- Marian College Kuttikkanam Autonomous, Kerala, India
Artrepreneurship is the process of bringing an artist’s creative capabilities into a physical form so that it can be commercialized widely. Social media can be used as a tool to leverage artrepreneurial ventures. The paper analyses the influence of social media on artrepreneurial practices in a purely inductive approach. The paper is based on the results of a pilot study conducted through semi-structured interviews using a phenomenological qualitative design from 15 respondents, focusing on their views on social media usage and outcomes derived. Data was analysed using NVIVO 14 based on thematic analysis, which generated the following themes: Social media usage, Artistic expression and content strategy, audience engagement and interactions, perceived benefits and challenges and Artrepreneurial outcomes. Findings suggest that social media acts as a catalyst in creative entrepreneurship by acting as a strategic enabler tool. The study contributes to literature on digital entrepreneurship and offers insights for future quantitative research, scale development and practical guidance for artists in the digital.
1 Introduction
Introduction of social media has made significant transformation in the landscape of entrepreneurship, influencing various aspects of how various types of entrepreneurs operate and connect with their audiences (Blanco-González-Tejero et al., 2024). Art world is no exception. By the introduction of social media, the art world has undergone a drastic revolutionary reshaping, shifting from the conventional gallery and show oriented arts to a virtual era. The rise of digital platforms has reshaped the landscape of art, democratizing access to art. Formerly the success of artists was based on the sale of art, which has now expanded to new definitions of artistic success, making creativity a viable business. Artrepreneur is a resourceful person who merges his creative ability and business acumen to establish a sustainable artist career. Artrepreneurship is the process of bringing an artist’s creative capabilities into a physical form so that it can be commercialized widely (Hoffmann et al., 2021). Artrepreneurship is a unique blend of art and entrepreneurship, focusing on individuals who leverage their creativity and artistic skills to create economic value (Elliot et al., 2018). Social media has paved the way for disrupting traditional art practices, enabling more accessibility and democracy in the creative community. The virtual world enabled the artists to attain wider exposure and broader audience reach. Despite the rising prominence of social media in various entrepreneurial domains, limited research explores the role of social media in shaping artrepreneurial practices. This study addresses the gap by exploring the lived experiences of artrepreneurs in the digital era using a phenomenological qualitative lens. Thus, the study seeks to explore the role of social media in artrepreneurship through the following research questions:
1. What factors influence art entrepreneurs’ choices of social media platforms?
2. Why do art entrepreneurs consider social media as a crucial tool for promoting their work?
3. What behavioural patterns do they follow on social media in their artrepreneurial process?
4. What are the primary benefits and key challenges that artrepreneurs encounter while using social media for entrepreneurial purposes?
5. How does strategic use of social media influence the outcome of artrepreneurs?
This study seeks to explore the ways in which social media influences artrepreneurship by investigating how artrepreneurs use these platforms to enhance their creative output, build networks, and achieve business success. The study aims to contribute to the understanding of how social media shapes entrepreneurial experiences in the arts sector, offering valuable insights for practitioners and researchers alike.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Research design
The study adopts an exploratory qualitative design which employs a phenomenological inductive approach to understand the lived experiences of artrepreneurs. Qualitative research is exploratory in nature, in cases where existing literature is not sufficient enough to explain the unique context of the study. It is particularly valuable for understanding complex data and capturing rich insights from the phenomena being studied. Qualitative research can also be used to enhance the process of sensemaking and emergence of theories (Hlady-Rispal et al., 2021). Qualitative inducive approach allows research findings to emerge into themes from collected raw data. This is beneficial in exploring a phenomenon where there are no pre-existing theories. By coding data, major themes can be identified and relationships between these major themes can be established. This enhances the depth of analysis and provides insights that are relevant to the research questions (Thomas, 2006). Phenomenological qualitative research focuses on studying the lived experiences of individuals, where personal narratives and subjective experiences are valuable and can provide rich insights. Deeper understanding of complexities of the phenomena paves the way to theory development (Hlady-Rispal et al., 2021).
2.2 Sampling strategy and data collection
Purposive sampling technique was used to select artrepreneurs who use their entrepreneurial skills to market their art through social media actively. The sample size of the original qualitative study is fixed as 30. Phenomenological studies often involve smaller sample sizes, generally ranging from 5 to 30 participants. This range is suggested to ensure that researchers can delve deeply into the experiences of each participant (Ahmed, 2025). Phenomenological studies reach saturation with fewer participants compared to other qualitative study types (Fusch and Ness, 2015). A sample size of 15 participants is taken for the trial phase of the original qualitative phase, which incorporates a sample size of 25–30 based on data saturation levels. Semi-structured interviews ranging from 45 to 60 min were conducted to obtain data from the respondents. Participants were asked about their strategies of social media engagement, role, benefits, challenges of using social media and outcomes. Participants were encouraged to express their experiences in their own words for rich exploration of opinions.
