- 1Institute for Communication Science, Technische Universitaet Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany
- 2Institute of Communication Science, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany
The comprehensibility of scientific experts is fundamentally important but presents a challenge for experts and their audiences. The definition and evaluation of comprehensibility are central to developing approaches for improvement. On the one hand, comprehensibility can be indicated by linguistic measures; on the other hand, audience assessments represent comprehensibility perceptions. However, the extent of overlap between these perspectives remains unknown. We conducted two studies to address this gap by analyzing five debates on various scientific topics, each featuring three experts. Our approach involved an integration of computational linguistic analyses, surveys, and real-time response measurements. The findings demonstrate that content and linguistic complexity appear complementary in their relationships with audience ratings for comprehensibility. Interestingly, more complex expert statements corresponded to higher overall debate ratings, hinting at the potential influence of human factors. Therefore, recognizing this influence is critical for improving the communication between experts and laypeople.
Introduction
Conveying scientific expertise to the general public is crucial not only at the individual and societal levels, particularly during crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic or the current climate crisis, but also in everyday life (Freiling et al., 2023; Taddicken et al., 2020). The challenge is that science is complex and abstract, and its relevance is often not immediately apparent to laypeople (Guenther et al., 2018). Additionally, the inherent epistemic nature of science often results in communications that present conflicting and even contradictory findings. Moreover, scientific information, particularly on controversial issues, is usually open to potential risks, threats, novel findings, and unexpected occurrences. Scientific information is inherently uncertain (Popper, 2002), making it challenging for laypeople who lack access to scientific sources, methodologies, and processes (Fischhoff and Scheufele, 2013).
Scientific experts offer assistance (König and Jucks, 2019) and help laypersons form opinions as well as make informed decisions through behavioral recommendations for everyday actions (Bromme and Thomm, 2016). They possess high levels of technical, practical, or experiential expertise, which has a practical impact and guides others; expertise is therefore defined by both knowledge and skills, and is also a social attribution (Bromme and Jucks, 2018).
Successful expert-layperson communication requires experts to convey their knowledge appropriately and comprehensibly (Bromme et al., 2001; Taddicken et al., 2020). As members of the scientific system, they are subject to communicative habits and peculiarities that make it difficult for others to understand science (Schimel, 2012; Sharon and Baram-Tsabari, 2014). Moreover, systematic knowledge divergence between experts and laypeople fundamentally fosters communication problems (Bromme et al., 2001). Although expert-laity communication is not aimed at equalizing the respective levels of knowledge (Bromme et al., 2001), reducing knowledge asymmetry is necessary. Bromme and Goldman (2014) argued that research must focus on a layperson’s understanding of science, who may not possess the same depth and breadth of knowledge as scientific experts. This highlights the relevance of (lay) audience perspectives on science communication (Taddicken et al., 2020; Wicke, 2022; Wicke and Taddicken, 2020). Therefore, research should investigate not only how communicating scientists can improve their comprehensibility (Dean, 2012; Meredith, 2021), but also how the public perceives the communications of scientists.
We conducted two studies to elucidate the extent to which the linguistic measures of the comprehensibility of scientists coincide with the subjective assessment of the audience. In the first study, we employed an innovative multimethod approach to compare computational linguistic analyses with existing survey data. In the second study, we incorporated real-time response measurements. As various science communication formats have been established with very different aims, and contexts (Fähnrich, 2017), we focused on a specific format of science communication, the expert debate.
Theoretical background
Communication requirements of science communication and their repercussions on language
Generally, science communication is subject to specific pragmatic conditions and exhibits specific linguistic features. Based on the assumption that the generation of knowledge is the central goal of science, Czicza and Hennig (2011) identified four communication requirements that serve this goal. They are reflected in the grammatical structure of science communication and, consequently, appear in the language used (Czicza and Hennig, 2011, pp. 50–54). These four requirements and their linguistic implementation can have decisive consequences for the comprehensibility of science communication.
The economy of scientific language, as the first requirement, is expressed in concise, succinct language. Precision, the second requirement, involves conveying content as unambiguously and clearly as possible. Origo-exclusion, the third requirement, involves neutral wording, which manifests itself, among others, in the use of the passive voice and avoidance of deictic references (e.g., avoidance of first-person formulations). These three requirements can sometimes result in a dense and impersonal style, making texts challenging to process for those less-skilled in this language (Bullock et al., 2019; Sharon and Baram-Tsabari, 2014; Willoughby et al., 2020). As the fourth requirement, discussion is characterized by the perception and reflection of other peoples’ findings in one’s own work. Discussing the state of research on a particular topic can involve reconciling conflicting findings and communicating uncertainty (Guenther and Ruhrmann, 2016; Maier et al., 2016). This is likely accompanied by an increase in the complexity of the ideas expressed (Owens and Wedeking, 2011), which is also likely to be reflected in language (Czicza and Hennig, 2011). It is important to note that the authors assume an idealized notion of written science communication. Naturally, spoken and popular forms of science communication may deviate from this ideal (e.g., Fandrych, 2018). However, we assume that these forms are still oriented toward the ideal type of scientific communication and thus differ systematically from other forms of spoken communication. Moreover, starting from such an ideal type—while recognizing that it may rarely manifest in its pure form—can be useful for understanding why scientific language is particularly prone to certain linguistic features that hinder comprehension.
Implementing these requirements enhances communication efficiency within the scientific community (Oppenheimer, 2006, p. 152). However, the associated linguistic idiosyncrasies, and the intrinsic complexity of contradictions and uncertainties can make communication between experts and laypeople more difficult. There are both knowledge and linguistic divergences between experts and laypersons (Bromme et al., 2001; Rink, 2024). Experts tend to underestimate the complexity of their knowledge and language, leading to inadequate adaptation to the needs of laypeople (Bromme et al., 2001; Bromme and Jucks, 2018; Hinds, 1999; Reif et al., 2020; Taddicken et al., 2020).
Although the dissemination of complex knowledge is an intrinsic aspect of the role of an expert and a prerequisite for defining someone as such, excessive complexity in language is not. Therefore, experts must endeavor to reduce language barriers and make the complexity of the matter more accessible to effectively convey appropriate knowledge to laypersons. This approach can also facilitate the knowledge development of a layperson (Bullock et al., 2019; Kleinnijenhuis, 1991; Tolochko et al., 2019).
Comprehensibility of science communication: how to measure a highly subjective variable
Research on the comprehensibility of scientific information often examines the presence or absence of technical terms and scientific jargon (e.g., Scharrer et al., 2012; Sharon and Baram-Tsabari, 2014; Willoughby et al., 2020). Scientists are often advised to reduce the use of jargon to increase its comprehensibility (Bullock et al., 2019; Dean, 2012; Meredith, 2021). As word comprehension is a crucial factor in understanding statements (Perfetti et al., 2011), considering technical terms and scientific jargon in determining the complexity of scientific language makes sense. This ties in with readability research, which is a subfield of comprehensibility research. Research on both comprehensibility and readability reveals additional important factors.
Comprehension refers to the (re)construction of the meaning of a text (Britt et al., 2018, pp. 9–21). It is both a process and a product (McNamara and Magliano, 2009). Comprehension involves sub-processes that build on linguistic, conceptual, and general knowledge (van den Broek and Espin, 2012). These are integrated to form a coherent mental representation of the text message, which is a product of comprehension (van den Broek et al., 1999). Comprehensibility refers to the ease with which (written or spoken) text can be comprehended (Klare, 1984, p. 681). This is related to the efficiency and effectiveness of comprehension. For example, it can lead to faster reading, higher comprehension performance, and higher subjective perceptions of comprehensibility (Kercher, 2013, pp. 159–161, 201–203). Such measures are used to approximate comprehension and have been previously used as indicators to determine the importance of different comprehensibility predictors (Ballstaedt and Mandl, 1988; Kercher, 2013, pp. 159–161; Klare, 1971).
As evident from the definition of comprehension, several factors are involved in this process and can affect comprehensibility (Kercher, 2013). Textual and recipient-related characteristics play a central role because every text is always processed against the background of the recipient’s prior knowledge, language, and reading skills, and processing capacities (for a review, see Thoms, 2023). Consequently, comprehensibility is subjective and varies from person to person and situation to situation (van den Broek et al., 1999, p. 90). Different strands of research have approached these challenges in various ways (Kercher, 2013).
Readability research examines the portion of comprehensibility that emerges from quantifiable text features known to influence average text processing (Fry, 1989; Groeben, 1982; Kercher, 2010, 2013), neglecting the individual comprehensibility of a text for a particular user, instead potential linguistic complexity is determined. Klare (1984) noted that numerous factors have been explored for their impact on readability indicators (or, more generally, comprehensibility indicators), with semantic and syntactic complexity considered key, with the former often explaining more variance in predicting readable writing (p. 715). Readability research utilizes the fact that easily measurable influencing factors, such as word and sentence lengths, often correlate with other features (also) known to affect word and sentence comprehension. For example, word frequency and familiarity correlate with word length (Balota et al., 2006; Piantadosi et al., 2011). Accordingly, the use of technical language in a text, which can be particularly difficult for laypeople to understand, can often be estimated from the (longer) average word length. Similarly, at the sentence level, longer sentences indicate a higher amount of information being conveyed, thus requiring increased effort and time to process the information (Tiffin-Richards and Schroeder, 2018). Therefore, the sentence complexity can be estimated from the average sentence length. In readability analyses, multiple text features are often integrated to form readability formulas intended to estimate overall complexity. Although these formulas have been criticized, they remain surprisingly good predictive tools (e.g., Benjamin, 2012; Kercher, 2013; Schoonvelde et al., 2019). Furthermore, they can be used to compare the readability of different texts, allowing at least relative statements about linguistic complexity (Thoms et al., 2020, p. 162).
