- 1Department of Oncology, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2The Second Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 4Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shandong Provincial Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 5The Third Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China
PLK1 plays a crucial role in cell cycle regulation and cancer development, and its dysregulation has been implicated in the prognosis of a variety of malignancies. The potential of PLK1 inhibitors as cancer therapeutics has been extensively investigated. However, the underlying biology and mechanisms of PLK1 remain incompletely understood. In recent years, numerous studies have demonstrated that PLK1 overexpression is associated with resistance to certain chemotherapeutic agents, while its inhibition can enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy. In addition, PLK1 inhibitors have been shown to selectively target cancer cells as radiation sensitizers and exert synergistic effects in combination immunotherapy. The underlying mechanisms may involve the regulation of multiple immune cells and inflammatory factors, as well as alterations in the tumor microenvironment, ultimately influencing tumor genesis, migration, and invasion. Moreover, PLK1 can regulate the expression of immune checkpoint-related proteins, thereby playing a synergistic role in cancer therapy. Furthermore, PLK1 represents a promising target antigen for cancer immunotherapy, with potential applications in optimizing cancer vaccines. Therefore, this review focuses on the applications and underlying mechanisms of PLK1 in tumor immunotherapy, aiming to provide new insights for improving patient outcomes and prognosis.
1 Introduction
PLK1, a member of the polo-like kinase (PLK) subfamily of Ser/Thr protein kinases, plays a pivotal role in regulating diverse cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, differentiation, survival, DNA damage response, autophagy, apoptosis, and cytokine signaling (1, 2). Given its frequent overexpression in various tumor types and its association with poor clinical outcomes, PLK1 has emerged as a highly attractive target for the development of anti-cancer therapies (3). However, due to its critical role in cell cycle regulation, inhibiting PLK1 activity can lead to aberrant mitosis and chromosomal instability in normal tissues. As a result, the use of PLK1 inhibitors carries the risk of inducing new tumors or causing significant side effects in some patients (4).
In recent years, studies have demonstrated that combining PLK1 inhibitors with other therapies can achieve superior efficacy compared to monotherapy. By inhibiting PLK1, these combinations can address the issue of drug resistance to certain chemotherapy agents and act as radiation sensitizers, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of tumor chemoradiotherapy (5–7). Additionally, PLK1 is closely linked to tumor immunotherapy, with its expression showing significant correlations with immunophenotyping, immune cell infiltration, tumor mutational burden (TMB), microsatellite instability (MSI), immune checkpoint gene activity, and therapeutic outcomes across various tumor types (8). In this review, we discuss the structure and function of PLK1, its multifaceted role in cancer biology, and its significance and underlying mechanisms in the context of cancer immunotherapy.
2 PLK1 structure and function
In humans, five PLK paralogues have been identified, including PLK1, PLK2 (Snk), PLK3 (Fnk/Prk), PLK4 (Sak), and PLK5 (9). PLK proteins typically comprise two C-terminal Polo-box domains (PBDs) and an N-terminal catalytic kinase domain (10). But PLK4 has three polo box regions, making it the most structurally differentiated member of the PLK family (11). In contrast, PLK5 lacks part of the kinase domain but is still considered a member of the PLK family due to the retention of the PBD sequence (9, 12).
PLK1 is the most highly conserved member of the polo-like kinase family (Figure 1). However, PLK1 gene polymorphisms (such as rs27770, rs40076, rs57973275) may regulate cancer risk and treatment response by affecting its expression, mRNA stability, or function. rs27770 is located in the PLK1 coding region, which can lead to threonine (Thr) to methionine (Met) at position 609. Its allele shows different secondary mRNA structure (13). There are studies have shown that the higher frequency of G allele in Asian population can make PLK1 more susceptible to the inhibition of human microrna: hsa-miR-100-5p, which is more conducive to the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (14). rs40076 is located in the intronic region of PLK1, affects mRNA splicing or transcriptional regulation, and can be used as a predictor of bladder cancer susceptibility and survival (15). rs57973275 is located in the 3 ‘-UTR region, and studies have shown that targeting this region can inhibit the expression of PLK1, thereby inhibiting the progression of lung cancer (16).
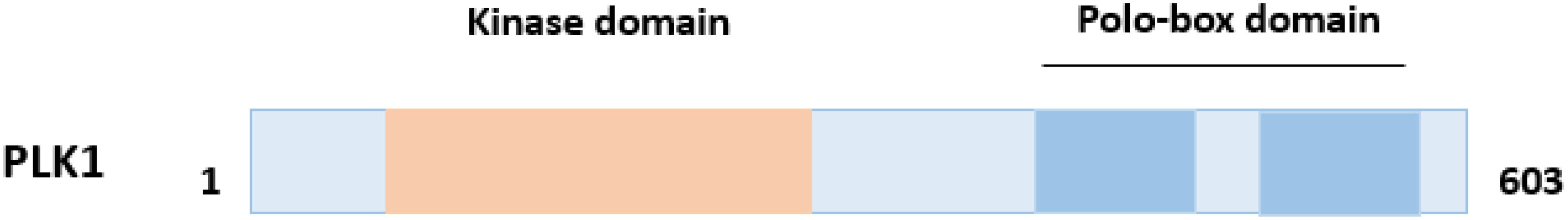
Figure 1. PLK1 protein domains. PLK1 structure includes two functional polo-box domains (PBDs) at C-terminal and the kinase domain at N-terminal.
PLK1 plays a critical role in cell division and is predominantly localized in three distinct subcellular regions: the mitotic centrosomes, kinetochores, and the cytokinetic midbody (17). PLK1 plays a crucial role in centrosome maturation. It also affects the process of centrosome separation in G2/M phase to form bipolar spindle. PLK1 promotes the recruitment of the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC) and other Plasma Membrane Calcium-transporting ATPase (PMC) proteins to centrosomes, while phosphorylating key proteins such as the kinase Nek9 and the mitotic motor protein Eg5 (18, 19). On one hand, PLK1 recruits PP2A to BubR1, facilitating the attachment of centromeres to microtubules and maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) (20). On the other hand, once all centromeres are properly attached to spindle microtubules during metaphase, PLK1 is ubiquitinated by the active anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), leading to its dissociation from centrosomes and the transition out of metaphase (21, 22). Furthermore, PLK1 activity is essential for cytokinesis, as it regulates phosphorylated microtubule-associated protein (PRC1) and intermediate localization protein (CEP55) to mediate cytoplasmic division and abscission (23–25). If PLK1/PRC1 signaling is blocked, tumor growth is inhibited, and drug-resistant tumors become more sensitive to conventional chemotherapy (26).
The process of epithelial cells transdifferentiate into motor mesenchymal cells is called epithelial-mesenchymal transition(EMT). Although EMT is integral in development, wound healing, and stem cell behavior, it also contributes pathologically to fibrosis and cancer progression (27). Studies have shown that PLK1 is a key regulator of EMT in tumor cells. In non-small cell lung cancer, the invasion and metastasis of tumor cells can be promoted by activating the PLK1/β-catenin/AP-1 or PLK1/TGF β axis (28, 29). In addition, PLK1 can accelerate or reverse EMT by regulating the AKT pathway. This phenomenon has been verified in gastric cancer and osteosarcoma (30, 31). In the prostate, PLK1 acts primarily as a potent activator of the MAPK signaling pathway, stimulating cell migration and invasion (32).
