- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Aerospace Center Hospital, Peking University Aerospace School of Clinical Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, St. John’s University, New York, NY, United States
- 3Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 4Department of Peripheral Vascular Intervention, Aerospace Center Hospital, Peking University Aerospace School of Clinical Medicine, Beijing, China
The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)/stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway are crucial elements of the type I interferon (type I IFN) response. cGAS senses both exogenous and endogenous DNA within cells, labeling cGAS-STING as a pivotal anti-tumor immunity mechanism, autoimmunity, sterile inflammatory responses, and cellular senescence. The cGAS-STING pathway, a pivotal innate immune axis, modulates tumorigenesis via diverse effector responses. Emerging evidence have shown that activating of cGAS-STING pathway functions as a therapy to kill cancers. Insights into the biology of the cGAS-STING pathway have enabled the discovery of small-molecule agents which have the potential to activate cGAS-STING axis in cancers. In this review, we first outline the principal components of the cGAS-STING signaling cascade. Then we explore recent advancements in understanding the cGAS-STING signaling pathway, with particular emphasis on its activation mechanisms and roles in tumor cancer killing. Next, we summarize a list of bioactive small-molecule compounds which activate the cGAS-STING axis, reviewing their potential applications. Finally, we discuss key limitations of this new proposed therapeutic approach and provide possible techniques to overcome them. This review highlights a novel groundbreaking therapeutic possibilities through activating cGAS-STING in cancers.
1 Introduction
Cyclic GMP/AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS), along with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated stimulator of interferon genes (STING), are crucial elements of the innate immune response (1, 2). Microbial DNA is a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP), the main ‘‘molecular threat’’ needed to activate the DNA sensing protein cGAS. cGAS promotes the synthesis of the cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP which binds to STING, initiating trafficking and migration from the ER to the Golgi, where it recruits TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3). Phosphorylated IRF3 dimerizes and translocates into the nucleus, enhancing the expression of type I interferons (IFN-I) and IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) (2–4). Increasing evidence reveals that the over-activation and aberrant regulation of the cGAS-STING axis triggers undesired outcomes such as neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration, contributing to neurological disorders and accelerating disease progression (1–3, 5–8).
In the past decade, interest has increased in elucidating the role of cGAS-STING in cancers. cGAS-STING pathway modulators are new and attractive targets for targeted medicine against cancers. Unlike chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., PD-1/PD-L1 blockers) that primarily modulate adaptive immunity or directly kill cells, cGAS-STING agonists broadly activate the innate immune system (9–11). This triggers dendritic cell maturation, cross-presentation of tumor antigens, and recruitment of diverse immune cells, fostering a more systemic and sustained anti-tumor response. It can convert immunologically “cold” tumors (T cell-poor) into “hot” tumors (T cell-inflamed), addressing a limitation of many conventional therapies. cGAS-STING activation enhances tumor immunogenicity and primes the tumor microenvironment for checkpoint inhibitors. By promoting antigen presentation and cytokine production (e.g., type I interferons), it amplifies T cell responses that checkpoint inhibitors rely on, overcoming resistance to monotherapy (12–19). Given the essential role of cGAS-STING signaling in the pathogenesis of cancers, drug discovery targeting the cGAS-STING axis has expanded rapidly (20, 21).
In this review, we first outline the principal components of the cGAS-STING signaling cascade. From such we discuss recent research that highlights general mechanisms by which cGAS-STING contributes to cancers. Then, we summarize a list of bioactive small-molecule compounds which modulate the cGAS-STING axis, reviewing their potential clinical applications. Finally, we discuss key limitations of this new proposed therapeutic approach and provide possible techniques to overcome them.
2 cGAS-STING pathway
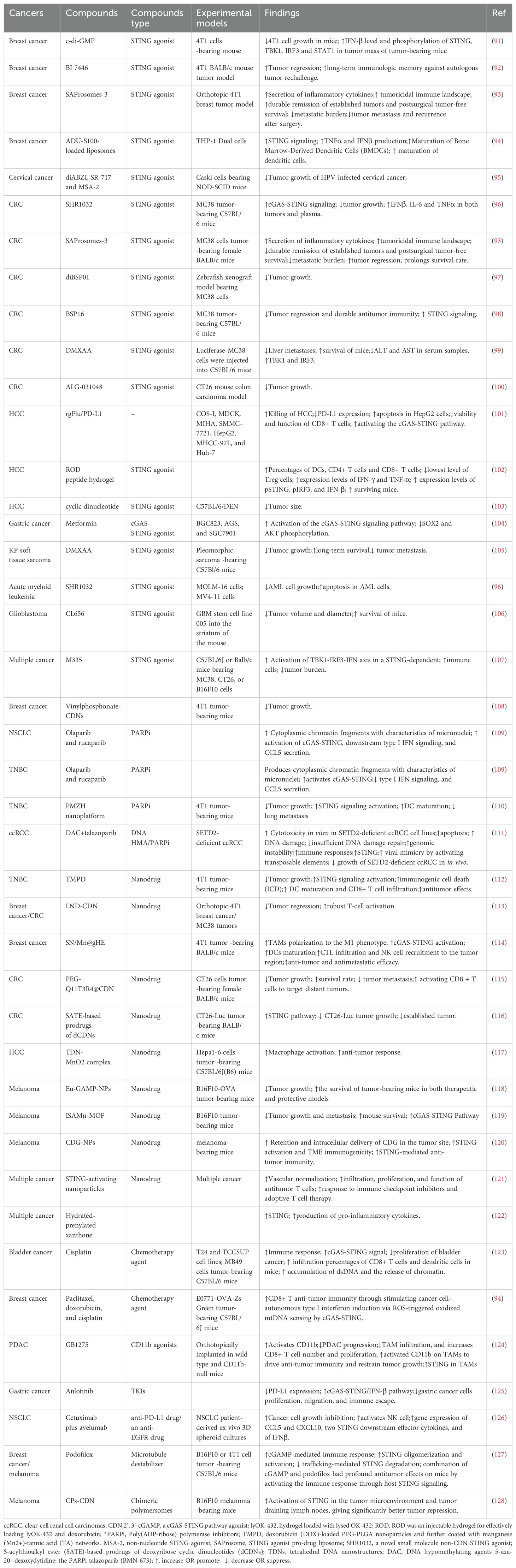
The DNA-sensing nucleotidyl transferase enzyme cyclic GMP/AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) is upstream of STING (22, 23). Key developments in cGAS-STING research is shown in Figure 1. Timeline depicting the scientific discoveries of the cGAS-STING pathway The cGAS-STING signaling axis detects pathogenic extranuclear DNA and initiates a type I interferon innate immune activation, physiologically used against microbial infections, making cGAS-STING an integral component the innate immune response (24). Belonging to a member of the nucleotidyl transferase (NTase) enzyme family, cGAS is also known as MB21D1 (24). STING is otherwise known as endoplasmic reticulum interferon stimulator (ERIS) (25), N-terminal methionine-proline-tyrosine-serine plasma membrane transpanner (MPYS) (26, 27), mediator of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) activation (MITA) (28) or transmembrane protein 173 (TMEM173) (24). The DNA sensor cGAS senses microbial (i.e. viral, bacterial, protozoal) double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), independent of sequence. cGAS may be activated by either endogenous DNA, mitochondrially-released DNA, or genotoxic stress-mediated extranuclear chromatin, placing cGAS-STING as a crucial signaling axis in autoimmunity, the sterile inflammatory response, and the induction of cellular senescence (24). An overview of the cGAS-STING signaling axis is illustrated in Figure 2. In mammalian cells, cGAS induces the synthesis of the secondary-messenger cyclic GMP/AMP (cGAMP), forming a crucial cytosolic DNA-sensing mechanism. cGAS binding to dsDNA induces a conformational change, activating it and initiating enzymatic activity (29–33). Active cGAS catalyzes and converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into 2′,3′-cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) (23). Subsequently, cGAMP binds to and activates STING, a ~40-kDa endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-localized transmembrane protein adaptor (23, 34, 35), to form homomeric quaternary ensembles of varying stoichiometry (36, 37). After activation, STING translocates from the ER to the Golgi, where it recruits TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and IκB kinase (IKK), which respectively phosphorylate interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) inhibitor IκBα (24). TBK1 transphosphorylates itself, the C-terminal domains of STING, and subsequently IRF3 (24). Meanwhile, STING engages and activates IKK to trigger NF-κB signaling (24), which works together with a robust IFN response to orchestrate the immunologically-driven clearance of intracellular bacteria, retroviruses, and DNA viruses (24). IRF3 dimerizes and translocates to enter the nucleus, transcriptionally activating genes which encode type I interferons, such as interferon-β (IFNβ), initiating antiviral defense mechanisms (24). The phosphorylation of IκBα leads to the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, enhancing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-6 (3). STING is trafficked to endolysosomes for degradation after activation (24). cGAS and STING are tightly regulated by transcriptional, posttranslational, and protein degradation mechanisms, for which we refer readers to a specific review for further discussion (24). cGAS senses cytosolic dsDNA in response to tissue injury or pathogenic invasion, which allows for the cGAS-STING axis to regulate various cellular functions, such as protein synthesis, IFN/cytokine production, autophagy, senescence, metabolism, and specific mechanisms of cell death (24). The cGAS-STING axis is vital for tissue homeostasis and host defense, while dysfunction of cGAS-STING activates pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, leading to inflammatory, autoimmune, degenerative diseases, and cancer (24).
