- Department of Journalism and Digital Media, Zarqa University, Zarqa, Jordan
Introduction: The study aimed to explore the role of podcasts in enhancing cultural awareness among the Jordanian public. The study examines the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects of following cultural topics through podcasts.
Methods: The present study employed a mixed-methods research design, integrating both quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the role of podcasts in shaping cultural awareness among the Jordanian public. The study population comprised Jordanian residents representing a range of age groups, educational levels, and geographical regions. The principal sample consisted of 498 participants, selected using quota sampling.
Results: A large percentage showed medium or high interest in podcasts, reflecting its growing role in transferring cultural knowledge. The results showed that providing rich and diverse content that meets the interests of listeners was a major factor in enhancing knowledge and awareness. Jordanians also benefited cognitively by learning about current events. Also, emotionally by enhancing cultural pride and changing negative attitudes, and behaviorally by encouraging knowledge exchange and adopting positive behaviors. The study proved the effect of podcasts as an educational and media tool that contributes to enhancing cultural understanding and community interaction.
Discussion: The study recommended developing the cultural content of podcasts and increasing interaction with the audience to maximize its impact and enhance its role in shaping an integrated cultural awareness in society.
1 Introduction
In recent years, advanced media and communication technologies have emerged, significantly increasing communication and public accessibility. These developments have transformed the media landscape into an interactive space where audiences can engage directly with content and participate in shaping social and political discourse (Nielsen and Ganter, 2022). The rise of digital media and social platforms has also enabled individuals to express their views more openly and to share information more rapidly than ever before. Technologies such as live streaming and on-demand videos allow users to interact with events in real time, thus enhancing the role of media as a primary source of live news and information (Luttrell and Wallace, 2024).
By 2005, platforms like “Podcast Alley” emerged to organize and index podcasts, marking the beginning of a new era in digital audio content (Morris, 2019). The medium gained traction in 2008, with 639 podcasts available, and experienced exponential growth from 2011 to 2021, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, which fueled demand for on-demand audio entertainment and education (Abdel-Razzaq, 2023). The latest statistics indicate that the number of global podcast listeners reached more than 500 million users in 2023, with expectations to increase to more than 650 million by 2027 (Statista, 2023). Additionally, the podcast market size was estimated at around $27 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow at a CAGR of around 15% from 2024 to 2032 (Global Market Insights, 2023). This growth is driven by advancements in technology, the rise of podcast platforms like Spotify, and increasing interest in diverse and localized content, with the Asia-Pacific region emerging as a key market.
Furthermore, podcasts have emerged as an effective tool in education and culture, providing educational and cultural episodes accessible to all individuals, regardless of geographic location or socio-economic status. The rapid expansion of podcasts has facilitated greater intercultural exchange, transcending traditional barriers and promoting the right to cultural expression (Bousbat and Laouira, 2022). Continual exploration and openness to new ideas are crucial for raising cultural awareness, and digital media serve as effective mediums for disseminating knowledge and expanding cultural boundaries. Cultural awareness is essential to understanding how social and cultural factors create individual and societal identity. It involves a deep understanding of a culture’s traditions, values, and rituals, and openness to different cultures (Alsharu et al., 2025; Usborne and De La Sablonnière, 2014).
Jordanian podcasts promote and enrich local culture by addressing heritage, arts, social issues, and economic developments. By offering episodes focused on local customs, traditions, and the personal experiences and achievements of community members, these platforms have contributed to a deeper cultural and social understanding within Jordan. Social media, including podcasting, enabled Jordanians from diverse backgrounds to connect with a global audience, promoting cultural comprehension and discourse (Al-Rifai, 2019; Aljalabneh et al., 2023). The growing number of podcast audiences and content creators in Jordan, especially among young people, has made podcasts an important medium for expressing opinions and creativity. Consequently, podcasts have become a key element of the Jordanian cultural landscape and an effective tool for engaging with contemporary issues in an interactive manner (Al-Zoubi, 2021).
Technological developments and the proliferation of digital platforms have made podcasting an excellent medium for developing cultural awareness among the general public in Jordan (Ahmad, 2022). Podcasting that addresses cultural and social concerns enhances listeners’ awareness of cultural identity and promotes openness to diverse cultures. Therefore, this study seeks to investigate the impact of podcasting on the attitudes and behaviors of the Jordanian people, as well as to understand the mechanisms by which this medium promotes cultural awareness. In addition, this study is one of the few that examines how podcasts influence Jordanian cultural awareness and highlights the impact of the media on society. The study examines how podcast content influences Jordanian public behavior, particularly cultural identification and openness to other cultures. The study also sheds light on the podcast audience in Jordan, including their listening habits and interests, which guide the objectives of cultural content. The study contributes to highlighting the importance of podcasts as an effective media tool that parallels traditional media while emphasizing its role in innovatively disseminating information and cultural content. It also highlights how podcasts can be used to enhance cultural awareness among individuals and employ them in areas such as education and health education, which helps build an aware and educated society.
2 Study questions
1. To what extent does the Jordanian public follow cultural topics through podcasts?
2. What are the reasons Jordanian public follows cultural topics through podcasts?
3. What are the reasons for the Jordanian public’s confidence in the cultural content presented through podcasts?
4. What are the Jordanian public’s cognitive, emotional, and behavioral effects following cultural topics through podcasts?
3 Study hypotheses
1. There is a correlation between the degree to which respondents follow cultural topics through podcasts in shaping cultural awareness; and the effects resulting from this follow-up.
2. There is a correlation between the cognitive effects of the respondents’ following cultural topics via podcasts in shaping cultural awareness and the emotional effects of this following.
4 Literature review
The expanding body of research on podcasts underscores their multifaceted role in shaping cultural awareness, social discourse, and educational engagement across diverse populations and contexts. Over the past decade, scholars have increasingly examined how podcasts function not merely as entertainment media but as dynamic platforms for cultural exchange, personal development, and public deliberation. Existing literature encompasses a spectrum of approaches from uses and gratifications theory to audience analysis and psychological inquiry, highlighting podcasts’ capacity to influence cognitive, emotional, and behavioral outcomes among listeners. The following review synthesizes key empirical contributions that have explored podcast consumption within varying socio-cultural milieus, delineating both thematic breadth and methodological diversity characterizing this emerging research field. These studies collectively inform the distinct focus of the present work, which examines the unique influence of podcasts on cultural awareness among Jordanian audiences, a context that has thus far received limited scholarly attention.
Bin Suwaidan (2024) investigated how Saudi youth interact with cultural podcasts that highlight social topics. The study uses the uses and gratifications framework to assess the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral effects of this information. 400 Saudi 18–34-year-old males and women were sampled. It found that cultural topics in podcasts attracted 54.4% of the respondents. These apps prefer to openly address cultural concerns and events, unlike established platforms. The initial form of cultural content interaction was icons (like, follow, share), followed by comments. Participants wanted to create cultural audio content and communicate with their audience. The following was driven by content quality, cultural diversity, app usability, and entertainment.
Ifedayo (2023) examined podcast-related educational tweets to comprehend educational discourse’s diversity and globality. The sample included tweets from CAMH Education and Remake Learning on topics like artificial intelligence’s psychological effects, innovation and diversity, organizational accountability, and Nigeria’s education challenges. The results showed that 71.43% of the tweets were international, reflecting the role of podcasts in promoting cultural interaction. The study recommended encouraging the production of educational podcasts, promoting international collaboration, and integrating technology into education.
