- 1Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, VA, United States
- 2Department of Basic Science Education, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, VA, United States
Medical education increasingly emphasizes the development of communication, empathy, and teaching skills alongside scientific knowledge. Community outreach programs offer a unique opportunity for medical students to cultivate these competencies in real-world settings. This pilot study investigates the impact of participation in science outreach programs on the engagement and perceived professional development of medical students. Thirty medical students from the Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine volunteered in two community-based outreach programs—Kids’ Tech University (KTU) and Medical Discovery of Careers (MedDOCs). These programs involved interactive, hands-on teaching of physiological concepts to middle and high school students. Engagement levels were assessed using a modified Utrecht Work Engagement Scale (UWES), comparing students’ self-reported experiences during teaching versus studying. Thematic analysis was applied to qualitative reflections. Students reported significantly higher engagement scores while teaching compared to studying (5.8 ± 0.1; 4.4 ± 0.1) on a 7-point Likert scale, p < 0.05. Thematic analysis revealed four key themes: community engagement and social responsibility, personal and professional growth, educational creativity and communication skills, and inspiration through role modeling. Participation in community outreach programs may enhance medical students’ engagement, communication skills, and sense of purpose. These findings support the integration of structured outreach opportunities into medical education to foster holistic professional development.
1 Introduction: background and rationale for the educational activity
Medical education presents numerous challenges, often prompting students to prioritize academics at the expense of their physical and mental well-being. The demands of rigorous coursework, exams, and the competitive pursuit of residency can narrow students’ focus, limiting opportunities for personal and professional growth (Dyrbye and Shanafelt, 2016). Beyond mastering medical knowledge, medical students must cultivate essential skills critical for holistic patient care, such as communication, adaptability, empathy, and teaching. The shift to a pass/fail STEP 1 exam further underscores the need for students to distinguish themselves through extracurricular experiences that foster these skills.
Medical schools could address this need by offering meaningful, engaging opportunities that enhance students’ competencies, for example, as supplemental training in communication that helps to meet the LCME accreditation standard (Restini et al., 2024; Butterfield et al., 2024; Vollbrecht et al., 2024). However, care must be taken to avoid contributing to burnout (Morcos and Awan, 2023) by adding extracurricular activities. Community outreach programs and service-learning provide an ideal platform for experiential learning, allowing students to develop practical skills while benefiting the community (Fatton et al., 2021). Outreach initiatives can, for example, involve students in health needs assessments and the development of health promotion interventions, potentially fostering a deeper understanding of social determinants of health and improving population health outcomes.
Furthermore, outreach programs provide students with a “boots on the ground” experience, enhancing their understanding of community health literacy and their ability to communicate effectively with diverse populations.(Butterfield et al., 2024; Vollbrecht et al., 2024). This hands-on experience can foster critical communication and adaptability skills essential for addressing future patients’ health literacy needs. Volunteering also may boost students’ happiness and engagement, improving their relationships with peers and the community.
These experiences potentially enhance students’ preparedness for the multifaceted demands of patient care while providing insight into the social and behavioral factors that impact health. Community outreach aligns with social learning theory (Cheng and Shelnutt, 2020), emphasizing learning through interaction, role modeling, and humanistic education to foster empathy. By teaching others, students may broaden their understanding of health concepts and expand their social awareness by witnessing the effect of health literacy on individuals. Despite other qualitative reports, few studies have quantified medical-student engagement while teaching community learners.
VTCSOM medical students were invited to volunteer in outreach community programs like Kids’ Tech University (KTU) and Medical Discovery of Careers (MedDOCs). Recent literature highlights the value of such peer education and service-learning programs, where health professions students can develop mentorship skills while promoting STEM engagement and health literacy in their communities (Butterfield et al., 2024). Through interactive, hands-on activities in real-world settings, students help learners explore complex physiological concepts in an accessible way while simultaneously enhancing their own abilities to employ innovative teaching approaches, simplify intricate information, and improve communication skills essential for their future medical careers (Fatton et al., 2021).
This manuscript describes a Community Case Study and explores medical students’ self-reported engagement when teaching science in community outreach programs. The authors hypothesized that medical students volunteering in these outreach programs would be more engaged in teaching compared to studying.
