- 1The School of Humanities, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- 2Faculty of Applied Sciences, Macao Polytechnic University, Macao, Macao SAR, China
Background: In an era of rapid media technology and AI advancement, deep learning (DL)-driven visual images (VI) is emerging as a critical mode of cultural transmission (CT). Despite the growing application of DL in the VI domain, there is a lack of a systematic review that comprehensively explores its transmission pathways, mechanisms of influence, and associated challenges. This study aims to systematically explore the pathways and impacts of DL-driven VI in CT and identify key trends and issues in the field through a systematic scoping review of existing literature.
Methods: This review analyzes 18 studies published between 2015 and 2024. The literature search was conducted across five databases: WOS, ScienceDirect, Scopus, ACM, and A&HCI. The research was undertaken rigorously following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines, ensuring systematic selection, extraction, and analysis of the identified studies.
Results: The study analyzed the literature from four aspects: transmission pathways, content, technology, and cultural context, identifying three main research areas: (1) the influence mechanisms of AI and social media on cultural transmission; (2) the role of VI in cross-cultural communication; and (3) the application of AI and digital technology in the conservation of Cultural Ecosystem Services (CES). The study finds that AI-driven visual technologies significantly enhance the breadth and impact of CT, particularly through DL algorithms. However, the field faces critical challenges such as algorithmic bias, cultural homogenization, and the reliability of user-generated content.
Conclusion: By systematically synthesizing the existing literature, this study provides a theoretical foundation for future research and points to emerging research directions, such as how to use DL to address ethical challenges in cultural communication and explore the differences in the application of DL and VI in different cultural contexts.
1 Introduction
Human behavior, shaped by preferences, beliefs, and norms, is partly a result of genetic evolution and partly acquired through generations via learning and other forms of social interaction (Panchanathan, 2024). This transmission occurs through both inter-generational and inter-generational social interactions and is referred to as CT (Bisin and Verdier, 2025). CT is a unique human behavior, central to which is the high-fidelity replication of cultural traits (Crema et al., 2024), accurately copying elements, values, and customs so that each generation can build upon the knowledge and practices of the previous one (Hewlett et al., 2024). This process distinguishes human culture from that of non-human primates and is a key mechanism in fostering intercultural understanding, respect, and global diversity (Legare, 2017). While traditional CT media such as language, writing, and rituals have deep historical roots, they are prone to information loss during cross-temporal and cross-spatial transmission, resulting in discontinuities in CT (Della Lena and Panebianco, 2021; Schönpflug, 2008).
Against this backdrop, VI has increasingly become a vital mode of CT. As one of the primary channels for CT, imagery has a long history (Eerkens and Lipo, 2007). From prehistoric cave paintings to medieval religious art, and from modern photography to digital media, the patterns and impacts of image dissemination have evolved alongside technological advancements (Homer, 1998; Robb, 2020). Early images were primarily used to record societal values and religious beliefs, while modern VI focuses on the immediacy and diversity of visuals, effectively conveying different cultural lifestyles, societal values, and aesthetic ideals (Heise, 2004; Mirzoeff, 1999). With the rapid development of globalization and digital technologies, the widespread use of visual media has greatly enhanced the efficiency of CT and facilitated emotional resonance between individuals, especially in cross-cultural communication, where the influence of VI now surpasses that of traditional textual communication (Fahmy et al., 2014).
Compared to textual dissemination, VI’s intuitive nature breaks down language barriers, extending the reach and scope of cultural transmission (Soreanu and German, 2022). The dissemination of urban imagery and landscapes utilizes VI to vividly depict the historical and cultural evolution of cities, making it an effective CT tool for showcasing unique cultural characteristics and historical heritage (Bai, 2023; Huang and Yang, 2016). While VI demonstrates significant advantages across various CT domains, its limitations are equally evident. Due to its intuitive and emotionally resonant nature, VI is regarded by scholars as an effective tool for fostering intercultural understanding (Mirzoeff, 1999). Despite these challenges, AI technology presents new opportunities to enhance the application of VI in CT. By combining AI, VI has significantly accelerated the global flow of CT (Somaini, 2023). Moreover, integrating AI and digital technologies offers innovative solutions for preserving and reconstructing cultural heritage, such as image restoration driven by DL and the digital reconstruction of virtual cultural sites (Basu et al., 2023). The advances in AI technology, especially DL, provide innovative solutions to these challenges with their powerful image processing and generation capabilities, playing a core role in the cultural transmission of visual imagery (Li and Wang, 2022; Somaini, 2023). DL plays a core role in the CT of VI through its powerful image processing and generation capabilities. This study primarily focuses on DL algorithms such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) (Xia et al., 2025), Large Language Models (LLMs) (Luo et al., 2025), and Natural Language Processing (NLP) (Jiang et al., 2023). However, despite its breakthroughs, AI’s limitations in generating and disseminating VI remain substantial, particularly regarding dataset representativeness and the simplicity of algorithmic designs, which could introduce biases in the CT process (Laba, 2024; Shahbazi et al., 2023).
Current reviews on CT, especially those focusing on VI, still exhibit certain limitations in scope and methodological frameworks (see Appendix A). First, these studies have not sufficiently addressed the complexity and diversity of CT mechanisms, often focusing on a single perspective or partial analysis. For example, the study by Wang et al. focuses solely on gamification in cultural heritage, without considering the broader applications of VI (Wang et al., 2024). Similarly, Romanazzi et al. limit their analysis to economic evaluation methods based on a single database (Romanazzi et al., 2023). Research by Plieninger et al. and Scholte et al. lacks a systematic review and focuses solely on ecological service systems (Plieninger et al., 2015; Scholte et al., 2015), while Hegetschweiler et al. concentrate only on the European context (Hegetschweiler et al., 2017).
In the context of the AI era, exploring pathways and methods for VI in CT can promote the effective dissemination and preservation of cultural heritage across regions. The specific research questions are as follows:
1. What are the scientific outcomes and geographical distributions of studies related to VI in CT (e.g., country distribution, publication years)?
2. Which DL has been used?
3. What are the CT themes and VI processing methods?
4. What platforms and dissemination paths can be used for VI-based CT?
5. What are the impacts of different forms of VI processing on CT?
This study systematically explores the pathways and impacts of VI in CT, examining its potential for CT. By comprehensively addressing these topics, this research contributes to understanding how VI affects CT and identifying key trends and issues in the field of VI research in CT.
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy
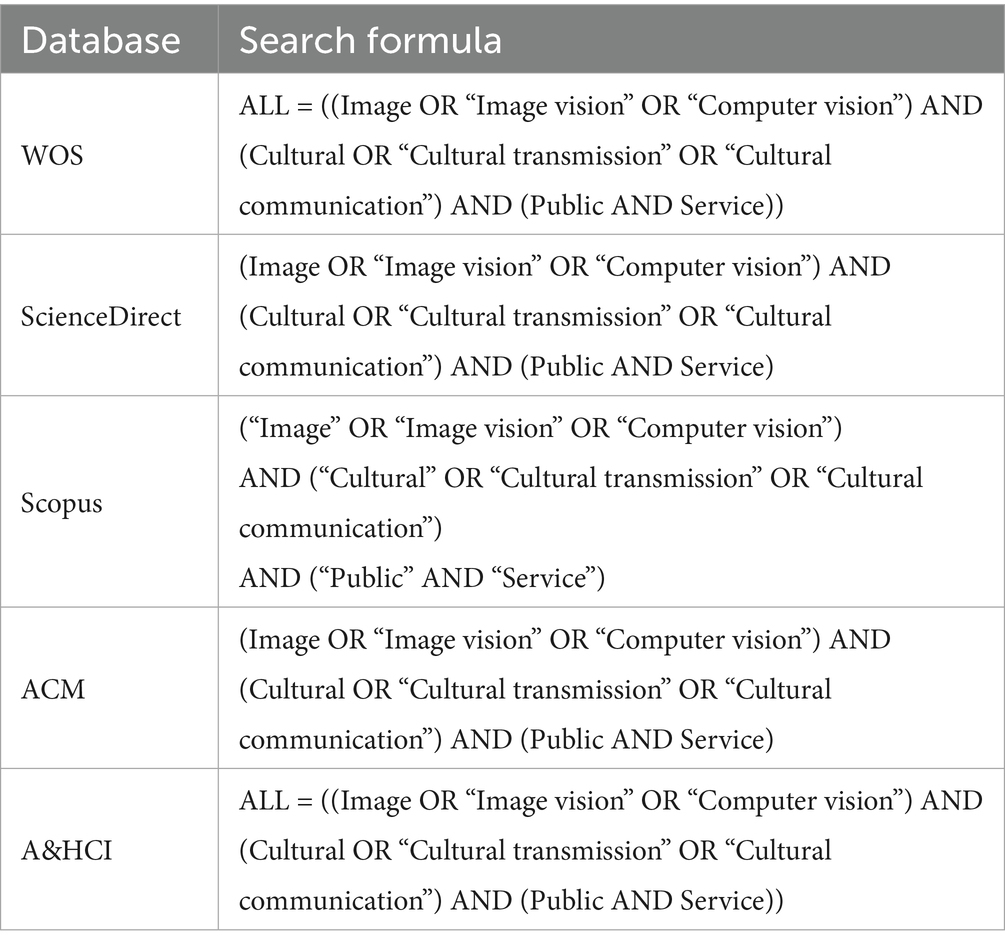
This study employs the PRISMA method for conducting a systematic scoping review, aiming to enhance the transparency and reproducibility of the literature screening process. The literature searches spans five databases: Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Scopus, ACM Digital Library, and A&HCI. The PRISMA approach ensures the structural rigor of the research process while increasing the transparency and consistency of the review process. This systematic scoping review adheres to the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR).
