- 1Center for Animal Disease Control and Prevention in Xiangcheng, Xiangcheng, Sichuan, China
- 2State Key Laboratory for Animal Disease Control and Prevention, Harbin Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Harbin, China
- 3Agriculture, Animal Husbandry, Rural and Science and Technology Bureau of Xiangcheng, Xiangcheng, Sichuan, China
This study developed a rapid, sensitive, and specific TaqMan MGB based qPCR assay for detecting Lawsonia intracellularis in Tibetan pigs by targeting the aspA gene. The method showed no cross-reactivity with other common porcine enteric pathogens, and exhibited high sensitivity (detection limit: 7.056 copies/μL) and excellent repeatability (CV < 2%). A standard curve with good linearity (R² = 0.998) and 110.95% amplification efficiency was established. The assay was applied to 237 fecal samples collected from Tibetan pigs across eight townships in Xiangcheng County, Sichuan Province, in parallel with a national standard method. Results indicated a 19% overall positivity rate (45/237), with regional rates ranging from 11.11% to 26.67%. The established qPCR provides a reliable tool for field surveillance, and findings underscore the need to integrate L. intracellularis monitoring into local prevention systems to support healthy Tibetan pig production.
1 Introduction
Porcine proliferative enteropathy (PPE), also known as porcine ileitis, is an important intestinal infectious disease caused by Lawsonia intracellularis (L. intracellularis) (Campillo et al., 2021). The clinical manifestations can be divided into three forms: acute, chronic, and subclinical. The acute form, primarily seen in pigs aged 4–12 months, is characterized by hemorrhagic proliferative enteritis with clinical signs including bloody diarrhea, tarry feces, and even sudden death (Obradovic and Wilson, 2020). The chronic form, often occurring in growing pigs aged 6–20 weeks and referred to as porcine intestinal adenomatosis, presents with intermittent diarrhea, reduced appetite, growth retardation, and decreased herd uniformity (Obradovic and Wilson, 2020). The subclinical form, which is the most common, typically shows no obvious symptoms but still leads to reduced growth performance and economic losses (Campillo et al., 2021). It is estimated that feed cost increases by $2–20 per infected pig, posing a substantial economic burden on the global pig industry (Mcorist et al., 1997). For instance, annual losses in the United States and the United Kingdom reach approximately $20 million and £2–4 million, respectively (Mcorist et al., 1997).
L. intracellularis is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, obligate intracellular bacterium (Xiao et al., 2022). The bacilli are curved or straight rods measuring approximately 1.25–1.75 μm in length and 0.25–0.43 μm in width, and do not form spores. This bacterium cannot be cultured on conventional media and requires eukaryotic cell lines (e.g., IEC-18, IPEC-J2) for in vitro propagation (Xie et al., 2025). Its isolation and maintenance are technically challenging, leading to relatively underdeveloped detection methods and somewhat limiting in-depth research. Serological and molecular surveys indicate that L. intracellularis infection is highly prevalent in pig farms worldwide. As the world’s largest producer of pigs and pork, China also shows a high infection rate, with some reports even exceeding 90% (Wang et al., 2024). However, epidemiological data in specific local pig breeds—particularly Tibetan pigs—remain scarce.
Xiangcheng County in Ganzi Prefecture, Sichuan Province, is located in a high-altitude mountainous region. Its local breed, the Xiangcheng Tibetan pig, is well-adapted to high-altitude environments, resistant to rough feeding, and known for excellent meat quality, making it an important genetic resource and a distinctive local industry (Yang et al., 2024). Yet, the health status of this herd is largely unknown, and no information is available on L. intracellularis infection. This complete absence of data, coupled with the known economic impact of PPE, underscores the critical necessity for a reliable detection method to facilitate timely and accurate diagnosis and effective intervention. Thus, we established a qPCR assay for L. intracellularis and applied it to fecal samples from Tibetan pig farms across eight townships in Xiangcheng County to investigate the local prevalence. Our results fill a key knowledge gap and offer a practical tool for early detection and control of L. intracellularis in this important pig breed, which is crucial for mitigating economic losses and ensuring sustainable production.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Nucleic acids and clinical samples
Nucleic acids of L. intracellularis, Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC), Salmonella Choleraesuis, Pasteurella multocida, Clostridium perfringens, Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), Transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV), Porcine group A rotavirus (PoRVA), and Porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) were preserved in our laboratory. A total of 237 fecal samples from Tibetan pigs were collected from eight townships in Xiangcheng County, Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province, including Ranwu Township (n = 30), Shuiwa Township (n = 22), Reda Town (n = 18), Zhengdou Township (n = 20), Baiyi Township (n = 30), Shagong Standard Farm (n = 50), Xiangbala Town (n = 30), and Qingde Town (n = 37). A total of 237 fecal samples of healthy Tibetan pigs were collected from some farms in Xiangcheng County, Garze Prefecture. It is imperative to underscore that no additional harm or intervention was imposed on the animals involved in this study. The Institutional Review Board of the Harbin Veterinary Research Institute has determined that this study is exempt from the requirement for ethical review or approval.
