- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Clinical Laboratory Medicine Research Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Sichuan Clinical Research Center for LaboratoryMedicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chengdu Shangjin Nanfu Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Medicine Research Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Sichuan Clinical Research Center for Laboratory Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4Department of Radiology, Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children of Ministry of Education, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
As an important inhibitory neurotransmitter, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) not only plays a key role in the central nervous system, but also has attracted wide attention in the tumor immune microenvironment in recent years. Studies have shown that tumor cells can synthesize GABA and use it to remodel the tumor microenvironment, thereby promoting the occurrence, development and metastasis of tumors. Although previous studies have revealed the important role of GABA in tumor immune escape, there are still many unknown areas of its mechanism, especially the heterogeneous manifestations in different tumor types and tissue environments. This review summarizes the immunomodulatory mechanisms of GABA in tumor-associated macrophages, CD8+ T cells and dendritic cells in the tumor immune microenvironment, and discusses its potential role in tumor immune escape and immunotherapy resistance, providing new ideas for the development of immunotherapeutic drugs targeting GABA receptors.
1 Introduction
Cancer remains a major global public health challenge, with incidence and mortality rates continuing to rise. According to the “Cancer Statistics, 2024” report, over 19 million new cancer cases were diagnosed worldwide in 2023, with certain tumor types such as breast cancer and lung cancer maintaining high incidence rates and showing significant variability in five-year survival rates among patients (1). Reviewing the history of cancer treatments, based on the NIH’s “Cancer Treatments: Past, Present, and Future” (2024), therapeutic approaches have evolved from traditional surgery and radiotherapy to chemotherapy, followed by targeted therapies and immunotherapies, greatly improving patient outcomes (2, 3). However, current treatments still face challenges posed by tumor heterogeneity and therapeutic resistance. Regarding cancer treatment strategies, recent research in “Different Strategies for Cancer Treatment: Targeting Cancer Cells or Their Neighbors?” (2025) highlights two primary approaches: direct targeting of tumor cells and modulation of the tumor microenvironment (4). The former achieves rapid tumor cell killing by targeting tumor-specific molecules but is prone to resistance development; the latter improves immune infiltration by regulating immune cells and stromal components, with complex mechanisms but considerable potential. Integrative treatment strategies that combine the advantages of both approaches are considered the future direction in oncology.
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA), a principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, plays a critical role in modulating neuronal excitability, exerting calming and sedative effects (5). Traditionally recognized for its neurological functions, GABA has recently garnered attention in oncology due to its aberrant upregulation in a variety of solid tumors, where elevated GABA levels have been correlated with poor clinical outcomes (6). Emerging evidence indicates that tumor cells not only possess the capacity to synthesize GABA but also exploit it to modulate the tumor microenvironment, thereby promoting tumor progression and metastasis (7).
Within the landscape of tumor immune evasion, cancer cells deploy multifaceted mechanisms to escape host immune surveillance, ultimately undermining the efficacy of immunotherapy (8). A well-characterized strategy involves the upregulation of immune checkpoint molecules such as programmed death-ligand 1, which inhibits T cell activation and effector function (9). Beyond checkpoint pathways, GABA has been shown to reprogram tumor-associated macrophages toward an immunosuppressive M2 phenotype, thereby fostering an immune-permissive tumor microenvironment (10). Moreover, GABA signaling through GABAA receptors can directly impair the cytotoxic activity of CD8+ T cells and reduce their production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). Simultaneously, GABA facilitates the infiltration and activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), contributing to a multilayered immune evasion network (11).
Therefore, it is of great significance to further study the immunomodulatory role of GABA in the tumor microenvironment. A deeper understanding of how GABA mediates immune escape and resistance to immunotherapy may not only shed light on the biological underpinnings of cancer progression but also pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies. This review aims to examine the emerging role of GABA in tumor immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance, and to explore its implications for the future of cancer immunotherapy.
