- 1College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 2College of Biomedicine and Health, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 3Research Center for Translational Medicine, Xiangyang No.1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang, China
- 4Department of Clinical Medical Research, Binhai County People’s Hospital, Clinical Medical College of Yangzhou University, Yancheng, Jiangsu, China
- 5School of Life and Health Sciences, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Introduction: B7-H6, a tumor-specific immune checkpoint molecule within the B7 family, represents a promising therapeutic target due to its selective overexpression in malignancies and negligible expression in normal tissues.
Method: Here, we developed bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) targeting B7-H6 to redirect T and NK cells against solid tumors. Through phage display, 15 high-affinity B7-H6 monoclonal antibodies were generated.
Results: Two optimized BsAbs, B7-H6M4-OKT3 (T cell-engaging) and B7-H6M4-LC21 (NK cell-engaging), were constructed in and scFv-hFc-scFv format. Both demonstrated nanomolar affinity (EC50: 0.04–1.22 nM) and selective cytotoxicity against B7-H6+ cells (H446, Huh-7, HepG2), while showing minimal cytotoxicity against B7-H6-negative cells (A431). B7-H6M4LC21 exhibited enhanced tumor-killing efficacy (IC50: 5 ng/mL) compared to B7H6M4-OKT3(IC50: 1 ng/mL) when combined with an IL-15/IL-15Ra sushi fusion protein, which augmented NK cell proliferation and cytotoxicity. In H446 xenograft models, both BsAbs suppressed tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner (0.1–20 mg/kg) without significant toxicity. Combination therapy with B7-H6M4-LC21 (10 mg/kg) and B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Ra sushi (0.03 mg/kg) achieved synergistic tumor inhibition (p<0.05), surpassing the efficacy of T cell-based combinations.
Discussion: These findings establish B7-H6-targeted BsAbs combined with cytokine engineering as a viable strategy for treating refractory solid tumors.
1 Introduction
The B7 family of immune checkpoint proteins plays critical roles in tumor immune evasion, among which B7-H6 (NCR3LG1) has garnered significant attention as a tumor-selective antigen due to its minimal expression in healthy tissues and aberrant overexpression across multiple malignancies, including lung, hepatic, and pancreatic carcinomas (1–3). Distinct from PD-L1 or CTLA-4 that predominantly regulate T cell activity, B7-H6 directly activates natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity via NKp30 engagement—a mechanism circumventing T cell-centric immunosuppression (4, 5). This unique biological property positions B7-H6 as a strategic target for bispecific antibody (BsAb) platforms designed to coordinate innate and adaptive immune responses.
Despite the clinical success of CD3-directed BsAbs (e.g., mosunetuzumab, teclistamab) in hematologic malignancies, their efficacy in solid tumors remains constrained by insufficient T cell infiltration, immunosuppressive stromal components, and cytokine depletion (6–8). While CD16-targeted BsAbs (e.g., AFM13) demonstrate enhanced safety and allogeneic potential for NK cell engagement, their therapeutic impact is limited by poor NK cell persistence within hostile tumor microenvironments (TMEs) (9, 10). These challenges highlight the imperative for combinatorial approaches integrating BsAb-mediated tumor targeting with cytokine support to sustain effector cell functionality. IL-15, a pleiotropic cytokine essential for NK and CD8+ T cell homeostasis, holds therapeutic potential but is hampered by systemic toxicity and transient bioavailability (11, 12). Engineered IL-15/IL-15Rα heterodimers (e.g., N-803) mitigate but incompletely resolve these limitations through stabilized receptor interactions, while lacking spatial control over cytokine activity (13–16). Unrestricted IL-15 delivery risks off-target Treg activation, underscoring the necessity for tumor-localized cytokine delivery systems (17).
Recent advances in antibody-cytokine fusion technology, exemplified by PD-L1/IL-12 conjugates, demonstrate enhanced therapeutic precision through tumor-directed cytokine activation (18, 19). However, this paradigm remains unexplored for B7-H6-targeted therapies. To address this gap, we developed a modular immunotherapy platform combining B7-H6-specific BsAbs with a tumor-anchored IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi fusion protein. Through phage display screening, we identified 15 high-affinity B7-H6 monoclonal antibodies and engineered T/NK cell-engaging BsAbs (B7-H6M4-OKT3 and B7-H6M4-LC21, scFv-hFc(N297A)-scFv architecture) with nanomolar binding affinity. The B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi fusion protein enables tumor-localized cytokine activation while preserving effector cell specificity. Our findings demonstrate superior synergy between NK cell-redirected BsAbs and IL-15 fusion, achieving >90% tumor lysis in vitro and significant regression in xenograft models. This work establishes three key advances: (1) B7-H6-dependent spatial restriction of IL-15 activity, (2) dual T/NK cell engagement to combat effector heterogeneity, and (3) modular designs permitting flexible cytokine pairing. By simultaneously addressing spatial, temporal, and cellular barriers to immune efficacy, this strategy transforms B7-H6 from a passive target into an active orchestrator of precision immunotherapy.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Cell lines and culture conditions
Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2, Hep3B, Huh-7), pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PANC-1, KLM-1, T3M4, MiaPaCa-2), breast carcinoma (SKBR-3, ZR75, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231), lung carcinoma (H446, H82, H196, H226, H1975, H1299, PC9, H292, H358), and epidermal carcinoma (A431) cell lines were procured from the Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). All lines underwent short tandem repeat (STR) authentication and mycoplasma screening (PlasmoTest™, Invivogen). Cells were maintained in DMEM or RPMI-1640 medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone), 1% L-glutamine, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37°C under 5% CO2. Lentiviral transduction using a full-length human B7-H6 construct (GeneChem) generated stable B7-H6-expressing A431(B7-H6) cells, with parental A431 serving as negative controls.
2.2 Western blot
Cells were washed twice with PBS and lysed in buffer containing 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, and protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Applied Science). Lysates were agitated at 4°C for 30 min, centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 15 min, and protein concentrations determined via BCA assay (Pierce). Fifty micrograms of total protein per sample was resolved by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and transferred to PVDF membranes for immunoblotting.
2.3 Isolation of lymphocyte populations
Human PBMCs were isolated from whole blood of healthy donors (Wuhan Blood Center) by Ficoll separation (Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Total T cells were then isolated using a Pan T Cell Isolation Kit II (human, Miltenyi Biotec) through negative selection. Human NK cells were isolated from PBMCs by negative selection using magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) with a human NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi Biotec).
2.4 Dual-color flow cytometry for detection of CD69+ T and NK cells in PBMC co-cultures
Following 24-hour treatments, PBMCs per group were harvested and washed twice by centrifugation (300 × g, 5 min at 4°C), then resuspended in ice-cold PBS containing 5% BSA. For the purpose of T cell analysis, PBMCs were initially incubated with b12-OKT3 (anti-CD3, 5 μg/mL) in PBS/5% BSA for 30 minutes on ice, followed by a single wash with 2 mL cold PBS via centrifugation (300 × g, 5 minutes, 4°C). Subsequently, the samples were incubated with Cy5-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:500; Sangon Biotech, Shanghai) on ice under conditions that protected them from light. Following an additional PBS wash, final staining was performed using mouse anti-human CD69-FITC (1:100 dilution; ZenBio) for 30 minutes on ice prior to flow cytometric analysis. For the purpose of NK cell analysis, PBMCs were initially incubated with CD16M39-HisFlag (20) (5 μg/mL) in PBS/5% BSA for 30 minutes on ice, followed by a single wash with 2 mL cold PBS via centrifugation (300 × g, 5 minutes, 4°C). Subsequently, the samples were subjected to incubation with an Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated anti-Flag antibody (1:500 dilution; BioLegend) for a duration of 30 minutes at 0°C under conditions that provided protection from light. This antibody was designed to target the Flag-tag of bound CD16M39-HF. Following an additional PBS wash, final staining was performed using mouse anti-human CD69-FITC (1:100 dilution; ZenBio) for 30 minutes on ice prior to flow cytometric analysis. Immediate analysis of all samples was conducted on a CytoFLEX S flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, USA) utilizing a gating strategy that firstly categorized lymphocytes as live singlets, followed by the identification of the CD3 positive population for T cells (CD69 quantification) or the CD16 positive population for NK cells (CD69 quantification). A minimum of 10,000 gated events per sample were collected for the analysis.
2.5 Antibody development
2.5.1 B7-H6 monoclonal antibody production
The extracellular domain of human B7-H6 (NP_001189368.1, a.a. 25-262) was fused with 6 × His tag and expressed in HEK-293F cells and purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography (Qiagen). The Amino acid sequence of the B7-H6 extracellular domain: DLKVEMMAGGTQITPLNDNVTIFCNIFYSQPLNITSMGITWFWKSLTFDKEVKVFEFFGDHQEAFRPGAIVSPWRLKSGDASLRLPGIQLEEAGEYRCEVVVTPLKAQGTVQLEVVASPASRLLLDQVGMKENEDKYMCESSGFYPEAINITWEKQTQKFPHPIEISEDVITGPTIKNMDGTFNVTSCLKLNSSQEDPGTVYQCVVRHASLHTPLRSNFTLTAARHSLSETEKTDNFS. BALB/c mice (n=6) were immunized subcutaneously with 50 μg B7-H6-His emulsified in Freund’s adjuvant (Sigma) over six weeks. Splenic mRNA was reverse-transcribed, and scFv phage display libraries were constructed for three rounds of panning against immobilized B7-H6-His as previously described (21). Phage display yielded 15 high-affinity mAbs. And the antibody produced as scFv-rFc.