Note: Throughout this manuscript, the term “volunteers” or “students” refers to medical students, In contrast, middle and high school students are collectively referred to as “learners,” acknowledging their pivotal role in the educational process facilitated by the medical students.
2 Active learning: environment, approach, and objectives
The authors’ approach is grounded in the belief that medical student teachers and learners construct their understanding through individual experiences and interactions. The teaching methods focus on physical engagement with the material, emphasizing active participation rather than content delivery. These methods encourage “learning by doing,” ensuring students and learners are not passive recipients of information but are involved in the learning process (Carvalho and West, 2011).
Medical students’ training was a key part of this process before engagement with the community. To stimulate insight and ensure that students in the role as teachers/educators understand how the learners received or perceived the information, all volunteers experienced the activities as learners first. They practiced the same hands-on activities with their peers, which allowed them to become comfortable with the content and teaching methods. It also fostered insight as they “experienced” what the learners would experience later. This dual role as both teacher and student helped them better understand the challenges and perspectives of their audience and hopefully facilitate empathy.
Medical students leveraged interactive teaching methods to engage learners in outreach programs, utilizing various creative techniques to enhance understanding. These methods included manipulatives (Li and Carvalho, 2016; Giffen and Carvalho, 2015; Jagzape et al., 2021) and dramatizations (Dowlati et al., 2016; Connor and Carvalho, 2019; Halpin and Gopalan, 2021) to illustrate body parts and cost-effective approaches that utilize everyday household items (e.g., cotton balls represent ‘oxygen’ during the dramatization of gas transport), making abstract concepts more tangible. During outreach activities, medical students asked learners questions that sparked curiosity and helped learners focus on the task. Descriptions and lesson plans of the special senses and dramatization model are included in the appendices (Supplementary Appendices A–E). While this approach is intended to help medical students translate complex health science concepts for the learners in the community, this study did not directly measure comprehension or understanding.
2.1 IRB statement
The Virginia Tech Human Research Protection Program (HRPP) was consulted. At that point, it was determined that this protocol met the criteria for exemption from IRB review, as no sensitive or protected data were collected from either the medical students or children (learners) participants. This study was conducted in accordance with local legislation and institutional requirements.
2.2 Participants
Each class at VTCSOM, a medical school located in Roanoke, Virginia, consists of approximately fifty students, with some variation due to gap years or other factors. Students from all classes were invited to participate in KTU. In contrast, first and second-year students were specifically invited to participate in MedDOCs. Thirty medical students volunteered for these two outreach programs, representing approximately 15% (30/200) of the total eligible student population across all four years. Twenty medical students were part of KTU, including twelve first-, six second-, and two third-year medical students. In MedDOCs, there were ten participants (five first-and second-year medical students), representing about 10% of eligible first-and second-year students. In total, within class years, this equates to 24% of M1s, 16% of M2s, 4% of M3s, and 0% of M4s.
2.3 Learning environment: Kids’ Tech University (KTU)
KTU is an annual program that caters to middle school learners and is hosted by Virginia Tech University on its Blacksburg, Virginia campus. The KTU program focuses on learners ages 9 through 12. Approximately 160 kids attended the day-long festivities in 2024, which are comprised of a morning lecture from a scientist, followed by 20–30 interactive stations on Science, Technology, Engineer, and Mathematics (STEM) subjects in the afternoon.
Medical students from VTCSOM have actively participated in the KTU program since 2011. The data presented here were obtained during the 2024 outreach program. Medical students are setting up stations featuring hands-on activities and plastic anatomical models. These stations focused on educating learners about taste, olfaction, and the auditory and visual senses. The curriculum also offered a dramatization where each learner personified a red blood cell transporting gases in the blood circulation in the cardiovascular system. Lastly, the curriculum also includes discussions on nutrition, featuring simulations that illustrate the appropriate proportions of food on a plate.