2 Mechanisms and functions of GABA signaling
Recent studies have demonstrated that the role of GABA signaling within the tumor immune microenvironment shows significant heterogeneity across different cancer types and tissue contexts. For example, in glioblastoma, activation of the GABAB receptor on granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (gMDSCs) enhances L-arginine metabolism and NOS2 expression, promoting tumor growth; conversely, inhibition of GABABR prolongs survival in mouse models (12). In breast cancer, GABAergic signaling modulates tumor progression through distinct mechanisms: activation of the GABAA receptor δ subunit (GABRD) enhances GPT2-mediated metabolic reprogramming, promoting metastasis, while upregulation of the β3 subunit fosters clonal expansion and cell migration in triple-negative breast cancer (13). In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), GABA has been shown to promote proliferation via the GABAA receptor π subunit; paradoxically, some studies suggest it may suppress migration, indicating a complex bidirectional role. Moreover, in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), GABAergic signaling through distinct receptor subunits (such as α3, β3, π, θ) may exert context-dependent effects, with certain receptor profiles linked to tumor suppression (13). Recent studies have revealed significant differences in the expression of various GABA receptor subunits within immune cells. For example, the expression levels of the α3 and β2 subunits differ between T cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), which may lead to distinct responses to GABA signaling. Specifically, the α3 subunit may be involved in regulating immune cell activation and cytokine secretion, whereas the β2 subunit may influence cell polarization and immunosuppressive functions (10, 14). Selective modulation of different subunits not only helps to uncover the complex roles of GABA signaling in immune regulation but also provides a theoretical basis for the development of highly selective targeted drugs, thereby enabling precise immunotherapy strategies that improve efficacy while minimizing side effects. Collectively, these findings emphasize that the immunomodulatory effects of GABA are highly context-dependent and are shaped by tumor-intrinsic characteristics, tissue-specific microenvironments, and the composition of immune cell populations. GABA synthesis primarily depends on glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), which converts glutamate into GABA. GAD exists in two isoforms, GAD65(GAD2) and GAD67(GAD1), which play roles at the nerve terminals and in areas such as the cerebral cortex, respectively (15, 16). After synthesis, GABA undergoes metabolism via GABA transaminase (ABAT), which converts it into succinic semialdehyde, which is further transformed into succinate by succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH), entering the tricarboxylic acid(TCA) cycle for energy metabolism(Figure 1). Previous studies have observed GAD1 upregulation and ABAT downregulation in tumor cells (6). Additionally, GABA is taken up by glial cells and neurons through GABA transporters (GAT) and is either converted back into glutamate or used for the synthesis of new GABA (17). The balance between GABA synthesis and metabolism is crucial for the proper function of the nervous system, and its dysregulation is closely associated with various neurological disorders, such as epilepsy and anxiety (18, 19).
