- 1State Key Laboratory for Quality and Safety of Agro-Products, School of Marine Sciences, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
- 2Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Marine Sciences, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Aquacultural Biotechnology of Ministry of Education, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) represent an evolutionarily conserved component of innate immunity with broad-spectrum antimicrobial and antiviral activities. However, the antiviral potential of fish-specific piscidins against emerging aquatic viruses largely remains to be explored. In this study, we evaluated the antiviral properties of three piscidins (designated here as MsPiscidin1, MsPiscidin2 and MsPiscidin3) identified from largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) against Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus (MSRV), a major pathogen causing high mortality in farmed largemouth bass. Computational prediction and expression profiling revealed inducible expression of MsPiscidins upon MSRV infection, with distinct tissue-specific patterns. Functional assays demonstrated that while MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3 primarily modulated host antiviral responses, MsPiscidin2 exhibited direct virucidal activity against MSRV. Molecular docking predicted potential interactions between MsPiscidin2 and the MSRV glycoprotein, where histidine and glutamic acid residues of MsPiscidin2 are positioned in close proximity to cysteine and methionine residues of the MSRV glycoprotein, supporting its capacity to directly target viral particles. In vitro assays further confirmed that MsPiscidin2 significantly suppressed MSRV replication and attenuated cytopathic effects in a dose-dependent manner. Further, MsPiscidin2 treatment conferred significant in vivo protection, delaying disease progression and improving survival rates in MSRV-infected juvenile bass. These findings provide the first evidence of piscidin-mediated antiviral defense against MSRV and highlight MsPiscidin2 as a promising candidate for developing novel antiviral strategies in largemouth bass aquaculture.
1 Introduction
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are evolutionarily conserved components of the innate immune system that serve as the first line of defense against a wide range of pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites (1). These small peptides, typically 10 ~ 50 amino acid in length, can be constitutively expressed in epithelia cells to provide continuous protection by suppressing microbial replication, or be rapidly induced in immune cells in response to infection (2, 3). Initially discovered for their potent bactericidal properties (4), AMPs have been extensively studied for their ability to disrupt bacterial membranes and inhibit microbial growth (5, 6). Recently, accumulating evidence suggests that AMPs also possess broad-spectrum antiviral activities (7). These peptides can interfere with viral infections through multiple mechanisms, including direct virucidal activity, inhibition of viral entry and replication, and modulation of host immune responses (8, 9).
AMPs with antiviral activity have been identified in a wide range of phylogenetically distinct species, such as mammals, birds, amphibians, and teleost fish (10). LL-37, the active form of human cathelicidin, has been reported to exert potent antiviral activities against respiratory viruses, such as influenza A virus and respiratory syncytial virus (11). Similarly, avian β-defensins have been implicated in host protection against avian influenza virus (12, 13). Further, temporins isolated from the skin of European common frog (Rana temporaria) were demonstrated to inhibit replications of Frog virus 3 (14). In teleost fish, hepcidins have been implicated in the suppression of nervous necrosis virus (NNV) replication in grouper species by regulating iron metabolism and immune signaling (15). Collectively, the ubiquitous presence of antiviral AMPs in various species indicated that AMP-mediated antiviral activity represents an evolutionarily conserved mechanism to enhance host resistance to viral infections.
Among fish-derived AMPs, piscidin is a unique family only present in teleost fish (16). Structurally, these small peptides are initially produced as a prepropeptide consisting of ~64 to 89 amino acids, which undergoes proteolytic cleavage to remove the N-terminal signal peptide and the C-terminal prodomain prior to the release of the mature peptide of 18 to 26 amino acids in length (17). To date, a number of small peptides, such as piscidin, epinecidin and pleurocidin, belong to the piscidin family has been identified, and functional characterizations further demonstrated their potent antiviral activities. For example, epinecidin derived from orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) effectively inhibited NNV and foot-and-mouth disease virus via distinct modes of action (15, 18). This broad-spectrum antiviral activity further underscores its promise as an alternative candidate against viral infections.
Largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) is one of the most economically important freshwater species in aquaculture. However, the expansion of largemouth bass farming has been accompanied by a rise in infectious diseases, which threaten the sustainability of the industry. Among these, Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus (MSRV) represents a major threat and has caused severe hemorrhagic disease outbreaks associated with high mortality rates in farmed juvenile fish, primarily due to its ability to establish systemic infection with pathological lesions detected in multiple tissues, including intestine, liver, muscle, brain and spleen (19–21). Despite efforts to develop vaccines and chemical treatments, current control measures remain inadequate, necessitating the search for alternative antiviral strategies. Three largemouth bass piscidins (MsPiscidin), designated as MsPiscidin1, MsPiscidin2 and MsPiscidin3 here, have been identified in a previous study and functional characterizations demonstrated potent bactericidal activity against multiple aquatic pathogens (22). Although the antibacterial properties of MsPiscidin are well characterized, their involvement in antiviral defense remains largely unexplored. A detailed investigation into their activity against MSRV infection will broaden our understanding of teleost-specific AMPs, extending their functional relevance beyond antibacterial action.
In the present study, the antiviral potential of MsPiscidins was first predicted in silico and validated by temporal expression analysis following MSRV infection. Functional assays revealed that MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3 modulated host immune responses, while MsPiscidin2 directly suppressed MSRV replication in a dose-dependent manner and reduced cytopathic effects (CPE) in vitro. Further in vivo assay demonstrated that MsPiscidin2 significantly improved survival in infected juvenile largemouth bass. Taken together, this represents the first report on antiviral activities of MsPiscidins against MSRV infection and highlight their potential as novel antiviral agents in aquaculture.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Cell culture and fish rearing
Epithelioma Papulosum Cyprini (EPC) cells were kindly provided by Dr. Yi-bing Zeng in Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute (Wuhan, China) and cultured as previously described (23). Briefly, cells were grown in medium 199 (M199; HyClone, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; SIJIQING, China), penicillin (100 IU/mL; Thermo fisher scientific, USA) and streptomycin (100 μg/mL; Thermo fisher scientific, USA) at 25 °C and 5% CO2.