2.2 Primer design
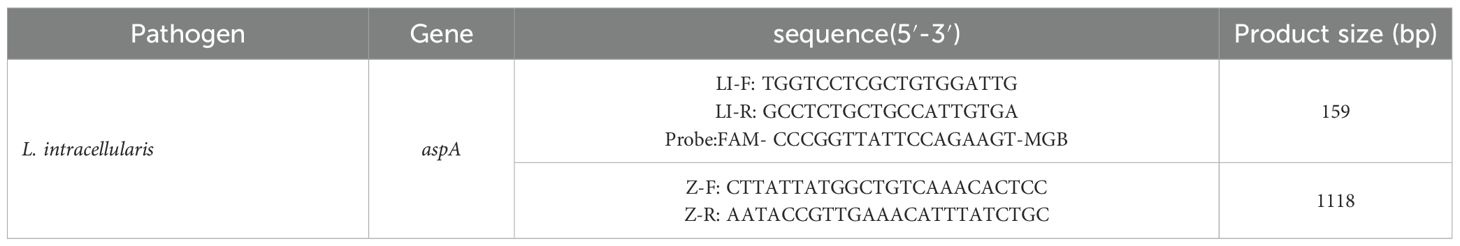
Based on the aspA gene of L. intracellularis (GenBank ID: CP107054.1), primers and a probe for qPCR, as well as primers for constructing the recombinant plasmid standard, were designed using Primer Express 3.0.1 and Primer Premier 5 software (Table 1). All primers and the probe were synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. and working concentrations were diluted to 10 μM. The 1118 bp fragment used to construct the recombinant plasmid standard fully contains the 159 bp qPCR target region.
2.3 Construction of recombinant plasmid standard
The recombinant plasmid standard was constructed by amplifying the target gene from L. intracellularis using primers Z-F/Z-R. The PCR product was purified, cloned into pMD19-T vector, and transformed into E. coli DH5α. After sequencing verification, positive clones were cultured and the plasmid was extracted. Determination of plasmid concentration using Nanodrop. The copy number was determined spectrophotometrically and calculated using the formula:Copies/µL = (6.02 × 10²³) × (concentration in ng/µL × 10⁻9)/(plasmid length in bp × 660) (Tian et al., 2025).
2.4 Optimization of qPCR conditions
The qPCR assay was optimized using a single-variable approach for primer concentration, probe concentration, annealing temperature, and cycle number. The reaction mixture consisted of: 10 μL of 2× TaqMan Fast qPCR Master Mix, 0.1–0.6 μM each of LI-F and LI-R primers, 0.1–0.6 μM probe, 2 μL of template DNA, and nuclease-free water added to a final volume of 20 μL. The thermal cycling conditions were as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, followed by 35–50 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 s and combined annealing/extension at 58–63°C for 30 s.
2.5 Assay validation
The specificity of the qPCR assay was confirmed using genomic DNA or cDNA from common swine enteric pathogens, including EPEC, Salmonella Choleraesuis, Pasteurella multocida, Clostridium perfringens, PEDV, TGEV, PoRVA, and PDCoV. L. intracellularis nucleic acid and nuclease-free water were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. For sensitivity evaluation, a standard curve was generated using 10-fold serial dilutions of the recombinant plasmid standard (from 0.5×107 to 0.5 copies/μL), with each dilution tested in triplicate. The limit of detection (LOD) was determined by probit regression analysis (IBM SPSS Statistics 25) at 95% confidence level using 40 replicates of low-copy samples (ranging from 100 to 3.125 copies/μL) (Tian et al., 2025). Repeatability was assessed through intra- and inter-assay tests using standards at 107, 105, and 10³ copies/μL, with results expressed as mean Ct and coefficient of variation (CV).
