- 1Center for Translational Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Longevity and Aging-Related Diseases, Ministry of Education, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 3Guangxi Key Laboratory of Brain Science, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) immunotherapy has been revolutionized by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), yet response heterogeneity persists due to dynamic tumor-immune interactions. This review summarizes recent studies in understanding tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) biology, highlighting CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) as pivotal regulators of immune surveillance and suppression. We summarize emerging biomarkers such as TCR clonality, spatial distribution of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and exhaustion markers including PD-1, TCF1, and TIM-3, which predict immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) efficacy beyond PD-L1 expression. This review specifically describes radiotherapy-induced immunogenic remodeling and peripheral T cell dynamics as innovative strategies to monitor immune response and resistance mechanisms. By integrating results from single-cell omics and AI-driven spatial analysis, we propose multidimensional frameworks of TIL in NSCLC to overcome resistance and optimize immunotherapy combinations. These insights collectively advance NSCLC immunotherapy toward precision modulation of the tumor immune microenvironment.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of malignancy-related mortality worldwide, with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounting for over 85% of histological subtypes (1). Although immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting axes such as PD-1/PD-L1 have revolutionized therapeutic paradigms, patient response rates remain constrained by the dynamic heterogeneity of the tumor microenvironment (TME) (2). Studies demonstrate that tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TILs), as core TME components, form dual regulatory networks through subtype distribution and functional states: CD8+ T cells mediate tumor cell killing via the perforin-granzyme system (3), while regulatory T cells (Tregs) foster disease progression by establishing an immunosuppressive niche through IL-10/TGF-β (4–6).
The cancer immunoediting framework further reveals that tumor cells drive T cell exhaustion via PD-1, CTLA-4, and Tim-3, characterized by loss of effector function, inhibitory receptor upregulation, and metabolic reprogramming (7–11). Notably, exhausted T cells retain partial clonal expansion potential, offering therapeutic targets for ICI intervention (12–15). Single-cell sequencing identifies PD-1+CD8+ T cell clonal expansion as a predictive biomarker for ICI efficacy (16), while CD4+ T cells synergistically amplify antitumor immunity by regulating dendritic cell antigen presentation (17, 18) and inducing CD8+ T cell IFN-γ secretion (17). Recent advances highlight activated CD8+ T cells as inducers of tumor ferroptosis (19), though their efficacy is compromised by Treg/CD8+ ratio imbalance (12) and spatial distribution heterogeneity (20–23). Current research focuses on deciphering epigenetic remodeling mechanisms underlying T cell exhaustion and integrating single-cell omics with spatial transcriptomics to transcend limitations of traditional biomarkers like PD-L1, thereby propelling NSCLC immunotherapy from empirical practice toward multidimensional precision modulation.
2 Multidimensional regulatory networks of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in NSCLC
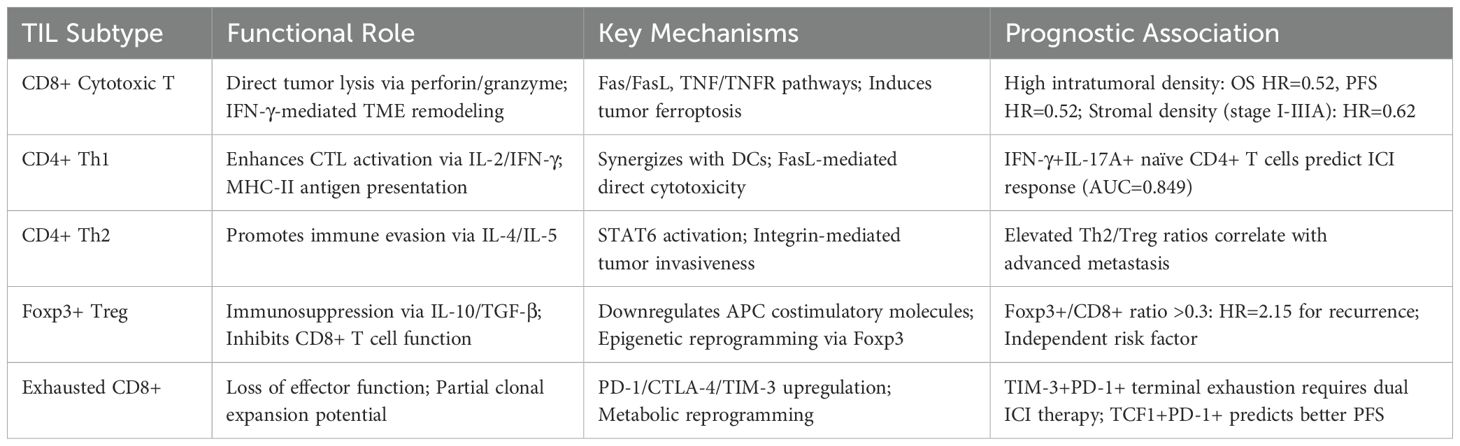
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, as key effectors within the tumor immune microenvironment, play a pivotal role in determining NSCLC prognosis and therapeutic response. TILs are primarily composed of T lymphocytes (24), including CD8+ cytotoxic T cells that mediate tumor cell lysis through perforin–granzyme pathways (25, 26), CD4+ helper T cells (Th1/Th2) that regulate cellular and humoral immunity via IL-2/IFN-γ and IL-4/IL-5, respectively, and Foxp3+ Tregs that exert immunosuppressive effects through IL-10 and TGF-β secretion (27–29). Single-cell sequencing reveals spatial-specific functional specialization in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (24), with their equilibrium predicting immunotherapy outcomes. Current biomarkers face limitations: PD-L1, the sole FDA-approved ICI marker, remains limited by tissue heterogeneity and detection variability (30), while threshold ambiguities and translational challenges hinder TMB and ctDNA clinical application (31, 32). Novel strategies leverage baseline TCR diversity (3) and spatial CD8+ TIL patterns, including associated with prognosis in stage I–IIIA NSCLC (33) and tumor nest localization observed in stage IV disease (34). Terminally exhausted CD8+ TILs (TIM-3+PD-1+) require CTLA-4 inhibitor-driven Treg depletion combined with PD-1 blockade (4, 35, 36), while epigenetic reversal of exhaustion (16) and adoptive therapy dose-responses (3) offer multidimensional interventions. Future integration of single-cell omics and spatial transcriptomics must map TIL functional subsets and spatial niches, propelling NSCLC immunotherapy toward systems biology-driven precision (37, 38).