Juvenile largemouth bass were purchased from the Yangyang fishery breeding company in Guangdong, China and all fish were maintained at 28 ± 0.5°C in a flow-through water system on a simulated natural photoperiod. Fish were acclimated to this environment for at least two weeks prior to any experiment. All experiments involving animals were approved by the Ningbo University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and were carried out in compliance with the National Institutes of Health’s Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
2.2 Viral propagations
Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus (MSRV) strain (MSRV-YH01) was kindly provided by Dr. Jia-yun Yao in Zhejiang Institute of Freshwater Fisheries (Huzhou, China) and propagated in EPC cells as previously described (24, 25). Briefly, supernatants containing viral particles originally stored at -80°C were thawed. Prior to the viral infection, concentration of FBS in the culturing medium was reduced to 2% and then 100 μL of aforementioned viral supernatants were added to EPC cells (1×105 cells). After 72 h, the supernatant was collected, aliquoted and stored at -80°C. The tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) was determined using Reed-Muench method (26).
2.3 Synthetic peptides
Three largemouth bass piscidins, i.e., MsPiscidin1(GenBank: MT681907), MsPiscidin2 (GenBank: MT681908) and MsPiscidin3 (GenBank: MT681909) were identified and their structures were analyzed in a previous study (22). In this study, mature peptides of three MsPiscidins were provided by GL Biochem Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The synthesized MsPiscidins were purified by RP-HPLC and the purity was >95%.
2.4 Characterization of physiochemical properties and prediction of antiviral potentials of MsPiscidins
Physicochemical characteristics, i.e., isoelectric point (pI) and charge of MsPiscidins were calculated using PepDraw (https://pepdraw.com). Antiviral potentials of MsPiscidins were predicted using AI4AVP (http://axp.iis.sinica.edu.tw/AI4AVP/).
2.5 RT-qPCR analysis of MsPiscidins expression in tissues of infected largemouth bass
To profile the expression of MsPiscidins in response to the viral infection, largemouth bass were infected by intraperitoneal injection of MSRV containing supernatants at 5×102 TCID50 or virus negative supernatants alone as controls. After 24 h infection, selected immune-relevant tissues, including liver, spleen, intestine, skin, and gills were collected for total RNA extraction, reverse transcription and RT-qPCR analysis as previously described (27). Briefly, Total RNA was extracted using TriQuick Reagent (Solarbio, China) and reverse transcribed using HiScript® III All-in-one RT SuperMix Perfect for qPCR (Vazyme, China) following the manufacturers’ instructions. Obtained cDNAs were then analyzed for MsPiscidins expression by RT-qPCR using Taq Pro Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme, China). Then the RT-qPCR analysis was performed on an ABI QuantStudio 3 real-time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, USA) using primers listed in Supplementary Table S1. Thermocycling parameters were as follows: 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 10 s at 95 °C and 30 s at 60 °C. The relative gene expression of MsPiscidins was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCT method normalized to the endogenous control gene (i.e., β-actin).
2.6 Cytotoxicity assay
To evaluate cytotoxic effects and determine safe dose of MsPiscidins, synthesized peptides used in this study were serially diluted and then added to EPC cells (~90% confluency in 96-well plates). After 24h incubation, cell viability was measured using CCK-8 assay following the manufacturers’ instructions (Beyotime, China). The optical density (OD) of each sample at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader. Percentage of cell viability was calculated using the following equation:(OD experimental group – OD blank group)/(OD control group – OD blank group) × 100%. EPC cells treated with PBS were used as the control group, while wells contain only reaction solution were used as the blank group. Cell viability > 90% after MsPiscidins incubation is considered as non-toxic.
2.7 Molecular docking
The tertiary structures of the MSRV glycoprotein (MSRV G protein; accession number: QBF51718.1) and MsPiscidin2 were predicted using AlphaFold3 (https://alphafoldserver.com/). The predicted structures were evaluated based on the per-residue confidence score, and the highest-ranked models were selected and protein data bank (PDB) files were downloaded for molecular docking analysis using HADDOCK2.4 (28, 29). Specifically, the resulting PDB files of predicted MSRV G protein and MsPiscidin2 structures were uploaded to the HADDOCK web server (https://rascar.science.uu.nl/haddock2.4/), and default docking parameters were applied. The top-ranked cluster with the lowest HADDOCK score was selected and visualized using PyMOL (version 2.1, Schrödinger, LLC). Briefly, MSRV G protein-MsPiscidin2 complex generated from HADDOCK2.4 was rendered in cartoon representation, with critical contact points highlighted using stick models.
2.8 Functional characterization of antiviral activities of MsPiscidins
To screen the antiviral potential of MsPiscidins, a viral dose of 1×103 TCID50 MSRV was pre-incubated with MsPiscidin1 (6.25 μg/mL), MsPiscidin2 (6.25 μg/mL), MsPiscidin3 (6.25 μg/mL) or equal volume of serum-free M199 for 2 h at room temperature. EPC cells were then exposed to the pre-treated MSRV for 2 h, followed by three washes with PBS and cultured as aforementioned with the exception that the FBS concentration in the culturing medium was reduced to 2%. Alternatively, EPC cells were pre-incubated with MsPiscidin1, MsPiscidin2 or MsPiscidin3 at the concentration of 6.25 μg/mL for 12 h, followed by three washes with PBS, then infected and cultured as described above. After 48 h, EPC cells and supernatants were collected for total RNA extraction, reverse transcription and RT-qPCR analysis as described above to assess the expression of viral G gene using the primers listed in Supplementary Table S1.
To confirm the direct antiviral capability of MsPiscidin2, a viral dose of 1×103 TCID50 MSRV was pre-incubated with serially diluted MsPiscidin2 (i.e., 100 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 25 μg/mL, 12.5 μg/mL, 6.25 μg/mL and 3.125 μg/mL) before infecting EPC cells as detailed above to assess the CPE using light microscope and expression of viral G gene.
To further investigate the temporal effects of MsPiscidin2 treatment on the viral replication of infected cells, a viral dose of 1×103 TCID50 MSRV was pre-incubated with MsPiscidin2 (i.e., 6.25 μg/mL) and EPC cells were infected as detailed above. Cells and supernatants were collected at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h for evaluating the expression of viral G gene using RT-qPCR as detailed above.