2.6 Clinical sample testing
Genomic DNA was extracted from 237 Tibetan pig fecal samples using an automated nucleic acid extraction system. Both the newly developed qPCR assay and the method specified in the Chinese industry standard SN/T 3488-2013 (using primers and probe for Lawsonia intracellularis detection) were applied in parallel to evaluate the accuracy of the established assay (Quarantine protocol for real-time PCR of Lawsona intracellularis). Additionally, the prevalence of L. intracellularis across different townships in Xiangcheng County was investigated.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Optimization of qPCR conditions
To improve amplification efficiency, key parameters including primer/probe concentration, annealing temperature, and cycle number were optimized using a single-variable approach. Optimal results were achieved with 0.3 μM primers, 0.2 μM probe, and an annealing temperature of 59°C, yielding low Ct values and high efficiency. Cycle number optimization revealed that 35 cycles resulted in insufficient amplification, whereas more than 40 cycles led to non-specific amplification and an elevated background. Therefore, 40 cycles were selected for subsequent experiments.
3.2 Specificity validation
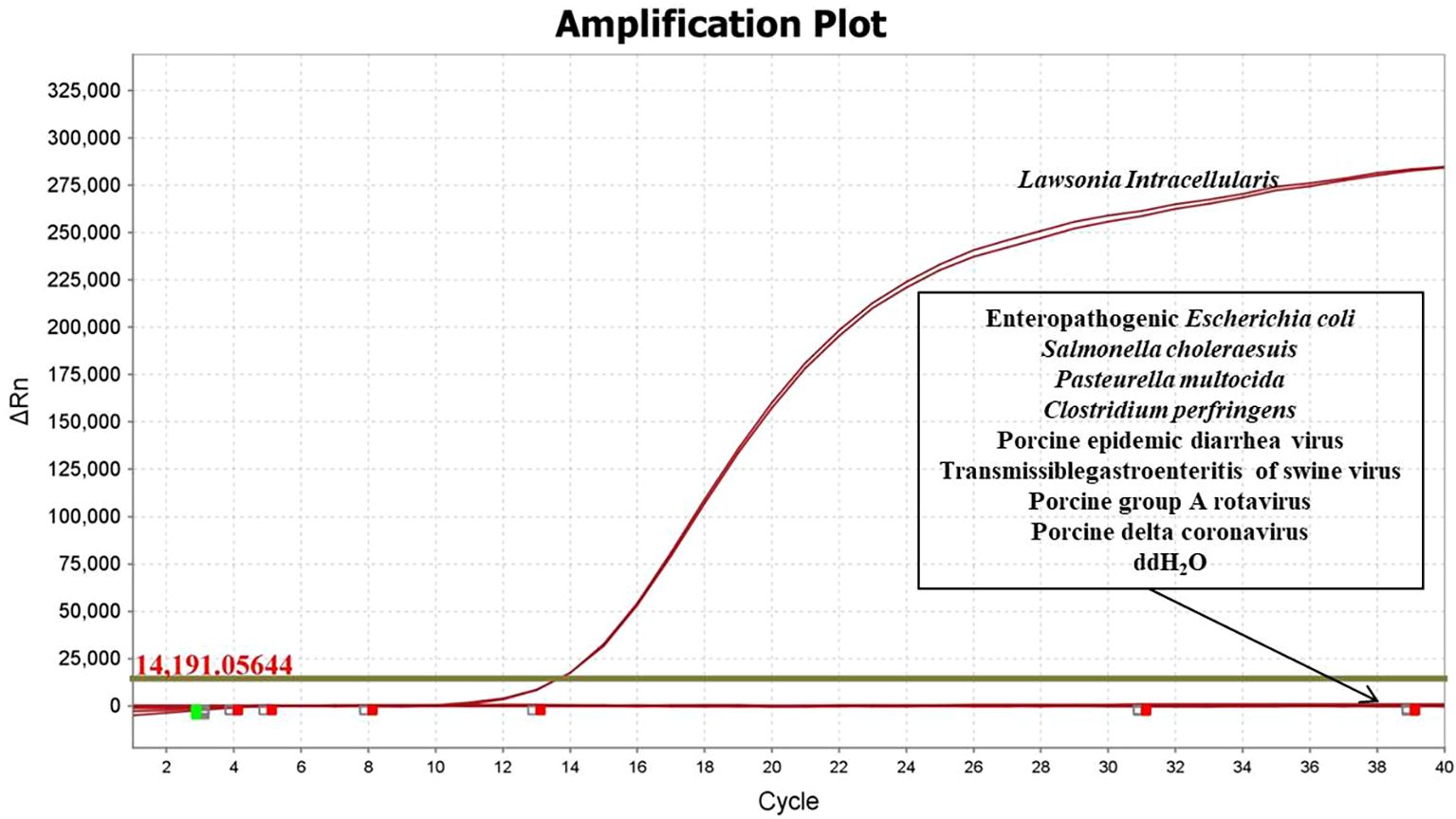
The specificity of the developed qPCR assay was evaluated using DNA/cDNA from EPEC, Salmonella Choleraesuis, Pasteurella multocida, Clostridium perfringens, PEDV, TGEV, PoRVA, and PDCoV. The results demonstrated that amplification occurred only in the presence of L. intracellularis nucleic acid, with no cross-reactivity observed with any of the other tested pathogens (Figure 1), confirming high specificity of the assay.