2.3 Data analysis
Analysis of the pilot study interview was conducted using thematic analysis to derive themes for the exploratory study. NVIVO 14 was selected as the primary tool for data analysis as it provides advanced capabilities to handle unstructured textual data. It also supports inductive and exploratory research. The interviews were transcribed in intelligent transcription mode, which focuses on the core content spoken, removing unnecessary elements, rather than verbatim transcripts, which focus on filler words, tone, repetitions, etc. Transcripts were imported into NVIVO 14 for initial open coding. The transcripts were read line-by-line repeatedly to familiarize oneself with the data and initial codes were generated inductively. The codes were then iteratively reviewed and grouped into categories, providing for generation of 6 major themes. Thematic coding is employed to identify themes derived directly from participants’ narratives. The inductive phenomenological approach ensured that themes are derived from real-world experiences rather than pre-existing conceptual frameworks. Thematic analysis can be employed to reflect participants’ experiences and meanings or to explore how these meanings are constructed within broader social discourses. This versatility makes thematic analysis an accessible method for researchers, particularly those new to qualitative research (Braun and Clarke, 2006).
To ensure reliability of coding, peer debriefing was conducted with two qualitative researchers. Additionally, member checking was used with 5 participants to confirm participant validation of the findings.
3 Results and discussions
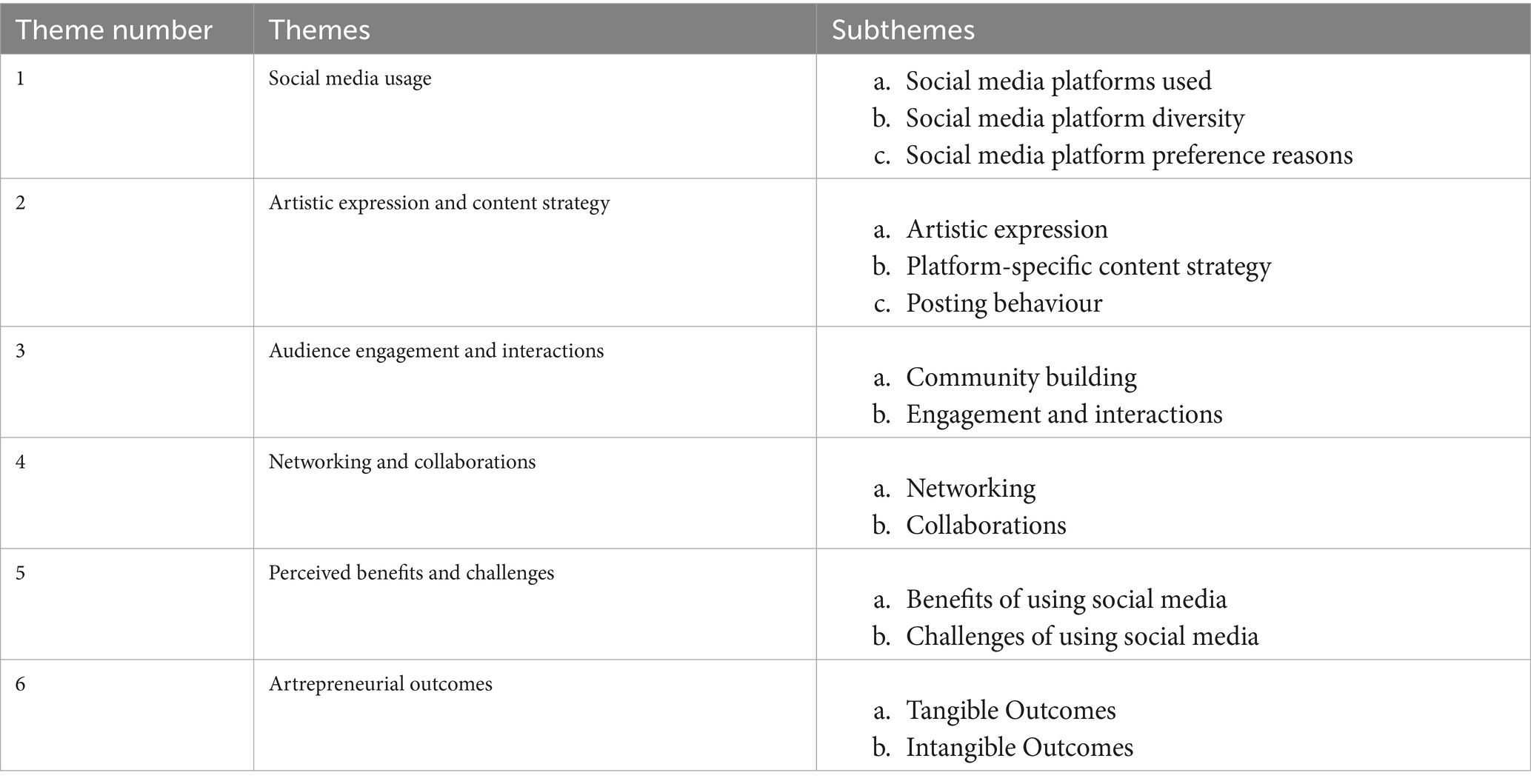
The analysis of the interview transcript revealed 6 major thematic areas which illustrate the role of social media on artrepreneurship. These themes explain the choices, behaviours and experiences of artrepreneurs, highlighting how social media functions on their artistic and entrepreneurial ventures. The findings offer insights to the decisions of artrepreneurs in their creative expressions on both their muse and contents, interactions in community, co-working with other artists, reaping the rewards and dealing with the challenges.
The 6 major themes identified, purely based on an inductive approach, are presented below with representative quotes. The discussion integrates these findings with existing literature (see Table 1).
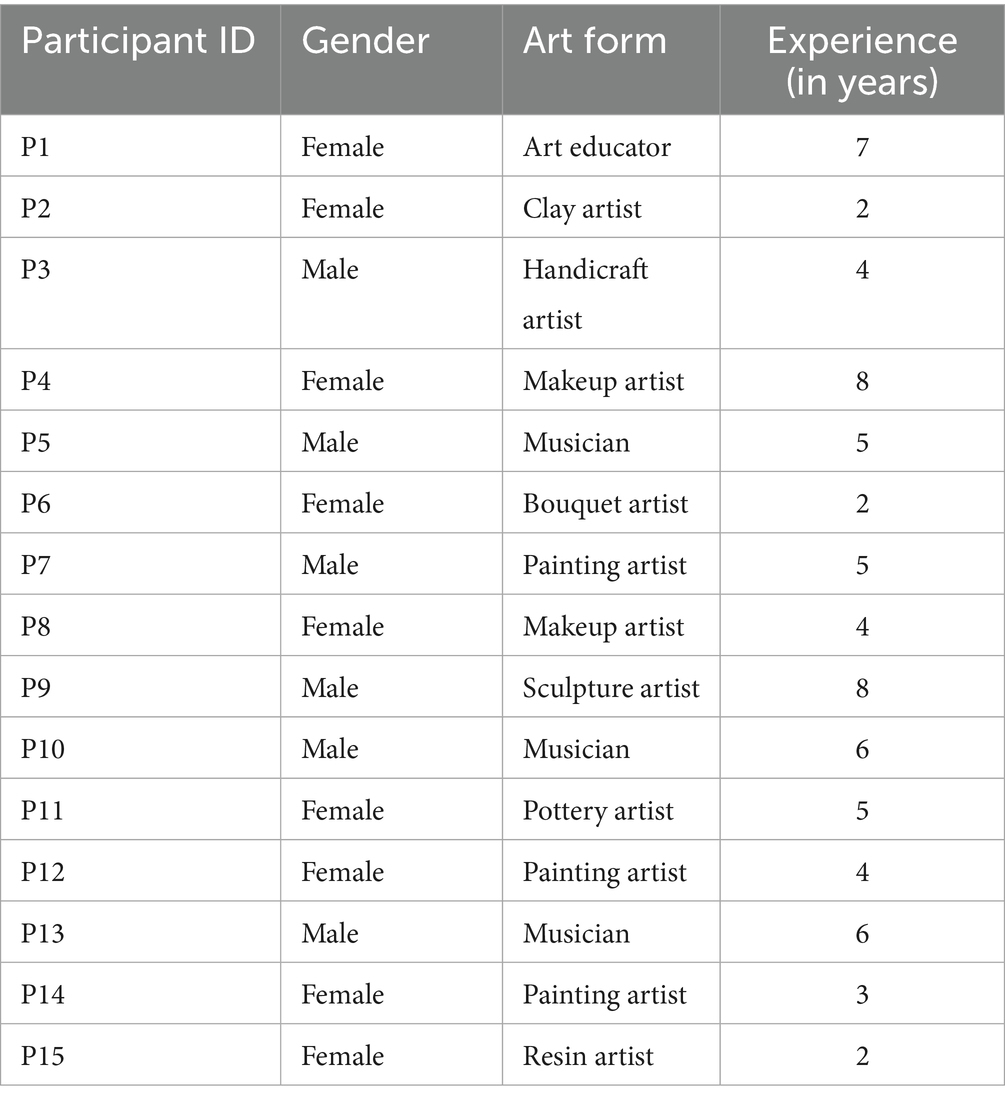
The data was collected from 15 respondents, out of which 9 were females and 6 were males. Their primary area of art includes painting, sculpting, music, makeup and clay modelling. The experience in the concerned field ranges from 2 to 8 years, among which the majority of the respondents showed the experience of 4 years or more (see Table 2).
