- 1Graduate School, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
- 2First Affiliated Hospital, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by synovial inflammation and destruction of articular cartilage and bone, which seriously affects patients’ quality of life. In recent years, with the in-depth research on natural medicines, the application of polysaccharides in the treatment of RA has gradually gained attention due to their unique bioactive components and diverse pharmacological effects. Polysaccharides were reported to exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and protective effects on cartilage and bone tissues. This review briefly introduces RA, its etiology and pathogenesis, and the different sources and structures of polysaccharides. It focuses on the mechanisms of polysaccharides in the alleviation of RA, mainly through the modulation of immune cell function, inhibition of inflammation, regulation of gut microbiota, promotion of bone formation and repair, and influence on related pathways. The aim of this review is to summarize the polysaccharides and their mechanisms of action in the alleviation of RA, with a view to providing new ideas for the clinical treatment of RA.
1 Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common chronic autoimmune diseases (1). Its pathogenesis involves a complex interaction between abnormal activation of the immune system, inflammatory response and gut microbial homeostasis (2). Epidemiology shows that the global prevalence of RA is about 0.5%-1%, and the incidence in women is 2–3 times higher than that in men, which seriously affects the quality of life of patients (3). Once diagnosed, RA requires lifelong treatment (4). It also brings a heavy economic burden to the society. Currently, the treatment strategies for RA mainly include drug therapy, physiotherapy, surgery (5–8). However, in view of its complex pathogenesis and diverse clinical manifestations, the search for safer and more effective treatments has always been a research hotspot in the field of rheumatology (9–11). In recent years, polysaccharides, as a class of natural products with a wide range of biological activities, have gradually attracted attention for their potential in alleviating rheumatoid arthritis (12, 13). The aim of this article is to review the role of polysaccharides and their potential mechanisms in the alleviation of RA, with a view to providing new ideas and strategies for the treatment of RA.
Polysaccharides are a class of macromolecular compounds consisting of multiple monosaccharide molecules linked by glycosidic bonds, which are widely found in plants, animals and microorganisms (14–16). Depending on the source, polysaccharides can be classified as plant polysaccharides, animal polysaccharides and microbial polysaccharides (17–19). Polysaccharides have a variety of biological activities, such as immunomodulation, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumour (20, 21). These activities are closely related to their complex chemical structures. In recent years, more and more studies have shown that polysaccharides can regulate the immune system, inhibit the inflammatory response, promote tissue repair and other pathways to produce therapeutic effects on a variety of diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (22, 23). The pathogenesis of RA is complex and involves a variety of aspects, such as genetics, the environment, immunity (24, 25). In the pathogenesis of RA, the immune system is abnormally activated and attacks its own synovium, leading to synovial inflammation and joint damage (26, 27). Synovial inflammation further triggers the formation of pannus, which invade the articular cartilage and bone, releasing a variety of inflammatory mediators and proteases and accelerating joint destruction (28, 29). In addition, RA patients suffer from pathological changes such as enhanced oxidative stress and imbalanced cytokine networks, which together contribute to disease progression (30, 31). Therefore, therapeutic strategies for RA need to take multiple aspects into account, including inhibiting the inflammatory response, regulating immune balance, and promoting tissue repair (32, 33).
Over the past decade, mentions of polysaccharides and RA increased from 19 in 2015 to 25 in 2024 (Figure 1A). Figure 1B shows the co-occurrence of keywords related to polysaccharides and RA. Among them, there are many keywords related to RA, such as inflammation, Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and B cells. This review provides a reference for further research and application of developing new therapeutic strategies for RA. The aim of this review is to provide a comprehensive overview of current research involving plant polysaccharides, animal polysaccharides and microbial polysaccharides, the therapeutic rheumatological activity of polysaccharides from different sources and their mechanisms, with a particular focus on the relevant signaling pathways for the treatment of RA, NF-κB, PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT and MAPK. This work also centers around the need for further research to better understand the limitations of clinical therapy with polysaccharides. It also critically examines the challenges associated with its clinical use, especially the safety concerns.
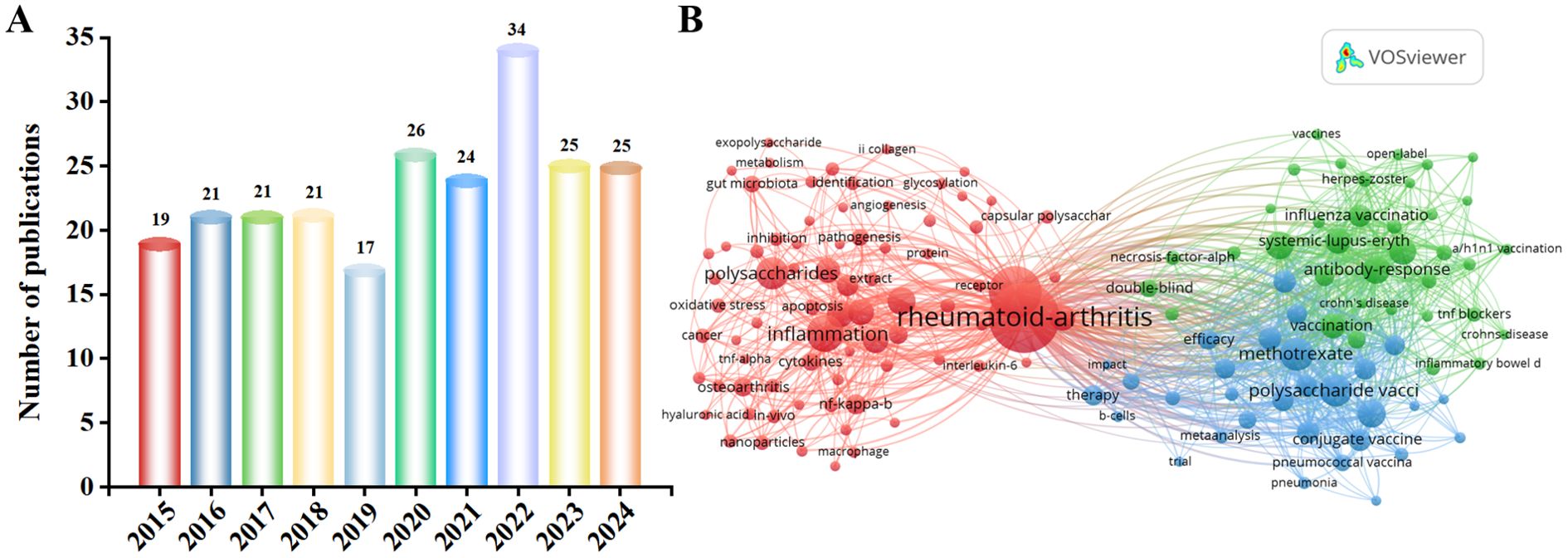
Figure 1. (A) Number of polysaccharide- and RA-related papers obtained from the Web of Science core database from 2015 to 2024. (B) Keyword co-occurrence map of bibliographic data created using VOSviewer from 2015 to 2024. Specifically, this area remains underexplored from 2015 to 2024. In 2022, polysaccharides for RA were published to a near-decade high of 34 articles, and have remained at 25 articles in 2023 and 2024. Thus, research findings on polysaccharides for RA have been of interest.
2 Methods
This narrative review searched PubMed, Web of Science, SpringerLink and Science Direct databases using keywords and related terms. It used certain keywords, i.e. polysaccharides and RA, and combined these terms with the following keywords: plant, microorganism, animal, immune, inflammatory, oxidative, bone tissue, pathway, etc. The last search was conducted in March 2025. The language of literature search was English and references were selected based on their relevance. Duplicate studies and irrelevant references were excluded, and abstracts of the remaining articles were reviewed to ensure they met the inclusion criteria for the review.
3 RA background
3.1 Etiology and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
RA is an autoimmune disease that is characterized by focusing on articular cartilage erosion and bone destruction, ultimately leading to joint deformity and loss of function (34). The main clinical manifestations of patients are symmetrical morning stiffness, pain and swelling of multiple joints to varying degrees, accompanied by limited movement, and joint deformity may occur in patients with a longer course of the disease (35, 36). RA-related extra-articular manifestations (EAM) can involve all organ systems, with a wide range of symptoms (37, 38). As shown in Figure 2, in addition to intra-articular manifestations, there may be secondary tissue and organ damage such as cardiovascular, pulmonary, renal, ocular, cutaneous ulcer, digestive and neurological disorders (39). Approximately 17.6 million people worldwide suffer from RA, and more than 3 million are disabled. As the population continues to age, the number of RA cases is projected to reach 31.7 million by 2050, increasing burden on society (39). Epidemiological studies have shown that the prevalence of RA in China is 0.42 per cent, affecting about 5 million people, with a male-to-female ratio of about 1:4 (40).
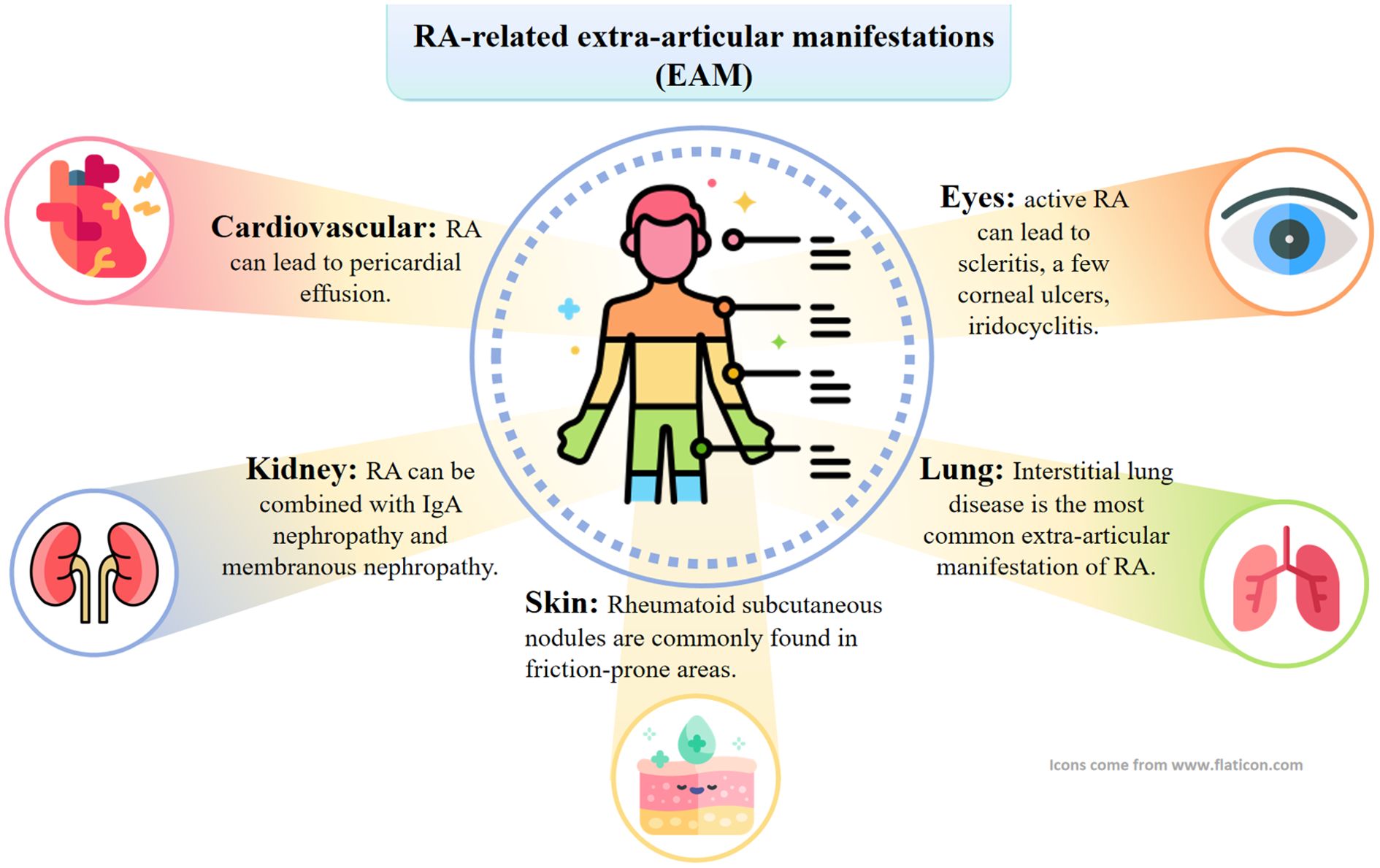
Figure 2. RA can also involve internal organs other than joints. Specifically, this can manifest as interstitial lung lesions, rheumatoid nodules, skin ulcers, and neurologic, cardiac, and eye lesions.
