- 1Department of Administrative Science, College of Administrative and Financial Science, Gulf University, Sanad, Bahrain
- 2Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, College of Engineering, Gulf University, Sanad, Bahrain
- 3Department of Business Administration, College of Administrative Sciences, Applied Science University, Al Eker, Bahrain
- 4Dubai Business School, University of Dubai, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Background: Employee performance (EP) is a key factor in organizational success. Nonetheless, the impact of particular factors on EP remains variable across research. This study investigated the influence of Communication and Collaboration (CC), Employee Efficiency (EE), Level of HRIS Training (LHT), and Performance Analysis (PA) on Employee Performance (EP) within the Ministry of Communications and Transport (MCCT) in Bahrain.
Methods: A quantitative, descriptive-correlational methodology was employed. Data were obtained from 243 convenience-sampled participants, with 167 valid responses subjected to analysis. Reliability was established through Cronbach’s alpha (α = 0.827). Descriptive statistics were conducted using SPSS v28, and Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) was executed with SmartPLS 4. The model’s validity was assessed through reliability indices, AVE, VIF, and goodness-of-fit indices.
Results: The analysis indicated that CC (β = 0.268, p = 0.002), EE (β = 0.280, p = 0.012), and LHT (β = 0.261, p = 0.006) exerted significant positive influences on EP. Conversely, PA (β = 0.067, p = 0.272) exhibited no statistical significance. Effect size analysis (f2) revealed minimal contributions (0.029–0.094), although CC and EE revealed a comparatively greater impact. The model accounted for R2 = 0.335 (33.5%) of the variance in EP, indicating moderate explanatory efficacy. The fit indices satisfied the prescribed thresholds (e.g., CFI = 0.982, TLI = 0.977, RMSEA = 0.072).
Conclusion: The study concludes that CC, EE, and LHT are substantial determinants of PE, whereas AP shown no direct effect. The findings underscore the significance of communication, efficiency, and training in enhancing employee outcomes, while also indicating the need for further research on the contextual role of performance analysis.
1 Introduction
The swift development of the digital transformation period has facilitated significant technological improvement, that is aimed at enhancing and streamlining operational processes across diverse industries (Ersoy et al., 2022). An important advancement in the field of Human Resources (HR) is the introduction and subsequent integration of Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) (Bhakuni and Totlani, 2023). This novel system is designed to enhance the administration, decision-making processes, and general efficacy of HR departments by proficiently gathering, storing, arranging, and examining data relevant to an organization’s workforce (Islam and Tamzid, 2023).
The use of HRIS has been widely recognized and accepted by many sectors worldwide, leading to a significant shift in the management of HR and operational effectiveness (Qamari and Rakotoarizaka, 2022). However, despite being widely recognized and used, there is still a notable study deficiency about the concrete effects of HRIS on employee performance (Kaushal et al., 2023). The Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain serves as an outstanding instance of a significant sector that has not only acknowledged the promise of these technologies but has also effectively incorporated them into its operational framework.
According to Sikandar et al. (2022), the advancement of digital improvement encompasses more than just technical advancements. Furthermore, this highlights the Kingdom’s commitment to developing a workforce that has advanced digital skills and is not just proficient but also highly motivated, engaged, and in alignment with the nation’s overarching goals (Alhajeri, 2022). By examining the potential relationship between the implementation of HRIS and improvements in EP, stakeholders may make well-informed choices on future investments in these technologies. This will assist in ensuring that the Kingdom maintains its position as a leader in digital advancement within the region.
The objective of this study is to thoroughly examine the challenges surrounding the implementation of a HRIS and its potential impact on enhancing EP, particularly within the context of the Ministry. Considering the Kingdom of Bahrain’s ambitious goal of strengthening its digital infrastructure and enhancing the quality-of-service provision, it is crucial to comprehend the relationship between the adoption of HRIS and the subsequent performance of its workforce.
In conclusion, it can be inferred that the use of HRIS will undoubtedly have a significant impact on the digital landscape of the Kingdom of Bahrain as it progresses forward. Hence, this study functions as a conduit, establishing a connection between technological ambitions and concrete workforce results.
1.1 Research objectives (RO)
1. To examine the effect of Communication and Collaboration (CC) on Employee Performance (EP) at Bahrain’s Ministry of Communications and Transportation.
2. To investigate the impact of Employee Efficiency (EE) on Employee Performance (EP) at the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in Bahrain.
3. To analyze the role of Level of HRIS Training (LHT) in influencing Employee Performance (EP) at the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in Bahrain.
4. To assess the effect of Performance Analysis (PA) on Employee Performance (EP) at the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain.
2 Literature review
In the era of digital transformation, the HRIS have become a crucial element in the transformation of conventional human resource management practices. This has led to increased efficiency and the adoption of a decision-making culture that is based on data. When examined through the lens of the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain, the ramifications of HRIS have become apparent in several aspects.
The enhancement of employee performance is contingent upon many crucial aspects, including staff efficiency, training, and performance analysis (Diawati et al., 2023; Saputra et al., 2024). The enhancement of efficiency not only serves to increase individual production, additionally contributes to the cultivation of a favorable work environment. Training provides individuals with the necessary skills and information to effectively perform their duties and achieve exceptional performance in their respective positions (Bandura, 2023). Performance analysis is a crucial tool that offers significant insights, enabling staff to effectively address areas of weakness and use their strengths. These components jointly lead to enhanced employee performance and corporate achievement.
The advent of HRIS have undeniably transformed the international HR domain. According to Abuhantash (2023), the contemporary HR process benefits greatly from the systematic and streamlined approach offered by HRIS. This enhanced agility is seen across several HR functions, including recruiting, payroll, and training. The remark made by Magege and Ngirwa (2023), reaffirms the notion that the integration of HRIS has led to a noticeable improvement in administrative efficiency inside Bahrain’s governmental institutions, particularly its ministries. Efficient optimization is of utmost importance in sectors such as the Ministry of Communications and Transportation, where the timely and accurate implementation of tasks is crucial for achieving operational excellence (Mohsan et al., 2023). Moreover, Hoai et al. (2022) emphasize the system’s capacity to enhance the efficiency of data retrieval, hence facilitating timely job completion and mitigating bureaucratic stagnation.
Nevertheless, the discourse around HRIS is not exclusively characterized by positive aspects. Although the system has gained international recognition for its benefits, such as less paperwork, improved real-time PA, and proactive predictive analytics, it also presents certain challenges (Jain et al., 2023; Diraco et al., 2023). The aforementioned factors include a variety of concerns, including a tangible aversion to change, the possibility of data breaches, and the possible drawbacks associated with excessive dependence on automation (Devaki and Leena Jenifer, 2022). In the case of Bahrain, the dynamics provide an additional level of intricacy. Feng (2023) discusses the nuanced relationship between entrenched hierarchical decision-making and the democratizing, and often disruptive, effect of HRIS.
One may argue that the substantial influence of HRIS can be observed in its ability to reconfigure the interconnected aspects of communication, cooperation, and decision-making within organizational settings. The use of a centralized repository, as suggested by Tejedo-Romero et al. (2022) facilitates enhanced transparency, consistency, and efficiency in communication. McLean (2023) further elaborates on this narrative by proposing that HRIS has the potential to remove information silos, hence creating an environment conducive to the development of cross-departmental synergy. Decision-makers are now equipped with a wealth of real-time data analytics, enabling them to make timely, relevant, and well-informed judgments (Testa and Karpova, 2022; Ling and Verma, 2023; Abdalla et al., 2023).
The significant implications for EP arise from the intersection of these changes with the degree of HRIS training and performance analysis, resulting in ripple effects (Gwiza et al., 2022). Mideksa (2023) highlights the significant importance of training in HRIS, highlighting that the effective usage of HRIS can only be achieved when personnel possess proficient training. This element has a strong positive correlation with the improvement of communication and collaboration capabilities offered by HRIS (Bhakuni and Totlani, 2023; Koech et al., 2022; Koech, 2022). In addition, the potential of HRIS to provide detailed and specific analysis of performance, at both the individual and departmental levels, represents a significant shift in the way performance metrics and evaluation systems are evaluated and adjusted (McCartney and Fu, 2024; Štaffenová and Kucharčíková, 2023; Madid, 2023).