3.1 Social media usage
The theme “Social Media Usage” captures the various social media platforms that the artrepreneurs use for the artrepreneurship process. The study highlights the strategic use of various social media platforms that the artrepreneurs use and the reasons behind the platform selection. These findings align with previous research suggesting that visual-based platforms provide a competitive edge for creative entrepreneurs. Different social media platforms serve distinct purposes, and users should analyse which platform aligns best with their entrepreneurial goals. The study also highlights that social media can be utilized in various ways, from professional interactions to personal engagement. This diversity allows entrepreneurs to leverage multiple platforms, and this strategic diversification enhances audience reach and engagement, reinforcing the importance of platform-specific content strategies (Blanco-González-Tejero et al., 2024).
3.1.1 Social media platforms used
Platforms include Instagram, WhatsApp, Facebook, YouTube, Threads, Spotify, etc. Each platform has platform specific peculiarities which influences the choice of artrepreneurs.
3.1.2 Social media platform diversity
Most of the artrepreneurs use a combination of these social media platforms to maximize the benefits effectively.
3.1.3 Social media platform preference reasons
The theme also explains the reasons why various social media platforms are preferred by artrepreneurs. Most of the artrepreneurs prefer Instagram as a platform for artistic entrepreneurship, followed by YouTube.
3.2 Artistic expression and content strategy
The theme “Artistic Expression and Content Strategy” explores how artrepreneurs create and curate content to showcase their work via social media platforms. Artistic expression is not mere showcase of creativity but curating content that resonates with the audience. Social media facilitates storytelling, allowing artists to exhibit their creative ideas. Artistic expression can lead to strong positive impacts as artists engage in pursuit of their passion, which fuels their creativity and contributes to their identity as an artrepreneur. The role of content strategy is particularly evident in the way artists tailor their posts according to platform-specific algorithms (Hoffmann et al., 2021).
3.2.1 Artistic expression
This category relates to the creative abilities of artrepreneurs and how they strategize them for social media platforms. It relates to authentic expression of the artist’s creative skills and story telling techniques. They make use of showcasing their unique creative abilities to connect with their audiences.
3.2.2 Platform-specific content strategy
Artists use various content on social media, ranging from images to videos. They adopt diverse strategies tailored to specific platforms, as follows:
Content strategy on Instagram: on Instagram the contents usually shared are images, reels, stories etc. This can be of any content that the artist intends to share, such as completed artwork, process reels, behind-the-scene contents or even personal images and posts.
Content strategy on WhatsApp: WhatsApp can be used for sharing images, videos and audios directly as Status or can be used to share content personally to clients.
Content strategy on YouTube: On YouTube, contents include full length videos of creations, tutorial, behind-the-scenes videos etc.
3.2.3 Posting behaviour
The sub-theme posting behaviour deals with the frequency, consistency, strategic timing and audience centric posting of contents. In the opinion of artrepreneurs, these are significant factors that influence their existence and visibility in social media platforms.
3.3 Audience engagement and interactions
This theme deals with how regular engagements and interactions with the followers is crucial for maintaining a successful artrepreneurial career. The theme discusses the process of community building through engagements and interactions and what various modes of interactions are. Existing literature highlights that social media facilitates significant user interactions and engagements, influencing thoughts and behaviours through social ties and collective influences within networks and it serves as a supportive tool for fostering connections (Elliot et al., 2018).