3 PLK1 and tumors
3.1 Effect of PLK1 on tumor development
3.1.1 Tumor-promoting role of PLK1
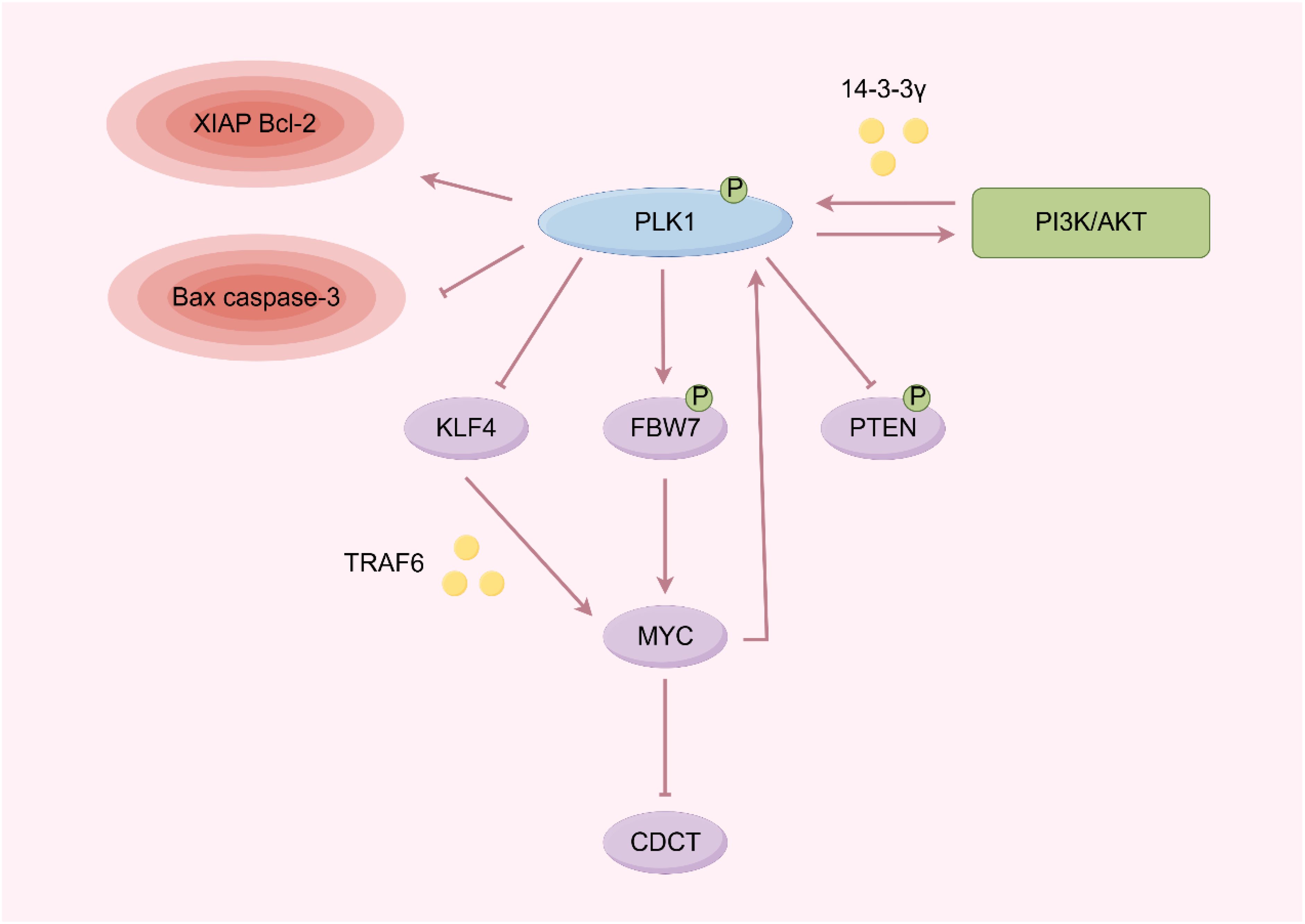
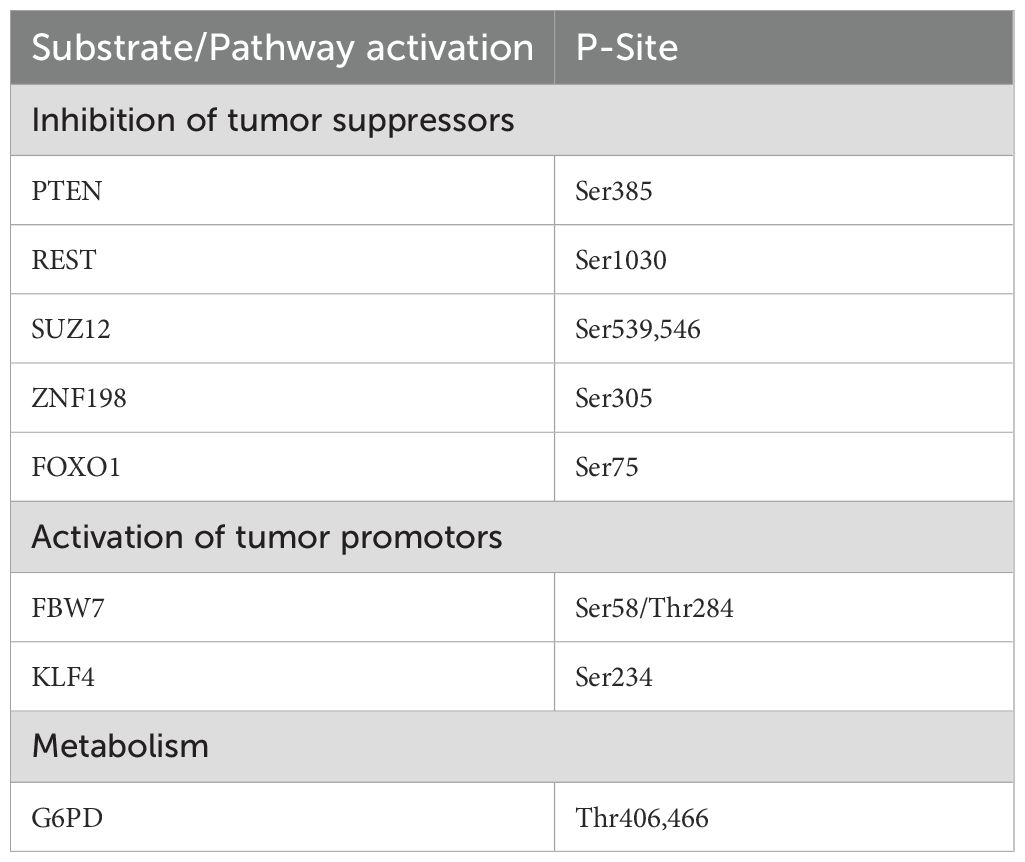
PLK1 is a key regulator of mitosis and cytokinesis, and its overexpression is frequently observed in various tumors, often correlating with poor prognosis (Figure 2). PLK1 phosphorylation can inactivate the tumor suppressor gene PTEN, thereby activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, which enhances aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumorigenesis (33). Meanwhile, PTEN is also known to be an important regulator of Plk1 dephosphorylation and chromosome stability during cell division (34). PI3K/AKT could reduce the binding of PLK1 to 14-3-3γ protein, eventually leading to the inability of PLK1 to be activated by catalysis (35). Inhibition of PLK1 can further regulate the downstream genes, including the up-regulation of caspase-3 and Bax and the down-regulation of XIAP and Bcl-2, ultimately affecting the occurrence and development of tumors (36). Furthermore, the combined inhibition of PLK1 and PI3K/AKT, along with FOXO1, exerts synergistic anticancer effects in anaplastic thyroid cancer and non-small cell lung cancer (37, 38). Additionally, PLK1 inhibitors have been shown to enhance the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer to chemotherapy (39).
PLK1 also enhances the stability of the oncogene MYC protein (40, 41). Inhibition of PLK1 reduces the phosphorylation of FBW7, preventing its autoubiquitination and proteasome degradation, thereby promoting the degradation of MYC and reducing tumor cell proliferation while increasing apoptosis (42, 43). PLK1 expression can promote MYC to activate Hedgehog signaling pathway by degrading PDCD4, and then promote the proliferation of tumor cells (44). PLK1 inhibitors also synergistically with mTOR inhibitors to compensatively induce MYC expression, overcome the oxaliplatin resistance of colon cancer, and enhance the radiosensitivity of medulloblastoma (6, 45, 46). At the same time, MYC can deactivate PLK1, preventing PLK1 inhibitors from exerting their effects of sustained activation of SAC and hindering intermediate separation (40, 43, 47, 48).
In nasopharyngeal carcinoma, PLK1 promotes tumorigenesis by mediating KLF4 overexpression. PLK1 directly phosphorylates the Ser234 site of KLF4, leading to the recruitment and binding of the E3 ligase TRAF6, which stabilizes KLF4 through K63-linked ubiquitination. This stabilization enhances the transcriptional activity of KLF4, which in turn activates the MYC oncogenic program, creating a feedforward loop that drives tumor progression (49).
Regulation of the PLK1-p53 signaling axis eventually induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits tumor growth (50). P53 can promote the cytotoxicity of PLK1-targeted therapy and reduce tumor recurrence and metastasis (51). Other transcription factors regulated by PLK1 include PLK1 phosphorylation-dependent REST degradation in triple-negative breast cancer (52), SUZ12 and ZNF198 in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-mediated liver cancer (53), and transcription of the key tumor suppressor FOXO1 in prostate cancer cells and rhabdomyosarcoma (54, 55). PLK1 can also exert a synergistic effect with FOXM1 to affect the prognosis of liver cancer (56), papillary thyroid cancer (57), bladder cancer (58),diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (59), kidney cancer (60), lung cancer (61), breast cancer (62), esophageal cancer (63) and other tumors.
In addition, PLK1 can also coordinate cancer progression by influencing metabolic reprogramming. PLK1 plays a key role in the biosynthesis of cancer cells by promoting the formation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) active dimers, interacting with them and directly phosphorylation, thereby activating the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) (64). PLK1 is also a valuable molecular target for angiogenesis, and inhibition of its expression can inhibit the formation of new tubular structures in non-small cell lung cancer and prostate cancer, and enhance the chemotherapy sensitization of paclitaxel in cancer cells (65) (Table 1). Recent studies have also found that PLK1 is involved in ferroptosis pathway, and PLK1-CBx8-GPX4 can overcome the drug resistance mechanism of colorectal cancer by inducing ferroptosis (66, 67).
3.1.2 PLK1 as a tumor suppressor
Despite its predominant role as a tumor promoter, PLK1 can also exhibit tumor-suppressive effects under certain conditions. For instance, PLK1 overexpression has been shown to inhibit the development of Kras- or Her2-induced breast tumors by interfering with mitotic processes and cytokinesis (68). Additionally, high levels of PLK1 have been associated with improved survival rates in colorectal cancer patients with APC mutations. In these cases, inhibition of PLK1 in colon cells expressing mutant APC-ΔC disrupts spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) recruitment by reducing the localization of BUBR1 and MAD1 at the centromere, leading to chromosomal abnormalities and an increased number of intestinal tumors in APC Min/+ mice (69).
