- 1Medical Research and Experiment Center, Yan’an Medical College of Yan’an University, Yan’an, China
- 2Nursing Department of Yan’an University Affiliated Hospital, Yan’an, China
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease with severe complications. Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of apoptosis, encompasses mechanisms including iron overload, lipid peroxidation, redox homeostasis, and reactive oxygen species accumulation, all of which are closely related to RA pathogenesis. This study focused on the mechanism of ferroptosis and RA, detailing their relationship and outlining the reported roles of ferroptosis inhibitors in RA treatment to provide a useful research basis in drug discovery and development and for clinicians.
1 Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease (1), initially described by Dr. Landré-Beauvais in 1880 (2). It occurs in individuals aged 30–50 years, especially women, smokers, or those with a familial predisposition (3). RA is typically characterized by synovial joint pain, swelling, and morning stiffness lasting up to 1 h, with initial symptoms usually affecting the hands and feet, particularly the metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints (4). Additionally, RA is characterized by symmetric joint inflammation (5), resulting in damage to articular cartilage and bones, potentially leading to disability (6), and affects approximately 1% of the global population (7), with a two- to three-fold higher prevalence in females than in males (8).The impact on the patient’s quality of life is profound.The pathogenesis mainly involves the interaction of genetic and environmental factors with the immune system, leading to disruption of immune tolerance, autoantibody production, and excessive release of inflammatory cytokines, which in turn leads to chronic synovitis and joint damage.These inflammatory responses are amplified through the activation of multiple signaling pathways (e.g., JAK/STAT, NF-κB, etc.) and cell types (e.g., T-cells, B-cells, synovial fibroblasts, etc.), with the abnormal activation of T-cells leading to an amplified inflammatory response, and the excessive proliferation and activation of synovial fibroblasts directly participating in the inflammation and destruction of joints, which further exacerbates the joint inflammation and tissue destruction (9). Current treatments for RA include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and small-molecule-targeted drugs (JAK inhibitors). NSAIDs relieve symptoms but do not slow RA progression and may cause gastrointestinal adverse reactions with long-term administration. DMARDs, including methotrexate, are the drugs of choice; however, some patients may not tolerate them, and they have poor efficacy. Biologics and targeted drugs are effective in controlling inflammation; however, they are expensive, have the potential risk of infection, and have non-response in some patients (10).
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of apoptosis (11) characterized by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, a reduction in glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) activity, and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced lipid peroxidation (12). Ferroptosis exacerbates the inflammatory response by releasing inflammatory mediators (tumor necrosis factor-alpha [TNF-α], IL-1β, and IL-6). Recently, the role of ferroptosis in RA pathogenesis has been gaining attention. In synoviocytes from patients with RA, RSL3 can induce intracellular lipid peroxidation buildup and subsequently trigger ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 activity (13). In addition, ferroptosis inhibitors, including liproxstatin-1, exhibited significant anti-inflammatory benefits in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) (14), indicating that ferroptosis may be implicated in the pathologic process of RA. Therefore, this review initially introduces the relationship between ferroptosis and RA, examines the mechanism of ferroptosis in RA, assesses its viability as a therapeutic target, outlines existing compounds that mitigate RA by inhibiting ferroptosis, and anticipates future avenues for ferroptosis research in RA, essential for a comprehensive understanding of the pathophysiological process of RA, and for uncovering the potential of targeted inhibition of ferroptosis. A comprehensive understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms of RA and the development of treatment options for RA aimed at inhibiting ferroptosis hold substantial scientific and therapeutic importance.
2 Pathogenesis of RA
2.1 Environment and genetics
RA pathogenesis involves the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic factors include specific alleles of the essential key gene HLA-DRB1, which trigger autoimmune responses by activating T cells through misrecognition of self-antigens, and non-HLA genes, including PTPN22, STAT4, and TRAF1/C5, which affect immune tolerance and the release of inflammatory factors (15). Besides, epigenetic regulation, including aberrant DNA methylation and histone modification, may result in overexpression of pro-inflammatory genes (16). Environmental factors include smoking, which increases the risk of RA by inducing protein citrullination and oxidative stress, infections including Epstein-Barr virus and porphyromonas gingivalis that may trigger autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, dysbiosis of the intestinal flora that could activate toll-like receptors to facilitate Th17 differentiation, and hormonal and metabolic factors including estrogen and obesity that may affect the development of RA. Collectively, these genetic and environmental factors result in the disruption of immune tolerance, autoantibody production, activation of the complement system and inflammatory cells, and, eventually, joint destruction (17).
2.2 Abnormalities in the immune system
The primary manifestations of immune system abnormalities are disruption of immunological tolerance and autoantibody production. Disruption of immunological tolerance involves several genes, including specific alleles of the HLA-DRB1 gene HLA-DRB1*04:01) which activate T cells through misrecognition of self-antigens (citrullinated proteins), triggering autoimmune responses (18); the PTPN22 R620W mutation affects T-cell receptor signaling, leading to enhanced T-cell recognition of and response to self-antigens (19); the STAT4 gene participates in pro-inflammatory cytokine signaling and enhances the activation of Th1 and Th17 cells (20); the TRAF1/C5 genes are associated with the NF-κB pathway and modulate the release of inflammatory factors (21). Autoantibody generation includes rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA). RF exacerbates joint inflammation by activating the complement system and inflammatory cells, while ACPA production is closely associated with the “shared epitope” configuration of the HLA-DRB1 gene, which exacerbates joint inflammation by activating the complement system and inflammatory cells. These immune system anomalies result in the breakdown of immunological tolerance and the generation of autoantibodies, subsequently leading to joint inflammation and destruction (22).
2.3 Inflammation and joint damage
In RA, the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, is implicated in disease progression, and these factors promote the inflammatory response and are directly involved in joint tissue destruction (23). For instance, TNF-α, a pleiotropic cytokine synthesized by many cell types, is essential for the immune cascade response, primarily mediating stress-activated protein kinase/milk mitogen-activated protein kinase (SAPK/MAPK) pathway signaling and activating JAK/STAT signaling, which serves as the major trigger of inflammation and joint damage in RA (24). IL-1β and IL-6 can exacerbate the inflammatory state of joints by increasing the inflammatory response (25). The inflammatory response results in the destruction of articular cartilage and bone, which is the primary cause of disability in patients with RA. Inflammatory cytokines stimulate the activation of synovial fibroblasts and osteoclasts through the activation of multiple signaling pathways, and these cells release matrix metalloproteinases and osteoclast-specific enzymes, leading to the degradation of cartilage and bone. Additionally, synovial fibroblasts proliferate abnormally in the inflammatory environment, forming aggressive cell clusters that exacerbate articular cartilage and bone (26). The persistence of these inflammatory cycles leads to the destruction of bone and cartilage from several angles, rendering RA a disease that cannot be cured by monotherapy (27).
3 Mechanisms of ferroptosis
3.1 Iron metabolism
Iron is the most abundant and in-demand trace element in the human body (28). All the iron in the human body is derived from the daily diet, and when (Fe3+) in food reaches the small intestine, most of it is reduced to (Fe2+) by duodenal cytochrome B reductase 1 (duodenal cytochrome b) (29). Subsequently, divalent iron is transferred from the intestinal lumen to the intracellular space through the divalent metal transporter protein 1 (DMT1) (30). The storage and utilization of divalent iron within the cell predominantly rely on transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) and ferritin, primarily expressed on the cell membrane, and bind to transferrin (Tf) to form the Tf-TfR1 complex, facilitating endocytosis of iron. Ferritin can store ferric ions in its internal iron pool (31). When cells require iron, iron ions are released from ferritin into the iron pool, thereby maintaining the unstable iron pool at low levels and preventing cytotoxicity (32, 33). The released (Fe2+) is sensitive to a Fenton reaction catalyzed by O2-ions with H2O2 in the cell, generating ROS, namely hydroxyl radicals, thus inducing ferroptosis in the cell (34).
3.2 Lipid peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation is the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids within cell membranes to generate lipid peroxides, which destroy cell structure and function (35). However, GPX4 mitigates lipid peroxides (including phospholipid hydroperoxides) by converting them into their respective alcohols, thereby inhibiting the chain reaction of lipid peroxidation and protecting the cell membrane from further oxidative damage (36). Additionally, in the Fenton reaction, LOOH (lipid peroxides) react with ferrous ions (Fe2+) to generate hydroxyl radicals (-OH), potent oxidants that can damage phospholipids in the cell membrane, especially those abundant in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), leading to cell membrane destruction (37). Another feature of lipid peroxidation in Ferroptosis is the autoxidation of esterified PUFA in cell membranes; for instance, arachidonic acid or adenosine deaminase is the most oxidized lipids that are most susceptible to oxidation in Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long-Chain Family Member 4 (ALSL4) and Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3). LPCAT3 and those form phosphatidylacetamide (lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3, PES), which is converted to lipid peroxides by lipoxygenase (38).
3.3 Imbalance in the antioxidant system
3.3.1 System Xc/GSH/GPX4 axis
The Xc/GSH/GPX4 axis comprises the catalytic subunit (solute carrier family 7 member 11 SLC7A11) and the regulatory subunit (solute carrier family 3 member 2 SLC3A2) interconnected by a disulfide bond. This axis facilitates the retrograde transport of extracellular cysteine and intracellular glutamate in a 1:1 ratio, restoring redox balance in cells subjected to oxidative stress, amino acid starvation, and metabolic and genotoxic stress (39). Additionally, it is an important antioxidant pathway in ferroptosis. In this system, GPX4 belongs to a family of selenoproteins containing selenocysteine (Sec), which can reduce hydroperoxides, including H2O2. Humans possess eight isoforms, five of which contain Sec residues (40). GPX4 can reduce phospholipid peroxide to lipohydrol, which is essential for resistance to oxidative stress. The absence of GPX4 renders cells highly sensitive to oxidative stress. Hence, GPX4 activity is essential for ferroptosis triggered by ferroptosis inducers (41). In addition, glutathione (GSH), a tripeptide comprising glutamate, cysteine, and glycine, has important antioxidant functions (42). Intracellularly, GSH, functioning as a cofactor of GPX4, is essential for the antioxidant activity of GPX4 and can bind to free iron, thereby facilitating iron storage and inhibiting ferroptosis (43).GSH, as a major intracellular antioxidant, exists in reduced GSH and oxidized GSSG forms, with the ratio of these forms directly reflecting the redox status of the cell (44). The Xc/GSH/GPX4 system initially facilitates the intracellular transport of cysteine into the cell by the Xc transport system, subsequently enhancing GSH synthesis (45). Subsequently, GPX4 utilizes GSH to mitigate lipid peroxidation by preventing the cascade of lipid peroxidation by reducing phospholipid hydroperoxides to the corresponding alkyl phospholipids, protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage (46).