3.3 Standard curve
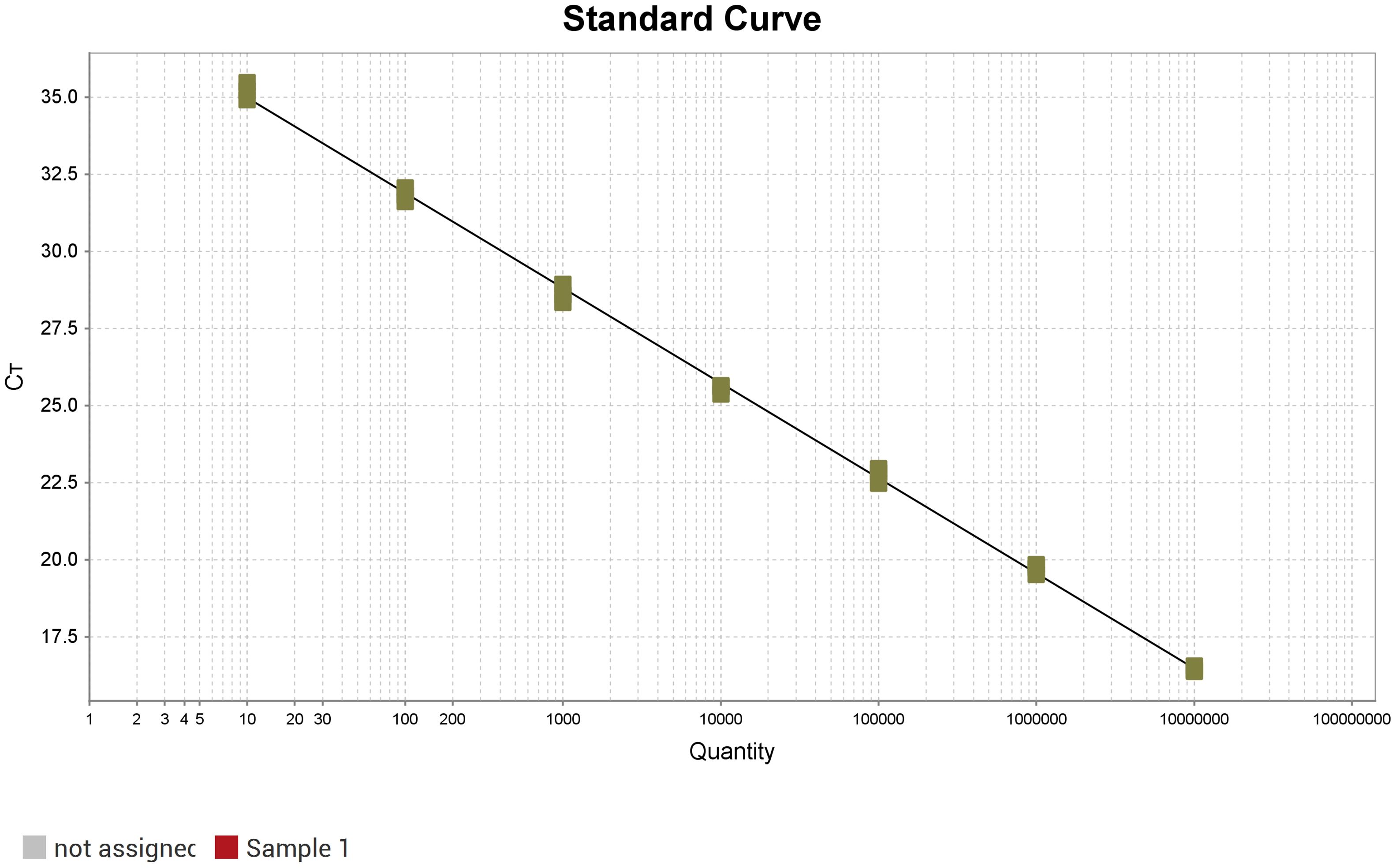
A standard curve was generated using 10-fold serial dilutions of the recombinant plasmid, ranging from 0.5×107 to 0.5 copies/μL. The plasmid copy number (X-axis) and Ct values (Y-axis) were plotted using QuantStudio™ Design & Analysis Software v1.3.1. The assay demonstrated excellent linearity (R² = 0.998) and high amplification efficiency (110.95%), with a linear regression equation of Y = –3.085log(X) + 38.07 (Figure 2).
