- 1Department of Health Technology and Informatics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- 2Infectious Diseases Research Directorate, Ethiopian Public Health Institute, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Microbiology, Immunology, and Parasitology, St. Paul’s Hospital Millennium Medical College, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Acinetobacter baumannii is a major global healthcare-associated pathogen with increased antibiotic resistance, underscoring the urgent need to develop novel antibiotics, immunotherapies, and vaccines. However, a critical gap in combating A. baumannii infections is the lack of a systematic approach to selecting appropriate host models for studying host-pathogen interactions. This review analyses previously published research articles on host interactions with A. baumannii. The articles were searched from electronic databases, including PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, covering publications from 2015 to 2024. These studies, encompassing both in vitro and in vivo research, aim to elucidate the virulence factors and host responses during host-pathogen interactions. The review analysis shows that mouse and Galleria mellonella are well-established animal models. Meanwhile, A549, HEK-293, HeLa, and Hep-G2 cell lines are the main in vitro models for studying A. baumannii pathogenesis. Key considerations for in vitro host model selection include necessitating a minimum of biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) laboratory conditions, the specific pathogens involved, relevance of the cell lines, immune responsiveness, and ease of manipulation. Challenges such as the heterogeneity of bacterial strains, initial bacterial dose, incubation duration, and infection multiplicity should be considered in host-pathogen studies. This review could serve as a roadmap for optimizing experimental models to accelerate the development of targeted strategies against A. baumannii.
1 Introduction
Acinetobacter baumannii is a healthcare-associated pathogen, Gram-negative, aerobic, catalase-positive, oxidase-negative, and nonfermenting coccobacilli (Yehya et al., 2025). It is a significant global health threat, which is an emerging pan-drug-resistant pathogen with high morbidity and mortality (Lim et al., 2019). It can survive for an extended time, particularly in hospital environments, on different surfaces such as beds, bedside tables, soft surfaces, and medical equipment (Alsan and Klompas, 2010). It also has the capacity to form resistant biofilms, which enables it to resist antibiotics and host immune responses (Sharma et al., 2023). These all increase the risk of transmission to patients and healthcare workers (Sharma et al., 2023). This bacterium is associated with healthcare-associated infections (HAIs)that primarily affect immunocompromised patients and can also lead to life-threatening conditions (Thacharodi et al., 2024). The most common diseases it causes are ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), followed by bacteremia, urinary tract infections (UTI), wound infections, skin infections, and meningitis (Abdallah and Abdalla, 2021).
It has been recently recognized that it is a challenging pathogen resistant to last-resort antibiotics, environmental stresses, hospital disinfectants, and host immune effector cells (Maure et al., 2023). To date, minimum antibiotic choices have demonstrated a significant ability to improve outcomes in patients with carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii (CRAB) infections (Bassetti et al., 2021; Yehya et al., 2025). Over the past decade, mortality rates for patients with CRAB infections are alarmingly elevated, ranging from 13.6% to 78%, mainly in patients with septic shock (Appaneal Haley et al., 2022; Boutzoukas and Doi, 2025; Russo et al., 2018). In 2021, the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators estimated that 1.14 million deaths were associated with deadly multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria, with A. baumannii being the most significant contributor (GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators, 2024). They forecasted that a total of 39.1 million people could die from antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) bacterial infections, including those caused by A. baumannii, between 2025 and 2050 (GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators, 2024). Thus, the WHO has ranked the CRAB as the top critical pathogen that requires new vaccines and drug developments (WHO, 2024).
To effectively combat this bacterium, it is crucial to understand the mechanisms that favor its survival under different conditions. According to previously published reports, the pathogen utilizes a range of virulence factors at various stages of pathogenicity, thereby favoring its survival under diverse conditions, including antibiotics, host immune responses, and environmental stresses (Karampatakis et al., 2024; Shadan et al., 2023). Several virulence factors of A. baumannii, including those involved in biofilm formation, drug resistance, cell adhesion, invasion, and persistence in the host, have been investigated (Lucidi et al., 2024). To uncover the pathogenesis of A. baumannii, scientists have extensively researched using various in vitro and in vivo experimental models. Various host models, including in vitro cell lines and in vivo animal models, have been employed to decipher the bacterial virulence mechanisms and host responses during A. baumannii infections. Despite the plethora of studies that leverage host models to investigate host-pathogen interactions, certain scientific questions, such as model relevance, remain unexplored in selecting appropriate host models. In addition, to date, there are no standardized laboratory methods for host-A. baumannii interaction studies. Accordingly, exploring different laboratory experiment-related factors that may contribute to the unsuccessful translation of preclinical studies to clinical studies is crucial. Thus, this review aims to provide an overview of the current progress of in vitro and in vivo host models used in studying host-pathogen interactions during A. baumannii infections. This review also highlights the challenges involved in study designs that may affect the translation of preclinical studies to clinical studies.
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy and study selection criteria
This review article was conducted on published articles to summarize the progress in using host models to decipher virulence factors of A. baumannii and to emphasize the strain and methodological differences that may contribute to the unsuccessful translation of A. baumannii preclinical studies to clinical studies. A comprehensive literature search was conducted for this narrative review using the following electronic databases: PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar. The search strategy included the following keywords in combination using Boolean operators (AND, OR): “Acinetobacter baumannii,” “A. baumannii,” “host models,” “host-microbe,” “host-bacterial,” “virulence factors,” “animal models,” and “cell lines” both in Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) and free text terms.
The peer-reviewed original research articles published in English from 2015 to 2024 were included in this study. The articles relevant to the topic of host models used in studying A. baumannii virulence and pathogenesis were included. TLG and AMS carried out the article search and screening independently. Case report studies, conference abstracts, and duplicated articles were excluded from this study (Figure 1). During the initial search, the two reviewers independently identified 2,561 records through comprehensive searches of electronic databases. Numerous (2,447) articles were excluded by title screening. More articles were excluded due to duplications (18), case report (1), and conference abstracts (3) during the abstract screening process. Finally, 49 full articles were selected based on their relevance to this review article and the quality of the whole article (Figure 1).
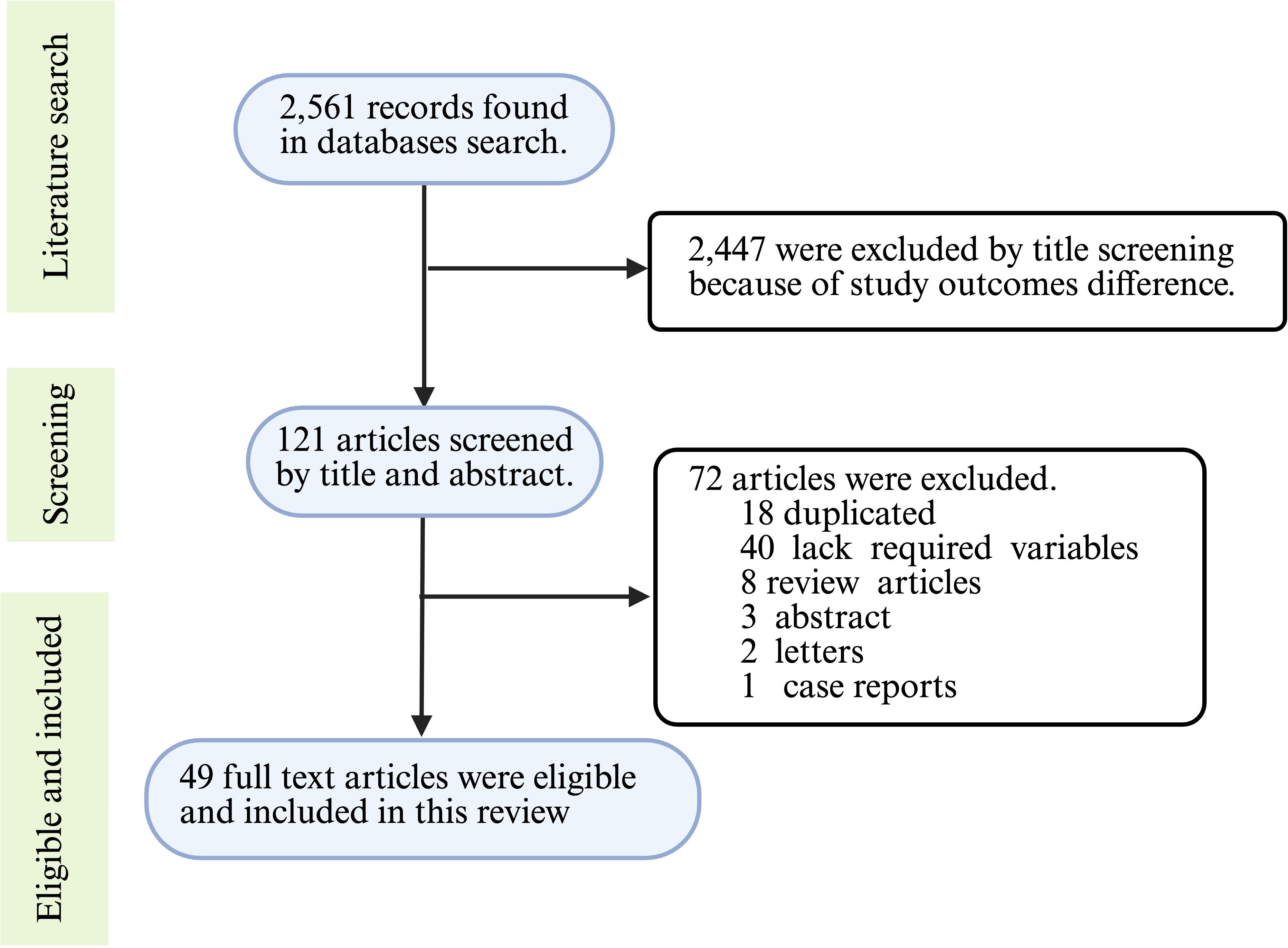
Figure 1. Article selection process flowchart. The data extracted from the selected articles included in vivo animal models, in vitro cell cultures, virulence factors of A. baumannii, the roles of virulence factors in pathogenesis, inoculum size, multiplicity of infection, and incubation and monitoring times. This information was synthesized and presented to provide a comprehensive overview of the current progress in host models for uncovering virulence factors of A. baumannii, with an emphasis on the challenges posed by strain and method heterogeneity. The figure was created with BioRender (https://www.biorender.com/).
3 Virulence factors and pathogenesis of A. baumannii
A. baumannii utilizes different arsenals of virulence factors, including outer membrane proteins (OMPs), lipopolysaccharide (LPS), lipooligosaccharide (LOS), pili, biofilm formation, capsular polysaccharides (CPS), metal ion acquisition systems, efflux pumps, two-component systems (TCSs), and secretion systems to favor its survival in the environment and host (Karampatakis et al., 2024; Shadan et al., 2023). In general, these virulence factors enable A. baumannii to adhere to and invade the host, evade the host’s immune response, proliferate, and successfully establish an infection in the host (Chen, 2020).
OMPs are beta barrel-shaped porins that facilitate the flow of tiny particles into and out of the periplasmic space of Gram-negative bacteria, including A. baumannii (Slusky and Dunbrack, 2013). They are major immunogenic proteins in A. baumannii, helping in bacterial environmental stress tolerance, antibiotic resistance, and host immune evasion. Immunization with A. baumannii OMPs resulted in a significant increase in protective immune responses (Mirali et al., 2023). Passive antibodies against OMPs of A. baumannii also safeguarded experimental animals from disease (Rafiei Delfan et al., 2024; Rajabzadeh et al., 2024). OmpA, CarO, outer membrane carboxylate channels, OmpW, and Omp33–36 are the major outer membrane proteins involved in different pathogenesis roles. Lipopolysaccharide and lipooligosaccharide, the A. baumannii surface adhesins, are important virulence factors (Eijkelkamp et al., 2014). Various genes of LPS and LOS of A. baumannii have been reported to activate Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and trigger the host innate immune response (Moffatt et al., 2013).
Capsular polysaccharide is a critical virulence factor responsible for resisting complement-mediated killing and evading phagocytosis by host immune cells (Zierke et al., 2025). More than 100 types of capsule loci have been identified from A. baumannii (Shashkov et al., 2017) which substantially influences virulence. Pili are found on the surface of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. In A. baumannii, they play a crucial in facilitating attachment, biofilm formation, and twitching and surface-associated motility, employing different genes involved in various pathogenesis roles (Ahmad et al., 2023). Most A. baumannii strains express genes involved in biofilm formation and associated with the virulence level of the bacterium (Wiradiputra et al., 2025). Mostly, these genes include biofilm-associated protein (BAP) and pili genes (Wiradiputra et al., 2025). The efflux systems and transcriptional regulators have been reported to regulate biofilm formation (Vareschi et al., 2025). These genes are involved in biofilm growth, and the biofilm, in turn, helps with adhesion and drug resistance (Vareschi et al., 2025).
Efflux pumps are also important A. baumannii virulence factors involved in virulence, extruding the antibiotics from bacterial cells and surface-associated motility (Pérez-Varela et al., 2019). The efflux pump has six classes with different roles in pathogenesis. The major facilitator superfamily (MFS) and resistance nodulation division (RND) are mainly involved in the resistance of multiple classes of antibiotics (Fournier et al., 2006). A. baumannii can uptake essential metal ions from the host for its survival using different metal ion acquisition mechanisms. Iron (Fe²+) and manganese (Mn²+) ions are the most critical and essential metal ions for the survival of A. baumannii. This bacterium uses siderophores to uptake Fe²+ (Gaddy et al., 2012) and MumT (manganese and urea metabolism transporter) to uptake Mn²+ (Green et al., 2020). This system can be used to help in introducing specific antibiotics inside bacteria by using the Trojan Horse strategy using specific siderophores to fight antimicrobial resistance in pathogenic bacteria, including A. baumannii (Tillotson, 2016). Thus, targeting the metal acquisition systems can be a future perspective to fight antimicrobial resistance in pathogenic bacteria, including A. baumannii (Ezzeddine and Ghssein, 2023). Another important virulence factor discovered in A. baumannii is the secretion systems. So far, five secretion systems, namely type I secretion system (T1SS), type II secretion system (T2SS), type IV secretion system (T4SS), type V secretion system (T5SS), and type VI secretion system (T6SS), have been identified. The T5SS and T6SS play a crucial role in A. baumannii pathogenesis, including biofilm formation, attachment to host cells, delivery of toxic effector proteins to host cells or neighboring bacterial cells, and survival in systemic infection.