A study by Ghazal and Bourhali (2021) examined the influence of podcasts and social media on fostering social responsibility and shaping public opinion. The research utilized a media audience survey methodology with a targeted sample of 70 podcast listeners. The findings indicated that the material was insufficient in fostering community awareness, as it predominantly concentrated on crime reports and youth issues. Sixty percent of participants indicated that podcasts enhanced their social awareness and improved community interactions, whilst 40 % perceived no effect. The study advised reevaluating the content to improve its effectiveness in promoting cultural awareness and social responsibility.
Tobin and Guadagno (2022) examined how personal characteristics affect podcast listening and psychological effects. The study examined curiosity, demand for knowledge, and openness to experience in 306 people from different nations, as well as listening time, type, surroundings, and potential outcomes like meaning and connectedness. The study found that the need for connection and neuroticism adversely predicted listening, while openness, curiosity, and need for information favorably predicted it. Parasocial interactions and social engagement were linked to beneficial psychological outcomes while listening time was not. The study demonstrated that informational motivations improve podcast listening and psychological features.
The study (Al-Nabulsi, 2021) sought to ascertain the degree of consolidation of social and human values among adolescents, with the study population comprising students from designated schools in the ninth, tenth, and first secondary grades. Subsequently, a purposive sample of 50 students was selected after they viewed the series “Walid Al-Sadfa.” The study revealed statistically significant variations among respondents regarding the social and human values influenced by exposure to the series “Walid Al-Sadfa.” The study discovered that respondents had satisfaction after seeing the series, attributable to the effects of class and gender characteristics.
Berg (2021) examines the analysis of independent podcasts produced on the prominent podcasting platform Apple Podcasts. The study provides insights into independent podcasting, its media and content, and the conditions under which independent podcasters operate in the transitional space between traditional radio broadcasting methods and shared online behaviors. The study reveals that the dominant elements of independent podcasting consist of conversations, interviews, personal narratives, and popular hobbies such as movies, football, and television. The increased exposure to discussions and interviews related to hobbies and personal narratives suggests that independent podcasters are influenced by the promotion and marketing of podcasting.
This study is distinguished from previous studies by its emphasis on the role of podcasts in influencing the cultural awareness of the general public in Jordan, unlike previous studies that dealt with the impact of podcasts on a broad scale or in different social contexts. The study addresses the impact of podcasts on societal culture and individual cultural awareness in Jordan, focusing on podcasts as an independent variable that significantly affects cultural awareness, a topic that deserves to be addressed in the Jordanian context.
5 Methodology
5.1 Research design
The present study employed a mixed-methods research design, integrating both quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the role of podcasts in shaping cultural awareness among the Jordanian public. The primary rationale for adopting a mixed-methods approach was to combine the statistical breadth afforded by a structured survey with the in-depth, contextual insights obtainable through semi-structured interviews. The quantitative component enabled us to identify trends and measure the extent of podcast engagement and its cognitive, emotional, and behavioral impacts across a representative sample. In contrast, the qualitative component offered a deeper exploration of individual motivations, subjective perceptions, and lived experiences regarding podcast consumption.
This methodological choice was guided by the study’s complex research questions, which necessitated this approach. Alternative designs such as a purely quantitative survey or an exclusively qualitative approach were considered but deemed insufficient. A solely quantitative design would have constrained the study to surface-level statistical patterns without uncovering the underlying mechanisms and meanings attached to podcast use. Conversely, a purely qualitative design would have limited the ability to draw conclusions about the broader Jordanian public. Thus, the mixed-methods approach was selected in line with leading recommendations for media audience research (Creswell, 2014; Riffe et al., 2023), ensuring both analytical rigor and contextual richness.
5.2 Study population and sample
The study population comprised Jordanian residents representing a range of age groups, educational levels, and geographical regions. The principal sample consisted of 498 participants, selected using quota sampling. The quotas were systematically determined based on the latest national demographic data to achieve proportional representation by gender, age, education, and region (central, northern, and southern Jordan). No further exclusion criteria were applied, apart from respondents being 18 years or older and resident in Jordan. Quota sampling was deemed suitable to reduce sampling bias and increase the generalizability of the findings within the Jordanian context (Wimmer and Dominick, 2011).
To minimize selection bias, the survey was distributed widely through multiple channels, including social media platforms (Facebook & Twitter). All participants were informed about the study’s purpose and provided consent prior to participation.
The survey was designed using a three-point Likert scale (agree, neutral, disagree) to measure the extent of participants’ agreement with the questionnaire axes. The scale was interpreted as 1.00–1.66 = low, 1.67–2.00 = medium, and 2.34–3.00 = high. To answer the fourth question, a four-point Likert scale was adopted to assess the behavioral, cognitive, and emotional effects of the exposure (high, medium, low, no). The scale was interpreted as 1.00–2.33 = low, 2.34–3.67 = medium, and 3.68–5.00 = high.
5.3 Data collection
Data collection was conducted in two phases. The first phase involved the administration of an online survey via Google Forms between March 10 and April 5, 2024. No financial or material incentives were provided to participants, thereby mitigating potential response bias. Survey invitations were disseminated through social media, to maximize reach and demographic diversity. The survey instrument was pilot-tested with a small group to ensure clarity and relevance.
The second phase consisted of 14 semi-structured interviews. Interviewees were purposively selected from among survey respondents who had indicated a high level of engagement with cultural podcasts and expressed willingness to participate in follow-up research. The interviews were conducted via Zoom to accommodate participants’ preferences and logistical constraints. Each interview lasted approximately 30 min and was recorded with consent and transcribed verbatim for analysis.
5.4 Validity and reliability tests
The apparent validity or content validity method was used to measure the accuracy of the study tool (questionnaire) and its ability to achieve the study objectives and answer its questions. To achieve this, the questionnaire was presented to a group of academics specialized in media colleges to evaluate the statements’ clarity and validity and suitability for measuring the phenomenon under study.
In addition, the SPSS program was used to calculate the reliability coefficient (Cronbach’s alpha) to assess the internal consistency of the questionnaire items. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is considered acceptable if it reaches 60% or more. The results showed that the reliability coefficient ranged between 92.3 and 93.5% for each scale, which indicate a high level of stability, which enhances the reliability of the study tool in social research.
5.5 Data analysis
The study data were analyzed using SPSS, which used statistical methods appropriate to the study’s goals. Frequencies and percentages were used to analyze respondents’ demographics and questionnaire answers, while the arithmetic mean and standard deviation measured the answers’ general trend and dispersion from the average. They also employed the T-test and One-Way ANOVA tests to compare the averages of two or more independent groups in several study variables. The direction and intensity of the variables’ relationships were determined via Pearson’s Correlation coefficient. These statistical measures help analyze data and produce accurate results that meet study goals.
While for qualitative data, responses to open-ended interview questions were coded thematically according to the predefined axes of the quantitative questionnaire specifically, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral effects, motivations for podcast use, and factors influencing trust. Thematic categories were established in advance, ensuring direct alignment between qualitative and quantitative findings. The coding process was conducted by the lead researcher and independently reviewed by a second academic for clarity and consistency. Discrepancies were discussed until consensus was reached. This deductive thematic approach enabled robust triangulation of quantitative and qualitative findings while maintaining focus on the study objectives.