3.4 Sensitivity and limit of detection
The sensitivity of the fluorescence qPCR assay was evaluated by testing serial dilutions of the recombinant plasmid standard. The results indicated that the method could reliably detect as low as 10 copies (Figure 3A). Determine the approximate range of sensitivity through gradient dilution detection. To determine the limit of detection (LOD), gradients ranging from 100 to 3.125 copies/μL were tested with 40 replicates each. Probit regression analysis (IBM SPSS Statistics 25) established the LOD at 7.056 copies/μL (95% CI: 6.541–7.995) (Figure 3B), with detailed average Ct values and detection rates shown in Table 2. The assay was considered valid when positive controls produced typical amplification curves and negative controls showed no amplification (Ct = 40 or undetermined). A sample was determined positive for L. intracellularis if the FAM channel exhibited a typical amplification curve with a Ct value ≤ 35.4. Samples with Ct values between 35.4 and 40 were considered suspected positives and were retested with a doubled template volume. A sample was confirmed positive if the Ct value in the retest was below the threshold; otherwise, it was deemed negative. Samples with no amplification in the FAM channel (Ct = 40 or undetermined) were classified as negative for L. intracellularis.
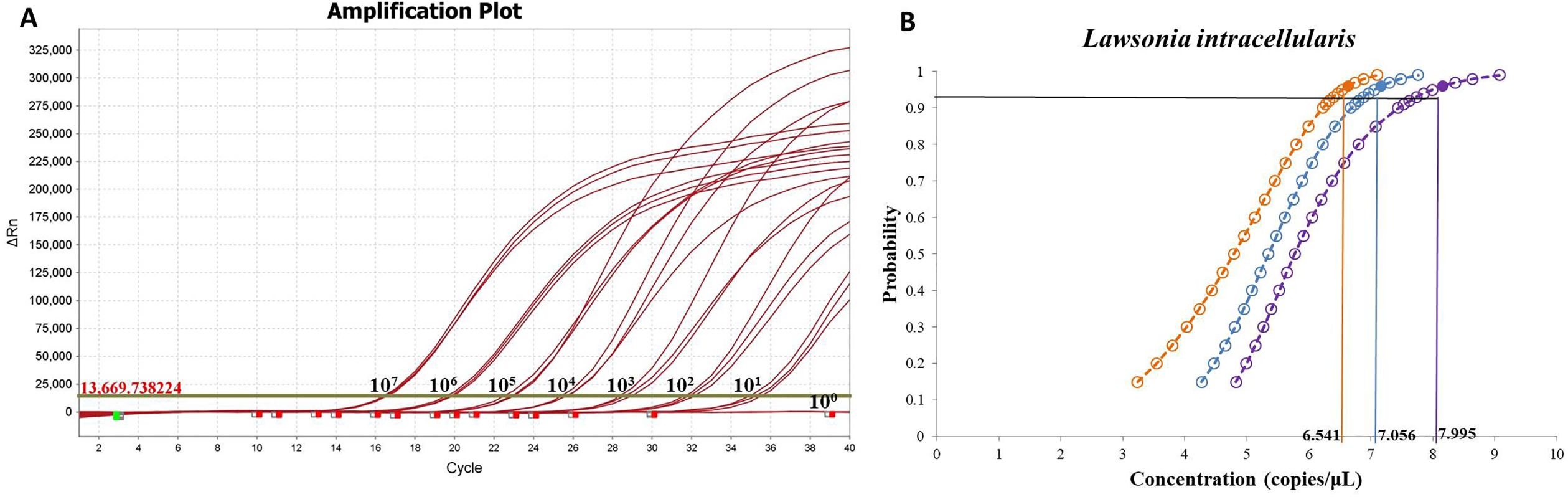
Figure 3. Sensitivity and limit of detection of fluorescence qPCR method for L. intracellularis. (A) Detection of plasmid standards from 107 to 100 copies using fluorescence quantitative PCR method; (B) Probability regression analysis of fluorescence qPCR.