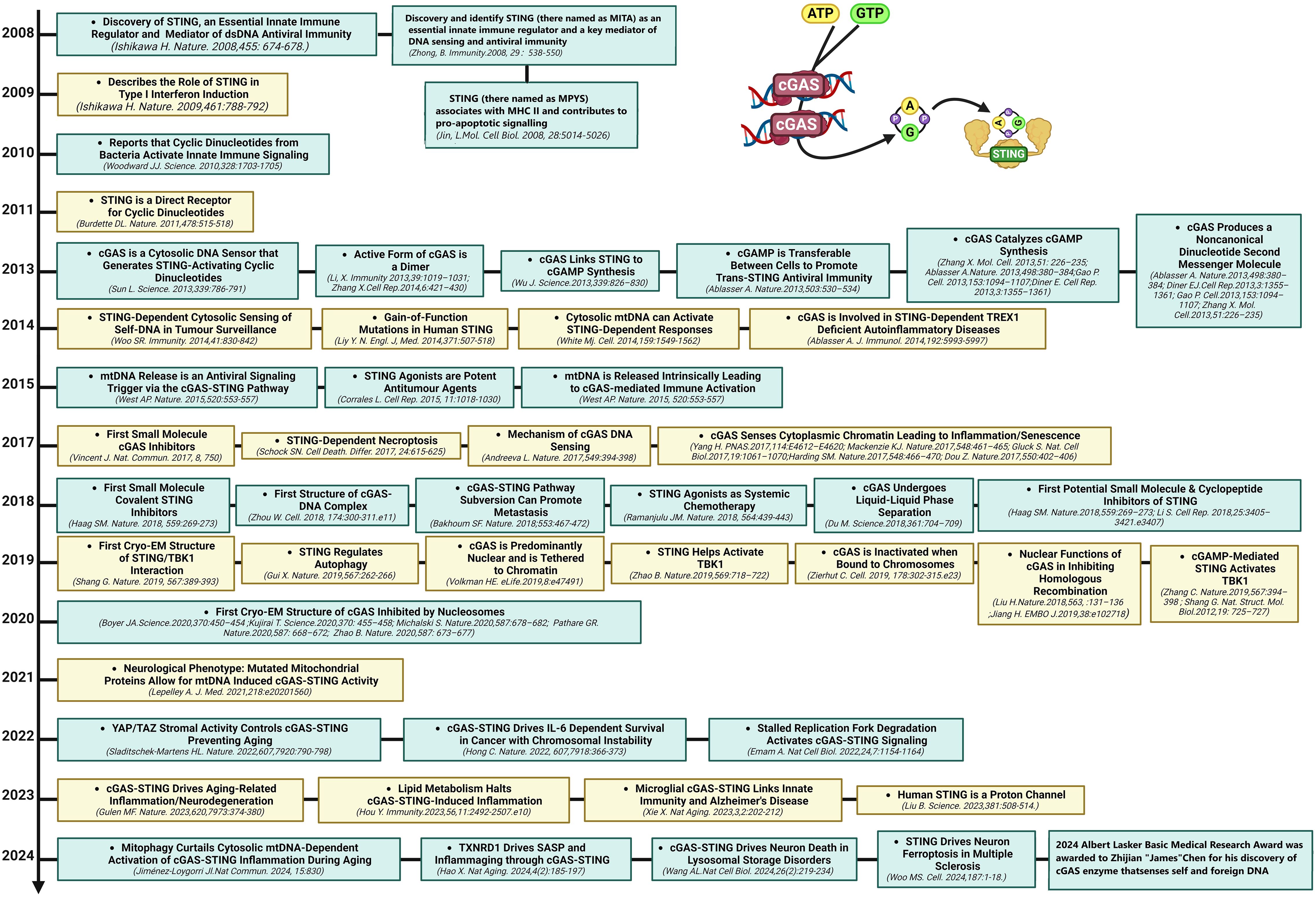
Figure 1. Milestones in cGAS-STING research. Timeline depicting the scientific discoveries of the cGAS-STING pathway from 2008 to 2024.
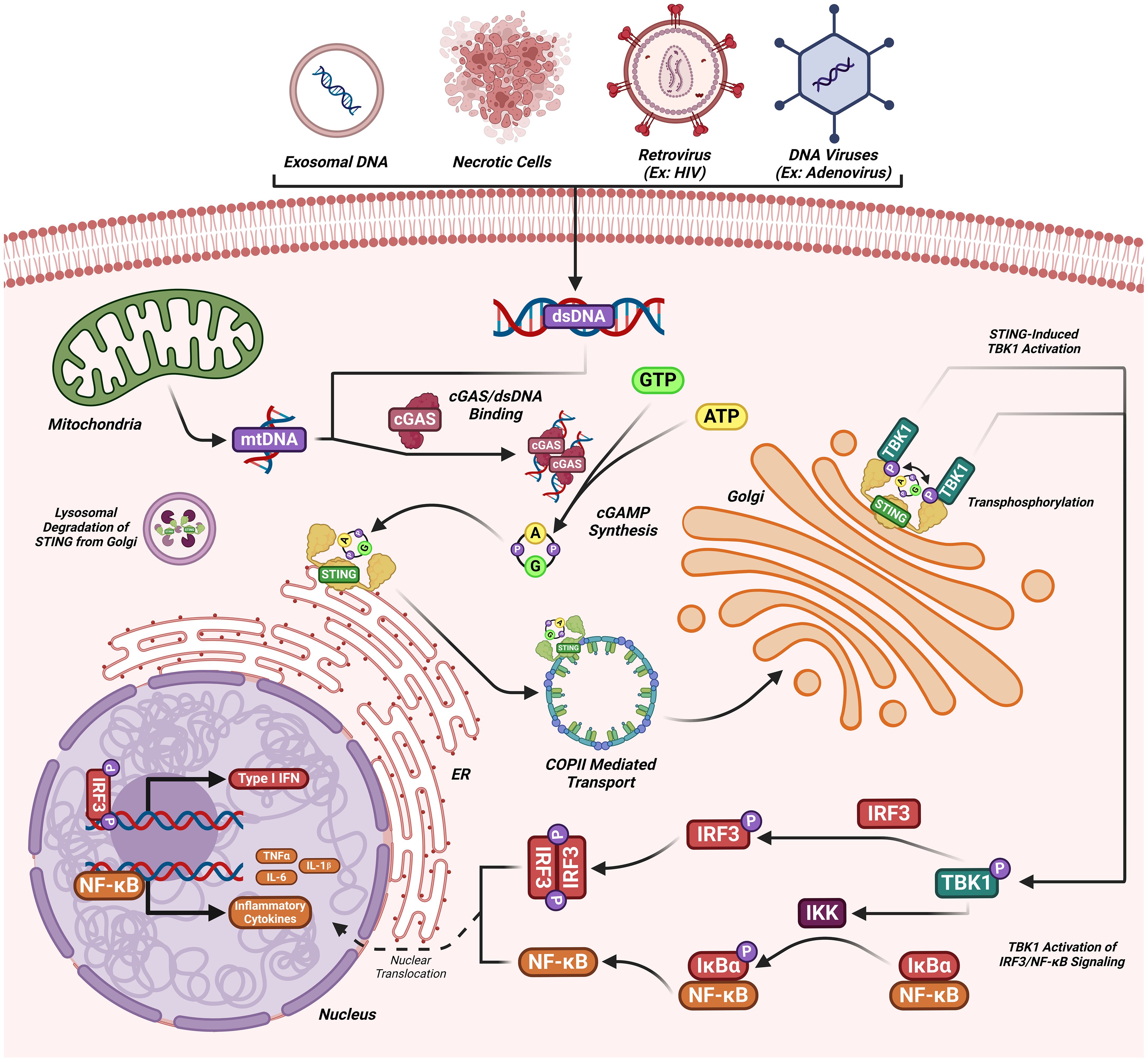
Figure 2. The cGAS-STING signaling cascade. dsDNA (introduced by viral or extracellular origins) binds to cGAS catalyzing the synthesis of cGAMP. cGAMP upon binding to STING transports to the Golgi where TBK1 transphosphorylation occurs. Phosphorylated TBK1 can then phosphorylate IRF3 inducing the nuclear transcription of IFN 1 genes or can activate IKK, inducing NF-kB mediated cytokine synthesis. STING is then recycled from the Golgi apparatus and degraded.
3 cGAS-STING in cancers
New evidence reveals that the cGAS-STING axis is crucial in cancer development (38), impacting all aspects of tumorigenesis from initial malignancy to metastasis (39). The cGAS-STING axis is a well-known double-edged sword, in which acute activation promotes antitumor effects and chronic inflammation promotes oncogenic growth/metastasis (40–42). In this upcoming section we will discussion how endogenous oncogenic processes are further modified by cGAS-STING axis activity. We refer readers to a recent excellent review for detailed discussion of the detrimental outcomes of cGAS-STING in cancer (40, 41, 43). The activation of cGAS-STING exerts an antitumor role by inducing spontaneous antitumor immunity, enhancing senescence in premalignant cells, responding to classic cancer therapies, and inducing regulated cell death via IFN-dependent and IFN-independent pathways (41, 44)(Figures 3, 4).
Figure 3. The activation of cGAS-STING exerts antitumor activity. Short-term cGAS-STING activity is antitumor, while long-term activity is oncogenic. Antitumor activity induces antitumor immunity, enhances premalignant cell senescence, enhances responsiveness to traditional chemotherapy, and induces IFN-dependent/independent regulated cell death.
