- 1Department of Communication Sciences, Telkom University, Bandung, Indonesia
- 2Department of Communication Sciences, Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Veteran Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia
In the era of digital transformation, social media has become a primary communication channel for local governments in fostering public engagement. This study analyzes how the structuring of the digital environment influences public engagement on the Instagram and Twitter (X) accounts of the Bandung City Government in 2022. Employing a qualitative case study approach, data were collected through in-depth interviews with social media administrators, active users, and practitioners. The findings reveal that account profiles (name and descriptions) and highlighted themes contribute to building identity and accessibility but do not significantly enhance engagement. In contrast, content design and feature optimization play a more substantial role in driving user interaction. Visually appealing content increases audience retention, while the use of interactive features strengthens two-way communication. This study contributes to digital engagement theory by underscoring the impact of digital environment structuring on public interaction. Practically, it offers insights for government social media administrators in designing more effective engagement strategies. This includes actionable recommendations for optimizing content formats, timing, and platform-specific features to improve citizen involvement.
1 Introduction
In the era of digital transformation, social media has emerged as one of the primary channels for government institutions to engage with the public (Sobaci, 2016). Local governments utilize digital platforms to disseminate policy information, establish two-way communication, and enhance public engagement (Bertot et al., 2010; Bertot et al., 2012; Kavanaugh et al., 2012; Graham, 2014; Guillamón et al., 2016; Romero, 2016; Park and Lee, 2018). Achieving optimal levels of engagement requires more than simply increasing the volume of content production. The management and optimization of the digital environment are also critical factors in fostering active user participation (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016; O’Brien and McKay, 2018; Johnston, 2023).
The concept of the digital environment in social media refers to the various elements that shape user experience, including content governance, user-to-user interaction, interface design, and moderation policies (Johnston, 2023). Previous studies have shown that a well-structured digital environment can promote higher-quality engagement—characterized not only by the volume of interaction but also by the relevance and depth of public participation in online discourse (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016; O’Brien and McKay, 2018). Accordingly, understanding how the structuring of the digital environment influences engagement is a critical aspect of managing governmental social media platforms.
The Municipal Government of Bandung is among the public institutions actively utilizing social media—particularly Instagram and Twitter (X)—to engage with the public (Atnan and Abrar, 2023). In 2022, there was a marked increase in content production; however, the anticipated level of user interaction was not optimally achieved (Atnan et al., 2024). This phenomenon suggests that factors beyond content volume—specifically elements of the digital environment—may influence patterns of public interaction. Accordingly, this study seeks to analyze how the Bandung City Government structures its digital environment across official social media platforms and to what extent these elements impact the level of public engagement.
A substantial body of research has examined public engagement on local government social media platforms. Scholars such as Bonsón et al. (2019), Manetti et al. (2017), Rahmanto and Dirgatama (2018), Roengtam (2017), and Romero (2016) have investigated the role of social media in fostering interaction between local governments and citizens. Meanwhile, studies by Bonsón et al. (2019), Dominic and Gisip (2021), Furqon et al. (2018), and Santoso et al. (2020) have emphasized the importance of content management as a strategic approach to enhancing public engagement.
Other studies, such as those conducted by Alam et al. (2022), Al-Masaeed (2019), Evans et al. (2018), Gálvez- Rodríguez et al. (2018), Izzati et al. (2018), Purwadi et al. (2019), and Rexhepi et al. (2021), discuss the management of local government social media, focusing on communication strategies and interactions (Evans et al., 2018; Gálvez- Rodríguez et al., 2018; Izzati et al., 2018; Al-Masaeed, 2019; Purwadi et al., 2019; Rexhepi et al., 2021; Alam et al., 2022). Meanwhile, Haro-de-Rosario et al. (2018) examined the factors influencing public engagement levels on local government social media platforms (Haro-de-Rosario et al., 2018).
Previous research has predominantly focused on specific aspects of public engagement, such as content, interaction intensity, or dialog techniques. In contrast, this study highlights the role of digital environment structuring in shaping engagement. With a more focused approach, this research explores the extent to which digital environmental factors influence public engagement. Referring to Kim A. Johnston’s Digital Engagement Theory (2023), this study offers a new perspective on understanding the dynamics of digital engagement. Furthermore, this research opens opportunities to identify digital environment indicators that have not been extensively discussed in the literature, thus enriching both the theoretical discourse and practical implications.
2 Literature review
2.1 Digital environment and engagement
The study of the digital environment in governmental social media and its impact on audience engagement remains relatively limited. Most of the existing research has focused primarily on the relationship between content design and the level of audience engagement in interactions with government institutions or corporations. Johnston (2023) emphasizes that content design is an integral component of the digital environment, playing a significant role in shaping user experience and engagement (Johnston, 2023). Therefore, understanding how content design can create a conducive digital environment for audience interaction becomes an important aspect that warrants further investigation.
An effective digital environment plays a crucial role in enhancing engagement on social media. A study conducted in Aotearoa, New Zealand, identified that audience engagement with local government social media accounts is influenced by content quality, creativity in active posts, an increase in followers, a combination of passive and active posts, and the creation of a diverse and inclusive digital environment (Alam et al., 2022). The findings of this study indicate that the primary factors contributing to engagement are not the scheduling or frequency of posts, but rather the quality and appeal of the content presented to the audience.
In regard to content type, several studies have indicated that the use of visual content—such as photographs and videos—is more effective in enhancing audience engagement. Bonsón et al. (2019), in their analysis of Twitter accounts from 29 local governments in Andalusia, found that visual-based content was more appealing to the public than text-based content (Bonsón et al., 2019). Similarly, a study by Santoso et al. (2020) involving 114 local governments in Indonesia confirmed that photos and video contents possessed a higher level of audience appeal compared to other content formats. These findings suggest that local government social media accounts should prioritize and optimize the use of visual content to increase public engagement (Santoso et al., 2020).