3.2 PLK1 as a target for cancer therapy
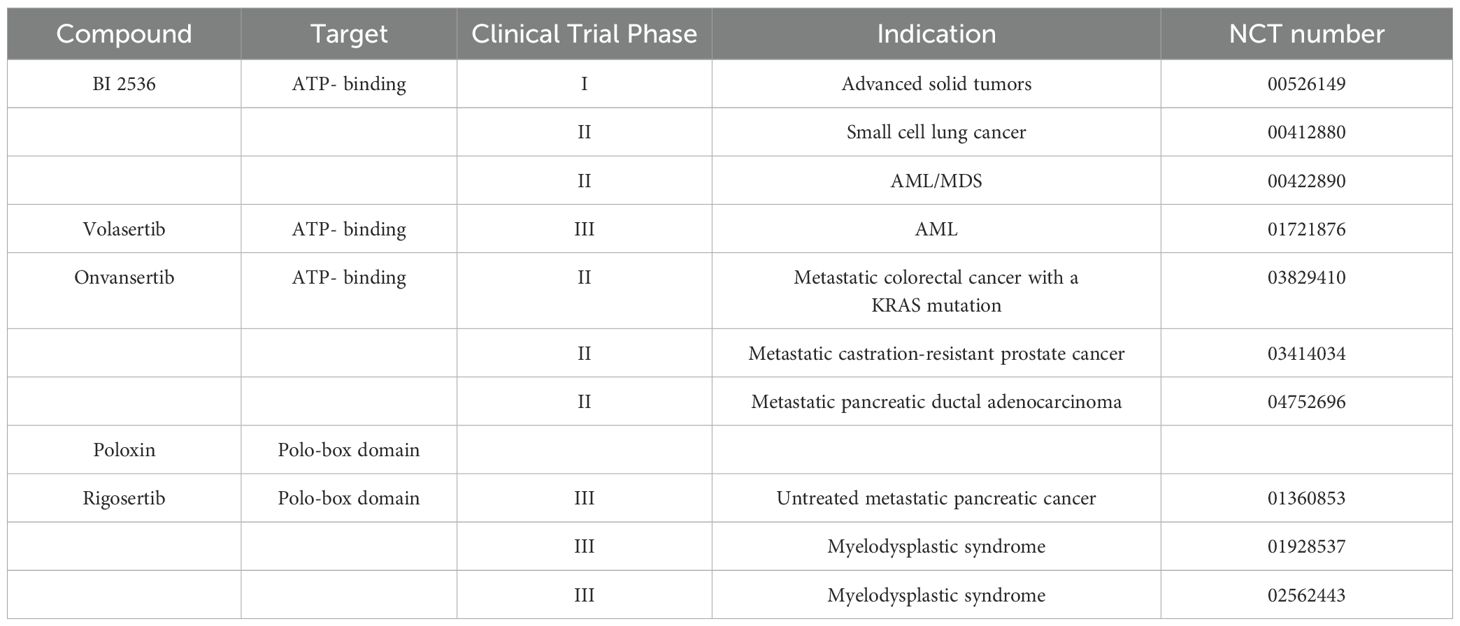
Given its central role in cell cycle regulation and its elevated expression in various cancers, PLK1 has emerged as a promising target for cancer therapy. Inhibition of PLK1 has been shown to enhance the sensitivity of tumors to chemotherapy and radiotherapy (70). PLK1 inhibitors can be broadly categorized into ATP-competitive inhibitors that target the kinase domain (KD) and compounds that target the polo-box domain (PBD) (71).
BI 2536 is a potent ATP-competitive inhibitor that inhibits tumor growth in vivo and in vitro (72). Clinical trials have shown that BI 2536 can exert synergistic anti-tumor effects when combined with other chemotherapeutic agents, but the efficacy of single therapy is poor (73). Volasertib, an ATP-competitive inhibitor, exhibits sustained high-dose exposure in tumor tissues and has demonstrated antitumor activity and a favorable safety profile in multiple xenograft models (74). Overexpression of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) drug transporter ABCB1 has been shown to cause ATP hydrolysis, which contributes to drug resistance in Volasertib. Therefore, combination therapy with ABCB1 modulators can be considered as a way to solve the problem of drug resistance (75). In addition, Volasertib exerts synergistic effects when combined with both MEK inhibitors and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors (76, 77). Onvansertib is a novel ATP-competitive PLK1 specific inhibitor, which can induce mitotic cycle arrest and apoptosis in tumor cells. Thus, the growth of xenograft tumors was inhibited (78). It is currently being tested in three clinical trials in combination with standard therapy (KRAS-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer, acute myeloid leukemia, and castration-resistant prostate cancer) and has shown promising drug resistance and safety profiles (79–81). However, this ATP-competitive PLK1 inhibitor has certain limitations. Firstly, the kinase domains of PLK family members (such as PLK1/2/3) are highly similar, resulting in reduced selectivity of existing drugs and easy to cause off-target effects. Secondly, PLK1 has complex and pleiotropic functions in the cell cycle regulatory network. When the inhibitor concentration is too high, PLK2/3 and other paraloproteins are unspecifically inhibited, resulting in dose-dependent cytotoxicity (such as bone marrow suppression and gastrointestinal reactions) (4). Finally, acquired mutations in the ATP-binding domain in tumor cells, such as Gatekeeper mutations in the kinase domain, may lead to decreased drug-binding affinity for PLK1 inhibitors and thus the phenomenon of acquired resistance (82).
Non-ATPcompetitive inhibitors, such as Rigosertib, which targets the PBD and inhibits both PLK1 and PI3K, have shown efficacy in killing tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. PBD inhibitors are more specific because of their high affinity for specific residues of PLK1 compared to ATP competitive inhibitors (71). Poloxin, a PBD inhibitor developed in 2008, causes mitotic arrest and apoptosis of cancer cells by inducing centrosome fragmentation and abnormal arrangement of spindles and chromosomes. In the xenograft mouse model, Poloxin was also shown to inhibit tumor growth. However, Poloxin is easily degraded in vitro and in vivo, resulting in a short half-life and difficult to maintain its efficacy. Moreover, due to its large molecular polarity and poor transmembrane permeability, it is difficult to reach an effective concentration in tumor cells (83, 84). However, Rigosertib has underperformed in clinical trials for high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and metastatic pancreatic cancer, with patients showing no significant benefits over standard care. On the one hand, the phosphopeptide binding interface of PBD is relatively shallow. On the other hand, it may activate other mitotic kinases (such as Aurora A/B, WEE1) to compensate for PLK1 function (71, 85). However, some studies have shown that Rigosertib can also target the RAS pathway and overcome chemotherapy resistance. Therefore, combining this inhibitor with chemotherapy may improve efficacy in patients with KRAS mutations (86). Therefore, further research is needed to improve the specificity and reduce the resistance of PLK1 inhibitors, making them more effective in clinical applications. Recent studies have found that dual-target inhibitors targeting PLK1/BRD4 and PLK1/MEK can produce cumulative effects and exert long-term inhibitory effect on cancer cell growth (87–89) (Table 2).
4 PLK1 and immunity
PLK1 has been found to play a significant immunomodulatory role in almost all types of cancer. The following pathways are mainly involved: immune cell infiltration, inflammatory signaling, immune checkpoint inhibitors and cancer vaccines. Increased PLK1 expression can inhibit the function of immune cells, such as NK cells and T cells, thereby promoting tumor immune escape (90). PLK1 also regulates inflammatory mediators and cellular effectors, thereby altering the local tumor microenvironment to promote tumor cell proliferation and survival while disrupting the adaptive immune response (91). Additionally, PLK1 exhibits positive associations with multiple immune checkpoints, encompassing both immunosuppressive and immunostimulatory checkpoints (92, 93). Moreover, PLK1 represents an attractive target antigen for cancer immunotherapy, playing a crucial role in the optimization of cancer vaccines (94) Figure 3).
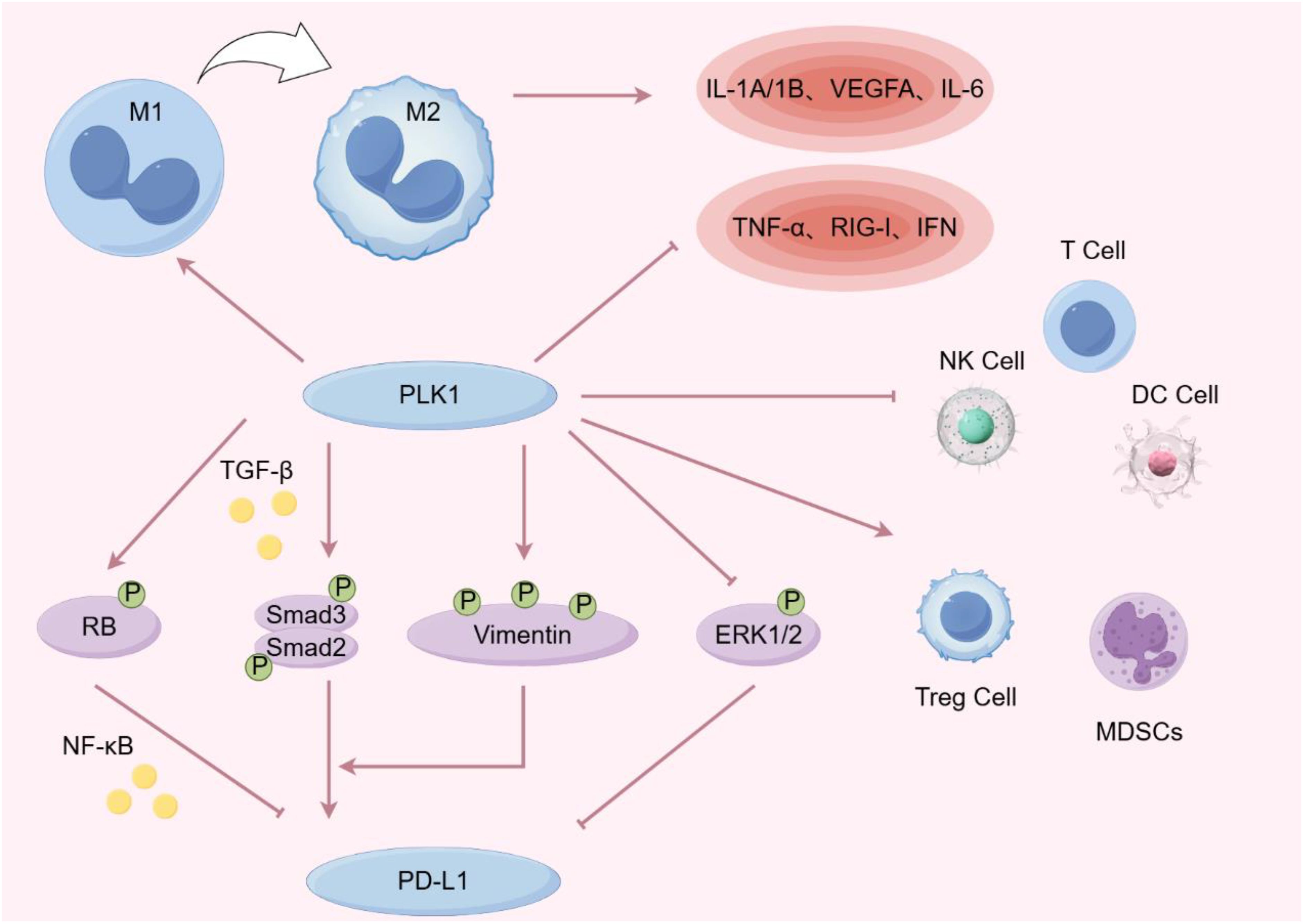
Figure 3. PLK1 decreased the levels of TNF-α, RIG-1 and IFN, promoted the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages from M1 to M2, and increased the levels of IL-1A, VEGFA and IL-6. PLK1 was negatively correlated with DC cells, T cells and NK cells, and positively correlated with myeloid suppressor cells (MDSCs) and regulatory T cells. PLK1 affects PD-L1 expression by regulating MAPK, TGF-β and NF-ĸB signal transduction pathways. (By Figdraw).