3.2 The development and pathogenesis of RA
As shown in Figure 3, the pathogenesis of RA is complex and is the result of a combination of factors. An imbalance in the immune system is key. The immune imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by T-cell abnormalities and an imbalance of pro-inflammatory/anti-inflammatory factors that trigger joint destruction (41, 42). Articular cartilage and bone are destroyed by inflammatory mechanisms involving a variety of pro-inflammatory factor-secreting cells, including immune cells (e.g., mast cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, T-cells, and B-cells) and synoviocytes (synovial macrophages (SMs) and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS)) (43). Similarly, inflammatory cytokines play a key role in the development of RA, the synovial inflammatory response and bone destruction (44, 45). Among them, the involvement of TNF and IL-6 is central to the pathogenesis of RA, and other cytokines such as IL-17, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-18, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) also play important roles (46). These cytokines, together with immune cells and autoantibodies, induce and maintain joint inflammation in RA, ultimately leading to cartilage and bone damage in the affected joints (Table 1). RA has a recognized genetic component, and studies have shown that in identical twins, if one twin has RA, the other has a probability of developing the disease of about 15 per cent. Certain genes are associated with the development of RA, such as HLA-DR4, which affects the immune system’s recognition and response, increasing the risk of the disease (47). In addition, a variety of infections are associated with the development of RA, such as EBV, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Helicobacter pylori. Infections may activate the immune system, and some components of pathogens are similar to the body’s own antigens, so that the immune system attacks the pathogen by attacking its own tissues by mistake, i.e., a molecular mimicry mechanism (48). General endocrine factors can also trigger rheumatoid arthritis, such as sex hormones. The incidence of RA is higher in women than in men. The risk of RA in women particularly increases during pregnancy, postpartum and around the time of menopause due to hormonal fluctuations (49). Estrogen regulates immune cell function, affects cytokine secretion, alters the immune balance and increases the susceptibility of RA. Lifestyle habits and environment can trigger rheumatoid arthritis (49). For example, long-term smoking disrupts the immune balance in the lungs and produces inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-8, CCL20), increasing the likelihood of RA onset (50). Cold and humid environments can affect blood circulation and immune function, increasing the risk of developing RA (51). Exposure of the body to certain chemicals, such as silica dust, may also trigger RA (52). With advances in high-throughput sequencing, it has been widely recognized that the host microbiota, particularly the gut microbiota, plays a key role in the pathogenesis and progression of RA (53). The gut microbiota and gut-associated lymphoid tissues work together to maintain immune homeostasis within the host and can serve as an indicator of host health status, and if their interactions are disrupted, they can have an impact on mucosal and systemic immunity and lead to the development of a variety of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases (54). Therefore, further elucidation of the pathogenesis of RA and promotion of RA-related drug research are of great significance in improving treatment efficacy of RA.
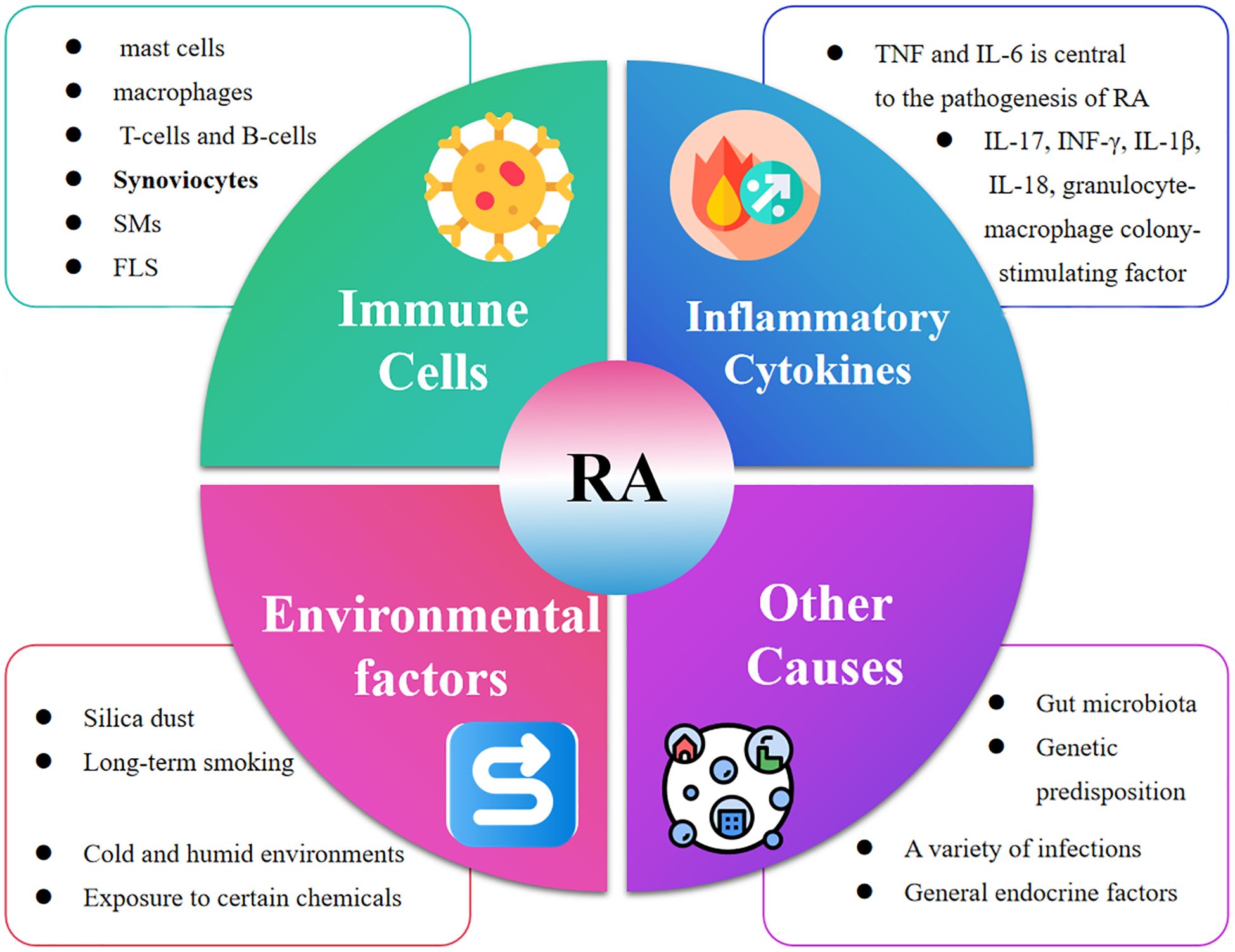
Figure 3. The development of RA is the result of a combination of factors. Specifically, Immune Cells (mast cells, macrophages, T-cells and B-cells, Synoviocytes, SMs, FLS), Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF and IL-6), Environmental factors (Silica dust, Long-term smoking, Cold and humid environments Exposure to certain chemicals and Other Causes (Gut microbiota, Genetic predisposition, A variety of infections, General endocrine factors) jointly accelerated the development of RA.
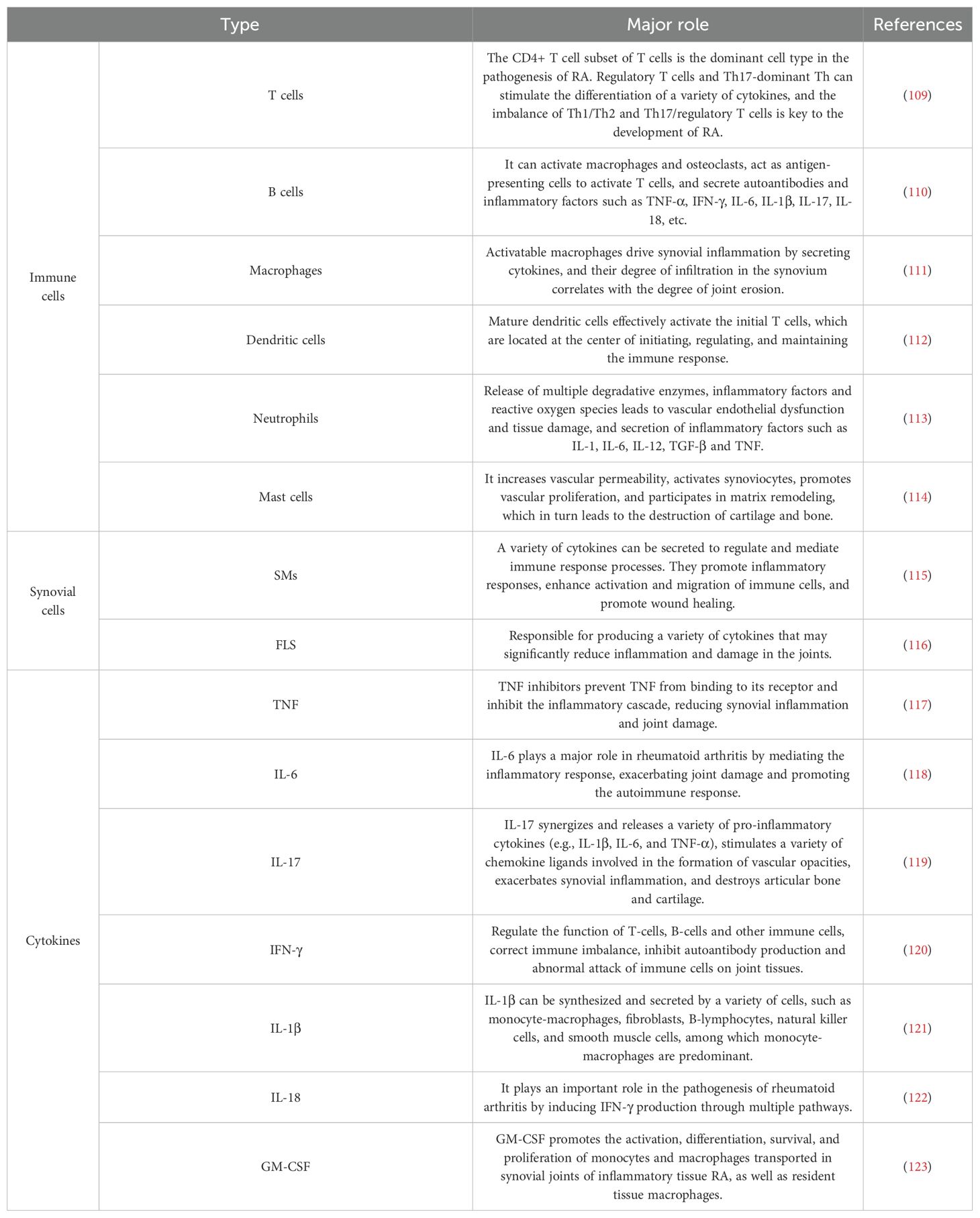
Table 1. Multiple immune cells and cytokines play important roles in RA intrinsic and adaptive immunity and its development.
