- 1School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 2Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescription and Syndrome Differentiation Translational Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 3Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Oncology of Hunan Province, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 4Department of Gynaecology, The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 5College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 6Medical School, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 7Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changsha Hospital for Maternal and Child Health Care, Changsha, Hunan, China
Ovarian cancer(OC) is the second most common gynecological malignancy worldwide. While traditional treatments such as cytoreductive surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted drugs have made progress, patients with advanced disease still face high recurrence rates and resistance to treatment. As a result, there is an urgent need to develop new therapeutic strategies. Ferroptosis, a novel form of programmed cell death characterized by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, has recently gained attention for its potential in cancer therapy. Studies indicate that OC cells are highly sensitive to ferroptosis, and targeting this pathway can effectively overcome chemotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes. This review systematically examines the molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in OC, with a focus on its involvement in tumor initiation, progression, TME and resistance. Furthermore, we highlight the research advancements on various ferroptosis inducers, including natural products, small molecule compounds, and nanotechnology, and explore their potential in overcoming resistance and enhancing patient prognosis. We also discuss the challenges facing ferroptosis-based treatments for OC, such as species differences, drug resistance, personalized treatment needs, and clinical translation issues. Ultimately, targeted modulation of ferroptosis offers new hope for OC therapy. Future research should focus on further elucidating its molecular mechanisms and exploring effective inducers and combination therapies to enhance its clinical applicability in precision and personalized medicine.
1 Introduction
Ovarian cancer(OC) ranks as the second most common malignant tumor among gynecological cancers worldwide, accounting for an estimated 3.7% of cases and 4.7% of cancer deaths in 2020 (1). OC is a highly heterogeneous disease, with only about half of patients surviving 5 years after diagnosis (2). Although cytoreductive surgery, taxane-based platinum chemotherapy, and targeted therapies—such as bevacizumab and PARP inhibitors— have made significant progress in clinical settings, the majority of patients with advanced stages still experience disease recurrence and treatment failure (3). Consequently, the prognosis for patients with advanced OC remains poor, characterized by high relapse rates and resistance to conventional therapies (4).This highlights the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies, particularly those targeting resistance mechanisms, to improve survival outcomes (5).
In recent years, ferroptosis has attracted widespread attention as a type of programmed cell death. First proposed by Dixon et al. in 2012, ferroptosis differs from other cell death pathways, such as apoptosis and necrosis, and is characterized by the accumulation of iron-dependent lipid peroxides (6).This process is driven by factors including intracellular iron overload, glutathione(GSH) depletion, and excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS)generation, which ultimately result in irreversible damage to the cell membrane and cell death (7). Given its unique regulation of cancer cell metabolic reprogramming and iron metabolism, ferroptosis plays a crucial role in tumors and has emerged as a hot topic in anti-cancer research (8–10).OC cells exhibit a high dependence on iron metabolism, making them significantly more susceptible to ferroptosis compared to normal cells (11). Studies have demonstrated that activating ferroptosis can inhibit OC growth and reverse chemotherapy resistance (12, 13). Particularly in chemotherapy-resistant OC, ferroptosis can selectively target tumor cells while sparing normal tissues by modulating redox homeostasis and lipid metabolism (14–16). As a result, targeting ferroptosis offers a promising strategy to overcome chemotherapy resistance and improve the prognosis of advanced OC patients (17–21). However, despite significant progress in understanding the molecular mechanisms and regulatory networks of ferroptosis, its clinical application in treating OC still faces challenges, including the need for efficient and selective induction of ferroptosis and the integration of existing therapies to enhance treatment efficacy.
This article reviews the research progress on targeted ferroptosis in OC treatment, with a focus on the molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis, its role in treating OC, the relationship between chemoresistance and ferroptosis, and the potential of natural products and small molecule drugs in inducing ferroptosis. Additionally, the article explores the potential of natural products and small molecule drugs in inducing ferroptosis and the potential applications of emerging nanotechnologies and combination treatment strategies. It also addresses the limitations of current research and offers insights for future studies on targeted ferroptosis in OC therapy.
2 Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis
2.1 Overview of ferroptosis
The term ferroptosis is derived from the Latin word ferrum, meaning iron. Research on lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and iron homeostasis forms the foundation for understanding ferroptosis. In 1876, Henry John Horstman Fenton proposed the Fenton reaction. Iron, a key trigger and mediator of ferroptosis signaling, can catalyze the formation of harmful free radicals through the Fenton reaction (22). In 1929, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as linoleic acid and linolenic acid, were recognized as crucial substrates for lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis (23). Phospholipids (PLs), which are integral components of cell membranes, contain PUFA groups and play a critical role in the process of ferroptosis (24).In 1955, Harry Eagle and colleagues discovered that cysteine (Cys) is essential for cell survival, and its deficiency, leading to GSH depletion, can result in cell death (25). In 1985, Helmut Sies coined the term “oxidative stress” (26), referring to a process where an excess of oxidizing substances—such as free radicals and peroxides—disrupts intracellular redox balance, triggering a range of harmful biological effects (27). GSH depletion impairs the cell’s ability to counteract oxidative stress, making it more susceptible to damage from oxidants like hydrogen peroxide (28). Regarding lipid metabolism, several studies have identified key mechanisms involved in lipid metabolism during ferroptosis (23, 29). These foundational studies provide key insights into the mechanisms driving ferroptosis.
Since 2012, ferroptosis has emerged as a prominent topic in biomedical research, with a rapid increase in related studies (30, 31). It has been implicated in a wide range of biological processes, including development, aging, immunity, and cancer. Over the past decade, significant breakthroughs have been made in understanding the mechanisms of ferroptosis and harnessing it for therapeutic benefits.
2.2 Regulation of ferroptotic signaling
2.2.1 Classical ferroptotic pathway
2.2.1.1 GPX4 and the GSH-dependent antioxidant system
Glutathione peroxidase4 (GPX4) is a key molecule in inhibiting ferroptosis, primarily by preventing the propagation of the lipid peroxidation chain reaction through the reduction of lipid hydroperoxide (LOOH) to inactive LOH(phospholipid alcohols). The activity of GPX4 relies on the tripeptide GSH as a reducing agent, and GSH synthesis is central to its function. This synthesis is driven by two enzymatic reactions: Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase (GCL) and Glutathione Synthetase(GSS).GCL catalyzes the binding of glutamate to cysteine, while GSS facilitates the attachment of glycine to glutamylcysteine, forming GSH. To support GSH synthesis, cells uptake cysteine from the extracellular environment via the system Xc-, which consists of the Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11(SLC7A11) and Solute Carrier Family 3 Member 2 (SLC3A2) subunits. Inhibition of GPX4 disrupts intracellular iron homeostasis and lipid peroxide reduction, inducing ferroptosis (32).
2.1.1.2 Lipid peroxidation and PUFA
Lipid peroxidation is a key determinant of ferroptosis sensitivity. It is a biochemical process in which free radicals, such as ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), attack and oxidize lipids in cell membranes and organelles. During lipid peroxidation, ROS and RNS react with PUFAs in plasma and organelle membranes to generate lipid peroxides (33). ROS are oxygen-containing, chemically reactive molecules that can initiate or amplify ferroptosis sensitivity in various cell types and tissues (34). RNS, which are reactive chemical species derived from nitrogen sources, include peroxynitrite, nitrosyl radicals and nitroxides. Studies have shown that ferroptosis can be induced by modulating cellular lipid peroxidation using peroxynitrite generators (35).
The mechanism of the lipid peroxidation chain reaction involves three stages: initiation, propagation, and termination, along with various regulatory mechanisms and key molecules. In the initiation stage, promoters such as hydroxyl radicals remove allylic hydrogen atoms, generating lipid radicals with a carbon core. During propagation, these lipid radicals rapidly combine with oxygen to form lipid peroxyl radicals. This stage is driven by divalent iron (Fe²+), which reacts with hydrogen peroxide through the Fenton reaction to produce highly reactive hydroxyl (•OH) radicals. These •OH radicals can directly attack PUFAs, such as linoleic acid and arachidonic acid, in cell membranes. Due to their multiple double bonds, these fatty acids are highly susceptible to reaction with free radicals, resulting in lipid peroxide formation. The accumulation of iron ions exacerbates lipid peroxidation, particularly in PUFAs within cell membranes. In addition to Fenton-type chemistry, enzymes like lipoxygenases and P450(Cytochrome P450) oxidoreductases can also promote lipid peroxidation in membranes. Once initiated, the lipid peroxidation chain reaction accelerates, with lipid peroxides such as LOOH further cleaving to produce new free radicals, like peroxyl radicals, which attack other lipid molecules and perpetuate the chain reaction.
The termination phase of lipid peroxidation relies on antioxidant systems, such as Ferroptosis Suppressor Protein 1(FSP1), vitamin E, and free radical scavengers, to neutralize free radicals and inhibit ferroptosis. FSP1 reduces coenzyme Q10(CoQ10) to its reduced form, coenzyme QH2, using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). Vitamin E reacts with lipid peroxyl radicals, forming a non-radical product and preventing further radical propagation. Free radical scavengers, such as reactive antioxidants (RTAs), block the lipid peroxidation chain reaction by directly interacting with free radicals. The lipid peroxidation chain reaction continues until these antioxidant systems intervene and the termination product is formed (36). Exogenous supplementation of Monounsaturated Fatty Acid(MUFA), stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD1)-mediated cellular MUFA production, and Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long-Chain Family Member 3 (ACSL3)-dependent MUFA membrane enrichment have been reported to reduce the propensity of cells to die by ferroptosis (37).The main byproduct of lipid peroxidation is lipid hydroperoxides. Lipid peroxidation produces a variety of aldehydes, including as Malondialdehyde (MDA), propionaldehyde, hexanal, and 4-HNE. PLs are the major lipid structures involved in ferroptosis, and lipid peroxidation of the phospholipid bilayer can promote ferroptosis. Among the fatty acids in PLs, PUFAs are the most susceptible to autoxidation—a free radical chain reaction that converts lipids into lipid hydroperoxides (38). Phospholipid hydroperoxides (PLOOH) are the key executors of ferroptosis. PLs containing two PUFA tails are particularly potent drivers of this process (39). PL-PUFA2, rather than PL-PUFA1, represents the key lipid class involved in ferroptosis (40).
PLs containing PUFAs are the primary substrates for lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis and are upregulated by enzymes such as acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4), lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3), ALOXs, and Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase(POR) (41).The membrane remodeling enzymes, ACSL4 (42) and LPCAT3, are key drivers of ferroptosis. ACSL4 enhances ferroptosis by promoting lipid oxidation. Interestingly, in certain cell types, ACSL4 may also play a protective role against ferroptosis (43). This may be related to the metabolic state of cells and the tumor microenvironment. LPCAT3 is transcriptionally regulated by the YAP/ZEB/EP300 axis and works in conjunction with ACSL4 and YAP to modulate ferroptosis sensitivity (44). Lipoxygenase (LOX) is a dioxygenase that catalyzes the conversion of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as linoleic acid and arachidonic acid, into their corresponding hydroperoxides (45). POR is an enzyme essential for various metabolic processes (46) and plays a role in initiating lipid peroxidation. Studies have shown that POR can induce ferroptosis by promoting the peroxidation of membrane polyunsaturated PLs (47).
Guanine cyclohydrolase 1 (GCH1) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) biosynthesis pathway. BH4 is not only a crucial cofactor for various enzymes, such as nitric oxide synthase, but also plays a key role in ferroptosis defense by inhibiting lipid peroxidation. Studies have shown that BH4 can protect against ferroptosis by directly scavenging lipid peroxides and inhibiting the generation of ROS (48). In addition, GCH1 and BH4 can also support the regeneration of coenzyme Q, working synergistically with the FSP1 system to protect cells from lipid oxidative damage (49).
2.1.1.3 Iron metabolism and the Fenton reaction
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of cell death closely associated with disorders of iron metabolism (50). Iron is both a catalyst and a key regulator of ferroptosis. As an essential mineral, it is involved in numerous physiological processes. Fe²+ from heme and non-heme sources is transported to the basal surface of enterocytes, reoxidized to Fe³+ by ferroferrin (HEPH), exported via the export protein ferroportin (FPN) (51), and then loaded onto the circulating iron transporter transferrin (TF) for systemic delivery. TF-bound iron is transported to peripheral cells, where it binds to transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1). The binding activates the non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src, which, in turn, triggers the endocytosis of the TF-TFR1 complex (52). Once inside the cell, Fe³+ is released and reduced to Fe²+ by the six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate (STEAP) family reductase (53). This Fe²+ participates in DNA synthesis, cellular respiration, and energy metabolism. Iron can also be stored in ferritin or exported to the circulation via FPN (54). A portion of Fe²+ is transported from endosomes to the cytosol by Divalent metal transporter 1(DMT1), becoming part of the metabolically active labile iron pool (LIP).
The first step of ferroptosis is the excessive accumulation of intracellular iron ions. Increased iron intake due to diet, environmental factors, or other pathological conditions disrupts systemic iron homeostasis. This leads to enhanced TfR-mediated iron influx, while iron storage proteins, such as ferritin, become saturated and can no longer store excess iron. As a result, free iron (Fe²+) levels rise, contributing to ferroptosis. The liver regulates iron absorption, recycling, and tissue levels by secreting hepcidin, which reduces iron efflux by negatively regulating FPN (55). Increased hepcidin secretion binds to FPN and triggers its degradation (55). Iron regulatory proteins (IRPs) bind to the 5’ IRE of FPN1 and FT mRNAs, resulting in translational repression (56). Additionally, IRPs bind to the 3’ IRE of TFR1 mRNA, stabilizing it and enhancing TFR1 protein synthesis. As a consequence, TFR1 levels increase while FT and FPN levels decrease. Moreover, STEAP (54) and DMT1 are upregulated (57). Ultimately, these changes lead to an increase in intracellular iron (58).
In cancer and inflammation, hepcidin secretion from the liver and peripheral tissues increases, leading to decreased FPN expression, which limits iron circulation and contributes to anemia. Cancer cells exhibit an “iron-seeking” phenotype by upregulating iron-related proteins (TFR1, STEAP, DMT1, hepcidin, SLC39A14) and downregulating FPN, thereby promoting iron uptake and accumulation (59). Studies have shown that exogenous iron supplementation, in the form of ammonium ferric citrate at submillimolar doses, induces ROS and lipid peroxidation in mitochondria (60). This also suggests that intracellular iron accumulation increases cellular susceptibility to ferroptosis.
2.2.2 Noncanonical ferroptotic pathway
2.2.2.1 p53 signaling in ferroptosis
p53 is a classic tumor suppressor that plays an important role in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, metabolic regulation and maintenance of genomic stability (61). p53 directly inhibits the expression of SLC7A11, limiting the uptake of L-cysteine, thereby reducing the synthesis of GSH and reducing the activity of GPX4 (62).In addition, SAT1 and GLS2 are transcriptional targets of p53. Studies have shown that p53 enhances ferroptosis by upregulating the expression of SAT1 and GLS2 (63). p53 can also enhance iron uptake and increase the accumulation of the LIP by upregulating the expression of TFR1 (64). This effect makes the iron-dependent Fenton reaction more likely to occur, thus generating more hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and inducing lipid peroxidation. In addition, p53 promotes lipid remodeling of intracellular PUFAs by regulating the expression of ACSL4, thereby exacerbating lipid peroxidation (65).
2.2.2.2 Ferritinophagy and autophagy-dependent ferroptosis
Ferritinophagy is a form of selective autophagy that targets ferritin for degradation, releasing stored iron and increasing the level of the LIP (66).During ferritinophagy, the ferritin receptor nuclear receptor coactivator 4(NCOA4) binds to ferritin and transports it to the autophagosome for degradation, releasing the stored iron. Studies have shown that inhibiting NCOA4 or blocking ferritinophagy can significantly reduce ferroptosis (67).
In some cases, autophagy can enhance the sensitivity of cells to ferroptosis. Autophagy-related genes (ATG5, ATG7) significantly affect the occurrence of ferroptosis by promoting mitochondrial autophagy and regulating the level of lipid peroxidation (68, 69). Additionally, studies have shown that overactivation of autophagy may accelerate ferritinophagy and the release of free iron, promoting the Fenton reaction and lipid peroxidation chain reaction, which in turn exacerbates ferroptosis (70).
2.2.2.3 Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and ferroptosis
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress (ERS) is a cellular stress response triggered by protein misfolding or calcium imbalance in the ER. Studies have shown that ERS plays a crucial role in cell death by regulating ferroptosis-related molecules and signaling pathways (71).
Studies have found that the ER stress-induced IRE1α-XBP1 signaling pathway regulates the expression of ACSL4, promotes the phospholipidation of PUFAs, enhances Lipid Peroxidation(LPO), and aggravates ferroptosis (72, 73). ER stress promotes ferroptosis by activating the PERK pathway, upregulating the expression of ATF4, and further enhancing the expression of ferroptosis-driving factors, ACSL4 and LPCAT3 (74, 75). Overactivation of ATF4 may also induce the downregulation of SLC7A11, reduce intracellular GSH levels, and further aggravate ferroptosis (76). Regulation of ferroptotic signaling is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Regulation of ferroptotic signaling (A) Classical Ferroptosis Pathway: This pathway primarily involves the synthesis of GSH and the reduction of lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) by GPX4, which prevents ferroptosis. Cells take up cysteine (Cys) through the System Xc- to support GSH synthesis. GSH then inhibits the propagation of lipid peroxidation through GPX4, avoiding ferroptotic cell death. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and phospholipids (PLs) play crucial roles in this process, with lipoxygenases (ALOXs) and other enzymes like POR, ACSL4, and LPCAT3 driving lipid peroxidation. (B) Noncanonical Ferroptosis Pathway: This pathway involves different molecular mechanisms, including the regulation of p53, GLS2, and SAT1, and affects ferroptosis through the expression of transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1) and ferritin. Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and autophagy also play significant roles in ferroptosis, with key players like ATG5 and ATG7 regulating the autophagic process.