4.1 PLK1 and immune cells infiltration
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a critical determinant of cancer cell survival and metastasis, and the infiltration of immune cells into the tumor is a key factor influencing the efficacy of immunotherapy (95, 96). Accumulating evidence indicates that PLK1, beyond its well-established role in mitosis, exerts significant effects on the tumor microenvironment and is involved in tumor cell metastasis and immune cell infiltration (8, 97).
On one hand, PLK1 regulates the infiltration of a variety of immune cells. In lung cancer, PLK1 inhibits DC maturation and T-cell enrichment (98, 99).Moreover, PLK1 expression is positively correlated with myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and regulatory T cells. In addition, PLK1 was positively correlated with myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and regulatory T cells in breast cancer and node-predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma (100–102). In summary, PLK1 modulates the function of immune cell infiltration, providing a foundation for the development of inhibitors targeting innate immune maintenance.
On the other hand, PLK1 has been shown to promote the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) from the M1 to the M2 phenotype (103). Tumor-associated macrophages can be polarized into two distinct phenotypes: M1 macrophages, which activate T-helper type 1 (Th1) T cells to induce a cytotoxic T-cell response against pathogens, thereby exerting tumor-killing activity and increasing hypoxia; and M2 macrophages, which promote tissue repair and wound healing, participate in angiogenesis, and secrete a variety of pro-inflammatory factors with pro-tumorigenic effects, thereby contributing to cancer progression (104, 105). In hepatocellular carcinoma, PLK1 interacts with PTEN and interferes with its nuclear translocation, leading to the inhibition of natural killer (NK) cell and T cell function by enhancing aerobic glycolysis and promoting M2 macrophage polarization (106). High expression of PLK1 inhibits the infiltration of M1 macrophages and their associated chemokines and marker genes into the glioblastoma immune microenvironment, whereas knockdown of PLK1 increases the infiltration and polarization of M1 macrophages (107).
In addition, PLK1 inhibitors can prevent and treat acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD) that may occur after leukemia transplantation by preventing activation and inducing apoptosis of already activated alloreactive T cells (Tallo cells) while inhibiting the molecular chaperone Hsp90 and inhibiting Tallo cell proliferation (108). There is also a link between PLK1 and Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling, which plays a key role in innate immunity. TLRs are important sentinels of bacterial and viral infections, and PLK inhibitor-mediated blockade of TLR signaling can lead to adverse effects. Thus, in some patients receiving PLK1 inhibitors during cancer treatment, the risk of infection with invading microorganisms may be increased due to the impaired ability of the TLR recognition system to sense and initiate a cytokine response (109).
4.2 PLK1 and inflammatory factor
Inflammatory factors are a wide range of effector molecules involved in inflammatory response, including a variety of cytokines and chemokines. Many cancers arise from sites of infection, chronic irritation, and inflammation. Studies have shown that inflammatory factors can act directly on tumor cells. Inflammatory cells also modulate tumor growth by orchestrating the tumor microenvironment and influencing the adaptive immune response. Exploring the role of inflammatory factors in tumor immunity can provide a new way for cancer treatment in the future (110, 111).
An earlier study in 2013 found that PLK1 inhibitors could help treat colon cancer or early-stage lesions with high levels of inflammatory cell infiltration (112). Some studies have suggested that the high selectivity of PLK1 inhibitors for the BET bromodomain is the reason why PLK1 inhibitors can be used as drug targets for cancer and inflammation (113). Further studies have found that the activation of PLK1 inhibits the expression of TNF-induced cyclin D1, providing a potential mechanism for TNF-α’s involvement in inflammation-induced cancer (114). Recently, PLK1 has been identified as a novel negative regulator of the RIG-I and IFN-inducing pathways. RIG-I is capable of upregulating the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, inducing inflammation in the tumor environment, and activating neighboring immune cells, while IFN plays an important role in T cell proliferation, antigen sensitivity, cytokine production, and migration (115, 116). PLK1 also promotes the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages to upregulate the expression of IL-1A/1B, VEGFA, and IL-6, and the increased activity of these genes and factors is inversely associated with survival in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma (61).
Studies have highlighted the role of PLK1 in regulating inflammatory factors in sepsis and related diseases, offering potential insights for anti-inflammatory strategies in tumor treatment. Sepsis and cancer share several pathophysiological features, and the immune dysfunction associated with sepsis may influence the progression of malignant tumors (117, 118). For instance, in sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI), the activation of the ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome is suppressed through modulation of the PLK1/AMPK/DRP1 signaling axis (119). Additionally, PLK1 has been identified as a key contributor to sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD). Its expression is upregulated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated mouse hearts and neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCM). Inhibition of PLK1 attenuates the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby mitigating LPS-induced myocardial injury, inflammation, and cardiac dysfunction (120). In contrast, PLK1 exhibits a protective role in sepsis-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction. Overexpression of PLK1 reduces IL-6 levels by suppressing NF-κB signaling, thereby alleviating intestinal epithelial damage (121, 122).
4.3 PLK1 and immune checkpoint inhibitors
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is widely expressed in human tumors and plays a critical role in immune evasion. By binding to its receptor PD-1 on activated T cells, PD-L1 inhibits T cell activation signaling, thereby promoting tumor immune escape (123). Blockade of the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway has shown significant anti-tumor effects in patients with advanced cancer and is considered the gold standard for developing new immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies and combination treatments. However, the response rate to anti-PD-L1 antibodies remains limited in several solid tumors (124). Consequently, improving the sensitivity of cancer patients to immune checkpoint inhibitors and expanding the population benefiting from immunotherapy are critical areas of future research.
Recent studies have revealed that PLK1 inhibitors can synergize with PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in tumor immunotherapy. Analysis of the TCGA dataset identified PLK1 as one of the proliferation-related kinases highly expressed in cancers with chromosome 9p copy number gains (CNGs) involving PD-L1. This finding is relevant to a variety of cancers, including lung cancer, melanoma, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, cervical cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, prostate cancer, gastric cancer, ovarian cancer, and triple-negative breast cancer (125).
Research has shown that PLK1-induced phosphorylation of Vimentin promotes PD-L1 expression by activating TGF-β signaling and interacting with p-Smad2/3, contributing to metastatic progression in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) (126). Meanwhile, in vivo experiments confirmed that PLK1 inhibitor combined with PD-L1 inhibitor could significantly reduce tumor progression in mice compared with the two drugs alone. Because inhibition of PLK1 can induce the up-regulation of PD-L1 through the MAPK pathway and enhance the sensitivity of tumor cells to immune checkpoint inhibitors (127). Additionally, there are studies reported that PLK1 inhibition suppresses Rb phosphorylation in lung cancer. In various cancer cell lines, phosphorylated Rb inhibits the transcriptional activity of NF-κB and the expression of PD-L1 mRNA (128, 129). These findings suggest that PLK1 inhibitors may influence tumor immunotherapy efficacy in lung cancer by modulating the Rb/NF-κB/PD-L1 axis.
In pancreatic cancer, PLK1 inhibition similarly upregulates PD-L1 expression but also enhances sensitivity to PD-L1 blockade, ultimately leading to tumor suppression. This combination therapy can transform immunologically “cold” tumors into “hot” tumors, thereby improving anti-tumor immune responses. Mechanistically, PLK1 inhibition or depletion increases nuclear localization of NF-κB by reducing Rb phosphorylation, which upregulates PD-L1 expression (130). This mechanism supports the proposed role of the PLK1/Rb/NF-κB/PD-L1 axis in lung cancer and highlights its potential relevance across multiple cancer types.
