- Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong, China
Tumor immunotherapy, a novel and rapidly progressing cancer treatment, has experienced remarkable advancements over recent years. It focuses on augmenting the patient’s immune defenses and remodeling the immune microenvironment (IME) of tumors, rather than directly targeting malignant cells. The efficacy of immunotherapy relies substantially on multiple components within the tumor microenvironment (TME), extending beyond adaptive immunity alone. Immune cells within the TME play critical roles in both promoting immune surveillance and facilitating immune evasion. This complexity emphasizes the importance of immune checkpoint regulation in immunotherapeutic interventions. Therapeutically targeting specific immune cell subsets and metabolic pathways in combination treatments can transform an immunosuppressive TME into one that is immunologically activated, facilitating enhanced immune cell infiltration and consequently improving immunotherapy efficacy. Nevertheless, comprehensive research remains necessary to fully elucidate the mechanisms underlying TME interactions and immune checkpoint regulation, ultimately enabling more effective immunotherapeutic approaches.
Introduction
Over the past decade, tumor immunotherapy has rapidly evolved into a promising therapeutic modality. Rather than directly attacking tumor cells, immunotherapy leverages the body’s immune response by enhancing innate defenses and reshaping the IME. Its primary objective is to potentiate natural anti-tumor immunity through increased infiltration of adaptive and innate immune cells into the TME. The formation of a favorable IME and enhanced immune responsiveness holds substantial clinical potential for predicting therapeutic outcomes and exploring new treatment avenues. Immunotherapy is associated with fewer adverse effects compared to conventional chemoradiotherapy. Targeting immune checkpoints, a cornerstone of immunotherapy, exhibits synergistic effects when combined with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or targeted therapies. The contemporary paradigm of advanced cancer management has progressively transitioned from chemotherapy and targeted therapies toward immunotherapy, increasingly integrating neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment modalities.
Immune checkpoints represent crucial inhibitory molecules within the immune system, predominantly expressed on immune and tumor cell surfaces. Upon receptor engagement, these molecules inhibit immune cell activation or promote immune exhaustion, exerting immunosuppressive effects. Under physiological conditions, immune checkpoints are essential for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity. Recently, extensive studies have primarily focused on immune checkpoints, both pivotal in mediating tumor immune evasion. Continuing research efforts have identified additional checkpoints. Immune checkpoint blockades (ICBs), mainly antibodies targeting programmed death protein-1 (PD-1), programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4), represent the primary immunotherapeutic strategy currently employed.
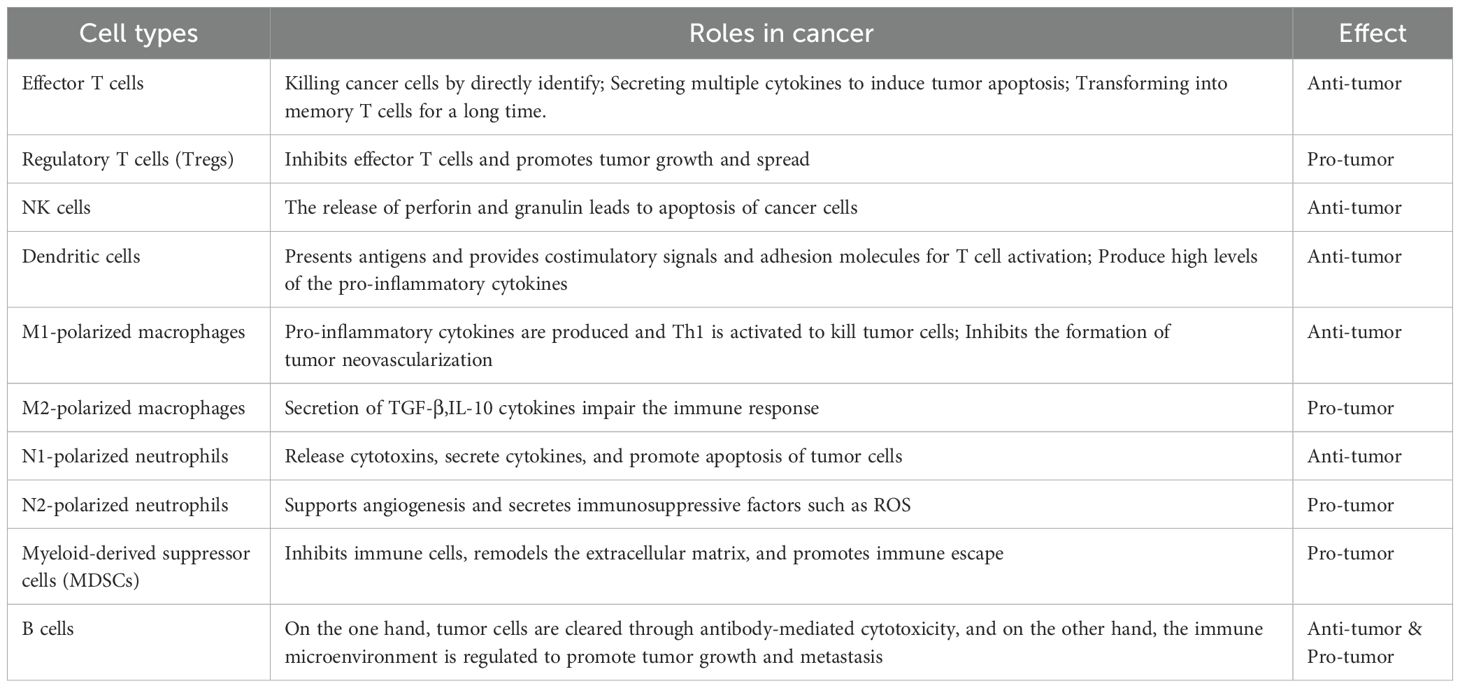
Presently, a significant limitation of immunotherapy, particularly ICB, is its restricted therapeutic response observed in subsets of cancer patients. Response rates vary widely across distinct cancer types and among patients diagnosed with identical malignancies, considerably restricting ICB’s broader clinical utility. Differential responses to immunotherapy, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIS), are predominantly attributed to variations in tumor IMEs across cancer types and subtypes. Immunosuppressive TMEs inhibit immune effector cells, leading to their exhaustion or functional impairment, thus hindering effective tumor eradication. Consequently, exploring novel molecular targets aimed at improving the IME constitutes a key direction in immunotherapy research. The roles and functions of immune cells within tumor contexts are summarized in Table 1.
TME and immunotherapy
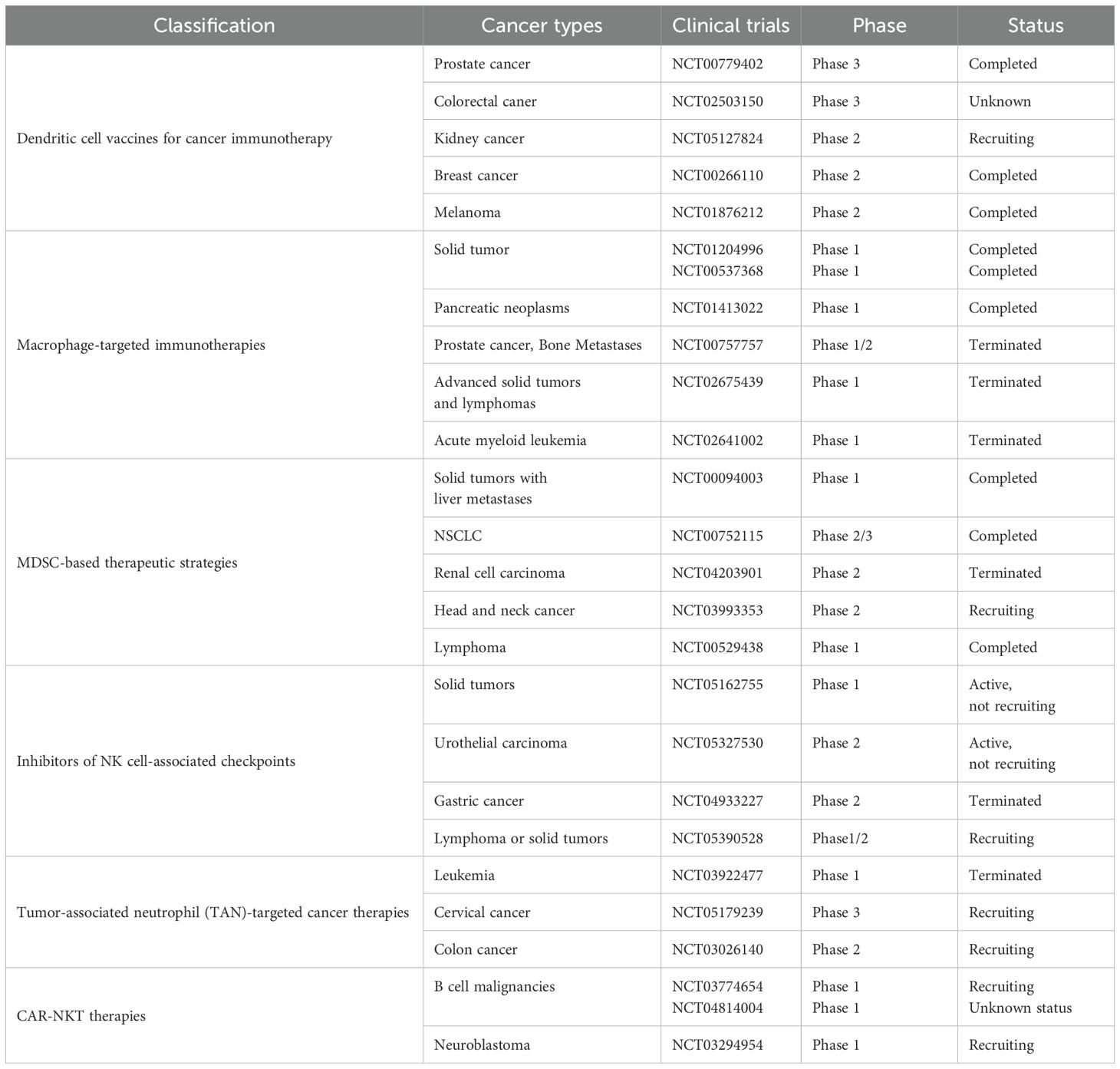
The TME encompasses the local surroundings in which tumor cells exist (1–4). Rapid proliferation of tumor cells accompanied by underdeveloped vasculature results in insufficient oxygen delivery, creating a hypoxic environment within tumor tissue (5, 6). Additionally, tumor cells preferentially generate energy through aerobic glycolysis, causing lactic acid buildup (7–9). Vascular anomalies and metabolic dysfunction trigger cascades of signaling pathways that foster the establishment of an immunosuppressive TME (5). Tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIICs) critically influence cancer cell activity within this microenvironment. These cells exhibit considerable heterogeneity and plasticity, exerting dual roles that either suppress or promote tumor growth. TIICs primarily encompass cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, dendritic cells (DCs), neutrophils, natural killer (NK) cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) (10). Microscopically, the TME is distinguished by pronounced fibrosis, limited vascularization, extensive interstitial fibrosis, abundant CAFs, and marked infiltration of immune cells with pro-inflammatory and tumor-promoting characteristics. Moreover, the immunosuppressive nature of the TME represents a defining feature of malignancies and constitutes a critical site for interactions between tumor cells and host immunity (11, 12). Therefore, modulation of immune cells within the TME to regulate anti-tumor responses has increasingly become a research priority. ICB therapy, representing a major recent advance in tumor immunotherapy, has exhibited notable effectiveness against various cancers Figure 1. Emerging technologies and novel research paradigms promise continued improvements in TME-focused immunotherapeutic strategies. Relevant points are summarized in Table 2.