2.9 In vivo analysis of MsPiscidin2 against MSRV infection
To determine the in vivo toxicity of MsPiscidin2, largemouth bass (n=20 per group) were intraperitoneally injected 40 μL PBS, or 40 μL MsPiscidin2 of different concentrations (i.e., 0.1, 1 and 10 mg/kg). The survival was monitored for 15 days and plotted accordingly. To further investigate the protective effect of MsPiscidin2 on MSRV infection in vivo, ninety juvenile largemouth bass were randomly selected and distributed into three groups and intraperitoneally injected with 20 μL PBS, 20 μL MSRV (5×102 TCID50) and 20 μL MSRV (5×102 TCID50) combined with the same volume of MsPiscidin2 (1 mg/kg), respectively. In the next 15 days, the number of live fish was monitored every day to plot the survival curve.
3 Results
3.1 MSRV infection induces tissue-specific upregulation of MsPiscidin genes in largemouth bass
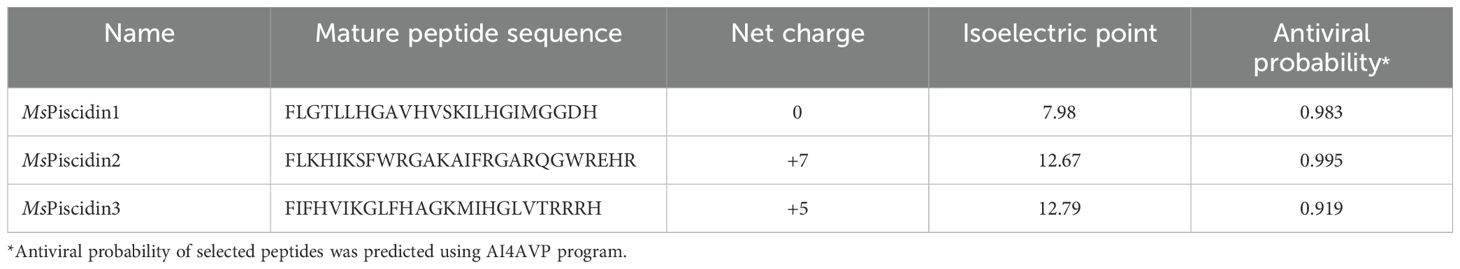
To investigate the innate immune response of largemouth bass to MSRV infection, RT-qPCR analysis was performed to evaluate expression profiles of three MsPiscidin genes in selected tissues after 48 h infection. Specifically, MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3 exhibited similar tissue-specific expression profiles that significant up-regulations were observed in all examined tissues except spleen following MSRV infection, though with differing magnitudes (Figures 1A, C). The highest expression was found in the gill (~470-fold) and intestine (~270-fold) for MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3, respectively. Marked increases were also observed in liver and skin tissues. Of note, a significant reduction in MsPiscidin genes expression was found in spleen. In contrast, Mspiscidin2 expression was only up-regulated ~5-fold in gill, whereas expression in the intestine, liver, and skin slightly increase but not significantly different compared to the control; similarly, a significant reduction of gene expression level was also obvious in the spleen (Figure 1B). Further computational predictions revealed potential antiviral potentials of MsPiscidins, with antiviral probabilities of 0.983, 0.995 and 0.919 for MsPiscidin1, MsPiscidin2 and MsPiscidin3, respectively (Table 1).
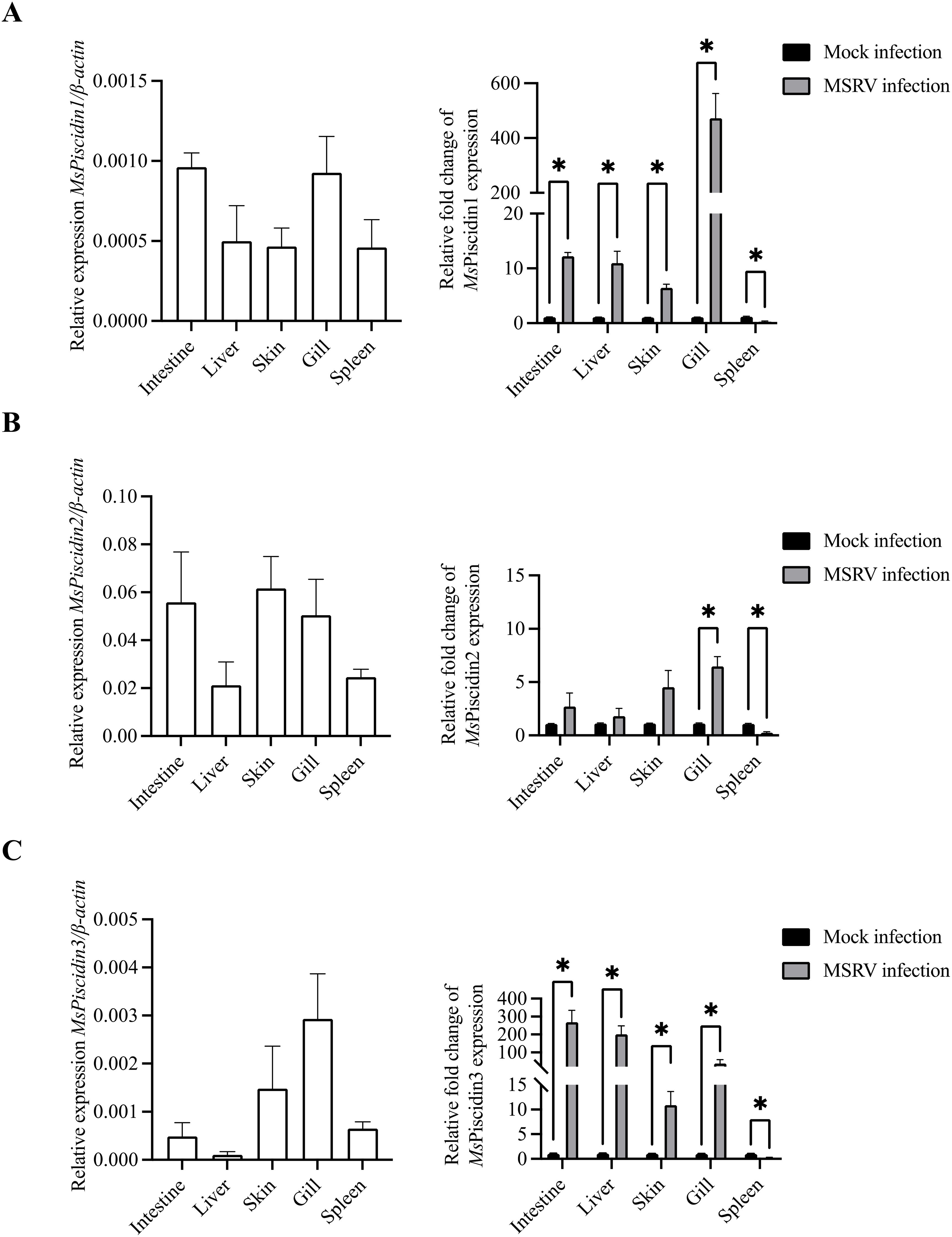
Figure 1. Tissue-specific expression profiles of MsPiscidins in largemouth bass under basal and MSRV-infected conditions. qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA expression levels of MsPiscidin1 (A), MsPiscidin2 (B), and MsPiscidin3 (C) under the basal condition or following MSRV infection. The left panels show the basal expression levels of each gene in healthy fish, normalized to the endogenous β-actin. The right panels show relative expression of MsPiscidin transcript levels following MSRV infection compared to the mock infection group using 2-△△Ct method. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three biological replicates (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to the control group (*p < 0.05).