4 Polysaccharide and RA
4.1 Sources of polysaccharides
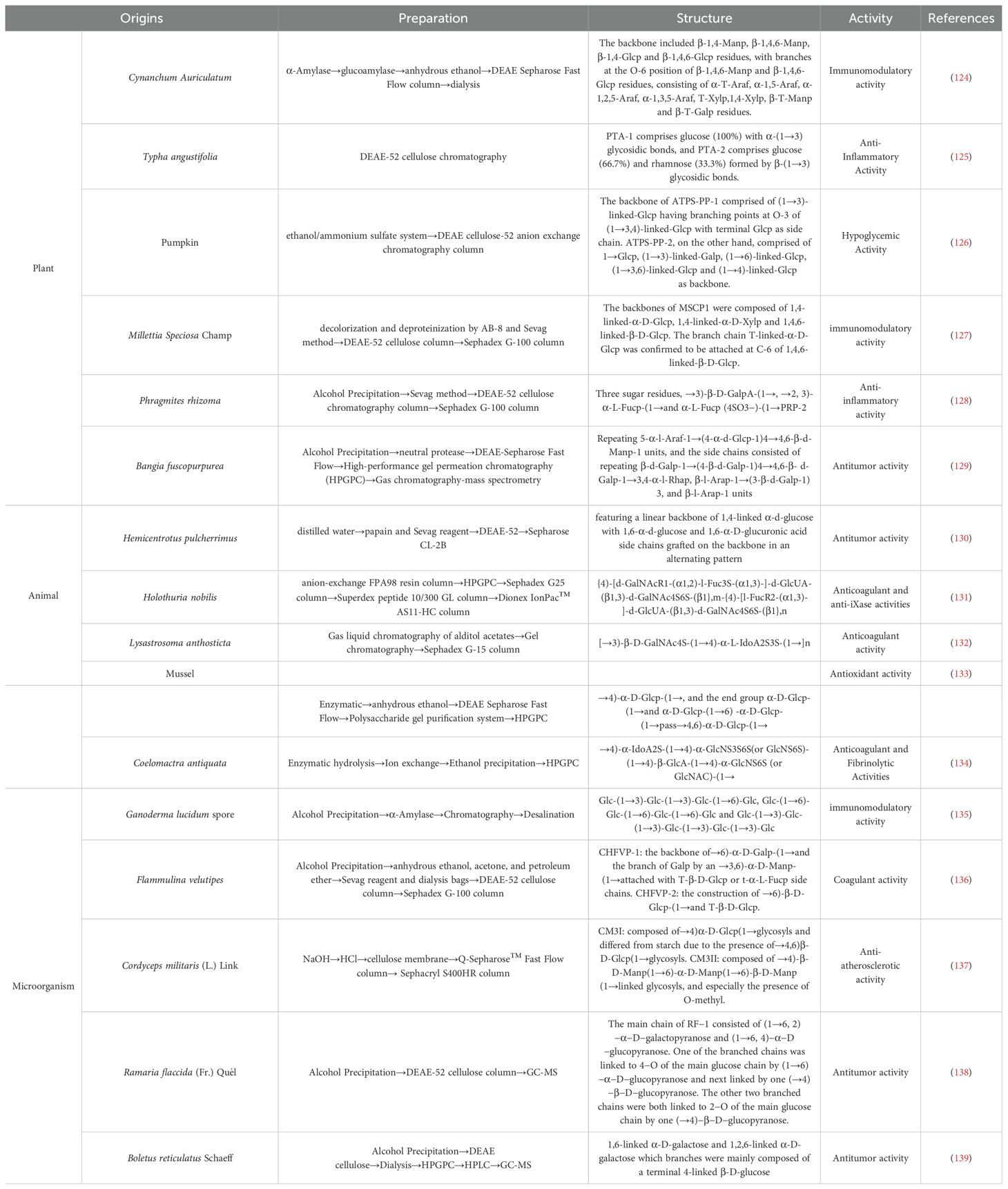
Polysaccharides are macromolecular compounds consisting of multiple monosaccharide molecules linked by glycosidic bonds and are widely found in living organisms. Depending on the source, polysaccharides can be classified into three main categories: plant polysaccharides, animal polysaccharides and microbial polysaccharides. As shown in Table 2, the preparation, structure, activity, and references of polysaccharides from different origins were listed. In addition, polysaccharides from different sources (plants, animals, microorganisms) exhibit unique mechanisms in RA therapy due to differences in chemical structure and targets of action. Plant polysaccharides are mainly heteropolysaccharides, which often contain hydroxyl and carboxyl groups, have high molecular weights, and some of them have helical conformations (55). Plant polysaccharides can inhibit the autoimmune response of RA by regulating Th17/Treg (56). Animal polysaccharides act directly on the joint microenvironment by virtue of sulfation modification to alleviate acute inflammation and cartilage damage (57). Microbial polysaccharides regulate systemic immune homeostasis through the “gut-joint axis” and are suitable for RA associated with gut dysbiosis (58).
4.2 Mechanisms associated with the alleviation of RA by polysaccharides
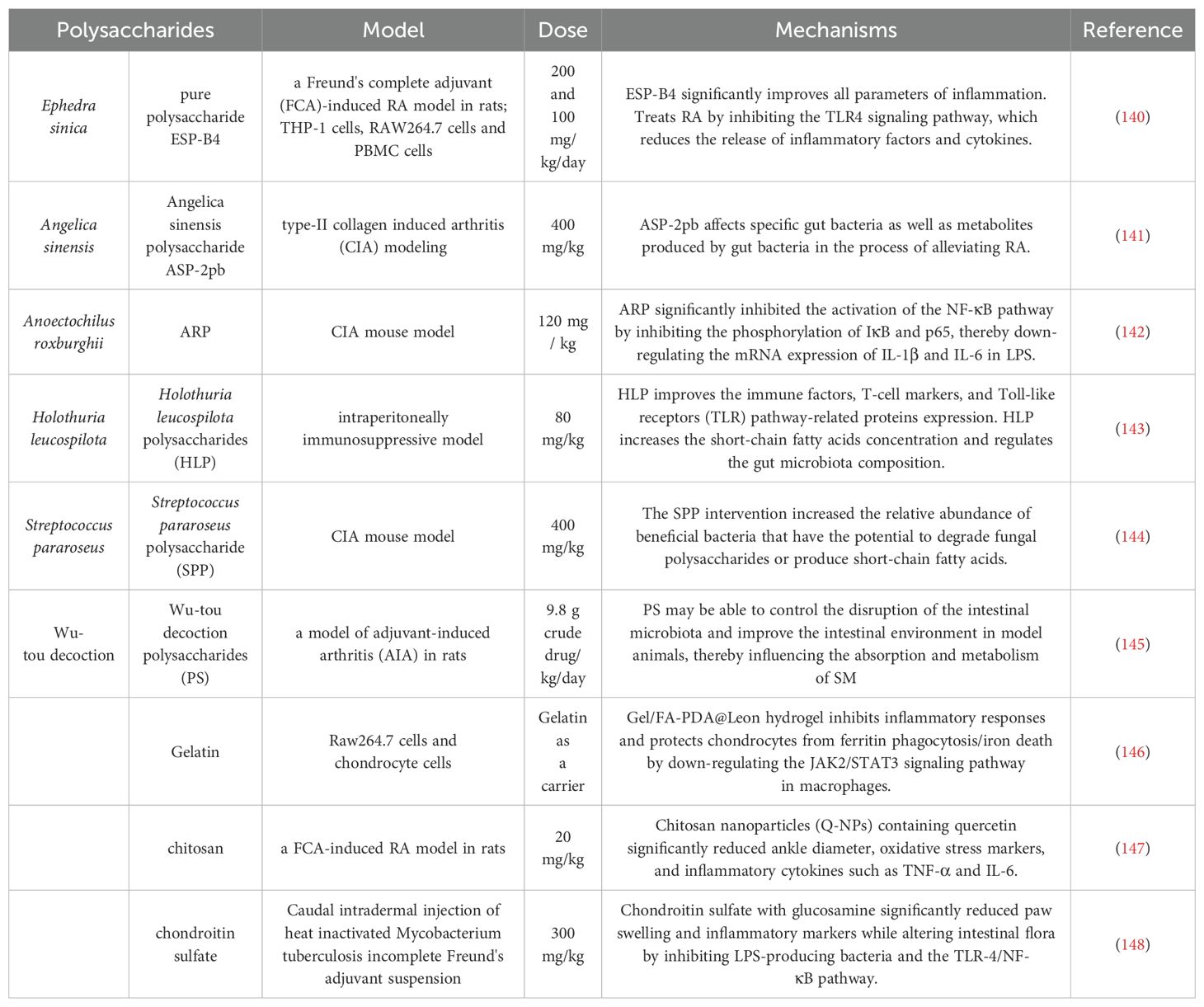
Polysaccharides, as natural active ingredients, have a variety of mechanisms of action to alleviate RA, which may provide new ideas for the treatment of RA, such as by regulating immune cell function, inhibiting inflammation, regulating the gut microbiota, promoting bone formation and repair and related pathways (Table 3). As shown in Figure 4, polysaccharides exhibit multiple mechanisms of action in alleviating RA.
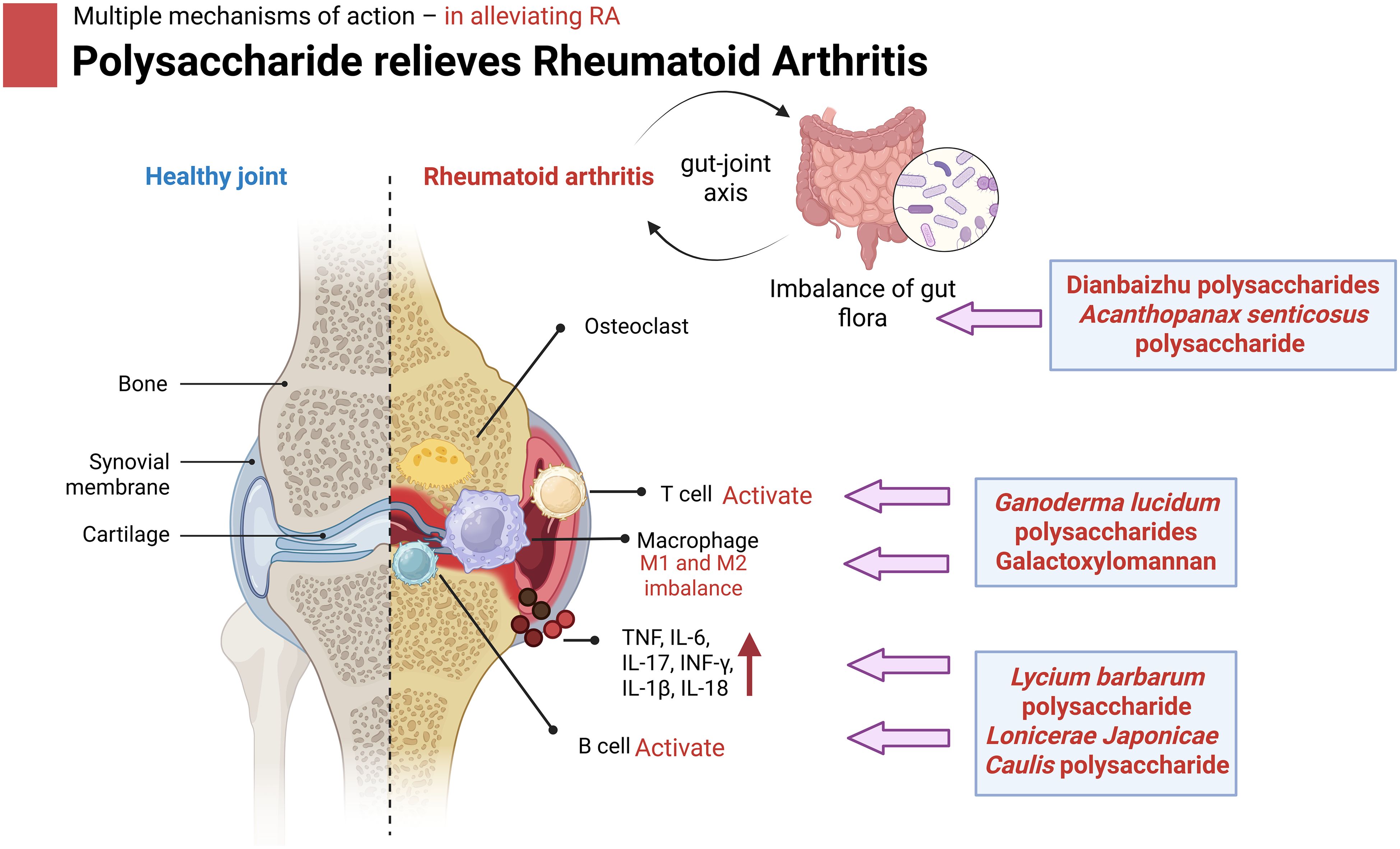
Figure 4. Mechanism of action of polysaccharides to alleviate OA in mouse. Specifically, polysaccharides of different origins treat RA progression by modulating immune macrophages, inhibiting inflammatory factors, improving the gut microbiota and its metabolites, promoting cartilage and bone tissue repair, and modulating related pathways. Image created with BioRender.com, with permission.