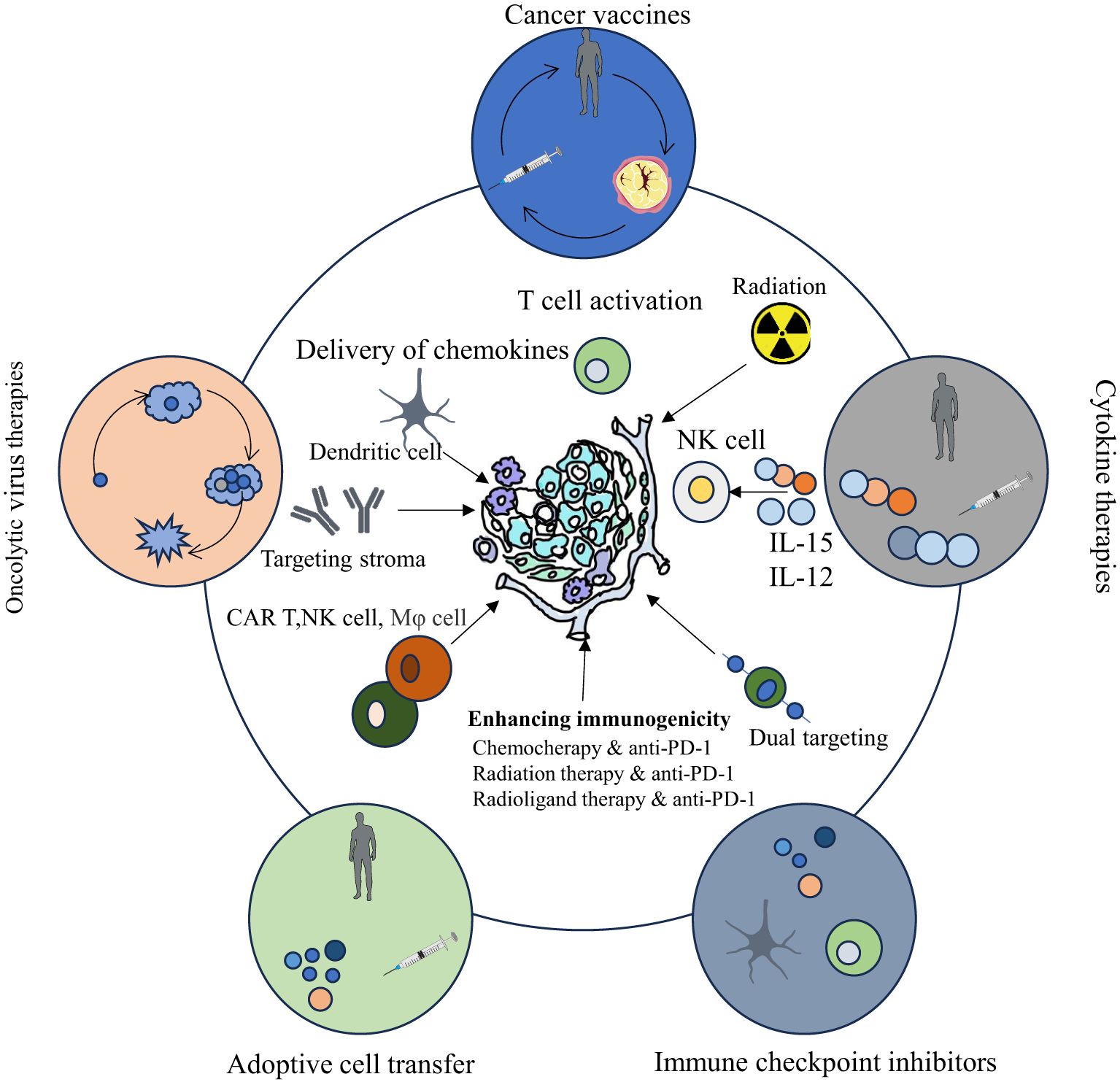
Figure 1. Cancer immunotherapy categories (oncolytic viruses, vaccines, cytokines, cell transfer, checkpoint inhibitors) have evolved, showing clinical promise, with their principles and cellular/molecular underpinnings depicted.
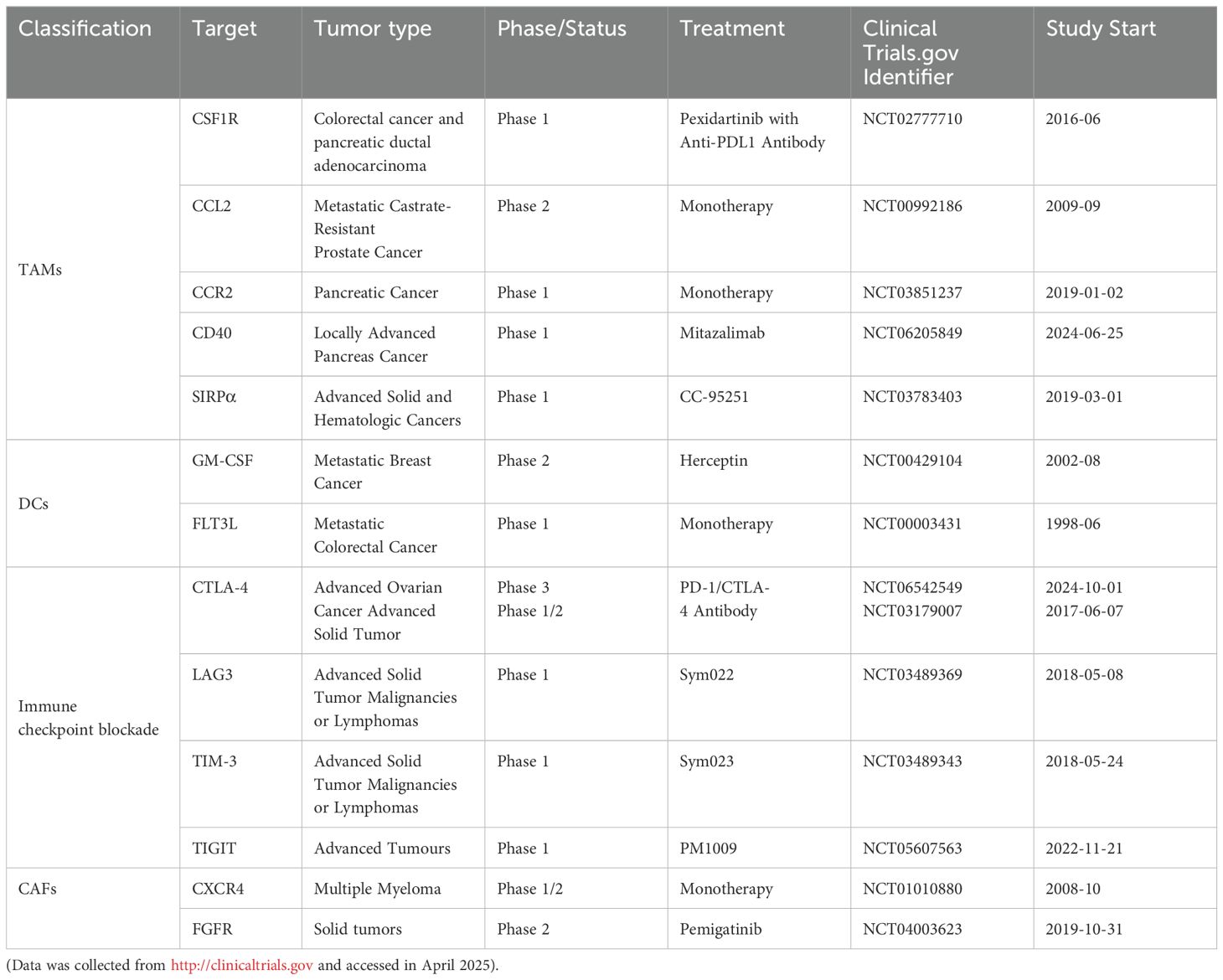
Table 2. Therapeutic targets that focus on the tumor-associated immune and stromal compartments, either investigated in interventional clinical trials or approved by the FDA.
Targeted TME therapy
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) comprise diverse lymphocyte subsets predominantly residing within the TME. These cells primarily include T cells, B cells, NK cells, DCs, macrophages, and MDSCs, with T cells being most abundant. CD4+ T cells mainly differentiate into helper T cells (Th cells) and regulatory T cells (Tregs) (13–15). Th cells further differentiate into specific subsets such as Th1 and Th2 cells, which typically release various inflammatory cytokines to enhance the activity of immune cells. T cells play a pivotal role in orchestrating anti-tumor immune responses. However, infiltrating CD8+ T cells exhibit elevated expression of co-inhibitory molecules, coupled with reduced proliferation markers like Ki-67, indicative of functional exhaustion and impaired effector capabilities. An acidic microenvironment further diminishes T-cell-derived pro-inflammatory cytokines, while increasing CTLA-4 expression. Consequently, infiltrating T cells become increasingly susceptible to inhibitory signals (5, 16, 17). Hypoxic conditions within tumors lead to diminished CD4+ T cell populations and elevated expression of immunoregulatory factors, such as VEGF and IDO. These molecules inhibit antigen-specific immune responses and decrease IFN-γ production from CTLs (18–20).
Alterations in metabolism constitute key hallmarks of tumors. Tumor cells modify metabolic pathways and nutrient uptake to sustain rapid proliferation. In the immunosuppressive TME, tumor cells limit nutrient availability required for T cell activation and generate abundant lactic acid, resulting in nutrient scarcity and metabolic waste accumulation. These conditions prompt phenotypic and functional shifts in TIL populations (21, 22). In the hypoxic and nutrient-deficient TME, tumor cells preferentially acquire and rapidly consume glucose, favoring glycolysis over oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) due to its metabolic advantages. This intense glycolytic activity results in substantial lactic acid accumulation (23, 24). Inhibiting lactate production using inhibitors of lactate transporters can enhance IL-2 and IFN-γ secretion in T cells and promote T cell activation. Alterations in tumor lipid metabolism also significantly affect T cell activity. Cholesterol and its derivatives critically regulate T lymphocyte function, including chemotaxis, cell cycle, and effector functions (25, 26). Interventions targeting membrane cholesterol represent a potential strategy for modulating T cell activation. Studies have shown that genetic knockout or pharmacological inhibition of ACAT1 in CD8+ T cells suppresses intracellular cholesterol esterification. Consequently, increased free cholesterol translocates to the cell membrane, raising membrane cholesterol levels and enhancing CD8+ T cell activation (27, 28). In preclinical melanoma and lung cancer models, deletion of ACAT1 in CD8+ T cells significantly suppressed tumor progression and metastasis (29–31). Additionally, attaching liposomes loaded with the ACAT1 inhibitor Avasimibe onto T cell surfaces increases membrane cholesterol content, facilitates rapid T cell receptor clustering, and sustains T cell activation, enhancing their cytotoxic effects against glioblastoma and melanoma. Studies revealed that RORα suppresses genes associated with cholesterol esterification in CD8+ T cells by inhibiting NF-κB signaling, thereby strengthening CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxic responses (32–34). Elevated cholesterol levels in CD8+ T cells induce ER stress, activating the ER stress-related protein XBP1. XBP1, functioning as a transcription factor, enhances expression of inhibitory molecules, resulting in functional exhaustion and suppression of CD8+ T cells, and ultimately promoting tumor progression (35–37).
Regulatory B cells are crucial to immune regulation, suppressing inflammatory responses primarily through IL-10 secretion. Recent studies have linked cholesterol metabolism to the anti-inflammatory functions of B cells. Specifically, the synthesis of GGPP, a cholesterol pathway metabolite, is essential for inducing IL-10 production. This process suppresses the Th1 response and limits overall immune reactivity, highlighting cholesterol metabolism as a pivotal pathway in IL-10 production and B cell regulation (38–40).