3 Role of ferroptosis in OC
3.1 Ferroptosis in the onset and metastasis of OC
OC is widely considered to be a “hidden killer” of women. Due to its high mortality rate, it remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in women worldwide. Recent studies have found that ferroptosis, a special type of programmed cell death, plays a significant role in the occurrence, development and metastasis of OC (77, 78). Ferroptosis causes cell death by inducing intracellular oxidative stress and destroying lipid peroxides on the cell membrane. Acording to Figure 2, this mechanism plays a crucial role in the proliferation, drug resistance and metastasis of OC cells (79, 80).
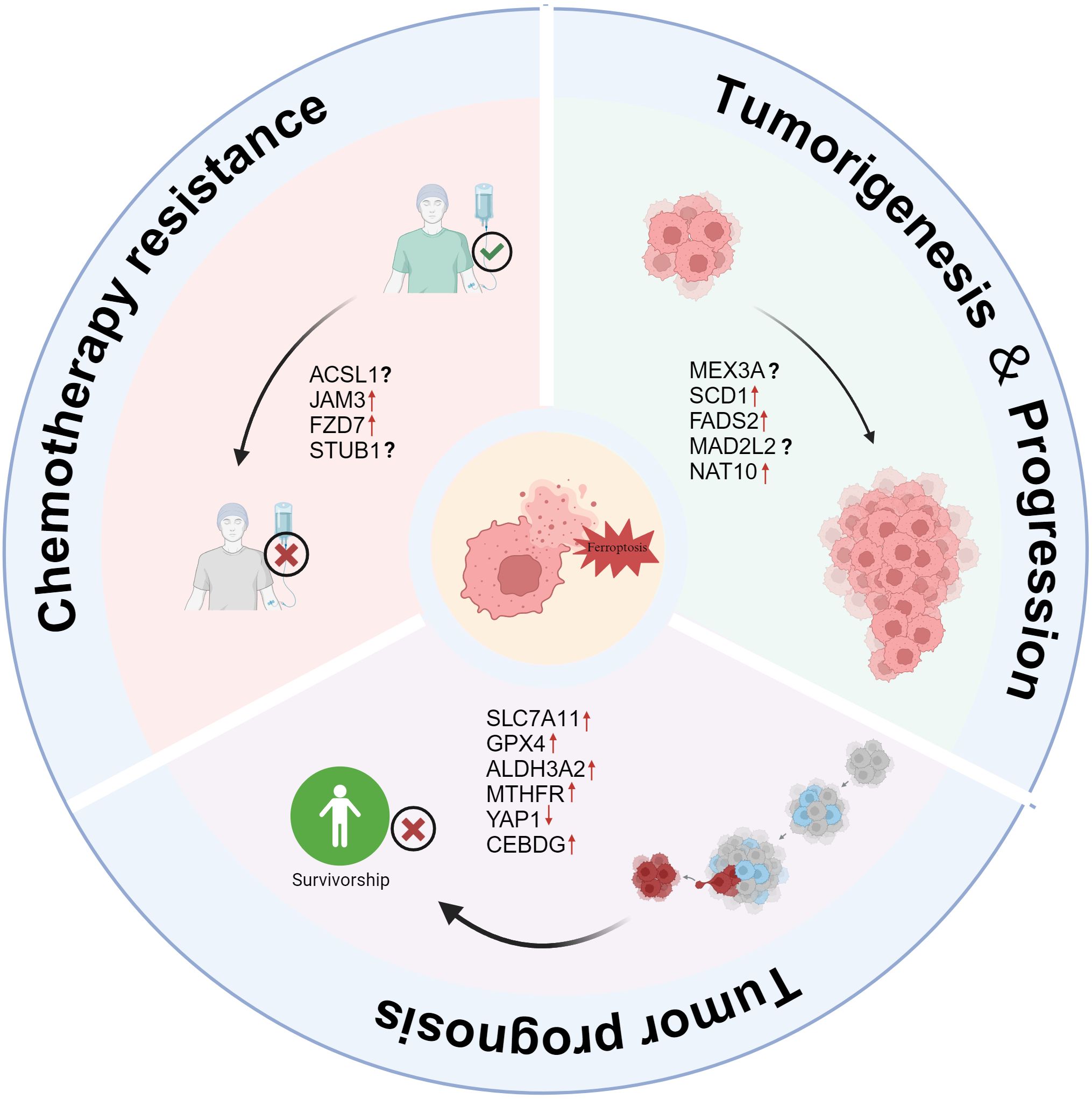
Figure 2. The role of ferroptosis in OC tumorigenesis, progression, and chemotherapy resistance. Tumorigenesis & Progression: Several factors, including MEX3A, SCD1, FADS2, MAD2L2, and NAT10, contribute to OC development and progression by suppressing ferroptosis, promoting tumor growth. Chemotherapy Resistance: ACSL1, JAM3, FZD7, and STUB1 are linked to resistance against chemotherapeutic agents, potentially reducing ferroptosis susceptibility and enabling tumor survival. Tumor Prognosis: High expression of SLC7A11, GPX4, ALDH3A2, MTHFR, YAP1, and CEBPG correlates with poor prognosis by inhibiting ferroptosis, whereas ferroptosis induction could improve patient outcomes.
In a study exploring the different cellular origins and pathogenesis of endometriosis-related OC (CCOC and ENOC), Ian Beddows et al. found (81) that CCOC cells enhance the gene expression of cysteine and GSH synthesis pathways and downregulate iron transporters. Battaglia, A.M. et al. also found that (82) iron metabolism plays a key role in the sphere-forming ability of OC cells. Under non-adhesive culture conditions, increased iron promoted the growth and maintenance of OC stem-like cells, while iron chelators significantly inhibited this process.
OC cells promote survival by inhibiting ferroptosis, a mechanism that not only facilitates the early initiation of tumors but also enables them to remain invasive during progression. For example, MEX3A promotes the proliferation of OCCC cells and tumor progression by regulating the stability of wild-type p53 and inhibiting ferroptosis (83). In addition, abnormal upregulation of SCD1 and FADS2 enhances lipid metabolism activity and tumor invasiveness in ascites-derived OC cells by inhibiting ferroptosis (84). Furthermore, studies have shown that OC metastasis-derived cells exhibit higher ferroptosis sensitivity and increased PUFA content, suggesting a close link between ferroptosis and the potential for OC metastasis (85). The relationship between ferroptosis susceptibility and poor prognosis in OC has also been further verified. Additionally, other molecules, such as MAD2L2 and NAT10, also promote OC progression by inhibiting the ferroptosis pathway. As a key regulatory factor, MAD2L2 further accelerates tumor progression by suppressing ferroptosis (86). Upregulation of NAT10 promotes ovarian tumor development by enhancing fatty acid metabolism and inhibiting ferroptosis (87). These findings suggest that ferroptosis plays a critical role in the onset and metastasis of OC. Therefore, regulating ferroptosis and its associated signaling pathways may offer new insights and strategies for the clinical treatment of OC. In summary, ferroptosis and its related regulatory molecules could become promising targets for future OC therapies.
3.2 Ovarian cancer tumor microenvironment and ferroptosis
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a dynamic, complex system that significantly influences cancer progression and therapeutic response. Recent studies have highlighted ferroptosis, a novel form of programmed cell death, as being regulated by various components of the TME, particularly through interactions among immune cells, stromal cells, and the extracellular matrix (88–90). These intricate interactions not only impact the effectiveness of ferroptosis inducers but also shape the tumor’s overall biological characteristics. For instance, Wei C et al.’s (91)immune and ferroptosis-related risk scoring model underscores the pivotal role of ferroptosis within the TME. Similarly, the prognostic risk model developed by Gao J et al. (92), which focuses on ferroptosis-related long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), further demonstrates how these lncRNAs regulate the TME in ovarian cancer.
A key interaction in the TME involves the regulation of immune cells, particularly macrophages. Ji H-Z et al. (93) discovered that in ovarian cancer, tumor-associated macrophages secrete CXCL8, activate CXCR2, and upregulate the expression of SLC7A11 and GPX4 in endothelial cells via the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby protecting endothelial cells from ferroptosis. This mechanism not only explains ferroptosis resistance within the TME but also underscores the crucial role of ferroptosis in tumor progression. Additionally, Wang Y et al. (94) identified that growth factors such as FGF2, 3, 8, 17, 18, 19, and 23 are closely linked to the ferroptosis signaling pathway in ovarian cancer. Their study found that FGF co-expresses with ferroptosis-related genes like GPX4, FTH1, and HMOX1, and that the level of FGF expression is negatively correlated with immune cell infiltration. This suggests that FGF influences ovarian cancer progression by modulating iron metabolism and immune responses. Li Z et al. (95) also pointed out that in the fatty acid-rich TME of ovarian cancer, the upregulation of SLC27A4 enhances tumor cell resistance to ferroptosis by promoting the selective uptake of MUFA, thereby inhibiting lipid peroxidation. Moreover, Atiya HI et al. (96)found that endometriosis-derived mesenchymal stem cells (enMSC) contribute to ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) growth through iron regulation. Specifically, when CD10-negative enMSC were co-cultured with OCCC cells, significant changes were observed in iron transport and export, highlighting the crucial role of iron homeostasis in the TME for ovarian cancer progression.
3.3 Chemoresistance and ferroptosis in OC
As is shown in Figure 2, ferroptosis plays a crucial role in the chemoresistance of OC (97, 98). Various molecular mechanisms work together to suppress ferroptosis, thereby enhancing cancer cell resistance to chemotherapy. However, research indicates that targeting these resistance-related pathways can restore ferroptosis sensitivity and improve chemotherapy efficacy.
ACSL1 enhances the stability and activity of FSP1 by promoting its N-myristoylation, thereby inhibiting lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. This mechanism contributes to significant resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy in OC cells. Notably, Zhang et al. found that inhibiting ACSL1 or targeting the N-myristoylation process of FSP1 can restore ferroptosis sensitivity and significantly improve the efficacy of platinum-based drugs (99). Meanwhile, JAM3, a transmembrane protein from the junctional adhesion molecule family, plays a crucial role in cell adhesion and signal transduction, particularly in cell migration and tumor metastasis (100, 101). Studies have shown that high JAM3 expression is closely associated with cisplatin resistance and poor prognosis in OC patients. Specifically, JAM3 enhances the resistance of highly adhesive OC cells to ferroptosis by activating the NRF2/FSP1 pathway and inhibiting lipid peroxidation. Targeting the JAM3-NRF2/FSP1 pathway presents a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome drug resistance and increase ferroptosis sensitivity (102).Additionally, Frizzled-7 (FZD7) is a key marker of platinum-resistant OC cells (103, 104). Wang et al. (105) found that OC cells maintain redox balance and resist oxidative damage by activating the FZD7–β-catenin–Tp63–GPX4 signaling pathway, further promoting chemotherapy resistance. Therefore, targeting FZD7 and its downstream pathways may be an effective strategy for improving chemotherapy sensitivity. Furthermore, as a ubiquitin ligase, STUB1 plays a crucial role in regulating ferroptosis in OC cells and enhancing sensitivity to the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel. STUB1 promotes ferroptosis by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of HOXB3, thereby inhibiting PARK7 expression (106). Understanding this mechanism provides a potential new approach for overcoming paclitaxel resistance in OC and lays the groundwork for future targeted therapy research.
In summary, the inhibition of ferroptosis is one of the important mechanisms of OC resistance. With the in-depth study of these molecular mechanisms, more and more evidence shows that targeting these key regulatory factors can effectively restore the sensitivity of OC cells to ferroptosis and improve the therapeutic effect of chemotherapy drugs. In the future, intervention strategies targeting these molecular mechanisms may become an effective way to break through the bottleneck of OC resistance and bring more clinical benefits to patients with resistant OC.
3.4 OC prognosis and ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is closely related to the metabolic regulation of tumor cells, drug resistance and the prognosis of patients (Figure 2). The importance of ferroptosis-related molecules in the prognosis of OC has been demonstrated by an increasing number of studies. Wu, X et al. found that high levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 co-expression are important predictors of platinum resistance and poor prognosis in patients with epithelial OC. According to mechanistic research, SLC7A11 and GPX4 stop ferroptosis by boosting cells’ antioxidant potential and preventing lipid peroxidation (107). ALDH3A2 is an enzyme involved in lipid metabolism that catalyzes the oxidation of long-chain fatty aldehydes to fatty acids, thereby regulating cellular lipid homeostasis and antioxidant capacity. Studies have shown that ALDH3A2 affects the sensitivity of tumor cells to ferroptosis by regulating lipid metabolism, GSH metabolism, phospholipid metabolism, and aldehyde metabolism pathways (108). Using TCGA and GTEx data, Dong, H. et al. also discovered that a poor prognosis for patients with OC was linked to high expression of ALDH3A2 (109). In addition to being closely linked to intracellular methylation processes, MTHFR is a crucial metabolic enzyme involved in the metabolism of folate and homocysteine (110). According to studies, women with OC who have high MTHFR expression had a far worse prognosis (111). Wang, X. et al. also discovered that MTHFR knockdown can greatly increase the anti-tumor effect and boost the lethal effect of ferroptosis inducers (such Erastin and RSL3) (112). In addition to metabolic regulation, transcription factors also play an important role in ferroptosis-related prognostic mechanisms. According to Furutake, Y. et al., YAP1 activation greatly increased the sensitivity of OCCC cells to ferroptosis inducers (such Erastin) via boosting lipid peroxidation, and low nuclear YAP1 expression was strongly linked to a poor prognosis in OCCC (113). This discovery suggests that YAP1 may play a part in controlling ferroptosis during the treatment of OC. Zhang et al. found that CEBPG expression is significantly higher in OC tissue than in benign ovarian tissue and is associated with poor prognosis in OC patients. Further studies revealed that CEBPG inhibits ferroptosis by regulating SLC7A11 transcription, thereby promoting the proliferation, migration, and invasion of OC cells (114).
These ferroptosis-related molecules not only reveal the key biological mechanisms for the prognosis of OC patients, but also provide new directions for precision treatment strategies targeting ferroptosis.
3.5 Molecular mechanisms and regulatory networks of ferroptosis in OC
3.5.1 The role of miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in ferroptosis of OC
As is shown in Figure 3, the occurrence of ferroptosis in OC cells is closely related to the expression of multiple RNA molecules, among which miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA play an important role as regulatory factors in the sensitivity and tolerance of ferroptosis. These RNA molecules influence the ferroptosis process through distinct mechanisms, significantly impacting the growth, migration, invasion, and prognosis of OC.
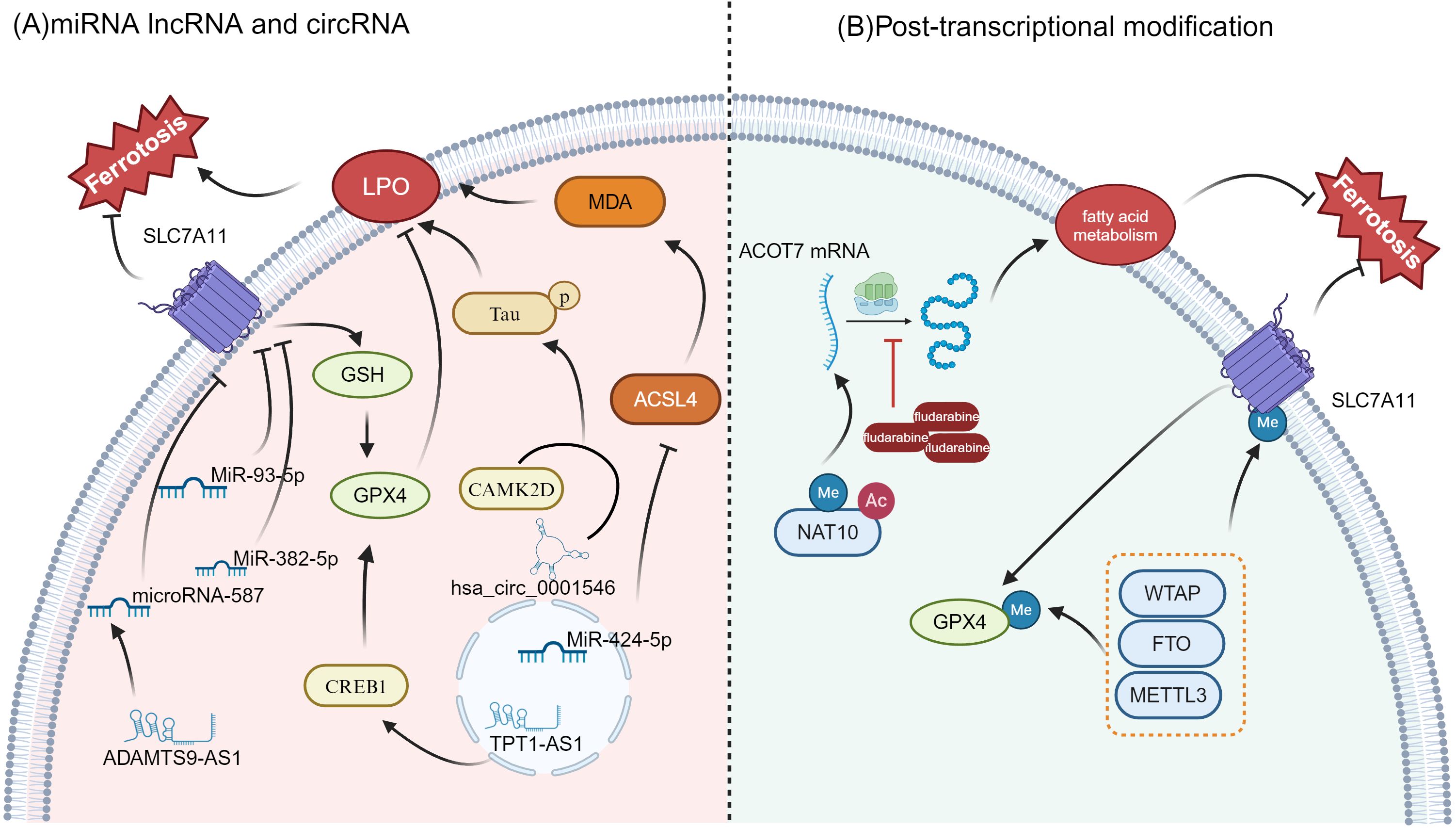
Figure 3. Regulation of ferroptosis by miRNAs, lncRNAs, circRNAs, and post-transcriptional modifications (A) miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA regulation in ferroptosis: Key miRNAs like MiR-93-5p, MiR-382-5p, and MiR-424-5p influence ferroptosis by modulating critical genes such as SLC7A11, GPX4, and ACSL4. hsa_circ_0001546 and TPT1-AS1 also contribute to lipid peroxidation (LPO) and ferroptosis sensitivity. Additionally, CREB1 plays a role in ferroptosis regulation through lipid metabolism and by impacting ACSL4 activity (B) Post-transcriptional Modifications: Modifications such as methylation (Me) and acetylation (Ac) are involved in regulating the expression and function of key proteins like SLC7A11 and GPX4, both of which are essential for ferroptosis regulation. The enzyme NAT10 influences fatty acid metabolism and ferroptosis by modifying mRNA stability, particularly for genes like ACOT7. In addition, methyltransferases such as METTL3, FTO, and WTAP are critical in the regulation of GPX4 and SLC7A11, further modulating the ferroptotic process.
