- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou, Shandong, China
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute, Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan, Shandong, China
As a core mechanism regulating intracellular protein homeostasis, the dynamic equilibrium between ubiquitination and deubiquitination profoundly impacts the functionality and fate of target proteins. The Ovarian tumor domain (OTU) family, a vital subclass of deubiquitinating enzymes, comprises 16 members that mediate ubiquitin binding and hydrolysis through their characteristic OTU domain. Recent years have witnessed growing interest in OTU family members in oncology and immunology research. This review comprehensively elucidates the core mechanisms by which OTU members regulate tumor-associated signaling networks via substrate-specific deubiquitination. On one hand, they directly govern tumor cell proliferation, metastasis, and apoptosis by modulating the stability of key substrates. On the other hand, they orchestrate tumor progression through dynamic regulation of inflammatory intensity, immune response duration, and immune evasion mechanisms within the tumor microenvironment (TME), thereby constructing a multidimensional regulatory network in tumor development. These findings not only unveil the pivotal role of OTU family members in tumorigenesis and immune modulation but also establish a theoretical foundation for developing novel anti-tumor therapeutics targeting deubiquitination processes. Notably, OTUs emerge as high-potential therapeutic targets with high translational relevance for refining precision-guided tumor-immunotherapy integration strategies.
Introduction
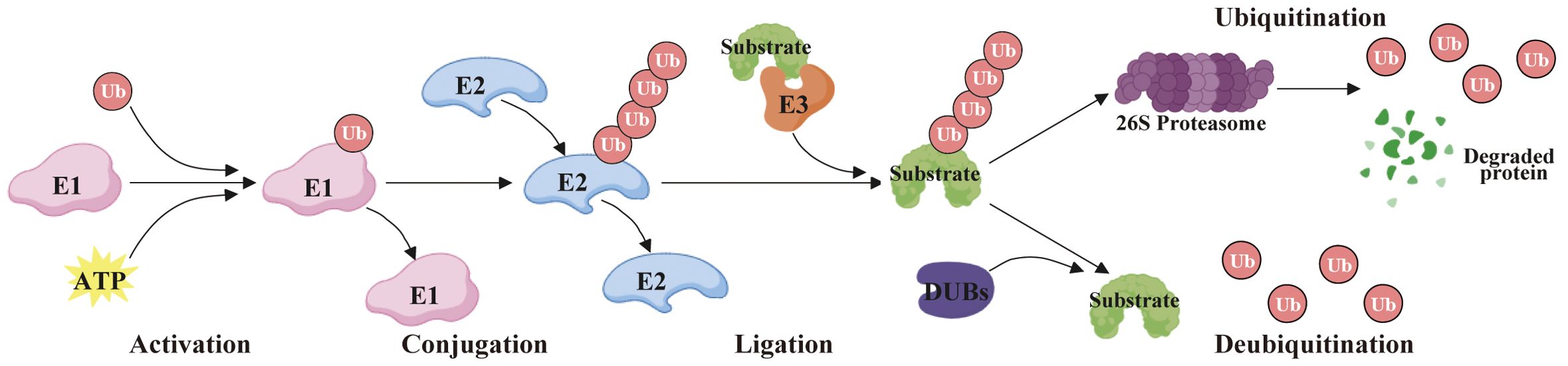
Protein ubiquitination is a significant post-translational modification process that denotes the covalent attachment of ubiquitin to specific lysine residues of a target protein via an enzymatic reaction. During this procedure, the ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) first forms the ubiquitin-acyl acylase complex by activating the ubiquitin molecule. Second, the activated ubiquitin is transferred to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), forming the ubiquitin-E2 complex. Then, ubiquitin ligase (E3) is responsible for recognizing specific target proteins and transferring ubiquitin from E2 to lysine residues of the target protein. Ultimately, the ubiquitin on the target protein can further bind to other ubiquitin molecules to form polyubiquitin chains, which are usually a hallmark of signal transduction or degradation (1) (Figure 1). Protein ubiquitination is essential in protein degradation, signal transduction, DNA repair, and immune response, and the reason for its functional diversity is the variety of ubiquitination types, categorized as mono-ubiquitination and polyubiquitination. Generally, the polyubiquitin chains are formed by seven lysine residues (K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48, and K63) and one N-terminal Met1 (2). Of these, the K48 polyubiquitin chains (K48-Ub) are the most prevalent form, which usually symbolizes that the protein is about to be degraded by the proteasome, whereas the K63 polyubiquitin chains (K63-Ub) are typically implicated in signaling and DNA repair, etc., and is not directly engaged in the degradation of proteins (3). These various types of ubiquitination mechanisms permit the cell to precisely regulate protein function, reflecting the sophisticated intracellular regulatory network.
Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are a class of proteases that reverse protein ubiquitination by specifically removing ubiquitin molecules from substrate proteins, thereby regulating their stability, activity, and biological functions. As critical regulators of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), DUBs modulate cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and stress responses through the removal or editing of ubiquitin chains. Dysregulation of DUB activity is closely associated with tumorigenesis and cancer progression (4). Based on their catalytic domain features, DUBs are categorized into five major families: Ubiquitin-specific proteases (USP), Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCH), Machado-Joseph disease proteases (MJD), Ovarian tumor proteases (OTU), and JAMM/MPN metalloproteases. Members of these families exhibit marked functional heterogeneity in cancer contexts (5).
Taking OTUB1 (from the OTU family) and USP7 (from the USP family) as examples, their mechanisms in tumorigenesis and therapeutic targeting diverge significantly. OTUB1 drives malignancy by mediating tumor immune evasion, promoting cell migration, and regulating tumor grading-associated signaling pathways (e.g., in glioma) (6); USP7 predominantly facilitates oncogenesis by stabilizing oncoproteins (e.g., in hepatocellular carcinoma) (7), enhancing tumor cell proliferation (e.g., in non-small cell lung cancer) (8), and suppressing tumor suppressor activity (e.g., p53) (9). This functional divergence informs distinct therapeutic strategies: interventions targeting OTUB1 prioritize immunomodulation and migration inhibition, whereas USP7-focused therapies aim to restore tumor suppressor function and block pro-proliferative signaling (10).
To date, research on the OTU family is rapidly evolving, revealing significant potential in disease onset, progression, and treatment. Thus in this review, we describe comprehensively the roles of OTU family members in oncology and immunity, including the functions of OTUs in tumorigenesis, tumor stemness, ferroptosis, DNA repair, chemo- and radiotherapy, clinical relevance, inflammatory response, autoimmunity, anti-viral immunity, and anti-tumor immunity.
Essential characteristics of the OTUs
The OTU family comprises DUBs that regulate protein stability and function by removing ubiquitin modifications. These enzymes are integral to diverse cellular processes, including signaling, cell cycle control, immune responses, and stress adaptation. To date, 16 OTU deubiquitylases have been identified, classified into four subfamilies: (a) the OTUB subfamily (OTUB1 and OTUB2); (b) the OTUD subfamily (OTUD1, YOD1/OTUD2, OTUD3, OTUD4, OTUD5/DUBA, OTUD6A, and OTUD6B); (c) the A20-like subfamily (TNFAIP3/A20, OTUD7A/Cezanne2, OTUD7B/Cezanne, ZRANB1/TRABID, and VCPIP1); (d) the OTULIN subfamily: OTULIN/FAM105B and OTULINL/FAM105A) (11–13). All members harbor a conserved OTU domain (OTUD) responsible for catalytic activity, although OTULINL lacks catalytic triad residues. Most OTU enzymes also contain auxiliary domains (e.g., UBDs) that refine substrate specificity (14) (Figure 2).
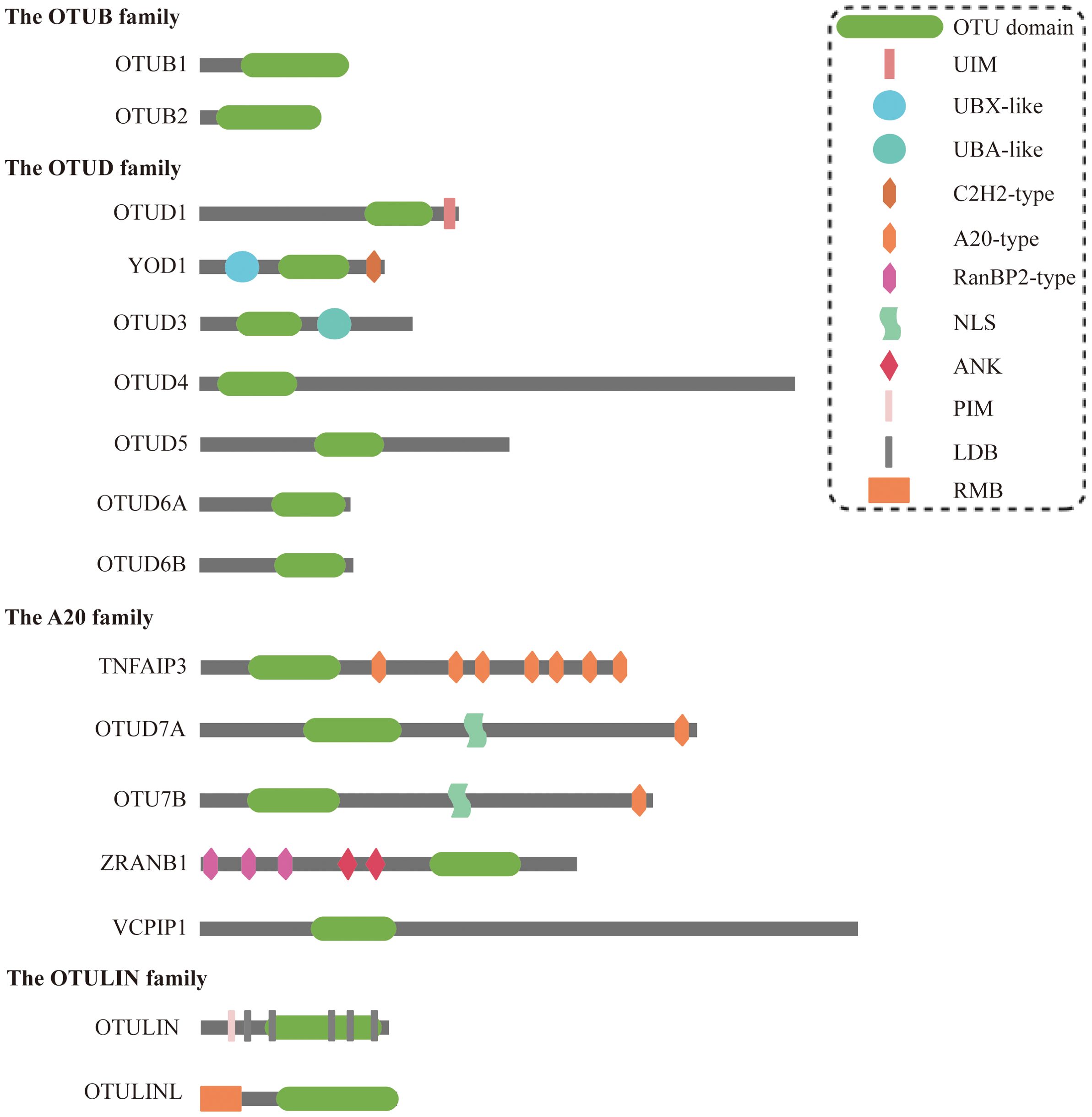
Figure 2. Structural characteristics of OTU family members. OTU domain, ovarian tumor domain; UIM, ubiquitin-interacting motif; UBX-like, ubiquitin regulatory X-like; UBA-like, ubiquitin-associated-like; NLS, nuclear localization signals; ANK, ankyrin motif; PIM, PUB interacting motif; LDB, linear diubiquitin binding; RMB, required for membrane binding.
Interestingly, various OTU family members exhibit obvious disparities in specificity against the eight ubiquitin linkage types. At low concentrations, the six OTUs preferentially cleave only one ubiquitin chain (OTUD7A/OTUD7B-K11, OTUB1/OTUD4-K48, OTUD1-K63, and OTULIN-Met1); the four OTUs cleave two ubiquitin chains (OTUD3-K6/K11, TNFAIP3/VCPIP-K11/K48, and phosphorylated OTUD5-K48/K63); and four OTUs (OTUB2, OTUD2, OTUD6A, and ZRANB1) cleaved three or more chains preferentially (14). Elevated enzyme concentrations expand substrate promiscuity, but Met1 linkage hydrolysis remains uniquely dependent on OTULIN (14). These activities enable OTUs to regulate both proteasomal degradation and non-degradative signaling, positioning them as critical players in tumorigenesis.
Members of the OTU family, particularly OTUB1, rely not only on their deubiquitinase activity but also engage in non-canonical mechanisms to participate in tumorigenesis and progression. For example, (a) Ubiquitin transfer blockade: In multiple myeloma, OTUB1 interacted with the E2 enzyme UBE2D3 to inhibit ubiquitination of the transcription factor c-Maf, stabilizing its expression and promoting tumor cell survival (15). (b) Direct target protein binding: OTUB1 suppressed ubiquitination of proteins (e.g., HIF-1α and RACK1) through non-catalytic binding, thereby driving tumor progression (16, 17). (c) Phosphorylation-dependent functional switching: Phosphorylation of the Tyr26 residue in OTUB1 enabled its interaction with the cell cycle regulator p27, modulating p27 stability and cell cycle progression (18). The non-canonical mechanisms of the OTU family expand the functional landscape of DUBs in cancer, offering novel avenues for the development of precision anticancer strategies.
OTUs in tumorigenesis, progression and metastasis
Members of the OTU superfamily are pivotal in carcinogenesis and progression, with their roles varying between oncogenic and tumor-suppressive capabilities depending on the type of cancer and the function of the substrate proteins (Figure 3).