In recent years, non-coding RNAs (miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA) have been identified as critical for the development of various cancers, and their aberrant expression serves as diagnostic and therapeutic markers (41, 42). miRNAs can bind directly to the 3’-UTR or target other genes to regulate PD-L1 expression. Cortez et al. found that in NSCLC, wild-type P53-induced miR-34 directly binds to the 3′-UTR of PD-L1 to inhibit PD-L1 mRNA expression, representing a potential therapeutic strategy by modulating the tumor immune escape mechanism via the p53/miR-34/PD-L1 axis (43). Xia et al. reported that LINC01140 overexpression protects PD-L1 mRNA from miRNA-mediated suppression, facilitating immune evasion in lung cancer cells (44). Additionally, exosomes secreted by cells are rich in miRNA, mRNA, and functional proteins, mediating cell-to-cell signaling within the TME (45). In gastric cancer, increased PD-L1 expression through EV-mediated miR-675-3p promotes immune evasion by cancer cells (46).
CAFs
Fibroblasts are critical multifunctional cells within connective tissues, responsible for synthesizing extracellular matrix and basement membrane components, modulating immune responses, influencing epithelial differentiation, and sustaining tissue integrity (47). Tumor cells induce activation and differentiation of fibroblasts into CAFs through direct intercellular contact or secretion of soluble signaling factors. CAFs prominently secrete proteins of the TGF-β family, particularly TGF-β1 (48). Additionally, CAFs suppress CD8+ T cell activity by expressing immune checkpoint ligands, thereby facilitating tumor immune evasion (49, 50). Therapeutic strategies targeting CAFs enhance the anti-tumor activities of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and NK cells while reducing regulatory Treg and MDSC populations (51, 52). Current research mainly focuses on CAF-targeted approaches by inhibiting their secreted cytokines and chemokines. For instance, combining TGF-β pathway inhibitors with anti-PD-1 antibodies disrupts TGF-β signaling, increases T cell infiltration, and augments anti-tumor immunity. Khalili et al. demonstrated that melanoma-derived IL-1α and IL-1β increase CAF density, whereas cytokine neutralization mitigates CAF-mediated suppression of T cell activation (53). Multiple studies confirm the significant role of CAFs in resistance to immunotherapy, indicating CAF interactions with diverse immune cells as promising therapeutic intervention targets. Several clinical trials involving CAF-targeted drugs combined with existing therapies are underway (4, 49). Despite progress, CAF heterogeneity has hindered therapeutic efficacy, potentially causing off-target effects (54–56).
MDSCs
MDSCs are a heterogeneous population of immature myeloid cells from bone marrow, including granulocytes and monocytes. Their primary feature is potent suppression of T cell responses, positioning them as key mediators of tumor-induced immunosuppression (57, 58). Activated MDSCs release immunosuppressive factors, which inhibit CTLs, NK cells, and their subsets, promoting tumor immune evasion and resistance to immunotherapy (59, 60). High-fat diets and obesity can enhance MDSC accumulation in tumor-bearing mice (61). CYP27A1 synthesizes 27-HC, a cholesterol metabolite positively correlated with poor prognosis. Studies have shown 27-HC promotes M-MDSC differentiation and proliferation, facilitating tumor progression by creating an immunosuppressive environment (59, 60). Tumor-derived chemokines recruit MDSCs into primary or metastatic sites in cancers such as breast, gastric, and ovarian tumors (58, 59). Macrophage-derived ApoE in pancreatic cancer binds LDLR on tumor cells, activating the NF-κB pathway and elevating CXCL1 and CXCL5 expression (62). CXCL1 and CXCL5 recruit M-MDSCs, mediating immunosuppression by inhibiting CD8+ T cell infiltration, thereby promoting tumor progression (63). In ovarian cancer (OC) and melanoma, ApoE binds LRP8 on MDSCs, enhancing anti-tumor immunity (64, 65). The LXR/ApoE axis influences MDSC survival, and LXR agonists (RGX-104/GW3965) have demonstrated efficacy in mouse models, significantly reducing tumor growth and metastasis by inducing MDSC apoptosis (66–68). LXR agonists also potentiate PD-1 blockade efficacy by targeting TAMs and MDSCs. Currently, the LXR agonist RGX-104/GW3965 is undergoing clinical trials for stage I solid tumors (NCT02922764) to investigate MDSC-mediated immunosuppression mechanisms and therapeutic potential (68, 69).
Tregs are immunosuppressive cells that inhibit anti-tumor immune responses. They suppress effector T cells via CTLA-4 expression and cytokines (70). IL-10 primarily mediates Treg immunosuppression by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines from monocytes and macrophages, reducing IL-12 synthesis, and hindering Th1 differentiation. Neutralizing antibodies against IL-10 can block Treg-mediated effector T cell suppression (71, 72). Tregs highly express CD25, enabling them to compete effectively for IL-2, resulting in effector T cell depletion and apoptosis (73).
TGF-β critically mediates immunosuppression by inhibiting effector T cell activation and promoting the differentiation of Tregs and Th17 cells (74). Tregs maintain immune tolerance partly by promoting activation of latent TGF-β1 (74). Additionally, Tregs express integrin αvβ8, activating TGF-β and mediating immunosuppression through cytotoxic mechanisms. Granzyme B, a serine protease delivered into target cells via perforin, initiates caspase-3-dependent apoptosis. By secreting granzyme B, Tregs induce apoptosis of effector T cells, thus modulating immune responses. The expression of granzyme B in Tregs relies significantly on TCR/CD28 signaling through activation of the PI3K-mTOR pathway (75). CCL1 activates Tregs by increasing surface expression of CCR8, and interaction between CCL1 and CCR8 induces Stat3-dependent Granzyme B expression, enhancing Treg inhibitory activity. Tregs also mediate immunosuppressive responses by altering cell metabolism. They require more glucose than effector T cells to execute immunosuppressive functions, leading to effector T cell exhaustion due to competitive glucose consumption (76, 77).
cAMP inhibits T cell activation and function. In Tregs, FOXP3 increases intracellular cAMP by enhancing AC9 expression through suppression of miR-142-3p and PDE3b. Subsequently, Tregs directly transfer cAMP to effector T cells through cell-to-cell contact, impairing their proliferation and reducing IL-2 secretion. Furthermore, Treg interactions with DCs elevate DC cAMP levels, downregulating expression of co-stimulatory molecules CD80/CD86. Surface-expressed CTLA-4 on Tregs further suppresses CD80/CD86 expression, impairing DC-mediated T cell activation. Tregs also secrete IL-10, inhibiting DC maturation and reducing their antigen-presenting capability (78–81).
CD70, a TNF family member expressed on dendritic and thymic medullary epithelial cells, enhances cytotoxic T cell function. Tregs down-regulate DC membrane CD70 expression via a CD27-dependent mechanism, thus impairing DC function. Selective depletion of Tregs from the TME improves anti-tumor immune responses. Current immunotherapies targeting Tregs primarily involve surface molecules overexpressed on Tregs but not conventional T cells. CD25 (IL-2Rα) is the earliest identified Treg marker. Tregs competitively bind IL-2 through CD25, inhibiting effector T cell proliferation and activation. Administration of anti-CD25 monoclonal antibodies before tumor inoculation significantly suppresses tumor growth in mice and enhances CD8+ T cell infiltration. Recombinant IL-2-diphtheria toxin conjugates selectively remove CD25+ Tregs from cancer patients, enhancing cytotoxic T cell proliferation and cytotoxicity in vitro.
CTLA-4, highly expressed on Tregs, functions as an immunosuppressive molecule that facilitates tumor cell survival. Tumor-infiltrating CTLA-4+ Tregs evade anti-tumor immune responses by dampening effector T cell activities. Anti-CTLA-4 antibodies enhance anti-tumor effects of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes (82, 83). CTLA-4 also inhibits glycolytic metabolism in T cells within the TME; therefore, CTLA-4 blockade enhances glycolysis in Tregs, altering their stability and facilitating activation of CD8+ TILs in vivo, especially in tumors with limited glycolysis (84). Ipilimumab, an FDA-approved anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody, is currently employed for treating melanoma, and several other cancers. It selectively reduces intratumoral Treg populations via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) mediated by CD16+ monocytes. Additionally, intratumoral ipilimumab treatment recruits CD68+CD16+ M1 macrophages, facilitating Treg clearance (85, 86).
Chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 are preferentially expressed on Tregs; CCR4 interacts with ligands CCL17 and CCL22. CCR4-positive Tregs secrete increased levels of IL-10 and IL-35. CCR4 antagonists markedly reduce tumor-infiltrating Treg numbers and enhance responsiveness to sorafenib in murine liver cancer models (87, 88). Moreover, Mogamulizumab, an anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody, effectively eliminates Tregs through ADCC in adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma patients, significantly increasing tumor-specific CD8+ T cells and promoting secretion of IFN-γ and TNF-α. Fc-optimized anti-CCR8 antibodies selectively deplete CCR8-expressing Tregs within tumors without affecting CCR8+ T cells elsewhere, effectively suppressing tumor growth (89, 90). Additionally, anti-CCR8 treatment induces persistent anti-tumor responses without triggering harmful autoimmune effects. Although several differentially expressed molecules distinguishing tumor-infiltrating Tregs from conventional T cells have been identified, the paucity of Treg-specific targets significantly restricts clinical translation (91–94). Further research is thus required to elucidate Treg-specific expression markers, as well as their development, differentiation, and biological functions within tumors Figure 2.
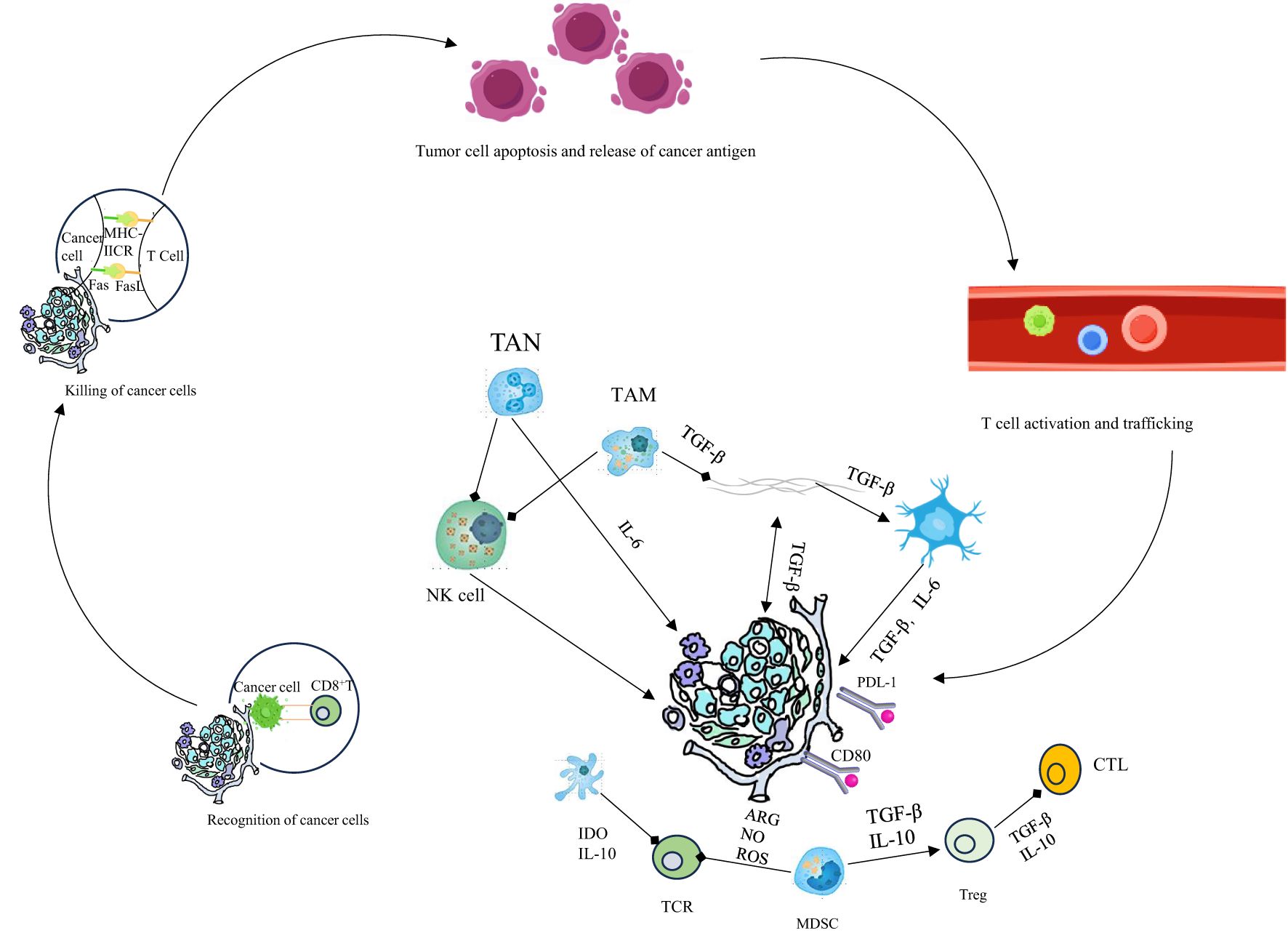
Figure 2. Innate immunity is crucial for the cancer - immunity cycle. Activated by tumors, its cells kill tumor cells directly and prime, expand, and infiltrate tumor - specific T - cells. Therapeutic manipulation of it stimulates antitumor immunity and overcomes immune evasion.