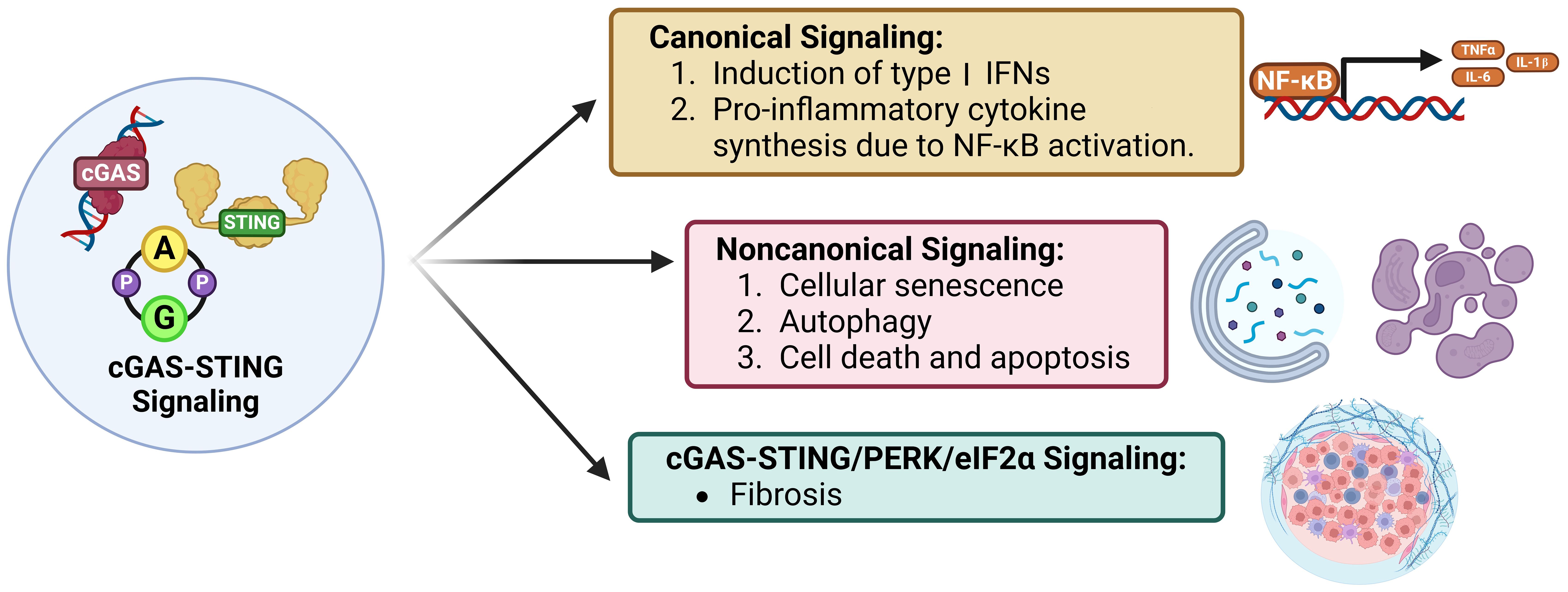
Figure 4. Signaling modes of cGAS-STING. Canonical cGAS-STING signaling induces type I IFN expression and an NF-kB-mediated pro-inflammatory response. STING dependent, cGAS, IFN, and TBK1 independent non-canonical signaling induces cellular senescence, autophagy, and apoptosis. Lastly, cGAS-STING/PERK/eIF2a signaling induces intra-organ fibrosis.
3.1 Activation of cGAS-STING induces regulated cell death
Studies have categorized cell death mechanisms as ‘uncontrolled necrosis’ and ‘regulated cell death (RCD)’, which contains ‘regulated necrosis (or non-apoptotic RCD)’ and apoptosis (45–48). Non-apoptotic RCD consists of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, cuproptosis, disulfidptosis, and autophagic cell death,et.al (49, 50). Activation of cGAS-STING induces RCD (51) (Figure 5).
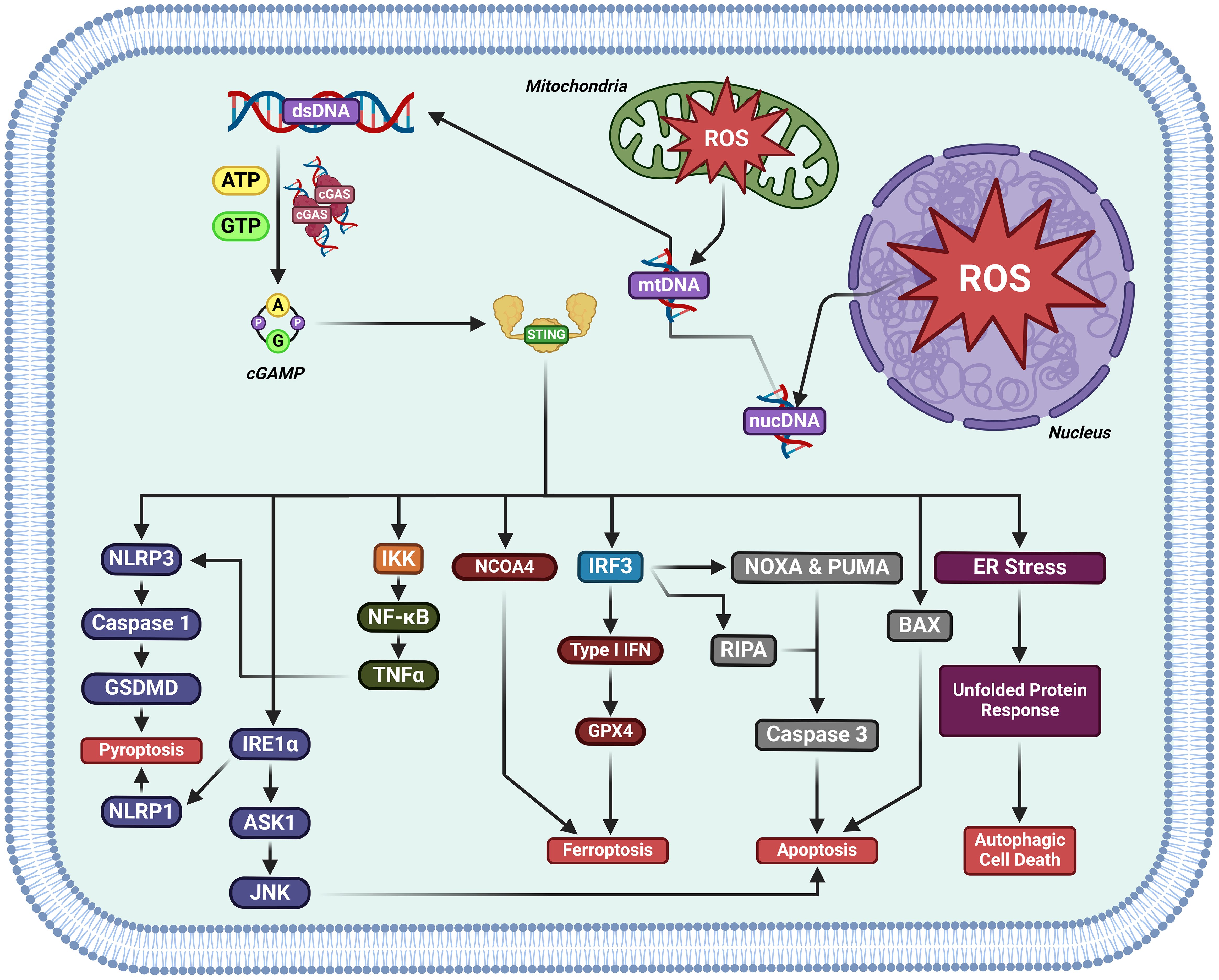
Figure 5. The activation of cGAS-STING induces regulated cell death in cancer. cGAS-STING pathway activation has been documented to kill cancer cells by either inducing pyroptosis, ferroptosis, apoptosis, or autophagic cell death.
3.1.1 Apoptosis
STING activity induces apoptosis. STING agonists have been found to induce apoptosis in B and T cells in vitro/vivo (52–54). STING/IRF3/p53 axis activity upregulates Noxa and Puma, directly promoting apoptosis (55).
3.1.2 Autophagy
cGAS-STING and autophagy have been shown to be interplayed, which may influence the progression of cancer. STING mediates autophagy.cGAS-STING pathway can trigger autophagy in several ways in innate immunity (reviewed in ref (56, 57)).
3.1.3 Ferroptosis
The nuclear cysteine protease cathepsin B (CTSB) triggers DNA damage and cGAS-STING1 activation to induce autophagydependent ferroptosis by degrading GPX4, thereby facilitating the anticancer activity of sorafenib in PDAC (58). STING promotes ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer by promoting MFN1/2-dependent mitochondrial fusion. Erastin, the pro-ferroptotic inducer enhances STING accumulation of in the mitochondria, where it interacts with MFN1/2 and promotes mitochondrial fusion, enhancing ROS production and lipid peroxidation. STING or MFN1/2 knockout reduces the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer samples to ferroptosis in vitro xenograft mice. Cumulatively, STING promotes ferroptosis via MFN1/2-dependent mitochondrial fusion (59). cGAS-STING axis activity promoted by manganese enhances mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and ROS production by upregulating IFN-1 release, directly preventing DHODH activity and therefore inducing ferroptosis in tumors (60).
3.1.4 Pyroptosis
Radium-223 inhibits tumor progression through triggering pyroptosis. DNA damage from 223 Ra promotes STING/NLRP3 axis activity, resulting in pyroptosis, dendritic cell, and T cell maturation (61).
3.2 Activation of cGAS-STING induces cancer-immunity cycle
The cancer-immunity cycle (CI cycle) provides a framework to understand what events promote an anticancer immunological response (62). Antigen-presenting cells (APCs), phagocytose cancer antigens and display them to T cells, which activates effector T cells to infiltrate the tumor, activate cytotoxic T cells, and kill tumor cells. In turn, newly killed cancer cells release more cancer-specific antigens which further promotes immunologically-driven cancer targeting (62, 63). This cycle teaches that T cell activity is promoted by a series of steps, some of which being extrinsic to the immune system and the cancer (63). cGAS-STING axis activity promotes every step of T cell immune defenses against cancer, effectively turning an immunologically “cold” tumor into a “hot” tumor being targeted by multiple immune responses (Figure 6) (64). cGAS-STING axis activity directly promotes tumor cell death. STING activity within DCs induces IFN-1 secretion and promotes maturation, whereas STING activity in T cells enhances their priming, activation, and chemokine output. STING activity enhances normalization of tumor blood vessels, allowing for easier T cell infiltration and upregulates MHC Class I expression, enhancing T cell-tumor recognition (reviewed in ref (43, 64)).
