- 1The State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Division of Immunology, Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 2Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Division of Immunology, Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
A Corrigendum on
17β-Estradiol promotes trained immunity in female against sepsis via regulating nucleus translocation of RelB
By Sun Z, Pan Y, Qu J, Xu Y, Dou H and Hou Y (2020). Front. Immunol. 11:1591. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01591
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 6F as published. The incorrect flow-cytometry results pictures were used in E2+TI+LPS group due to the inconsistent use of gating strategy and the misuse of the same picture. The corrected Figure 6F appears below.
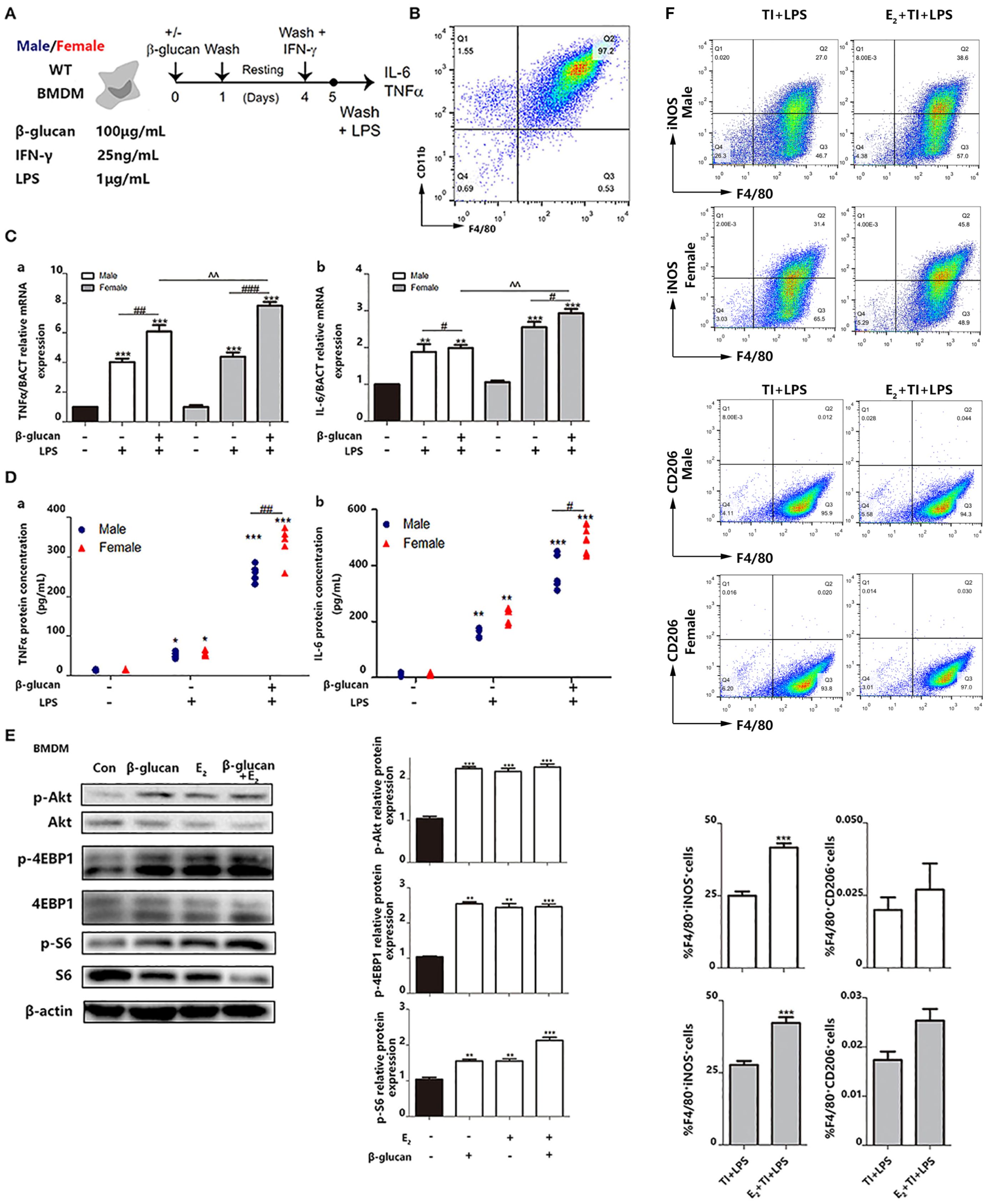
Figure 6. E2 is verified to facilitate trained immunity in primary BMDMs from female and male mice. (A) In vitro trained immunity model for BMDMs. (B) Flow cytometry was used for testing the purity of BMDMs induced by in vitro culture. (C) The mRNA levels of TNFα and IL-6 in male/female BMDMs were detected by qPCR to determine the different intensity of trained immunity between genders. (D) The protein concentrations of TNFα and IL-6 from the supernatant from male/female BMDM cultures were detected by ELISA to determine the different intensity of trained immunity between genders. (E) E2 activated hallmarks of trained immunity, such as Akt, 4EBP1, and S6 by western blot. (F) E2 promoted M1 polarization in TI + LPS group from male and female mice. Meanwhile, E2 maintained the M2 polarization to inhibit the effect of TI (n ≥ 3/group). #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001, paired Student’s t-test comparing β-glucan + LPS group and LPS group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, paired Student's t-test comparing with control group. ^^p < 0.01, paired Student’s t-test comparing between β-glucan + LPS groups with or without E2.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: estradiol, gender difference, macrophages, sepsis, trained immunity
Citation: Sun Z, Pan Y, Qu J, Xu Y, Dou H and Hou Y (2025) Corrigendum: 17β-Estradiol promotes trained immunity in female against sepsis via regulating nucleus translocation of RelB. Front. Immunol. 16:1629629. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1629629
Received: 16 May 2025; Accepted: 29 May 2025;
Published: 13 June 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Francesca Granucci, University of Milano-Bicocca, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Sun, Pan, Qu, Xu, Dou and Hou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huan Dou, ZG91aGF1bkBuanUuZWR1LmNu; Yayi Hou, eWF5aWhvdUBuanUuZWR1LmNu
 Zhiheng Sun
Zhiheng Sun Yuchen Pan1
Yuchen Pan1 Yayi Hou
Yayi Hou