TAM
Macrophages are crucial components of innate immunity, exhibiting remarkable functional plasticity. Under varying physiological and pathological states, macrophages polarize into either classically activated M1 or alternatively activated M2 phenotypes. M1 macrophages directly eliminate tumor cells and amplify adaptive immunity by upregulating antigen-presenting genes and co-stimulatory molecules. Conversely, M2 macrophages facilitate tumor progression (95–97). Within the TME, tumor-derived signals recruit monocytes and induce their polarization into TAMs, promoting tumor cell proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and suppressing CD8+ T-cell-mediated anti-tumor effects. Elevated TAM density correlates with enhanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis, whereas TAM depletion restores immune functions in the TME, inhibiting tumor growth. TAM-depleting agents include bisphosphonates and inhibitors targeting colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and its receptor (CSF-1R) (98, 99).
Bader et al. demonstrated that clodronate-mediated TAM depletion reduces polyp formation in colon cancer mouse models, down-regulates transcription factors related to carcinogenesis, and modulates intestinal flora, thus inhibiting tumor progression (100, 101). CSF-1, a critical growth factor for the monocyte-macrophage lineage, significantly regulates macrophage chemotaxis, survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Many tumors overexpress CSF-1, while its receptor CSF-1R is broadly expressed on monocytes. Therefore, inhibiting the CSF-1/CSF-1R pathway effectively depletes TAMs in tumors. CSF-1R inhibitors, such as BLZ945 and PLX5622, are widely utilized. Inhibitors targeting monocyte and macrophage recruitment effectively block monocyte/macrophage infiltration into the TME, suppressing tumor progression.
Metabolic regulation also critically influences macrophage polarization. Directly targeting intrinsic macrophage metabolism alters polarization states (5). TAMs in tumors exhibit enhanced glutamine and fatty acid metabolism, essential for maintaining their M2 phenotype. Elevated fatty acid oxidation in macrophages enhances mitochondrial OXPHOS, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, phosphorylation of tyrosine protein kinase 1, and activation of STAT6, thus promoting TAM polarization (102, 103). Tumor-derived metabolites further affect macrophage polarization, impacting tumor progression. Specifically, tumor-derived lactic acid binds the lipid receptor G2A on macrophages, activating STAT3 and promoting TAM polarization. Depleting macrophage G2A significantly inhibits their polarization toward TAMs. CD47, expressed on the surface of tumor cells, binds signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) on macrophages, preventing macrophage-mediated tumor clearance through phagocytosis (104). Inhibiting the CD47/SIRPα interaction between macrophages and tumor cells has the potential to restore macrophage-driven anti-tumor immune responses mediated by TAMs (105). Combining CD47/SIRPα-targeted treatments with other therapeutic modalities, including angiogenesis inhibitors and ICIS, can further suppress tumor progression.
Currently, several principal therapeutic agents targeting CD47/SIRPα include: (1) Hu5F9-G4 monoclonal antibody, a macrophage checkpoint inhibitor targeting CD47, promotes tumor cell elimination via macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. Advani et al. demonstrated that combining Hu5F9-G4 with rituximab effectively enhanced antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) to treat B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clinical trials have confirmed significant therapeutic efficacy of Hu5F9-G4 in aggressive and indolent lymphomas (106, 107). (2) CC-90002, a high-affinity humanized monoclonal antibody against CD47, disrupts CD47-SIRPα interactions. Narla et al. indicated significant dose-dependent anti-tumor effects of CC-90002 (108, 109). (3) ALX148 (Evorpacept), an engineered fusion protein comprising a modified SIRPαD1 domain and inactive human IgG1 Fc, binds CD47 with high affinity to block interactions with native SIRPα. ALX148 promotes innate anti-tumor immunity by increasing macrophage phagocytosis, DC activation, and inflammatory TAM polarization. Combining Evorpacept with anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies markedly boosts macrophage phagocytic activity, pro-inflammatory polarization, and DC stimulation, thus potentiating tumor cytotoxicity. Consequently, Evorpacept has emerged as a promising therapeutic candidate targeting CD47 (110). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Evorpacept to treat head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), and HER2-positive gastric or gastroesophageal junction malignancies.
Although TAM depletion strategies inhibit tumor progression, the non-specific effects necessitate further investigation to determine the selective impact on TAM populations and potential collateral effects on beneficial resident macrophages and other immune cells.
DCs
DCs are professional antigen-presenting cells capable of initiating strong anti-tumor immune responses. Increased infiltration of DCs into tumor tissue correlates positively with improved patient prognosis (111). Studies indicate that patients with higher DC infiltration at tumor margins show lower lymph node metastasis rates and better overall survival compared to those lacking DCs. Therefore, DC-based immunotherapy represents a promising strategy for treating cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) (112). Agents that activate DCs or reverse their immunosuppressive functions enhance both DC and T cell activation. GM-CSF directly promotes DC maturation, activation, and migration (113). TLR7/TLR8 agonists stimulate NF-κB signaling, promoting secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increasing the expression of co-stimulatory molecules. Imiquimod, a synthetic TLR7/TLR8 agonist, enhances DC-mediated cytotoxicity and is approved for topical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancers. Clinical trials involving TLR7/TLR8 agonists (e.g., NCT02574377, NCT02692976) are currently underway (114). Additionally, unmethylated CpG oligodeoxynucleotides, representing major TLR9 agonists, activate human DCs, facilitating Th1-biased immune responses and CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity. Clinical evaluations combining CpG oligodeoxynucleotides with ICIS are ongoing (NCT02521870, NCT03831295) (115).
DCs bridge innate and adaptive immunity by activating and programming T cells. Studies suggest that cholesterol, hydroxysteroids, and cholesterol transporters influence DC differentiation and maturation. For instance, 27-HC induces monocyte differentiation into mature DCs, promoting surface expression of characteristic molecules such as MHC-II and CD80, thereby enhancing immune responses (5). Cyclosporin A, a broad-spectrum immunosuppressant, inhibits 27-HC-induced DC differentiation by interacting with calcineurin, down-regulating specific DC markers (116). The absence of ApoE leads to cholesterol accumulation on DC membranes, enhancing antigen presentation through increased aggregation of MHC-II molecules, thus strengthening CD4+ T cell-mediated immune responses. Conversely, oxidized lipids impair DC cross-presentation in cancer by promoting accumulation of triacylglycerols, and fatty acids in DCs, reducing MHC-I expression and exogenous antigen presentation (5). Additionally, liver X receptor (LXR) activation impairs DC migration to lymphoid organs by suppressing CCR7 expression, promoting tumor immune escape.
Several clinical trials have explored DC vaccines, involving the isolation, expansion, and in vitro manipulation of autologous DCs for re-injection into patients. These studies primarily targeted immunogenic cancers, such as prostate cancer and glioblastoma, confirming the safety and clinical efficacy of DC-based vaccines in stimulating NK cells and CD8+ T cell responses (117). Currently, sipuleucel-T (Provenge), an autologous APC vaccine loaded with prostate-specific antigen-GM-CSF fusion proteins, represents the only clinically approved APC-based vaccine. Clinical trials demonstrated that sipuleucel-T extends median overall survival by approximately four months in prostate cancer patients. DC-based therapies have the potential to enhance current cancer treatments; however, developing optimal vaccine strategies requires deeper understanding of DC biology and function (118). Preclinical studies indicate that DC-based anti-tumor immunotherapy holds considerable promise, warranting further clinical validation.
Neutrophils represent an important immune cell population within the TME. Increased proportions of tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) occur frequently in various solid tumors, exhibiting similar pro-tumor activities as PMN-MDSCs (119). Tumor-derived 22-HC recruits Tumor-derived 22-HC recruits TANs through CXCR2 signaling, promoting angiogenesis, immunosuppression, and tumor growth. Additionally, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) induces 24-HC synthesis via CYP46A1, facilitating anti-inflammatory neutrophil infiltration and angiogenesis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (120). TANs mediate immunosuppression via PD-L1, impaired antigen presentation, ROS, and related pathways, representing emerging therapeutic targets and prognostic indicators (121, 122). The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a potential biomarker for tumor prognosis. TAN infiltration closely associates with tumor progression, and quantitative analysis of TANs, Tregs, and TAMs interactions can predict cancer patient outcomes (123).
Targeting TANs with small-molecule inhibitors or neutralizing antibodies is a promising therapeutic strategy. Studies indicate down-regulation of methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) elevates IL-8 expression, enhancing N2 TAN recruitment. IL-8 antagonists eliminate N2 TAN accumulation, significantly delaying tumor growth in mice (124). CXCR1/2 inhibitors can prevent immunosuppressive neutrophil recruitment, enhancing PD-1 therapy efficacy and treatment response rates (119). TANs also inhibit CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity via JAG2 signaling. Blocking the Notch pathway with gamma-secretase inhibitor LY3039478 and anti-JAG2 antibodies delays tumor growth and improves CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity. Additionally, TAN-secreted IL-17a promotes gastric cancer EMT through JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Neutralizing IL-17a or blocking JAK2/STAT3 signaling with inhibitor AG490 reduces TAN-mediated tumor migration and invasion (125).
TANs demonstrate high plasticity and heterogeneity, necessitating further research into their characteristics. Current studies employing single-cell sequencing investigate TAN polarization reprogramming to identify new immunotherapy targets. Tumor cell response to immunotherapy depends not only on intrinsic genetic reprogramming but also on the complex interactions and cytokine/chemokine regulation within the TME (121), Understanding TAN-TME molecular interactions and signaling pathways presents new avenues for targeted tumor immunotherapy, reshaping the TME and hindering tumor cell colonization, growth, and invasion (126). Combined therapeutic strategies targeting TANs, tumor cells, and TME components may enhance tumor immunotherapy outcomes.
NK cells, innate lymphoid cells, possess intrinsic capacity to recognize and eliminate malignant cells independently of prior sensitization. NK cells exhibit potent tumoricidal activity, promoting apoptosis via secretion of perforin, cytotoxic molecules, and TNF. The activating receptor natural killer group 2D (NKG2D), predominantly found on NK cells, mediates tumor recognition and cytotoxicity (127). Cholesterol accumulation in NK cells promotes their activation and enhances their cytotoxic function, significantly influencing cancer progression, notably in hepatocellular carcinoma. Additionally, activation of LXR signaling in multiple myeloma cells elevates NK-cell-mediated cytotoxicity by upregulating NKG2D ligands, including MICA and MICB (128).