In conclusion, the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain finds itself at a critical turning point. The incorporation of HRIS represents a significant change in operations, culture, and performance, rather than being a simple technological improvement. The appeal of efficient operations and improved performance indicators is unquestionably enticing. Nevertheless, it is important to navigate this course while being aware of the obstacles, particularly those that are specific to Bahrain’s socio-cultural context. The success of Bahrain’s digital journey will depend on effectively managing the opportunities and difficulties presented by HRIS, to achieve continuous development and a steadfast dedication to achieving high standards. Consequently, this has resulted in the formulation of the following hypothesis (Figure 1).
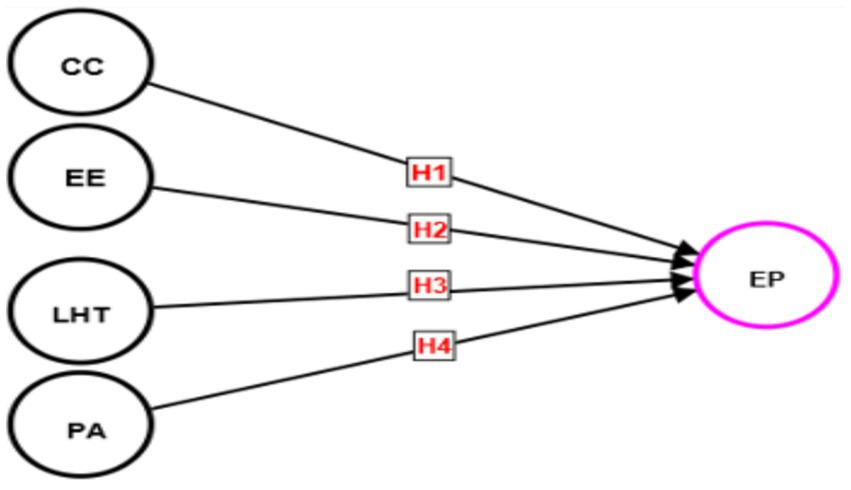
Figure 1. Conceptual framework. EE, Employee Efficiency; CC, Communication and Collaboration; LHT, Level of HRIS Training; PA, Performance Analysis; EP, Employee Performance.
2.1 Hypotheses
H1: Communication and Collaboration (CC) has a significant positive effect on Employee Performance (EP) on the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain.
H2: Employee Efficiency (EE) has a significant positive effect on Employee Performance (EP) on the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain.
H3: Level of HRIS Training (LHT) has a significant positive effect on Employee Performance (EP) on the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain.
H4: Performance Analysis (PA) has a significant positive effect on Employee Performance (EP) on the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain.
3 Methodology
This research examined the influence of HRIS on Employee Performance (EP) within Bahrain’s Ministry of Communications and Transportation employing a quantitative, descriptive correlational methodology. Data had been collected from 243 employees via structured online questionnaires. Reliability testing showed a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.827, confirming internal consistency. The data analysis occurred in two phases: SPSS version 28 facilitated descriptive statistics and preliminary evaluations, while SmartPLS 4 used PLS-SEM to examine the measurement and structural models. Diagnostics included reliability, validity, collinearity (VIF), and predictive relevance (R2), used bootstrapping (5,000 resamples) to evaluate hypotheses. Ethical norms were upheld, guaranteeing the anonymity and confidentiality of all participants.
4 Results
4.1 Background characteristics of the respondents
The research examined a sample of 167 participants, with a predominant representation of males (70%). With regard to the distribution of age, around 49% of the participants were between the 31–40 year age range, while 12.5% were below the age of 20. A substantial majority of individuals, namely 86.5%, have less than 10 years of professional experience. It is worth noting that a significant majority of the participants had a bachelor’s degree, accounting for 65.8% of the total responses. The proportion of those with high school or diploma qualifications was comparatively lower, with 7.1 and 4.1%, respectively. The group labeled as “Others” within the context of schooling constituted 22.7% of the total sample (Table 1).
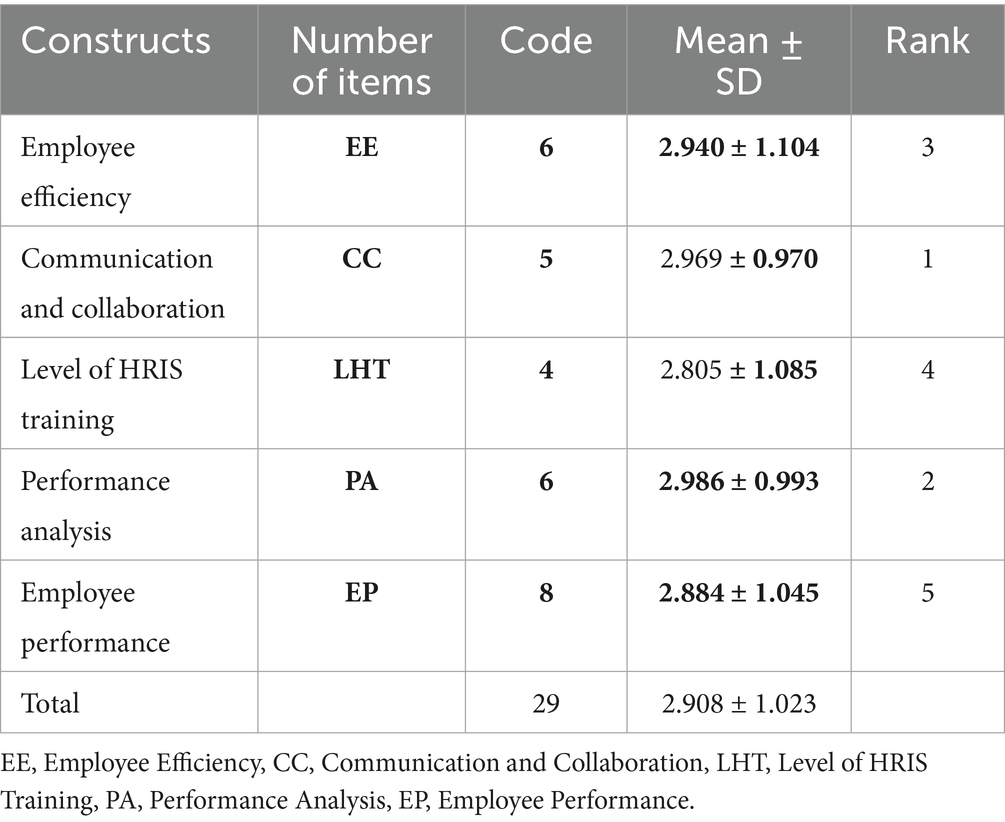
4.2 Μ ± SD and rank for the variables
The provided data illustrates an ordered set of five constructs, determined by their respective average scores. CC is ranked highest, with a mean score of 2.969 ± 0.970, indicating that it is considered the most successful among the other groupings. PA closely trails behind with a mean value of 2.986 ± 0.993. It is worth noting that each of these constructs has a standard deviation that is less than 1, suggesting a pretty high level of consistency in the assessments. The variables of EE and LHT exhibit a moderate level of ranking. However, their standard deviations exceed 1, suggesting a greater variability in the scores. The EP metric, although having the highest number of elements, is ranked last with a mean score of 2.884 ± 1.045. The mean value for all constructions is 2.908 with a standard deviation of 1.023. The data presented indicates that the domain of CC has the highest level of proficiency. However, there is still potential for improvement across all structures (Table 2).
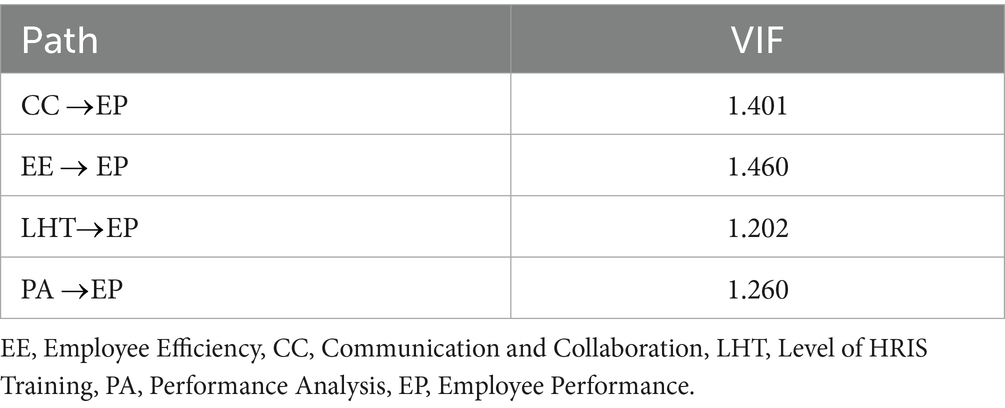
4.3 Multicollinearity test
The Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) quantifies the extent to which the variance of an estimated regression coefficient is augmented due to the presence of correlation among the predictors (Venkatesh et al., 2023; Abulibdeh, 2022). According to accepted knowledge, a general guideline is that a VIF above a range of 5–10 indicates the presence of significant multicollinearity (Waqar et al., 2023; Wen and Wang, 2022). The VIF values for all variables (CCEP: 1.401, EE EP: 1.460, LHT EP: 1.202, PA EP: 1.260) are below the established threshold, suggesting the absence of substantial multicollinearity among the predictors in the model. This suggests that the predictors may be regarded as providing unique, non-overlapping information to the model, consequently validating their incorporation (Table 3).