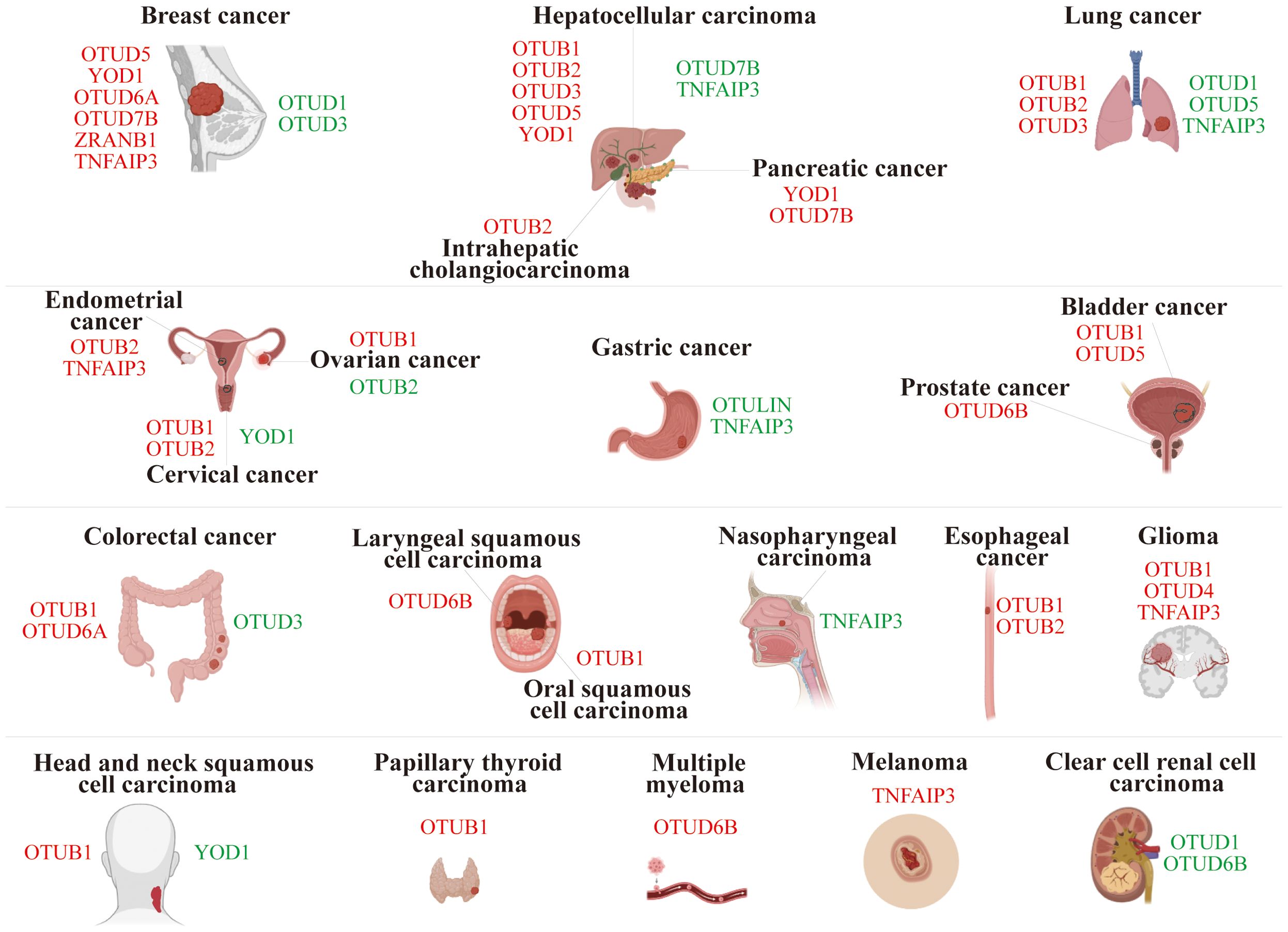
Figure 3. Role of OTU family members in tumor progression. The red font represents OTUs exerting an oncogenic effect in specific cancers, while the green font is for an inhibitory effect.
Breast cancer
In breast cancer (BC), OTUD5, YOD1, OTUD6A, OTUD7B, ZRANB1, and TNFAIP3 were characterized as carcinogenic drivers. Specifically, OTUD5 mediated the deubiquitination of Yes-associated protein (YAP), leading to increased YAP expression in THP-1-derived macrophages. Overexpression of YAP in M2 macrophages promoted triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) progression both in vitro and in vivo (19). Similarly, YOD1 facilitated the deubiquitination of Cyclin dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), resulting in its upregulation, which enhanced the proliferation, migration, and invasion of TNBC cells (20). The study revealed that in breast cancer, OTUD6A stabilized DNA topoisomerase 2 binding protein 1 (TopBP1) by inhibiting its K48-Ub (21). OTUD7B’s deubiquitination and ubiquitin-binding functions enabled EGFR to evade cellular degradation (22), while ZRANB1 bound to and deubiquitinated EZH2, stabilizing it (23). Additionally, TNFAIP3 promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in TGF-β1-induced breast cancer cells by facilitating multiple monoubiquitinations of Snail (24). Together, these processes enhanced cell proliferation, migration, and malignancy in breast lesions.
However, OTUD1 and OTUD3 could curb the progression of breast cancer. For example, OTUD1 weakened the tumor response to TGF-β by removing ubiquitin from SMAD7, thereby inhibiting breast cancer proliferation (25). OTUD3 effectively inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells by directly deubiquitinating and stabilizing p53 (26). Inversely, OTUD3 deficiency activated the AKT signaling pathway and propagated the transformation and metastasis of breast cancer cells (27).
Hepatocellular carcinoma
In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), OTUB2, OTUD3, and OTUD5 stabilized the expression of PJA1 (28), ACTN4 (29), and SLC38A1 (30) by deubiquitination, respectively, which facilitated the proliferation and metastasis of HCC. Interestingly, OTUB1 reduced the K1-Ub of RACK48 through its non-classical inhibition of ubiquitination activity, thereby stabilizing RACK1 protein levels in HCC cells (17). YOD1, a key regulator of the Hippo pathway, stabilized ITCH and potentiated ITCH-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of LATS1/2, which resulted in elevated YAP/TAZ levels (31, 32). Both of these ultimately exacerbated the progression of HCC.
However, both OTUD7B and TNFAIP3 can exert anti-tumor effects by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in HCC (33, 34). Additionally, TNFAIP3 restrained the onset of EMT in HCC cells by diminishing Twist1 expression (34, 35).
Lung cancer
In lung cancer, OTUB1 triggered lung cancer development by inhibiting RAS monoubiquitination (36); OTUB2 stabilized U2AF2 through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to promote the Warburg effect and tumorigenesis (37); and OTUD3 stabilized GRP78 to augment the malignancy (38). These play a crucial driving role in the progression of lung cancer.
Conversely, OTUD1 and OTUD5 deubiquitinated and stabilized KLF4, FHL1, and PTEN, respectively, which effectively suppressed the progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (39–41). Furthermore, silencing TNFAIP3 promoted lung cancer invasion and proliferation (42).
Ovarian cancer
OTUB1 drove ovarian cancer (OV) progression by stabilizing FOXM1 via cleavage of K48-Ub of FOXM1 (43). Whereas OTUB2 acted as a tumor suppressor in OV, mechanistically, OTUB2 silencing destabilized SNX29P2, which subsequently prevented the degradation of HIF-1α. Elevated HIF-1α activated CA9 transcription and drove OV progression via promoting glycolysis (44).
Bladder cancer
OTUB1 promoted bladder cancer (BLCA) progression by deubiquitinating and stabilizing ATF6 in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress (45). In addition, OTUD5 can activate the mTOR signaling pathway and facilitate BLCA progression. Mechanistically, OTUD5 deubiquitinated and stabilized RNF186, which further led to the degradation of sestrin2, an inhibitor of the mTOR signaling pathway (46).
Endometrial cancer
OTUB2 contributed to endometrial cancer (EC) progression by regulating the PKM2-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (47). Furthermore, TNFAIP3 impeded ERα protein degradation through deubiquitinating enzyme activity, which enhanced estrogen-driven EC cell proliferation (48).
Gastric cancer
Knockdown of OUTLIN, a gastric cancer (GC) biomarker, suppressed GC cell viability and metastasis (49). Chronic Helicobacter pylori infection, a major contributing factor to gastric carcinogenesis, induced TNFAIP3 to suppress caspase-8 activity through promoting K63-linked deubiquitination of procaspase-8 during infection, thereby reducing apoptotic cell death in infected cells (50, 51). Furthermore, TNFAIP3 was shown to promote gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by stabilizing Snail and ZEB1 proteins (52).
Pancreatic cancer
YOD1 and OTUD7B were highly expressed in pancreatic cancer (PC) tissues and could propagate the proliferation and metastasis of PC cells (53, 54). Specifically, OTUD7B enhanced the EGFR and MAPK signaling pathways (54).
Colorectal cancer
In colorectal cancer (CRC), OTUB1 and OTUD6A promoted tumor growth by stabilizing β-catenin (55) and Drp1 (56), respectively. However, silencing OTUD3 enhanced the proliferation and migration of CRC cells (57).
Esophageal cancer
OTUB1 and OTUB2 potentiated esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) proliferation and metastasis by regulating the stability of Snail and YAP1/TAZ proteins, respectively (58, 59).
Other cancers
In various cancer types, OTU family members exhibit various oncogenic mechanisms. In brief, certain OTU members were oncogenic in specific cancers, such as OTUB1 in glioma (6), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) (60), oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) (61), and papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) (62); OTUB2 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) (63) and cervical cancer (64); OTUD4 in glioblastoma (GBM) (65); OTUD6A in prostate cancer (66); OTUD6B in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (67) and multiple myeloma (68); TNFAIP3 in glioma (69) and melanoma (70).
In contrast, other OTU members exert anti-cancer effects in specific cancers, such as YOD1 in HNSCC (71) and cervical cancer (72); OTUD1 and OTUD6B in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) (73, 74); TNFAIP3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) (75).
Overall, OTU family members manifest diverse and complex roles in cancer biology, offering promising targets for therapeutic strategies and deeper insights into cancer mechanisms.
Dual role of OTUs in specific cancers
The dual roles of OTU family members in specific cancers present intriguing mechanistic complexities, exemplified by OTUB1 in breast cancer, OTUD7B in lung cancer, and TNFAIP3 in CRC (Figure 4A).
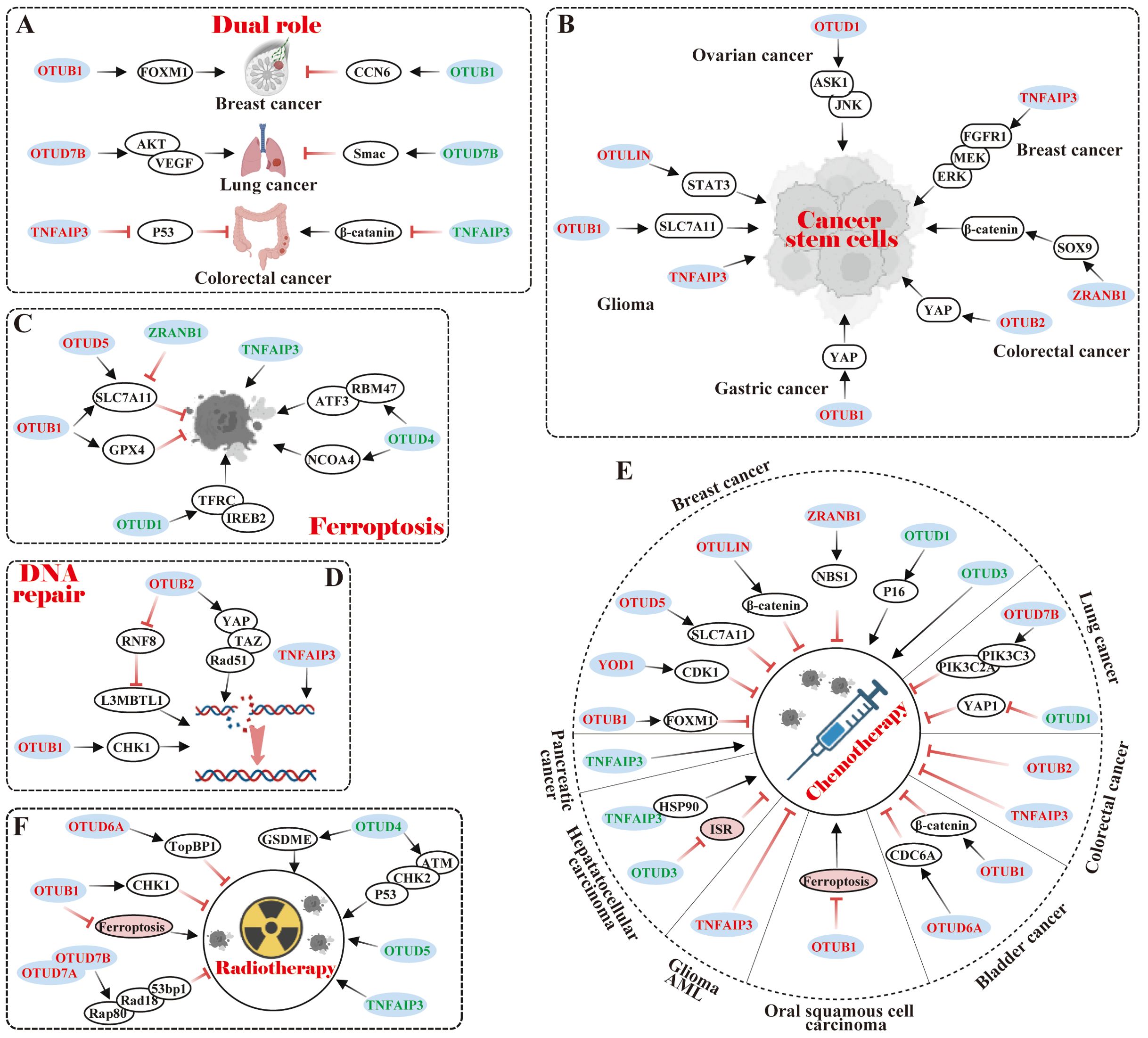
Figure 4. Relationship of OTU family members to tumor characteristics. (A) Dual role of OTUs in specific cancers. (B) OTUs maintain cancer stem cell-like properties. (C) OTUs regulate tumor ferroptosis. (D) OTUs participate in DNA repair. (E, F) OTUs are involved in tumor chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The red font represents OTUs exerting an oncogenic effect in specific cancers, while the green font is for an inhibitory effect.
Notably, OTUB1 exhibits context-dependent functional duality in breast cancer progression. Karunarathna U et al. (76) demonstrated that OTUB1 stabilized the oncogenic transcription factor FOXM1 by removing K48-Ub, thereby enhancing proliferation and epirubicin resistance in MCF-7 cells. Paradoxically, Zhao Y et al. (77) revealed that OTUB1 suppressed tumorigenic properties in 4T1 cells through a non-catalytic inhibition of CCN6 ubiquitination, ultimately impairing cell migration, proliferation, and viability. These opposing effects highlight the cell type-specific regulatory mechanisms of OTUB1 in breast cancer.
In lung cancer, OTUD7B displays multifaceted roles in lung cancer pathogenesis with divergent clinical implications. Pang Z et al. (78) correlated elevated OTUD7B expression with poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma tissues; Lin DD et al. (79) further showed that OTUD7B promoted in vitro proliferation and in vivo tumorigenicity of NCI-H358 cells via the AKT/VEGF pathway. In contrast, Sun C et al. (80) reported that OTUD7B exacerbated hyperthermia-induced cytotoxicity in A549 and CALU-3 cells by amplifying Smac-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction, while Zhang B et al. (81) identified its tumor-suppressive role in impeding LCL161-induced A549 and H1299 cells invasion and migration through TRAF3 deubiquitination-mediated NIK suppression. These findings suggest microenvironment-dependent functional switching of OTUD7B.
In CRC, TNFAIP3 exhibits paradoxical regulatory effects in colorectal carcinogenesis. Shao L (82) utilized TNFAIP3fl/fl villin-Cre APCmin/+ genetic mouse model to demonstrate its tumor-suppressive role in restricting Wnt signaling and suppressing colon tumorigenesis. Conversely, Liu J et al. (83) observed TNFAIP3 overexpression in human CRC tissues and adenomatous polyps, where it attenuated p53 expression in HEK293 cells, suggesting a potential oncogenic contribution to polyp malignancy. This duality underscores the need for context-specific evaluation of TNFAIP3 in CRC progression.