In addition to content type, other studies have demonstrated that design and esthetic elements also play a critical role in fostering audience engagement. O’Brien and McKay (2018) identified that appealing design characteristics can evoke emotional responses from users. The use of high-quality imagery, evocative music, and compelling interface layouts are among the factors that significantly influence audience attention. Effective visual design includes strategic choices of color schemes, element sizing, and the use of headers that capture attention optimally. Digital esthetics likewise exert a substantial influence on user engagement. Before accessing further content, audiences form initial impressions based on layout, color selection, and other visual elements. In many cases, compelling esthetics can override rational considerations of a platform’s utility, thereby encouraging users to engage more actively (O’Brien and McKay, 2018).
Based on this review of the literature, it is evident that the digital environment—shaped through content design, design characteristics, and esthetics—has a significant impact on audience engagement. Previous studies have emphasized that content quality, creative presentation, and visual elements are key factors in enhancing engagement on government social media platforms. However, a research gap persists in understanding how these elements can be specifically optimized to improve audience engagement in the context of official government social media accounts. Accordingly, this study seeks to address the central question: to what extent does the structuring of the digital environment on government social media accounts influence public engagement? This inquiry aims to contribute both theoretically and practically to the body of knowledge concerning the effective management of governmental social media, with the objective of fostering more optimal engagement in the digital era.
2.2 Social media engagement theory
Engagement in the context of organizational–public relationships has been conceptualized in various ways within communication studies. Bortree (2011) and Johnston (2010) define engagement as the interaction that occurs between the public and an organization (Johnston, 2010; Bortree, 2011). Heath (2011), on the other hand, emphasizes that engagement arises when stakeholders actively participate in organizational programs (Heath, 2011). Taylor and Kent (2014) further argue that engagement constitutes a component of dialog that facilitates the interaction process between groups. From interpretivist and constructionist perspectives, engagement is understood as a process of co-creating meaning through communication (Taylor and Kent, 2014). In addition, Ledingham (2010) highlights that engagement is characterized by a form of social exchange among the involved parties (Ledingham, 2010).
The concept of engagement has since evolved within the context of digital media into what is now recognized as the Social Media Engagement theory. This theoretical framework emphasizes how organizations utilize social media platforms to communicate with the public and sustain their engagement in pursuit of organizational objectives (Bruce et al., 2023). Prahalad and Ramaswamy (2001) assert that technology plays a pivotal role in constructing platforms that facilitate social interaction, with social media serving as a primary instrument for optimizing public engagement in a manner that is rapid, accessible, and far-reaching (Prahalad and Ramaswamy, 2001).
Paul M. Di Gangi and Molly Wasko are scholars who advanced the theory of Social Media Engagement by adapting the user–organization interaction model originally proposed by Prahalad and Ramaswamy to the context of social media platforms. Di Gangi and Wasko (2016) define engagement as a form of intensified individual involvement that yields cognitive benefits and fulfills specific user needs. The higher the level of user engagement, the greater the utilization of social media platforms. Operationally, engagement on social media is manifested through user contributions, information retrieval, and content exploration within the platform (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016).
This theory posits that engagement is formed through user experience, which is shaped by two primary factors: social interaction and technical features. Social interaction refers to communication among users within a social media platform, whereas technical features encompass the extent to which users can access information, use platform functionalities flexibly, integrate content, and customize features to meet their individual needs (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016).
Social interaction experiences on social media consist of several key dimensions. First, personalization, which denotes social interactions shaped by user preferences and mutual concern among users. Second, access to social resources, referring to users’ ability to access social assets such as information, expertise, and social networks. Third, risk, which reflects users’ perceptions of potential risks associated with engaging on social media. Fourth, transparency, which pertains to the degree of information symmetry among users and plays a critical role in fostering trust within online communities (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016).
Meanwhile, the experience of technical features in social media also comprises several dimensions. First, completeness, referring to the comprehensiveness of information provided by the platform to meet user needs. Second, flexibility, which denotes the degree to which the platform can be adapted to align with users’ interests and requirements. Third, evolvability, indicating the platform’s capacity to develop and adapt in response to evolving user needs. Fourth, integration, which reflects users’ ability to incorporate diverse content that aligns with their preferences (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016).
Although the Social Media Engagement theory developed by Di Gangi and Wasko does not explicitly address the influence of the digital environment on engagement, several aspects of the theory are closely aligned with the concept of digital engagement. According to Johnston (2023), the technical features of social media constitute a key component of the digital environment that can significantly influence user engagement levels (Johnston, 2023). Di Gangi and Wasko argue that features which provide enjoyable and engaging user experiences are likely to enhance audience participation on social media platforms (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016).
In the context of this study, the primary focus is to examine how the technical features of the digital environment contribute to engagement on the social media platforms of the Bandung City Government. This research aims to analyze whether the optimization of technical features in the management of local government social media accounts has a significant impact on public engagement. Furthermore, the study seeks to identify the most influential indicators of the digital environment in enhancing engagement, particularly within the domain of public communication in Indonesia.
2.3 Digital engagement theory
The theory of Digital Engagement, as developed by Johnston (2023), represents an evolution of the Social Media Engagement concept and is increasingly pertinent in today’s digital context. This theory is built upon four core dimensions: the digital environment, user attributes, engagement processes, and outcomes. Together, these dimensions provide a comprehensive framework for understanding user digital engagement and how it can be strategically cultivated (Johnston, 2023).
The digital environment dimension underscores the importance of systems and attributes that are simple, user-friendly, and beneficial to users. In the context of organizational social media, system design and functionality are central factors influencing public appeal. Well-designed attributes can enhance user experience through esthetic quality, interactivity, and functional value. Moreover, social media as an interactive platform has shifted the pattern of information consumption from passive observation to active participation—even to the extent of institutionalizing digital participation (Johnston, 2023). Consequently, this dimension holds significant relevance for the analysis of social media management strategies, particularly in fostering high-quality engagement.
The remaining dimensions of the Digital Engagement theory—namely user attributes, engagement processes, and outcomes—also play important roles in shaping digital engagement, although they are not the primary focus of this study. User attributes refer to users’ intentions and motivations in interacting with digital media. Engagement processes denote the varying levels of user involvement, ranging from simple reactions to deeper forms of participation that contribute to the co-creation of social meaning. Meanwhile, outcomes pertain to the shared value generated through digital interactions and their impact on social capital (Johnston, 2023).