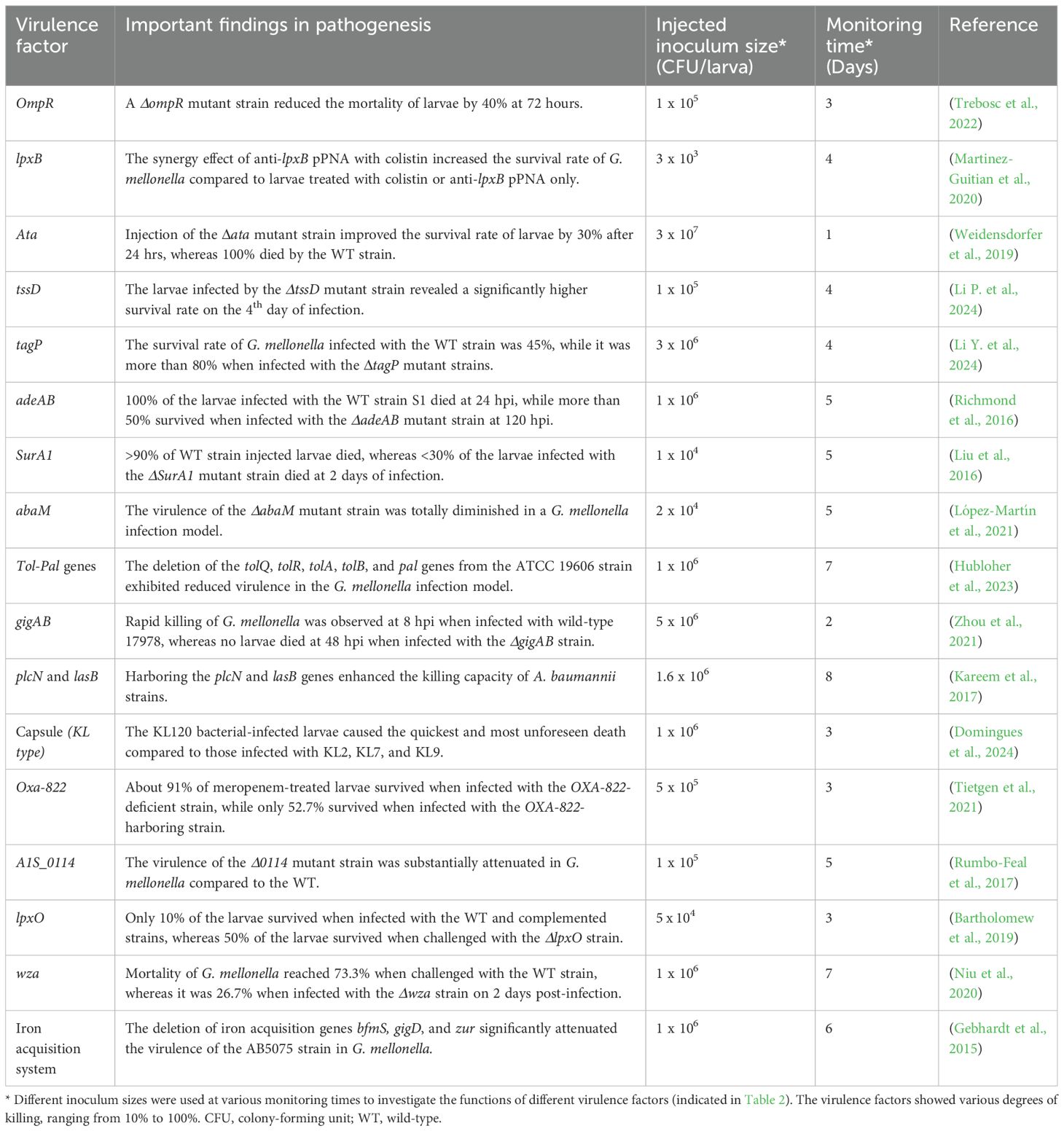
In general, multiple genes within specific arsenals of virulence factors are involved in the pathogenesis process of A. baumannii. The pathogenicity roles of some crucial genes are illustrated in Tables 1-3. Figure 2 illustrates the key virulence determinants of A. baumannii that play various roles in pathogenesis.
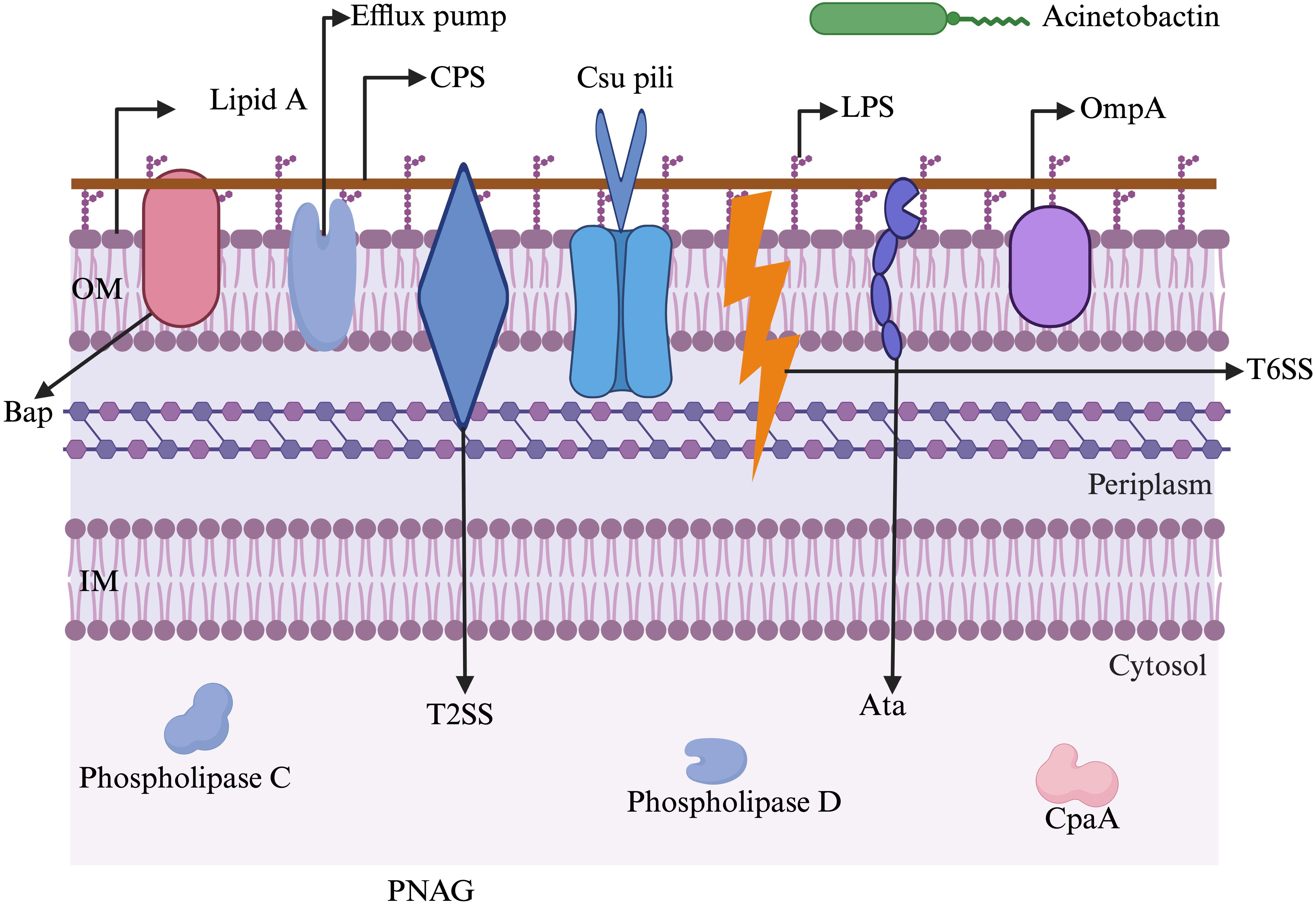
Figure 2. A schematic representation of major virulence factors possessed by A. baumannii to withstand harsh environments and establish infection. Acinetobactin: involved in nutrition/metal uptake; Ata: Acinetobacter trimeric autotransporter (involved in adherence to host membranes); Bap: biofilm-associated protein (involved in maturation of biofilms); CpaA: Coagulation targeting metallo-endopeptidase of A. baumannii (involved in blood coagulation); CPS: capsular polysaccharide (involved in immune modulation, antiphagocytosis); Csu pili: chaperon/usher pilus system (involved in biofilm formation and adherence); Efflux pump: involved in antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation; IM: inner membrane; LPS: lipopolysaccharide (involved in evasion of the host immune response and triggering the host inflammatory response); OM: outer membrane; OmpA: outer membrane protein A (involved in apoptosis, biofilm formation, avoiding complement-mediated killing, and adherence and invasion of epithelial cells); Phospholipase C: involved in lysis of host cells; Phospholipase D: aids in bacterial persistence in human serum; PNAG: poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine (aids in biofilm formation and adhesion); T2SS: type II secretion system (aids in secreting multiple effectors); T6SS: type VI secretion system (helps in delivering protein effectors and bacterial competition). The figure was created with BioRender (https://www.biorender.com/).
4 Host models in studying A. baumannii virulence
Since A. baumannii is the top priority human pathogen requiring urgent new drug development, studying the pathogenic mechanisms involved during the infection process is crucial for identifying potential therapeutic targets. Various host models, including in vitro cell lines and in vivo animal models, have been reported for studying host and pathogen interactions.
4.1 In vitro cell culture models
Compared to animal models, cell culture is more convenient because it is easier to manipulate. The primary use of in vitro cell culture models is to create model systems for studying basic cell biology, reproducing disease mechanisms to mimic in vivo activity, or examining the toxicity of new drugs, vaccines, or immunotherapies (Segeritz and Vallier, 2017). Investigating host-pathogen interactions is crucial for understanding host cellular responses to infections. Nowadays, various cell cultures have been established to study a wide range of assays related to host-pathogen interactions, including 2D and 3D cell cultures (Park et al., 2021). The 2D cell culture models include immortalized cell lines that grow as a monolayer on flat surfaces, such as Petri dishes and flasks. In contrast, 3D cell cultures grow in three-dimensional structures, which have limited growth and higher costs. To date, different types of cell models, such as 2D-immortalized cell lines, primary cells, 3D-organoids, 3D-spheroids, and organs-on-a-chip, have been developed for infectious disease studies.
4.1.1 Cell line models
In vitro cell lines are easier to be manipulated, they divide continuously and can be cultured for long periods of time. Cell lines can either be finite or continuous immortalized cells. Most of the cell lines that have been implemented in investigating host A. baumannii interactions so far are continuous immortalized cells (Figure 3). Over 60 cell culture models have been used in studying A. baumannii pathogenesis, including adhesion and invasion, cellular viability and toxicity, and cellular immune responses to the bacteria. The human alveolar basal epithelial cell (A549) was the most successful and extensively used immortalized cell line in the last decade, with more than 100 publications. Other commonly used cell lines include the human embryonic kidney (HEK-293) cell, human cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cell, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells were also commonly used cell lines in studying A. baumannii pathogenesis (Figure 3). The immune system-derived cells are crucial in studying infection-related inflammatory responses. The RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line, HL-60, and THP-1 monocytic cells were among the most used in modeling disease-associated inflammatory pathways (Barron et al., 2021). Over the last decade, because they are well characterized and stable, RAW 264.7 macrophage and THP-1 monocytic cells have gained significant attention from scientists and have been extensively utilized in studying inflammatory pathways in response to A. baumannii infection. The top ten established cell lines used in the last decade to study A. baumannii pathogenesis are summarized in Figure 3.
