).
Technologies, O.N Automated preparation for streamlined answers. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/products/prepare/automated-library-prep (Accessed October 23, 2025).
Technologies, O.N (2025). Elysion. Available online at: https://nanoporetech.com/products/prepare/automation-solutions/elysion (Accessed October 23, 2025).
Tešović, B., Nišavić, J., Banović Đeri, B., Petrović, T., Radalj, A., Šekler, M., et al. (2023). Development of multiplex PCR based NGS protocol for whole genome sequencing of West Nile virus lineage 2 directly from biological samples using Oxford Nanopore platform. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 105, 115852. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2022.115852
Tham, C. Y., Tirado-Magallanes, R., Goh, Y., Fullwood, M. J., Koh, B. T. H., Wang, W., et al. (2020). NanoVar: accurate characterization of patients’ genomic structural variants using low-depth nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol. 21, 1–15. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-01968-7
Theuns, S., Vanmechelen, B., Bernaert, Q., Deboutte, W., Vandenhole, M., Beller, L., et al. (2018). Nanopore sequencing as a revolutionary diagnostic tool for porcine viral enteric disease complexes identifies porcine kobuvirus as an important enteric virus. Sci. Rep. 8, 9830. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28180-9
Thøfner, I. and Christensen, J.-P. (2021). “Bacterial diseases in poultry,” in Advancements and technologies in pig and poultry bacterial disease control (Elsevier), 199–227.
Thomas, C., Methner, U., Marz, M., and Linde, J. (2023). Oxford nanopore technologies-a valuable tool to generate whole-genome sequencing data for. Front. Vet. Sci. 10, 1178922. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1178922
Thormann, A., Halachev, M., McLaren, W., Moore, D. J., Svinti, V., Campbell, A., et al. (2019). Flexible and scalable diagnostic filtering of genomic variants using G2P with Ensembl VEP. Nat. Commun. 10, 2373. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10016-3
Toh, X., Wang, Y., Rajapakse, M. P., Lee, B., Songkasupa, T., Suwankitwat, N., et al. (2022). Use of nanopore sequencing to characterize african horse sickness virus (AHSV) from the African horse sickness outbreak in Thailand in 2020. Transboundary emerging Dis. 69, 1010–1019. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14056
Trigodet, F., Lolans, K., Fogarty, E., Shaiber, A., Morrison, H. G., Barreiro, L., et al. (2022). High molecular weight DNA extraction strategies for long-read sequencing of complex metagenomes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 22, 1786–1802. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13588
Ulrich, J.-U., Lutfi, A., Rutzen, K., and Renard, B. Y. (2022). ReadBouncer: precise and scalable adaptive sampling for nanopore sequencing. Bioinformatics 38, i153–i160. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac223
Ultima_Genomics (2022). Ultima Genomics Delivers the $100 Genome. Available online at: https://www.ultimagenomics.com/blog/ultima-genomics-delivers-usd100-genome/ (Accessed February 7, 2025).
Usui, M., Akiyoshi, M., Fukuda, A., Iwano, H., and Kato, T. (2023). 16S rRNA nanopore sequencing for rapid diagnosis of causative bacteria in bovine mastitis. Res. Veterinary Sci. 161, 45–49. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2023.06.006
van Dijk, E. L., Auger, H., Jaszczyszyn, Y., and Thermes, C. (2014). Ten years of next-generation sequencing technology. Trends Genet. 30, 418–426. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.07.001
Van Dijk, E. L., Jaszczyszyn, Y., Naquin, D., and Thermes, C. (2018). The third revolution in sequencing technology. Trends Genet. 34, 666–681. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.05.008
van Dijk, E. L., Naquin, D., Gorrichon, K., Jaszczyszyn, Y., Ouazahrou, R., Thermes, C., et al. (2023). Genomics in the long-read sequencing era. Trends Genet. 39, 649–671. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2023.04.006
Vanmechelen, B., Meurs, S., Horemans, M., Loosen, A., Joly Maes, T., Laenen, L., et al. (2022). The characterization of multiple novel paramyxoviruses highlights the diverse nature of the subfamily Orthoparamyxovirinae. Virus Evol. 8, veac061. doi: 10.1093/ve/veac061
Vaser, R. and Šikić, M. (2021). Time-and memory-efficient genome assembly with Raven. Nat. Comput. Sci. 1, 332–336. doi: 10.1038/s43588-021-00073-4
Vibin, J., Chamings, A., Klaassen, M., Bhatta, T. R., and Alexandersen, S. (2020). Metagenomic characterisation of avian parvoviruses and picornaviruses from Australian wild ducks. Sci. Rep. 10, 12800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69557-z
Viehweger, A., Krautwurst, S., Lamkiewicz, K., Madhugiri, R., Ziebuhr, J., Holzer, M., et al. (2019). Direct RNA nanopore sequencing of full-length coronavirus genomes provides novel insights into structural variants and enables modification analysis. Genome Res. 29, 1545–1554. doi: 10.1101/gr.247064.118