MiR-93-5p is a small noncoding RNA belonging to the microRNA (miRNA) family. Li, C et al. reported that miR-93-5p down-regulated SLC7A11, reduced GSH levels, increased the accumulation of ROS and lipid peroxides, and ultimately induced ferroptosis (115). In addition, Sun et al. showed that miR-382-5p can promote ferroptosis by inhibiting SLC7A11 and may become a potential target for the future treatment of OC (116). Another microRNA, miR-424-5p, can reduce the accumulation of lipid peroxidation end products (such as MDA) and reduce ferroptosis-related cell death by directly targeting ACSL4. In contrast, inhibition of miR-424-5p can enhance the sensitivity of OC cells to ferroptosis (117).
Through multi-omics analysis, Wang, K. et al. revealed the significant role of ferroptosis-related long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in OC. Eight ferroptosis-related lncRNAs were screened (such as RP11-443B7.3, TRAM2-AS1, FAM13A-AS1, AC107959.3, AC068870.2, ACBD3-AS1, LINC01857, and AL031186.1), and were found to be closely associated with the prognosis of OC patients. A risk scoring model based on these lncRNAs was constructed to assess the potential benefits of immunotherapy (118). In addition, TPT1-AS1, a long noncoding RNA, promotes the transcription of GPX4 by upregulating the transcription factor CREB1, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis and enhancing the proliferation, migration, and invasion of OC cells (119). In epithelial OC (EOC), ADAMTS9-AS1 upregulation indirectly promotes SLC7A11 expression and inhibits ferroptosis by suppressing microRNA-587. Silencing ADAMTS9-AS1, on the other hand, increases microRNA-587 levels, leading to reduced SLC7A11 expression, which in turn promotes ferroptosis and inhibits the proliferation and migration of OC cells (120).
In terms of circular RNA regulation, Chai, B. et al. reported that hsa_circ_0001546, functioning as a molecular chaperone for the 14-3–3 protein, interacts with CAMK2D to promote the abnormal phosphorylation of Tau protein at Ser324, thereby driving lipid peroxidation-dependent ferroptosis. This mechanism effectively inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of OC cells, offering a potential new strategy for targeted therapy (121).
3.5.2 Post-transcriptional modifications and ferroptosis
Recent studies have increasingly highlighted the crucial role of post-transcriptional modifications in regulating ferroptosis, as well as in tumorigenesis and cancer progression (Figure 3) (122–124). A study found that NAT10 enhances the stability and translation of ACOT7 mRNA through m6A-driven translational regulation and ac4C RNA modification, thereby remodeling fatty acid metabolism, inhibiting ferroptosis and promoting the occurrence and progression of OC. More importantly, the study pointed out that the small molecule inhibitor fludarabine can target NAT10 and inhibit the acetylation modification of ACOT7 mRNA, inhibiting the acetylation modification of ACOT7 mRNA and effectively preventing tumor development. This offers a promising new strategy for treating OC (87).
Other studies have also highlighted the critical role of post-transcriptional modifications in regulating ferroptosis. For instance, research has shown that m6A modification influences ferroptosis sensitivity by modulating the expression of key genes, such as GPX4 and SLC7A11 (125). m6A-related enzymes such as METTL3, WTAP, and FTO affect mRNA stability and translation efficiency by regulating RNA methylation modification, thereby participating in the regulation of lipid peroxidation and cell ferroptosis (126, 127). These findings further suggest that post-transcriptional modifications play an important role in regulating ferroptosis in OC cells, offering new insights for potential therapeutic strategies.
3.5.3 Ferroptosis inhibitors and promoters
3.5.3.1 Ferroptosis inhibitors
NRF2 is a transcription factor that helps maintain cellular redox balance by regulating antioxidant gene expression. It plays a crucial role in responding to oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular metabolism (128). Studies show that NRF2 impacts iron homeostasis in OC cells by regulating the expression of HERC2 and VAMP8. Specifically, NRF2 upregulates HERC2 expression, promoting ferritin degradation and increasing free iron levels. Conversely, NRF2 downregulates VAMP8 expression, inhibiting ferritin autophagy, and thereby modulating ferroptosis sensitivity (129). Additionally, SGK1 (serum and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1) inhibits ferroptosis in OC through both NRF2-dependent and -independent pathways. Sang et al. reported that SGK1 enhances antioxidant defense and reduces lipid peroxide production by activating the NRF2 pathway. Furthermore, SGK1 directly regulates intracellular iron and lipid metabolism through NRF2-independent pathways, further inhibiting ferroptosis (130).
SLC2A12 and SLC27A4 also contribute to cellular metabolism. Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1A binds to HIF-1B and upregulates SLC2A12 expression by binding to the hypoxia response element (HRE) in the SLC2A12 promoter. This regulation enhances GSH metabolism, promotes GPX4 expression, and inhibits lipid peroxide formation, thereby preventing ferroptosis (131). In contrast, SLC27A4 inhibits lipid peroxide production and ferroptosis in OC by promoting monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and phospholipid remodeling (123). PTRF/Cavin-1 is a protein involved in cell membrane structure and signal transduction. It inhibits ferroptosis by maintaining cell membrane integrity and lipid homeostasis. Xiang et al. identified PTRF/Cavin-1 as a key regulator in OC, preventing ferroptosis. Knockdown of PTRF/Cavin-1 increased OC cells’ sensitivity to ferroptosis inducers, such as Erastin and RSL3 (132).
PAX8, a transcription factor, enhances the antioxidant capacity of OC cells by upregulating genes related to GSH synthesis, such as GCLC and GSS, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (133). FXN, a mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster assembly protein, regulates the degradation of mitochondrial antioxidant protein PRDX3 and inhibits ferroptosis in OC stem cells. FXN deficiency increases ROS accumulation, disrupts the intracellular redox balance, and induces ferroptosis, impairing the survival and self-renewal of tumor stem cells (134). Moreover, Miyahara et al. found that FDX2 prevents ferroptosis, cell senescence, and apoptosis in OC cells by maintaining mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster homeostasis. Knockdown of FDX2 causes ROS accumulation and increased lipid peroxidation, significantly heightening the sensitivity of OC cells to ferroptosis inducers. In vivo experiments also demonstrated that the loss of FDX2 inhibited tumor growth (135). Finally, SQLE, the rate-limiting enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway, is significantly overexpressed in OC (136, 137). Zhang et al. discovered that SQLE inhibits lipid peroxide generation and ROS accumulation by regulating cholesterol and lipid metabolism, reducing ferroptosis occurrence. Knockdown of SQLE significantly increased the sensitivity of OC cells to ferroptosis inducers, such as GPX4 inhibitors, and markedly inhibited tumor growth in in vivo experiments (138). The ferroptosis inhibitors is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Ferroptosis regulatory network in OC cells. Ferroptosis-promoting factors (highlighted in red) include LIF/LIFR, STAT3, HRD1, and SKP2, which are involved in regulating iron metabolism, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation (LPO), all of which contribute to ferroptosis. SLC7A11, SLC2A12, and STEAP3 play important roles in iron uptake and GSH synthesis, while VAMP8 and ferritin autophagy regulate intracellular iron storage. Ferroptosis inhibitory factors (highlighted in green) such as GPX4, NRF2, PAX8, and p53 help prevent ferroptosis by maintaining cellular redox balance and suppressing lipid peroxidation. FXN, FDX2, and PTRF/Cavin-1 contribute to iron homeostasis and mitochondrial function.
3.5.3.2 Ferroptosis promoting factors
STEAP3, a key regulator of iron metabolism, has been shown by Han, Y. et al. to inhibit the expression of SLC7A11 through activation of the p53 signaling pathway. This reduces GSH levels, increases lipid peroxidation and ROS accumulation, ultimately inducing ferroptosis and inhibiting OC progression (139). The LIF/LIFR autocrine loop enhances OC cells’ sensitivity to ferroptosis by suppressing the antioxidant defense system downstream of the STAT3/NRF2/SLC7A11-GPX4 axis. Ebrahimi, B. et al. demonstrated that the LIFR inhibitor EC359 not only inhibited OC cell growth and stem cell properties, but also induced lipid peroxidation and cell death by downregulating anti-ferroptosis genes, ultimately slowing tumor progression in both in vivo and in vitro models (140). HRD1 inhibits tumor proliferation and metastasis by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of SLC7A11. Wang, Y. et al. found that elevated HRD1 expression increases ROS and lipid peroxidation levels, triggers ferroptosis, and limits tumor growth (141). In addition, Yang, W.-H. et al. reported that the Hippo pathway effector YAP promotes ferroptosis by regulating the E3 ubiquitin ligase SKP2. Knockdown of YAP significantly decreased the sensitivity to lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis, while genetic or chemical inhibition of SKP2 protected cancer cells from ferroptosis. This discovery reveals the critical regulatory roles of YAP and SKP2 in ferroptosis and offers new therapeutic avenues for targeting YAP or SKP2 in cancer treatment (142). The ferroptosis promoters is shown in Figure 4.
4 Preclinical strategies for ferroptosis-based OC therapy
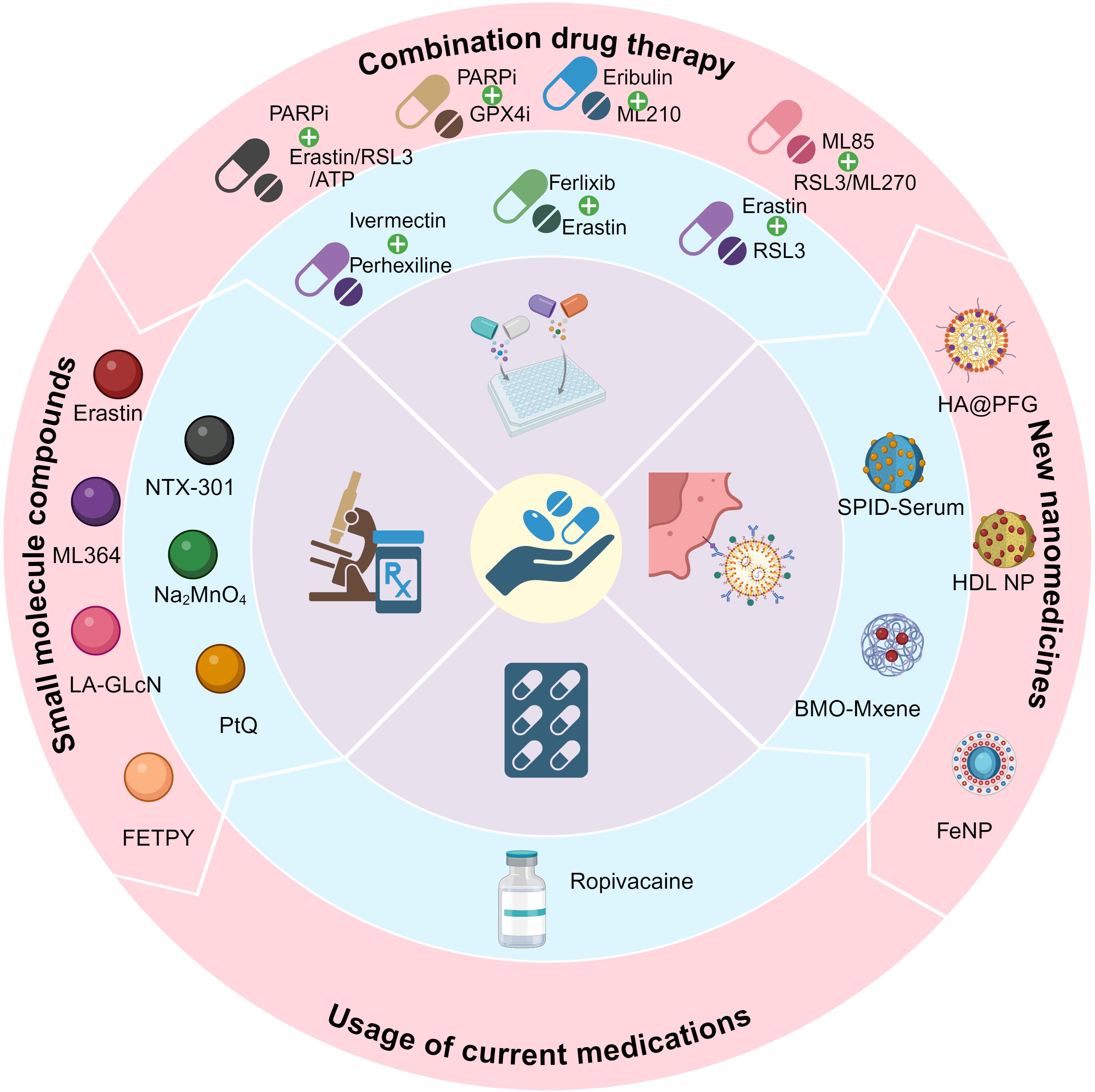
Figures 5 and 6 show the preclinical strategies for ferroptosis-based OC treatment.
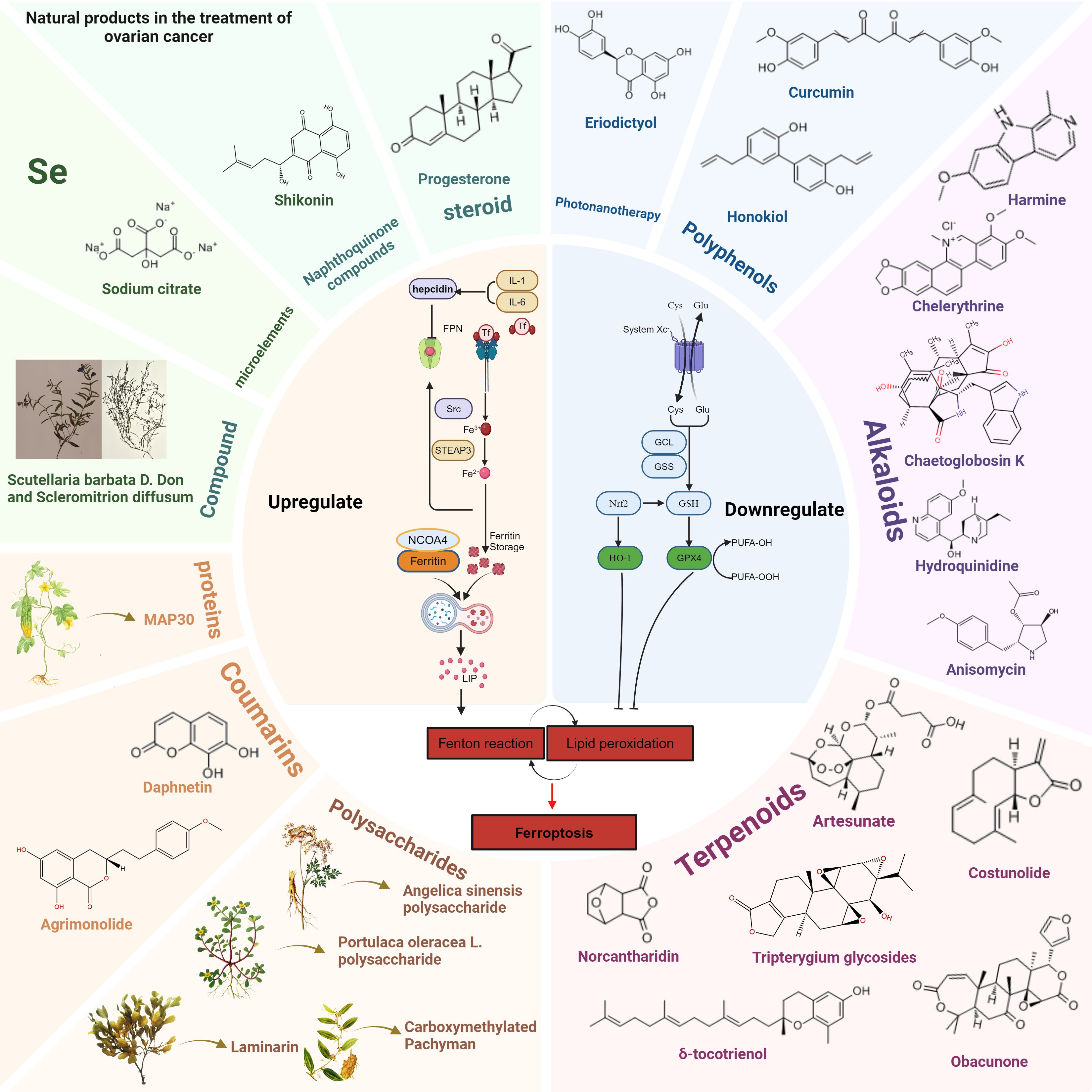
Figure 6. Natural products modulate ferroptosis in OC by upregulating or downregulating key molecular pathways. Natural compounds are categorized into different groups, including polyphenols, alkaloids, terpenoids, steroids, naphthoquinones, coumarins, polysaccharides, proteins, trace elements (Se), and traditional Chinese medicine (Scutellaria barbata D. Don and Scleromitrion diffusum). Left Panel: Compounds that upregulate ferroptosis, such as sodium citrate, shikonin, and progesterone, promote lipid peroxidation and Fenton reactions, increasing free iron and oxidative stress. Key proteins such as NCOA4 mediate ferritinophagy, leading to intracellular iron accumulation. Right Panel: Compounds that downregulate ferroptosis, such as curcumin, honokiol, and eriodictyol, act by enhancing antioxidant pathways. These include upregulation of GPX4, HO-1, and GSH metabolism, reducing lipid peroxidation and preventing ferroptotic cell death.