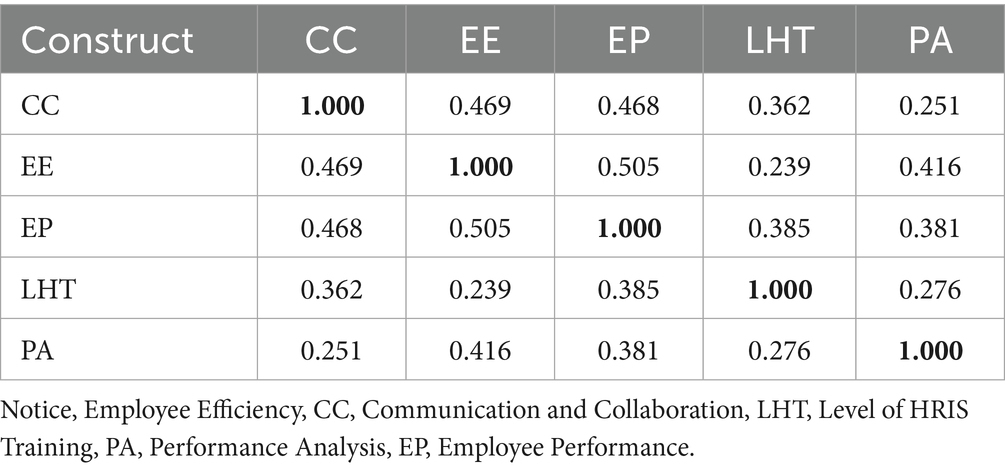
4.4 Correlations
The demonstrated table presents a correlation matrix illustrating the relationships among five variables, namely CC, EE, EP, LHT, and PA. A value that is in proximity to 1 indicates a higher degree of correlations (Statistics Solutions, 2016). The correlation coefficients between CC and EE, as well as CC and EP, are modest, with values of 0.469 and 0.468, respectively. There exists a significant association (r = 0.505) between the variables EE and EP. The variable LHT has the greatest correlation coefficient of 0.385 with the variable EP, indicating a significant link. Conversely, the variable PA demonstrates the strongest association with the variable EE, with a correlation coefficient of 0.416. In general, the data indicates that there are different levels of dependency among the variables, with EE and EP revealing the strongest correlation (Table 4).
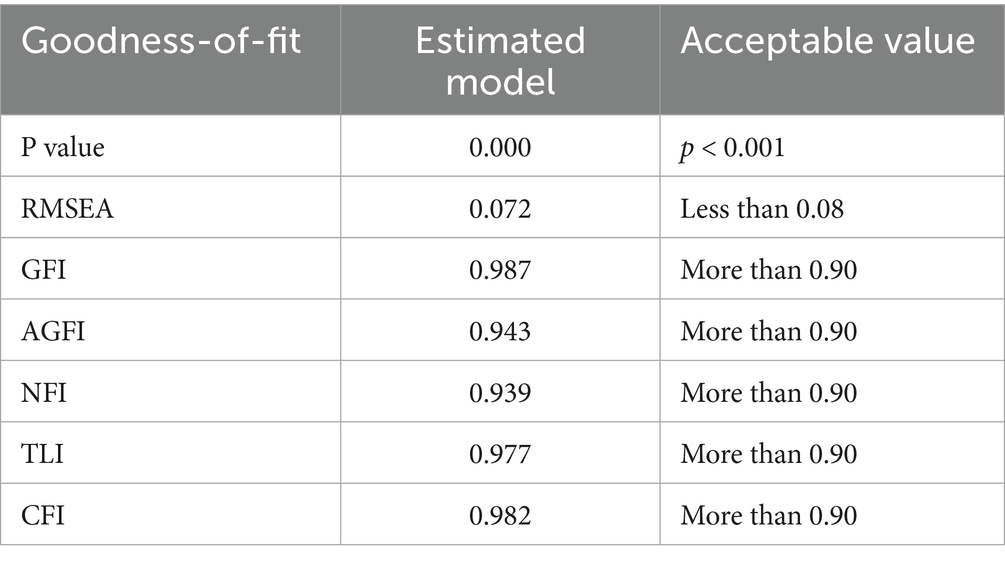
4.5 Goodness-of-fit of the model
The model has an acceptable degree of goodness-of-fit when evaluated using different indices. The p-value is congruent with the predetermined significance level (0.000), suggesting that the model adequately aligns with the observed data (Ren et al., 2023; Abraham et al., 2023). The root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) value of 0.072 falls below the commonly acknowledged criterion of 0.08, indicating a strong fit (Kudubeş et al., 2023). In addition, it is worth noting that the GFI, AGFI, NFI, TLI, and CFI values all above the threshold of 0.90, which suggests a strong correspondence between the proposed model and the empirical data (Sahoo, 2019; Bhakuni et al., 2021), it can be argued that the model has a high degree of reliability and validity in accurately capturing the fundamental data structure (Table 5).
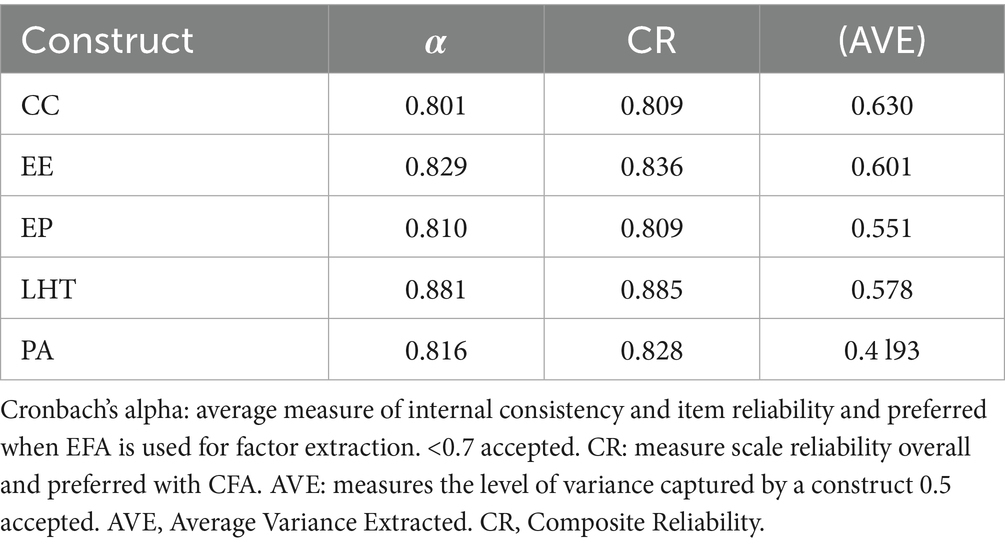
4.6 Construct reliability and validity
The data provided indicates that all constructs present a high level of reliability, shown by Cronbach’s alpha (α) and CR values beyond the suggested threshold of 0.7 (Mansour et al., 2023). This implies that all of the elements within each construct reveal a high degree of consistency in assessing their intended theoretical constructs (Clark and Watson, 1995). Nevertheless, while examining construct validity, it is seen that only the constructs CC and EE above the recommended level of 0.5 as Bedford and Speklé (2018) recommendations, indicating possible concerns about the validity of EP, LHT, and PA. Therefore, while the constructs exhibit reliability, more examination may be necessary to show strong validity for particular constructs (Figure 2; Table 6).