The article published reported that PLK1 has the ability to alter the transcriptional profile of Her2+ breast tumors in the living environment, affecting the effector capacity of NK and T cells. This coordinated interaction in the tumor microenvironment ultimately upregulates PD-L1 and CD206 in the later stages of tumor progression and induces the NF-kb signaling pathway, promoting immune evasion (131).
4.4 PLK1 and cancer vaccines
Genetic instability in tumor cells often results in a high frequency of mutations, and the expression of non-synonymous mutations can generate tumor-specific antigens known as neoantigens. These neoantigens are highly immunogenic because they are not expressed in normal tissues. Neoantigen-targeting cancer vaccines primarily include nucleic acid vaccines, dendritic cell vaccines, tumor cell vaccines, and synthetic long-peptide vaccines (SLPs) (132).
In recent years, it has been found that PLK1 may be a universal tumor antigen recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes for cancer immunotherapy. PLK1-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells can be induced by mPLK1 RNA/DC vaccine and exert anti-tumor effects (94). Inoculation of bone marrow cells CD8 T against the cellular epitope synthesis of PLK1: PLK1122 (DSDFVFVVL) yields a large number of long-lasting antigen-specific CD8 T cells. The use of a peptide vaccine that simultaneously targets PLK1 and blocks PD-L1 can lead to complete tumor eradication and long-term survival in mice with clonal heterologous C1498 myeloid leukemia (133).
However, PLK1 as a target of direct immunotherapy still faces multiple challenges, mainly involving target specificity, immunogenicity and tumor heterogeneity. PLK1 still has basal expression in normal proliferating cells. Systemic targeting of PLK1 may cause “on-target, off-tumor” toxicity, leading to bone marrow suppression or gastrointestinal injury. Such risks may be further amplified by the long-term activating effects of immunotherapy (134). PLK1 did not show strong immunogenicity in human models, and experimental data showed that PlK1-derived peptides only weakly activated T cells in peripheral blood of patients (135). In addition, in a study utilizing a DNA vaccine model to compare the immunogenicity of G2/M-related antigens, it was observed that PLK1-immunized mice did not exhibit any anti-tumor effects. This may be related to the fact that PLK1 is not preferentially expressed in the cancer stem cell (CSC) or cancer initiation cell (CIC) population (136). In summary, PLK1 may be an attractive target antigen for cancer immunotherapy, but is more likely to act as an accessory target rather than an independent immunotherapy antigen.
5 Conclusions and future perspectives
PLK1 is a key regulator of mitosis, playing critical roles in centrosome maturation and separation, spindle assembly formation, and cytokinesis. Due to its central role in cell division, aberrant expression of PLK1 can have profound detrimental effects, particularly in carcinogenesis. This review focuses on the relationship between PLK1 and cancer development. On one hand, PLK1 promotes tumor progression through the PLK1/β-catenin/AP-1 axis or the PLK1/TGF-β axis, while on the other hand, it activates the AKT and MAPK pathways, leading to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and ultimately facilitating tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Additionally, PLK1 is widely recognized as a cancer-promoting gene that regulates multiple tumor suppressor gene inactivation and proto-oncogene expression. Inhibition of PLK1 has been shown to enhance chemosensitivity, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target.
PLK1 also modulates the expression of transcription factors across various cancer types, further contributing to its tumor-promoting functions. However, despite its oncogenic role, only a limited number of PLK1 inhibitors have demonstrated promising therapeutic effects in clinical trials. This is largely due to challenges such as toxicity at high doses, the pleiotropic functions of PLK1 in mitotic cells, and off-target effects. Interestingly, PLK1 overexpression has been found to inhibit tumor development in certain contexts by disrupting mitotic progression, spindle assembly checkpoint recruitment, and cytokinesis. These dual roles suggest that PLK1 acts as a double-edged sword, capable of either promoting or suppressing tumor development depending on the context. This complexity complicates the therapeutic application of PLK1 inhibitors and underscores the need for further research to fully understand its functions.
In recent years, increasing evidence has highlighted the significant role of PLK1 in cancer immunotherapy. Firstly, PLK1 plays a crucial role in cancer progression by modulating the tumor microenvironment, particularly through the regulation of immune cell infiltration and inflammatory factors. PLK1 inhibits the recruitment of immune-promoting cells such as dendritic cells (DCs), T cells, and NK cells, while positively correlating with the presence of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and regulatory T cells. Additionally, PLK1 acts as a negative regulator of key inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, RIG-1, and IFN, and is implicated in inflammation-driven cancer processes. Furthermore, PLK1 promotes the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) from the M1 to the M2 phenotype, upregulating the expression of chemokines such as IL-1A/1B, VEGFA, and IL-6, which are associated with poor survival outcomes in cancer patients.
Secondly, PLK1 inhibitors have shown synergistic effects when combined with PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in tumor immunotherapy. These effects are primarily mediated through the TGF-β, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling pathways, enhancing the anti-tumor immune response. Lastly, PLK1 has emerged as a universal tumor antigen recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes, making it a promising target for cancer immunotherapy. Dendritic cell vaccines targeting PLK1-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells have demonstrated potent anti-tumor effects. Similarly, peptide vaccines derived from PLK1 epitopes have been shown to generate long-lasting antigen-specific CD8 T cells, leading to complete tumor eradication and prolonged survival in murine models. Notably, a polypeptide vaccine targeting both PLK1 and PD-L1 has shown remarkable efficacy in eliminating tumors and improving survival outcomes in mice.
In conclusion, expanding our understanding of PLK1 signaling in immunotherapy offers new avenues to enhance the efficacy of PLK1 inhibitors and improve the sensitivity of immunotherapeutic approaches. These insights also provide a foundation for the development of novel therapeutic strategies, paving the way for more effective cancer treatments.
Author contributions
WW: Writing – original draft. RZ: Writing – original draft. YW: Writing – original draft. LP: Writing – original draft. FL: Writing – review & editing. GF: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant/Award Number: 81802284); Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant/Award Number: tsqn202103179); 2021 Shandong Medical Association Clinical Research Fund (Grant/Award Number: YXH2022ZX02176); Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation (Grant/Award Number: Y-HR2022MS-0257); Shandong provincial medical and health technology development program (Grant/Award Number: 202403110985); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant/Award Number: ZR2022MH088); Key Development Program of Shandong Province (Grant/Award Number: 2018GSF118116) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant/Award Number: 81101484).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
References
1. Iliaki S, Beyaert R, and Afonina IS. Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) signaling in cancer and beyond. Biochem Pharmacol. (2021) 193. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114747
2. Dwivedi D and Meraldi P. Balancing Plk1 activity levels: The secret of synchrony between the cell and the centrosome cycle. Bioessays. (2024) 46:e2400048. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400048
3. Stafford JM, Wyatt MD, and McInnes C. Inhibitors of the PLK1 polo-box domain: drug design strategies and therapeutic opportunities in cancer. Expert Opin Drug Discovery. (2023) 18:65–81. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2023.2159942
4. Chopra P, Sethi G, Dastidar SG, and Ray A. Polo-like kinase inhibitors: an emerging opportunity for cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2010) 19:27–43. doi: 10.1517/13543780903483191
5. Guerrero-Zotano Á, Belli S, Zielinski C, Gil-Gil M, Fernandez-Serra A, Ruiz-Borrego M, et al. CCNE1andPLK1Mediate Resistance to Palbociclib in HR+/HER2– Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:1557–68. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-22-2206
6. Yu Z, Deng P, Chen Y, Liu S, Chen J, Yang Z, et al. Inhibition of the PLK1-coupled cell cycle machinery overcomes resistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Advanced Sci. (2021) 8. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100759
7. Reda M, Ngamcherdtrakul W, Gu S, Bejan DS, Siriwon N, Gray JW, et al. PLK1 and EGFR targeted nanoparticle as a radiation sensitizer for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. (2019) 467:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.09.014
8. Shen C, Wang T, Li K, Fu C, Yang S, Zhang Z, et al. The prognostic values and immune characteristics of polo-like kinases (PLKs) family: A pan-cancer multi-omics analysis. Heliyon. (2024) 10. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28048
9. de Cárcer G, Manning G, and Malumbres M. From Plk1 to Plk5: functional evolution of polo-like kinases. Cell Cycle. (2011) 10:2255–62. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.14.16494
10. Combes G, Alharbi I, Braga LG, and Elowe S. Playing polo during mitosis: PLK1 takes the lead. Oncogene. (2017) 36:4819–27. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.113
11. Maniswami RR, Prashanth S, Karanth AV, Koushik S, Govindaraj H, Mullangi R, et al. PLK4: a link between centriole biogenesis and cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2018) 22:59–73. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1410140
12. Raab CA, Raab M, Becker S, and Strebhardt K. Non-mitotic functions of polo-like kinases in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2021) 1875:188467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188467
13. Akdeli N, Riemann K, Westphal J, Hess J, Siffert W, and Bachmann HS. A 3'UTR polymorphism modulates mRNA stability of the oncogene and drug target Polo-like Kinase 1. Mol Cancer. (2014) 13:87. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-87
14. Liao Z, Zhang Q, Yang L, Li H, Mo W, Song Z, et al. Increased hsa-miR-100-5p expression improves hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis in the asian population with PLK1 Variant rs27770A>G. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010129