4.2.1 Regulation of immune cell function
RA is an autoimmune disease mainly characterized by chronic synovial inflammation, and its pathogenesis is complex, involving the abnormal activation of multiple immune cells and cytokines. In recent years, the role of polysaccharides in the treatment of RA has received widespread attention, and related studies have shown that polysaccharides can attenuate the immune response of RA by regulating the function and number of immune cells and balancing the immune system (59). However, although these studies have provided new ideas for the treatment of RA, there are also some problems that deserve in-depth discussion. Studies have shown that polysaccharides can enhance the activity of T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes and natural killer cells (NK cells), and promote the secretion of immune factors, while inhibiting excessive inflammatory responses (60, 61). For example, in a study that included 60 patients with RA and 40 patients with Huntington’s disease (HD), the microbial polysaccharide Galactoxylomannan (GalXM) was able to increase the activation of caspase-3 and ultimately increase the rate of apoptosis in T cells subset. GalXM was able to reduce STAT3 phosphorylation, IL-17 production and Th17 cell proliferation. It was also demonstrated that CD45 expression on target T cells was required to mediate the immunomodulatory effects of GAlXM (62). In terms of the studies themselves, most of the existing studies on the mechanisms of polysaccharides in RA therapy have focused on in vitro cellular experiments and animal models and small sample sizes. The limitation of sample size may lead to the bias of research results, and it is difficult to fully reflect the real efficacy and safety of GalXM in RA patients. In addition, there are differences between animal experiments and human physiological environments, and whether the mechanism of action of polysaccharides in animals is fully applicable to humans needs to be further verified (63). Guo et al. (13) prepared a novel self-assembled nanoparticle containing Celastrol (Cel) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-sensitive chemo-acoustic kinetic therapies targeting macrophages at the site of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis from Achyranthes polysaccharide. The final results show that DS-PVGLIG-Cel&Abps-thioketal-Cur@Cel nanomicelles (DPC&ATC@Cel) has a favorable in vitro and in vivo ability to treat RA with a good in vivo safety profile. Natural polysaccharides such as chitosan, alginate and hyaluronic acid are widely used in RA therapy because they are biocompatible and can be easily functionalized to enhance drug loading and targeting (64). However, in the human body, the targeting of nanoparticles, the in vivo metabolic process, and the safety of long-term use still need to be studied in depth (65). In a review, Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides (GLP) inhibited the proliferation and migration of synovial fibroblasts (RASF) in RA, modulated pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and reduced synovial inflammation. Secondly, GLP regulates the proliferation and differentiation of antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, inhibits the phagocytosis of monocyte-derived macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells, and regulates the ratio of M1, M2 and related inflammatory cytokines. In addition, GLP produces activities that balance humoral and cellular immunity, such as regulating the production of immunoglobulins, the proliferative response of T and B lymphocytes and cytokine release, thus demonstrating immunomodulatory effects (43).
4.2.2 Inflammation suppression
Polysaccharides have significant anti-inflammatory activity, inhibiting the infiltration of inflammatory cells and the release of inflammatory factors, and reducing joint swelling and pain (66, 67). In a study, different doses of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide (ASP) alleviated paw swelling in rat models of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Antibody levels in the ASP-treated group also showed varying degrees of reduction. Anti-CII IgG and anti-CII IgG2a levels were reduced in a dose-dependent manner, and ASP reduced the effects of CIA by attenuating TNF-α pro-inflammatory factors (68). In another study, administration of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide (LBP) significantly reduced serum IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-12, and IL-17 levels and restored and normalized IL-10 levels in a rat model of CIA. LBP reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and restored anti-inflammatory cytokine levels (69). Lonicerae Japonicae Caulis polysaccharide (LJCP-2b) is a homogeneous heteropolysaccharide. Its structure mainly consisted of 1,3,6-β-D-Galp, 1,4-α-D-Glcp, 1,4,6-α-D-Glcp, 1,4-β-D-Galp, 1,2,4-α-L-Rhap and 1,4-α-D-GalpA. In vitro experiments demonstrated that LJCP-2b affected TNF-α-induced rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte (RA-FLS) functions, including attenuation of cell viability, increase in apoptosis, decrease in the number of migratory movements and adhesion capacity, and reduction in the levels of IL-6 and IL-1β. These results suggest that LJCP-2b has the activity to inhibit RA-FLS hyperproliferation and inflammatory response (70). Glycosaminoglycans (GAG) play a crucial role in the pathophysiology of RA (71). One of the main pathways by which these long-chain polysaccharides in the extracellular matrix and on the cell surface interact with growth factors, cytokines, and proteases that influence cell behavior is the TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) signaling pathway, where GAGs enhance the anti-inflammatory effects of TGF-β, promote the differentiation of regulatory T-cells (Tregs), and inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine production (72). In addition, Sun et al. extracted polysaccharides with anti-inflammatory activity from Large-leaf Yellow tea (LYT) and identified the presence of β-d-Xylp(1→, →2, 4)-β-d-Xylp(1→, →3)-β-d-Manp(1→, α-d-Glcp(1→ and →2, 4)-α-d-GalAp(1→ linkages. They found that LYT polysaccharides inhibited the migration and proliferation of MH7A cells and reduced NO production in a TNF-α-induced inflammation model. NO regulates the production of a variety of inflammatory factors, and its reduced production can upset the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory factors, leading to difficulty in effectively controlling the inflammatory response and affecting immune homeostasis. The abundant presence of xylose accounts for 39% of the polysaccharide structure of LYT, and its unique linkage pattern (→2, 4)-β-d-Xylp(1→) appears to be a major contributor to its anti-inflammatory effects (73). Lin et al. introduced an alginate nanogel embedded in liposomes designed to enhance in vivo stability while retaining the inherent benefits of liposomes for RA. By incorporating an alginate network, the liposomes showed increased stiffness, reduced drug leakage, and improved cellular uptake by inflammatory macrophages. In addition, the encapsulated anti-inflammatory chlorogenic acid significantly inhibited ROS production and inflammatory response in arthritic rats, resulting in better therapeutic efficacy (74). Existing studies have relied on the CIA model, which mimics the acute inflammatory response but is fundamentally different from the chronic, progressive synovial lesions of human RA (75). The collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model involves both cellular (particularly Th17-mediated) and humoral immune responses, and its inflammatory microenvironment involves more complex cell-cell interactions (76). Furthermore, whether the structural complexity of polysaccharides acts through multi-target regulation remains to be systematically evaluated.
4.2.3 Ameliorating gut microbiota and its metabolites
Gut microbiota as one of the factors that can directly influence the body’s immune response, the role of gut microbiota in the field of RA has been gradually explored (77). Improving the gut microbiota and its metabolites can jointly have an impact on the development of diseases such as RA. Regulating the intestinal microbiota to restore its balanced state, as well as improving the composition and level of metabolites, can reduce the release of pro-inflammatory factors, inhibit the activation of inflammatory vesicles, etc., thereby alleviating the inflammatory response, relieving the symptoms of RA, and playing a protective role for the body (58). Some studies have shown that probiotics such as Lactobacillus reuteri can improve the symptoms of RA, which can be a promising novel target, with the ‘gut-joint’ axis as an important potential mechanism. The gut-joint axis refers to the stable, bi-directionally regulated interaction between the gut microbiota and the joints. Imbalances in the intestinal microbiota can affect the development of joint diseases such as RA. At the same time, joint diseases also change the structure and function of the gut microbiota (58, 78, 79). In the intestinal microbiota of RA patients, there is a significant increase in the abundance of pathogenic bacteria such as Ruminococcus gnavus group and a decrease in beneficial short-chain fatty acid (SCFAs) producing bacteria such as Roseburia, and these microbiota imbalances promote IL-6 by impairing antioxidant capacity, TNF-α and other pro-inflammatory factors release, exacerbating the development of RA (80). In addition, gut microbiota metabolites such as trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) in RA patients may promote synovial inflammation by activating NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles (81). For example, polysaccharides from Dianbaizhu (DBZP) treatment can affect the abundance of several specific bacteria in CIA mice, such as Lactobacillus, Anaplasma spp. Alistipes, Enterorhabdus, Mucispirillum and Candidatus_Saccharimonas, as well as a number of fecal or urinary Metabolites, such as 11β-hydroxytestosterone, pregnanediol 3-O-glucuronide, p-cresol sulfate and several amino acids and peptides, were also altered. The results suggest that DBZP has a protective effect on CIA in mice by modulating the gut microbiota (82). Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) is one of the core tools for microbiome research by integrating non-parametric tests and effect size analysis to efficiently identify biomarkers of intergroup differences. In addition, researchers identified 12 bacterial strains enriched in Acanthopanax senticosus polysaccharide (ASPS)-treated mice and 2 strains enriched in CIA mice after initial immunization by LEfSe analysis. ASPS treatment significantly reversed the trend of increased abundance of Bacteroides and the ratio of Bacteroidota/Bacillota induced by the progression of arthritis. Similar results were observed at the class, order, and family levels finding Acetatifactor, Ruminalococcus, Colidextribacter, Blautia, and were significantly enriched at the genus level in ASPS-treated mice (83). The “gut-joint axis” theory of RA reveals that intestinal microbiota are involved in the pathogenesis of joint inflammation through bidirectional regulation, and polysaccharides have been shown to alleviate the symptoms of RA in mouse models by remodeling the structure of intestinal microbiota and metabolites (84). However, there may be fundamental differences in the regulatory targets of polysaccharides on different host microbiota. Different polysaccharides are preferentially degraded by specific groups of bacteria due to differences in glycosidic bond type and branching structure (85). Segatella copri is a bacterium widely found in the human gut (86). A variety of lactic acid bacteria convert primary bile acids to secondary bile acids via bile salt hydrolases, which activate farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and inhibit intestinal Th17 cells (87). Segatella copri lacks Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH) activity and is unable to participate in bile acid metabolism. However, its overproliferation may indirectly weaken the anti-inflammatory pathway by decreasing the metabolic substrate for beneficial bacteria through consumption of bile salts (88). In addition, excessive inhibition of Bacteroides may affect dietary fiber metabolism, and enrichment of Lactobacillus may increase the risk of bloating in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (89). Therefore, future assessments regarding the intestinal tolerance of polysaccharide interventions need to be focused.