This study focuses specifically on the impact of the digital environment on engagement. Accordingly, this dimension is prioritized due to its significant influence on user engagement through the design and functional attributes of well-constructed social media systems.
In light of the above discussion, the Digital Engagement theory is highly pertinent to the context of this research, as it offers a systematic theoretical framework for analyzing digital engagement on organizational social media platforms. By emphasizing the influence of the digital environment, this study aims to explore how social media design and system features can be optimized to foster more meaningful and sustainable forms of user engagement.
3 Data and methods
This study employs a qualitative approach with a case study design to analyze the digital environment management strategies implemented on the official social media accounts of the Bandung City Government. Furthermore, the research evaluates the impact of these strategies on public engagement. The case study method was selected as it allows for an in-depth exploration of complex phenomena and the uncovering of underlying mechanisms, as emphasized by Yin (2018) and Yin (2018).
The research focuses on the management of the digital environment on the Bandung City Government’s social media accounts throughout the year 2022. This period was chosen based on preliminary observations indicating a high volume of content production accompanied by relatively low levels of audience interaction. By examining this dynamic, the study aims to identify key elements within the digital environment that social media administrators should consider in order to enhance public engagement.
This study explores two primary aspects. First, it examines the strategies employed by the Department of Communication and Informatics of the Bandung City Government in managing the digital environment of its official Instagram and Twitter (X) accounts. The analysis includes the identification of key factors in the management of the digital environment, as well as the strategic approaches implemented in the operationalization of these official social media platforms. Data were collected through in-depth interviews with officials and social media staff at the Department of Communication and Informatics. The collected data were then analyzed through stages of selection, categorization, presentation, and interpretation.
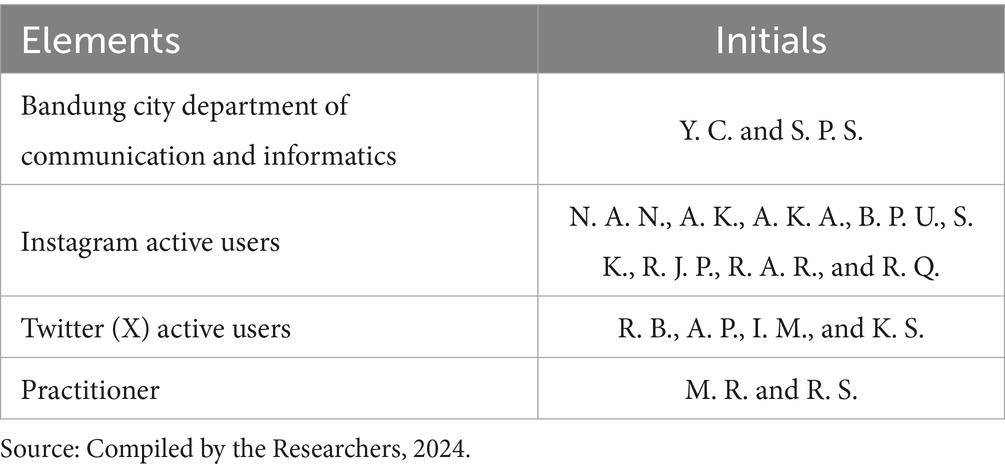
The second aspect investigated is the impact of digital environment management on public engagement. This research aims to identify elements within the digital environment that exert the most significant influence on engagement levels. To understand user perceptions, in-depth interviews were conducted with eight active followers of the Bandung City Government’s Instagram account and four active followers of its Twitter (X) account. Respondents were selected using a snowball sampling technique, which enabled the researchers to identify relevant individuals based on referrals from previous participants (Table 1).
The respondents in this study were social media activists who consistently monitor the official social media accounts of the Bandung City Government. Their insights are thus considered to possess a high degree of credibility and validity. The interviews focused on the respondents’ experiences and perspectives concerning how the management of the digital environment influences their participation and interaction with government social media accounts. The data collected were analyzed through the processes of selection, categorization, presentation, and interpretation, following the analytical approach applied in previous stages of the study.
In addition to interviews with active social media users, this study also engaged two social media practitioners as complementary sources. Their insights offered alternative perspectives on best practices for structuring and managing the digital environment to enhance public engagement. Furthermore, the practitioners’ viewpoints were utilized to reinforce the findings derived from user interviews, thereby contributing to a more comprehensive and multi-angled analysis.
4 Result
This section presents two principal findings of the study. First, it delineates the strategies employed by the Department of Communication and Informatics of the City of Bandung in structuring the digital environment to enhance public engagement. Second, it examines the influence of individual elements within the digital environment on public interaction with the official social media accounts of the local government, identifying both the indicators that exert a significant impact and those that have minimal effect.
4.1 Structuring the digital environment on social media accounts
4.1.1 Administrators prefer the use of formal account names
The official Instagram and Twitter (X) accounts of the Bandung City Government have undergone multiple name changes as part of their digital communication strategy. Initially, the accounts adopted the name “bandung.go.id,” aligning with the official government website. However, this name was considered overly formal and insufficiently engaging for social media users, thus limiting its effectiveness in fostering public engagement.
In response to this challenge, the Bandung City Government experimented with the name “Bewara”—a Sundanese term meaning “announcement” and an acronym for berita bawa gembira (news that brings joy). This strategy was inspired by the success of the Surabaya City Government, which adopted a more casual account name such as “Sapa Warga.” Nonetheless, the name change did not automatically lead to increased public engagement. This was confirmed by Y. C., the Social Media Coordinator at the Bandung City Government’s Department of Communication and Informatics (Diskominfo), who stated that:
“We tried using ‘bandung.go.id’ and ‘Halo Bandung’, then ‘Bewara’, but they still did not attract much interest. Eventually, we switched to ‘Humas Bandung’, and it’s been fairly effective so far.” (Interview, March 5, 2024).