Other strands of research, such as the Hamburg concept of comprehensibility, or more sophisticated concepts based on processing models of text comprehension, place greater emphasis on how an individual or group of individuals perceive a specific text (Kercher, 2013). Generally, these involve the assessment of comprehensibility judgments or comprehension performance. For example, the Hamburg concept of comprehensibility is based on the evaluation of texts along four dimensions of comprehensibility: linguistic simplicity, organizational clarity, conciseness of presentation, and additional stylistic stimulation (Ballstaedt and Mandl, 1988). In this context, the crucial role of culture in comprehension can be emphasized. Following Rink (2024), cultural barriers arise when readers lack the necessary cultural knowledge to fully understand a text. This includes familiarity with discourse and text types, as well as their linguistic, media-specific, and conceptual design. Consequently, culture can be an additional filter for perceiving texts. In addition, Friedrich and Heise (2022) emphasized the significance of subjective judgments as indicators of ease of comprehension. They corroborated the findings of previous studies by demonstrating that readability measures, perceived comprehensibility, and comprehension performance are correlated.
Hereafter, the terms readability and linguistic complexity are used synonymously to refer to the portion of comprehensibility that emerges from text features. When the focus is on perception, it is explicitly referred to as perceived comprehensibility (or similarly, as assessments, ratings, or evaluations of comprehensibility). This perception is the result of the interplay between text and reader characteristics. Analyzing the readability of science communication provides insights into the linguistic attributes that impact its comprehensibility. This includes, but is not limited to, the use of technical vocabulary. This approach presents a significant advantage for science communication research, given that readability and perceived comprehensibility are correlated. However, it is important to note that these analyses focus solely on text mode, and do not consider voice-based para-verbal information, such as speech rate, pauses, or intonation. In addition to the aforementioned factors, the topic and characteristics of the communicator may influence perceived comprehensibility (Kercher, 2013), hence the necessity to investigate the extent to which readability and perceived comprehensibility overlap in science communication.
The science communication format expert debate
A multitude of formats, marked by increased audience engagement and a distinct sense of “eventification” (Fähnrich, 2017), have gained popularity. Expert debates are a popular science communication format that promotes fact-based exchanges between experts and laypersons, and highlights different scientific perspectives. Similar to political discussions and expert panels, they aim to shape public opinion, provide guidance on how to apply scientific findings to everyday actions, offer suggestions for arguments, and provide a framework for evaluating social discourse (Bromme and Thomm, 2016; Wicke and Taddicken, 2020). Expert debates are a well-known and prevalent format that regularly takes place on various topics. In Germany, approximately a quarter of the population occasionally attends expert debates or open lectures (Wissenschaft im Dialog, 2018). Attendance is driven by different motivations, such as learning more about the scientific topic being debated, understanding different scientific perspectives, or interacting with scientific researchers. The highest expectation is to provide complex information comprehensibly (Wicke and Taddicken, 2020).
Considering that science spans a wide range of research fields, disciplines, associated methods, and theories, socioscientific issues frequently attract public interest. Social issues with conceptual or technological ties to science often gain public attention and become central to political debate. They are characterized by typical science-inherent dimensions such as complexity, uncertainty, and contestedness (Funtowicz and Ravetz, 1994; Ruhrmann et al., 2015). Different topics may be associated with varying levels of individual or societal relevance and interest, as well as differing levels of uncertainty and complexity. Topics that are closely related to individuals may generally be perceived as less complex and easier to understand than those related to technology.
Research questions
Our research questions compare linguistic measures with audience perceptions. Therefore, we fulfilled Sharon and Baram-Tsabari’s (2014) demand for an integration of computational data and human evaluations of the use of jargon in science communication. As mentioned previously, assessments are context- and situation-sensitive. Therefore, it is important to highlight that we decided to focus on expert debates:
RQ: To what extent do linguistic measures overlap with audience perceptions of science communication during expert debates?
To answer this research question, we first captured the comprehensibility of science communication. Here, we examine audience perceptions and linguistic measures. We applied a linguistic approach by conceptualizing comprehensibility as readability, thereby capturing semantic and syntactic complexity. Moreover, content characteristics were identified as relevant for the assessment of the comprehensibility of audiences. Therefore, we ask three further research questions as the first step:
RQ1a: How comprehensible does the audience perceive the statements of scientific experts in the context of expert debates (audience perceptions)?
RQ1b: How readable are the statements of scientific experts in the context of expert debates (linguistic measure)?
RQ1c: How complex is the content of the statements made by scientific experts in the context of expert debates (linguistic measure)?
Second, we focused on comparing linguistic measures and audience perceptions:
RQ2a: Do the readability characteristics match the perceptions of the audience in the context of expert debates?
RQ2b: Do the content characteristics match the perceptions of the audience in the context of expert debates?
We applied an innovative multi-method approach using computational linguistic analyses and surveys in Studies 1 and 2, and an additional real-time response measurement of the audience perspective in Study 2. The audience perceptions used for Study 1 were collected for another research study and analyzed secondarily. This integration of methods allows for findings at the aggregate level of debate and additional expert- and statement-specific assessments to capture the influence of personal and statement-related factors more precisely.
We analyzed a series of expert debates referred to as “Die Debatte” (https://www.die-debatte.org). This format was based on a “classic” expert discussion and aimed at introducing scientific facts and various scientific perspectives on controversial scientific topics into societal discourse comprehensibly. Expert debates regularly occured in various German cities. Three experts from different scientific disciplines and two moderators participated in the panel, and attendance was free and open to the public. Each debate was streamed through various media, such as YouTube channels and the website of a German media partner. During the 90-min discussion, the audience could ask questions through paper cards and social media.
Study 1: Comparing linguistic measures and survey data
Methods1
In Study 1, we used paper questionnaires to evaluate the audience’s perceptions of five expert debates on various scientific topics: Autonomous Driving (n = 76), Opinion Research (n = 51), Digitized Childhood (n = 114), the Housing Market (n = 31), and Geoengineering (n = 26), with a total of N = 298 participants. These topics were selected for their presumably different degrees of societal interest, impact, and consequences, as well as their varying levels of uncertainty and complexity. While Autonomous Driving and Geoengineering are primarily technology-oriented issues with no direct, immediate impact on individuals, Digitized Childhood and the Housing Market are less distant from individuals, and may be less complex owing to their more direct impact. The debate on Opinion Research occurred during election times, making it more relatable to the public.
Participants were, on average, 39.7 years old (SD = 17.31), ranging from 17 to 81 years. Gender was well distributed (females: 45%, males: 47%, while the remaining participants chose not to report their gender). The sample was highly educated overall (secondary school leaving certificate [Realschulabschluss]: 5.1%, advanced technical college certificate [Fachhochschulreife]: 4.3%, university entrance qualification [Abitur]: 20.3%, university degree: 61.2%, and doctoral degree: 5.8%), which is typical for expert debate audiences (Wicke and Taddicken, 2020). Participation in the survey was voluntary and completely anonymous.
We prepared transcripts of these debates as the foundation for linguistic analyses using F4 software and standards on the recordings (Dresing and Pehl, 2020). Certain features of spoken language (e.g., non-fluencies and colloquial expressions) were standardized. Comma placement and sentence endings followed transcription rules supported by grammar-checking software. However, subjective judgments in determining sentence boundaries, which may affect sentence length, are inherent in the transcription of spoken language. This should be considered in readability analyses, and the interpretation of results.
Linguistic measures
Our linguistic analyses included an investigation of (1) readability characteristics, evaluating linguistic complexity, and (2) content characteristics, using measures for content-related complexity. Both sets of analyses were aimed at operationalizing the communication requirements proposed in Czicza and Hennig (2011). Readability analyses aim to capture semantic and syntactic complexity by focusing on linguistic features resulting from economy, precision, and origo-exclusion requirements. Measures of content-related (un)certainty and cognitive complexity appear to be appropriate operationalizations of the requirement of discussion.
(1) Linguistic complexity was evaluated using variables indicative of semantic and/or syntactic complexity. At the semantic level, we considered two related measures: the proportion of long words and the proportion of frequent words. Long words are defined as those with more than six letters (Björnsson, 1968). The longer a word, the more difficult it becomes. Therefore, with a higher proportion of long words, the complexity of the text increases. We determined the frequent words based on corpus data from the Leipzig Corpora Collection from 2018 (Goldhahn et al., 2012).2 For this purpose, we considered entries from frequency classes3 0 to 8, representing the 1,212 most frequent (German) words. The higher the proportion of frequent words, the more straightforward the text tends to be because it may contain fewer rare and potentially unknown terms. With this second measurement, we followed previous research that primarily considered the use of technical vocabulary. The advantage of focusing on frequent words is that they eliminate the requirement for topic-specific technical word lists.