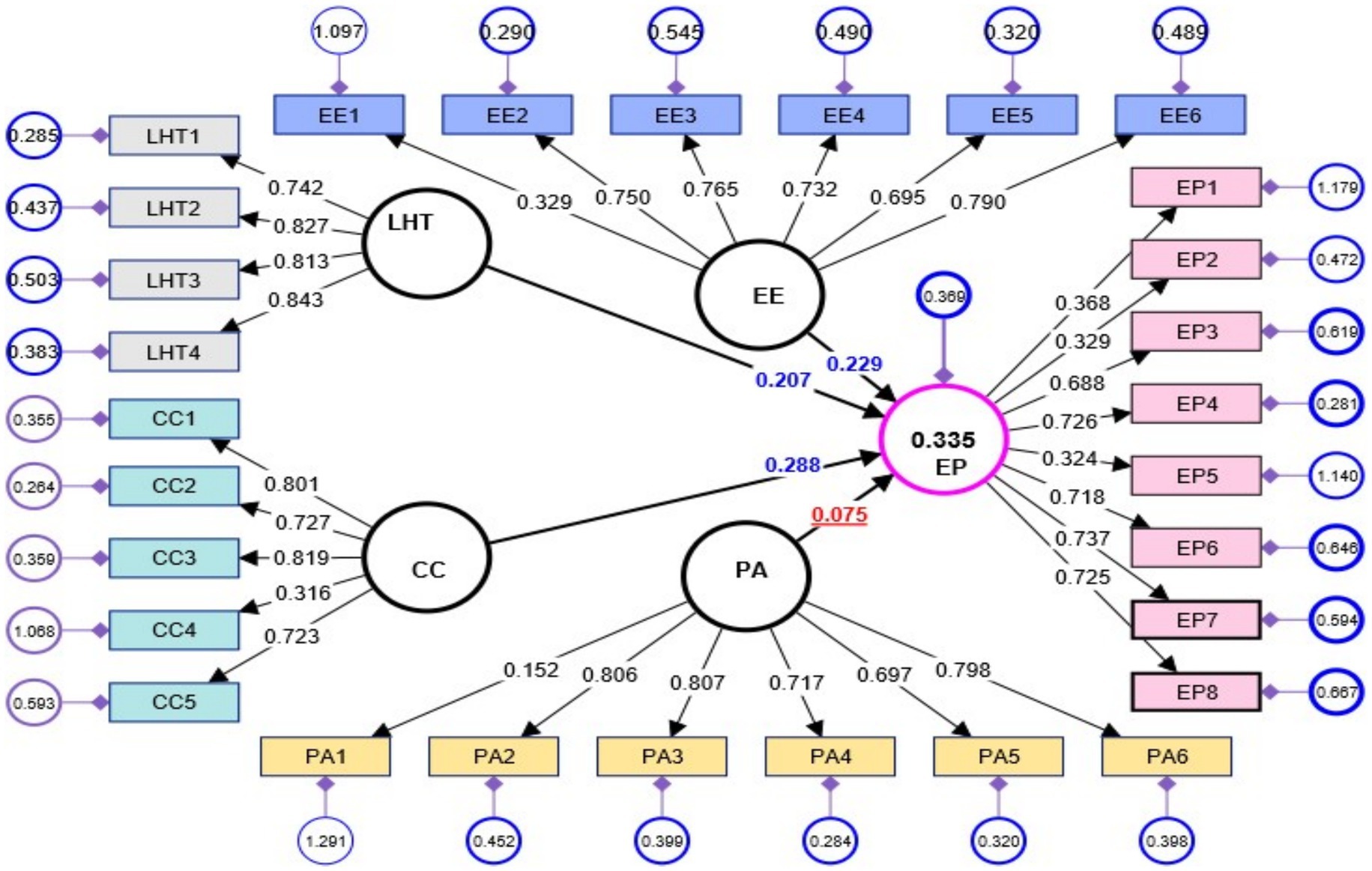
Figure 2. Assessment of measurement model. EE, Employee Efficiency; CC, Communication and Collaboration; LHT, Level of HRIS Training; PA, Performance Analysis; EP, Employee Performance.
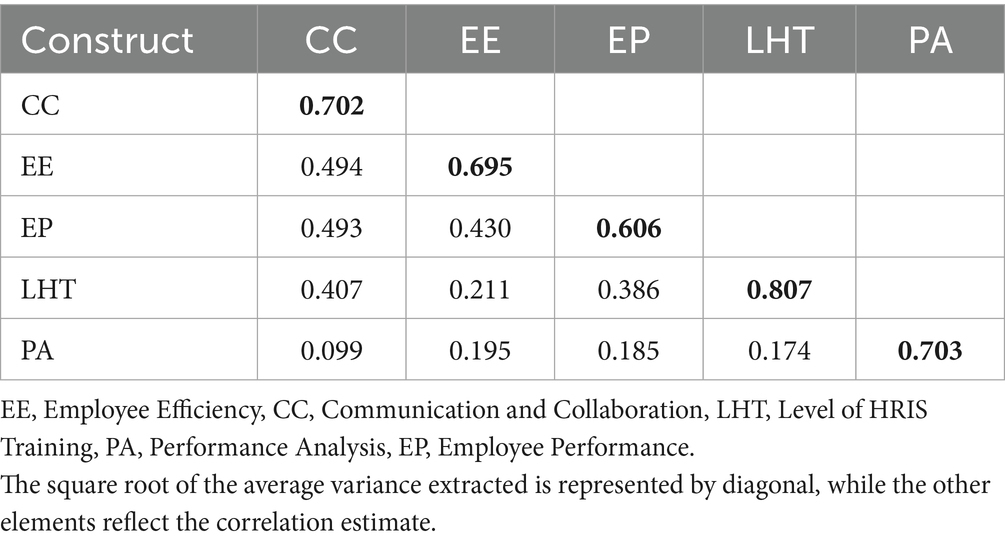
4.7 Discriminant validity
The discriminant validity of the constructs is supported by the structure of the matrix, shown by the higher values of the square root of the average variance extracted (AVE) on the diagonal (e.g., CC = 0.702, EE = 0.695) compared to the correlations between constructs (off-diagonal values). As an illustration, the correlation coefficient (CC) of 0.702 is higher than its maximum correlation with other constructions, which is 0.494 with EE. This finding provides evidence that the conceptions under consideration are separate and distinguishable from one another (Kurbi et al., 2023; Alshuhumi et al., 2025) (Table 7).
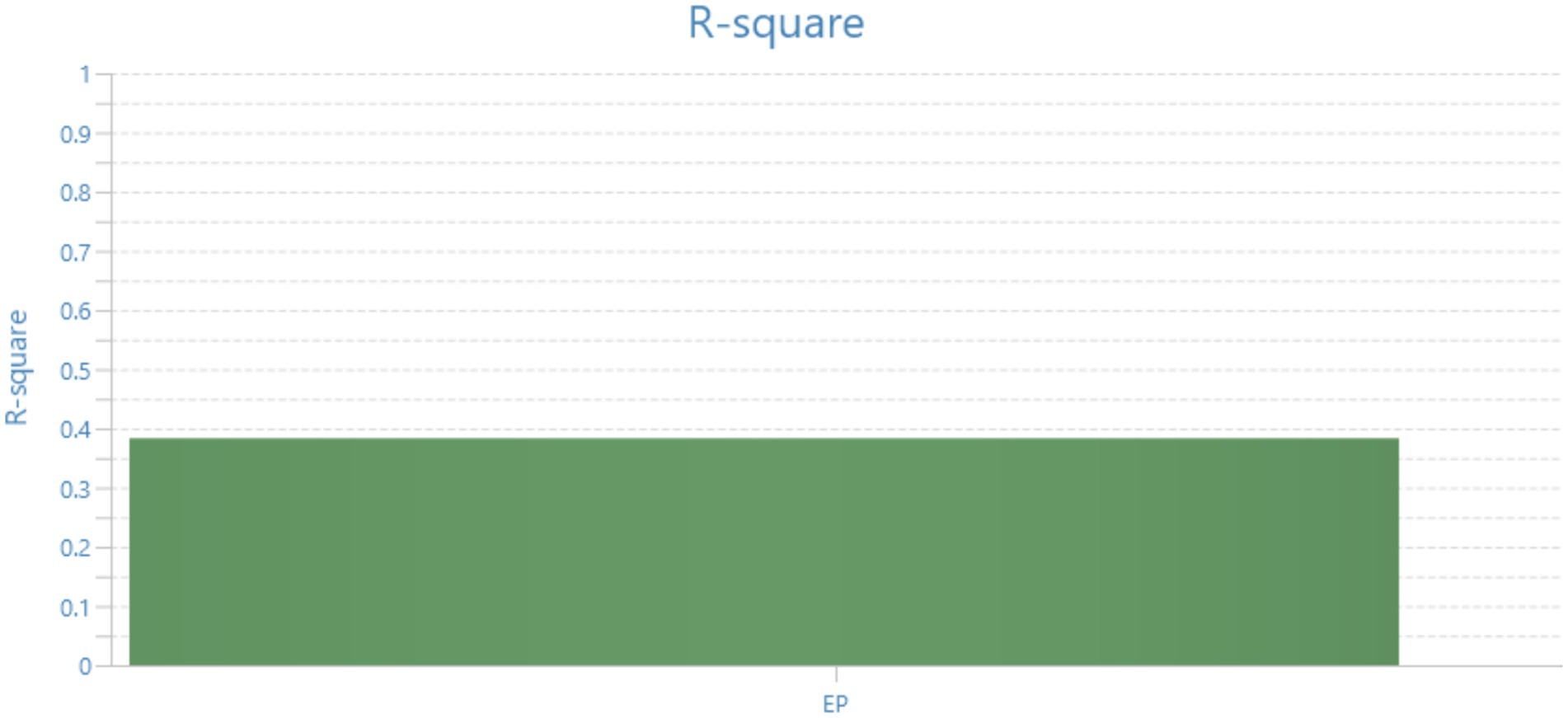
4.8 Coefficient of determination result R2
The coefficient of determination (R-square) for employee performance is 0.335, suggesting that about 33.5% of the variability in employee performance can be accounted for by the independent variables included in the model. This indicates that while a certain amount of performance variability is accounted for, a substantial 66.5% remains unaccounted for by the existing predictors. Hence, it is plausible that other variables have an influence on performance that have not been accounted for in the present model (Chen et al., 2019) (Figure 3; Table 8).