The literature search was conducted on November 20, 2024, using search terms including “image,” “image vision,” “computer vision,” “cultural,” “cultural transmission,” “cultural communication,” “public,” and “service.” The search strategy included the following steps: (1) a preliminary screening in all databases to exclude irrelevant studies; (2) removal of duplicate references using EndNote 21.4 software; (3) detailed screening of titles and abstracts to identify studies relevant to the research topic; and (4) full-text review to exclude studies that were not directly related to the research topic. The specific search formula is shown in Table 1 (The PRISMA-ScR checklist is provided in Appendix B).
2.2 Data selection and extraction
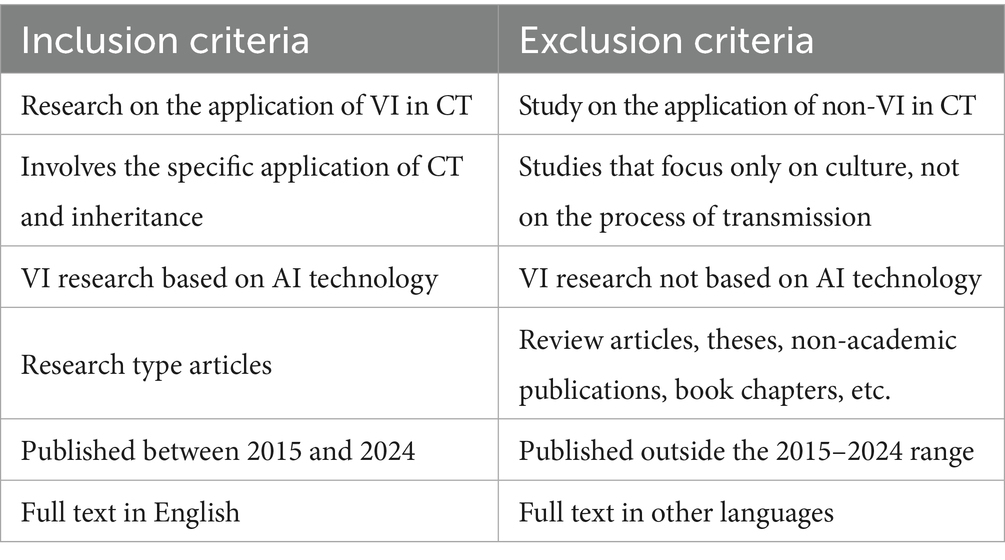
All retrieved records were imported into the reference management software EndNote version 21.5, and duplicate entries were removed using the software. Two independent reviewers (JY and TL) screened the titles and abstracts of the articles based on predefined inclusion criteria. In cases of discrepancies between the reviewers, a third reviewer (PP) was consulted to reach a consensus. The inclusion criteria (see Table 2) for selecting studies were as follows: (1) research involving the application of VI in CT; (2) involves the specific application of CT and inheritance; (3) VI studies based on AI technology; (4) studies presenting original research; (5) published between 2015 and 2024; (6) full text in English.
2.3 Data charting
A data extraction form was developed based on the scoping review methodology guidelines provided by the Joanna Briggs Institute. After conducting a preliminary trial with five articles, the form was revised to enhance its effectiveness and accuracy. The form includes the following key data extraction items: author, publication year, country, AI technology, topic, VI type, target group, dissemination platform, dissemination path, and findings. Data extraction was performed by two independent reviewers, and any discrepancies were resolved through consultation with a senior reviewer to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the extracted data.