2.4 Learning environment: MedDOCs
MedDOCs is a weekly after-school enrichment program designed to span six weeks. It is tailored for high school students living in underserved neighborhoods in Roanoke Valley, Virginia and who are demographically underrepresented in medicine. There were 25 high school students during this session, resulting in groups of five. Medical student volunteers worked in pairs (one M1 and one M2) and oversaw a group of high school learners interested in science and medicine. The curriculum, curated by medical students, featured interactive lectures and hands-on activities that immersed learners in anatomy, physiology, and pathology while providing volunteers opportunities to hone their teaching and communication skills. For this study, each pair of medical students set up a station focused on one of the special senses. Each station involved a brief lecture followed by a hands-on activity specifically tailored to mirror the special senses activities of KTU.
2.5 Learning objectives for community learners
Although not assessed in the current study, the overall learning objective for learners (middle and high school students) participating in the outreach programs was to expose them to and improve their understanding of science and health literacy, as described in the literature (Vollbrecht et al., 2019). Our program activities focused on the physiology of the special senses (taste, smell, vision, hearing, and touch) and the circulatory system. By engaging with these concepts through interactive, hands-on experiences, the authors aimed to foster a deeper appreciation of the health sciences in the learners (Restini et al., 2024). In addition to building foundational knowledge, the study sought to inspire learners by exposing them to a diverse group of medical students, illustrating that careers in science and medicine are accessible to anyone, regardless of background.
2.6 Learning objectives for medical students
As the objective of this study, these outreach programs were designed for medical students to contribute to the community and enhance their engagement during teaching activities. The authors assessed medical students’ self-reported engagement levels using a simplified survey instrument (Schaufeli et al., 2006). The focus was on comparing engagement between studying and teaching activities, with particular attention to energy levels, happiness, immersion, and flow experience (Table 1). By providing medical students with opportunities to teach in community settings, the program aimed to create a more engaging learning environment that could potentially translate to improved communication skills, as described in the literature (Restini et al., 2024).
3 Data collection and analysis
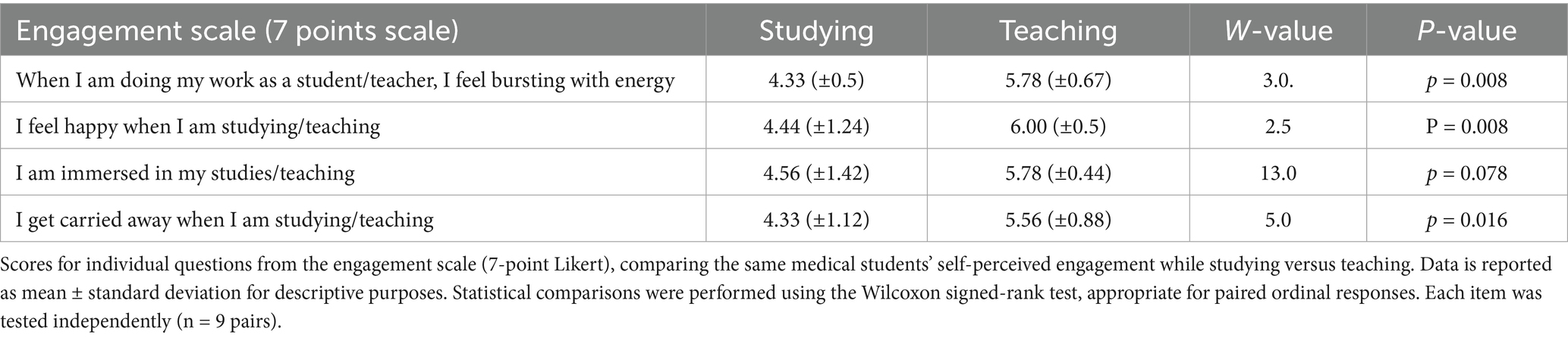
The authors simplified the Utrecht Work Engagement Survey (Schaufeli et al., 2006) (UWES) to assess medical students’ engagement, comparing their perception of teaching versus studying activities. The original UWES contains 17 items. For this pilot study, the authors selected four questions derived from the original scale that were most relevant to the comparison between studying and teaching contexts (Table 1). The questions were adapted to specifically reference either teaching or studying activities, maintaining the same structure and format while adjusting context. An additional free-text question was included, asking students to “share any thoughts reflecting on your time participating in these activities.” We applied thematic analysis to the free-text question, obtaining insight into the medical students’ perception of their role in the outreach programs (Table 2). The thematic analysis was supported by Microsoft Copilot, a generative AI tool based on OpenAI’s GPT-4 model, integrated by Microsoft to assist with qualitative data interpretation and theme development.