15. Andrew AS, Gui J, Sanderson AC, Mason RA, Morlock EV, Schned AR, et al. Bladder cancer SNP panel predicts susceptibility and survival. Hum Genet. (2009) 125:527–39. doi: 10.1007/s00439-009-0645-6
16. Wang XH, Lu Y, Liang JJ, Cao JX, Jin YQ, An GS, et al. MiR-509-3-5p causes aberrant mitosis and anti-proliferative effect by suppression of PLK1 in human lung cancer A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2016) 478:676–82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.006
17. Colicino EG and Hehnly H. Regulating a key mitotic regulator, polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1). Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). (2018) 75:481–94. doi: 10.1002/cm.21504
18. Joukov V, Walter JC, and De Nicolo A. The Cep192-organized aurora A-Plk1 cascade is essential for centrosome cycle and bipolar spindle assembly. Mol Cell. (2014) 55:578–91. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.06.016
19. Kalous J and Aleshkina D. Multiple Roles of PLK1 in Mitosis and Meiosis. Cells. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/cells12010187
20. Ikeda M and Tanaka K. Plk1 bound to Bub1 contributes to spindle assembly checkpoint activity during mitosis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:8794. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09114-3
21. Kim T. Recent Progress on the Localization of PLK1 to the Kinetochore and Its Role in Mitosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095252
22. Beck J, Maerki S, Posch M, Metzger T, Persaud A, Scheel H, et al. Ubiquitylation-dependent localization of PLK1 in mitosis. Nat Cell Biol. (2013) 15:430–9. doi: 10.1038/ncb2695
23. Hu CK, Ozlü N, Coughlin M, Steen JJ, and Mitchison TJ. Plk1 negatively regulates PRC1 to prevent premature midzone formation before cytokinesis. Mol Biol Cell. (2012) 23:2702–11. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-01-0058
24. Fabbro M, Zhou BB, Takahashi M, Sarcevic B, Lal P, Graham ME, et al. Cdk1/Erk2- and Plk1-dependent phosphorylation of a centrosome protein, Cep55, is required for its recruitment to midbody and cytokinesis. Dev Cell. (2005) 9:477–88. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.09.003
25. Bastos RN and Barr FA. Plk1 negatively regulates Cep55 recruitment to the midbody to ensure orderly abscission. J Cell Biol. (2010) 191:751–60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201008108
26. Li P, Zhao Y, Lu M, Chen C, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of PLK1/PRC1 triggers mitotic catastrophe and sensitizes lung cancers to chemotherapy. Cell Death Dis. (2025) 16:374. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07708-8
27. Lamouille S, Xu J, and Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2014) 15:178–96. doi: 10.1038/nrm3758
28. Kim DE, Shin SB, Kim CH, Kim YB, Oh HJ, and Yim H. PLK1-mediated phosphorylation of β-catenin enhances its stability and transcriptional activity for extracellular matrix remodeling in metastatic NSCLC. Theranostics. (2023) 13:1198–216. doi: 10.7150/thno.79318
29. Shin SB, Jang HR, Xu R, Won JY, and Yim H. Active PLK1-driven metastasis is amplified by TGF-β signaling that forms a positive feedback loop in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. (2020) 39:767–85. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1023-z
30. Cai XP, Chen LD, Song HB, Zhang CX, Yuan ZW, and Xiang ZX. PLK1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric carcinoma cells. Am J Transl Res. (2016) 8:4172–83.
31. Jin B, Jin D, Zhuo Z, Zhang B, and Chen K. MiR-1224-5p activates autophagy, cell invasion and inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma cells by directly targeting PLK1 through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. (2020) 13:11807–18. doi: 10.2147/ott.S274451
32. Wu J, Ivanov AI, Fisher PB, and Fu Z. Polo-like kinase 1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes epithelial cell motility by activating CRAF/ERK signaling. Elife. (2016) 5. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10734
33. Li Z, Li J, Bi P, Lu Y, Burcham G, Elzey BD, et al. Plk1 Phosphorylation of PTEN Causes a Tumor-Promoting Metabolic State. Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 34:3642–61. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00814-14
34. Li W, Wang X, Liu J, Liu B, and Hao Y. Crosstalk between Plk1 and PTEN in mitosis affects chromosomal stability. DNA Cell Biol. (2025). doi: 10.1089/dna.2024.0246
35. Kasahara K, Goto H, Izawa I, Kiyono T, Watanabe N, Elowe S, et al. PI 3-kinase-dependent phosphorylation of Plk1–Ser99 promotes association with 14-3-3γ and is required for metaphase–anaphase transition. Nat Commun. (2013) 4. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2879
36. Mao Y, Xi L, Li Q, Cai Z, Lai Y, Zhang X, et al. Regulation of cell apoptosis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer through PI3K/Akt pathway via Polo-like kinase 1. Oncol Rep. (2016) 36:49–56. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4820
37. De Martino D, Yilmaz E, Orlacchio A, Ranieri M, Zhao K, and Di Cristofano A. PI3K blockage synergizes with PLK1 inhibition preventing endoreduplication and enhancing apoptosis in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Cancer Lett. (2018) 439:56–65. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.09.024
38. Zhao S, Li Y, Li G, Ye J, Wang R, Zhang X, et al. PI3K/mTOR inhibitor VS-5584 combined with PLK1 inhibitor exhibits synergistic anti-cancer effects on non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 957. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176004
39. Mao Y, Xi L, Li Q, Wang S, Cai Z, Zhang X, et al. Combination of PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition and Plk1 depletion can enhance chemosensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic carcinoma. Trans Oncol. (2018) 11:852–63. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.04.011
40. Ren Y, Bi C, Zhao X, Lwin T, Wang C, Yuan J, et al. PLK1 stabilizes a MYC-dependent kinase network in aggressive B cell lymphomas. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:5517–30. doi: 10.1172/jci122533
41. Mo H, He J, Yuan Z, Wu Z, Liu B, Lin X, et al. PLK1 contributes to autophagy by regulating MYC stabilization in osteosarcoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. (2019) 12:7527–36. doi: 10.2147/ott.S210575
42. Wang D, Pierce A, Veo B, Fosmire S, Danis E, Donson A, et al. A regulatory loop of FBXW7-MYC-PLK1 controls tumorigenesis of MYC-driven medulloblastoma. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030387
43. Xiao D, Yue M, Su H, Ren P, Jiang J, Li F, et al. Polo-like Kinase-1 regulates myc stabilization and activates a feedforward circuit promoting tumor cell survival. Mol Cell. (2016) 64:493–506. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.016
44. Zhang Q, Peng J, Zhang Y, Liu J, He D, Zhao Y, et al. The kinase PLK1 promotes Hedgehog signaling-dependent resistance to the antiandrogen enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer. Sci Signal. (2025) 18:eadi5174. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adi5174
45. Tan J, Li Z, Lee PL, Guan P, Aau MY, Lee ST, et al. PDK1 signaling toward PLK1-MYC activation confers oncogenic transformation, tumor-initiating cell activation, and resistance to mTOR-targeted therapy. Cancer Discovery. (2013) 3:1156–71. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-12-0595
46. Wang D, Veo B, Pierce A, Fosmire S, Madhavan K, Balakrishnan I, et al. A novel PLK1 inhibitor onvansertib effectively sensitizes MYC-driven medulloblastoma to radiotherapy. Neuro Oncol. (2022) 24:414–26. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab207
47. Gao X, You J, Gong Y, Yuan M, Zhu H, Fang L, et al. WSB1 regulates c-Myc expression through β-catenin signaling and forms a feedforward circuit. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:1225–39. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.10.021
48. Littler S, Sloss O, Geary B, Pierce A, Whetton AD, and Taylor SS. Oncogenic MYC amplifies mitotic perturbations. Open Biol. (2019) 9:190136. doi: 10.1098/rsob.190136
49. Mai J, Zhong ZY, Guo GF, Chen XX, Xiang YQ, Li X, et al. Polo-Like Kinase 1 phosphorylates and stabilizes KLF4 to promote tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Theranostics. (2019) 9:3541–54. doi: 10.7150/thno.32908
50. Li L, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Shi S, Liu S, Huang K, et al. Dehydrodiisoeugenol targets the PLK1-p53 axis to inhibit breast cancer cell cycle. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1545498. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545498
51. Louwen F and Yuan J. Battle of the eternal rivals: restoring functional p53 and inhibiting Polo-like kinase 1 as cancer therapy. Oncotarget. (2013) 4:958–71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1096
52. Karlin KL, Mondal G, Hartman JK, Tyagi S, Kurley SJ, Bland CS, et al. The oncogenic STP axis promotes triple-negative breast cancer via degradation of the REST tumor suppressor. Cell Rep. (2014) 9:1318–32. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.10.011
53. Zhang H, Diab A, Fan H, Mani SK, Hullinger R, Merle P, et al. PLK1 and HOTAIR Accelerate Proteasomal Degradation of SUZ12 and ZNF198 during Hepatitis B Virus-Induced Liver Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:2363–74. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-2928
54. Gheghiani L, Shang S, and Fu Z. Targeting the PLK1-FOXO1 pathway as a novel therapeutic approach for treating advanced prostate cancer. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:12327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69338-8
55. Thalhammer V, Lopez-Garcia LA, Herrero-Martin D, Hecker R, Laubscher D, Gierisch ME, et al. PLK1 phosphorylates PAX3-FOXO1, the inhibition of which triggers regression of alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:98–110. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-1246
56. Fan W, Ma H, and Jin B. Expression of FOXM1 and PLK1 predicts prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. (2022) 23:146. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13266
57. Poyil PK, Siraj AK, Padmaja D, Parvathareddy SK, Thangavel S, Alobaisi K, et al. PLK1 and FoxM1 expressions positively correlate in papillary thyroid carcinoma and their combined inhibition results in synergistic anti-tumor effects. Mol Oncol. (2024) 18:691–706. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13610
58. Seyedabadi S, Saidijam M, Najafi R, Mousavi-Bahar SH, Jafari M, MohammadGanji S, et al. Assessment of CEP55, PLK1 and FOXM1 expression in patients with bladder cancer in comparison with healthy individuals. Cancer Invest. (2018) 36:407–14. doi: 10.1080/07357907.2018.1514504
59. Yu F, He H, Nastoupil LJ, Xu-Monette ZY, Pham K, Liang Y, et al. Targetable vulnerability of deregulated FOXM1/PLK1 signaling axis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Am J Cancer Res. (2022) 12:4666–79.
