- 1Department of Oncology, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Luzhou, China
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Sichuan Cancer Hospital and Institute, Sichuan Cancer Center, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 3Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
A Corrigendum on
Low-Dose Total Body Irradiation Can Enhance Systemic Immune Related Response Induced by Hypo-Fractionated Radiation
By Liu J, Zhou J, Wu M, Hu C, Yang J, Li D, Wu P, Chen Y, Chen P, Lin S, Cui Y, Fu S and Wu J (2019). Front. Immunol. 10:317. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00317
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figures 3C and 4C as published. The authors regret that the wrong images were used. The reason may be owing to layer fusion leading the images to be duplicated (primary tumor and secondary tumor images were repeated in the L-TBI group; secondary tumor images were repeated in the control group and L-TBI group). The corrected Figures 3 and 4 appear below. Furthermore, the authors have ensured that the arrows now point to identifiable structures within the images. The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
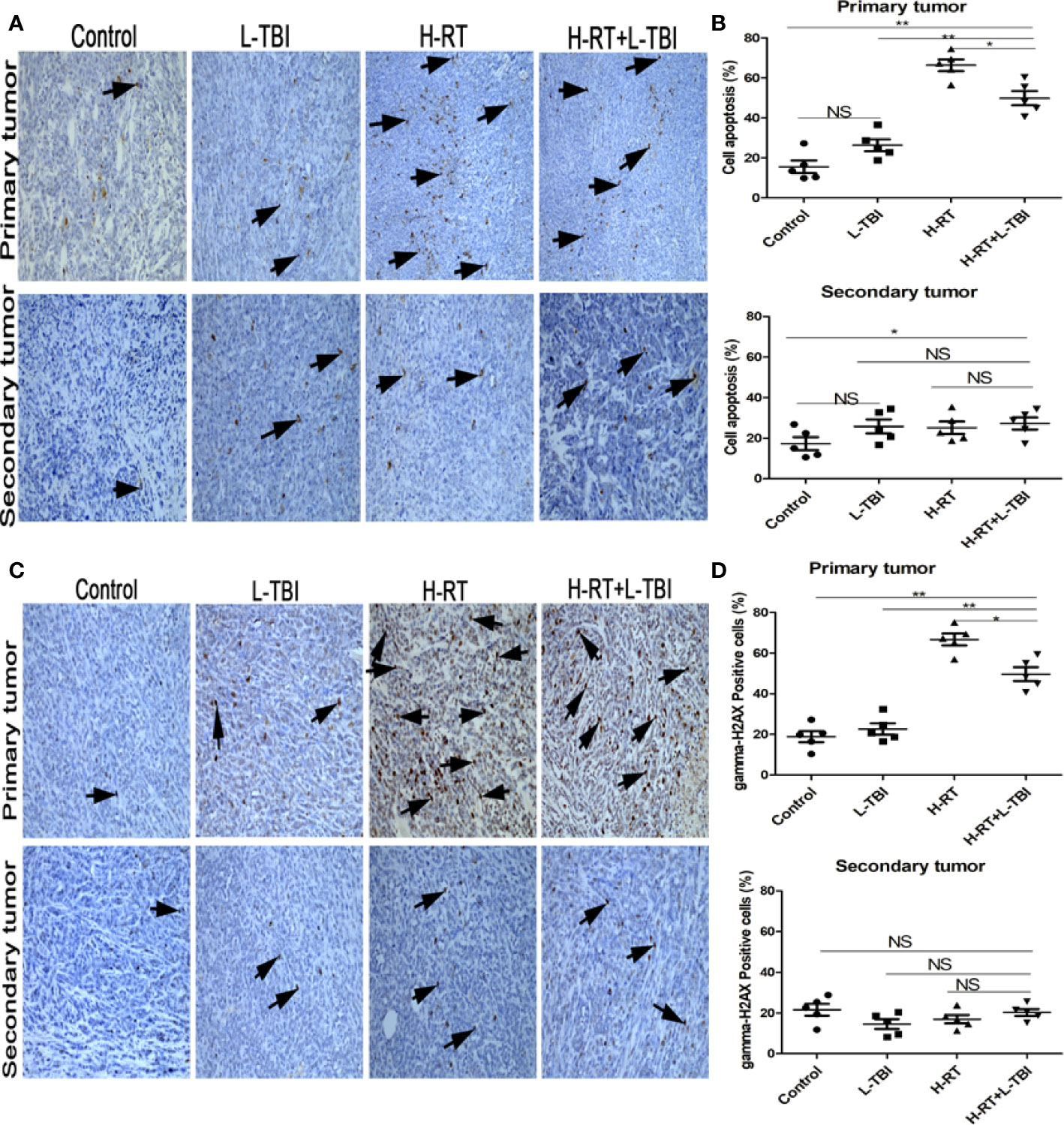
Figure 3 Effect of combination H-RT and L-TBI therapy on apoptosis in 4T1 tumor bearing tissues. (A) Comparison of representative TUNEL IHC-stained in different treatment groups. (B) Percentage of TUNEL positive cells in the primary and secondary tumor. (C) Representative gamma-H2AX IHC staining image in different treatment groups. (D) Percentage of gamma H2AX positive cells in the primary and secondary tumor. The arrows point to the TUNEL and gamma-H2AX positive cells in the tumor tissue (original magnification ×200). Data are expressed as mean ± SE of 5 mice/group. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and N, not significant).