The survey was anonymous and administered via the QuestionPro platform at the end of the outreach program, with access through a link and QR code. All thirty medical students who volunteered for KTU and MedDOCs outreach programs began responding to the engagement survey, and nine completed it.
3.1 Statistical analysis
Data was presented as means and standard deviations, and test results are reported with degree of freedom, t statistic, and p-value. To assess the effect of the teaching activity on student engagement, we compared responses between studying and teaching situations. Engagement was measured using a four-item questionnaire, with each item rated on a 7-point Likert scale.
For each student, an average engagement score was calculated by taking the mean of their responses to the four items, providing an average measure for each phase (“studying” and “teaching”). To analyze the change in engagement, a paired sample t-test was conducted comparing the mean engagement scores. For each individual question, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare paired responses for studying and teaching, as this nonparametric test is appropriate for ordinal data. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. All analyses were performed using Python (pandas, scipy, matplotlib).
4 Results
The medical students responded about their overall engagement during studying compared to their teaching engagement (Figure 1). They reported higher engagement scores when teaching compared with studying: 5.8 ± 0.1 and 4.4 ± 0.1, respectively [mean ± SD, p < 0.05, t(8)-3.93] on a seven-point Likert scale (1 = Strongly Disagree, 2 = Disagree, 3 = Slightly Disagree, 4 = Neutral, 5 = Slightly Agree, 6 = Agree, 7 = Strongly Agree). The average score for each question is presented in Table 1.
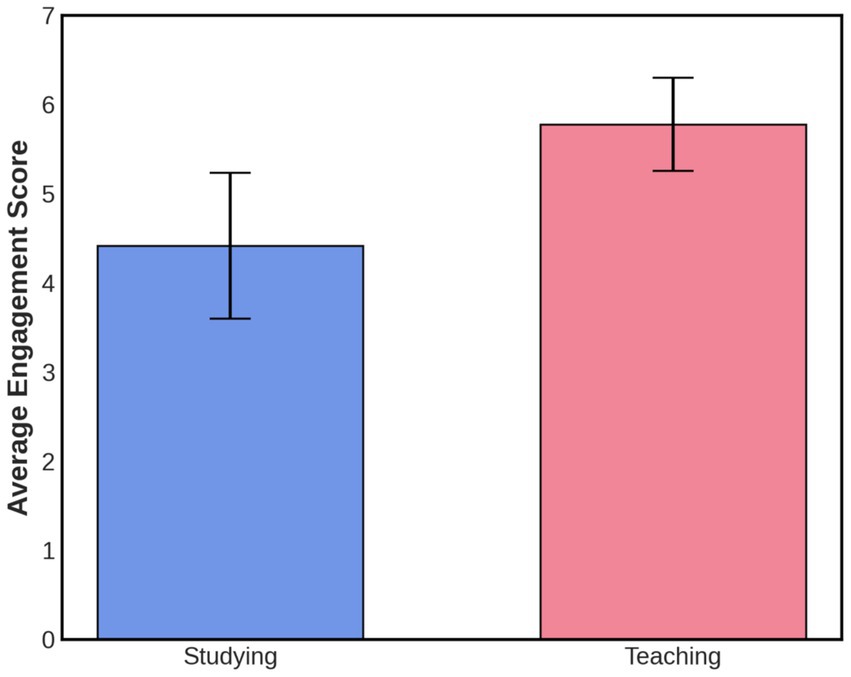
Figure 1. Overall engagement scale during studying versus teaching. Teaching has a higher value 5.78 ± 0.52; than studying 4.42 ± 0.82 (mean ± SD), indicating that participants generally feel more engaged while teaching than studying.
4.1 Comments from medical student
Table 2 displays medical students’ responses to the optional free-text question. The thematic analysis of their reflection on participation in the outreach programs were divided into themes.