4.9 Effect size f2
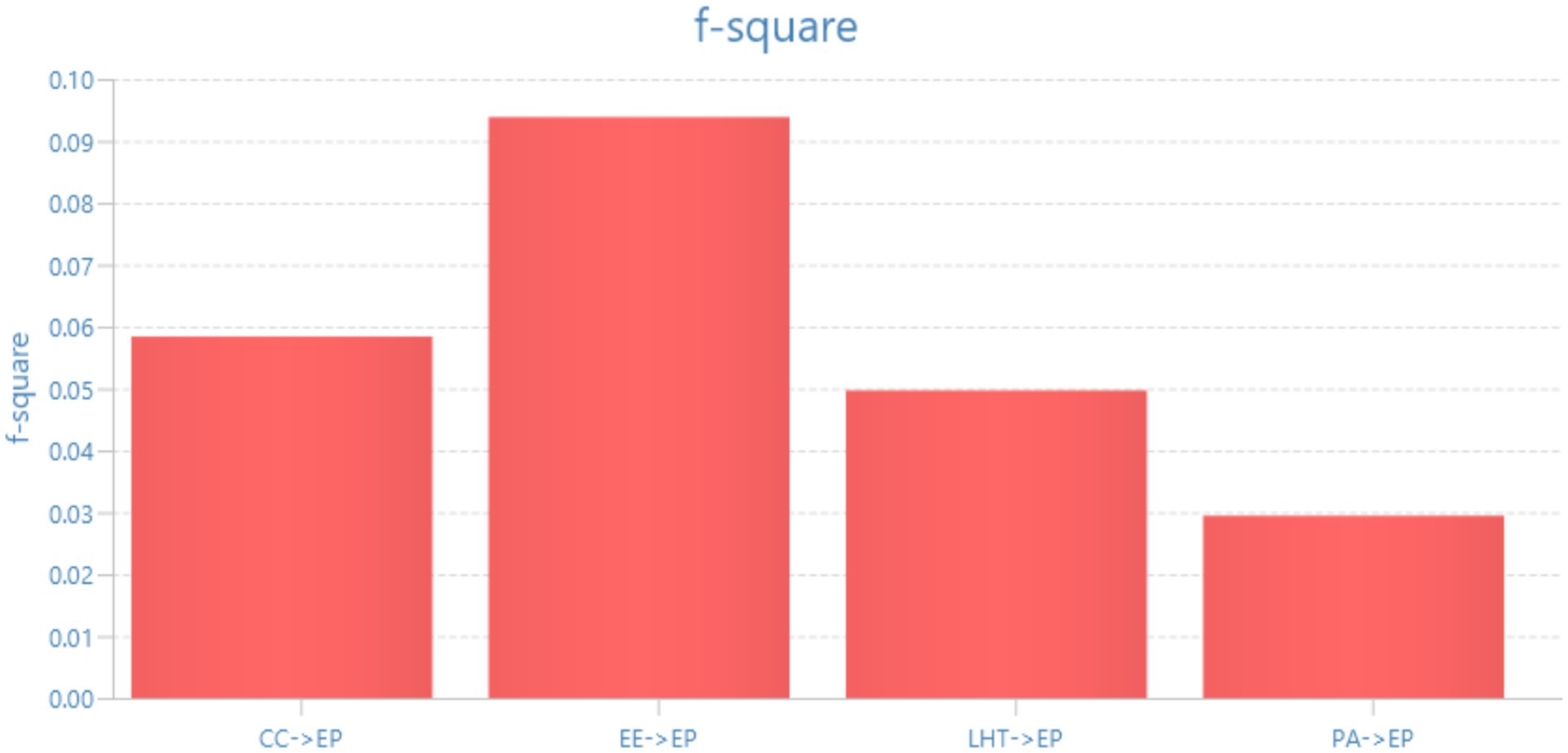
In the examination of f-square values, EE EP has the largest impact size at 0.094, suggesting that it has a larger partial contribution than other variables. CC EP and LHTEP come in second and third, with 0.058 and 0.050, respectively, while PA EP had the smallest impact at 0.029. The findings indicate that the predictors have varied degrees of importance, with EE clearly dominating (Amici et al., 2020). These magnitudes should be considered while making model refinement decisions (Figure 4; Table 9).
4.10 The assessment of the inner model and hypotheses testing procedures
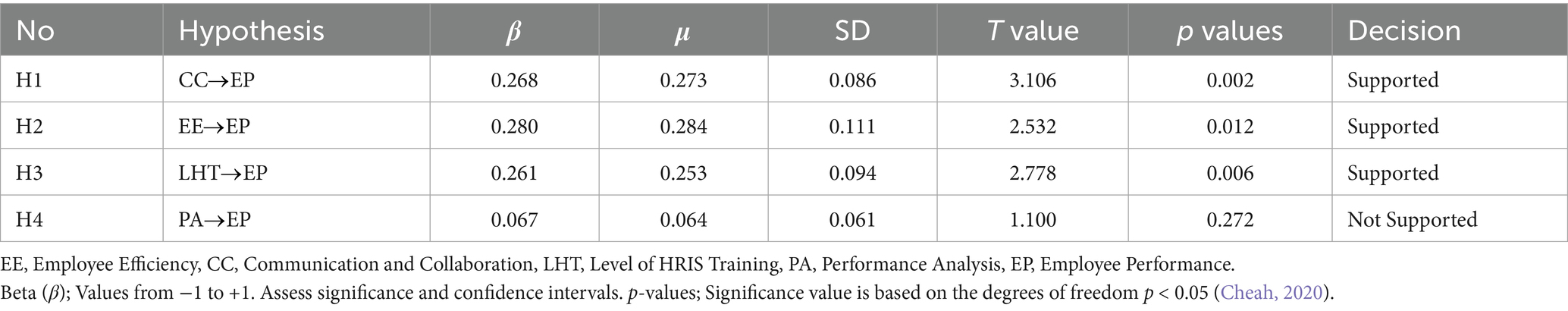
The findings of the hypothesis testing demonstrate differing degrees of endorsement for the suggested relationships. The study examined four hypotheses to investigate the influence of several variables (CC, EE, LHT, and PA) on EP.
4.10.1 Analysis of hypothesis testing results
Hypothesis 1 (CC EP): The hypothesis posits that there exists a positive relationship between CC and EP. The estimated t-value, given a β value of 0.268, a mean (μ) of 0.273, and a standard deviation of 0.086, is 3.106. The observed significance level of this finding is 0.002, which falls below the standard alpha threshold of 0.05. Consequently, substantial evidence exists to support this hypothesis.