2.5.2 Bispecific antibody construction
Variable domains from B7-H6 mAbs (M4 for NK-targeting BsAbs, Mx for T-cell targeting BsAbs), CD3ϵ (OKT3), and CD16a (LC21) were cloned into a scFv-hFc(N297A)-scFv backbone. The B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi fusion protein was engineered with human Fc(N297A) linking the B7-H6M18 scFv and IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi domain. Anti-HIV scFv b12 (VH and VL sequences are from 2NY7_H and 2NY7_L, respectively) was used to make an irrelevant control. Constructs were transiently transfected into HEK-293F cells using polyethylenimine (PEI, Polysciences), with culture supernatants harvested at 120 h post-transfection. Proteins were purified by Protein A affinity chromatography (Cytiva) and analyzed via non-reducing SDS-PAGE.
2.6 Binding characterization
2.6.1 ELISA
96-well plates (Corning) were coated with 5 μg/mL B7-H6-His overnight at 4°C, blocked with 5% BSA, and incubated with serially diluted antibodies (0.001–100 nM). Binding was detected using HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:5,000; Sangon Biotech) and TMB substrate (Thermo Fisher), with absorbance measured at 450 nm (BioTek Synergy H1).
2.6.2 Flow cytometry
Cells (1×106/mL) were stained with 5 μg/mL antibodies in PBS/5% BSA for 30 min at 4°C. After washing, samples were incubated with Cy5-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:500; Sangon Biotech) and analyzed on a CytoFLEX S flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter). Data processing utilized FlowJo v10 software.
2.7 Functional assays
2.7.1 In vitro cytotoxicity
Tumor cells stably expressing firefly luciferase (ffLuc2) were plated in 96-well plates (5×10³ cells/well). Freshly isolated human PBMCs (Wuhan Blood Center) were added at effector-to-target (E:T) ratios of 10:1. This outcome was attributed to the laboratory’s prior publication on bispecific antibodies (22). The findings indicated that an effector-to-target ratio of 10:1 was an optimal choice, as it exhibited substantial tumor-killing capability against positive tumor cells, i.e., antibody dose-dependent cell killing, while concomitantly evading pronounced non-specific killing. Antibodies or fusion proteins were incubated with the cells at variable concentrations starting from 10,000 ng/mL and followed by 1:10 serial dilutions. After 48 h, residual luciferase activity was quantified using the Bright-Glo™ Assay System (Promega) on a SpectraMax M5 microplate reader (Molecular Devices). Cytotoxicity was calculated as: Cytotoxicity (%) = [(1 – (luminescencesample/luminescencecontrol)] × 100.
2.7.2 In vivo efficacy
All animal procedures were approved by the Huazhong Agricultural University Animal Care Committee. Female NSG mice (6-week-old, Vital River Laboratories) received subcutaneous injections of 5×106 H446 cells. When tumors reached ~100 mm³, mice were pretreated with intraperitoneal cyclophosphamide (100 mg/kg) for lymphocyte depletion. Weekly intravenous PBMC infusions (1×107 cells) and bispecific antibody administration (0.1–20 mg/kg every 4 days) were performed. Tumor volumes were calculated as (length × width²)/2 using caliper measurements. Body weights were monitored biweekly for toxicity assessment.
2.8 Statistical analysis
Data represent mean ± SEM. Two-group comparisons utilized unpaired Student’s t-tests (two-tailed). Multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (GraphPad Prism 9). Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Tumor-selective B7-H6 expression patterns
Western blot and flow cytometry analyses revealed differential B7-H6 expression patterns across solid tumor cell lines (Figure 1). Among lung cancer models, nine cell lines (H446, H82, H196, H226, H1975, H1299, PC9, H358, H292) demonstrated detectable B7-H6 expression, while A549 and H1703 remained negative (Figure 1A). Hepatocellular carcinoma (Hep3B, Huh-7, HepG2), pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PANC-1, KLM-1, T3M4, MiaPaCa-2), and MCF-7 breast cancer cells exhibited strong B7-H6 positivity, contrasting with negative expression in SKBR-3, ZR75, and MDA-MB-231 lines. Lentiviral-transduced A431(B7-H6) cells served as stable overexpression controls, while parental A431 cells confirmed baseline negativity (Figure 1B). This expression profile corroborates previous reports of tumor-restricted B7-H6 distribution (4).
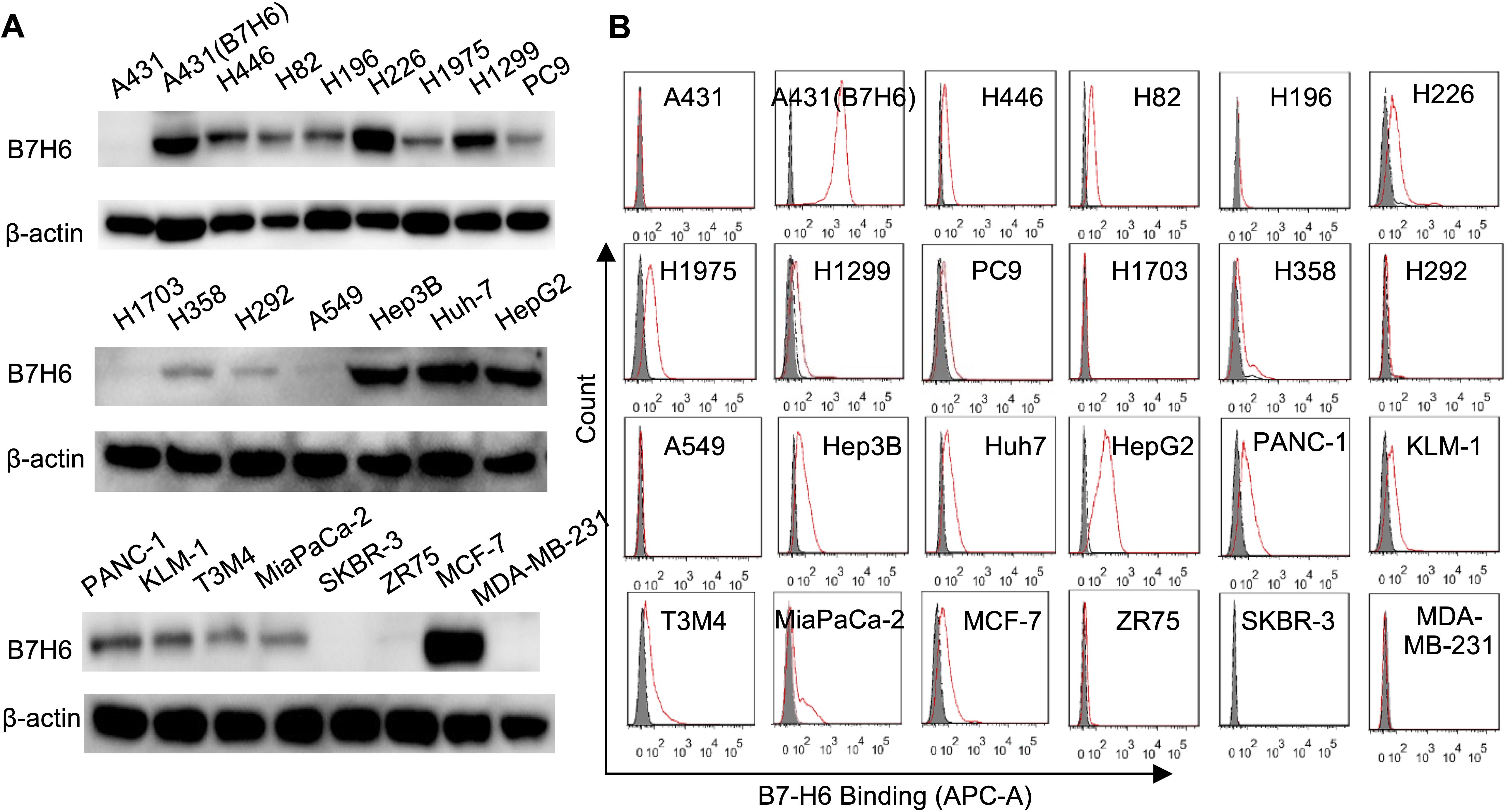
Figure 1. Comparative analysis of B7-H6 protein expression across solid tumor cell lines. (A) Western blot analysis of B7-H6 protein expression in lung cancer (H446, H82, H196, H226, H1975, H1299, PC9, H1703, H358, H292, A549), hepatocellular carcinoma (Hep3B, Huh7, HepG2), pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PANC-1, KLM-1, T3M4, MiaPaCa-2), and breast carcinoma (SKBR-3, ZR75, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231) cell lines. A431 epidermal carcinoma cells served as B7-H6-negative controls, while lentiviral-transduced A431(B7-H6) stable transfectants were used as positive controls. Total protein lysates (50 μg/lane) were resolved by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and probed with HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:5,000). β-Actin served as the loading control. (B) Flow cytometric quantification of surface B7-H6 expression. Cells were incubated with 5 μg/mL primary B7-H6-specific antibody followed by Cy5-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:500). Shaded histograms represent untreated controls; red lines indicate antibody-treated groups.