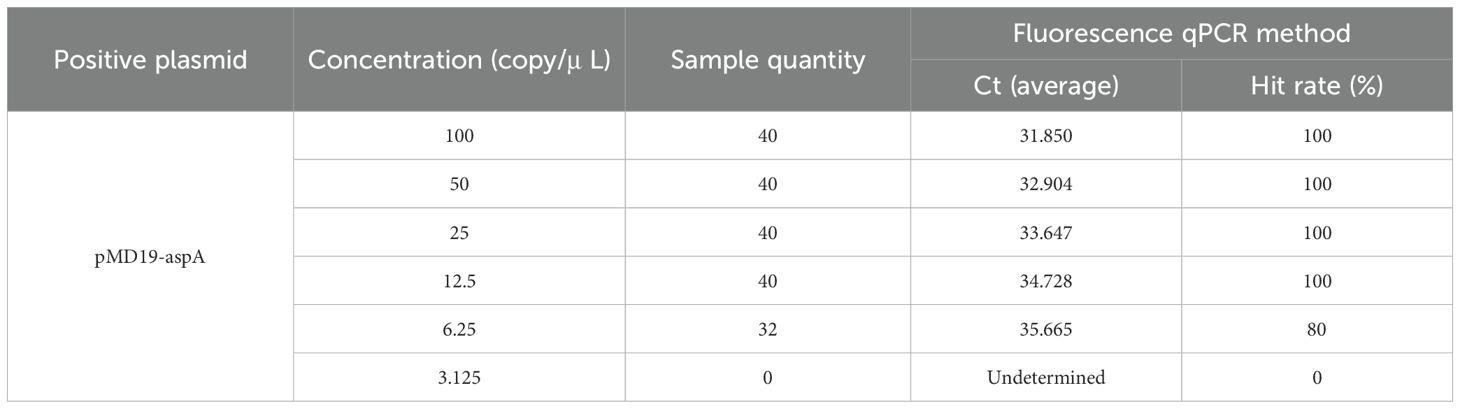
Table 2. shows the average Ct values and hit rates for the detection of continuously diluted plasmid standards.
3.5 Repeatability
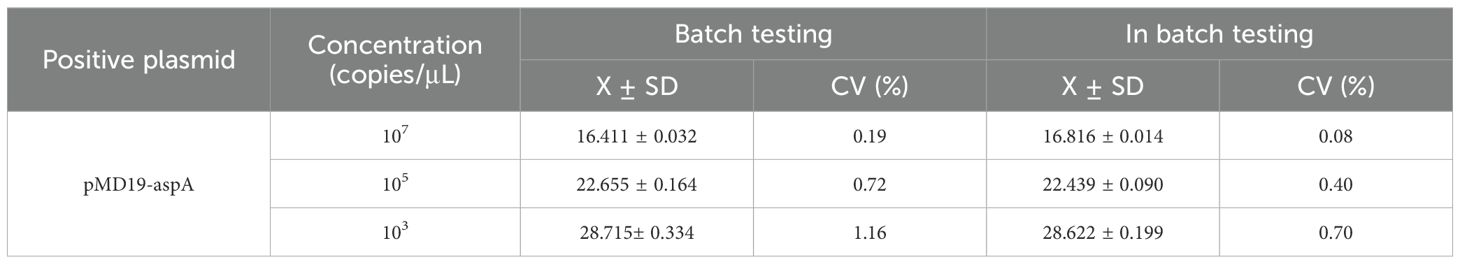
To evaluate the reproducibility of the assay, intra- and inter-assay tests were performed using plasmid standards at concentrations of 107, 105, and 10³ copies/μL. The coefficients of variation (CV) for both intra- and inter-assay replicates were below 2% (Table 3), demonstrating high repeatability and stability of the established fluorescence qPCR method.