Viñes, J., Cuscó, A., and Francino, O. (2020). Hybrid assembly from a pathogenic methicillin-and multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strain Isolated from a case of canine otitis in Spain. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 9. doi: 10.1128/mra.01121-19
Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Bollas, A., Wang, Y., and Au, K. F. (2021). Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 39, 1348–1365. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01108-x
Wang, K., Wang, S., Ji, X., Chen, D., Shen, Q., Yu, Y., et al. (2023). Epigenome-wide association studies of meat traits in Chinese Yorkshire pigs highlights several DNA methylation loci and genes. Front. Genet. 13, 1028711. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1028711
Wang, J., Yang, L., Cheng, A., Tham, C. Y., Tan, W., Darmawan, J., et al. (2024). Direct RNA sequencing coupled with adaptive sampling enriches RNAs of interest in the transcriptome. Nat. Commun. 15, 481. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44656-3
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M., and Snyder, M. (2009). RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 57–63. doi: 10.1038/nrg2484
Wang, K., Li, M., and Hakonarson, H. (2010). ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, e164–e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq603
Warburton, P. E. and Sebra, R. P. (2023). Long-read DNA sequencing: recent advances and remaining challenges. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 24, 109–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-101722-103045
Weigl, S., Dabernig-Heinz, J., Granitz, F., Lipp, M., Ostermann, L., Harmsen, D., et al. (2025). Improving Nanopore sequencing-based core genome MLST for global infection control: a strategy for GC-rich pathogens like Burkholderia pseudomallei. J. Clin. Microbiol. 63, e01569–e01524. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01569-24
Wenger, A. M., Peluso, P., Rowell, W. J., Chang, P.-C., Hall, R. J., Concepcion, G. T., et al. (2019). Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1155–1162. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0217-9
Wheeler, D. A., Srinivasan, M., Egholm, M., Shen, Y., Chen, L., McGuire, A., et al. (2008). The complete genome of an individual by massively parallel DNA sequencing. Nature 452, 872–876. doi: 10.1038/nature06884
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L., and Holt, K. E. (2017). Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PloS Comput. Biol. 13, e1005595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595
Wick, R. R. (2021). Trycycler: consensus long-read assemblies for bacterial genomes. Genome Biol. 22, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02483-z
Wick, R. R. and Holt, K. E. (2021). Benchmarking of long-read assemblers for prokaryote whole genome sequencing. F1000Research 8, 2138. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.21782.4
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., and Holt, K. E. (2023). Assembling the perfect bacterial genome using Oxford Nanopore and Illumina sequencing. PloS Comput. Biol. 19, e1010905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010905
Wilm, A., Aw, P. P. K., Bertrand, D., Yeo, G. H. T., Ong, S. H., Wong, C. H., et al. (2012). LoFreq: a sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 11189–11201. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks918
Wingett, S. W. and Andrews, S. (2018). FastQ Screen: A tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control. F1000Research 7, 1338. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.15931.2
Wolff, J., Abd El Rahman, S., King, J., El-Beskawy, M., Pohlmann, A., Beer, M., et al. (2020). Establishment of a challenge model for sheeppox virus infection. Microorganisms 8, 2001. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8122001
Wongsurawat, T., Jenjaroenpun, P., Taylor, M. K., Lee, J., Tolardo, A. L., Parvathareddy, J., et al. (2019). Rapid sequencing of multiple RNA viruses in their native form. Front. Microbiol. 10, 260. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00260
Wood, D. E., Lu, J., and Langmead, B. (2019). Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 20, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1891-0
Wu, Z., Li, M., Qu, L., Zhang, C., and Xie, W. (2024). Metagenomic insights into microbial adaptation to the salinity gradient of a typical short residence-time estuary. Microbiome 12, 115. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01817-w
Wu, Z., Sahin, O., and Zhang, Q. (2021). Complete genome sequence of campylobacter hepaticus USA52, associated with chicken spotty liver disease. Microbiol. Resource Announcements 10. doi: 10.1128/mra.01266-20
Xu, Y., Lewandowski, K., Lumley, S., Pullan, S., Vipond, R., Carroll, M., et al. (2018). Detection of viral pathogens with multiplex nanopore MinION sequencing: be careful with cross-talk. Front. Microbiol. 9, 2225. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02225
Xu, L., Berninger, A., Lakin, S. M., O'Donnell, V., Pierce, J. L., Pauszek, S. J., et al. (2024). Direct RNA sequencing of foot-and-mouth disease virus genome using a flongle on minION. Bio Protoc. 14, e5017. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5017