60. Zhang Z, Zhang G, and Kong C. FOXM1 participates in PLK1-regulated cell cycle progression in renal cell cancer cells. Oncol Lett. (2016) 11:2685–91. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4228
61. Xu R, Lee YJ, Kim CH, Min GH, Kim YB, Park JW, et al. Invasive FoxM1 phosphorylated by PLK1 induces the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages to promote immune escape and metastasis, amplified by IFITM1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:302. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02872-1
62. Zhang Z, Liu W, Bao X, Sun T, Wang J, Li M, et al. USP39 facilitates breast cancer cell proliferation through stabilization of FOXM1. Am J Cancer Res. (2022) 12:3644–61.
63. Dibb M, Han N, Choudhury J, Hayes S, Valentine H, West C, et al. The FOXM1-PLK1 axis is commonly upregulated in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. (2012) 107:1766–75. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.424
64. Ma X, Wang L, Huang D, Li Y, Yang D, Li T, et al. Polo-like kinase 1 coordinates biosynthesis during cell cycle progression by directly activating pentose phosphate pathway. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:1506. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01647-5
65. Gomes CP, Gomes-da-Silva LC, Ramalho JS, de Lima MC, Simões S, and Moreira JN. Impact of PLK-1 silencing on endothelial cells and cancer cells of diverse histological origin. Curr Gene Ther. (2013) 13:189–201. doi: 10.2174/1566523211313030004
66. Zhao Z, He J, Qiu S, Wang L, Huangfu S, Hu Y, et al. Targeting PLK1-CBX8-GPX4 axis overcomes BRAF/EGFR inhibitor resistance in BRAFV600E colorectal cancer via ferroptosis. Nat Commun. (2025) 16:3605. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58992-z
67. Shen S, Xue G, Zeng Z, Peng L, Nie W, and Zeng X. Toosendanin promotes prostate cancer cell apoptosis, ferroptosis and M1 polarization via USP39-mediated PLK1 deubiquitination. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03916-3
68. de Cárcer G, Venkateswaran SV, Salgueiro L, El Bakkali A, Somogyi K, Rowald K, et al. Plk1 overexpression induces chromosomal instability and suppresses tumor development. Nat Commun. (2018) 9. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05429-5
69. Raab M, Sanhaji M, Matthess Y, Hörlin A, Lorenz I, Dötsch C, et al. PLK1 has tumor-suppressive potential in APC-truncated colon cancer cells. Nat Commun. (2018) 9. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03494-4
70. Liu Z, Sun Q, and Wang X. PLK1, A Potential Target for Cancer Therapy. Transl Oncol. (2017) 10:22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2016.10.003
71. Lee KS, Burke TR Jr., Park JE, Bang JK, and Lee E. Recent advances and new strategies in targeting plk1 for anticancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2015) 36:858–77. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.08.013
72. Steegmaier M, Hoffmann M, Baum A, Lénárt P, Petronczki M, Krssák M, et al. BI 2536, a potent and selective inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1, inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Curr Biol. (2007) 17:316–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.12.037
73. Czaplinski S, Hugle M, Stiehl V, and Fulda S. Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition sensitizes neuroblastoma cells for vinca alkaloid-induced apoptosis. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:8700–11. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3901
74. Rudolph D, Steegmaier M, Hoffmann M, Grauert M, Baum A, Quant J, et al. BI 6727, a Polo-like kinase inhibitor with improved pharmacokinetic profile and broad antitumor activity. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:3094–102. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-08-2445
75. Komrokji RS, Raza A, Lancet JE, Ren C, Taft D, Maniar M, et al. Phase I clinical trial of oral Rigosertib in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. (2013) 162:517–24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12436
76. Posch C, Cholewa BD, Vujic I, Sanlorenzo M, Ma J, Kim ST, et al. Combined inhibition of MEK and Plk1 has synergistic antitumor activity in NRAS mutant melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. (2015) 135:2475–83. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.198
77. Wissing MD, Mendonca J, Kortenhorst MS, Kaelber NS, Gonzalez M, Kim E, et al. Targeting prostate cancer cell lines with polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors as a single agent and in combination with histone deacetylase inhibitors. FASEB J. (2013) 27:4279–93. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-222893
78. Valsasina B, Beria I, Alli C, Alzani R, Avanzi N, Ballinari D, et al. NMS-P937, an orally available, specific small-molecule polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor with antitumor activity in solid and hematologic malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther. (2012) 11:1006–16. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-11-0765
79. Ahn DH, Barzi A, Ridinger M, Samuëlsz E, Subramanian RA, Croucher PJP, et al. Onvansertib in combination with FOLFIRI and Bevacizumab in second-line treatment of KRAS-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: A phase Ib clinical study. Clin Cancer Res. (2024) 30:2039–47. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-23-3053
80. Zeidan AM, Ridinger M, Lin TL, Becker PS, Schiller GJ, Patel PA, et al. A Phase Ib study of onvansertib, a novel oral PLK1 Inhibitor, in combination therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:6132–40. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-2586
81. Patterson JC, Varkaris A, Croucher PJP, Ridinger M, Dalrymple S, Nouri M, et al. Plk1 inhibitors and abiraterone synergistically disrupt mitosis and kill cancer cells of disparate origin independently of androgen receptor signaling. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:219–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-22-1533
82. Burkard ME, Santamaria A, and Jallepalli PV. Enabling and disabling polo-like kinase 1 inhibition through chemical genetics. ACS Chem Biol. (2012) 7:978–81. doi: 10.1021/cb200551p
83. Reindl W, Yuan J, Krämer A, Strebhardt K, and Berg T. Inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 by blocking polo-box domain-dependent protein-protein interactions. Chem Biol. (2008) 15:459–66. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.03.013
84. Yuan J, Sanhaji M, Krämer A, Reindl W, Hofmann M, Kreis NN, et al. Polo-box domain inhibitor poloxin activates the spindle assembly checkpoint and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Am J Pathol. (2011) 179:2091–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.031
85. Monfort-Vengut A and de Cárcer G. Lights and shadows on the cancer multi-target inhibitor Rigosertib (ON-01910.Na). Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041232
86. Zhou X, Xiao Q, Fu D, Zhang H, Tang Y, He J, et al. Efficacy of Rigosertib, a small molecular RAS signaling disrupter for the treatment of KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Med. (2021) 19:213–28. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0532
87. Song S, Yang W, and Tai W. Proteolysis targeting chimera of BI-2536 induces potent dual degradation of PLK1 and BET proteins. Bioorg Med Chem. (2025) 120:118087. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2025.118087
88. Zhao B, Fang R, Schürmann H, Hemmer EJ, Mayer GL, Trajkovic-Arsic M, et al. PLK1 blockade enhances the anti-tumor effect of MAPK inhibition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Rep. (2025) 44:115541. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115541
89. Kim DE, Oh HJ, Kim HJ, Kim YB, Kim ST, and Yim H. Synergistic two-step inhibition approach using a combination of trametinib and onvansertib in KRAS and TP53-mutated colorectal adenocarcinoma. BioMed Pharmacother. (2025) 182:117796. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117796
90. Raab M, Strebhardt K, and Rudd CE. Immune adaptor SKAP1 acts a scaffold for Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) for the optimal cell cycling of T-cells. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:10462. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45627-9
91. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, and Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. (2008) 454:436–44. doi: 10.1038/nature07205
92. Li M, Liu Z, and Wang X. Exploration of the Combination of PLK1 Inhibition with Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment. J Oncol. (2018) 2018:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2018/3979527
93. Zhao G, Wang Y, Zhou J, Ma P, Wang S, and Li N. Pan-cancer analysis of polo-like kinase family genes reveals polo-like kinase 1 as a novel oncogene in kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e29373. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29373
94. Park JS, Sohn HJ, Park GS, Chung YJ, and Kim TG. Induction of antitumor immunity using dendritic cells electroporated with Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) mRNA in murine tumor models. Cancer Sci. (2011) 102:1448–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01974.x
95. Zhang Y and Zhang Z. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:807–21. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6
96. Wang F, Yang M, Luo W, and Zhou Q. Characteristics of tumor microenvironment and novel immunotherapeutic strategies for non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Cent. (2022) 2:243–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2022.10.002
97. Kim CH, Kim DE, Kim DH, Min GH, Park JW, Kim YB, et al. Mitotic protein kinase-driven crosstalk of machineries for mitosis and metastasis. Exp Mol Med. (2022) 54:414–25. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00750-y
98. Zhou J, Yang Q, Lu L, Tuo Z, Shou Z, and Cheng J. PLK1 Inhibition Induces Immunogenic Cell Death and Enhances Immunity against NSCLC. Int J Med Sci. (2021) 18:3516–25. doi: 10.7150/ijms.60135
99. Zhang P, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Cui Y, Xu J, and Zhang W. Polo-like kinase 1 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma immunity through necroptosis. Oncol Res. (2023) 31:937–53. doi: 10.32604/or.2023.030933