4.2 Theme 1: Community engagement and social responsibility
This theme reflects a growing awareness among students of their roles not just as future healthcare providers, but as active community members. Many students expressed a deep sense of fulfillment from contributing to their communities. They highlighted the importance of giving back and the meaningfulness of their involvement.
• “Outreach was valuable to me because I felt as though I was truly doing something valuable for the community.”
• “Spending the afternoon demonstrating science and engaging with the participants truly reminded me of what it means to be connected to a community.”
4.3 Theme 2: Personal and professional growth
This suggests that outreach programs can serve as powerful reminders of students’ core values and aspirations. Students noted that the outreach experience contributed to their personal development and reinforced their motivation for pursuing a career in medicine.
• “I had opportunities to get involved as a school-aged child myself, and leading these activities now was incredibly meaningful to me.”
• “The positive impact that I made on the kids was so much more meaningful than sitting in the library.”
4.4 Theme 3: Educational creativity and communication skills
This theme highlights the development of communication and pedagogical skills, which are essential for effective patient education in clinical practice. Participants emphasized the challenge and satisfaction of translating complex scientific concepts into engaging, age-appropriate content.
• “It felt really good breaking down those complex physiological processes, like vision or smell, for kids in ways that really clicked for them.”
• “Wanting to come up with more engaging activities! I think having a stethoscope and allowing the kids to listen to hearts would be exciting…”
4.5 Theme 4: Inspiration and role modeling
This underscores the cyclical nature of outreach—today’s learners becoming tomorrow’s leaders and educators. Some students reflected on the importance of being a role model and inspiring the next generation, especially those from backgrounds similar to their own.
• “I had opportunities to get involved as a school-aged child myself…”
The students’ comments aligned with findings from other studies where medical students gained valuable health and science communication skills through similar outreach programs. The comments, while limited, provide some qualitative context to the quantitative findings on engagement. They suggest these volunteer experiences may have value beyond the classroom setting.
5 Discussion
Experience with community outreach programs, such as KTU and MedDOCs, at VTCSOM offer valuable lessons for medical education. This manuscript presents preliminary data indicating that medical students who volunteer in an outreach program show increased engagement in teaching compared with studying. Medical students’ self-reported happiness and energy bursts underscore the effectiveness of moving beyond traditional classroom learning.
Furthermore, the act of translating complex physiological concepts into accessible formats, exemplified by KTU’s dramatizations of cardiovascular processes, reinforces learning (Carvalho and West, 2011). This experience offers a dual benefit for medical students: a better grasp of science alongside the crucial skill of clear communication that is essential for future patient interactions. As one student noted, the challenge of explaining concepts like vision or smell in a way that ‘really clicked’ with younger learners provides direct practice in this skill.
The authors advocate that elements of community-based teaching could be more formally integrated into the curriculum as required training modules prior to starting clerkships or for elective credits aimed at fulfilling specific communication or health advocacy learning objectives.
While the current study did not directly measure changes in communication skills or mentorship abilities, qualitative feedback from participants suggests that these outreach experiences may provide opportunities for practicing these skills in real-world settings. A recent publication (Restini et al., 2024) advocates for the early involvement of medical students in community outreach to strengthen individual and community health literacy.
5.1 Impact
The findings from this pilot study underscore the potential of community outreach programs to enhance student engagement while simultaneously building essential clinical communication skills. To enhance benefits, medical education institutions could consider several key strategies: actively promoting outreach opportunities as recognized avenues for personal and professional growth, ensuring acknowledgment of program and student time and efforts, and nurturing strong, reciprocal relationships with community partners (Restini et al., 2024).
Incorporating creative teaching methods, including arts-based approaches like dramatization (Dowlati et al., 2016; Connor and Carvalho, 2019; Halpin and Gopalan, 2021) as a pedagogical method and hands-on manipulatives (Li and Carvalho, 2016; Giffen and Carvalho, 2015; Jagzape et al., 2021) represent a promising direction for medical education. These approaches can provide a crucial outlet from intense academic pressures. This aligns with other research suggesting that humanities integration within medical curricula can help mitigate burnout and enhance well-being among medical students (Volpe et al., 2022; Mangione et al., 2018).