At the syntactic level, we consider the average sentence length in words an approximate indicator of sentence complexity. Finally, as an indicator of overall linguistic complexity, we use the readability index LIX (Björnsson, 1968). The sum index integrates the proportion of long words and average sentence length. Higher LIX scores indicate greater linguistic complexity as the proportion of more extended (and potentially more complex) sentences and words increases. Analyses were performed using the R packages quanteda.textstats (Version 0.96 Benoit et al., 2018), koRpus (Version 0.13–8), and koRpus.lang.de (Version 0.1–2) (Michalke, 2020, 2021).
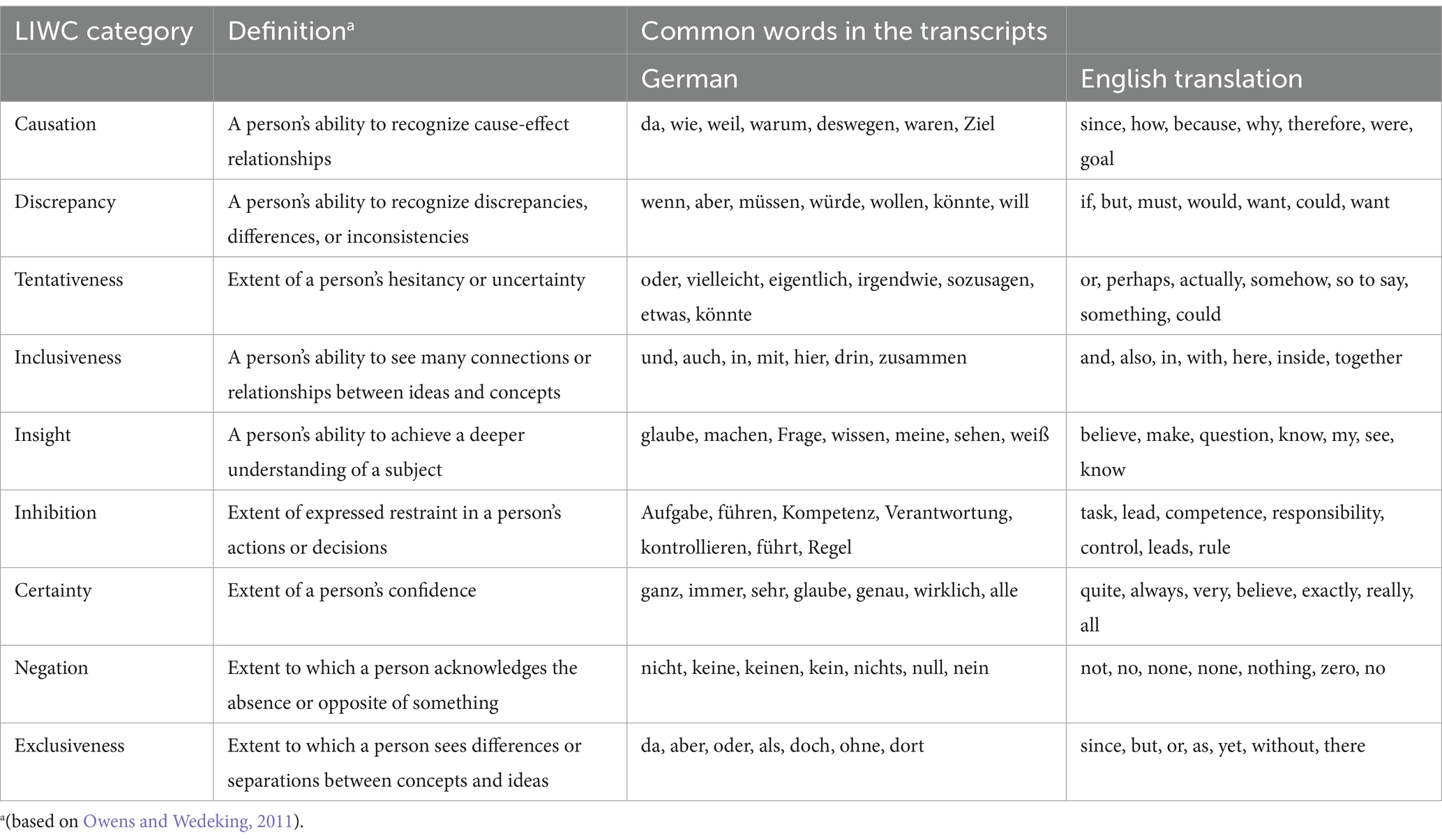
(2) Content complexity is operationalized through certainty and cognitive complexity. We used a dictionary-based approach with the German adaptation of Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC) (Version LIWC2001; Wolf et al., 2008).4 The main idea behind LIWC is that “while words are part of rhetoric, words themselves also can inform us of deeper cognitive issues” (Owens and Wedeking, 2011: 1041). “The function and emotion words people use provide important psychological cues to their thought processes, emotional states, intentions, and motivations” (Tausczik and Pennebaker, 2010: 37). LIWC has been applied to the transcription of spoken language (e.g., Wyss et al., 2015).
Our net certainty score is calculated in ways comparable to sentiment scores (Young and Soroka, 2012: 215) by subtracting the proportion of tentative words from the proportion of certain words. In theory, values between −100 (all words are tentative) and +100 (all words are certain) are possible, with values between the extremes being more likely. Similar to the determination of the sentiments in texts, the question here is which form of expression predominates. The lower the value, the more tentative expressions predominate over certain expressions, such that the text appears more uncertain overall.
Cognitive complexity describes the ability and willingness of actors to perceive and acknowledge different positions on a topic, establish connections, and, thus, develop a differentiated view (Owens and Wedeking, 2011; Wyss et al., 2015). This mental complexity is also reflected in language but is not the same as linguistic complexity (Owens and Wedeking, 2011, p. 1040). Inspired by Owens and Wedeking (2011), cognitive complexity was calculated using nine LIWC categories. As we want to separate mental complexity from linguistic complexity, we deviate from Owens and Wedeking’s (2011) formula by excluding the proportion of words with six or more letters as “a commonly used measure of a person’s linguistic sophistication” (p. 1057). The categories were standardized and integrated using the following formula:
The higher the value, the more cognitively complex the text.
Regarding the calculations, proportions rather than raw word counts were used to account for different text lengths (see Table 1 for LIWC category definitions and word examples).
The analyses were performed using the R package quanteda.dictionaries (Version 0.4) (Benoit and Müller, 2023) using the function liwkalike.
Survey measures
To capture subjective perceptions of comprehensibility, we included one to three single items in the questionnaire provided to the audience:
• Comprehensibility of the expert debate as a whole (“How do you assess the expert debate?” Answer on a five-point semantic differential with left “incomprehensible” and right “comprehensible”) (conducted in all five debates).
• Comprehensibility of the experts (“How do you assess the experts?” Answer on a five-point semantic differential with left “incomprehensible” and right “comprehensible”) (conducted in three debates).
• Comprehensibility of the content (“In the expert debate, the complex scientific content was explained comprehensibly.” Answer from “1–do not agree at all” to “5–fully agree”) (conducted in four debates).
Although these questions concern global assessments of the perceived comprehensibility of debates and certain aspects thereof, analogous measures of “subjective comprehensibility” have demonstrated correlations with comprehension performance (Friedrich and Heise, 2022). Additionally, we asked for the general assessment of the expert debate (“Overall, how did you find the expert debate?,” from “1–did not like at all” to “5–liked very much”) (conducted in all five debates).
Findings
RQ1a: How comprehensible does the audience perceive the statements of scientific experts in the context of expert debates (audience perceptions)?
Overall, the evaluations of the expert debates indicated a high level of perceived comprehensibility, with both the debate and experts receiving ratings higher than four out of five (Table 2). Although the comprehensibility of the complex content was slightly lower, it remained well above average. Overall, the audience expressed positive sentiments toward the debates.