3.2 Development and characterization of B7-H6-specific mAbs
The recombinant B7-H6 extracellular domain (B7-H6-His) expressed in HEK-293F cells showed an apparent molecular weight of ~42 kDa via SDS-PAGE (theoretical 28.1 kDa), consistent with post-translational glycosylation (Figure 2A). The phage display library was subjected to four rounds of panning, with the input and output of each round illustrated in Figure 2B. It was observed that there was an enrichment of specific antibody sequences at various points throughout the panning rounds. Phage display yielded 15 high-affinity mAbs (M4, M9, M14, M18, M26, M39, M44, M49, M53, M56, M59, M65, M73, M88, M90) (Figure 2C). The antibody produced as scFv-rFc fusions with >90% purity (Figure 2C). ELISA quantification revealed sub-nanomolar binding affinities (EC50: 0.02–0.43 nM; Figure 2D). Flow cytometric screening confirmed tumor-specific recognition, with M4 demonstrating superior specificity, while M90 was excluded due to non-specific binding (Figure 2E).
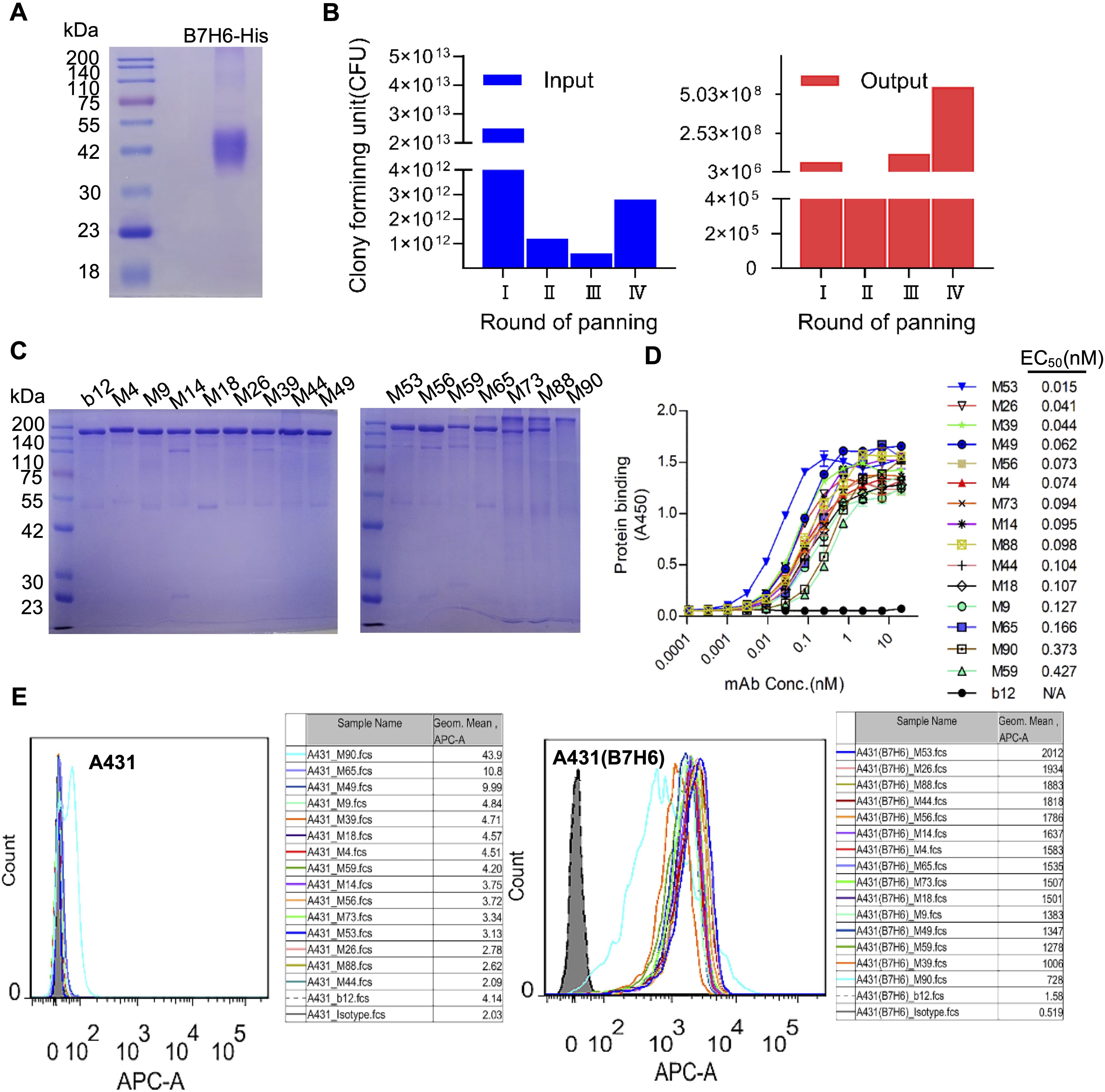
Figure 2. Phage display-derived B7-H6-specific monoclonal antibodies show nanomolar affinity. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant B7-H6-His protein under reducing conditions. (B) Phage display library screening. Input and output phage titers were quantified via bacterial colony counts. (C) Non-reducing SDS-PAGE of scFv-rFc monoclonal antibodies (2 μg/lane), confirming dimeric assembly. (D) ELISA-based affinity measurement. Plates coated with 5 μg/mL B7-H6-His were incubated with serially diluted antibodies (0.01–100 nM) and detected using HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:5,000). (E) Flow cytometric validation of antibody specificity. A431(B7-H6)+ (red line) and A431− (shaded histogram) cells were stained with 5 μg/mL B7-H6 mAbs and Cy5-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:500).
3.3 Bispecific antibody binding characteristics
Ten scFv-hFc(N297A)-scFv format B7-H6/CD3 bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) demonstrated proper assembly and >90% purity by SDS-PAGE (Figures 3A, B). ELISA binding analyses showed nanomolar-range affinity for B7-His (EC50: 0.04–1.22 nM; Figure 3C). Flow cytometry confirmed dual specificity: B7-H6M53-OKT3 selectively bound B7-H6+ tumor cells (A431(B7-H6), H446, Huh-7) and PBMCs, while maintaining specificity against B7-H6-negative controls (Figure 3D).
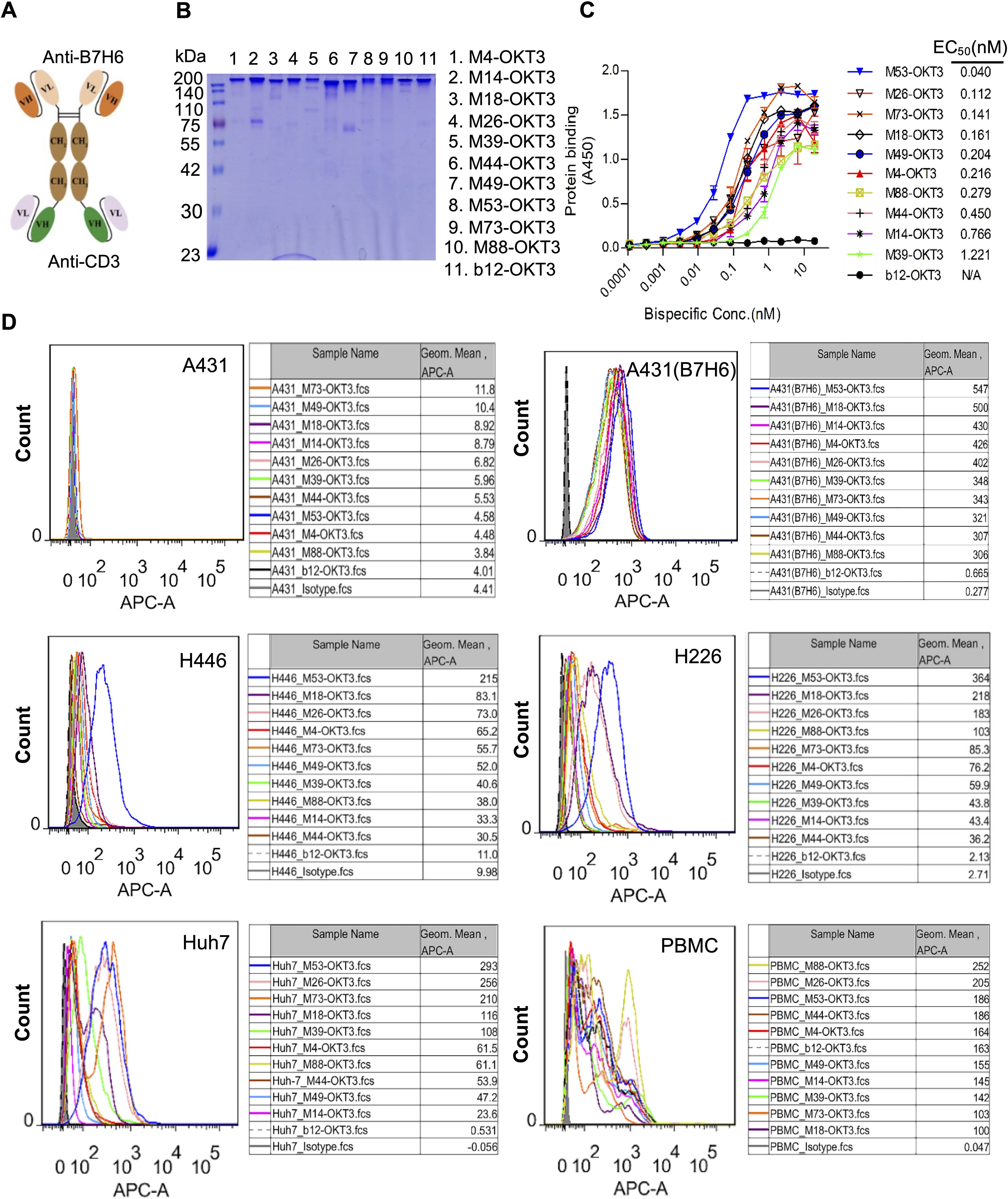
Figure 3. Design framework and functional validation of B7-H6/CD3 bispecific antibodies. (A) Schematic of the B7-H6/CD3 bispecific antibody (BsAb) architecture. (B) Non-reducing SDS-PAGE of purified BsAbs (2 μg/lane), confirming dimeric assembly. (C) ELISA affinity assessment. Plates coated with 5 μg/mL B7-H6-His were incubated with serially diluted BsAbs (100 nM starting concentration) and detected using HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:5,000). (D) Flow cytometric validation of BsAb binding to B7-H6+ tumor cells (A431(B7-H6), H446, H226, Huh7) and healthy donor PBMCs. Cells were stained with 5 μg/mL BsAbs followed by Cy5-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:500). Shaded profiles: unstained controls; solid lines: BsAb-treated groups. Isotype control (pooled human IgG).