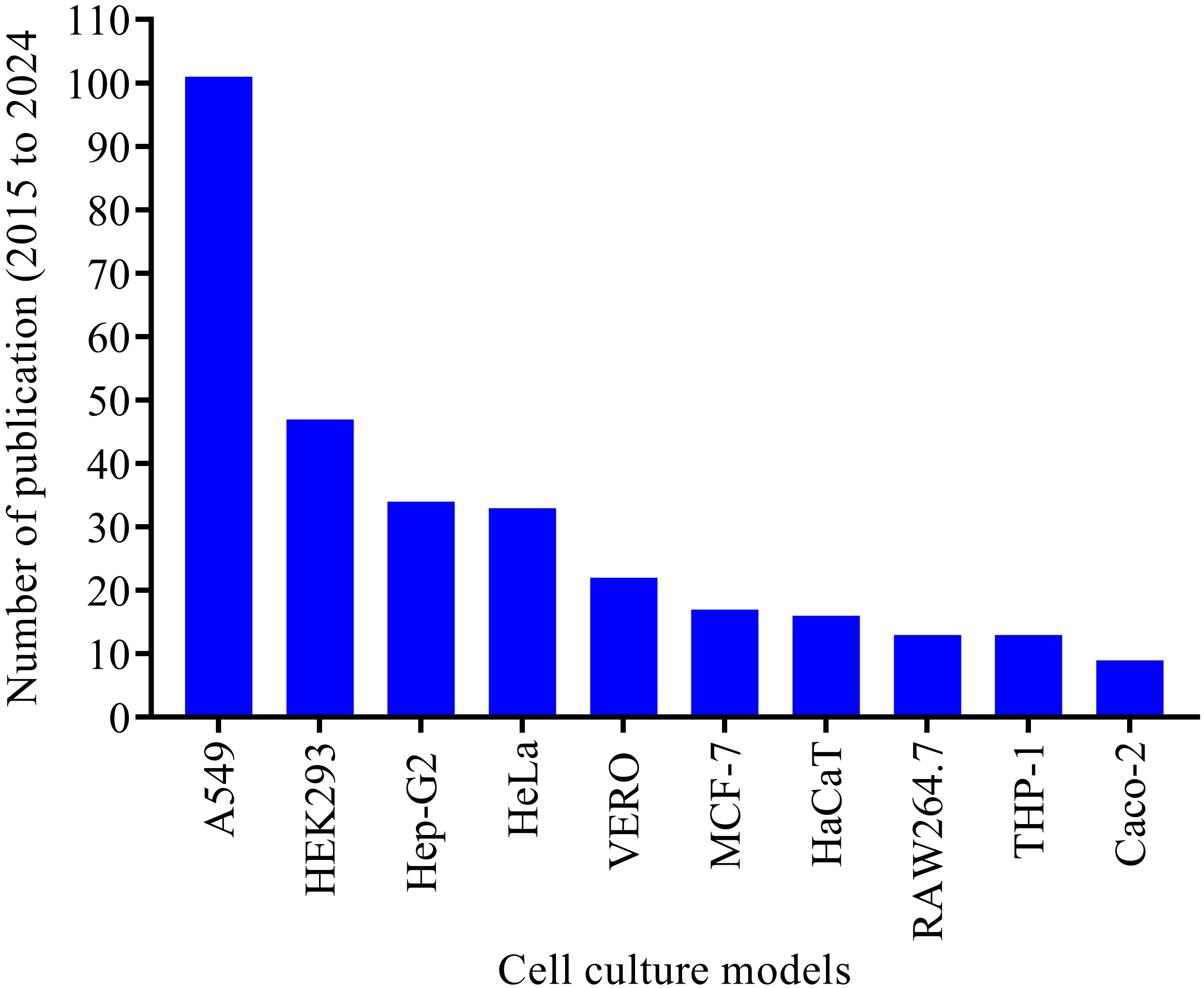
Figure 3. Top ten cell culture models tested and established in studying A. baumannii pathogenesis over the last decade (2015 to 2024). The electronic database search was made for the period from 2015 to 2024. More than 60 cell culture models were extracted, and only the top ten cell models extensively used in the last decade were illustrated in this figure.
During the study of A. baumannii pathogenesis, cell culture models were widely used to investigate various virulence factors of A. baumannii. Bacterial adherence and internalization, host cell viability or cytotoxicity, and host cell immune response are among the most assessed parameters in cell culture models [Table 1]. For instance, OmpA has been evaluated for its effectiveness as a vaccine candidate, and A. baumannii adherence, internalization, proliferation, and viability assay were assessed on the HeLa cell line in the presence and absence of anti-OmpA serum, highlighting that OmpA plays a crucial role in A. baumannii epithelial cell interactions (Rafiei Delfan et al., 2024). The A. baumannii strain with the mutant CarO showed a reduced ability to adhere to and invade A549 cells, indicating that CarO is an important virulence factor and a potential target for new drugs against CRAB (Labrador-Herrera et al., 2020). Furthermore, the deletion of chaperone protease-encoding genes, such as clpA, clpB, and clpS, affected the survival and proliferation of A. baumannii in J774.16 cells (Belisario et al., 2021), indicating that these genes are essential for bacterial proliferation within host cells.
Additionally, QS genes are essential in aiding the adherence and invasiveness of A. baumannii. According to the report by (Tang et al., 2020), strains carrying abaI and abaR genes or producing acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) signaling molecules exhibited substantial levels of adherence and invasion into A549 cells compared to strains lacking the QS genes or AHL signaling molecules. Furthermore, the Acinetobacter trimeric autotransporter adhesin, Ata, is reported to be an essential virulence factor involved in the adhesion of A. baumannii to host cells, as Ata-producing strains adhered more efficiently to the epithelial and endothelial cells compared to Ata-deficient strains (Weidensdorfer et al., 2019). Some recombinant proteins were also assessed for cytotoxicity on different cell lines (Table 1). For instance, rSurA1 was exposed to A549 and Hep-2 cells at varying concentrations, including 20, 40, and 80 μg/mL. The results showed that, 20 μg/mL caused 10% cell death in A549 and 15% in Hep-2 cells, whereas 40 and 80 μg/mL of rSurA1 were highly cytotoxic to both cells (Liu et al., 2016), indicating that SurA1 is a critical virulence factor in A. baumannii infection.
The 2D immortalized cell lines are inexpensive, easy to handle, and enable high-throughput screening of drugs and virulence factors. Despite this, because most cell lines are immortalized, they are unable to fully replicate the in vivo cell conditions, particularly those involved in host-pathogen interactions (Barron et al., 2021). Thus, primary human immune cells are crucial for studying host-pathogen interactions, as they closely mimic human body physiology.
4.1.2 Primary cell models
Primary human immune cells have been developed and are used to address challenges in cell lines when studying the interaction between A. baumannii and host immune cells. These include primary monocytes, alveolar and interstitial macrophages, bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs), dendritic cells, and neutrophils (Lazaro-Diez et al., 2020; Sabatini et al., 2024; Wang H. et al., 2024). When these cells are exposed to A. baumannii, they produce cytokines and/or chemokines. For instance, neutrophils infected with A. baumannii produce proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-1β, and CXCL-8, in response to this bacterium (Lazaro-Diez et al., 2020). Macrophages and monocytes have been shown to mediate bacterial clearance, while dendritic cells produce cytokines and chemokines (Sabatini et al., 2024). Alveolar and interstitial macrophages can undergo polarization toward the M1 phenotype, which can trigger a cytokine storm and usually cause the death of the host (Wang H. et al., 2024). This cytokine storm could be due to the high virulence level of the strain, which hyperactivates the host immune cells to produce high levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Virulence factors of A. baumannii are involved in evading the host’s immune responses, enabling them to survive and proliferate within immune cells. For example, a 10-fold reduction in intracellular live bacteria occurred at 2 hours post-infection (hpi) when BMDMs were infected with the wild-type (WT) 17978 strain. In contrast, a 300-fold reduction was observed at 2 hpi when infecting BMDMs with the ΔgigAB mutant strain. To verify this observation, the complementation strain displayed survival and replication levels comparable to those of the WT strain (Zhou et al., 2021). Table 1 represents the key virulence factors examined in cell lines and primary cells over the past decade. It illustrates the virulence factors elucidated and their roles in pathogenesis across different cell lines. Different multiplicities of infection (MOI) and cell lines have been employed to assess the pathogenesis roles of the virulence factors. Various concentrations of purified proteins, but not the bacterial strains, were used to infect the cell lines to evaluate the cytotoxic effects of SurA1 and trxA.
4.1.3 3D organoids, spheroids, and organs-on-a-chip models
To address the limitations of 2D cell culture models, such as their lack of complexity and physiological relevance, the 3D cell culture model has gained attention from the scientists in the recent years. The 3D cell cultures of organoids, spheroids, and organs-on-a-chip are emerging as advanced in vitro cell culture technologies for elucidating the pathophysiology of infectious diseases. Organoids are 3D cell cultures formed from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), or adult stem cells (ASCs) (Huch and Koo, 2015). They form cellular organization through self-renewal. So far, numerous organoids have been generated from human and mouse origins. They are genetically stable, can be manipulated indefinitely, and can be frozen for future use. To date, a few organoids, such as lung organoids for respiratory bacterial and viral infections, gastric and intestinal organoids for gastrointestinal infections caused by bacteria and viruses, and cerebral organoids for brain infections caused by viruses, have been well established. Other organoids for elucidating infectious diseases are in a very early stage.
Spheroids are spherical self-assembling 3D cell culture models, or are forced to grow as cell aggregates from single-cell suspensions (Yamada and Cukierman, 2007). These models are primarily used in cancer research, drug discovery, and regenerative medicine. They are rarely applied in infectious disease research. Even though lung spheroids are used to elucidate SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis, they have not been harmonized for bacterial infection studies (Medina et al., 2025; Rosa et al., 2021). Organs-on-a-chip are emerging technologies that integrate organoids and organ chips to simulate relevant pathophysiology. Respiratory-on-a-chip, gut-on-a-chip, vasculature-on-a-chip, liver-on-a-chip, and kidney-on-a-chip are organ-on-a-chips utilized by infectious disease research so far. They have been employed to elucidate the pathophysiology of a very limited number of bacteria and viruses. None of these 3D organoids, spheroids, and organs-on-a-chip models has been established to study the pathogenesis of A. baumannii.
While 3D cell models have advantages over 2D cell models, they have some limitations, such as a lack of vascular and immune systems, low reproducibility, a lack of newly developed biomaterials (Williams, 2022), complexity of biofabrication technologies (Skardal et al., 2015), expense, and difficulty in setting up. In a natural disease state, various cell types can simultaneously interact with the pathogen to clear it from the host, whereas in vitro cell culture models typically utilize only a limited number of cell types, which cannot fully mimic the host’s immune response. Thus, as in vitro cell models are the first step in deciphering the virulence factors involved in host-pathogen interactions, it is crucial to validate the in vitro results with in vivo host models to examine hypotheses that might be translated into clinical settings.
4.2 In vivo nonmammalian animal models
The complex and dynamic nature of host-microbe interactions presents significant challenges for fully replicating and elucidating these processes within in vitro cell culture models (Lemaitre and Ausubel, 2008). To address these challenges, numerous non-mammalian animal models have been tested and established to study A. baumannii pathogenesis. These models are crucial to the proof of concept for in vivo activity, enabling scientists to identify the key virulence factors responsible for host damage. To date, Galleria mellonella is the most widely used non-mammalian model (Tao et al., 2021), and has been experimentally validated for uncovering the virulence factors of A. baumannii. It is followed by Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) (Mylonakis et al., 2016), zebrafish (Danio rerio) (Plumet et al., 2024), Drosophila melanogaster (Drosophila) (Qin et al., 2020), Dictyostelium discoideum (D. discoideum) (Iwashkiw et al., 2012), marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) (Gong et al., 2022), Zophobas morio (Rakovitsky et al., 2024), and Lucilia sericata (McKenna et al., 2022) (Figure 4). Over the last decade (2015-2024), G. mellonella (354) and C. elegans (167) have been extensively utilized in in vivo studies of A. baumannii pathogenesis, whereas zebrafish were used intermittently (Figure 4).
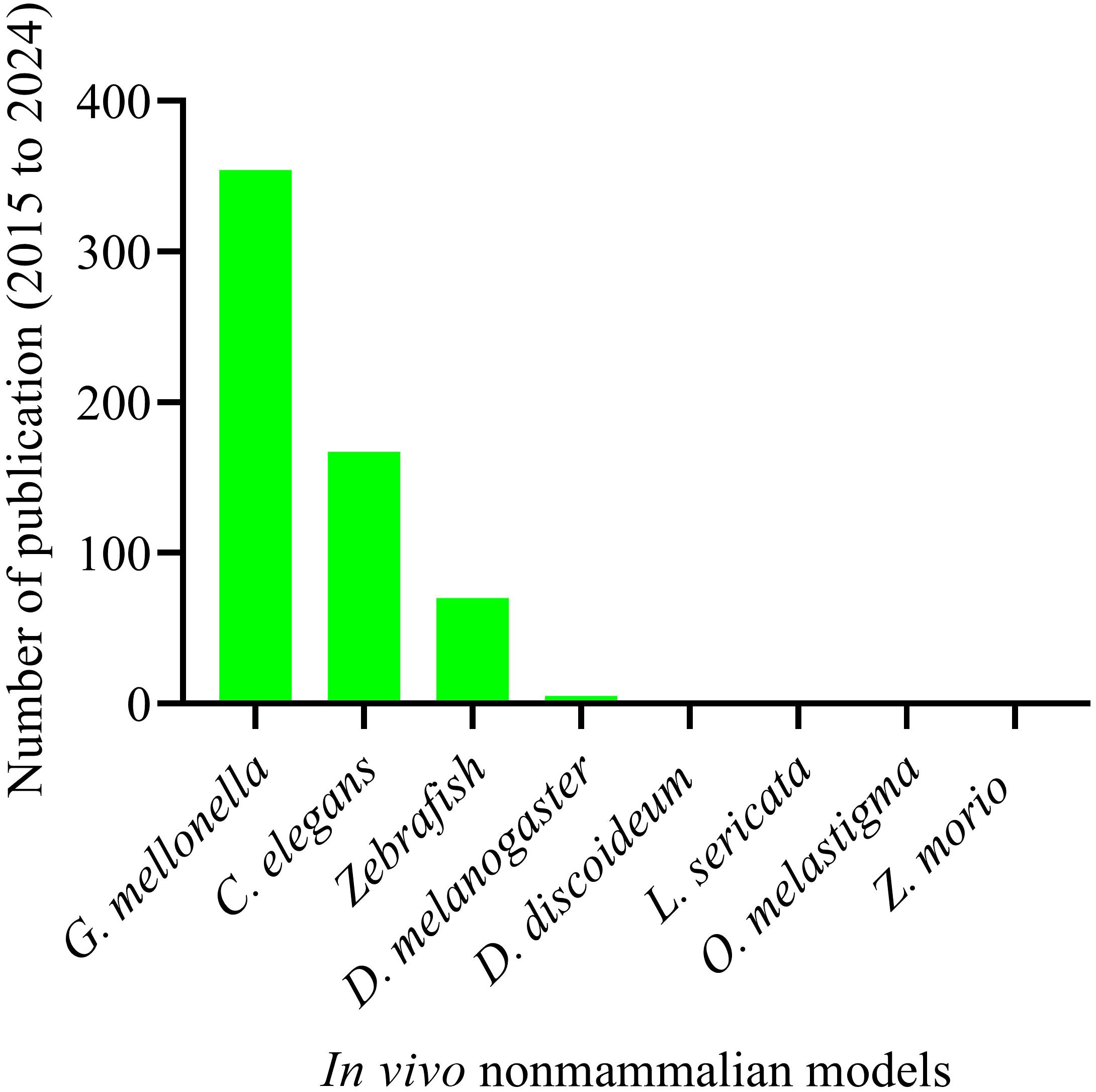
Figure 4. Non-mammalian animal models tested and established in studying A. baumannii pathogenesis over the last ten years. Total number of publications on non-mammalian animal host models and A. baumannii pathogenesis. Animal models: “G. mellonella” (354); “C. elegans” (167); “Zebrafish” (70); “Drosophila” (5); “D. discoideum” (2); “L. sericata” (2); “O. melastigma” (1); and “Z. morio” (1). Systematic search was made for the period from 2015 to 2024.