6 Results and discussion
6.1 The degree to which the Jordanian public follows cultural topics via podcasts
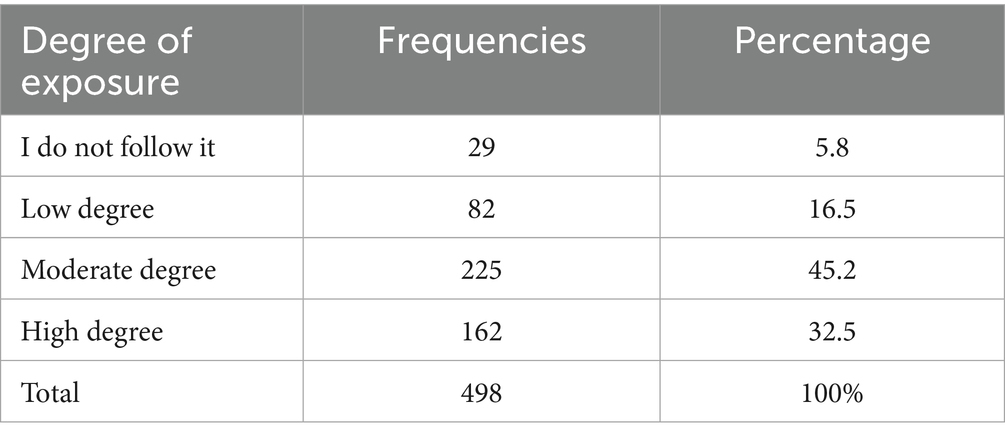
According to Table 1, the results showed that the Jordanian audience’s following of cultural topics via podcasts varies to varying degrees. The largest percentage of participants (45.2%) follow these topics to a moderate degree, while 32.5% of participants reported that they follow cultural topics to a high degree. Those who follow them to a low degree amounted to 16.5%, while 5.8% of participants reported that they do not follow them at all.
These findings indicate that a significant proportion of the Jordanian public engages with cultural content through podcasts, although a notable segment exhibits minimal or no interest. While the data reveal varying degrees of engagement, the study did not directly assess the specific reasons underlying lower participation. Future research may be needed to examine whether factors such as content quality, audience interests, or promotional strategies play a role in influencing podcast engagement among these groups.
The study’s findings align with Bin Suwaidan (2024), indicating a widespread public interest in cultural content via podcast platforms. The findings reveal that a majority of the Jordanian populace engages with cultural subjects to a moderate or significant extent, corroborating the conclusions of the Saudi study regarding the growing interest in cultural content.
However, the differences between the 32.5% in the current survey who follow cultural matters closely and the 54.4% in the Saudi study who do may indicate a disparity in cultural participation between the two countries. The data indicate that a considerable proportion of participants report low or no engagement with cultural podcasts. Although the current study did not directly investigate the reasons for this, prior research (Ghazal and Bourhali, 2021) suggests that content quality and diversity may affect podcast effectiveness in promoting awareness. Thus, these factors could represent areas for further inquiry within the Jordanian context.
This comparison highlights the presence of an audience segment with lower engagement in cultural podcasts. While the present study does not directly evaluate content quality or promotional strategies, the results suggest that further exploration of these factors may be beneficial for increasing audience engagement, especially among those currently less interested.
These insights were further reflected during the interviews phase with the participants. For instance, one participant noted, “I have been listening to cultural podcasts for years. They offer a great way to stay informed about our heritage and current cultural trends. I usually listen while driving, and it has become a part of my daily routine.” (Participant 3, Male, 34). Another emphasized the selective nature of their engagement, explaining, “I follow cultural podcasts occasionally, especially when a particular topic interests me. However, I believe more efforts should be made to promote them among younger audiences.” (Participant 7, Female, 27). Meanwhile, some listeners remain hesitant, preferring alternative formats, as one participant shared, “To be honest, I rarely listen to cultural podcasts because I prefer video content. If podcasts included more interactive elements, I might be more interested.” (Participant 12, Male, 22). These participant statements illustrate the diversity of engagement experiences reported in the qualitative interviews. Several interviewees expressed interest in greater promotion of podcasts or inclusion of more interactive elements, suggesting possible areas for future development in cultural podcast content.
6.2 The reasons why the Jordanian public follows cultural topics through podcasts
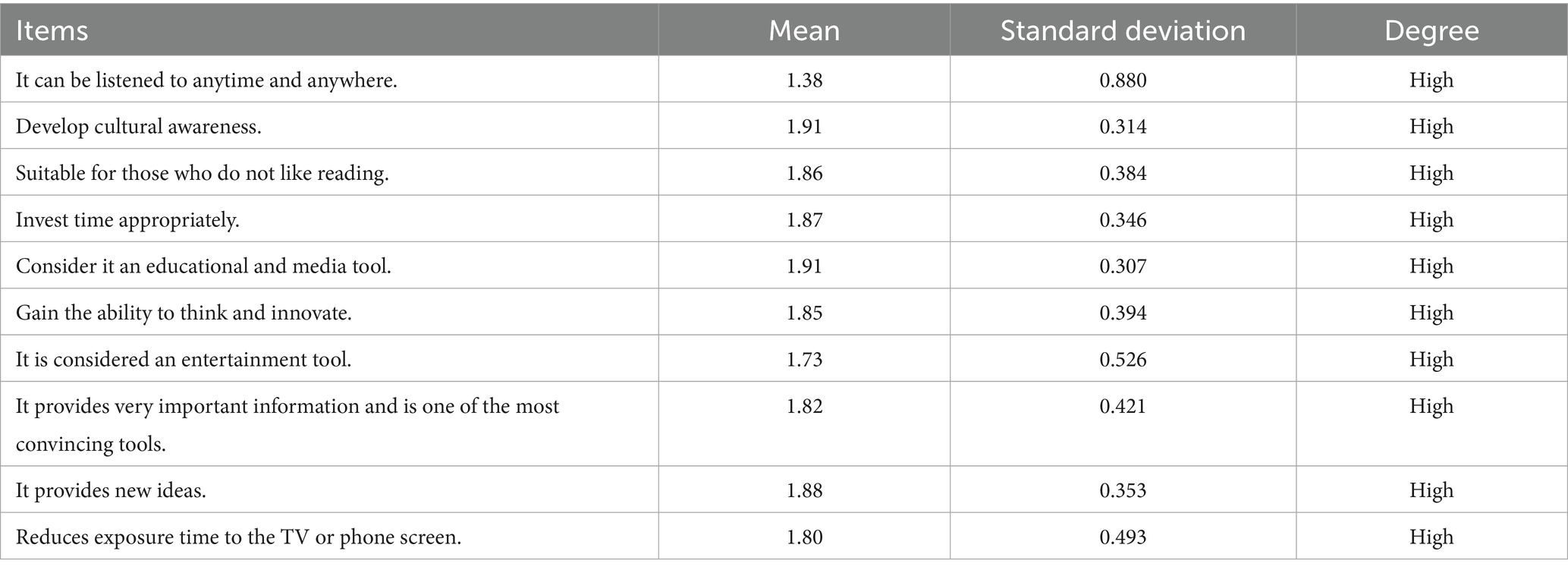
The study’s results in Table 2 reveal multiple factors that motivate the Jordanian people to engage with cultural subjects via podcasts. The findings indicate that all evidence received high ratings based on the mean and standard deviation. The primary reason is that podcasts serve as an educational and media tool that encourages cultural awareness, evidenced by a high mean (1.91) and standard deviations (0.307 and 0.314, respectively), indicating participants’ recognition of the significance of podcasts in education and cultural awareness.
On the other hand, podcasts serve as an entertainment medium that reduces exposure to TV or smartphone screens, as evidenced by the mean of 1.80 and standard deviation of 0.493, confirming their contribution to improving the quality of time unconventionally spent on entertainment. The results indicate that the Jordanian audience chooses podcasts as a versatile medium that can be accessed anytime and anywhere (1.38), which meets their educational, cultural, and entertainment requirements. The main elements influencing podcast participation are providing rich and diverse material and offering a practical alternative to reading or traditional media.