3.4 T B7-H6/CD3 BsAb cytotoxic activitys
At 10:1 E:T ratio, B7-H6M4-OKT3 induced significant target cell lysis in B7-H6+ lines (H446: 85% ± 3.2%; A431(B7-H6): 78% ± 2.8%; Huh-7: 72% ± 4.1%; HepG2: 68% ± 3.5%), while showing minimal activity against B7-H6-negative A431 cells (Figures 4A–F). Dose-response analyses revealed superior potency of B7-H6M4-OKT3 (IC50: 1.0 nM) compared to other BsAbs (IC50: 2.5–8.0 nM).
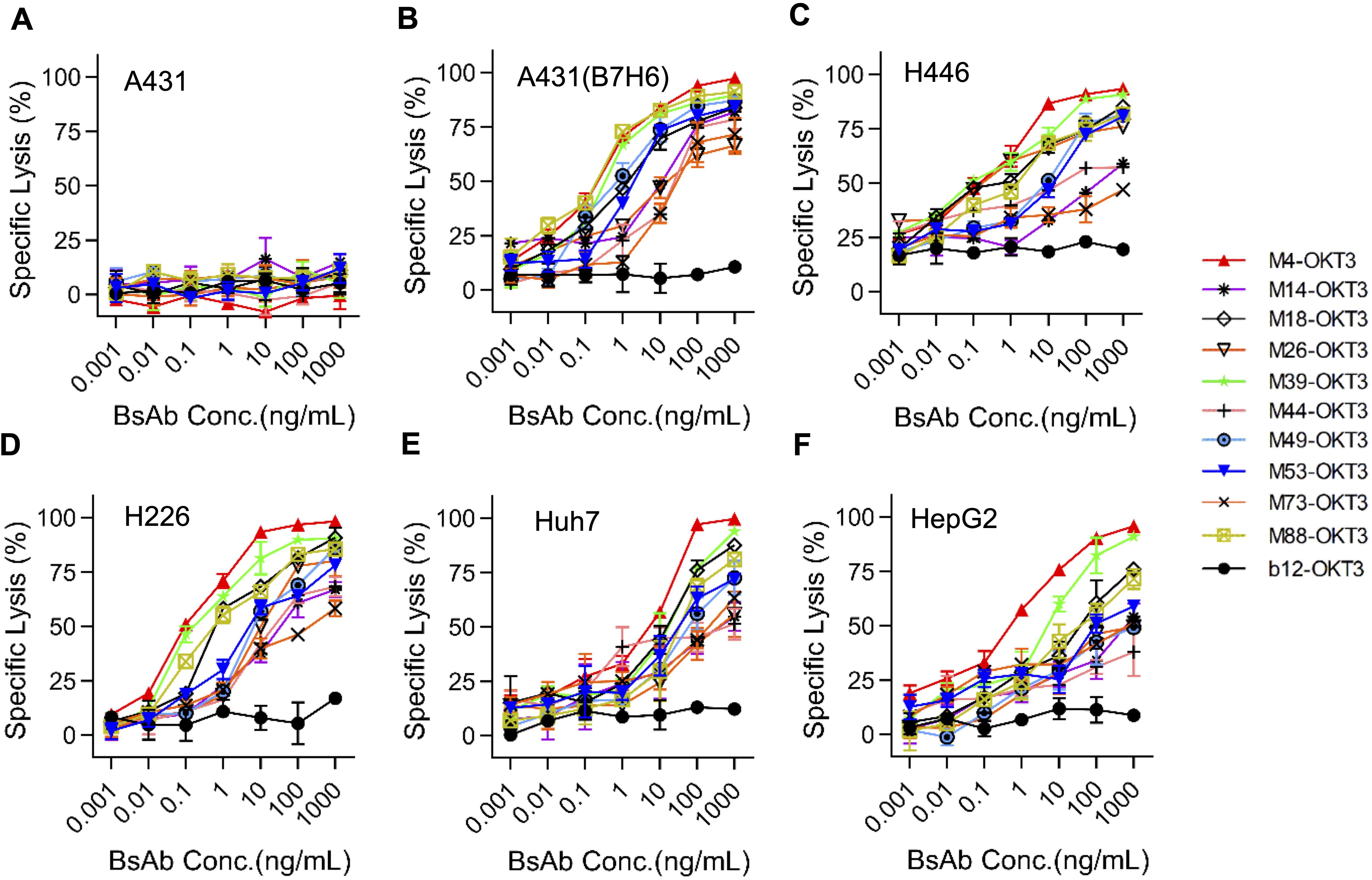
Figure 4. B7-H6/CD3 bispecific antibodies induce antigen-dependent cytotoxicity in vitro. (A–F) Cytotoxic activity of ten B7-H6/CD3 BsAbs against tumor cell lines at an effector-to-target (E:T) ratio of 10:1. Target cells (A431, A431(B7-H6), H446, H226, Huh7, HepG2) stably expressed firefly luciferase (ffLuc2). Residual luminescence inversely correlates with cytotoxicity. A431 (B7-H6−): negative control for antigen-independent killing; b12: isotype control. Data represent mean ± SEM.
3.5 NK cell synergy with IL-15 fusion protein
Purified proteins (>90% purity by SDS-PAGE; Figure 5A) demonstrated high B7-H6-His affinity (EC50: 0.01–0.1 nM), with control b12/CD3 showing no binding (Figure 5B). B7-H6M4-LC21 (NK-engaging BsAb) mediated 60% ± 2.3% H446 lysis at 10 ng/mL (IC50: 5 ng/mL). Co-administration with B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi (0.1 nM) enhanced cytotoxicity to 90% ± 1.8% (p < 0.01 vs monotherapy; Figures 5D, E). Flow cytometry confirmed simultaneous engagement of B7-H6+ tumors and PBMCs (Figure 5C).