PD-1, conventionally recognized as an exhaustion marker on T cells, is also expressed on NK cells. Tumor-derived exosomal circUHRF1 from hepatocellular carcinoma enhances PD-1 expression in NK cells, thus weakening their anti-tumor capacity (129). Similarly, in gastrointestinal malignancies, elevated PD-1 levels on NK cells impair their cytotoxic activities due to PD-L1 binding; disrupting PD-1/PD-L1 interactions restores NK cell functions. Additionally, TIM-3 is another marker of NK cell exhaustion; dual TIM-3 and PD-1-positive NK cells exhibit reduced secretion of IFN-γ and granzyme B, limiting their cytotoxic effectiveness (130). NK cell effector functions in tumors are compromised by inhibitory TME interactions.
Clinical approaches enhancing NK cell function have yielded promising outcomes. A phase III/IVA trial in head and neck cancer demonstrated that PD-1+ NK cell enrichment induced by anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab predicts favorable prognosis. Subsequent anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab administration significantly enhanced cetuximab-induced NK cell activity. In colon cancer, TIGIT blockade prevents NK cell exhaustion, thereby augmenting NK-driven anti-tumor responses and improving T-cell-mediated immunity in an NK-dependent manner. Moreover, re-administration of anti-PD-L1 antibodies enhances persistent immune memory (131). Monalizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting NKG2A, enhances NK cell cytotoxicity and restores CD8+ T cell functions. Phase II clinical trials combining monalizumab with cetuximab in head and neck carcinoma showed an objective response rate of 31%. TGF-β, an important immunosuppressive molecule that induces NKG2A expression, is also an emerging therapeutic target. Inhibitors such as galunisertib block TGF-β, thereby augmenting NK and T cell cytotoxicity and improving outcomes from anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies (132). Future developments will likely increase NK-targeted therapies, offering personalized treatment strategies based on tumor-specific characteristics.
Tumor immunotherapy
Immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI): Upon activation, T lymphocytes involved in anti-tumor immunity up-regulate various inhibitory receptors. These receptors bind ligands highly expressed on tumor cells, suppress immune responses, and weaken anti-tumor immunity. These negative regulatory mechanisms of immune activation are termed immune checkpoints. ICI has emerged as a major area of immunotherapy research. Among extensively studied immune checkpoints are CTLA-4 and PD-1, co-inhibitory receptors expressed by T cells that negatively regulate their function (133). Tumor cells inhibit T cell-mediated immunity primarily by expressing high levels of checkpoint ligands. Immunotherapy strategies employ monoclonal antibodies targeting these checkpoints to enhance endogenous anti-tumor responses. Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of ICIs in reversing tumor-induced immunosuppression. Currently, PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors represent the most actively investigated checkpoint inhibitors. Additionally, CD40, a co-stimulatory receptor on APCs, has emerged as another promising immunotherapy target. Several CD40 agonists are undergoing clinical trials in oncology and immune disorders. ICIs have shown therapeutic success in various malignancies, including melanoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Response rates to ICIs correlate closely with tumor-specific genetic profiles, particularly DNA mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) and microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) status (134). In 2017, the FDA approved pembrolizumab and nivolumab specifically for MSI-H/dMMR CRC. The Phase III clinical trial KEYNOTE-177, involving 307 treatment-naive metastatic CRC patients with MSI-H/dMMR, randomized patients 1:1 to pembrolizumab (200 mg every 3 weeks) or standard chemotherapy. Median progression-free survival (PFS) improved significantly to 16.5 months with pembrolizumab versus 8.2 months with chemotherapy. At 24-month follow-up, the mean survival duration was 13.7 months for pembrolizumab-treated patients compared to 10.8 months for chemotherapy recipients. Adverse event incidence rates were comparable, at 97% (149/153) for pembrolizumab and 99% (142/143) for chemotherapy (135). Pembrolizumab has also entered Phase II clinical studies targeting PD-1 in CCA, significantly improving overall survival (OS) and objective response rates (ORR) in patients harboring mismatch repair defects. FDA-approved ICIs, including pembrolizumab, nivolumab, durvalumab, atezolizumab, and avelumab, have demonstrated efficacy in various solid tumors (Table 3). Emerging checkpoint inhibitors targeting molecules such as TIGIT, TIM-3, and inhibitory ligands (B7-H3, B7-H4, B7-H5) are currently being intensively studied for solid tumor therapy (136).
Combination therapy
To enhance the therapeutic efficacy of immunotherapy, combinations of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies with anti-CTLA-4 antibodies or tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have frequently been explored (137). Combination therapies generally exhibit superior efficacy compared to TKI monotherapy. Although both PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibit T cell activation, CTLA-4 acts primarily during early T cell activation, whereas PD-1 mainly inhibits activated CD8+ T cells within the TME (138). Simultaneous inhibition of CTLA-4 and PD-1 significantly enhances CD8+ T cell activation in tumors, exerting synergistic therapeutic effects. The Phase III CheckMate 214 trial demonstrated that nivolumab plus ipilimumab improved PFS, OS, and ORR compared to sunitinib monotherapy in patients with intermediate- or poor-risk advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), subsequently leading to FDA approval of this combination therapy (139). In preclinical mouse breast cancer models, ICIs induced CD8+ T cell activation and vascular normalization in tumors, alleviating immune suppression within the TME and enhancing ICI. This positive feedback between immune activation and vascular normalization provides a rationale for combining immunotherapy strategies. The Phase III JAVELIN Renal 101 trial indicated that combining the anti-PD-L1 antibody avelumab with axitinib extended median PFS by 6.6 months compared to axitinib alone in advanced renal carcinoma patients (140). Similarly, KEYNOTE-426 demonstrated that pembrolizumab (anti-PD-1 antibody) plus axitinib improved OS, PFS, and ORR versus sunitinib monotherapy. Consequently, the FDA approved these combination therapies in 2019 for advanced renal cancer treatment. In metastatic pancreatic cancer, pembrolizumab combined with CXCR4 inhibitor BL-8040 markedly increased disease control and median OS, associated with elevated CD8+ T cell infiltration, decreased MDSCs, and stable regulatory Treg levels (141). Furthermore, CXCR4 inhibition enhanced the effectiveness of PD-1 blockade combined with chemotherapy in advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Animal models of pancreatic cancer liver metastasis demonstrated that gemcitabine combined with PD-1 blockade improved survival outcomes, increased tumor infiltration of Th1 lymphocytes, and enhanced M1 macrophage activity. Additionally, gemcitabine combined with DC vaccines promoted systemic chemotherapy and T cell-mediated responses. Murine studies further indicated that IL-6 combined with PD-L1 blockade significantly inhibited pancreatic cancer growth. Combining GM-CSF vaccines with PD-1 blockade notably prolonged survival in pancreatic cancer models (142).
However, combination therapy does not universally benefit all patients and can induce severe adverse reactions. In KEYNOTE-426, diarrhea and hypertension were common with pembrolizumab and axitinib, and liver-related adverse events increased compared with monotherapy, forcing treatment discontinuation in 30.5% of patients. Identifying suitable biomarkers and clarifying drug interactions in combination therapies are thus essential to minimize adverse effects and economic burdens (143).
Stem cell therapy that reprograms the TME provides a novel strategy for overcoming tumor immune escape and enhancing treatment sensitivity by intervening in key aspects such as immunity and vascularization in the TME (127, 144, 145). Macrophages have long been utilized in ACT, but the development of macrophage therapies requires a more cost-effective and durable approach for generating M1 macrophages. Among these approaches, macrophages are engineered to express CAR (CAR-M) (146). Zhang et al. found that induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived macrophages (CAR-iMac) have emerged as a promising cellular immunotherapy source (147). In March 2021, the first patient in a phase I multicenter clinical trial received CAR-M therapy targeting HER2 to overcome solid tumors (148). Additionally, promising results have been achieved in preclinical ACT studies using genetically engineered T-cell receptors (TCRs) and chimeric antigen receptors (CARs). In NSCLC, anti-PD-1/PD-L1 combined with CAR-T cell therapy promotes the restoration of normal immune recognition and maintenance of immune system homeostasis (149). Fang et al. reported that PD-1-meso CAR-T cells were effective and safe for advanced ovarian cancer, rapidly improving the TME without obvious adverse reactions (150). However, the long-term efficacy of CAR-T cells remains uncertain in most clinical studies, even for leukemia. Nevertheless, CRISPR/Cas9 technology has significantly advanced the understanding of tumor genomics and contributed to cancer immunotherapy. Lu’s team used CRISPR/Cas9-edited PD-1 knockout T cells in patients with advanced NSCLC. The results showed a median PFS of 7.7 weeks, an OS of 42.6 weeks, and stable disease in two patients (151).
Overall, single-agent immunotherapy exhibits limited efficacy, whereas combination therapies effectively transform the TME from immunosuppressive to immuno-activated states and enhance immune cell infiltration. Additional therapeutic targets in the TME, present opportunities for targeted drug development. Combining such strategies with ICIs is potentially beneficial. Personalized treatment strategies based on patient-specific tumor characteristics will improve treatment outcomes and extend patient survival.
Predictive biomarkers
Predictive biomarkers are critical for population stratification and efficacy assessment, providing an essential pathway for translating basic research into clinical practice. With the advent of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and mass spectrometry flow cytometry, many additional predictive markers have emerged due to the generation of abundant genetic information. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) significantly contribute to tumor heterogeneity. CSCs can drive tumor growth, promote disease progression, and are associated with distant metastasis and treatment resistance. Fendler et al. identified a small CSC population through single-cell sequencing and evaluated CSC heterogeneity, providing new insights for clinical applications related to tumor drug resistance and CSC-targeted treatments (152). ctDNA has demonstrated associations with clinical response or survival in patients with melanoma, colorectal cancer (CRC), and gastric cancer receiving anti-PD-1 therapy. Another analysis of 18 patients with MSS metastatic CRC identified ctDNA as a biomarker predictive of responses to nivolumab immunotherapy (153). Single-cell multi-omics studies and innovative high-throughput sequencing technologies have opened new avenues for personalized patient treatments. For example, in heterogeneous diseases such as bladder cancer, gene expression models based on multi-omics sequencing can identify patient populations likely to respond well to cytotoxic drugs, enabling precise targeted therapies (154).
Noninvasive imaging modalities (e.g., PET, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)) can facilitate monitoring of T-cell activation and anticancer T-cell responses (155–158). Radiomics captures features such as tissue morphology, lesion heterogeneity, and changes during continuous imaging throughout treatment or monitoring (159, 160). Studies report a strong correlation between radiomics features and cellular-level heterogeneity indices. Furthermore, PET and MRI can assess T-cell density by detecting energy metabolism-related substances in tumor tissues (161–163). These non-invasive analytical methods allow dynamic observation of patient responsiveness after treatment.
Summary and prospects
As more combination therapies emerge, involving ICIS, adoptive cell therapy, and chemoradiotherapy or targeted agents, promising outcomes are increasingly evident. However, immunotherapy efficacy requires further improvement. Currently, no reliable predictive indicators for immunotherapy responsiveness exist. Resistance involves complex multifactorial mechanisms, including T cell exhaustion, immunosuppressive cell infiltration, ineffective tumor immune infiltration, and epigenetic factors. Treatment-related adverse reactions present significant clinical challenges. Tumor heterogeneity and dynamic TME interactions account for varied immunotherapy responses and adverse events. Selecting precise targets, identifying suitable patients, and using combination treatments can partly address immunotherapy limitations. Understanding TME impact on immunotherapy is crucial for identifying more effective targets and therapeutic strategies. A deeper understanding of the spatial-temporal heterogeneity within the TME and its interactions with immunotherapy could guide individualized immunotherapy approaches. Concurrently, sensitive and specific biomarker identification will accelerate translating basic research into clinical practice.