In this review, we focus on the invertebrates G. mellonella, C. elegans, and zebrafish, as they have attracted significant interest from scientists for their use in discovery of virulence factors. These models offer distinct advantages over other in vivo non-mammalian animal models.
4.2.1 Galleria mellonella model
G. mellonella, the greater wax moth, has been utilized to study host-pathogen interactions in various organisms, including pathogenic bacteria and fungi. This larva is the most extensively used invertebrate model for investigating the host-pathogen interaction of A. baumannii (Figure 4), with 354 publications over the past decade. Most importantly, this larva offers many advantages over other non-mammalian models, as it mimics the human body. It can survive at 37 °C, which resembles human body temperature, a crucial factor for deciphering the virulence factors of human pathogens, such as A. baumannii. They possess innate cellular immunity (hemocytes) and humoral immunity (antimicrobial peptides, lysozymes, reactive oxygen species) but lack adaptive immune responses against bacterial infections (Kay et al., 2019). Furthermore, it can be purchased at a low cost, reproduces rapidly, and is easier to handle in the laboratory (Figure 5). The complete life cycle of the larva takes about 8–13 weeks. Mature, healthy larvae (2–3 cm in length) are used for experiments. G. mellonella does not require ethics approval for the studies. Considering this, G. mellonella has significant advantages in studying host-pathogen interactions and antibacterial efficacy. G. mellonella can be used for various purposes, including killing assays, bacterial burden assays, host immune response studies, and the isolation of bacterial or host RNA from infected larvae (Ten et al., 2023). Figure 5 below illustrates the complete life cycle and mass production of G. mellonella.
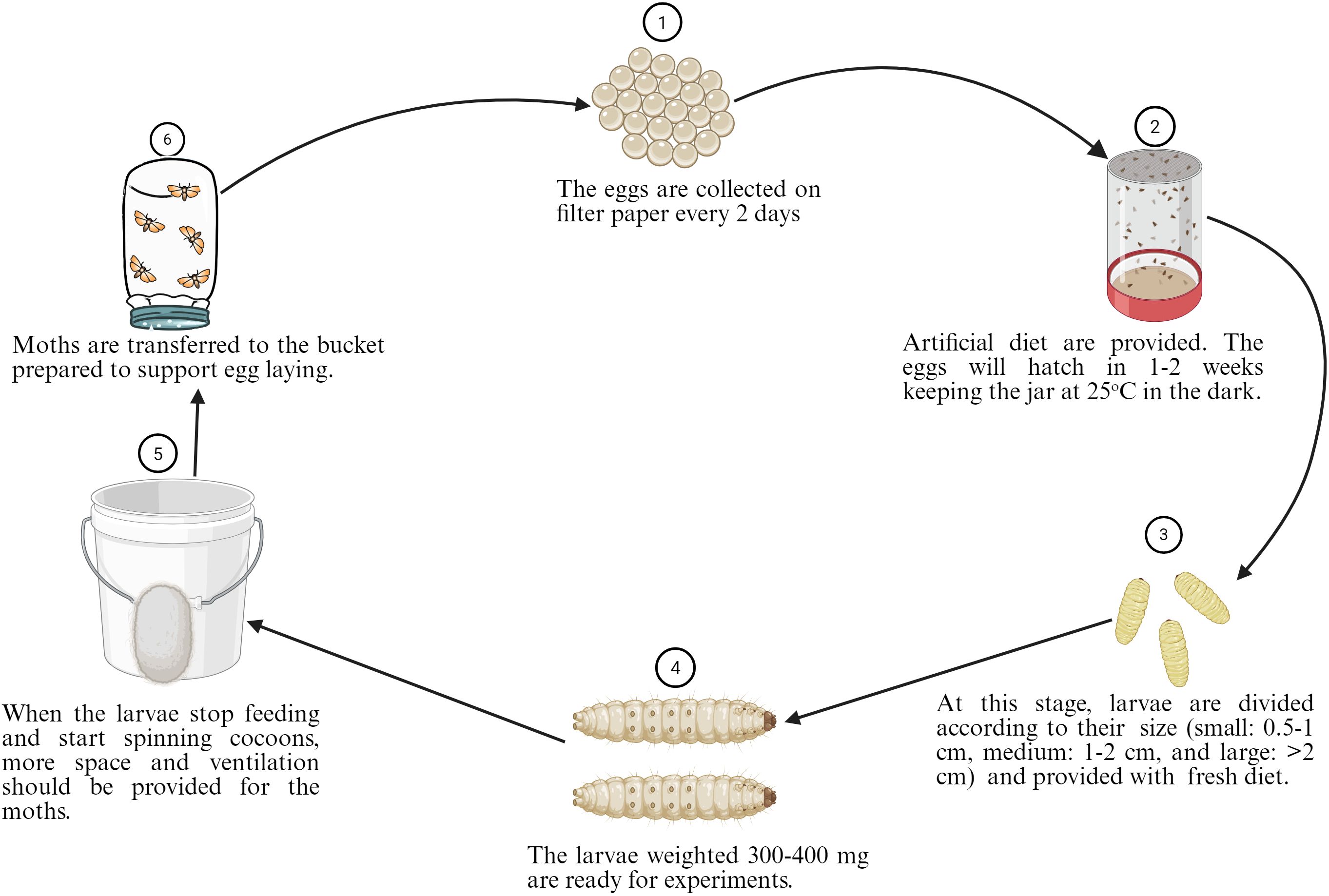
Figure 5. Steps for the standardized breeding of G. mellonella starting from eggs to moths. The composition of the optimized G. mellonella diet was composed of 54 g (9.5%) of rice flour, 54 g (9.5%) of oatmeal, 28 g (5%) of wheat germ, 84 g (14.8%) of torula yeast, 22 g (3.9%) of beeswax, 136 g (24%) of honey, 128 g (22.6%) of glycerol, and 60 g (10.7%) of water. The figure was created with BioRender (https://www.biorender.com/).
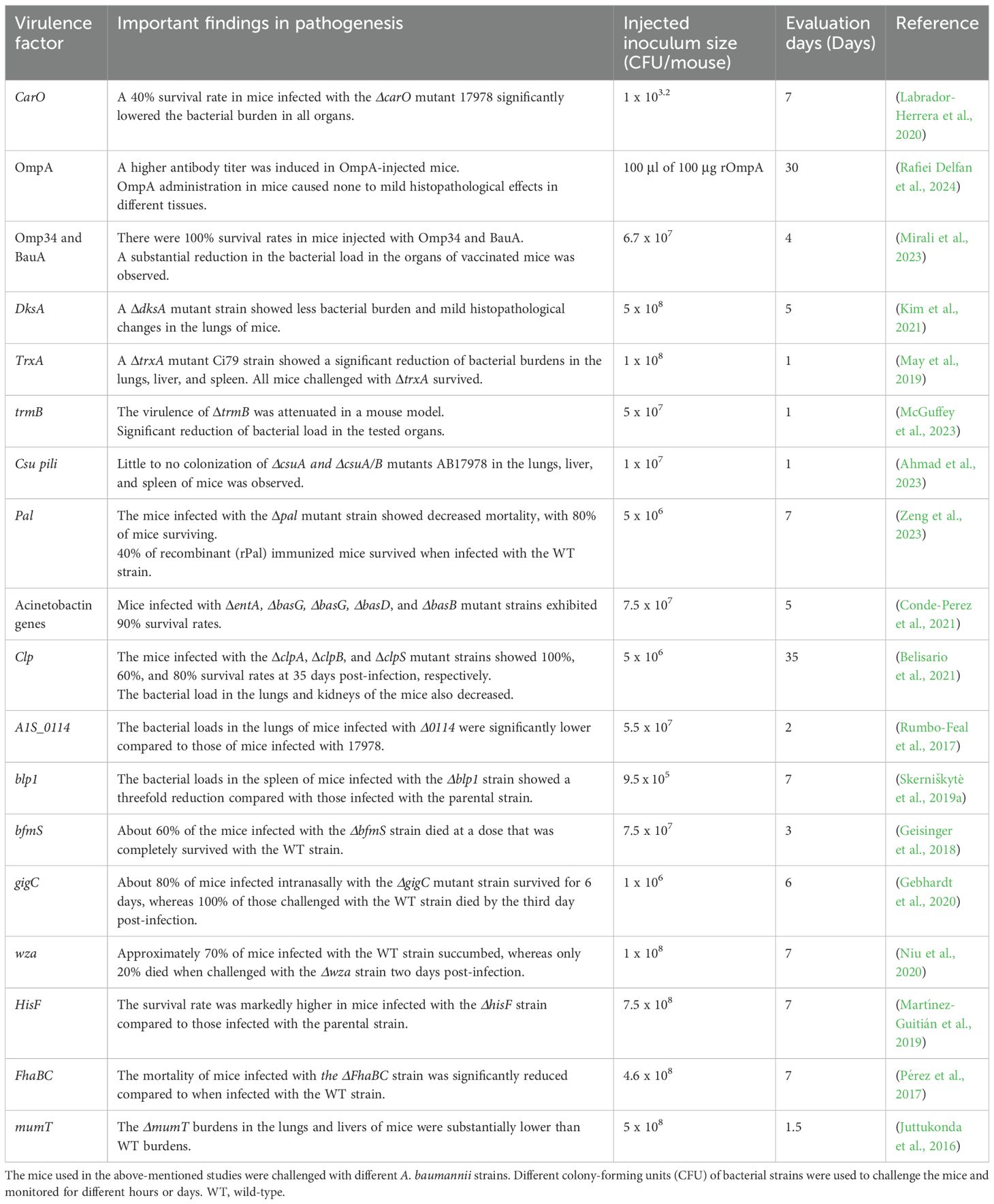
Various arsenals of virulence factors of A. baumannii have been deciphered in this nonmammalian model. The T6SS is a critical key virulence factor in the host-A. baumannii interaction. The T6SS genes tssB, tssD (hcp), and tssM were reported to be essential for A. baumannii pathogenesis, as their mutants impaired lethality in G. mellonella (Li P. et al., 2024). Additionally, the TagP (T6SS-Associated Gene PAAR) mutant strain was attenuated in numerous examined phenotypes, including its ability to cause disease in G. mellonella, showing a significant influence on pathogenicity (Li Y. et al., 2024). Acinetobacter trimeric autotransporter adhesin (Ata) is a key virulence factor of A. baumannii, exhibiting multiple functions including mediating adhesion and invasion. A Δata mutant strain was less effective in killing the larvae of G. mellonella (Weidensdorfer et al., 2019). Furthermore, disrupting the production of BasD and BauA, proteins vital for acinetobactin biosynthesis and transport, impaired the virulence of the ATCC 19606 strain. Infection assay of G. mellonella larvae demonstrated that impairing the acinetobactin-mediated iron acquisition system substantially reduced the killing ability of the ATCC 19606 strain (Gaddy et al., 2012).
The contribution of quorum-sensing (QS) genes to the pathogenesis of A. baumannii is also significant. The abaM, the third gene located between abaI and abaR, significantly influences the virulence of the A. baumannii 5075 strain, in which the killing ability of the abaM::T26 mutant was diminished entirely in the killing assay of G. mellonella (López-Martín et al., 2021). Furthermore, scientists have reported that two-component system genes can regulate the pathogenesis of A. baumannii. For instance, the adeAB mutant of strain S1 substantially affected the virulence of this strain when G. mellonella was infected with 106 CFU of bacteria (Richmond et al., 2016). The SurA1, the most dominant gene involved in biofilm formation, exhibited a decreased survival rate and limited dissemination when the SurA1 mutant strain was injected into the G. mellonella infection model, indicating that this gene plays a significant role in the virulence of A. baumannii (Liu et al., 2016). The gigAB genes also play an essential role in the growth and virulence of this bacterium. The study revealed that when G. mellonella was inoculated with WT 17978, rapid larval killing commenced at 8 hpi. In contrast, no larval killing was observed within 48 hours of infection among those infected with the ΔgigAB mutant strain (Zhou et al., 2021), indicating that this gene is crucial in the pathogenesis of A. baumannii.