Currently, the “Humas Bandung” account serves as the primary official account; however, other accounts such as “Halo Bandung” remain active as well. The existence of multiple official accounts has caused confusion among the public. This concern was expressed by N. A. N., an active Instagram user, who stated:
“There’s @humas_bandung, @halobandung, and also accounts from sub-districts and villages. It’s confusing. They should clarify which one is the main official account.” (Interview, January 12, 2024).
To address this issue, the Bandung City Government has implemented various outreach strategies, including collaborations with educational institutions and radio stations. According to S. P. S., a member of the city’s social media team:
“We conduct outreach to schools so that students know the official government accounts. We also collaborate with PRFM radio.” (Interview, June 5, 2023).
In addition, the government has also established collaborations with academic institutions and other social media platforms to enhance the visibility of the main account. Y. C. further added that:
“We’re collaborating with Parahyangan University and PRFM’s social media to popularize the ‘Humas Bandung’ account.” (Interview, March 5, 2024).
There are various perspectives from users regarding the account name. A. K. argues that the use of a formal name facilitates the identification of the official account:
“A formal name like ‘Humas Bandung’ makes it easier to search for information.” (Interview, 26 May 2024).
Conversely, A. P. expressed a preference for a non-formal account name, considering it more communicative and inclusive:
“Halo Bandung’ feels more friendly and invites interaction.” (Interview, 16 May 2024).
However, the majority of users consider that the most critical factor in enhancing public engagement lies in the quality of content and the level of interaction offered by the government’s social media account. This view aligns with the perspective of I. M., who stated:
“The name is important, but the content is what really matters.” (Interview, 17 May 2024).
Findings from both observations and interviews reveal a range of user preferences regarding account names, with memorability identified as a key consideration. Nevertheless, this study finds that the primary driver of public engagement is not the account name itself, but rather the quality of interaction and the relevance of the content provided. Users show greater interest in informative and practical updates—such as traffic conditions and disaster-related news—than in accounts with merely appealing names.
For government social media administrators, a more effective strategy for enhancing public engagement lies in providing relevant content and fostering meaningful interaction. Thus, while the choice of account name contributes to recognizability, the quality of content and interaction remains the central determinant of successful engagement on government social media platforms.
4.1.2 The profile description serves to strengthen the identity of the account
The Government of Bandung City structures the profile description of its social media accounts with a simple, credibility-oriented approach. Observations indicate that the Instagram and Twitter (X) profiles of the City of Bandung include the phrase “Pusat Informasi Pemerintah Kota Bandung,” emphasizing that the account is managed by the Bandung City Department of Communication and Informatics (Diskominfo). Additionally, the Instagram profile lists complaint channels such as @ppidlaporkotabandung and @bandungsiaga112, while the Twitter (X) account only includes @bandungsiaga112.
The Social Media Administrator of the City of Bandung, Y. C., stated that the profile description is not a primary factor in enhancing public interaction. The main focus of the social media adminstrators is on providing quality content and more comprehensive news through the official website, bandung.go.id.
“We keep the profile description simple because our main focus is not there. We prioritize the website as the primary source of information. Essentially, we want to build public trust that every post on social media always links back to more detailed news on the bandung.go.id website. For us, the profile description does not really impact engagement.” (Interview, March 5, 2024).
The views on the profile description received varied responses from social media users. A. K., an active Instagram user, believed that the profile description plays a crucial role in helping users understand the account’s purpose. He argued that without a clear description, users might struggle to determine the account’s relevance to their needs.
“If a large or general account does not include information about its purpose or the type of content it provides in the profile description, users might get confused about the content and scope of the information shared.” (Interview, May 26, 2024).
A similar viewpoint was expressed by S. K., who emphasized the importance of the profile description in clarifying the identity and purpose of the account.
“Basically, an account should have a description that we can read, so we can understand its purpose and its benefits.” (Interview, May 27, 2024).
However, some informants argued that the profile description is not the main factor in increasing engagement. A. K. A. stated that other features, such as the inclusion of complaint accounts, are more effective in capturing users’ attention.
“The profile description may not directly increase engagement on Instagram. However, the presence of private channels or specialized services can attract users’ interest.” (Interview, May 15, 2024).
K. S., an active Twitter (X) user, emphasized that meaningful interactions are far more effective in increasing user engagement than simply improving the profile description.
“In my opinion, the social media administrators of the Bandung City Government should focus on building meaningful interactions, not just adding a profile description, but also actively engaging and being relevant with followers.” (Interview, May 16, 2024).
Thus, these findings indicate that although the profile description can provide an initial overview of the account, the primary factors in enhancing user engagement are the presentation of relevant content, active interaction, and the credibility of the information provided by the official account.
4.1.3 Highlight themes should address public issues
Highlight themes are a popular feature on Instagram that enable users to organize content by specific categories. This feature, however, is not available on twitter (X). The accounts’ administrators retain full autonomy in curating highlight themes that align with the needs and interests of their target audience.
The Government of Bandung utilizes highlight themes to showcase seven priority agendas: champion, excellent, livable, prosperous, religious, cultural, and tourism. The city’s social media management is conducted under the directive of the Head of the Department of Communication and Informatics, ensuring alignment with the broader vision and mission of the city. According to Y. C., the social media coordinator for the Bandung City Government, the primary objective of employing highlight themes is to facilitate public understanding of the city’s development priorities.
“The themes come from Bandung’s seven priority agendas. Basically, they reflect the city’s development priorities—things the leadership is really focused on.” (Interview, March 5, 2024).
In addition to the seven core agendas, the Bandung City Government also introduced supplementary themes such as Kata Wargi, Ngawartosan, Ruang Publik, and Layanan. The first two themes employ the Sundanese language to foster a closer cultural connection with the community. Kata Wargi features citizen testimonials regarding public services, while Ngawartosan serves as a channel for disseminating public service information.
“So this came from our leadership—specifically the Head of the Bandung City Communication and Information Office. The content follows the set themes, but we added a few of our own, like Kata Wargi and Ngawartosan.” (Interview, March 5, 2024).
However, the effectiveness of the highlight theme feature in enhancing engagement remains debatable. Y. C. acknowledged that while the feature facilitates information delivery, it does not necessarily succeed in capturing public attention. Some Instagram users, however, reported positive experiences with the use of highlight themes. R. J. P. noted that the feature made it easier to locate specific information. Similarly, S. K. and R. A. R. emphasized that it helps users save time when searching for relevant content.