3.3.1 Community building
The artrepreneurs emphasized the importance of creation of a loyal follower base through various interactions. This process can be defined as community building.
3.3.2 Engagement and interactions
Modes of engagements and interactions: The subtheme discusses how the artrepreneurs interact with their audiences or followers. The various modes of interactions include comments, direct messages, group interactions, live sessions, personal calls, polls, etc.
Benefits of engagements and interactions: The theme discusses how various interactions lead to an increase in opportunities.
3.4 Networking and collaborations
This theme explores how social media enables networking and collaborative opportunities. Networks and collaborations can be built through working with various artists, engaging in partnerships and sponsorships, etc. Social media serves as a tool for fostering networking and collaborations in entrepreneurial endeavours, which is essential in enhancing creativity and skills. Effective use of social media can facilitate co-creation of content and interactions among peers, thereby supporting the success of entrepreneurial ventures (Barrera-Verdugo and Villarroel-Villarroel, 2022).
3.4.1 Networking
Networking can be done by the artists to work with various industries, which can lead to an increase in professional connections and industry relationship building.
3.4.2 Collaborations
Collaborations include working in partnership with other artists and cross-promotions.
3.5 Perceived benefits and challenges
This theme deals with the benefits and hurdles of using social media as a tool for entrepreneurship. It explains that social media provides multiple advantages for artrepreneurship, but despite these advantages, it is not free from certain drawbacks or challenges. While social media offers numerous benefits for entrepreneurs, such as expanded networks and increased social capital, it also presents challenges that need to be navigated to maximize its potential (Wang et al., 2020). An artrepreneur must be able to tackle these challenges and maintain a balance between these two, to attain a successful career.
3.5.1 Benefits of using social media
Social media platforms offer multiple advantages that empower artists to build their brand, connect with a global audience, and monetize their work without relying on traditional marketing.
3.5.2 Challenges of using social media
Despite its advantages, social media presents several obstacles that artrepreneurs must navigate to sustain success. The challenges include platform-specific limitations, pressure to follow trends, content burnout and consistency pressure, financial frauds, and so on.
3.6 Artrepreneurial outcomes
The theme artrepreneurial outcome discusses the results of using social media as a tool for entrepreneurship by artists. This can be measured in terms of both tangible and intangible outcomes. This theme thoroughly illustrates the success of artrepreneurial ventures. The study suggests that social media is not just a promotional tool but a transformative medium that reshapes traditional art entrepreneurship models.
3.6.1 Tangible outcomes
Tangible outcomes are the gains of artrepreneurial activities which are measurable, financially in nature and which are career-oriented. This includes an increase in sales, an increase in visibility, an increase in follower count, invitations to events, etc. This aligns with previous research stating popular measures of entrepreneurial success such as growth, profitability, and survival. These measures reflect different aspects of entrepreneurial performance and may be more or less appropriate depending on specific policy agendas and objectives (Yusuf, 2010).
3.6.2 Intangible outcomes
Intangible outcomes are the non-monetary benefits that the artrepreneurs gain by using social media as a platform for showcasing their works. This includes self-confidence, personal satisfaction, feeling of fulfilment, etc. These intangible outcomes highlight the importance of personal fulfilment and subjective measures of success in entrepreneurship, emphasizing that success is not solely defined by financial gain but also by personal growth and satisfaction (Baluku et al., 2020).
4 Conceptual framework from pilot study findings
The pilot study aims to explore the influence of Social Media on Artrepreneurship by examining the lived experiences of artist entrepreneurs who use social media as a platform for promoting their artworks. The pilot study, which is purely inductive in nature, followed an exploratory qualitative study, and used a phenomenological approach to derive six key themes-Social Media Usage, Artistic Expression and Content Strategy, Audience Engagement and Interactions, Networking and Collaborations, Perceived Benefits and Challenges, and Artrepreneurial Outcomes. These themes aided in the development of a preliminary conceptual framework that narratively and visually represents the interrelations between social media usage and artrepreneurial outcomes.
4.1 Purpose and rationale of the framework
The framework, purely conceptual, is grounded in empirical data drawn from participant narratives. It explains how social media acts as a catalyst in shaping artrepreneurial processes and its outcomes. It depicts how social media acts as a strategic, interactive and adaptive mechanism which converges creativity, community and commerce, altogether. The framework is solely tentative based on exploratory data, which acts as a foundation for further theory building, instrument development, its validation and subsequent large scale research stages.