G. mellonella has also been utilized to study the virulence of A. baumannii by exposing the bacteria to various conditions, including antibiotics. For example, Schmitt et al. reported the virulence of persister and regular cells of A. baumannii after exposure to meropenem, and their study revealed that persister cells were more virulent than regular cells after injecting the cells into G. mellonella (Schmitt et al., 2023). Furthermore, the presence of OXA-822 in A. baumannii 19606 significantly decreased the survival rate of infected larvae after treatment with meropenem compared to the control group without the OXA-822 (Tietgen et al., 2021), indicating that meropenem is not protective in the presence of the OXA-822 gene. The effect of bacterial biofilm formation on the survival of G. mellonella has also been reported. According to Khalil et al, the killing capacity of the strong biofilm-producing A. baumannii was considerably higher than that of the moderate and poor biofilm-producers (Khalil et al., 2021). Overall, G. mellonella has been extensively utilized in studying A. baumannii pathogenesis, and various virulent genes have been investigated using this model organism. Some of the recently examined virulent genes in G. mellonella are summarized in Table 2.
4.2.2 Caenorhabditis elegans
The nematode C. elegans is one of the most utilized invertebrates for bacterial pathogenesis studies over the past decade. It has a short life cycle of about three days to grow and an overall lifespan of three weeks. C. elegans has been widely used in host-pathogen studies with several advantages, such as sharing extensive genome similarity (30%–60%) with mammals, including humans (Culetto and Sattelle, 2000); its small size; ease of cultivation and storage; being able to be humanized by transgenesis; lack of ethical concerns; and a transparent body, which allows real-time observation of what occurs inside the body of the nematode after bacterial infection, including A. baumannii (Vallejo et al., 2015). It has been used to study innate immune response to identify genes and signaling pathways, such as TIR-1, which is essential in activating the MAPK signaling pathway (Wang D. et al., 2024). Additionally, it has also been employed to assess the effectiveness of various antibacterial agents against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including multi-drug-resistant A. baumannii, their antibiofilm potencies, and toxic effects in nematode C. elegans (Chai et al., 2022; Khadke et al., 2021; Lee et al., 2019).
Most importantly, this nematode has been widely used to explore the virulence factors in host-pathogen interaction studies. According to Rumbo-Feal et al, inactivating the A1S_0114 gene, which is involved in the production of acinetin 505, substantially reduced the virulence of the ATCC 17978 strain (Rumbo-Feal et al., 2017). The abeD mutant A. baumannii showed a significant reduction in virulence capability in C. elegans (Srinivasan et al., 2015), indicating that this gene contributes to the bacteria’s ability to withstand osmotic and oxidative stress and to kill the host. Reports also suggest that both RecA and CheW-like proteins are essential for full virulence of A. baumannii, as knocking out either gene impaired bacterial virulence in C. elegans (Corral et al., 2020).
The knockout of the Omp 33–36 kDa protein affected the virulence level of A. baumannii in the C. elegans infection model (Espinal et al., 2019). Likewise, deletion of the blp1 gene impaired the virulence of A. baumannii during infection of the C. elegans (Skerniškytė et al., 2019a). This nematode is commonly used in killing assays to evaluate antimicrobial efficacy, analyze the virulence level of specific genes, and study host immune responses. It allows high-throughput screening of multiple bacterial strains more quickly and cost-effectively.
4.2.3 Zebrafish (Danio rerio) model
Zebrafish is a small freshwater fish that has been primarily developed for embryogenesis studies. In the past decade, it has become a valuable model organism for studying human pathogens. This model offers several advantages, including small size, cost-effectiveness, ease of breeding, high reproduction, rapid development, and not being subject to ethical concern (Sullivan et al., 2017), in accordance with the 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement). Most importantly, transparency in their embryos facilitates visualization of host-microbe interactions and live imaging of infection dynamics (Schmitz et al., 2024). Indeed, this host model is excellent for immune response studies, because the zebrafish’s innate and adaptive immune systems shares considerable similarities with those of humans (H Meijer and P Spaink, 2011). During its first four days of life, exhibits only innate immunity. Its adaptive immune system becomes fully functional in 4–6 weeks (Lam et al., 2002). Thus, zebrafish is most suitable for studying innate immune responses in the first two weeks and adaptive immune responses later after about a month.
Zebrafish has been utilized to elucidate the role of the virulence factors of A. baumannii. For instance, the role of AbaI quorum sensing in pathogenesis has been examined in this model. Deletion of AbaI from the A. baumannii strain substantially decreased the virulence of the bacterium and recruitment of neutrophils to the infection site of zebrafish (Jiang et al., 2024). Compared to those infected with the wild-type strain, zebrafish infected with a strain lacking the carboxy-terminal processing protease (Ctp) gene showed a significantly higher survival rate (Roy et al., 2020), highlighting the importance of the Ctp gene in virulence. Additionally, zebrafish embryo has been used to demonstrate the virulence of eight capsule types. The strains with capsule types of K2, K9, K32, and K45 proved to be the most virulent; K1, K38, and K67 exhibited medium; and the K44 strain was less virulent (Neto et al., 2023). Another study demonstrated that A. baumannii ΔgacS and ΔgacA mutants had significantly reduced virulence in a zebrafish infection model compared to the wild-type strain (Bhuiyan et al., 2016), suggesting that these genes are crucial virulence regulators.
This host model has also been employed to investigate various therapeutic agents, including antimicrobials, antibiofilm formers, and anti-virulence, for their effective bactericidal activities, biofilm inhibition, and cytotoxicity level (Abirami et al., 2023; Jayathilaka et al., 2022).
Overall, due to their small size, ease of handling, cost-effectiveness, and lack of ethical concerns for non-mammalian animal models, zebrafish are highly suitable for experimental purposes. They address some challenges associated with in vitro cell culture. However, many gaps remain in the application of nonmammalian infection models for fully understanding of A. baumannii pathogenesis, such as growth at room temperature where bacterial pathogens may not express virulence factors, differences in target organs compared to humans, and the absence of complete mammalian immune responses. Therefore, confirming in vivo results from nonmammalian models with a mammalian model is essential to further understand bacterial pathogenesis and translating preclinical findings to clinical studies.
4.3 In vivo mammalian models
To address the challenges of nonmammalian models, mammalian models are crucial for a detailed understanding of the A. baumannii pathogenesis. Mammalian models offer significant advantages by closely mimicking human diseases, facilitating the investigation of potential virulence factors and the comprehensive testing of complex host-bacterial interactions. To date, mammalian animal models such as mice (Arrazuria et al., 2022), porcine (Zurawski et al., 2019), rabbits (Hansen et al., 2009), and guinea pigs (Bernabeu-Wittel et al., 2005) have been tested and established in studying A. baumannii pathogenesis (Figure 6). Over the last ten years (2015 to 2024), mice have been the paramount mammalian model extensively used in in vivo studies of A. baumannii pathogenesis, with 1,356 publications (Figure 6).
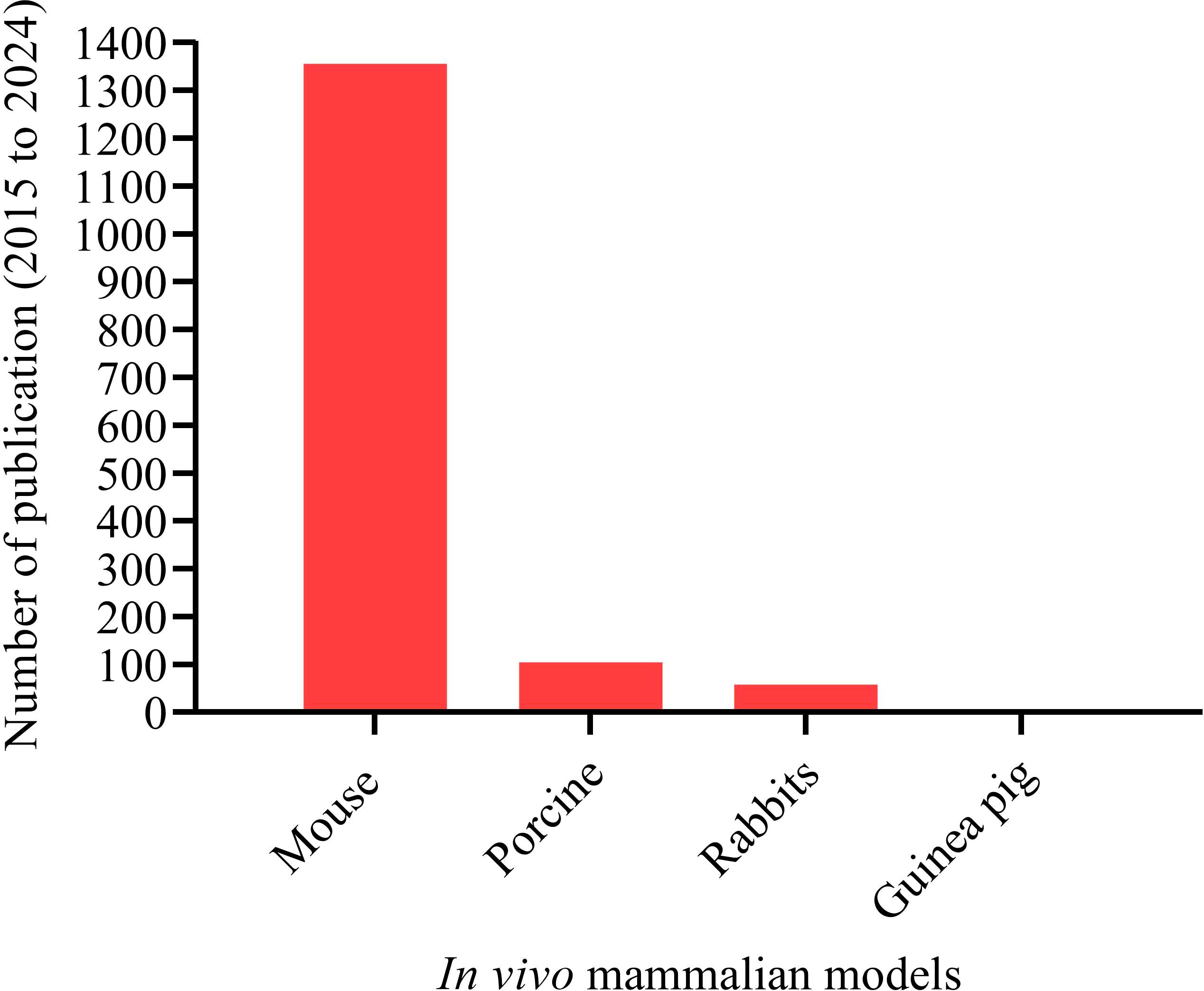
Figure 6. Mammalian animal models have been tested and established for studying A. baumannii pathogenesis. Total number of publications on mammalian animal host models and A. baumannii interaction. Mammalian animal models: “Mouse” (1,356); “Porcine” (105); “Rabbits” (58); and “Guinea pig” (3). A systematic search was made for the period from 2015 to 2024.
4.3.1 Mouse model
We selected the mouse model to focus on in this review because scientists have consistently shown a strong interest in using mice as the primary and most common laboratory animal. Mice are used not only to decipher virulence factors but also for drug discovery, vaccine development, and anti-virulence approach studies. Over the last decade, more than 1,300 articles on A. baumannii pathogenesis using mouse models have been published. Porcine, rabbit, and guinea pig were less frequently used in A. baumannii studies compared to mice. However, these animals offer advantages, including anatomical and physiological similarities to humans. Their use in infectious disease research has decreased over the past decade due to certain limitations (Figure 6). Because of their large size, it isn’t easy to breed in large numbers, handle in a laboratory, and genetically modify (Mukherjee et al., 2022). Small animal models like mice are easier to breed in large quantities, handled in laboratory, and are suitable for genetic modification.
The use of mice as laboratory animals began with genetic research in the early 20th century and remains the main choice (Figure 6). Since humans and mice share over 90% of their genes, laboratory mice are essential in studying bacterial pathogenesis. They are crucial for identifying specific virulence factors associated with pathogens and understanding the immune responses elicited against them (Sarkar and Heise, 2019).
There are various types of mice used in biological research, including inbred, outbred, transgenic, knockout, and immunodeficient. Scientists have extensively used all except outbred mouse for studies of pathogen infection, including A. baumannii (Masopust et al., 2017). The inbred C57BL/6 and BALB/c are the most well-characterized and genetically stable mouse models for studying a variety of immunological and human pathogen studies, including A. baumannii.
Mouse models have been used for many years in studying specific virulence factors that contribute to the pathogenesis of microorganisms, including A. baumannii (Rumbo-Feal et al., 2017; Sams et al., 2012). In addition, they are essential to assess the effectiveness of new therapeutic agents and vaccines, where mouse models are immunized by the whole bacterial strain or specific bacterial cell components (such as virulence factors) and then assessed for any cytotoxicity and host immune response (Harris et al., 2013, 2019; Rafiei Delfan et al., 2024). Various types of mouse models can be utilized for diverse research objectives to mimic different types of infections. Common models include acute infection (intranasal, intraperitoneal, or intravenous routes) (Harris et al., 2013, 2019), pneumonia infection (Arrazuria et al., 2022; Ranjbar et al., 2022), wound infection (Ruamsap et al., 2022), sepsis model (Mirali et al., 2023), and immunocompromised mouse model (Huo et al., 2022; Kim et al., 2021), which are among the most commonly used mouse models in A. baumannii virulence studies.
Mouse models have been employed to identify virulence factors associated with the pathogenesis of A. baumannii. Outer membrane proteins are the most abundant surface proteins and key virulence factors in host-pathogen interactions, as explored in mouse models. For instance, the virulence of OmpW, Omp34, and BauA was elucidated and reported as potential vaccine candidates after confirming their effects using immunized mice (Gil-Marqués et al., 2022; Mirali et al., 2023). The synergistic effect of Omp34 and BauA was observed, with the combination providing greater protection than either protein alone in the immunized mice (Mirali et al., 2023). A substantial reduction of A. baumannii load was detected in the lungs, livers, and spleens vaccinated with Omp34 and BauA, indicating the potential virulence of these proteins (Mirali et al., 2023).