“In general, the highlight feature is helpful—it makes it easier to find specific information.” (Interview, 15 May 2024).
However, some users expressed that the highlighted themes were not entirely relevant to their needs. A. K. observed that although the feature facilitates easier navigation, the information presented often does not align with their specific interests.
“The highlight themes on the Bandung City Government’s Instagram account do not really meet my personal information needs.” (Interview, 26 May 2024).
N. A. N. further noted that the highlight themes tend to reflect the image-building efforts of the Bandung City Government rather than providing information that meets the public’s actual needs.
“The basis has not really addressed the public’s needs. It still seems focused on disseminating the city’s performance.” (Interview, May 16, 2024).
From the perspective of Digital Engagement theory, as outlined by Kim A. Johnston (2023), effective digital communication strategies should be bottom-up, where the public’s needs are prioritized in the delivery of the organization’s messages. M. R., a social media practitioner, suggested that the ideal composition should be 40 percent organizational mandatory themes and 60 percent content that aligns with public trends and needs.
“So, this approach is balanced—it still meets the organization’s directives, but also provides content that’s relevant to the public.” (Interview, March 5, 2024).
This approach is crucial for enhancing public engagement. If the highlight themes are predominantly driven by governmental interests without addressing the information needs of the public, their effectiveness in fostering engagement will diminish. Therefore, the social media administrators of the Bandung City Government must develop a deeper understanding of public needs, ensuring that the highlight themes function not only as a one-way communication tool but also as a means of actively boosting public participation and involvement.
Overall, the highlight theme feature can assist users in quickly accessing relevant information; however, its effectiveness is contingent upon the relevance and quality of the content. To achieve maximal impact, the Bandung City Government must better comprehend the public’s informational needs and ensure that the themes presented align with the community’s expectations. By balancing mandatory organizational themes with emerging user needs, the social media platforms of the Bandung City Government can become more dynamic and appealing to a broader audience.
4.1.4 Content design: visual appeal and comfort
Content design plays a crucial role in the management of official social media accounts of the Bandung City Government, such as Instagram and Twitter (X). The visual appearance of an account can significantly influence public perception of the credibility and professionalism of the local government. In practice, there are two main approaches to content design: first, the application of a consistent color theme, and second, a more flexible and natural approach.
Initially, the social media administrators of the City of Bandung utilized a thematic color scheme that changed every month, reflecting the city’s characteristic colors—blue, yellow, and green. However, this approach did not yield a significant impact on increasing public interaction. Additionally, the production team felt that their creativity was constrained by the rigid color scheme. Following an internal evaluation, this strategy was eventually abandoned, and the City of Bandung’s social media team reverted to a more flexible and natural design approach.
The decision to switch to a more natural design proved to be a positive one. Since the change, the City of Bandung’s social media accounts have received recognition and awards in various social media competitions, both at the regional (West Java) and national levels. This success indicates that flexibility in content design can enhance engagement and public appeal.
According to Y. C., the Social Media Administrator of the City of Bandung, content design plays a crucial role in attracting user interest. He estimated that the influence of design on engagement is approximately 50 to 60 percent. Video content has emerged as the most popular format, as it is able to convey information in a more engaging and dynamic manner compared to static images or text. Therefore, the social media team focuses on producing high-quality videos with clear and meaningful messages (Interview, March 5, 2024).
From the users’ perspective, an appealing content design plays a crucial role in enhancing the attractiveness of an account. Several Instagram users noted that disorganized or monotonous designs could decrease their interest in accessing the official City of Bandung social media account. A. K., for example, emphasized the importance of a neat layout and esthetics to maintain the account’s appeal and professionalism (Interview, May 26, 2024). Meanwhile, S. K. argued that variation in design is more effective in sustaining audience interest compared to the repetitive use of the same template (Interview, May 27, 2024).
Similar opinions were also expressed by Twitter (X) users. K. S. highlighted the importance of engaging visuals in boosting user loyalty. If the account’s appearance is captivating, users are more likely to revisit the account (Interview, May 16, 2024). However, some users complained that the content design on the City of Bandung’s Twitter (X) account lacked appeal, as it was overly monotonous and dominated by news text with minimal visual elements.
While content design is considered important, some users noted that its implementation on Bandung City’s social media remains inadequate. A. K. A., for instance, noted that many posts are overly text-heavy, making the intended message unclear (Interview, May 15, 2024). Similarly, R. Q. suggested that an unappealing design could reduce user interaction with the account (Interview, May 28, 2024).
However, not all users viewed design as the primary factor. R. J. P., for example, stated that while design is not the main concern, a cleaner and more organized visual appearance would add value to the City of Bandung’s account (Interview, May 15, 2024). On Twitter (X), K. S. emphasized that meaningful interaction between account administrators and users is more critical than content design itself. Unfortunately, the official City of Bandung account was perceived as lacking in user engagement, which diminishes its overall appeal (Interview, May 16, 2024).
In conclusion, content design plays a crucial role in the management of local government social media, but it must be complemented by a more interactive communication strategy. Flexibility in design, a focus on content quality, and enhanced user engagement are key elements in fostering higher levels of public interaction. The success of the Bandung City Government in transitioning to a more natural and adaptive design approach demonstrates that creativity and content relevance have a greater impact than rigid color schemes. By adopting a more dynamic and user-responsive strategy, government social media management can become more effective in reaching and engaging with the public.
4.1.5 Feature optimization remains overlooked
Instagram offers a range of features, including feed, stories, reels, highlights, live, insights, ads, and the explore tab. The feed serves as the main space for permanent posts, while stories enable users to share ephemeral content visible for 24 h. Reels facilitate the creation of engaging short videos, and highlights allow users to archive selected stories for ongoing visibility. The live feature supports real-time interaction, while insights provide analytics on content performance. Paid advertisements (ads) enhance reach, and the explore feature helps users discover new content aligned with their interests.