4.1 Combination drug therapy for OC
In recent years, OC treatment has increasingly focused on combination therapies, particularly the use of ferroptosis inducers alongside chemotherapy drugs. This approach has shown promise in enhancing treatment efficacy and overcoming drug resistance. For example, Battaglia et al. reported that Ferlixit can mitigate Erastin resistance by increasing intracellular iron levels, inducing mitochondrial dysfunction, and activating lipid peroxidation. Thus, the combination of Erastin and Ferlixit can synergistically enhance ferroptosis induction (82). The combination of Erastin and RSL3 significantly enhances cytotoxicity, particularly in multidrug-resistant and Ras-mutated OC cells, demonstrating strong therapeutic potential (143). Meanwhile, NRF2 and GPX4 play key roles in the antioxidant defense system of OC cells. Studies have shown that co-administering the NRF2 inhibitor ML85 with the GPX4 inhibitors RSL3 and ML210 induces lipid peroxidation and ROS accumulation, triggering both ferroptosis and apoptosis. This combination effectively inhibits OC cell growth and metastasis. Further animal studies confirm its efficacy in reducing abdominal implanted tumors, offering a promising strategy for OC treatment (144).Additionally, Eribulin, a non-taxane microtubule inhibitor widely used for advanced breast and OC, has shown effectiveness in patients resistant to other treatments. Research indicates that Eribulin induces ferroptosis in ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) cells by enhancing ROS generation, increasing intracellular iron levels, promoting lipid peroxidation, and inhibiting the NRF2-HO-1 antioxidant pathway. Furthermore, Eribulin exacerbates ferroptosis by disrupting mitochondrial function and reducing DHODH protein expression. Its combination with the GPX4 inhibitor ML210 further enhances its anti-tumor effects, presenting a potential therapeutic target for OCCC (145).
Targeting DNA repair pathways, the PARP inhibitor Olaparib has also shown potential in regulating ferroptosis. Hong T. et al. found that Olaparib suppresses SLC7A11 expression and reduces GSH synthesis, thereby promoting lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in OC. Further studies indicate that combining PARP inhibitors with ferroptosis inducers significantly enhances treatment sensitivity in BRCA wild-type OC (146). Additionally, the combination of Olaparib and arsenic trioxide (ATO) has been shown to enhance chemotherapy sensitivity in platinum-resistant OC by promoting both ferroptosis and apoptosis. Specifically, ATO strengthens Olaparib’s anti-cancer effects by activating the AMPK pathway and inhibiting SCD1, offering a promising combination therapy strategy to overcome platinum resistance (147). BRCA1 also enhances OC cell sensitivity to ferroptosis by promoting GPX4 degradation through K6-linked polyubiquitination. Conversely, BRCA1 deficiency leads to increased GPX4 levels, inhibiting ferroptosis and promoting tumor growth. In BRCA1-deficient OC cells, PARP inhibitors (PARPi) can induce ferroptosis, and their combination with GPX4 inhibitors exhibits significant synergistic anti-tumor effects. This approach presents a promising strategy for optimizing the treatment of BRCA1-deficient cancers (148). Additionally, in the context of drug resistance, HSP27 and fatty acid oxidation (FAO) reduce ROS levels induced by cisplatin, thereby inhibiting its cytotoxic effects in platinum-resistant OC. Studies have shown that combining ivermectin and perhexiline to inhibit HSP27 and FAO significantly enhances cisplatin’s effectiveness against drug-resistant OC cells. This finding suggests that targeting HSP27 and FAO could offer a promising strategy for overcoming drug resistance in OC treatment (149).
In summary, combining ferroptosis inducers with chemotherapy or targeted therapies can enhance the sensitivity of OC cells to treatment while overcoming drug resistance, offering new options for clinical management. However, further research is needed to evaluate the long-term effects, safety, and impact of these combination strategies on the tumor microenvironment. Such studies will help develop more precise and effective treatments for OC patients.
4.2 Development of new nanomedicines
The creation of medications based on nanomaterials has created new avenues for the treatment of OC in recent years. When paired with the ferroptosis process, nanomaterials can improve therapeutic efficacy and demonstrate great promise in targeted therapy. A promising new treatment approach for OC is provided by this combo.
Zhang, Y. et al. created the nanomedicine known as SPIO-Serum, which is made up of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles attached to human serum. By increasing iron absorption, causing mitochondrial damage, and causing lipid peroxidation, the nanoparticles dramatically increase ferroptosis in OC cells (150). This finding offers a fresh theoretical foundation for iron oxide nanomaterial-based OC treatment. Furthermore, Cheng, S. et al. created a novel ferroptosis inducer using an ultrasound-responsive Bi2MoO6-MXene (BMO-MXene) heterojunction. By increasing ROS production and suppressing GPX4 and SLC7A11 expression, BMO-MXene markedly increased ferroptosis in OC cells. Subsequent research revealed that BMO-MXene may stimulate immunogenic cell death (ICD) when ultrasound is applied, which would activate the tumor immune microenvironment and stop OC from growing (151). This research offers a novel approach to the accurate and non-invasive management of OC. Li, G. et al. created HA@PFG nanoparticles based on hyaluronic acid in another study. By releasing Fe³+ into the OC tumor microenvironment, these nanoparticles triggered ferroptosis by causing lipid peroxidation and GSH consumption (152). Furthermore, by targeting the highly expressed cholesterol receptor SR-B1 in OC cells, HDL-like nanoparticles (HDL NPs) caused lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis, which blocked cholesterol absorption and decreased GPX4 expression. HDL NPs can greatly increase the killing effect of chemotherapy-resistant OC cells when combined with chemotherapeutic medications (like carboplatin) (153). This study targets SR-B1 and cholesterol metabolism, offering a novel approach to treating OC.
Iron Nitroprusside (FeNP) is an iron-based self-therapeutic nanomaterial that exerts significant anti-tumor effects in OC by inducing ferroptosis and chemodynamic therapy (CDT). In the acidic lysosomal environment, FeNP releases Fe²+, which catalyzes the Fenton reaction, converting endogenous H2O2 into ·OH. This generates ROS and lipid peroxides, triggering ferroptosis. Additionally, FeNP disrupts redox homeostasis by inhibiting GPX4 expression, further promoting ferroptosis (154).The development of novel nanomedicines offers an innovative therapeutic strategy for treating OC.
4.3 Application of small molecule compounds
Since the mechanism of ferroptosis has been gradually revealed, the use of small molecule drugs in the treatment of OC has shown great promise, particularly in causing ferroptosis, which offers a novel approach to OC treatment.
Erastin is a classic ferroptosis inducer. According to research by Zhan, S. et al., Erastin induces ferroptosis in OC cells by inhibiting xCT transporters and inducing the accumulation of ROS, and significantly enhances the sensitivity of OC cells to chemotherapeutic drugs such as cisplatin (155). In addition, Cang, W. et al. found that Erastin induces TAMs to polarize to M2 phenotype by activating the STAT3 signaling pathway and secreting IL-8, which significantly enhances the migration and invasion ability of ferroptosis-resistant OC cells (156). ABCB1 is a drug efflux transporter, and its overexpression is closely related to multidrug resistance in OC. Erastin can also enhance the sensitivity of ABCB1-overexpressing OC cells to Docetaxel by inhibiting the drug efflux activity of ABCB1 (157). In recent years, sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4) has steadily gained attention because of its potential for treating cancer (158, 159). Mao, G. et al. showed that Na2MoO4 significantly induced ferroptosis of OC cells by increasing the level of LIP, promoting the production of NO, and depleting GSH (160). Based on ferroptosis, the novel small molecule USP2 inhibitor ML364 has demonstrated anti-tumor potential (161). Yang, D. et al.showed that ML364 significantly enhanced RSL3-induced ferroptosis by downregulating Cyclin D1 and increasing ROS levels, providing new ideas for the development of ferroptosis-based therapeutic strategies (162). Another novel small molecule compound, linoleic acid-glucosamine hybrid (LA-GlcN), has the ability to enter tumor cells and selectively recognize overexpressed glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), thereby inducing ferroptosis in HGSOC cells and offering a new approach to the precision treatment of high-grade serous OC (163). Mihajlović, E. et al. showed that FETPY, a novel diiron(I)sulfur-carbene complex, triggers ferroptosis in OC cells by promoting iron uptake and inducing membrane lipid peroxidation (164). Shen, X. et al. found that the platinum (II) complex PtQ induced ferroptosis in OC cells by downregulating the SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling axis and significantly enhancing lipid peroxidation and the accumulation of ROS (165). NTX-301 is a novel DNA demethylating agent. Wang, Y. et al. showed that NTX-301 enhances the ferroptosis sensitivity of OC cells by upregulating the expression of ACSL4. In addition, NTX-301 induces increased lipid peroxidation levels and further exacerbates cell ferroptosis by regulating iron metabolism-related genes (166). The identification of these small molecule compounds shows the potential clinical use of ferroptosis-based treatment for OC and offers a new anti-cancer method.
4.4 Increasing the usage of current medications
One of the key tactics in the treatment of cancer is the repurposing of current medications for new uses. A growing number of research have started to investigate the novel function of conventional medications in the treatment of cancer, particularly through the anti-tumor effects of ferroptosis, a novel mechanism of cell death (167, 168).
Ropivacaine is a local anesthetic drug that belongs to the amide anesthetic class. The amide anesthetic class includes the local anesthetic medication ropivacaine. Apart from its use in clinical anesthesia, research has demonstrated that ropivacaine causes ferroptosis by raising intracellular levels of ROS and free iron (Fe²+) and dramatically reduces the stemness of OC cells by blocking the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. In addition to preventing cancer cells from proliferating, this form of action may also successfully overcome tumor stem cell resistance to treatment. The anti-tumor activity of ropivacaine was further confirmed by in vivo tests, which offered a theoretical foundation for its use in the treatment of OC (169). Meanwhile, there has been modest advancement in the repurposing of other widely used medications for the treatment of tumors. For instance, the sedative dexmedetomidine has been shown to control immunological responses in the tumor microenvironment and may potentially influence pathways linked to ferroptosis by causing oxidative stress (170). Furthermore, recent research has demonstrated that some medicines, such doxycycline, can also cause ferroptosis by disrupting lipid metabolism or triggering oxidative stress pathways, offering a possible novel therapy approach for OC (171, 172). Future advancements in the treatment of OC are anticipated to come from the expansion of the use of current medications by focusing on ferroptosis.
4.5 Natural products in the treatment of OC via targeting ferroptosis
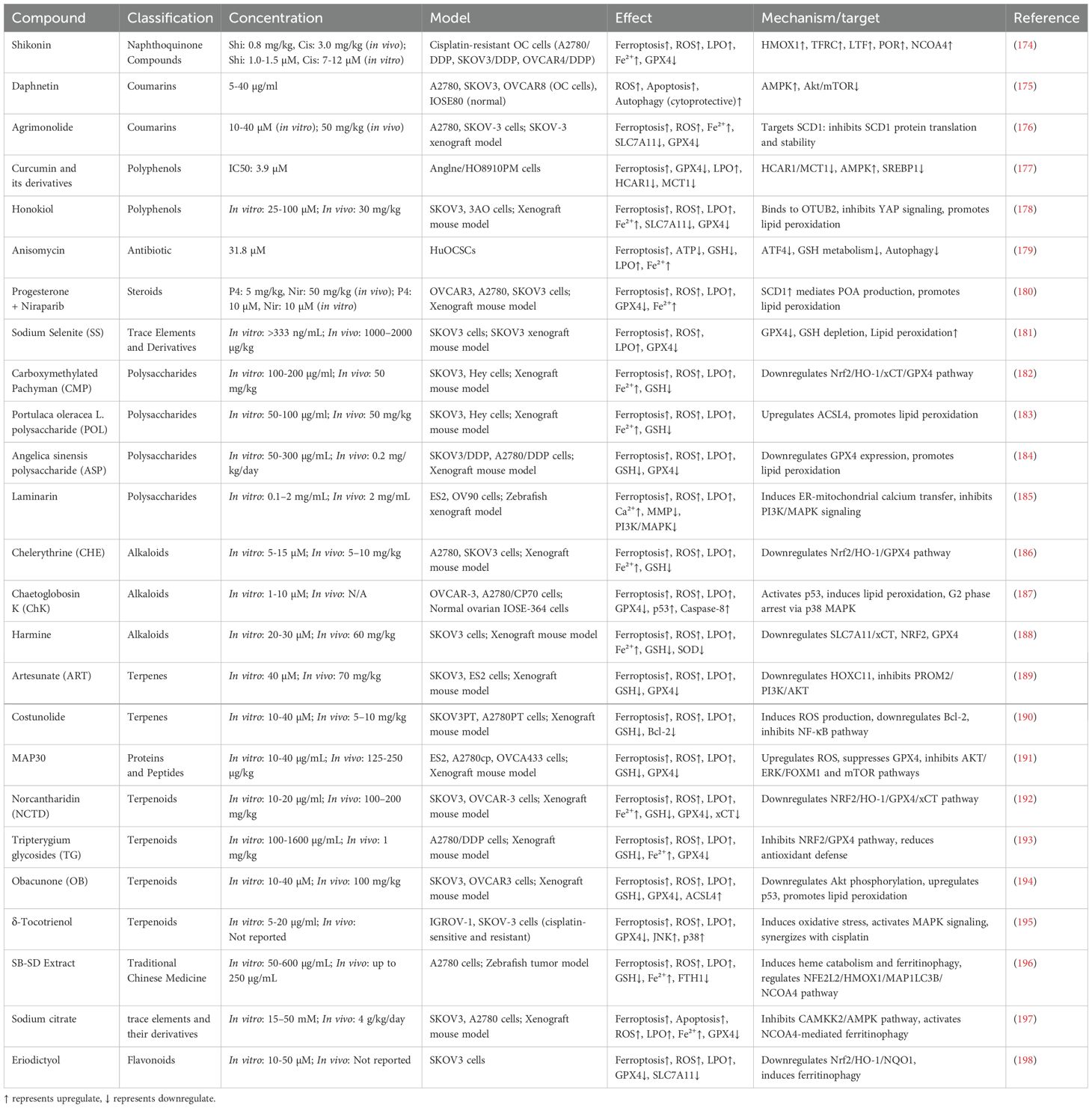
As is shown in Figure 6, in recent years, natural products have become an important direction in cancer treatment research due to their wide range of biological activities and low side effects (Table 1). Several studies have shown that natural products have the potential to regulate the expression levels of ferroptosis-related factors (173). Natural products in particular are considered to be a potentially effective therapy option for OC. In the treatment of OC, natural products can not only promote the death of cancer cells by promoting ferroptosis, but also enhance the sensitivity of cancer cells to ferroptosis, forming a synergistic effect with existing therapies (such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.), thereby improving the treatment effect.
In this review, we summarized the roles of several natural products, including flavonoids, polyphenols, alkaloids, terpenes, polysaccharides, coumarins, proteins and peptides, trace elements and their derivatives, Traditional Chinese Medicine, naphthoquinone compounds, steroid compounds, etc., in OC and the mechanisms by which they regulate ferroptosis-related pathways to achieve their anti-cancer effects. We also analyzed their potential clinical application prospects, providing a new perspective for the development and application of natural products in the treatment of OC.
4.5.1 Flavonoids
Eriodictyol is a natural flavonoid compound that regulates the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway, inhibits the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11, thereby significantly enhancing the levels of intracellular ROS and LPO, and ultimately inducing ferroptosis. In addition, eriodictyol promotes mitochondrial dysfunction and ferritinophagy, exacerbating oxidative stress and effectively inhibiting the proliferation of OC cells (such as SKOV3), and its ferroptosis effect can be reversed by Ferrostatin-1 (198).
4.5.2 Polyphenols
Curcumin is a natural polyphenolic compound derived from the rhizome of turmeric, which has been widely studied for cancer treatment in recent years (199). In an OC model, curcumin and its derivatives significantly induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the activity of GPX4 and downregulating the expression of key molecules such as MCT1 and HCAR1. Curcumin can enhance the generation of ROS and lipid peroxides, while causing lipid metabolism imbalance by inhibiting cellular antioxidant capacity. In addition, curcumin activated the AMPK signaling pathway and inhibited the SREBP1-mediated fatty acid synthesis pathway, further exacerbating the ferroptosis effect. In vivo studies have shown that the curcumin derivative NL01 can significantly inhibit the growth of OC transplanted tumors without causing obvious toxicity (177).