Investigation of other virulence factors using a mouse sepsis model revealed that virulence genes such as bauE, abaI, and pgAB played essential roles in the virulence of polymyxin B-resistant A. baumannii, indicating promising therapeutic targets (de Souza et al., 2024). Furthermore, pili are among the most important virulence factors for establishing A. baumannii infections. The Csu pili was known to mediate biofilm formation but was recently reported to enhance colonization of A. baumannii into various organs of mouse model such as liver, spleen, and lungs, which suggests it as a major virulence factor mediating A. baumannii adherence to initiate a disease in host models (Ahmad et al., 2023). The role of thioredoxin-A protein (TrxA) in A. baumannii biofilm formation has also been explored in the pulmonary infection model, and the mutant TrxA (ΔTrxA) was less virulent than the WT strain (May et al., 2019). Moreover, the transcriptomic analysis of the mutant revealed that loss of feoA, mtnN, yfgC, basB, hisF, oatA, and bfnL resulted in a significant loss of virulence in the mouse pneumonia model, highlighting these genes as promising therapeutic targets (Martinez-Guitian et al., 2021). The mice infected with a lethal dose of mutant strains showed higher survival rates compared to those infected with the WT strain. The virulence factors examined in mouse model in the last decade are summarized in Table 3.
5 Challenges and key considerations for model selection
Heterogeneity of strains is the most common challenge encountered in studying host and A. baumannii interactions. Due to its high genome plasticity, pan-genome analysis of 2,500 strains revealed nearly 20,000 different genes present across various A. baumannii strains (Mangas et al., 2019). It is important to note that different strains of A. baumannii employ distinct strategies to adhere, invade, internalize, and replicate within host cells. Some strains may possess specific virulence factors involved in pathogenesis or may share these factors with other strains. A comparative genomic analysis of 14,159 clinical isolates showed that only nine ST1791°/ST2P strains carried 11 unique genes involved in pathogenesis, which are not found in other clinical strains (He et al., 2024). In contrast, Ata adhesin is present in 78% of all sequenced A. baumannii isolates, indicating that this gene is available in most sequenced strains (Weidensdorfer et al., 2019). The virulence factor lasB genes were present in 53.33% (16/30) of the strains, while plcN genes were present in 23.3% (7/30) of the strains. These differences suggest that the pathogenesis of the standard strains, ATCC 19606 and ATCC 17978, which are primarily used in numerous studies, may not accurately represent the recently circulating strains, as the genetic variability of most A. baumannii strains is significant.
Experimental variations in laboratory testing present another challenge in studying interactions between the host and A. baumannii. To explore how A. baumannii interacts with both animal and cell culture models, scientists have employed various animal models with different immune systems, varying bacterial doses, and different incubation periods after infection (Tables 2 and 3), which may complicate efforts to translate preclinical studies to clinical trials. Indeed, the virulence levels of the bacterial strains injected into the host models in these studies vary. When the bacterium is highly virulent, it can trigger a cytokine storm that even leads to the host’s death (Wang H. et al., 2024), highlighting the importance of managing host immune response to save the infected individuals. The infectivity level of A. baumannii influences the multiplicity of infection in cell culture models (Table 1). Different incubation durations and infection doses have been established and utilized for studying bacterial adhesion, invasion, and cell cytotoxicity.
When G. mellonella is used for survival studies or killing assays, the outcomes depend on several factors, including the number of A. baumannii cells inoculated into the larvae, incubation temperature, incubation time after injection, and the volume of injection. For instance, about 75% of the G. mellonella larvae inoculated with 3.7 × 105 CFU of A. baumannii were killed after 48 hours, while very few were killed when inoculated with 3.7 × 104 CFU, indicating that the killing ability depends on the inoculation dose (Peleg et al., 2009). This study also reported that the killing capacity of pathogenic A. baumannii is temperature-dependent. The rate of G. mellonella killing by A. baumannii was higher at 37 °C than at 30 °C (Peleg et al., 2009). Different studies used different incubation times (Table 2) and various injection volumes (Gaddy et al., 2012; Lin et al., 2023; Tang et al., 2020; Trebosc et al., 2022), which suggests that there are no standardized laboratory methods established for A. baumannii pathogenesis studies.
In laboratory experiments using a mouse infection model, various inoculum sizes per mouse have been employed so far (Gebhardt et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2021; Labrador-Herrera et al., 2020; Mirali et al., 2023). Highly diverse evaluation days after bacterial inoculation into mice have also been used to study the pathogenesis of A. baumannii in the mouse model (Ahmad et al., 2023; Belisario et al., 2021; Labrador-Herrera et al., 2020). There is also heterogeneity in immune responses against different A. baumannii strains with varying levels of virulence among both mammalian and nonmammalian models. Overall, no standardized methods, such as incubation durations and infection doses, are available for both cell culture and animal models. These heterogeneities could be among the major factors that hinder the translation from preclinical to clinical studies.
6 Conclusions
In this review, we focus on successful and well-established host models, including animal and cell culture models, to decipher the virulence factors of A. baumannii. Although many virulence factors have been identified and assessed for their abilities to stimulate immune responses using either in vivo animal models or in vitro culture systems, there is a gap in selecting the most appropriate models to elucidate the role of these factors in A. baumannii pathogenesis. This review compiles evidence that numerous cell culture and animal models have been thoroughly developed for studying the pathogenesis of A. baumannii. Over the past decade, A549, followed by HEK-293, HeLa, and HepG2 cells, have been the most successful, well-characterized, and extensively used cell lines in A. baumannii pathogenesis research. For studies on the inflammatory pathway, choosing immune-derived cells is essential. The RAW 264.7 macrophage and THP-1 monocytic cells are well-established immune cell models for studying inflammatory responses to A. baumannii infection. Among the nonmammalian models, G. mellonella larvae stand out as a more suitable model than others due to their capacity to be maintained at 37 °C, which is critical for host-pathogen interaction studies. C. elegans and zebrafish are also well-established nonmammalian models. Mice, as well-established mammalian models, provide diverse infection models that enable researchers to address varied objectives in A. baumannii pathogenesis studies. More works are needed to standardize methods, such as the selection of bacterial strains, initial bacterial inoculum, incubation duration, and follow-up time, when using both animal and cell culture models, as well as the multiplicity of infection in the case of cell culture systems. Notably, the 3D culture models, including organoid models, have yet to be developed for studying A. baumannii pathogenesis. Because 3D organoid models better replicate the physiology of human organs, they are crucial for understanding the complex interactions between host and pathogen. Overcoming these challenges could help translate preclinical findings into clinical applications.
Author contributions
TG: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AS: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. PL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Department of Health Technology and Informatics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdallah, E. M. and Abdalla, R. M. (2021). Acinetobacter baumannii, a global health-threatening bacterium: a short review. J. Microbiol. Expe. 9, 181–184. doi: 10.15406/jmen.2021.09.00341
Abirami, G., Alexpandi, R., Sudhin, S., Durgadevi, R., Roshni, P. S., Kumar, P., et al. (2023). Pyrogallol downregulates the expression of virulence-associated proteins in Acinetobacter baumannii and showing anti-infection activity by improving non-specific immune response in zebrafish model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 226, 853–869. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.045
Ahmad, I., Nadeem, A., Mushtaq, F., Zlatkov, N., Shahzad, M., Zavialov, A. V., et al. (2023). Csu pili dependent biofilm formation and virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii. NPJ Biofilms Microb. 9, 101. doi: 10.1038/s41522-023-00465-6
Alsan, M. and Klompas, M. (2010). Acinetobacter baumannii: an emerging and important pathogen. J. Clin. Outcomes Manage. 17, 363–369.
Alvarez-Fraga, L., Rumbo-Feal, S., Perez, A., Gomez, M. J., Gayoso, C., Vallejo, J. A., et al. (2017). Global assessment of small RNAs reveals a non-coding transcript involved in biofilm formation and attachment in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978. PloS One 12, e0182084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182084
Appaneal Haley, J., Lopes Vrishali, V., LaPlante Kerry, L., and Caffrey Aisling, R. (2022). Treatment, Clinical Outcomes, and Predictors of Mortality among a National Cohort of Admitted Patients with Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 66, e01975–e01921. doi: 10.1128/aac.01975-21
Arrazuria, R., Kerscher, B., Huber, K. E., Hoover, J. L., Lundberg, C. V., Hansen, J. U., et al. (2022). Variability of murine bacterial pneumonia models used to evaluate antimicrobial agents. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.988728
Barron, S. L., Saez, J., and Owens, R. M. (2021). In vitro models for studying respiratory host-pathogen interactions. Adv. Biol. (Weinh) 5, e2000624. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202000624
Bartholomew, T. L., Kidd, T. J., Sá Pessoa, J., Conde Álvarez, R., and Bengoechea, J. A. (2019). 2-Hydroxylation of Acinetobacter baumannii lipid A contributes to virulence. Infect. Immun. 87, 10-1128. doi: 10.1128/iai.00066-00019
Bassetti, M., Echols, R., Matsunaga, Y., Ariyasu, M., Doi, Y., Ferrer, R., et al. (2021). Efficacy and safety of cefiderocol or best available therapy for the treatment of serious infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria (CREDIBLE-CR): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, pathogen-focused, descriptive, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 21, 226–240. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30796-9
Belisario, J. C., Lee, H. H., Luknauth, H., Rigel, N. W., and Martinez, L. R. (2021). Acinetobacter baumannii strains deficient in the clp chaperone-protease genes have reduced virulence in a murine model of pneumonia. Pathogens 10, 204. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020204
Bernabeu-Wittel, M., Pichardo, C., Garcia-Curiel, A., Pachon-Ibanez, M. E., Ibanez-Martinez, J., Jimenez-Mejias, M. E., et al. (2005). Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic assessment of the in-vivo efficacy of imipenem alone or in combination with amikacin for the treatment of experimental multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 11, 319–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01095.x
Bhuiyan, M. S., Ellett, F., Murray, G. L., Kostoulias, X., Cerqueira, G. M., Schulze, K. E., et al. (2016). Acinetobacter baumannii phenylacetic acid metabolism influences infection outcome through a direct effect on neutrophil chemotaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 9599–9604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1523116113
Boutzoukas, A. and Doi, Y. (2025). The global epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 7, dlaf134. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlaf134
Chai, W. C., Whittall, J. J., Polyak, S. W., Foo, K., Li, X., Dutschke, C. J., et al. (2022). Cinnamaldehyde derivatives act as antimicrobial agents against Acinetobacter baumannii through the inhibition of cell division. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.967949
Chen, W. (2020). Host innate immune responses to Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00486
Conde-Perez, K., Vazquez-Ucha, J. C., Alvarez-Fraga, L., Ageitos, L., Rumbo-Feal, S., Martinez-Guitian, M., et al. (2021). In-depth analysis of the role of the acinetobactin cluster in the virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.752070
Corral, J., Pérez-Varela, M., Barbé, J., and Aranda, J. (2020). Direct interaction between RecA and a CheW-like protein is required for surface-associated motility, chemotaxis and the full virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii strain ATCC 17978. Virulence 11, 315–326. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1748923
Culetto, E. and Sattelle, D. B. (2000). A role for Caenorhabditis elegans in understanding the function and interactions of human disease genes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 869–877. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.6.869
de Souza, C. M., Silverio de Oliveira, W., Fleitas Martinez, O., Dos Santos Neto, N. A., Buccini, D. F., Nieto Marin, V., et al. (2024). Evaluating virulence features of Acinetobacter baumannii resistant to polymyxin B. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 77, ovae061. doi: 10.1093/lambio/ovae061
Domingues, R., Oliveira, R., Silva, S., Araújo, D., Almeida, C., Cho, G.-S., et al. (2024). Molecular detection of carbapenemases in Acinetobacter baumannii strains of Portugal and association with sequence types, capsular types, and virulence. Clin. Ther. 46, e9–e15. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2024.09.005
Eijkelkamp, B. A., Stroeher, U. H., Hassan, K. A., Paulsen, I. T., and Brown, M. H. (2014). Comparative analysis of surface-exposed virulence factors of Acinetobacter baumannii. BMC Genomics 15, 1020. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1020
Espinal, P., Pantel, A., Rolo, D., Marti, S., López-Rojas, R., Smani, Y., et al. (2019). Relationship between different resistance mechanisms and virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Drug Resist. 25, 752–760. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0182
Ezzeddine, Z. and Ghssein, G. (2023). Towards new antibiotics classes targeting bacterial metallophores. Microb. Pathog. 182, 106221. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106221
Fournier, P.-E., Vallenet, D., Barbe, V., Audic, S., Ogata, H., Poirel, L., et al. (2006). Comparative genomics of multidrug resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. PloS Genet. 2, e7. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020007