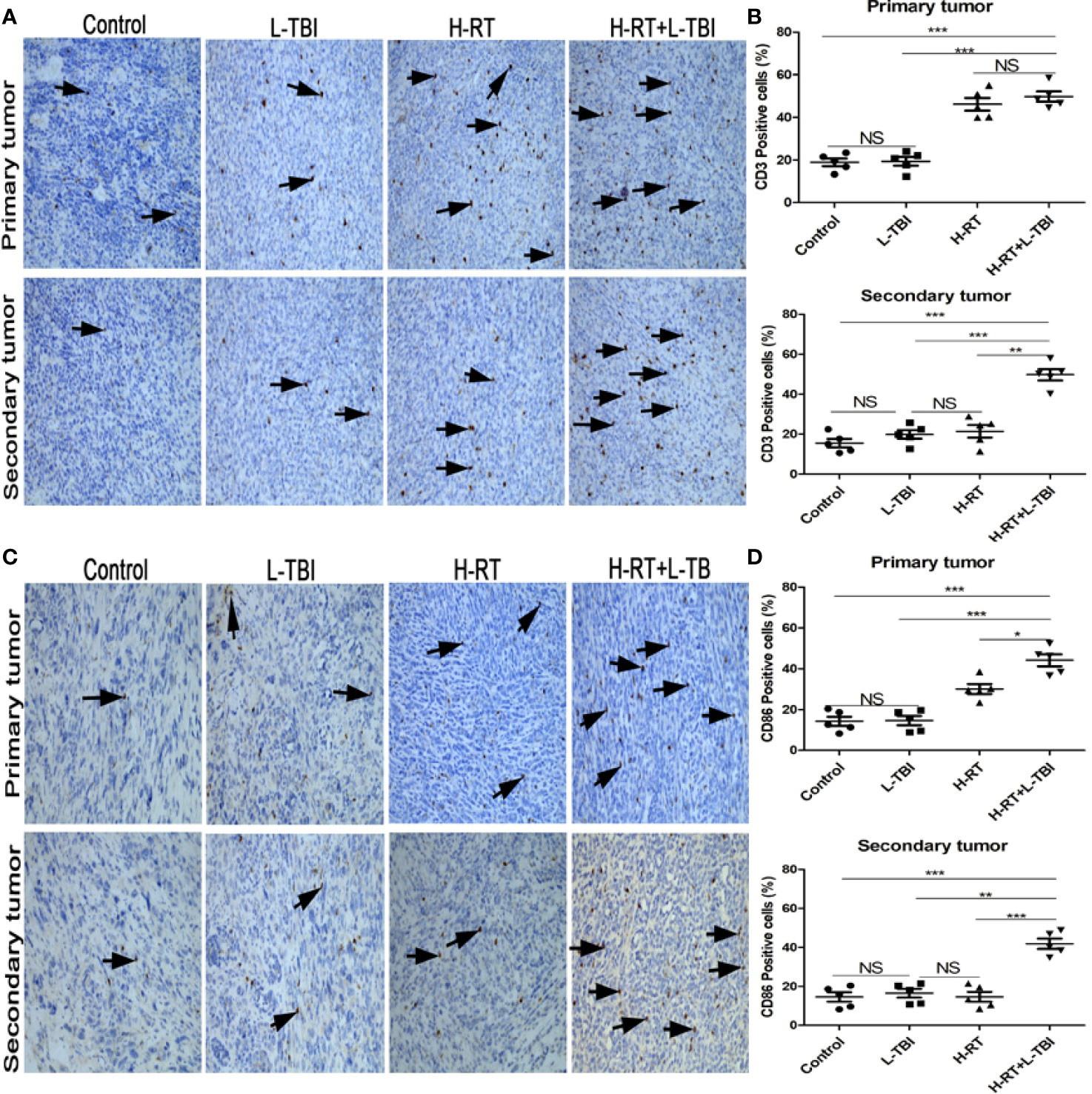
Figure 4 Comparison of CD3+ and CD86+ lymphocytes in different treatment groups. (A) Representative images of CD3 IHC in tumor tissues of different treatment groups. (B) Percentage of CD3 positive cells in the primary and secondary tumor. (C) Representative IHC images of CD86 infiltration in the tumor tissue of different treatment groups. (D) Percentage of CD86 positive cells in the primary and secondary tumor. The arrows point the CD3 and Cd86 positive cells in tumor tissues from mice that received different treatments (original magnification ×200). Data are expressed as mean ± SE of 5 mice/group. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and NS, not significant).
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: systemic immune related response, hypo-fractionated radiation therapy, low-dose total body irradiation, immune enhancement, immunosuppressive microenvironment
Citation: Liu J, Zhou J, Wu M, Hu C, Yang J, Li D, Wu P, Chen Y, Chen P, Lin S, Cui Y, Fu S and Wu J (2021) Corrigendum: Low-Dose Total Body Irradiation Can Enhance Systemic Immune Related Response Induced by Hypo-Fractionated Radiation. Front. Immunol. 12:745787. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.745787
Received: 22 July 2021; Accepted: 06 August 2021;
Published: 03 September 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Franz Rödel, University Hospital Frankfurt, GermanyCopyright © 2021 Liu, Zhou, Wu, Hu, Yang, Li, Wu, Chen, Chen, Lin, Cui, Fu and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: JingBo Wu, d2piNjE0N0AxNjMuY29t; ShaoZhi Fu, c2hhb3poaWZ1NTEzQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jing Liu
Jing Liu Jie Zhou2†
Jie Zhou2† ShaoZhi Fu
ShaoZhi Fu JingBo Wu
JingBo Wu