- Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Bacterial infections continue to pose a serious threat to global health, especially with the growing challenge of multidrug-resistant pathogens. While traditional vaccines have been pivotal in reducing disease burden, they come with limitations such as variable efficacy, safety concerns, and limited ability to address the diversity of bacterial strains. This review highlights the promise of peptide-based vaccines as an innovative approach to overcoming these hurdles. By targeting specific regions of bacterial proteins, peptide vaccines can elicit precise immune responses with improved safety and broader applicability. Advances in technology, including bioinformatics and delivery systems, have enhanced their design, making them more stable, effective, and easier to produce. These vaccines work by activating both antibody and T-cell responses through well-defined mechanisms. Different types, such as linear peptides, cyclic peptides, and synthetic long peptides, offer diverse strategies to tailor immune protection. The role of adjuvants and advanced delivery methods, like nanoparticles and liposomes, further improve their potential. Exciting progress has been made against the ESKAPE pathogens — Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp. Peptide vaccines offer a forward-thinking, adaptable solution to reduce bacterial infections and mitigate the rise of antibiotic resistance, paving the way for safer and more effective prevention strategies. This review underscores the critical role of peptide-based vaccines in combating bacterial infections, advocating for ongoing research to unlock their full potential.
1 Introduction
Bacterial infections remain a major global health problem, causing substantial morbidity and mortality; notably in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) with challenging healthcare system resources (1, 2). Tens of millions die from bacterial diseases, including respiratory infections caused by tuberculosis and pneumonia (3). These infections predominantly affect young children, elder people and people with compromised immune systems (4). Among the top five global causes of death are lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs); pneumonia is the most common (5). Along with pneumonia, other bacterial infections—such as bloodstream infections (sepsis), urinary tract infections (especially catheter-associated), and bacterial meningitis—contribute significantly to global mortality, particularly when caused by multidrug-resistant organisms (6).
Vaccination remains one of the most effective public health interventions to prevent bacterial infections. Vaccines prime the immune system, enabling it to recognize and respond to pathogens before an infection can be established (7). Conventional vaccines — live-attenuated, inactivated, and subunit vaccines — have significantly decreased the incidence of various bacterial diseases. However, these approaches have intrinsic limitations. For instance, although live-attenuated vaccines are highly immunogenic, they pose safety concerns since the attenuated strains can revert to a virulent form, particularly in the immunocompromised host (8–10). Inactivated vaccines are safer but they often trigger only moderate immune responses, requiring the use of adjuvants or booster doses (9, 10). Subunit vaccines, which employ purified pathogen components, frequently fail to generate durable immunity (10, 11). Additionally, the diversity of bacterial antigens is a major problem. Traditional vaccines are often strain- or serotype-specific, limiting their broad use (12).
The increase in multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria highlights the need for new vaccines. Antibiotic resistance has reached a global crisis, with MDR pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, emerging as major public health threats (13). These so-called “superbugs” (14) are particularly alarming as they cause hard-to-treat infections, leading to increased morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs (15).
In addition to their resistance to antibiotics, MDR bacteria have evolved multiple immune evasion strategies that enable persistence and pathogenicity (16). These include biofilm formation, which creates a physical barrier that impedes phagocytosis and limits immune cell access (17); secretion of immunomodulatory toxins, such as leukocidins and hemolysins, which damage immune cells or disrupt cytokine signaling (18); antigenic variation, involving changes in surface antigens that help bacteria escape recognition by antibodies and T-cells (19); inhibition of phagocytosis, via surface proteins (e.g., protein A in S. aureus) that bind antibodies in a non-opsonizing orientation (20); and downregulation of antigen presentation, where bacterial factors interfere with major histocompatibility complex (MHC)" expression, limiting T-cell activation (21). These sophisticated strategies enable pathogens to evade both innate and adaptive immunity, establish chronic infections, and challenge vaccine-mediated protection. Consequently, there is an imperative to develop innovative vaccine platforms that not only prevent infection but also reduce antibiotic reliance and effectively counter bacterial immune evasion strategies.
The bacterial peptide-based vaccine is a new paradigm of bacterial immunization that uses short sequences of amino acids from pathogen-specific antigens to elicit a targeted response against specific epitopes (the portions of antigens that the immune system uses to recognize pathogens). Peptide vaccines bypass risks associated with using whole pathogens, such as reversion to virulence, associated with traditional approaches. Peptide vaccines targeting conserved protein regions critical to bacterial survival and less prone to mutation offer the possibility of broad immunity and can effectively combat antigenic variation (22). New insights from bioinformatics and proteomics have played a major role in discovering immunogenic peptides. This allows the rational design of vaccines against individual pathogens or multiple strains (23). In addition to providing immunological advantages, peptide vaccines offer significant logistical and economic benefits. Their synthetic derivation makes them easy to manufacture, which lowers production costs and simplifies storage and distribution (10). Innovative delivery systems, such as nanoparticle-based carriers, enhance peptide stability and facilitate targeted endocytic uptake by antigen-presenting cells. This promotes efficient processing and presentation of epitopes on MHC class I and II molecules, thereby eliciting robust humoral and cellular immune responses and optimizing overall vaccine immunogenicity and efficacy (24, 25).
In general, peptide-based vaccines present a promising, flexible approach to overcoming many of the challenges faced by traditional bacterial vaccines. Offering a targeted, customizable, and potentially safer solution, they have the potential to significantly reduce the global impact of bacterial infections, especially as antibiotic resistance continues to rise. Continued research into peptide immunization is essential to harness their full potential in creating effective, lasting vaccines against a wide range of bacterial pathogens. In this review, we examined the benefits and future approaches of peptide vaccines.
2 Mechanisms of peptide vaccines in immunity against bacterial infections
2.1 Immunological basis of peptide vaccines
Peptide vaccines offer several advantages, including precise antigen targeting, favorable safety profiles, and the ability to induce both humoral and cellular immune responses (22). The fundamental mechanism underlying their immunogenicity involves the presentation of antigenic peptides by MHC molecules to T-cells, thereby initiating an adaptive immune response against bacterial pathogens (Figure 1) (26).
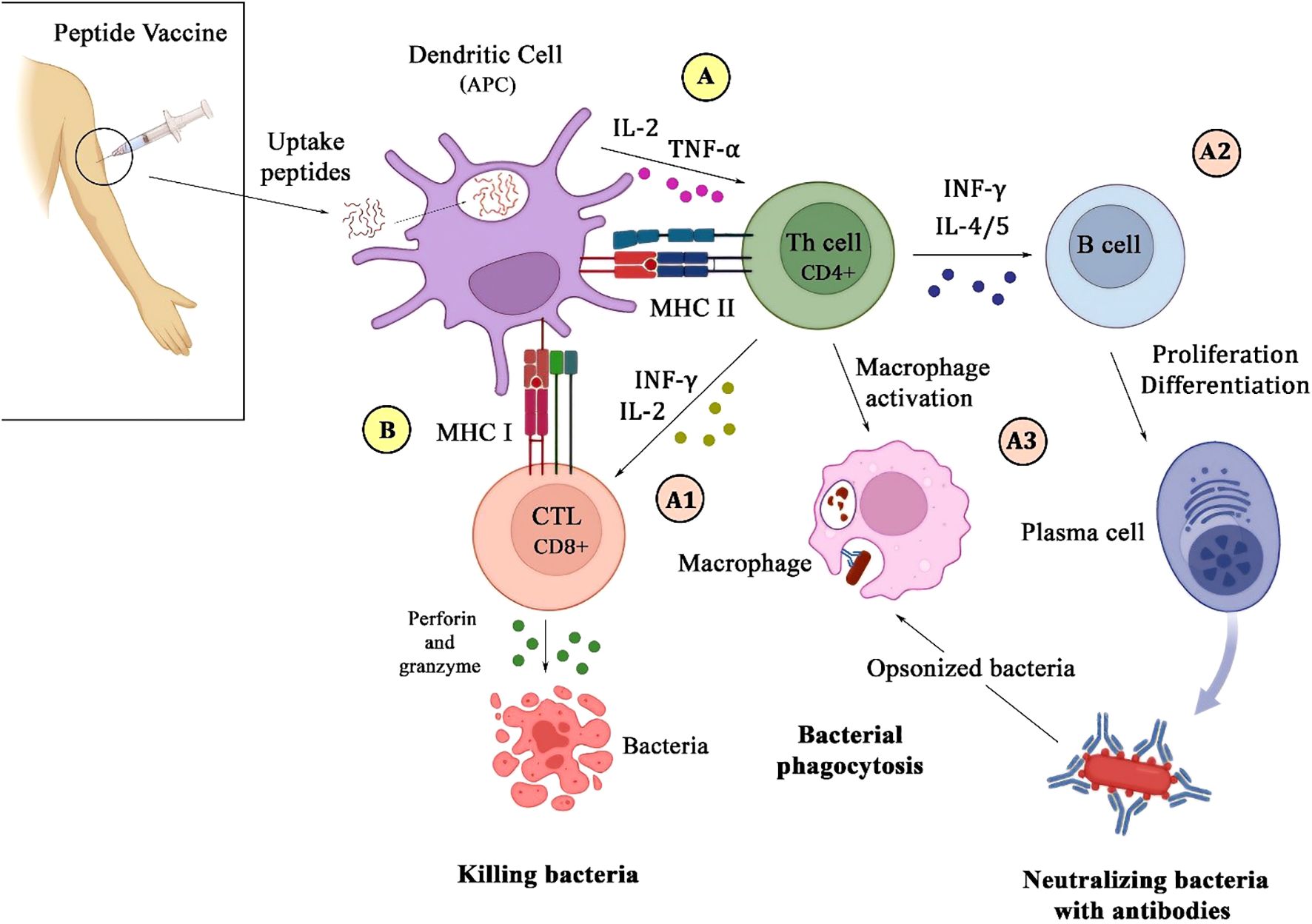
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the immune response to a peptide vaccine. Upon injection of the vaccine, microbial peptides are internalized by dendritic cells, which then process and present them via MHC class II (A) and I (B) molecules to CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells. This interaction leads to the secretion of IL-2 and TNF-α by DC on CD4+ T-cells (A). Activated CD4+ T-cells enhance CD8+ T-cells function by secreting IFN-γ and IL-2, which promote bacterial killing through perforin and granzyme release (A1). Additionally, CD4+ T-cells stimulate B-cells to differentiate into plasma cells to produce antibodies (A2), and also activate macrophages to recognize and phagocytose antibody-opsonized bacteria (A3).