4.2.4 Promotes cartilage and bone tissue repair
At the same time, polysaccharide can also intervene in the core signaling axis of RANKL/OPG (Key factor in the regulation of bone metabolism), remodel the microenvironment of immune-bone metabolism interaction to regulate the function of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, maintain the balance of bone metabolism, and promote the repair and regeneration of bone tissue (90). At the same time, polysaccharides can also regulate the functions of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, maintain the balance of bone metabolism, and promote the repair and regeneration of bone tissue (91). Ma et al. found that Ephedra sinica polysaccharide (ESP) treatment attenuated the significant infiltration of inflammatory cells, fibroblast proliferation and neovascularization, unevenness of articular cartilage surfaces, localized vascular shadowing, and damage to articular cartilage surfaces, and poorly defined borders of cartilage and subchondral tissues in ankle joints of mice in the CIA group (92). Similarly, the expression of osteogenesis-related genes (ALP and RUNX2) was significantly upregulated by Sporidiobolus pararoseus polysaccharides (SPP), which is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. On the other hand, the bone remodeling signaling pathway was stimulated by SPP, which significantly reduced the RANKL/OPG ratio and TRAF6 (Tumor necrosis factor receptor-related factor 6) expression, indicating reduced osteoclast activity and differentiation (93). The chemical structures of polysaccharides in the existing studies were roughly analyzed, such as the monosaccharide composition of ESP and the conformational relationship between bone protective activity were not clarified, and different extraction processes may lead to differences in the degree of sulfation modification (94), which directly affects its binding ability to RANKL. In addition, most of the trials in the efficacy assessment indexes were based on histopathologic scores. In contrast, human RA needs to be assessed by imaging hard endpoints for bone protection, such as X-ray Sharp score and MRI bone marrow edema score, which were completely missing in the existing studies.
4.2.5 Polysaccharides alleviate RA through related signaling pathways
As shown in Figure 5, polysaccharides inhibit the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF-κB, PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT and MAPK, and reduce the expression and release of inflammatory factors. By inhibiting the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways, polysaccharides reduce the inflammatory response of synovial tissues, thus alleviating the symptoms of RA. The occurrence of RA is closely related to the dysfunction of NF - κB, and the expression level of NF - κB in the lesion synovial tissue of RA patients is significantly increased. Highly activated NF - κB induces the production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF - α, IL-1 β and IL-6), and the pro-inflammatory cytokines regulate the activation of NF - κB through positive feedback, forming a vicious cycle to aggravate the progression of RA. Relevant studies have shown that the development of RA is closely related to NF-κB dysfunction, and the expression level of NF-κB is significantly elevated in the lesional synovial tissues of RA patients (95, 96). Highly activated NF-κB induces the production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), and IL-6, accelerating the progression of the disease. The upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines can in turn regulate the activation of NF-κB through positive feedback, forming a vicious circle and aggravating the progression of RA (97, 98). GAGs affect the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is essential for cartilage homeostasis and repair (99). GAGs are involved in the NF-κB signaling pathway, which reduces the activation of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, which both play a central role in RA. For example, administration of Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) to CIA rats reversed the expression levels of NF-κB-p65 and IκBα, thereby blocking the harmful feedback and loop (increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines→activation of NF-κB signaling→induced release of pro-inflammatory cytokines) (100). Similarly, Researchers investigated SD-a from Saposhnikovia divaricata (Trucz.) Schischk and investigated the molecular mechanism of the anti-rheumatoid effect of SD-a in a rat model of CIA. The results showed that SD-a could inhibit the significantly elevated expression of TLR4 and TRAF6 proteins in the CIA group, and significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of IκB-α and the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 (101). Chitosan reduces the expression of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, which are central to the pathogenesis of RA, by inhibiting NF-κB activation (102).
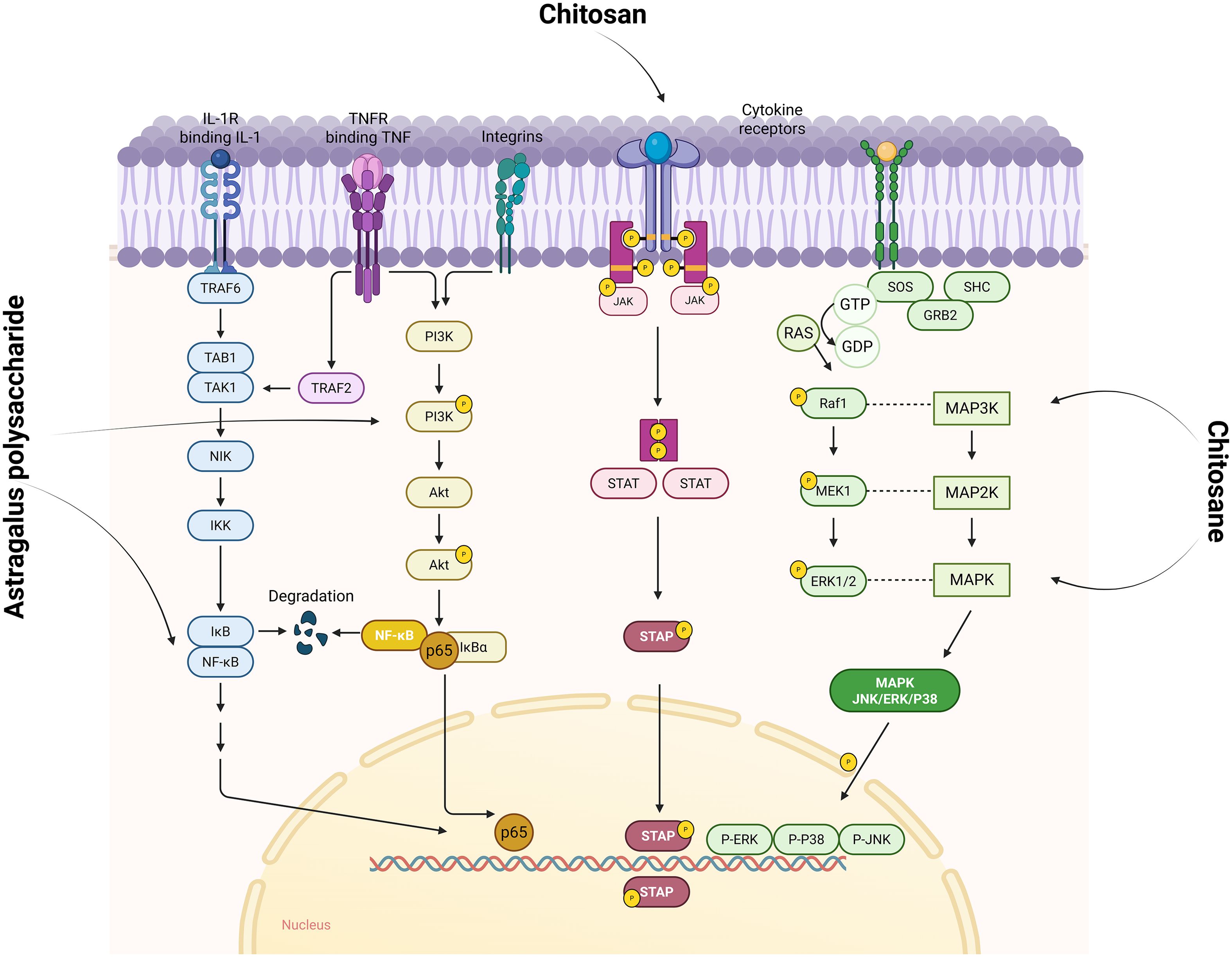
Figure 5. Polysaccharides affect signaling pathways such as NF-κB, PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT, and MAPK to improve RA. IL-1R (interleukin-1 receptor) is a key upstream initiator of the NF-κB signaling pathway activating NF-κB through the TRAF6-TAK1-IKK cascade reaction, a central driver of the inflammatory response. While TNFR initiates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, it can also lead to phosphorylated degradation of IκBα through activation of the IKK complex, which in turn releases and activates NF-κB transcription factors. In the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, cytokine binding to the receptor activates JAK, which in turn catalyzes STAT phosphorylation, and the phosphorylated STAT forms a dimer that enters the nucleus to regulate gene expression. In the MAPK (including JNK, ERK, and P38) signaling pathway, upstream growth factors bind to the receptor to phosphorylate SHC, recruiting GRB2 and SOS. SOS prompts activation by exchanging Ras-bound GDP for GTP. Activated Ras activates Raf1 (a MAP3K), MAP3K activates MEK1 (MAP2K), and MEK1 phosphorylates ERK1/2 (MAPK). ERK enters the nucleus and regulates gene expression, while JNK and P38 function through a similar cascade. Image created with BioRender.com, with permission.
The JAK/STAT pathway is one of the important signal transduction pathways of cytokines, regulating the growth, activation, differentiation, apoptosis and functions of cells. In the hematopoietic tissues of RA patients, JAK3, STAT and phosphorylated STAT are mainly highly expressed in activated T cells, B cells and FLS in the synovial lining layer. Chitosan also affects the JAK/STAT signaling pathway by modulating Janus kinase (JAK) activity, thereby reducing downstream transcription of inflammatory mediators (103). It has been reported that the phosphorylation levels of IκB and p65 in the NF-κB pathway in synovial tissues of CIA mice in the model group were increased to a very high level, whereas the phosphorylation levels in the Dendrobium huoshanense stem polysaccharide (cDHPS)-L group and the cDHPS-H group were reduced by 0-70%, respectively. 30-70%, respectively. Similarly, cDHPS also significantly reduced the elevated phosphorylation of JNK, p38, ERK1/2, PI3K, AKT, JAK1 and STAT3 in a dose-dependent manner in CIA mice. Apparently, cDHPS significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of IκB, p65, JNK, p38, ERK1/2, AKT, PI3K, JAK1 and STAT3 in CIA mice (104). The MAPK pathway, which contains components of JNK, p38, and ERK1/2, plays an important role in RA pathogenesis. In addition, chitosan has been shown to modulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which influences cell proliferation, differentiation, and cytokine release in synovial tissue. This characteristic of chitosan oligosaccharides may have a potential adverse effect on bone homeostasis (105).
RANKL was abundantly expressed in the joint cavity of RA patients and combined with RANK on the surface of osteoclasts and osteoclast precursor cells, inducing the proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells, increasing the activity of osteoclasts, and promoting bone resorption, as well as inhibiting the differentiation and function of osteoblasts. For example, the intervention of SPP significantly reduced rheumatoid factor, M1 macrophage activation and pro-inflammatory factors in CIA mice. Comprehensive metabolomics and gene expression analyses showed that SPP alleviated RA through arachidonic acid metabolism and OPG/RANKL/TRAF6 signaling pathway, played a key role in regulating metabolism and osteoblastic/osteoclastic gene expression in RA progression, and stimulated osteogenic remodeling (93). An in vitro and in vivo study of the therapeutic effects of ASP on RA showed that ASP inhibited TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of components of the JAK2/STAT3 and MAPK signaling pathways in CIA-FLS cells.ASP also inhibited inflammatory cytokine invasion and secretion via JAK2/STAT3 and MAPK signaling by FLS cells from CIA rats (106).
Existing studies have shown that polysaccharides often act through non-specific inhibition of multiple pathways, such as cDHPS, which simultaneously inhibits NF-κB-p65 nuclear translocation, JNK/p38/ERK phosphorylation and JAK1/STAT3 activation (104). However, the NF-κB pathway not only mediates inflammation, but also participates in apoptosis, and long-term inhibition may increase the risk of infection and tumor (107). The overall protein phosphorylation levels (p-NF-κB-p65, p-STAT3) in synovial tissues were mostly detected by Western blot in animal experiments, but there was a significant heterogeneity in pathway activation among different cell subpopulations in the synovial membranes of human RA (108).
5 Limitations
The review of the role and mechanisms of polysaccharides in the alleviation of RA does have some limitations. As a class of complex biomolecules, the specific mechanisms of action of polysaccharides have not been fully elucidated. Although some studies have shown that polysaccharides possess biological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory activities, the specific mechanisms of these effects in RA still need further investigation. Therefore, this evaluation may not be able to elaborate in detail and accurately on the mechanism of action of polysaccharides in the treatment of RA in vitro and in vivo (in mice and humans). In addition, due to the differences in experimental conditions, animal models, polysaccharide sources and extraction methods, the experimental data derived from different studies may differ significantly. This makes it challenging for reviews to integrate and analyse these data and to draw consistent conclusions. Currently, polysaccharide studies have shown some efficacy in the animal and in vitro experimental stages, but the effects in clinical applications still need to be further verified.