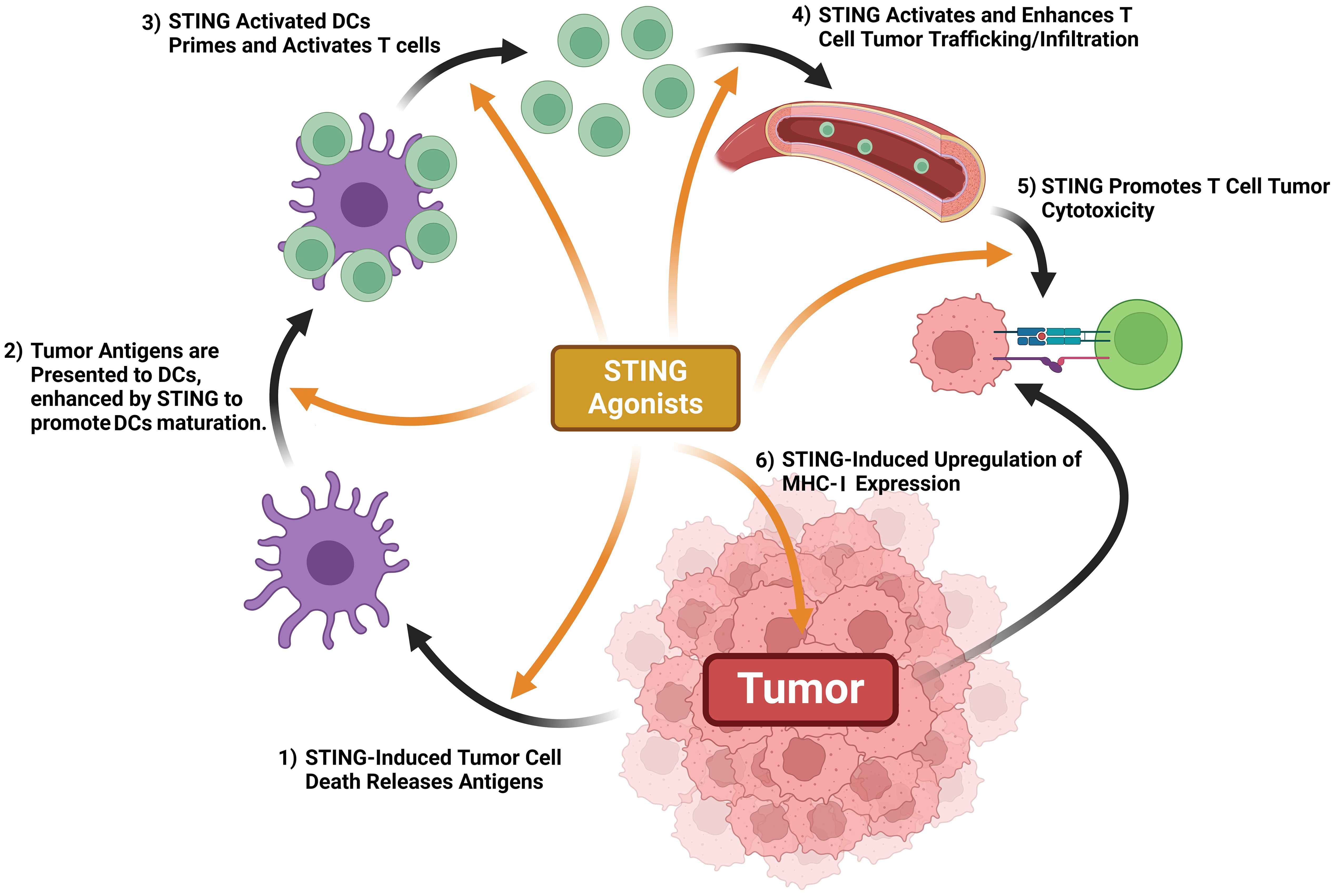
Figure 6. STING activation promotes antitumor immune mechanisms. STING activation promotes tumor antigen release, DC maturation once exposed to tumor antigens, T cell priming, T cell trafficking & tumor infiltration, tumor expression of MHC-1, and T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
3.3 Activation of cGAS-STING enhances senescence in premalignant cells
Senescence is a stress-inducible state of terminal cell cycle arrest and complex proinflammatory secretions, including chemokines, proteases, cytokines, and is also referred to as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) (65). Senescence is a hallmark of both cancer/aging (66, 67). The SASP facilitates growth inhibition in a paracrine manner (68). SASP-associated chemokines can recruit immune cells to remove cells which contain damaged DNA (69). Senescence is normally associated with telomere shortening or the steady-state accumulation of DNA damage (70). Exogenous stresses such as ROS or ionizing radiation may also induce senescence, including that of classical chemotherapy and targeted therapy (65). Inducing cellular senescence may function as a defense mechanism against oncogenesis and metastasis. From such, it may be currently used as a common mechanism underlying current anticancer therapies (65, 71–73). Together, senescence, and more importantly the mechanisms underlying its induction hold much importance in the development of novel anticancer therapies (71–73).
New studies have displayed that the DNA sensing functionality of the cGAS-STING axis directly promotes senescence and the SASP (74–77). Decreased senescence was observed cGAS or STING knockout cells after irradiation, oncogene expression, serial passage, or treatment with DNA-damaging drugs, all of these are known to create micronuclei and activate cGAS-senescence (74–77). cGAS or STING knockout prevented the SASP, where impaired clearance of RasV12-expressing cells tumorigenesis (74, 75). STING knockout increased tumor susceptibility in colitis-related mice cancer models (78, 79), inevitably indicating that the SASP-promoted cGAS-STING axis prevents tumorigenesis by reinforcing senescence or enhancing the immune-targeted clearance of aberrant cells. Decreased cGAS or STING expression was observed in several cancer cell lines (22, 80). Lower cGAS or STING expression in cancer samples was correlated to worse patient outcomes with hepatocellular carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma, suggesting the importance of functional cGAS-STING axis activity in proper tumor suppression (77, 81).
3.4 Ubiquitination-mediated inhibition of cGAS-STING in cancers
Emerging research has revealed multiple E3 ubiquitin ligases as critical regulators of the cGAS-STING pathway in cancer biology. Recent studies by Fu et al. (82) and Li et al. (83) demonstrated distinct mechanisms through which different TRIM family members modulate this pathway. TRIM41 was identified as a negative regulator that interacts with IDI1, a key enzyme in the mevalonate pathway, to promote cGAS ubiquitination and subsequent degradation, effectively dampening cGAS-STING signaling (82). Meanwhile, TRIM21 exerts its suppressive effect through mitochondrial regulation, enhancing VDAC2 ubiquitination to prevent mtDNA release via inhibition of VDAC2 oligomerization, thereby blocking radiation-induced STING activation and antitumor immunity (83). Concurrently, Liu et al. uncovered the paradoxical role of ARIH1 in cancer immunotherapy resistance (84). Their work revealed that ARIH1 deficiency promotes ICB resistance by disrupting the DNA-PKcs-STING signaling axis, while cisplatin-treated ICB-insensitive tumors showed compensatory ARIH1 upregulation. Mechanistically, ARIH1 overexpression facilitates DNA-PKcs ubiquitination and degradation, thereby activating STING signaling to enhance cytotoxic T-cell infiltration and synergize with PD-L1 blockade (84). This STING-mediated immunostimulatory effect was specifically dependent on non-phosphorylated cGAS, as demonstrated by the abolished response in cells expressing the phosphomimetic T68E/S213D mutant (84). Collectively, these findings highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting E3 ligase networks to modulate cGAS-STING pathway activity. TRIM29 restricts antiviral innate immunity against DNA virus infections by targeting STING for degradation (85). Recently, TRIM29 was also shown to promote viral myocarditis by enhancing ROS-mediated TBK1 oxidation and inhibition (86). Additionally, TRIM29 deficiency has been shown to control viral enteritis by regulating inflammasome activation (87). Furthermore, TRIM18 knockout has been demonstrated to control viral myocarditis and organ inflammation through the upregulation of TBK1-mediated antiviral immunity (88). Given the critical roles of TRIM29 and TRIM18 in controlling cGAS-STING pathway and cancer development, it is deserved to investigate the role of TRIM29 and TRIM18 in controlling cGAS-STING pathway in cancers.
4 Therapeutic potential of cGAS-STING activation in cancers
Suppression of cGAS-STING was found in various human malignancies, leading to growing interest in small-molecule agonists that reactivate this pathway to kill cancer (89, 90). Several compounds have already demonstrated therapeutic potential by targeting cGAS-STING in cancers (Figure 7). A summary of compounds functions as cGAS-STING agonists that include STING agonist, Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi), nanodrug, chemotherapy agent and others drugs are itemized in Table 1.