The observed functional duality of OTU family members in cancer pathogenesis arises from three interconnected mechanistic layers: substrate-specific modulation, signaling pathway plasticity, and therapeutic context dependency. Primarily driven by their context-dependent substrate engagement, OTUs can selectively stabilize oncoproteins (e.g., FOXM1) while destabilizing tumor suppressors (e.g., CCN6) through precise ubiquitin chain editing, creating opposing biological outcomes within the same cancer type. This functional dichotomy is further amplified by their ability to differentially regulate critical signaling hubs—such as simultaneously modulating NF-κB activation through TRAF3 deubiquitination while suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling via APC complex stabilization—effectively rewiring tumor cell fate decisions. Furthermore, OTUs establish dynamic feedback loops in drug response pathways, exemplified by their capacity to confer chemoresistance through drug target stabilization (e.g., epirubicin resistance via FOXM1 protection) while sensitizing cells to targeted therapies by enhancing pro-apoptotic signaling (e.g., Smac-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction). These multilayered regulatory mechanisms, operating through spatial-temporal control of ubiquitin code interpretation, ultimately dictate the paradoxical tumor-promoting versus tumor-suppressing phenotypes observed across cancer subtypes.
OTUs in cancer therapy and patient prognosis
Currently, some OTUs have been reported to possess roles in preserving the cancer stemness and ferroptosis properties, which are intimately implicated not only in tumor aggressiveness and recurrence but also in the treatment and prognosis of patients.
OTUs-mediated cancer stem cell properties
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are characterized by their high metastatic potential, tumor initiation abilities, and capabilities for self-renewal, differentiation, and drug resistance traits similar to normal stem cells. Recent studies have emphasized the critical role that some OTU members play in maintaining CSC characteristics by regulating core transcription factors such as SLC7A1, YAP, ASK1, and SOX9 (Figure 4B).
Specifically, OTUB1 stimulated glioma cell stemness by stabilizing the SLC7A11 protein to suppress ferroptosis (84). Additionally, OTUB1 and OTUB2 served as pivotal components in maintaining cancer stemness and promoting metastasis via deubiquitination and stabilization of YAP proteins in gastric and colon cancer, respectively (85, 86). Multi-omics screening has identified that OTUD1 stabilized ASK1 by recruiting it in a deubiquitinase-independent manner, which activated the downstream JNK signaling pathway to maintain ovarian cancer stem cells (87). Interestingly, ALDH-positive breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) were reduced in TNFAIP3 knockout in BCSCs, possibly since TNFAIP3 facilitated the growth of ALDH-positive BCSCs in part through the FGFR1/MEK/ERK pathway (88). ZRANB1 modulated SOX9 stability in CRC cells by diminishing its ubiquitination, which in turn potentiated the SOX9-mediated USP22/Wnt/β-catenin pathway to uphold CRC stemness characteristics (89). In GBM, TNFAIP3 and OTULIN maintained the stemness and self-renewal capacity of GBM stem-like cells (GSCs) (90, 91). Specifically, preferential expression of OTULIN in GSCs restricted linear ubiquitination on STAT3 and drove persistent STAT3 signaling (91).
Overall, OTU members have been shown to provide a critical role in the sustainment of CSC properties via the regulation of cellular signaling pathways and core transcription factors. Several studies have illustrated that CSC properties can significantly confer drug resistance in cancer cells, which seriously affects tumor response to treatment and patient prognosis. Thus, the OTU family may hold a pivotal position in chemo- or radiotherapy resistance in tumors.
OTUs in Ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is a type of programmed cell death, distinct from apoptosis and necrosis, characterized by iron-dependent accumulation of lipid peroxides. Research has shown that in cancer, ferroptosis can inhibit the growth of tumor cells. Therefore, inducing ferroptosis in cancer cells may be a novel anti-cancer therapeutic strategy, and OTUs influence tumor progression by modulating the stability of ferroptosis-related proteins (Figure 4C).
SLC7A11, also known as xCT, is a transporter protein that influences glutathione (GSH) synthesis, a vital anti-oxidant, by regulating intracellular cysteine levels. In many malignancies, upregulation of SLC7A11 expression contributes to tumor cell resistance to ferroptosis, which promotes tumor growth, metastasis, and drug resistance. Currently, several OTU family members, such as OTUB1 (84, 92) and OTUD5 (93), can positively regulate the protein stability of SLC7A11, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis. Interestingly, the deubiquitinase ZRANB1 was identified as the E3 ligase of SLC7A11 to degrade it, which suppressed GSH synthesis and led to lipid peroxidation and elevated ferroptosis (94).
In addition to that, OTUs can govern ferroptosis in tumor cells via other pathways. For instance, OTUB1 inhibited ferroptosis by improving GPX4 protein stability and reducing intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), which in turn promoted gastric cancer metastasis (95). In contrast, OTUD1, OTUD4, and TNFAIP3 could induce the genesis of ferroptosis. Specifically, OTUD1 facilitated TFRC-mediated iron transport via deubiquitination and stabilization of IREB2, causing ROS production and increased ferroptosis in CRC (96). OTUD4 potentiated ferroptosis in ICC and ccRCC by regulating the stability of NCOA4 protein and RBM47/ATF3 axis, respectively (97, 98). In A549 lung cancer cells, TNFAIP3 exhibited a significant induction of ferroptosis (99).
In short, ferroptosis represents a promising prospect for extensive research in cancer therapy, but additional clinical trials and studies are necessary to gain insight into its mechanisms and applications.
OTUs in DNA repair
DNA repair is a fundamental cellular process aimed at restoring damaged DNA to its normal state. However, cancer cells often exploit this mechanism to survive chemotherapy and thus evade treatment. Recent studies have emphasized the critical role of several OTU members in DNA repair (Figure 3D). In lung cancer, for example, OTUB1 stabilized the CHK1 protein through deubiquitination, enhancing the cell’s ability to repair DNA and aiding cancer cell survival (100). In endometrial cancer, OTUB2 promoted Rad51 expression via the YAP/TAZ pathway, supporting homologous recombination repair and protecting cells from drugs like cisplatin (101). Additionally, OTUB2 regulated L3MBTL1 at DNA break sites by counteracting RNF8, optimizing DNA repair pathways (102). TNFAIP3, which was highly expressed in invasive breast cancer, increased the efficiency of error-free DNA homologous recombination and diminished error-prone non-homologous DNA end-joining, which stabilized the genome and conferred resistance to DNA damage (103). These data indicate that OTUs exert effects on DNA repair by regulating protein stability and influencing the choice of repair mechanism, etc.
OTUs in chemotherapy
Chemotherapy attacks cancer cells by interfering with their DNA replication, repair, and cell division. Many studies have pointed out that the expression level of OTUs was related to the efficacy of chemotherapy. Comparatively, it was identified that the majority of OTUs conferred chemoresistance to tumor cells, while a small percentage of OTUs sensitized tumor cells to chemotherapy (Figure 4E).
Currently, members of OTUs were reported to both promote resistance and sensitization in specific cancers. In breast cancer, for instance, OTUB1, YOD1, OTUD5, OTULIN, TNFAIP3, and ZRANB1 drove chemoresistance, whereas OTUD1 and OTUD3 were sensitized to chemotherapy. Specifically, OTUB1 deubiquitinated and stabilized FOXM1, thereby conferring epirubicin resistance (76). YOD1 positively regulated CDK1 stability and drove cisplatin and paclitaxel resistance (20). OTUD5 inhibited ferroptosis by stabilizing SLC7A11, thereby diminishing paclitaxel susceptibility (104). OTULIN enhanced doxorubicin resistance by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (105, 106).TNFAIP3 could confer tamoxifen resistance (107). ZRANB1 was implicated in radioresistance and PARPi resistance, such as olaparib and tarazoparib, by modulating the stability of NBS1 and upregulation of the MRN complex (108). On the contrary, OTUD1 rendered TNBC cells sensitive to doxorubicin by up-regulating P16 expression (109). OTUD3 overexpression significantly enhanced the responsiveness of MCF-7 cells to paclitaxel (110). In lung cancer, OTUD7B facilitated osimertinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma cells through PIK3C3 stabilization and PIK3C2A transcription (111). However, OTUD1 conferred erlotinib susceptibility in NSCLC by repressing the nuclear translocation of YAP1 (112).OTUD5 knockdown also potentiated resistance to doxorubicin and cisplatin in NSCLC cells (113).
Members of OTUs were also reported to confer chemotherapy resistance in specific cancers. In CRC, for example, OTUB2 and TNFAIP3 confer cisplatin resistance to CRC cells (114, 115). In BLCA, OTUB1 and OTUD6A potentiated BLCA resistance to cisplatin and gemcitabine by deubiquitinating and stabilizingβ-catenin and CDC6, respectively (116, 117). In OSCC, OTUB1 induced cisplatin resistance by suppressing ferroptosis (118). Furthermore, TNFAIP3 enhanced the resistance of GBM and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells to O6 alkylating agents and daunorubicin, respectively (119, 120).
Surely, OTUs were reported to be sensitized to chemotherapy in specific cancers. Such as in HCC, OTUD3 and TNFAIP3 rendered HCC cells responsive to sorafenib by antagonizing the integrative stress response (ISR) and binding to HSP90, respectively (121, 122). In SW1990 pancreatic cancer cells, overexpression of TNFAIP3 increased chemosensitivity to gemcitabine (123).
In view of the fact that many OTUs confer chemoresistance to tumor cells, the future is dedicated to the study of OTU inhibitors as candidates for targeted therapy. Meanwhile, combining OTU inhibitors with other means, such as radiotherapy and immunotherapy, may improve therapeutic efficacy.
OTUs in radiotherapy
Radiotherapy suppresses the growth of cancer cells by directly destroying their DNA with high-energy radiation, which is mainly applied for localized tumor control. OTUs impact the efficacy of radiotherapy by regulating cellular response mechanisms, DNA repair and ferroptosis, and other mechanisms (Figure 4F).
Currently, OTUB1, OTUD6A, and OTUD7B were reported to be engaged in resistance to radiotherapy. Mechanistically, OTUB1 inhibited radiation-induced cellular ferroptosis, which triggered radiotherapy resistance in NPC (124). Furthermore, OTUB1 and OTUD6A deubiquitinated and stabilized CHK1 and TopBP1, which regulated DNA damage and repair and promoted radiation resistance in lung and breast cancer, respectively (21, 100). Analogously, OTUD7A interacted with OTUD7B to promote OTUD7B recruitment of Rap80/BRCA1-A, Rad18, and 53bp1, which enhanced cellular resistance to ionizing radiation, and DNA damage repair (125).
On the contrary, high expression of OTUD4, OTUD5, and TNFAIP3 could enhance the sensitivity of cancer cells to radiotherapy. Specifically, OTUD4 sensitized NSCLC cells to radiotherapy through ATM/CHK2/P53 signaling and suppressed homology-directed repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks (126). OTUD4-mediated GSDME deubiquitination also enhanced radiosensitivity in NPC by inducing pyroptosis (127). Furthermore, OTUD5 overexpression enhanced the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to radiotherapy (128), whereas TNFAIP3 knockdown decreased the sensitivity of NPC cells to radiotherapy (129).
Collectively, OTUs influence the efficacy of radiotherapy through a variety of mechanisms, emerging as valuable targets in cancer research and treatment. Inhibitors or agonists targeting OTUs can potentially improve the efficacy of radiotherapy in specific cancers.
Clinical significance of OTUs
Numerous studies have shown that members of the OTU family exhibited significant differences in clinical expression between cancerous tissues and normal tissues. The expression levels of some members were associated with TNM stage or lymph node metastasis or shortened overall survival in cancer patients, indicating a poor prognosis. For instance, OTUB1 in glioma (6), CRC (130), GC (131), and HCC (132); OTUB2 in BC (133); OTUD2 in NSCLC (134); TNFAIP3 in BC (135, 136) and ESCC (137).
In contrast, other OTU family members were positively observed to be linked to patients’ overall and disease-free survival. In HCC, for example, decreased OTUD7B expression was related to increased tumor volume, presence of satellite nodules, vascular invasion, and early recurrence (138, 139). In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), TNFAIP3 expression was positively correlated with tumor differentiation, TNM stage, and patient survival, suggesting a potential anti-cancer role (140). Reduced expression of ZRANB1, a favorable factor, in HCC tissues and cell lines, facilitated tumor recurrence and metastasis (141).
To broaden our understanding of the expression patterns of OTU family members in tumors and their association with patient prognosis, we conducted a pan-cancer analysis utilizing The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, providing a comprehensive landscape of OTUs’ expression and prognostic relevance (Figure 5). Through these studies, we can notice that the expression patterns of OTUs family proteins in various cancers are closely related to the biological behaviors of tumors and the clinical prognosis of patients, providing important biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prognostic assessment.
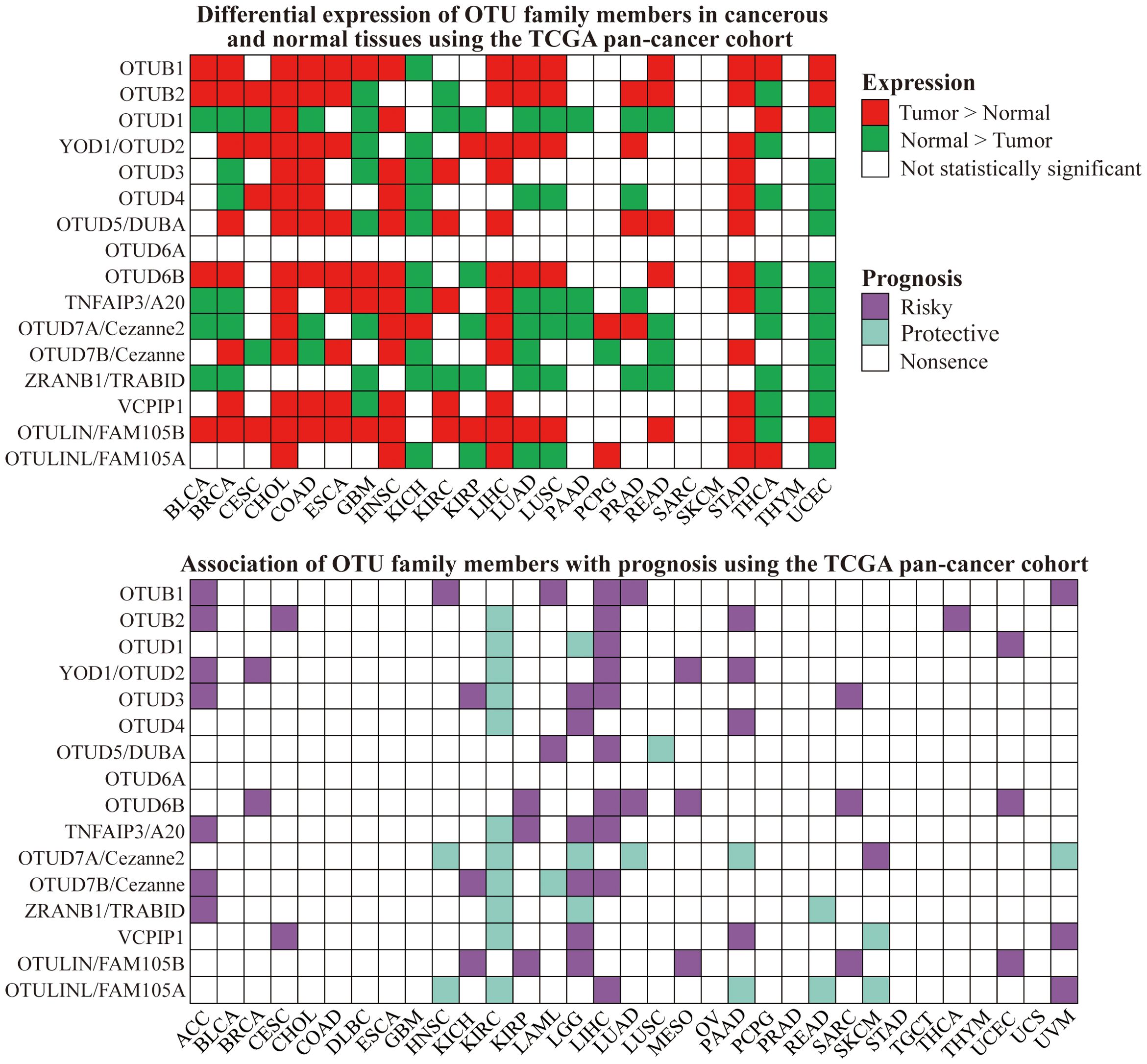
Figure 5. Differential expression and prognostic value of OTU family members in cancer and normal tissues using the TCGA pan-cancer cohort.