2.4 Collating, summarizing, and reporting the results
During this process, all three authors concurred on narrowing the scope of categories to ensure that they specifically address the research questions of this study. Descriptive statistics were employed to systematically organize, summarize, and report the results. The findings were presented in a narrative format, complemented by figures and tables to enhance clarity.
3 Results
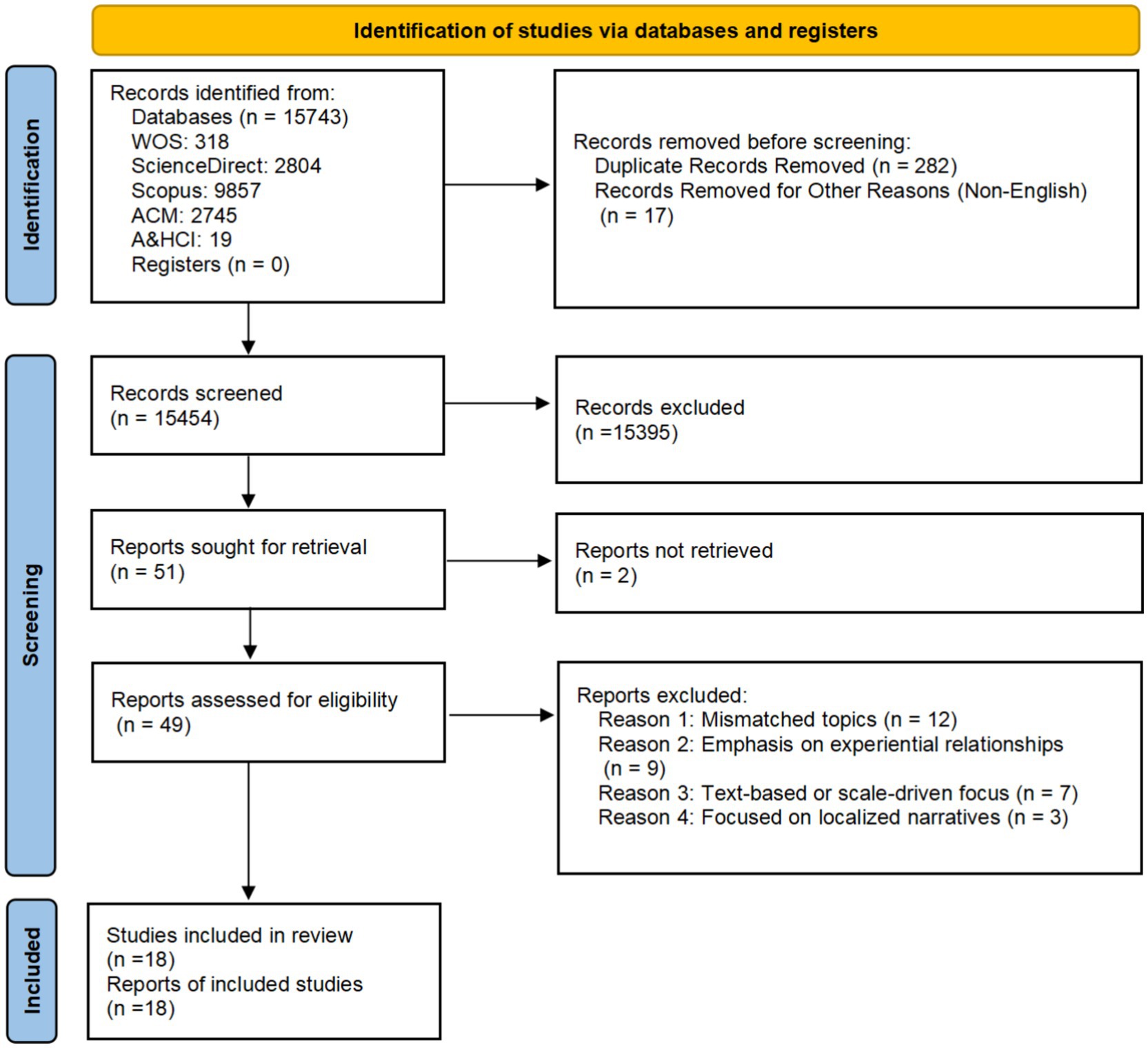
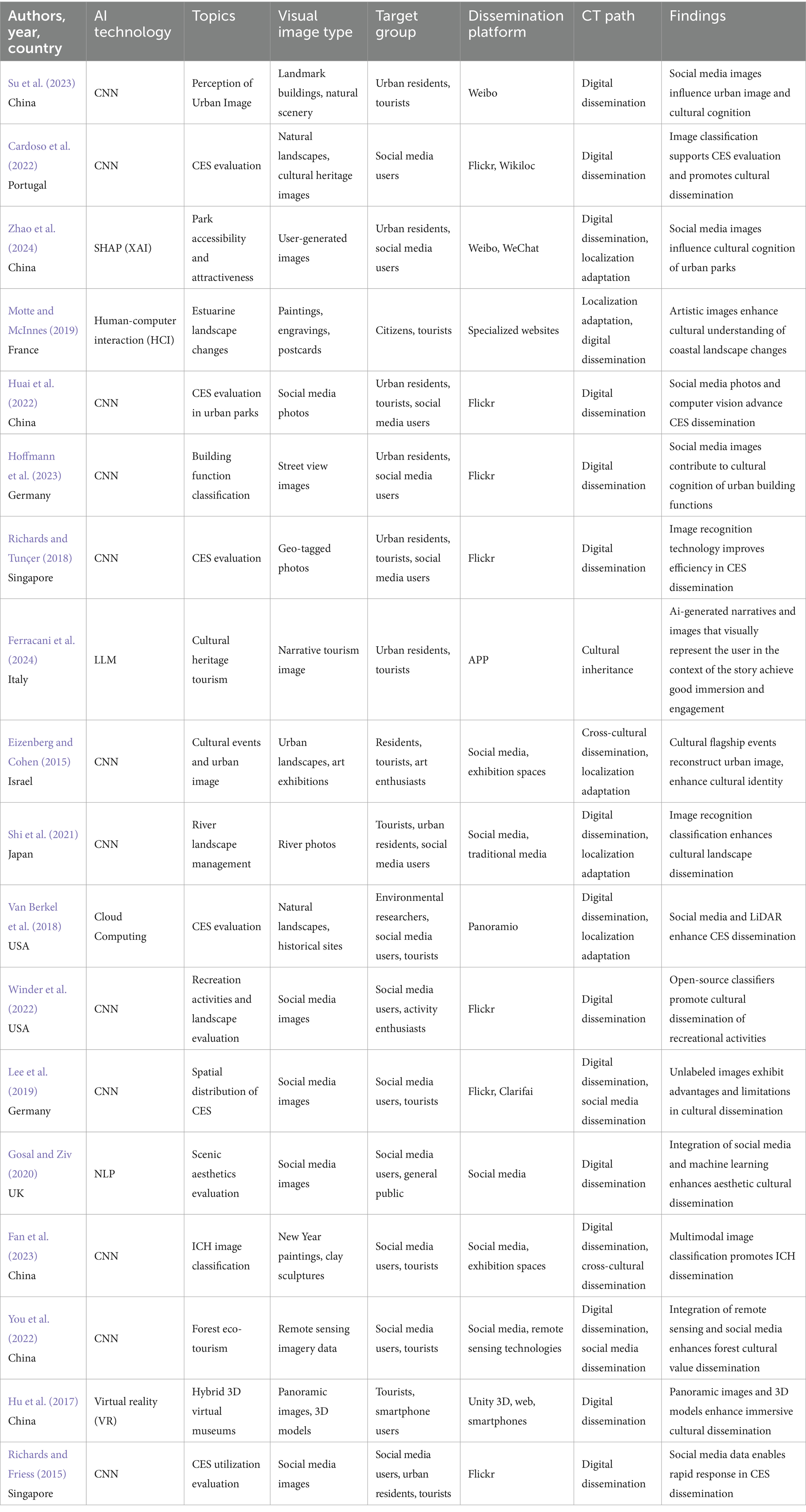
As illustrated in Figure 1, a total of 15,743 articles were retrieved through the systematic search. After removing duplicate entries using EndNote software, 15,461 articles remained. Two reviewers independently screened the titles and abstracts, excluding 15,395 articles that were not directly related to the research topic and 17 non-English articles. Studies focusing on image usage in advertising and marketing, corporate image construction, and body image perception were excluded due to their lack of direct relevance to the CT theme. Additionally, excluded studies primarily emphasized the functionality of images in business, education, or health promotion rather than the specific analysis or application of CT. The remaining 49 articles underwent a thorough evaluation by both reviewers, resulting in the exclusion of 30 articles. Ultimately, 18 articles were included in the scope evaluation of the system (see Table 3).
3.1 Publication characteristics of studies
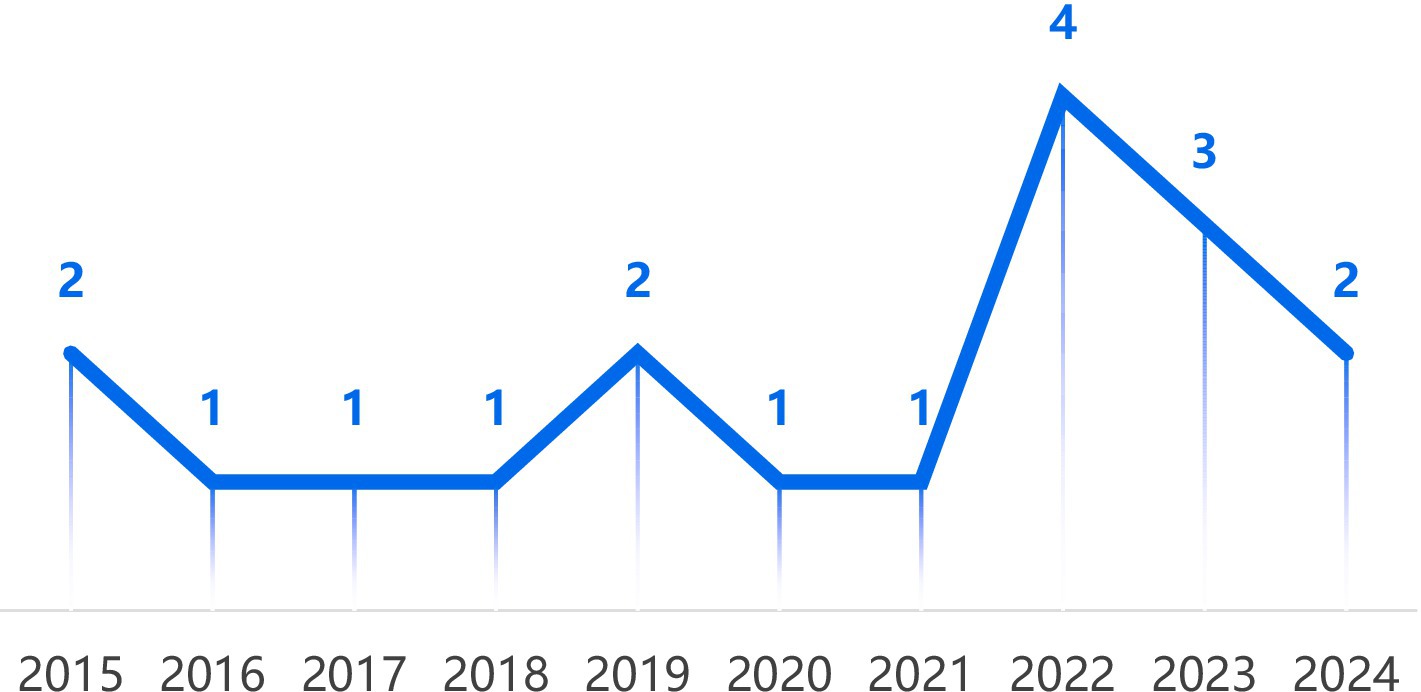
Figure 2 illustrates the annual evolution trend of the included literature. The time series indicates that relevant research began in 2015, gradually developing thereafter, and reaching a peak in 2022 with a total of four studies published. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the closure of cultural institutions and the global shift to online spaces prompted a transition of cultural content toward virtual engagement. This increased the need to explore the role of digital and virtual media in CT, which may explain the rise in publications in 2022 and the following year (Li et al., 2022).