4.2 Description of the framework components
4.2.1 Social media usage
Artrepreneurs choose the social media platforms based on their strategies of diversification, affordability, audience demographic and artrepreneurial goals.
4.2.2 Artistic expression and content strategy
Artists use social media as a platform to deliver content by aligning with the needs of the audience. This involves creation of art based on both creative abilities of the artrepreneur as well as requirements of the audience. This involves sharing artistic output with platform-specific norms and algorithms.
4.2.3 Audience engagement and interactions
Social media usage enables the artrepreneurs to engage and interact with the followers to build an emotional connection with the followers which leads to the development of a loyal follower community. The emotional resonance fuels ongoing content creation and brand identity.
4.2.4 Networking and collaborations
Social media provides a digital space for discovering other artists, initiating communications with them, and sustaining interactions with co-artists. It is a dynamic virtual space for interacting with influencers and organizations. This enables co-creation, widens follower circle, fosters innovations, expands brand image, thereby leading to enhanced artrepreneurial success.
4.2.5 Perceived benefits and challenges
Social Media usage creates a perception in the minds of artrepreneurs which can be both positive and negative in nature. While social media offers larger market access, increased visibility and community building, it is not free from possible challenges like algorithm fluctuations, content creation pressure, digital burnout and so on. Navigating these dual aspects is vital in ensuring sustainable artrepreneurial practices and outcomes.
4.2.6 Artrepreneurial outcomes
Artrepreneurial outcomes can be both tangible and intangible. Tangible outcomes include increased sales, growth, visibility, brand image etc., whereas intangible outcomes include enhanced self-identity, satisfaction, mental empowerment and so on. The study suggests that social media can act as a stimulus for creative ventures by integrating art and strategic digital engagement soundly.
4.3 Interconnections among themes
The conceptual framework (see Figure 1) illustrates the dynamic and interconnected nature of these themes. Social Media Usage is the foundational input in the artrepreneurial process. Social Media Usage aids in more Artistic Expression and Content Strategy, drives Audience Engagement and Interactions, leads to richer Networking and Collaborative Opportunities and shapes the artrepreneur’s perception of the Benefits and Challenges of using social media. Together, these experiences influence the eventual artrepreneurial outcomes.
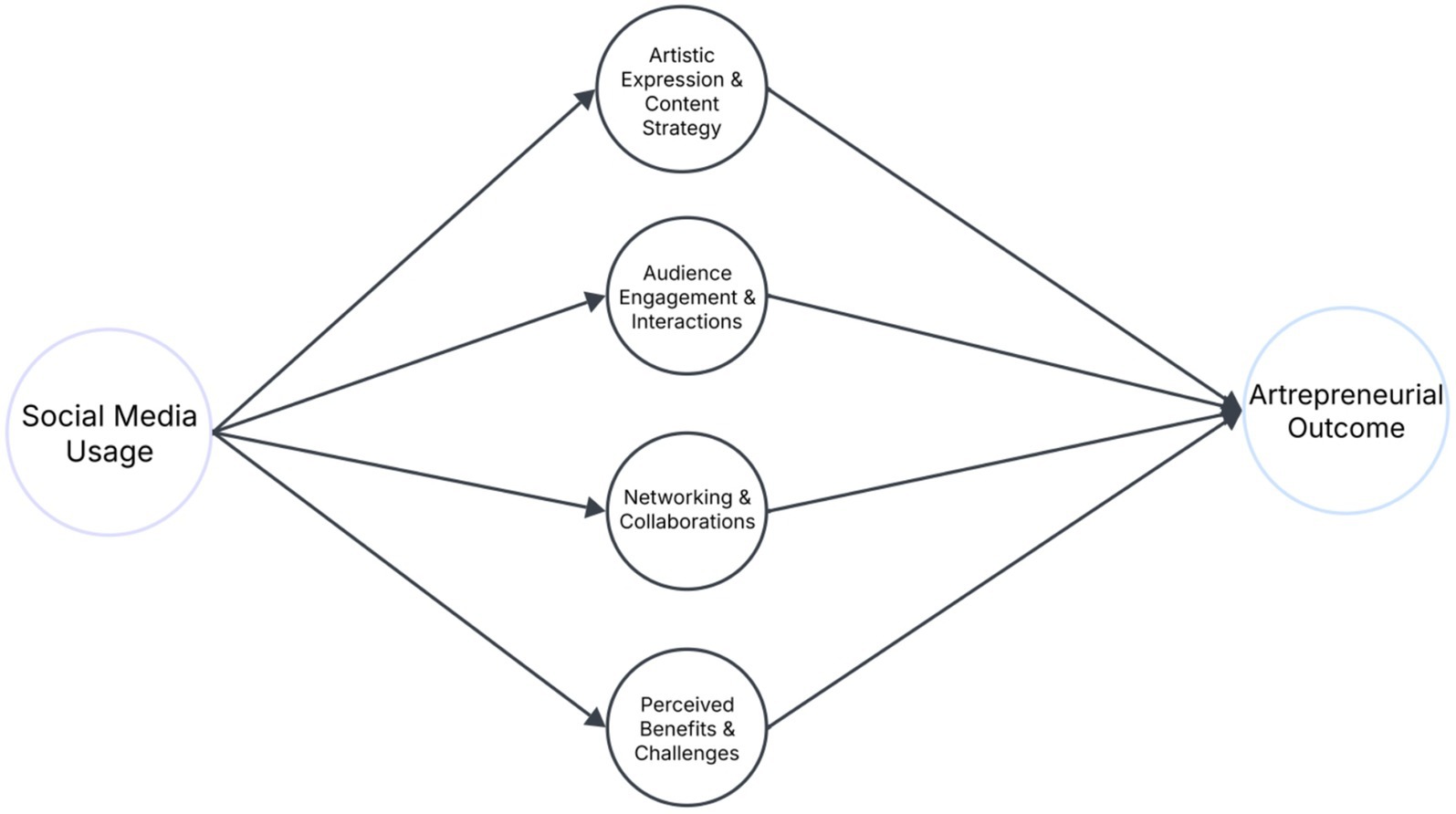
Figure 1. Conceptual framework of social media-driven artrepreneurship based on findings of thematic analysis.
4.4 Visual model of the framework
The framework shows Social Media Usage as the entry point, leading to Artistic Expression and Content Strategy, Audience Engagement and Interactions, Networking and Collaborations, Perceived Benefits and Challenges, together culminating into Artrepreneurial Outcomes.