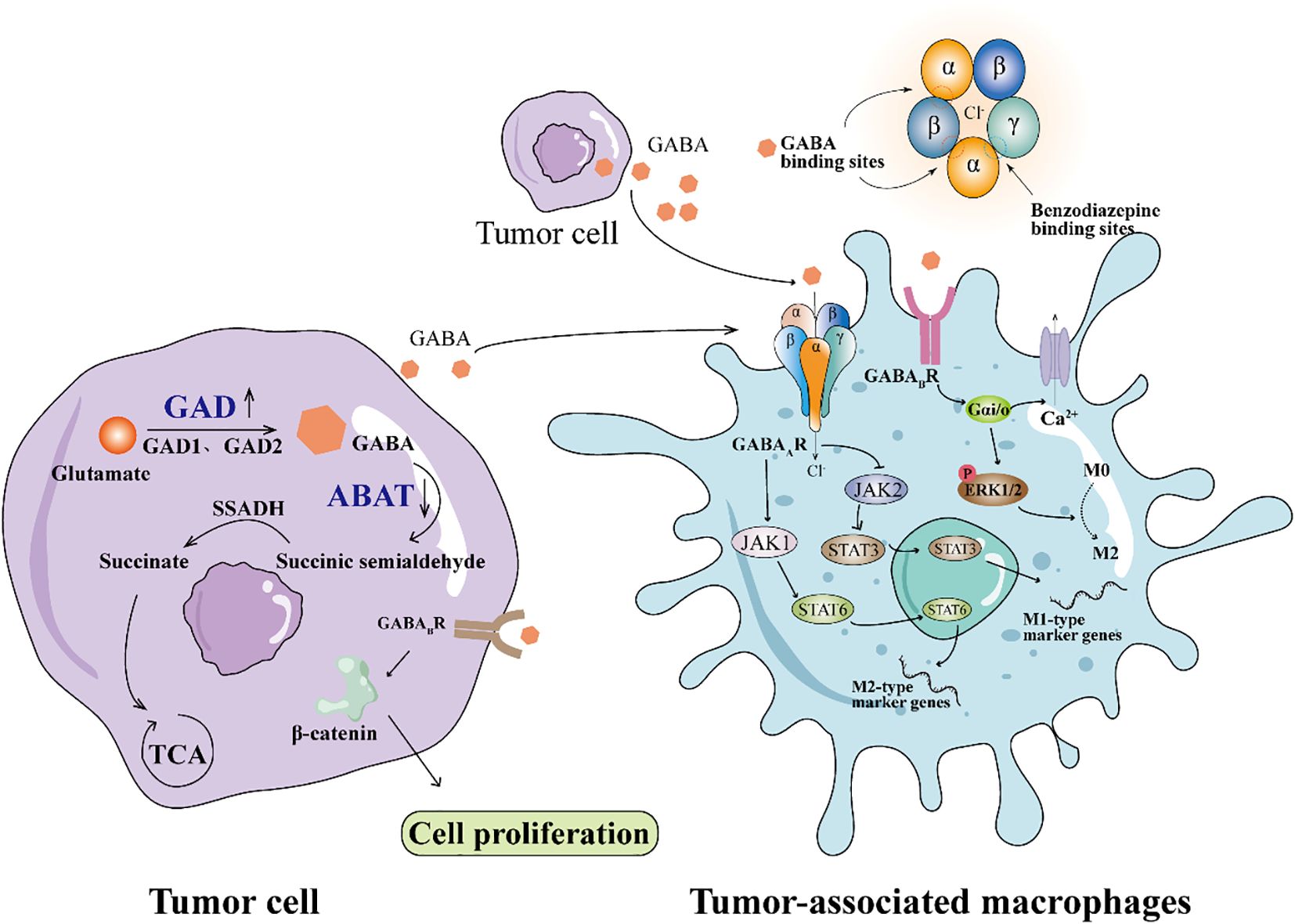
Figure 1. GABA signaling pathway in tumor microenvironment stimulates the polarization of macrophages to M2 type. Downregulation of GAD expression and downregulation of ABAT expression in tumor cells leads to GABA accumulation. GABAAR on the surface of TAMs binds GABA from tumor cells to activate JAK1/STAT6 signaling and promote M2 polarization. GABA couples GABABR to Gαi, activates ERK1/2 signaling pathway, and promotes M2 polarization.
The biological effects of GABA are primarily mediated through its receptors, including GABAA, GABAB, and GABAC receptors (20–22). GABAA receptors are ion channel receptors, and when GABA binds to them, Cl- flow into the cell, causing hyperpolarization of the neuron and inhibiting neural activity, thus mediating rapid inhibitory synaptic transmission (23). GABAA receptors are drug targets, and benzodiazepines enhance their effects, providing sedative and anti-anxiety properties (24, 25). In contrast, GABAB receptors are G-protein coupled receptors, which regulate Ca2+ and K+ channels to produce slower inhibitory effects, involved in long-term neural regulation, and play a broad role in learning, memory, and pain control (26, 27). GABAC receptors, primarily located in the retina (28), are ion channel receptors responsible for the rapid inhibitory transmission of visual information. These three receptor types each play a unique role in the nervous system, collectively maintaining the balance of neural function.
3 Role of GABA in tumor microenvironment
Tumor immune evasion refers to the ability of tumor cells to evade recognition and clearance by the host immune system, allowing the tumor to survive and develop under immune surveillance (29, 30). The primary function of the immune system is to maintain the health of the body by recognizing and attacking foreign substances, mutated cells, and tumor cells. However, tumor cells avoid this clearance by altering their surface characteristics or by modulating the immune environment. Tumor immune evasion is one of the major causes of cancer resistance and the progression of malignant tumors (31). Through immune evasion, tumor cells not only avoid detection by the immune system but may also accelerate tumor growth, metastasis, and the development of resistance to treatment. Studies have shown that GABA stimulates tumor cell proliferation by activating GABAB receptors (32). This process involves the inhibition of the GSK-3 signaling pathway, leading to the activation of β-catenin, which subsequently inhibit tumor cell proliferative capacity and impairs CD8+ T cell infiltration into tumors (6, 33). Mohita et al. (34) found that GABA promotes melanoma development by releasing a SNAR-dependent vesicle pathway. GABA signaling has an immunosuppressive effect in the tumor microenvironment, which makes GABA receptors a potential therapeutic target for cancer immunotherapy (35).