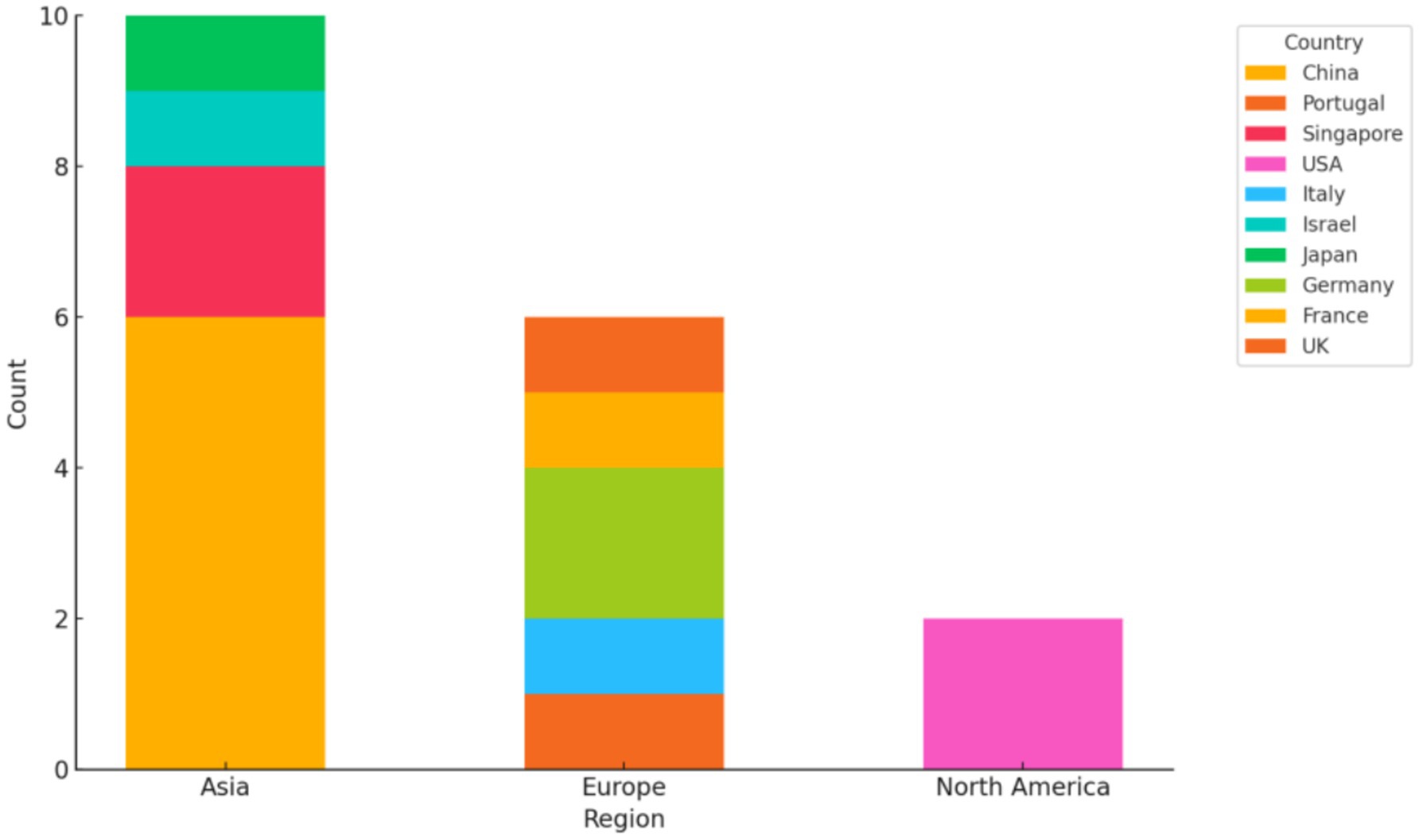
Regarding the geographical distribution of the research, Figure 3 displays the number of contributions by country and region. China published six papers, accounting for 33.3% of the total, temporarily leading the field. China has 56 cultural and natural heritage sites listed on the UNESCO World Heritage List, ranking second globally. This leadership is likely closely related to the rapid development of China’s digital cultural industry in recent years and government support for visual culture research. At the regional level, Asia dominates with ten articles, representing 55.6%, followed by Europe with six articles (33.3%), and North America with two articles (11.1%).
3.2 AI technology
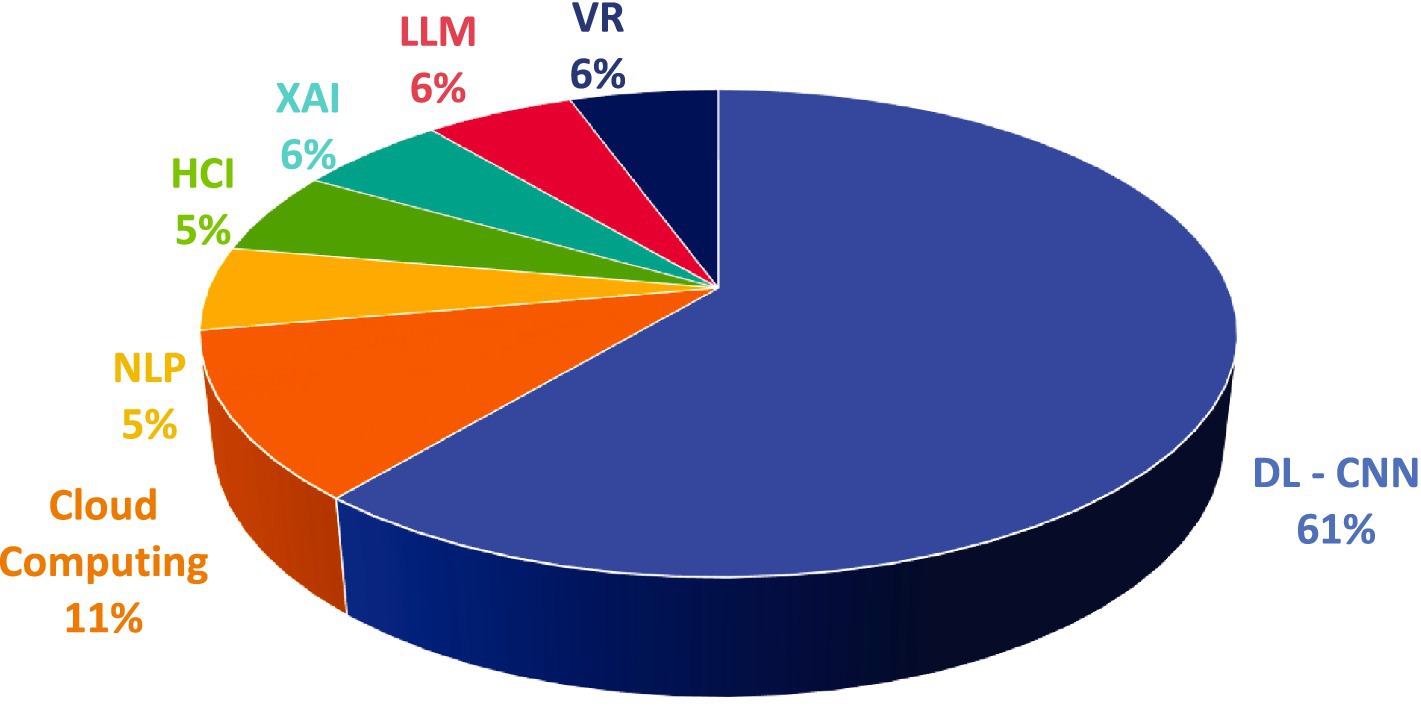
In the included studies, the majority employed DL algorithms for AI-based VI processing in CT applications, particularly CNN. 11 studies utilized CNN to process and generate image data. CNN has significant advantages in handling image data, enabling tasks such as image classification and detection. Secondly, cloud computing was used for data processing in two studies. Image processing often involves textual data; for example, input text data can be transformed into VI through generative AI, thereby involving LLM and NLP. However, HCI and XAI were less frequently employed in the research (see Figure 4).