Navigating the challenges inherent in these real-world teaching environments, such as adapting content on the fly or managing group dynamics, may potentially help build resilience and practical problem-solving skills that could be beneficial for future clinical roles. Similarly, the challenges observed when volunteers work with kids require creativity, adaptability, and communication (Butterfield et al., 2024). Though further research would be needed to substantiate these potential benefits, our preliminary findings suggest that community outreach programs could serve as complementary activities to traditional medical education, contributing to personal and professional development.
Integrating community outreach opportunities into the medical education curriculum cannot be overstated. These programs provide students with hands-on teaching experiences that enrich their academic and professional development while potentially contributing to their personal growth and well-being. As medical schools prioritize holistic training approaches, incorporating outreach initiatives can nurture well-rounded, empathetic physicians capable of addressing diverse community needs. Also, participation in KTU and MedDoc created opportunities for some volunteer students to develop and present posters (Prabhakar et al., 2024) and talks (Prabhakar and Carvalho, 2025).
In summary, this pilot study suggests that community outreach programs serve as more than just opportunities for medical students to give back to society; they serve as catalysts for personal and professional development. Active participation in such initiatives enriches students’ educational experiences and cultivates essential skills and values that will benefit them throughout their medical careers.
5.2 Challenges, limitations, and future directions
The small sample size is a limitation of the study. With only thirty participants representing approximately 15% of the eligible student population, the findings may not fully represent the experiences and perspectives of all VTCSOM medical students. This limited representativeness affects the generalizability of the results and underscores the preliminary design and results of this pilot study. The authors intend to address this by continuing data collection over the next four years and tracking the engagement of this group of medical students’ volunteers in their teaching roles as they progress from preclinical to clinical years, years one through four.
This study is also constrained by the preliminary nature of its self-reported and simplified data collection methods. While the adapted questionnaire provides valuable insights, future iterations could benefit from more comprehensive data collection methods. The authors recognize the need to explore potential confounding factors in the study design, especially given the varied engagement levels observed among students who participated in different outreach activities and interacted with middle versus high school students, as certain things could be influenced by audience maturity.
Ongoing outreach efforts will focus on identifying alternative assessment tools that offer more comprehensive evaluations of the impacts of community outreach programs on medical students’ communication skills. Future research can include longitudinal studies comparing participant and non-participant outcomes throughout their medical school journey. Through rigorous evaluation of the impact of community teaching initiatives, the authors aim to adapt and enhance our programs to serve better both medical students and the communities in which they engage.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine IRB. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
SP: Writing – original draft, Resources, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. BC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation. KR: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. HC: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Resources, Formal analysis, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to thank the Department of Basic Science Education at Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine for supporting the publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Dr. Hans Vink for his reviewing and discussing the manuscript and Daniel Contaifer for their invaluable contributions with the statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Authors want to disclosure that the thematic analysis was supported by the Microsoft Copilot, a generative AI tool based on OpenAI’s GPT-4 model, integrated by the Microsoft to assist with qualitative data interpretation and theme development.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcomm.2025.1613259/full#supplementary-material
References
Butterfield, K., Wesley, M., Carvalho, H., Holt, E., Toy, S., Powell, C., et al. (2024). Bodies and bites: a medical school program that teaches anatomy, physiology, and nutrition to elementary school kids. Front. Public Health 12:1398124. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1398124