2.1.1 Antigen presentation by MHC molecules and T-cell activation
These studies generally design peptide vaccines that are composed of selected amino acid sequences, termed epitopes, which correspond to the immunogenic regions of bacterial antigens. Following administration, such epitopes are internalized by antigen-presenting cells, mainly dendritic cells (27). The cell processes the peptides and then presents them on the surface in association with MHC molecules. MHC class I and II present peptides to cytotoxic CD8+ T and CD4+T helper cells, which play a crucial role in coordinating the immune response through the elimination of intracellular pathogens and secretion of cytokines that support both cellular and humoral immunity (28). Dendritic cells, along with the presentation of peptides with MHC class II, secrete interleukin 2 and TNF-α on CD4+T to activate it (29). The efficacy of peptide vaccines is strongly influenced by the ability of the epitopes to bind to MHC molecules, which promotes T-cell activation and a potent immune defense against bacterial infections.
2.1.2 Stimulation of humoral and cellular immune responses
A well-designed vaccine should trigger both humoral and cellular immune responses to provide comprehensive protection against bacterial pathogens. Activated CD4+T activates B-cells by secreting INF-γ and interleukins such as 4 and 5. The humoral immune response, driven by B-cell activation and antibody production, is essential for neutralizing extracellular bacteria and preventing colonization. The antibodies can neutralize bacterial toxins, inhibit bacterial adhesion to host tissues, and facilitate opsonization, marking bacteria for phagocytosis (29, 30). Cellular immunity, primarily mediated by T-cells, plays a crucial role in the defense against intracellular pathogens. Cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells recognize and eliminate infected cells, and CD4+ helper T-cells stimulate phagocytic activity and also enhance the responses of cytotoxic T-cells by secreting INF-γ and interleukin 2, contributing to the development of lasting immunity (28, 29). Peptide vaccines aim to induce a comprehensive and durable immune response against bacterial infections by targeting epitopes that engage both humoral and cellular immunity.
2.2 Types of peptide vaccines
Peptide vaccines are classified based on the structure of the peptide as well as its targeted immune response. There are a few categories of peptides, such as linear peptides, cyclic peptides, epitope-based peptides, and synthetic long peptides (SLPs). Different types have distinct advantages for bacterial vaccine development.
2.2.1 Linear vs. cyclic peptides
Most peptide vaccines are based on linear epitopes—short, sequential amino acid fragments derived from pathogenic proteins. These are relatively easy to identify, synthesize, and screen using high-throughput platforms. However, linear peptides often fail to replicate the native three-dimensional structure of proteins, leading to reduced stability and suboptimal immune recognition in vivo. In contrast, conformational epitopes—formed by amino acid residues brought together by protein folding—are typically more immunogenic as they better resemble the native surface of pathogens recognized by B-cell receptors. Peptide vaccines face a fundamental limitation in effectively presenting these conformational structures due to the inherent flexibility and lack of structural complexity of linear peptides. Cyclic peptides, by forming stable and rigid ring structures, can mimic conformational epitopes more accurately. Their restricted conformational mobility enhances binding specificity to MHC molecules and immune receptors, and increases resistance to enzymatic degradation. Thus, employing cyclic peptides in vaccine design can partially overcome the challenge of inducing immune responses against conformational epitopes, though reproducing full protein structures remains difficult in synthetic constructs (31–33).
2.2.2 Epitope-based peptides
Epitope-based vaccines are composed of peptides representing either T-cell or B-cell epitopes. T-cell epitopes are selected based on their ability to bind MHC molecules, leading to the activation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) or helper T-cell responses that are essential for combating intracellular pathogens. In contrast, B-cell epitopes—often derived from surface-exposed regions of bacterial proteins—aim to induce robust antibody responses, which are critical for neutralizing extracellular pathogens (34, 35). To enhance immunogenic breadth, multiple epitopes can be combined into a single construct, resulting in multiepitope-based peptide vaccines (36). These constructs are designed through a rational, immunoinformatics-driven process involving the prediction and selection of highly antigenic, non-toxic, and non-allergenic epitopes with broad population coverage. Then, the selected epitopes are assembled using appropriate peptide linkers and, in some cases, fused to molecular adjuvants or carrier sequences to enhance immunogenicity (37). The choice of linker is critical for maintaining proper antigen processing and structural integrity. Flexible linkers such as AAY or KK are often used to join CTL and B-cell epitopes due to their capacity to promote proteasomal cleavage and enhance epitope presentation. However, their high conformational mobility may result in reduced structural integrity, unwanted interactions between adjacent epitopes, or impaired biological activity. On the other hand, rigid linkers like EAAAK provide fixed spatial separation between functional domains, helping to maintain proper folding and minimize domain interference but may hinder the conformational flexibility needed for antigen processing by APCs. Thus to ensure optimal structural conformation and antigen processing, peptide linkers are chosen based on the structural and immunological demands of the vaccine construct (37–39). Following design, the synthetic gene encoding the multi-epitope construct is codon-optimized and recombinantly expressed in suitable host systems. The suitability of these vaccine candidates depends on several critical parameters, including physicochemical stability, expression yield, proper folding, epitope accessibility, and cost-effectiveness of production. (37). Multiepitope vaccines have demonstrated promise against antigenically diverse or drug-resistant pathogens—such as ESKAPE bacteria—by eliciting multi-faceted immune responses and potential cross-protection.
2.2.3 Synthetic long peptides
SLPs are longer peptides, 20 to 35 amino acids long, that contain multiple T-and B-cell epitopes within a single structure. This enables the activation of both arms of the immune system. SLPs often have multiple MHC-binding sites, enabling a broader T-cell response and increased potential for cross-reactivity. Their design imitates natural antigens in a way that enhances antigen presentation and immune recognition. These features make SLPs promising for inducing strong and lasting immunity in bacterial vaccine development (40, 41).
2.3 Adjuvants and delivery systems
To enhance the immunogenicity of peptide vaccines, adjuvants and advanced delivery systems are often used. Adjuvants amplify the immune response to an antigen, while delivery systems control the release of the vaccine and target its delivery, overcoming the low immunogenicity of isolated peptide antigens (42).
2.3.1 Adjuvants in enhancing immunogenicity
Adjuvants stimulate immune cells and prolong antigen exposure, thereby enhancing vaccine efficacy. Traditional adjuvants, such as alum, play a major role in promoting antibody responses. However, newer adjuvants, including Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists, saponins, and liposomes, are designed to boost cellular immunity by activating dendritic cells and promoting antigen presentation. In peptide vaccines, adjuvants are particularly valuable as they provide “danger signals” that amplify the immune response (42, 43). Despite their efficacy, the use of adjuvants comes with potential risks, particularly concerning their safety. Overuse or inappropriate selection of adjuvants can result in allergic reactions and, in some cases, autoimmune disorders. For example, TLR agonists may overstimulate the immune system, leading to unwanted inflammatory responses or hypersensitivity, especially in vulnerable individuals. Additionally, some adjuvants, such as saponins, have been linked to local reactions and systemic toxicity. These risks necessitate careful optimization and controlled usage of adjuvants in peptide vaccines to prevent any adverse effects (44, 45).
2.3.2 Delivery systems: nanocarriers, liposomes, and conjugate vaccines
New delivery systems, including nanocarriers and liposomes, have been developed that protect peptides from degradation, control their release rate, and target the immune cells with high precision. Nanocarriers, consisting of nanoparticles and polymer systems, can encapsulate peptides for protection and assured delivery to the APCs. Nanoparticles may be prepared as pathogen imitations that can be taken up by dendritic cells at enhanced rates, therefore promoting antigen presentation (46). Since liposomes are vesicular carriers of lipids, they would, in turn, encapsulate the peptides for longer circulation and specific delivery to immune cells. They also act as an adjuvant and enhance humoral and cellular responses (47). Conjugate vaccines link peptides to carrier proteins such as tetanus or diphtheria toxoids. They enhance immunogenicity by providing extra T-cell epitopes. This approach is quite useful in groups where immune responses are generally poor, such as older adults and young children (48).
Despite their advantages, each delivery modality carries specific safety concerns. Nanocarriers may induce dose−dependent cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and pro−inflammatory cytokine release—effects that vary with particle size, surface charge, and composition, and can lead to tissue damage or systemic inflammation (49). Liposomes are prone to complement activation−related pseudo-allergy (CARPA), manifesting as infusion−related hypersensitivity (flushing, dyspnea, hypotension) in susceptible individuals (50). Conjugate vaccines, while generally well tolerated, can cause local injection−site reactions and, in rare cases, carrier−induced epitope suppression, whereby pre−existing immunity to the protein carrier (e.g., tetanus toxoid) diminishes the response to the linked peptide antigen (51, 52).