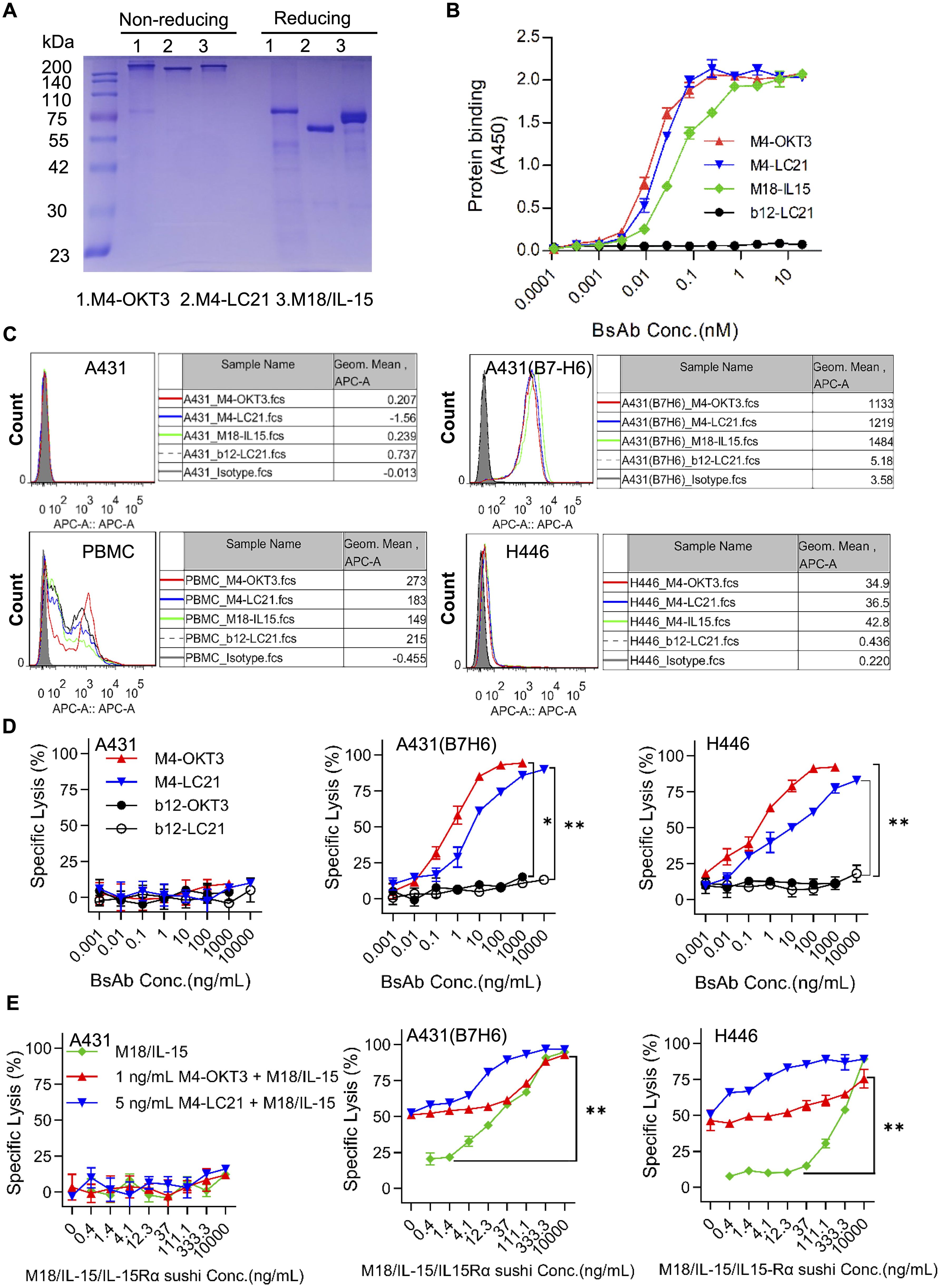
Figure 5. Synergistic activity of NK cell-engaging BsAbs and tumor-localized IL-15 delivery. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of B7-H6M4-OKT3, B7-H6M4-LC21, and B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi under non-reducing (−βME) and reducing (+βME) conditions (2 μg/lane). The structures of all proteins are scFv (Anti B7H6)-hFc (N297A)-scFv. (B) ELISA-based affinity measurement. Plates coated with B7-H6-His (5 μg/mL) were incubated with serially diluted proteins (0.01–100 nM) and detected using HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:5,000). (C) Flow cytometric validation of BsAb binding to B7-H6+ tumor cells (A431 (B7-H6), H446). PBMC were used to evaluate the binding ability of the bispecific antibodies. Cells were stained with 5 μg/mL antibodies followed by Cy5-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:500). Isotype control (pooled human IgG) (D) In vitro cytotoxicity of B7-H6M4-OKT3 and B7-H6M4-LC21 against tumor cell lines (E:T = 10:1). (E) Synergistic cytotoxicity of BsAbs combined with B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi. Data: mean ± SEM. Statistical significance determined by unpaired t-test or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
3.6 Bispecific antibodies M4-OKT3 and M4-LC21 mediate targeted engagement and functional activation of T and NK effector cells
Flow cytometry analysis confirmed specific binding of M4-OKT3 to purified T cells and M4-LC21 to purified NK cells (Figure 6A), demonstrating effective target engagement by both bispecific antibodies. To assess functional activation, surface CD69 expression—an early activation marker—was quantified on T cells (gated as CD3+ lymphocytes) and NK cells (gated as CD16+ lymphocytes) in PBMC-tumor co-culture systems using multiparameter staining with anti-CD3/anti-CD69 and anti-CD16/anti-CD69 antibody pairs.B7-H6M4-OKT3 significantly upregulated CD69 on T cells (Figure 6B), while B7-H6M4-LC21 potently induced CD69 expression on NK cells (Figure 6C). The B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi activated both T and NK cell populations (Figures 6C, D). Consistent with these findings, B7-H6M4-OKT3 showed the highest CD69 induction among T cell-targeting agents (Supplementary Figure S1), and B7-H6M4-LC21 demonstrated superior activation of NK cells (Supplementary Figure S2). Collectively, these results establish that M4-OKT3 and M4-LC21 bispecific antibodies selectively engage and activate their respective effector cells (T and NK lymphocytes) within PBMC, enabling potent cytotoxic function against tumor targets.
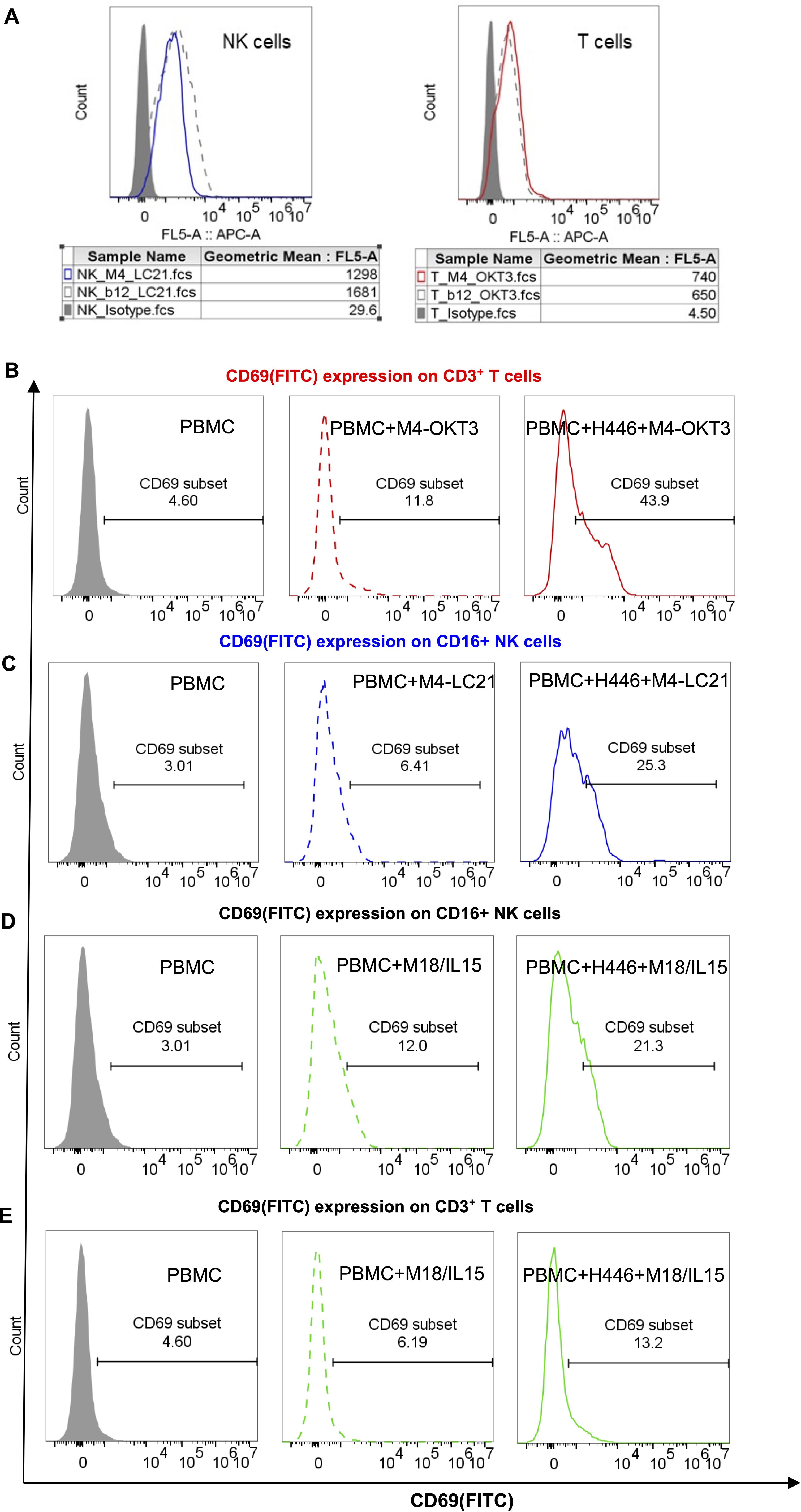
Figure 6. Target binding and functional activation of bispecific antibodies. (A) Flow cytometric binding specificity of NK/T cells purified from healthy donor PBMCs. NK cells were stained with 5 μg/mL M4-LC21 followed by Cy5-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:500). T cells were stained with 5 μg/mL M4-OKT3 followed by Cy5-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (1:500). (B–E) CD69 expression after 24-hour treatments: Gray-shaded histogram: PBMC alone (control). Dashed line: PBMC+antibody co-culture. Solid line: PBMC+tumor cells+antibody triple co-culture (B) CD69 expression on T cells (gated as CD3+ lymphocytes). (C) CD69 expression on NK cells (gated as CD16+ lymphocytes). (D, E) CD69 co-expression profiles on T and NK cell subsets.
3.7 Combination therapy efficacy and safety profile
In H446 xenografts, B7-H6M4-OKT3 (1.0 mg/kg) and B7-H6M4-LC21 (10 mg/kg) monotherapies achieved 69.5% ± 10.2% and 66.9% ± 11.2% tumor growth inhibition, respectively, versus PBS (p < 0.05; Figures 7A, B). B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi demonstrated dose-dependent efficacy (0.06 mg/kg: 25.0% ± 7.4% inhibition; 0.5 mg/kg: 57.5% ± 9.0%) with associated toxicity at higher doses (7.4% ± 2.2% weight loss; p < 0.05; Figures 7C, D). The combination regimen (B7-H6M4-LC21 + IL-15 fusion) significantly enhanced tumor suppression versus monotherapies (achieved 76.1% ± 14.8% tumor growth inhibition; p < 0.05; Figures 7E, F) without significant weight changes at therapeutic doses.