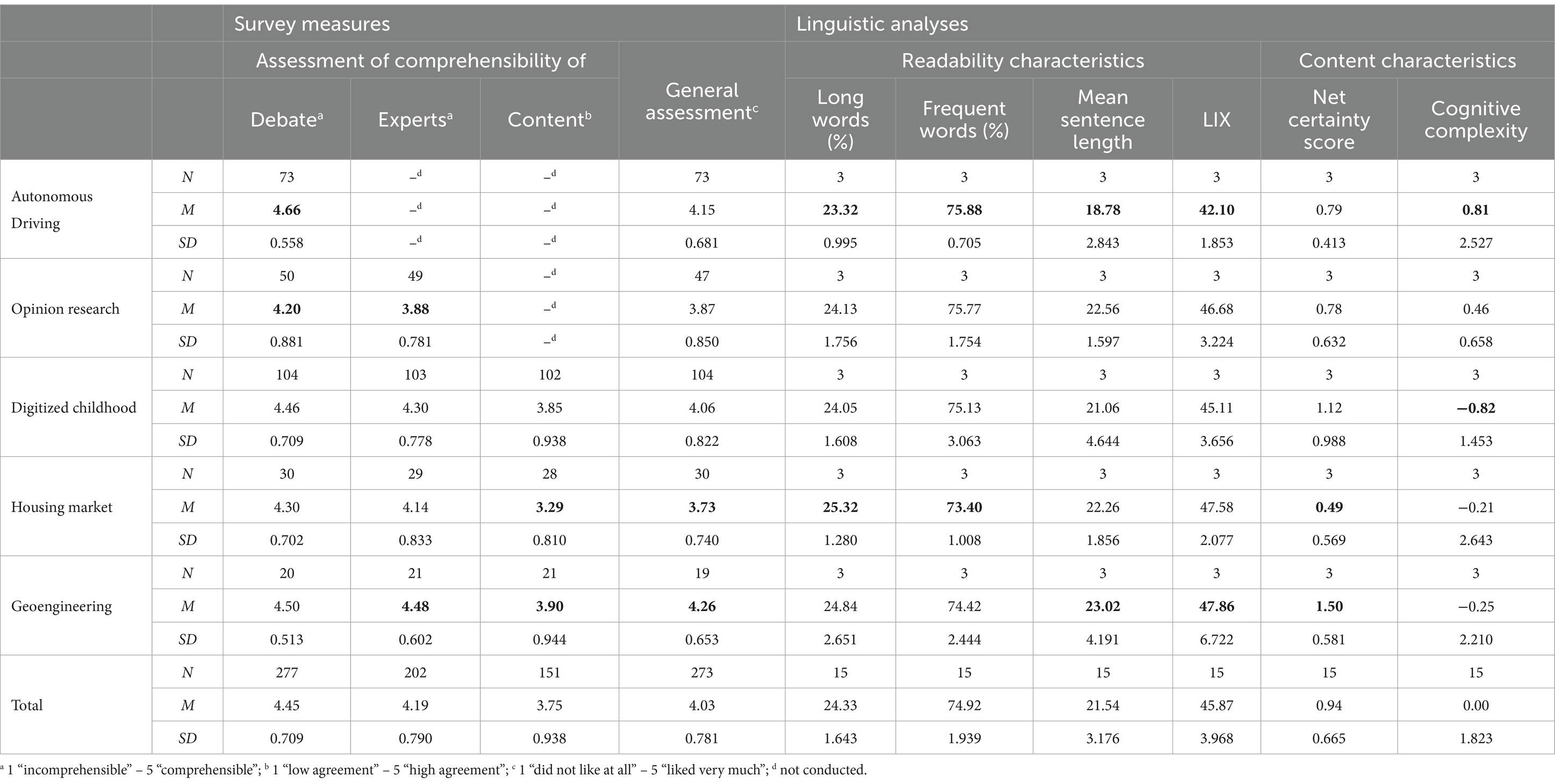
Table 2. Comparison of the debates based on their mean values across survey measures and linguistic analyses.
When comparing the five debates featuring various science topics and different scientific experts, noticeable differences emerged in both general assessments and evaluations of comprehensibility. Nevertheless, a consistent pattern can be observed: the perceived comprehensibility of the debate consistently ranks highest, while the perceived comprehensibility of the explanations for complex content remains comparatively lower. However, the data do not present a clear picture of the assumed differences in individual relevance or immediate societal impact. Autonomous Driving was perceived as the most comprehensible debate, whereas experts in the Geoengineering debate were rated as the most comprehensible. The initial assumption that topics more closely related to individuals are perceived as more comprehensible has not yet been confirmed.
RQ1b: How readable are statements of scientific experts in the context of expert debates (linguistic measure)?
RQ1c: How complex is the content of the statements made by scientific experts in the context of expert debates (linguistic measure)?
To assess the linguistic and content-related complexity of the experts’ statements during the debates, we analyzed the transcripts of the three experts from each of the five debates separately (see an overview in Table 2).
The readability characteristics indicate that the debate on Autonomous Driving was the most readable: the choice of words was simpler, and sentences were shorter. Accordingly, the LIX score as a measure of overall linguistic complexity was also the lowest at (rounded) 42 points. The remaining debates have demonstrated relatively minor differences. Debates on Geoengineering and the Housing Market have the highest linguistic complexity levels in comparison with a LIX of 48 points (rounded). However, the debate on Geoengineering shows significant variability among the experts involved, as reflected by the large standard deviation.
The content characteristics indicated that there was no particularly high degree of (un)certainty in the statements. The greatest certainty is evident in the debate on Geoengineering and the greatest uncertainty in the Housing Market. In the comparison of debates, there were no major differences in cognitive complexity. Interestingly, the Autonomous Driving debate exhibits the highest cognitive complexity but ranks among the best in terms of readability. The digitized Childhood debate showed the lowest cognitive complexity.
RQ2a: Do the readability characteristics match the perceptions of the audience in the context of expert debates?
RQ2b: Do the content characteristics match the perceptions of the audience in the context of expert debates?
To explore the relationship between audience assessments and computational linguistic analyses, we compared the mean values of the linguistic analyses for the five debates with the survey scores (Table 2), which were also collected at the debate level, and could not be attributed to individual experts. Owing to the sample size, this analysis can only serve as a trend analysis. Therefore, we compared debates according to their rankings in the subjective assessments of the debates, readability characteristics, and content characteristics (Table 3). The debates were sorted from the least complex (1) to the most complex value (5) for each measure. The question is how well different measures reproduce consistent rankings. We refrained from making statements about statistical significance. Based on the relevant literature, lower levels of content and linguistic complexity should be associated with higher levels of perceived comprehensibility. This implies that the rankings should be consistent across different variables.
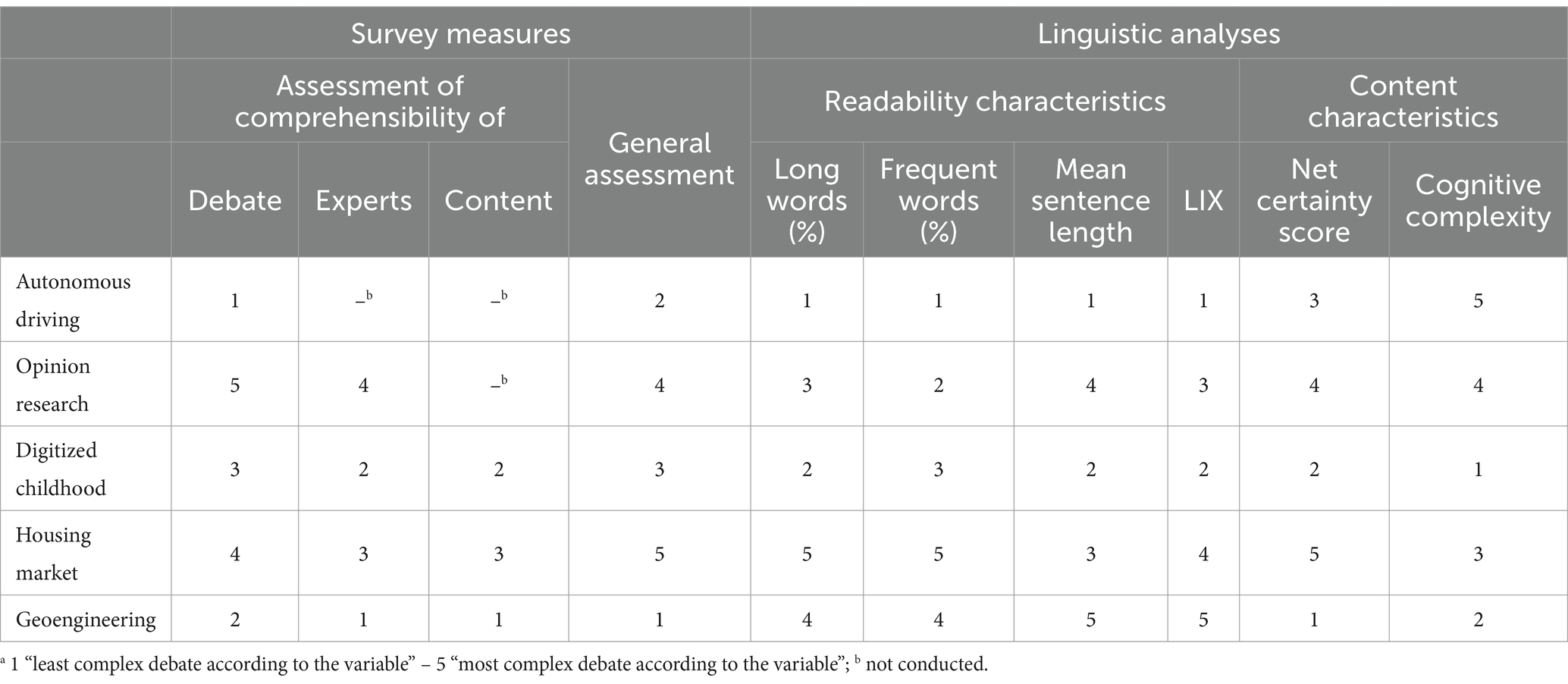
Table 3. Comparison of the debates based on their ranksa across survey measures and linguistic analyses.
The audience’s ratings of comprehensibility and their general assessment of the debates showed a tendency toward agreement. The two debates with the highest perceived comprehensibility values, Autonomous Driving and Geoengineering, were also rated the best overall.
Comparing readability and content characteristics showed some apparent differences. While the rankings within each group of variables are relatively consistent, the more readable debates are not necessarily those that convey less complex content. The debate on Autonomous Driving is the most complex in terms of the content conveyed; however, it is also the most readable. Geoengineering, however, is more straightforward in terms of content and more complex in terms of language. Housing Market and Opinion Research seem to be cases in which both language and content are complex. Conversely, Digitized Childhood is simpler in terms of language, but also less complex in terms of content.