Author contributions
HJ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YG: Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – review & editing. SL: Funding acquisition, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.81802888), the Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong (No.2018GSF118088), and the General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M592143).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ACAT, Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; CAF, Cancer-associated fibroblast; CCL, Chemoattractant cytokine ligand; CTLA-4, Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; CTLs, Cytotoxic T lymphocytes; CXCL17, C-X-C motif chemokine 17; DCs, Dendritic cells; GGPP, Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphat; ICBs, Immune checkpoint blockades; IDO, Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase; IFN-γ, Interferon-γ; LAG-3, Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3; LDLR, Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor; MCT, Monocarboxylate transporter; MDSCs, Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; OXPHOS, Oxidative phosphorylation; PD-1, Programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, Programmed death ligand 1; PDGF, Platelet-derived growth factor; RORα, Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor α; TAMs, Tumor-associated macrophages; TILs, Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes; TIGIT, T cell immune receptor with Ig and ITIM domains; TME, Tumor microenvironment; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain-3; TIICs, Tumor-infiltrating immune cells; VEGF, Vascular endothelial growth factor; XBP-1, X-box-binding protein-1.
References
1. Lu C, Liu Y, Ali NM, Zhang B, and Cui X. The role of innate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment and research progress in anti-tumor therapy. Front Immunol. (2023) 13:1039260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039260
2. Petitprez F, Meylan M, de Reyniès A, Sautès-Fridman C, and Fridman WH. The tumor microenvironment in the response to immune checkpoint blockade therapies. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00784
3. Hinshaw DC and Shevde LA. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res. (2019) 79:4557–66. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3962
4. Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, Liang C, Hua J, Liu J, et al. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:131. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01428-1
5. Xia L, Oyang L, Lin J, Tan S, Han Y, Wu N, et al. The cancer metabolic reprogramming and immune response. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01316-8
6. Dai E, Zhu Z, Wahed S, Qu Z, Storkus WJ, and Guo ZS. Epigenetic modulation of antitumor immunity for improved cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:171. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01464-x
7. Greville G, Llop E, Huang C, Creagh-Flynn J, Pfister S, O’Flaherty R, et al. Hypoxia alters epigenetic and N-glycosylation profiles of ovarian and breast cancer cell lines in-vitro. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:1218. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01218
8. Al Tameemi W, Dale TP, Al-Jumaily RMK, and Forsyth NR. Hypoxia-modified cancer cell metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2019) 7:4. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00004
9. S K, B K, D J, J P-T, E G, Sk B, et al. Molecular and functional imaging insights into the role of hypoxia in cancer aggression. Cancer metastasis Rev. (2019) 38:51–64. doi: 10.1007/s10555-019-09788-3
10. Chen Y, Jia K, Sun Y, Zhang C, Li Y, Zhang L, et al. Predicting response to immunotherapy in gastric cancer via multi-dimensional analyses of the tumor immune microenvironment. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4851. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32570-z
11. Xiong J, Chi H, Yang G, Zhao S, Zhang J, Tran LJ, et al. Revolutionizing anti-tumor therapy: unleashing the potential of B cell-derived exosomes. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1188760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188760
12. Du M, Sun L, Guo J, and Lv H. Macrophages and tumor-associated macrophages in the senescent microenvironment: From immunosuppressive TME to targeted tumor therapy. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 204:107198. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107198
13. Sidaway P. Efficacy of TILs confirmed. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:64–4. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00723-0
14. Stanton SE and Disis ML. Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2016) 4:59. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0165-6
15. Savas P, Salgado R, Denkert C, Sotiriou C, Darcy PK, Smyth MJ, et al. Clinical relevance of host immunity in breast cancer: from TILs to the clinic. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2016) 13:228–41. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.215
16. Yu X, Yang J, Xu J, Pan H, Wang W, Yu X, et al. Histone lactylation: from tumor lactate metabolism to epigenetic regulation. Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:1833–54. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.91492
17. Liu W, Wang Y, Bozi LHM, Fischer PD, Jedrychowski MP, Xiao H, et al. Lactate regulates cell cycle by remodeling the anaphase promoting complex. Nature. (2023) 616:790–7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05939-3
18. Huang Z, Gan J, Long Z, Guo G, Shi X, Wang C, et al. Targeted delivery of let-7b to reprogram tumor-associated macrophages and tumor infiltrating dendritic cells for tumor rejection. Biomaterials. (2016) 90:72–84. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.03.009
19. Liu N, Zhang J, Yan M, Chen L, Wu J, Tao Q, et al. Supplementation with α-ketoglutarate improved the efficacy of anti-PD1 melanoma treatment through epigenetic modulation of PD-L1. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:170. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05692-5
20. Xing Y, Ruan G, Ni H, Qin H, Chen S, Gu X, et al. Tumor immune microenvironment and its related miRNAs in tumor progression. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:624725. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.624725
21. Marullo R, Castro M, Yomtoubian S, Calvo-Vidal MN, Revuelta MV, Krumsiek J, et al. The metabolic adaptation evoked by arginine enhances the effect of radiation in brain metastases. Sci Adv. (2021) 7:eabg1964. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg1964
22. Harmon C, O’Farrelly C, and Robinson MW. The immune consequences of lactate in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1259:113–24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-43093-1_7
23. Rostamian H, Khakpoor-Koosheh M, Jafarzadeh L, Masoumi E, Fallah-Mehrjardi K, Tavassolifar MJ, et al. Restricting tumor lactic acid metabolism using dichloroacetate improves T cell functions. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:39. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09151-2
24. Brand A, Singer K, Koehl GE, Kolitzus M, Schoenhammer G, Thiel A, et al. LDHA-associated lactic acid production blunts tumor immunosurveillance by T and NK cells. Cell Metab. (2016) 24:657–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.011
25. Amersfoort J, Schaftenaar FH, Douna H, van Santbrink PJ, van Puijvelde GHM, Slütter B, et al. Diet-induced dyslipidemia induces metabolic and migratory adaptations in regulatory T cells. Cardiovasc Res. (2020) 117:1309–24. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa208
26. Chang HR, Josefs T, Scerbo D, Gumaste N, Hu Y, Huggins L-A, et al. Role of lpL (Lipoprotein lipase) in macrophage polarization in vitro and in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39:1967–85. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312389
27. Ma X, Bi E, Lu Y, Su P, Huang C, Liu L, et al. Cholesterol induces CD8+ T-cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. (2019) 30:143–156.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.04.002
28. Hu C, Qiao W, Li X, Ning Z-K, Liu J, Dalangood S, et al. Tumor-secreted FGF21 acts as an immune suppressor by rewiring cholesterol metabolism of CD8+T cells. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:630–647.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.01.005
29. Szántó M, Gupte R, Kraus WL, Pacher P, and Bai P. PARPs in lipid metabolism and related diseases. Prog Lipid Res. (2021) 84:101117. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2021.101117
30. Yang W, Bai Y, Xiong Y, Zhang J, Chen S, Zheng X, et al. Potentiating the antitumor response of CD8(+) T cells by modulating cholesterol metabolism. Nature. (2016) 531:651–5. doi: 10.1038/nature17412
31. Hartmann P, Trufa DI, Hohenberger K, Tausche P, Trump S, Mittler S, et al. Contribution of serum lipids and cholesterol cellular metabolism in lung cancer development and progression. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:5662. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31575-y
32. Choi W-S, Lee G, Song W-H, Koh J-T, Yang J, Kwak J-S, et al. The CH25H-CYP7B1-RORα axis of cholesterol metabolism regulates osteoarthritis. Nature. (2019) 566:254–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0920-1
33. Park JH, Lee J, Lee G-R, Kwon M, Lee HI, Kim N, et al. Cholesterol sulfate inhibits osteoclast differentiation and survival by regulating the AMPK-Sirt1-NF-κB pathway. J Cell Physiol. (2023) 238:2063–75. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31064
34. Wang Y-N, Ruan D-Y, Wang Z-X, Yu K, Rong D-L, Liu Z-X, et al. Targeting the cholesterol-RORα/γ axis inhibits colorectal cancer progression through degrading c-myc. Oncogene. (2022) 41:5266–78. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02515-3
35. Zhu C, Xie Y, Li Q, Zhang Z, Chen J, Zhang K, et al. CPSF6-mediated XBP1 3’UTR shortening attenuates cisplatin-induced ER stress and elevates chemo-resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. Drug Resist Update. (2023) 68:100933. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2023.100933
36. Yang Z, Huo Y, Zhou S, Guo J, Ma X, Li T, et al. Cancer cell-intrinsic XBP1 drives immunosuppressive reprogramming of intratumoral myeloid cells by promoting cholesterol production. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:2018–2035.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.10.010
37. Urra H, Dufey E, Avril T, Chevet E, and Hetz C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the hallmarks of cancer. Trends Cancer. (2016) 2:252–62. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.03.007
38. Perucha E, Melchiotti R, Bibby JA, Wu W, Frederiksen KS, Roberts CA, et al. The cholesterol biosynthesis pathway regulates IL-10 expression in human Th1 cells. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:498. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08332-9
39. Salkeni MA and Naing A. Interleukin-10 in cancer immunotherapy: from bench to bedside. Trends Cancer. (2023) 9:716–25. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.05.003
40. Sun H, Wu Y, Zhang Y, and Ni B. IL-10-producing ILCs: molecular mechanisms and disease relevance. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:650200. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.650200
41. Xu Z, Chen Y, Ma L, Chen Y, Liu J, Guo Y, et al. Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:3133–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.01.046
42. Chen B, Dragomir MP, Yang C, Li Q, Horst D, and Calin GA. Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy resistance. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:121. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00975-3
43. Cortez MA, Ivan C, Valdecanas D, Wang X, Peltier HJ, Ye Y, et al. PDL1 Regulation by p53 via miR-34. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2015) 108:djv303. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv303
44. Xia R, Geng G, Yu X, Xu Z, Guo J, Liu H, et al. LINC01140 promotes the progression and tumor immune escape in lung cancer by sponging multiple microRNAs. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002746. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002746
45. Lo Cicero A, Stahl PD, and Raposo G. Extracellular vesicles shuffling intercellular messages: for good or for bad. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2015) 35:69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.04.013
46. Li P, Luo X, Xie Y, Li P, Hu F, Chu J, et al. GC-derived EVs enriched with microRNA-675-3p contribute to the MAPK/PD-L1-mediated tumor immune escape by targeting CXXC4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 22:615–26. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.08.020
47. Melchionna R, Trono P, Di Carlo A, Di Modugno F, and Nisticò P. Transcription factors in fibroblast plasticity and CAF heterogeneity. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:347. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02934-4
48. Peng D, Fu M, Wang M, Wei Y, and Wei X. Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:104. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01569-x
49. Liu Y, Xun Z, Ma K, Liang S, Li X, Zhou S, et al. Identification of a tumor immune barrier in the HCC microenvironment that determines the efficacy of immunotherapy. J Hepatol. (2023) 78:770–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.01.011
50. Zhu G-Q, Tang Z, Huang R, Qu W-F, Fang Y, Yang R, et al. CD36+ cancer-associated fibroblasts provide immunosuppressive microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma via secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Cell Discov. (2023) 9:25. doi: 10.1038/s41421-023-00529-z
51. Lee YE, Go G-Y, Koh E-Y, Yoon H-N, Seo M, Hong S-M, et al. Synergistic therapeutic combination with a CAF inhibitor enhances CAR-NK-mediated cytotoxicity via reduction of CAF-released IL-6. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006130. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006130
52. Mhaidly R and Mechta-Grigoriou F. Fibroblast heterogeneity in tumor micro-environment: Role in immunosuppression and new therapies. Semin Immunol. (2020) 48:101417. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2020.101417