Ghazal and Bourhali (2021) demonstrated that podcasts and new media contribute to the dissemination of cultural awareness and the promotion of social responsibility, corroborating the findings of the present study, which revealed that “developing cultural awareness” was a primary motivation for engaging with cultural topics through podcasts. The findings of the present study indicated that the ability to listen “anytime and anywhere” is a significant factor, corroborating the research of Lundström and Lundström (2021), which highlighted the flexibility of podcasts as a primary attribute that enhances audience preference.
In addition to, Mazio (2020), which examined the impact of social media on cultural awareness among Saudi youth, the current study found that these sites spread cultural awareness through platforms other than podcasts. Ifedayo (2023) focused on podcasts in education, however, this study concentrated on educational podcasts rather than cultural ones. These findings align with many participants as they emphasized the accessibility and convenience of podcasts. One listener shared, “The flexibility of podcasts is what attracts me the most. I can listen to them while cooking, driving, or even before bed. They help me expand my cultural knowledge without feeling like a chore.” (Participant 5, Female, 29). Others highlighted the role of podcasts as an alternative to reading, with one stating, “For someone who dislikes reading, podcasts provide an excellent alternative. I can engage with cultural content in an audio format, which makes learning much more enjoyable for me.” (Participant 9, Male, 31). Furthermore, the entertainment and informative aspects of podcasts were recognized as another major draw, as one participant noted, “I think podcasts are a great source of education and entertainment. The way they present cultural topics is engaging, and I often find myself looking up more information on subjects I hear about.” (Participant 13, Female, 23).
These perspectives reinforce the study’s conclusions that podcasts effectively balance educational and entertainment elements, making them a compelling medium for cultural engagement in Jordan.
Based on participant responses highlighting the educational and entertainment value of podcasts, it may be beneficial for content producers to consider diversifying topics and further publicizing the unique features of podcasts, such as ease of access and flexibility. However, additional research is warranted to determine which specific enhancements would be most effective in reaching different audience segments.
6.3 Reasons for the Jordanian public’s confidence in cultural content presented via podcasts
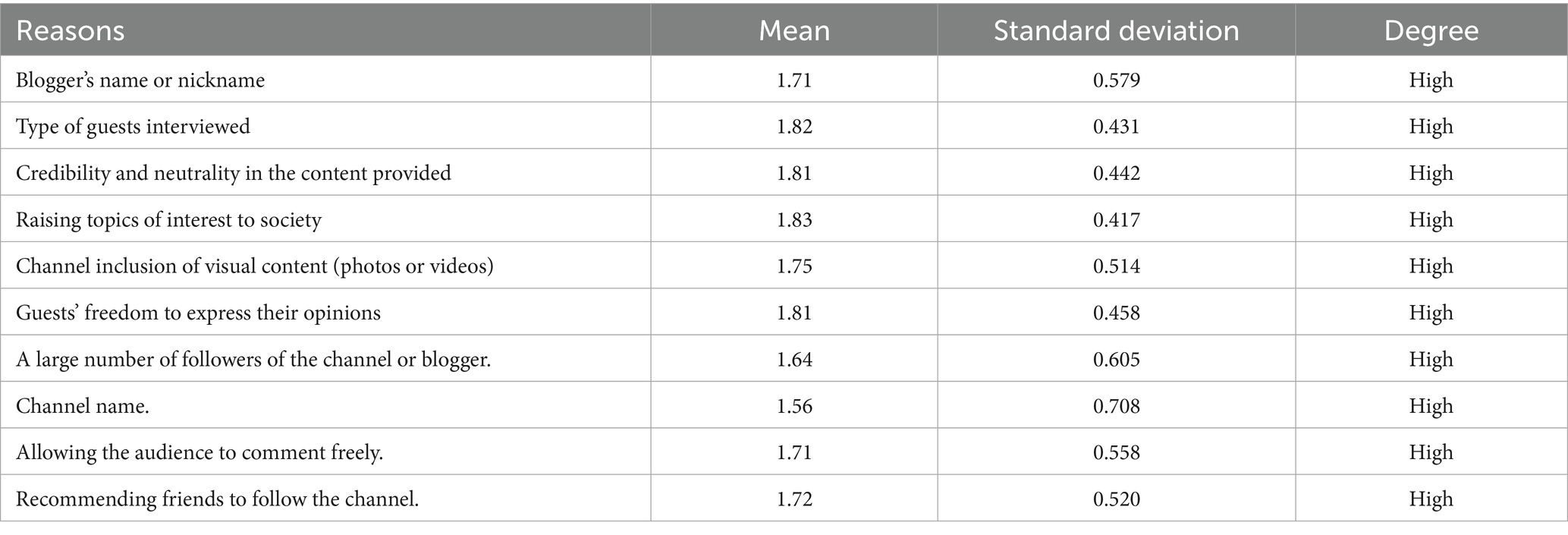
Table 3 shows that the Jordanian public’s confidence in the cultural content published via podcasts is linked to multiple elements that differ in their impact. Presenting topics relevant to society was an important factor in enhancing this confidence, as it achieved the highest arithmetic mean (1.83) with a standard deviation (0.417), which confirms the importance of the content’s connection to reality and societal needs.
The results indicated that the qualifications of the interviewed guests and the credibility and integrity of the content provided were important factors in enhancing trust, with arithmetic means of 1.82 and 1.81, respectively, accompanied by standard deviations of 0.431 and 0.442, confirming the importance of the quality of the guest and the nature of the content in developing a positive impression among the audience.
On the other hand, participants noted that the freedom given to guests to express their opinions and use visual elements, such as photos or videos, on the channel contributed to building trust, as evidenced by their means (1.81 and 1.75). The blogger’s name and fame, along with the channel name, had a moderate effect, with means of 1.71 and 1.56, respectively, highlighting the importance of personal branding and reputable channels in establishing trust.
This study’s conclusions align with other research on the factors influencing audience confidence in digital content, especially podcasts. Hashem and Abdel Rahman (2023) study demonstrated the significance of content credibility and popularity in audience preferences, aligning with the current findings that highlight the influence of the blogger’s identity and the kind of guests in fostering trust. Tobin and Guadagno (2022) study demonstrated that social interactions, including personal recommendations and sharing on social networks, positively influence feelings of belonging and credibility. The importance of media literacy and the ability to critically assess visual and audio content has also been highlighted in recent research. For instance, Aljalabneh (2024) found that strategies for developing visual media literacy, such as teaching audiences to evaluate the authenticity of images and videos on social media, play a crucial role in building trust and combating misinformation in the digital sphere. This finding is directly relevant to the present study’s observation that the inclusion of visual elements in podcasts enhances trust by promoting transparency and audience engagement. Furthermore, Al-Bousbat (2020) study demonstrated the significance of transparency and neutrality in content for fostering trust, aligning with findings that indicated the audience’s preference for information that embodies neutrality and emphasizes critical societal issues. These findings were reflected within the interviews as one participant shared, “I tend to trust podcasts that feature well-known experts or reputable guests. If the host invites credible speakers, I feel more confident in the information being presented.” (Participant 8, Male, 36). Another highlighted the importance of neutrality, stating, “The neutrality of the podcast is crucial for me. If a podcast presents balanced views without bias, I am more likely to trust and recommend it to others.” (Participant 2, Female, 28). Similarly, audience engagement plays a role in trust, as expressed by one listener: “I follow podcasts that allow open discussions and audience interactions. If I see that the podcast creators engage with their listeners, it reassures me that their content is authentic and reliable.” (Participant 11, Male, 24). These statements emphasize the critical role of content credibility, guest expertise, and audience interaction in shaping listener trust, reinforcing the study’s quantitative findings.