OTUs participate in the host immune response
Recent studies have shown that the role of the OTUs family of proteins in the body’s immune system has received increasing attention. For instance, certain OTUs possess crucial roles in the differentiation, proliferation, and functional maintenance of T and B cells. Moreover, they can also influence the inflammatory response and anti-viral immune response by governing the NF-κB and interferon pathways, respectively (Figure 6).
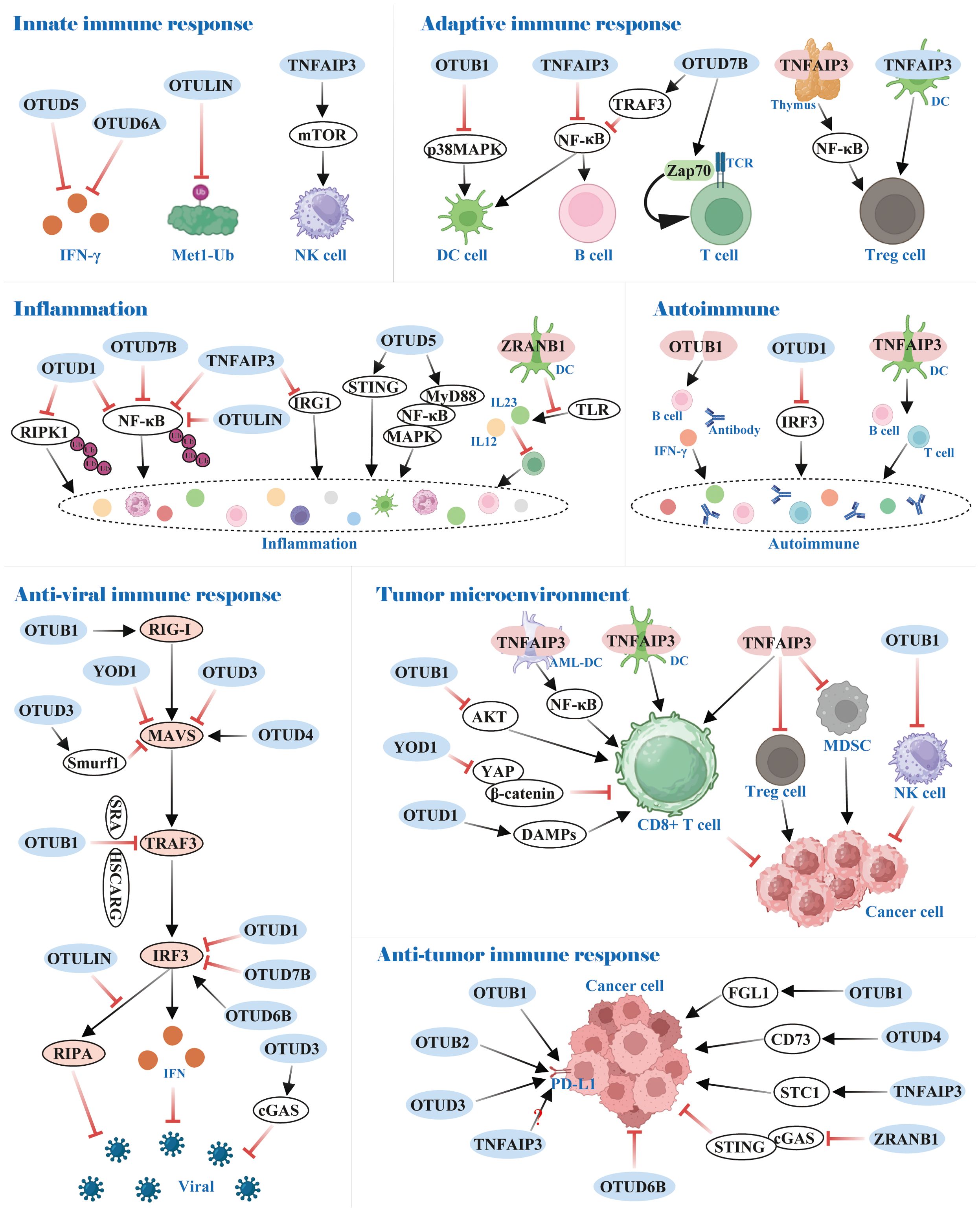
Figure 6. Functions of OTUs in immunity. OTUs are involved in innate and adaptive immune responses, inflammation and autoimmunity, and anti-viral and anti-tumor immune responses.
OTUs participate in the body’s immune response by regulating the differentiation and development of immune cells
The innate immune system serves as the body’s rapid first-line defense against invading pathogens, with type I interferon (IFN-I) production constituting a central protective mechanism in this initial response. Research has identified OTUD5 and OTUD6A as potent suppressors of IFN-I generation, establishing their roles as negative regulators of innate immunity (142, 143). Notably, while Met1-linked ubiquitin chains (M1-Ub) were crucial for amplifying innate immune signaling, the deubiquitinating enzyme OTULIN counteracted this process by selectively dismantling M1-Ub chains, thereby restraining excessive inflammatory activation (144).
OTUs also maintain the homeostasis of a portion of innate immune cells. In NK cells, for example, TNFAIP3 controlled NK cell homeostasis by regulating mTOR activity to prevent its spontaneous death (145). Dendritic cells (DCs), an antigen-presenting cell (APC), link innate and adaptive immune responses. OTUB1 and TNFAIP3 restrained p38MAPK and NF-κB activation, respectively, which prevented DCs hyper-activation under homeostatic conditions (146–148).
In adaptive immunity, OTUs mediate the stability and activity of key proteins linked to immune cells by removing the ubiquitin chain. In B cells, for instance, OTUD7B deubiquitinated TRAF3 and prevented its degradation, thereby hindering aberrant nonclassical NF-κB activation (149). Also, TNFAIP3 was reported to be a negative regulator of NF-κB signaling, which impeded B cells’ hyper-activation to maintain immune homeostasis (150). Importantly, OTUD7B promoted T cell activation by deubiquitinating and activating Zap70, a central mediator of TCR proximal signaling (151). Regulatory T cells (Treg), essential for maintaining immune tolerance, are also activated by NF-κB transcription factor. In the thymus, TNFAIP3 deficiency dominated differentiation over Treg cells owing to enhanced NF-κB activation, but silencing TNFAIP3 in DCs dampened Treg cells activation (152, 153). Conversely, TNFAIP3 overexpression in DCs led to the development of tolerogenic DCs, which facilitated the induction of Treg cells (154). All of these provide a promising potential in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
OTUs-mediated inflammatory response and autoimmunity
Investigations have indicated that distinct OTUs family proteins exert either anti-inflammatory or pro-inflammatory responses, e.g., OTUD1, OTUD7B, OTULIN, and TNFAIP3 function as anti-inflammatory, whereas the contrary is true for OTUD5 and ZRANB1.
In OTUD1-/- mice, inflammation was augmented in models of inflammatory bowel disease, acute hepatitis, and sepsis. Mechanistically, OTUD1 inhibited inflammation by cleaving K63-Ub from RIPK1 and NF-κB, respectively, thereby dampening NF-κB signaling pathway transduction (155, 156). Analogously, OTUD7B and OTULIN attenuated NF-κB activation by selectively removing K63-Ub and M1-Ub on NF-κB, respectively, thereby inhibiting inflammation induced by TNF receptor (TNFR) signaling (157–159). TNFAIP3, also a negative regulator of NF-κB signaling, predominantly used its zinc finger structural domain 7 (ZF7) to curb inflammatory signaling. Additionally, TNFAIP3 negatively regulated immune response gene 1 (IRG1) expression at the transcriptional level (160, 161).
In radiation pneumonitis (RIP), OTUD5 upregulated by USP11 acclimated endothelial cell inflammation through the STING signaling pathway (162). In inflammatory bowel disease, OTUD5 was significantly overexpressed and increased TNF-α release (163). Mechanistically, OTUD5 interacted with MyD88 and cleaved its K11-Ub, which enhanced MyD88 oligomerization and subsequently promoted Myddosome formation, activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling, and inflammatory cytokine production (164). Furthermore, ZRANB1 deletion in DCs inhibited Toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced expression of IL12 and IL23, which impaired inflammatory T cell differentiation and protected mice from autoimmune inflammation (165).
Consistent with the aforementioned results, OTUB1, OTUD1, and TNFAIP3 restricted the development of autoimmune diseases through anti-inflammatory responses. Specifically, OTUB1 deficiency exhibited an aberrantly activated phenotype in B cells, causing B cell proliferation, antibody, and IL-6 hyper-production, and lupus-like autoimmunity (166). OTUD1 prevented excessive interferon production-induced autoimmune disease by removing K63-Ub on Lys98 of IRF3, thereby dampening IRF3 nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity, which blocked RIG-I-like receptor signaling (167). Furthermore, TNFAIP3 ablation in DCs altered T-cell and B-cell homeostasis, which primarily promoted the progression of autoimmune liver disease (168).
OTUs-mediated anti-viral immune response
RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) pathway activates downstream signaling primarily through recognition of viral RNA, which, involves the participation of multiple molecules including, but not limited to, RIG-I, MAVS, TRAF3, and IRF3, and ultimately facilitates interferon-mediated anti-viral immune responses. OTUs, as deubiquitinases, regulate these pivotal molecules in post-transcriptional modifications, thereby impacting on the organism’s anti-viral immunity.
RIG-I is an intracellular pattern recognition receptor that recognizes viral 5’triphosphate RNA and double-stranded RNA. During influenza A virus (IAV) infection, OTUB1 activated RIG-I via a dual mechanism of K48-Ub hydrolysis and formation of an E2-repressive complex with UBCH5c, which stimulated the RIG-I signaling cascade and the anti-viral response (169).
The adaptor protein MAVS binds to activated RIG-I and further triggers a series of signal transduction events, such as recruitment of the TRAF family and activation of the transcription factor IRF3. YOD1 and OTUD3 abrogated the formation of prion-like aggregates of MAVS by interacting with MAVS and cleaving K63-Ub, leading to attenuation of IRF3 and IFN-β production (170, 171). Additionally, OTUD1 up-regulated E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 expression via deubiquitination, which increased the degradation of MAVS and the MAVS/TRAF3/TRAF6 signalosome (172, 173). Yet, viral infection induced an IRF3/7-dependent up-regulation of OTUD4, which bound to MAVS to remove K48-Ub, thereby maintaining MAVS stability and promoting innate anti-viral signaling (174).
TRAF3 interacts with MAVS, contributing to signaling and enhancing the downstream anti-viral response. OTUB1 was recruited to TRAF3 by Scavenger receptor A (SRA) and HSCARG to negatively regulate its protein stability, which counterbalanced anti-viral innate immunity (175, 176).
IRF3 was identified as a key regulator of interferon production. Currently, several OTU proteins have been reported to negatively regulate the protein abundance of IRF3, including OTUB1 (177), OTUD1 (178), OTUD7B (179), OTULIN (180), and TNFAIP3 (181, 182). Mechanistically, OTUD1 caused the dissociation of IRF3 from the promoter region of the target gene by cleaving K6-Ub from IRF3, without disturbing its protein stability, dimerization, and nuclear translocation (178). In addition, OTUD7B promoted the degradation of IRF3 by removing K63-Ub at the IRF3 Lys7 residue (179). Interestingly, IRF3 activates another interferon-independent anti-viral pathway termed the RIG-I-induced apoptotic pathway (RIPA). OTULIN suppressed RIPA by deubiquitinating IRF3 to prevent its mitochondrial translocation (180). Nevertheless, OTUD6B positively modulated the IRF3-mediated anti-viral immune response by stabilizing IRF3 protein abundance via hydrolysis of K33-Ub on IRF3 Lys315 residue (183).
In addition, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) behaves as a major DNA sensor and initiates DNA-stimulated innate immune responses. OTUD3 was reported to stabilize and potentiate cGAS enzyme activity, which facilitated the anti-DNA viral immune response (184).
The RLR pathway initiates antiviral immunity by detecting viral RNA through a RIG-I/MAVS/TRAF3/IRF3 signaling cascade to drive interferon production, while OTUs dynamically fine-tune this response via spatiotemporal regulation of post-translational modifications. These enzymes establish bidirectional control networks across RLR signaling nodes through targeted deubiquitination, providing molecular precision for antiviral immune modulation. Furthermore, OTUs play dual roles in antibacterial immunity, as structurally and pharmacologically elucidated by Dirk Schlüter et al. (185). Pathogens evade immune surveillance by secreting OTU-mimicking effector proteins that hijack the host ubiquitination system through specific ubiquitin chain hydrolysis, thereby suppressing NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses and attenuating chemokine or cytokine storms. Conversely, host OTUs like TNFAIP3 maintain immune homeostasis via dynamic regulation of signaling pathways, particularly through negative feedback modulation of the NF-κB cascade to balance protective immunity and inflammatory control.
Role of OTUs in the tumor microenvironment and immune escape
The tumor microenvironment (TME) describes the sophisticated landscape of cells, signaling molecules, and stroma surrounding tumor cells, which contributes to tumourigenesis, progression, and therapeutic response. As deubiquitinases, OTU family proteins exert an influential role in tumor progression and immune escape by regulating intracellular ubiquitination levels, which affects the tumor microenvironment and immune cell function.
OUTs-mediated anti-tumor immunity in TME
In TME, partial OTUs attenuated anti-tumor immunity by dampening CD8+ T-cell function. For instance, OTUB1 was recruited to the membrane mediated by IL-15, which restrained the ubiquitin-dependent activation of AKT and thus inhibited the activation of CD8+ T and NK cells (186). In the B16 mouse melanoma tumor model, TNFAIP3 silencing in DCs resulted in an augmented amount of tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells (187); in AML, TNFAIP3 depletion in AML-DCs potentiated autologous cytolysing T cell (CTL)-specific killing of progenitor AML cells via the NF-κB pathway (188). Likewise, adoptively transferred anti-tumor CD8+ T cells harboring a deletion of TNFAIP3 enhanced IFN-γ and TNF-α production and reduced PD-1 expression, which exhibited superior anti-tumor activity in vivo (189, 190).