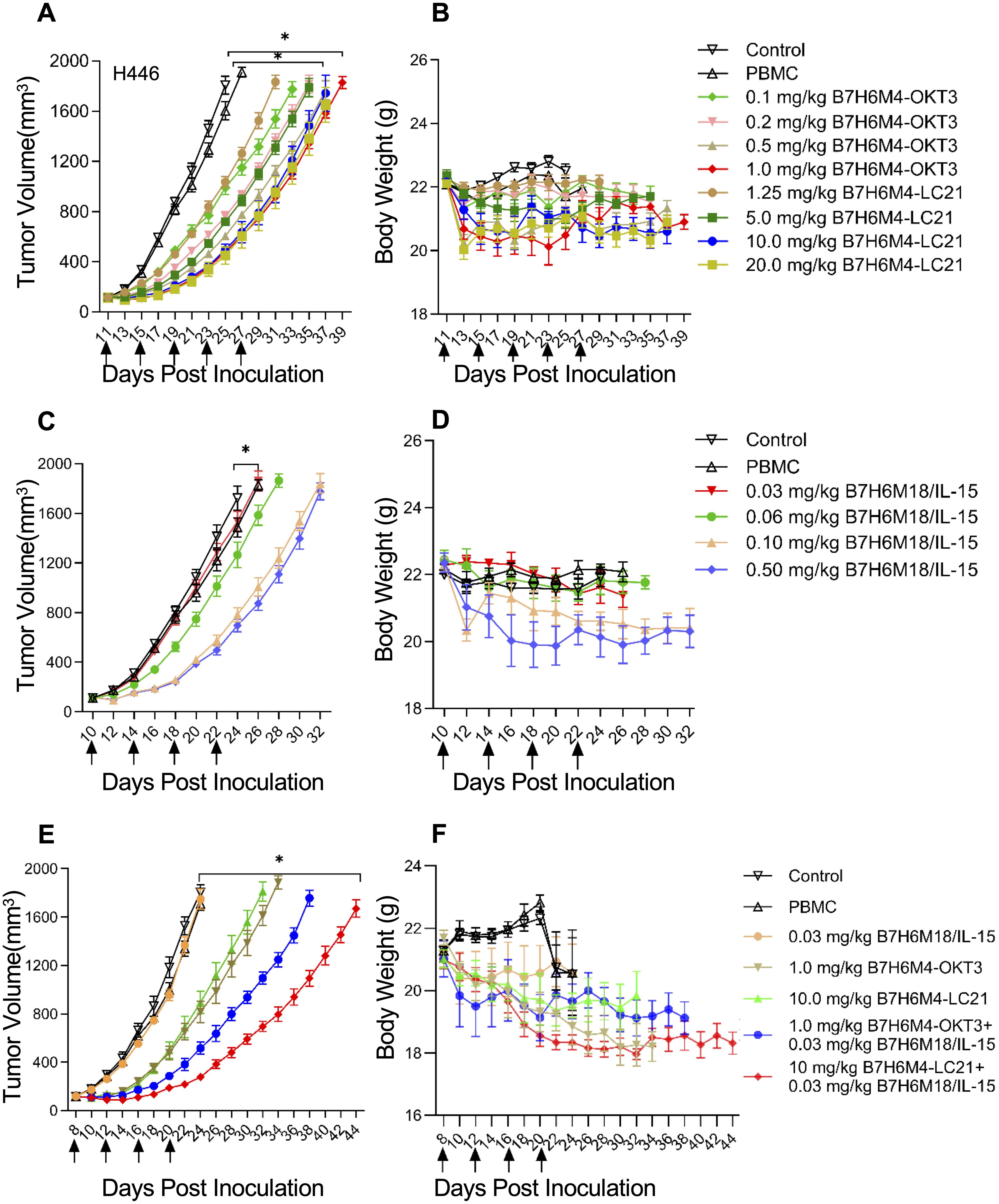
Figure 7. Dose-dependent tumor suppression by B7-H6-targeted bispecific antibodies in xenograft models. (A, B) Tumor growth curves in H446 xenografts treated with escalating doses of B7-H6M4-OKT3 or B7-H6M4-LC21. Controls: untreated mice and PBMC-only groups. (C, D) Dose-dependent efficacy of B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi. (E, F) Combination therapy (B7-H6M4-OKT3: 1.0 mg/kg; B7-H6M4-LC21: 10.0 mg/kg; IL-15 fusion: 0.03 mg/kg). Arrows: treatment timepoints of antibodies (intravenous injection via tail vein). PBMCs (1×107 cells) administered weekly (×2). Tumor volume calculated as V=length×width2/2. Body weight monitored for toxicity. Data: mean ± SEM. Significance determined by unpaired t-test. *p<0.05.
4 Discussion
This study establishes B7-H6 as a therapeutically actionable immune checkpoint in solid malignancies through three principal advances: (1) development of high-affinity bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) redirecting T/NK cells against B7-H6+ tumors, (2) design of a tumor-localized IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi fusion protein to amplify effector cell activity, and (3) identification of NK cell-redirected therapy as the optimal strategy for overcoming immunosuppressive tumor microenvironments (TMEs). Phage display-derived B7-H6M4-OKT3 (T cell-targeting) and B7-H6M4-LC21 (NK cell-targeting) BsAbs demonstrated tumor-selective cytotoxicity with nanomolar binding affinity (EC50: 0.01–1.22 nM). Notably, B7-H6M4-LC21 combined with IL-15 fusion protein elicited synergistic tumor lysis (>90% at 10 ng/mL in vitro) and enhanced in vivo antitumor efficacy, surpassing T cell-based modalities. These observations align with emerging evidence supporting NK cell engagement to bypass T cell exhaustion and stromal resistance in solid tumors (9, 23). The effectiveness of our B7-H6/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi fusion further underscores the value of spatial cytokine regulation—a concept validated in recent PD-L1/IL-12 fusion studies (24, 25). Tumor-restricted IL-15 delivery reduced systemic toxicity while enhancing effector cell persistence, a critical advantage for treating chemoresistant malignancies like small-cell lung cancer (SCLC).
4.1 B7-H6 as a tumor-restricted immune checkpoint for solid cancers
B7-H6 has been identified as a marker in various types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (26), small cell lung cancer (2), gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer (3), oral squamous cell carcinoma (27), and cervical cancer (28). This finding indicates the possible utilization of B7-H6-targeted therapy in a range of solid tumor indications. Conversely, B7-H6 expression is minimal in normal human tissues. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of 48 normal human tissues did not detect B7-H6 mRNA expression (4). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis has confirmed that normal pancreatic, colonic, and gastric tissues do not express B7-H6 membrane protein (29). B7-H6/CD3 T cell conjugates (for example, BI 765049) have been shown to bind specifically to tumor cells that express B7-H6. In addition, they have been demonstrated to have no cytotoxic effect on B7-H6-negative cells, thereby reducing off-target toxicity (3).
Systematic analysis of B7-H6 expression confirms its tumor-selective distribution, with negligible detection in normal tissues. Elevated expression in lung (H446, H1299), hepatic (Hep3B, Huh-7), and pancreatic (PANC-1, MiaPaCa-2) carcinomas supports prior associations between B7-H6 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-driven metastasis (30–32). Heterogeneity observed in breast cancer lines (e.g., MCF-7+ vs. MDA-MB-231−) suggests context-dependent regulation, potentially involving STAT3 or Wnt/β-catenin signaling (33, 34). This tumor-restricted expression profile, coupled with B7-H6’s role in NKp30-mediated NK cell activation (4), establishes its dual utility as both a therapeutic target and diagnostic biomarker. In summary, the low toxicity of B7-H6-targeted therapy is primarily attributable to its tumor-specific expression and precise targeting mechanism, thus rendering it a promising low-toxicity immunotherapy strategy.
4.2 Dual-arm immunotherapy: NK cell engagement outperforms T cell strategies
While T cell-redirecting BsAbs (e.g., B7-H6M4-OKT3) exhibited potent in vitro cytotoxicity (IC50: 1 ng/mL), their in vivo efficacy plateaued—likely due to limited T cell infiltration, a well-documented challenge in solid tumors (35). In contrast, NK cell-engaging B7-H6M4-LC21 achieved superior tumor control with reduced cytokine release risk, mirroring outcomes of CD16-targeted BsAbs in lymphoma models (9, 10). This advantage may stem from NK cells’ intrinsic ability to lyse MHC-I-deficient tumors and resist TME-mediated suppression (23, 36). Furthermore, IL-15 fusion synergized more robustly with B7-H6M4-LC21 (>90% lysis) than T cell-BsAbs, likely attributable to IL-15’s preferential enhancement of NK cell metabolic fitness and granzyme B production (13, 37, 38).
In this study, both T/NK cell-type bispecific antibodies demonstrated significant cytolytic activity and tumor growth inhibition in NSG mice in both in vitro experiments and in vivo experiments in NSG mice. When the M18 antibody was combined with the IL-15/IL-15Rα fusion protein and the two types of bispecific antibody, significant activity was observed both in vivo and in vitro. The combination with the NK cell-type bispecific antibody proved to be the most significant. Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a cytokine that plays a pivotal role in regulating the development, balance, and function of natural killer (NK) cells and T cells (39). The IL-15/IL-15Rα complex signaling pathway is stimulated, thereby promoting the survival, proliferation, and effector functions of NK cells and T cells (39). Consequently, therapeutic IL-15 pathway agonists have the potential to enhance the activity of immunotherapies that induce NK and T cell activity, such as monoclonal antibodies, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and T cell bispecific antibodies, by expanding NK/T cell expansion and enhancing antitumor immune responses.