6.4 Cognitive effects on the Jordanian public after following cultural topics through podcasts
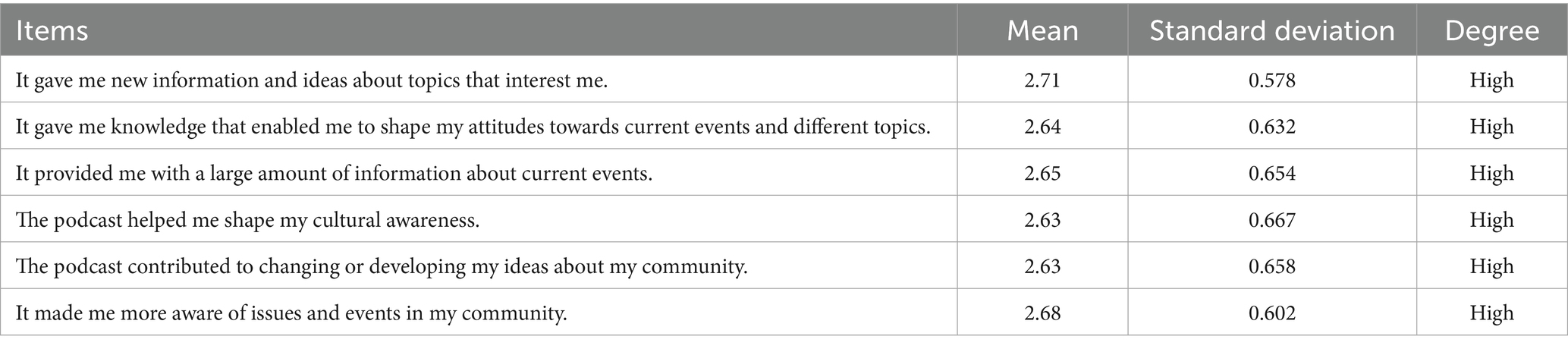
Table 4 shows that following cultural topics via podcasts contributes significantly to enhancing knowledge and increasing awareness among the Jordanian public. It was found that providing new information and ideas about topics of interest to followers had the most prominent impact with the highest arithmetic mean (2.71), which reflects the importance of podcasts as a cognitive tool that enriches followers’ thinking with new information.
The results also indicated that podcasts provide followers with knowledge that helps them form their attitudes towards current events and various topics, with an arithmetic mean of (2.64), in addition to the fact that podcasts provide listeners with a large amount of information about current events with an arithmetic mean of (2.65), which enhances its role as a news and cultural source. Moreover, podcasts helped listeners form cultural awareness with an arithmetic mean of (2.63) and contributed to changing or developing their ideas about their society and environment with an average of (2.63). It also showed a significant effect in making listeners more aware of issues and events in their community with an average of (2.68).
The current study found that podcasts on cultural issues increase audience cultural understanding. The study (Tobin and Guadagno, 2022) found that podcasts stimulate curiosity and the need for knowledge, enhancing cultural and cognitive awareness. It showed that podcasts helped listeners gain new information and ideas about cultural topics (mean = 2.71). It found that podcasts shape attitudes towards current events and other topics (mean = 2.64), supporting the findings of the previous study (Mashhadi and Jalilifar, 2016) that podcasts improve English speaking skills and broaden students’ horizons.
The current study found that podcasts helped listeners shape their cultural awareness (mean = 2.63), which is consistent with Bin Suwaidan (2024) findings that podcasts were effective in building cultural awareness among Saudi youth because they captured 54.4% of the sample due to their freely and transparently addressed cultural topics. Podcasts changed listeners’ views of their communities and homes (mean = 2.63), supporting the study (Ghazal and Bourhali, 2021) that found podcasts promote social responsibility and public opinion on important social issues. Podcasts also increased listeners’ awareness of community issues and events (mean = 2.68), supporting the study’s findings (Ifedayo, 2023) that podcasts improve cultural interaction and purposeful discussions.
Thus, the results demonstrate that podcasts serve as an effective cognitive instrument for enhancing cultural awareness and broadening listeners’ cognitive perspectives, aligning with numerous prior studies that emphasize the significance of this medium in disseminating cultural knowledge and influencing public cultural perceptions.
These findings were also reinforced by listeners insights. One participant expressed, “I have learned so much about Jordanian history and culture through podcasts. They have helped me develop a deeper appreciation for our traditions and heritage.” (Participant 6, Female, 33). Another reflected on the influence of podcasts on personal perspectives, stating, “Listening to cultural podcasts has changed my perspective on many social issues. They provide context and depth that I rarely get from mainstream media.” (Participant 10, Male, 25). Similarly, another respondent shared, “Before listening to podcasts, I was unaware of many cultural topics. Now, I feel more informed and capable of discussing these issues with my peers.” (Participant 1, Female, 26). These testimonials highlight the transformative cognitive impact of podcasts, reinforcing their role as a crucial medium for cultural education and awareness building in Jordan.
6.5 Emotional effects of following cultural topics through podcasts
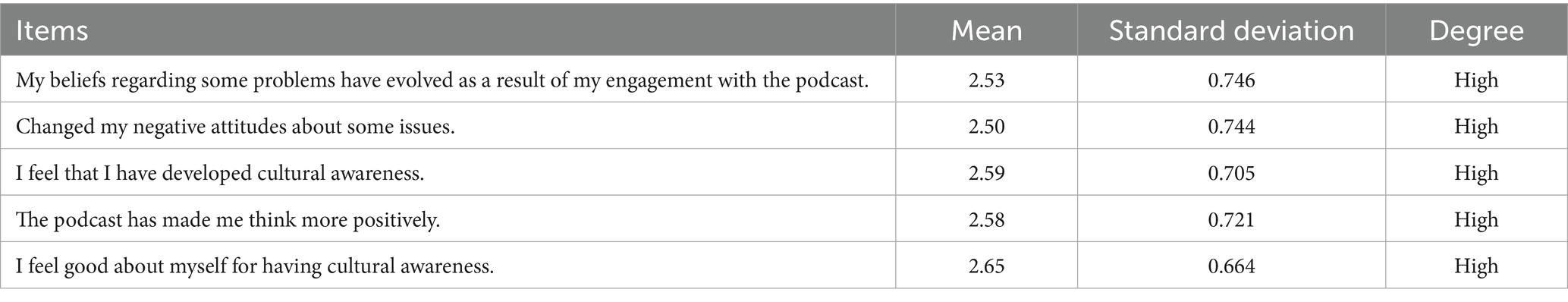
Table 5 demonstrates that exploring cultural subjects through podcasts substantially enhanced the emotional impact on the Jordanian audience. Listening to the podcast influenced certain beliefs regarding various subjects, as seen by a mean score of 2.53 and a standard deviation of 0.746, indicating a moderate emotional effect on belief formation.
The podcast also contributed to changing listeners’ negative attitudes towards some issues, with an average of (2.50), which indicates its role in improving intellectual and emotional orientations. In addition, the results confirmed that following the podcast contributed to shaping cultural awareness among listeners, with an arithmetic mean of (2.59) indicating its contribution to promoting pride and awareness.