2.1 The dual roles of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes in NSCLC tumorigenesis and progression
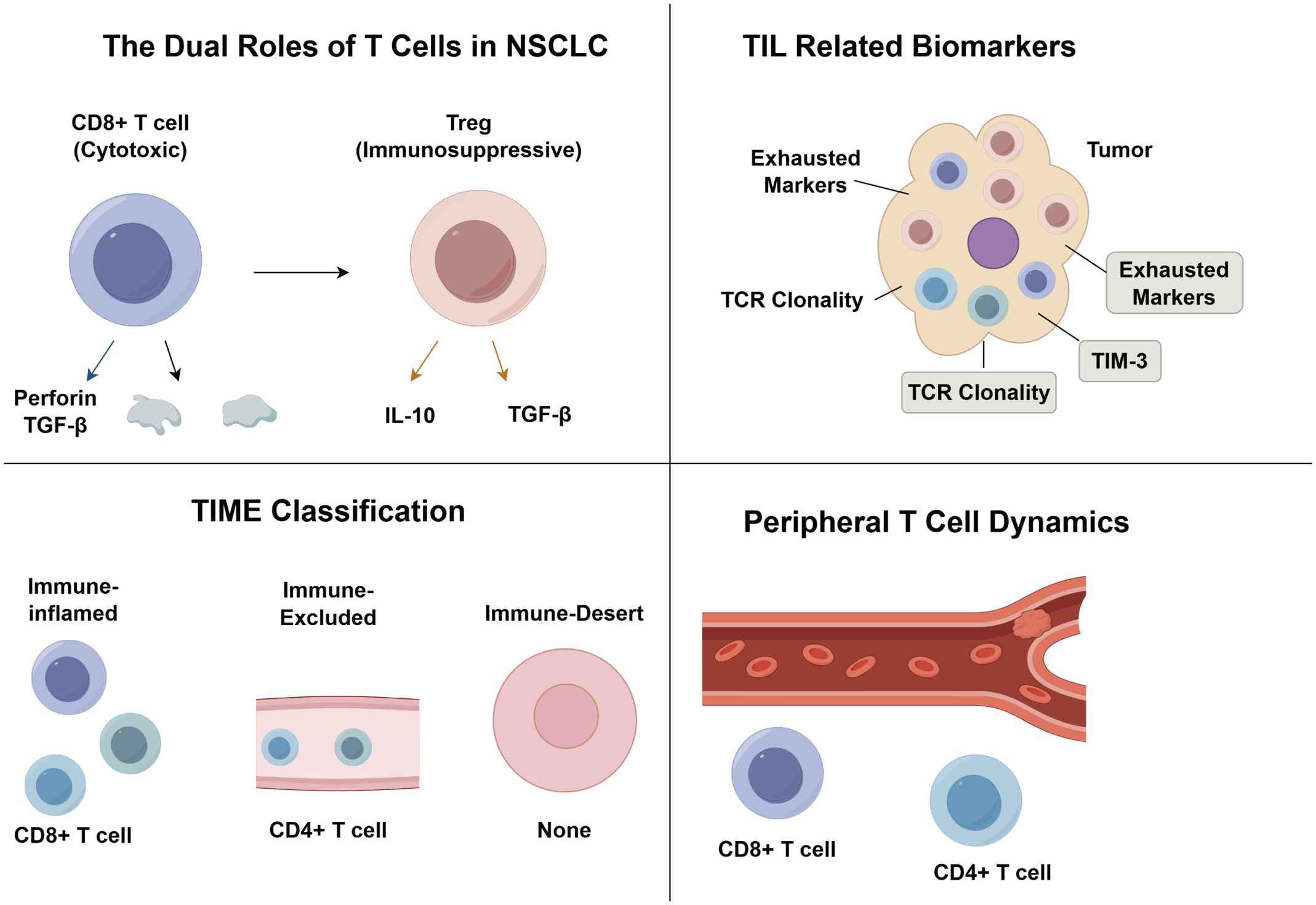
Tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes in NSCLC exhibit dual functions, either suppressing or promoting tumor progression. This dynamic interplay reflects the immune system’s balance between resisting immune evasion and sustaining antitumor responses (39). As primary antitumor effectors, CD8+ CTLs eliminate tumor cells via perforin/granzyme-induced membrane disruption, Fas/FasL-mediated apoptosis, and TNF/TNFR signaling amplification (40). CD4+ Th1 cells further support this by presenting antigens (MHC-II), secreting IFN-γ and TNF-α to activate antigen-presenting cells and enhance MHC-I expression, and mediating direct tumoricidal effects via FasL (41). Together, these cells coordinate spatiotemporally to form a robust T cell-mediated cytotoxic network. Conversely, Foxp3+ Tregs and Th2 cells foster tumor immune evasion. Tregs enhance tumor invasiveness through Foxp3-dependent epigenetic reprogramming (42), secrete IL-10 and TGF-β to inhibit CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity (43), and downregulate costimulatory molecules, hindering effective T cell activation. Th2 cells complement this by activating the IL-4/Gata3/STAT6 axis, inducing genes linked to proliferation and metastasis, and promoting integrin-mediated tumor invasion (44). The synergistic action of Tregs and Th2 cells reshapes tumor immunoediting via paracrine cytokine signaling and cell–cell interactions, ultimately undermining immune surveillance and advancing malignancy (Table 1).