3.2 MsPiscidins exhibit dose-dependent cytotoxicity in EPC cells
To evaluate the cytotoxic potential of synthetic MsPiscidin peptides, EPC cells were treated with increasing concentrations of MsPiscidin1, MsPiscidin2, or MsPiscidin3 and after 24 h, CCK-8 assay was performed to assess cell viability. Specifically, MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3 demonstrated a similar dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on EPC cells. Both synthetic peptides impaired cell survival at 12.5 µg/mL, with viability dropping below 50% at concentrations ≥50 µg/mL (Figures 2A, C). In contrast, MsPiscidin2 exhibited a markedly different cytotoxic profile that cell viability remained above 90% up to 50 µg/mL. However, at higher concentrations (i.e., 100, 150 and 200 µg/mL), percentage of viable cells was reduced to ~86%, ~64% and ~51%, respectively (Figure 2B).
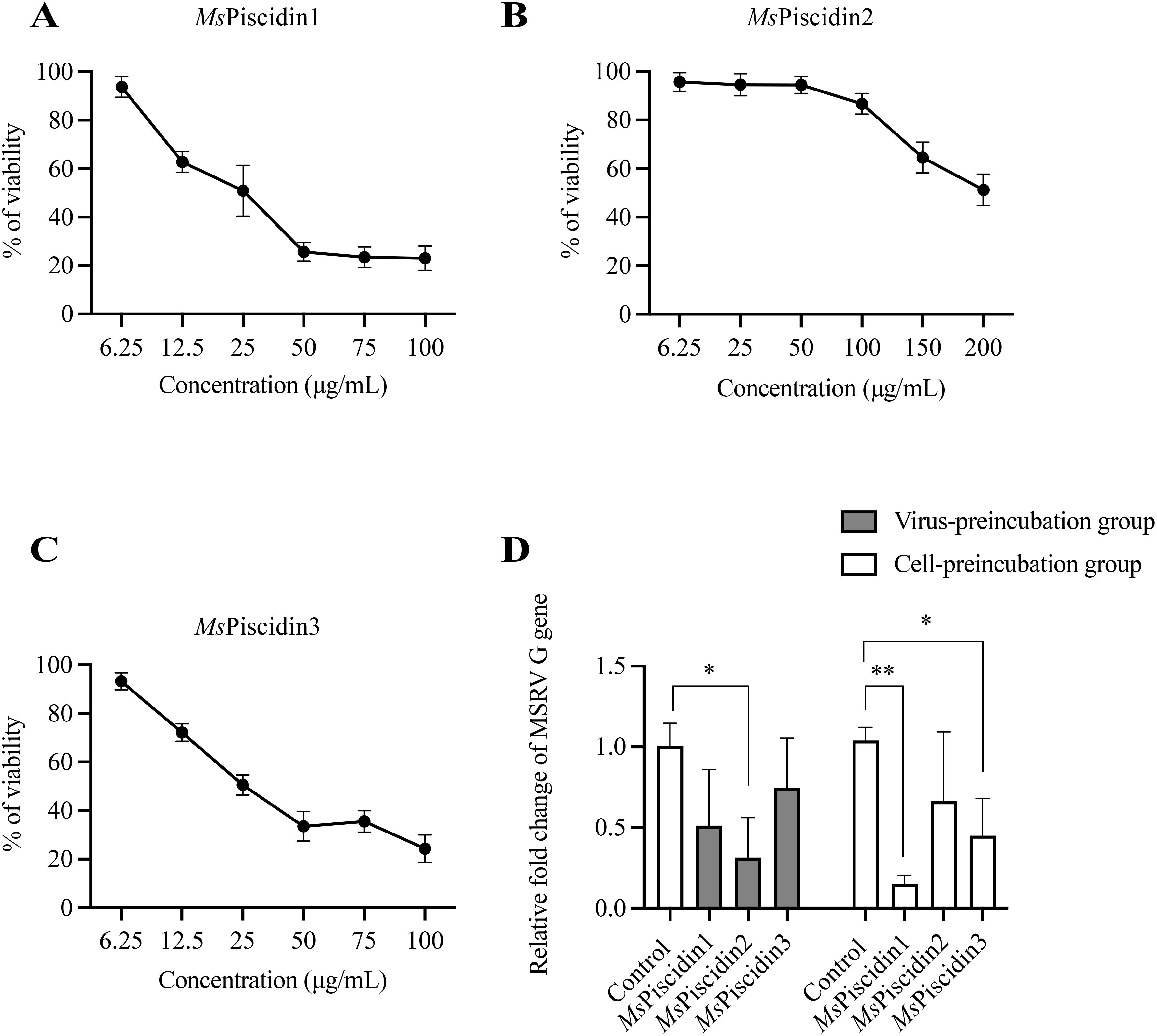
Figure 2. Cytotoxicity and antiviral activity of MsPiscidins in EPC cells. EPC cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of MsPiscidin1 (A), MsPiscidin2 (B), or MsPiscidin3 (C) and after 48 h incubation, cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 assay. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiment, each performed in triplicates. (D) In the virus-preincubation group (grey bar), 1×103 TCID50 MSRV virus were pre-incubated with PBS (i.e., control group) or respective MsPiscidins at the concentration of 6.25 μg/mL. After 2 h incubation, pre-incubated MSRV viruses were further used to infect EPC cells for 2h. In the cell-preincubation group (white bar), EPC cells were pre-treated with PBS or respective MsPiscidins at the concentration of 6.25 μg/mL. After 12 h treatment, EPC cells were further infected with 1×103 TCID50 MSRV for 2h. EPC cells were collected after 48 h and the relative expression levels of MSRV G gene were calculated using 2-△△Ct method and relative to the control group. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three biological replicates (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to the control group (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
3.3 MsPiscidins inhibit MSRV replication via distinct mechanisms
To assess the antiviral activity of MsPiscidin peptides against MSRV, EPC cells or MSRV were pre-incubated with MsPiscidin peptides, followed by RT-qPCR analysis of MSRV G gene expression to examine infectivity of pre-treated MSRV and viral resistance of pre-treated EPC cells. As shown in Figure 2D, pre-incubating MSRV only with MsPiscidin2 significantly reduced viral gene expression compared to the control, indicating that MsPiscidin2 capable of inactivating MSRV directly. In comparison, a significant reduction in MSRV G gene expression was only seen when EPC cells were pre-treated with MsPiscidin1 or MsPiscidin3, suggesting that both peptides indirectly exert antiviral effects, likely through modulation of host cell resistance to viral infection.