Hypothesis 2 (EE EP): The hypothesis suggesting an advantageous impact of EE on EP is also confirmed. The value of β is 0.280, the value of μ is 0.284, and the standard deviation is 0.111. The obtained t-value of 2.532, accompanied by a p-value of 0.012, demonstrates statistical significance. However, it is important to note that this significance is somewhat lower compared to the first hypothesis, however, it remains far below the conventional threshold of 0.05.
The impact of H3 (LHT EP) is also observable, as shown by the β coefficient of 0.261, the mean (μ) of 0.253, and the standard deviation of 0.094. The obtained t-value in this analysis is 2.778, which, when combined with a p-value of 0.006, offers compelling support for the hypothesized relationship.
Hypothesis 4 (PAEP): In contrast, the quantity of evidence for a relationship between PA and EP is not equivalent. The t-value of 1.100 is obtained from the given parameters: a beta (β) of 0.067, a mean (μ) of 0.064, and a standard deviation of 0.061. The p-value associated with this association is 0.272, which is above the significance level of 0.05. This finding suggests that there is no statistically significant relationship between (PA EP). Hence, drawing on the existing evidence, it is not possible to assert with certainty that (PA) has a significant impact on (EP).
In a comparative analysis, it is evident that the first three hypotheses (namely, the effect of CC, EE, and LHT on EP) have been substantiated by compelling statistical evidence. However, the fourth hypothesis, which proposes the influence of PA on EP, lacks empirical support. It is essential to comprehend that the absence of evidence does not automatically invalidate the association between PA and EP; rather, it indicates that, within the confines of this particular dataset and the circumstances examined, the relationship is not prominent.
In conclusion, the aforementioned results emphasize the significance of CC, EE, and LHT in the context of EP, accordingly, emphasizing the need for a more comprehensive investigation into the function of PA. Decision-makers and researchers need to take into account these findings when formulating strategies or interventions, with a particular emphasis on factors that have the most significant influence (Figure 5; Table 10).
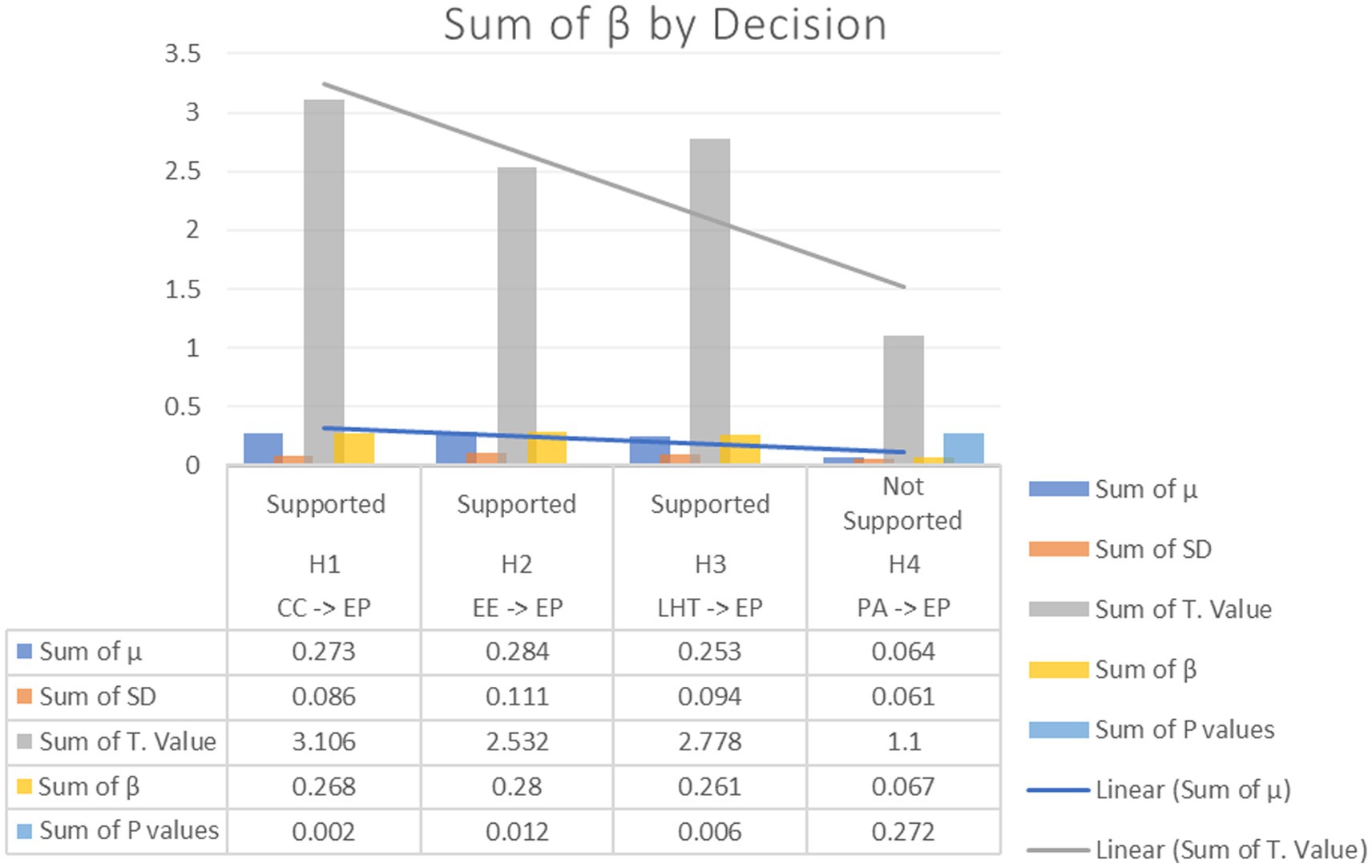
Figure 5. Mean, STDEV, T values, p values, Decision. Notice, Employee Efficiency; CC, Communication and Collaboration; LHT, Level of HRIS Training; PA, Performance Analysis; EP, Employee Performance.
5 Discussion
The previously mentioned findings provide compelling insights into the relationships between different variables and EP, shedding light on their relative efficacy and significance. It is essential to comprehend the significant difference between the statistical data substantiating the first three hypotheses and the fourth hypothesis.
The present study provides empirical evidence supporting a beneficial relationship between CC and EP as shown by a t-value of 3.106 and a p-value of 0.002. These results align with the previous research conducted by Chowdhury et al. (2022), which also revealed an advantageous relationship between CC and EP. With a beta coefficient of 0.268, it can be inferred that an increase of one value in the variable CC is associated with a corresponding rise of 0.268 values in the variable EP, while holding all other variables constant. This observation suggests that organizations that emphasize CC may have equivalent enhancements in EP. The statistical significance of this relationship is significantly above the stringent alpha level of 0.05.
Similarly, the findings of this study indicate a significant relationship between EE and EP as shown by a t-value of 2.532 and a p-value of 0.012. These results are consistent with the conclusions reached by Abdullahi et al. (2023). A correlation was shown between firms that allocated resources toward improving EE and their subsequent achievement of improved EP results. The close closeness between the mean (0.284) and the beta value (0.280) highlights the strength of the influence of EE on EP, although significantly lower than the impact of CC. The little variation seen may be ascribed to the varying significance of these characteristics across various businesses or environments, thereby necessitating more investigation.
The third hypothesis reveals a significant statistical relationship between LHT and EP, as shown by a t-value of 2.778 and a p-value of 0.006. The present observation is noteworthy as it aligns with the conclusions drawn in the research conducted by Ololade et al. (2023), which suggested that variables such as LHT may have a significant influence on EP. It is worth mentioning that there is a significant similarity between the mean value (0.253) and the beta coefficient (0.261), indicating a strong linear relationship between LHT and EP. Considering the growing global focus on strategic planning with long-term perspectives, it is reasonable to recognize the significance of this outcome.
The suggested impact of PA on EP, on the other hand, seems to be unsupported in the present study. The estimated t-value of 1.100 and the much higher p-value of 0.272 show an insignificant connection. This finding contradicts prior claims made by Charles and Ochieng (2023) who claimed that PA had a significant impact on EP. The gap in results might be related to methodological discrepancies, contextual variables, or even shifting dynamics in the market.