As demonstrated in previous studies, the combination of XmAb24306 (IL-15/IL-15Rα Fc fusion protein) with T cell bispecific antibodies has been shown to enhance the proliferation and expansion of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells induced by these antibodies (40). The present study hypothesizes that T cell bispecific antibody stimulation can serve as an initiator for XmAb24306, thereby enhancing T cell responsiveness to IL-15. It has been reported that IL-15 can promote TCR sensitization, resulting in stronger T cell responses (41). NK cells have been observed to constitutively overexpress IL-2/15Rβγ (CD122/CD132) on their surface, and it has been demonstrated that IL-15/IL-15Rα can directly bind to this receptor, resulting in the rapid activation of the JAK-STAT5 pathway and the subsequent expression of perforin/granzyme B. In contrast, T cells require higher concentrations of IL-15 and are inhibited by Tregs. Consequently, the combination of NK cell-type bispecific antibodies has been demonstrated to be the most efficacious approach (23, 42).
4.3 Spatial control of IL-15 activity through tumor anchoring
The B7-H6M18/IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi fusion represents an innovative cytokine delivery paradigm. Unlike systemic IL-15 therapies (e.g., ALT-803) that promote Treg expansion and hepatotoxicity (14, 43, 44), our design confines IL-15 activity to B7-H6+ tumors, analogous to PD-L1-targeted IL-12 strategies that improve tumor-specific immunity (18, 19). Mechanistically, the sushi domain stabilizes IL-15 binding to CD122/CD132 on NK cells, prolonging STAT5 activation without requiring dendritic cell-mediated trans-presentation (45–47). Dose-dependent toxicity at 0.5 mg/kg underscores the necessity for precise cytokine dosing—a challenge mitigated by tumor-localized delivery.
4.4 Clinical translation and therapeutic implications
Our findings position B7-H6 as a pivotal target in refractory solid tumors, particularly cisplatin-resistant SCLC (H446 model). The observed tumor regression parallels PD-1 inhibitor efficacy in similar models (2), suggesting complementary innate-adaptive immune mechanisms. Clinically, this regimen could benefit patients with B7-H6+ tumors identifiable via standard immunohistochemistry—a feasible approach using existing diagnostic antibodies (1). The modular BsAb platform also permits rapid integration with alternative cytokines (e.g., IL-18, IFN-α), costimulatory molecules (4-1BB, OX40), or nanoparticle-based delivery systems such as microrobots, which show promise in enhancing tumor-targeted drug penetration and overcoming biological barriers (48), enabling tailored combination therapies.
4.5 Limitations and future perspectives
Despite promising results, several limitations require resolution. First, validation in patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models of B7-H6+ pancreatic/hepatic cancers is essential. Second, the role of endogenous immune cells in PBMC-humanized NSG mice remains unclear; single-cell RNA sequencing of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes could clarify NK/T cell interactions. Third, IL-15 fusion dosing optimization demands comprehensive pharmacokinetic studies in non-human primates to balance efficacy and safety. Finally, issues related to treatment safety were explored. With regard to the weight loss phenomenon referenced in Figure 7, it is imperative to elucidate its correlation with cytokine storms. It is regrettable that, owing to an absence of foresight regarding the possibility of toxicity risks during the study design stage, serum or tissue samples were not retained for the purpose of cytokine detection. Nevertheless, the controllability of toxicity is a pivotal focal point of subsequent analyses. The extant data support the hypothesis that toxicity is unrelated to the storm, with limited weight loss: the maximum recorded weight loss was 15% of initial body weight (Figure 7F), consistent with temporary stress responses (e.g. suppression of appetite) rather than the explosive characteristics of a storm (49). No clinical symptoms related to the storm were observed in the subjects. The experimental mice administered the treatment did not display the customary indications of the storm, including hair erection, lethargy, or respiratory distress (50). A review of the clinical data for analogous bispecific antibodies (for example, CD3×CD19 Blinatumomab) yielded the following results: The incidence of weight loss was approximately 18% (CTCAE Grade 1–2) (51). The incidence of cytokine storm was only 3–5% (≥ Grade 3) (51). Therefore, weight loss is not necessarily storm-related and is more likely attributed to energy expenditure caused by T-cell activation.
5 Conclusion
This study establishes an integrative platform for solid tumor immunotherapy combining B7-H6-targeted bispecific antibodies with tumor-anchored cytokine delivery. High-affinity NK cell-engaging B7-H6M4-LC21 (IC50: 5 ng/mL) and T cell-redirecting B7-H6M4-OKT3 (IC50: 1 ng/mL) demonstrate the therapeutic versatility of B7-H6, a tumor-selective immune checkpoint. Co-administration of B7-H6M4-LC21 with IL-15/IL-15Rα sushi fusion achieved synergistic tumor inhibition, outperforming T cell-based strategies and emphasizing NK cells’ unique capacity to overcome stromal immunosuppression. Tumor-localized IL-15 delivery minimized systemic toxicity—a critical advancement given the dose-limiting hepatotoxicity of conventional IL-15 therapies.
These results hold immediate clinical relevance for cisplatin-resistant SCLC (H446 model) and other B7-H6+ malignancies where current immunotherapies show limited efficacy. The modular BsAb design facilitates adaptation to alternative cytokines (e.g., IL-18, IFN-α) or costimulatory molecules (4-1BB, OX40), providing a framework for personalized regimens. Future priorities include (1) biomarker-driven patient stratification via B7-H6 IHC, (2) pharmacokinetic optimization of IL-15 fusion dosing, and (3) combinatorial trials with PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibitors to exploit innate-adaptive immune synergy. By unifying targeted antibody engineering with precision cytokine delivery, this work repositions B7-H6 as both a diagnostic marker and therapeutic cornerstone in immuno-oncology.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used. All animal procedures were approved by the Huazhong Agricultural University Animal Care Committee. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XM: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Formal analysis, Resources, Data curation, Project administration, Validation, Conceptualization, Visualization. HH: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Validation, Project administration, Data curation. YZ: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Resources, Formal analysis, Methodology. DZ: Writing – original draft, Validation, Data curation, Methodology. FW: Project administration, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. MF: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Resources, Validation. KJ: Writing – review & editing, Software, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Conceptualization, Visualization. XC: Supervision, Methodology, Conceptualization, Visualization, Investigation, Data curation, Software, Validation, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32300783 and 32270992), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (2021CFB155), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M701338).
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to the Public Instrument Platform of the College of Life Science and Technology at Huazhong Agricultural University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1625813/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Pulanco MC, Madsen AT, Tanwar A, Corrigan DT, and Zang X. Recent advancements in the B7/CD28 immune checkpoint families: new biology and clinical therapeutic strategies. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:694–713. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01019-8
2. Thomas PL, Groves SM, Zhang YK, Li J, Gonzalez-Ericsson P, Sivagnanam S, et al. Beyond programmed death-ligand 1: B7-H6 emerges as a potential immunotherapy target in SCLC. J Thorac Oncol. (2021) 16:1211–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.03.011
3. Zhang W, Auguste A, Liao X, Walterskirchen C, Bauer K, Lin YH, et al. A novel B7-H6-targeted igG-like T cell-engaging antibody for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 28:5190–201. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2108
4. Brandt CS, Baratin M, Yi EC, Kennedy J, Gao Z, Fox B, et al. The B7 family member B7-H6 is a tumor cell ligand for the activating natural killer cell receptor NKp30 in humans. J Exp Med. (2009) 206:1495–503. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090681
5. Zhang H, Dai Z, Wu W, Wang Z, Zhang N, Zhang L, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40:184. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01987-7
6. June CH, O’Connor RS, Kawalekar OU, Ghassemi S, and Milone MC. CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science. (2018) 359:1361–5. doi: 10.1126/science.aar6711
7. Budde LE, Sehn LH, Assouline S, Flinn IW, Isufi I, Yoon S-S, et al. Mosunetuzumab, a full-length bispecific CD20/CD3 antibody, displays clinical activity in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL): interim safety and efficacy results from a phase 1 study. Blood. (2018) 132:399–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-99-118344
8. Usmani SZ, Garfall AL, van de Donk N, Nahi H, San-Miguel JF, Oriol A, et al. Teclistamab, a B-cell maturation antigen × CD3 bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (MajesTEC-1): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 1 study. Lancet. (2021) 398:665–74. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01338-6
9. Kerbauy LN, Marin ND, Kaplan M, Banerjee PP, Berrien-Elliott MM, Becker-Hapak M, et al. Combining AFM13, a bispecific CD30/CD16 antibody, with cytokine-activated blood and cord blood-derived NK cells facilitates CAR-like responses against CD30(+) Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:3744–56. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0164
10. Wu J, Fu J, Zhang M, and Liu D. AFM13: a first-in-class tetravalent bispecific anti-CD30/CD16A antibody for NK cell-mediated immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. (2015) 8:96. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0188-3
11. Propper DJ and Balkwill FR. Harnessing cytokines and chemokines for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2022) 19:237–53. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
12. Patidar M, Yadav N, and Dalai SK. Interleukin 15: A key cytokine for immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2016) 31:49–59. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.06.001
13. Conlon KC, Lugli E, Welles HC, Rosenberg SA, Fojo AT, Morris JC, et al. Redistribution, hyperproliferation, activation of natural killer cells and CD8 T cells, and cytokine production during first-in-human clinical trial of recombinant human interleukin-15 in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:74–82. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.3329
14. Wrangle JM, Velcheti V, Patel MR, Garrett-Mayer E, Hill EG, Ravenel JG, et al. ALT-803, an IL-15 superagonist, in combination with nivolumab in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. (2018) 19:694–704. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30148-7
15. Guo Y, Luan L, Patil NK, and Sherwood ER. Immunobiology of the IL-15/IL-15Rα complex as an antitumor and antiviral agent. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2017) 38:10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.08.002
16. Foltz JA, Hess BT, Bachanova V, Bartlett NL, Berrien-Elliott MM, McClain E, et al. Phase I trial of N-803, an IL15 receptor agonist, with rituximab in patients with indolent non-hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:3339–50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4575
17. Klebanoff CA, Finkelstein SE, Surman DR, Lichtman MK, Gattinoni L, Theoret MR, et al. IL-15 enhances the in vivo antitumor activity of tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2004) 101:1969–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307298101
18. Zou Z, Shen J, Xue D, Li H, Xu L, Cao W, et al. Anti-PD-1 cis-delivery of low-affinity IL-12 activates intratumoral CD8(+)T cells for systemic antitumor responses. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:4701. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49034-1
19. Liao J, Pan H, Huang G, Gong H, Chen Z, Yin T, et al. T cell cascade regulation initiates systemic antitumor immunity through living drug factory of anti-PD-1/IL-12 engineered probiotics. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114086. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114086
20. Chen L, Zhu Y, Feng M, Zuo D, Chen G, and Ji K. Targeting CD16A on NK cells and GPC3 in hepatocellular carcinoma: development and functional validation of a therapeutic bispecific antibody. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1599764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1599764
21. Xu M, Lei G, Chen M, Wang K, Lv W, Zhang P, et al. Development of a novel, fully human, anti-PCSK9 antibody with potent hypolipidemic activity by utilizing phage display-based strategy. EBioMedicine. (2021) 65:103250. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103250
22. Chen X, Chen Y, Liang R, Xiang L, Li J, Zhu Y, et al. Combination therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma by GPC3-targeted bispecific antibody and irinotecan is potent in suppressing tumor growth in mice. Mol Cancer Ther. (2022) 21:149–58. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-1025
23. Myers JA and Miller JS. Exploring the NK cell platform for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:85–100. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0426-7
24. Yang Z, Pietrobon V, Bobbin M, Stefanson O, Yang J, Goswami A, et al. Nanoscale, antigen encounter-dependent, IL-12 delivery by CAR T cells plus PD-L1 blockade for cancer treatment. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:158. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04014-9
25. Di Trani CA, Cirella A, Arrizabalaga L, Alvarez M, Bella Á, Fernandez-Sendin M, et al. Intratumoral injection of IL-12-encoding mRNA targeted to CSFR1 and PD-L1 exerts potent anti-tumor effects without substantial systemic exposure. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2023) 33:599–616. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.07.020
26. Zhang X, Zhang G, Qin Y, Bai R, and Huang J. B7-H6 expression in non-small cell lung cancers. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2014) 7(10):6936–42.