3.3.2 P53
P53 is a protein that functions as a cellular “guardian” (47). Inside the cell, P53 concentration is typically maintained at a low level to prevent excessive interference with normal cellular activities (48). Upon encountering a crisis, including DNA damage, nutritional deficiencies, insufficient oxygen supply, or free radical attack, the concentration of P53 protein increases rapidly in response to these threats (49). Moreover, P53 is involved in the regulation of the ferroptosis. During ferroptosis, P53 promotes iron endocytosis by regulating long-chain non-coding RNA PVT1 (lncRNA PVT1) to increase the expression of transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1) and by modulating SLC25A28 and ferric reductase (FDXR) to augment iron production (50). Furthermore, P53 stimulates ferroptosis by increasing the expression of glutaminase 2 and ROS production (51). P53 promotes lipid peroxidation and induces ferroptosis by increasing the levels of the SAT1-ALOX15 pathway (52). In addition, P53 can transcriptionally inhibit the expression of the cystine transporter protein SLC7A11, which reduces intracellular cystine uptake, subsequently reduces GSH synthesis, and indirectly inhibits GPX4 enzymatic activities, leading to the accumulation of intracellular lipid peroxides, which promotes ferroptosis. Additionally, p53 can inhibit ferroptosis by promoting its essential target gene p21, thereby inhibiting the cell cycle and diverting some of the raw materials used for synthesizing nucleic acids to synthesize the reducing power NADPH and GSH (53).
3.3.3 Nrf2
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a protein crucial to cellular function. It primarily regulates cellular antioxidant responses to protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress (54). NRF2, a key regulator in ferroptosis, controls the expression of many antioxidant enzymes and associated annotates through its downstream antioxidant response element (ARE) to maintain intracellular redox homeostasis (55). During ferroptosis, NRF2 activation enhances the antioxidant capacity of cells, inhibits lipid peroxidation, and prevents ferroptosis by upregulating the expression of key enzymes, including GPX4 (56). Furthermore, the activity of NRF2 is inhibited by Keap1; under oxidative stress, NRF2 dissociates from Keap1 and translocates to the nucleus to activate the expression of downstream genes while regulating iron metabolism and affecting iron uptake, storage, and release, thus playing a protective role in ferroptosis (57).
3.3.4 Mevalonate pathway
The MVA pathway facilitates the intracellular synthesis of cholesterol and several important non-cholesterol steroids, with 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase) serving as the rate-limiting enzyme that regulates cholesterol synthesis in the cell (58). It is essential in GPX4 biosynthesis by providing the isoprenoid moiety necessary for GPX4 synthesis and other selenoproteins (59). When the MVA pathway is inhibited, GPX4 synthesis is compromised, accumulating intracellular lipid peroxides, which may subsequently induce ferroptosis (60). Furthermore, treatment of cells with the ferroptosis inducer FIN56 does not cause GSH depletion; instead, it leads to post-translational GPX4 deletion and a decrease in MVA-derived lipophilic antioxidants (61), indicating that FIN56-induced cellular ferroptosis occurs mainly through MVA pathway modulation.
3.3.5 FSP1-CoQ10-NAD(P)H axis
The mechanism of action of ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1) and coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in ferroptosis involves a parallel system independent of GPX4 and GSH (62). In this mechanism, FSP1 acts as a flavoproteinase, catalyzing the reduction of coenzyme Q10 from its oxidized form (ubiquinone) to its reduced form (ubiquinol) utilizing NAD(P)H as an electron donor. Panthenol acts as a potent antioxidant that traps and neutralizes lipid peroxyl radicals, resulting in lipid peroxidation and inhibiting ferroptosis (63). In the absence of GPX4 function, FSP1 can independently resist lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis, offering an extra layer of protection for cells (64).
3.3.6 GCH1-BH4 axis
The GCH1-BH4 pathway is an important anti-lipid peroxidation pathway in ferroptosis, which is independent of the conventional Xc-GSH-GPX4 axis and the NADPH-FSP1-CoQ10 pathway (65). GCH1 functions as a rate-limiting enzyme in tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis and inhibits ferroptosis through its metabolites BH4 and dihydrobiopterin (BH2) (66). BH4 functions as an antioxidant in the cell and can directly trap free radicals and prevent the overoxidation of phospholipids, which contain two polyunsaturated fatty acid tails, thereby protecting the cell membrane from damage (67). Furthermore, the synthesis and cycling pathways of BH4 are regulated by GCH1 and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), respectively, indicating that the metabolic status of BH4 is essential for sustaining cellular redox homeostasis (68). GCH1 overexpression selectively protects membrane phospholipids from peroxidation, and the level of GCH1 expression exhibited a substantial correlation with the sensitivity of cancer cells to ferroptosis (69). BH4 may affect lipid peroxidation-regulated pathways involving CoQ10 by influencing the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine, which subsequently interferes with the synthesis of CoQ10 precursors (70).
3.3.7 Antioxidant pathway of peroxiredoxin 6
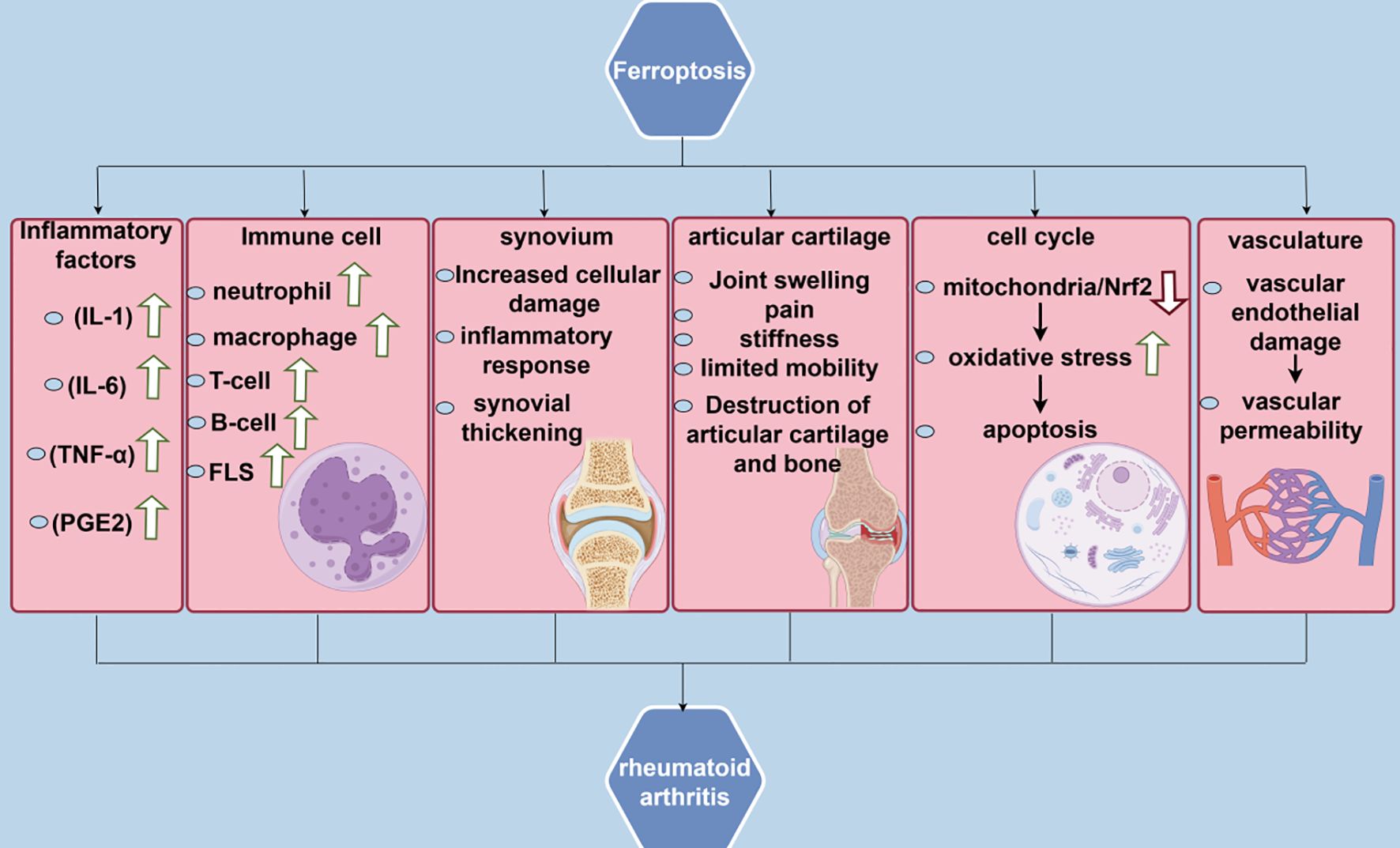
PRDX6 is an enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of H2O2, short-chain, and phospholipid hydroperoxides. In the antioxidant defense system, PRDX6 protects cells from oxidative stress-induced damage through its GSH peroxidase and acidic Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 activities (71). PRDX6 negatively regulates ferroptosis in tumor cells. A reduction in PRDX6 expression increases tumor cells’ sensitivity to ferroptosis inducers, indicating that PRDX6 may affect the sensitivity of cells to ferroptosis inducers (72). Besides, PRDX6 deficiency reduces the expression of the intracellular selenoprotein GPX4, which induces ferroptosis. PRDX6 contributes to selenoprotein synthesis by increasing the efficiency of selenium (Se) utilization as a Se-delivering protein, inhibiting ferroptosis (73) (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11(SLC7A11); Solute Carrier Family 3 Member 2(SLC3A2); Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 4 Gene(ALSL4); Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyltransferase 3(LPCAT3); Tumor Protein P53(P53); Glutaminase 2(GLS2); Glutathione(GSH); Glutathione Disulfide GSSG); Glutathione Peroxidase 4(GPX4); Mevalonate(MVA); 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase(HMGCR); Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate(IPP); Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (NRF2); Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate(NADPH); Oenzyme Q10(COQ10); Progression-Free Survival 1 (PFS1); Tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4); Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids(PUFAS).
4 Correlation between ferroptosis and RA
Recent findings indicate that iron metabolism disorders in ferroptosis, lipid peroxidation, and antioxidant system imbalance are related to the pathomechanism of RA. This indicates a significant association between ferroptosis and RA, implying that inhibiting ferroptosis may mitigate damage to RA.