The inconsistency with past research suggests two possibilities: either PA’s influence on EP is indeed minor, or the present dataset and context analyzed are not suitable for exposing this relationship. As Albert Einstein famously said, “Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence.” Thus, although the present dataset’s findings do not support the impact of PA on EP, it would be unfair to dismiss its potential relevance, particularly given contradictory evidence in earlier studies.
As the current data are compared to previous research, the main disparity is in the PA and EP relationship. Inconsistencies such as these are common in empirical research and may be attributed to differing sample sizes, regional settings, industry-specific subtleties, or time-period concerns.
Based on the findings that have been addressed, it is apparent that CC, EE, and LHT play a significant role in affecting EP. However, the lack of conclusive proof about the effects of Performance Analysis necessitates a more thorough examination. It is essential for decision-makers and researchers to carefully evaluate these data, particularly when formulating strategies, interventions, or future research priorities. Most of the attention should be placed on identifying the elements that have the most significant impact, enabling informed and strategic decision-making in the realm of EP.
5.1 Limitations
The conclusions of the research are predicated upon a particular dataset, therefore potentially limiting their generalizability to other groups or circumstances. Insufficient details were provided on the sample size, possible biases, and measuring procedures, hence potentially impacting the validity and reliability of the findings. Furthermore, while the effect of PA on EP was not shown to be statistically significant in the present dataset, it is important to acknowledge that this does not exclude the possibility of its influence in other contexts or under alternative circumstances.
5.2 Recommendations
It is recommended that future research endeavors use varied datasets to enhance the generalizability of their results. The use of several analytical techniques might potentially enhance the comprehension of the function of PA’s role concerning EP. It is of utmost importance to give priority to initiatives targeting established elements, including CC, EE, and LHT, while simultaneously investigating the potential impact of public awareness of PA in particular contexts.
5.3 The implication
The findings of the research emphasize the significant impact of Communication and Collaboration (CC), Employee Engagement (EE), and Level of HRIS Training (LHT) on enhancing Employee Performance (EP). These characteristics play a crucial role in determining the success of a business. Nevertheless, the dearth of robust information pertaining to the influence of Performance Analysis (PA) necessitates more inquiry. When formulating plans, decision-makers need to give careful consideration to prioritizing CC (Communication and Collaboration), EE (Employee Efficiency), and LHT (Level of HRIS Training). It is essential to recognize that study outcomes may exhibit variability as a result of contextual influences, hence underscoring the need for methodologies adapted to individual contexts. The aforementioned insights serve as a fundamental basis for making well-informed decisions, developing strategic plans, and identifying future research avenues within the area of EP.
6 Conclusion
The hypotheses under examination provide statistical evidence that supports the existence of positive relationships between CC, EE, and LHT with EP, hence indicating their substantial effect. Nevertheless, the empirical evidence supporting the supposed relationship PA and EP is insufficient, since the observed level of significance is beyond the accepted threshold. While this does not invalidate a potential correlation PA and EP, it emphasizes that the relationship is not apparent within the dataset provided. Therefore, it is evident that CC, EE, and LHT play significant roles in the setting of EP. However, further study is required to fully comprehend the precise function and significance of PA. It is important for decision-makers to accord priority to these results when formulating strategies.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
AA: Writing – original draft, Software, Resources, Formal analysis, Project administration, Visualization, Supervision, Methodology, Validation, Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation. MA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization. MAA: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Resources, Conceptualization, Validation. NA: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Validation, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdalla, W., Renukappa, S., and Suresh, S. (2023). Managing COVID-19-related knowledge: a smart cities perspective. Knowl. Process. Manag. 30, 87–109. doi: 10.1002/kpm.1706
Abdullahi, M. S., Raman, K., Solarin, S. A., and Adeiza, A. (2023). Employee engagement as a mediating variable on the relationship between employee relation practice and employee performance in a developing economy. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 15, 83–97. doi: 10.1108/JARHE-06-2021-0222
Abdulsamad, A., Ateeq, A. A., Al-Zubaidi, R., and Al-refaei, A. A.-A. (2025). Entrepreneurial orientation and innovation capabilities as drivers of sustainable innovation performance: a conceptual framework for SMEs. Tech. Fusion Bus. Soc. 6, 845–858. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-84636-6_76
Abraham, I., Mensah, C. K. O., Howard, E. K., and Asinyo, B. K. (2023). Impact of technological capabilities, design innovation, and operations on the performance of small and medium textile enterprises in Ghana. Int. J. Sm. Med. Ent. 6, 41–55. doi: 10.46281/ijsmes.v6i1.2048
Abuhantash, A. (2023). The impact of human resource information systems on organizational performance: a systematic literature review. Eur J Bus Manag Res 8, 239–245. doi: 10.24018/ejbmr.2023.8.3.1992
Abulibdeh, A. (2022). Time series analysis of environmental quality in the state of Qatar. Energy Policy 168:113089. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113089
Alhajeri, M. (2022). Developing a digital competence framework for UAE law enforcement agencies to enhance cyber security of Critical Physical Infrastructure (CPI). United Kingdom: University of Salford.
Alshuhumi, S., Al-Hidabi, D., Aldaba, A., and Ateeq, A. A. (2025). Examining the impact of Omani primary school climate and teacher self-efficacy on innovative teaching practices: a structural equation modeling approach. Front. Educ. 10:1487857. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1487857
Amici, F., Widdig, A., MacIntosh, A. J. J., Francés, V. B., Castellano-Navarro, A., Caicoya, A. L., et al. (2020). Dominance style only partially predicts differences in neophobia and social tolerance over food in four macaque species. Sci. Rep. 10:22069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79246-6
Bandura, A. (2023). “Cultivate self-efficacy for personal and organizational effectiveness” in Principles of organizational behavior: the handbook of evidence-based management. ed. E. A. Locke (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons), 113–135.
Bedford, D. S., and Speklé, R. F. (2018). Construct validity in survey-based management accounting and control research. J. Manage. Account. Res. 30, 23–58. doi: 10.2308/jmar-51995
Bhakuni, P., Rajput, S., Sharma, B. K., and Bhakar, S. S. (2021). Relationship between brand image and store image as drivers of repurchase intention in apparel stores. Gurukul Bus. Rev. 17, 63–73. doi: 10.48205/gbr.v17.6
Bhakuni, S., and Totlani, N. (2023). The application of human resources information systems for enhancing output in agricultural companies. World J. Manag. Econ. 16, 25–42. doi: 10.18488/35.v10i4.3521
Charles, M., and Ochieng, S. B. (2023). Strategic outsourcing and firm performance: a review of literature. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Hum. Res 1, 20–29. doi: 10.61108/ijsshr.v1i1.5
Cheah, C. S. (2020). Factors contributing to the difficulties in teaching and learning of computer programming: a literature review. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 12:ep272. doi: 10.30935/cedtech/8247
Chen, J., de Hoogh, K., Gulliver, J., Hoffmann, B., Hertel, O., Ketzel, M., et al. (2019). A comparison of linear regression, regularization, and machine learning algorithms to develop Europe-wide spatial models of fine particles and nitrogen dioxide. Environ. Int. 130:104934. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.104934
Chin, W. W. (1998). The partial least squares approach for structural equation modeling. In Modern methods for business research. Ed. G. A. Marcoulides. (pp. 295–336). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Chowdhury, S., Budhwar, P., Dey, P. K., Joel-Edgar, S., and Abadie, A. (2022). AI-employee collaboration and business performance: integrating knowledge-based view, socio-technical systems and organisational socialisation framework. J. Bus. Res. 144, 31–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.01.069
Clark, L. A., and Watson, D. (1995). Constructing validity: basic issues in objective scale development. Psychological Assessment, 7, 309–319. doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.7.3.309
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers.
Devaki, K., and Leena Jenifer, L. (2022). “A study on challenges in data security during data transformation” in Computer networks, big data and IoT: proceedings of ICCBI 2021. ed. K. Devaki (Cham: Springer), 49–66.