Carvalho, H., and West, C. (2011). Voluntary participation in an active learning exercise leads to a better understanding of physiology. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 35, 53–58. doi: 10.1152/advan.00011.2010
Cheng, Z., and Shelnutt, K. (2020). Integrating experiential learning theory and citizen science practice through community outreach projects to enhance student learning. NACTA J. 65, 398–405. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/27157867
Connor, B. W., and Carvalho, H. (2019). Using dramatization to teach Starling forces in the microcirculation to first-year medical students. MedEdPORTAL 15:10842. doi: 10.15766/mep_2374-8265.10842
Dowlati, E., Musick, D. W., Zhang, L., Thornton, K., and Carvalho, H. (2016). Use of dramatization to teach cardiac cycle physiology to medical students. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 4, 100–108. doi: 10.11114/jets.v4i9.1603
Dyrbye, L., and Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Med. Educ. 50, 132–149. doi: 10.1111/medu.12927
Fatton, M., Schneiter, A., Allisiardi, M., Hänni, L., Hauser, G., Fernandes, Y., et al. (2021). Microbes go to school: using microbiology and service-learning to increase science awareness and fostering the relationship between universities and the general public. Front. Educ. 6. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.735297
Giffen, Z. C., and Carvalho, H. (2015). Development of a manipulative for nephron physiology education. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 39, 39–41. doi: 10.1152/advan.00087.2013
Halpin, P. A., and Gopalan, C. (2021). Using dramatizations to teach cell signaling enhances learning and improves students’ confidence in the concept. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 45, 89–94. doi: 10.1152/advan.00177.2020
Jagzape, A., Gupta, A., and Ghritlahre, N. (2021). Simple manipulative of gross organization of skeletal muscle: enhancing learning among students offline and online. Adv. Physiol. Educ., 461–463. doi: 10.1152/advan.00236.2020
Li, A. Y. L., and Carvalho, H. (2016). Active learning in neuroscience: a manipulative to simulate visual field defects. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 40, 462–464. doi: 10.1152/advan.00071.2016
Mangione, S., Chakraborti, C., Staltari, G., Harrison, R., Tunkel, A. R., Liou, K. T., et al. (2018). Medical students’ exposure to the humanities correlates with positive personal qualities and reduced burnout: a multi-institutional U.S. survey. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 33, 628–634. doi: 10.1007/s11606-017-4275-8
Morcos, G., and Awan, O. A. (2023). Burnout in medical school: a medical student’s perspective. Acad. Radiol. 30, 1223–1225. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2022.11.023
Prabhakar, S., and Carvalho, H. (2025). Physiology and outreach: dual benefits for teachers and learners. Physiology 40:1697. doi: 10.1152/physiol.2025.40.S1.1697
Prabhakar, S., chang, B., and Carvalho, H. (2024). Edutainment on display: enhancing learning experiences through scientific dramatizations of gas transport. Physiology 39:1810. doi: 10.1152/physiol.2024.39.S1.1810
Restini, C. B. A., Weiler, T., Porter-Stransky, K. A., Vollbrecht, P. J., and Wisco, J. J. (2024). Empowering the future: improving community wellbeing and health literacy through outreach and service-learning. Front. Public Health 12:1778. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1441778/full
Schaufeli, W. B., Bakker, A. B., and Salanova, M. (2006). The measurement of work engagement with a short questionnaire: a cross-national study. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 66, 701–716. doi: 10.1177/0013164405282471
Vollbrecht, P. J., Cooper, C. E. A., Magoline, J. A., Chan, T. M., and Porter-Stransky, K. A. (2024). Evaluation of content knowledge and instructor impacts in a middle school outreach program: lessons from brain explorers. Front. Educ. 9. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1446205
Vollbrecht, P. J., Frenette, R. S., and Gall, A. J. (2019). An effective model for engaging faculty and undergraduate students in neuroscience outreach with middle schoolers. J. Undergrad. Neurosci. Educ. 17, A130–A144.
Keywords: medical education, community outreach, student engagement, health communication, active learning, service learning
Citation: Prabhakar S, Chang BS, Rau KK and Carvalho H (2025) Teaching science in outreach programs may enhance health science communication and engagement in medical students. Front. Commun. 10:1613259. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1613259
Edited by:
Jonathan J. Wisco, Boston University, United StatesReviewed by:
Akshata R. Naik, Oakland University, United StatesCarolina Restini, Michigan State University, United States
Kirsten A. Porter-Stransky, University of South Carolina, United States
Copyright © 2025 Prabhakar, Chang, Rau and Carvalho. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Helena Carvalho, aGVsZW5hQHZ0LmVkdQ==
 Shruthi Prabhakar
Shruthi Prabhakar Brianna S. Chang1
Brianna S. Chang1 Kristofer K. Rau
Kristofer K. Rau Helena Carvalho
Helena Carvalho