3 Peptide vaccines against bacterial infections
As mentioned, peptide vaccines have emerged as a therapeutic strategy by targeting specific antigenic determinants, which can induce precise and potent immune responses against a wide range of bacterial pathogens in the fight against bacterial infections. One of the most promising strategies in this context involves the use of conserved regions of bacterial proteins. These conserved sequences are shared across multiple strains or species of a pathogen and are less prone to mutation, making them ideal targets for vaccine development. Targeting such regions ensures broader coverage against diverse bacterial variants, including multidrug-resistant strains. Furthermore, these proteins are predicted to be highly antigenic and essential for pathogen survival and reduces the risk of immune escape due to antigenic variation. Moreover, peptides derived from conserved epitopes are more likely to elicit cross-protective immune responses, which is crucial for combating the genetic variability characteristic of ESKAPE pathogens (53, 54).
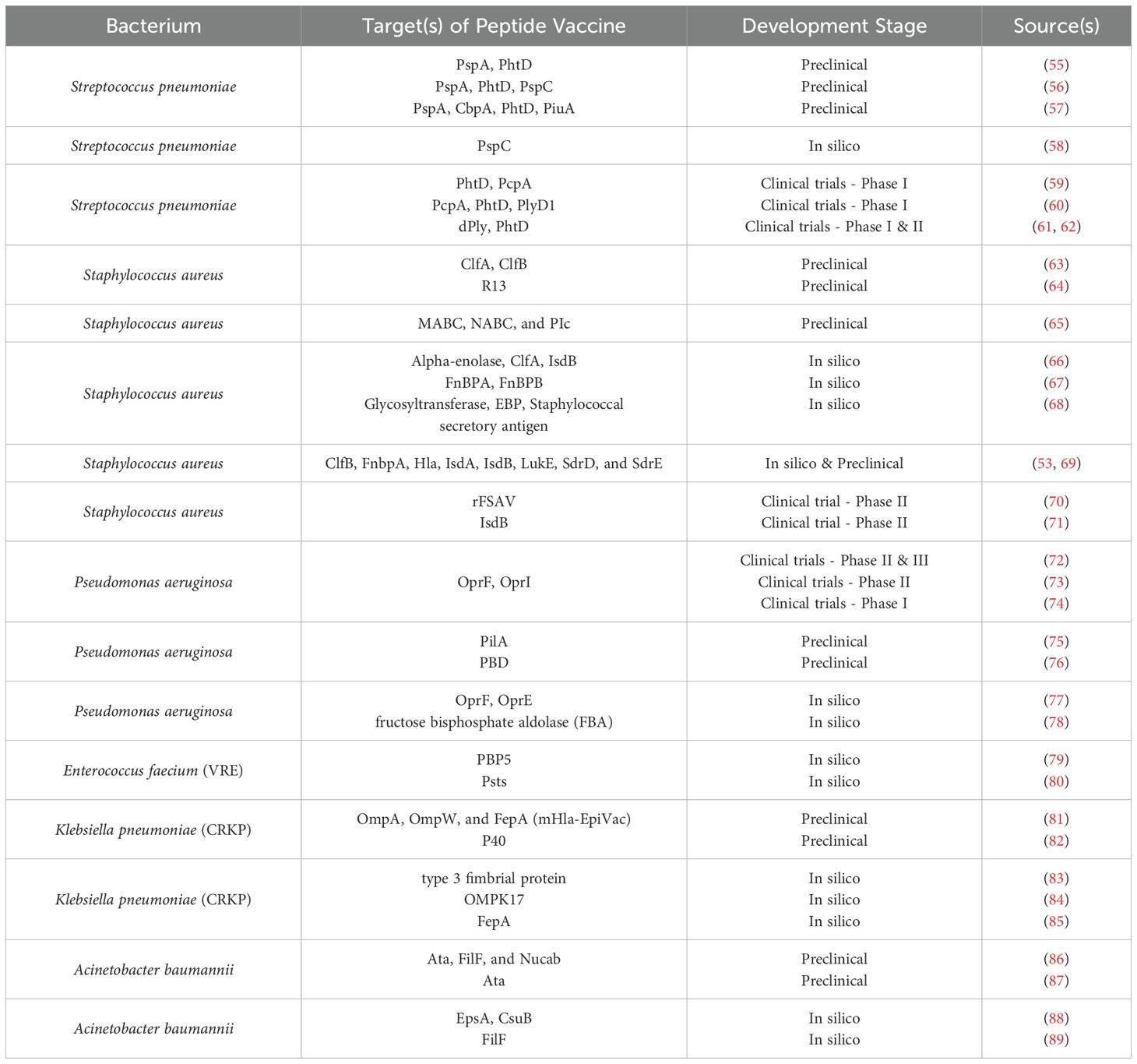
This review analyzes the development of peptide vaccines for the ESKAPE pathogens — Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter spp. — each of which presents unique challenges in immunogenicity and pathogen persistence. Peptide vaccines in development against ESKAPE are shown in Table 1.
3.1 Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus)
Streptococcus pneumoniae remains a significant global health burden, causing a range of severe infections, including pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. While pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) have significantly reduced the incidence of pneumococcal disease, serotype diversity and the emergence of non-vaccine serotypes limit their effectiveness (90, 91).
Peptide vaccines offer a promising alternative by targeting conserved antigens present across multiple pneumococcal strains. This approach has the potential to provide broader protection against a wider range of serotypes, including those not covered by current vaccines. PspA (Pneumococcal Surface Protein A) is the most promising vaccine candidate (92). This protein—along with several other surface proteins—is highly conserved across pneumococcal strains and is recognized by both B and T-cells. Recently Bahadori et al. demonstrated the efficacy of the fusion PhtD-PspA-PspC-based peptide vaccine in inducing protective antibody responses and improving survival in animal models of pneumococcal infection in a preclinical study (56). Researchers have also conducted clinical trials combining the peptide vaccine and the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for greater efficacy (60–62). However the multiepitope peptide vaccine against Streptococcus pneumoniae showed limited efficacy in a clinical trial for otitis media, likely due to antigenic polymorphism among strains. The selected epitopes did not cover the full antigenic diversity, resulting in weak cross-protection. Additionally, synthetic peptides may fail to replicate the native structure of full-length proteins, reducing their immunogenicity (62). Preclinical and clinical trials are still ongoing in this field, and if successful, peptide vaccines could provide a valuable tool in the fight against pneumococcal disease, providing broader protection and overcoming the limitations of current vaccine strategies.
3.2 Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus, particularly methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), remains a significant cause of hospital-acquired infections worldwide. Its ability to form biofilms, evade host immune responses, and develop resistance to multiple antibiotics has made it a challenging pathogen to combat (93).
Peptide-based vaccines represent a promising approach to combat Staphylococcus aureus infections by targeting key virulence factors to elicit robust immune responses and prevent bacterial colonization. Notably, clumping factors A and B (ClfA and ClfB) have emerged as important targets, as explored by Dey et al. ClfA facilitates bacterial adhesion to host tissues, while ClfB promotes attachment to nasal corneocytes and triggers human platelet aggregation. These antigens are both highly immunogenic and conserved, making them suitable candidates for vaccine development, especially against multidrug-resistant strains (63). Also, the newest study developed a peptide vaccine using B and T-cell epitopes from MABC, NABC, and PIc proteins to combat Staphylococcus aureus. Mice immunized with this vaccine showed the best skin lesion healing, with high IgG levels, increased INF-γ, and enhanced CD4/CD8 T-cell counts. This approach improved both humoral and cellular immunity, demonstrating promising results for S. aureus vaccine development (65).
Several multi-antigenic peptide vaccines have been evaluated in preoperative settings. For example, the V710 vaccine targeting IsdB did not reduce the incidence of postoperative infections in cardiac surgery patients and was paradoxically associated with increased mortality in those who became infected—likely due to insufficient preexisting IL-2 and IL-17 responses (71, 94). Conversely, the rFSAV vaccine, which incorporates five different antigens, demonstrated good safety and strong, rapid humoral responses in a phase II clinical trial among patients undergoing elective orthopedic surgery (70). These findings highlight the challenges inherent in developing effective vaccines against S. aureus, including the need for appropriate antigen selection and consideration of host immune profiles.
Despite these findings, no peptide-based S. aureus vaccine has yet reached clinical application, underscoring the need for further experimental and clinical investigations (95).
3.3 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a versatile opportunistic pathogen that can cause a wide range of infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. Its intrinsic antibiotic resistance and ability to form biofilms make it a significant challenge in healthcare settings (96).
Peptide vaccines represent a promising strategy to combat P. aeruginosa infections. Key targets for peptide-based vaccines against P. aeruginosa include outer membrane proteins (OMPs) and also the receptor-binding domains (RBD) of pili. Studies to develop a peptide vaccine against RBD have been conducted in the past (97, 98). Recently, in the study by Adlbrecht et al., a peptide vaccine against OprI and OprF was evaluated in phase II and III clinical trials, and it showed that while the vaccine was highly immunogenic, it did not reduce mortality from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (72). Additionally, Roy et al. designed an in silico multiepitope peptide vaccine targeting the OprF and OprE proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which are conserved across various serogroups and phenotypically stable within biofilms. While the computational predictions regarding immunogenicity, antigenicity, and safety were promising, no experimental validation has been reported to date. Therefore, extensive preclinical and clinical studies are still required to confirm its real-world efficacy (77). Currently, more clinical trials are underway to assess the safety and immunogenicity of peptide vaccine candidates against P. aeruginosa. If successful, these vaccines could provide much-needed protection for high-risk individuals, particularly those with underlying medical conditions or undergoing invasive procedures.