6 Prospects and future directions
In the therapeutic exploration of RA, polysaccharides have demonstrated multifaceted potential and promise. In the field of targeted delivery systems, polysaccharides can deliver drugs directly, which not only ensures the sustained release of drugs, but also reduces the frequency of local drug delivery and toxic side effects, improves therapeutic safety, and provides a new idea for the development of highly efficient and low-toxicity drug delivery systems. In terms of synergistic combination therapy, dexamethasone in combination with hyssop polysaccharide has been shown to have better therapeutic effects on rheumatoid arthritis than either drug alone, reducing pathological symptoms, improving osteoporosis, and restoring athletic ability, which suggests that the combination of polysaccharides and other drugs is expected to play a synergistic role in providing a better solution for clinical treatment. In addition, in-depth investigation of the role of the gut microbiota-joint axis in the pathogenesis and therapeutic response of RA is also an important direction for the future. Studies have shown that intestinal microbiota dysbiosis is closely related to the development of RA, and polysaccharide vaccines can regulate the intestinal microbiota, maintain the homeostasis of intestinal microbiota, and prevent the autoimmune response caused by intestinal microbiota dysbiosis. Perhaps in the future, based on the modulation of the gut microbiota by polysaccharides, precise therapeutic strategies targeting the gut microbiota-joint axis could be developed. At present, no public information on ongoing clinical trials of polysaccharide in the treatment of RA has been retrieved, but as the research on polysaccharide in the treatment of RA continues to deepen, it is expected that more clinical trials will be conducted in the future to further validate the safety and efficacy of polysaccharide in the treatment of RA, and to promote the development of polysaccharide from basic research to clinical application, which will bring a new hope of treatment to the majority of patients with RA.
7 Conclusions
Polysaccharides, as a class of natural active ingredients, have shown therapeutic potential to alleviate RA by modulating immune responses, inhibiting inflammation, combating oxidative stress and promoting articular cartilage repair. However, the evidence for their use as stand-alone therapies is insufficient, and they are more often used as a complement to conventional therapies to synergize with mainstream drugs. In clinical application, it is necessary to strictly evaluate the patient’s condition, including metabolic status and intestinal microecology, to avoid blindly replacing standardized therapeutic regimens.
Author contributions
WL: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. YK: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. XW: Writing – original draft. YY: Writing – review & editing. QY: Writing – original draft, Visualization. ZL: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Gholijani N, Azarpira N, Abolmaali SS, Tanideh N, Ravanrooy MH, Taki F, et al. Piperine and piperine-loaded albumin nanoparticles ameliorate adjuvant-induced arthritis and reduce IL-17 in rats. Exp Mol Pathol. (2024) 140:104937. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2024.104937
2. Veale DJ, Orr C, and Fearon U. Cellular and molecular perspectives in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. (2017) 39:343–54. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0633-1
3. Stainer A, Tonutti A, De Santis M, Amati F, Ceribelli A, Bongiovanni G, et al. Unmet needs and perspectives in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A critical review. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1129939. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1129939
4. Liu S, Liu J, Cheng X, Fang D, Chen X, Ding X, et al. Application value of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a novel indicator in rheumatoid arthritis: A review based on clinical evidence. J Inflammation Res. (2024) 17:7607–17. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S477262
5. Yi J, Liu Y, Xie H, An H, Li C, Wang X, et al. Hydrogels for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Front bioengineering Biotechnol. (2022) 10:1014543. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1014543
6. Prasad P, Verma S, Surbhi, Ganguly NK, Chaturvedi V, and Mittal SA. Rheumatoid arthritis: advances in treatment strategies. Mol Cell Biochem. (2023) 478:69–88. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04492-3
7. Jeong M and Park JH. Nanomedicine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol pharmaceutics. (2021) 18:539–49. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00295
8. Wang Y, Chen S, Du K, Liang C, Wang S, Owusu Boadi E, et al. Traditional herbal medicine: Therapeutic potential in rheumatoid arthritis. J ethnopharmacology. (2021) 279:114368. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114368
9. He YC, Yao YM, Xue QW, Fang X, and Liang S. Anti-rheumatoid arthritis potential of diterpenoid fraction derived from Rhododendron molle fruits. Chin J Natural medicines. (2021) 19:181–7. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(21)60019-5
10. Dai C, Wang L, You X, Zhao Y, Cao Z, and Wu J. Coffee-derived self-anti-inflammatory polymer as drug nanocarrier for enhanced rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Chin Chem Letters. (2025) 36:109869. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109869
11. Wijesinghe SN, Lindsay MA, and Jones SW. Oligonucleotide therapies in the treatment of arthritis: A narrative review. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:902. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080902
12. Mo X, Shen A, Han Y, Xu L, Miao J, Xu D, et al. Polysaccharide nanoadjuvants engineered via phenotype-specific nanoprobe-assisted phenotypic screen reprogram macrophage cell functions for cancer and rheumatoid arthritis therapy. ACS nano. (2025) 19:12920–36. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c16671
13. Guo C, Diao N, Zhang D, Cao M, Wang W, Geng H, et al. Achyranthes polysaccharide based dual-responsive nano-delivery system for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2023) 234:123677. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123677
14. Noorbakhsh H and Khorasgani MR. Date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) polysaccharides: a review on Chemical structure and nutritional properties. J Food Measurement Characterization. (2022) 16:3240–50. doi: 10.1007/s11694-022-01425-y
15. El Asri S, Ben Mrid R, Zouaoui Z, Roussi Z, Ennoury A, Nhiri M, et al. Advances in structural modification of fucoidans, ulvans, and carrageenans to improve their biological functions for potential therapeutic application. Carbohydr Res. (2025) 549:109358. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2024.109358
16. Yin M, Zhang Y, and Li H. Advances in research on immunoregulation of macrophages by plant polysaccharides. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:145. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00145
17. Qi M, Zheng C, Wu W, Yu G, and Wang P. Exopolysaccharides from marine microbes: source, structure and application. Mar Drugs. (2022) 20:512. doi: 10.3390/md20080512
18. Liu S, Hu J, Zhong Y, Hu X, Yin J, Xiong T, et al. A review: Effects of microbial fermentation on the structure and bioactivity of polysaccharides in plant-based foods. Food Chem. (2024) 440:137453. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137453
19. Paul S, Parvez SS, Goswami A, and Banik A. Exopolysaccharides from agriculturally important microorganisms: Conferring soil nutrient status and plant health. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 262:129954. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129954
20. Wang W, Tan J, Nima L, Sang Y, Cai X, and Xue H. Polysaccharides from fungi: A review on their extraction, purification, structural features, and biological activities. Food chemistry: X. (2022) 15:100414. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100414
21. Shi Y and Ma P. Pharmacological effects of Astragalus polysaccharides in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1449101. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1449101
22. Yin Y, Shi X, Cai X, Liu F, Ni W, Li B, et al. Isolation techniques, structural characteristics, and pharmacological effects of phellinus polysaccharides: A review. Molecules (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 29:3047. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133047
23. Liu Y, Shi Y, Zou J, Zhang X, Zhai B, Guo D, et al. Extraction, purification, structural features, biological activities, modifications, and applications from Taraxacum mongolicum polysaccharides: A review. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 259:129193. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.129193
24. McInnes IB and Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl J Med. (2011) 365:2205–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1004965
25. McInnes IB and Schett G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London England). (2017) 389:2328–37. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31472-1
26. Wang X, Fan D, Cao X, Ye Q, Wang Q, Zhang M, et al. The role of reactive oxygen species in the rheumatoid arthritis-associated synovial microenvironment. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2022) 11:1153. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061153
27. Lin Y, Zhao YJ, Zhang HL, Hao WJ, Zhu RD, Wang Y, et al. Regulatory role of KCa3.1 in immune cell function and its emerging association with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:997621. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.997621
28. Shen PC, Huang SH, Liu ZM, Lu CC, Chou SH, and Tien YC. Suramin ameliorates osteoarthritis by acting on the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways in chondrocytes and promoting M2 polarization in macrophages. Int immunopharmacology. (2023) 120:110295. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110295
29. Jo HG, Baek CY, Hwang Y, Baek E, Park C, Song HS, et al. Investigating the anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and chondroprotective effects of gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) makino in osteoarthritis: an in vitro and in vivo study. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:9594. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179594
30. Qi P, Chen X, Tian J, Zhong K, Qi Z, Li M, et al. The gut homeostasis-immune system axis: novel insights into rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis and treatment. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1482214. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1482214
31. Lu H, Yao Y, Yang J, Zhang H, and Li L. Microbiome-miRNA interactions in the progress from undifferentiated arthritis to rheumatoid arthritis: evidence, hypotheses, and opportunities. Rheumatol Int. (2021) 41:1567–75. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04798-3
32. Zhang Z, Wang G, Zhang Z, Liang X, Wang G, Xu M, et al. Locally administered liposomal drug depot enhances rheumatoid arthritis treatment by inhibiting inflammation and promoting cartilage repair. J nanobiotechnology. (2025) 23:69. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03110-w
33. Blagov AV, Grechko AV, Nikiforov NG, Zhuravlev AD, Sadykhov NK, and Orekhov AN. Effects of metabolic disorders in immune cells and synoviocytes on the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Metabolites. (2022) 12:634. doi: 10.3390/metabo12070634
34. Scherer HU, Häupl T, and Burmester GR. The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J autoimmunity. (2020) 110:102400. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102400
35. Tian X, Wang Q, Jiang N, Zhao Y, Huang C, Liu Y, et al. Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: 2024 update. Rheumatol Immunol Res. (2024) 5:189–208. doi: 10.1515/rir-2024-0028
36. England BR, Smith BJ, Baker NA, Barton JL, Oatis CA, Guyatt G, et al. 2022 American college of rheumatology guideline for exercise, rehabilitation, diet, and additional integrative interventions for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. (2023) 75:1603–15. doi: 10.1002/acr.25117
37. Mitrović J, Hrkač S, Tečer J, Golob M, Ljilja Posavec A, Kolar Mitrović H, et al. Pathogenesis of extraarticular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis-A comprehensive review. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:1262. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051262.