3.6 Sample testing results
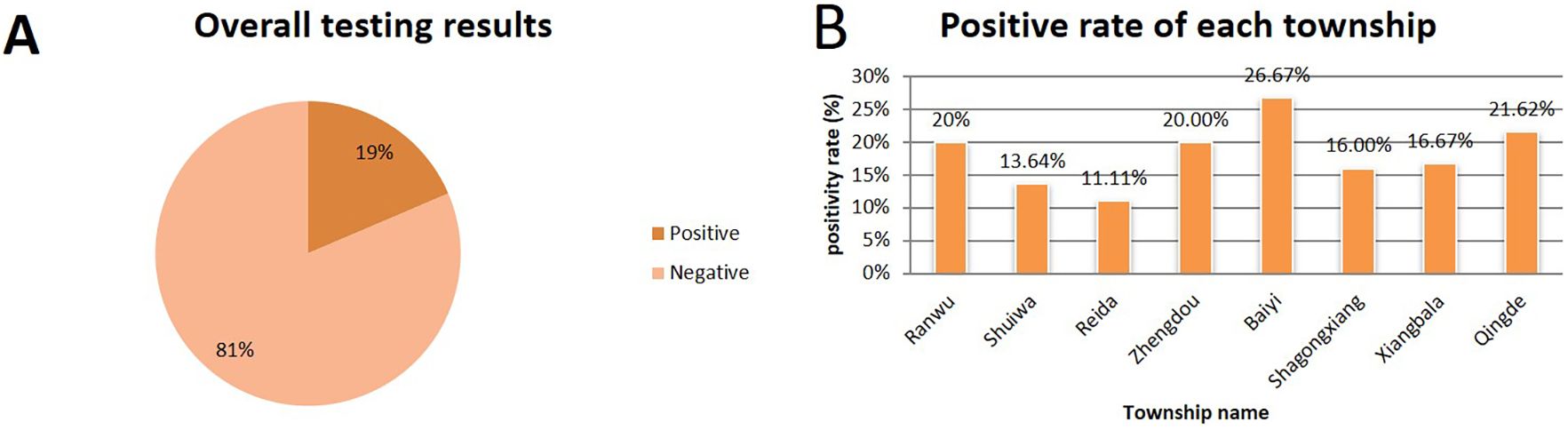
To evaluate the clinical applicability of the established method and investigate the prevalence of L. intracellularis in Tibetan pig farms across Xiangcheng County, Ganzi Prefecture, a total of 237 fecal samples were tested using both the newly developed qPCR assay and a previously published standard method. The results showed an overall positivity rate of 19% and a negativity rate of 81% (Figure 4A). The positivity rates in Ranwu Township, Shuiwa Township, Reda Town, Zhengdou Township, Baiyi Township, Shagong Standard Farm, Xiangbala Town, and Qingde Town were 20%, 13.64%, 11.11%, 20.00%, 26.67%, 16.00%, 16.67%, and 21.62%, respectively (Figure 4B). The detection results of these two methods have a 100% agreement rate.
4 Discussion
Porcine proliferative enteropathy (PPE), caused by Lawsonia intracellularis, is a globally significant infectious intestinal disease associated with substantial economic losses in the swine industry (Wang et al., 2024). This study developed a TaqMan-based qPCR assay targeting the aspA gene of L. intracellularis and conducted the first molecular epidemiological investigation of this pathogen in Tibetan pigs from Xiangcheng County, Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province.
The established fluorescence qPCR method demonstrated excellent performance, including high specificity with no cross-reactivity with other common swine enteric pathogens, high sensitivity with a detection limit of 7.056 copies/μL (95% CI: 6.541–7.995), a wide linear range (107 to 10¹ copies/μL) with good linear correlation (R² = 0.998), and high repeatability with both intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation below 2%. Compared with the current industry standard method (SN/T 3488-2013), the developed assay showed improved sensitivity and stability while maintaining high consistency, making it suitable for application in basic laboratories.
Epidemiological investigation revealed an overall positivity rate of 19% (45/237) in Tibetan pigs from Xiangcheng County, indicating a certain degree of endemicity. Positivity rates varied among townships, ranging from 11.11% (Reda Town) to 26.67% (Baiyi Township). This rate is lower than many reports from commercial pig herds domestically and internationally. For example, Wang et al. reported a fecal positivity rate of 37.3% (95% CI: 34.1–40.5%) and a farm-level positivity rate of 93.6% (95% CI: 65.3–94.4%) using qPCR (Wang et al., 2024). Notably, the highest positivity rate (26.67%) was observed in Baiyi Township, where samples were collected from a local intensive farm. In contrast, the lower rates in other townships were associated with free-range or backyard farming practices. This striking disparity strongly suggests that the discrepancy in overall prevalence may reflect the unique characteristics of Tibetan pigs as a local breed, which are typically raised under low-density free-range or semi-intensive systems in high-altitude regions, resulting in reduced pathogen exposure and transmission pressure. The intensive farming conditions in Baiyi Township, characterized by higher animal density, likely facilitated fecal-oral transmission of L. intracellularis, aligning it more closely with the epidemiological patterns observed in commercial herds (Wang et al., 2024). Although the overall infection rate was not high, positive samples were detected in all surveyed townships, indicating that L. intracellularis is widely present in the local Tibetan pig farming environment. Subclinical infections are common in PPE and can lead to reduced feed efficiency and impaired growth performance even in the absence of obvious diarrheal symptoms (Wang et al., 2024; Hu et al., 2025). Therefore, although no large-scale outbreaks have been reported in Xiangcheng Tibetan pigs, the potential economic losses should not be overlooked, especially as farming practices shift toward standardization and intensification, which may increase infection pressure. Continuous monitoring and integration into routine disease prevention systems are necessary. This study has several limitations. The sample size was relatively small (n = 237) and collected during a single time period, which may not reflect seasonal dynamics or age-related differences. Additionally, the lack of bacterial isolation prevented genetic characterization of local strains.