3.3 Research topics
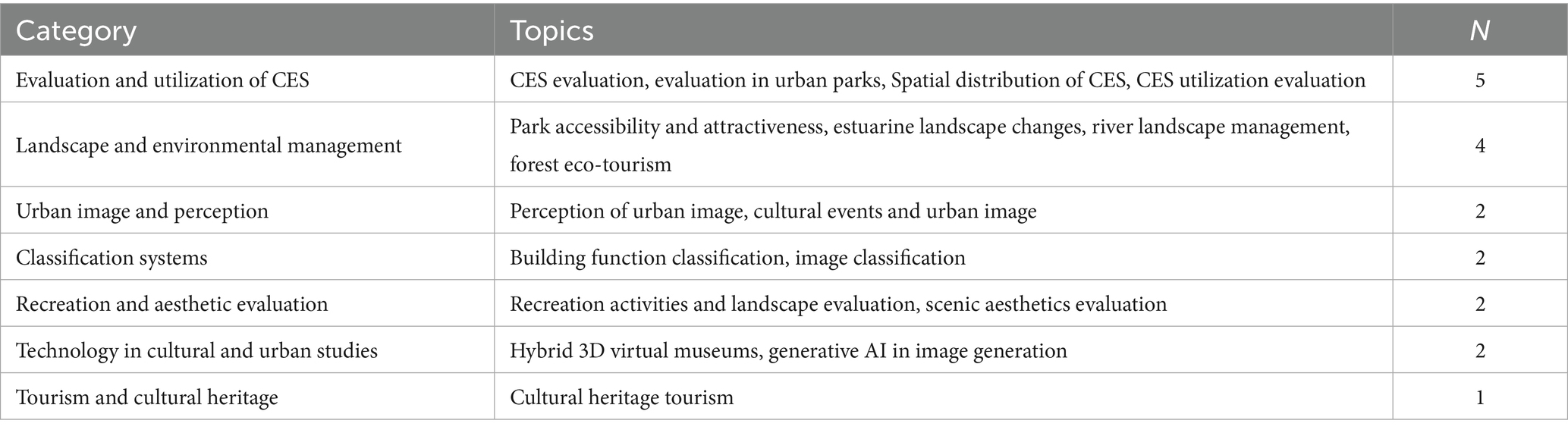
The thematic classification identified 18 topics across seven major categories. CES evaluation and utilization was the most prominent, encompassing five topics, highlighting researchers’ focus on assessing and applying CES in various contexts, essential for urban planning and environmental management. Landscape & environmental management, as well as urban image & perception, included four and two topics, respectively, emphasizing the role of landscape management and urban image in enhancing sustainability and residents’ quality of life. Classification systems and recreation & aesthetic evaluation each comprised two topics, indicating the need for specific classification methodologies and aesthetic value assessments. Cultural heritage and technology in urban Studies featured one and two topics, respectively. This reflects the increasing recognition of cultural heritage tourism and emerging technologies, such as hybrid 3D virtual museums and generative AI, in enriching cultural experiences and research. Overall, the distribution of topics underscores current academic interests in CES, landscape management, and technological applications (see Table 4).
3.4 Target group
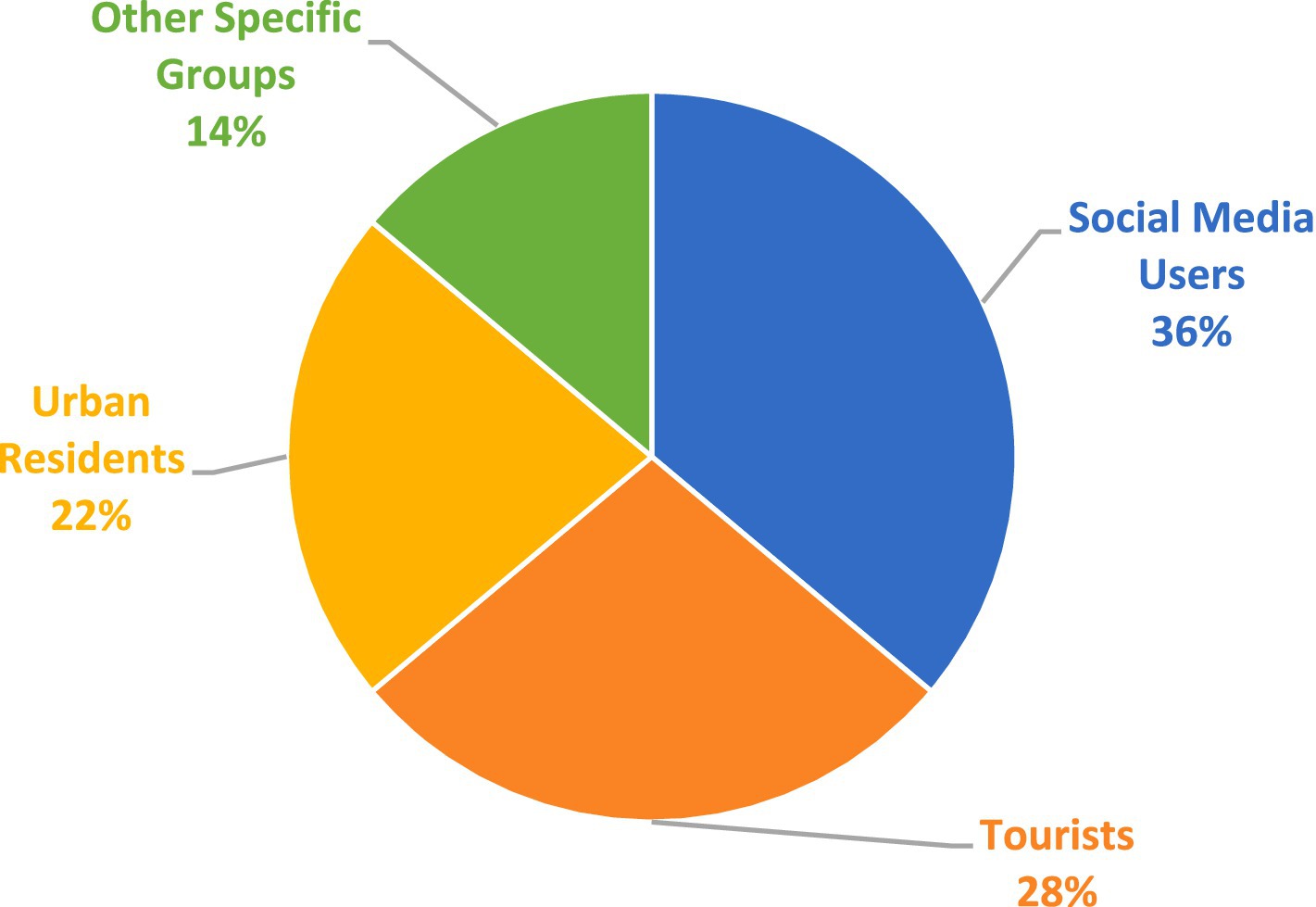
The analysis reveals that social media users (36%), tourists (28%), and urban residents (22%) are the primary target groups across the studies. The frequent combination of these groups highlights the importance of social media in urban and tourism research, as well as the need to understand the dynamics between local residents and visitors. Additionally, the inclusion of niche groups points to diverse research interests that can be further explored to enrich the understanding of cultural and urban ecosystems (see Figure 5).
3.5 Dissemination platforms
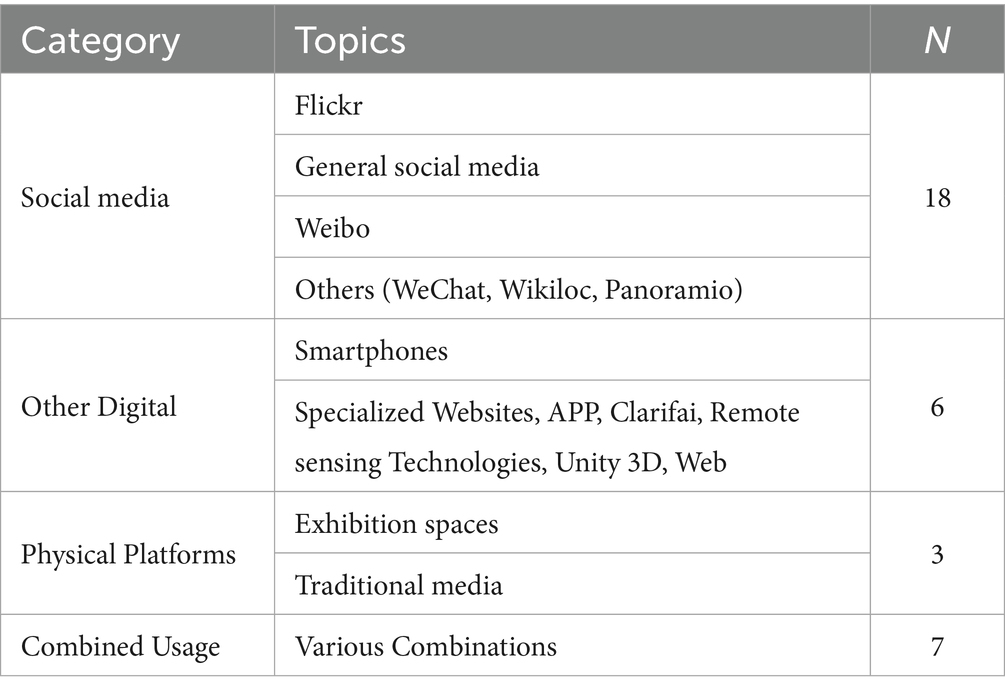
The analysis reveals that Flickr and social media are the predominant dissemination platforms, with usage frequencies of 41 and 35%, respectively. This emphasizes the importance of visual content and social interactions in information dissemination. The strategic combination of multiple platforms underscores the need to reach a broader and more varied audience. While emerging technologies are currently underutilized, their potential for enhancing dissemination strategies is evident, presenting opportunities for future research and application. The integration of physical and digital dissemination methods also highlights the evolving landscape of information sharing, aiming for more comprehensive and effective communication (see Table 5).