The most evident support for the assumptions of readability research can be seen when comparing the rankings of the readability characteristics and the subjective assessments of the debate on Autonomous Driving: It is the most readable debate with the best assessments of perceived comprehensibility. In the case of Opinion Research, Digitized Childhood, and Housing Market, the agreement is not perfect but at least goes in a similar direction, showing that slightly worse readability scores are accompanied by slightly worse assessments of perceived comprehensibility. The most evident deviation from this pattern can be observed in the Geoengineering debate. This debate, which received one of the highest perceived comprehensibility assessments, had the lowest readability rating.
In this context, the results on the interactions between readability and content characteristics provide interesting insights. The positive audience assessment of the debate on Autonomous Driving, with its relatively high content complexity and low linguistic complexity, provides evidence of the appreciation for expert communication that conveys complex knowledge accessibly. However, this was not the case in the Geoengineering debate. Although the content of this debate is simpler and more linguistically complex, it is still one of the best and most comprehensible debates for the respondents. In this case, respondents’ assessments may have been less influenced by linguistic complexity because the content was already less demanding. Another explanation might be that the audience unconsciously rated the experts’ “scientificness” or “expertness” rather than solely focusing on their comprehensibility (Thomm and Bromme, 2012).
Individual and societal relevance, along with immediate impact, served as an assumption heuristic prior to analysis. However, audience assessments have indicated that the evaluation of comprehensibility does not appear closely related to the expected complexity, uncertainty, or immediate relevance of the topic. This lack of relationship is also mirrored in linguistic measures, with Autonomous Driving being the most readable debate. However, the Geoengineering debate showed the highest values for sentence length and complexity, as indicated by LIX, indicating a readability level closer to the previously assumed topic complexity.
Investigating the relationship between content and linguistic complexity suggests that expert communication, which makes complexity accessible, may be beneficial. These findings are based on comparing debates without considering the absolute differences in the variables. Additionally, factors such as speech rate, intonation, and communicators’ likability or position were omitted. To further explore individual assessments, we conducted Study 2.
Study 2: Comparing linguistic analyses and real-time-response measurement
Measures5
For Study 2, we invited 40 participants to participate in an expert debate on the Housing Market. Participation was voluntary, the data were collected anonymously, and participants were informed about their data protection rights before the study. The participants were asked to answer pre- and post-questionnaires, and assess the debate using a real-time response (RTR) measurement system. Post-receptive methods evaluate the perception and processing of content rather unreliably, as memory difficulties may occur and judgments may be rationalized or biased owing to the effects of social desirability (Ottler, 2013). Moreover, they represent only cumulative judgments. We were interested in individual perception and judgment formation processes with regard to specific linguistic patterns. Reception-accompanying second-by-second recordings of individual impressions using RTR allows them to be traced back to individual parts of the material shown (West and Biocca, 1996).
Sample
Participants were recruited online, and flyers were distributed in local urban areas. An expense allowance of 20 EUR was offered. The sample consisted of 40 participants with an average age of 31.8 years (SD = 1.68), ranging from 21 to 64 years, and gender was well distributed (females: 45%, males: 55%). The sample was highly educated overall (secondary school leaving certificate [Realschulabschluss]: 2.5%, advanced technical college certificate [Fachhochschulreife]: 12.5%, university entrance qualification [Abitur]: 40%, university degree: 45%), which is typical for expert debate audiences (Wicke and Taddicken, 2020).
Real-time-response-measurement
The RTR measurement was conducted on the participants’ Internet-enabled personal iOS or Android devices using the pre-installed RTR system “RTRmobile”6. The slider is operated using a smartphone touchscreen. The system operated in the latched mode, that is, a continuous second-by-second recording of the controller status. The color-coded rating scale ranges from “0″ (bad, red) to “100″ (good, green). We did not directly ask about perceived comprehensibility, rather for an overall assessment to prevent participants from focusing too much on linguistic features.
Survey measures
Similar to Study 1, the measurements included the perceived comprehensibility of the expert debate, individual experts, content presented, and overall assessment (see above). Additionally, we inquired about the comprehensibility of each expert to enable clear differentiation between them.
Findings
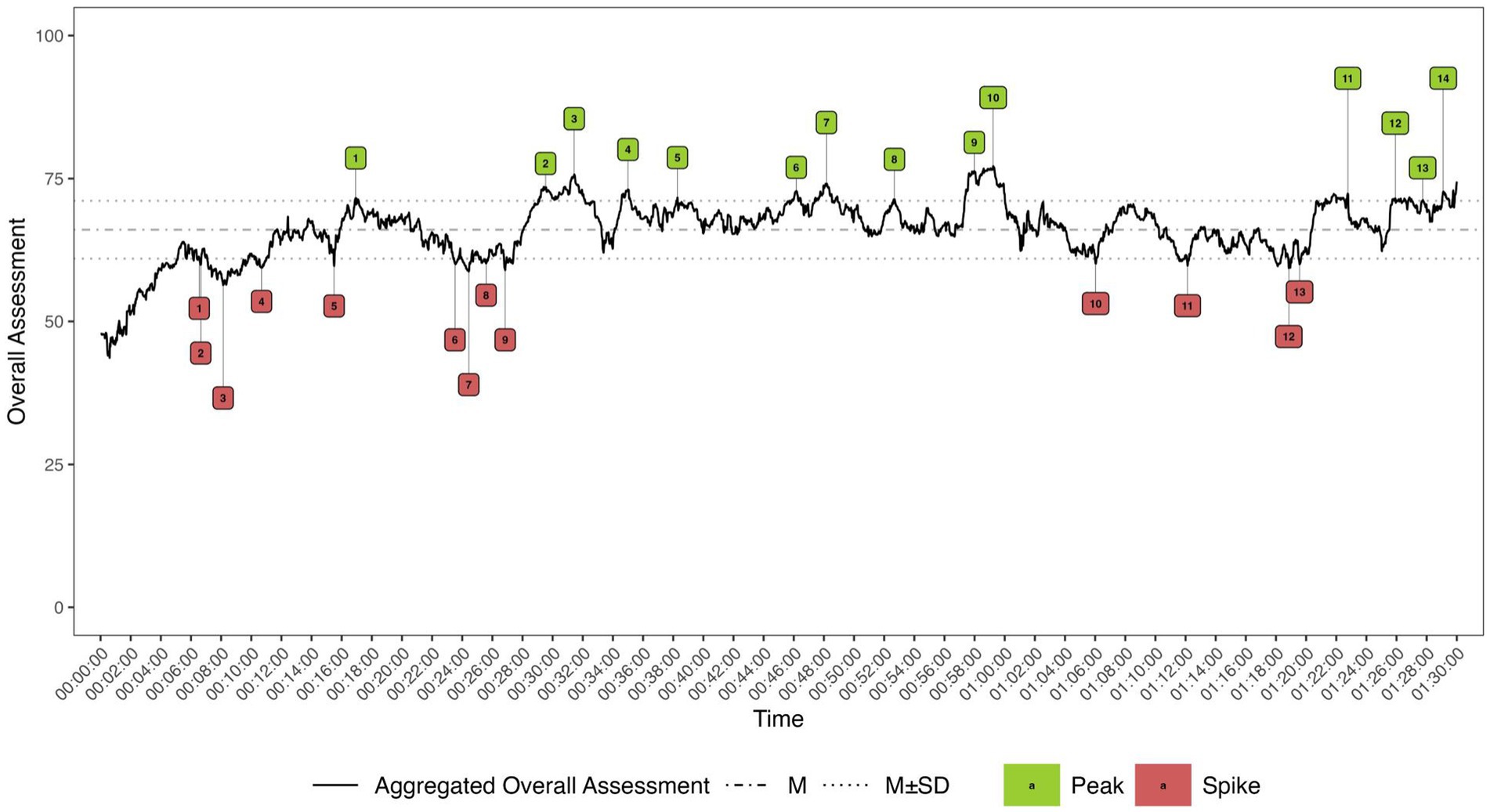
The RTR provides audience judgments for each time point across all participants, resulting in a global “fever curve” for the stimulus course that reflects the average audience response at a given second. This enabled us to apply a peak-spike analysis (Bachl, 2014; Biocca et al., 2014), which revealed passages of expert debate that the audience evaluated most positively (peaks) or negatively (spikes). To determine whether this particularly positive or negative assessment of certain parts of the debate was related to the experts’ comprehensibility, we identified and analyzed 27 peaks (n = 14) and spikes (n = 13) (Figure 1).7
Examination of the experts’ passages revealed that the readability characteristics of the peaks and spikes aligned with the expected pattern for only one expert, Expert B. From a linguistic perspective, the peaks were more readable than the spikes, displaying simpler vocabulary, shorter sentences, and lower LIX scores (Table 4). The situation was reversed for the other two experts. Moreover, the peaks of all experts exhibited higher uncertainty and greater cognitive complexity than their spikes.8
Therefore, real-time assessment indicates that employing scientific language, which is characterized by greater complexity, results in a more favorable evaluation. This increased linguistic complexity can enhance the perceptions of expertise, aligning with Kercher’s (2013) view that complexity positively influences the assessment of arguments and statements. The RTR measurement provides a general evaluation of the debate rather than a specific assessment of comprehensibility. This suggests that the overall debate evaluation is not solely driven by the complexity of the experts’ language. Factors such as the persuasiveness of the content and its alignment with the audience’s predispositions may have also influenced their ratings. However, these factors were not examined.