Regarding the qPCR assay used in this study, the calculated amplification efficiency was 110.95%, which is slightly above the ideal range of 90-110%. This elevated efficiency is most likely attributable to minor inaccuracies during the serial dilution of the standard DNA for the standard curve. Such technical variations, including pipetting errors or slight inaccuracies in the initial DNA quantification, are common and can lead to a miscalculation of the slope, thereby yielding an efficiency value marginally above 110%. Despite this, the high coefficient of determination (R² > 0.99) of the standard curve confirms excellent linearity, and the distinct separation between positive and negative results validates the reliability of our data for qualitative prevalence assessment.
In conclusion, a highly sensitive, specific, and reproducible fluorescence qPCR method was successfully established for the rapid detection and quantification of L. intracellularis. This study provides the first systematic insight into the prevalence and distribution of L. intracellularis in Tibetan pigs from Xiangcheng County, offering critical scientific evidence and epidemiological data to support early monitoring, precise prevention and control, and health management of this pathogen in this unique local breed.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
CdX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. TC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LX: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. HZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. CyX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The research was supported by grants from the 2023 Xiangbala Talent Program (Team Project) in Xiangcheng County, National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFF0724603-6).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
SN/T 3488-2013. Quarantine protocol for real-time PCR of Lawsona intracellularis. SN/T 3488-2013. doi: 10.1177/10406387211003551
Campillo, M., Smith, S. H., Gally, D. L., and Opriessnig, T. (2021). Review of methods for the detection of Lawsonia intracellularis infection in pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 33, 621–631. doi: 10.1177/10406387211003551
Hu, Z., Lai, R., Xu, W., Guan, R., Zhang, Z., Yan, G., et al. (2025). Establishment of a taqMan quantitative real-time PCR for detecting. Lawsonia intracellularis. Vet. Sci. 12:450. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050450
Mcorist, S., Smith, S. H., and Green, L. E. (1997). Estimate of direct financial losses due to porcine proliferative enteropathy. Vet. Rec. 140, 579–581. doi: 10.1136/vr.140.22.579
Obradovic, M. R. and Wilson, H. L. (2020). Immune response and protection against Lawsonia intracellularis infections in pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 219, 109959. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2019.109959
Tian, X., Wang, H., Liu, Z., Wei, Z., Yang, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2025). The updated duplex fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR assay for simultaneous detection of PRRSV-1 and PRRSV-2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1616898
Wang, H., Sun, Y., Chen, J., Wang, W., Yu, H., Gao, C., et al. (2024). Development and application of a quadruplex TaqMan real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR assay for four porcine digestive pathogens. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1468783
Wang, L., Wu, W., Zhao, L., Zhu, Z., Yao, X., Fan, J., et al. (2024). Fecal PCR survey and genome analysis of Lawsonia intracellularis in China. Front. Vet. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1324768
Xiao, N., Li, J., Li, M., Zhou, H., Lin, H., and Fan, H. (2022). Isolation and in Vitro cultivation of Lawsonia intracellularis from China. Vet. Microbiol. 270, 109457. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109457
Xie, R., Luo, Y., Peng, C., Wu, W., Cui, Y., Sun, X., et al. (2025). Isolation, passage, and pathogenicity of a newly isolated lawsonia intracellularis strain from Hubei, China. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2025, 2501719. doi: 10.1155/tbed/2501719
Keywords: Tibetan pig, Lawsonia endocellularis, aspA, quantitative PCR, epidemiology
Citation: Xiao C, Wang Y, Chen T, Xue L, Zhao H, Xia C and Zhao X (2025) Development and application of a qPCR assay for Lawsonia intracellularis in Tibetan pigs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1711578. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1711578
Received: 23 September 2025; Accepted: 12 November 2025; Revised: 07 November 2025;
Published: 03 December 2025.
Edited by:
Qiang Zhang, Huazhong Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Xiao, Wang, Chen, Xue, Zhao, Xia and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaogang Zhao, MTA3ODUwMTgyMUBxcS5jb20=; Changyou Xia, eGlhY2hhbmd5b3VAY2Fhcy5jbg==
 Chendong Xiao
Chendong Xiao Yanqiong Wang1
Yanqiong Wang1