Gaddy, J. A., Arivett, B. A., McConnell, M. J., Lopez-Rojas, R., Pachon, J., and Actis, L. A. (2012). Role of acinetobactin-mediated iron acquisition functions in the interaction of Acinetobacter baumannii strain ATCC 19606T with human lung epithelial cells, Galleria mellonella caterpillars, and mice. Infect. Immun. 80, 1015–1024. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06279-11
GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators (2024). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990-2021: a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 404, 1199–1226. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01867-1
Gebhardt, M. J., Czyz, D. M., Singh, S., Zurawski, D. V., Becker, L., and Shuman, H. A. (2020). GigC, a LysR family transcription regulator, is required for cysteine metabolism and virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii. Infect. Immun. 89. doi: 10.1128/iai.00180-00120
Gebhardt, M. J., Gallagher, L. A., Jacobson, R. K., Usacheva, E. A., Peterson, L. R., Zurawski, D. V., et al. (2015). Joint transcriptional control of virulence and resistance to antibiotic and environmental stress in Acinetobacter baumannii. mBio 6. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01660-01615
Geisinger, E., Mortman, N. J., Vargas-Cuebas, G., Tai, A. K., and Isberg, R. R. (2018). A global regulatory system links virulence and antibiotic resistance to envelope homeostasis in Acinetobacter baumannii. PloS Pathog. 14, e1007030. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007030
Gil-Marqués, M. L., Pachón, J., and Smani, Y. A.-O. (2022). iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Acinetobacter baumannii under Hypoxia and Normoxia Reveals the Role of OmpW as a Virulence Factor. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0232821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02328-21
Gong, R., An, Z., Zhang, W., Chen, F., and Wang, K. J. (2022). The Antimicrobial Peptide LJ-hep2 from Lateolabrax japonicus Exerting Activities against Multiple Pathogenic Bacteria and Immune Protection In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 20, 651. doi: 10.3390/md20100651
Green, E. R., Juttukonda, L. J., and Skaar, E. P. (2020). The manganese-responsive transcriptional regulator mumR protects Acinetobacter baumannii from oxidative stress. Infect. Immun. 88, 10-1128. doi: 10.1128/iai.00762-19
Hansen, L. K., Brown, M., Johnson, D., Palme Ii, D. F., Love, C., and Darouiche, R. (2009). In vivo model of human pathogen infection and demonstration of efficacy by an antimicrobial pouch for pacing devices. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 32, 898–907. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2009.02406.x
Harris, G., Kuo Lee, R., Lam, C. K., Kanzaki, G., Patel, G. B., Xu, H. H., et al. (2013). A mouse model of Acinetobacter baumannii-associated pneumonia using a clinically isolated hypervirulent strain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57, 3601–3613. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00944-13
Harris, G., KuoLee, R., Xu, H. H., and Chen, W. (2019). Acute intraperitoneal infection with a hypervirulent Acinetobacter baumannii isolate in mice. Sci. Rep. 9, 6538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43000-4
He, Z. A.-O., Huang, Y., Li, W., Zhang, H., Cao, R., Ali, M. A.-O., et al. (2024). Characterization and genomic analysis of the highly virulent Acinetobacter baumannii ST1791 strain dominating in Anhui, China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 69, e0126224. doi: 10.1128/aac.01262-24
H Meijer, A. and P Spaink, H. (2011). Host-pathogen interactions made transparent with the zebrafish model. Curr. Drug Targets 12, 1000–1017. doi: 10.2174/138945011795677809
Hubloher, J. J., van der Sande, L., Schaudinn, C., Müller, V., and Averhoff, B. (2023). The Tol-Pal system of Acinetobacter baumannii is important for cell morphology, antibiotic resistance and virulence. Int. Microbiol. 26, 543–550. doi: 10.1007/s10123-022-00319-9
Huch, M. and Koo, B.-K. (2015). Modeling mouse and human development using organoid cultures. Development 142, 3113–3125. doi: 10.1242/dev.118570
Huo, W. W., Busch, L. M., Hernandez-Bird, J., Hamami, E., Marshall, C. W., Geisinger, E., et al. (2022). Immunosuppression broadens evolutionary pathways to drug resistance and treatment failure during Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 7, 796–79+. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01126-8
Iwashkiw, J. A., Seper, A., Weber, B. S., Scott, N. E., Vinogradov, E., Stratilo, C., et al. (2012). Identification of a general O-linked protein glycosylation system in Acinetobacter baumannii and its role in virulence and biofilm formation. PloS Pathog. 8, e1002758. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002758
Jackson-Litteken, C. A.-O. X., Di Venanzio, G., Le, N. H., Scott, N. A.-O., Djahanschiri, B., Distel, J. S., et al. (2022). InvL, an invasin-like adhesin, is a type II secretion system substrate required for Acinetobacter baumannii uropathogenesis. mBio 13, e0025822. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00258-22
Jayathilaka, E., Rajapaksha, D. C., Nikapitiya, C., Lee, J., De Zoysa, M., and Whang, I. (2022). Novel Antimicrobial Peptide “Octoprohibitin” against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Pharm. (Basel) 15, 928. doi: 10.3390/ph15080928
Jiang, X., Shan, X., Jia, J., Yang, X., Yang, M., Hou, S., et al. (2024). The role of AbaI quorum sensing molecule synthase in host cell inflammation induced by Acinetobacter baumannii and its effect on zebrafish infection model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 278, Article 134568. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134568
Juttukonda, L. J., Chazin, W. J., and Skaar, E. P. (2016). Acinetobacter baumannii coordinates urea metabolism with metal import to resist host-mediated metal limitation. mBio 7, 10-1128. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01475-01416
Karampatakis, T., Tsergouli, K., and Behzadi, P. (2024). Pan-genome plasticity and virulence factors: A natural treasure trove for Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics (Basel) 13, 257. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030257
Kareem, S. M., Al-Kadmy, I. M. S., Al-Kaabi, M. H., Aziz, S. N., and Ahmad, M. (2017). Acinetobacter baumannii virulence is enhanced by the combined presence of virulence factors genes phospholipase C (plcN) and elastase (lasB). Microb. Pathog. 110, 568–572. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.08.001
Kay, S., Edwards, J., Brown, J., and Dixon, R. (2019). Galleria mellonella Infection Model Identifies Both High and Low Lethality of Clostridium perfringens Toxigenic Strains and Their Response to Antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01281
Khadke, S. K., Lee, J. H., Kim, Y. G., Raj, V., and Lee, J. (2021). Assessment of Antibiofilm Potencies of Nervonic and Oleic Acid against Acinetobacter baumannii Using In Vitro and Computational Approaches. Biomedicines 9, 1133. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091133
Khalil, M. A. F., Ahmed, F. A., Elkhateeb, A. F., Mahmoud, E. E., Ahmed, M. I., Ahmed, R. I., et al. (2021). Virulence Characteristics of Biofilm-Forming Acinetobacter baumannii in Clinical Isolates Using a Galleria mellonella Model. Microorganisms 9, 2365. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112365
Kim, N., Son, J. H., Kim, K., Kim, H. J., Kim, Y. J., Shin, M., et al. (2021). Global regulator DksA modulates virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 12, 2750–2763. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1995253
Labrador-Herrera, G., Perez-Pulido, A. J., Alvarez-Marin, R., Casimiro-Soriguer, C. S., Cebrero-Cangueiro, T., Moran-Barrio, J., et al. (2020). Virulence role of the outer membrane protein CarO in carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 11, 1727–1737. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1855912
Lam, S., Chua, H., Gong, Z., Wen, Z., Lam, T., and Sin, Y. (2002). Morphologic transformation of the thymus in developing zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 225, 87–94. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10127
Lazaro-Diez, M., Chapartegui-Gonzalez, I., Suberbiola, B., Ocejo-Vinyals, J. G., Lopez-Hoyos, M., and Ramos-Vivas, J. (2020). Gene expression profiling in human neutrophils after infection with Acinetobacter baumannii in vitro. PloS One 15, e0242674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242674
Lee, J. H., Kim, Y. G., Khadke, S. K., Yamano, A., Woo, J. T., and Lee, J. (2019). Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of prenylated flavanones from Macaranga tanarius. Phytomedicine 63, 153033. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153033
Lemaitre, B. and Ausubel, F. M. (2008). Animal models for host-pathogen interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 11, 249–250. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.05.002
Li, Y., Cui, Y., Song, K., Shen, L., Xiao, L., Jin, J., et al. (2024). TagP, a PAAR-domain containing protein, plays roles in the fitness and virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1379106
Li, P., Zhang, S. R., Wang, J. D., Al-Shamiri, M. M., Luo, K., Liu, S. Y., et al. (2024). The role of type VI secretion system genes in antibiotic resistance and virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1297818
Lim, S. M. S., Abidin, A. Z., Liew, S., Roberts, J., and Sime, F. (2019). The global prevalence of multidrug-resistance among Acinetobacter baumannii causing hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia and its associated mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 79, 593–600. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2019.09.012
Lin, Y. S., Zhao, D. Y., Huang, N., Liu, S. X., Zheng, J. Y., Cao, J. M., et al. (2023). Clinical impact of the type VI secretion system on clinical characteristics, virulence and prognosis of Acinetobacter baumannii during bloodstream infection. Microb. Pathog. 182, Article 106252. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106252
Liu, D., Liu, Z. S., Hu, P., Cai, L., Fu, B. Q., Li, Y. S., et al. (2016). Characterization of surface antigen protein 1 (SurA1) from Acinetobacter baumannii and its role in virulence and fitness. Vet. Microbiol. 186, 126–138. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.02.018
López-Martín, M., Dubern, J. A.-O., Alexander, M. R., and Williams, P. A.-O. (2021). AbaM Regulates Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii. LID - 10.1128/JB.00635–20 [doi] LID - e00635-20. J. Bacteriol. 203, e00635–e00620. doi: 10.1128/JB.00635-20
Lucidi, M., Visaggio, D., Migliaccio, A., Capecchi, G., Visca, P., Imperi, F., et al. (2024). Pathogenicity and virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii: Factors contributing to the fitness in healthcare settings and the infected host. Virulence 15, 2289769. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2289769
Mangas, E. L., Rubio, A., Alvarez-Marin, R., Labrador-Herrera, G., Pachon, J., Pachon-Ibanez, M. E., et al. (2019). Pangenome of Acinetobacter baumannii uncovers two groups of genomes, one of them with genes involved in CRISPR/Cas defence systems associated with the absence of plasmids and exclusive genes for biofilm formation. Microb. Genom. 5, e000309. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000309
Martinez-Guitian, M., Vazquez-Ucha, J. C., Alvarez-Fraga, L., Conde-Perez, K., Bou, G., Poza, M., et al. (2020). Antisense inhibition of lpxB gene expression in Acinetobacter baumannii by peptide-PNA conjugates and synergy with colistin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75, 51–59. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz409
Martínez-Guitián, M., Vázquez-Ucha, J. C., Álvarez-Fraga, L., Conde-Pérez, K., Lasarte-Monterrubio, C., Vallejo, J. A., et al. (2019). Involvement of HisF in the persistence of Acinetobacter baumannii during a pneumonia infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 9, 310. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00310
Martinez-Guitian, M., Vazquez-Ucha, J. C., Alvarez-Fraga, L., Conde-Perez, K., Vallejo, J. A., Perina, A., et al. (2021). Global transcriptomic analysis during murine pneumonia infection reveals new virulence factors in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Infect. Dis. 223, 1356–1366. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa522
Masopust, D., Sivula, C. P., and Jameson, S. C. (2017). Of mice, dirty mice, and men: using mice to understand human immunology. J. Immunol. 199, 383–388. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700453
Maure, A., Robino, E., and Van der Henst, C. (2023). The intracellular life of Acinetobacter baumannii. Trends Microbiol. 31, 1238–1250. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2023.06.007
May, H. C., Yu, J. J., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Cap, A. P., Chambers, J. P., et al. (2019). Thioredoxin-A is a virulence factor and mediator of the type IV pilus system in Acinetobacter baumannii. PloS One 14, e0218505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218505
McGuffey, J. C., Jackson-Litteken, C. D., Di Venanzio, G., Zimmer, A. A., Lewis, J. M., Distel, J. S., et al. (2023). The tRNA methyltransferase TrmB is critical for Acinetobacter baumannii stress responses and pulmonary infection. mBio 14, e0141623. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01416-23
McKenna, C. H., Asgari, D., Crippen, T. L., Zheng, L., Sherman, R. A., Tomberlin, J. K., et al. (2022). Gene expression in Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae) larvae exposed to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii identifies shared and microbe-specific induction of immune genes. Insect Mol. Biol. 31, 85–100. doi: 10.1111/imb.12740
Medina, A., Chen, Y. C., Zhang, J., Ogden, S. C., Cotsmire, S., Vishwasrao, H. D., et al. (2025). Modeling neurotropic virus infection with functional human neural spheroids as a platform for high-throughput antiviral screening and pathogenesis. Antiviral Res. 242, 106248. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2025.106248
Mirali, M., Jahangiri, A., Jalali Nadoushan, M., and Rasooli, I. (2023). A two-protein cocktail elicits a protective immune response against Acinetobacter baumannii in a murine infection model. Microb. Pathog. 182, 106262. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106262
Moffatt, J. H., Harper, M., Mansell, A., Crane, B., Fitzsimons, T. C., Nation, R. L., et al. (2013). Lipopolysaccharide-deficient Acinetobacter baumannii shows altered signaling through host Toll-like receptors and increased susceptibility to the host antimicrobial peptide LL-37. Infect. Immun. 81, 684–689. doi: 10.1128/iai.01362-12
Mukherjee, P., Roy, S., Ghosh, D., and Nandi, S. (2022). Role of animal models in biomedical research: a review. Lab. Anim. Res. 38, 18. doi: 10.1186/s42826-022-00128-1
Mylonakis, E., Podsiadlowski, L., Muhammed, M., and Vilcinskas, A. (2016). Diversity, evolution and medical applications of insect antimicrobial peptides. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 371, 20150290. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0290
Neto, S., Vieira, A., Oliveira, H., and Espiña, B. (2023). Assessing Acinetobacter baumannii virulence and treatment with a bacteriophage using zebrafish embryos. FASEB J. 37, e23013. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300385R