2.2 Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes in NSCLC
The prognostic value of TILs hinges on subtype-specific distribution, spatial localization, and functional states (45, 46), with CD8+ CTLs exhibiting marked prognostic heterogeneity. MANDARANO et al. (47) demonstrated that intratumoral CD8+ TILs correlate with favorable outcomes, while a meta-analysis by LI et al. (48) further revealed that high intratumoral CD8+ TIL density associates with prolonged overall survival, progression-free survival, and a 4.08-fold increase in objective response rate following immunotherapy, though peripheral blood CD8+ T cell levels show no clinical relevance. XIA et al. (49) identified significant enrichment of IFN-γ+IL-17A+CD4+ naïve T cells and PD-1+CTLA-4+CD4+ memory T cells in responders to anti-PD-1 therapy, whereas elevated CTLA-4+CD4+ memory T cells predict poor prognosis in anti-PD-L1 treatment. Notably, while increased CD8+ TIL density paradoxically correlated with reduced 5-year survival, both CD3+ TIL abundance and IL-2-high subgroups demonstrated significant survival benefits. This counterintuitive observation suggests that functional activation status may serve as a more reliable prognostic indicator than mere lymphocyte subtype density (50). Mechanistic studies on Foxp3+ Treg-mediated protumor effects (42) reveal their suppression of CD8+ CTL cytotoxicity and enhancement of tumor invasiveness, with elevated Foxp3+/CD8+ and Foxp3+/CD4+ ratios confirmed as independent risk factors for postoperative recurrence (51). Current heterogeneity in findings likely stems from methodological disparities, sampling sites, and analytical threshold variability, underscoring the urgent need for standardized multidimensional frameworks integrating TIL spatial distribution, clonal diversity, and functional activation to establish reliable prognostic models for NSCLC precision immunotherapy.
2.3 The role of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes in NSCLC immunotherapy
Despite the transformative clinical impact of ICIs in NSCLC, heterogeneous patient responses underscore the urgent need for precision biomarkers. High TIL density is significantly associated with prolonged progression-free and overall survival following immunotherapy (52), underscoring TILs as predictive biomarkers of treatment responsiveness. Immune-inflamed tumors with high TIL infiltration demonstrate superior clinical outcomes compared to immune-desert phenotypes lacking immune cells, while immune-excluded and immune-suppressed subtypes exhibit intermediate responses (53). Multidimensional immunohistochemical analysis by KIM et al. (54) revealed that ICI responders display elevated CD3+ and CD8+ TIL densities, increased CD8+/CD3+ ratios (reflecting effector T cell activation), and reduced Foxp3+/CD8+ ratios (indicative of immunosuppressive microenvironment attenuation). Multivariate regression identified CD3+ TIL densityand Foxp3+/CD8+ ratio as independent predictors of ICI clinical benefit. Notably, EGFR-mutant tumors exhibit markedly diminished CD3+ TIL infiltration, providing a microenvironmental basis for their reduced ICI responsiveness. Collectively, these findings advocate for composite predictive models integrating T cell subset spatial distribution (intratumoral vs. stromal) and functional activation/exhaustion markers, thereby advancing precision stratification beyond PD-L1 monotherapy paradigms (Figure 1).
3 Roles of T cells in defining the NSCLC tumor immune microenvironment
3.1 Tumor immune microenvironment classification
The TIME classification system, based on TIL spatial patterns, stratifies tumors into immune-inflamed, immune-excluded, and immune-desert subtypes (55, 56). Immune-inflamed tumors feature dense CD8+/CD4+ T cell infiltration and PD-1/PD-L1 activation near tumor nests, correlating with better responses to ICIs. In contrast, immune-excluded tumors are characterized by stromal T cell accumulation without infiltration into the tumor parenchyma, while immune-desert tumors are devoid of T cells altogether, both exhibiting limited sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibitors. To overcome the subjectivity of traditional histopathology, Park et al. (57) developed an AI-based whole-slide imaging (WSI) model to classify TIME phenotypes using H&E slides. This system predicted clinical outcomes, with immune-inflamed tumors showing significantly improved progression-free survival and overall survival versus immune-excluded and immune-desert subtypes. Expanding on this, Teng et al. (58) introduced a four-tier model incorporating PD-L1 status and TIL density: Type I (PD-L1+/TIL+), Type II (PD-L1-/TIL-), Type III (PD-L1+/TIL-), and Type IV (PD-L1-/TIL+). Shirasawa et al. (59) validated its prognostic value, showing that Type I had the highest response rate and longest median PFS, while Type III reflected resistance due to immune exhaustion. Further refinements include Wu et al’s (60) identification of stage-specific TIME features and transcriptomic model (61), which defines immune-enriched, immune-enriched fibrotic, fibrotic, and depleted TIME subtypes. Notably, immune-excluded subtypes respond best to ICIs, and therapy-induced TIME transitions highlight the plasticity of the immune landscape. Together, these evolving frameworks support multidimensional TIME classification, but require further multicenter validation and mechanistic dissection of treatment-induced remodeling.
3.2 T Cell-related biomarkers in TIME
The dual PD-L1 expression on tumor and immune cells confers dynamic biological functions. High infiltration of CD8+PD-L1+ TILs exhibited hot tumor features but correlated with shorter progression-free survival due to concurrent CD68+ macrophage and CD163+ M2 polarization fostering an immunosuppressive niche (62). Conversely, in advanced patients receiving PD-1 inhibitors, the high CD8+PD-L1+ TILs group showed improved objective response rate and PFS via T cell exhaustion reversal. This duality underscores PD-L1’s spatiotemporal regulatory role—exacerbating Treg-mediated suppression in native immunity while serving as a therapeutic vulnerability under ICI intervention—complementing TIME classification theories and offering a novel composite biomarker for precision immunotherapy stratification.
