- 1Queensland Research Centre for Peripheral Vascular Disease, College of Medicine and Dentistry, James Cook University, Townsville, QLD, Australia
- 2Ulcer and Wound Healing Consortium (UHEAL), Australian Institute of Tropical Health and Medicine, James Cook University, Townsville, QLD, Australia
- 3Faculty of Health and Medicine, School of Health Sciences, University of Newcastle, Newcastle, NSW, Australia
- 4Australian Institute of Tropical Health and Medicine, James Cook University, Townsville, QLD, Australia
- 5Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Townsville University Hospital, Townsville, QLD, Australia
By Fernando ME, Seng L, Drovandi A, Crowley BJ and Golledge J (2022) Front. Endocrinol. 13:848695. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.848695
In the original article, there were mistakes in Figure 2B, Figure 2C, Figure 3A and Figure 3B as published. The corrected Figures 2 and 3 appear here.
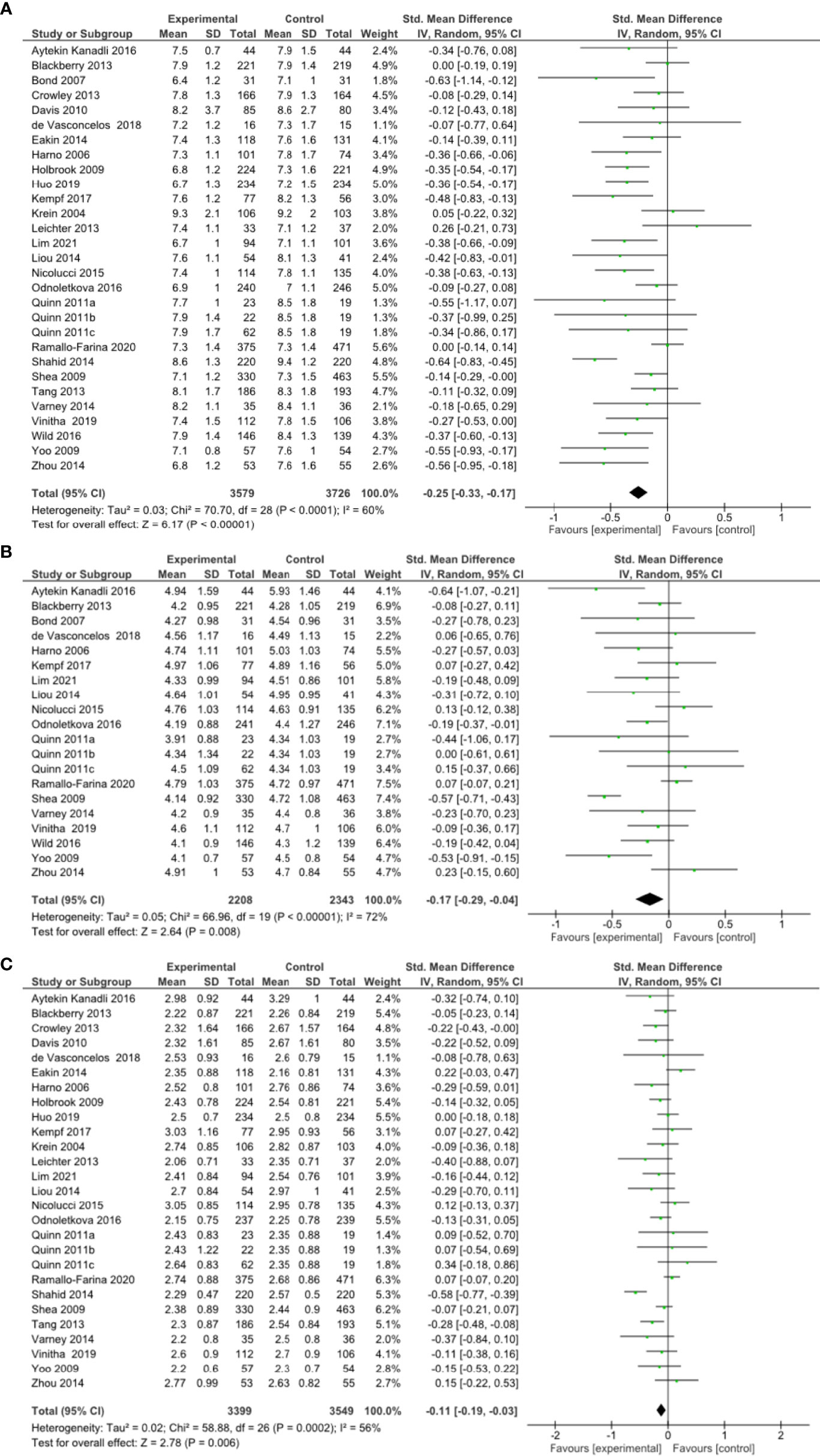
Figure 2 (A) Forest plot showing the effect of remote risk factor management on HbA1c, (B) Forest plot showing the effect of remote management on total cholesterol, (C) Forest plot showing the effect of remote risk factor management on LDL-cholesterol.