3.4 MsPiscidin2 directly inactivates MSRV replication in vitro
Molecular docking analysis was firstly performed to assess potential interactions between MsPiscidin2 and MSRV, which might account for the direct antiviral activities of this peptide. Indeed, two residues in MsPiscidin2 (i.e., histidine at position 26 and glutamic acid at position 47) were identified as likely interacting with cysteine and methionine residues in MSRV G protein (Figure 3A). To further confirm the direct viral inactivation of MsPiscidin2, RT-qPCR analysis was performed to investigate the infectivity of MSRV after pre-incubation with increasing concentration of MsPiscidin2. The result shown that MsPiscidin2 significantly suppressed the replication of MSRV in a dose-dependent manner; the highest concentration (i.e., 25 μg/mL) tested reduced the relative expression of viral G gene to ~ 20% compared to the control group (Figure 3B). Consistently, CPE was also attenuated in cells infected with pre-treated MSRV in a manner proportional to MsPiscidin2 concentrations (Figure 3B).
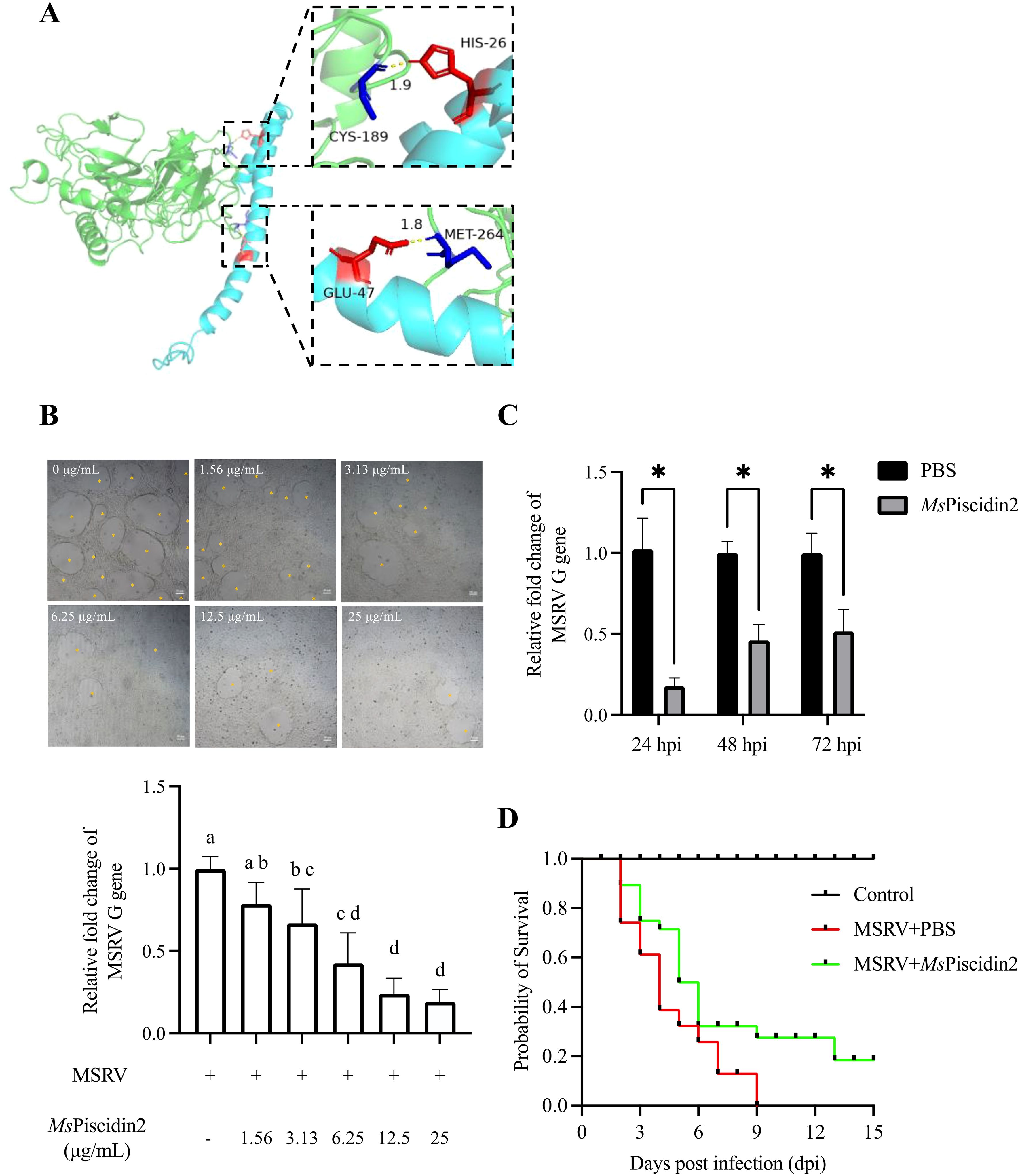
Figure 3. Mechanistic and functional analysis of MsPiscidin2 in vitro and in vivo activity against MSRV infection. (A) Molecular docking analysis illustrating the interaction between the MSRV G protein (green) and the Mspiscidin2 (cyan). Predicted binding interfaces are highlighted with dashed boxes, showing key interacting residues in red and blue. In the upper inset, CYS-189 (blue) of MSRV G protein is positioned near HIS-26 (red) of Mspiscidin2 with an interatomic distance of 1.9 Å, suggesting potential hydrogen bonding or van der Waals interaction. In the lower inset, GLU-47 (red) of Mspiscidin2 is in close proximity (1.8 Å) to MET-264 (blue) of MSRV G protein, indicating another potential interaction hotspot. Distances are given in angstroms (Å). (B) EPC cells were infected with 1×103 TCID50 MSRV pre-treated with indicated concentrations of MsPiscidin2 or PBS as a positive control. After 48 hours, cells were imaged using light microscope and the cytopathic effect was indicated by yellow asterisks (top pane), followed by the qRT-PCR analysis of the relative mRNA expression of the MSRV G gene (bottom histogram). The relative expression levels were calculated using 2-△△Ct method and relative to the positive control group. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three biological replicates (n = 3). Different letters indicate significantly different between groups (p < 0.05). (C) EPC cells were infected with MSRV virus pre-incubated with either MsPiscidin2 or PBS (control group) for 2 hours. After infection, the medium was replaced with 2% FBS-containing medium. Cells and supernatants were harvested at indicated time points to quantify MSRV G gene expression using qRT-PCR. Gene expression levels are shown as relative fold changes normalized to respective control groups. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of three biological replicates (n = 3). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between MsPiscidin2 and respective control groups (p < 0.05). (D) Survival curves of largemouth bass following MSRV infection. Ninety juvenile fish were randomly divided into three groups, i.e., control group that fish were intraperitoneally injected with PBS (black line), infection group that fish were intraperitoneally injected with 5×102 TCID50 MSRV (red line), and treatment group that fish received intraperitoneal injection of 5×102 TCID50 MSRV co-administrated with MsPiscidin2 (green line). Fish were then monitored over 15 days and number of surviving individuals was recorded and plotted accordingly.