3.4 Enterococcus faecium
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VRE) has emerged as a significant healthcare-associated pathogen, causing a range of serious infections, including bloodstream infections, surgical site infections, and endocarditis. The increasing prevalence of VRE, coupled with its resistance to multiple antibiotics, has necessitated the development of novel therapeutic strategies (99).
Peptide vaccines provide a new potential strategy for the prevention of VRE infections. These vaccines may target surface proteins, such as Penicillin-Binding Protein 5 (PBP5), which is necessary for the cell wall strength and stability, inducing specific immune responses neutralizing bacteria, and preventing their biofilm formation. Since this protein is an important metabolic target for beta-lactam antibiotic resistance, peptide vaccines against its epitopes can be a preventive measure (100). Additionally, this protein’s multiepitope vaccine with B-cell and T-cell epitopes can elicit both humoral and cellular immune responses, which Dey et al. evaluated in silico, and were promising for experimental testing. Humoral immunity, mediated by antibodies, can neutralize VRE and promote its clearance by phagocytic cells. Cellular immunity, mediated by T-cells, can eliminate infected cells and provide long-lasting protection (79). By enhancing immune system recognition and overcoming immune evasion mechanisms, peptide vaccines have the potential to improve outcomes for patients infected with VRE. Although preclinical and clinical research is needed for a vaccine against this bacterium, they represent a promising strategy to combat this challenging pathogen.
3.5 Klebsiella pneumoniae
Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) has emerged as a major global health threat, causing severe infections such as pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). The increasing prevalence of CRKP, coupled with its resistance to multiple antibiotics, has led to significant morbidity and mortality (101, 102).
Unfortunately, there is no effective vaccine available against Klebsiella pneumoniae (103). Peptide vaccines are considered promising approaches for fighting CRKP infections. Major candidates for peptide-based vaccines against CRKP include outer membrane proteins (OMPs) such as OmpA which are involved in bacterial survival and virulence. In a study conducted by Liao et al., was produced a peptide vaccine to target the OmpA-OmpW-FepA combination protein and then administered that vaccine to mice. Induced by such antigens, the peptide vaccine confers the capabilities of opsonization of bacteria by antibodies; they make them more amenable to clearance by an immune cell and evoke IgG antibodies above any other tested immunoglobulins (81). These peptide vaccines may be used against CRKP, which will improve the outcomes. However, we need more studies to test the safety and efficacy of these peptide vaccines.
3.6 Acinetobacter baumannii
Acinetobacter baumannii is a gram-negative bacterium with increasing trends toward multidrug resistance, which has constituted a severe health threat worldwide during recent years. This microorganism is thus quasi-invincible due to its ability to form biofilm and its resistance to most known antibiotics, including last-resort antimicrobials including colistin (104).
One of the most interesting strategies to overcome the problems caused by these bacteria is peptide vaccines that important approach is in the targeting of biofilm-related proteins such as Ata, FilF, and Nucab. They are important in bacterial adhesion, biofilm development, and immune evasion (105). Ren et al. developed peptide vaccines targeting these antigens, which inhibit biofilm formation, reduce bacterial colonization, and accelerate immune clearance. In addition, this study developed a peptide vaccine that generated opsonizing antibodies capable of promoting phagocytosis and clearance of developing bacterial infections. This is especially crucial in the setting of chronic infections, in which bacteria can avoid host defenses (86). Peptide vaccines are in progress to combat A. baumannii and improve patient outcomes. They are a potentially powerful weapon against this ornery bug. Many need to be further tested for safety and effectiveness.
4 Preclinical and clinical evaluation of peptide vaccines against bacterial infections
Significant progress has been made in the development of peptide vaccines for bacterial infections, and promising results have been obtained from both preclinical and clinical studies.
4.1 Animal models
Mice, non-human primates, and other animal models are invaluable for assessing immunogenicity and efficacy of peptide vaccines. Such models enable studies to study the induction of particular immune responses, such as T-cell activation, antibody production and cytokine profiles. For bacterial pathogens, effector-encoded peptide vaccines have shown promise in animal models, including for organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus. S. aureus peptide vaccines reduce bacterial load and improve survival in animal models of infection (65, 106). While animal models provide valuable insights, it is important to acknowledge their limitations. Differences in immune responses between animals and humans can impact the interpretation of preclinical data. Therefore, studies must carefully consider the selection of appropriate animal models and how to apply findings to human populations (107).
4.2 Clinical trials
The transition from preclinical studies to clinical trials is a critical step in the development of peptide vaccines. Phase I clinical trials focus on assessing the safety and tolerability of the vaccine in a small group of healthy volunteers. Phase II trials involve larger groups of participants and aim to determine the optimal dose and evaluate the vaccine’s effectiveness. Phase III trials, the final stage of clinical development, involve large-scale randomized controlled trials to confirm the vaccine’s efficacy and safety in diverse populations. Several peptide-based vaccines targeting bacterial infections are currently undergoing clinical trials, which were mentioned earlier. For example, peptide vaccines for Pseudomonas aeruginosa have shown promising safety profiles in Phase I trials. Ongoing Phase II trials are evaluating their immunogenicity and efficacy in larger populations. While these early-phase clinical trials have shown encouraging results, challenges remain in advancing peptide vaccines to Phase III trials. Factors such as peptide stability, immunogenicity, and the development of effective adjuvants and delivery systems are crucial for generalizing preclinical findings into clinical applications (108).
5 A Critical appraisal of the safety, stability, and manufacturability of peptide vaccines
5.1 Safety considerations
Peptide vaccines have unprecedented safety over traditional vaccines because they are well-defined in their composition. However, the potential risk of autoimmune reactions and off-target effects is a cautious approach. If administered, peptides are highly homologous with host proteins, autoimmunity might develop. The risk of cross-reactivity has been mitigated through careful epitope selection strategies that include targeting sequences with minimal structural similarity to self-antigens. Rigorous preclinical testing — including evaluation of the long-term immune response and assessment of delayed adverse events — is important in these discussions to ensure safety (109). However, advanced bioinformatic tools and structural analyses may also be used to detect peptides with low sequence homology to host proteins. This will lower the possibility of autoimmune reactions (110). However, if not carefully characterized, off-target effects where the immune response targets unrelated strains of bacteria and other commensal microbiota can also pose potential safety issues. Utilizing pathogen-specific peptide sequences and limiting structural similarities with commensal bacteria might mitigate these dangers (111, 112).
5.2 Enhanced stability for improved logistics
Peptide vaccines provide significant logistical advantages in stability and storage, particularly in resource-limited environments. Unlike live-attenuated or inactivated vaccines, which often cause stringent cold-chain logistics (113), synthetic peptides exhibit greater stability at room temperature or require only moderate refrigeration. Lyophilization (freeze-drying) further extends shelf life, simplifying distribution and minimizing associated costs. Recent studies demonstrate the viability of specific peptide formulations under diverse storage conditions for extended durations. It’s particularly helpful for deploying them in remote regions (114).
5.3 Simplified manufacturing and scalability
Peptide vaccines benefit from streamlined manufacturing processes compared to conventional vaccines. Unlike traditional methods rely on pathogen cultivation, peptide vaccines can be produced through chemical synthesis or recombinant DNA technology. This approach gives greater control over production, which helps achieve high purity and consistency, reduces costs, and speeds up vaccine development. However, scaling up peptide synthesis presents challenges, including potential batch-to-batch variability and high cost influenced by peptide length and complexity. Advancements in automated synthesis techniques and cost-effective production methods are addressing these limitations, which pave the way for wider use and large-scale production of peptide vaccines (108, 115, 116).
6 Future directions in peptide vaccine development for bacterial infections
Peptide vaccines are promising tools for the prevention and management of bacterial infections, with ongoing advances in bioinformatics, immunology, and delivery technologies forming the future of their development.
6.1 Innovations in peptide design; bioinformatics and artificial intelligence
Due to the development of immunoinformatic tools, the implementation of computational biology has primarily eased the way in the advancement of peptide vaccine development. High-throughput sequencing and structural biology data can be integrated by these technologies to map the immunogenic bacterial epitopes. Using these tools, researchers can predict B-cell and T-cell epitopes, model peptide–MHC and peptide–TCR interactions, and determine binding affinities and epitope stability. Machine learning can help guide this step by finding conserved peptides across multiple strains of bacteria to develop vaccines capable of eliciting long-lived and specific immune responses (117–119).
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has played a transformative role in vaccine design by streamlining several key steps such as antigen selection, epitope prioritization, and adjuvant discovery. Machine learning and deep learning algorithms analyze genomic sequences, protein structures, and immune system interactions to assess immunogenicity and optimize candidate peptides. These AI-driven methods not only reduce the time and cost of vaccine development but also improve precision by integrating emerging technologies like single-cell omics and synthetic biology. Despite challenges such as data heterogeneity and interpretability of models, the incorporation of AI into vaccine research represents a promising approach to accelerate the design of safe and effective peptide vaccines against a broad range of infectious diseases (120).
6.2 Personalized peptide vaccines
The concept of personalized medicine is being applied more often to vaccine development. Differences in immune response among individuals, often due to genetic differences in HLA allele distribution, influence peptide presentation and recognition. Tuning frequencies for specific human genetic profiles can rescue vaccine efficacy and reduce their unwanted effects. This is especially useful for high-risk groups, including healthcare workers and people with immunodeficiency (Figure 2) (121).