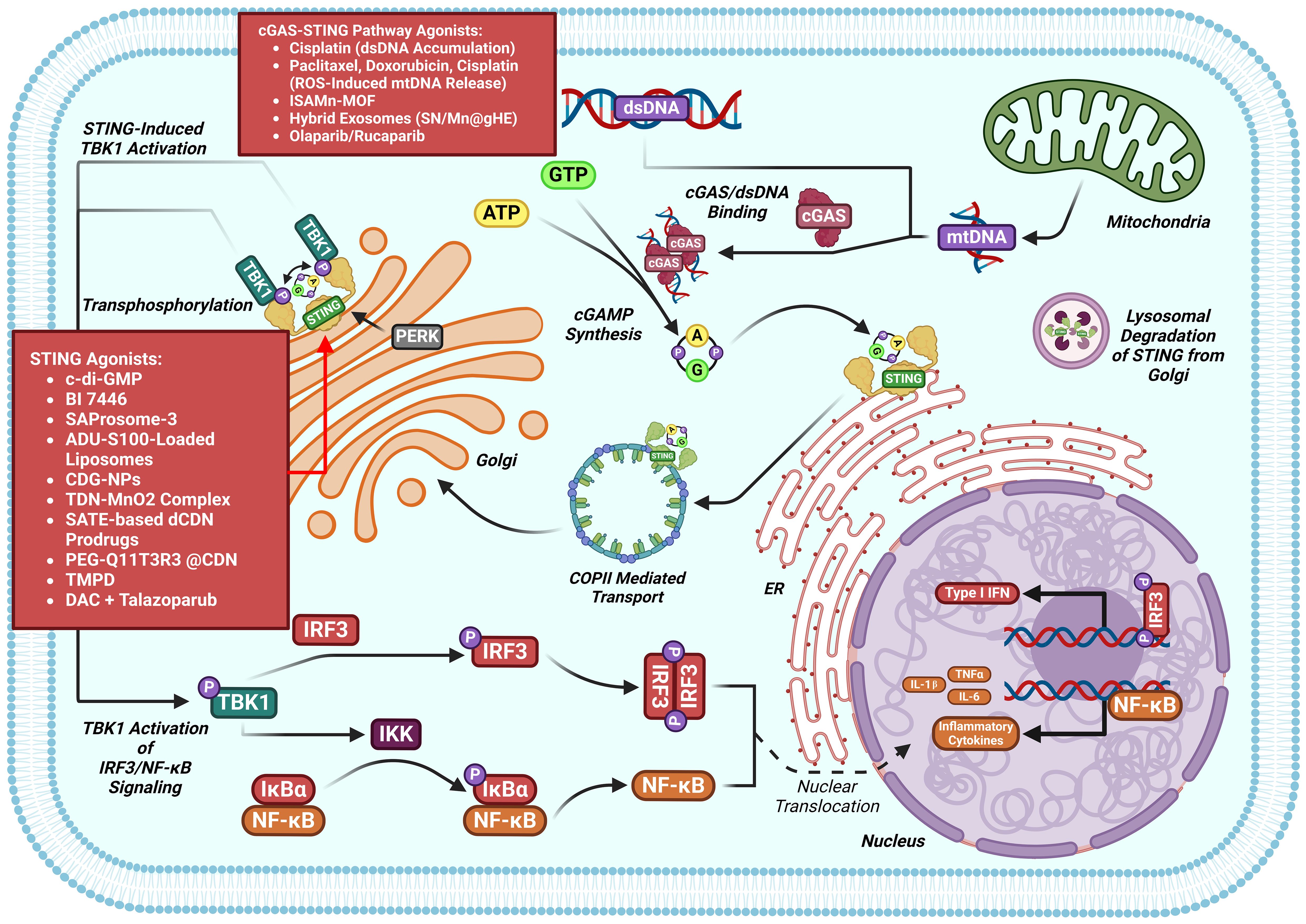
Figure 7. cGAS-STING pathway modulators in the setting of cancers. Multiple classes of cGAS-STING antagonists have shown benefit against cancers models.
4.1 STING agonist
c-di-GMP inhibits 4T1 cell growth and increases phosphorylation of STING, TBK1, IRF3 and STAT1 and the IFN-β level in tumor-bearing mice (91). BI 7446, a potent cyclic dinucleotide STING agonist, produces a durable and potent tumor inhibition and a long-term immunologic memory against autologous tumor rechallenge (92). SAProsomes-3 decreases metastatic burden and elicits durable remission of established tumors through stimulating secretion of inflammatory cytokines and creates a tumoricidal immune landscape (93). SAProsomes-3 promotes postsurgical tumor-free survival and decreases tumor metastasis and recurrence after surgery (93). ADU-S100-loaded liposomes facilitates the maturation of Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells (BMDCs) and promotes the maturation of dendritic cells through activating STING signaling to enhance TNFα and IFNβ production (94).
The STING agonists SHR1032 (96), SAProsomes-3 (93), diBSP01 (97), BSP16 (98), DMXAA (99), and ALG-031048 (100) all inhibit tumor growth through inhibiting activation of STING in colorectal cancer. The injectable hydrogel loaded with doxorubicin (DOX) and lysed OK-432 (lyOK-432) promotes an antitumor immunity through activating the STING pathway, conferring effective therapy for residual hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after incomplete radiofrequency ablation (102). The cyclic dinucleotide 3′3′-cAIMP reduces tumor size in DEN-induced C57BL/6 HCC model (103). Metformin functions as a cGAS-STING agonist to promote immunotherapy through activating the cGAS-STING signaling pathway by blocking SOX2 and AKT phosphorylation in gastric cancer (104).
4.2 PARPi
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) that targets poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase are currently approved to treat a range of tumor types harboring defects of genes contribute to homologous repair (HR), including BRCA1 and BRCA2 (129). Olaparib and rucaparib produces cytoplasmic chromatin fragments with characteristics of micronuclei, which activate cGAS-STING and downstream type I IFN signaling to enhance CCL5 secretion in NSCLCL and TNBC (109). The combination of DNA hypomethylating agents 5-aza-2’-dexoxydytidine (DAC) with BMN-673 (the PARPi talazoparib) increases cytotoxicity in SETD2-deficient ccRCC cell lines (111). DAC and talazoparib induces apoptotic, increases genomic instability, DNA damage, and insufficient DNA damage repair. DAC and talazoparib elevates immune responses, upregulates STING, and enhances viral mimicry through activating transposable elements (111). DAC and talazoparib suppresses the growth of SETD2-deficient ccRCC in vivo (111).
4.3 Nanodrugs
The manganese-phenolic network platform (TMPD) inhibits tumor growth and elicits strong antitumor effects 4T1 tumor-bearing mice through promoting STING signaling activation and promotes DC maturation and CD8+ T cell infiltration, thus (112). LND-CDN that conjugates STING-activating cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) to PEGylated lipids via a cleavable linker and incorporated them into lipid nanodiscs (LNDs), elicits tumor regression and facilitates robust T-cell activation in breast cancer and CRC (113). The SN/Mn@gHE, multifunctional hybrid exosomes that fuses genetically engineered exosomes carrying tumor cells-derived CD47 with M1 macrophages-derived exosomes, which are further encapsulated with DNA-targeting agent (SN38) and STING-agonist (MnO2). SN/Mn@gHE have tumor-targeting capacity and induce TAMs polarization to the M1 phenotype. SN/Mn@gHE release SN38 and Mn2+ to induce DNA damage and stimulate cGAS-STING activation, respectively. SN/Mn@gHE enhances maturation of DCs and promotes NK cell recruitment to the tumor region and CTL infiltration, resulting in significant antimetastatic and anti-tumor efficacy (114). PEG-Q11T3R4 @CDN inhibits tumor growth and suppresses tumor metastasis through activating the STING pathway in CRC (115). SATE-based prodrugs of dCDNs decreases CT26-Luc tumor growth and eliminates the established tumor through activating STING pathway (116). Tetrahedral DNA nanostructures synergize with MnO2(TDN-MnO2 complex) exerts anti-tumor response through activating the STING pathway in HCC (117). ISAMn-MOF inhibits tumor growth and metastasis through activating the cGAS-STING pathway in melanoma (119). CDG-NPs enhance the retention and intracellular delivery of CDG in the tumor site and facilitates activation of STING and TME immunogenicity to enhance STING-mediated anti-tumor immunity in melanoma-bearing mice (120).
4.4 Chemotherapy agents
Cisplatin inhibits the proliferation of bladder cancer through enhancing accumulation of dsDNA to activate cGAS-STING signal in bladder cancer (123). Paclitaxel, doxorubicin, and cisplatin promote CD8+ T anti-tumor immunity through enhancing induction of cancer cell-autonomous type I interferon via ROS-triggered oxidized mtDNA to activate cGAS-STING in breast cancer (94).
5 Conclusions and perspectives
Mounting evidence indicates that cGAS-STING pathway activation plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of diseases, including cancers. Emerging studies have demonstrated that pharmacological activation of the cGAS-STING pathway offers a novel therapeutic opportunities to treat cancers. Many bioactive compounds exert potential therapeutic effects against cancers by activating or inactivating the cGAS-STING pathway. In this review, we first outline the principal core mechanisms of activation for cGAS-STING signaling, then summarize recent research mechanistically connecting cGAS-STING signaling to the pathogenesis of cancers. Finally, we outlined several bioactive compounds serving as potential pharmacological antagonists of the cGAS-STING pathway, delineating their beneficial effects against the phenotypes in cancers. This review spotlights the novel potential of cGAS-STING agonists as novel therapeutic agents against cancers.
However, many questions remain to be answered. First, cGAS-STING signaling is tightly regulated at the level of transcriptional regulation, posttranslational modifications, and epigenetic modifications in various diseases, especially in cancer. An area that merits future study is the interplay between the activation of cGAS-STING and various regulated cell death (RCD) contributory to disease pathogenesis, such as: ferroptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, etc. These interplay needs to be explored on a per-disease basis. The role played by the cGAS-STING pathway is disease dependant, and places the cGAS-STING pathway as a doubled-edged sword, which may be inhibited or activated to arrive at the desired outcome. cGAS-STING activation may result in pathological conditions in non-cancer diseases. For instance, tumor cells evade cGAS-STING, and activation of this axis offers benefits in specific forms of cancer. Activation of cGAS-STING may kill cancer by overcoming resistance to targeted therapy, conventional chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. It is essential to uncover which genes and proteins regulate cGAS-STING in specific diseases, along with what their initial triggering insults are. Identifying the diverse regulators of ferroptosis in cancers remains a challenge to be resolved. Lastly, most results reported in the literature on the role played by cGAS-STING in diseases are derived from experimental studies, which do not directly related to clinical implications and applications. Many agonists of STING have been tested in clinical trials for cancer immunotherapy (2, 130). So far, these clinical trials have yielded disappointing results, with a general failure of efficacy either in combination with checkpoint blockade or as a monotherapy (131). The reasons underlying these outcomes remain unclear and remains an open conundrum for future investigate on. Cumulatively, we need to conduct more clinical studies to inform the development of practical targeted treatment strategies in the future. Translational potential of agonists of cGAS and STING is our ultimate goals. However, the laboratory insights move into clinical trials have potential barriers. cGAS-STING is highly versatile and context-dependent, and cGAS-STING axis is discovered to respond to a wide range of endogenous nucleic acids implicated in cellular stress and damage, and that its signaling outputs reach far beyond IRF3 activation and cytokine induction, such as ferroptosis, autophagy, senescence, cell death, metabolism regulation, DNA damage response, and RNA replication restriction. The in-depth cGAS-STING interactome and mechanisms of versatile outputs deserve further investigation. Our understanding of the functions and mechanisms of the DNA-sensing pathway cGAS-STING has grown exponentially since the descriptions of intracellular DNA sensing (132, 133), the discovery of STING (28, 34), and the identification of cGAS and cGAMP (22, 23). These remarkable achievements benefit from two important technologies, cryo-EM and CRISPR-Cas9 editing (2). Recent technological advancements such as single-cell RNA sequencing and genetic lineage tracing maybe help to reveal novel cell types and enriched functional properties of existing cell types in different organs that express cGAS-STING.