3.6 The path of CT
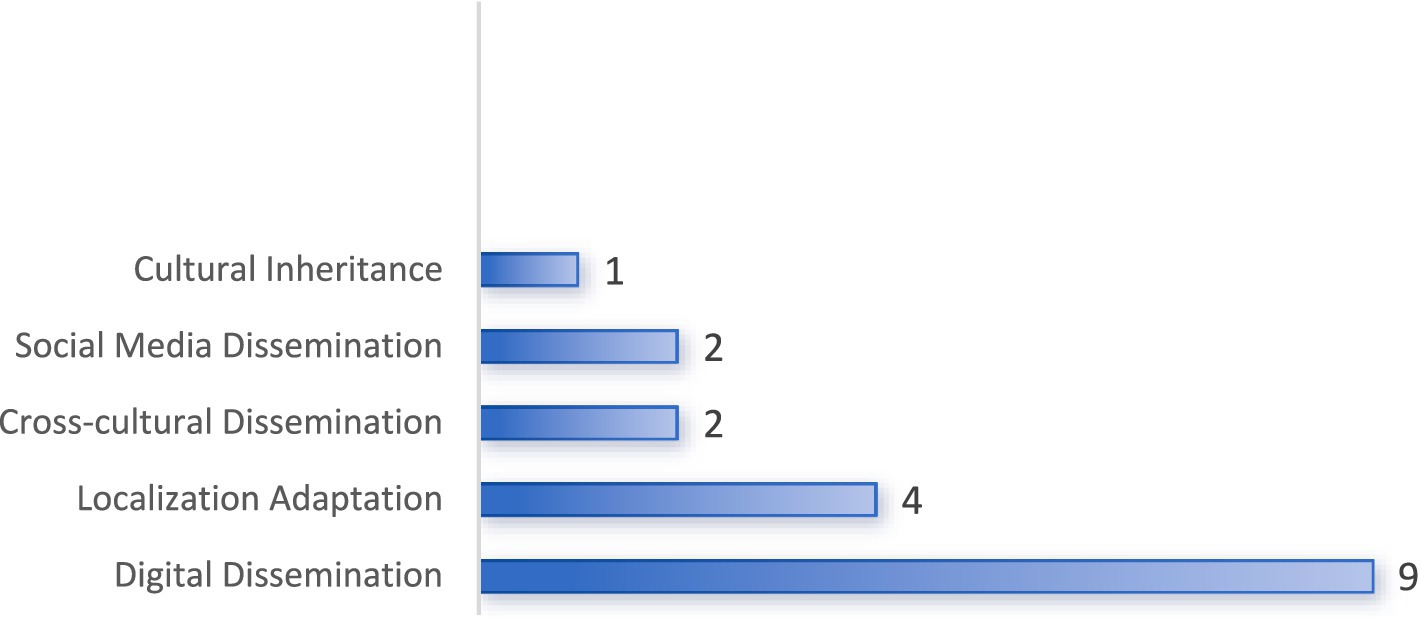
The analysis reveals that digital dissemination (50%) is the predominant pathway for CT, highlighting its central role in contemporary cultural exchange. The strategic combination of digital dissemination with localization adaptation (22%) and social media dissemination (11%) underscores the importance of contextual and interactive approaches in enhancing the effectiveness of CT. Cross-cultural dissemination (11%) also plays a notable role, reflecting the interconnectedness of global cultures. Cultural inheritance (6%) maintains a unique position, emphasizing the preservation of traditional cultural elements (see Figure 6).
3.7 Findings
The analysis of the findings reveals several key themes underpinning the mechanisms of CT within urban contexts. Social media images emerge as a predominant factor, influencing both urban image and cultural cognition across various domains such as urban parks, building functions, and coastal landscapes. Specifically, SMP facilitates the dissemination and enhancement of cultural understanding through visual content, as evidenced by multiple findings.
Image classification and recognition technologies play a crucial role in supporting CES evaluation and promoting broader cultural dissemination. These technologies enhance the efficiency and accuracy of disseminating cultural landscapes and intangible cultural heritage, leveraging tools such as computer vision, open-source classifiers, and multi-modal image classification. DL further augments CT by generating immersive narratives and facilitating aesthetic dissemination. The integration of advanced technologies like LiDAR, remote sensing, and 3D models enhances the depth and reach of cultural dissemination efforts, enabling more comprehensive and interactive cultural experiences. Cultural flagship events significantly contribute to the reconstruction of urban images and the enhancement of cultural identity. The use of unlabeled images presents both advantages and limitations, indicating a need for balanced approaches in CT strategies. Overall, the findings underscore the synergistic interplay between social media, advanced image technologies, and DL in fostering effective CT.
4 Discussion
4.1 The role of AI technologies in visual imagery cultural transmission
DL enhances CT by generating immersive narratives and promoting aesthetic dissemination. Studies show that AI-generated narratives and images that visually present users in a story context can achieve good immersion and engagement (Dong, 2025). Image classification and recognition technologies play a crucial role in supporting CES evaluations and promoting broader cultural dissemination (Ju, 2024). DL improves the efficiency and accuracy of disseminating cultural landscapes and intangible cultural heritage by leveraging tools such as computer vision and multimodal image classification (Gîrbacia, 2024). Pre-trained CNNs have shown high effectiveness in accurately identifying cultural heritage elements from social media images (Belhi et al., 2021). For instance, some studies have used pre-trained VGG19 and Xception models to significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of traditional cultural heritage image classification through transfer learning (Janković Babić, 2024). The integration of advanced technologies such as LiDAR, remote sensing, and 3D modeling enhances the depth and breadth of CT by creating interactive cultural experiences for urban populations (Y. Li et al., 2023), as such technologies enable computers to capture in-depth environmental data and generate artistic output based on sensing. A hybrid 3D virtual museum combines panoramic images and models to offer a more realistic and interactive cultural experience (Barrile et al., 2022).
4.2 The impact of social media platforms on visual imagery cultural transmission
Social media images, through a collective construction process, significantly influence cultural cognition and the formation of urban identity across different urban contexts (Loughran et al., 2015). Unlike the unidirectional dissemination of traditional media, SMP facilitate two-way cultural exchange through user-generated content and interactive functions (such as comments, reposts, and likes), encouraging users to actively participate in content creation and sharing (Eroglu, 2023). This collective construction process significantly influences cultural cognition and enhances the role of visual content in promoting cultural understanding (Gooding, 2004). Moreover, real-time content dissemination on SMP significantly accelerates CT relative to the slower, fixed schedules of traditional broadcast media (Chukwu, 2023). On a technical level, image classification and recognition technologies play a crucial role in supporting CES evaluations and promoting broader cultural dissemination. These technologies, utilizing tools like computer vision and multimodal image classification, improve the efficiency and accuracy of transmitting cultural landscapes and intangible cultural heritage. Research indicates that platforms like Flickr and Weibo are core channels for disseminating visual content and facilitating social interaction (Liang et al., 2022).
4.3 Visual imagery and cross-cultural transmission
VI, due to its intuitive and universal nature, can transcend language barriers, simplifying complex cultural concepts and promoting understanding without the need for translation (Vishwakarma, 2023). For example, traditional Chinese New Year pictures express themes of happiness, good fortune, and prosperity through symbols like figures, animals, and plants, which helps audiences from different cultural backgrounds understand core Chinese cultural values (Welch, 2013). Algorithmic diversification strategies, such as “explore mode” and randomized recommendations (Fang et al., 2020), are effective in broadening users’ exposure to cross-cultural content by correcting the “filter bubble” effect often found in recommendation systems (Grossetti et al., 2021).
Furthermore, AI-driven visual technologies are pivotal in creating immersive and interactive cultural experiences that drive cross-cultural communication. In the context of digital cultural tourism, technologies like virtual tours and 3D modeling allow global audiences to explore cultural heritage sites and traditions regardless of physical distance (Napolitano et al., 2018). These visual mediums not only attract tourists but also serve as educational tools, enabling a deeper appreciation of diverse cultures. The application of AI in this domain transforms passive viewing into an active, engaging experience, fostering a more direct and personal connection between individuals and foreign cultures.