Honokiol is a biphenyl lignan extracted from the bark extract of Magnolia plant species, which has a wide range of antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, anti-aggregant, analgesic, antitumor, antiviral and neuroprotective activities (200). Honokiol inhibits the YAP signaling pathway by binding to the deubiquitinase OTUB2, significantly upregulating LPO and ROS, and inducing ferroptosis in OC cells. At the same time, Honokiol can reduce the expression of key antioxidant factors SLC7A11 and GPX4, further weakening the antioxidant capacity of tumor cells. Its in vivo experimental results show good safety and significant anti-tumor effects (178).
4.5.3 Alkaloids
Harmine is a natural alkaloid derived from the plant Peganum harmala, which has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anti-diabetic, anti-malarial, anti-depressant and significant anti-tumor effects (201). Harmine significantly reduces the risk of OC. Studies have shown that Harmine significantly induces ferroptosis in OC cells SKOV3 by downregulating ferroptosis inhibitors such as SLC7A11/xCT, NRF2, and GPX4, promoting Fe²+ accumulation, LPO, and ROS generation. Additionally, Harmine also leads to a decrease in GSH and SOD levels, further exacerbating oxidative damage (188).
Chelerythrine (CHE) is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid derived from plants. Studies have shown that CHE can trigger ferroptosis by downregulating the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 signaling pathway, reducing antioxidant defense capacity, and increasing lipid peroxidation and ROS accumulation. In addition, CHE significantly reduced intracellular GSH levels, accompanied by an increase in Fe²+. In vitro experiments showed that CHE could inhibit the proliferation of OC cells A2780 and SKOV3 and induce ferroptosis, while combined treatment with the Nrf2 activator TBHQ could reverse the CHE-induced ferroptosis effect. In vivo, CHE significantly inhibited tumor growth in the SKOV3 xenograft model and further enhanced the ferroptosis effect by inhibiting the expression of Nrf2 and related antioxidant proteins (186).
Anisomycin is an antibiotic purified from Streptomyces lividans and is a potential anticancer drug. Anisomycin weakens the cell’s ability to clear ROS and lipid peroxidation by inhibiting intracellular GSH levels and the activity of the key antioxidant enzyme GPX4, leading to the accumulation of lipid peroxides and the occurrence of cellular ferroptosis. In addition, Anisomycin can further aggravate the effects of ferroptosis by regulating the autophagy signaling pathway, and its mechanism of action is closely related to the inhibition of GSH metabolism mediated by ATF4. In the OC model, Anisomycin not only significantly promoted the accumulation of Fe²+, but also induced oxidative damage to cell membrane lipids, ultimately triggering ferroptosis signals (179).
Hydroquinidine (HQ) is a natural alkaloid derived from cinchona bark, which has significant anticancer effects in OC cells. HQ activates the oxidative stress pathway by inhibiting the expression of cell cycle-related proteins CDK1 and CDK6, significantly enhancing the apoptotic effect associated with ferroptosis. In addition, HQ can further aggravate the accumulation of intracellular lipid peroxides by reducing the expression level of GPX4 and inhibiting the activity of ferroportin. In SKOV-3 OC cells, HQ showed significant anti-proliferation, migration inhibition and apoptosis induction effects, and had low toxicity to normal cells, providing a new strategy for the treatment of OC (202).
Chaetoglobosin K (ChK) belongs to the class of natural products called mycotoxins and is also classified as an alkaloid, specifically an indole-diterpenoid alkaloid. This compound is extracted from fungi and has shown significant anticancer activity in platinum-resistant OC cells (203). ChK can inhibit cancer cell growth through multiple mechanisms, including inducing ferroptosis and apoptosis (204). Studies have shown that ChK triggers ferroptosis by downregulating the expression of the antioxidant factor GPX4 and increasing the levels of ROS and lipid peroxidation. In addition, ChK can further enhance cancer cell death by upregulating the p53 signaling pathway and activating the caspase-8-dependent extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments have shown that ChK has low toxicity to normal ovarian cells, showing good selectivity and therapeutic potential (187).
4.5.4 Terpenoids
Artesunate (ART) is a well-tolerated antimalarial drug and a potential anti-OC drug that induces ferroptosis (205). Artesunate has been widely studied. Studies have shown that (206) ART inhibits the transcription factor HOXC11, reduces the activity of the downstream PROM2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, significantly induces lipid peroxidation and ROS production, and reduces GSH levels, thereby triggering ferroptosis. In addition, ART further aggravates oxidative damage by inhibiting the expression of GPX4. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments have shown that ART significantly inhibits the proliferation, migration and growth of OC cells, and its effect of inducing ferroptosis can be partially reversed by overexpression of HOXC11 (189).
Costunolide is a natural sesquiterpene lactone compound that has shown significant inhibitory effects on platinum-resistant OC cells in research. Costunolide significantly increases the generation of ROS while reducing the level of antioxidant factor GSH, triggering lipid peroxidation and leading to cell death. Its induced ferroptosis mechanism is achieved by downregulating Bcl-2 protein, enhancing mitochondrial membrane permeability and inhibiting NF-κB pathway. In addition, costunolide also exhibits synergistic effects with cisplatin, effectively overcoming the chemotherapy barriers of platinum-resistant OC by promoting the accumulation of ROS and increasing the sensitivity of cells to cisplatin (190).
Obacunone (OB) is a natural bioactive compound extracted from citrus fruits. OB activates the Akt/p53 signaling pathway by downregulating Akt phosphorylation and upregulating p53 expression, thereby promoting iron-dependent lipid peroxidation and ROS production and inducing ferroptosis in OC cells. In addition, OB significantly reduces the levels of GSH and GPX4, while upregulating the expression of ACSL4, further enhancing the ferroptosis effect (194).
Norcantharidin (NCTD) is an effective anticancer drug. Studies have shown that NCTD is a potential anti-OC therapeutic agent, and its mechanism of action depends on the regulation of the NRF2/HO-1/GPX4/xCT axis, thereby promoting the accumulation of ROS, lipid peroxidation and Fe²+, inducing OC cell death. In vivo and in vitro experiments, NCTD not only significantly reduced the survival rate of OC cells, but also inhibited the growth of transplanted tumors, while significantly increasing the levels of ferroptosis-related markers MDA and PTGS2 (192).
Tripterygium glycosides (TG) is an active ingredient extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Tripterygium wilfordii, which has anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and anti-cancer effects. Studies have shown that TG induces ferroptosis by regulating the NRF2/GPX4 signaling axis. TG treatment can significantly promote the accumulation of ROS and lipid peroxidation, while exacerbating the depletion of GSH and increasing the concentration of intracellular Fe²+. Studies have also shown that when TG is used in combination with cisplatin, it can significantly enhance the toxicity of cisplatin to drug-resistant OC cells (such as A2780/DDP) through a synergistic effect. In vivo studies have shown that TG alone or in combination with cisplatin significantly inhibited the growth of transplanted tumors and prolonged the survival time of tumor-bearing mice without showing obvious toxic side effects (193). Tripterygium wilfordii glycosides provide a potential new strategy for the treatment of OC resistance.
δ-Tocotrienol is a natural derivative of vitamin E and a type of terpenoid. δ-Tocotrienol is widely found in plants and exhibits unique antioxidant and anti-tumor activities. Studies have shown that δ-tocotrienol effectively inhibits the growth of OC cells (OC) by inducing ferroptosis. In addition, δ-tocotrienol activated JNK and p38 protein phosphorylation in the MAPK signaling pathway, further enhancing the oxidative stress-induced cell death response. In cisplatin-resistant OC cells (such as SKOV-3), δ-tocotrienol not only significantly reduced cell proliferation, but also synergized with cisplatin treatment to significantly improve the anti-cancer effect (195).
4.5.5 Polysaccharides
Carboxymethylated Pachyman (CMP) is a polysaccharide derivative derived from Poria cocos. CMP weakens the antioxidant defense capacity of tumor cells by downregulating the Nrf2/HO-1/xCT/GPX4 signaling pathway, thereby inducing lipid peroxidation and ROS accumulation, and ultimately leading to ferroptosis. In vitro studies have shown that CMP significantly reduced GSH levels and increased the accumulation of Fe²+ and MDA in SKOV3 and Hey OC cells. At the same time, CMP significantly upregulated the expression of ferroptosis marker genes PTGS2 and CHAC1, and this effect could be reversed by the ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1. In vivo, CMP significantly inhibited the growth of OC xenografts and reduced the expression levels of Nrf2, HO-1, xCT and GPX4 in tumor tissues (182).
Purslane polysaccharide is a natural polysaccharide derived from Purslane. Studies have shown that POL can significantly upregulate the expression of ACSL4, promote the accumulation of lipid peroxidation, ROS and Fe²+, and reduce the level of GSH, thereby inducing ferroptosis. In addition, the survival rate of OC cells decreased significantly after POL treatment, while the ferroptosis inhibitors Ferrostatin-1 and Deferoxamine were able to reverse this phenomenon, further proving that POL induces cell death through iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. In vivo studies also confirmed that POL can significantly inhibit the growth of OC xenografts, as manifested by a decrease in tumor volume and weight, and a significant increase in ACSL4, MDA and ROS levels in tumor tissues (183).
Angelica sinensis polysaccharide (ASP) is derived from the traditional Chinese medicine Angelica sinensis. Studies by Guo W et al. have shown that ASP significantly downregulates the expression level of the key antioxidant factor GPX4, weakens the antioxidant capacity of tumor cells, promotes the accumulation of ROS and lipid peroxidation, and thus enhances the ferroptosis effect. In addition, ASP exhibits a synergistic effect when used in combination with cisplatin, significantly inhibiting the proliferation, migration and invasion of cisplatin-resistant OC cells (such as SKOV3/DDP and A2780/DDP), while significantly increasing their apoptosis levels. In vivo studies have shown that the combination of ASP and cisplatin can significantly inhibit the growth of transplanted tumors, while having no obvious toxicity to normal tissues and organs, showing a good safety profile (184).
Laminarin is a natural polysaccharide derived from brown algae that achieves anti-cancer effects by inducing ferroptosis. Laminarin induces intracellular Ca²+ accumulation and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential by regulating the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial axis-related proteins GRP75 and MFN2, significantly increasing ROS and lipid peroxidation levels. In addition, Laminarin also significantly reduces the proliferation ability of OC cells by inhibiting the phosphorylation of the PI3K/MAPK signaling pathway, and induces the synergistic effect of apoptosis and ferroptosis. In animal experiments, Laminarin showed significant anti-tumor activity in the zebrafish transplant tumor model, and no obvious toxicity was observed (185).
4.5.6 Coumarins
Daphnetin is a natural coumarin compound. Ma N et al. showed that Daphnetin can inhibit NQO1 activity, leading to intracellular iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, thereby activating ferroptosis, a non-apoptotic cell death pathway (207). Fan X et al.’s research showed that Daphnetin can also trigger cell death by inducing the generation of ROS and induce protective autophagy by regulating the AMPK/Akt/mTOR pathway (175). Ferroptosis mechanism provides theoretical support for the potential application of Daphnetin in the treatment of OC.
Agrimonolide is a natural isocoumarin product derived from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb and has multiple functional activities (208). Liu Y et al.’s study showed that vanilloids significantly induced ferroptosis in OC cells A2780 and SKOV-3 by targeting and inhibiting the expression of SCD1. Specifically, vanilloids treatment increased intracellular ROS, total iron, and Fe²+ levels, and reduced the expression of ferroptosis marker proteins SLC7A11 and GPX4. SCD1 overexpression can significantly reverse the ferroptosis effect induced by vanilloids. In in vivo studies, vanilloids inhibited the growth of OC xenografts in a dose-dependent manner, while reducing the expression level of SCD1 in tumor tissues (176).
4.5.7 Protein and peptide compounds
Momotarin (MAP30) is a natural active protein extracted from the seeds of Momordica charantia, which has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-obesity and immunomodulatory activities (209). Momordica protein is a potential drug for adjuvant therapy of OC (210). Research by Chan DW et al. showed that (191)MAP30 significantly increased the Ca²+ concentration in OC cells. This change led to oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, further inducing the accumulation of ROS and lipid peroxidation. The experiment also found that the ferroptosis-inducing effect of MAP30 could be partially reversed by the ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1. In addition, MAP30 can significantly inhibit the proliferation and migration of OC cells by inhibiting the AKT/ERK/FOXM1 and mTOR signaling pathways. MAP30 is a safe and effective natural product that can be used as a potential drug for the adjuvant treatment of OC.
4.5.8 Trace elements and their derivatives
Sodium citrate is a naturally derived citrate. Sodium citrate chelates intracellular Ca²+, significantly reducing Ca²+ concentrations, thereby inhibiting the activity of the Ca²+/CAMKK2/AMPK signaling pathway. On the one hand, this mechanism induces cell apoptosis by inhibiting the HIF1α-dependent glycolysis pathway; on the other hand, sodium citrate triggers ferroptosis by activating NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy, leading to iron ion (Fe²+) accumulation and increased lipid peroxidation levels. Studies have also found that sodium citrate can significantly enhance the sensitivity of OC cells to chemotherapeutic drugs, especially cisplatin and carboplatin (197).
Selenium (Se) is a trace element widely present in the natural environment and is also one of the important components of natural products. Studies have shown that high-dose sodium selenite (SS) significantly induces ferroptosis of OC cells by promoting ROS generation, weakening GPX4 expression, and inducing lipid peroxidation. In addition, in vivo experiments have verified that high-dose Se can significantly inhibit the growth of SKOV3 xenograft tumors and exhibit tumor-specific toxicity (181).
4.5.9 Traditional Chinese medicine
Scutellaria barbata D. Don and Scleromitrion diffusum (SB-SD) is a traditional Chinese medicine combination for the treatment of OC. SB-SD extract significantly increases intracellular free iron (Fe²+),ROS, and lipid peroxidation levels by promoting heme catabolism and ferritinophagy, while reducing GSH and mitochondrial membrane potential, ultimately leading to cell death. Multi-omics analysis found that SB-SD forms a complex ferroptosis regulatory network by upregulating the expression of NFE2L2, HMOX1, MAP1LC3B, and NCOA4, and downregulating the expression of FTH1. In addition, the anti-tumor effect of SB-SD has been verified in both in vivo (zebrafish tumor model) and in vitro experiments. SB-SD is a potential natural anti-cancer treatment option (196).
4.5.10 Naphthoquinones
Shikonin is a natural naphthoquinone compound derived from Lithospermum erythrorhizon. Studies have shown that shikonin can effectively overcome the resistance of OC to cisplatin by inducing ferroptosis. In cisplatin-resistant OC cells (such as A2780/DDP, SKOV3/DDP, and OVCAR4/DDP), the combination of shikonin and cisplatin significantly enhanced the level of cellular ferroptosis, including ROS generation, lipid peroxidation accumulation, and increased Fe²+. Its mechanism of action is related to the upregulation of HMOX1, which produces Fe²+ by promoting heme degradation, thereby exacerbating ROS generation and lipid peroxidation. In addition, shikonin also regulates the expression levels of other ferroptosis-related proteins (such as TFRC, LTF, POR, NCOA4) and key enzymes (such as GPX4) (174).
4.5.11 Steroids
Progesterone is derived from steroidal natural products and is usually produced in vivo through cholesterol metabolism. Progesterone significantly promotes ferroptosis of OC cells by enhancing the production of POA and lipid oxidation. Studies have shown that progesterone can activate the expression of SCD1, a gene related to fatty acid metabolism, increase the expression of GPX4, and weaken the cell’s ability to clear lipid peroxides. In addition, progesterone combined with the PARP inhibitor Niraparib can further enhance DNA damage, leading to increased ROS and aggravated ferroptosis. In vivo studies have shown that this combined treatment can significantly inhibit the growth of OC transplanted tumors and prolong the survival of mice (180).
5 Limitations and considerations for future research directions
Ferroptosis is a regulated form of cell death characterized by iron accumulation and uncontrolled lipid peroxidation. This leads to plasma membrane disruption and the release of intracellular contents. Initially studied as a targeted therapy for cancer cells with oncogenic RAS mutations, ferroptosis induction now shows potential to complement chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy in various cancer types. However, it can cause side effects, including immune cell death, bone marrow damage, liver and kidney damage, cachexia (severe weight loss and muscle wasting), and secondary tumorigenesis (211). Currently, most studies on ferroptosis focus on animal models and cell lines, and there are significant differences between different species. Although mouse models and human cell lines provide preliminary evidence for the potential of ferroptosis in the treatment of OC, there is still uncertainty as to whether their results can accurately reflect the clinical situation of human patients. For example, the expression levels and mechanisms of key molecules in the ferroptosis pathway, such as FSP1 and GPX4, may vary between species (212–214). Therefore, validation using more clinically relevant animal models and human samples is critical in future studies.
Although some laboratory research progress has been made in ferroptosis as a new target for the treatment of OC, there are still challenges in translating these findings into effective clinical treatments. The regulatory pathways of ferroptosis are relatively complex and may involve multiple cross-signaling pathways, such as ROS generation, lipid peroxidation, autophagy, inflammatory response, etc. In clinical studies, the regulation of these mechanisms may be affected by factors such as individual differences among patients and tumor heterogeneity. Therefore, future studies need more clinical data to verify the actual effect of ferroptosis-targeted therapy and optimize treatment strategies. Ferroptosis is not an isolated cell death pathway. Studies have found that it interacts with other cell death pathways such as apoptosis, necrosis, and pyroptosis (97). For example, ferroptosis may work together with apoptosis pathways or be regulated by other cell death pathways in some cases. Therefore, future studies need to explore the interactions between these cell death pathways in more depth and consider jointly targeting multiple cell death pathways to improve the therapeutic effect. Although targeted therapy for ferroptosis has shown potential in laboratory studies, OC cells may develop resistance in clinical treatment. The resistance mechanism may be related to factors such as the regulation of key molecules in the ferroptosis pathway, the balance of ROS generation, and changes in iron metabolism. Future studies need to reveal the resistance mechanism associated with ferroptosis and explore how to overcome this resistance to achieve more lasting therapeutic effects. Individual differences in ferroptosis regulation may affect its effectiveness as a therapeutic target. Different OC patients may respond differently to ferroptosis inducers due to differences in gene mutations, tumor microenvironment, immune response, and other factors. Therefore, the development of personalized treatment strategies is critical. Future studies can explore the use of multidimensional data such as genomics and proteomics to analyze the response of OC patients to ferroptosis therapy, so as to develop personalized treatment plans.