Emerging evidence highlights the clinical significance of T cell exhaustion states in NSCLC. Pre-exhausted TCF1+PD-1+ populations demonstrate superior prognostic value compared to terminally exhausted TIM-3+TIGIT+ subsets, as revealed through single-cell sequencing (63). In clinical validation, abundant TCF1+PD-1+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes correlated with sustained treatment benefit in a 116-patient surgical cohort receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors, suggesting these pre-exhausted cells maintain functional memory potential (64). However, CD8+PD-1High TILs exhibiting TIM-3/CTLA-4 co-expression along with impaired IFN-γ/TNF production showed opposite associations with reduced disease-free survival (65), a pattern subsequently confirmed in advanced NSCLC cohorts (66). This dichotomy mirrors PD-L1+CD8+ TIL dualism, advocating dynamic models integrating exhaustion-stage-specific markers. While limited by retrospective designs, these findings highlight multidimensional T cell functional assessment as a breakthrough beyond PD-L1 limitations.
Beyond CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cell subsets demonstrate distinct prognostic value in NSCLC through neoantigen recognition and immunomodulatory functions. In advanced NSCLC, elevated FoxP3+CD4+ TIL infiltration was associated with improved progression-free and overall survival (67), potentially reflecting regulatory T cell-mediated mitigation of T cell exhaustion. Spatial transcriptomic analyses using digital profiling further revealed that CD4+ T cell localization within specific immune niches significantly enhanced survival outcomes, with observed synergistic effects from co-localized CD56+ NK cells (68). This spatially resolved approach advances beyond conventional immunohistochemistry by precisely mapping topological relationships between CD4+ T cells and NK cells, offering three-dimensional insights into tumor immune microenvironment heterogeneity. When integrated with T cell exhaustion profiling, these spatial and functional characterization methods collectively enhance precision immunotherapy strategies.
4 T Cell-based immunotherapy in NSCLC treatment
4.1 Predictive value of T cell receptor dynamics in immunotherapy efficacy
As the central molecular determinant of T cell antigen recognition, TCR diversity metrics and clonal evolution are emerging as novel biomarkers for predicting immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy. Han et al. (69) demonstrated in a seminal study that patients with high TCRβ chain CDR3 region diversity in peripheral PD-1+CD8+ T cells exhibited significantly superior disease control rates and survival benefits, with treatment-induced TCR clonal expansion correlating positively with tumor regression. The team further proposed the Tumor-Immune Repertoire (TIR) index—quantifying shared TCR clones between tumor and peripheral blood—showing that high TIR index patients achieved improved PFS and OS, mechanistically linked to elevated immunomodulatory cytokine levels (70). Notably, TCR clonal dynamics analysis effectively differentiates pseudoprogression. For instance, pseudoprogressive patients exhibit clonal expansion patterns and dominant clone overlap rates akin to partial responders, distinct from true progression cohorts, providing critical molecular insights for clinical decision-making. Zhang et al. (71) identified via multi-site TCR sequencing that only the top 1% high-frequency clones correlate with therapeutic response, with elevated tumor-peripheral TCR clonal concordance significantly enhancing major pathological response rates. These findings functionally complement prior CD4+/CD8+ T cell subset studies, collectively establishing a multidimensional predictive framework integrating T cell quantity and functional activity. Despite current limitations in sample sizes, TCR clonal monitoring demonstrates transformative potential in efficacy prediction, toxicity management, and progression discrimination, necessitating standardized sequencing protocols for clinical translation.
4.2 Radiotherapy-mediated remodeling of the tumor immune microenvironment
Radiotherapy remodels the TIME in NSCLC through multidimensional mechanisms, exhibiting dose-dependent biphasic immunomodulation. Preclinical studies demonstrate that conventional-dose radiotherapy activates PI3K/AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways to upregulate tumor cell PD-L1 expression while reducing immunosuppressive regulatory T cells (iTregs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) infiltration, thereby promoting CD8+ T cell clonal expansion to establish an immunologically active niche (72). Preclinical models confirm synergistic antitumor effects when combining radiotherapy with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, mechanistically linked to enhanced TCR diversity and spatial CD8+ T cell infiltration remodeling (73, 74). Notably, radiation fractionation patterns critically dictate immunomodulatory outcomes: hypofractionated radiotherapy outperforms conventional fractionation in activating systemic antitumor immunity via immunogenic cell death induction and proinflammatory cytokine release (75). A prospective cohort study by Theelen et al. (76) revealed that early-phase immune checkpoint inhibitor co-administration during radiotherapy synchronizes CD8+ T cell expansion peaks with radiation cycles, significantly improving objective response rates, though radiation pneumonitis risks require further evaluation. Current evidence highlights that spatiotemporal synergy between radiotherapy and ICIs transcends conventional therapeutic paradigms by reprogramming TIME immunoediting equilibria, offering advanced NSCLC patients a dual strategy for local control and systemic efficacy. Optimal intervention timing and safety management warrant validation through multicenter phase III trials.
4.3 Immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
The therapeutic paradigm for non-small cell lung cancer has evolved from chemotherapy and radiotherapy to targeted therapies and, most recently, immune checkpoint inhibitors, which reprogram antitumor immunity by reversing T cell functional suppression. PD-1, a pivotal inhibitory receptor on T cells, initiates downstream immunosuppressive signaling upon interaction with tumor-expressed PD-L1/L2 ligands, driving T cell exhaustion and immune evasion (77, 78). ICIs restore T cell cytotoxic function by blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 axis while reactivating clonal expansion capabilities of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells, thereby re-establishing antitumor immune surveillance networks (79, 80). Globally, multiple PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been approved for NSCLC treatment, with over 200 related agents in clinical trials demonstrating synergistic therapeutic potential in combination with chemoradiotherapy or targeted therapies (81, 82). This precision strategy focused on reversing immunosuppression represents a paradigm shift in NSCLC treatment, moving beyond single-target approaches to achieve comprehensive immunomodulation.