In Study 1, the general assessment was related to the subjective perception of debate comprehensibility, influenced by the interaction between linguistic and content complexity. Our results further demonstrate that this observation applies not only to debate-based assessments, but also to expert-based assessments. As in Study 1, Table 5 compares experts’ rankings across variables. The readability characteristics appear to align more with perceived comprehensibility than the content characteristics. This is particularly evident for (un)certainty, where the rankings are entirely reversed: Expert B, with the highest certainty score, is rated the worst, and Expert C, with the lowest certainty score, is rated the best.
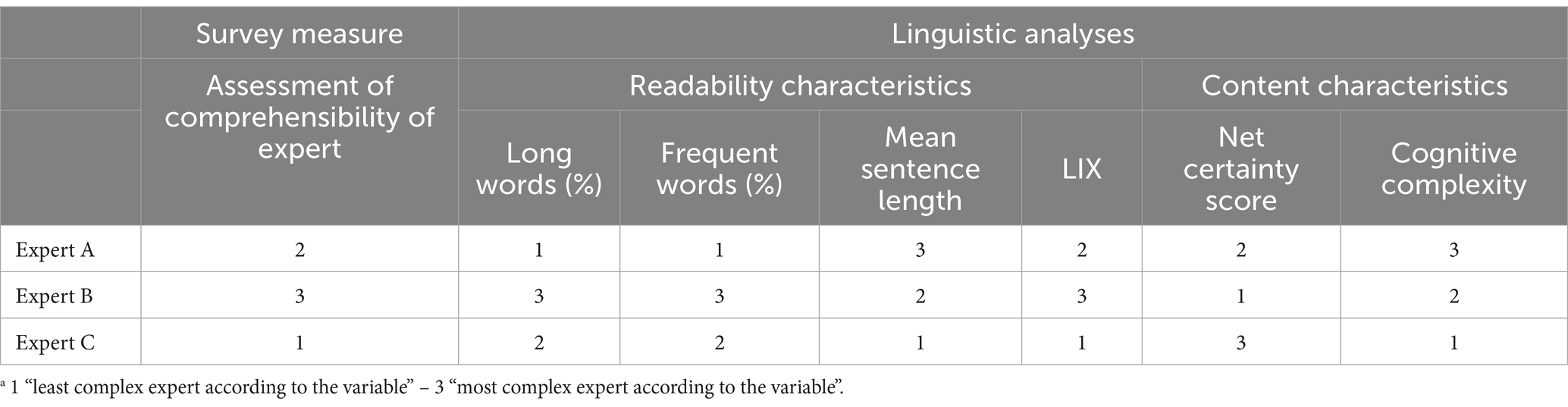
Table 5. Comparison of the experts based on their ranks a across survey measures and linguistic analyses.
Generally, Expert B exhibited lower content but higher linguistic complexity. Contrary to the observations made in Study 1 regarding the interaction between content and linguistic complexity in the Geoengineering debate, the perceived comprehensibility of Expert B is the lowest. A possible explanation for this discrepancy between the studies could be that the linguistic complexity of Expert B exceeded the audience’s tolerance. Experts A and C showed similar readability rankings that were less complex than those of Expert B. However, content complexity was higher for Expert A than for Expert C. This may explain the different rankings of perceived comprehensibility.
Studies 1 and 2 showed a link between linguistic complexity and perceived comprehensibility. Study 1 found that readability might enhance the overall evaluation of debates, but Study 2 suggested this might not apply to individual statements or human assessments, as examined with RTR measurements. Additional data is needed for generalization. Factors like speaker likability or content agreement may influence second-by-second evaluations more than comprehensibility. However, respondents generally preferred clearer communication from experts during the debate.
Discussion and conclusion
This study examines the comprehensibility of scientific experts engaged in public debates by comparing linguistic analyses and audience assessments. We aimed to discover the depth of concurrence between these perspectives to gauge the alignment between audience assessments and the identified linguistic attributes. A thorough understanding of what audiences find comprehensible and valuable in science communication, encompassing pragmatic and grammatical linguistic features, is an attainable and worthy goal that might help scientists develop an awareness of this issue.
Previous research has frequently examined scientific jargon, which often includes technical terminology. By implementing a readability analysis approach, we expanded our scope to incorporate diverse textual elements, encompassing parameters such as word and sentence length, and the overarching linguistic complexity evaluated via the LIX formula. Additionally, we examined content characteristics, considering (un)certainty and the degree of cognitive complexity. These linguistic features represent grammatical equivalents of the fundamental requirements of science communication (Czicza and Hennig, 2011).
We employed expert debates on five distinct scientific topics as case studies to juxtapose linguistic analyses with audience assessments. Our findings indicate high levels of perceived comprehensibility, particularly in the format of expert debates and, to a lesser extent, concerning the experts themselves. Thus, the format generally met the audience preferences for clear communication of scientific content identified in previous studies. However, differences have emerged between the debates on various scientific topics. The debate on Autonomous Driving scored the highest for cognitive complexity, which aligns with the expectation that this topic would be relatively distant and less immediately impactful. Notably, it was still the most comprehensible from both the audience’s perspective and the readability metrics. Conversely, despite lower content complexity and higher linguistic complexity, the Geoengineering debate still received favorable comprehensibility ratings. This challenges the expectation of a uniform relationship among content complexity, linguistic complexity, and perceived comprehensibility, suggesting that these complexity sources interact in their impact on audience perceptions.
Although the patterns observed in Study 1 regarding the interactions between sources of complexity are plausible, further research is warranted. Particularly, a “human factor” can be at play in expert communication, not only in terms of the credibility of science communication (Reif et al., 2020), but also for comprehensibility perception. Audience judgments on the comprehensibility of scientific experts and their communication are influenced by the perceived level of “scientificness” or “expertness” (Hafer et al., 1996; Thomm and Bromme, 2012). In cases where an expert is perceived as particularly knowledgeable, a more incomprehensible language is perceived as conforming to status, and the messages conveyed are perceived as persuasive.
The integrated approach of computational linguistic analysis and survey measures in Study 1 did not allow for an in-depth analysis of individual experts and specific statements. To better understand the relationships among readability, content characteristics, and audience assessments, we conducted a second study using real-time response measurements. This approach allowed us to identify specific statements from different experts rated either positively or negatively by the audience. We then subjected these statements to linguistic analysis and compared them with the audience’s assessments of the experts, which were collected through an accompanying survey.
This approach aims to provide a clearer understanding of what the audience finds comprehensible, and how this aligns with linguistic measures. However, the real-time response measurements did not reveal a straightforward relationship between readability characteristics, content characteristics, and general assessments. Only one of the experts exhibited the expected higher readability in peaks. In contrast, the content characteristics consistently indicated that peaks were associated with a higher average level of cognitive complexity and uncertainty.
These findings suggest that audiences value detailed scientific information, reflecting the inherent complexity and uncertainty of scientific topics. The accompanying survey data show that shorter sentences and simpler language might still be beneficial.
Future research should further explore these dynamics, particularly with different audience groups. The audience for expert debates is often highly engaged and knowledgeable (Wicke and Taddicken, 2020). As less interested citizens are often key targets for science communication (Dawson, 2014), it is important to explore how other groups assess the content complexity inherent in science communication.
Our study has some limitations. First, it involved a limited number of respondents and topics and should therefore be replicated using different samples, topics, and formats, including online formats, such as ScienceTubes or TikTok videos. Second, it focused on textual elements, neglecting voice-based para-verbal and other cues such as appearance, attire, empathy, and warmth, which can affect overall impressions, comprehension, and listenability. Additionally, the results may not be generalizable beyond the context of a country where debate attendance is prevalent. Other limitations, in Study 2, include the small number of identified peaks and spikes, the method used for their identification, the specific context of the science topic, the Housing Market, and individual experts. We focused on a general evaluation of science communication rather than a specific assessment of perceived comprehensibility in the RTR setting.
Our findings make an important contribution to current debates in science communication by challenging the widespread assumption that simplification is the most effective strategy for public engagement. Instead, our findings show that audiences responded more favorably to scientific language characterized by greater complexity and content density. This suggests that audiences appreciate a blend of intricate language and higher content complexity, particularly when it reflects the inherent uncertainty and nuanced nature of scientific topics. Such appreciation may stem from the perception that complexity signals epistemic rigor and trustworthiness.
These results align with research demonstrating that communicating scientific uncertainty can, in some contexts, positively affect audience evaluations (Gustafson and Rice, 2019). This is also confirmed by Retzbach et al. (2016) who distinguish between objective uncertainty, which is the general perception of the uncertainty inherent in scientific content, and subjective uncertainty, as the reflection of perceived uncertainty in the individual’s everyday life—emphasizing that reactions to uncertainty can not only vary across individuals but also across contexts and situations. Here, subjective uncertainty perceptions were positively related to science-friendly attitudes and engagement. Our findings also indicate that making complexity and uncertainty explicit may enhance audience engagement, potentially because it aligns with expectations of scientific discourse as a space for diverse perspectives and interpretations—a quality marker highlighted in prior research (Anhäuser and Wormer, 2012; Rögener and Wormer, 2017; Wicke, 2022; Wicke and Taddicken, 2020). While it is crucial to examine whether this holds true for diverse and less educated target groups, often neglected in research, the acceptance of complexity is promising concerning the “easiness effect” (Scharrer et al., 2012). This suggests that oversimplifying science communication can lead to an underestimation of scientific complexity and contentiousness, ultimately fostering an overconfident understanding among laypeople. Our results thus support a more nuanced approach to science communication: one that moves beyond mere simplification and embraces complexity and uncertainty as integral to fostering epistemic humility and trust.