38. Wang D, Zhang J, Lau J, Wang S, Taneja V, Matteson EL, et al. Mechanisms of lung disease development in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2019) 15:581–96. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0275-x
39. Wu D, Luo Y, Li T, Zhao X, Lv T, Fang G, et al. Systemic complications of rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on pathogenesis and treatment. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1051082. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1051082
40. Song X, Wang YH, Li MT, Duan XW, Li HB, and Zeng XF. Chinese registry of rheumatoid arthritis: IV. Correlation and consistency of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity indices in China. Chin Med J. (2021) 134:1465–70. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001517
41. Romero-Figueroa MDS, Ramírez-Durán N, Montiel-Jarquín AJ, and Horta-Baas G. Gut-joint axis: Gut dysbiosis can contribute to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis via multiple pathways. Front Cell infection Microbiol. (2023) 13:1092118. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1092118
42. He Y, Huang Y, Mai C, Pan H, Luo HB, Liu L, et al. The immunomodulatory role of PDEs inhibitors in immune cells: therapeutic implication in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 161:105134. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105134
43. Meng M, Yao J, Zhang Y, Sun H, and Liu M. Potential anti-rheumatoid arthritis activities and mechanisms of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides. Molecules (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 28:2483. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062483
44. Suto T, Tosevska A, Dalwigk K, Kugler M, Dellinger M, Stanic I, et al. TNFR2 is critical for TNF-induced rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte inflammation. Rheumatol (Oxford England). (2022) 61:4535–46. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac124
45. Taghadosi M, Adib M, Jamshidi A, Mahmoudi M, and Farhadi E. The p53 status in rheumatoid arthritis with focus on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Immunologic Res. (2021) 69:225–38. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09202-7
46. Kondo N, Kuroda T, and Kobayashi D. Cytokine networks in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:10922. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010922
47. Lim JJ, Jones CM, Loh TJ, Ting YT, Zareie P, Loh KL, et al. The shared susceptibility epitope of HLA-DR4 binds citrullinated self-antigens and the TCR. Sci Immunol. (2021) 6:eabe0896. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe0896
48. Erre GL, Phan NDT, Diaz N, Congiargiu A, Mundula N, Mangoni AA, et al. Microbial players in autoimmunity: multicentric analysis of the association between Mycoplasma hominis serostatus and rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiol spectrum. (2025) 13:e0147724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01477-24
49. Pathi A, Wright M, Smed MK, Nelson JL, Olsen J, Hetland ML, et al. The rheumatoid arthritis gene expression signature among women who improve or worsen during pregnancy: A pilot study. J Rheumatol. (2021) 48:985–91. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.201128
50. GianFrancesco MA and Crowson CS. Where there’s smoke, there’s a joint: passive smoking and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken NJ). (2021) 73:2161–2. doi: 10.1002/art.41940
51. Smid DJ, Klous L, Ballak SB, Catoire M, De Hoogh IM, and Hoevenaars FPM. Exploring the role of nutritional strategies to influence physiological and cognitive mechanisms in cold weather operations in military personnel. Front Physiol. (2025) 16:1539615. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1539615
52. Min YS, Kim MG, and Ahn YS. Rheumatoid arthritis in silica-exposed workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:12776. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182312776
53. Zhong X, Wang X, Xu L, Zhang J, Yu W, Ji L, et al. Alterations in gut microbiota in Rheumatoid arthritis patients with interstitial lung Disease: A Comparative study. Hum Immunol. (2025) 86:111239. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2025.111239
54. Shao T, Hsu R, Rafizadeh DL, Wang L, Bowlus CL, Kumar N, et al. The gut ecosystem and immune tolerance. J autoimmunity. (2023) 141:103114. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103114
55. Xu M, Ren J, Jiang Z, Zhou S, Wang E, Li H, et al. Structural characterization and immunostimulant activities of polysaccharides fractionated by gradient ethanol precipitation method from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1388206. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1388206
56. Li N, Xu T, Wu Z, Zhao Y, Ruan M, Xu H, et al. Arabinogalactan from Cynanchum atratum induces tolerogenic dendritic cells in gut to restrain autoimmune response and alleviate collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Phytomedicine. (2025) 136:156269. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156269
57. Li X, Zhou Y, Chen X, Wang H, Yang S, Yang J, et al. Semi-synthetic chondroitin sulfate CS-semi5 upregulates miR-122-5p, conferring a therapeutic effect on osteoarthritis via the p38/MMP13 pathway. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2024) 14:3528–42. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.016
58. Bodkhe R, Balakrishnan B, and Taneja V. The role of microbiome in rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Ther Adv musculoskeletal Dis. (2019) 11:1759720x19844632. doi: 10.1177/1759720X19844632
59. Rong X, Shen C, and Shu Q. Interplay between traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharides and gut microbiota: The elusive “polysaccharides-bond-bacteria-enzyme” equation. Phytotherapy research: PTR. (2024) 38:4695–715. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8284
60. Shibuya A and Shibuya K. DNAM-1 versus TIGIT: competitive roles in tumor immunity and inflammatory responses. Int Immunol. (2021) 33:687–92. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxab085
61. Cai G, Wu C, Zhu T, Peng S, Xu S, Hu Y, et al. Structure of a Pueraria root polysaccharide and its immunoregulatory activity on T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, and immunosuppressive mice. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2023) 230:123386. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123386
62. Alunno A, Pericolini E, Gabrielli E, Bistoni O, Caterbi S, Bartoloni E, et al. THU0129 Selective elimination of pathogenic TH17 cells from peripheral blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients by a purified fungal polysaccharide. Ann Rheumatic Diseases. (2012) 71:198. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-eular.2094
63. Van Norman GA. Limitations of animal studies for predicting toxicity in clinical trials: is it time to rethink our current approach? JACC Basic Transl Sci. (2019) 4:845–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.10.008
64. Serrano-Sevilla I, Artiga Á, Mitchell SG, De Matteis L, and de la Fuente JM. Natural polysaccharides for siRNA delivery: nanocarriers based on chitosan, hyaluronic acid, and their derivatives. Molecules (Basel Switzerland). (2019) 24:2570. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142570
65. Fernandes Q and Billa N. Amygdalin in antineoplastic medicine and the relevance of nanotechnology. BioMed Pharmacother. (2025) 182:117772. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117772
66. Alenazi F, Moursi S, Mahmoud MR, Shahid SMA, Khatoon F, Shahid Khan M, et al. Withaferin A alleviates inflammation in animal models of arthritis by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway and cytokine release. Chemico-biological interactions. (2024) 398:111114. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111114
67. Huang D, Jiang S, Du Z, Chen Y, Xue D, Wang X, et al. Analgesic and anti-arthritic activities of polysaccharides in chaenomeles speciosa. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:744915. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.744915
68. Hu Q, Wu C, Yu J, Luo J, and Peng X. Angelica sinensis polysaccharide improves rheumatoid arthritis by modifying the expression of intestinal Cldn5, Slit3 and Rgs18 through gut microbiota. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2022) 209:153–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.090
69. Lai W, Wang C, Lai R, Peng X, and Luo J. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide modulates gut microbiota to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis in a rat model. NPJ Sci Food. (2022) 6:34. doi: 10.1038/s41538-022-00149-z
70. Bi Z, Zhao Y, Hu J, Ding J, Yang P, Liu Y, et al. A novel polysaccharide from Lonicerae Japonicae Caulis: Characterization and effects on the function of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Carbohydr polymers. (2022) 292:119674. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119674
71. Xu XL, Shu GF, Wang XJ, Qi J, Jin FY, Shen QY, et al. Sialic acid-modified chitosan oligosaccharide-based biphasic calcium phosphate promote synergetic bone formation in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J Control Release. (2020) 323:578–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.04.047
72. Iacob S and Cs-Szabo G. Biglycan regulates the expression of EGF receptors through EGF signaling pathways in human articular chondrocytes. Connect Tissue Res. (2010) 51:347–58. doi: 10.3109/03008200903427695
73. Sun Q, Du J, Wang Z, Li X, Fu R, Liu H, et al. Structural characteristics and biological activity of a water-soluble polysaccharide HDCP-2 from Camellia sinensis. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 277:134437. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134437
74. Lin X, Li Y, Zhang B, Li J, Ren J, Tang Y, et al. Alginate nanogel-embedded liposomal drug carriers facilitate drug delivery efficiency in arthritis treatment. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 273:133065. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133065
75. de Molon RS, Thurlings RM, Walgreen B, Helsen MM, van der Kraan PM, Cirelli JA, et al. Systemic resolvin E1 (RvE1) treatment does not ameliorate the severity of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice: A randomized, prospective, and controlled proof of concept study. Mediators Inflamm. (2019) 2019:5689465. doi: 10.1155/2019/5689465
76. Yao F, Zhao Y, Yu Q, Hu W, Lin Y, Chen Y, et al. Extracellular CIRP induces abnormal activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with RA via the TLR4-mediated HDAC3 pathways. Int immunopharmacology. (2024) 128:111525. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111525
77. Wang H, Cai Y, Wu W, Zhang M, Dai Y, and Wang Q. Exploring the role of gut microbiome in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Autoimmun Rev. (2024) 23:103654. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103654
78. Fujimoto K and Uematsu S. Vaccine therapy for dysbiosis-related diseases. World J gastroenterology. (2020) 26:2758–67. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2758
79. Asoudeh F, Djafarian K, Akhalghi M, Mahmoudi M, Jamshidi AR, Farhadi E, et al. The effect of probiotic cheese consumption on inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers, disease severity, and symptoms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Trials. (2022) 23:180. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06113-2
80. Liu Z, Wu Y, Luo Y, Wei S, Lu C, Zhou Y, et al. Self-balance of intestinal flora in spouses of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2020) 7:538. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00538
81. Li X, Geng J, Zhao J, Ni Q, Zhao C, Zheng Y, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide exacerbates cardiac fibrosis via activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Physiol. (2019) 10:866. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00866
82. Dong Y, Wang Y, Zhang F, Ma J, Li M, Liu W, et al. Polysaccharides from Gaultheria leucocarpa var. yunnanensis (DBZP) alleviates rheumatoid arthritis through ameliorating gut microbiota. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 281:136250. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136250
83. Liu A, Zhang M, Wu Y, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Su X, et al. ASPS exhibits anti-rheumatic effects by reprogramming gut microbiota and increasing serum γ-glutamylcysteine level. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2023) 10:e2205645. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205645
84. Li X, Qin Y, Yue F, and Lü X. Comprehensive analysis of fecal microbiome and metabolomics uncovered dl-norvaline-ameliorated obesity-associated disorders in high-fat diet-fed obese mice by targeting the gut microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. (2025) 73:2381–92. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06638
85. Xue H, Liang B, Wang Y, Gao H, Fang S, Xie K, et al. The regulatory effect of polysaccharides on the gut microbiota and their effect on human health: A review. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 270:132170. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132170
86. Blanco-Míguez A, Gálvez EJC, Pasolli E, De Filippis F, Amend L, Huang KD, et al. Extension of the Segatella copri complex to 13 species with distinct large extrachromosomal elements and associations with host conditions. Cell Host Microbe. (2023) 31:1804–19.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.09.013
87. Olotu T and Ferrell JM. Lactobacillus sp. for the attenuation of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in mice. Microorganisms. (2024) 12:2488. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122488
88. Wang L, Hu R, Ma S, Yang X, Gong J, Xiang H, et al. Dihydroquercetin attenuated Prevotella copri-caused intestinal injury by modulating gut microbiota and bile acids in weaned piglets. Anim Nutr. (2025) 20:303–10. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.10.002
89. Kwon H, Nam EH, Kim H, Jo H, Bang WY, Lee M, et al. Effect of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus IDCC 3201 on irritable bowel syndrome with constipation: a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:22384. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72887-x
90. Bourdon B, Cassé F, Gruchy N, Cambier P, Leclercq S, Oddoux S, et al. Marine collagen hydrolysates promote collagen synthesis, viability and proliferation while downregulating the synthesis of pro-catabolic markers in human articular chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:3693. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073693
91. Kim S-H, Park KH, Lee J, Lee SH, and Baek J-H. The effect of Schizophyllan on the differentiation of osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2024) 710:149860. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149860
92. Ma Y, Wei X, Peng J, Wei F, Wen Y, Liu M, et al. Ephedra sinica polysaccharide regulate the anti-inflammatory immunity of intestinal microecology and bacterial metabolites in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1414675. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1414675
93. Zhu H, Shen F, Liao T, Qian H, and Liu Y. Sporidiobolus pararoseus polysaccharides relieve rheumatoid arthritis by regulating arachidonic acid metabolism and bone remodeling signaling pathway. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 281:136272. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136272