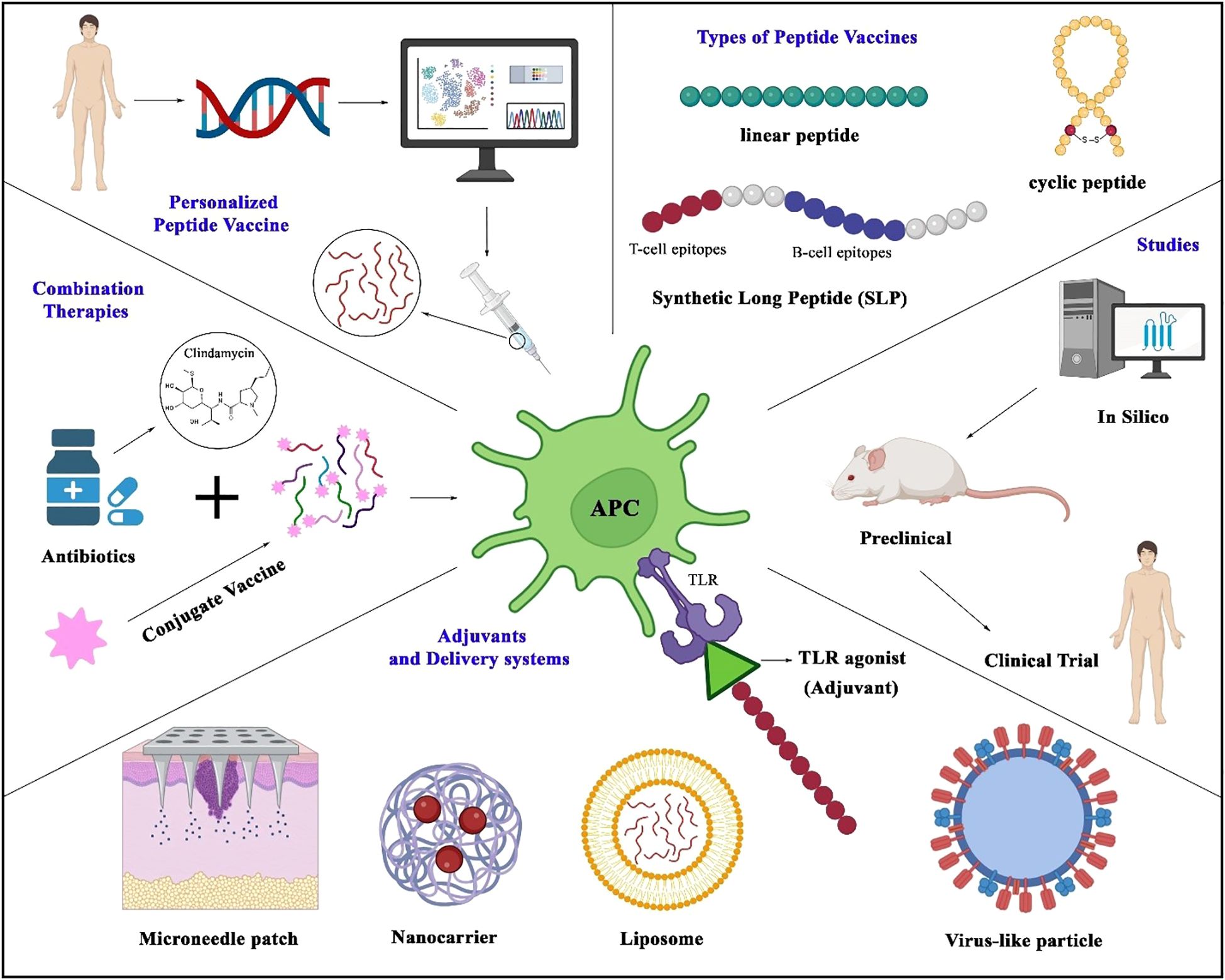
Figure 2. Strategies in peptide vaccine design and application. The figure illustrates key approaches in developing peptide vaccines, centered around antigen-presenting cells that process peptides to activate T-cell immunity. Represented vaccine modalities include linear peptides, cyclic peptides, and synthetic long peptides (SLPs) incorporating both B- and T-cell epitopes. Genomic advances enable personalized vaccines tailored to individual genetic profiles. Delivery platforms (liposomes, nanocarriers, microneedle patches, virus-like particles) and adjuvants (e.g., TLR agonists) enhance immunogenicity. The development pipeline spans in silico epitope prediction, preclinical testing, and clinical trials. Emerging strategies—such as antibiotic-conjugated peptide vaccines—highlight combinatorial approaches to boost efficacy and counter antimicrobial resistance.
6.3 Next-generation delivery systems
Delivery System of the Next Generation Improving peptide stability and immunogenicity by optimizing vaccine delivery systems is of great significance. Innovative approaches for stable, efficient delivery of peptide vaccines are emerging, such as with virus-like particles (VLPs) and microneedle patches (Figure 2). Virus-like particles serve as efficient delivery systems for peptide vaccines by mimicking the structure of viruses while lacking genetic material, allowing safe presentation of antigens to immune cells. VLPs have been modified to present peptide epitopes on their surface to promote antigen uptake and immune activation. This approach has shown promising efficacy against preclinical models and is currently being evaluated for various infectious diseases (10, 122). Microneedle patches penetrate the outer layers of the skin and deliver their payloads—such as peptide antigens—directly to dendritic cells in the dermis in a minimally invasive manner. By targeting these key antigen-presenting cells, microneedles facilitate robust immune activation. Moreover, due to their ease of administration, pain-free application, and potential for self-use, microneedle technologies significantly improve vaccine accessibility and compliance, particularly in low-resource settings (10, 123).
6.4 Combination therapies
As shown in Figure 2, combining peptide vaccines with antibiotics or other vaccines can enhance their efficacy and expand their activity. For infections resistant to antibiotics, combining peptide vaccines with them can reduce bacterial load and limit the rise of drug-resistant strains (14, 124). Additionally, combining peptide vaccines with other vaccine platforms, such as conjugate vaccines, can provide broader immune coverage against complex pathogens. In this regard, Laura L. Hammitt and colleagues conducted a clinical trial based on a protein-based pneumococcal vaccine (dPly/PhtD) containing pneumolysin toxoid and pneumococcal histidine triple protein D (62).
6.5 Harnessing the power of immunomodulation
Combining peptide vaccines with immunomodulators, such as checkpoint inhibitors, can amplify immune responses. Checkpoint inhibitors can enhance T-cell responses, particularly beneficial for chronic bacterial infections that require a strong cell-mediated immune response. Such combination therapies may allow for lower antibiotic doses, which could reduce side effects and the risk of antibiotic resistance (125, 126).
7 Conclusion
Peptide vaccines offer a promising approach to combat bacterial infections. By targeting specific antigens, these vaccines can induce targeted immune responses, enhancing the body’s ability to recognize and eliminate bacterial pathogens. Key advantages include rapid production, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for immunocompromised individuals. However, challenges such as improving immunogenicity, stability, and delivery methods remain. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing peptide design, developing advanced delivery systems, and exploring combination therapies to enhance vaccine efficacy. With continued advancements, peptide vaccines have the potential to become a crucial tool in the struggle against antibiotic resistance and emerging infectious diseases.