4.4 TLS-mature CD8+ T cells to durable ICI responses in NSCLC
The immunological heterogeneity of NSCLC manifests in the spatial distribution of immune cells across tumor cores, invasive margins, and TLS, with hierarchical compartmentalization of effector populations: T lymphocytes and macrophages dominate as primary immune effectors, while plasma cells, NK cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells exhibit limited representation (83–86). In addition to core tumor and invasive margin compartments, tertiary lymphoid structures have emerged as crucial immunological hubs influencing NSCLC immunotherapy outcomes. These ectopic lymphoid aggregates, composed of B cells, T cells, follicular dendritic cells, and high endothelial venules, support local antigen presentation and clonal expansion. This profoundly immunosuppressive microenvironment subverts antitumor immunity through multifaceted mechanisms—defective antigen presentation impairs immune recognition, aberrant recruitment of Tregs establishes immune-tolerant niches, and sustained inhibitory cytokine networks suppress CD8+ T cell functional activity (12, 87). Recent studies have shown that TLS presence—particularly those containing mature CD8+ T cells—correlates strongly with durable responses to immune checkpoint inhibitor and improved overall survival. Spatial transcriptomic profiling confirmed that TLS-rich tumors exhibit enhanced infiltration of stem-like TCF1+CD8+ T cells, sustaining antitumor activity during prolonged ICI exposure (88–90). Furthermore, TLS density and maturation status may stratify patients beyond PD-L1 expression, offering a reproducible and spatially resolved biomarker for precision immunotherapy (91, 92). Integrating TLS profiling into prognostic models may substantially improve patient selection, therapeutic monitoring, and understanding of immune resistance dynamics (93).
5 Conclusion
Non-small cell lung cancer represents a paradigm of immune heterogeneity. The spatial distribution, phenotypic diversity, and functional states of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes critically determine disease progression and immunotherapeutic outcomes. This review highlights how distinct T cell subsets, particularly CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes and Foxp3+ regulatory T cells, exert opposing immunological influences that shape the tumor immune microenvironment. The prognostic and predictive utility of these subsets depends not only on their density but also on their exhaustion status, clonal diversity, and localization within tumor compartments. Incorporating spatial transcriptomics, single-cell omics, and AI-assisted histopathological tools offers novel opportunities to refine TIME classification and advance immunotherapeutic precision.
Looking ahead, several actionable directions warrant attention. These include the development of standardized, spatially resolved biomarkers integrating TIL function and topography; dynamic monitoring frameworks that combine peripheral immune signatures with intratumoral exhaustion markers; personalization of immune checkpoint blockade through TCR repertoire analysis; and combinatorial strategies leveraging radiotherapy, ICIs, and adoptive T cell therapies to overcome resistance in non-inflamed tumor phenotypes. Multidimensional profiling and systems-level therapeutic design will be essential to transform NSCLC immunotherapy into a more precise, effective, and patient-tailored modality.
Author contributions
YL: Writing – original draft. DQ: Writing – original draft. JF: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 82060532).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. He T, Cao J, Xu J, Wang L, and Hu J. Minimally invasive therapies for early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. (2020) 23:479–86. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.101.01
2. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente D, Murakami S, Hui R, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:1919–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
3. Jiménez-Reinoso A, Nehme-Álvarez D, Domínguez-Alonso C, and Álvarez-Vallina L. Synthetic TILs: engineered tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes with improved therapeutic potential. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:593848. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.593848
4. Hendry S, Salgado R, Gevaert T, Russell PA, John T, Thapa B, et al. Assessing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in solid tumors: A practical review for pathologists and proposal for a standardized method from the international immuno-oncology biomarkers working group: part 2: TILs in melanoma, gastrointestinal tract carcinomas, non-small cell lung carcinoma and mesothelioma, endometrial and ovarian carcinomas, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, genitourinary carcinomas, and primary brain tumors. Adv Anat Pathol. (2017) 24:311–35. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000161
5. Dunn GP, Old LJ, and Schreiber RD. The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annu Rev Immunol. (2004) 22:329–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104803
6. Wei J, Zheng W, Chapman NM, Geiger TL, and Chi H. T cell metabolism in homeostasis and cancer immunity. Curr Opin Biotechnol. (2021) 68:240–50. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.02.003
7. Baitsch L, Baumgaertner P, Devêvre E, Raghav SK, Legat A, Barba L, et al. Exhaustion of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in metastases from melanoma patients. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121:2350–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI46102
8. Zajac AJ, Blattman JN, Murali-Krishna K, Sourdive DJ, Suresh M, Altman JD, et al. Viral immune evasion due to persistence of activated T cells without effector function. J Exp Med. (1998) 188:2205–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.12.2205
9. Verdon DJ, Mulazzani M, and Jenkins MR. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of CD8(+) T cell differentiation, dysfunction and exhaustion. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:7357. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197357
10. McLane LM, Abdel-Hakeem MS, and Wherry EJ. CD8 T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection and cancer. Annu Rev Immunol. (2019) 37:457–95. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055318
11. Blank CU, Haining WN, Held W, Hogan PG, Kallies A, Lugli E, et al. Defining ‘T cell exhaustion’. Nat Rev Immunol. (2019) 19:665–74. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0221-9
12. Woo EY, Yeh H, Chu CS, Schlienger K, Carroll RG, Riley JL, et al. Cutting edge: Regulatory T cells from lung cancer patients directly inhibit autologous T cell proliferation. J Immunol. (2002) 168:4272–6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.9.4272
13. Reina-Campos M, Scharping NE, and Goldrath AW. CD8(+) T cell metabolism in infection and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21:718–38. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00537-8