Yang, X., Zhang, T., Lei, C.-W., Wang, Q., Huang, Z., Chen, X., et al. (2022). Florfenicol and oxazolidone resistance status in livestock farms revealed by short-and long-read metagenomic sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 13, 1018901. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1018901
Yinda, C. K., Seifert, S. N., Macmenamin, P., van Doremalen, N., Kim, L., Bushmaker, T., et al. (2020). A novel field-deployable method for sequencing and analyses of henipavirus genomes from complex samples on the minION platform. J. Infect. Dis. 221, S383–s388. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz576
Yip, C. C.-Y., Chan, W.-M., Ip, J. D., Seng, C. W.-M., Leung, K.-H., Poon, R. W.-S., et al. (2020). Nanopore sequencing reveals novel targets for detection and surveillance of human and avian influenza A viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 58. doi: 10.1128/jcm.02127-19
Young, K. T., Lahmers, K. K., Sellers, H. S., Stallknecht, D. E., Poulson, R. L., Saliki, J. T., et al. (2021). Randomly primed, strand-switching, MinION-based sequencing for the detection and characterization of cultured RNA viruses. J. Veterinary Diagn. Invest. 33, 202–215. doi: 10.1177/1040638720981019
Young, K. T., Stephens, J. Q., Poulson, R. L., Stallknecht, D. E., Dimitrov, K. M., Butt, S. L., et al. (2022). Putative novel avian paramyxovirus (AMPV) and reidentification of APMV-2 and APMV-6 to the species level based on wild bird surveillance (United States, 2016–2018). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 88, e00466–e00422. doi: 10.1128/aem.00466-22
Zeng, H.-X., Zu, W.-H., Wang, H.-Y., Yuan, J., Cheng, L. L., Xu, G., et al. (2024). The intra-host evolution of SARS-CoV-2 after neutralizing antibody therapy, revealed by nanopore sequencing. Zoonoses 4, 992. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2023-0032
Zhang, M., Huang, Y., Godson, D. L., Fernando, C., Alexander, T. W., and Hill, J. E. (2020). Assessment of metagenomic sequencing and qPCR for detection of influenza D virus in bovine respiratory tract samples. Viruses 12, 814. doi: 10.3390/v12080814
Zhang, L., Chen, F., Zeng, Z., Xu, M., Sun, F., Yang, L., et al. (2021). Nanopore-based direct RNA-sequencing reveals a high-resolution transcriptional landscape of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Viruses 13, 2531. doi: 10.3390/v13122531
Zhang, R., Wang, P., Ma, X., Wu, Y., Luo, C., Qiu, L., et al. (2021). Advances in metagenomics and its application in environmental microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 12, 766364. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.766364
Zhang, L., Chen, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Lv, Q., Kong, D., et al. (2022). Comparison analysis of different DNA extraction methods on suitability for long-read metagenomic nanopore sequencing. Front. Cell. Infection Microbiol. 12, 919903. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.919903
Zhang, Z., Yang, C., Veldsman, W. P., Fang, X., and Zhang, L. (2023). Benchmarking genome assembly methods on metagenomic sequencing data. Briefings Bioinf. 24, bbad087. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad087
Zhang, J.-Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Guo, F., Yun, Q., Zeng, T., et al. (2024). A single-molecule nanopore sequencing platform. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.19.608720
Zhao, G., Krishnamurthy, S., Cai, Z., Popov, V. L., Travassos da Rosa, A. P., Guzman, H., et al. (2013). Identification of novel viruses using VirusHunter–an automated data analysis pipeline. PLoS One 8, e78470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078470
Keywords: nanopore, NGS, sequencing, Oxford nanopore technologies, veterinary medicine, diagnostics, clinical applications and challenges, infectious diseases
Citation: Chaves M, Hashish A, Goraichuk IV, Casserta LC, Mears MC, Gadu E, Bakre A, Alexander Morris ER, Shelkamy MMS, Nadendla S, Perez DR and El-Gazzar M (2025) Nanopore sequencing in veterinary medicine: from concepts to clinical applications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1701570. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1701570
Received: 08 September 2025; Accepted: 27 October 2025;
Published: 18 November 2025.
Edited by:
Rebecca P. Wilkes, University of Kentucky, United StatesReviewed by:
Tirth Uprety, University of Kentucky, United StatesBrianna Stenger, North Dakota State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Chaves, Hashish, Goraichuk, Casserta, Mears, Gadu, Bakre, Alexander Morris, Shelkamy, Nadendla, Perez and El-Gazzar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maria Chaves, bXBlaXhvdG9AaWFzdGF0ZS5lZHU=; Amro Hashish, YW1yby5oYXNoaXNoX3BzZ0B2ZXQuc3Vlei5lZHUuZWc=; Iryna V. Goraichuk, Z29yYWljaHVrQG91dGxvb2suY29t
 Maria Chaves
Maria Chaves Amro Hashish
Amro Hashish Iryna V. Goraichuk
Iryna V. Goraichuk Leonardo Cardia Casserta
Leonardo Cardia Casserta Megan C. Mears3
Megan C. Mears3 Eman Gadu
Eman Gadu Abhijeet Bakre
Abhijeet Bakre Ellen Ruth Alexander Morris
Ellen Ruth Alexander Morris Daniel R. Perez
Daniel R. Perez Mohamed El-Gazzar
Mohamed El-Gazzar