4.1 RA in iron metabolism
Regarding iron metabolism, some studies have demonstrated that disorders of iron metabolism in the body have a strong relationship with the progression of RA disease (74). Hiroe Sato et al. assessed iron metabolism markers, including ferritin, fibroblast growth factor 23, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D, by collecting blood samples of patients with RA for biochemical analysis. They subsequently measured the bone mineral density using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Their statistical analysis revealed that in patients with RA, serum iron tends to correlate positively with ferritin and ferromodulin; however, inflammatory markers correlate negatively with serum iron and positively with ferromodulin (75). In addition, synovial tissue is an important site for RA pathogenesis as well as for the identification of targets (76). A G Mowat’s study demonstrated that iron levels in synovial tissue of patients with RA may be significantly different from those of normal individuals and that the use of medications such as sebaceous steroids in the treatment of patients with RA can inhibit inflammatory activity, while at the same time leading to an increase in the levels of plasma iron and hemoglobin (77). Additionally, animal experiments by A J Dabbagh et al. have demonstrated that intravenous iron administration results in increased synovial inflammation in RA (78). Furthermore, iron is an essential immune response regulator, and its association with iron metabolism has a great impact on autoimmune diseases, including RA, especially in neutrophils, macrophages, and T cells (79). In neutrophils, iron overload can diminish their bactericidal efficacy and disrupt intracellular ROS homeostasis, consequently impairing cellular function. Macrophages may experience impaired function in an iron-overloaded state, including reduced phagocytosis and diminished ferroportin response, limiting their role in immune responses. Moreover, T-cells may experience adverse effects on their activation, proliferation, and cytokine production due to iron overload (80).
4.2 RA in lipid peroxidation
Regarding lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress is a major feature of RA, which involves the activation and involvement of various inflammatory cells that release large amounts of ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) in response to inflammation. This process results in the peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the cell membranes and the generation of harmful lipid peroxidation products (81). These products can affect the function of T cells, B cells, and macrophages, thereby affecting the immune response in RA. Besides, they can directly affect chondrocytes, promoting the release of cartilage-degrading enzymes, leading to cartilage damage, and stimulating the activation of osteoclasts, which enhances bone resorption and results in bone destruction (82). Shengpeng Zhang et al. reported that the synovial membrane of joints in patients with RA contains lipid peroxidation metabolites that can recognize and bind to cell surface receptors, including toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), thereby altering the properties of the cell membrane, interfering with cell signaling, and exacerbating the pathological process of RA (83). In patients with RA, high lipid peroxidation levels result in the formation of harmful lipid hydroperoxides and electrophilic reactive lipid compounds, which contribute to an increase in biomarkers of oxidative damage (84). The accumulation of ROS and RNS in cells can activate the transcription factor NF-κB (85). Under normal conditions, NF-κB binds to the inhibitory protein IκB in the cytoplasm (86). Following ROS-induced phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, NF-κB is released and translocated to the nucleus (87). In the nucleus, activated NF-κB binds to the promoter regions of target genes, facilitating the transcription of many inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, interleukin 1β (IL-1β), and IL-6 increased expression of these cytokines, leading to amplification of the inflammatory response, as well as the stimulation of synoviocytes proliferation and production of matrix metalloproteinases, thus facilitating inflammation and joint damage in RA (88).
4.3 RA in antioxidant system imbalances
Regarding antioxidant system imbalance, Hanzhi Ling et al. reported that the expression level of long-chain specific lipoyl coenzyme A synthetase 4 (ACSL4) was significantly reduced in synovial and fibroblast-like synovial cells (FLS) from patients with RA, while the expression levels of ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), GPX4, and solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) expression levels were comparatively increased (89). Moreover, P53 induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits the proliferation of damaged cells by regulating the expression of cell cycle-related genes, including P21, hence contributing to erythrocyte stability (90).P53 mitigates the symptoms of patients with RA by inhibiting pro-inflammatory factor production, including TNF-α, and by modulating the activation, proliferation, and differentiation of T- and B-cells (91). In the synovium of RA joints, p53 activates apoptosis-promoting pathways, eliminates damaged and inflammatory cells, and reduces inflammatory responses and joint damage (92).
In RA treatment, NRF2 serves as a double-edged sword that scavenges ROS and mitigates oxidative stress damage on joint cells by activating ARE and enhancing the expression of antioxidant enzymes, including GSH peroxidase and superoxide dismutase (93). Meanwhile, NRF2 inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory factors, including TNF-α and IL-6, thereby exerting an anti-inflammatory effect through the regulation of downstream heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and protecting the cells against inflammation-induced damage (94). However, NRF2 activation may affect the efficacy of conventional antirheumatic medications by diminishing their effectiveness through enhanced drug efflux (95). Consequently, careful consideration should be given to the contraindications of dosing NRF2 for RA. Additionally, statins, inhibitors of the MVA pathway, may mitigate inflammation by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, thereby decreasing downstream metabolites of the MVA pathway and modulating the immune response (96).There are also some unresolved issues in the study of the antioxidant system in RA.For example, the degree of activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway in RA and the mechanism of its interaction with other signaling pathways are still not fully understood.In addition, although several studies have shown that there is an imbalance of the antioxidant system in RA patients, there is still a lack of effective strategies and methods on how to precisely regulate the antioxidant system for the purpose of treating RA (Figure 2).
5 Medications that inhibit ferroptosis in RA treatment
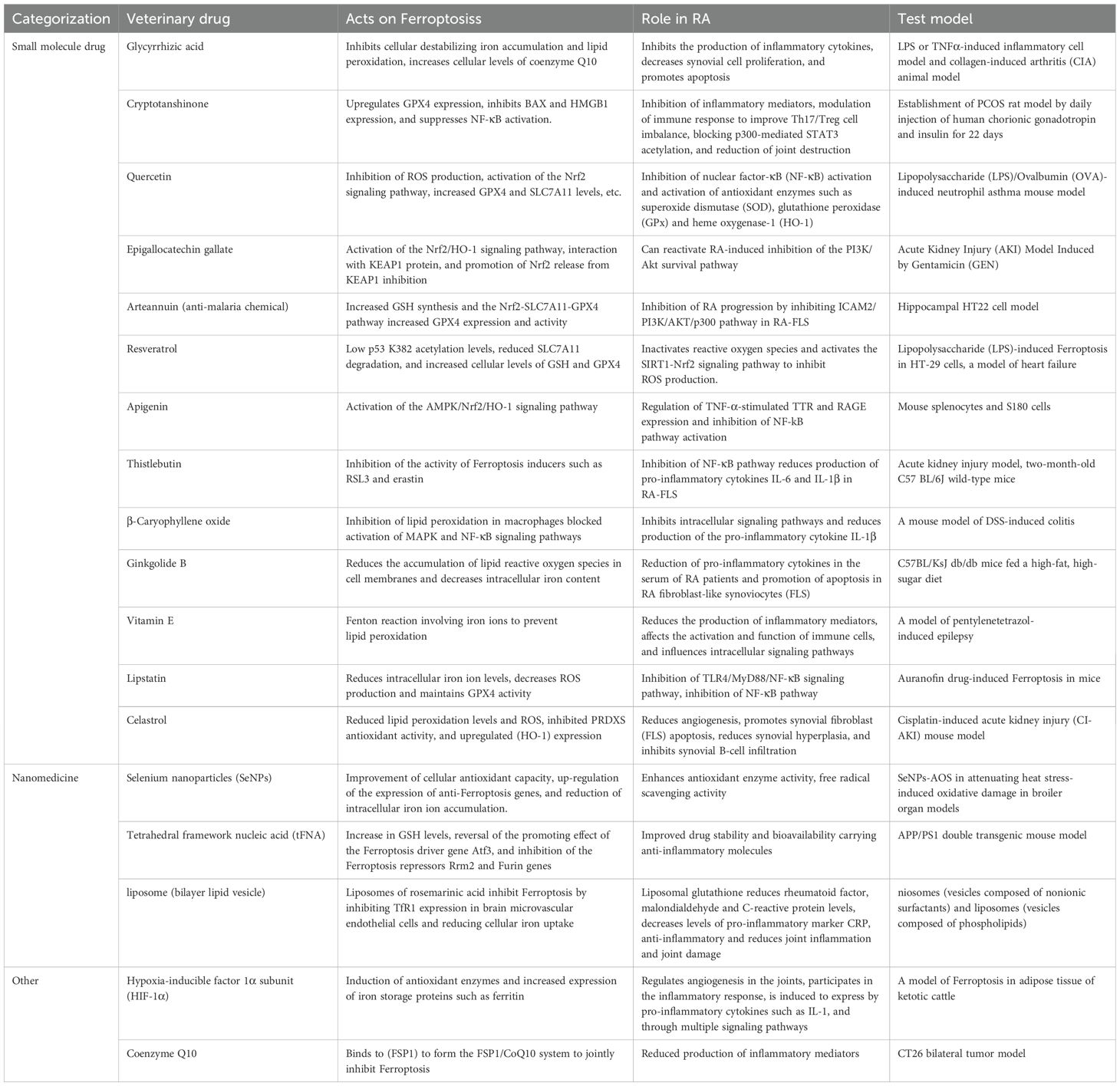
A comprehensive study of the mechanism of ferroptosis increasingly demonstrates that medications that inhibit ferroptosis may have potential applications in RA treatment. These medications inhibit ferroptosis and mitigate the harmful effects of RA by affecting iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation, immuno-inflammatory dysregulation, oxidative stress, GSH depletion, and GPX4 inactivation.
5.1 Small molecule medications
5.1.1 Glycyrrhizic acid
GA is the primary bioactive constituent of Glycyrrhiza glabra, which possesses numerous bioactivities and neuroprotective effects (97). Xuan Ma et al. reported that GA could inhibit Fin56-induced cellular destabilization by inhibiting iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation while simultaneously increasing the cellular levels of coenzyme Q10. This mechanism mitigates ferroptosis-induced inflammatory injury and protects neurons from damage (98). Yunhui Feng et al. reported that 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (18β-GA) may inhibit inflammatory cytokine production by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway and enhancing FOXO3 signaling, hence reducing synoviocyte proliferation and facilitating apoptosis. Furthermore, 18β-GA mitigated arthropathic changes, reduced serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and alleviated drug-induced hepatic damage in RA model mice (99).
5.1.2 Cryptotanshinone
CRY exhibits biological activities for the treatment of coronary heart disease, renal failure, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, obesity, aging, diabetes, and fibrosis of the liver, lungs, heart, and kidneys (100). CRY upregulates GPX4 expression and enhances cellular antioxidant capacity. In addition, CRY inhibits BAX expression (Bcl-2-associated X-protein) and HMGB1 (High Mobility Group Protein 1), thereby reducing iron release, lipid peroxidation, inflammatory response, and cellular damage. Besides, CRY inhibits NF-κB activation and reduces inflammatory factor production, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (101). In patients with RA, CRY exerts its anti-inflammatory effects primarily by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators, modulating the immune response to ameliorate the Th17/Treg cell imbalance, and inhibiting the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways by blocking p300-mediated STAT3 acetylation. Furthermore, CRY reduces joint destruction and protects joint structures (102).