Niu, T., Guo, L., Luo, Q., Zhou, K., Yu, W., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Wza gene knockout decreases Acinetobacter baumannii virulence and affects Wzy-dependent capsular polysaccharide synthesis. VIRULENCE 11, 1–13. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1700659
Park, A. J., Wright, M. A., Roach, E. J., and Khursigara, C. M. (2021). Imaging host-pathogen interactions using epithelial and bacterial cell infection models. J. Cell Sci. 134, jcs250647. doi: 10.1242/jcs.250647
Peleg, A. Y., Jara, S., Monga, D., Eliopoulos, G. M., Moellering, R. C., Jr., and Mylonakis, E. (2009). Galleria mellonella as a model system to study Acinetobacter baumannii pathogenesis and therapeutics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53, 2605–2609. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01533-08
Pérez, A., Merino, M., Rumbo-Feal, S., Álvarez-Fraga, L., Vallejo, J., Beceiro, A., et al. (2017). The FhaB/FhaC two-partner secretion system is involved in adhesion of Acinetobacter baumannii AbH12O-A2 strain. Virulence 8, 959–974. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1262313
Pérez-Varela, M., Corral, J., Aranda, J., and Barbé, J. (2019). Roles of efflux pumps from different superfamilies in the surface-associated motility and virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63, 10-1128. doi: 10.1128/aac.02190-18
Plumet, L., Magnan, C., Ahmad-Mansour, N., Sotto, A., Lavigne, J. P., Costechareyre, D., et al. (2024). The zebrafish embryo model: unveiling its potential for investigating phage therapy against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 68, e0056124. doi: 10.1128/aac.00561-24
Qin, Q. M., Pei, J., Gomez, G., Rice-Ficht, A., Ficht, T. A., and de Figueiredo, P. (2020). A tractable drosophila cell system enables rapid identification of Acinetobacter baumannii host factors. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00240
Rafiei Delfan, R., Fekrirad, Z., Jalali Nadoushan, M., and Rasooli, I. (2024). Adherence and cytotoxicity of Acinetobacter baumannii on human cervical carcinoma epithelial cells: Exploring the role of anti-OmpA antibodies. Med. Microecol. 22, 100113. doi: 10.1016/j.medmic.2024.100113
Rajabzadeh, M., Fekrirad, Z., Jalali Nadoushan, M., and Rasooli, I. (2024). Characterizing the interplay between Acinetobacter baumannii, A549 cells, and anti-Omp34 antibodies: implications for adherence, internalization, and cytotoxicity. Folia Microbiol. (Praha). 70 (3), 699–709. doi: 10.1007/s12223-024-01218-4
Rakovitsky, N., Temkin, E., Hameir, A., Lurie-Weinberger, M., Keren-Paz, A., and Carmeli, Y. (2024). Zophobas morio larvae as a novel model for the study of Acinetobacter virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1375787
Ranjbar, A., Rasooli, I., Jahangiri, A., and Ramezanalizadeh, F. (2022). Specific egg yolk antibody raised to biofilm associated protein (Bap) is protective against murine pneumonia caused by Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 12, 12576. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16894-w
Richmond, G. E., Evans, L. P., Anderson, M. J., Wand, M. E., Bonney, L. C., Ivens, A., et al. (2016). The Acinetobacter baumannii two-component system AdeRS regulates genes required for multidrug efflux, biofilm formation, and virulence in a strain-specific manner. mBio 7, e00430–e00416. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00430-16
Rosa, R. B., Dantas, W. M., do Nascimento, J. C., da Silva, M. V., de Oliveira, R. N., and Pena, L. J. (2021). In vitro and in vivo models for studying SARS-CoV-2, the etiological agent responsible for COVID-19 pandemic. Viruses 13, 379. doi: 10.3390/v13030379
Roy, R., You, R.-I., Lin, M.-D., and Lin, N.-T. (2020). Mutation of the carboxy-terminal processing protease in Acinetobacter baumannii affects motility, leads to loss of membrane integrity, and reduces virulence. Pathogens 9, 322. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050322
Ruamsap, N., Thomas, C. S., Imerbsin, R., Reed, M. C., Gonwong, S., Lurchachaiwong, W., et al. (2022). Chronic wound infection model of Acinetobacter baumannii in outbred mice. Mil Med. 188 (7-8), e1708-e1716. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usac020
Rumbo-Feal, S., Perez, A., Ramelot, T. A., Alvarez-Fraga, L., Vallejo, J. A., Beceiro, A., et al. (2017). Contribution of the A. baumannii A1S_0114 gene to the interaction with eukaryotic cells and virulence. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00108
Russo, A., Giuliano, S., Ceccarelli, G., Alessandri, F., Giordano, A., Brunetti, G., et al. (2018). Comparison of septic shock due to multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii or Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae in intensive care unit patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, 10-1128. doi: 10.1128/aac.02562-02517
Sabatini, A., Lucidi, M., Ciolfi, S., Vuotto, C., De Bardi, M., Visca, P., et al. (2024). Innate immune mechanisms promote human response to Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 54 (11), 2451170. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451170
Sams, V. G., Lawson, C. M., Coan, P., Bemis, D., Newkirk, K., Karlstad, M., et al. (2012). Effect of local anesthetic on microorganisms in a murine model of surgical site infection. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 73, 441–446. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3182583e4f
Sarkar, S. and Heise, M. T. (2019). Mouse models as resources for studying infectious diseases. Clin. Ther. 41, 1912–1922. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.08.010
Schmitt, B. L., Leal, B. F., Leyser, M., de Barros, M. P., Trentin, D. S., Ferreira, C. A. S., et al. (2023). Increased ompW and ompA expression and higher virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii persister cells. BMC Microbiol. 23, 157. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02904-y
Schmitz, D. A., Wechsler, T., Li, H. B., Menze, B. H., and Kümmerli, R. (2024). A new protocol for multispecies bacterial infections in zebrafish and their monitoring through automated image analysis. PloS One 19, e0304827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304827
Segeritz, C.-P. and Vallier, L. (2017). “Cell culture,” in Basic Science Methods for Clinical Researchers (USA: Academic Press, Inc.), 151–172. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-803077-6.00009-6
Shadan, A., Pathak, A., Ma, Y., Pathania, R., and Singh, R. P. (2023). Deciphering the virulence factors, regulation, and immune response to Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1053968
Sharma, S., Mohler, J., Mahajan, S. D., Schwartz, S. A., Bruggemann, L., and Aalinkeel, R. (2023). Microbial biofilm: A review on formation, infection, antibiotic resistance, control measures, and innovative treatment. Microorganisms 11, 1614. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061614
Shashkov, A. S., Liu, B., Kenyon, J. J., Popova, A. V., Shneider, M. M., Senchenkova, S., et al. (2017). Structures of the K35 and K15 capsular polysaccharides of Acinetobacter baumannii LUH5535 and LUH5554 containing amino and diamino uronic acids. Carbohydr. Res. 448, 28–34. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2017.05.017
Shrihari, S., May, H. C., Yu, J. J., Papp, S. B., Chambers, J. P., Guentzel, M. N., et al. (2022). Thioredoxin-mediated alteration of protein content and cytotoxicity of Acinetobacter baumannii outer membrane vesicles. Exp. Biol. Med. 247, 282–288. doi: 10.1177/15353702211052952
Skardal, A., Devarasetty, M., Soker, S., and Hall, A. R. (2015). In situ patterned micro 3D liver constructs for parallel toxicology testing in a fluidic device. Biofabrication 7, 031001. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/7/3/031001
Skerniškytė, J., Karazijaitė, E., Deschamps, J., Krasauskas, R., Armalytė, J., Briandet, R., et al. (2019a). Blp1 protein shows virulence-associated features and elicits protective immunity to Acinetobacter baumannii infection. BMC Microbiol. 19, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1615-3
Skerniškytė, J., Krasauskas, R., Péchoux, C., Kulakauskas, S., Armalytė, J., and Sužiedėlienė, E. (2019b). Surface-related features and virulence among Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates belonging to international clones I and II. Front. Microbiol. 9, 3116. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03116
Slusky, J. S. and Dunbrack, R. L., Jr. (2013). Charge asymmetry in the proteins of the outer membrane. Bioinformatics 29, 2122–2128. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt355
Srinivasan, V. B., Venkataramaiah, M., Mondal, A., and Rajamohan, G. (2015). Functional characterization of AbeD, an RND-type membrane transporter in antimicrobial resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. PloS One 10, e0141314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141314
Sullivan, C., Matty, M., Jurczyszak, D., Gabor, K., Millard, P., Tobin, D., et al. (2017). Infectious disease models in zebrafish. Methods Cell Biol. 138, 101–136. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.10.005
Tang, J., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Ding, Y., Sun, X., and Ni, Z. (2020). Contribution of the AbaI/AbaR quorum sensing system to resistance and virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains. Infect. Drug Resist. 13, 4273–4281. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S276970
Tao, Y., Duma, L., and Rossez, Y. (2021). Galleria mellonella as a Good Model to Study Acinetobacter baumannii Pathogenesis. Pathogens 10, 1483. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10111483
Ten, K. E., Muzahid, N. H., Rahman, S., and Tan, H. S. (2023). Use of the waxworm Galleria mellonella larvae as an infection model to study Acinetobacter baumannii. PloS One 18, e0283960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283960
Thacharodi, A., Vithlani, A., Hassan, S., Alqahtani, A., and Pugazhendhi, A. (2024). Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii raises global alarm for new antibiotic regimens. iScience 27, 111367. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111367
Tietgen, M., Leukert, L., Sommer, J., Kramer, J. S., Brunst, S., Wittig, I., et al. (2021). Characterization of the novel OXA-213-like beta-lactamase OXA-822 from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 76, 626–634. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa488
Tillotson, G. S. (2016). Trojan horse antibiotics-A novel way to circumvent gram-negative bacterial resistance? Infect. Dis. (Auckl) 9, 45–52. doi: 10.4137/idrt.S31567
Trebosc, V., Lucchini, V., Narwal, M., Wicki, B., Gartenmann, S., Schellhorn, B., et al. (2022). Targeting virulence regulation to disarm Acinetobacter baumannii pathogenesis. Virulence 13, 1868–1883. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2135273
Vallejo, J. A., Beceiro, A., Rumbo-Feal, S., Rodriguez-Palero, M. J., Russo, T. A., and Bou, G. (2015). Optimisation of the Caenorhabditis elegans model for studying the pathogenesis of opportunistic Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.05.021
Vareschi, S., Jaut, V., Vijay, S., Allen, R. J., and Schreiber, F. (2025). Antimicrobial efflux and biofilms: an interplay leading to emergent resistance evolution. Trends Microbiol. 33, 1018–1032. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2025.04.012
Wang, H., Xu, Q., Heng, H., Zhao, W., Ni, H., Chen, K., et al. (2024). High mortality of Acinetobacter baumannii infection is attributed to macrophage-mediated induction of cytokine storm but preventable by naproxen. EBioMedicine 108, 105340. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105340
Wang, D., Zhou, X., Zheng, X., and Dai, H. (2024). Editorial: Caenorhabditis elegans: a model organism for research on medicinal plants and their metabolites. Front. Pharmacol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1472276
Weidensdorfer, M., Ishikawa, M., Hori, K., Linke, D., Djahanschiri, B., Iruegas, R., et al. (2019). The Acinetobacter trimeric autotransporter adhesin Ata controls key virulence traits of Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 10, 68–81. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1558693
WHO (2024). WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List 2024: bacterial pathogens of public health importance to guide research, development and strategies to prevent and control antimicrobial resistance (Geneva: World Health Organization). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Williams, D. F. (2022). Biocompatibility pathways and mechanisms for bioactive materials: The bioactivity zone. Bioactive Mater. 10, 306–322. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.08.014
Wiradiputra, M. R. D., Khuntayaporn, P., Thirapanmethee, K., Wanapaisan, P., and Chomnawang, M. T. (2025). Genomic insights into biofilm-associated virulence in extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 9, 100434. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2025.100434
Yamada, K. M. and Cukierman, E. (2007). Modeling tissue morphogenesis and cancer in 3D. Cell 130, 601–610. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.006
Yehya, A., Ezzeddine, Z., Chakkour, M., Dhaini, Z., Bou Saba, M. S., Bou Saba, A. S., et al. (2025). The intricacies of Acinetobacter baumannii: a multifaceted comprehensive review of a multidrug-resistant pathogen and its clinical significance and implications. Front. Microbiol. 16. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1565965
Zeng, X., Wang, N., Xiang, C., Liu, Q., Li, D., Zhou, Y., et al. (2023). Peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein contributes to the virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii and serves as a vaccine candidate. Genomics 115, 110590. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110590
Zhou, H., Gebhardt, M. J., Czyz, D. M., Yao, Y., and Shuman, H. A. (2021). The gigA/gigB Genes Regulate the Growth, Stress Response, and Virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 Strain. Front. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.723949
Zierke, L., Mourad, R., Kohler, T. P., Musken, M., and Hammerschmidt, S. (2025). Influence of the polysaccharide capsule on virulence and fitness of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 16. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1450984
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii, virulence factors, animal models, cell culture, pathogenesis
Citation: Garomsa TL, Shenkutie AM and Leung PHM (2025) Recent advances in host models in studying virulence factors and pathogenesis of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1715193. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1715193
Received: 29 September 2025; Accepted: 20 October 2025;
Published: 10 November 2025.
Edited by:
Percy Schröttner, Technische Universität Dresden, GermanyReviewed by:
Ghassan Ghssein, Islamic University of Lebanon, LebanonDaryoush Babazadeh, Shiraz University, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Garomsa, Shenkutie and Leung. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Polly H. M. Leung, cG9sbHkuaG0ubGV1bmdAcG9seXUuZWR1Lmhr
 Tadesse Lejisa Garomsa
Tadesse Lejisa Garomsa Abebe Mekuria Shenkutie
Abebe Mekuria Shenkutie Polly H. M. Leung
Polly H. M. Leung