At present, drug development for ferroptosis is still in its infancy, and the development of targeted drugs is progressing slowly. The diversity and complexity of ferroptosis regulatory molecules pose huge challenges to drug development. Future research should focus on developing more efficient and selective ferroptosis inducers and solving problems such as drug biocompatibility, dose control, and targeting. In clinical applications, physiological conditions such as liver and kidney function of patients should also be considered to avoid treatment-related side effects. Although ferroptosis, as an emerging target for the treatment of OC, has been supported by laboratory and small-scale preclinical studies, it is still necessary to verify its efficacy and safety in extensive clinical trials. Large-scale, long-term clinical trials are needed in the future to evaluate the true effect of ferroptosis-targeted therapy in the treatment of OC and provide strong data support for drug approval.
6 Discussions
This review systematically summarizes the research progress on ferroptosis in OC treatment, focusing particularly on its potential to overcome chemotherapy resistance and enhance treatment efficacy. Targeting ferroptosis can effectively inhibit the growth, metastasis, and drug resistance of OC cells, while improving chemotherapy outcomes. Ferroptosis plays a crucial role in the onset, progression, and metastasis of OC. OC cells often have a high dependence on iron metabolism, which makes them more prone to ferroptosis than normal cells. Key mechanisms of ferroptosis include lipid peroxidation, ROS accumulation, and membrane rupture. Molecular pathways such as GPX4, SLC7A11, and ACSL4 are central in regulating this process. By targeting these key molecules, and by modulating iron metabolism and antioxidant defense systems, ferroptosis can be induced directly to kill OC cells and overcome chemotherapy resistance. Research on natural products, small molecule compounds, and novel nanomedicines has opened new avenues for clinical ferroptosis application. Natural products like rutin, curcumin, and magnolol can induce ferroptosis and enhance OC cells’ sensitivity to chemotherapy by regulating antioxidant factors and lipid metabolism. Small molecules, such as Erastin and RSL3, further promote ferroptosis by inhibiting critical factors like GPX4 and SLC7A11. The development of novel nanomedicines offers targeted treatment options, especially in combination with ferroptosis mechanisms, to improve treatment efficacy and overcome drug resistance.
Despite its promising potential, ferroptosis-based therapy faces several challenges. First, efficient induction of ferroptosis still suffers from selectivity issues. While ferroptosis can selectively target tumor cells, the lack of fully specific ferroptosis inducers remains a limitation. Ensuring accurate control over ferroptosis induction and minimizing damage to normal tissues is an ongoing challenge. Second, individual variation in iron metabolism, antioxidant capacity, and ferroptosis sensitivity among OC patients complicates the individualized regulation of ferroptosis-related molecules. As a result, future ferroptosis therapies will need more personalized approaches. Moreover, optimizing the combination of ferroptosis inducers with other treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies, warrants further investigation. Future research should focus on the following areas: first, deepen understanding of ferroptosis regulation to improve its selectivity and therapeutic effectiveness; second, develop more selective ferroptosis inducers and explore their combination with existing chemotherapy or targeted therapies; third, identify biomarkers for ferroptosis-related molecules to guide individualized treatment strategies; last but not least, investigate the synergistic effects of ferroptosis with other treatments, such as immunotherapy and radiotherapy, to provide more comprehensive treatment options for OC.
In conclusion, ferroptosis represents a promising therapeutic target for OC, with great potential for clinical application. By advancing our understanding of its mechanisms, developing more selective ferroptosis inducers, and optimizing combination therapies, we hope to provide OC patients with more precise and effective treatment options in the future.
Author contributions
XW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QL: Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GW: Writing – review & editing. LL: Writing – original draft. XY: Writing – original draft. MX: Writing – review & editing. HS: Writing – original draft. QL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Hunan Provincial Health and Health High-level Talent Major Scientific Research Project (R2023168); Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2022JJ30035); Hunan Provincial Health Commission Scientific Research Project Key Guidance Project (C202305017379); Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Graduate Innovation Project(2023CX28, 2023CX107);Hunan Province College Students Innovation Training Program General Project (S202410541102).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the BioRender (www.biorender.com), as figures in this review were created with the BioRender platform.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
OC, Ovarian cancer; GSH, Glutathione; GCL, Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase; GSS, Glutathione Synthetase; SLC7A11, Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11; SLC3A2, Solute Carrier Family 3 Member 2; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; PLs, Phospholipids; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; PLOOHs, phospholipid peroxides; PLOHs, phospholipid alcohols; FSP1, Ferroptosis Suppressor Protein 1; P450, Cytochrome P450; RTAs, reactive antioxidants; MUFA, Monounsaturated Fatty Acid; SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase; ACSL3, Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long-Chain Family Member 3; MDA, Malondialdehyde; CoQ10, Coenzyme Q10; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; POR, Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase; Nrf2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; FTH1, ferritin heavy chain 1; NQO1, quinone oxidoreductase 1; CHE, Chelerythrine; MDR, multidrug resistance; HIPEC, Hyperthermic intraperitoneal peroperative chemotherapy; VEGF, Vascular endothelial growth factor; BEV, bevacizumab; SPIO, superparamagnetic iron oxide; TFR1, Transferrin Receptor 1; FPN, ferroportin; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase4; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; GCH1, GTP cyclohydrolase 1; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; SAS, Sulfasalazine; DMT1, Divalent metal transporter 1; LIP, labile iron pool; TF, transferrin; STEAP, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate; NTBI, non-transferrin-bound iron; SLC39A14, metal transport proteins; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; ERS, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress; IRE, Iron responsive element; IRP, Iron responsive protein.
References
1. Webb PM and Jordan SJ. Global epidemiology of epithelial ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2024) 21:389–400. doi: 10.1038/s41571-024-00881-3
2. Rodriguez IV, Ghezelayagh T, Pennington KP, and Norquist BM. Prevention of ovarian cancer: where are we now and where are we going? Curr Oncol Rep. (2024) 26:1355–66. doi: 10.1007/s11912-024-01587-6
3. Webb PM, Green AC, and Jordan SJ. Trends in hormone use and ovarian cancer incidence in US white and Australian women: implications for the future. Cancer Causes Control CCC. (2017) 28:365–70. doi: 10.1007/s10552-017-0868-0
4. Mize BK, Salvi A, Ren Y, Burdette JE, and Fuchs JR. Discovery and development of botanical natural products and their analogues as therapeutics for ovarian cancer. Nat Prod Rep. (2023) 40:1250–70. doi: 10.1039/d2np00091a
5. Li X, Li Z, Ma H, Li X, Zhai H, Li X, et al. Ovarian cancer: Diagnosis and treatment strategies (Review). Oncol Lett. (2024) 28:441. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14574
6. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
7. Grzelak MM, Chmura Ł, Wróbel PM, Adamek D, Lankosz M, Jach R, et al. Investigation of the role and chemical form of iron in the ovarian carcinogenesis process. J Trace Elem Med Biol. (2020) 60:126500. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126500
8. Hou K, Liu L, Fang Z-H, Zong W-X, Sun D, Guo Z, et al. The role of ferroptosis in cardio-oncology. Arch Toxicol. (2024) 98:709–34. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03665-3
9. Bhatia T, Doshi G, and Godad A. PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer: Mechanisms, resistance, and the promise of combination therapy. Pathol - Res Pract. (2024) 263:155617. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155617
10. Huang Z, Ma Y, Sun Z, Cheng L, and Wang G. Ferroptosis: potential targets and emerging roles in pancreatic diseases. Arch Toxicol. (2024) 98:75–94. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03625-x
11. Ćwiertnia A, Kozłowski M, and Cymbaluk-Płoska A. The role of iron and cobalt in gynecological diseases. Cells. (2022) 12:117. doi: 10.3390/cells12010117
12. Wang Y, Wu X, Ren Z, Li Y, Zou W, Chen J, et al. Overcoming cancer chemotherapy resistance by the induction of ferroptosis. Drug Resist Update. (2023) 66:100916. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2022.100916
13. Nie Z, Chen M, Gao Y, Huang D, Cao H, Peng Y, et al. Ferroptosis and tumor drug resistance: current status and major challenges. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:879317. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.879317
14. Lu B, Chen XB, Ying MD, He QJ, Cao J, and Yang B. The role of ferroptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Front Pharmacol. (2018) 8:992. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00992
15. Ren Y, Mao X, Xu H, Dang Q, Weng S, Zhang Y, et al. Ferroptosis and EMT: key targets for combating cancer progression and therapy resistance. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2023) 80:263. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04907-4
16. Zuo S, Yu J, Pan H, and Lu L. Novel insights on targeting ferroptosis in cancer therapy. biomark Res. (2020) 8:50. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00229-w
17. Li D, Geng D, and Wang M. Advances in natural products modulating autophagy influenced by cellular stress conditions and their anticancer roles in the treatment of ovarian cancer. FASEB J. (2024) 38:e70075. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401409R
18. Zhang X, Wei X, Shi L, Jiang H, Ma F, Li Y, et al. The latest research progress: Active components of traditional Chinese medicine as promising candidates for ovarian cancer therapy. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 337:118811. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118811
19. Zhou J, Jiang Y-Y, Wang H-P, Chen H, Wu Y-C, Wang L, et al. Natural compound Tan-I enhances the efficacy of Paclitaxel chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. Ann Transl Med. (2020) 8:752–2. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4072
20. Zhou L, Xu T, Zhang Y, Zhu M, Zhu W, Wang Z, et al. Transcriptional network in ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3 treated with pinellia pedatisecta schott extract. Oncol Rep. (2016) 36:462–70. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4779
21. Zhou J, Jiang Y-Y, Wang X-X, Wang H-P, Chen H, Wu Y-C, et al. Tanshinone IIA suppresses ovarian cancer growth through inhibiting Malignant properties and angiogenesis. Ann Transl Med. (2020) 8:1295–5. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5741
22. Dixon SJ and Stockwell BR. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol. (2014) 10:9–17. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1416
23. Gaschler MM and Stockwell BR. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 482:419–25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086
25. Spector AA and Kim H-Y. Discovery of essential fatty acids. J Lipid Res. (2015) 56:11–21. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R055095
26. Sies H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. (2015) 4:180–3. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.002
27. Forman HJ and Zhang H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:689–709. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
28. Yang WS and Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis: Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. (2016) 26:165–76. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014
29. Stockwell BR and Jiang X. The chemistry and biology of ferroptosis. Cell Chem Biol. (2020) 27:365–75. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.03.013
30. Yang S, Hu C, Chen X, Tang Y, Li J, Yang H, et al. Crosstalk between metabolism and cell death in tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:71. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01977-1
31. Jiang X, Stockwell BR, and Conrad M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 22:266–82. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
32. Li D, Zhang M, and Chao H. Significance of glutathione peroxidase 4 and intracellular iron level in ovarian cancer cells-”utilization” of ferroptosis mechanism. Inflammation Res Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc Al. (2021) 70:1177–89. doi: 10.1007/s00011-021-01495-6
33. Chen F, Kang R, Tang D, and Liu J. Ferroptosis: principles and significance in health and disease. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. (2024) 17:41. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01564-3
34. Endale HT, Tesfaye W, and Mengstie TA. ROS induced lipid peroxidation and their role in ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2023) 11:1226044. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1226044
35. Li R, Yuan H, Zhang C, Han D, Wang Y, and Feng L. Induced ferroptosis pathway by regulating cellular lipid peroxidation with peroxynitrite generator for reversing “cold” tumors. Small Weinh Bergstr Ger. (2024) 20:e2404807. doi: 10.1002/smll.202404807
36. Wang B, Wang Y, Zhang J, Hu C, Jiang J, Li Y, et al. ROS-induced lipid peroxidation modulates cell death outcome: Mechanisms behind apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Arch Toxicol. (2023) 97:1439–51. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03476-6
37. Akiyama H, Carter BZ, Andreeff M, and Ishizawa J. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and updates of ferroptosis studies in cancers and leukemia. Cells. (2023) 12:1128. doi: 10.3390/cells12081128
38. Pope LE and Dixon SJ. Regulation of ferroptosis by lipid metabolism. Trends Cell Biol. (2023) 33:1077–87. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.05.003
39. Lu C, Zhou X, and Zhang L. Phospholipids with two polyunsaturated fatty acyl tails: An important driver of ferroptosis. MedComm. (2024) 5:e606. doi: 10.1002/mco2.606
40. Qiu B, Zandkarimi F, Bezjian CT, Reznik E, Soni RK, Gu W, et al. Phospholipids with two polyunsaturated fatty acyl tails promote ferroptosis. Cell. (2024) 187:1177–1190.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.030
41. Liu J, Kang R, and Tang D. Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. FEBS J. (2022) 289:7038–50. doi: 10.1111/febs.16059
42. Lin J, Lai Y, Lu F, and Wang W. Targeting ACSLs to modulate ferroptosis and cancer immunity. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2024.09.003
43. Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, et al. Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. (2017) 171:273–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
44. Cui J, Wang Y, Tian X, Miao Y, Ma L, Zhang C, et al. LPCAT3 is transcriptionally regulated by YAP/ZEB/EP300 and collaborates with ACSL4 and YAP to determine ferroptosis sensitivity. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2023) 39:491–511. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0237
45. Mashima R and Okuyama T. The role of lipoxygenases in pathophysiology; new insights and future perspectives. Redox Biol. (2015) 6:297–310. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.006
46. Pandey AV and Flück CE. NADPH P450 oxidoreductase: Structure, function, and pathology of diseases. Pharmacol Ther. (2013) 138:229–54. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.01.010
47. Zou Y, Li H, Graham ET, Deik AA, Eaton JK, Wang W, et al. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase contributes to phospholipid peroxidation in ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. (2020) 16:302–9. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0472-6
48. Kraft VAN, Bezjian CT, Pfeiffer S, Ringelstetter L, Müller C, Zandkarimi F, et al. GTP cyclohydrolase 1/tetrahydrobiopterin counteract ferroptosis through lipid remodeling. ACS Cent Sci. (2020) 6:41–53. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b01063
49. Vasquez-Vivar J, Shi Z, and Tan S. Tetrahydrobiopterin in cell function and death mechanisms. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2022) 37:171–83. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0136
50. Patanè GT, Putaggio S, Tellone E, Barreca D, Ficarra S, Maffei C, et al. Ferroptosis: Emerging role in diseases and potential implication of bioactive compounds. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:17279. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417279
51. Dlouhy AC, Bailey DK, Steimle BL, Parker HV, and Kosman DJ. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer links membrane ferroportin, hephaestin but not ferroportin, amyloid precursor protein complex with iron efflux. J Biol Chem. (2019) 294:4202–14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005142
52. Cao H, Schroeder B, Chen J, Schott MB, and McNiven MA. The endocytic fate of the transferrin receptor is regulated by c-abl kinase. J Biol Chem. (2016) 291:16424–37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.724997
53. Oosterheert W, van Bezouwen LS, Rodenburg RNP, Granneman J, Förster F, Mattevi A, et al. Cryo-EM structures of human STEAP4 reveal mechanism of iron(III) reduction. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:4337. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06817-7
54. Torti SV, Manz DH, Paul BT, Blanchette-Farra N, and Torti FM. Iron and cancer. Annu Rev Nutr. (2018) 38:97–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-082117-051732
55. Habashy HO, Powe DG, Staka CM, Rakha EA, Ball G, Green AR, et al. Transferrin receptor (CD71) is a marker of poor prognosis in breast cancer and can predict response to tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2010) 119:283–93. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0345-x
56. Katsarou A and Pantopoulos K. Basics and principles of cellular and systemic iron homeostasis. Mol Aspects Med. (2020) 75:100866. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2020.100866
57. Brookes MJ, Hughes S, Turner FE, Reynolds G, Sharma N, Ismail T, et al. Modulation of iron transport proteins in human colorectal carcinogenesis. Gut. (2006) 55:1449–60. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.094060
58. Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, and Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:280–96. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00462-0
59. Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J, He D, Zhang C, Duan C, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: Opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. (2019) 12:34. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0720-y
60. Lyamzaev KG, Huan H, Panteleeva AA, Simonyan RA, Avetisyan AV, and Chernyak BV. Exogenous iron induces mitochondrial lipid peroxidation, lipofuscin accumulation, and ferroptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:730. doi: 10.3390/biom14060730
61. Kang R, Kroemer G, and Tang D. The tumor suppressor protein p53 and the ferroptosis network. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 133:162–8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.05.074
62. Fantone S, Piani F, Olivieri F, Rippo MR, Sirico A, Di Simone N, et al. Role of SLC7A11/xCT in ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:587. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010587
63. Ou Y, Wang S-J, Li D, Chu B, and Gu W. Activation of SAT1 engages polyamine metabolism with p53-mediated ferroptotic responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2016) 113:E6806–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1607152113
64. Xu R, Wang W, and Zhang W. Ferroptosis and the bidirectional regulatory factor p53. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:197. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01517-8
65. Chen D, Chu B, Yang X, Liu Z, Jin Y, Kon N, et al. iPLA2β-mediated lipid detoxification controls p53-driven ferroptosis independent of GPX4. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3644. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23902-6
66. Li J-Y, Feng Y-H, Li Y-X, He P-Y, Zhou Q-Y, Tian Y-P, et al. Ferritinophagy: A novel insight into the double-edged sword in ferritinophagy-ferroptosis axis and human diseases. Cell Prolif. (2024) 57:e13621. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13621
67. Huang G, Cai Y, Ren M, Zhang X, Fu Y, Cheng R, et al. Salidroside sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to ferroptosis by SCD1-mediated lipogenesis and NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy. J Adv Res. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.09.027
68. Zhou B, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, and Tang D. Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. (2020) 66:89–100. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.03.002
69. Liu M, Fan Y, Li D, Han B, Meng Y, Chen F, et al. Ferroptosis inducer erastin sensitizes NSCLC cells to celastrol through activation of the ROS-mitochondrial fission-mitophagy axis. Mol Oncol. (2021) 15:2084–105. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12936
70. Lee S, Hwang N, Seok BG, Lee S, Lee S-J, and Chung SW. Autophagy mediates an amplification loop during ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:464. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05978-8
71. Lee Y-S, Lee D-H, Choudry HA, Bartlett DL, and Lee YJ. Ferroptosis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res MCR. (2018) 16:1073–6. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0055
72. Ji X, Chen Z, Lin W, Wu Q, Wu Y, Hong Y, et al. Esculin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and drives apoptosis and ferroptosis in colorectal cancer via PERK regulating eIF2α/CHOP and Nrf2/HO-1 cascades. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 328:118139. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118139
73. Tak J, Kim YS, Kim TH, Park G-C, Hwang S, and Kim SG. Gα12 overexpression in hepatocytes by ER stress exacerbates acute liver injury via ROCK1-mediated miR-15a and ALOX12 dysregulation. Theranostics. (2022) 12:1570–88. doi: 10.7150/thno.67722