The podcast also showed an increase in listeners’ positive perceptions of various issues, with an arithmetic mean (2.58). In addition, it raised the level of psychological satisfaction among individuals stemming from their cultural awareness, as this aspect achieved the highest arithmetic mean (2.65).
These findings confirm the significant impact of podcasts in shaping listeners’ emotions and attitudes. It transcends mere information provision, influencing beliefs and attitudes while augmenting satisfaction and cultural awareness. Podcasters should concentrate on uplifting and inspirational themes to amplify emotional resonance and boost listener engagement. The findings of the study regarding the emotional impact of engaging with cultural topics through podcasts align with prior research, as evidenced by Ghazal and Bourhali (2021), which indicated that podcasts augment listeners’ cultural awareness and positively influence their social orientations, while Bousbat and Laouira (2022) demonstrated the role of digital media in cultivating cultural awareness among youth.
These results were echoed in the experiences of several interviewees. One participant described how podcasts instill cultural pride, stating, “I feel a strong sense of pride in my culture after listening to podcasts that highlight Jordanian traditions and success stories.” (Participant 4, Male, 28). Another participant reflected on how podcasts challenged and reshaped their views, explaining, “Some episodes have made me rethink my previous biases. The way certain topics are presented encourages reflection and emotional engagement.” (Participant 9, Female, 30). Additionally, a respondent highlighted the emotional connection podcasts foster, sharing, “Listening to cultural podcasts has given me a greater sense of belonging. I feel more connected to my community and its cultural identity.” (Participant 13, Male, 26). These views show the emotional dimension of podcast engagement, illustrating their power to foster cultural pride, reshape perspectives, and strengthen a sense of community among the participants.
6.6 Behavioral effects of following cultural topics through podcasts
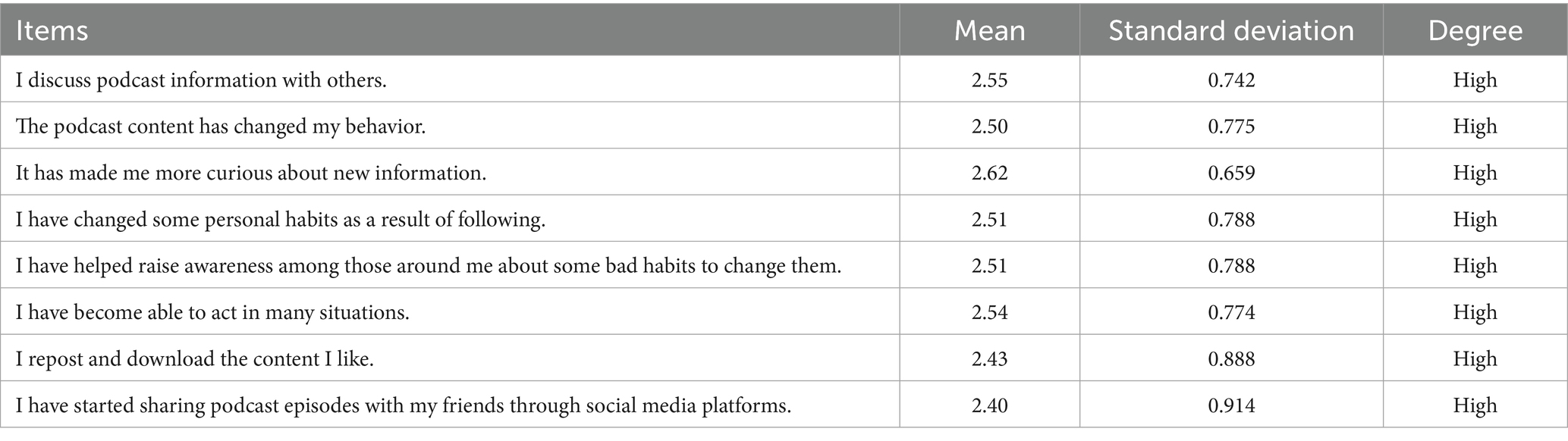
Table 6 demonstrates that listening to podcasts about cultural subjects had a major impact on the audience’s behaviors in Jordan. The arithmetic mean for this statement was (2.55) with a standard deviation of (0.742), confirming that listening to the podcast encouraged listeners to share the knowledge they acquired with others. It also showed that the content provided through the podcast brought about a change in the behaviors of followers, with an average of (2.50), indicating a moderate positive impact on changing individual behavior patterns. In addition, the podcast aroused the curiosity of listeners to learn new information, which was reflected in this statement achieving the highest arithmetic mean (2.62) among the studied statements.
Also, following the podcast helped change some personal habits of listeners, with an average of (2.51), and contributed to raising awareness among those around them about some negative habits and working to change them. Listeners also became more capable of acting in many daily situations, as this statement received an average of (2.54). As for publishing and interacting with content, the results showed that listeners republish and download content that catches their attention, with an average of (2.43). Participants also began to share podcast episodes with their friends via social media platforms, with an average of (2.40), which reflects the wider spread of the influence of podcasts in society.
These results show that podcasting connects with audiences and improves cultural engagement. Changes in personal behavior, increased curiosity for learning, and social awareness are evident. Previous studies on the behavioral impacts of podcasting cultural themes are consistent with the current findings. Although the current findings confirm that following podcasts stimulates discussion with others and changes personal behaviors, previous studies (Tobin and Guadagno, 2022) have shown that podcasts enhance social interaction and participation, while other studies (Ifedayo, 2023) show cognitive curiosity and behavior change. The current findings that podcasts promote cultural and social awareness are consistent with other research (Berg, 2021; Ghazal and Bourhali, 2021) which stresses the power of podcasts to change cultural and social behavior. These findings were also highlighted when discussing the impact of podcasts on personal and social behaviors with the participants. One participant discussed, “Since I started listening to cultural podcasts, I have become more engaged in discussions about heritage and social issues. I actively share what I learn with friends and family.” (Participant 1, Female, 22). Another participant emphasized the role of podcasts in motivating real-life actions, stating, “I now make a conscious effort to attend cultural events and participate in community discussions. Podcasts have motivated me to be more active in preserving our traditions.” (Participant 6, Male, 29). Furthermore, another listener reflected on the transformative nature of podcast content, explaining, “One podcast episode made me realize how little I knew about my own culture. It inspired me to start a blog where I share insights and reflections on Jordanian heritage.” (Participant 11, Female, 27). These statements demonstrate how cultural podcasts act as catalysts for individual and collective action, further strengthening their influence beyond passive listening.