4.4 Challenges and risks posed by AI
Despite advancements, AI technology introduces several challenges in CT. A primary concern is algorithmic bias, as many AI models are trained on datasets dominated by Western aesthetic standards, leading to biases in recognizing non-Western cultural content. This can distort cultural heritage representations and exacerbate cultural inequalities (Gosal and Ziv, 2020). AI models often lack a deep understanding of cultural symbols and contexts, resulting in misinterpretations, especially with religious or historical images (Fan et al., 2023). Another significant risk is cultural homogenization and the loss of creativity. In creative fields, reliance on repetitive data can stifle innovation, leading to homogenized cultural products (Fan et al., 2023).
Privacy and data security also present pressing concerns. Training facial recognition models requires vast amounts of personal images, raising issues of privacy infringement (Su et al., 2023). AI can be misused to create fake images or videos, which can mislead the public and undermine social trust, such as fabricated political videos used as propaganda (SHI et al., 2021). To mitigate these issues, both technological and methodological improvements are essential. Expanding AI training datasets to include diverse cultural elements such as language, music, and text can help reduce bias (Fan et al., 2023). Incorporating cultural context into algorithm design through cultural tagging or building knowledge bases can enhance the understanding of cultural nuances and reduce misinterpretations (Huai et al., 2022). Developing explainable AI algorithms is crucial for improving transparency in decision-making and identifying potential biases (Huai et al., 2022).
4.5 Future directions
Future research should expand its methodological scope to provide more balanced insights into the application of AI and SMP in diverse cultural contexts. This can be achieved by incorporating a wider range of sources from various cultural backgrounds and conducting more nuanced analyses of the practical challenges and ethical implications. Additionally, the potential of digital tools such as VR, 3D modeling, and panoramic imaging to simultaneously strengthen cultural engagement and ecological conservation should be explored. This could be achieved by creating virtual tours of heritage sites that highlight both their cultural significance and the need for ecological protection. Ultimately, future studies should investigate the potential of user-generated content in supporting CES by developing collaborative cultural-ecological conservation models that foster public participation and promote conservation efforts.
4.6 Limitations
This scoping review has several limitations and strengths that warrant discussion. Many studies relied heavily on user-generated content from SMP, which inherently introduces biases. Factors such as sample selection, tagging practices, and subjective interpretations may distort the representativeness of cultural narratives. These limitations are compounded by the under-representation of diverse cultural contexts, particularly from regions with limited access to advanced technological tools. Addressing this imbalance would require broader geographic and demographic inclusion in future research. In conclusion, while this systematic scoping review provides valuable insights into the role of VI in CT, particularly in the era of DL, it is crucial for future research to address these limitations by expanding the scope of the literature review, incorporating a broader range of sources, and providing a more nuanced analysis of the challenges and practicalities of implementing AI and SMP strategies in diverse cultural contexts.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we conducted a systematic scoping review to analyze the role of DL-driven VI in CT. We have identified that DL-driven visual technologies, especially DL algorithms, significantly enhance the breadth and impact of CT. One of our contributions also highlighted key challenges, including algorithmic bias, cultural homogenization, and the reliability of user-generated content. Future research should focus on improving the inclusivity of DL algorithms, addressing biases in cultural representation, and enhancing the accuracy and authenticity of content through advanced image recognition technologies. This research provides a foundational framework for understanding the complex interplay between AI, VI, and CT, paving the way for more nuanced and effective applications in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JY: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft. TL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YL: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Methodology, Investigation. PP: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bai, Y. (2023). Historical changes of urban landscape in the field of visual culture: take the bund as an example. Lecture Notes Educ. Psychol. Pub. Media 22, 23–34. doi: 10.54254/2753-7048/22/20230209
Barrile, V., Bernardo, E., Fotia, A., and Bilotta, G. (2022). A combined study of cultural heritage in archaeological museums: 3D survey and mixed reality. Heritage 5, 1330–1349. doi: 10.3390/heritage5030069
Basu, A., Paul, S., Ghosh, S., Das, S., Chanda, B., Bhagvati, C., et al. (2023). Digital restoration of cultural heritage with data-driven computing: a survey. IEEE Access 11, 53939–53977. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3280639
Belhi, A., Ahmed, H. O., Alfaqheri, T., Bouras, A., Sadka, A. H., and Foufou, S. (2021). Study and evaluation of pre-trained CNN networks for cultural heritage image classification. In Belhi, A., A. Bouras, A. K. Al-Ali, and A. H. Sadka Data analytics for cultural heritage: Current trends and concepts (pp. 47–69): Cham Springer.
Cardoso, A. S., Renna, F., Moreno-Llorca, R., Alcaraz-Segura, D., Tabik, S., Ladle, R. J., et al. (2022). Classifying the content of social media images to support cultural ecosystem service assessments using deep learning models. Ecosystem Serv. 54:101410. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2022.101410
Chukwu, O. J. (2023). Interrogating the online internet-based broadcast media stations: platforms, implications and emerged paradigms. J. Manage. Sci. 13, 74–81. doi: 10.26524/jms.13.36
Crema, E. R., Bortolini, E., and Lake, M. (2024). How cultural transmission through objects impacts inferences about cultural evolution. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 31, 202–226. doi: 10.1007/s10816-022-09599-x
Della Lena, S., and Panebianco, F. (2021). Cultural transmission with incomplete information. J. Econ. Theory 198:105373. doi: 10.1016/j.jet.2021.105373
Dong, A. (2025). LUMIEA: Enhancing user engagement in storytelling: Empowering personal narratives through AI-generated environments and tactile interaction in mixed reality. Toronto, ON: OCAD University.
Eerkens, J. W., and Lipo, C. P. (2007). Cultural transmission theory and the archaeological record: providing context to understanding variation and temporal changes in material culture. J. Archaeol. Res. 15, 239–274. doi: 10.1007/s10814-007-9013-z
Eizenberg, E., and Cohen, N. (2015). Reconstructing urban image through cultural flagship events: the case of bat-yam. Cities 42, 54–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2014.09.003
Eroglu, D. I. (2023). Medium is the message: Unraveling the social media platforms' effects on communication and opinions. Blacksburg VI: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Fahmy, S., Bock, M., and Wanta, W. (2014). Visual communication theory and research: A mass communication perspective. Cham: Springer.
Fan, T., Wang, H., and Deng, S. (2023). Intangible cultural heritage image classification with multimodal attention and hierarchical fusion. Expert Syst. Appl. 231:120555. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120555
Fang, H., Zhang, D., Shu, Y., and Guo, G. (2020). Deep learning for sequential recommendation: algorithms, influential factors, and evaluations. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 39, 1–42. doi: 10.1145/3426723
Ferracani, A., Bertini, M., Pala, P., Nannotti, G., Principi, F., and Becchi, G. (2024). “Personalized generative storytelling with AI-visual illustrations for the promotion of knowledge in cultural heritage tourism,” in Paper Presented at the Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on the Analysis, Understanding and Promotion of Heritage Contents.