94. Guo H, Li HY, Liu L, Wu CY, Liu H, Zhao L, et al. Effects of sulfated modification on the physicochemical properties and biological activities of β-glucans from Qingke (Tibetan hulless barley). Int J Biol macromolecules. (2019) 141:41–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.245
95. Shi L, Zhao Y, Feng C, Miao F, Dong L, Wang T, et al. Therapeutic effects of shaogan fuzi decoction in rheumatoid arthritis: Network pharmacology and experimental validation. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:967164. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.967164
96. Shen Y, Teng L, Qu Y, Liu J, Zhu X, Chen S, et al. Anti-proliferation and anti-inflammation effects of corilagin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. J ethnopharmacology. (2022) 284:114791. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114791
97. Liao H, Zheng J, Lu J, and Shen HL. NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Mol Neurobiol. (2025) 62:6998–7021. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04634-2
98. Ilchovska DD and Barrow DM. An Overview of the NF-kB mechanism of pathophysiology in rheumatoid arthritis, investigation of the NF-kB ligand RANKL and related nutritional interventions. Autoimmun Rev. (2021) 20:102741. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102741
99. Praxenthaler H, Krämer E, Weisser M, Hecht N, Fischer J, Grossner T, et al. Extracellular matrix content and WNT/β-catenin levels of cartilage determine the chondrocyte response to compressive load. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2018) 1864:851–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.12.024
100. Cao L, Yu M, Wang C, Bao Y, Zhang M, He P, et al. Cellulase-assisted extraction, characterization, and bioactivity against rheumatoid arthritis of astragalus polysaccharides. Int J Polymer Science. (2019) 2019:8514247. doi: 10.1155/2019/8514247
101. Sun X, Zhang T, Liu S, Zhao Y, and Sun X. The prepared and characterized polysaccharide polymer in Saposhnikovia divaricata(Trucz.) Schischk effectively controls the course of rheumatoid arthritis via TLR4/TRAF6–NF-κB/IκB-α signaling pathway. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2023) 160:114416. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114416
102. Xu L, Qin J, Ma X, Wang Q, Wu W, Huang H, et al. Chitosan-based self-healing thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with siHMGB1 for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis via macrophage repolarization. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 282:137102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137102
103. Kong Y, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Wang G, and Liu Q. Carboxymethyl-chitosan attenuates inducible nitric oxide synthase and promotes interleukin-10 production in rat chondrocytes. Exp Ther Med. (2017) 14:5641–6. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5258
104. Shang ZZ, Qin DY, Li QM, Zha XQ, Pan LH, Peng DY, et al. Dendrobium huoshanense stem polysaccharide ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis in mice via inhibition of inflammatory signaling pathways. Carbohydr polymers. (2021) 258:117657. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117657
105. Bai BL, Xie ZJ, Weng SJ, Wu ZY, Li H, Tao ZS, et al. Chitosan oligosaccharide promotes osteoclast formation by stimulating the activation of MAPK and AKT signaling pathways. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. (2018) 29:1207–18. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2018.1448336
106. Xue Y, Zhou S, Yang Z, Hao P, Wang L, Cui W, et al. Angelica sinensis polysaccharide inhibits inflammation of collagen-induced arthritis rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 and MAPK signaling. Arabian J Chem. (2023) 16:105320. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105320
107. Lalle G, Twardowski J, and Grinberg-Bleyer Y. NF-κB in cancer immunity: friend or foe? Cells. (2021) 10:355. doi: 10.3390/cells10020355
108. MaChado CRL, Dias FF, Resende GG, Oliveira PG, Xavier RM, Andrade MVM, et al. Morphofunctional analysis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in human rheumatoid arthritis and mouse collagen-induced arthritis. Adv Rheumatol. (2023) 63:1. doi: 10.1186/s42358-022-00281-0
109. Jiang Q, Yang G, Liu Q, Wang S, and Cui D. Function and role of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:626193. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626193
110. Wu F, Gao J, Kang J, Wang X, Niu Q, Liu J, et al. B cells in rheumatoid arthritis:Pathogenic mechanisms and treatment prospects. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:750753. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.750753
111. Baasch S, Ruzsics Z, and Henneke P. Cytomegaloviruses and macrophages-friends and foes from early on? Front Immunol. (2020) 11:793. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00793
112. Edilova MI, Akram A, and Abdul-Sater AA. Innate immunity drives pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed J. (2021) 44:172–82. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.06.010
113. Karmakar U and Vermeren S. Crosstalk between B cells and neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology. (2021) 164:689–700. doi: 10.1111/imm.13412
114. Kim KW, Kim BM, Won JY, Min HK, Lee KA, Lee SH, et al. Regulation of osteoclastogenesis by mast cell in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2021) 23:124. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02491-1
115. Yan Y, Lu A, Dou Y, Zhang Z, Wang XY, Zhai L, et al. Nanomedicines reprogram synovial macrophages by scavenging nitric oxide and silencing CA9 in progressive osteoarthritis. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2023) 10:e2207490. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207490
116. Németh T, Nagy G, and Pap T. Synovial fibroblasts as potential drug targets in rheumatoid arthritis, where do we stand and where shall we go? Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) 81:1055–64. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-222021
117. Vial G, Lambert C, Pereira B, Couderc M, Malochet-Guinamand S, Mathieu S, et al. The effect of TNF and non-TNF-targeted biologics on body composition in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Med. (2021) 29:487. doi: 10.3390/jcm10030487
118. Pandolfi F, Franza L, Carusi V, Altamura S, Andriollo G, and Nucera E. Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155238
119. Zhao R, Zhang YW, Yao JY, Qiao J, Song S, Zhang SX, et al. Genetic association between interleukin-17 and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Med Genomics. (2023) 16:277. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01713-6
120. Han L, Tu S, Shen P, Yan J, Huang Y, Ba X, et al. A comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of alternate interferon signaling pathways in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Aging. (2021) 13:20511–33. doi: 10.18632/aging.203432
121. Hatipoğlu M, Daltaban Ö, Uğur S, Üstün K, Kaçar C, Tuncer T, et al. B cell depletion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is associated with reduced IL-1β in GCF. Clin Oral investigations. (2022) 26:4307–13. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04378-0
122. Min HK, Kim S, Lee JY, Kim KW, Lee SH, and Kim HR. IL-18 binding protein suppresses IL-17-induced osteoclastogenesis and rectifies type 17 helper T cell/regulatory T cell imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis. J Trans Med. (2021) 19:392. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03071-2
123. de la Aleja AG, Herrero C, Torres-Torresano M, Schiaffino MT, Del Castillo A, Alonso B, et al. Inhibition of LXR controls the polarization of human inflammatory macrophages through upregulation of MAFB. Cell Mol Life sciences: CMLS. (2023) 80:96. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04745-4
124. Wang Y, Han J, Yue Y, Wu Y, Zhang W, Xia W, et al. Purification, structure identification and immune activity of a neutral polysaccharide from Cynanchum Auriculatum. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2023) 237:124142. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124142
125. Wei H, Shi Y, Yuan Z, Huang Z, Cai F, Zhu J, et al. Isolation, identification, and anti-inflammatory activity of polysaccharides of typha angustifolia. Biomacromolecules. (2021) 22:2451–9. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00235
126. ShanChen, Khan BM, Cheong KL, and Liu Y. Pumpkin polysaccharides: Purification, characterization and hypoglycemic potential. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2019) 139:842–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.053
127. Huang Z, Zong M-H, and Lou W-Y. Preparation, structural elucidation and immunomodulatory activity of a polysaccharide from Millettia Speciosa Champ. Ind Crops Products. (2022) 182:114889. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114889
128. Zhou R, Cui M, Wang Y, Zhang M, Li F, and Liu K. Isolation, structure identification and anti-inflammatory activity of a polysaccharide from Phragmites rhizoma. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2020) 161:810–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.124
129. Wu J, Chen X, Qiao K, Su Y, and Liu Z. Purification, structural elucidation, and in vitro antitumor effects of novel polysaccharides from Bangia fuscopurpurea. Food Sci Hum Wellness. (2021) 10:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2020.05.003
130. Jiang Y, Shang Z, Lv X, Du M, Ma L, Hou G, et al. Structure elucidation and antitumor activity of a water soluble polysaccharide from Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. Carbohydr polymers. (2022) 292:119718. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119718
131. Li S, Zhong W, Pan Y, Lin L, Cai Y, Mao H, et al. Structural characterization and anticoagulant analysis of the novel branched fucosylated glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber Holothuria nobilis. Carbohydr polymers. (2021) 269:118290. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118290
132. Ustyuzhanina NE, Bilan MI, Dmitrenok AS, Tsvetkova EA, Nifantiev NE, and Usov AI. Oversulfated dermatan sulfate and heparinoid in the starfish Lysastrosoma anthosticta: Structures and anticoagulant activity. Carbohydr polymers. (2021) 261:117867. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117867
133. Xiang X-W, Wang R, Chen H, Chen Y-F, Shen G-X, Liu S-L, et al. Structural characterization of a novel marine polysaccharide from mussel and its antioxidant activity in RAW264.7 cells induced by H2O2. Food Bioscience. (2022) 47:101659. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101659
134. Du Z, Jia X, Chen J, Zhou S, Chen J, Liu X, et al. Isolation and characterization of a heparin-like compound with potent anticoagulant and fibrinolytic activity from the clam coelomactra antiquata. Mar Drugs. (2019) 18:6. doi: 10.3390/md18010006
135. Sheng Z, Wen L, and Yang B. Structure identification of a polysaccharide in mushroom Lingzhi spore and its immunomodulatory activity. Carbohydr polymers. (2022) 278:118939. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118939
136. Liang Z, Zheng K, Zhao Q, Shao W, Li C, Wang J, et al. Structural identification and coagulation effect of flammulina velutipes polysaccharides. Appl Sci [Internet]. (2021) 11:1736. doi: 10.3390/app11041736
137. Yang X, Lin P, Wang J, Liu N, Yin F, Shen N, et al. Purification, characterization and anti-atherosclerotic effects of the polysaccharides from the fruiting body of Cordyceps militaris. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2021) 181:890–904. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.083
138. Dong M, Hou Y, and Ding X. Structure identification, antitumor activity and mechanisms of a novel polysaccharide from Ramaria flaccida (Fr.) Quél. Oncol Lett. (2020) 20:2169–82. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11761
139. Su S, Ding X, Hou Y, Liu B, Du Z, and Liu J. Structure elucidation, immunomodulatory activity, antitumor activity and its molecular mechanism of a novel polysaccharide from Boletus reticulatus Schaeff. Food Sci Hum Wellness. (2023) 12:647–61. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.067
140. Wang Q, Shu Z, Xing N, Xu B, Wang C, Sun G, et al. A pure polysaccharide from Ephedra sinica treating on arthritis and inhibiting cytokines expression. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2016) 86:177–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.010
141. Luo J, Yang Q, Jiang W, Liu Y, Hu Q, and Peng X. The interaction between Angelica sinensis polysaccharide ASP-2pb and specific gut bacteria alleviates rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2025) 301:140473. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140473
142. Guo Y, Ye Q, Yang S, Wu J, Ye B, Wu Y, et al. Therapeutic effects of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2019) 122:882–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.015
143. Zhao F, Ma T, Zhang X, Zhao Q, Zhu K, Cao J, et al. Holothuria leucospilota polysaccharides improve immunity and the gut microbiota in cyclophosphamide-treated immunosuppressed mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2023) 67:e2200317. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202200317
144. Liao T, Shen F, Zhu H, Mu W, Qian H, and Liu Y. Extracellular polysaccharides from Sporidiobolus pararoseus alleviates rheumatoid through ameliorating gut barrier function and gut microbiota. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2024) 260:129436. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129436
145. Yang D, Cheng X, Fan M, Xie D, Liu Z, Zheng F, et al. Regulation of polysaccharide in Wu-tou decoction on intestinal microflora and pharmacokinetics of small molecular compounds in AIA rats. Chin Med. (2024) 19:9. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00878-1
146. Yang R, Yan L, Xu T, Zhang K, Lu X, Xie C, et al. Injectable bioadhesive hydrogel as a local nanomedicine depot for targeted regulation of inflammation and ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials. (2024) 311:122706. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122706
147. Hannan A, Akhtar B, Sharif A, Anjum F, Pasha I, Khan A, et al. Quercetin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles ameliorate adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats by regulating anti-oxidant enzymes and downregulating pro- and inflammatory cytokines. Inflammopharmacology. (2023) 31:287–300. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01118-4
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis (RA), polysaccharides, mechanism, immune cells, cytokines
Citation: Liu W, Kong Y, Wang X, Yang Y, Yan Q and Li Z (2025) Therapeutic mechanisms of polysaccharides in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive review. Front. Immunol. 16:1608909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1608909
Received: 09 April 2025; Accepted: 12 June 2025;
Published: 01 July 2025.
Edited by:
Carolina Otero, Universidad Andrés Bello, ChileReviewed by:
Sebastian Makuch, Wroclaw Medical University, PolandKatina Schinnerling, Andres Bello University, Chile
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Kong, Wang, Yang, Yan and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zeguang Li, aGxqenlfbHpnQDE2My5jb20=
 Wenlong Liu1
Wenlong Liu1 Youqian Kong
Youqian Kong Xiaoyu Wang
Xiaoyu Wang Zeguang Li
Zeguang Li