To further investigate the temporal dynamics of MsPiscidin2 antiviral effect, MSRV was pre-incubated with MsPiscidin2 prior to infection. RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that viral replication was significantly suppressed at 24, 48, and 72 hours post infection (hpi), with maximum reduction to ~17% at 24 hpi (Figure 3C).
3.5 MsPiscidin2 protects largemouth bass from MSRV infection in vivo
To determine the in vivo toxicity of MsPiscidin2 and define a safe concentration range, largemouth bass were intraperitoneally injected with increasing doses of MsPiscidin2 (0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg), and results shown no mortality was observed in the control group (PBS injection) and in groups treated with 0.1 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg MsPiscidin2, indicating that these doses were tolerated; in contrast, deceased fish were observed at day 2 and day 3 in the group receiving the highest dose (Supplementary Figure S1). To further evaluate the in vivo protective efficacy of MsPiscidin2 against MSRV infection, survival analysis was performed and MSRV-infected fish exhibited rapid mortality, with survival rate dropping below 50% by 4 days post infection (dpi) and all fish died by 9 dpi. In comparison, survival rate of infected fish co-administrated with MsPiscidin2 was pronouncedly increased, with delayed onset of mortality and a final survival rate of ~20% (Figure 3D).
4 Discussion
AMPs represent a critical component of innate immunity in teleost fish and contribute to defending against a range of incoming infectious agents (30). To date, a number of AMPs identified in teleost has been demonstrated potent antiviral activities against aquatic viruses, such as Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) and NNV (31, 32). However, antiviral potentials of piscidin, the fish-specific AMPs, remain largely unknown. In this study, we provide the first evidence that MsPiscidin2 exerts potent antiviral activity against MSRV. Using computational prediction, expression profiling, in vitro functional assays and in vivo infection models, we demonstrate that MsPiscidin2 directly inactivates MSRV particles, significantly suppresses viral replication along with reduced CPE, and confers partial protection in infected juvenile fish. These findings highlight MsPiscidin2 as a promising candidate for antiviral therapy in aquaculture and provide new insights into the antiviral capacity of fish-specific AMPs.
The computational prediction program used in this study (i.e., AI4AVP) infers antiviral potential by analyzing peptide sequence features, such as net charge, hydrophobicity, and structural motifs, through machine learning models trained on large, curated datasets of experimentally validated antiviral peptides (33). Importantly, the relatively short length and well-defined physicochemical properties of AMP make them especially amenable to computational modeling, allowing for more precise identification of functional motifs and prediction of bioactivity. Indeed, this in silico approach has been widely used as an initial step to prioritize AMP candidates with high antiviral potential for subsequent experimental validation.
The observed tissue-specific upregulation of MsPiscidins upon MSRV infection suggests their likely role in anti-viral immunity. MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3 were robustly induced in key barrier tissues, including the gills, intestine and skin, consistent with expression profiles of piscidins observed in other teleost species when challenged with bacteria and viral mimics (34, 35). Interestingly, MsPiscidin2 expression was only significantly induced in gills and remained largely unchanged in other tissues, indicating that its antiviral role may not rely on pathogen-induced upregulation but rather on constitutive expression, of which is sufficient for antiviral effects.
Functional assays revealed distinct antiviral mechanisms among the MsPiscidins. Specifically, MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3 indirectly suppressed viral replication, likely by priming host cells through up-regulating immune-relevant genes (e.g., interferons and interferon-stimulated genes) as seen in other immunomodulatory AMPs (36–38). This immunomodulatory effect can enhance the basal antiviral state of the cells, rendering them more resistant to subsequent MSRV infection. In comparison, MsPiscidin2 directly inactivated viral particles. The polycationic nature of MsPiscidin2 may account for this discrepancy in the mode of action and mechanistically, MsPiscidin2 could directly inserted into the outer membrane of MSRV via electrostatic interactions as enveloped viruses are normally negatively charged (39). Similar membrane-disrupting properties have been observed in other AMPs, such as LL-37 and temporins, which target enveloped viruses (40, 41). Consistently, hepcidin and epinecidin identified in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) can cause aggregation of viral particles after incubation, likely disrupting the viral membrane (15, 42). Although the potential interactions between MsPiscidin2 and MSRV G protein were shown using molecular docking analysis and two residues within the MsPiscidin2 were identified, further mutagenesis analysis is required to validate the contribution of these two residues to the antiviral activity of MsPiscidin2. The direct anti-viral activity of MsPiscidin2 was further confirmed via pre-incubation of MSRV with increasing concentrations of MsPiscidin2, of which led to a significant and dose-dependent reduction in the viral replication and CPE. Consistently, temporal analysis of viral replication demonstrated significant inhibitions of viral replication at all tested time points and further confirmed that MsPiscidin2 exhibited sustained inhibitory effects on MSRV replication.