53. Hu Y, Recouvreux MS, Haro M, Taylan E, Taylor-Harding B, Walts AE, et al. INHBA(+) cancer-associated fibroblasts generate an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2024) 8:35. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00523-y
54. Taylor JL, Kokolus KM, Basse PH, Filderman JN, Cosgrove CE, Watkins SC, et al. Therapeutic anti-tumor efficacy of DC-based vaccines targeting TME-associated antigens is improved when combined with a chemokine-modulating regimen and/or anti-PD-L1. Vaccines (Basel). (2024) 12:777. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070777
55. Kundu M, Butti R, Panda VK, Malhotra D, Das S, Mitra T, et al. Modulation of the tumor microenvironment and mechanism of immunotherapy-based drug resistance in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:92. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01990-4
56. Piwocka O, Piotrowski I, Suchorska WM, and Kulcenty K. Dynamic interactions in the tumor niche: how the cross-talk between CAFs and the tumor microenvironment impacts resistance to therapy. Front Mol Biosci. (2024) 11:1343523. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1343523
57. Li Z, Xia Q, He Y, Li L, and Yin P. MDSCs in bone metastasis: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Cancer Lett. (2024) 592:216906. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216906
58. Hegde S, Leader AM, and Merad M. MDSC: Markers, development, states, and unaddressed complexity. Immunity. (2021) 54:875–84. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.04.004
59. J C, X L, Y Z, J G, Z G, X L, et al. A high-fat diet promotes cancer progression by inducing gut microbiota-mediated leucine production and PMN-MDSC differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2024) 121:e2306776121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2306776121
60. Matsushita M, Fujita K, Hatano K, Hayashi T, Kayama H, Motooka D, et al. High-fat diet promotes prostate cancer growth through histamine signaling. Int J Cancer. (2022) 151:623–36. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34028
61. Ruan H, Zhang J, Wang Y, Huang Y, Wu J, He C, et al. 27-Hydroxycholesterol/liver X receptor/apolipoprotein E mediates zearalenone-induced intestinal immunosuppression: A key target potentially linking zearalenone and cancer. J Pharm Anal. (2024) 14:371–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.08.002
62. Pushalkar S, Hundeyin M, Daley D, Zambirinis CP, Kurz E, Mishra A, et al. The pancreatic cancer microbiome promotes oncogenesis by induction of innate and adaptive immune suppression. Cancer Discov. (2018) 8:403–16. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1134
63. Chen H, Pan Y, Zhou Q, Liang C, Wong C-C, Zhou Y, et al. METTL3 inhibits antitumor immunity by targeting m6A-BHLHE41-CXCL1/CXCR2 axis to promote colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. (2022) 163:891–907. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.024
64. Marks ZRC, Campbell NK, Mangan NE, Vandenberg CJ, Gearing LJ, Matthews AY, et al. Interferon-ϵ is a tumor suppressor and restricts ovarian cancer. Nature. (2023) 620:1063–70. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06421-w
65. Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob J-J, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, et al. Long-term outcomes with nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone versus ipilimumab in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:127–37. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02229
66. Tavazoie MF, Pollack I, Tanqueco R, Ostendorf BN, Reis BS, Gonsalves FC, et al. LXR/apoE activation restricts innate immune suppression in cancer. Cell. (2018) 172:825–840.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.026
67. LXR agonism depletes MDSCs to promote antitumor immunity. Cancer Discov. (2018) 8:263. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2018-010
68. Zhang W, Luo M, Zhou Y, Hu J, Li C, Liu K, et al. Liver X receptor agonist GW3965 protects against sepsis by promoting myeloid derived suppressor cells apoptosis in mice. Life Sci. (2021) 276:119434. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119434
69. Liang X, Cao Y, Xiang S, and Xiang Z. LXRα-mediated downregulation of EGFR suppress colorectal cancer cell proliferation. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:17391–404. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29003
70. Ohkura N and Sakaguchi S. Transcriptional and epigenetic basis of Treg cell development and function: its genetic anomalies or variations in autoimmune diseases. Cell Res. (2020) 30:465–74. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0324-7
71. Proto JD, Doran AC, Gusarova G, Yurdagul A, Sozen E, Subramanian M, et al. Regulatory T cells promote macrophage efferocytosis during inflammation resolution. Immunity. (2018) 49:666–677.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.015
72. Whiteside SK, Grant FM, Alvisi G, Clarke J, Tang L, Imianowski CJ, et al. Acquisition of suppressive function by conventional T cells limits antitumor immunity upon Treg depletion. Sci Immunol. (2023) 8:eabo5558. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abo5558
73. Abbas AK, Trotta E R, Simeonov D, Marson A, and Bluestone JA. Revisiting IL-2: Biology and therapeutic prospects. Sci Immunol. (2018) 3:eaat1482. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aat1482
74. Gu J, Zhou J, Chen Q, Xu X, Gao J, Li X, et al. Tumor metabolite lactate promotes tumorigenesis by modulating MOESIN lactylation and enhancing TGF-β signaling in regulatory T cells. Cell Rep. (2022) 39:110986. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110986
75. Huo R, Yang W-J, Liu Y, Liu T, Li T, Wang C-Y, et al. Stigmasterol: Remodeling gut microbiota and suppressing tumor growth through Treg and CD8+ T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Phytomedicine. (2024) 129:155225. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155225
76. Josefowicz SZ, Lu L-F, and Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. (2012) 30:531–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141623
77. de Candia P, Procaccini C, Russo C, Lepore MT, and Matarese G. Regulatory T cells as metabolic sensors. Immunity. (2022) 55:1981–92. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.10.006
78. Yin X, Chen S, and Eisenbarth SC. Dendritic cell regulation of T helper cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2021) 39:759–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-101819-025146
79. Moreno Ayala MA, Campbell TF, Zhang C, Dahan N, Bockman A, Prakash V, et al. CXCR3 expression in regulatory T cells drives interactions with type I dendritic cells in tumors to restrict CD8+ T cell antitumor immunity. Immunity. (2023) 56:1613–1630.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.06.003
80. Shevach EM and Thornton AM. tTregs, pTregs, and iTregs: similarities and differences. Immunol Rev. (2014) 259:88–102. doi: 10.1111/imr.12160
81. Hafkamp FMJ, Groot Kormelink T, and de Jong EC. Targeting DCs for tolerance induction: don’t lose sight of the neutrophils. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:732992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732992
82. Dong S, Guo X, Han F, He Z, and Wang Y. Emerging role of natural products in cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:1163–85. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.08.020
83. Sharma N, Fan X, Atolagbe OT, Ge Z, Dao KN, Sharma P, et al. ICOS costimulation in combination with CTLA-4 blockade remodels tumor-associated macrophages toward an antitumor phenotype. J Exp Med. (2024) 221:e20231263. doi: 10.1084/jem.20231263
84. Chow A, SChad S, Green MD, Hellmann MD, Allaj V, Ceglia N, et al. Tim-4+ cavity-resident macrophages impair anti-tumor CD8+ T cell immunity. Cancer Cell. (2021) 39:973–988.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.05.006
85. Rahma OE and Hodi FS. The intersection between tumor angiogenesis and immune suppression. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:5449–57. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1543
86. Wu X, Giobbie-Hurder A, Liao X, Connelly C, Connolly EM, Li J, et al. Angiopoietin-2 as a biomarker and target for immune checkpoint therapy. Cancer Immunol Res. (2017) 5:17–28. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0206
87. Korbecki J, Kojder K, Simińska D, Bohatyrewicz R, Gutowska I, Chlubek D, et al. CC chemokines in a tumor: A review of pro-cancer and anti-cancer properties of the ligands of receptors CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, and CCR4. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:8412. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218412
88. Chiang Y, Lu L-F, Tsai C-L, Tsai Y-C, Wang C-C, Hsueh F-J, et al. C-C chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4)-positive regulatory T cells interact with tumor-associated macrophages to facilitate metastatic potential after radiation. Eur J Cancer. (2024) 198:113521. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113521
89. de Masson A, Darbord D, Dobos G, Boisson M, Roelens M, Ram-Wolff C, et al. Macrophage-derived CXCL9 and CXCL11, T-cell skin homing, and disease control in mogamulizumab-treated CTCL patients. Blood. (2022) 139:1820–32. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021013341
90. Strobl J and Haniffa M. Functional heterogeneity of human skin-resident memory T cells in health and disease. Immunol Rev. (2023) 316:104–19. doi: 10.1111/imr.13213
91. Zagorulya M, Yim L, Morgan DM, Edwards A, Torres-Mejia E, Momin N, et al. Tissue-specific abundance of interferon-gamma drives regulatory T cells to restrain DC1-mediated priming of cytotoxic T cells against lung cancer. Immunity. (2023) 56:386–405.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.01.010
92. Twyman-Saint Victor C, Rech AJ, Maity A, Rengan R, Pauken KE, Stelekati E, et al. Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature. (2015) 520:373–7. doi: 10.1038/nature14292
93. Wang Y, Yang H, Jia A, Wang Y, Yang Q, Dong Y, et al. Dendritic cell Piezo1 directs the differentiation of TH1 and Treg cells in cancer. Elife. (2022) 11:e79957. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79957
94. Levine AG, Mendoza A, Hemmers S, Moltedo B, Niec RE, Schizas M, et al. Stability and function of regulatory T cells expressing the transcription factor T-bet. Nature. (2017) 546:421–5. doi: 10.1038/nature22360
95. Xiang X, Wang J, Lu D, and Xu X. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to synergize tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6:75. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00484-9
96. Zhang H, Liu L, Liu J, Dang P, Hu S, Yuan W, et al. Roles of tumor-associated macrophages in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for solid cancers. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:58. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01725-x
97. Chen D, Zhang X, Li Z, and Zhu B. Metabolic regulatory crosstalk between tumor microenvironment and tumor-associated macrophages. Theranostics. (2021) 11:1016–30. doi: 10.7150/thno.51777
98. Huang M, Lin Y, Wang C, Deng L, Chen M, Assaraf YG, et al. New insights into antiangiogenic therapy resistance in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic aspects. Drug Resist Update. (2022) 64:100849. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2022.100849
99. Cannarile MA, Weisser M, Jacob W, Jegg A-M, Ries CH, and Rüttinger D. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Immunother Cancer. (2017) 5:53. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0257-y
100. Bader JE, Enos RT, Velázquez KT, Carson MS, Sougiannis AT, McGuinness OP, et al. Repeated clodronate-liposome treatment results in neutrophilia and is not effective in limiting obesity-linked metabolic impairments. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 316:E358–72. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00438.2018
101. Rohm TV, Keller L, Bosch AJT, AlAsfoor S, Baumann Z, Thomas A, et al. Targeting colonic macrophages improves glycemic control in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Commun Biol. (2022) 5:370. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03305-z
102. Leone RD, Zhao L, Englert JM, Sun I-M, Oh M-H, Sun I-H, et al. Glutamine blockade induces divergent metabolic programs to overcome tumor immune evasion. Science. (2019) 366:1013–21. doi: 10.1126/science.aav2588
103. Oh M-H, Sun I-H, Zhao L, Leone RD, Sun I-M, Xu W, et al. Targeting glutamine metabolism enhances tumor-specific immunity by modulating suppressive myeloid cells. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:3865–84. doi: 10.1172/JCI131859
104. Tang L, Yin Y, Cao Y, Fu C, Liu H, Feng J, et al. Extracellular vesicles-derived hybrid nanoplatforms for amplified CD47 blockade-based cancer immunotherapy. Adv Mater. (2023) 35:e2303835. doi: 10.1002/adma.202303835
105. Huang C, Wang X, Wang Y, Feng Y, Wang X, Chen S, et al. Sirpα on tumor-associated myeloid cells restrains antitumor immunity in colorectal cancer independent of its interaction with CD47. Nat Cancer. (2024) 5:500–16. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00691-z
106. Sikic BI, Lakhani N, Patnaik A, Shah SA, Chandana SR, Rasco D, et al. First-in-human, first-in-class phase I trial of the anti-CD47 antibody hu5F9-G4 in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol. (2019) 37:946–53. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.02018
107. Kayser S and Levis MJ. The clinical impact of the molecular landscape of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. (2023) 108:308–20. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.280801
108. Russ A, Hua AB, Montfort WR, Rahman B, Riaz IB, Khalid MU, et al. Blocking “don’t eat me” signal of CD47-SIRPα in hematological Malignancies, an in-depth review. Blood Rev. (2018) 32:480–9. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2018.04.005
109. Kaur S, Reginauld B, Razjooyan S, Phi T, Singh SP, Meyer TJ, et al. Effects of a humanized CD47 antibody and recombinant SIRPα proteins on triple negative breast carcinoma stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1356421. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1356421