4.5 Alignment with research objectives
This framework supports the study’s qualitative objectives:
• Objective 1 is addressed through insights on platform preferences in Social Media Usage.
• Objective 2 is captured in Audience Engagement and Interactions, highlighting community-building effects.
• Objective 3 emerges from Perceived Benefits, such as identity formation and visibility.
• Objective 4 is reflected in challenges like algorithm fatigue and performance anxiety.
• Objective 5 is incorporated into Artrepreneurial Outcomes, capturing both psychological and entrepreneurial dimensions of social media use.
4.6 Conclusion and future implications
This preliminary conceptual framework offers a grounded representation of how artrepreneurs utilize, experience, and navigate social media in their professional practice. As an evolving structure, it will inform future phases of this study, including the development of a measurement scale and validation through broader mixed-methods research. The model invites future exploration into the nuanced, symbiotic relationship between digital platforms and art-based entrepreneurship in the contemporary creative economy.
5 Conclusion and practical implications
This study sheds light on the profound impact of social media on artrepreneurship, highlighting its multifaceted role in shaping artistic expression, audience engagement, networking, and business outcomes. Through an inductive thematic analysis, six major themes emerged—Social Media Usage, Artistic Expression and Content Strategy, Audience Engagement and Interactions, Networking and Collaborations, Perceived Benefits and Challenges, and Artrepreneurial Outcomes.
The findings reveal that social media serves as a dynamic ecosystem where artrepreneurs strategically leverage various platforms to promote their work, connect with audiences, and establish their entrepreneurial presence. The study underscores the importance of platform-specific content strategies, engagement techniques, and the potential for collaborations in enhancing artrepreneurial success. Additionally, while social media offers numerous benefits, such as increased visibility, income generation, and community-building, challenges like algorithm dependence, content burnout, and financial risks persist.
The study contributes to the existing literature by reinforcing the evolving nature of digital entrepreneurship in the creative sector. It emphasizes that social media is not merely a promotional tool but a transformative medium that redefines traditional art entrepreneurship models. By understanding the nuances of social media usage, artists can better navigate digital spaces, optimize their strategies, and sustain their careers in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
5.1 Practical implications
5.1.1 For artrepreneurs
The findings provide rich insights for actionable strategies not only for established but also emerging artrepreneurs. Artists can develop sustainable and strategy-oriented practices in creation of content, engagement with followers, networking stragies and successful pursuit of artrepreneurship.