5.1.3 Quercus dentata
Quercetin is a flavonoid that offers many benefits for the human body, including providing cardiovascular protection, anti-inflammatory properties, anticancer activity, anti-ulcer effects, and anti-allergic and antiviral effects (103). In liver injury, it ameliorated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diminished triglyceride and cholesterol accumulation, and inhibited mitochondrial ROS production. In the central nervous system, it protects dopaminergic neurons, activates the Nrf2 signaling pathway, and increases the levels of GPX4 and SLC7A11. In BMSC (bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells) injury, it prevents oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis and promotes cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. In type 2 diabetes, it decreases iron levels and ferritin levels in pancreatic β-cells and reduces ROS and MDA levels (104). Quercetin inhibits the activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in RA, thereby diminishing the inflammatory response. In addition, quercetin can activate antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), GPx, and HO-1, which enhances the cellular antioxidant defense system (105).
5.1.4 Epigallocatechin gallate
EGCG is a polyphenolic compound in green tea that possesses many biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antimetabolic disease, cardiovascular, and neuroprotective effects (106). Lin Yue et al. reported that EGCG can enhance the antioxidant capacity of the cells by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway, mitigating oxidative stress during ferroptosis. Ming-Shan Chen et al. reported that adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) exhibited neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory functions in patients with RA, while EGCG-pretreated ADSCs demonstrated significantly enhanced neuroprotection and were able to reactivate RA-induced inhibition of the PI3K/Akt survival pathway (107), thereby inhibiting RA progression.
5.1.5 Artemisinin
ATT, a sesquiterpene lactone extracted from the Chinese herb Artemisia annua with a specific peroxyl group, is a first-line drug for malaria treatment globally (108). Peng-Xi Deng et al. reported that Nrf2 can be activated and translocated to the nucleus in the presence of ATT, subsequently binds to the ARE, which upregulates the expression of various antioxidant genes and enhances GSH synthesis, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (109). Additionally, ATT increased the expression and activity of GPX4 through the Nrf2-SLC7A11-GPX4 pathway, thereby diminishing intracellular phospholipid peroxide accumulation, preserving cell membrane integrity, reducing oxidative stress, and preventing Erastin-induced cell death (110). In RA treatment, Jian Chen et al. identified intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2) as a key factor promoting RA progression in RA-FLS by RNA sequencing analysis. ATT inhibited RA progression by inhibiting the ICAM2/PI3K/AKT/p300 pathway in RA-FLS and inhibited METTL3-mediated ICAM2N6-methyladenosine modification of mRNA. Furthermore, p300 directly promotes METTL3 transcription, which can be inhibited by ATT in RA-FLS. Expressions of METTL3, ICAM2, and p300 in synovial tissues of patients with RA are correlated with clinical features and response to therapy, serving as potential biomarkers of therapy response (111).
5.1.6 Resveratrol
Res is a non-flavonoid polyphenolic compound and an antitoxin secreted by plants in response to stressors or pathogenic threats, with synthesis significantly increased, especially in response to UV irradiation, mechanical injury, and fungal infections (112). In a heart failure model, resveratrol mitigates ferroptosis by decreasing p53 K382 acetylation levels, reducing SLC7A11 degradation, and increasing cellular concentrations of GSH and GPX4. Furthermore, in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ferroptosis model of HT-29 cells, resveratrol downregulated the expression of pro-oxidant indicators, inflammatory factors, total cellular ferric ions, and the negatively regulated ferroptosis gene, GPX4, while upregulating the expression of the positively regulated factor for ferroptosis, ACSL4, and the pathway indicators, SIRT1 and NRF2, leading to ferroptosis inhibition (113). Additionally, resveratrol exerts an inhibitory effect on inflammation-associated signaling pathways, including NF-κB, hence diminishing inflammation-mediated ROS generation. Besides, it inhibits ROS production by activating the SIRT1-Nrf2 signaling pathway, thereby reducing RA prevalence (114).
5.1.7 Apigenin
Apigenin is a flavonoid prevalent in fruits and vegetables and is recognized for its several health benefits, including antitumor, cardiovascular protection, anti-neurodegenerative diseases, and anti-type 2 diabetes (115). Apigenin upregulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes and downregulates pro-inflammatory factors through activation of the AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. It inhibits oxidative stress, reduces reactive oxygen species generation, and enhances intracellular antioxidant capacity, resulting in significant inhibition of ferroptosis at the cellular level (116). Monu et al. reported that apigenin can regulate transthyretin (TTR) by modulating TNF-α-stimulated expression of TTR and receptor for advanced glycosylation end-products, thereby attenuating the inflammatory response and cartilage destruction in RA. Furthermore, silymarin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in patients with RA by reducing the levels of p65 (a key component of the NF-kB pathway), inhibiting NF-kB pathway activation, and reducing inflammatory factors production (117).
5.1.8 Silymarin
Silymarin is an antioxidant extracted from the milk thistle plant. Silymarin can inhibit iron autophagy by directly targeting FTH1 and consequently affecting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction in acute kidney injury mouse models (118). In patients with RA, silymarin exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway and diminishing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β in RA-FLS. In vitro, silymarin inhibits Th17 cell differentiation and reduces IL-17 and RORγ expression, thereby alleviating RA symptoms (119).
5.1.9 β-Stilbene
Beta-caryophyllene (BCP) is a naturally occurring chemical compound, especially in the essential oils of many plants, and is often used as a natural flavoring agent for foods (120). Yan-Ting Wu et al. reported that BCP inhibits ferroptosis and reduces the expression of ferroptosis-associated inflammatory factors by inhibiting lipid peroxidation in macrophages through activation of the type 2 cannabinoid receptor (CB2R). In addition, BCP diminished the mRNA expression of Tnf-α and Ptgs2 and blocked the activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, which significantly inhibited ferroptosis-induced inflammatory responses (121). BCP effectively treats RA by inhibiting intracellular signaling pathways, including the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway or the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway, thereby diminishing the formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines during inflammation and attenuating the inflammatory response. Furthermore, BCP effectively inhibits the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β production, thereby reducing inflammatory symptoms in patients with RA (122).
5.1.10 Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a class of fat-soluble compounds that are antioxidants and perform various physiological functions in the body, including safeguarding cell membranes from free radical damage, bolstering the immune system, facilitating blood coagulation, and aiding the nervous system and muscle function (123). It significantly contributes to ferroptosis by inhibiting the Fenton reaction involving iron ions (particularly Fe2+) by binding to them, thereby reducing the generation of ROS (124). Moreover, vitamin E maintains GPX4 activity and synergizes with other antioxidants (vitamin C and coenzyme Q10) to prevent lipid peroxidation and inhibit ferroptosis (125). However, in patients with RA, vitamin E reduces the synthesis of inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α and ILs, thereby reducing the inflammatory response (126). It may affect immune cell activation and function, including T and B cells, regulating the immune response and reducing autoimmune attacks, or by affecting intracellular signaling pathways, including nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which subsequently affect inflammatory and immune responses (127). In addition, some drugs, including methotrexate (MTX), may cause hepatotoxicity in RA treatment, and vitamin E may help minimize the side effects of these drugs (128).
5.1.11 Ginkgolide B
Ginkgo biloba is an ancient tree species of significant medicinal potential, with its leaves and seeds containing abundant biologically active components for treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases (129). Jing Chen et al. reported that GB can mitigate lipid metabolism disorders by lowering ROS levels and diminishing the accumulation of lipid ROS in cell membranes by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination, thereby maintaining its antioxidant properties and inhibiting ferroptosis (130). GB successfully diminished pro-inflammatory cytokines in the sera of patients with RA, including IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α, thereby inhibiting the activation of inflammatory cells and the release of inflammatory mediators and thus mitigating the inflammatory response in patients with RA. Additionally, GB effectively induced apoptosis in RA FLS, which contributed to the attenuation of synoviocytes, thereby slowing down the pathological progression of RA (131).
5.1.12 Lipistatin
Lipstatin is a secondary metabolite synthesized by streptomyces toxins (132). Hong-Fa Yan et al. reported that lipstatin decreased intracellular iron ion levels and mitigated the Fenton reaction involving iron ion levels, thus reducing ROS production and maintaining GPX4 activity. Furthermore, lipstatin inhibited the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to the transformation of the immune response into an anti-inflammatory response. Statins can inhibit the NF-κB pathway and exert their anti-inflammatory effects, thereby reducing the inflammatory response in patients with RA (133).
5.1.13 Celastrol
Celastrol, a naturally occurring compound extracted from the thunder god vine (Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F), has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory activities (134). Minling Pan et al. reported that tretinoin inhibits ferroptosis and protects cells from damage through multiple mechanisms, including activation of the AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway, the reduction of lipid peroxidation levels and mitochondrial ROS, and attenuation of ferroptosis. Additionally, tretinoin modulates intracellular iron metabolism and antioxidant responses by upregulating the expression of heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), further inhibiting ferroptosis (135). Tretinoin, as a potential therapeutic agent for RA, reduces angiogenesis and promotes FLS apoptosis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor, which slows down the progression of the disease and reduces synovial hyperplasia (136). Moreover, tretinoin can reduce joint inflammation by inhibiting Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-β-AMP-activated protein kinase-mTOR pathway and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and interfere with the COMMD protein interactions to inhibit synovial B-cell infiltration and exert immunosuppressive effects (137).
5.2 Nanomaterials
Se possesses beneficial antioxidant qualities and is an essential trace element for health maintenance; it is specifically due to these antioxidant properties that Se nanoparticles can also be used for ferroptosis inhibition (138). For instance, SeNPs activated the Nrf2 signaling pathway and enhanced the expression of antioxidant genes, including GST, SOD, and GPX, thereby enhancing the antioxidant capacity of cells (139). SeNPs effectively upregulated the expression of antioxidant genes associated with ferroptosis, including GPX4, SLC7A11 (cystine/glutamate transporter), FTH1 (ferritin heavy chain), and Fpn1 (iron transporter protein 1), thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (140). In addition, SeNPs can regulate iron metabolism and reduce the accumulation of intracellular iron ions, thereby reducing the risk of ferroptosis (141). In RA models, SeNPs exhibited anti-inflammatory effects by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and improving the redox state of the inflamed synovium. Furthermore, SeNPs exhibited free radical scavenging activity in vivo, which helps reduce oxidative stress and thereby alleviate RA symptoms (142).
Tetrahedral framework nucleic acid (tFNA) is a new nanomaterial (143). tFNA, as a novel nanoparticle, was found by Lu Tan et al. to inhibit ferroptosis by promoting cell viability, reducing iron levels 2+, lipid peroxidation, MDA, and LDH, and increasing GSH levels in Aβ-treated N2a cells (144). Additionally, RNA sequencing in the experiment demonstrated that tFNA could counteract the stimulatory effect of Aβ on the ferroptosis driver gene Atf3 and the inhibitory effect on the ferroptosis repressor Rrm2 and Furin genes (145). Simultaneously, tFNA has demonstrated considerable potential in RA treatment. Some medications for RA treatment, including poorly water-soluble or easily degradable medications, can be encapsulated or conjugated by tFNA to improve their stability and bioavailability. For instance, curcumin (Cur) is a natural compound with anti-inflammatory effects; however, its rapid degradation and poor water solubility impede therapeutic efficacy (146). The therapeutic efficacy of Cur can be enhanced by tFNA delivery. Besides, tFNA can transport anti-inflammatory molecules, including miRNAs, to regulate the inflammatory response. For instance, the integration of miR-23b into tFNA enhances its stability, facilitating effective delivery into organisms to inhibit synovial inflammation and cartilage matrix degradation (147).