The in vivo protective efficacy of MsPiscidin2 treatment further supports its antiviral potentials against MSRV infection. Co-administration of MsPiscidin2 with MSRV significantly delayed disease progression and increased survival rates in infected juvenile largemouth bass. Although MsPiscidin1 and MsPiscidin3 also demonstrated promising in vitro activities in enhancing cellular resistance to MSRV infection, their in vivo protective effects are not examined in this study due to their immunomodulatory nature. As their antiviral efficacy may depend on complex host immune dynamics that vary with the timing of peptide administration and viral infection, making it more challenging to interpret their in vivo antiviral activities using the current infection model. However, the encouraging in vitro data warrants further investigation and their in vivo protective effects will be explored when more mechanistic details regarding to their in vitro antiviral activities are obtained. In contrast to the potent in vitro antiviral efficacy of MsPiscidins2, the survival rate of infected fish following MsPiscidins2 is not optimal. This observed discrepancy may derive from the differing nature of in vitro and in vivo systems; in vitro models offer a controlled environment where the MsPiscidins2 concentration and exposure duration to viral particles are precisely maintained, whereas in vivo conditions involve rapid degradation of peptides by endogenous proteases, different clearance rates and variable distribution sites, all of which can reduce antiviral efficacy of MsPiscidins2 in vivo. Consequently, the practical application of AMPs in combating viral infection in aquaculture is still limited and further engineering of MsPiscidins2 (e.g., peptide cyclization) to increase its stability and optimization of delivery system to prolong the presence of administrated peptides are required.
In conclusion, our study identifies MsPiscidin2 as a potent antiviral peptide capable of directly inactivating MSRV, reducing viral replication in vitro, and enhancing fish survival in vivo. These findings expand our knowledge of antiviral functions of piscidins and establish a foundation for the development of AMP-based interventions against viral pathogens in aquaculture.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Ningbo University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. LN: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JC: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was funded by the Science and Technology Innovation Yongjiang 2035 Key Research and Development Project of Ningbo, grant number 2024Z279; the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, grant number LZYQ25C190001; the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo City, grant number 2024J447.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI was only used to check grammars, typos and revise ambiguous/misleading sentences in the manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1629256/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Chen N and Jiang C. Antimicrobial peptides: structure, mechanism, and modification. Eur J Med Chem. (2023) 255:115377. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115377
2. Li H, Niu J, Wang X, Niu M, and Liao C. The contribution of antimicrobial peptides to immune cell function: A review of recent advances. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:2278. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092278
3. Johnstone KF and Herzberg MC. Antimicrobial peptides: Defending the mucosal epithelial barrier. Front Oral Health. (2022) 3:958480. doi: 10.3389/froh.2022.958480
4. Steiner H, Hultmark D, Engström A, Bennich H, and Boman HG. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature. (1981) 292:246–8. doi: 10.1038/292246a0
5. Benfield AH and Henriques ST. Mode-of-action of antimicrobial peptides: membrane disruption vs. intracellular mechanisms. Front Med Technol. (2020) 2:610997. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2020.610997
6. Chen EH-L, Wang C-H, Liao Y-T, Chan F-Y, Kanaoka Y, Uchihashi T, et al. Visualizing the membrane disruption action of antimicrobial peptides by cryo-electron tomography. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5464. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41156-2
7. Qureshi A. A review on current status of antiviral peptides. Discov Viruses. (2025) 2:3. doi: 10.1007/s44370-024-00006-5
8. Vilas Boas LCP, Campos ML, Berlanda RLA, de Carvalho Neves N, and Franco OL. Antiviral peptides as promising therapeutic drugs. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. (2019) 76:3525–42. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03138-w
9. Zhao H, To KKW, Lam H, Zhou X, Chan JF-W, Peng Z, et al. Cross-linking peptide and repurposed drugs inhibit both entry pathways of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1517. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21825-w
10. Lee Y-CJ, Shirkey JD, Park J, Bisht K, and Cowan AJ. An overview of antiviral peptides and rational biodesign considerations. Biodesign Res. (2022) 2022:9898241. doi: 10.34133/2022/9898241
11. Barlow PG, Svoboda P, Mackellar A, Nash AA, York IA, Pohl J, et al. Antiviral activity and increased host defense against influenza infection elicited by the human cathelicidin LL-37. PloS One. (2011) 6:e25333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025333
12. Kalenik BM, Góra-Sochacka A, Stachyra A, Pietrzak M, Kopera E, Fogtman A, et al. Transcriptional response to a prime/boost vaccination of chickens with three vaccine variants based on HA DNA and Pichia-produced HA protein. Dev Comp Immunol. (2018) 88:8–18. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.07.001
13. Jang H-J, Lee H-J, Kang KS, Song K-D, Kim T-H, Song C-S, et al. Molecular responses to the influenza A virus in chicken trachea-derived cells. Poult Sci. (2015) 94:1190–201. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev033
14. Chinchar VG, Bryan L, Silphadaung U, Noga E, Wade D, and Rollins-Smith L. Inactivation of viruses infecting ectothermic animals by amphibian and piscine antimicrobial peptides. Virology. (2004) 323:268–75. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.02.029
15. Wang Y-D, Kung C-W, and Chen J-Y. Antiviral activity by fish antimicrobial peptides of epinecidin-1 and hepcidin 1–5 against nervous necrosis virus in medaka. Peptides. (2010) 31:1026–33. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.02.025
16. Masso-Silva JA and Diamond G. Antimicrobial peptides from fish. Pharmaceuticals. (2014) 7:265–310. doi: 10.3390/ph7030265
17. Katzenback BA. Antimicrobial peptides as mediators of innate immunity in teleosts. Biology. (2015) 4:607–39. doi: 10.3390/biology4040607
18. Huang H-N, Pan C-Y, and Chen J-Y. Grouper (Epinephelus coioides) antimicrobial peptide epinecidin-1 exhibits antiviral activity against foot-and-mouth disease virus in vitro. Peptides. (2018) 106:91–5. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.07.003