74. Cheng R, Wang X, Huang L, Lu Z, Wu A, Guo S, et al. Novel insights into the protective effects of leonurine against acute kidney injury: Inhibition of ER stress-associated ferroptosis via regulating ATF4/CHOP/ACSL4 pathway. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) 395:111016. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111016
75. Zhong P, Li L, Feng X, Teng C, Cai W, Zheng W, et al. Neuronal ferroptosis and ferroptosis-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress: Implications in cognitive dysfunction induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 138:112579. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112579
76. He F, Zhang P, Liu J, Wang R, Kaufman RJ, Yaden BC, et al. ATF4 suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by inducing SLC7A11 (xCT) to block stress-related ferroptosis. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:362–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.016
77. Ruan D, Wen J, Fang F, Lei Y, Zhao Z, and Miao Y. Ferroptosis in epithelial ovarian cancer: a burgeoning target with extraordinary therapeutic potential. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:434. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01721-6
78. Liu M, Wu K, and Wu Y. The emerging role of ferroptosis in female reproductive disorders. BioMed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 166:115415. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115415
79. Kapper C, Oppelt P, Arbeithuber B, Gyunesh AA, Vilusic I, Stelzl P, et al. Targeting ferroptosis in ovarian cancer: Novel strategies to overcome chemotherapy resistance. Life Sci. (2024) 349:122720. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122720
80. Liu D, Hu Z, Lu J, and Yi C. Redox-regulated iron metabolism and ferroptosis in ovarian cancer: molecular insights and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:791. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070791
81. Beddows I, Fan H, Heinze K, Johnson BK, Leonova A, Senz J, et al. Cell state of origin impacts development of distinct endometriosis-related ovarian carcinoma histotypes. Cancer Res. (2024) 84:26–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1362
82. Battaglia AM, Sacco A, Perrotta ID, Faniello MC, Scalise M, Torella D, et al. Iron administration overcomes resistance to erastin-mediated ferroptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:868351. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.868351
83. Wang C-K, Chen T-J, Tan GYT, Chang F-P, Sridharan S, Yu C-HA, et al. MEX3A mediates p53 degradation to suppress ferroptosis and facilitate ovarian cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:251–63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-1159
84. Xuan Y, Wang H, Yung MM, Chen F, Chan W-S, Chan Y-S, et al. SCD1/FADS2 fatty acid desaturases equipoise lipid metabolic activity and redox-driven ferroptosis in ascites-derived ovarian cancer cells. Theranostics. (2022) 12:3534–52. doi: 10.7150/thno.70194
85. Wang Y, Hu M, Cao J, Wang F, Han JR, Wu TW, et al. ACSL4 and polyunsaturated lipids support metastatic extravasation and colonization. Cell. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.047
86. Xu K, Zheng X, Shi H, Ou J, and Ding H. MAD2L2, a key regulator in ovarian cancer and promoting tumor progression. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:130. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50744-7
87. Liu Y, Li J, Xu J, Long Y, Wang Y, Liu X, et al. m6A-driven NAT10 translation facilitates fatty acid metabolic rewiring to suppress ferroptosis and promote ovarian tumorigenesis through enhancing ACOT7 mRNA acetylation. Oncogene. (2024) 43:3498–516. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03185-z
88. Li X-X, Xiong L, Wen Y, and Zhang Z-J. Comprehensive analysis of the tumor microenvironment and ferroptosis-related genes predict prognosis with ovarian cancer. Front Genet. (2021) 12:774400. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.774400
89. Li Y, Gong X, Hu T, and Chen Y. Two novel prognostic models for ovarian cancer respectively based on ferroptosis and necroptosis. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:74. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09166-9
90. Wang H, Cheng Q, Chang K, Bao L, and Yi X. Integrated analysis of ferroptosis-related biomarker signatures to improve the diagnosis and prognosis prediction of ovarian cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:807862. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.807862
91. Wei C, Zhao G, Gao M, Liu Y, Lei P, and Cao T. Construction of an immunity and ferroptosis-related risk score model to predict ovarian cancer clinical outcomes and immune microenvironment. Front Biosci Landmark Ed. (2023) 28:4. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2801004
92. Gao J, Pang X, Ren F, and Zhu L. Identification of a ferroptosis-related long non-coding RNA signature for prognosis prediction of ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2023) 44:80–92. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgac082
93. Ji H-Z, Chen L, Ren M, Li S, Liu T-Y, Chen H-J, et al. CXCL8 promotes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition of endothelial cells and protects cells from erastin-induced ferroptosis via CXCR2-mediated activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Pharm Basel Switz. (2023) 16:1210. doi: 10.3390/ph16091210
94. Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhan Y, Li Z, Li S, and Guo S. Comprehensive in silico analysis of prognostic and immune infiltrates for FGFs in human ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:197. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01496-z
95. Li Z, Liao X, Hu Y, Li M, Tang M, Zhang S, et al. SLC27A4-mediated selective uptake of mono-unsaturated fatty acids promotes ferroptosis defense in hepatocellular carcinoma. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 201:41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.013
96. Atiya HI, Frisbie L, Goldfeld E, Orellana T, Donnellan N, Modugno F, et al. Endometriosis-associated mesenchymal stem cells support ovarian clear cell carcinoma through iron regulation. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:4680–93. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-1294
97. Zhang C and Liu N. Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:920059. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.920059
98. Chen J, Wei Z, Fu K, Duan Y, Zhang M, Li K, et al. Non-apoptotic cell death in ovarian cancer: Treatment, resistance and prognosis. BioMed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 150:112929. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112929
99. Zhang Q, Li N, Deng L, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Lee LTO, et al. ACSL1-induced ferroptosis and platinum resistance in ovarian cancer by increasing FSP1 N-myristylation and stability. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:83. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01385-2
100. Zhang Y, Xia F, Liu X, Yu Z, Xie L, Liu L, et al. JAM3 maintains leukemia-initiating cell self-renewal through LRP5/AKT/β-catenin/CCND1 signaling. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:1737–51. doi: 10.1172/JCI93198
101. Yamaguchi M, Hirai S, Idogawa M, Sumi T, Uchida H, Fujitani N, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule 3 is a potential therapeutic target for small cell lung carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. (2023) 426:113570. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113570
102. Wang N, Chen M, Wu M, Liao Y, Xia Q, Cai Z, et al. High-adhesion ovarian cancer cell resistance to ferroptosis: The activation of NRF2/FSP1 pathway by junctional adhesion molecule JAM3. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 228:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.12.040
103. Atwani R, Nagare RP, Rogers A, Prasad M, Lazar V, Sandusky G, et al. Integrin-linked kinase-frizzled 7 interaction maintains cancer stem cells to drive platinum resistance in ovarian cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. (2024) 43:156. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03083-y
104. Cabarca S, Ili C, Vanegas C, Gil L, Vertel-Morrinson M, and Brebi P. Drug resistance biomarkers in ovarian cancer: a bibliometric study from 2017 to 2022. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1450675. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1450675
105. Wang Y, Zhao G, Condello S, Huang H, Cardenas H, Tanner EJ, et al. Frizzled-7 identifies platinum-tolerant ovarian cancer cells susceptible to ferroptosis. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:384–99. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1488
106. Zhao L, Yang H, Wang Y, Yang S, Jiang Q, Tan J, et al. STUB1 suppresses paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer through mediating HOXB3 ubiquitination to inhibit PARK7 expression. Commun Biol. (2024) 7:1439. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07127-z
107. Wu X, Shen S, Qin J, Fei W, Fan F, Gu J, et al. High co-expression of SLC7A11 and GPX4 as a predictor of platinum resistance and poor prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Bjog- Int J Obstet Gynaecol. (2022) 129 Suppl 2:40–9. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.17327
108. Yusuf RZ, Saez B, Sharda A, van Gastel N, Yu VWC, Baryawno N, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3a2 protects AML cells from oxidative death and the synthetic lethality of ferroptosis inducers. Blood. (2020) 136:1303–16. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001808
109. Dong H, He L, Sun Q, Zhan J, Li J, Xiong X, et al. Inhibit ALDH3A2 reduce ovarian cancer cells survival via elevating ferroptosis sensitivity. Gene. (2023) 876:147515. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147515
110. Zhang S, Zheng F, Zhang L, Huang Z, Huang X, Pan Z, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR-mediated MTHFR methylation inhibits 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in esophageal cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. (2020) 39:131. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01610-1
111. Woloszynska-Read A, Zhang W, Yu J, Link PA, Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Collamat G, et al. Coordinated cancer germline antigen promoter and global DNA hypomethylation in ovarian cancer: Association with the BORIS/CTCF expression ratio and advanced stage. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2011) 17:2170–80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2315
112. Wang X, Xu Z, Ren X, Chen X, Yi Q, Zeng S, et al. MTHFR inhibits TRC8-mediated HMOX1 ubiquitination and regulates ferroptosis in ovarian cancer. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12:e1013. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1013
113. Furutake Y, Yamaguchi K, Yamanoi K, Kitamura S, Takamatsu S, Taki M, et al. YAP1 suppression by ZDHHC7 is associated with ferroptosis resistance and poor prognosis in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2024) 23:1652–65. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-24-0145
114. Zhang X, Zheng X, Ying X, Xie W, Yin Y, and Wang X. CEBPG suppresses ferroptosis through transcriptional control of SLC7A11 in ovarian cancer. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:334. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04136-0
115. Li C, Wang Z, Wang Y, Liu H, and Cheng Y. MiR-93-5p inhibits ovarian cancer through SLC7A11-mediated-ferroptosis. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e35457. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35457
116. Sun D, Li Y-C, and Zhang X-Y. Lidocaine promoted ferroptosis by targeting miR-382-5p/SLC7A11 axis in ovarian and breast cancer. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:681223. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.681223
117. Ma L-L, Liang L, Zhou D, and Wang S-W. Tumor suppressor miR-424-5p abrogates ferroptosis in ovarian cancer through targeting ACSL4. Neoplasma. (2021) 68:165–73. doi: 10.4149/neo_2020_200707N705
118. Wang K, Mei S, Cai M, Zhai D, Zhang D, Yu J, et al. Ferroptosis-related long noncoding RNAs as prognostic biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:888699. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.888699
119. Cao L, Wang Y, Liu J, Bai X, and Chi X. Long non-coding RNA TPT1-AS1 inhibits ferroptosis in ovarian cancer by regulating GPX4 via CREB1 regulation. Am J Reprod Immunol N Y N 1989. (2024) 92:e13864. doi: 10.1111/aji.13864
120. Cai L, Hu X, Ye L, Bai P, Jie Y, and Shu K. Long non-coding RNA ADAMTS9-AS1 attenuates ferroptosis by targeting microRNA-587/solute carrier family 7 member 11 axis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:8226–39. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2049470
121. Chai B, Wu Y, Yang H, Fan B, Cao S, Zhang X, et al. Tau aggregation-dependent lipid peroxide accumulation driven by the hsa_circ_0001546/14-3-3/CAMK2D/tau complex inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis. Adv Sci Weinh Baden-Wurtt Ger. (2024) 11:e2310134. doi: 10.1002/advs.202310134
122. Chen J, Ye M, Bai J, Hu C, Lu F, Gu D, et al. Novel insights into the interplay between m6A modification and programmed cell death in cancer. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:1748–63. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.81000
123. Shi J-X, Zhang Z-C, Yin H-Z, Piao X-J, Liu C-H, Liu Q-J, et al. RNA m6A modification in ferroptosis: Implications for advancing tumor immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:213. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02132-6
124. Pu X, Wu Y, Ji Q, Fu S, Zuo H, Chu L, et al. Mechanisms of N6−methyladenosine modification in tumor development and potential therapeutic strategies (review). Int J Oncol. (2023) 62:75. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5523
125. Lou Y, Huang K, Xu B, and Chen X. METTL14 plays an oncogenic role in NSCLC by modulating ferroptosis and the m6A modification of GPX4. Arch Physiol Biochem. (2024) 130:962–73. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2024.2376813
126. Tao X, Kang N, Zheng Z, Zhu Z, Ma J, and He W. The regulatory mechanisms of N6-methyladenosine modification in ferroptosis and its implications in disease pathogenesis. Life Sci. (2024) 355:123011. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123011
127. Li Y, Guo M, Qiu Y, Li M, Wu Y, Shen M, et al. Autophagy activation is required for N6-methyladenosine modification to regulate ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Redox Biol. (2024) 69:102971. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102971
128. Dodson M, de la Vega MR, Cholanians AB, Schmidlin CJ, Chapman E, and Zhang DD. Modulating NRF2 in disease: timing is everything. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2019) 59:555–75. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010818-021856
129. Anandhan A, Dodson M, Shakya A, Chen J, Liu P, Wei Y, et al. NRF2 controls iron homeostasis and ferroptosis through HERC2 and VAMP8. Sci Adv. (2023) 9:eade9585. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade9585
130. Sang X, Han J, Wang Z, Cai W, Liao X, Kong Z, et al. SGK1 suppresses ferroptosis in ovarian cancer via NRF2-dependent and -independent pathways. Oncogene. (2024) 43:3335–47. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03173-3
131. Li M, Li L, Cheng X, Li L, and Tu K. Hypoxia promotes the growth and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells by suppressing ferroptosis via upregulating SLC2A12. Exp Cell Res. (2023) 433:113851. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113851
132. Xiang H, Wang M, Chen Y-F, Wu H-M, Li M-G, Guo L, et al. Regulation of cancer cell ferroptosis by PTRF/cavin-1. Free Radic Res. (2024) 58:417–29. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2024.2386457
133. Luo Y, Liu X, Chen Y, Tang Q, He C, Ding X, et al. Targeting PAX8 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to ferroptosis by inhibiting glutathione synthesis. Apopt Int J Program Cell Death. (2024) 29:1499–514. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01985-y
134. Xu S, Liu Y, Yang S, Fei W, Qin J, Lu W, et al. FXN targeting induces cell death in ovarian cancer stem-like cells through PRDX3-mediated oxidative stress. iScience. (2024) 27:110506. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110506
135. Miyahara S, Ohuchi M, Nomura M, Hashimoto E, Soga T, Saito R, et al. FDX2, an iron-sulfur cluster assembly factor, is essential to prevent cellular senescence, apoptosis or ferroptosis of ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem. (2024) 300:107678. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107678
136. Hou R, Sun X, Cao S, Wang Y, and Jiang L. Stabilization of SQLE mRNA by WTAP/FTO/IGF2BP3-dependent manner in HGSOC: Implications for metabolism, stemness, and progression. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:872. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07257-6
137. He J, Siu MKY, Ngan HYS, and Chan KKL. Aberrant cholesterol metabolism in ovarian cancer: Identification of novel therapeutic targets. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:738177. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.738177
138. Zhang R, Zhang L, Fan S, Wang L, Wang B, and Wang L. Squalene monooxygenase (SQLE) protects ovarian cancer cells from ferroptosis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:22646. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72506-9
139. Han Y, Fu L, Kong Y, Jiang C, Huang L, and Zhang H. STEAP3 affects ovarian cancer progression by regulating ferroptosis through the p53/SLC7A11 pathway. Mediators Inflammation. (2024) 2024:4048527. doi: 10.1155/2024/4048527
140. Ebrahimi B, Viswanadhapalli S, Pratap UP, Rahul G, Yang X, Pitta Venkata P, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the LIF/LIFR autocrine loop reveals vulnerability of ovarian cancer cells to ferroptosis. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2024) 8:118. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00612-y
141. Wang Y, Wang S, and Zhang W. HRD1 functions as a tumor suppressor in ovarian cancer by facilitating ubiquitination-dependent SLC7A11 degradation. Cell Cycle Georget Tex. (2023) 22:1116–26. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2178102
142. Yang W-H, Lin C-C, Wu J, Chao P-Y, Chen K, Chen P-H, et al. The hippo pathway effector YAP promotes ferroptosis via the E3 ligase SKP2. Mol Cancer Res MCR. (2021) 19:1005–14. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0534
143. Sinha BK, Murphy C, Brown SM, Silver BB, Tokar EJ, and Bortner CD. Mechanisms of cell death induced by erastin in human ovarian tumor cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:8666. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168666
144. Yue W, Yupeng G, Jun C, and Kui J. Apatinib combined with olaparib induces ferroptosis via a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:8681–9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04811-1
145. Azumi M, Kusama K, Yoshie M, Nakano S, Tsuru A, Kato T, et al. Involvement of ferroptosis in eribulin-induced cytotoxicity in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Eur J Pharmacol. (2024) 971:176544. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176544
146. Hong T, Lei G, Chen X, Li H, Zhang X, Wu N, et al. PARP inhibition promotes ferroptosis via repressing SLC7A11 and synergizes with ferroptosis inducers in BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer. Redox Biol. (2021) 42:101928. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101928
147. Tang S, Shen Y, Wei X, Shen Z, Lu W, and Xu J. Olaparib synergizes with arsenic trioxide by promoting apoptosis and ferroptosis in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:826. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05257-y
148. Xie X, Chen C, Wang C, Guo Y, Sun B, Tian J, et al. Targeting GPX4-mediated ferroptosis protection sensitizes BRCA1-deficient cancer cells to PARP inhibitors. Redox Biol. (2024) 76:103350. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103350
149. Heiserman JP, Minhas Z, Nikpayam E, and Cheon D-J. Targeting heat shock protein 27 and fatty acid oxidation augments cisplatin treatment in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:12638. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612638
150. Zhang Y, Xia M, Zhou Z, Hu X, Wang J, Zhang M, et al. p53 promoted ferroptosis in ovarian cancer cells treated with human serum incubated-superparamagnetic iron oxides. Int J Nanomed. (2021) 16:283–96. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S282489
151. Cheng S, Zhou T, Luo Y, Zhang J, Dong K, Zhang Q, et al. Ultrasound-responsive Bi2MoO6-MXene heterojunction as ferroptosis inducers for stimulating immunogenic cell death against ovarian cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. (2024) 22:408. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02658-3
152. Li G, Shi S, Tan J, He L, Liu Q, Fang F, et al. Highly efficient synergistic chemotherapy and magnetic resonance imaging for targeted ovarian cancer therapy using hyaluronic acid-coated coordination polymer nanoparticles. Adv Sci Weinh Baden-Wurtt Ger. (2024) 11:e2309464. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309464
153. Wang Y, Calvert AE, Cardenas H, Rink JS, Nahotko D, Qiang W, et al. Nanoparticle targeting in chemo-resistant ovarian cancer reveals dual axis of therapeutic vulnerability involving cholesterol uptake and cell redox balance. Adv Sci Weinh Baden-Wurtt Ger. (2024) 11:e2305212. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305212
154. Asif K, Adeel M, Rahman MM, Caligiuri I, Perin T, Cemazar M, et al. Iron nitroprusside as a chemodynamic agent and inducer of ferroptosis for ovarian cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B. (2023) 11:3124–35. doi: 10.1039/d2tb02691k
155. Zhan S, Yung MMH, Siu MKY, Jiao P, Ngan HYS, Chan DW, et al. New insights into ferroptosis initiating therapies (FIT) by targeting the rewired lipid metabolism in ovarian cancer peritoneal metastases. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:15263. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315263
156. Cang W, Wu A, Gu L, Wang W, Tian Q, Zheng Z, et al. Erastin enhances metastatic potential of ferroptosis-resistant ovarian cancer cells by M2 polarization through STAT3/IL-8 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 113:109422. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109422
157. Zhou H-H, Chen X, Cai L-Y, Nan X-W, Chen J-H, Chen X-X, et al. Erastin reverses ABCB1-mediated docetaxel resistance in ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:1398. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01398
158. Manchester DK, Gordon SK, Golas CL, Roberts EA, and Okey AB. Ah receptor in human placenta: Stabilization by molybdate and characterization of binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, 3-methylcholanthrene, and benzo(a)pyrene. Cancer Res. (1987) 47:4861–8.