On the contrary, YOD1 and OTUD1 positively regulated CD8+ T cells. Specifically, YOD1 prevented CD8+ T cell exhaustion by inactivating the YAP/β-catenin pathway in HCC (191). OTUD1 facilitated the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which in turn recruited tumor-responsive T cells and curbed colon cancer progression (96).
Tregs, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), and DCs collectively form a dynamic immunosuppressive network within the TME, collaboratively driving tumor immune evasion. Although the mechanistic roles of these cells have been partially elucidated, the regulatory functions of OTUs in modulating their activities remain underexplored. For instance, recent studies demonstrate that TNFAIP3 silencing dampened infiltration of Treg cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), while the numbers of dendritic cells and macrophages remained unaffected (187, 192). This finding underscores the potential therapeutic value of targeting OTUs to remodel the immunosuppressive TME.
Overall, OTUs serve a complicated role in TME, and further investigations could provide insights into their functions and mechanisms, thus shedding new light on tumor prevention and treatment.
OTUs influence the efficacy of immunotherapy via the regulation of immune checkpoints
Immune checkpoints work as regulators of the immune system, and immunotherapy can be applied to combat cancer by strengthening the immune response through the regulation of these immune checkpoints.
PD-L1, a crucial immune checkpoint protein, is up-regulated in tumor cells to evade surveillance by the immune system, preventing T cells from effectively recognizing and attacking the tumor. Currently, certain OTUs stabilize PD-L1 expression to propagate tumor immune escape. In the A549 lung cancer and 4T1 breast cancer mouse models, OTUB1 knockdown significantly enhanced the anti-tumor immune response of mice. Mechanistically, OTUB1 attenuated tumor immunity in NSCLC and breast cancer by cleaving the K48-Ub of PD-L1 to prevent degradation of PD-L1 via the ERAD pathway (193, 194). Consistent with this, analogous phenomena were observed in OTUB2 in NSCLC and OTUD3 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (195, 196). Nevertheless, TNFAIP3 was controversial in regulating PD-L1 expression. Guo W et al. (197) suggested that TNFAIP3 knockdown significantly down-regulated PD-L1 expression in melanoma A375 and A2958 cells. However, Zou J et al. (198) noted that as the concentration of TNFAIP3 plasmid transfected in MDA-MB231 and A375 cells increased, the abundance of PD-L1 decreased. Breitenecker K et al. (199) also showed that PD-L1 was highly expressed in TNFAIP3 knockout in lung adenocarcinomas. Further investigations are required concerning the role of TNFAIP3 in regulating the expression of PD-L1.
In addition to their core regulatory functions, various OTUs participate in tumor immune regulation by specifically modulating key immune checkpoint molecules. Specifically, OTUD1 enhanced FGL1 stability through deubiquitination, which mediated immune escape and progression of metastatic colorectal cancer (200). OTUD4 deubiquitinated CD73 to offset the ubiquitination of TRIM21, causing CD73 stabilization to suppress the immune response in breast cancer (201). TNFAIP3 suppressed STC1 phosphorylation at Thr86 by GSK3β to alleviate STC1 protein degradation, which promoted immune evasion in colorectal cancer (202). ZRANB1 could stabilize the entire chromosome, and its inhibition prevented autophagic degradation of cGAS to further stimulate the cGAS/STING innate immune pathway. ZRANB1 inhibition facilitated anti-tumor immune surveillance and was sensitive to anti-PD-1 therapy (203). Notably, these regulatory mechanisms provide novel directions for developing combination immunotherapy strategies targeting OTUs.
The OTU family proteins profoundly shape the tumor immune microenvironment through diverse molecular mechanisms, offering novel targeted strategies to enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. For example, in DLBCL, the OTUD3 inhibitor Rupatadine competitively bond to OTUD3 to block PD-L1 deubiquitination, promoting its proteasomal degradation, thereby alleviating PD-1/PD-L1-mediated immune suppression and enhancing anti-tumor T-cell activity (196). In TNBC, ST80 disrupted OTUD4-dependent stabilization of CD73, reducing immunosuppressive adenosine levels, reactivating CD8+ T-cell function, and reversing resistance to anti-PD-L1 therapy (201). Additionally, in ESCC, all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) suppressed the Snail signaling pathway by inducing OTUD6B expression, synergistically improving responses to anti-PD-1 therapy (204). Collectively, these studies highlight the potential of OTU family members as “immune regulatory hubs”. Targeted modulation of specific OTU proteins may achieve multi-layered synergies with existing immunotherapies, though further elucidation of their substrate specificity and dynamic regulatory networks is required to mitigate potential antagonistic risks.
Directions and challenges for future research
The OTU family deubiquitinases play pivotal roles in tumorigenesis, immune evasion, and tumor microenvironment remodeling by regulating ubiquitination modification networks. Recent studies have uncovered their diverse functions in tumor proliferation, metastasis, and therapy resistance. For instance, OTUB1 promoted NPC progression by regulating ferroptosis and radioresistance (124), while OTUD3 and OTUD4 impaired anti-tumor immune responses by stabilizing PD-L1 and CD73, respectively (196, 201). These findings position OTU family members as emerging therapeutic targets, yet their functional complexity and clinical translation challenges require systematic resolution.
Modern cancer research demonstrates an integrated innovation chain spanning from molecular mechanisms to clinical translation in the context of interdisciplinary convergence. At the molecular regulatory level, functional exploration of the OTU deubiquitinase family has opened new avenues for targeted therapies. For example, OTUB1 has emerged as a hotspot for small-molecule inhibitor design through its Asn45/Arg86 hydrogen-bond network (205), while the OTUD3 inhibitor OTUDin3 significantly suppresses NSCLC progression by targeting the S1 ubiquitin-binding site (206). Epigenetic regulation mechanisms, such as FTO-mediated m6A modification, further reveal OTUB1’s critical role in conferring radiotherapy resistance in NPC (124). These discoveries are driving the integration of single-cell multi-omics technologies with spatial metabolomic imaging to map the dynamic regulatory landscape of OTU enzymes within tumor immune-metabolic networks.
In therapeutic strategy development, structure biology-based precision designs (e.g., PROTAC degraders) and combination therapies—such as ST80 enhancing TNBC immunotherapy by disrupting the OTUD4-CD73 complex (201) and crizotinib suppressing NSCLC via targeting the OTUB1/pSTAT3 axis (207)—are overcoming functional redundancy challenges, while the combined use of ERRα inhibitors and metabolic modulators underscores the necessity of multi-target interventions (208). Concurrently, diagnostic and therapeutic innovations continue to advance. For instance, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are associated with distant tumor metastasis and poor prognosis (209), while dynamic imaging of TAMs based on a two-step click chemistry protocol enables real-time visualization of breast cancer progression (210), while copper-based nanomaterials integrate diagnostic functions with photothermal/electromagnetic synergistic therapeutic capabilities through heterostructure doping (211, 212). Additionally, low-frequency rotating magnetic fields significantly inhibit breast cancer metastasis by disrupting F-actin polymerization (213). These technologies synergize with physical microenvironment modulation tools like ionizing radiation and ultrasound, forming a three-dimensional therapeutic network.
At the clinical translation level, biomarker stratification (e.g., the FTO-OTUB1 axis in NPC prognosis) and adaptive clinical trial designs (e.g., basket trials for OTUD3-high DLBCL) may improve precision. Dynamic monitoring techniques (e.g., ctDNA analysis) enable real-time tracking of therapeutic responses and compensatory pathway activation. However, vigilance is required regarding potential immune homeostasis disruption risks associated with OTU-targeted therapies. The deep integration of traditional medicine and modern technology is exemplified by the synergistic interplay between herbal formulations—which exert systemic regulatory effects in cancer management—and mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes that modulate mitochondrial gene functions (214–216). These approaches, combined with exercise-induced tumor immune microenvironment reprogramming and immunotherapy, establish a multi-tiered defense framework (217). Artificial intelligence further enriches early screening by uncovering associations between craniofacial genes and cancer susceptibility (218). Current research is advancing toward magnetic field-nanomaterial synergy platforms and imaging-guided dynamic monitoring systems, with a focus on integrating physical interventions, metabolic reprogramming, and gene-editing technologies to achieve a closed-loop precision therapy spanning OTU molecular network regulation to systemic immune activation. This evolution marks a comprehensive transformation in oncology toward a spatiotemporal dynamic regulation paradigm.
In conclusion, OTU family research is shifting from single-target exploration to multidimensional network analysis. By integrating structural biology, computational modeling, and clinical big data, future research may develop OTU-based molecular subtyping strategies for personalized treatment, synergizing with existing immunotherapies. However, overcoming functional complexity, optimizing inhibitor specificity, and ensuring clinical safety remain pivotal for translational breakthroughs. Advances in this field could redefine the landscape of cancer immunotherapy, offering novel strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Conclusions
Collectively, OTU family members performs critical roles in tumorigenesis and immunomodulation. In the present review, we illustrated that OTUs can modulate multiple signaling pathways through deubiquitination, thereby affecting tumor growth, migration, and apoptosis. Alternatively, OTUs were able to influence the intensity and duration of the immune response and promote tumorigenesis and progression in the TME by regulating the inflammatory response and immune escape mechanisms. Hence, an in-depth investigation of the specific mechanisms of the OTU family and their roles in tumor and immunity will be significant for the development of novel anti-tumor therapeutic strategies.
Author contributions
XT: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – original draft. YaL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YoL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Taishan Scholarship (tsqn202312362) and the National Natural Science Foundations of China (81802400).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Popovic D, Vucic D, and Dikic I. Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Med. (2014) 20:1242–53. doi: 10.1038/nm.3739
2. Swatek KN and Komander D. Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res. (2016) 26:399–422. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.39
3. Tracz M and Bialek W. Beyond K48 and K63: non-canonical protein ubiquitination. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2021) 26:1. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-00245-6
4. Dewson G, Eichhorn P, and Komander D. Deubiquitinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2023) 23:842–62. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00633-y
5. Snyder NA and Silva GM. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs): Regulation, homeostasis, and oxidative stress response. J Biol Chem. (2021) 297:101077. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101077
6. Xu L, Li J, Bao Z, Xu P, Chang H, Wu J, et al. Silencing of OTUB1 inhibits migration of human glioma cells. vitro NEUROPATHOL. (2017) 37:217–26. doi: 10.1111/neup.2017.37.issue-3
7. Wang X, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Zhuang H, and Chen B. Clinical significance of ubiquitin specific protease 7 (USP7) in predicting prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and its functional mechanisms. Med Sci Monit. (2018) 24:1742–50. doi: 10.12659/MSM.909368
8. Zhang C, Lu J, Zhang QW, Zhao W, Guo JH, Liu SL, et al. USP7 promotes cell proliferation through the stabilization of Ki-67 protein in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2016) 79:209–21. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.08.025
9. Saha G and Ghosh MK. The key vulnerabilities and therapeutic opportunities in the USP7-p53/MDM2 axis in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2025) 1872:119908. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2025.119908
10. Poondla N, Chandrasekaran AP, Kim KS, and Ramakrishna S. Deubiquitinating enzymes as cancer biomarkers: new therapeutic opportunities? BMB Rep. (2019) 52:181–9. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.3.048
11. Enesa K and Evans P. The biology of A20-like molecules. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2014) 809:33–48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0398-6_3
12. Weinelt N and van Wijk S. Ubiquitin-dependent and -independent functions of OTULIN in cell fate control and beyond. Cell Death DIFFER. (2021) 28:493–504. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00675-x
13. Du J, Fu L, Sui Y, and Zhang L. The function and regulation of OTU deubiquitinases. Front Med. (2020) 14:542–63. doi: 10.1007/s11684-019-0734-4
14. Mevissen TE, Hospenthal MK, Geurink PP, Elliott PR, Akutsu M, Arnaudo N, et al. OTU deubiquitinases reveal mechanisms of linkage specificity and enable ubiquitin chain restriction analysis. CELL. (2013) 154:169–84. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.046
15. Xu Y, Xu M, Tong J, Tang X, Chen J, Chen X, et al. Targeting the Otub1/c-Maf axis for the treatment of multiple myeloma. BLOOD. (2021) 137:1478–90. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020005199
16. Liu X, Deng H, Tang J, Wang Z, Zhu C, Cai X, et al. OTUB1 augments hypoxia signaling via its non-canonical ubiquitination inhibition of HIF-1alpha during hypoxia adaptation. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:560. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05008-z
17. Peng L, Wu T, Liu Y, Zhao D, He W, and Yuan Y. OTUB1 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing RACK1 via its non-canonical ubiquitination. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2024) 47:987–1004. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00913-7
18. Lee SG, Woo SM, Seo SU, Lee HS, Kim SH, Chang YC, et al. Non-canonical deubiquitination of OTUB1 induces IFNgamma-mediated cell cycle arrest via regulation of p27 stability. ONCOGENE. (2024) 43:1852–60. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03042-z
19. Zhang Y, Fan Y, Jing X, Zhao L, Liu T, Wang L, et al. OTUD5-mediated deubiquitination of YAP in macrophage promotes M2 phenotype polarization and favors triple-negative breast cancer progression. Cancer Lett. (2021) 504:104–15. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.02.003
20. Han Z, Jia Q, Zhang J, Chen M, Wang L, Tong K, et al. Deubiquitylase YOD1 regulates CDK1 stability and drives triple-negative breast cancer tumorigenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:228. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02781-3
21. Zhao Y, Huang X, Zhu D, Wei M, Luo J, Yu S, et al. Deubiquitinase OTUD6A promotes breast cancer progression by increasing TopBP1 stability and rendering tumor cells resistant to DNA-damaging therapy. Cell Death DIFFER. (2022) 29:2531–44. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01036-6
22. Pareja F, Ferraro DA, Rubin C, Cohen-Dvashi H, Zhang F, Aulmann S, et al. Deubiquitination of EGFR by Cezanne-1 contributes to cancer progression. ONCOGENE. (2012) 31:4599–608. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.587
23. Zhang P, Xiao Z, Wang S, Zhang M, Wei Y, Hang Q, et al. ZRANB1 is an EZH2 deubiquitinase and a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cell Rep. (2018) 23:823–37. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.078
24. Lee JH, Jung SM, Yang KM, Bae E, Ahn SG, Park JS, et al. A20 promotes metastasis of aggressive basal-like breast cancers through multi-monoubiquitylation of Snail1. Nat Cell Biol. (2017) 19:1260–73. doi: 10.1038/ncb3609
25. Zhang Z, Fan Y, Xie F, Zhou H, Jin K, Shao L, et al. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor OTUD1 deubiquitinates SMAD7. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:2116. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02029-7