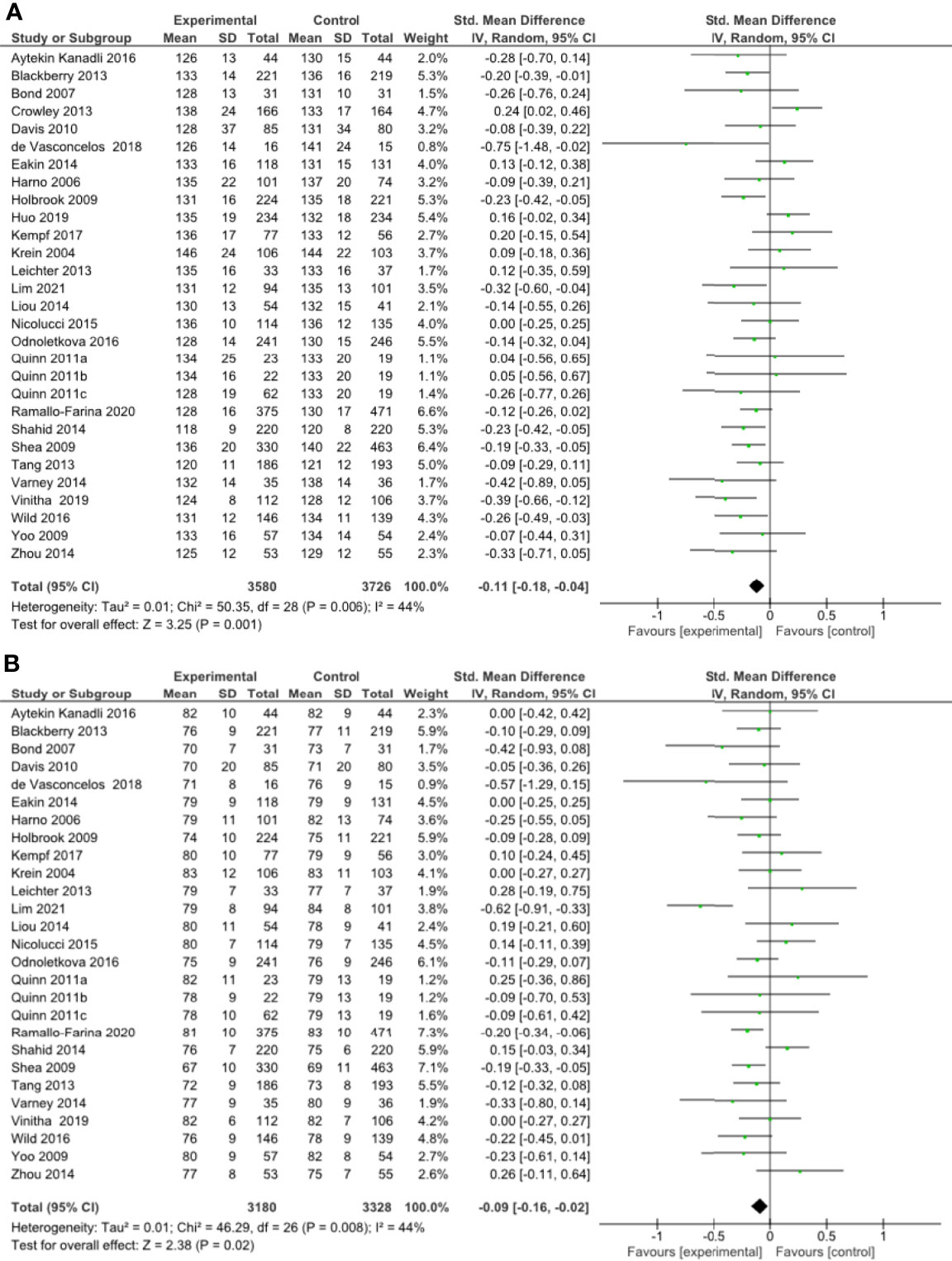
Figure 3 (A) Forest plot showing the effect of remote management on systolic blood pressure, (B) Forest plot showing the effect of remote risk factor management on diastolic blood pressure.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: blood pressure, cholesterol, lipids, systematic review, telehealth
Citation: Fernando ME, Seng L, Drovandi A, Crowley BJ and Golledge J (2022) Corrigendum: Effectiveness of Remotely Delivered Interventions to Simultaneously Optimize Management of Hypertension, Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in People With Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 13:916377. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.916377
Received: 09 April 2022; Accepted: 19 April 2022;
Published: 09 May 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Fariba Ahmadizar, University Medical Center Utrecht, NetherlandsCopyright © 2022 Fernando, Seng, Drovandi, Crowley and Golledge. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jonathan Golledge, Sm9uYXRoYW4uR29sbGVkZ2VAamN1LmVkdS5hdQ==
 Malindu E. Fernando
Malindu E. Fernando Leonard Seng
Leonard Seng Aaron Drovandi
Aaron Drovandi Benjamin J. Crowley1
Benjamin J. Crowley1 Jonathan Golledge
Jonathan Golledge