110. Lakhani NJ, Chow LQM, Gainor JF, LoRusso P, Lee K-W, Chung HC, et al. Evorpacept alone and in combination with pembrolizumab or trastuzumab in patients with advanced solid tumors (ASPEN-01): a first-in-human, open-label, multicenter, phase 1 dose-escalation and dose-expansion study. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:1740–51. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00584-2
111. Worbs T, Hammerschmidt SI, and Förster R. Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:30–48. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.116
112. Tiberio L, Del Prete A, Schioppa T, Sozio F, Bosisio D, and Sozzani S. Chemokine and chemotactic signals in dendritic cell migration. Cell Mol Immunol. (2018) 15:346–52. doi: 10.1038/s41423-018-0005-3
113. Achuthan AA, Lee KMC, and Hamilton JA. Targeting GM-CSF in inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Semin Immunol. (2021) 54:101523. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2021.101523
114. Murphy TL and Murphy KM. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology. Cell Mol Immunol. (2022) 19:3–13. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00741-5
115. Ding L, Liang M, Li Y, Zeng M, Liu M, Ma W, et al. Zinc-organometallic framework vaccine controlled-release zn2+ Regulates tumor extracellular matrix degradation potentiate efficacy of immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2302967. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302967
116. Fervenza FC, Appel GB, Barbour SJ, Rovin BH, Lafayette RA, Aslam N, et al. Rituximab or cyclosporine in the treatment of membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:36–46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1814427
117. Huang L, Rong Y, Tang X, Yi K, Qi P, Hou J, et al. Engineered exosomes as an in situ DC-primed vaccine to boost antitumor immunity in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:45. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01515-x
118. Chang R, Gulley JL, and Fong L. Vaccinating against cancer: getting to prime time. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006628. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006628
119. Que H, Fu Q, Lan T, Tian X, and Wei X. Tumor-associated neutrophils and neutrophil-targeted cancer therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2022) 1877:188762. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188762
120. Li H, Liu Y, Xue Z, Zhang L, Ruan X, Yang J, et al. Adamantaniline derivatives target ATP5B to inhibit translation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2301071. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301071
121. Wu Y, Ma J, Yang X, Nan F, Zhang T, Ji S, et al. Neutrophil profiling illuminates anti-tumor antigen-presenting potency. Cell. (2024) 187:1422–1439.e24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.02.005
122. Giese MA, Hind LE, and Huttenlocher A. Neutrophil plasticity in the tumor microenvironment. Blood. (2019) 133:2159–67. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-11-844548
123. Hu J, Zhang L, Xia H, Yan Y, Zhu X, Sun F, et al. Tumor microenvironment remodeling after neoadjuvant immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Genome Med. (2023) 15:14. doi: 10.1186/s13073-023-01164-9
124. Zhou Y, Guo S, Li Y, Chen F, Wu Y, Xiao Y, et al. METTL3 is associated with the Malignancy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and serves as a potential immunotherapy biomarker. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:824190. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.824190
125. Cheng Y, Mo F, Li Q, Han X, Shi H, Chen S, et al. Targeting CXCR2 inhibits the progression of lung cancer and promotes therapeutic effect of cisplatin. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:62. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01355-1
126. Maas RR, Soukup K, Fournier N, Massara M, Galland S, Kornete M, et al. The local microenvironment drives activation of neutrophils in human brain tumors. Cell. (2023) 186:4546–4566.e27. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.043
127. Wu S-Y, Fu T, Jiang Y-Z, and Shao Z-M. Natural killer cells in cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:120. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01238-x
128. Bilotta MT, Abruzzese MP, Molfetta R, Scarno G, Fionda C, Zingoni A, et al. Activation of liver X receptor up-regulates the expression of the NKG2D ligands MICA and MICB in multiple myeloma through different molecular mechanisms. FASEB J. (2019) 33:9489–504. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900319R
129. Zhang P-F, Gao C, Huang X-Y, Lu J-C, Guo X-J, Shi G-M, et al. Cancer cell-derived exosomal circUHRF1 induces natural killer cell exhaustion and may cause resistance to anti-PD1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:110. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01222-5
130. Dong W, Wu X, Ma S, Wang Y, Nalin AP, Zhu Z, et al. The mechanism of anti-PD-L1 antibody efficacy against PD-L1-negative tumors identifies NK cells expressing PD-L1 as a cytolytic effector. Cancer Discov. (2019) 9:1422–37. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1259
131. Kyrysyuk O and Wucherpfennig KW. Designing cancer immunotherapies that engage T cells and NK cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2023) 41:17–38. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-101921-044122
132. André P, Denis C, Soulas C, Bourbon-Caillet C, Lopez J, Arnoux T, et al. Anti-NKG2A mAb is a checkpoint inhibitor that promotes anti-tumor immunity by unleashing both T and NK cells. Cell. (2018) 175:1731–1743.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.014
133. Helmink BA, Reddy SM, Gao J, Zhang S, Basar R, Thakur R, et al. B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response. Nature. (2020) 577:549–55. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1922-8
134. Li J, Wu C, Hu H, Qin G, Wu X, Bai F, et al. Remodeling of the immune and stromal cell compartment by PD-1 blockade in mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41:1152–1169.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.04.011
135. André T, Shiu K-K, Kim TW, Jensen BV, Jensen LH, Punt C, et al. Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-instability-high advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:2207–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2017699
136. Overman MJ, Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, Wong M, Limon Miron ML, Leonard G, et al. Nivolumab plus relatlimab in patients with previously treated microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: the phase II CheckMate 142 study. J Immunother Cancer. (2024) 12:e008689. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008689
137. Ribas A and Wolchok JD. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. (2018) 359:1350–5. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4060
138. Postow MA, Callahan MK, and Wolchok JD. Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:1974–82. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.4358
139. Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Bourlon MT, Zurawski B, et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:829–41. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2026982
140. Yi M, Zheng X, Niu M, Zhu S, Ge H, and Wu K. Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: current advances and future directions. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01489-2
141. Schmid P, Cortes J, Dent R, Pusztai L, McArthur H, Kümmel S, et al. Event-free survival with pembrolizumab in early triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:556–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2112651
142. Huseni MA, Wang L, Klementowicz JE, Yuen K, Breart B, Orr C, et al. CD8+ T cell-intrinsic IL-6 signaling promotes resistance to anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy. Cell Rep Med. (2023) 4:100878. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100878
143. Powles T, Plimack ER, Soulières D, Waddell T, Stus V, Gafanov R, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): extended follow-up from a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:1563–73. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8
144. Rafae A, van Rhee F, and Al Hadidi S. Perspectives on the treatment of multiple myeloma. Oncologist. (2024) 29:200–12. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad306
145. Li Y-R, Dunn ZS, Yu Y, Li M, Wang P, and Yang L. Advancing cell-based cancer immunotherapy through stem cell engineering. Cell Stem Cell. (2023) 30:592–610. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.02.009
146. Maalej KM, Merhi M, Inchakalody VP, Mestiri S, Alam M, Maccalli C, et al. CAR-cell therapy in the era of solid tumor treatment: current challenges and emerging therapeutic advances. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:20. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01723-z
147. Zhang L, Tian L, Dai X, Yu H, Wang J, Lei A, et al. Pluripotent stem cell-derived CAR-macrophage cells with antigen-dependent anti-cancer cell functions. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:153. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00983-2
148. Li W, Wang F, Guo R, Bian Z, and Song Y. Targeting macrophages in hematological Malignancies: recent advances and future directions. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:110. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01328-x
149. Sui H, Ma N, Wang Y, Li H, Liu X, Su Y, et al. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: toward personalized medicine and combination strategies. J Immunol Res. (2018) 2018:6984948. doi: 10.1155/2018/6984948
150. Fang J, Ding N, Guo X, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Xie B, et al. αPD-1-mesoCAR-T cells partially inhibit the growth of advanced/refractory ovarian cancer in a patient along with daily apatinib. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e001162. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001162
151. Lu Y, Xue J, Deng T, Zhou X, Yu K, Deng L, et al. Safety and feasibility of CRISPR-edited T cells in patients with refractory non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Med. (2020) 26:732–40. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0840-5
152. Fendler A, Bauer D, Busch J, Jung K, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Kunz S, et al. Inhibiting WNT and NOTCH in renal cancer stem cells and the implications for human patients. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:929. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14700-7
153. Kasi PM, Budde G, Krainock M, Aushev VN, Koyen Malashevich A, Malhotra M, et al. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) serial analysis during progression on PD-1 blockade and later CTLA-4 rescue in patients with mismatch repair deficient metastatic colorectal cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e003312. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003312
154. Baysoy A, Bai Z, Satija R, and Fan R. The technological landscape and applications of single-cell multi-omics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 24:695–713. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00615-w
155. Li K, Liu W, Yu H, Chen J, Tang W, Wang J, et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET imaging monitors response to combined TGF-βR inhibition and immunotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134:e170490. doi: 10.1172/JCI170490
156. Mu W, Jiang L, Shi Y, Tunali I, Gray JE, Katsoulakis E, et al. Non-invasive measurement of PD-L1 status and prediction of immunotherapy response using deep learning of PET/CT images. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002118. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002118
157. Tong H, Sun J, Fang J, Zhang M, Liu H, Xia R, et al. A machine learning model based on PET/CT radiomics and clinical characteristics predicts tumor immune profiles in non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective multicohort study. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:859323. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.859323
158. Liu L, Yoon CW, Yuan Z, Guo T, Qu Y, He P, et al. Cellular and molecular imaging of CAR-T cell-based immunotherapy. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2023) 203:115135. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115135
159. Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, Häggström I, Szczypiński P, Gibbs P, et al. Introduction to radiomics. J Nucl Med. (2020) 61:488–95. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.222893
160. Chen M, Copley SJ, Viola P, Lu H, and Aboagye EO. Radiomics and artificial intelligence for precision medicine in lung cancer treatment. Semin Cancer Biol. (2023) 93:97–113. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.05.004
161. Magistretti PJ and Allaman I. A cellular perspective on brain energy metabolism and functional imaging. Neuron. (2015) 86:883–901. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.035
162. Hyder F and Rothman DL. Quantitative fMRI and oxidative neuroenergetics. Neuroimage. (2012) 62:985–94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.04.027
Keywords: immune checkpoint, tumor microenvironment, cancer immunotherapy, immune cells, immunotherapy resistance
Citation: Jing H, Gao Y, Sun Z and Liu S (2025) Recent advances in novel tumor immunotherapy strategies based on regulating the tumor microenvironment and immune checkpoints. Front. Immunol. 16:1529403. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1529403
Received: 16 November 2024; Accepted: 28 May 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025.
Edited by:
Juana Serrano Lopez, Health Research Institute Foundation Jimenez Diaz (IIS-FJD), SpainReviewed by:
Paula Dobosz, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, PolandKhalil Hajiasgharzadeh, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Jing, Gao, Sun and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shanglong Liu, bGl1c2hhbmdsb25nQHFkdS5lZHUuY24=
 Hanhui Jing
Hanhui Jing Yan Gao
Yan Gao Shanglong Liu
Shanglong Liu