We thus argue that balancing comprehensibility with the awareness of a subject’s complexity is crucial in science communication. This balance enables laypeople acquire scientific knowledge, form informed opinions, and understand the inherent complexities and uncertainties of scientific processes. Therefore, scientists must be prepared to address this communication challenge.
Recent advancements in AI-assisted text production offer exciting opportunities for practical applications and research, bringing us closer to tailoring text to individual readers’ needs, potentially allowing for more personalized science communication. To effectively leverage these tools, it is essential to deeply understand how to enhance perceived comprehensibility, and its effects on science communication. This knowledge will ensure that new technologies are used to improve science communication meaningfully.
Data availability statement
General information, datasets and replication script can be found online: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/62KRQ.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
MT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CT: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was part of the science communication format “The Debate” (https://www.die-debatte.org/). This project was carried out in cooperation between Wissenschaft im Dialog, the Science Media Center Germany, and the TUBraunschweig. It was funded by the Volkswagen Foundation (reference number: 92741), the Klaus Tschira Stiftung, and the Stifterverband.
Acknowledgments
We thank all our partners for their support as well as the reviewers for their helpful and constructive feedback. We acknowledge the support by the Open Access Publication Funds of the Technische Universitaet Braunschweig.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1. ^General information, datasets and replication script can be found online: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/62KRQ.
2. ^We used the corpus deu_news_2018_1M (https://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/de/download).
3. ^Groups of words that occur with similar frequency in a language (Keibel et al., 2012).
4. ^We used this older version of the dictionary to be able to orient ourselves to the operationalizations of other authors. The newer version (LIWC2015) does not contain all the categories required.
5. ^General information, datasets and replication script can be found online: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/62KRQ.
6. ^http://www.real-time-response.com/
7. ^Statements made by moderators or audience members were excluded.
8. ^Since eight of the 27 analyzed passages were under 100 words, potentially affecting reliability, we conducted further checks comparing all peak and spike passages of a speaker. The results showed minimal variation, with spikes consistently displaying lower complexity than peaks, with few exceptions.
References
Anhäuser, M., and Wormer, H. (2012). “A question of quality: criteria for the evaluation of science and medical reporting and testing their applicability” in Quality, honesty and beauty in science and technology communication : PCST 2012 Book of Papers. eds. B. Trench and M. Bucchi (Vicenza: Observa Science in Society), 335–337.
Bachl, M. (2014). Analyse rezeptionsbegleitend gemessener Kandidatenbewertungen in TV-Duellen: Erweiterung etablierter Verfahren und Vorschlag einer Mehrebenenmodellierung. Berlin: epubli GmbH.
Ballstaedt, S. P., and Mandl, H. (1988). “The assessment of comprehensibility” in Sociolinguistics: An international handbook of the science of language and society. eds. U. Ammon, N. Dittmar, and K. J. Mattheier (Berlin: De Gruyter), 1039–1052.
Balota, D. A., Yap, M. J., and Cortese, M. J. (2006). “Visual word recognition: the journey from features to meaning (a travel update)” in Handbook of psycholinguistics. eds. M. J. Traxler and M. A. Gernsbacher (London: Elsevier), 285–375.
Benjamin, R. G. (2012). Reconstructing readability: recent developments and recommendations in the analysis of text difficulty. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 24, 63–88. doi: 10.1007/s10648-011-9181-8
Benoit, K, and Müller, S (2023) Quanteda. Dictionaries: dictionaries for text analysis and associated utilities [software]. Available online at https://github.com/kbenoit/quanteda.dictionaries
Benoit, K., Watanabe, K., Wang, H., Nulty, P., Obeng, A., Müller, S., et al. (2018). Quanteda: an R package for the quantitative analysis of textual data. J. Open Source Softw. 3, 1–4. doi: 10.21105/joss.00774
Biocca, F., David, P., and West, M. (2014). “Continuous response measurement (CRM): a computerized tool for research on the cognitive processing of communication messages” in Measuring psychological responses to media messages. ed. A. Lang (New York: Routledge), 15–64.
Britt, M. A., Rouet, J.-F., and Durik, A. M. (2018). Literacy beyond text comprehension: A theory of purposeful reading. New York, NY: Routledge.
Bromme, R., and Goldman, S. R. (2014). The Public's bounded understanding of science. Educ. Psychol. 49, 59–69. doi: 10.1080/00461520.2014.921572
Bromme, R., and Jucks, R. (2018). “Discourse and expertise: the challenge of mutual understanding between experts and laypeople” in The Routledge handbook of discourse processes. eds. M. F. Schober, D. N. Rapp, and M. A. Britt (New York: Routledge), 222–246.
Bromme, R., Rambow, R., and Nückles, M. (2001). Expertise and estimating what other people know: the influence of professional experience and type of knowledge. J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 7, 317–330. doi: 10.1037/1076-898X.7.4.317
Bromme, R., and Thomm, E. (2016). Knowing who knows: Laypersons' capabilities to judge Experts' pertinence for science topics. Cogn. Sci. 40, 241–252. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12252
Bullock, O. M., Colón Amill, D., Shulman, H. C., and Dixon, G. N. (2019). Jargon as a barrier to effective science communication: evidence from metacognition. Public Underst. Sci. 28, 845–853. doi: 10.1177/0963662519865687
Czicza, D., and Hennig, M. (2011). Zur Pragmatik und Grammatik der Wissenschaftskommunikation. Ein Modellierungsvorschlag. J. Profess. Sci. Commun. 33, 36–60. doi: 10.24989/fs.v33i1-2.1380
Dawson, E. (2014). Reframing social exclusion from science communication: moving away from ‘barriers’ towards a more complex perspective. J. Sci. Commun. 13:C02. doi: 10.22323/2.13020302
Dean, C. (2012). Am I making myself clear? A scientist's guide to talking to the public. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
Dresing, T., and Pehl, T. (2020). “Transkription” in Handbuch Qualitative Forschung in der Psychologie (Wiesbaden: Springer), 835–854.
Fähnrich, B. (2017). “Wissenschaftsevents zwischen Popularisierung, Engagement und Partizipation” in Forschungsfeld Wissenschaftskommunikation. eds. H. Bonfadelli, B. Fähnrich, C. Lüthje, J. Milde, M. Rhomberg, and M. S. Schäfer (Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden), 165–182.
Fandrych, C (2018). “Wissenschaftskommunikation” in Sprache im kommunikativen, interaktiven und kulturellen Kontext. eds. A. Deppermann and S. Reineke (Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter), 143–168. doi: 10.1515/9783110538601-007
Fischhoff, B., and Scheufele, D. A. (2013). The science of science communication. Proceed. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110 Suppl 3, 14031–14032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312080110
Freiling, I., Krause, N. M., Scheufele, D. A., and Brossard, D. (2023). Believing and sharing misinformation, fact-checks, and accurate information on social media: the role of anxiety during COVID-19. New Media Soc. 25, 141–162. doi: 10.1177/14614448211011451
Friedrich, M. C. G., and Heise, E. (2022). The influence of comprehensibility on interest and comprehension. Zeitschrift Pädagogische Psychol. 39, 139–152. doi: 10.1024/1010-0652/a000349
Funtowicz, S. O., and Ravetz, J. R. (1994). Uncertainty, complexity and post-normal science. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 13, 1881–1885. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620131203
Goldhahn, D., Eckart, T., and Quasthoff, U. (2012). “Building large monolingual dictionaries at the Leipzig corpora collection: from 100 to 200 languages” in Proceedings of the 8th international conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC '12). eds. N. Calzolari, K. Choukri, T. Declerck, M. U. Doğan, B. Maegaard, and J. Mariani, et al. (Istanbul: European Language Resources Association (ELRA)), 759–765.
Guenther, L., and Ruhrmann, G. (2016). Scientific evidence and mass media: investigating the journalistic intention to represent scientific uncertainty. Public Understanding Sci. 25, 927–943. doi: 10.1177/0963662515625479
Guenther, L., Weingart, P., and Meyer, C. (2018). “Science is everywhere, but no one knows it”: assessing the cultural distance to science of rural south African publics. Environ. Commun. 12, 1046–1061. doi: 10.1080/17524032.2018.1455724
Gustafson, A., and Rice, R. E. (2019). The effects of uncertainty frames in three science communication topics. Sci. Commun. 41, 679–706. doi: 10.1177/1075547019870811
Hafer, C. L., Reynolds, K. L., and Obertynski, M. A. (1996). Message comprehensibility and persuasion: effects of complex language in Counterattitudinal appeals to laypeople. Soc. Cogn. 14, 317–337. doi: 10.1521/soco.1996.14.4.317
Hinds, P. J. (1999). The curse of expertise: the effects of expertise and debiasing methods on prediction of novice performance. J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 5, 205–221.
Kercher, J. (2010). “Zur Messung der Verständlichkeit deutscher Spitzenpolitiker anhand quantitativer Textmerkmale” in Information – Wahrnehmung – Emotion. eds. T. Faas, K. Arzheimer, and S. Roßteutscher (Wiesbaden: VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften), 97–121.