Gîrbacia, F. (2024). An analysis of research trends for using artificial intelligence in cultural heritage. Electronics 13:3738. doi: 10.3390/electronics13183738
Gooding, D. (2004). Cognition, construction and culture: visual theories in the sciences. J. Cogn. Cult. 4, 551–593. doi: 10.1163/1568537042484896
Gosal, A., and Ziv, G. (2020). Landscape aesthetics: spatial modelling and mapping using social media images and machine learning. Ecol. Indic. 117:106638. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106638
Grossetti, Q., Du Mouza, C., Travers, N., and Constantin, C. (2021). Reducing the filter bubble effect on twitter by considering communities for recommendations. Int. J. Web Inf. Syst. 17, 728–752. doi: 10.1108/IJWIS-06-2021-0065
Hegetschweiler, K. T., de Vries, S., Arnberger, A., Bell, S., Brennan, M., Siter, N., et al. (2017). Linking demand and supply factors in identifying cultural ecosystem services of urban green infrastructures: a review of European studies. Urban For. Urban Green. 21, 48–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2016.11.002
Heise, D. (2004). Is visual culture becoming our canon of art? Art Educ. 57, 41–46. doi: 10.1080/00043125.2004.11653567
Hewlett, B. S., Boyette, A. H., Lew-Levy, S., Gallois, S., and Dira, S. J. (2024). Cultural transmission among hunter-gatherers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 121:e2322883121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2322883121
Hoffmann, E. J., Abdulahhad, K., and Zhu, X. X. (2023). Using social media images for building function classification. Cities 133:104107. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2022.104107
Hu, Q., Yu, D., Wang, S., Fu, C., Ai, M., and Wang, W. (2017). Hybrid three-dimensional representation based on panoramic images and three-dimensional models for a virtual museum: data collection, model, and visualization. Inf. Vis. 16, 126–138. doi: 10.1177/1473871616655467
Huai, S., Chen, F., Liu, S., Canters, F., and Van de Voorde, T. (2022). Using social media photos and computer vision to assess cultural ecosystem services and landscape features in urban parks. Ecosystem Serv. 57:101475. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2022.101475
Huang, Y., and Yang, S. (2016). “The orientation of urban image and the strategy of cultural communication,” in Paper Presented at the 2nd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 2017)
Janković Babić, R. (2024). A comparison of methods for image classification of cultural heritage using transfer learning for feature extraction. Neural Comput. & Applic. 36, 11699–11709. doi: 10.1007/s00521-023-08764-x
Jiang, Y., Pang, P. C.-I., Wong, D., and Kan, H. Y. (2023). Natural language processing adoption in governments and future research directions: a systematic review. Appl. Sci. 13:12346. doi: 10.3390/app132212346
Ju, F. (2024). Mapping the knowledge structure of image recognition in cultural heritage: a scientometric analysis using CiteSpace, VOSviewer, and bibliometrix. J. Imaging 10:272. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10110272
Laba, N. (2024). Engine for the imagination? Visual generative media and the issue of representation. Media Cult. Soc. 46, 1599–1620. doi: 10.1177/01634437241259950
Lee, H., Seo, B., Koellner, T., and Lautenbach, S. (2019). Mapping cultural ecosystem services 2.0–potential and shortcomings from unlabeled crowd sourced images. Ecol. Indic. 96, 505–515. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.08.035
Legare, C. H. (2017). Cumulative cultural learning: development and diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 7877–7883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620743114
Li, X., Liang, X., Yu, T., Ruan, S., and Fan, R. (2022). Research on the integration of cultural tourism industry driven by digital economy in the context of COVID-19—based on the data of 31 Chinese provinces. Front. Public Health 10:780476. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.780476
Li, R., and Wang, C. (2022). Cultural and creative product design and image recognition based on deep learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 1–9. doi: 10.1155/2022/7256584
Li, Y., Zhao, L., Chen, Y., Zhang, N., Fan, H., and Zhang, Z. (2023). 3D LiDAR and multi-technology collaboration for preservation of built heritage in China: a review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 116:103156. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2022.103156
Liang, X., Hua, N., Martin, J., Dellapiana, E., Coscia, C., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Social media as a medium to promote local perception expression in China’s world heritage sites. Land 11:841. doi: 10.3390/land11060841
Loughran, K., Fine, G. A., and Hunter, M. A. (2015). “Urban spaces, city cultures, and collective memories” in Routledge international handbook of memory studies. eds. A. L. Tota and T. Hagen (London: Routledge), 193–204.
Luo, Y. T., Liu, T., Pang, P. C.-I., Wang, Z., and Chan, K. I. (2025). Exploring information interaction preferences in an LLM-assisted learning environment with a topic modeling framework. Appl. Sci. 15:7515. doi: 10.3390/app15137515
Motte, E., and McInnes, R. (2019). Using artistic imagery to improve understanding of coastal landscape changes on the Rance estuary (French Channel coast). Geoheritage 11, 961–972. doi: 10.1007/s12371-018-00341-2
Napolitano, R. K., Scherer, G., and Glisic, B. (2018). Virtual tours and informational modeling for conservation of cultural heritage sites. J. Cult. Herit. 29, 123–129. doi: 10.1016/j.culher.2017.08.007
Plieninger, T., Bieling, C., Fagerholm, N., Byg, A., Hartel, T., Hurley, P., et al. (2015). The role of cultural ecosystem services in landscape management and planning. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 14, 28–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2015.02.006
Richards, D. R., and Friess, D. A. (2015). A rapid indicator of cultural ecosystem service usage at a fine spatial scale: content analysis of social media photographs. Ecol. Indic. 53, 187–195. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.01.034
Richards, D. R., and Tunçer, B. (2018). Using image recognition to automate assessment of cultural ecosystem services from social media photographs. Ecosystem Serv. 31, 318–325. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.09.004
Robb, J. (2020). Art (pre) history: ritual, narrative and visual culture in Neolithic and bronze age Europe. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 27, 454–480. doi: 10.1007/s10816-020-09471-w
Romanazzi, G. R., Koto, R., De Boni, A., Palmisano, G. O., Cioffi, M., and Roma, R. (2023). Cultural ecosystem services: a review of methods and tools for economic evaluation. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 20:100304. doi: 10.1016/j.indic.2023.100304
Scholte, S. S., Van Teeffelen, A. J., and Verburg, P. H. (2015). Integrating socio-cultural perspectives into ecosystem service valuation: a review of concepts and methods. Ecol. Econ. 114, 67–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015
Schönpflug, U. (2008). Cultural transmission: Psychological, developmental, social, and methodological aspects. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Shahbazi, N., Lin, Y., Asudeh, A., and Jagadish, H. (2023). Representation bias in data: a survey on identification and resolution techniques. ACM Comput. Surv. 55, 1–39. doi: 10.1145/3588433
Shi, J., Honjo, T., Yazawa, Y., and Furuya, K. (2021). Recognition and classification of homogeneous landscape with visitor–employed photography and cloud image annotation API—an example of the Riverscape in Nihonbashi, Tokyo, Japan. Landscape Architecture Frontiers 9, 12–31. doi: 10.15302/J-LAF-1-020054
Somaini, A. (2023). Algorithmic images: artificial intelligence and visual culture. Grey Room :93, 74–115. doi: 10.1162/grey_a_00383
Soreanu, C., and German, L. (2022). Visual communication in cultural media. The Rashomon effect in the image globalization paradigm. Rev. Art Educ. 26, 177–185. doi: 10.2478/rae-2023-0025
Su, L., Chen, W., Zhou, Y., and Fan, L. (2023). Exploring city image perception in social media big data through deep learning: a case study of Zhongshan City. Sustainability 15:3311. doi: 10.3390/su15043311
Van Berkel, D. B., Tabrizian, P., Dorning, M. A., Smart, L., Newcomb, D., Mehaffey, M., et al. (2018). Quantifying the visual-sensory landscape qualities that contribute to cultural ecosystem services using social media and LiDAR. Ecosystem Serv. 31, 326–335. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.03.022
Vishwakarma, V. K. (2023). Translating cultural nuances: challenges and strategies. ELT Voices 13:8268531. doi: 10.5281/ZENODO.8268531
Wang, H., Gao, Z., Zhang, X., Du, J., Xu, Y., and Wang, Z. (2024). Gamifying cultural heritage: exploring the potential of immersive virtual exhibitions. Telemat. Inform. Rep. 15:100150. doi: 10.1016/j.teler.2024.100150
Winder, S. G., Lee, H., Seo, B., Lia, E. H., and Wood, S. A. (2022). An open-source image classifier for characterizing recreational activities across landscapes. People Nat. 4, 1249–1262. doi: 10.1002/pan3.10382
Xia, S., Xia, Y., Liu, T., Luo, Y., and Pang, P. C.-I. (2025). Application of deep learning models in gastric cancer pathology image analysis: a systematic scoping review. BMC Cancer 25:1257. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14662-3
You, S., Zheng, Q., Chen, B., Xu, Z., Lin, Y., Gan, M., et al. (2022). Identifying the spatiotemporal dynamics of forest ecotourism values with remotely sensed images and social media data: a perspective of public preferences. J. Clean. Prod. 341:130715. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130715
Keywords: deep learning, cultural transmission, visual images, systematic scoping review, DL
Citation: Yang J, Liu T, Luo YT and Pang PC-I (2025) Deep learning in cultural imagery dissemination: a systematic scoping review of AI-driven visual transmission mechanisms. Front. Commun. 10:1645168. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1645168
Edited by:
Ankan Bhattacharya, Hooghly Engineering and Technology College, IndiaReviewed by:
Abhranil De, Hooghly Engineering and Technology College, IndiaKrishanu Kundu, GL Bajaj Group of Institutions, India
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Liu, Luo and Pang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Patrick Cheong-Iao Pang, bWFpbEBwYXRyaWNrcGFuZy5uZXQ=
†ORCID: Jinhua Yang, https://orcid.org/0009-0004-4633-1830
Ting Liu, https://orcid.org/0009-0001-0331-262X
Yiming Taclis Luo, https://orcid.org/0009-0002-6117-738X
Patrick Cheong-Iao Pang, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8820-5443
 Jinhua Yang
Jinhua Yang Ting Liu2†
Ting Liu2† Yiming Taclis Luo
Yiming Taclis Luo Patrick Cheong-Iao Pang
Patrick Cheong-Iao Pang