7 Hypotheses test
7.1 There is a correlation between the degree to which respondents follow cultural topics through podcasts in shaping cultural awareness; and the effects resulting from this follow-up
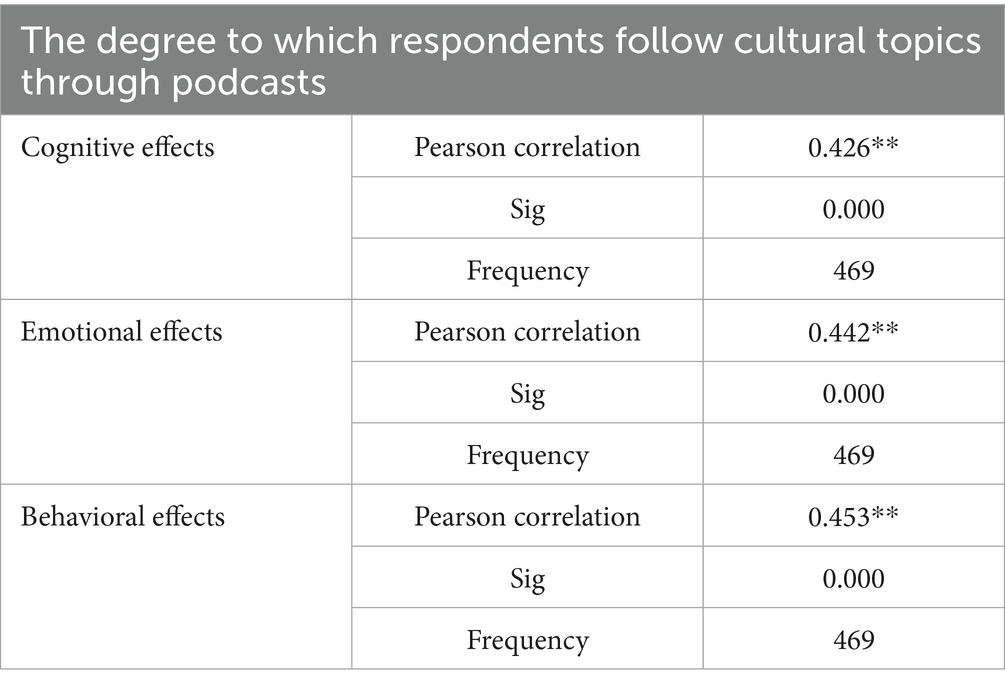
According to Table 7, the results of testing the hypothesis of the relationship between the degree of respondents’ following of cultural topics through podcasts and the effects indicated a statistically significant positive association between the variables. Pearson correlation coefficient analysis found a strong relationship between the degree of following cultural topics and cognitive effects, with a correlation coefficient of 0.426 and a significance level of 0.000, indicating a statistically significant positive correlation between the two variables. Further, the results indicated a positive association between listening to podcasts and emotional effects, with a correlation coefficient of 0.442 and a significance level of 0.000, and behavioral effects, with a correlation coefficient of 0.453 and a significance level of 0.000. This confirms the existence of a strong association between interaction with cultural content via podcasts and effects on knowledge, emotions, and behaviors.
The findings indicated that engaging with cultural topics through podcasts enhances listeners’ cultural knowledge and awareness, stimulates inspiration and empathy, and encourages the adoption of positive cultural behaviors, such as participating in cultural activities or embracing new practices. The findings align with McClung and Johnson (2010) research, which highlighted podcasts’ contribution to self-directed learning and awareness, and with Sajid et al.'s (2024) study, which underscored the significance of digital media in shaping emotional and social dimensions.
Moreover, our results corroborate the findings of López et al. (2020) regarding the capacity of podcasts to promote positive cultural behaviors, affirming its efficacy as a medium for disseminating culture and augmenting cognitive, emotional, and behavioral impacts on the audience.
7.2 There is a correlation between the cognitive effects of the respondents’ following cultural topics via podcasts in shaping cultural awareness and the emotional effects of this following
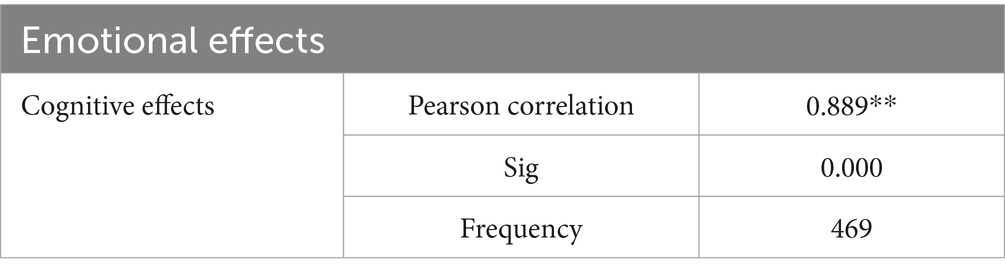
According to Table 8, the findings indicated a robust positive association of statistical significance between the cognitive and emotional effects experienced by respondents who engaged with cultural topics via podcasts. The Pearson correlation coefficient analysis revealed a significant correlation (correlation coefficient 0.889) between cognitive and emotional effects, with a significance level of 0.000, indicating a statistically significant relationship between the two effects.
The results show that information and emotion work together to shape cultural awareness, with the cognitive effects of podcasts significantly enhancing listeners’ emotional effects. Listeners gain cultural understanding and feel inspired, empathized, and proud, which enhances their connection to cultural issues. As Bandura (1986) stated, learning is influenced by emotional and social factors in addition to knowledge. McClung and Johnson (2010) add that podcasts enhance cognitive and emotional engagement, making learning inclusive. According to PM Ribeiro (2016), cultural digital information can lead to strong emotional responses that increase cultural awareness, while López et al. (2020) showed that the emotional effects of cultural media shape good cultural behaviors. Cultural podcasts demonstrate the need to combine cognitive and emotional elements to raise awareness and connect people to cultural concerns on many levels.
Building on the present findings, future research could take several specific directions to further elucidate the role of podcasts in cultural awareness. First, longitudinal studies are needed to track how sustained podcast engagement influences cognitive, emotional, and behavioral dimensions of cultural awareness over time. Second, experimental and quasi-experimental designs could be implemented to examine the effects of specific podcast formats, content types, or delivery strategies on different audience segments. Third, comparative studies across different mediasuch as contrasting podcasts with traditional radio, television, or social media, would provide valuable insights into the unique contributions of podcasts to cultural education. Additionally, future studies should investigate the role of individual differences, such as digital literacy, socio-economic status, and prior media habits, in moderating the effects of podcast consumption. Qualitative research that includes less-engaged or non-listeners could help identify barriers to adoption and inform strategies for broader cultural participation. Finally, partnership-based research involving collaborations between podcast creators and cultural institutions may reveal effective ways to expand podcast reach and cultural impact within diverse communities.
8 Conclusion
The study concluded that podcasts are an effective means of enhancing cultural awareness among the Jordanian public, as they have shown a positive impact on cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects. Despite the varying levels of audience follow-up, a large percentage showed medium or high interest in this medium, reflecting its growing role in transferring cultural knowledge. The results also showed that providing rich and diverse content that is in line with listeners’ interests was the most prominent factor in enhancing knowledge and awareness. The study found that Jordanians gained cognitive, emotional, and behavioral benefits from cultural podcasts. The findings suggest that podcasts are associated with enhanced cultural awareness, increased knowledge about current events, and greater cultural pride among listeners. Many participants reported that podcast engagement was linked to shifts in attitudes and behavioral intentions. Nevertheless, these outcomes are based on self-report data, and future research is needed to confirm the broader impact of podcasts on knowledge exchange and community interaction. Accordingly, the study recommends developing the cultural content of podcasts and increasing interaction with the public to maximize its impact, allowing it to continue as an effective educational and media tool capable of contributing to shaping an integrated cultural awareness among various societal groups.
8.1 Limitations
Despite its contributions, this study is subject to several limitations that should be acknowledged when interpreting the findings. First, the use of quota sampling, while intended to increase representativeness, cannot fully eliminate sampling bias and may restrict the generalizability of results beyond the surveyed population. Second, the cross-sectional survey design captures responses at a single point in time and does not account for potential changes in attitudes or behaviors over time, limiting the ability to infer causality. Third, the reliance on self-reported measures introduces the possibility of social desirability and recall bias, as participants may overstate positive impacts or underreport negative experiences related to podcast engagement. Additionally, while the mixed-methods approach provided both breadth and depth, the qualitative sample was relatively small and limited to highly engaged listeners, potentially skewing thematic findings toward more active podcast users. Furthermore, the study did not systematically explore other influential variables such as socio-economic status, media literacy, or prior exposure to digital technologies, which may also shape cultural awareness. Finally, as the research was conducted exclusively within the Jordanian context, caution should be exercised when generalizing the results to other cultural or national settings.