Kercher, J. (2013). Verstehen und Verständlichkeit von Politikersprache: Verbale Bedeutungsvermittlung zwischen Politikern und Bürgern. Wiesbaden: Springer VS.
Klare, G. R. (1971). “Some empirical predictors of readability” in Verbal learning research and the technology of written instructions. eds. E. Z. Rothkopf and P. E. Johnson (New York: Teacher’s College Press), 241–254.
Klare, G. R. (1984). “Readability” in Handbook of Reading research. ed. P. D. Pearson (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates), 681–744.
König, L., and Jucks, R. (2019). Hot topics in science communication: aggressive language decreases trustworthiness and credibility in scientific debates. Public Understand. Sci. 28, 401–416. doi: 10.1177/0963662519833903
Maier, M., Milde, J., Post, S., Günther, L., Ruhrmann, G., Barkela, B., et al. (2016). “Toward a comprehensive model of comprehension” in The psychology of learning and motivation: Advances in research and theory. ed. B. H. Ross 41, 239–264.
McNamara, D. S., and Magliano, J. (2009). “Chapter 9 toward a comprehensive model of comprehension” in Psychology of learning and motivation the psychology of learning and motivation (San Diego, CA: Elsevier), 297–384.
Meredith, D. (2021). Explaining research: How to reach key audiences to advance your work. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Michalke, M (2020) koRpus.lang.de: Language support for ‘koRpus' package: German [Software]. Available online at: https://reaktanz.de/?c=hacking&s=koRpus
Michalke, M (2021) koRpus: text analysis with emphasis on POS tagging, readability, and lexical diversity [software]. Available online at: https://reaktanz.de/?c=hacking&s=koRpus
Oppenheimer, D. M. (2006). Consequences of erudite vernacular utilized irrespective of necessity: problems with using long words needlessly. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 20, 139–156. doi: 10.1002/acp.1178
Ottler, S. (2013). “RTR-Messung: Möglichkeiten und Grenzen einer sozialwissenschaftlichen Methode” in Das TV-Duell in Baden-Württemberg 2011 eds. M. Bachl, F. Brettschneider and S. Ottler (Wiesbaden: Springer VS), 113–134.
Owens, R. J., and Wedeking, J. P. (2011). Justices and legal clarity: analyzing the complexity of U.S. Supreme Court opinions. Law Soc. Rev. 45, 1027–1061. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5893.2011.00464.x
Perfetti, C. A., Landi, N., and Oakhill, J. (2011). “The acquisition of reading comprehension skill” in The science of reading: A handbook eds. M. J. Snowling and C. Hulme (Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing), 227–247.
Piantadosi, S. T., Tily, H., and Gibson, E. (2011). Word lengths are optimized for efficient communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 3526–3529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012551108
Popper, K. R. (2002). Conjectures and refutations: The growth of scientific knowledge. London: Routledge.
Reif, A., Kneisel, T., Schäfer, M., and Taddicken, M. (2020). Why are scientific experts perceived as trustworthy? Emotional assessment within TV and YouTube videos. Media Commun. 8, 191–205. doi: 10.17645/mac.v8i1.2536
Retzbach, J., Otto, L., and Maier, M. (2016). Measuring the perceived uncertainty of scientific evidence and its relationship to engagement with science. Public Underst. Sci. 25, 638–655. doi: 10.1177/0963662515575253
Rink, I. (2024). “Communication barriers” in Handbook of accessible communication. eds. C. Maaß and I. Rink (Berlin: Frank & Timme GmbH), 33–68.
Rögener, W., and Wormer, H. (2017). Defining criteria for good environmental journalism and testing their applicability: an environmental news review as a first step to more evidence based environmental science reporting. Public Underst. Sci. 26, 418–433. doi: 10.1177/0963662515597195
Ruhrmann, G., Guenther, L., Kessler, S. H., and Milde, J. (2015). Frames of scientific evidence: how journalists represent the (un)certainty of molecular medicine in science television programs. Public Underst. Sci. 24, 681–696. doi: 10.1177/0963662513510643
Scharrer, L., Bromme, R., Britt, M. A., and Stadtler, M. (2012). The seduction of easiness: how science depictions influence laypeople’s reliance on their own evaluation of scientific information. Learn. Instr. 22, 231–243. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2011.11.004
Schimel, J. (2012). Writing science: How to write papers that get cited and proposals that get funded. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press.
Schoonvelde, M., Brosius, A., Schumacher, G., and Bakker, B. N. (2019). Liberals lecture, conservatives communicate: analyzing complexity and ideology in 381,609 political speeches. PLoS One 14, 1–15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208450
Sharon, A. J., and Baram-Tsabari, A. (2014). Measuring mumbo jumbo: a preliminary quantification of the use of jargon in science communication. Public Underst. Sci. 23, 528–546. doi: 10.1177/0963662512469916
Taddicken, M., Wicke, N., and Willems, K. (2020). Verständlich und kompetent? Eine Echtzeitanalyse der Wahrnehmung und Beurteilung von Expert*innen in der Wissenschaftskommunikation. Medien & Kommunikationswissenschaft 68, 50–72. doi: 10.5771/1615-634X-2020-1-2-50
Tausczik, Y. R., and Pennebaker, J. W. (2010). The psychological meaning of words: LIWC and computerized text analysis methods. J. Lang. Soc. Psychol. 29, 24–54. doi: 10.1177/0261927X09351676
Thomm, E., and Bromme, R. (2012). “It should at least seem scientific!” Textual features of “scientificness” and their impact on lay assessments of online information. Sci. Educ. 96, 187–211. doi: 10.1002/sce.20480
Thoms, C. (2023). Im Sinne der Medien: Textverständlichkeit im Nachrichtenauswahlkontext : Springer VS. doi: 10.1007/978-3-658-40007-1
Thoms, C., Degenhart, A., and Wohlgemuth, K. (2020). Is bad news difficult to read? A readability analysis of differently connoted passages in the annual reports of the 30 DAX companies. J. Bus. Tech. Commun. 34, 157–187. doi: 10.1177/1050651919892312
Tiffin-Richards, S. P., and Schroeder, S. (2018). The development of wrap-up processes in text reading: a study of children's eye movements. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 44, 1051–1063. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000506
Tolochko, P., Song, H., and Boomgaarden, H. (2019). “That looks hard!”: effects of objective and perceived textual complexity on factual and structural political knowledge. Polit. Commun. 36, 609–628. doi: 10.1080/10584609.2019.1631919
van den Broek, P., and Espin, C. A. (2012). Connecting cognitive theory and assessment: measuring individual differences in Reading comprehension. Sch. Psychol. Rev. 41, 315–325. doi: 10.1080/02796015.2012.12087512
van den Broek, P, Young, M, Tzeng, Y, and Linderholm, T. (1999). “The landscape model of reading: Inferences and the online construction of a memory representation” in The construction of mental representations during reading. eds. H. van Oostendorp and S. R. Goldman (Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum), 71–98.
West, M. D., and Biocca, F. A. (1996). “Dynamic Systems in Audience Response Measures” in Dynamic patterns in communication processes. eds. J. H. Watt and C. A. VanLear (Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications), 119–144.
Wicke, N. (2022). Eine Frage der Erwartungen? Publizistik 67, 51–84. doi: 10.1007/s11616-021-00701-z
Wicke, N., and Taddicken, M. (2020). Listen to the audience(s)! Expectations and characteristics of expert debate attendants. J. Sci. Commun. 19:A02. doi: 10.22323/2.19040202
Willoughby, S. D., Johnson, K., and Sterman, L. (2020). Quantifying scientific jargon. Public Underst. Sci. 29, 634–643. doi: 10.1177/0963662520937436
Wissenschaft im Dialog (2018). Wissenschaftsbarometer 2018. Available online at: https://wissenschaft-im-dialog.de/documents/188/180927_Wissenschaftsbarometer_Broschuere_2018.pdf (April 14, 2025).
Wolf, M., Horn, A. B., Mehl, M. R., Haug, S., Pennebaker, J. W., and Kordy, H. (2008). Computergestützte quantitative Textanalyse: Äquivalenz und Robustheit der deutschen Version des Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count. Diagnostica 54, 85–98. doi: 10.1026/0012-1924.54.2.85
Wyss, D., Beste, S., and Bächtiger, A. (2015). A decline in the quality of debate? The evolution of cognitive complexity in Swiss parliamentary debates on immigration (1968–2014). Swiss Polit. Sci. Rev. 21, 636–653. doi: 10.1111/spsr.12179
Keywords: comprehensibility, computational linguistic analyses, audience assessments, real-time response measurement, expert debates
Citation: Taddicken M and Thoms C (2025) How comprehensible are scientific experts? A multi-method comparison of linguistic analyses, surveys, and real-time audience responses. Front. Commun. 10:1580377. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1580377
Edited by:
Anke van Kempen, Munich University of Applied Sciences, GermanyReviewed by:
Nicole Kelp, Colorado State University, United StatesSylvia Jaki, University of Hildesheim, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Taddicken and Thoms. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Monika Taddicken, bS50YWRkaWNrZW5AdHUtYnJhdW5zY2h3ZWlnLmRl
 Monika Taddicken
Monika Taddicken Claudia Thoms
Claudia Thoms