14. Kallies A, Zehn D, and Utzschneider DT. Precursor exhausted T cells: key to successful immunotherapy? Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:128–36. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0223-7
15. Propper DJ and Balkwill FR. Harnessing cytokines and chemokines for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2022) 19:237–53. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
16. Hanahan D and Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. (2011) 144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
17. Tay RE, Richardson EK, and Toh HC. Revisiting the role of CD4(+) T cells in cancer immunotherapy-new insights into old paradigms. Cancer Gene Ther. (2021) 28:5–17. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-0183-x
18. Beuneu H, Garcia Z, and Bousso P. Cutting edge: cognate CD4 help promotes recruitment of antigen-specific CD8 T cells around dendritic cells. J Immunol. (2006) 177:1406–10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.3.1406
19. Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, Gijón M, Kennedy PD, Johnson JK, et al. CD8(+) T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature. (2019) 569:270–4. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1170-y
20. Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagès C, et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. (2006) 313:1960–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1129139
21. Pagès F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo F, Costes A, Molidor R, et al. Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2005) 353:2654–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa051424
22. Azimi F, Scolyer RA, Rumcheva P, Moncrieff M, Murali R, McCarthy SW, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol. (2012) 30:2678–83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.37.8539
23. Savas P, Virassamy B, Ye C, Salim A, Mintoff CP, Caramia F, et al. Single-cell profiling of breast cancer T cells reveals a tissue-resident memory subset associated with improved prognosis. Nat Med. (2018) 24:986–93. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0078-7
24. Stankovic B, Bjørhovde HAK, Skarshaug R, Aamodt H, Frafjord A, Müller E, et al. Immune cell composition in human non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:3101. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03101
25. Durgeau A, Virk Y, Corgnac S, and Mami-Chouaib F. Recent advances in targeting CD8 T-cell immunity for more effective cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:14. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00014
26. Martínez-Lostao L, Anel A, and Pardo J. How do cytotoxic lymphocytes kill cancer cells? Clin Cancer Res. (2015) 21:5047–56. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0685
27. Kim HJ and Cantor H. CD4 T-cell subsets and tumor immunity: the helpful and the not-so-helpful. Cancer Immunol Res. (2014) 2:91–8. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0216
28. Borst J, Ahrends T, Bąbała N, Melief CJM, and Kastenmüller W. CD4(+) T cell help in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. (2018) 18:635–47. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0044-0
29. Raphael I, Nalawade S, Eagar TN, and Forsthuber TG. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. (2015) 74:5–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.09.011
30. Bryant AK, Sankar K, Strohbehn GW, Zhao L, Daniel V, Elliott D, et al. Prognostic and predictive role of PD-L1 expression in stage III non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive chemoradiation and adjuvant durvalumab. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2022) 113:752–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.03.015
31. Hellmann MD, Ciuleanu TE, Pluzanski A, Lee JS, Otterson GA, Audigier-Valette C, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a high tumor mutational burden. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:2093–104. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801946
32. Yang Y, Zhang T, Wang J, Wang J, Xu Y, Zhao X, et al. The clinical utility of dynamic ctDNA monitoring in inoperable localized NSCLC patients. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:117. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01590-0
33. Al-Shibli KI, Donnem T, Al-Saad S, Persson M, Bremnes RM, and Busund LT. Prognostic effect of epithelial and stromal lymphocyte infiltration in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2008) 14:5220–7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0133
34. Kawai O, Ishii G, Kubota K, Murata Y, Naito Y, Mizuno T, et al. Predominant infiltration of macrophages and CD8(+) T Cells in cancer nests is a significant predictor of survival in stage IV nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. (2008) 113:1387–95. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v113:6
35. Philip M and Schietinger A. CD8+ T cell differentiation and dysfunction in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (2022) 22:209–23. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00574-3
36. Guan Q, Han M, Guo Q, Yan F, Wang M, Ning Q, et al. Strategies to reinvigorate exhausted CD8(+) T cells in tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1204363. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1204363
37. Yu Y, Zeng D, Ou Q, Liu S, Li A, Chen Y, et al. Association of survival and immune-related biomarkers with immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis and individual patient-level analysis. JAMA Netw Open. (2019) 2:e196879. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.6879
38. Sanmamed MF, Nie X, Desai SS, Villaroel-Espindola F, Badri T, Zhao D, et al. A burned-out CD8(+) T-cell subset expands in the tumor microenvironment and curbs cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. (2021) 11:1700–15. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0962
39. Wu J and Lin D. A review of artificial intelligence in precise assessment of programmed cell death-ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer. Adv Anat Pathol. (2021) 28:439–45. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000322
40. Zhu J, de Tenbossche CGP, Cané S, Colau D, Baren NV, Lurquin C, et al. Resistance to cancer immunotherapy mediated by apoptosis of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:1404. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00784-1
41. Laheurte C, Dosset M, Vernerey D, Boullerot L, Gaugler B, Gravelin E, et al. Distinct prognostic value of circulating anti-telomerase CD4(+) Th1 immunity and exhausted PD-1(+)/TIM-3(+) T cells in lung cancer. Br J Cancer. (2019) 121:405–16. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0531-5
42. Peng J, Yu Z, Xue L, Wang J, Li J, Liu D, et al. The effect of foxp3-overexpressing Treg cells on non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17:5860–8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8606