Author contributions
FTR: Visualization, Writing – original draft. NS: Writing – original draft. AE: Writing – original draft. DH: Writing – review & editing. RB: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The author(s) declare that generative AI was used to assist with language editing and refinement of this manuscript. All AI-processed content was carefully reviewed and approved by the authors, who take full responsibility for the work.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bergstrom C, Fischer NO, Kubicek-Sutherland JZ, and Stromberg ZR. mRNA vaccine platforms to prevent bacterial infections. Trends Mol Med. (2024) 30:524–6. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.02.013
2. Ikuta KS, Swetschinski LR, Robles Aguilar G, Sharara F, Mestrovic T, Gray AP, et al. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. (2022) 400:2221–48. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02185-7
3. Dheda K, Makambwa E, and Esmail A. The great masquerader: tuberculosis presenting as community-acquired pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. (2020) 41:592–604. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1710583
4. Uzoamaka M, Ngozi O, Johnbull OS, and Martin O. Bacterial etiology of lower respiratory tract infections and their antimicrobial susceptibility. Am J Med Sci. (2017) 354:471–5. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.06.025
5. Hanquet G, Theilacker C, Vietri J, Sepúlveda-Pachón I, Menon S, Gessner B, et al. Best practices for identifying hospitalized lower respiratory tract infections using administrative data: a systematic literature review of validation studies. Infect Dis Ther. (2024) 13:921–40. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-00949-8
6. Laxminarayan R, Matsoso P, Pant S, Brower C, Røttingen J-A, Klugman K, et al. Access to effective antimicrobials: a worldwide challenge. Lancet. (2016) 387:168–75. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00474-2
7. Curtiss R. Bacterial infectious disease control by vaccine development. J Clin investigation. (2002) 110:1061–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI0216941
8. Kamei K. Live attenuated vaccines in patients receiving immunosuppressive agents. Pediatr Nephrology. (2023) 38:3889–900. doi: 10.1007/s00467-023-05969-z
9. Chen Y. The advantages and disadvantages of different types of vaccines: DNA vaccine, mRNA vaccine, and inactivated vaccine. Theor Nat Sci. (2023) 6. doi: 10.54254/2753-8818/6/20230193
10. Lu B, Lim JM, Yu B, Song S, Neeli P, Sobhani N, et al. The next-generation DNA vaccine platforms and delivery systems: Advances, challenges and prospects. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1332939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332939
11. Hansson M, Nygren PA, and Ståhl S. Design and production of recombinant subunit vaccines. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (2000) 32:95–107. doi: 10.1042/BA20000034
12. Mullins LP, Mason E, Winter K, and Sadarangani M. Vaccination is an integral strategy to combat antimicrobial resistance. PLoS Pathogens. (2023) 19:e1011379. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011379
13. Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, Zaidi AK, Wertheim HF, Sumpradit N, et al. Antibiotic resistance—the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect diseases. (2013) 13:1057–98. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70318-9
14. Garza-Cervantes JA and León-Buitimea A. Editorial: Synergistic combinatorial treatments to overcome antibiotic resistance. Front Cell Infection Microbiol. (2024) 14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1369264
15. Sheu C-C, Chang Y-T, Lin S-Y, Chen Y-H, and Hsueh P-R. Infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: an update on therapeutic options. Front microbiology. (2019) 10:80. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00080
16. Rueckert C and Guzmán CA. Vaccines: from empirical development to rational design. PLoS pathogens. (2012) 8:e1003001. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003001
17. Flemming H-C and Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev microbiology. (2010) 8:623–33. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2415
18. Otto M. Staphylococcus aureus toxins. Curr Opin microbiology. (2014) 17:32–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.11.004
19. Van Der Woude MW and Bäumler AJ. Phase and antigenic variation in bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2004) 17:581–611. doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.3.581-611.2004
20. Kim HK, Thammavongsa V, Schneewind O, and Missiakas D. Recurrent infections and immune evasion strategies of Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Opin microbiology. (2012) 15:92–9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.10.012
21. Hughes EA and Cresswell P. The thiol oxidoreductase ERp57 is a component of the MHC class I peptide-loading complex. Curr Biol. (1998) 8:709–13. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(98)70278-7
22. Skwarczynski M and Toth I. Peptide-based synthetic vaccines. Chem science. (2016) 7:842–54. doi: 10.1039/C5SC03892H
23. Shafaghi M, Bahadori Z, Madanchi H, Ranjbar MM, Shabani AA, and Mousavi SF. Immunoinformatics-aided design of a new multi-epitope vaccine adjuvanted with domain 4 of pneumolysin against Streptococcus pneumoniae strains. BMC Bioinf. (2023) 24:67. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05175-6
24. Hasannejad-Asl B, Pooresmaeil F, Takamoli S, Dabiri M, and Bolhassani A. Cell penetrating peptide: A potent delivery system in vaccine development. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1072685. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1072685
25. Pati R, Shevtsov M, and Sonawane A. Nanoparticle vaccines against infectious diseases. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2224. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02224
26. Malonis RJ, Lai JR, and Vergnolle O. Peptide-based vaccines: current progress and future challenges. Chem Rev. (2019) 120:3210–29. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00472
27. Gutiérrez-Martínez E, Planès R, Anselmi G, Reynolds M, Menezes S, Adiko AC, et al. Cross-presentation of cell-associated antigens by MHC class I in dendritic cell subsets. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:363. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00363
28. Wieczorek M, Abualrous ET, Sticht J, Álvaro-Benito M, Stolzenberg S, Noé F, et al. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and MHC class II proteins: conformational plasticity in antigen presentation. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00292
29. Gong W, Pan C, Cheng P, Wang J, Zhao G, and Wu X. Peptide-based vaccines for tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.830497
30. Rastogi I, Jeon D, Moseman JE, Muralidhar A, Potluri HK, and McNeel DG. Role of B cells as antigen presenting cells. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:954936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.954936
31. Chia LY, Kumar PV, Maki MAA, Ravichandran G, and Thilagar S. A review: The antiviral activity of cyclic peptides. Int J Pept Res Ther. (2022) 29:7. doi: 10.1007/s10989-022-10478-y
32. Meuleman TJ, Dunlop JI, Owsianka AM, Van de Langemheen H, Patel AH, and Liskamp RM. Immobilization by surface conjugation of cyclic peptides for effective mimicry of the HCV-envelope E2 protein as a strategy toward synthetic vaccines. Bioconjugate Chem. (2018) 29:1091–101. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00755
33. Eriksson C, Gunasekera S, Muhammad T, Zhang M, Laurén I, Mangsbo SM, et al. Epitopes displayed in a cyclic peptide scaffold bind SARS-COV-2 antibodies. ChemBioChem. (2023) 24:e202300103. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202300103
34. Sajid M, Marriam S, Mukhtar H, Sohail S, Sajid M, and Sehgal SA. Epitope-based peptide vaccine design and elucidation of novel compounds against 3C like protein of SARS-CoV-2. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0264700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264700
35. Lim HX, Lim J, and Poh CL. Identification and selection of immunodominant B and T cell epitopes for dengue multi-epitope-based vaccine. Med Microbiol Immunol. (2021) 210:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s00430-021-00700-x
36. Saadi M, Karkhah A, and Nouri HR. Development of a multi-epitope peptide vaccine inducing robust T cell responses against brucellosis using immunoinformatics based approaches. Infection Genet Evolution. (2017) 51:227–34. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.04.009
37. Mortazavi B, Molaei A, and Fard NA. Multi-epitopevaccines, from design to expression; an in silico approach. Hum Immunol. (2024) 85:110804. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2024.110804
38. Wei Y, Qiu T, Ai Y, Zhang Y, Xie J, Zhang D, et al. Advances of computational methods enhance the development of multi-epitope vaccines. Brief Bioinform. (2024) 26. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf055
39. Hossen MS, Hasan MN, Haque M, Al Arian T, Halder SK, Uddin MJ, et al. Immunoinformatics-aided rational design of multiepitope-based peptide vaccine (MEBV) targeting human parainfluenza virus 3 (HPIV-3) stable proteins. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. (2023) 21:162. doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00623-5
40. Rosendahl Huber S, Camps MG, Jacobi RH, Mouthaan J, van Dijken H, van Beek J, et al. Synthetic long peptide influenza vaccine containing conserved T and B cell epitopes reduces viral load in lungs of mice and ferrets. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0127969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127969
41. Rosalia RA, Quakkelaar ED, Redeker A, Khan S, Camps M, Drijfhout JW, et al. Dendritic cells process synthetic long peptides better than whole protein, improving antigen presentation and T-cell activation. Eur J Immunol. (2013) 43:2554–65. doi: 10.1002/eji.201343324
42. Moynihan KD, Holden RL, Mehta NK, Wang C, Karver MR, Dinter J, et al. Enhancement of peptide vaccine immunogenicity by increasing lymphatic drainage and boosting serum stability. Cancer Immunol Res. (2018) 6:1025–38. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0607
43. Ho NI, Huis in’t Veld LG, Raaijmakers TK, and Adema GJ. Adjuvants enhancing cross-presentation by dendritic cells: the key to more effective vaccines? Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02874
44. Guimarães LE, Baker B, Perricone C, and Shoenfeld Y. Vaccines, adjuvants and autoimmunity. Pharmacol Res. (2015) 100:190–209. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.08.003
45. Azmi F, Ahmad Fuaad AA, Skwarczynski M, and Toth I. Recent progress in adjuvant discovery for peptide-based subunit vaccines. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2014) 10:778–96. doi: 10.4161/hv.27332
46. Saleemi MA, Zhang Y, and Zhang G. Current progress in the science of novel adjuvant nano-vaccine-induced protective immune responses. Pathogens. (2024) 13:441. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13060441
47. Liu M, Fang X, Yang Y, and Wang C. Peptide-enabled targeted delivery systems for therapeutic applications. Front Bioengineering Biotechnol. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.701504
48. Micoli F, Stefanetti G, and MacLennan CA. Exploring the variables influencing the immune response of traditional and innovative glycoconjugate vaccines. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1201693