In summary, despite these considerations, emerging evidence strongly suggests that cGAS-STING pathway induction for cancer is a significant new direction for treating diseases. Direct research on cGAS-STING aligned towards diseases pathogenesis is still needed, but pharmacological agonism of cGAS-STING may be a promising therapeutic approach for cancers.
Author contributions
YW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. JF: Formal analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. JC: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. MD: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82300089), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7252174), Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (320.6750.2024-13-59), Science Foundation of ASCH (YN202402; YN202423), the Science Foundation of AMHT (2022YK01; 2022YK27; 2024YK01; 2024YK04), and Grant of Chinese Medicine Education Association (2022KTZ019).
Acknowledgments
Figures were created by Biorender (biorender.com).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Skopelja-Gardner S, An J, and Elkon KB. Role of the cGAS-STING pathway in systemic and organ-specific diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2022) 18:558–72. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00589-6
2. Zhang Z, Zhou H, Ouyang X, Dong Y, Sarapultsev A, Luo S, et al. Multifaceted functions of STING in human health and disease: from molecular mechanism to targeted strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:394. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01252-z
3. Motwani M, Pesiridis S, and Fitzgerald KA. DNA sensing by the cGAS-STING pathway in health and disease. Nat Rev Genet. (2019) 20:657–74. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0151-1
4. Yang K, Tang Z, Xing C, and Yan N. STING signaling in the brain: Molecular threats, signaling activities, and therapeutic challenges. Neuron. (2024) 112:539–57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.10.014
5. Ferecskó AS, Smallwood MJ, Moore A, Liddle C, Newcombe J, Holley J, et al. STING-triggered CNS inflammation in human neurodegenerative diseases. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:1375. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051375
6. Fryer AL, Abdullah A, Taylor JM, and Crack PJ. The complexity of the cGAS-STING pathway in CNS pathologies. Front Neurosci. (2021) 15:621501. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.621501
7. Huang Y, Liu B, Sinha SC, Amin S, and Gan L. Mechanism and therapeutic potential of targeting cGAS-STING signaling in neurological disorders. Mol Neurodegener. (2023) 18:79. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00672-x
8. Paul BD, Snyder SH, and Bohr VA. Signaling by cGAS-STING in neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and aging. Trends Neurosci. (2021) 44:83–96. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.10.008
9. Shen M, Jiang X, Peng Q, Oyang L, Ren Z, Wang J, et al. The cGAS–STING pathway in cancer immunity: mechanisms, challenges, and therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. (2025) 18:40. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01691-5
10. Yue B, Gao W, Lovell JF, Jin H, and Huang J. The cGAS-STING pathway in cancer immunity: dual roles, therapeutic strategies, and clinical challenges. Essays Biochem. (2025) 69:EBC20253006. doi: 10.1042/EBC20253006
11. Corrales L, Glickman LH, McWhirter SM, Kanne DB, Sivick KE, Katibah GE, et al. Direct activation of STING in the tumor microenvironment leads to potent and systemic tumor regression and immunity. Cell Rep. (2015) 11:1018–30. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.031
12. Islam S, Islam MM, Akhand M, Park BY, and Akanda MR. Recent advancements in cGAS-STING activation, tumor immune evasion, and therapeutic implications. Med Oncol. (2024) 41:291. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02539-7
13. Chabanon RM, Morel D, Eychenne T, Colmet-Daage L, Bajrami I, Dorvault N, et al. PBRM1 deficiency confers synthetic lethality to DNA repair inhibitors in cancer. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:2888–902. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0628
14. Yang B, Li X, Fu Y, Guo E, Ye Y, Li F, et al. MEK inhibition remodels the immune landscape of mutant KRAS tumors to overcome resistance to PARP and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:2714–29. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2370
15. Oh G, Wang A, Wang L, Li J, Werba G, Weissinger D, et al. POLQ inhibition elicits an immune response in homologous recombination-deficient pancreatic adenocarcinoma via cGAS/STING signaling. J Clin Invest. (2023) 133:e165934. doi: 10.1172/JCI165934
16. Yang D, Huang FX, Wei W, Li QQ, Wu JW, Huang Y, et al. Loss of HRD functional phenotype impedes immunotherapy and can be reversed by HDAC inhibitor in ovarian cancer. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:1846–60. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.79654
17. Shakfa N, Li D, Conseil G, Lightbody ED, Wilson-Sanchez J, Hamade A, et al. Cancer cell genotype associated tumor immune microenvironment exhibits differential response to therapeutic STING pathway activation in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006170. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006170
18. Yildirim Z, Doğan E, Güler Kara H, Kosova B, and Bozok V. STING activation increases the efficiency of temozolomide in PTEN harbouring glioblastoma cells. Turk J Med Sci. (2024) 54:607–14. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5828
19. Zhang S, Song D, Yu W, Li J, Wang X, Li Y, et al. Combining cisplatin and a STING agonist into one molecule for metalloimmunotherapy of cancer. Natl Sci Rev. (2024) 11:nwae020. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwae020
20. Decout A, Katz JD, Venkatraman S, and Ablasser A. The cGAS-STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21:548–69. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00524-z
21. Sheridan C. Drug developers switch gears to inhibit STING. Nat Biotechnol. (2019) 37:199–201. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0060-z
22. Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, and Chen ZJ. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science. (2013) 339:786–91. doi: 10.1126/science.1232458
23. Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science. (2013) 339:826–30. doi: 10.1126/science.1229963
24. Gall A, Treuting P, Elkon KB, Loo YM, Gale M Jr, Barber GN, et al. Autoimmunity initiates in nonhematopoietic cells and progresses via lymphocytes in an interferon-dependent autoimmune disease. Immunity. (2012) 36:120–31. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.018
25. Sun W, Li Y, Chen L, Chen H, You F, Zhou X, et al. ERIS, an endoplasmic reticulum IFN stimulator, activates innate immune signaling through dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2009) 106:8653–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900850106
26. Jin L, Getahun A, Knowles HM, Mogan J, Akerlund LJ, Packard TA, et al. STING/MPYS mediates host defense against Listeria monocytogenes infection by regulating Ly6C(hi) monocyte migration. J Immunol. (2013) 190:2835–43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201788
27. Jin L, Waterman PM, Jonscher KR, Short CM, Reisdorph NA, and Cambier JC. MPYS, a novel membrane tetraspanner, is associated with major histocompatibility complex class II and mediates transduction of apoptotic signals. Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 28:5014–26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00640-08
28. Zhong B, Yang Y, Li S, Wang YY, Li Y, Diao F, et al. The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity. (2008) 29:538–50. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.09.003
29. Civril F, Deimling T, de Oliveira Mann CC, Ablasser A, Moldt M, Witte G, et al. Structural mechanism of cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS. Nature. (2013) 498:332–7. doi: 10.1038/nature12305
30. Gao P, Ascano M, Wu Y, Barchet W, Gaffney BL, Zillinger T, et al. Cyclic [G(2’,5’)pA(3’,5’)p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. Cell. (2013) 153:1094–107. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.046
31. Kranzusch PJ, Lee AS, Berger JM, and Doudna JA. Structure of human cGAS reveals a conserved family of second-messenger enzymes in innate immunity. Cell Rep. (2013) 3:1362–8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.05.008
32. Li X, Shu C, Yi G, Chaton CT, Shelton CL, Diao J, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is activated by double-stranded DNA-induced oligomerization. Immunity. (2013) 39:1019–31. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.019
33. Zhang X, Shi H, Wu J, Zhang X, Sun L, Chen C, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING. Mol Cell. (2013) 51:226–35. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.05.022
34. Ishikawa H and Barber GN. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature. (2008) 455:674–8. doi: 10.1038/nature07317
35. Ishikawa H, Ma Z, and Barber GN. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature. (2009) 461:788–92. doi: 10.1038/nature08476
36. Shang G, Zhang C, Chen ZJ, Bai XC, and Zhang X. Cryo-EM structures of STING reveal its mechanism of activation by cyclic GMP-AMP. Nature. (2019) 567:389–93. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0998-5
37. Shu C, Yi G, Watts T, Kao CC, and Li P. Structure of STING bound to cyclic di-GMP reveals the mechanism of cyclic dinucleotide recognition by the immune system. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2012) 19:722–4. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2331
38. Kwon J and Bakhoum SF. The cytosolic DNA-sensing cGAS-STING pathway in cancer. Cancer Discov. (2020) 10:26–39. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0761
39. Samson N and Ablasser A. The cGAS-STING pathway and cancer. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:1452–63. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00468-w
40. Wheeler O and Unterholzner L. DNA sensing in cancer: Pro-tumour and anti-tumour functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Essays Biochem. (2023) 67:905–18. doi: 10.1042/EBC20220241
41. Yum S, Li M, and Chen ZJ. Old dogs, new trick: classic cancer therapies activate cGAS. Cell Res. (2020) 30:639–48. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0346-1
42. Wang Y, Luo J, Alu A, Han X, Wei Y, and Wei X. cGAS-STING pathway in cancer biotherapy. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:136. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01247-w
43. Zhu Y, An X, Zhang X, Qiao Y, Zheng T, and Li X. STING: a master regulator in the cancer-immunity cycle. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:152. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1087-y
44. Zou SS, Qiao Y, Zhu S, Gao B, Yang N, Liu YJ, et al. Intrinsic strategies for the evasion of cGAS-STING signaling-mediated immune surveillance in human cancer: How therapy can overcome them. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 166:105514. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105514