Liposomes are biocompatible nanovesicles composed of natural phospholipids that protect medications, regulate targeted delivery, control the release rate, and can be enhanced through surface modifications (148). Rosmarinic acid (RosA) encapsulated in nanoliposomes can be prepared into a new delivery system, liposomes with rosmarinic acid (RosA-LIP). This rosmarinic acid liposome (RosA-LIP) leverages the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of rosmarinic acid to reduce cellular iron uptake by inhibiting the expression of TfR1 in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, thus inhibiting ferroptosis (149). As for RA treatment, GSH was sequestered in liposomes using methods including film dispersion, and liposomal GSH significantly reduced RF, MDA, and CRP levels but demonstrated its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. GSH itself is a potent antioxidant, and liposomal encapsulation improves its stability and bioavailability, allowing it to reach the site of inflammation more effectively. Additionally, liposomal GSH was able to reduce the levels of the pro-inflammatory marker CRP, indicating its anti-inflammatory and joint inflammation-reducing effects, reducing joint damage and pathology scores (150).
5.3 Others
5.3.1 Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α subunit
HIF-1α is a transcription factor that activates the expression of several genes involved in cellular adaptive responses to hypoxia, including angiogenesis, energy metabolism, cell survival, and apoptosis. HIF-1α works by inducing the expression of antioxidant enzymes, including GPX and SOD, which help to scavenge ROS that reduce oxidative stress, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (151). In addition, HIF-1α increases the expression of iron storage proteins, including ferritin, and reduces the availability of free iron ions in the cell, thereby reducing ferroptosis (152). HIF-1α is essential in RA treatment by regulating joint angiogenesis, participating in the inflammatory response, being induced to be expressed by pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1, and modulating the course of inflammation through multiple signaling pathways, including the PHDs/HIF-1α/pVHL pathway and the inhibitor HIF (153).
5.3.2 Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 is a prominent antioxidant that binds to ferroptosis inhibitory protein 1 (FSP1) to form the FSP1/CoQ10 system, collaboratively inhibiting ferroptosis (154). J Kucharská et al. reported that CoQ10 treatment of arthritic rats for 28 days slightly reduced inflammatory markers and increased plasma antioxidant capacity. Furthermore, CoQ10 can exert an anti-inflammatory effect by reducing the production of inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α and IL-1β (155).
In summary, iron death has an important role in the pathogenesis of RA, and a variety of iron death inhibitors show great promise in the treatment of RA.However, there are many challenges in the current study and differences in efficacy, translational potential and challenges among different inhibitors.In terms of small molecule drugs, although several drugs have shown promising efficacy in vitro and in animal models, their data in clinical studies are still limited, and long-term efficacy and safety need to be further validated. In addition, the issue of selectivity and potential toxicities of small molecule drugs are also challenges.For example, resveratrol, despite its multiple health benefits, has a relatively weak specific inhibitory effect on iron death and may act through multiple signaling pathways, which may lead to interference with its effects in RA treatment by other biological processes (156). In contrast, compounds such as mannuronic acid may have greater specificity, but their efficacy may be influenced by cell type and pathological environment (157). Nanomaterials, as a novel therapeutic tool, have the advantages of strong targeting, high bioavailability and delivery efficiency, but still face challenges in their preparation process, clinical translation and biocompatibility (158). For example, potential issues such as the toxicity of selenium nanoparticles and the immunogenicity of liposomes need to be further investigated and addressed.Future studies should focus more on the in-depth evaluation and optimization of iron death inhibitors to improve their efficacy and safety and accelerate their translational application in RA therapy.In addition, there are significant differences in specificity and off-target effects among different compounds.These differences suggest that we need to comprehensively consider the specificity, efficacy, and potential off-target effects when developing and selecting iron death inhibitors to optimize therapeutic strategies (Table 1).
6 Conclusion and outlook
RA treatment is advancing. However, it faces some challenges. Recently, the therapeutic approach for RA has gradually transitioned from pure symptom relief to early intervention and a (treat-to-target) strategy, which involves continual assessment and modification of the treatment regimen within six months of initiation, guided by setting clear treatment goals (clinical remission or low disease activity). This strategy has significantly improved patient prognosis and reduced joint damage and disability. However, challenges persist in RA treatment, including the poor response of some patients to the available medications and the long-term safety and drug resistance of biologics that need to be further studied. Furthermore, there is still room for improvement in the treatment compliance rate of patients with RA in China, and multidisciplinary comprehensive management and individualized treatment need to be strengthened (159). As a new form of apoptosis, ferroptosis has gradually gained attention in the study of RA in recent years. However, ferroptosis, which is characterized by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation and excessive accumulation of ROS, may exacerbate the disease progression by facilitating the activation of inflammatory cells and causing oxidative damage to joint tissues in patients with RA. For instance, most of the chemical compounds mentioned in this study mostly reduce inflammation and immunity in RA while inhibiting ferroptosis. Accordingly, we believe that inhibiting ferroptosis may provide new therapeutic options for RA, especially in regulating iron metabolism and antioxidant defense systems [157]. Despite the understanding of the role of iron death in RA, there are still many contradictions and limitations in existing studies.For example, there is current controversy about the specific role of iron death in different pathogenic stages of RA, with some studies pointing to a possible potential protective role in the early stages of the disease, while others emphasize its pro-inflammatory effects in disease progression.In addition, there is a lack of clarity regarding the interactions between iron death and other modes of cell death (e.g., apoptosis, necrosis, pyroptosis, etc.) in RA; for example, there may be a cross-regulatory mechanism between iron death and apoptosis, and the two may be both independent of each other and interact with each other in the pathologic process of RA.In some cases, iron death may promote an inflammatory response through the release of proinflammatory factors, while dysregulation of apoptosis may also exacerbate iron death.This complex interaction may lead to different cell death patterns exhibited at different pathological stages of RA, thereby affecting disease progression and therapeutic response (160). However, care should be taken when promoting ferroptosis in target cells to inhibit excessive death in other cells to prevent other damage (79).
The study of ferroptosis and RA should be advanced further to clarify the relationship between ferroptosis and RA, particularly regarding how iron metabolic imbalance affects inflammatory response, joint damage, and other mechanisms. However, developing ferroptosis inhibitors will become a research focus. Currently, most medications administered in clinical settings have significant side effects and poor water solubility after administering the drugs, resulting in decreased efficacy. Consequently, researchers are focusing on the advancement of delivery technologies that can overcome biological barriers, enhance drug efficacy, and minimize side effects. This includes the investigation of nanomedicines that work more precisely at the target site and natural drugs with lower resistance and side effects to achieve a more effective and efficient delivery of ferroptosis drugs. Besides, natural drugs with lower drug resistance and side effects achieve more efficacious RA treatments. Additionally, future gene therapy for RA needs to be focused on ferroptosis, with multi-targeted interventions to reshape the redox balance and inflammatory microenvironment. We can focus on developing intelligent delivery systems, investigating epigenetic-metabolic interaction networks, and establishing biomarker-based precision therapeutic systems. With the ongoing advancement in CRISPR technology and delivery vectors, ferroptosis-targeted gene therapy is expected to be a revolutionary strategy for RA treatment (161). The main mechanism of most current ferroptosis inhibitors involves the inhibition of the Nrf2 pathway and the inhibition of GPX4 and ROS generation. Further insights into the mechanisms and the effects of other ferroptosis pathways in relation to RA are needed.
Author contributions
ZW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. BX: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. HZ: Writing – review & editing. MY: Writing – review & editing. ML: Writing – review & editing. TN: Writing – review & editing. TL: Writing – review & editing. MZ: Writing – review & editing. XW: Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – review & editing. JH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This review was supported by the grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (82060521 to JH)Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2023-JC-QN-0125 to XL), Yan’ an science and technology bureau (2023-SFGG-141 to XL), Shaanxi Province Natural Science Foundation (2024JC-YBMS-683 to HZ), Special Scientific Research Program of Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (23JK0735 to HZ).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Koziel J and Potempa J. Pros and cons of causative association between periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Periodontol. (2000) 89:83–98. doi: 10.1111/prd.12432
2. Sokolova MV, Schett G, and Steffen U. Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: historical background and novel findings. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2022) 63:138–51. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08890-1
3. Singh SB, Bhandari S, Bhandari S, Bhandari S, Singh R, and Raynor WY. Role of PET/CT in diagnosing and monitoring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a review. Ann Nucl Med. (2024) 38:165–75. doi: 10.1007/s12149-023-01896-z
4. Brown P, Pratt AG, and Hyrich KL. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ (Clinical Res ed.). (2024) 384:e070856. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2022-070856
5. Ciofoaia EI, Pillarisetty A, and Constantinescu F. Health disparities in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv musculoskeletal Dis. (2022) 14:1759720x221137127. doi: 10.1177/1759720x221137127
6. Wang T, Wang Z, Qi W, Jiang G, and Wang G. Possible future avenues for rheumatoid arthritis therapeutics: hippo pathway. J Inflammation Res. (2023) 16:1283–96. doi: 10.2147/jir.S403925
7. Yang G, Li D, Deng D, Zhou Y, Zhang L, and Zhong Z. Epigenetic regulation in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:859400. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.859400
8. GBD 2021 Rheumatoid arthritis collaborators, et alGlobal, regional, and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5:e594–610. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(23)00211-4
9. McInnes IB and Schett G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London England). (2017) 389:2328–37. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)31472-1
10. Zhang L, Zhang Y, and Pan J. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis and the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. Intractab le rare Dis Res. (2021) 10:154–64. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2021.01022
11. Hirschhorn T and Stockwell BR. The development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radical Biol Med. (2019) 133:130–43. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.043
12. Djulbegovic MB and Uversky VN. Ferroptosis - An iron- and disorder-dependent programmed cell death. Int J Biol macromolecules. (2019) 135:1052–69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.221
13. Yin X, SriRamaratnam R, Wang M, Shimada K, Skouta R, and Viswanathan V. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. (2014) 156:317–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010
14. Li Y, Sun M, Cao F, Chen Y, Zhang L, and Cao J. The ferroptosis inhibitor liproxstatin-1 ameliorates LPS-induced cognitive impairment in mice. Nutrients. (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/nu14214599
15. Tsuji H, Ikari K, Ohmura K, Yano H, Furu M, and Hashimoto H. Significant joint-destructive association of HLA-DRB1*04:05 independent of DAS28 in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann rheumatic Dis. (2019) 78:284–6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214022
16. Padyukov L. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin immunopathology. (2022) 44:47–62. doi: 10.1007/s00281-022-00912-0
17. Bemis EA, Norris JM, Seifert JN, Fraser-Abel A, Okamoto Y, and Fessel M. Complement and its environmental determinants in the progression of human rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. (2019) 112:256–65. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.05.012
18. Larid G, Pancarte M, Offer G, Clavel C, Martin M, and Pradel V. In rheumatoid arthritis patients, HLA-DRB1*04:01 and rheumatoid nodules are associated with ACPA to a particular fibrin epitope. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:692041. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.692041
19. Taylor LH, Twigg S, Worthington J, Emery P, Morgan A, and Wilson AG. Metaanalysis of the association of smoking and PTPN22 R620W genotype on autoantibody status and radiological erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. (2013) 40:1048–53. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.120784
20. Gao W, Dong X, Yang Z, Mao G, and Xing W. Association between rs7574865 polymorphism in STAT4 gene and rheumatoid arthritis: An updated meta-analysis. Basel, Switzerland: Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI) (2023) doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2019.11.009.