49. Dobrovolskaia MA and McNeil SE. Immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Nat nanotechnology. (2007) 2:469–78. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.223
50. Lee Y, Jeong M, Park J, Jung H, and Lee H. Immunogenicity of lipid nanoparticles and its impact on the efficacy of mRNA vaccines and therapeutics. Exp Mol Med. (2023) 55:2085–96. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01086-x
51. Dagan R and van der Beek BA. Immune response to the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is reduced in infants immunized during the respiratory viral season. Clin Infect Dis. (2024), ciae619. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae619
52. Pichichero ME. Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines: characteristics, development, and clinical trials. Hum vaccines immunotherapeutics. (2013) 9:2505–23. doi: 10.4161/hv.26109
53. Chatterjee R, Sahoo P, Mahapatra SR, Dey J, Ghosh M, Kushwaha GS, et al. Development of a Conserved Chimeric Vaccine for Induction of Strong Immune Response against Staphylococcus aureus Using Immunoinformatics Approaches. Vaccines (Basel). (2021) 9:1038–58. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9091038
54. Kolla HB, Makam SS, and Reddy PN. Mapping of conserved immunodominant epitope peptides in the outer membrane porin (Omp) L of prominent Enterobacteriaceae pathogens associated with gastrointestinal infections. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. (2023) 21:146. doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00622-6
55. Shafaghi M, Bahadori Z, Barzi SM, Afshari E, Madanchi H, Mousavi SF, et al. A new candidate epitope-based vaccine against PspA PhtD of Streptococcus pneumoniae: a computational experimental approach. Front Cell Infection Microbiol. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1271143
56. Bahadori Z, Shafaghi M, Sabzevari J, Madanchi H, Ranjbar MM, Mousavi SF, et al. Design, development, and assessment of a novel multi-peptide vaccine targeting PspC, PsaA, and PhtD proteins of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2023), 128924. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128924
57. Dorosti H, Nezafat N, Heidari R, Ghoshoon MB, Gholami A, Dehshahri A, et al. Production and immunological evaluation of epitope-based preventative pneumococcal candidate vaccine comprising immunodominant epitopes from pspA, cbpA, phtD and piuA antigens. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. (2021) 22:1900–9. doi: 10.2174/1389201022666201231112029
58. Nahian M, Shahab M, Mazumder L, Oliveira JIN, Banu TA, Sarkar MH, et al. In silico design of an epitope-based vaccine against PspC in Streptococcus pneumoniae using reverse vaccinology. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. (2023) 21:166. doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00604-8
59. Bologa M, Kamtchoua T, Hopfer R, Sheng X, Hicks B, Bixler G, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of pneumococcal protein vaccine candidates: monovalent choline-binding protein A (PcpA) vaccine and bivalent PcpA-pneumococcal histidine triad protein D vaccine. Vaccine. (2012) 30:7461–8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.10.076
60. Brooks WA, Chang LJ, Sheng X, and Hopfer R. Safety and immunogenicity of a trivalent recombinant PcpA, PhtD, and PlyD1 pneumococcal protein vaccine in adults, toddlers, and infants: A phase I randomized controlled study. Vaccine. (2015) 33:4610–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.06.078
61. Pauksens K, Nilsson AC, Caubet M, Pascal TG, Van Belle P, Poolman JT, et al. Randomized controlled study of the safety and immunogenicity of pneumococcal vaccine formulations containing PhtD and detoxified pneumolysin with alum or adjuvant system AS02V in elderly adults. Clin Vaccine Immunol. (2014) 21:651–60. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00807-13
62. Hammitt LL, Campbell JC, Borys D, Weatherholtz RC, Reid R, Goklish N, et al. Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of a pneumococcal protein-based vaccine co-administered with 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against acute otitis media in young children: A phase IIb randomized study. Vaccine. (2019) 37:7482–92. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.09.076
63. Dey J, Mahapatra SR, Singh P, Patro S, Kushwaha GS, Misra N, et al. B and T cell epitope-based peptides predicted from clumping factor protein of Staphylococcus aureus as vaccine targets. Microbial pathogenesis. (2021) 160:105171. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105171
64. Yang G, Gao Y, Dong J, Xue Y, Fan M, Shen B, et al. A novel peptide isolated from phage library to substitute a complex system for a vaccine against staphylococci infection. Vaccine. (2006) 24:1117–23. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.09.004
65. Solyman SM, Kamal SA, and Hanora AS. Protection of mice vaccinated with a new B cell and T cell epitopes cocktail from staphylococcus aureus challenge in skin infection model. Curr Microbiology. (2025) 82:128. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04102-7
66. Hajighahramani N, Nezafat N, Eslami M, Negahdaripour M, Rahmatabadi SS, and Ghasemi Y. Immunoinformatics analysis and in silico designing of a novel multi-epitope peptide vaccine against Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Genet Evol. (2017) 48:83–94. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.12.010
67. Chatterjee R, Mahapatra SR, Dey J, Raj Takur K, Raina V, Misra N, et al. An immunoinformatics and structural vaccinology study to design a multi-epitope vaccine against Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Mol Recognit. (2023) 36:e3007. doi: 10.1002/jmr.v36.4
68. Tahir Ul Qamar M, Ahmad S, Fatima I, Ahmad F, Shahid F, Naz A, et al. Designing multi-epitope vaccine against Staphylococcus aureus by employing subtractive proteomics, reverse vaccinology and immuno-informatics approaches. Comput Biol Med. (2021) 132:104389. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104389
69. Ullah N, Anwer F, Ishaq Z, Siddique A, Shah MA, Rahman M, et al. In silico designed Staphylococcus aureus B-cell multi-epitope vaccine did not elicit antibodies against target antigens suggesting multi-domain approach. J Immunol Methods. (2022) 504:113264. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2022.113264
70. Jiang XY, Gong MQ, Zhang HJ, Peng AQ, Xie Z, Sun D, et al. The safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant five-antigen Staphylococcus aureus vaccine among patients undergoing elective surgery for closed fractures: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter phase 2 clinical trial. Vaccine. (2023) 41:5562–71. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.07.047
71. McNeely TB, Shah NA, Fridman A, Joshi A, Hartzel JS, Keshari RS, et al. Mortality among recipients of the Merck V710 Staphylococcus aureus vaccine after postoperative S. aureus infections: an analysis of possible contributing host factors. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2014) 10:3513–6. doi: 10.4161/hv.34407
72. Adlbrecht C, Wurm R, Depuydt P, Spapen H, Lorente JA, Staudinger T, et al. Efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of IC43 recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in mechanically ventilated intensive care patients—a randomized clinical trial. Crit Care. (2020) 24:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-2792-z
73. Rello J, Krenn C-G, Locker G, Pilger E, Madl C, Balica L, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled phase II study of a Pseudomonas vaccine in ventilated ICU patients. Crit Care. (2017) 21:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1601-9
74. Westritschnig K, Hochreiter R, Wallner G, Firbas C, Schwameis M, and Jilma B. A randomized, placebo-controlled phase I study assessing the safety and immunogenicity of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa hybrid outer membrane protein OprF/I vaccine (IC43) in healthy volunteers. Hum vaccines immunotherapeutics. (2014) 10:170–83. doi: 10.4161/hv.26565
75. Kao DJ and Hodges RS. Advantages of a synthetic peptide immunogen over a protein immunogen in the development of an anti-pilus vaccine for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem Biol Drug Des. (2009) 74:33–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2009.00825.x
76. Hackbarth C and Hodges RS. Synthetic peptide vaccine development: designing dual epitopes into a single pilin peptide immunogen generates antibody cross-reactivity between two strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem Biol Drug Des. (2010) 76:293–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2010.01021.x
77. Roy SK, Biswas MS, Foyzur Raman M, Hasan R, Rahmann Z, and Uddin PK MM. A computational approach to developing a multi-epitope vaccine for combating Pseudomonas aeruginosa–induced pneumonia and sepsis. Briefings Bioinf. (2024) 25:bbae401. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae401
78. Elhag M, Alaagib RM, Ahmed NM, Abubaker M, Haroun EM, Albagi SOA, et al. Design of Epitope-Based Peptide Vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase Protein Using Immunoinformatics. J Immunol Res. (2020) 2020:9475058. doi: 10.1155/2020/9475058
79. Dey J, Mahapatra SR, Raj TK, Kaur T, Jain P, Tiwari A, et al. Designing a novel multi-epitope vaccine to evoke a robust immune response against pathogenic multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecium bacterium. Gut Pathogens. (2022) 14:21. doi: 10.1186/s13099-022-00495-z
80. Alotaibi G, Khan K, Al Mouslem AK, Ahmad Khan S, Naseer Abbas M, Abbas M, et al. Pan genome based reverse vaccinology approach to explore Enterococcus faecium (VRE) strains for identification of novel multi-epitopes vaccine candidate. Immunobiology. (2022) 227:152221. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152221
81. Liao J, Zhang X, Zeng X, Zhao Z, Sun T, Xia Z, et al. A rational designed multi-epitope vaccine elicited robust protective efficacy against Klebsiella pneumoniae lung infection. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2024) 174:116611. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116611
82. Goetsch L, Gonzalez A, Plotnicky-Gilquin H, Haeuw JF, Aubry JP, Beck A, et al. Targeting of nasal mucosa-associated antigen-presenting cells in vivo with an outer membrane protein A derived from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. (2001) 69:6434–44. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.10.6434-6444.2001
83. Mahapatra SR, Dey J, Kaur T, Sarangi R, Bajoria AA, Kushwaha GS, et al. Immunoinformatics and molecular docking studies reveal a novel Multi-Epitope peptide vaccine against pneumonia infection. Vaccine. (2021) 39:6221–37. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.09.025
84. Ranjbarian P, Goudarzi F, Akya A, Heidarinia H, Farasat A, and Rostamian M. Finding epitopes of Klebsiella pneumoniae outer membrane protein-K17 (OMPK17) and introducing a 25-mer peptide of it as a vaccine candidate. Biol (Bratisl). (2023), 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11756-023-01371-0
85. Nemati Zargaran F, Akya A, Ghadiri K, Ranjbarian P, and Rostamian M. Detecting the dominant T and B epitopes of klebsiella pneumoniae ferric enterobactin protein (FepA) and introducing a single epitopic peptide as vaccine candidate. Int J Pept Res Ther. (2021) 27:2209–21. doi: 10.1007/s10989-021-10247-3
86. Ren S, Guan L, Dong Y, Wang C, Feng L, and Xie Y. Design and evaluation of a multi-epitope assembly peptide vaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii infection in mice. Swiss Med weekly. (2019) 149:w20052–w. doi: 10.4414/smw.2019.20052