45. Imre G. Pyroptosis in health and disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2024) 326:C784–94. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00503.2023
46. Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yang Y, Fleishman JS, Wang Y, et al. Cuproptosis: A novel therapeutic target for overcoming cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat. (2024) 72:101018. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2023.101018
47. Wang Y, Hu J, Wu S, Fleishman JS, Li Y, Xu Y, et al. Targeting epigenetic and posttranslational modifications regulating ferroptosis for the treatment of diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:449. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01720-0
48. Wang Y, Wu X, Ren Z, Li Y, Zou W, Chen J, et al. Overcoming cancer chemotherapy resistance by the induction of ferroptosis. Drug Resist Updat. (2023) 66:100916. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2022.100916
49. Hadian K and Stockwell BR. The therapeutic potential of targeting regulated non-apoptotic cell death. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2023) 22:723–42. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00749-8
50. Tang D, Kang R, Berghe TV, Vandenabeele P, and Kroemer G. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. (2019) 29:347–64. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0164-5
51. Hu A, Sun L, Lin H, Liao Y, Yang H, and Mao Y. Harnessing innate immune pathways for therapeutic advancement in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:68. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01765-9
52. Cerboni S, Jeremiah N, Gentili M, Gehrmann U, Conrad C, Stolzenberg MC, et al. Intrinsic antiproliferative activity of the innate sensor STING in T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:1769–85. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161674
53. Larkin B, Ilyukha V, Sorokin M, Buzdin A, Vannier E, and Poltorak A. Cutting edge: activation of STING in T cells induces type I IFN responses and cell death. J Immunol. (2017) 199:397–402. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601999
54. Tang CH, Zundell JA, Ranatunga S, Lin C, Nefedova Y, Del Valle JR, et al. Agonist-mediated activation of STING induces apoptosis in Malignant B cells. Cancer Res. (2016) 76:2137–52. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1885
55. Gulen MF, Koch U, Haag SM, Schuler F, Apetoh L, Villunger A, et al. Signalling strength determines proapoptotic functions of STING. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:427. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00573-w
56. Lu Q, Chen Y, Li J, Zhu F, and Zheng Z. Crosstalk between cGAS-STING pathway and autophagy in cancer immunity. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1139595. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1139595
57. Yamazaki T, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G, and Pietrocola F. Autophagy in the cancer-immunity dialogue. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2021) 169:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.12.003
58. Kuang F, Liu J, Li C, Kang R, and Tang D. Cathepsin B is a mediator of organelle-specific initiation of ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 533:1464–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.035
59. Li C, Liu J, Hou W, Kang R, and Tang D. STING1 promotes ferroptosis through MFN1/2-dependent mitochondrial fusion. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:698679. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.698679
60. Zhang S, Kang L, Dai X, Chen J, Chen Z, Wang M, et al. Manganese induces tumor cell ferroptosis through type-I IFN dependent inhibition of mitochondrial dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 193:202–12. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.10.004
61. Yang M, Liu H, Lou J, Zhang J, Zuo C, Zhu M, et al. Alpha-emitter radium-223 induces STING-dependent pyroptosis to trigger robust antitumor immunity. Small. (2024) 20:e2307448. doi: 10.1002/smll.202307448
62. Chen DS and Mellman I. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity. (2013) 39:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012
63. Mellman I, Chen DS, Powles T, and Turley SJ. The cancer-immunity cycle: Indication, genotype, and immunotype. Immunity. (2023) 56:2188–205. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.09.011
64. Zhao K, Huang J, Zhao Y, Wang S, Xu J, and Yin K. Targeting STING in cancer: Challenges and emerging opportunities. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2023) 1878:188983. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188983
65. Schmitt CA, Wang B, and Demaria M. Senescence and cancer - role and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2022) 19:619–36. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00668-4
66. Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. (2022) 12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059
67. López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, and Kroemer G. Hallmarks of aging: An expanding universe. Cell. (2023) 186:243–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.001
68. Coppé JP, Desprez PY, Krtolica A, and Campisi J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu Rev Pathol. (2010) 5:99–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102144
69. Xue W, Zender L, Miething C, Dickins RA, Hernando E, Krizhanovsky V, et al. Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas. Nature. (2007) 445:656–60. doi: 10.1038/nature05529
70. Campisi J and d’Adda di Fagagna F. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2007) 8:729–40. doi: 10.1038/nrm2233
71. Braig M, Lee S, Loddenkemper C, Rudolph C, Peters AH, Schlegelberger B, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development. Nature. (2005) 436:660–5. doi: 10.1038/nature03841
72. Chen Z, Trotman LC, Shaffer D, Lin HK, Dotan ZA, Niki M, et al. Crucial role of p53-dependent cellular senescence in suppression of Pten-deficient tumorigenesis. Nature. (2005) 436:725–30. doi: 10.1038/nature03918
73. Collado M, Gil J, Efeyan A, Guerra C, Schuhmacher AJ, Barradas M, et al. Tumour biology: senescence in premalignant tumours. Nature. (2005) 436:642. doi: 10.1038/436642a
74. Dou Z, Ghosh K, Vizioli MG, Zhu J, Sen P, Wangensteen KJ, et al. Cytoplasmic chromatin triggers inflammation in senescence and cancer. Nature. (2017) 550:402–6. doi: 10.1038/nature24050
75. Glück S, Guey B, Gulen MF, Wolter K, Kang TW, Schmacke NA, et al. Innate immune sensing of cytosolic chromatin fragments through cGAS promotes senescence. Nat Cell Biol. (2017) 19:1061–70. doi: 10.1038/ncb3586
76. Harding SM, Benci JL, Irianto J, Discher DE, Minn AJ, and Greenberg RA. Mitotic progression following DNA damage enables pattern recognition within micronuclei. Nature. (2017) 548:466–70. doi: 10.1038/nature23470
77. Yang H, Wang H, Ren J, Chen Q, and Chen ZJ. cGAS is essential for cellular senescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2017) 114:E4612–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705499114
78. Ahn J, Konno H, and Barber GN. Diverse roles of STING-dependent signaling on the development of cancer. Oncogene. (2015) 34:5302–8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.457
79. Zhu Q, Man SM, Gurung P, Liu Z, Vogel P, Lamkanfi M, et al. Cutting edge: STING mediates protection against colorectal tumorigenesis by governing the magnitude of intestinal inflammation. J Immunol (Baltimore Md. (2014) 1950) 193:4779–82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402051
80. Xia T, Konno H, Ahn J, and Barber GN. Deregulation of STING signaling in colorectal carcinoma constrains DNA damage responses and correlates with tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. (2016) 14:282–97. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.029
81. Bu Y, Liu F, Jia QA, and Yu SN. Decreased expression of TMEM173 predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0165681. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165681
82. Fu L, Ding H, Bai Y, Cheng L, Hu S, and Guo Q. IDI1 inhibits the cGAS-Sting signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e27205. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27205
83. Li JY, Zhao Y, Gong S, Wang MM, Liu X, He QM, et al. TRIM21 inhibits irradiation-induced mitochondrial DNA release and impairs antitumour immunity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumour models. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:865. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36523-y
84. Liu X, Cen X, Wu R, Chen Z, Xie Y, Wang F, et al. ARIH1 activates STING-mediated T-cell activation and sensitizes tumors to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:4066. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39920-5
85. Xing J, Zhang A, Zhang H, Wang J, Li XC, Zeng MS, et al. TRIM29 promotes DNA virus infections by inhibiting innate immune response. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:945. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00101-w
86. Wang J, Lu W, Zhang J, Du Y, Fang M, Zhang A, et al. Loss of TRIM29 mitigates viral myocarditis by attenuating PERK-driven ER stress response in male mice. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:3481. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44745-x
87. Wang J, Wang L, Lu W, Farhataziz N, Gonzalez A, Xing J, et al. TRIM29 controls enteric RNA virus-induced intestinal inflammation by targeting NLRP6 and NLRP9b signaling pathways. Mucosal Immunol. (2025) 18:135–50. doi: 10.1016/j.mucimm.2024.10.004
88. Fang M, Zhang A, Du Y, Lu W, Wang J, Minze LJ, et al. TRIM18 is a critical regulator of viral myocarditis and organ inflammation. J BioMed Sci. (2022) 29:55. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00840-z
89. Xia T, Konno H, and Barber GN. Recurrent loss of STING signaling in melanoma correlates with susceptibility to viral oncolysis. Cancer Res. (2016) 76:6747–59. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1404
90. Liu W, Kim GB, Krump NA, Zhou Y, Riley JL, and You J. Selective reactivation of STING signaling to target Merkel cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2020) 117:13730–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1919690117
91. Yin M, Hu J, Yuan Z, Luo G, Yao J, Wang R, et al. STING agonist enhances the efficacy of programmed death-ligand 1 monoclonal antibody in breast cancer immunotherapy by activating the interferon-β signalling pathway. Cell Cycle. (2022) 21:767–79. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2029996
92. Kuttruff CA, Fleck M, Carotta S, Arnhof H, Bretschneider T, Dahmann G, et al. Discovery of BI 7446: A potent cyclic dinucleotide STING agonist with broad-spectrum variant activity for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem. (2023) 66:9376–400. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00510
93. Chen X, Meng F, Xu Y, Li T, Chen X, and Wang H. Chemically programmed STING-activating nano-liposomal vesicles improve anticancer immunity. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:4584. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40312-y
94. Ji N, Wang M, and Tan C. Liposomal delivery of MIW815 (ADU-S100) for potentiated STING activation. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:638. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020638