9 Recommendations
The limitations identified above provide important directions for future research in this field. Subsequent studies should aim to employ probability-based sampling strategies and larger, more diverse samples to enhance the generalizability of findings across different segments of Jordanian society and in other cultural contexts. Longitudinal designs are recommended to examine how podcast engagement influences cultural awareness and related outcomes over time, thereby providing stronger evidence for causal relationships. Additionally, future research should incorporate objective measures of media exposure, such as digital tracking or usage analytics, to supplement self-reported data and reduce reporting bias. Expanding the qualitative component to include less engaged listeners or non-users may yield a more comprehensive understanding of barriers to podcast adoption and cultural participation. Researchers should also consider examining moderating variables such as socio-economic status, education, or digital literacy, which may interact with podcast consumption in shaping cultural awareness. Comparative studies analyzing the effects of podcasts relative to other media forms such as television, radio, and social media could further elucidate the distinctive contributions of podcasting to cultural education and engagement. Finally, experimental or intervention-based research could assess the effectiveness of specific podcast formats, content strategies, or collaborations with cultural institutions in promoting cultural understanding and knowledge exchange.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Zarqa University, Jordan (#ZU-ESA-MEDIA37/2024-2025). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The author declares that this research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Zarqa University, Jordan (No: 14055).
Acknowledgments
The researcher thanks all study participants who participated in the study.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel-Razzaq, S. (2023). The credibility of podcast programs as a source of information and news for the Egyptian public. J. Med. Res. 69, 903–1030. doi: 10.21608/jsb.2024.243961.1660
Ahmad, A. K. M. (2022). The impact of the use of social networking platforms on the Jordanian voters in the nineteenth Jordanian parliamentary elections during the emerging pandemic of the coronavirus (COVID-19). Zarqa J Research Studies Humanities 22, 333–350. doi: 10.12816/0061218
Aljalabneh, A. A. (2024). Visual media literacy: educational strategies to combat image and video disinformation on social media. Front. Commun. 9:1490798. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2024.1490798
Aljalabneh, A. A. S., Alzoubi, A. F., and Shlool, H. (2023). Facebook as a contemporary public sphere for opinion expression and participation: Jordan as a case study. Stud. Media Commun. 11, 70–78. doi: 10.11114/smc.v11i3.5984
Al-Nabulsi, A. (2021). The impact of podcast series on adolescents in consolidating social and human values [unpublished master’s thesis]. Middle East University.
Al-Rifai, A. (2019). The role of social media networks in promoting tourism in Jordan from the perspective of local and Arab tourists. J. Med. Res. 10, 25–50.
Alsharu, W. Z., Eneizat, M. F., and Safori, A. (2025). The impact of data journalism on Jordanian voters during the 2024 parliamentary elections. Int. J. Media Mass Commun. 7, 1–16. doi: 10.46988/IJMMC.07.01.2025.01
Al-Zoubi, M. (2021). Podcasts as a cultural and social communication tool in Jordan: an analytical study. J. Cult. Stud. 8, 45–70.
Bandura, A.National Inst of Mental Health. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Berg, F. S. A. (2021). Independent podcasts on the apple podcast platform in the streaming era. MedieKultur 37, 110–130. doi: 10.7146/mediekultur.v37i70.122390
Bin Suwaidan, A. (2024). The effectiveness of podcasts in building cultural awareness among Saudi youth. Arab J Media Communication Research 45, 101–147. doi: 10.21608/jkom.2024.360789
Bousbat, A., and Laouira, I.. (2022). The role of new media in developing cultural awareness among university youth [unpublished master’s thesis]. Mohamed Seddik Ben Yahia University.
Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
Ghazal, A., and Bourhali, W. (2021). Social podcast between developing responsibility and creating community awareness. J. Human Soc. Sci. 10, 645–663.
Global Market Insights (2023). Podcasting market size and forecast 2024–2032. Available online at: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/podcasting-market
Hashem, M., and Abdel Rahman, A. (2023). Trends of Egyptian and Arab news websites to use podcast technology and its relationship to the preferences of the Egyptian audience. Egyptian J Mass Commun. Res. 1, 737–834. doi: 10.21608/mebp.2022.181223.1053
Ifedayo, A. E. (2023). Podcasts shaping the educational landscape: a comparative analysis of Nigeria and foreign universities. J. Educ. Res. Libr. Pract. 2, 22–31.
López, M., García, A., and Pérez, J. (2020). The role of podcasts in promoting cultural behaviors: a qualitative analysis. Media Cult. Soc. 42, 589–605.
Lundström, M., and Lundström, T. P. (2021). Podcast ethnography. Int. J. Social Research Method., 24, 289–299.
Luttrell, R., and Wallace, A. A. (2024). Social media and society: An introduction to the mass media landscape. US: Rowman & Littlefield.
Mashhadi, A., and Jalilifar, A. (2016). The impact of podcasts on English vocabulary development in a blended educational model. Applied Research English Language 5, 145–172. doi: 10.22108/are.2016.20423
Mazio, M. (2020). The role of social media in developing cultural awareness among Saudi youth. Faculty Educ. Cairo. Educ. Magazine 188, 177–204. doi: 10.21608/jsrep.2020.128661
McClung, S., and Johnson, K. (2010). Examining the motives of podcast users. J. Radio Audio Media 17, 82–95. doi: 10.1080/19376521003719391
Morris, J. W. (2019). Hearing the past: The sonic web from MIDI to music streaming. The SAGE handbook of web history. Eds. N. Brügger and I. Milligan. Londres: SAGE Publications, 491–504.
Nielsen, R. K., and Ganter, S. A. (2022). The power of platforms: Shaping media and society. UK: Oxford University Press.
PM Ribeiro, S. (2016). Developing intercultural awareness using digital storytelling. Language Intercultural Commun. 16, 69–82. doi: 10.1080/14708477.2015.1113752
Riffe, D., Lacy, S., Watson, B. R., and Lovejoy, J. (2023). Analyzing media messages: Using quantitative content analysis in research. UK: Routledge.
Sajid, S., Anwer, M., Mufti, A. A., and Iqbal, M. (2024). Investigating how cultural contexts shape social media experiences and their emotional consequence. Rev. Educ. Adm. Law 7, 185–200. doi: 10.47067/real.v7i4.370
Statista. (2023). Number of podcast listeners worldwide from 2020 to 2027. Available online at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1291360/podcast-listeners-worldwide
Tobin, S. J., and Guadagno, R. E. (2022). Why people listen: motivations and outcomes of podcast listening. PLoS One 17:e0265806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265806
Usborne, E., and De La Sablonnière, R. (2014). Understanding my culture means understanding myself: the function of cultural identity clarity for personal identity clarity and personal psychological well-being. J. Theory Soc. Behav. 44, 436–458. doi: 10.1111/jtsb.12061
Keywords: podcast, cultural awareness, Jordanian audience, digital cultural content, digital content
Citation: Safori A (2025) The role of podcasts in shaping cultural awareness among the Jordanian public. Front. Commun. 10:1595098. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1595098
Edited by:
Syed Hassan Raza, Taylor’s University, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Ogadi Emenyeonu, University of Sharjah, United Arab EmiratesAmjad Ali Shah, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Safori. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Amjad Safori, YXNhZm9yaUB6dS5lZHUuam8=
 Amjad Safori
Amjad Safori