100. Shen J, Zhang W, Jin Q, Gong F, Zhang H, Xu H, et al. Polo-like kinase 1 as a biomarker predicts the prognosis and immunotherapy of breast invasive carcinoma patients. Oncol Res. (2023) 32:339–51. doi: 10.32604/or.2023.030887
101. Chen Y, You Y, Wu Q, Wu J, Lin S, Sun Y, et al. Performance of a PLK1-based immune risk model for prognosis and treatment response prediction in breast cancer. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:11020–39. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5813
102. Weiss J, Gibbons K, Ehyaee V, Perez-Silos V, Zevallos A, Maienschein-Cline M, et al. Specific polo-like kinase 1 expression in nodular lymphocyte-predominant hodgkin lymphoma suggests an intact immune surveillance program. Am J Pathol. (2024) 194:165–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.10.008
103. Jiang T, Sun L, Zhu J, Li N, Gu H, Zhang Y, et al. MicroRNA-23a-3p promotes macrophage M1 polarization and aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating PLK1/STAT1/STAT3 signalling. Int J Exp Pathol. (2022) 103:198–207. doi: 10.1111/iep.12445
104. Jeong H, Hwang I, Kang SH, Shin HC, and Kwon SY. Tumor-associated macrophages as potential prognostic biomarkers of invasive breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. (2019) 22:38–51. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e5
105. Boutilier AJ and Elsawa SF. macrophage polarization states in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136995
106. Xu D, Wang Y, Wu J, Zhang Z, Chen J, Xie M, et al. ECT2 overexpression promotes the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma via the ECT2/PLK1/PTEN pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:162. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03450-z
107. Luo L, Zhang XY, Zhen YW, Guo GC, Peng DZ, Wei C, et al. Polo-like kinase 1 is related with malignant characteristics and inhibits macrophages infiltration in glioma. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1058036. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1058036
108. Berges C, Chatterjee M, Topp MS, and Einsele H. Targeting polo-like kinase 1 suppresses essential functions of alloreactive T cells. Immunol Res. (2016) 64:687–98. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8778-2
109. El Maadidi S, Weber ANR, Motshwene P, Schüssler JM, Backes D, Dickhöfer S, et al. Putative link between Polo-like kinases (PLKs) and Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in transformed and primary human immune cells. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:13168. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49017-z
110. Coussens LM and Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. (2002) 420:860–7. doi: 10.1038/nature01322
111. Maiorino L, Daßler-Plenker J, Sun L, and Egeblad M. Innate Immunity and Cancer Pathophysiology. Annu Rev Pathol. (2022) 17:425–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-032221-115501
112. Chopra AS, Kuratnik A, Scocchera EW, Wright DL, and Giardina C. Identification of novel compounds that enhance colon cancer cell sensitivity to inflammatory apoptotic ligands. Cancer Biol Ther. (2013) 14:436–49. doi: 10.4161/cbt.23787
113. Ember SW, Zhu JY, Olesen SH, Martin MP, Becker A, Berndt N, et al. Acetyl-lysine binding site of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) interacts with diverse kinase inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol. (2014) 9:1160–71. doi: 10.1021/cb500072z
114. Higashimoto T, Chan N, Lee YK, and Zandi E. Regulation of I(kappa)B kinase complex by phosphorylation of (gamma)-binding domain of I(kappa)B kinase (beta) by Polo-like kinase 1. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:35354–67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806258200
115. Vitour D, Dabo S, Ahmadi Pour M, Vilasco M, Vidalain PO, Jacob Y, et al. Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) regulates interferon (IFN) induction by MAVS. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:21797–809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018275
116. Rady T, Erb S, Deddouche-Grass S, Morales R, Chaubet G, Cianférani S, et al. Targeted delivery of immune-stimulating bispecific RNA, inducing apoptosis and anti-tumor immunity in cancer cells. iScience. (2024) 27:109068. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109068
117. Vigneron C, Mirouse A, Merdji H, Rousseau C, Cousin C, Alby-Laurent F, et al. Sepsis inhibits tumor growth in mice with cancer through Toll-like receptor 4-associated enhanced Natural Killer cell activity. Oncoimmunology. (2019) 8:e1641391. doi: 10.1080/2162402x.2019.1641391
118. Mirouse A, Vigneron C, Llitjos JF, Chiche JD, Mira JP, Mokart D, et al. Sepsis and Cancer: An Interplay of Friends and Foes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2020) 202:1625–35. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1116TR
119. Liu Y, Zhang Y, You G, Zheng D, He Z, Guo W, et al. Tangeretin attenuates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation via regulating PLK1/AMPK/DRP1 signaling axis. Inflammation Res. (2024) 73:47–63. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01819-8
120. Gao Z, Zheng C, Xing Y, Zhang X, Bai Y, Chen C, et al. Polo-like kinase 1 promotes sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 125:111074. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111074
121. Cao YY, Zhang Y, Gerile W, Guo Y, Wu LN, Wu LL, et al. PLK1 protects intestinal barrier function during sepsis by targeting mitochondrial dynamics through TANK-NF-κB signalling. Mol Med. (2022) 28:163. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00597-z
122. Cao YY, Li J, Chen Q, Qi YP, Xu QC, He JM, et al. PLK1 protects intestinal barrier function in sepsis: A translational research. Cytokine. (2023) 162:156113. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.156113
123. Sun C, Mezzadra R, and Schumacher TN. Regulation and function of the PD-L1 checkpoint. Immunity. (2018) 48:434–52. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.014
124. Cha J-H, Chan L-C, Li C-W, Hsu JL, and Hung M-C. Mechanisms controlling PD-L1 expression in cancer. Mol Cell. (2019) 76:359–70. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.030
125. Budczies J, Denkert C, Győrffy B, Schirmacher P, and Stenzinger A. Chromosome 9p copy number gains involving PD-L1 are associated with a specific proliferation and immune-modulating gene expression program active across major cancer types. BMC Med Genomics. (2017) 10. doi: 10.1186/s12920-017-0308-8
126. Jang H-R, Shin S-B, Kim C-H, Won J-Y, Xu R, Kim D-E, et al. PLK1/vimentin signaling facilitates immune escape by recruiting Smad2/3 to PD-L1 promoter in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Differentiation. (2021) 28:2745–64. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00781-4
127. Reda M, Ngamcherdtrakul W, Nelson MA, Siriwon N, Wang R, Zaidan HY, et al. Development of a nanoparticle-based immunotherapy targeting PD-L1 and PLK1 for lung cancer treatment. Nat Commun. (2022) 13. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31926-9
128. Yoon H-E, Kim S-A, Choi H-S, Ahn M-Y, Yoon J-H, and Ahn S-G. Inhibition of Plk1 and Pin1 by 5′-nitro-indirubinoxime suppresses human lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. (2012) 316:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.029
129. Jin X, Ding D, Yan Y, Li H, Wang B, Ma L, et al. Phosphorylated RB Promotes Cancer Immunity by Inhibiting NF-κB Activation and PD-L1 Expression. Mol Cell. (2019) 73:22–35.e26. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.034
130. Zhang Z, Cheng L, Li J, Qiao Q, Karki A, Allison DB, et al. Targeting Plk1 Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer to Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:3532–48. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-22-0018
131. Kandala S, Ramos M, Voith von Voithenberg L, Diaz-Jimenez A, Chocarro S, Keding J, et al. Chronic chromosome instability induced by Plk1 results in immune suppression in breast cancer. Cell Rep. (2023) 42. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113266
132. Peng M, Mo Y, Wang Y, Wu P, Zhang Y, Xiong F, et al. Neoantigen vaccine: an emerging tumor immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:128. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1055-6
133. Shin AR, Lee SE, Choi H, Sohn HJ, Cho HI, and Kim TG. An effective peptide vaccine strategy circumventing clonal MHC heterogeneity of murine myeloid leukaemia. Br J Cancer. (2020) 123:919–31. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0955-y
134. Arber C, Feng X, Abhyankar H, Romero E, Wu MF, Heslop HE, et al. Survivin-specific T cell receptor targets tumor but not T cells. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:157–68. doi: 10.1172/jci75876
135. Andersen RS, Thrue CA, Junker N, Lyngaa R, Donia M, Ellebæk E, et al. Dissection of T-cell antigen specificity in human melanoma. Cancer Res. (2012) 72:1642–50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-11-2614
Keywords: cancer, PLK1, inflammation, immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines
Citation: Wang W, Zhao R, Wang Y, Pan L, Luan F and Fu G (2025) PLK1 in cancer therapy: a comprehensive review of immunomodulatory mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Front. Immunol. 16:1602752. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602752
Received: 30 March 2025; Accepted: 02 June 2025;
Published: 19 June 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Poggi, San Martino Hospital (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Dahmane Oukrif, University College London, United KingdomOi Kwan Wong, Consultant, California, United States
Hua Yang, University of South Florida, United States
Iryna Kolosenko, Karolinska Institutet (KI), Sweden
Tao Wang, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhao, Wang, Pan, Luan and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guobin Fu, Zmdic0BzaW5hLmNvbQ==; Fang Luan, bHVhbmZhbmcyMDA0QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Guobin Fu, orcid.org/0000-0003-0893-7714
 Weihao Wang
Weihao Wang Rui Zhao1†
Rui Zhao1† Liying Pan
Liying Pan Guobin Fu
Guobin Fu