87. Sun P, Li X, Pan C, Liu Z, Wu J, Wang H, et al. A short peptide of autotransporter ata is a promising protective antigen for vaccination against acinetobacter baumannii. Front Immunol. (2022) 13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.884555
88. Ahmad S and Azam SS. A novel approach of virulome based reverse vaccinology for exploring and validating peptide-based vaccine candidates against the most troublesome nosocomial pathogen: Acinetobacter baumannii. J Mol Graph Model. (2018) 83:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2018.04.020
89. Mahapatra SR, Dey J, Jaiswal A, Roy R, Misra N, and Suar M. Immunoinformatics-guided designing of epitope-based subunit vaccine from Pilus assembly protein of Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria. J Immunol Methods. (2022) 508:113325. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2022.113325
90. Qiu X, McGee L, Hammitt LL, Grant LR, O’Brien KL, Hanage WP, et al. Prediction of post-PCV13 pneumococcal evolution using invasive disease data enhanced by inverse-invasiveness weighting. mBio. (2024) 15:e03355–23. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03355-23
91. Du QQ, Shi W, Yu D, and Yao KH. Epidemiology of non-vaccine serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae before and after universal administration of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2021) 17:5628–37. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2021.1985353
92. Chandpa HH, Panda AK, Meena CL, and Meena J. Beyond the polysaccharide and glycoconjugate vaccines for Streptococcus pneumoniae: Does protein/peptide nanovaccines hold promises? Vaccine. (2023) 41:7515–24. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.11.020
93. Kaushik A, Kest H, Sood M, Steussy BW, Thieman C, and Gupta S. Biofilm producing methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections in humans: clinical implications and management. Pathogens. (2024) 13:76. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13010076
94. Clegg J, Soldaini E, McLoughlin RM, Rittenhouse S, Bagnoli F, and Phogat S. Staphylococcus aureus vaccine research and development: the past, present and future, including novel therapeutic strategies. Front Immunol. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.705360
95. Chung PY. Immunotherapies for the prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections: updates and challenges. Pathog Dis. (2023) 81. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftad016
96. Mansouri E, Blome-Eberwein S, Gabelsberger J, Germann G, and von Specht B-U. Clinical study to assess the immunogenicity and safety of a recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa OprF-OprI vaccine in burn patients. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. (2003) 37:161–6. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00072-5
97. Campbell AP, Wong WY, Houston M Jr., Schweizer F, Cachia PJ, Irvin RT, et al. Interaction of the receptor binding domains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili strains PAK, PAO, KB7 and P1 to a cross-reactive antibody and receptor analog: implications for synthetic vaccine design. J Mol Biol. (1997) 267:382–402. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0871
98. Campbell AP, Spyracopoulos L, Irvin RT, and Sykes BD. Backbone dynamics of a bacterially expressed peptide from the receptor binding domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilin strain PAK from heteronuclear 1H-15N NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR. (2000) 17:239–55. doi: 10.1023/A:1008311319998
99. Miller WR, Murray BE, Rice LB, and Arias CA. Resistance in vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Infectious disease clinics of North America. 2020;34(4):751
100. Hunashal Y, Kumar GS, Choy MS, D’Andréa ÉD, Da Silva Santiago A, Schoenle MV, et al. Molecular basis of β-lactam antibiotic resistance of ESKAPE bacterium E. faecium Penicillin Binding Protein PBP5. Nat Communications. (2023) 14:4268. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39966-5
101. Wang Q, Liu Y, Chen R, Zhang M, Si Z, Wang Y, et al. Genomic insights into the evolution and mechanisms of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae co-harboring blaKPC and blaNDM: implications for public health threat mitigation. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrobials. (2024) 23:27. doi: 10.1186/s12941-024-00686-3
102. Yao Y, Zha Z, Li L, Tan H, Pi J, You C, et al. Healthcare-associated carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections are associated with higher mortality compared to carbapenem-susceptible K. pneumoniae infections in the intensive care unit: a retrospective cohort study. J Hosp Infect. (2024) 148:30–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2024.03.003
103. Mehmood A, Naseer S, Ali A, Fatimah H, Rehman S, and Kiani AK. Identification of novel vaccine candidates against carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A systematic reverse proteomic approach. Comput Biol Chem. (2020) 89:107380. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107380
104. Sherif MM, Elkhatib WF, Khalaf WS, Elleboudy NS, and Abdelaziz NA. Multidrug resistant acinetobacter baumannii biofilms: evaluation of phenotypic–genotypic association and susceptibility to cinnamic and gallic acids. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.716627
105. Pereira IL and Hartwig DD. Unveiling the role of adhesin proteins in controlling Acinetobacter baumannii infections: a systematic review. Infection Immun. (2025), e00348–24. doi: 10.1128/iai.00348-24
106. Chen Z, Gou Q, Xiong Q, Duan L, Yuan Y, Zhu J, et al. Immunodominance of epitopes and protective efficacy of HI antigen are differentially altered using different adjuvants in a mouse model of staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Front Immunol. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.684823
107. Gong W, Liang Y, Mi J, Jia Z, Xue Y, Wang J, et al. Peptides-based vaccine MP3RT induced protective immunity against mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a humanized mouse model. Front Immunol. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.666290
108. Jiang S, Gong M, and Xu X-N. Research, development and clinical trials for peptide-based vaccines. Front Media SA;. (2022), 894989. doi: 10.3389/978-2-88976-146-3
109. Nelde A, Rammensee HG, and Walz JS. The peptide vaccine of the future. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2021) 20:100022. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R120.002309
110. Sanchez R, Tiwari S, Ferreira L, Oliveira F, Lopes M, and Passos M. Immunoinformatics design of multi-epitope peptide based vaccines against Schistosoma mansoni using transmembrane proteins a target. Front Immunol. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.621706
111. Becker JP and Riemer AB. The importance of being presented: target validation by immunopeptidomics for epitope-specific immunotherapies. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:883989. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.883989
112. Smith CC, Olsen KS, Gentry KM, Sambade M, Beck W, Garness J, et al. Landscape and selection of vaccine epitopes in SARS-CoV-2. Genome Med. (2021) 13:101. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00910-1
113. Kumru OS, Joshi SB, Smith DE, Middaugh CR, Prusik T, and Volkin DB. Vaccine instability in the cold chain: mechanisms, analysis and formulation strategies. Biologicals. (2014) 42:237–59. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2014.05.007
114. Ashkani EG, McKenna BD, Bryant JL, Trevisan-Silva D, Sherman NE, Chianese-Bullock KA, et al. Stability of multi-peptide vaccines in conditions enabling accessibility in limited resource settings. Int J Pept Res Ther. (2024) 30:42. doi: 10.1007/s10989-024-10620-y
115. Karahan M. Synthetic Peptide Vaccine Models: Design, Synthesis, Purification and Characterization. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; 2021.
116. Martin V, Egelund PH, Johansson H, Le Quement ST, Wojcik F, and Pedersen DS. Greening the synthesis of peptide therapeutics: an industrial perspective. RSC advances. (2020) 10:42457–92. doi: 10.1039/D0RA07204D
117. Chen H-Z, Tang L-L, Yu X-L, Zhou J, Chang Y-F, and Wu X. Bioinformatics analysis of epitope-based vaccine design against the novel SARS-CoV-2. Infect Dis poverty. (2020) 9:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00713-3
118. Chukwudozie OS, Gray CM, Fagbayi TA, Chukwuanukwu RC, Oyebanji VO, Bankole TT, et al. Immuno-informatics design of a multimeric epitope peptide based vaccine targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0248061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248061
119. Basmenj ER, Pajhouh SR, Ebrahimi Fallah A, Naijian R, Rahimi E, Atighy H, et al. Computational epitope-based vaccine design with bioinformatics approach; a review. Heliyon. (2025) 11. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41714
120. Olawade DB, Teke J, Fapohunda O, Weerasinghe K, Usman SO, Ige AO, et al. Leveraging artificial intelligence in vaccine development: A narrative review. J Microbiological Methods. (2024) 224:106998. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2024.106998
121. Somogyi E, Csiszovszki Z, Molnár L, Lőrincz O, Tóth J, Pattijn S, et al. A peptide vaccine candidate tailored to individuals’ Genetics mimics the multi-targeted T cell immunity of COVID-19 convalescent subjects. Front Genet. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.684152
122. Kheirvari M, Liu H, and Tumban E. Virus-like particle vaccines and platforms for vaccine development. Viruses. (2023) 15:1109–32. doi: 10.3390/v15051109
123. Caucheteux SM, Mitchell JP, Ivory MO, Hirosue S, Hakobyan S, Dolton G, et al. Polypropylene Sulfide Nanoparticle p24 Vaccine Promotes Dendritic Cell-Mediated Specific Immune Responses against HIV-1. J Invest Dermatol. (2016) 136:1172–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.01.033
124. Pizzolato-Cezar LR, Okuda-Shinagawa NM, and Machini MT. Combinatory therapy antimicrobial peptide-antibiotic to minimize the ongoing rise of resistance. Front Microbiol. (2019) 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01703
125. Du Y, Liu Y, Wang D, Bai H, Wang Z, He X, et al. Peptidic microarchitecture-trapped tumor vaccine combined with immune checkpoint inhibitor or PI3Kγ inhibitor can enhance immunogenicity and eradicate tumors. J ImmunoTherapy Cancer. (2022) 10:e003564. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003564
Keywords: peptide vaccines, Enterococcus faecium, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp
Citation: Tavassoli Razavi F, Salari N, Emami A, Haghmorad D and Baharlou R (2025) Peptide vaccines: an innovative therapeutic approach against antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Front. Immunol. 16:1567584. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567584
Received: 28 January 2025; Accepted: 28 April 2025;
Published: 21 May 2025.
Edited by:
Xingmin Sun, University of South Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Hasanain Odhar, Al-Zahrawi University College, IraqNeelam Sharma, B V Raju Institute of Technology, India
Copyright © 2025 Tavassoli Razavi, Salari, Emami, Haghmorad and Baharlou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rasoul Baharlou, YmFoYXJsb3VyQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Fatemeh Tavassoli Razavi
Fatemeh Tavassoli Razavi Nasrin Salari
Nasrin Salari Dariush Haghmorad
Dariush Haghmorad Rasoul Baharlou
Rasoul Baharlou