Meanwhile, Twitter (X) provides features such as tweets, hashtags, live tweeting, and Twitter analytics. Tweets allow users to share short-form messages containing text, images, or videos. Hashtags function to categorize content by topic, while live tweeting supports real-time updates during ongoing events. Twitter analytics offers performance metrics, including impressions and user engagement.
In this study, the features available on Instagram and Twitter (X) proved instrumental for social media administrators in creating engaging and interactive content. By leveraging these functionalities, account administrators were able to enhance user engagement and broaden audience reach. Moreover, data derived from Instagram Insights and Twitter Analytics facilitated a deeper understanding of user needs and preferences, thereby enabling more effective content strategies.
The City of Bandung’s official Instagram account frequently utilizes features such as feed posts, stories, reels, highlights, and live broadcasts, while paid advertisements (ads) are rarely employed. In contrast, the official Twitter (X) account relies primarily on tweets and hashtags. According to the social media administrator for the Bandung City Government, ads are typically reserved for crisis situations—for example, during the eviction controversy in Tamansari. In that instance, ads were used strategically to reach audiences in Jakarta, given the national attention the issue received and the need to counter negative narratives.
A social media practitioner, M. R., emphasized that advertising features (ads) can be effectively utilized to reach a broader audience with flexible budget options. When combined with insights, ads can also generate more accurate data on audience demographics and preferences. However, due to budgetary constraints, the City of Bandung relies solely on free analytics tools, which are less effective in evaluating content impact (Interview, December 21, 2023).
Instagram users have also offered feedback regarding feature utilization. A. K. A. noted that the City of Bandung has yet to fully capitalize on the potential of Instagram Reels, despite its wide reach—even among non-followers (Interview, May 15, 2024). R. A. R. highlighted the importance of Instagram Stories for enhancing interaction, particularly through polls and Q&A sessions. He further emphasized that the comment feature should be optimized by providing timely and empathetic responses (Interview, May 14, 2024).
In addition, the use of template responses has been recommended to accelerate replies to user inquiries. However, A. K. A. cautioned that such responses must be contextually appropriate to avoid user dissatisfaction (Interview, May 15, 2024). R. A. R. further suggested that template replies should be followed by a personalized response from the account administrator, as this can enhance the sense of appreciation among users (Interview, May 14, 2024).
The optimization of social media features, both on Instagram and Twitter (X), has the potential to significantly enhance the effectiveness of the City of Bandung’s communication strategies. Through a more deliberate and data-driven approach, account administrators can broaden audience reach, strengthen engagement, and improve the public image of the local government. Strategic utilization of these features will contribute to achieving more impactful and efficient communication outcomes.
4.2 The impact of digital environment structuring on social media account engagement
In the management of social media, various elements—such as account naming, profile descriptions, highlight themes, content design, and feature optimization—play distinct roles in fostering public engagement. A simple and memorable account name can enhance user recognition, optimize searchability, and strengthen brand identity. However, while it may create a strong first impression, this factor alone does not directly contribute to increased engagement. Users tend to prioritize meaningful interaction over mere ease of recognition. Therefore, an effective social media strategy must go beyond a memorable name and be complemented by the delivery of relevant content and active communication with the audience.
The profile description serves as an informational tool that helps audiences understand the purpose and value of a social media account. While it provides a general overview, it is not a primary factor influencing engagement levels. Many users tend to overlook this section, placing greater emphasis on the content being published. This suggests that although a clear and informative description can enhance credibility, the core appeal of an account ultimately lies in the quality of its content. Therefore, account administrators should not focus solely on crafting engaging descriptions but must also ensure that the content aligns with the audience’s needs and interests.
Highlight themes also play a role in organizing information to make it more accessible. This feature enables users to locate categorized topics without the need to scroll through content sequentially. However, its effectiveness in enhancing engagement depends largely on the relevance of the selected themes. Highlights that contain only static, outdated information tend to attract limited interest. Therefore, account administrators must ensure that the themes featured in highlights are genuinely aligned with public interests and provide added value to the audience.
On the other hand, content design exerts a more substantial influence on enhancing public engagement. Visually appealing and consistent content can encourage users to visit an account more frequently. Conversely, monotonous and unvaried design often leads to a decline in audience interest. Therefore, the use of fresh, esthetically pleasing visual elements that align with the account’s identity is essential for sustaining attention and fostering active participation. An engaging design serves not only an esthetic function but also acts as a tool for building audience appeal and loyalty.
Finally, feature optimization within social media platforms can serve as a critical factor in increasing engagement. Features such as analytics, polls, and other interactive tools assist account administrators in understanding audience preferences and tailoring content strategies accordingly. A data-driven approach enables more effective information delivery, enhanced interaction, and broader audience reach. Thus, the strategic utilization of social media features not only boosts engagement but also contributes to the development of a more cohesive and loyal online community.
5 Discussion
The structuring of the digital environment—which includes account management, profile descriptions, highlight themes, content design, and feature optimization—affects user engagement on social media. According to the Digital Engagement theory proposed by Johnston (2023), digital identity plays a crucial role in fostering audience engagement (Johnston, 2023). Meanwhile, Di Gangi and Wasko (2016) add that engagement becomes stronger when social media managers are able to create digital experiences that are engaging, useful, and easy to navigate (Di Gangi and Wasko, 2016).
The digital environment structuring undertaken by the Bandung City Government through its Department of Communication and Informatics reinforces both theoretical perspectives. However, this study highlights two elements of the digital environment that are particularly dominant in driving engagement: content design and feature optimization. Other elements, such as account name, profile description, and highlight themes, also contribute, but their impact is comparatively less substantial.
A study by Chen et al. (2016) emphasizes that an effective account name is one that clearly reflects the function of the organization, thereby optimizing user recognition and access to services (Chen et al., 2016). Nevertheless, the current findings suggest that while a memorable account name may improve recognition, it does not significantly enhance engagement. More influential factors include the quality of interaction and the relevance of the content presented.