43. Liu W, Wei X, Li L, Wu X, Yan J, Yang H, et al. CCR4 mediated chemotaxis of regulatory T cells suppress the activation of T cells and NK cells via TGF-β pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 488:196–203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.05.034
44. Suzuki A, Leland P, Joshi BH, and Puri RK. Targeting of IL-4 and IL-13 receptors for cancer therapy. Cytokine. (2015) 75:79–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.026
45. Barua S, Fang P, Sharma A, Fujimoto J, Wistuba I, Rao AUK, et al. Spatial interaction of tumor cells and regulatory T cells correlates with survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2018) 117:73–9. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.01.022
46. Giatromanolaki A, Anestopoulos I, Panayiotidis MI, Mitrakas A, Pappa A, and Koukourakis MI. Prognostic relevance of the relative presence of CD4, CD8 and CD20 expressing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in operable non-small cell lung cancer patients. Anticancer Res. (2021) 41:3989–95. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15196
47. Mandarano M, Bellezza G, Belladonna ML, Van den Eynde BJ, Chiari R, Vannucci J, et al. Assessment of TILs, IDO-1, and PD-L1 in resected non-small cell lung cancer: an immunohistochemical study with clinicopathological and prognostic implications. Virchows Arch. (2019) 474:159–68. doi: 10.1007/s00428-018-2483-1
48. Li F, Li C, Cai X, Xie Z, Zhou L, Cheng B, et al. The association between CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and the clinical outcome of cancer immunotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. (2021) 41:101134. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101134
49. Xia L, Wang H, Sun M, Yang Y, Yao C, He S, et al. Peripheral CD4(+) T cell signatures in predicting the responses to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy for Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Sci China Life Sci. (2021) 64:1590–601. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1861-5
50. Tian C, Lu S, Fan Q, Zhang W, Jiao S, Zhao X, et al. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ or CD3+ T lymphocytes and interleukin-2 expression in radically resected non-small cell lung cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). (2015) 128:105–10. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.147828
51. Mlika M, Saidi A, Mejri N, Abdennadher M, Haddouchi C, Labidi S, et al. Prognostic impact of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. (2022) 30:177–84. doi: 10.1177/02184923211042129
52. Gataa I, Mezquita L, Rossoni C, Auclin E, Kossai M, Aboubakar F, et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte density is associated with favourable outcome in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with immunotherapy. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 145:221–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.10.017
53. Galon J and Bruni D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2019) 18:197–218. doi: 10.1038/s41573-018-0007-y
54. Kim H, Kwon HJ, Han YB, Park SY, Kim ES, Kim SH, et al. Increased CD3+ T cells with a low FOXP3+/CD8+ T cell ratio can predict anti-PD-1 therapeutic response in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Mod Pathol. (2019) 32:367–75. doi: 10.1038/s41379-018-0142-3
55. Chen DS and Mellman I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature. (2017) 541:321–30. doi: 10.1038/nature21349
56. Hegde PS and Chen DS. Top 10 challenges in cancer immunotherapy. Immunity. (2020) 52:17–35. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.011
57. Park S, Ock CY, Kim H, Pereira S, Park S, Ma M, et al. Artificial intelligence-powered spatial analysis of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes as complementary biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:1916–28. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02010
58. Teng MW, Ngiow SF, Ribas A, and Smyth MJ. Classifying cancers based on T-cell infiltration and PD-L1. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:2139–45. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0255
59. Shirasawa M, Yoshida T, Shimoda Y, Takayanagi D, Shiraishi K, Kubo T, et al. Differential immune-related microenvironment determines programmed cell death protein-1/programmed death-ligand 1 blockade efficacy in patients with advanced NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. (2021) 16:2078–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.07.027
60. Wu F, Fan J, He Y, Xiong A, Yu J, Li Y, et al. Single-cell profiling of tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:2540. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22801-0
61. Bagaev A, Kotlov N, Nomie K, Svekolkin V, Gafurov A, Isaeva O, et al. Conserved pan-cancer microenvironment subtypes predict response to immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. (2021) 39:845–865.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.014
62. Zhang L, Chen Y, Wang H, Xu Z, Wang Y, Li S, et al. Massive PD-L1 and CD8 double positive TILs characterize an immunosuppressive microenvironment with high mutational burden in lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002356. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002356
63. Guo X, Zhang Y, Zheng L, Zheng C, Song J, Zhang Q, et al. Global characterization of T cells in non-small-cell lung cancer by single-cell sequencing. Nat Med. (2018) 24:978–85. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0045-3
64. Koh J, Kim S, Woo YD, Song SG, Yim J, Han B, et al. TCF1(+)PD-1(+) tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes predict a favorable response and prolonged survival after immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. (2022) 174:10–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.07.004
65. Kim CG, Kim G, Kim KH, Park S, Shin S, Yeo D, et al. Distinct exhaustion features of T lymphocytes shape the tumor-immune microenvironment with therapeutic implication in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002780. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002780
66. Mazzaschi G, Madeddu D, Falco A, Bocchialini G, Goldoni M, Sogni F, et al. Low PD-1 expression in cytotoxic CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes confers an immune-privileged tissue microenvironment in NSCLC with a prognostic and predictive value. Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 24:407–19. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2156
67. Kagamu H, Yamasaki SY, Kitano S, Yamaguchi O, Mouri A, Shiono A, et al. Single-cell analysis reveals a CD4+ T-cell cluster that correlates with PD-1 blockade efficacy. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:4641–53. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0112
68. Zugazagoitia J, Gupta S, Liu Y, Fuhrman K, Gettinger S, Herbst RS, et al. Biomarkers associated with beneficial PD-1 checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) identified using high-plex digital spatial profiling. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:4360–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-0175