26. Pu Q, Lv YR, Dong K, Geng WW, and Gao HD. Tumor suppressor OTUD3 induces growth inhibition and apoptosis by directly deubiquitinating and stabilizing p53 in invasive breast carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:583. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07069-9
27. Yuan L, Lv Y, Li H, Gao H, Song S, Zhang Y, et al. Deubiquitylase OTUD3 regulates PTEN stability and suppresses tumorigenesis. Nat Cell Biol. (2015) 17:1169–81. doi: 10.1038/ncb3218
28. Hu G, Yang J, Zhang H, Huang Z, and Yang H. OTUB2 promotes proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by PJA1 deubiquitylation. Cell Mol BIOENG. (2022) 15:281–92. doi: 10.1007/s12195-022-00720-4
29. Xie P, Chen Y, Zhang H, Zhou G, Chao Q, Wang J, et al. The deubiquitinase OTUD3 stabilizes ACTN4 to drive growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). (2021) 13:19317–38. doi: 10.18632/aging.203293
30. Yang Y, Jia S, Zhu N, Xiao X, Ma Y, Tu K, et al. OTUD5 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by deubiquitinating and stabilizing SLC38A1. Biol DIRECT. (2024) 19:31. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00475-0
31. Kim Y and Jho EH. Deubiquitinase YOD1: the potent activator of YAP in hepatomegaly and liver cancer. BMB Rep. (2017) 50:281–2. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2017.50.6.078
32. Kim Y, Kim W, Song Y, Kim JR, Cho K, Moon H, et al. Deubiquitinase YOD1 potentiates YAP/TAZ activities through enhancing ITCH stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2017) 114:4691–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620306114
33. Kanki K, Akechi Y, Ueda C, Tsuchiya H, Shimizu H, Ishijima N, et al. Biological and clinical implications of retinoic acid-responsive genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J HEPATOL. (2013) 59:1037–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.06.024
34. Chen H, Hu L, Luo Z, Zhang J, Zhang C, Qiu B, et al. A20 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through inhibition of Twist1 expression. Mol Cancer. (2015) 14:186. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0454-6
35. Yi PS, Shu Y, Bi WX, Zheng XB, Feng WJ, He LY, et al. Emerging role of zinc finger protein A20 as a suppressor of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:21479–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v234.12
36. Baietti MF, Simicek M, Abbasi AL, Radaelli E, Lievens S, Crowther J, et al. OTUB1 triggers lung cancer development by inhibiting RAS monoubiquitination. EMBO Mol Med. (2016) 8:288–303. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201505972
37. Li J, Cheng D, Zhu M, Yu H, Pan Z, Liu L, et al. OTUB2 stabilizes U2AF2 to promote the Warburg effect and tumorigenesis via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. THERANOSTICS. (2019) 9:179–95. doi: 10.7150/thno.29545
38. Du T, Li H, Fan Y, Yuan L, Guo X, Zhu Q, et al. The deubiquitylase OTUD3 stabilizes GRP78 and promotes lung tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:2914. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10824-7
39. Ma X, Wang L, Shi G, and Sun S. The deubiquitinase OTUD1 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by deubiquitinating and stabilizing KLF4. Thorac Cancer. (2022) 13:761–70. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14320
40. Zhang Q, Li J, Chen Z, Jiang K, Yang K, Huang F, et al. VE-822 upregulates the deubiquitinase OTUD1 to stabilize FHL1 to inhibit the progression of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2023) 46:1001–14. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00793-x
41. Li X, Lu B, Zhang L, Yang J, Cheng Y, and Yan D. Mechanism of OTUD5 in non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. (2022) 22:901–11. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.7206
42. Liao Y, Cao L, Wang F, and Pang R. miR-605-5p promotes invasion and proliferation by targeting TNFAIP3 in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Cell Biochem. (2020) 121:779–87. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v121.1
43. Wang Y, Zhou X, Xu M, Weng W, Zhang Q, Yang Y, et al. OTUB1-catalyzed deubiquitination of FOXM1 facilitates tumor progression and predicts a poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:36681–97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i24
44. Nan Y, Wu X, Luo Q, Chang W, Zhao P, Zhang L, et al. OTUB2 silencing promotes ovarian cancer via mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming and can be synthetically targeted by CA9 inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2024) 121:e1979619175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315348121
45. Zhang HH, Li C, Ren JW, Liu L, Du XH, Gao J, et al. OTUB1 facilitates bladder cancer progression by stabilizing ATF6 in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Sci. (2021) 112:2199–209. doi: 10.1111/cas.v112.6
46. Hou T, Dan W, Liu T, Liu B, Wei Y, Yue C, et al. Deubiquitinase OTUD5 modulates mTORC1 signaling to promote bladder cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:778. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05128-6
47. Zhang Q, Zhang J, Yao A, Tian X, Han Z, Yuan Y, et al. OTUB2 promotes the progression of endometrial cancer by regulating the PKM2-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int. (2023) 47:428–38. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11950
48. Lv Q, Xie L, Cheng Y, Shi Y, Shan W, Ning C, et al. A20-mediated deubiquitination of ERalpha in the microenvironment of CD163(+) macrophages sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to estrogen. Cancer Lett. (2019) 442:137–47. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.10.019
49. Huang Z, Zhang Z, Tu Y, He H, Qiu F, Qian H, et al. Integrated single-cell and transcriptome sequencing analyses develop a ubiquitination-associated signature in gastric cancer and identified OTULIN as a novel biomarker. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2023) 28:304. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2811304
50. Jantaree P, Chaithongyot S, Sokolova O, and Naumann M. USP48 and A20 synergistically promote cell survival in Helicobacter pylori infection. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2022) 79:461. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04489-7
51. Lim M, Maubach G, Sokolova O, Feige MH, Diezko R, Buchbinder J, et al. Pathogen-induced ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 bifunctionally shuts off NF-kappaB and caspase-8-dependent apoptotic cell death. Cell Death DIFFER. (2017) 24:1621–31. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.89
52. Du B, Liu M, Li C, Geng X, Zhang X, Ning D, et al. The potential role of TNFAIP3 in Malignant transformation of gastric carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. (2019) 215:152471. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152471
53. Zhang Z, Zhao W, Li Y, Li Y, Cheng H, Zheng L, et al. YOD1 serves as a potential prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22:203. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02616-9
54. Lei S, He Z, Chen T, Guo X, Zeng Z, Shen Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA 00976 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through OTUD7B by sponging miR-137 involving EGFR/MAPK pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:470. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1388-4
55. Ye D, Wang S, Wang X, Lin Y, Huang Y, and Chi P. Overexpression of OTU domain-containing ubiquitin aldehyde-binding protein 1 exacerbates colorectal cancer Malignancy by inhibiting protein degradation of beta-Catenin via Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. BIOENGINEERED. (2022) 13:9106–16. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2057897
56. Shi L, Liu J, Peng Y, Zhang J, Dai X, Zhang S, et al. Deubiquitinase OTUD6A promotes proliferation of cancer cells via regulating Drp1 stability and mitochondrial fission. Mol Oncol. (2020) 14:3169–83. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12825
57. Jin Y, Cheng H, Cao J, and Shen W. MicroRNA 32 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and suppresses apoptosis in colon cancer cells by targeting OTU domain containing 3. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:18629–39. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v120.11
58. Zhou H, Liu Y, Zhu R, Ding F, Cao X, Lin D, et al. OTUB1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through modulating Snail stability. ONCOGENE. (2018) 37:3356–68. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0224-1
59. Liu L, Cheng H, Ji M, Su L, Lu Z, Hu X, et al. OTUB2 regulates YAP1/TAZ to promotes the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biol PROCED Online. (2022) 24:10. doi: 10.1186/s12575-022-00169-9
60. Jin S, Tsunematsu T, Horiguchi T, Mouri Y, Shao W, Miyoshi K, et al. Involvement of the OTUB1-YAP1 axis in driving Malignant behaviors of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:22156–69. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v12.24
61. Li Y, Li R, Qin H, He H, and Li S. OTUB1’s role in promoting OSCC development by stabilizing RACK1 involves cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumor-associated macrophage M1 polarization. Cell Signal. (2023) 110:110835. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110835
62. Xie P, Chao Q, Mao J, Liu Y, Fang J, Xie J, et al. The deubiquitinase OTUB1 fosters papillary thyroid carcinoma growth through EYA1 stabilization. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:10980–9. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.v25.23
63. Wang J, Dong Y, Wei Z, Zhang Y, Wu N, Zhang C, et al. Deubiquitinase OTUB2 promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression by stabilizing the CTNNB1-ZEB1 axis. Exp Cell Res. (2023) 425:113537. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113537
64. Song Y and Wu Q. RBM15 m(6) A modification-mediated OTUB2 upregulation promotes cervical cancer progression via the AKT/mTOR signaling. Environ Toxicol. (2023) 38:2155–64. doi: 10.1002/tox.23852
65. Ci M, Zhao G, Li C, Liu R, Hu X, Pan J, et al. OTUD4 promotes the progression of glioblastoma by deubiquitinating CDK1 and activating MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:179. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06569-x
66. Peng Y, Liu J, Wang Z, Cui C, Zhang T, Zhang S, et al. Correction to: Prostate-specific oncogene OTUD6A promotes prostatic tumorigenesis via deubiquitinating and stabilizing c-Myc. Cell Death DIFFER. (2023) 30:224–5. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-00978-1
67. Ma B, Wei X, Zhou S, and Yang M. MCTS1 enhances the proliferation of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via promoting OTUD6B-1 mediated LIN28B deubiquitination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 678:128–34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.08.036
68. Paulmann C, Spallek R, Karpiuk O, Heider M, Schaffer I, Zecha J, et al. The OTUD6B-LIN28B-MYC axis determines the proliferative state in multiple myeloma. EMBO J. (2022) 41:e110871. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022110871
69. Guo Q, Dong H, Liu X, Wang C, Liu N, Zhang J, et al. A20 is overexpressed in glioma cells and may serve as a potential therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2009) 13:733–41. doi: 10.1517/14728220903045018
70. Ma J, Wang H, Guo S, Yi X, Zhao T, Liu Y, et al. A20 promotes melanoma progression via the activation of Akt pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:794. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03001-y
71. Wu Y, Duan Y, Han W, Cao J, Ye B, Chen P, et al. Deubiquitinase YOD1 suppresses tumor progression by stabilizing E3 ligase TRIM33 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:517. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06035-0
72. Wang LQ, Zhang Y, Yan H, Liu KJ, and Zhang S. MicroRNA-373 functions as an oncogene and targets YOD1 gene in cervical cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 459:515–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.138
73. Liu W, Yan B, Yu H, Ren J, Peng M, Zhu L, et al. OTUD1 stabilizes PTEN to inhibit the PI3K/AKT and TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathways and sensitize ccRCC to TKIs. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:1401–14. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.68980
74. Guo K, Wei Y, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhang X, Liu X, et al. Deubiquitylase OTUD6B stabilizes the mutated pVHL and suppresses cell migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:97. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04135-3
75. Huang T, Yin L, Wu J, Gu JJ, Ding K, Zhang N, et al. TNFAIP3 inhibits migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by suppressing epithelial mesenchymal transition. NEOPLASMA. (2017) 64:389–94. doi: 10.4149/neo_2017_309
76. Karunarathna U, Kongsema M, Zona S, Gong C, Cabrera E, Gomes AR, et al. OTUB1 inhibits the ubiquitination and degradation of FOXM1 in breast cancer and epirubicin resistance. ONCOGENE. (2016) 35:1433–44. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.208
77. Zhao Y, Ruan J, Li Z, Su X, Chen K, Lin Y, et al. OTUB1 inhibits breast cancer by non-canonically stabilizing CCN6. Clin Transl Med. (2023) 13:e1385. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.v13.8
78. Pang Z, Cui L, Ding N, Zhu L, Qu X, Dong W, et al. Expressions of insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 and cezanne-1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Med Oncol. (2017) 34:78. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0934-1
79. Lin DD, Shen Y, Qiao S, Liu WW, Zheng L, Wang YN, et al. Upregulation of OTUD7B (Cezanne) promotes tumor progression via AKT/VEGF pathway in lung squamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:862. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00862
80. Sun C, Bai J, Sun J, Sun Y, Zhang F, Li H, et al. OTU deubiquitinase 7B facilitates the hyperthermia-induced inhibition of lung cancer progression through enhancing Smac-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. Environ Toxicol. (2024) 39:1989–2005. doi: 10.1002/tox.24080
81. Zhang B, Yang C, Wang R, Wu J, Zhang Y, Liu D, et al. OTUD7B suppresses Smac mimetic-induced lung cancer cell invasion and migration via deubiquitinating TRAF3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 39:244. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01751-3
82. Shao L, Oshima S, Duong B, Advincula R, Barrera J, Malynn BA, et al. A20 restricts wnt signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and suppresses colon carcinogenesis. PloS One. (2013) 8:e62223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062223
83. Liu J, Yang S, Wang Z, Chen X, and Zhang Z. Ubiquitin ligase A20 regulates p53 protein in human colon epithelial cells. J BioMed Sci. (2013) 20:74. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-74
84. Zhao X, Zhou M, Yang Y, and Luo M. The ubiquitin hydrolase OTUB1 promotes glioma cell stemness via suppressing ferroptosis through stabilizing SLC7A11 protein. BIOENGINEERED. (2021) 12:12636–45. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2011633
85. Yan C, Yang H, Su P, Li X, Li Z, Wang D, et al. OTUB1 suppresses Hippo signaling via modulating YAP protein in gastric cancer. ONCOGENE. (2022) 41:5186–98. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02507-3
86. Zhang Z, Du J, Wang S, Shao L, Jin K, Li F, et al. OTUB2 promotes cancer metastasis via hippo-independent activation of YAP and TAZ. Mol Cell. (2019) 73:7–21. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.030
87. Chen Y, Qiang Y, Fan J, Zheng Q, Yan L, Fan G, et al. Aggresome formation promotes ASK1/JNK signaling activation and stemness maintenance in ovarian cancer. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:1321. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45698-x
88. Feng W, Gao M, Yang M, Li X, Gan Z, Wu T, et al. TNFAIP3 promotes ALDH-positive breast cancer stem cells through FGFR1/MEK/ERK pathway. Med Oncol. (2022) 39:230. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01844-3
89. Miao D, Wang Y, Jia Y, Tong J, Jiang S, and Liu L. ZRANB1 enhances stem-cell-like features and accelerates tumor progression by regulating Sox9-mediated USP22/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer. Cell Signal. (2022) 90:110200. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110200
90. Hjelmeland AB, Wu Q, Wickman S, Eyler C, Heddleston J, Shi Q, et al. Targeting A20 decreases glioma stem cell survival and tumor growth. PloS Biol. (2010) 8:e1000319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000319
91. Du X, Pang J, Gu B, Si T, Chang Y, Li T, et al. A bio-orthogonal linear ubiquitin probe identifies STAT3 as a direct substrate of OTULIN in glioblastoma. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:1050–66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad002