27. Wang J, Jin X, Liu J, Zhao K, Xu H, Wen J, et al. The prognostic value of B7-H6 protein expression in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. (2017) 46:766–72. doi: 10.1111/jop.12586
28. Gutierrez-Silerio GY, Franco-Topete RA, Haramati J, Navarrete-Medina EM, Gutierrez-Franco J, Bueno-Topete MR, et al. Positive staining of the immunoligand B7-H6 in abnormal/transformed keratinocytes consistently accompanies the progression of cervical cancer. BMC Immunol. (2020) 21:9. doi: 10.1186/s12865-020-0341-9
29. Zhu Z, Teng K-Y, Zhou J, Xu Y, Zhang L, Zhao H, et al. B7H6 serves as a negative prognostic marker and an immune modulator in human pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.814312
30. Mohammadi A, Najafi S, Amini M, Mansoori B, Baghbanzadeh A, Hoheisel JD, et al. The potential of B7-H6 as a therapeutic target in cancer immunotherapy. Life Sci. (2022) 304:120709. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120709
31. Hu Y, Zeng T, Xiao Z, Hu Q, Li Y, Tan X, et al. Immunological role and underlying mechanisms of B7-H6 in tumorigenesis. Clin Chim Acta. (2020) 502:191–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.12.030
32. Baragaño Raneros A, Rodriguez RM, Bernardo Flórez A, Palomo P, Colado E, Minguela A, et al. Bromodomain protein BRD4 is an epigenetic activator of B7-H6 expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncoimmunology. (2021) 10:1897294. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1897294
33. Xu X, Zhang M, Xu F, and Jiang S. Wnt signaling in breast cancer: biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:165. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01276-5
34. Ma JH, Qin L, and Li X. Role of STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Commun Signal. (2020) 18:33. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-0527-z
35. Gajewski TF. The next hurdle in cancer immunotherapy: overcoming the non-T-cell-inflamed tumor microenvironment. Semin Oncol. (2015) 42:663–71. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2015.05.011
36. Laskowski TJ, Biederstädt A, and Rezvani K. Natural killer cells in antitumour adoptive cell immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2022) 22:557–75. doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00491-0
37. Dubois SP, Miljkovic MD, Fleisher TA, Pittaluga S, Hsu-Albert J, Bryant BR, et al. Short-course IL-15 given as a continuous infusion led to a massive expansion of effective NK cells: implications for combination therapy with antitumor antibodies. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002193. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002193
38. Conlon KC, Potter EL, Pittaluga S, Lee CR, Miljkovic MD, Fleisher TA, et al. IL15 by continuous intravenous infusion to adult patients with solid tumors in a phase I trial induced dramatic NK-cell subset expansion. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:4945–54. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3468
39. Fehniger TA and Caligiuri MA. Interleukin 15: biology and relevance to human disease. Blood. (2001) 97:14–32. doi: 10.1182/blood.V97.1.14
40. Li J, Clark R, Slaga D, Avery K, Liu K, Schubbert S, et al. IL-15/IL-15Rα-fc-fusion protein xmAb24306 potentiates activity of CD3 bispecific antibodies through enhancing T-cell expansion. Mol Cancer Ther. (2024) 23:1305–16. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-23-0910
41. Deshpande P, Cavanagh MM, Le Saux S, Singh K, Weyand CM, and Goronzy JJ. IL-7– and IL-15–mediated TCR sensitization enables T cell responses to self-antigens. J Immunol. (2013) 190:1416–23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201620
42. Cai Y, Han Z, Shen J, Zou Z, Guo J, Liang Y, et al. Concurrent intratumoural Treg cell depletion and CD8+ T cell expansion via a cleavable anti-4-1BB–interleukin-15 fusion protein. Nat Biomed Eng. (2024) 9:952–66. doi: 10.1038/s41551-024-01303-6
43. Felices M, Chu S, Kodal B, Bendzick L, Ryan C, Lenvik AJ, et al. IL-15 super-agonist (ALT-803) enhances natural killer (NK) cell function against ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. (2017) 145:453–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.02.028
44. Rosario M, Liu B, Kong L, Collins LI, Schneider SE, Chen X, et al. The IL-15-based ALT-803 complex enhances fcγRIIIa-triggered NK cell responses and in vivo clearance of B cell lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:596–608. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1419
45. Gotthardt D, Putz EM, Grundschober E, Prchal-Murphy M, Straka E, Kudweis P, et al. STAT5 is a key regulator in NK cells and acts as a molecular switch from tumor surveillance to tumor promotion. Cancer Discov. (2016) 6:414–29. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0732
46. Monaghan KL, Aesoph D, Ammer AG, Zheng W, Rahimpour S, Farris BY, et al. Tetramerization of STAT5 promotes autoimmune-mediated neuroinflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2021) 118:e2116256118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2116256118
47. Maghsoodi N, Zareinejad M, Ghaderi A, Mahmoudi Maymand E, Irajie C, and Ramezani A. Anti-CD8/IL-15 (N72D)/sushi fusion protein: A promising strategy for improvement of cancer immunotherapy. Cytokine. (2025) 185:156822. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156822
48. Wang J and Liao Z-X. Research progress of microrobots in tumor drug delivery. Food Med Homol. (2024) 1:9420025. doi: 10.26599/FMH.2024.9420025
49. Lee DW, Santomasso BD, Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Turtle CJ, Brudno JN, et al. ASTCT consensus grading for cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity associated with immune effector cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. (2019) 25:625–38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.12.758
50. Teachey DT, Lacey SF, Shaw PA, Melenhorst JJ, Maude SL, Frey N, et al. Identification of predictive biomarkers for cytokine release syndrome after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Discov. (2016) 6:664–79. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0040
Keywords: B7-H6, bispecific antibodies, NK cells, IL-15Rα sushi, solid tumor
Citation: Ma X, He H, Zhu Y, Zuo D, Wang F, Feng M, Ji K and Chen X (2025) Dual T/NK cell engagement via B7-H6-targeted bispecific antibodies and IL-15 eradicates chemo-resistant solid tumors. Front. Immunol. 16:1625813. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1625813
Received: 09 May 2025; Accepted: 24 July 2025;
Published: 12 August 2025.
Edited by:
Miroslawa Puskulluoglu, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, PolandReviewed by:
Stefano Ugel, University of Verona, ItalyIlona Hagelstein, Tübingen University Hospital, Germany
Dennis Awuah, City of Hope National Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Ma, He, Zhu, Zuo, Wang, Feng, Ji and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Chen, Y2hlbnhpbjE5OTBAd2VibWFpbC5oemF1LmVkdS5jbg==; Kangkang Ji, a3lyaWVAbWFpbC51c3RjLmVkdS5jbg==
 Xuqian Ma1,2
Xuqian Ma1,2 Yuankui Zhu
Yuankui Zhu Dianbao Zuo
Dianbao Zuo Mingqian Feng
Mingqian Feng Kangkang Ji
Kangkang Ji Xin Chen
Xin Chen