21. Ahmadlou S, Akhiani M, and Salimzadeh A. et al: Lack of association between single nucleotide polymorphism rs10818488 in TRAF1/C5 region and rheumatoid arthritis in Iranian population. Iranian J allergy asthma Immunol. (2014) 13:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmhg.2012.08.007
22. Shelef MA. New relationships for old autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken N.J.). (2019) 71:1396–9. doi: 10.1002/art.40879
23. Dissanayake K, Jayasinghe C, Wanigasekara P, and Somathilaka A. Potential applicability of cytokines as biomarkers of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay-based evaluation of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10 and IL-17A. PloS One. (2021) 16:e0246111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246111
24. Ibrahim SSA and Huttunen KM. Orchestrated modulation of rheumatoid arthritis via crosstalking intracellular signaling pathways. Inflammopharmacology. (2021) 29:965–74. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00800-3
25. Akhter S, Irfan HM, Arshad L, Shajahan, Shahzad M, and Latif MB. Nerolidol: a potential approach in rheumatoid arthritis through reduction of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, NF-kB, COX-2 and antioxidant effect in CFA-induced arthritic model. Inflammopharmacology. (2022) 30:537–48. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00930-2
26. Lee ES, Kim HJ, Lee DE, Kang JY, Shin DM, and Jeong HH. Rheumatoid arthritis severity is mediated by crosstalk between synoviocytes and mature osteoclasts through a calcium and cytokine feedback loop. Exp Mol Med. (2025) 57:402–19. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01401-8
27. Matsuda K, Shiba N, and Hiraoka K. : new insights into the role of synovial fibroblasts leading to joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065173
28. Muckenthaler MU, Walter S, Mertens C, and Oettgen C. Cardiac iron metabolism during aging - Role of inflammation and proteolysis. Mech Ageing Dev. (2023) 215:111869. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2023.111869
29. Zhang Y, Lu Y, and Jin L. : iron metabolism and ferroptosis in physiological and pathological pregnancy. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169395
30. Fenaroli F, Valerio A, and Ingrassia R. : ischemic neuroprotection by insulin with down-regulation of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) expression and ferrous iron-dependent cell death. Biomolecules. (2024) 14. doi: 10.3390/biom14070856
31. Sha M, Zhu L, Wu H, Li Y, Wu J, and Zhang H. Casein phosphopeptide interferes the interactions between ferritin and ion irons. Food Chem. (2024) 454:139752. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.139752
32. Weichhart T. Transferrin: the iron transporter takes control. Blood. (2024) 144:9–10. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024024731
33. Chen S, Chen YM, Zhang YK, Kuang X, Liu Y, and Guo MW. Iron metabolism and ferroptosis in epilepsy. Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:601193. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.601193
34. Zheng D, Liu J, Piao H, Zhu Z, Wei R, and Liu K. ROS-triggered endothelial cell death mechanisms: Focus on pyroptosis, parthanatos, and ferroptosis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1039241. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039241
35. Lyamzaev KG, Panteleeva AA, Simonyan RA, Avetisyan AV, and Chernyak BV. Mitochondrial lipid peroxidation is responsible for ferroptosis. Cells. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/cells12040611
36. Yang WS and Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. (2016) 26:165–76. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014
37. Fujii J and Imai H. Oxidative Metabolism as a cause of lipid peroxidation in the execution of ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147544
38. Do Q and Xu L. How do different lipid peroxidation mechanisms contribute to ferroptosis? Cell reports. Phys Sci. (2023) 4. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2023.101683
39. Li F, Long H, Zhou Z, Luo H, Xu S, and Gao L. System X(c) (-)/GSH/GPX4 axis: An important antioxidant system for the ferroptosis in drug-resistant solid tumor therapy. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:910292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.910292
40. Xie Y, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, and Tang D. GPX4 in cell death, autophagy, and disease. Autophagy. (2023) 19:2621–38. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2218764
41. Zhang WZ, Liu Y, Liao Y, Zhu C, and Zou Z. GPX4, ferroptosis, and diseases. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2024) 174:116512. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116512
42. Jiang Y, Glandorff C, and Sun M. GSH and ferroptosis: side-by-side partners in the fight against tumors. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 13. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060697
43. Ursini F and Maiorino M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radical Biol Med. (2020) 152:175–85. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
44. Kalinovic S, Stamm P, Oelze M, Daub S, Kröller-Schön S, and Kvandova M. Comparison of three methods for in vivo quantification of glutathione in tissues of hypertensive rats. Free Radical Res. (2021) 55:1048–1061. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2021.2016735
45. Li XR, Liu XZ, Jin ZH, and Kang CX. : LKB1 regulates inflammation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis via AMPK-dependent SLC7A11-NOX4-ROS signaling. Cells. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/cells12091263
46. Lv Q, Niu H, Yue L, Liu J, Yang L, and Liu C. Abnormal ferroptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:1656. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01656
47. Lane DP and Crawford LV. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. (1979) 278:261–3. doi: 10.1038/278261a0
48. White E. Autophagy and p53. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. (2016) 6:a026120. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026120
49. Sabapathy K and Lane DP. Understanding p53 functions through p53 antibodies. J Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 11:317–29. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz010
50. Xu R, Wang W, and Zhang W. Ferroptosis and the bidirectional regulatory factor p53. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:197. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01517-8
51. Ji H, Wang W, Li X, Han X, Zhang X, and Wang J. p53: A double-edged sword in tumor ferroptosis. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 177:106013. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106013
52. Gao N, Tang A, Liu XY, Chen J, Zhang G, and Qin S. p53-Dependent ferroptosis pathways in sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 118:110083. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110083
53. Liu Y and Gu W. p53 in ferroptosis regulation: the new weapon for the old guardian. Cell Death differentiation. (2022) 29:895–910. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-00943-y
54. Hu M, Yuan L, and Zhu J. The dual role of NRF2 in colorectal cancer: targeting NRF2 as a potential therapeutic approach. J Inflammation Res. (2024) 17:5985–6004. doi: 10.2147/jir.S479794
55. Dodson M, Anandhan A, and Zhang DD. MGST1, a new soldier of NRF2 in the battle against ferroptotic death. Cell Chem Biol. (2021) 28:741–2. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.05.013
56. Roh JL. Nrf2 targeting in overcoming ferroptosis evasion in head and neck cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 671:225–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.06.022
57. Yan R, Lin B, Jin W, Tang L, Hu S, and Cai R. NRF2, a superstar of ferroptosis. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091739
58. Zhang JL, Lv M, Yang CF, Zhu YX, and Li CJ. Mevalonate pathway and male reproductive aging. Mol Reprod Dev. (2023) 90:774–81. doi: 10.1002/mrd.23705
59. Tang W, Xu D, Liang M, Guan-Qun W, Chen W, and Tang J. Pitavastatin induces autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells via the mevalonate pathway. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e27084. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27084
60. Xing K, Bian X, Shi D, Dong S, Zhou H, and Xiao S. miR-612 Enhances RSL3-Induced Ferroptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Mevalonate Pathway. J hepatocellular carcinoma. (2023) 10:2173–85. doi: 10.2147/jhc.S433332
61. Sun Y, Berleth N, Wu W, Schrötter D, Deitzen Y, and Stürderailer F. Fin56-induced ferroptosis is supported by autophagy-mediated GPX4 degradation and functions synergistically with mTOR inhibition to kill bladder cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:1028. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04306-2
62. Li W, Liang L, Liu S, Hong Y, and Zhou Y. FSP1: a key regulator of ferroptosis. Trends Mol Med. (2023) 29:753–64. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.05.013
63. Hadian K. Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1) and coenzyme Q(10) cooperatively suppress ferroptosis. Biochemistry. (2020) 59:637–8. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00030
64. Yang M, Tsui MG, Tsang JKW, Goit RK, Yao KM, and So KF. Involvement of FSP1-CoQ(10)-NADH and GSH-GPx-4 pathways in retinal pigment epithelium ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:468. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04924-4
65. Liu M, Kong X, Yuan Y, Wang X, Yang W, and Wu H. The critical role and molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis in antioxidant systems: a narrative review. Ann Trans Med. (2022) 10:368. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6942
66. Kraft VA, Bezgiyan K, Pfeiffer S, Ringelstetter L, Müller C, and Zandkarimi F. GTP cyclohydrolase 1/tetrahydrobiopterin counteract ferroptosis through lipid remodeling. ACS Cent Sci. (2020) 6:41–53. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b01063
67. Milski KV, Erle M, Quintic I, Quintic M, Kalinovic S, and Li HG. Measurement of tetrahydrobiopterin in animal tissue samples by HPLC with electrochemical detection-Protocol optimization and pitfalls. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061182
68. Tuy K, GC S, Chen W, Harrison D, Aleman J, and Hjelmeland A. Ddre-22. Disrupting redox balance via the tetrahydrobiopterin pathway in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology. (2021) 23(Supplement_6):vi79. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab196.306
69. Hu H, Wei W, Wu D, Huang F, Li M, and Li W. Blockade of GCH1/BH4 axis activates ferritinophagy to mitigate the resistance of colorectal cancer to erastin-Induced ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:810327. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.810327
70. Vancassel S, Fanet H, Castanon N, Monchaux De Oliveira C, Kusot S, and Capuron L. Tetrahydrobiopterin modulates the behavioral neuroinflammatory response to an LPS challenge in mice. Brain behavior Immun. (2022) 105:139–48. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2022.06.016
71. Chhunchha B, Kubo E, and Singh DP. Switching of redox signaling by prdx6 expression decides cellular fate by hormetic phenomena involving nrf2 and reactive oxygen species. Cells. (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/cells11081266
72. Torres-Villalobos J, Allen C, Salvador-Pascual A, Lea R, Liang Z, and Moreno-Santillan D. Peroxiredoxin 6 suppresses ferroptosis in lung endothelial cells. Free Radical Biol Med. (2024) 218:82–93. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.04.208
73. Fujita Hiroaki, Tanaka Yu-Ki, Ogata Seiryo, Suzuki Noriyuki, Kuno Sota, and Barayeu Uladzimir. PRDX6 augments selenium utilization to limit iron toxicity and ferroptosis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2024) 31:1277–85. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01329-z