92. Liu T, Jiang L, Tavana O, and Gu W. The deubiquitylase OTUB1 mediates ferroptosis via stabilization of SLC7A11. Cancer Res. (2019) 79:1913–24. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3037
93. Wang Z, Ouyang L, Liu N, Li T, Yan B, Mao C, et al. The DUBA-SLC7A11-c-Myc axis is critical for stemness and ferroptosis. ONCOGENE. (2023) 42:2688–700. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02744-0
94. Huang S, Zhang Q, Zhao M, Wang X, Zhang Y, Gan B, et al. The deubiquitinase ZRANB1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase for SLC7A11 and regulates ferroptotic resistance. J Cell Biol. (2023) 222(11):e202212072. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202212072
95. Li D, Wang Y, Dong C, Chen T, Dong A, Ren J, et al. CST1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating GPX4 protein stability via OTUB1. ONCOGENE. (2023) 42:83–98. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02537-x
96. Song J, Liu T, Yin Y, Zhao W, Lin Z, Yin Y, et al. The deubiquitinase OTUD1 enhances iron transport and potentiates host antitumor immunity. EMBO Rep. (2021) 22:e51162. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051162
97. Wang P, Hu Z, Yu S, Su S, Wu R, Chen C, et al. A novel protein encoded by circFOXP1 enhances ferroptosis and inhibits tumor recurrence in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. (2024) 598:217092. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217092
98. Li Z, Tian Y, Zong H, Wang X, Li D, Keranmu A, et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUD4 stabilizes RBM47 to induce ATF3 transcription: a novel mechanism underlying the restrained Malignant properties of ccRCC cells. APOPTOSIS. (2024) 29:1051–69. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01953-6
99. Gao C, Xiao F, Zhang L, Sun Y, Wang L, Liu X, et al. SENP1 inhibition suppresses the growth of lung cancer cells through activation of A20-mediated ferroptosis. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:224. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6909
100. Wang J, Liu Y, Wu D, Tian C, Gao J, Yang Q, et al. OTUB1 targets CHK1 for deubiquitination and stabilization to facilitate lung cancer progression and radioresistance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2024) 119:1222–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.01.202
101. Wan Q, Chen Q, Cai D, Zhao Y, and Wu X. OTUB2 promotes homologous recombination repair through stimulating rad51 expression in endometrial cancer. Cell Transplant. (2020) 29:2138924137. doi: 10.1177/0963689720931433
102. Kato K, Nakajima K, Ui A, Muto-Terao Y, Ogiwara H, and Nakada S. Fine-tuning of DNA damage-dependent ubiquitination by OTUB2 supports the DNA repair pathway choice. Mol Cell. (2014) 53:617–30. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.01.030
103. Yang C, Zang W, Tang Z, Ji Y, Xu R, Yang Y, et al. A20/TNFAIP3 regulates the DNA damage response and mediates tumor cell resistance to DNA-damaging therapy. Cancer Res. (2018) 78:1069–82. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2143
104. Liu X, Ma Z, Jing X, Wang G, Zhao L, Zhao X, et al. The deubiquitinase OTUD5 stabilizes SLC7A11 to promote progression and reduce paclitaxel sensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Lett. (2024) 604:217232. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217232
105. Wang W, Li M, Ponnusamy S, Chi Y, Xue J, Fahmy B, et al. ABL1-dependent OTULIN phosphorylation promotes genotoxic Wnt/beta-catenin activation to enhance drug resistance in breast cancers. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:3965. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17770-9
106. Wang W and Wu ZH. OTULIN couples WNT signaling to resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cell Oncol. (2020) 7:1825904. doi: 10.1080/23723556.2020.1825904
107. Vendrell JA, Ghayad S, Ben-Larbi S, Dumontet C, Mechti N, and Cohen PA. A20/TNFAIP3, a new estrogen-regulated gene that confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. ONCOGENE. (2007) 26:4656–67. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210269
108. Mei Y, Hang Q, Teng H, Yao F, Chen MK, Hung MC, et al. ZRANB1 is an NBS1 deubiquitinase and a potential target to overcome radioresistance and PARP inhibitor resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Genes Dis. (2023) 10:1739–42. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.09.013
109. Zhou T, Wu Y, Qian D, Tang H, Liu X, Qiu J, et al. OTUD1 chemosensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to doxorubicin by modulating P16 expression. Pathol Res Pract. (2023) 247:154571. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154571
110. Geng W, Song H, Zhao Q, Dong K, Pu Q, Gao H, et al. miR-520h stimulates drug resistance to paclitaxel by targeting the OTUD3-PTEN axis in breast cancer. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:9512793. doi: 10.1155/2020/9512793
111. Wang Y, Li J, Zheng H, Wang K, Ren X, Wang G, et al. Cezanne promoted autophagy through PIK3C3 stabilization and PIK3C2A transcription in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:302. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01599-4
112. Liu H, Zhong L, Lu Y, Liu X, Wei J, Ding Y, et al. Deubiquitylase OTUD1 confers Erlotinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of nuclear translocation of YAP1. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:403. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01119-w
113. Kang XY, Zhang J, Tang L, Huang L, Tong J, and Fu Q. OTU deubiquitinase 5 inhibits the progression of non-small cell lung cancer via regulating p53 and PDCD5. Chem Biol Drug Des. (2020) 96:790–800. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13688
114. Yu S, Zang W, Qiu Y, Liao L, and Zheng X. Deubiquitinase OTUB2 exacerbates the progression of colorectal cancer by promoting PKM2 activity and glycolysis. ONCOGENE. (2022) 41:46–56. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02071-2
115. Paul S, Bhardwaj M, and Kang SC. GSTO1 confers drug resistance in HCT−116 colon cancer cells through an interaction with TNFalphaIP3/A20. Int J Oncol. (2022) 61(5):136. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5426
116. Liao Y, Liang J, Wang Y, Li A, Liu W, Zhong B, et al. Target deubiquitinase OTUB1 as a therapeatic strategy for BLCA via beta-catenin/necroptosis signal pathway. Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:3784–801. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.94013
117. Cui J, Liu X, Shang Q, Sun S, Chen S, Dong J, et al. Deubiquitination of CDC6 by OTUD6A promotes tumour progression and chemoresistance. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:86. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01996-y
118. Liu Y, Bai Q, Pang N, and Xue J. TCF12 induces ferroptosis by suppressing OTUB1-mediated SLC7A11 deubiquitination to promote cisplatin sensitivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Biol Int. (2024) 48:1649–63. doi: 10.1002/cbin.v48.11
119. Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, Duran GE, Yu RX, Harsh GR, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced protein 3 as a putative regulator of nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated resistance to O6-alkylating agents in human glioblastomas. J Clin Oncol. (2006) 24:274–87. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.9405
120. Chen S, Xing H, Li S, Yu J, Li H, Liu S, et al. Up-regulated A20 promotes proliferation, regulates cell cycle progression and induces chemotherapy resistance of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leuk Res. (2015) 39:976–83. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.06.004
121. Dai H, Wu B, Ge Y, Hao Y, Zhou L, Hong R, et al. Deubiquitylase OTUD3 regulates integrated stress response to suppress progression and sorafenib resistance of liver cancer. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114487. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114487
122. Shen LJ, Sun HW, Chai YY, Jiang QY, Zhang J, Li WM, et al. The disassociation of the A20/HSP90 complex via downregulation of HSP90 restores the effect of A20 enhancing the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to molecular targeted agents. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:804412. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.804412
123. Yao J, Li Z, Wang X, Xu P, Zhao L, and Qian J. MiR-125a regulates chemo-sensitivity to gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer cells through targeting A20. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2016) 48:202–8. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv129
124. Huang WM, Li ZX, Wu YH, Shi ZL, Mi JL, Hu K, et al. m6A demethylase FTO renders radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via promoting OTUB1-mediated anti-ferroptosis. Transl Oncol. (2023) 27:101576. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101576
125. Wu X, Liu S, Sagum C, Chen J, Singh R, Chaturvedi A, et al. Crosstalk between Lys63- and Lys11-polyubiquitin signaling at DNA damage sites is driven by Cezanne. Genes Dev. (2019) 33:1702–17. doi: 10.1101/gad.332395.119
126. Wu Z, Qiu M, Guo Y, Zhao J, Liu Z, Wang H, et al. OTU deubiquitinase 4 is silenced and radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells via inhibiting DNA repair. Cancer Cell Int. (2019) 19:99. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0816-z
127. Di M, Miao J, Pan Q, Wu Z, Chen B, Wang M, et al. OTUD4-mediated GSDME deubiquitination enhances radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inducing pyroptosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 41:328. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02533-9
128. Yin F, He H, Zhang B, Zheng J, Wang M, Zhang M, et al. Effect of deubiquitinase ovarian tumor domain-containing protein 5 (OTUD5) on radiosensitivity of cervical cancer by regulating the ubiquitination of akt and its mechanism. Med Sci Monit. (2019) 25:3469–75. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912904
129. Huang T, Yin L, Wu J, Gu JJ, Wu JZ, Chen D, et al. MicroRNA-19b-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting TNFAIP3/NF-kappaB axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 35:188. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0465-1
130. Liu X, Jiang WN, Wang JG, and Chen H. Colon cancer bears overexpression of OTUB1. Pathol Res Pract. (2014) 210:770–3. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2014.05.008
131. Weng W, Zhang Q, Xu M, Wu Y, Zhang M, Shen C, et al. OTUB1 promotes tumor invasion and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Am J Transl Res. (2016) 8:2234–44.
132. Ni Q, Chen J, Li X, Xu X, Zhang N, Zhou A, et al. Expression of OTUB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its effects on HCC cell migration and invasion. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2017) 49:680–8. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmx056
133. Deng Y, Li J, He Y, Du D, Hu Z, Zhang C, et al. The deubiquitinating enzymes-related signature predicts the prognosis and immunotherapy response in breast cancer. Aging (Albany NY). (2024) 16:11553–67. doi: 10.18632/aging.206010
134. Deng J, Hou G, Fang Z, Liu J, and Lv XD. Distinct expression and prognostic value of OTU domain-containing proteins in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. (2019) 18:5417–27. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10883
135. Sharif-Askari FS, Al-Khayyal N, Talaat I, Sharif-Askari NS, Rawat S, Jundi M, et al. Immunohistochemical assessment of TNFAIP3/A20 expression correlates with early tumorigenesis in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. (2021) 41:739–45. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14825
136. Yoon CI, Ahn SG, Bae SJ, Shin YJ, Cha C, Park SE, et al. High A20 expression negatively impacts survival in patients with breast cancer. PloS One. (2019) 14:e221721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221721
137. Hadisaputri YE, Miyazaki T, Yokobori T, Sohda M, Sakai M, Ozawa D, et al. TNFAIP3 overexpression is an independent factor for poor survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. (2017) 50:1002–10. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3869
138. Wang JH, Zhong XP, Zhang YF, Wu XL, Li SH, Jian PE, et al. Cezanne predicts progression and adjuvant TACE response in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:e3043. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.428
139. Wang JH, Wei W, Guo ZX, Shi M, and Guo RP. Decreased Cezanne expression is associated with the progression and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. (2015) 13:41. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0396-1
140. Xu P, Wang X, Qian J, Li Z, Yao J, and Xu A. The prognostic evaluation of CA19-9, D-dimer and TNFAIP3/A20 in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Med (Baltimore). (2021) 100:e24651. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024651
141. Zhu Y, Qu C, Hong X, Jia Y, Lin M, Luo Y, et al. Trabid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by cleaving RNF8-induced K63 ubiquitination of Twist1. Cell Death DIFFER. (2019) 26:306–20. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0119-2
142. Kayagaki N, Phung Q, Chan S, Chaudhari R, Quan C, O’Rourke KM, et al. DUBA: a deubiquitinase that regulates type I interferon production. SCIENCE. (2007) 318:1628–32. doi: 10.1126/science.1145918
143. Li Z, Li G, Li Y, Luo Y, Jiang Y, Zhang Z, et al. Deubiquitinase OTUD6A regulates innate immune response via targeting UBC13. Viruses. (2023) 15(8):1761. doi: 10.3390/v15081761
144. Fiil BK, Damgaard RB, Wagner SA, Keusekotten K, Fritsch M, Bekker-Jensen S, et al. OTULIN restricts Met1-linked ubiquitination to control innate immune signaling. Mol Cell. (2013) 50:818–30. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.06.004
145. Vetters J, van Helden MJ, Wahlen S, Tavernier SJ, Martens A, Fayazpour F, et al. The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 controls NK cell homeostasis through regulation of mTOR activity and TNF. J Exp Med. (2019) 216:2010–23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20182164
146. Xuan NT, Trung DM, Minh NN, Nghia VX, Giang NV, Canh NX, et al. Regulation of p38MAPK-mediated dendritic cell functions by the deubiquitylase otubain 1. HLA. (2019) 93:462–70. doi: 10.1111/tan.2019.93.issue-6
147. Duy PN, Thuy NT, Trang BK, Giang NH, Van NTH, and Xuan NT. Regulation of NF-kappaB- and STAT1-mediated plasmacytoid dendritic cell functions by A20. PloS One. (2019) 14:e222697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222697
148. Xuan NT, Wang X, Nishanth G, Waisman A, Borucki K, Isermann B, et al. A20 expression in dendritic cells protects mice from LPS-induced mortality. Eur J Immunol. (2015) 45:818–28. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444795
149. Hu H, Brittain GC, Chang JH, Puebla-Osorio N, Jin J, Zal A, et al. OTUD7B controls non-canonical NF-kappaB activation through deubiquitination of TRAF3. NATURE. (2013) 494:371–4. doi: 10.1038/nature11831
150. Chu Y, Soberon V, Glockner L, Beyaert R, Massoumi R, van Loo G, et al. A20 and CYLD do not share significant overlapping functions during B cell development and activation. J Immunol. (2012) 189:4437–43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200396
151. Hu H, Wang H, Xiao Y, Jin J, Chang JH, Zou Q, et al. Otud7b facilitates T cell activation and inflammatory responses by regulating Zap70 ubiquitination. J Exp Med. (2016) 213:399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151426
152. Fischer JC, Otten V, Kober M, Drees C, Rosenbaum M, Schmickl M, et al. A20 restrains thymic regulatory T cell development. J Immunol. (2017) 199:2356–65. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1602102
153. Song XT, Evel-Kabler K, Shen L, Rollins L, Huang XF, and Chen SY. A20 is an antigen presentation attenuator, and its inhibition overcomes regulatory T cell-mediated suppression. Nat Med. (2008) 14:258–65. doi: 10.1038/nm1721
154. Javan MR, Rahimpour A, and Moazzeni SM. Simultaneous transduction of dendritic cells with A20 and BTLA genes stimulates the development of stable and efficient tolerogenic dendritic cells and induces regulatory T cells. Int IMMUNOPHARMACOL. (2021) 99:107966. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107966
155. Oikawa D, Gi M, Kosako H, Shimizu K, Takahashi H, Shiota M, et al. OTUD1 deubiquitinase regulates NF-kappaB- and KEAP1-mediated inflammatory responses and reactive oxygen species-associated cell death pathways. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:694. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05145-5
156. Wu B, Qiang L, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Zhao M, Lei Z, et al. The deubiquitinase OTUD1 inhibits colonic inflammation by suppressing RIPK1-mediated NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Mol Immunol. (2022) 19:276–89. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00810-9