In addition to the title of the account, profile descriptions also play a role in fostering engagement, as noted by Chen et al. (2016). A clear explanation of an account’s purpose and function can help the public understand its utility and encourage interaction (Chen et al., 2016). However, user interviews in this study indicate that while the profile description provides essential information, its direct impact on engagement is not always significant. Thus, although the profile description aids in facilitating access to information, higher levels of engagement continue to depend more heavily on other factors, such as content relevance and administrative responsiveness.
Highlight themes on social media also contribute to shaping engagement, although their effectiveness is largely contingent upon the relevance of the content presented. According to the digital engagement theory proposed by Johnston (2023), a bottom-up approach—one that prioritizes public needs and aspirations—is more effective in enhancing digital participation than a top-down strategy that primarily reflects organizational interests (Johnston, 2023).
Social media practitioners interviewed in this study emphasized that the ideal composition of highlight themes consists of 40 percent organizationally mandated content and 60 percent content aligned with prevailing public needs and trends. This balanced approach allows official social media accounts to remain dynamic and engaging, thereby increasing the likelihood of higher user interaction.
Content design also plays a significant role in influencing engagement. According to Johnston’s (2023) theory of Digital Engagement, compelling visual presentation enhances user interaction with digital platforms (Johnston, 2023). This is supported by O’Brien and McKay (2018), who found that visual design and esthetic appeal significantly affect user engagement with digital information. The present study corroborates these findings by showing that when content design is visually appealing and well-organized, users tend to stay longer on the account and explore more content, ultimately increasing both the duration and depth of engagement. Therefore, visual esthetics should not be viewed merely as decorative elements, but rather as strategic components for fostering public participation on social media platforms (O’Brien and McKay, 2018).
In addition to content design, the optimization of social media features—such as the use of reels, stories, and comment sections—also contributes to enhancing engagement. According to Johnston’s (2023) Digital Engagement theory, the effective utilization of available features can strengthen digital communication and encourage active user participation. This study found that interactive features can significantly boost engagement when managed with a well-planned strategy, such as providing more personalized responses during user interactions (Johnston, 2023).
The implications of this analysis suggest that social media administrators, particularly within local government contexts such as the Bandung City Government, must develop more integrated strategies for managing their digital environments. Elements such as account identity, profile descriptions, and highlight themes should be crafted to align more closely with user needs. Furthermore, content design should not only emphasize visual appeal but also prioritize functionality in delivering clear and engaging information. Equally important is the strategic and personalized use of interactive features, which can foster deeper and more sustainable forms of engagement.
6 Conclusion
Based on the findings above, it can be concluded that while the structuring of the digital environment does influence user engagement, its impact is largely indirect. Digital identity—manifested through account configuration and profile descriptions—plays a supportive role in fostering public recognition and facilitating access. However, the primary determinants of engagement remain the quality of content and the depth of interaction established with the audience. The use of highlight themes that align with public interests can stimulate user curiosity and encourage interaction, whereas visually appealing content design enhances user retention and promotes more active exploration of information. Furthermore, the strategic and personalized optimization of social media features can strengthen the relationship between institutions and the public, thereby fostering more meaningful and sustained engagement.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Head of Humanities and Media Studies Research Group School of Communication and Social Science Telkom University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
NA: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Validation, Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation. WS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by a research grant from Telkom University.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Communication and Informatics Office of Bandung City for being willing to be an informant in this research. We would also like to thank Telkom University for funding this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1681409.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alam, A., Meenar, M., Barraza, F., Khalil, M. B., and Knopp, K. (2022). Citizen engagement on local government Facebook pages: experience from Aotearoa New Zealand. Cities 123:584. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2022.103584
Al-Masaeed, S. (2019). Social media use by government: adoption and efficiency. Int. J. Electron. Gov. 11:497. doi: 10.1504/IJEG.2019.101497
Atnan, N., and Abrar, A. N. (2023). Relation of social media literacy, trust, and information quality on public communication behaviour in urban local government social media in Indonesia. J. Komun. Malays. J. Commun. 39, 210–226. doi: 10.17576/JKMJC-2023-3902-12
Atnan, N., Prajarto, N., and Kurnia, N. (2024). Social media management in local government: a case study of Bandung City government’s Instagram and twitter (X), Indonesia. J. Komun 40, 465–481. doi: 10.17576/JKMJC-2024-4002-27
Bertot, J. C., Jaeger, P. T., and Grimes, J. M. (2010). Using ICTs to create a culture of transparency: e-government and social media as openness and anti-corruption tools for societies. Gov. Inf. Q. 27, –271. doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2010.03.001
Bertot, J. C., Jaeger, P. T., and Hansen, D. (2012). The impact of polices on government social media usage: issues, challenges, and recommendations. Gov. Inf. Q. 29:4. doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2011.04.004
Bonsón, E., Perea, D., and Bednárová, M. (2019). Twitter as a tool for citizen engagement: an empirical study of the Andalusian municipalities. Gov. Inf. Q. 36:1. doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2019.03.001
Bortree, D. S. (2011). Mediating the power of antecedents in public relationships: a pilot study. Public Relat. Rev. 37:2. doi: 10.1016/j.pubrev.2010.11.002
Bruce, E., Keelson, S., Amoah, J., and Bankuoru Egala, S. (2023). Social media integration: an opportunity for SMEs sustainability. Cogent Bus. Manag. 10:859. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2023.2173859
Chen, Q., Xu, X., Cao, B., and Zhang, W. (2016). Social media policies as responses for social media affordances: the case of China. Gov. Inf. Q. 33:8. doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2016.04.008
Di Gangi, P. M., and Wasko, M. (2016). Social media engagement theory: exploring the infuence of user engagement on social media usage. J. Organ. End User Comput. 28:104. doi: 10.4018/JOEUC.2016040104
Dominic, D., and Gisip, I. A. (2021). ‘Effect of Social Media Usage in Government Agencies’ Communication Effort’, Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 11. doi: 10.6007/ijarbss/v11-i3/9277
Evans, L., Franks, P., and Chen, H. M. (2018). Voices in the cloud: social media and trust in Canadian and US local governments. Rec. Manag. J. 28:18. doi: 10.1108/RMJ-11-2016-0041
Furqon, A., Hermansyah, D., Sari, R., Sukma, A., Akbar, Y., and Rakhmawati, N. A. (2018). ‘Analisis sosial media pemerintah daerah di indonesia berdasarkan respons warganet analysis of local government social media in indonesia based on netizen response’, Jurnal Sosioteknologi, 17.