95. Huang X, Huo L, Xiao B, Ouyang Y, Chen F, Li J, et al. Activating STING/TBK1 suppresses tumor growth via degrading HPV16/18 E7 oncoproteins in cervical cancer. Cell Death Differ. (2024) 31:78–89. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01242-w
96. Song C, Liu D, Liu S, Li D, Horecny I, Zhang X, et al. SHR1032, a novel STING agonist, stimulates anti-tumor immunity and directly induces AML apoptosis. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:8579. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12449-1
97. Liu D, Yu B, Guan X, Song B, Pan H, Wang R, et al. Discovery of a photoactivatable dimerized STING agonist based on the benzoselenophene scaffold. Chem Sci. (2023) 14:4174–82. doi: 10.1039/D2SC06860E
98. Feng X, Pan L, Qian Z, Liu D, Guan X, Feng L, et al. Discovery of selenium-containing STING agonists as orally available antitumor agents. J Med Chem. (2022) 65:15048–65. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00634
99. Liu Y, Sun Q, Zhang C, Ding M, Wang C, Zheng Q, et al. STING-IRG1 inhibits liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by regulating the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. iScience. (2023) 26:107376. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107376
100. Jekle A, Thatikonda SK, Jaisinghani R, Ren S, Kinkade A, Stevens SK, et al. Tumor regression upon intratumoral and subcutaneous dosing of the STING agonist ALG-031048 in mouse efficacy models. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:16274. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216274
101. Sun F, Xu Y, Deng Z, and Yang P. A recombinant oncolytic influenza virus expressing a PD-L1 antibody induces CD8(+) T-cell activation via the cGas-STING pathway in mice with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 120:110323. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110323
102. Cao Y, Sun T, Sun B, Zhang G, Liu J, Liang B, et al. Injectable hydrogel loaded with lysed OK-432 and doxorubicin for residual liver cancer after incomplete radiofrequency ablation. J Nanobiotechnol. (2023) 21:404. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02170-0
103. Thomsen MK, Skouboe MK, Boularan C, Vernejoul F, Lioux T, Leknes SL, et al. The cGAS-STING pathway is a therapeutic target in a preclinical model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. (2020) 39:1652–64. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1108-8
104. Shen Q, Yang L, Li C, Wang T, Lv J, Liu W, et al. Metformin promotes cGAS/STING signaling pathway activation by blocking AKT phosphorylation in gastric cancer. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e18954. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18954
105. Marritt KL, Hildebrand KM, Hildebrand KN, Singla AK, Zemp FJ, Mahoney DJ, et al. Intratumoral STING activation causes durable immunogenic tumor eradication in the KP soft tissue sarcoma model. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1087991. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1087991
106. Joseph JV, Blaavand MS, Cai H, Vernejoul F, Knopper RW, Lindhardt TB, et al. STING activation counters glioblastoma by vascular alteration and immune surveillance. Cancer Lett. (2023) 579:216480. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216480
107. Zhao M, Fan W, Wang Y, Qiang P, Zheng Z, Shan H, et al. M335, a novel small-molecule STING agonist activates the immune response and exerts antitumor effects. Eur J Med Chem. (2024) 264:116018. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.116018
108. Dejmek M, Brazdova A, Otava T, Polidarova MP, Klíma M, Smola M, et al. Vinylphosphonate-based cyclic dinucleotides enhance STING-mediated cancer immunotherapy. Eur J Med Chem. (2023) 259:115685. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115685
109. Chabanon RM, Muirhead G, Krastev DB, Adam J, Morel D, Garrido M, et al. PARP inhibition enhances tumor cell-intrinsic immunity in ERCC1-deficient non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Invest. (2019) 129:1211–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI123319
110. Huang Y, Qin G, Cui T, Zhao C, Ren J, and Qu X. A bimetallic nanoplatform for STING activation and CRISPR/Cas mediated depletion of the methionine transporter in cancer cells restores anti-tumor immune responses. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:4647. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40345-3
111. Zhou X, Sekino Y, Li HT, Fu G, Yang Z, Zhao S, et al. SETD2 deficiency confers sensitivity to dual inhibition of DNA methylation and PARP in kidney cancer. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:3813–26. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0401
112. Pang X, Fu C, Chen J, Su M, Wei R, Wang Y, et al. A manganese-phenolic network platform amplifying STING activation to potentiate MRI guided cancer chemo-/chemodynamic/immune therapy. Biomater Sci. (2023) 11:3840–50. doi: 10.1039/D2BM02140D
113. Dane EL, Belessiotis-Richards A, Backlund C, Wang J, Hidaka K, Milling LE, et al. STING agonist delivery by tumour-penetrating PEG-lipid nanodiscs primes robust anticancer immunity. Nat Mater. (2022) 21:710–20. doi: 10.1038/s41563-022-01251-z
114. Cheng L, Zhang P, Liu Y, Liu Z, Tang J, Xu L, et al. Multifunctional hybrid exosomes enhanced cancer chemo-immunotherapy by activating the STING pathway. Biomaterials. (2023) 301:122259. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122259
115. Dong W, Xu L, Chang C, Jiang T, Chen CP, and Zhang G. A novel self-assembled nucleobase-nanofiber platform of CDN to activate the STING pathway for synergistic cancer immunotherapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2023) 232:113597. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113597
116. Xie Z, Lu L, Wang Z, Luo Q, Yang Y, Fang T, et al. S-acylthioalkyl ester (SATE)-based prodrugs of deoxyribose cyclic dinucleotides (dCDNs) as the STING agonist for antitumor immunotherapy. Eur J Med Chem. (2022) 243:114796. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114796
117. Liang S, Li J, Zou Z, Mao M, Ming S, Lin F, et al. Tetrahedral DNA nanostructures synergize with MnO(2) to enhance antitumor immunity via promoting STING activation and M1 polarization. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:2494–505. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.12.010
118. Luo Z, Liang X, He T, Qin X, Li X, Li Y, et al. Lanthanide-nucleotide coordination nanoparticles for STING activation. J Am Chem Soc. (2022) 144:16366–77. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c03266
119. Zheng SJ, Yang M, Luo JQ, Liu R, Song J, Chen Y, et al. Manganese-based immunostimulatory metal-organic framework activates the cGAS-STING pathway for cancer metalloimmunotherapy. ACS Nano. (2023) 17:15905–17. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03962
120. Xu L, Deng H, Wu L, Wang D, Shi L, Qian Q, et al. Supramolecular cyclic dinucleotide nanoparticles for STING-mediated cancer immunotherapy. ACS Nano. (2023) 17:10090–103. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c12685
121. Wang-Bishop L, Kimmel BR, Ngwa VM, Madden MZ, Baljon JJ, Florian DC, et al. STING-activating nanoparticles normalize the vascular-immune interface to potentiate cancer immunotherapy. Sci Immunol. (2023) 8:eadd1153. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.add1153
122. Tran T, Le PM, Nguyen T, Hoang T, Do T, Martel AL, et al. Novel human STING activation by hydrated-prenylated xanthones from Garcinia cowa. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2023) 75:1058–65. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgad038
123. Fu G, Wu Y, Zhao G, Chen X, Xu Z, Sun J, et al. Activation of cGAS-STING signal to inhibit the proliferation of bladder cancer: the immune effect of cisplatin. Cells. (2022) 11:3011. doi: 10.3390/cells11193011
124. Liu X, Hogg GD, Zuo C, Borcherding NC, Baer JM, Lander VE, et al. Context-dependent activation of STING-interferon signaling by CD11b agonists enhances anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41:1073–1090.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.04.018
125. Yuan M, Guo XL, Chen JH, He Y, Liu ZQ, Zhang HP, et al. Anlotinib suppresses proliferation, migration, and immune escape of gastric cancer cells by activating the cGAS-STING/IFN-β pathway. Neoplasma. (2022) 69:807–19. doi: 10.4149/neo_2022_211012N1441
126. Della Corte CM, Fasano M, Ciaramella V, Cimmino F, Cardnell R, Gay CM, et al. Anti-tumor activity of cetuximab plus avelumab in non-small cell lung cancer patients involves innate immunity activation: findings from the CAVE-Lung trial. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 41:109. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02332-2
127. Han J, Hu S, Hu Y, Xu Y, Hou Y, Yang Y, et al. Discovery of podofilox as a potent cGAMP-STING signaling enhancer with antitumor activity. Cancer Immunol Res. (2023) 11:583–99. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0483
128. Zheng H, Guo B, Qiu X, Xia Y, Qu Y, Cheng L, et al. Polymersome-mediated cytosolic delivery of cyclic dinucleotide STING agonist enhances tumor immunotherapy. Bioact Mater. (2022) 16:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.02.029
129. Bhamidipati D, Haro-Silerio JI, Yap TA, and Ngoi N. PARP inhibitors: enhancing efficacy through rational combinations. Br J Cancer. (2023) 129:904–16. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02326-7
130. Vanpouille-Box C, Hoffmann JA, and Galluzzi L. Pharmacological modulation of nucleic acid sensors - therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2019) 18:845–67. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0043-2
131. Meric-Bernstam F, Sweis RF, Kasper S, Hamid O, Bhatia S, Dummer R, et al. Combination of the STING agonist MIW815 (ADU-S100) and PD-1 inhibitor spartalizumab in advanced/metastatic solid tumors or lymphomas: an open-label, multicenter, phase ib study. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:110–21. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2235
132. Ishii KJ, Coban C, Kato H, Takahashi K, Torii Y, Takeshita F, et al. A Toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA. Nat Immunol. (2006) 7:40–8. doi: 10.1038/ni1282
Keywords: CGAS, STING, agonist, cancers contents, small-molecule compounds
Citation: Wang Y, Zhu Y, Cao Y, Li Y, Zhang Z, Fleishman JS, Cheng S, Chen J and Ding M (2025) The activation of cGAS-STING pathway offers novel therapeutic opportunities in cancers. Front. Immunol. 16:1579832. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1579832
Received: 19 February 2025; Accepted: 19 May 2025;
Published: 09 June 2025.
Edited by:
Abdullah Saeed, City of Hope National Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Junji Xing, Houston Methodist Research Institute, United StatesXiang Zhou, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhu, Cao, Li, Zhang, Fleishman, Cheng, Chen and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mingchao Ding, ZG1jX3p4bEB2aXAuc2luYS5jb20=; Jichao Chen, Y2hlbl9odHp4eXlAc2luYS5jb20=; Sihang Cheng, Y2hlbmdzaWhhbmdAcHVtY2guY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Yumin Wang, orcid.org/0000-0001-7023-7159
 Yumin Wang
Yumin Wang Yonglin Zhu1†
Yonglin Zhu1†