Diawati, P., Gadzali, S. S., Abd Aziz, M. K. N., Almaududi Ausat, A. M., and Suherlan, S. (2023). The role of information technology in improving the efficiency and productivity of human resources in the workplace. J. Teknol. Sist. Inf. Bisnis 5, 296–302. doi: 10.47233/jteksis.v5i3.872
Diraco, G., Rescio, G., Siciliano, P., and Leone, A. (2023). Review on human action recognition in smart living: sensing technology, multimodality, real-time processing, interoperability, and resource-constrained processing. Sensors 23:5281. doi: 10.3390/s23115281
Ersoy, P., Börühan, G., Kumar Mangla, S., Hormazabal, J. H., Kazancoglu, Y., and Lafcı, Ç. (2022). Impact of information technology and knowledge sharing on circular food supply chains for green business growth. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 31, 1875–1904. doi: 10.1002/bse.2988
Feng, Y. (2023). The nature of the human resource development research–practice gap: text data mining and topic modeling analysis of three decades of professional and academic literature from 1990 to 2022. Minnesota: University of Minnesota.
Gwiza, A., Hlungwani, P. M., Nyagadza, B., David, V., Masaruse, G., and Massimo, C. (2022). “Developin priority-driven leadership and supervisory skills within public sector low resource settings” in Transformational human resources Management in Zimbabwe: Solutions for the public sector in the 21st century. eds. M. Chiware, B. Nkala, and I. Chirisa (Cham: Springer), 75–98.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2017). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). 2nd Edition, Sage Publications Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA.
Hoai, T. T., Hung, B. Q., and Nguyen, N. P. (2022). The impact of internal control systems on the intensity of innovation and organizational performance of public sector organizations in Vietnam: the moderating role of transformational leadership. Heliyon 8:e08954. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08954
Islam, M. T., and Tamzid, P. M. (2023) Artificial intelligence in human resource management. In Management Education for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals in the Context of Bangladesh (pp. 61–80). doi: 10.57240/DUJMBK04
Jain, R., Dhingra, S., Joshi, K., Rana, A. K., and Goyal, N. (2023). Enhance traffic flow prediction with real-time vehicle data integration. J. Auton. Intell. 6:574. doi: 10.32629/jai.v6i2.574
Kaushal, N., Kaurav, R. P. S., Sivathanu, B., and Kaushik, N. (2023). Artificial intelligence and HRM: identifying future research agenda using systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Manag. Rev. Q. 73, 455–493. doi: 10.1007/s11301-021-00249-2
Koech, R. K. (2022). Relationship between human resource information system and management of human capital at James Finlay limited, Kenya. Kenya: University of Kabianga.
Koech, R. K., Kirui, J., and Langat, L. (2022). Relationship between recruitment information system and management of human capital: a case of James Finlay limited, Kenya. East Afr. J. Bus. Econ. 5, 11–19. doi: 10.37284/eajbe.5.1.523
Kudubeş, A. A., Semerci, R., Özbay, S. Ç., Ay, A., and Boztepe, H. (2023). Development and psychometric analysis of a pediatric oncology nurses’ educational needs scale. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 70:e30285. doi: 10.1002/pbc.30285
Kurbi, H. A., Abebe, S. M., Mengistu, N. W., Ayele, T. A., and Toni, A. T. (2023). Cultural adaptation and validation of the Amharic version of the World Health Organization’s self reporting questionnaire (SRQ-20) screening tool among pregnant women in north West Ethiopia, 2022: a psychometric validation. Int. J. Women's Health 15, 779–791. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S402865
Ling, M., and Verma, S. (2023). Enhancing cleaning operations with JSP and servlet-based management systems. Tensorgate J. Sustain. Technol. Infras. Dev. Ctries 6, 47–63.
Madid, H. R. (2023). Application of data analytics in the human resources information system in selected companies in metro Manila. Int. J. Mod. Dev. Eng. Sci. 2, 37–54. Available online at: https://journal.ijmdes.com/ijmdes/article/view/160
Magege, T. J., and Ngirwa, C. C. (2023). Effectiveness of human resources information system (HRIS) on organisational performance in the banking sector. International Journal of Business Management and Economic Review. 6, 39–52. doi: 10.35409/IJBMER.2023.3458
Mansour, M., Alaghbari, M. A., Beshr, B., and Al-Ghazali, B. M. (2023). Perceived CSR on career satisfaction: A moderated mediation model of cultural orientation (collectivism and masculinity) and organisational pride. Sustainability 15:5288. doi: 10.3390/su15065288
McCartney, S., and Fu, N. (2024). Enacting people analytics: Exploring the direct and complementary effects of analytical and storytelling skills. Human Resource Management, 63, 187–205. doi: 10.1002/hrm.22194
McLean, L. (2023). Developing expertise & expert teams for high performance: utilizing the expert-to-expert practice framework. Arizona: Arizona State University.
Mideksa, M. (2023). An assessment on the practices and challenges of human resource information system (HRIS) in commericl bank ethiopia. San Antonio, TX: St. Mary’s University.
Mohsan, S. A. H., Othman, N. Q. H., Li, Y., Alsharif, M. H., and Khan, M. A. (2023). Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs): practical aspects, applications, open challenges, security issues, and future trends. Intell. Serv. Robot. 16, 109–137. doi: 10.1007/s11370-022-00452-4
Ololade, A. J., Jadesola Ololade, A., Odunayo Paul, S., Tolulope Morenike, A., and Augustina Esitse, D. (2023). Bolstering the role of human resource information system on employees’ behavioural outcomes of selected manufacturing firms in Nigeria. Heliyon 9:12785. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12785
Qamari, I. N., and Rakotoarizaka, N. L. P. (2022). Impact of electronic human resource management toward excellent service–a bibliometric review. Expert J. Bus. Manag. 10:256.
Ren, L., Qu, G., Liu, G., Zhang, Y., Zhan, M., and Lau, S.-K. (2023). The perceptual variation of artificial light environment among college students due to the group defect of retinal light sensitivity. Energ. Buildings 294:113285. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2023.113285
Sahoo, M. (2019). “Structural equation modeling: threshold criteria for assessing model fit” in Methodological issues in management research: Advances, challenges, and the way ahead. eds. R. N. Subudhi and S. Mishra (Leeds: Emerald Publishing Limited), 269–276.
Saputra, N., Putera, R. E., and Zetra, A. (2024). Capacity building for organizational performance: a systematic review, conceptual framework, and future research directions. Cogent Bus Manag 11:2434966. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2024.2434966
Sikandar, H., Abbas, A. F., Khan, N., and Qureshi, M. I. (2022). Digital technologies in healthcare: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 18, 34–48. doi: 10.3991/ijoe.v18i08.31961
Štaffenová, N., and Kucharčíková, A. (2023). Digitalization in the human capital management. Systems 11:337. doi: 10.3390/systems11070337
Tejedo-Romero, F., Araujo, J. F. F. E., Tejada, Á., and Ramírez, Y. (2022). E-government mechanisms to enhance the participation of citizens and society: exploratory analysis through the dimension of municipalities. Technol. Soc. 70:101978. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101978
Testa, D. S., and Karpova, E. E. (2022). Executive decision-making in fashion retail: a phenomenological exploration of resources and strategies. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. 26, 700–716. doi: 10.1108/JFMM-08-2020-0169
Venkatesh, K., Mohanasundaram, K., and Pothyachi, V. (2023). “Regression tasks for machine learning” in Statistical modeling in machine learning. eds. T. Goswami and G. R. Sinha (Netherlands: Elsevier), 133–157.
Waqar, A., Qureshi, A. H., Othman, I., Saad, N., and Azab, M. (2023). Exploration of challenges to deployment of blockchain in small construction projects. Ain Shams Eng. J. 15:102362. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2023.102362
Keywords: employee performance, communication and collaboration, employee efficiency, level of training, performance analysis, statistically significant, Ministry of Communications and Transportation, Bahrain
Citation: Ateeq A, Alfiras M, Alaghbari MA and Almuraqab NAS (2025) The influence of human resource information systems on employee performance within the Ministry of Communications and Transportation in the Kingdom of Bahrain. Front. Commun. 10:1644487. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1644487
Edited by:
Khadija Al-Omran, Bahrain Polytechnic, BahrainReviewed by:
Roni Ekha Putera, Andalas University, IndonesiaMochamad Rizal Yulianto, Universitas Muhammadiyah Sidoarjo, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Ateeq, Alfiras, Alaghbari and Almuraqab. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ali Ateeq, ZHIuYWxpLmF0ZWVxQGd1bGZ1bml2ZXJzaXR5LmVkdS5iaA==
 Ali Ateeq
Ali Ateeq Mohanad Alfiras2
Mohanad Alfiras2 Mohammed Abdulrazzaq Alaghbari
Mohammed Abdulrazzaq Alaghbari Nasser A. Saif Almuraqab
Nasser A. Saif Almuraqab