74. Chen YH, Liu HM, Han R, Lin JY, Yang JY, and Guo MJ. Analyzing how SiMiao Wan regulates ferroptosis to prevent RA-ILD using metabolomics and cyberpharmacology. Phytomedicine: Int J phytotherapy phytopharmacology. (2024) 133:155912. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155912
75. Sato H, Takai C, Kazama JJ, Matsumatsu A, Hasegawa E, and Kobayashi D. Serum hepcidin level, iron metabolism and osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:9882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66945-3
76. Zhang F, Jonsson AH, Nathan A, Millard E, Curtis M, and Qian X. Deconstruction of rheumatoid arthritis synovium defines inflammatory subtypes. Nature. (2023) 623:616–24. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06708-y
77. Mowat AG and Hothersall TE. Nature of anaemia in rheumatoid arthritis. 8. Iron content of synovial tissue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in normal individuals. Ann rheumatic Dis. (1968) 27:345–51. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.4.345
78. Dabbagh AJ, Blake DR, and Morris CJ. Effect of iron complexes on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Ann rheumatic Dis. (1992) 51:516–21. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.4.516
79. Zhao H, Tang C, Wang M, Zhao H, and Zhu Y. Ferroptosis as an emerging target in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1260839. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1260839
80. Cronin SJ, Woolf C, Weiss G, and Penninger J. The role of iron regulation in immunometabolism and immune-Related disease. Front Mol Biosci. (2019) 6:116. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00116
81. Luo R, Su J, Zhang W, Huang W, Zhou Q, and Sun P. Targeted delivery of NO donor and ROS scavenger for synergistic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2024) 174:116540. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116540
82. Qian L, Yang J, Li L, Zhao N, Cheng L, and Lu A. Lipid metabolism and rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1190607. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190607
83. Zhang S, Zhu P, Yuan J, Cheng K, Xu Q, and Chen W. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease combined with rheumatoid arthritis exacerbates liver fibrosis by stimulating co-localization of PTRF and TLR4 in rats. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1149665. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1149665
84. Ferreira HB, Melo T, Paiva A, and Domingues MR. Insights in the role of lipids, oxidative stress and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis unveiled by new trends in lipidomic investigations. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 10. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010045
85. Jing M, Yang J, Zhang L, Liu J, Xu S, and Wang M. Celastrol inhibits rheumatoid arthritis through the ROS-NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 98:107879. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107879
86. Wang X, Huang X, Gao P, Ren Y, Li X, and Diao Y. Kallistatin attenuates inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 943:175530. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175530
87. Shu C, Chen J, Lv M, Yi Y, Zheng J, and Xu X. Plumbagin relieves rheumatoid arthritis through nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:13632–42. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2081756
88. Williams LM and Gilmore TD. Looking down on NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 40. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00104-20
89. Ling HZ, Li W, Yang CL, Sun SY, Zhang W, and Zhao L. Glycine increased ferroptosis via SAM-mediated GPX4 promoter methylation in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford England). (2022) 6:4521–34. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac069
90. Xian L, Tengyu L, Xiaocheng W, Jiaxin H, Gao X, and Shuyan L. Sesamol serves as a p53 stabilizer to relieve rheumatoid arthritis progression and inhibits the growth of synovial organoids. Phytomedicine: Int J phytotherapy phytopharmacology. (2023) 121:155109. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155109
91. Qiu CL, Chan JTW, Zhang W, Huang NL, Zeng YL, and Luo BYK. The potential development of drug resistance in rheumatoid arthritis patients identified with p53 mutations. Genes Dis. (2023) 10:2252–5. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.02.007
92. Adib M, Taghadosi M, Tamasebi MN, Sharafat-Vaziri A, Jamshidi AR, and Mahmoudi M. Anti-inflammatory effects of PRIMA-1(MET) (mutant p53 reactivator) induced by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB on rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammopharmacology. (2023) 31::385–394. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01094-9
93. Chada S, Tapan B, Kumar A, Kural G, and Arora S. Role of Nrf2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Res Trans Med. (2020) 68:171–81. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2020.05.002
94. Saha S. An overview of therapeutic targeting of nrf2 signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. ACS omega. (2024) 9:10049–57. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00163
95. Zhang A, Suzuki T, Adachi S, Yoshida E, Sakaguchi S, and Yamamoto M. Nrf2 activation improves experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Free Radical Biol Med. (2023) 207:279–95. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.07.016
96. Zeiser R. Immune modulatory effects of statins. Immunology. (2018) 154:69–75. doi: 10.1111/imm.12902
97. Wen Y, Chen H, Zhang L, Wu M, Zhang F, and Yang D. Glycyrrhetinic acid induces oxidative/nitrative stress and drives ferroptosis through activating NADPH oxidases and iNOS, and depriving glutathione in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Free Radical Biol Med. (2021) 173:41–51. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.019
98. Ma X, Chen H, Cao L, Zhao S, Zhao C, and Yin S. 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid protects neuronal cells from ferroptosis through inhibiting labile iron accumulation and preventing coenzyme Q10 reduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2022) 635:57–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.10.017
99. Feng Y, Mei L, Wang M, Huang Q, and Huang R. Anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic effects of 18beta-Glycyrrhetinic acid in vitro and in vivo models of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:681525. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.681525
100. Chen W, Lu Y, Chen G, and Huang S. Molecular evidence of cryptotanshinone for treatment and prevention of human cancer. Anti-cancer Agents medicinal Chem. (2013) 13:979–87. doi: 10.2174/18715206113139990115
101. Longevity O. Retracted: Cryptotanshinone Protects against PCOS-Induced Damage of Ovarian Tissue via Regulating Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, Inflammation, and Apoptosis via Regulating Ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2023) 2023:9875726. doi: 10.1155/2023/9875726
102. Wang Y, Zhou C, Gao H, Li C, Li D, and Liu P. Therapeutic effect of Cryptotanshinone on experimental rheumatoid arthritis through downregulating p300 mediated-STAT3 acetylation. Biochem Pharmacol. (2017) 138:119–29. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.05.006
103. Sun Y, Xie W, Kang N, Yi J, Ruan X, and Hu L. To explore the inhibitory mechanism of quercetin in thyroid papillary carcinoma through network pharmacology and experiments. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:9541080. doi: 10.1155/2022/9541080
104. Cruz-Gregorio A and Aranda-Rivera AK. : quercetin and ferroptosis. Life (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 13. doi: 10.3390/life13081730
105. Tang M, Zeng Y, Peng W, Xie X, Yang Y, and Ji B. Pharmacological aspects of natural quercetin in rheumatoid arthritis. Drug design Dev Ther. (2022) 16:2043–53. doi: 10.2147/dddt.S364759
106. Ding S-B, Chu X-L, Jin Y-X, Jiang J-J, Zhao X, and Yu M. Epigallocatechin gallate alleviates high-fat diet-induced hepatic lipotoxicity by targeting mitochondrial ROS-mediated ferroptosis. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1148814. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1148814
107. Chen MS, Tsai BC, Sitorus MA, Kuo CH, Kuo WW, and Chen TS. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate pretreatment improves autologous adipose-derived stem cells against rheumatoid arthritis-induced neuroinflammation in the brain of collagen-induced rats. Neurotoxicity Res. (2022) 40:1223–34. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00544-0
108. Yin Q, Xiang L, Han X, Zhang Y, Lyu R, and Yuan L. The evolutionary advantage of artemisinin production by Artemisia annua. Trends Plant Sci. (2025) 30:213–26. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2024.09.006
109. Deng PX, Silva M, Yang N, Wang Q, Meng X, and Ye KQ. Artemisinin inhibits neuronal ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease models by targeting KEAP1. Acta pharmacologica Sin. (2025) 46:326–37. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01378-6
110. Zhang G, Zhang Y, Shen Y, Wang Y, Zhao M, and Sun L. The potential role of ferroptosis in alzheimer’s disease. . J Alzheimer’s disease: JAD. (2021) 80:907–25. doi: 10.3233/jad-201369
111. Chen J, Lin X, He J, Liu D, He L, and Zhang M. Artemisitene suppresses rheumatoid arthritis progression via modulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of ICAM2 mRNA in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Clin Trans Med. (2022) 12:e1148. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1148
112. Tosun İ and İnkaya AN. Resveratrol as a health and disease benefit agent. Food Rev Int. (2009) 26:85–101. doi: 10.1080/87559120802525459
113. Liu P, Hu XZ, Liu ZQ, Liu WK, Huang Q, and Wen Y. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol through ferroptosis modulation: insights and future directions in disease therapeutics. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1473939. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1473939
114. Karimi A, Sefidmooye Azar P, Kadkhodayi M, Tandorost A, Vajdi M, and Shoorei H. A comprehensive insight into effects of resveratrol on molecular mechanism in rheumatoid arthritis: A literature systematic review. Int J Rheum Dis. (2022) 25:827–43. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.14356
115. Salehi B, Venditti A, Sharifi-Rad M, Kręgiel D, Sharifi-Rad J, and Durazzo A. The therapeutic potential of apigenin. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061305
116. Amini P, Moazamiyanfar R, Dakkali MS, Jafarzadeh E, Ganjizadeh M, and Rastegar-Pouyani N. Induction of cancer cell death by apigenin: A review on different cell death pathways. Mini Rev medicinal Chem. (2023) 23:1461–78. doi: 10.2174/1389557523666230119110744
117. Monu, Agnihotri P, Saquib M, and Biswas S. Targeting TNF-α-induced expression of TTR and RAGE in rheumatoid arthritis: Apigenin’s mediated therapeutic approach. Cytokine. (2024) 179:156616. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156616
118. Duan WT, Ou ZX, Huang YX, Zhang YF, Zhang L, and Zhao YN. Silibinin inhibits cell ferroptosis and ferroptosis-Related tissue injuries. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122119
119. Tong WW, Zhang C, Hong T, Liu DH, Wang C, and Li J. Silibinin alleviates inflammation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and has a therapeutic effect on arthritis in rats. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:3241. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21674-6
120. Li Y, Wu W, Song Y, Zhang J, Han D, and Shu C. β-caryophyllene confers cardioprotection by scavenging radicals and blocking ferroptosis. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:18003–12. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c03239