157. Ji Y, Cao L, Zeng L, Zhang Z, Xiao Q, Guan P, et al. The N-terminal ubiquitin-associated domain of Cezanne is crucial for its function to suppress NF-kappaB pathway. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:1979–91. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v119.2
158. Damgaard RB, Walker JA, Marco-Casanova P, Morgan NV, Titheradge HL, Elliott PR, et al. The deubiquitinase OTULIN is an essential negative regulator of inflammation and autoimmunity. CELL. (2016) 166:1215–30. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.019
159. Damgaard RB, Jolin HE, Allison M, Davies SE, Titheradge HL, McKenzie A, et al. OTULIN protects the liver against cell death, inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer. Cell Death DIFFER. (2020) 27:1457–74. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0532-1
160. Yang FM, Shen L, Fan DD, Bai Y, Li B, and Lee J. YAP9/A20 complex suppresses proinflammatory responses and provides novel anti-inflammatory therapeutic potentials. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:914381. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.914381
161. Van Quickelberghe E, Martens A, Goeminne L, Clement L, van Loo G, and Gevaert K. Identification of immune-responsive gene 1 (IRG1) as a target of A20. J Proteome Res. (2018) 17:2182–91. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00139
162. Tang Y, Wang T, Gu L, Xu Y, Yang Z, Zhu W, et al. USP11 exacerbates radiation-induced pneumonitis by activating endothelial cell inflammatory response via OTUD5-STING signaling. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2024) 119:1261–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.01.220
163. Dinallo V, Di Fusco D, Di Grazia A, Laudisi F, Troncone E, Di Maggio G, et al. The deubiquitinating enzyme OTUD5 sustains inflammatory cytokine response in inflammatory bowel disease. J CROHNS COLITIS. (2022) 16:122–32. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab121
164. Liu Y, Yuan J, Zhang Y, Qin F, Bai X, Sun W, et al. OTUD5 promotes the inflammatory immune response by enhancing MyD88 oligomerization and Myddosome formation. Cell Death DIFFER. (2024) 31:753–67. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01293-7
165. Jin J, Xie X, Xiao Y, Hu H, Zou Q, Cheng X, et al. Epigenetic regulation of the expression of Il12 and Il23 and autoimmune inflammation by the deubiquitinase Trabid. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:259–68. doi: 10.1038/ni.3347
166. Li Y, Yang JY, Xie X, Jie Z, Zhang L, Shi J, et al. Preventing abnormal NF-kappaB activation and autoimmunity by Otub1-mediated p100 stabilization. Cell Res. (2019) 29:474–85. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0174-3
167. Lu D, Song J, Sun Y, Qi F, Liu L, Jin Y, et al. Mutations of deubiquitinase OTUD1 are associated with autoimmune disorders. J AUTOIMMUN. (2018) 94:156–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.07.019
168. Das T, Bergen IM, Koudstaal T, van Hulst J, van Loo G, Boonstra A, et al. DNGR1-mediated deletion of A20/Tnfaip3 in dendritic cells alters T and B-cell homeostasis and promotes autoimmune liver pathology. J AUTOIMMUN. (2019) 102:167–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.05.007
169. Jahan AS, Biquand E, Munoz-Moreno R, Le Quang A, Mok CK, Wong HH, et al. OTUB1 is a key regulator of RIG-I-dependent immune signaling and is targeted for proteasomal degradation by influenza A NS1. Cell Rep. (2020) 30:1570–84. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.015
170. Liu C, Huang S, Wang X, Wen M, Zheng J, Wang W, et al. The otubain YOD1 suppresses aggregation and activation of the signaling adaptor MAVS through lys63-linked deubiquitination. J Immunol. (2019) 202:2957–70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800656
171. Zhang Z, Fang X, Wu X, Ling L, Chu F, Li J, et al. Acetylation-dependent deubiquitinase OTUD3 controls MAVS activation in innate antiviral immunity. Mol Cell. (2020) 79:304–19. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.020
172. Zhang L, Liu J, Qian L, Feng Q, Wang X, Yuan Y, et al. Induction of OTUD1 by RNA viruses potently inhibits innate immune responses by promoting degradation of the MAVS/TRAF3/TRAF6 signalosome. PloS PATHOG. (2018) 14:e1007067. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007067
173. Wang S, Hou P, Pan W, He W, He DC, Wang H, et al. DDIT3 targets innate immunity via the DDIT3-OTUD1-MAVS pathway to promote bovine viral diarrhea virus replication. J VIROL. (2021) 95(6):e02351-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02351-20
174. Liuyu T, Yu K, Ye L, Zhang Z, Zhang M, Ren Y, et al. Induction of OTUD4 by viral infection promotes antiviral responses through deubiquitinating and stabilizing MAVS. Cell Res. (2019) 29:67–79. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0107-6
175. Peng Y, Xu R, and Zheng X. HSCARG negatively regulates the cellular antiviral RIG-I like receptor signaling pathway by inhibiting TRAF3 ubiquitination via recruiting OTUB1. PloS PATHOG. (2014) 10:e1004041. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004041
176. Xie M, Yin Y, Chen L, Yin A, Liu Y, Liu Y, et al. Scavenger receptor A impairs interferon response to HBV infection by limiting TRAF3 ubiquitination through recruiting OTUB1. FEBS J. (2020) 287:310–24. doi: 10.1111/febs.v287.2
177. Su Y, Xu T, and Sun Y. Evolutionarily conserved Otub1 suppresses antiviral immune response by promoting Irf3 proteasomal degradation in miiuy croaker, Miichthys miiuy. Dev Comp Immunol. (2024) 159:105218. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2024.105218
178. Zhang Z, Wang D, Wang P, Zhao Y, and You F. OTUD1 negatively regulates type I IFN induction by disrupting noncanonical ubiquitination of IRF3. J Immunol. (2020) 204:1904–18. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900305
179. Xie W, Tian S, Yang J, Cai S, Jin S, Zhou T, et al. OTUD7B deubiquitinates SQSTM1/p62 and promotes IRF3 degradation to regulate antiviral immunity. AUTOPHAGY. (2022) 18:2288–302. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2026098
180. Raja R and Sen GC. The antiviral action of the RIG-I induced pathway of apoptosis (RIPA) is enhanced by its ability to degrade Otulin, which deubiquitinates IRF3. Cell Death DIFFER. (2022) 29:504–13. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00870-4
181. Martin-Vicente M, Gonzalez-Sanz R, Cuesta I, Monzon S, Resino S, and Martinez I. Downregulation of A20 expression increases the immune response and apoptosis and reduces virus production in cells infected by the human respiratory syncytial virus. Vacc (Basel). (2020) 8(1):100. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8010100
182. Feng W, Sun X, Shi N, Zhang M, Guan Z, and Duan M. Influenza a virus NS1 protein induced A20 contributes to viral replication by suppressing interferon-induced antiviral response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 482:1107–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.166
183. Wang J, Zheng H, Dong C, and Xiong S. Human OTUD6B positively regulates type I IFN antiviral innate immune responses by deubiquitinating and stabilizing IRF3. MBIO. (2023) 14:e33223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00332-23
184. Lyu H, Sun L, Guan Z, Li J, Yin C, Zhang Y, et al. Proximity labeling reveals OTUD3 as a DNA-binding deubiquitinase of cGAS. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:112309. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112309
185. Schluter D, Schulze-Niemand E, Stein M, and Naumann M. Ovarian tumor domain proteases in pathogen infection. Trends MICROBIOL. (2022) 30:22–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2021.04.002
186. Zhou X, Yu J, Cheng X, Zhao B, Manyam GC, Zhang L, et al. The deubiquitinase Otub1 controls the activation of CD8(+) T cells and NK cells by regulating IL-15-mediated priming. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:879–89. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0405-2
187. Braun FC, van den Brandt J, Thomas S, Lange S, Schrank J, Gand C, et al. In vivo silencing of A20 via TLR9-mediated targeted siRNA delivery potentiates antitumor immune response. PloS One. (2015) 10:e135444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135444
188. Zhang X, Su Y, Song H, Yu Z, Zhang B, and Chen H. Attenuated A20 expression of acute myeloid leukemia-derived dendritic cells increased the anti-leukemia immune response of autologous cytolytic T cells. Leuk Res. (2014) 38:673–81. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2014.03.011
189. Giordano M, Roncagalli R, Bourdely P, Chasson L, Buferne M, Yamasaki S, et al. The tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20) imposes a brake on antitumor activity of CD8 T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2014) 111:11115–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406259111
190. Verdeil G and Schmitt-Verhulst AM. Unleashing antitumor T-cell activation without ensuing autoimmunity: the case for A20-deletion in adoptive CD8(+) T-cell therapy. ONCOIMMUNOLOGY. (2014) 3:e958951. doi: 10.4161/21624011.2014.958951
191. Pu J, Xu Z, Nian J, Fang Q, Yang M, Huang Y, et al. M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate CD8+T cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-21-5p/YOD1/YAP/beta-catenin pathway. Cell Death Discov. (2021) 7:182. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00556-3
192. Shao B, Wei X, Luo M, Yu J, Tong A, Ma X, et al. Author Correction: Inhibition of A20 expression in tumor microenvironment exerts anti-tumor effect through inducing myeloid-derived suppressor cells apoptosis. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:4372. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31371-8
193. Liu Z, Wang T, She Y, Wu K, Gu S, Li L, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-modified circIGF2BP3 inhibits CD8(+) T-cell responses to facilitate tumor immune evasion by promoting the deubiquitination of PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:105. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01398-4
194. Zhu D, Xu R, Huang X, Tang Z, Tian Y, Zhang J, et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 promotes cancer cell immunosuppression via preventing ER-associated degradation of immune checkpoint protein PD-L1. Cell Death DIFFER. (2020) 28(6):1773–89. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00700-z
195. Ren W, Xu Z, Chang Y, Ju F, Wu H, Liang Z, et al. Pharmaceutical targeting of OTUB2 sensitizes tumors to cytotoxic T cells via degradation of PD-L1. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:9. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44466-7
196. Sui Y, Shen Z, Li X, Lu Y, Feng S, Ma R, et al. Rupatadine-inhibited OTUD3 promotes DLBCL progression and immune evasion through deubiquitinating MYL12A and PD-L1. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:561. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06941-x
197. Guo W, Ma J, Guo S, Wang H, Wang S, Shi Q, et al. A20 regulates the therapeutic effect of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma. J IMMUNOTHER Cancer. (2020) 8(2):e001866. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001866
198. Zou J, Xia H, Zhang C, Xu H, Tang Q, Zhu G, et al. Casp8 acts through A20 to inhibit PD-L1 expression: The mechanism and its implication in immunotherapy. Cancer Sci. (2021) 112:2664–78. doi: 10.1111/cas.v112.7
199. Breitenecker K, Homolya M, Luca AC, Lang V, Trenk C, Petroczi G, et al. Down-regulation of A20 promotes immune escape of lung adenocarcinomas. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 13(601):eabc3911. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abc3911
200. Li JJ, Wang JH, Tian T, Liu J, Zheng YQ, Mo HY, et al. The liver microenvironment orchestrates FGL1-mediated immune escape and progression of metastatic colorectal cancer. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:6690. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42332-0
201. Zhu Y, Banerjee A, Xie P, Ivanov AA, Uddin A, Jiao Q, et al. Pharmacological suppression of the OTUD4/CD73 proteolytic axis revives antitumor immunity against immune-suppressive breast cancers. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134(10):e176390. doi: 10.1172/JCI176390
202. Luo M, Wang X, Wu S, Yang C, Su Q, Huang L, et al. A20 promotes colorectal cancer immune evasion by upregulating STC1 expression to block “eat-me” signal. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:312. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01545-x
203. Chen YH, Chen HH, Wang WJ, Chen HY, Huang WS, Kao CH, et al. TRABID inhibition activates cGAS/STING-mediated anti-tumor immunity through mitosis and autophagy dysregulation. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:3050. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38784-z
204. Li L, Zhu R, Zhou H, Cui CP, Yu X, Liu Y, et al. All-trans retinoic acid promotes a tumor suppressive OTUD6B-beta-trCP-SNAIL axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and enhances immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2207458. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207458
205. Galindo-Hernandez O, Garcia-Salazar LA, Garcia-Gonzalez VG, Diaz-Molina R, and Vique-Sanchez JL. Potential inhibitors of the OTUB1 catalytic site to develop an anti-cancer drug using in-silico approaches. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. (2023) 11:684–93. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.11.4.684
206. Zhang Y, Du T, Liu N, Wang J, Zhang L, Cui CP, et al. Discovery of an OTUD3 inhibitor for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:378. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05900-2
207. Liu ZY, Zhang YW, Zhuang HX, Ou YJ, Jiang QY, Li PF, et al. Inhibiting the Otub1/phosphorylated STAT3 axis for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2025) 46:184–95. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01366-w
208. Zhao M, Xu C, and Zhu H. Ef fi cacy of glucose transporter inhibitors for the treatment of ERRalpha-overexpressed colorectal cancer. Acta Biochim Pol. (2022) 69:567–72. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5852
209. Tang J, He J, Guo H, Lin H, Li M, Yang T, et al. PTBP2-mediated alternative splicing of IRF9 controls tumor-associated monocyte/macrophage chemotaxis and repolarization in neuroblastoma progression. Res (Wash D C). (2023) 6:33. doi: 10.34133/research.0033
210. Xu Y, Zeng Y, Xiao X, Liu H, Zhou B, Luo B, et al. Targeted imaging of tumor associated macrophages in breast cancer. Bio Integr. (2023) 4(3):114–24. doi: 10.15212/bioi-2022-0010
211. Xu H, Guo Z, Li M, Chaves HV, Pinto VDPT, Filho GC, et al. Copper-based nanomaterials for image-guided cancer therapy. Bio Integr. (2024) 5:24. doi: 10.15212/bioi-2024-0013
212. Guo Z, Saw PE, and Jon S. Non-invasive physical stimulation to modulate the tumor microenvironment: unveiling a new frontier in cancer therapy. Bio Integr. (2024) 5:14. doi: 10.15212/bioi-2024-0012
213. Ji X, Tian X, Feng S, Zhang L, Wang J, Guo R, et al. Intermittent F-actin perturbations by magnetic fields inhibit breast cancer metastasis. Res (Wash D C). (2023) 6:80. doi: 10.34133/research.0080
214. Mokashi A and Bhatia NM. Integrated network ethnopharmacology, molecular docking, and ADMET analysis strategy for exploring the anti-breast cancer activity of ayurvedic botanicals targeting the progesterone receptor. Bio Integr. (2024) 5:31. doi: 10.15212/bioi-2024-0066
215. Liao K, Gong L, Yang Y, He Y, Wang F, Huang Y, et al. A comprehensive review of research progress in Chinese medicines for primary liver cancer treatment. Traditional Med Res. (2022) 7:10. doi: 10.53388/TMR20220207263
216. Guo XF, Gu SS, Wang J, Sun H, Zhang YJ, Yu PF, et al. Protective effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal treatment of hippocampal neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced injury. World J Emerg Med. (2022) 13:46–53. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.015
217. Luo Z, Mei J, Wang X, Wang R, He Z, Geffen Y, et al. Voluntary exercise sensitizes cancer immunotherapy via the collagen inhibition-orchestrated inflammatory tumor immune microenvironment. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114697. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114697
Keywords: OTU family, deubiquitinating enzymes, tumorigenesis, immune regulation, ubiquitination-deubiquitination balance
Citation: Tang X, Li Y and Liu Y (2025) Dissecting the dual role of OTU family proteins in tumor progression and immune escape. Front. Immunol. 16:1544341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1544341
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 30 April 2025;
Published: 21 May 2025.
Edited by:
Zhiwen Luo, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Bikesh Kumar Nirala, Emory University, United StateDehui Chang, University of Oxford, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongshuo Liu, bGl1eW9uZ3NodW9AcGt1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiaolong Tang
Xiaolong Tang Yadan Li
Yadan Li Yongshuo Liu
Yongshuo Liu