69. Han J, Duan J, Bai H, Wang Y, Wan R, Wang X, et al. TCR repertoire diversity of peripheral PD-1(+)CD8(+) T cells predicts clinical outcomes after immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. (2020) 8:146–54. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0398
70. Han J, Yu R, Duan J, Li J, Zhao W, Feng G, et al. Weighting tumor-specific TCR repertoires as a classifier to stratify the immunotherapy delivery in non-small cell lung cancers. Sci Adv. (2021) 7:eabd6971. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd6971
71. Zhang J, Ji Z, Caushi JX, Asmar ME, Anagnostou V, Cottrell TR, et al. Compartmental analysis of T-cell clonal dynamics as a function of pathologic response to neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:1327–37. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2931
72. Gong X, Li X, Jiang T, Xie H, Zhu Z, Zhou F, et al. Combined radiotherapy and anti-PD-L1 antibody synergistically enhances antitumor effect in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. (2017) 12:1085–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.04.014
73. Yoneda K, Kuwata T, Kanayama M, Mori M, Kawanami T, Yatera K, et al. Alteration in tumoural PD-L1 expression and stromal CD8-positive tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes after concurrent chemo-radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. (2019) 121:490–6. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0541-3
74. Dovedi SJ, Adlard AL, Lipowska-Bhalla G, McKenna C, Jones S, Cheadle EJ, et al. Acquired resistance to fractionated radiotherapy can be overcome by concurrent PD-L1 blockade. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:5458–68. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1258
75. Cortiula F, Reymen B, Peters S, Mol PV, Wauters E, Vansteenkiste J, et al. Immunotherapy in unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: state of the art and novel therapeutic approaches. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:893–908. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.06.013
76. Theelen W, Chen D, Verma V, Hobbs BP, Peulen HMU, Aerts JGJV, et al. Pembrolizumab with or without radiotherapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Respir Med. (2021) 9:467–75. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30391-X
77. Patsoukis N, Wang Q, Strauss L, and Boussiotis VA. Revisiting the PD-1 pathway. Sci Adv. (2020) 6:eabd2712. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd2712
78. Dyck L and Mills KHG. Immune checkpoints and their inhibition in cancer and infectious diseases. Eur J Immunol. (2017) 47:765–79. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646875
79. Raskov H, Orhan A, Christensen JP, and Gögenur I. Cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells in cancer and cancer immunotherapy. Br J Cancer. (2021) 124:359–67. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01048-4
80. Shen Y, Chen J, and Li XP. Research advances in immune checkpoint drugs for non-small cell lung cancer. J Drug Target. (2023) 31:700–13. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2023.2235098
81. Cella E, Zullo L, Marconi S, Rossi G, Coco S, Dellepiane C, et al. Immunotherapy-chemotherapy combinations for non-small cell lung cancer: current trends and future perspectives. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2022) 22:1259–73. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2022.2116273
82. Tang S, Qin C, Hu H, Liu T, He Y, Guo HG, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: progress, challenges, and prospects. Cells. (2022) 11:320. doi: 10.3390/cells11030320
83. Bremnes RM, Al-Shibli K, Donnem T, Sirera R, Al-Saad S, Andersen S, et al. The role of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and chronic inflammation at the tumor site on cancer development, progression, and prognosis: emphasis on non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. (2011) 6:824–33. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182037b76
84. Bremnes RM, Busund LT, Kilvær TL, Andersen S, Richardsen E, Paulsen EE, et al. The role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in development, progression, and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. (2016) 11:789–800. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.01.015
85. Ishibashi Y, Tanaka S, Tajima K, Yoshida T, and Kuwano H. Expression of Foxp3 in non-small cell lung cancer patients is significantly higher in tumor tissues than in normal tissues, especially in tumors smaller than 30 mm. Oncol Rep. (2006) 15:1315–9. doi: 10.3892/or.15.5.1315
86. Kataki A, Scheid P, Piet M, Marie B, Martinet N, Martinet Y, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and macrophages have a potential dual role in lung cancer by supporting both host-defense and tumor progression. J Lab Clin Med. (2002) 140:320–8. doi: 10.1067/mlc.2002.128317
87. Rosenberg SA. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. (2005) 2:115. doi: 10.1038/ncponc0101
88. Elfving H, Yu H, Fessehatsion KK, Brunnström H, Botling J, Gulyas M, et al. Spatial distribution of tertiary lymphoid structures in the molecular and clinical context of non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2025). doi: 10.1007/s13402-025-01052-x
89. Weng Y, Yuan J, Cui X, Wang J, Chen H, Xu L, et al. The impact of tertiary lymphoid structures on tumor prognosis and the immune microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:16246. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64980-y
90. Tooley KA, Escobar G, and Anderson AC. Spatial determinants of CD8(+) T cell differentiation in cancer. Trends Cancer. (2022) 8:642–54. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2022.04.003
91. Vanhersecke L, Brunet M, Guégan JP, Rey C, Bougouin A, Cousin S, et al. Mature tertiary lymphoid structures predict immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy in solid tumors independently of PD-L1 expression. Nat Cancer. (2021) 2:794–802. doi: 10.1038/s43018-021-00232-6
92. Liu Y, Ye SY, He S, Chi DM, Wang XZ, Wen YF, et al. Single-cell and spatial transcriptome analyses reveal tertiary lymphoid structures linked to tumour progression and immunotherapy response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:7713. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52153-4
Keywords: melanoma, T lymphocyte, CD8 + T cell, PD-1, NRAS mutations, immunotherapy combination therapy, biomarkers
Citation: Liu Y, Qin D and Fu J (2025) T lymphocyte heterogeneity in NSCLC: implications for biomarker development and therapeutic innovation. Front. Immunol. 16:1604310. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1604310
Received: 01 April 2025; Accepted: 12 May 2025;
Published: 29 May 2025.
Edited by:
Zhijie Zhao, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xin Zhang, Affiliated Foshan Hospital of Southern Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Liu, Qin and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiejun Fu, ZnVqaWVqdW5AZ3htdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yu Liu
Yu Liu Denghui Qin1,2†
Denghui Qin1,2†