Gálvez- Rodríguez, M. d. M., Sáez-Martín, A., García-Tabuyo, M., and Caba-Pérez, C. (2018). Exploring dialogic strategies in social media for fostering citizens’ interactions with Latin American local governments. Public Relat. Rev. 44:265. doi: 10.1016/j.pubrev.2018.03.003
Graham, M. W. (2014). Government communication in the digital age: social media’s effect on local government public relations. Public Relat. Inq. 3:371. doi: 10.1177/2046147X14545371
Guillamón, M. D., Ríos, A.-M., Gesuele, B., and Metallo, C. (2016). Factors influencing social media use in local governments: the case of Italy and Spain. Gov. Inf. Q. 33:5. doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2016.06.005
Haro-de-Rosario, A., Sáez-Martín, A., and del Carmen Caba-Pérez, M. (2018). Using social media to enhance citizen engagement with local government: twitter or Facebook? New Media and Society 20, 29–49. doi: 10.1177/1461444816645652
Heath, R. L. (2011). External organizational rhetoric: bridging management and sociopolitical discourse. Manag. Commun. Q. 25:532. doi: 10.1177/0893318911409532
Izzati, A. N., Pratama, A., Aristamy, I. G. A. A. M., Najwa, N. F., and Rakhmawati, N. A. (2018). Kategorisasi Jenis Interaksi Antara Pemerintah dan Masyarakat dan Popularitas Media Sosial Pemerintah Daerah. J. Sist. Inf. 14, 1–8. doi: 10.21609/jsi.v14i1.567
Johnston, K. A. (2010). Community engagement: exploring a relational approach to consultation and collaborative practice in Australia. J. Promot. Manag. 16, 217–234. doi: 10.1080/10496490903578550
Johnston, K. A. (2023). “Theorizing digital engagement in public relations” in Public relations theory III: In the age of publics. ed. K. A. Johnston (New York: Taylor and Francis).
Kavanaugh, A. L., Fox, E. A., Sheetz, S. D., Yang, S., Li, L. T., Shoemaker, D. J., et al. (2012). Social media use by government: from the routine to the critical. Gov. Inf. Q. 29:480. doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2012.06.002
Ledingham, J. A. (2010). Relationship management: a general theory of public relations’, in: J. A. Ledingham Public relations theory II. New York: Taylor and Francis, pp. 412–427.
Manetti, G., Bellucci, M., and Bagnoli, L. (2017). ‘Stakeholder Engagement and Public Information Through Social Media: A Study of Canadian and American Public Transportation Agencies’, Am. Rev. Public Adm. 47. doi: 10.1177/0275074016649260
O’Brien, H. L., and McKay, J. (2018). “Modeling antecedents of user engagement” in The handbook of communication engagement. eds. K. A. Johnston and M. Taylor (New York: John Wiley & Sons).
Park, H., and Lee, T. D. (2018). Adoption of e-government applications for public health risk communication: government trust and social media competence as primary drivers. J. Health Commun. 23:1013. doi: 10.1080/10810730.2018.1511013
Prahalad, C. K., and Ramaswamy, V. (2001). The future of competition. Ind. Mark. Manag. 30, 379–389. doi: 10.1016/S0019-8501(00)00152-8
Purwadi, A., Pratama, A. B., and Mahendradi, R. M. (2019). Mengukur Engagement Warga Negara dalam Interaksi Media Sosial (Studi Pada 32 Akun Resmi Facebook Pemerintah Kabupaten/Kota di Jawa Tengah). Natapraja 7, –17. doi: 10.21831/jnp.v7i1.24895
Rahmanto, A. N., and Dirgatama, C. H. A. (2018). ‘The implementation of e-government through social media use in local government of Solo Raya’, in 2018 International Conference on Information and Communications Technology, ICOIACT 2018. doi: 10.1109/ICOIACT.2018.8350763
Rexhepi, A., Filiposka, S., and Trajkovik, V. (2021). Adoption of social networks as web 2.0 citizen engagement tool in the local e-government context. Int. J. Electron. Gov. 13:276. doi: 10.1504/IJEG.2021.114276
Roengtam, S. (2017). ‘Social Media Use and Citizen Engagement in Local Government of Thailand’, in Management of Cities and Regions. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.70982
Romero, L. D. (2016). Social media, civic engagement, and local governments. Int. J. Civic Engagem. Soc. Change 3, 14–24. doi: 10.4018/IJCESC.2016100102
Santoso, A. D., Rinjany, D. K., and Bafadhal, O. M. (2020). Social media and local government in Indonesia: adoption, use and stakeholder engagement. Rom. J. Commun. Public Relat. 22, 21–35. doi: 10.21018/RJCPR.2020.3.307
Sobaci, M. Z. (2016). Social media and local governments: an overview. In: Public administration and information technology.
Taylor, M., and Kent, M. L. (2014). Dialogic engagement: clarifying foundational concepts. J. Public Relat. Res. 26:106. doi: 10.1080/1062726X.2014.956106
Keywords: digital environment, social media engagement, government communication, municipal government, Bandung City government
Citation: Atnan N and Sembada WY (2025) An analysis of digital environment structuring and its impact on engagement: a case study of the Bandung City government’s social media accounts, Indonesia. Front. Commun. 10:1628346. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1628346
Edited by:
Maria Matsiola, University of Western Macedonia, GreeceReviewed by:
Prasongchai Setthasuravich, The University of Tokyo, JapanKhoirudin Khoirudin, Universitas Buana Perjuangan, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Atnan and Sembada. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nur Atnan, bnVyYXRuYW5AdGVsa29tdW5pdmVyc2l0eS5hYy5pZA==; Windhiadi Yoga Sembada, eW9nYS5zZW1iYWRhQHVwbnZqLmFjLmlk
 Nur Atnan
Nur Atnan Windhiadi Yoga Sembada
Windhiadi Yoga Sembada