5.1.2 For art educators
Educators providing training in creative art and entrepreneurship can integrate social media strategy and digital literacy into their syllabi. Emerging artrepreneurs can enhance their entrepreneurial potential by such programs that equip artists with the skills in content creation, branding, community management and networking.
5.1.3 For policy makers
Policy makers and art incubators can offer workshops, funding opportunities and self-employment schemes which supports potential artists to navigate through vast horizons of digital art world.
5.1.4 For social media platform developers
Platforms can create art-oriented features like artist-friendly algorithms, artist-tailored professional dashboards and analytics, customizable portfolios, authentic collaborations, art-nurturing audience engagement strategies etc. which can foster a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
While the pilot study provides valuable insights on the role of social media on artrepreneurship, several avenues for future research remain. Since this study followed an inductive qualitative approach, a future quantitative study can be conducted. Further research can develop and validate a scale based on these findings to measure the impact of social media on different dimensions of artrepreneurship. Future studies can be conducted on the effectiveness of social media platforms in enhancing artrepreneurial success separately, in-depth exploration of algorithms of platforms, monetization strategies of platforms, audience behaviours etc. A longitudinal approach could provide deeper insights into how social media influences artrepreneurial outcomes over time, including trends in platform preferences, content evolution, and sustainability challenges. Future research can also explore the cognitive and affective consequences of social media usage on work-life balance for artrepreneurs, including stress, burnout, and the pressure of maintaining an online presence. The role of AI integration and emerging technologies in art and content creation, audience engagement etc. can be explored.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Marian Research Ethics Committee, Marian College Kuttikanam. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AG: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MM: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmed, S. K. (2025). Sample size for saturation in qualitative research: debates, definitions, and strategies. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 5:100171. doi: 10.1016/j.glmedi.2024.100171
Baluku, M. M., Matagi, L., and Otto, K. (2020). Exploring the link between mentoring and intangible outcomes of entrepreneurship: the mediating role of self-efficacy and moderating effects of gender. Front. Psychol. 11:1556. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01556
Barrera-Verdugo, G., and Villarroel-Villarroel, A. (2022). Evaluating the relationship between social media use frequency and entrepreneurial perceptions and attitudes among students. Heliyon 8:e09214. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09214
Blanco-González-Tejero, C., Ulrich, K., and Ribeiro-Navarrete, S. (2024). Can social media be a key driver to becoming an entrepreneur? J. Knowl. Econ. 15, 16780–16798. doi: 10.1007/s13132-024-01764-9
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 3, 77–101. doi: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Elliot, E. A., Jamal, A., and Cherian, J. (2018). Artrepreneurship and learning in ethnic markets. J. Bus. Res. 82, 391–399. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.01.018
Fusch, P., and Ness, L. (2015). Are we there yet? Data saturation in qualitative research. Qual. Rep. 20, 1408–1416. doi: 10.46743/2160-3715/2015.2281
Hlady-Rispal, M., Fayolle, A., and Gartner, W. B. (2021). In search of creative qualitative methods to capture current entrepreneurship research challenges. J. Small Bus. Manage. 59, 887–912. doi: 10.1080/00472778.2020.1865541
Hoffmann, R., Coate, B., Chuah, S.-H., and Arenius, P. (2021). What makes an artrepreneur?: an exploratory study of artrepreneurial passion, personality and artistry. J. Cult. Econ. 45, 557–576. doi: 10.1007/s10824-021-09413-8
Thomas, D. R. (2006). A general inductive approach for analyzing qualitative evaluation data. Am. J. Eval. 27, 237–246. doi: 10.1177/1098214005283748
Wang, W., Liang, Q., Mahto, R. V., Deng, W., and Zhang, S. X. (2020). Entrepreneurial entry: the role of social media. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 161:120337. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120337
Keywords: social media, artrepreneurship, creative entrepreneurship, thematic analysis, digital platforms
Citation: George A and Mathew MS (2025) Exploring the role of social media in artrepreneurship: initial empirical insights. Front. Commun. 10:1643963. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1643963
Edited by:
Douglas Ashwell, Massey University Business School, New ZealandReviewed by:
Fayyaz Hussain Qureshi, Oxford Business College, United KingdomFerry Darmawan, Mining Engineering Bandung Islamic University, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 George and Mathew. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maria Susan Mathew, bWFyaWEuMjRyc0BtYXJpYW5jb2xsZWdlLm9yZw==
 Ajimon George
Ajimon George Maria Susan Mathew
Maria Susan Mathew