159. El-Waseif EG, Sharawy MH, and Suddek GM. The modulatory effect of sodium molybdate against cisplatin-induced CKD: Role of TGF-β/smad signaling pathway. Life Sci. (2022) 306:120845. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120845
160. Mao G, Xin D, Wang Q, and Lai D. Sodium molybdate inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells via inducing both ferroptosis and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 182:79–92. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.02.023
161. Yi J, Tavana O, Li H, Wang D, Baer RJ, and Gu W. Targeting USP2 regulation of VPRBP-mediated degradation of p53 and PD-L1 for cancer therapy. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:1941. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37617-3
162. Yang D, Liu X, Yang Y, Long Y, Nan D, Shi B, et al. Pharmacological USP2 targeting suppresses ovarian cancer growth by potentiating apoptosis and ferroptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2024) 762:110193. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.110193
163. Chen Y, Liao X, Jing P, Hu L, Yang Z, Yao Y, et al. Linoleic acid-glucosamine hybrid for endogenous iron-activated ferroptosis therapy in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Mol Pharm. (2022) 19:3187–98. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00333
164. Mihajlović E, Biancalana L, Jelača S, Chiaverini L, Dojčinović B, Dunđerović D, et al. FETPY: A diiron(I) thio-carbyne complex with prominent anticancer activity in vitro and in vivo. J Med Chem. (2024) 67:7553–68. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00377
165. Shen X, Peng Y, Zhou H, Ye X, Han Z, and Shi X. A pt(II) complex bearing N-heterocycle ring induced ferroptotic cell death in ovarian cancer. J Inorg Biochem. (2024) 253:112502. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2024.112502
166. Wang Y, Situ X, Cardenas H, Siu E, Alhunayan SA, Keathley R, et al. Preclinical evaluation of NTX-301, a novel DNA hypomethylating agent in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2024) 30:1175–88. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-2368
167. Gonzalez-Fierro A and Dueñas-González A. Drug repurposing for cancer therapy, easier said than done. Semin Cancer Biol. (2021) 68:123–31. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.012
168. Xia Y, Sun M, Huang H, and Jin W-L. Drug repurposing for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:92. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01808-1
169. Lu Y, Mao J, Xu Y, Pan H, Wang Y, and Li W. Ropivacaine represses the ovarian cancer cell stemness and facilitates cell ferroptosis through inactivating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2022) 41:9603271221120652. doi: 10.1177/09603271221120652
170. Gao X and Wang X-L. Dexmedetomidine promotes ferroptotic cell death in gastric cancer via hsa_circ_0008035/miR-302a/E2F7 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2023) 39:390–403. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12650
171. Tourville A, Viguier S, González-Lizárraga F, Tomas-Grau RH, Ramirez P, Brunel J-M, et al. Rescue of dopamine neurons from iron-dependent ferroptosis by doxycycline and demeclocycline and their non-antibiotic derivatives. Antioxid Basel Switz. (2023) 12:575. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030575
172. Crissey MAS, Versace A, Bhardwaj M, Jain V, Liu S, Singh A, et al. Divergent effects of acute and chronic PPT1 inhibition in melanoma. Autophagy. (2024) 1–13. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2403152
173. Koeberle SC, Kipp AP, Stuppner H, and Koeberle A. Ferroptosis-modulating small molecules for targeting drug-resistant cancer: Challenges and opportunities in manipulating redox signaling. Med Res Rev. (2023) 43:614–82. doi: 10.1002/med.21933
174. Ni M, Zhou J, Zhu Z, Xu Q, Yin Z, Wang Y, et al. Shikonin and cisplatin synergistically overcome cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer by inducing ferroptosis via upregulation of HMOX1 to promote Fe2+ accumulation. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharm. (2023) 112:154701. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154701
175. Fan X, Xie M, Zhao F, Li J, Fan C, Zheng H, et al. Daphnetin triggers ROS-induced cell death and induces cytoprotective autophagy by modulating the AMPK/akt/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharm. (2021) 82:153465. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153465
176. Liu Y, Liu X, Wang H, Ding P, and Wang C. Agrimonolide inhibits cancer progression and induces ferroptosis and apoptosis by targeting SCD1 in ovarian cancer cells. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharm. (2022) 101:154102. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154102
177. Shi M, Zhang M-J, Yu Y, Ou R, Wang Y, Li H, et al. Curcumin derivative NL01 induces ferroptosis in ovarian cancer cells via HCAR1/MCT1 signaling. Cell Signal. (2023) 109:110791. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110791
178. Liu F, Zhang Y, Xia X, Han J, and Cao L. Honokiol induces ferroptosis in ovarian cancer cells through the regulation of YAP by OTUB2. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. (2024) 50:864–72. doi: 10.1111/jog.15922
179. Xiong Y, Liu T, and Chen J. Anisomycin has the potential to induce human ovarian cancer stem cell ferroptosis by influencing glutathione metabolism and autophagy signal transduction pathways. J Cancer. (2023) 14:1202–15. doi: 10.7150/jca.83355
180. Wu N, Zhang X, Fang C, Zhu M, Wang Z, Jian L, et al. Progesterone enhances niraparib efficacy in ovarian cancer by promoting palmitoleic-acid-mediated ferroptosis. Res Wash DC. (2024) 7:371. doi: 10.34133/research.0371
181. Choi J-A, Lee EH, Cho H, and Kim J-H. High-dose selenium induces ferroptotic cell death in ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:1918. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031918
182. Jing T, Guo Y, and Wei Y. Carboxymethylated pachyman induces ferroptosis in ovarian cancer by suppressing NRF1/HO-1 signaling. Oncol Lett. (2022) 23:161. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13281
183. Xia L, Yang M, and Liu Y. Portulaca oleracea L. polysaccharide inhibits ovarian cancer via inducing ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis. Aging. (2024) 16:5108–22. doi: 10.18632/aging.205608
184. Guo W, Wang W, Lei F, Zheng R, Zhao X, Gu Y, et al. Angelica sinensis polysaccharide combined with cisplatin reverses cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer by inducing ferroptosis via regulating GPX4. BioMed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 175:116680. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116680
185. Bae H, Song G, Lee J-Y, Hong T, Chang M-J, and Lim W. Laminarin-derived from brown algae suppresses the growth of ovarian cancer cells via mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress. Mar Drugs. (2020) 18:152. doi: 10.3390/md18030152
186. Zhou J, Wang Y, Fu Y, Lin Z, Lin H, Lv G, et al. Chelerythrine induces apoptosis and ferroptosis through Nrf2 in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol Noisy–Gd Fr. (2024) 70:174–81. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2024.70.3.26
187. Li B, Gao Y, Rankin GO, Rojanasakul Y, Cutler SJ, Tu Y, et al. Chaetoglobosin K induces apoptosis and G2 cell cycle arrest through p53-dependent pathway in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. (2015) 356:418–33. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.023
188. Zhu J, Zhu H, Zhu Q, Xu SL, Xiao L, Zhang MY, et al. The roles of autophagy, ferroptosis and pyroptosis in the anti-ovarian cancer mechanism of harmine and their crosstalk. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:6504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57196-7
189. Li J, Feng L, Yuan Y, He T, Zou X, Su B, et al. Inhibition of HOXC11 by artesunate induces ferroptosis and suppresses ovarian cancer progression through transcriptional regulation of the PROM2/PI3K/AKT pathway. World J Surg Oncol. (2024) 22:268. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03544-w
190. Yang Y-I, Kim J-H, Lee K-T, and Choi J-H. Costunolide induces apoptosis in platinum-resistant human ovarian cancer cells by generating reactive oxygen species. Gynecol Oncol. (2011) 123:588–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.08.031
191. Chan DW, Yung MM, Chan Y-S, Xuan Y, Yang H, Xu D, et al. MAP30 protein from momordica charantia is therapeutic and has synergic activity with cisplatin against ovarian cancer in vivo by altering metabolism and inducing ferroptosis. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 161:105157. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105157
192. Wu J, Zhou T, Wang Y, Jiang Y, and Wang Y. Mechanisms and advances in anti-ovarian cancer with natural plants component. Mol Basel Switz. (2021) 26:5949. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195949
193. Ma B, Zhong Y, Chen R, Zhan X, Huang G, Xiong Y, et al. Tripterygium glycosides reverse chemotherapy resistance in ovarian cancer by targeting the NRF2/GPX4 signal axis to induce ferroptosis of drug-resistant human epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 665:178–86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.04.111
194. Zhao Y, Liang H, and Cui X. Obacunone regulates ferroptosis in ovarian cancer through the akt/p53 pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2024). doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03738-9
195. Fontana F, Marzagalli M, Raimondi M, Zuco V, Zaffaroni N, and Limonta P. δ-tocotrienol sensitizes and re-sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin via induction of G1 phase cell cycle arrest and ROS/MAPK-mediated apoptosis. Cell Prolif. (2021) 54:e13111. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13111
196. Wang Z, Liu M, Li G-X, Zhang L, Ding K-Y, Li S-Q, et al. A herbal pair of scutellaria barbata D. Don and scleromitrion diffusum (willd.) R.J. wang induced ferroptosis in ovarian cancer A2780 cells via inducing heme catabolism and ferritinophagy. J Integr Med. (2024) 22. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2024.10.001
197. Wu Y, Jia C, Liu W, Zhan W, Chen Y, Lu J, et al. Sodium citrate targeting Ca2+/CAMKK2 pathway exhibits anti-tumor activity through inducing apoptosis and ferroptosis in ovarian cancer. J Adv Res. (2024) 65:89–104. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.033
198. Wang X, Chen J, Tie H, Tian W, Zhao Y, Qin L, et al. Eriodictyol regulated ferroptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell viability via Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2023) 37:e23368. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23368
199. Nelson KM, Dahlin JL, Bisson J, Graham J, Pauli GF, and Walters MA. The essential medicinal chemistry of curcumin. J Med Chem. (2017) 60:1620–37. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975
200. Rauf A, Olatunde A, Imran M, Alhumaydhi FA, Aljohani ASM, Khan SA, et al. Honokiol: A review of its pharmacological potential and therapeutic insights. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharm. (2021) 90:153647. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153647
201. Hu Y, Yu X, Yang L, Xue G, Wei Q, Han Z, et al. Research progress on the antitumor effects of harmine. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1382142. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1382142
202. Yavuz M, Şahin B, Baykal AT, and Demircan T. Hydroquinidine displays a significant anticarcinogenic activity in breast and ovarian cancer cells via inhibiting cell-cycle and stimulating apoptosis. Turk J Biol Turk Biyol Derg. (2023) 47:44–60. doi: 10.55730/1300-0152.2640
203. Luo H, Li B, Li Z, Cutler SJ, Rankin GO, and Chen YC. Chaetoglobosin K inhibits tumor angiogenesis through downregulation of vascular epithelial growth factor-binding hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Anticancer Drugs. (2013) 24:715–24. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e3283627a0b
204. Cutler HG, Crumley FG, Cox RH, Cole RJ, Dorner JW, Springer JP, et al. Chaetoglobosin K: a new plant growth inhibitor and toxin from diplodia macrospora. J Agric Food Chem. (1980) 28:139–42. doi: 10.1021/jf60227a011
205. Greenshields AL, Shepherd TG, and Hoskin DW. Contribution of reactive oxygen species to ovarian cancer cell growth arrest and killing by the anti-malarial drug artesunate. Mol Carcinog. (2017) 56:75–93. doi: 10.1002/mc.22474
206. Koike T, Takenaka M, Suzuki N, Ueda Y, Mori M, Hirayama T, et al. Intracellular ferritin heavy chain plays the key role in artesunate-induced ferroptosis in ovarian serous carcinoma cells. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2022) 71:34–40. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.21-82
207. Ma N, Zhang M, Hu J, Wei Z, and Zhang S. Daphnetin induces ferroptosis in ovarian cancer by inhibiting NAD(P)H:Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharm. (2024) 132:155876. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155876
208. Huang T, Zhao C-C, Xue M, Cao Y-F, Chen L-K, Chen J-X, et al. Current progress and outlook for agrimonolide: A promising bioactive compound from agrimonia pilosa ledeb. Pharm Basel Switz. (2023) 16:150. doi: 10.3390/ph16020150
209. Dandawate PR, Subramaniam D, Padhye SB, and Anant S. Bitter melon: A panacea for inflammation and cancer. Chin J Nat Med. (2016) 14:81–100. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(16)60002-X
210. Yung MMH, Ross FA, Hardie DG, Leung THY, Zhan J, Ngan HYS, et al. Bitter melon (momordica charantia) extract inhibits tumorigenicity and overcomes cisplatin-resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting AMPK signaling cascade. Integr Cancer Ther. (2016) 15:376–89. doi: 10.1177/1534735415611747
211. Diao J, Jia Y, Dai E, Liu J, Kang R, Tang D, et al. Ferroptotic therapy in cancer: Benefits, side effects, and risks. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:89. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01999-9
212. Hendricks JM, Doubravsky CE, Wehri E, Li Z, Roberts MA, Deol KK, et al. Identification of structurally diverse FSP1 inhibitors that sensitize cancer cells to ferroptosis. Cell Chem Biol. (2023) 30:1090–1103.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.04.007
213. Pontel LB, Bueno-Costa A, Morellato AE, Carvalho Santos J, Roué G, and Esteller M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia necessitates GSH-dependent ferroptosis defenses to overcome FSP1-epigenetic silencing. Redox Biol. (2022) 55:102408. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102408
Keywords: OC, ferroptosis, lipid peroxidation, drug resistance, targeted therapy
Citation: Wu X, Liu Q, Jiang Z, Wang G, Liao L, Ye X, Xing M, Sun H, Liu Q and Liu H (2025) Targeting ferroptosis: a promising avenue for ovarian cancer treatment. Front. Immunol. 16:1578723. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1578723
Received: 18 February 2025; Accepted: 23 May 2025;
Published: 05 June 2025.
Edited by:
César Antonio Echeverría, Universidad de Atacama, ChileReviewed by:
Jiawen Bu, China Medical University, ChinaDingxi Li, Henan Provincial Cancer Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Liu, Jiang, Wang, Liao, Ye, Xing, Sun, Liu and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huiping Liu, MDAzNDMzQGhudWNtLmVkdS5jbg==; Qiying Liu, Mjg0MzQwMzY1M0BxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiaolan Wu1,2,3,4†
Xiaolan Wu1,2,3,4† Qizhi Liu
Qizhi Liu Zhili Jiang
Zhili Jiang Min Xing
Min Xing Han Sun
Han Sun Huiping Liu
Huiping Liu