121. Wu YT, Zhong LS, Huang C, Guo YY, Jin FJ, and Hu YZ. β-caryophyllene acts as a ferroptosis inhibitor to ameliorate experimental colitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416055
122. Li WX, Qian P, Guo YT, Gu L, Jurat J, and Bai Y. Myrtenal and β-caryophyllene oxide screened from Liquidambaris Fructus suppress NLRP3 inflammasome components in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC complementary Med therapies. (2021) 21:242. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03410-2
123. Miyazawa T, Burdeos GC, Itaya M, Nakagawa K, and Miyazawa T. Vitamin E: regulatory redox interactions. IUBMB Life. (2019) 71:430–41. doi: 10.1002/iub.2008
124. Zhang X, Wu S, Guo C, Guo K, Hu Z, and Peng J. Vitamin E exerts neuroprotective effects in pentylenetetrazole kindling epilepsy via suppression of ferroptosis. Neurochemical Res. (2022) 47:739–47. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03483-y
125. Tavakol S and Seifalian AM. Vitamin E at a high dose as an anti-ferroptosis drug and not just a supplement for COVID-19 treatment. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (2022) 69:1058–60. doi: 10.1002/bab.2176
126. Kou H, Qing Z, Guo H, Zhang R, and Ma J. Effect of vitamin E supplementation in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2023) 77:166–72. doi: 10.1038/s41430-022-01148-9
127. Turk MA, Liu Y, and Pope JE. Non-pharmacological interventions in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev. (2023) 22:103323. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103323
128. Yin Y, Dong Y, Cao Y, and Dong G. Association of vitamin E intake with all-Cause mortality among individuals with rheumatoid arthritis: A cohort study from the NHANES 1999-2018. J Am Nutr Assoc. (2025) 44:89–95. doi: 10.1080/27697061.2024.2401055
129. Boateng ID. Ginkgols and bilobols in Ginkgo biloba L. A review of their extraction and bioactivities. Phytotherapy research: PTR. (2023) 37:3211–23. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7877
130. Chen J, Ou Z, Gao T, Yang Y, Shu A, and Xu H. Ginkgolide B alleviates oxidative stress and ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination to improve diabetic nephropathy. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2022) 156:113953. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113953
131. Xie C, Jiang J, Liu J, Yuan G, and Zhao Z. Ginkgolide B attenuates collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis and regulates fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated apoptosis and inflammation. Ann Trans Med. (2020) 8:1497. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-6420
132. Zhou J, Wu G, Zheng J, Abdalmegeed D, Wang M, and Sun S. Research on the regulation of plipastatin production by the quorum-Sensing comQXPA system of bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Agric Food Chem. (2023) 71:10683–92. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c03120
133. Aminifar E, Tavakkol Afshari HS, Sathyapalan T, Abbasifard M, and Sahebkar A. The pleiotropic effects of statins in rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2023) 75:910–20. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgad024
134. Shen W, Li C, Liu Q, Cai J, Wang Z, and Pang Y. Celastrol inhibits oligodendrocyte and neuron ferroptosis to promote spinal cord injury recovery. Phytomedicine: Int J phytotherapy phytopharmacology. (2024) 128:155380. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155380
135. Pan M, Wang Z, Wang Y, Jiang X, Fan Y, and Gong F. Celastrol alleviated acute kidney injury by inhibition of ferroptosis through Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2023) 166:115333. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115333
136. Zeng L, Yu G, Yang K, He Q, Hao W, and Xiang W. Exploring the mechanism of Celastrol in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on systems pharmacology and multi-omics. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:1604. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48248-5
137. Liu S, Liu M, Xiu J, Zhang T, Zhang B, and Cun D. Celastrol-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticles target inflamed neutrophils for improved rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Acta biomaterialia. (2024) 174:345–57. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.11.028
138. Zuo ZY, Luo M, Liu ZY, Liu T, Wang X, and Huang XR. Selenium nanoparticles alleviate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferritinophagy via the XBP1/NCOA4 pathway. Cell communication signaling: CCS. (2024) 22:376. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01751-2
139. Zhao JG, Dong CY, Zhang YY, Xu DD, Zhang W, and Huang HB. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles synthesized with alginate oligosaccharides alleviate heat stress-Induced oxidative damage to organs in broilers through activating nrf2-Mediated anti-Oxidation and anti-Ferroptosis pathways. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 12:2032. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111973
140. Huang MY, An YC, Zhang SY, Qiu SJ, Yang YY, and Liu WC. Metabolomic analysis reveals biogenic selenium nanoparticles improve the meat quality of thigh muscle in heat-stressed broilers is related to the regulation of ferroptosis pathway. Poultry Sci. (2024) 103:103554. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103554
141. Li XN, Lin L, Li XW, Zhu Q, Xie ZY, and Hu YZ. BSA-stabilized selenium nanoparticles ameliorate intracerebral hemorrhage’s-like pathology by inhibiting ferroptosis-mediated neurotoxicology via Nrf2/GPX4 axis activation. Redox Biol. (2024) 75:103268. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103268
142. Qamar N, John P, and Bhatti A. Toxicological and anti-rheumatic potential of trachyspermum ammi derived biogenic selenium nanoparticles in arthritic balb/c mice. nternational J nanomedicine. (2020) 15:3497–509. doi: 10.2147/ijn.S243718
143. Li X, Li L, Fu X, Huang S, Wang Y, and Yang Y. A novel tetrahedral framework nucleic acid-derived chemodynamic therapy agent for effective glioblastoma treatment. Cell proliferation. (2025) 58:e13736. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13736
144. Tan L, Xie J, Liao C, Li X, Zhang W, and Cai C. Tetrahedral framework nucleic acids inhibit Aβ-mediated ferroptosis and ameliorate cognitive and synaptic impairments in Alzheimer’s disease. J nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:682. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02963-x
145. Li Y, Cai Z, Ma W, Bai L, Luo E, and Lin Y. A DNA tetrahedron-based ferroptosis-suppressing nanoparticle: superior delivery of curcumin and alleviation of diabetic osteoporosis. . Bone Res. (2024) 12:14. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00319-7
146. Zhang M, Zhang X, Tian T, Zhang Q, Wen Y, and Zhu J. Anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin-loaded tetrahedral framework nucleic acids on acute gouty arthritis. Bioactive materials. (2022) 8:368–80. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.06.003
147. Wang L, Wang Y, Lu T, Luo C, Qiu B, and Huang S. Tetrahedral framework nucleic acid loaded miR-23b inhibits synovial inflammation and cartilage matrix degradation in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Advanced Funct Materials. (2023) 34:1074. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202310749
148. Bartelds R, Nematollahi MH, Pols T, Stuart MCA, Pardakhty A, and Asadikaram G. Niosomes, an alternative for liposomal delivery. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0194179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194179
149. Jia CL, Gou Y, Gao Y, Pei X, Jin X, and Li BL. Rosmarinic acid liposomes suppress ferroptosis in ischemic brain via inhibition of TfR1 in BMECs. Phytomedicine: Int J phytotherapy phytopharmacology. (2024) 132:155835. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155835
150. Kadry MO. Liposomal glutathione as a promising candidate for immunological rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Heliyon. (2019) 5:e02162. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02162
151. Fan YH, Ma L, Fang XX, Du SY, Mauck J, and Loor JJ. Role of hypoxia-inducible-factor-1α (HIF-1α) in ferroptosis of adipose tissue during ketosis. J dairy Sci. (2024) 107:10611–27. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-24822
152. Wang Z, Tian J, Wang L, Yan H, Feng S, and Zhang Y. PGK1 is involved in the HIF-1 signaling pathway as a hub gene for ferroptosis after traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol. (2025) 62:233–45. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04170-z
153. Park SY, Lee SW, Kim HY, Lee WS, Hong KW, and Kim CD. HMGB1 induces angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis via HIF-1α activation. Eur J Immunol. (2015) 45:1216–27. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444908
154. Peng Z, Ding YN, Yang ZM, Li XJ, Zhuang Z, and Lu Y. Neuron-targeted liposomal coenzyme Q10 attenuates neuronal ferroptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage by activating the ferroptosis suppressor protein 1/coenzyme Q10 system. Acta biomaterialia. (2024) 179:325–339. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.03.023
155. Kucharská J, Poništ S, Vančová O, Gvozdjáková A, Uličná O, and Slovák L. Treatment with coenzyme Q10, omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids and their combination improved bioenergetics and levels of coenzyme Q9 and Q10 in skeletal muscle mitochondria in experimental model of arthritis. Physiol Res. (2021) 70:723–33. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934664
156. Chen L, Ge H, Huang J, Si L, Sun L, and Wu L. Resveratrol alleviates depression-like behaviors by inhibiting ferroptosis via AKT/NRF2 pathway. Brain Res Bull. (2025) 220:111136. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111136
157. Rocher DF, Myburgh MW, Viljoen-Bloom M, and Cripwell RA. Recombinant alginate lyases and mannitol dehydrogenase enhance hydrolysis of macroalgal carbohydrates. Enzyme Microb Technol. (2025) 186:110618. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2025.110618
158. Fernández-Acosta R, Iriarte-Mesa CI, Alvarez-Alminaque D, Hassannia B, Wiernicki BW, and Díaz-García AM. Novel iron oxide nanoparticles induce ferroptosis in a panel of cancer cell lines. Molecules (Basel Switzerland). (2022) 27. doi: 10.3390/molecules27133970
159. Prasad P, Verma S, Surbhi S, Ganguly NK, Chaturvedi V, and Mittal SA. Rheumatoid arthritis: advances in treatment strategies. Mol Cell Biochem. (2023) 478:69–88. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04492-3
160. Tong L, Qiu J, Xu Y, Lian S, Xu Y, and Wu X. Programmed cell death in rheumatoid arthritis. J Inflammation Res. (2025) 2025:2377–2393. doi: 10.2147/jir.s499345
Keywords: ferroptosis, rheumatoid arthritis, lipid peroxidation, natural medicine, nanomedicine
Citation: Wang Z, Bai X, Zhang H, Yang M, Liu M, Nie T, Li T, Zhang M, Wang X, Wang J, Han J and Liu X (2025) Targeting the ferroptosis pathway for rheumatoid arthritis: molecular mechanisms and prospects for inhibitor development. Front. Immunol. 16:1610121. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1610121
Received: 11 April 2025; Accepted: 23 May 2025;
Published: 10 June 2025.
Edited by:
Matheus Mattos, KU Leuven, BelgiumReviewed by:
Yong Chen, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, ChinaSenlin Ji, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Bai, Zhang, Yang, Liu, Nie, Li, Zhang, Wang, Wang, Han and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaolong Liu, bHhsMzI4MUAxNjMuY29t; Jiming Han, eWFkeGhqbUAxNjMuY29t; Jin Wang, MjcwNjEzMjc1QHFxLkNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Zhuoling Wang
Zhuoling Wang Xinyue Bai
Xinyue Bai Huahua Zhang1†
Huahua Zhang1† Jiming Han
Jiming Han Xiaolong Liu
Xiaolong Liu