19. Wu Y, Yi S, Cheng Y, Yang S, and Fei H. A concise review on advancement of Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus (MSRV): Current status and challenges. Aquac Rep. (2023) 30:101551. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2023.101551
20. Yue G and Guo C. Strategies for managing major diseases in Asian seabass aquaculture. Anim Dis. (2025) 5:6. doi: 10.1186/s44149-025-00159-w
21. Qin Y, Zhang P, Zhang M, Guo W, Deng S, Liu H, et al. Isolation and identification of a new strain Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus (MSRV) from largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides in China. Aquaculture. (2023) 572:739538. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739538
22. Duan Y, Ouyang J, Mo G, Hao W, Zhang P, Yang H, et al. Defensing role of novel piscidins from largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) with evidence of bactericidal activities and inducible expressional delineation. Microbiol Res. (2022) 256:126953. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126953
23. Zhang X, Wang H, Wang Z, Shan L, Shen Y, He J, et al. New use of praziquantel as a broad-spectrum anti-parasitic agent in blocking MSRV infection. Aquaculture. (2025) 596:741847. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741847
24. Lyu S-J, Yuan X-M, Zhang H-Q, Shi W, Hang X-Y, Liu L, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel strain (YH01) of Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus and expression of its glycoprotein by the baculovirus expression system. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2019) 20:728–39. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900027
25. Zhang X, Xue M, Liu L, Wang H, Qiu T, Zhou Y, et al. Rhein: A potent immunomodulator empowering largemouth bass against MSRV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2024) 144:109284. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.109284
26. Reed LJ and Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am J Epidemiol. (1938) 27:493–7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118408
27. Nie L, Wu X-Y, Zhao Z-Y, Fei C-J, Zhu T-F, Shao J-Z, et al. Palmitoylation-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in teleosts highlights evolutionary divergence in immune regulation. Zool Res. (2025) 46:3–14. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.409
28. Honorato RV, Trellet ME, Jiménez-García B, Schaarschmidt JJ, Giulini M, Reys V, et al. The HADDOCK2.4 web server for integrative modeling of biomolecular complexes. Nat Protoc. (2024) 19:3219–41. doi: 10.1038/s41596-024-01011-0
29. Honorato RV, Koukos PI, Jiménez-García B, Tsaregorodtsev A, Verlato M, Giachetti A, et al. Structural biology in the clouds: The WeNMR-EOSC ecosystem. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:729513. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.729513
30. Valero Y, Saraiva-Fraga M, Costas B, and Guardiola FA. Antimicrobial peptides from fish: beyond the fight against pathogens. Rev Aquac. (2020) 12:224–53. doi: 10.1111/raq.12314
31. Cervera L, Arizcun M, Mercado L, Chaves-Pozo E, and Cuesta A. Synthetic antimicrobial Nkl and Dic peptides are immunomodulatory but only Dic peptide can be therapeutic against nodavirus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2024) 152:109772. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109772
32. Guo M, Wei J, Huang X, Huang Y, and Qin Q. Antiviral effects of β-defensin derived from orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2012) 32:828–38. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2012.02.005
33. Lin T-T, Sun Y-Y, Wang C-T, Cheng W-C, Lu I-H, Lin C-Y, et al. AI4AVP: an antiviral peptides predictor in deep learning approach with generative adversarial network data augmentation. Bioinform Adv. (2022) 2:vbac080. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbac080
34. Pan C-Y, Chen J-Y, Cheng Y-SE, Chen C-Y, Ni I-H, Sheen J-F, et al. Gene expression and localization of the epinecidin-1 antimicrobial peptide in the grouper (Epinephelus coioides), and its role in protecting fish against pathogenic infection. DNA Cell Biol. (2007) 26:403–13. doi: 10.1089/dna.2006.0564
35. Yang J, Lu X-J, Chai F-C, and Chen J. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of a piscidin gene in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Zool Res. (2016) 37:347–55. doi: 10.13918/j.issn.2095-8137.2016.6.347
36. Takiguchi T, Morizane S, Yamamoto T, Kajita A, Ikeda K, and Iwatsuki K. Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 augments interferon-β expression and antiviral activity induced by double-stranded RNA in keratinocytes. Br J Dermatol. (2014) 171:492–8. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12942
37. Sato E, Hiromatsu K, Murata K, and Imafuku S. Loss of ATP2A2 allows herpes simplex virus 1 infection of a human epidermis model by disrupting innate immunity and barrier function. J Invest Dermatol. (2018) 138:2540–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.05.019
38. Ahmed A, Siman-Tov G, Keck F, Kortchak S, Bakovic A, Risner K, et al. Human cathelicidin peptide LL-37 as a therapeutic antiviral targeting Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infections. Antiviral Res. (2019) 164:61–9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.02.002
39. Bohan D and Maury W. Enveloped RNA virus utilization of phosphatidylserine receptors: Advantages of exploiting a conserved, widely available mechanism of entry. PloS Pathog. (2021) 17:e1009899. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009899
40. Watts S, Hänni E, Smith GN, Mahmoudi N, Freire RVM, Lim S, et al. Human antimicrobial peptide inactivation mechanism of enveloped viruses. J Colloid Interface Sci. (2024) 657:971–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.11.055
41. Roy M, Lebeau L, Chessa C, Damour A, Ladram A, Oury B, et al. Comparison of anti-viral activity of frog skin anti-microbial peptides temporin-Sha and [K3]SHa to LL-37 and temporin-Tb against herpes simplex virus type 1. Viruses. (2019) 11:77. doi: 10.3390/v11010077
Keywords: piscidin, antimicrobial peptide, largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus, antiviral activity
Citation: Fei C, Wang Z, Hu Y, Nie L and Chen J (2025) A fish-specific antimicrobial peptide MsPiscidin2 inactivates MSRV and confers protection in largemouth bass. Front. Immunol. 16:1629256. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1629256
Received: 15 May 2025; Accepted: 09 June 2025;
Published: 23 June 2025.
Edited by:
Li Wang, Henan Institute of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Qingpi Yan, Jimei University, ChinaKang Yu, National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIH), United States
Copyright © 2025 Fei, Wang, Hu, Nie and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiong Chen, Y2hlbmppb25nQG5idS5lZHUuY24=
 Chenjie Fei
Chenjie Fei Ziwen Wang2,3
Ziwen Wang2,3 Li Nie
Li Nie Jiong Chen
Jiong Chen