4 The influence of GABA on immune cells
4.1 The effect of GABA on TAM
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are important immune cells within the tumor microenvironment, primarily originating from circulating monocytes (36, 37). Tumors recruit these monocytes by secreting chemokines such as CCL2 and growth factors like CSF-1. These recruited monocytes differentiate into macrophages and become TAMs in response to local signals. The functional phenotype of TAMs is highly plastic and influenced by multiple signals within the tumor microenvironment. Pro-inflammatory stimuli such as IFN-γ and LPS drive TAMs toward an M1 phenotype, characterized by anti-tumor activity through the production of inflammatory cytokines and antigen presentation (38). In contrast, anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-4 and IL-13 promote M2 polarization, which supports tumor progression by facilitating immune suppression, angiogenesis, and tissue remodeling. Increasing evidence suggests that GABA signaling can modulate TAM polarization. GABA binds to GABA receptors on macrophages, leading to downstream signaling changes that favor M2 polarization. Dong et al. (39) showed that macrophages activate the JAK1/STAT6 signaling pathway via GABA, which promotes the expression of Arg1, a gene related to M2. GABA aiso inhibited the NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways, and decreased the expression of iNos related to M1 (Figure 1). This finding is consistent with previous research, and Zhang et al. (40) also confirmed that GABA can significantly reduce the nuclear localization of p65 in the NF-κB signaling pathway.
The changes in GABAA receptor (GABAAR) expression may form the basis for macrophage polarization. During the differentiation of monocytes into the M0 macrophage phenotype, the expression of the GABAAR β2 subunit increases significantly, while the expression of the GABAAR α4 subunit shows no significant change. When M0 macrophages polarize to the M1 phenotype, the expression of the GABAAR α4 subunit and GAD1 decreases, while the β2 subunit expression returns to monocyte levels, and the expression of GAT2 increases significantly (41). These changes diminish the response of GABAAR to GABA, thereby relieving GABA’s anti-inflammatory suppression and supporting the pro-inflammatory function of M1 macrophages. GABA Transporters(GAT) belongs to the SLC6A family, which includes GAT1–4 and is responsible for transporting GABA from the synaptic cleft or extracellular environment to the cell to maintain GABA homeostasis.Xia et al. (42) GAT2 deficiency in macrophages can increase intracellular betaine content, leading to hypoxanthine and S-adenosylmethionine accumulation (SAM), and the intracellular betaine/SAM/hypoxanthine metabolic pathway affects the methylation of the transcription factor KID3. It inhibits the formation of NLRP3-ASC-Caspase-1 complex and increases the intracellular OXPHOS level, thereby inhibiting the production of IL-1β in M1 macrophages. Liu et al. (43) found that GABA receptor agonists can promote the polarization of macrophages towards the M2 phenotype. Sun et al. (44) found that GABA-related genes can be used to judge the prognosis of glioma. Dou et al. (45) found that GABA secreted by oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) promotes macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype by activating the GABAB R1 and its downstream ERK and Ca²+ signaling pathways, which promoted EMT of OSCC in vivo(Figure 1). These results suggest that GABA may play a role in tumor immune escape by regulating the polarization of macrophages in the tumor microenvironment.
4.2 The effect of GABA on T cell
CD8+ T cells are a major subset of cytotoxic T lymphocytes, which express CD8 coreceptors and recognize antigens through MHC class I molecules. In the tumor microenvironment, CD8+ T cells are the core effector cells of anti-tumor immunity, and their activity is positively correlated with the prognosis of patients. Tharp et al. (46) found that in the fibrotic tumor microenvironment, TAMs initiate collagen biosynthesis through TGF-β signaling, creating a metabolic environment that depletes arginine and secretes proline and ornithine, thereby inhibiting CD8+ T cell antitumor responses. Previous studies have found that PMVK expression is increased in tumor tissues (47). Zhou et al. (11) observed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells that PMVK activity is negatively correlated with CD8+ T cell infiltration and immune evasion. Their study demonstrated that PMVK promotes the conversion of glutamate to GABA by phosphorylating threonine 576 at the C-terminus of GAD1, thereby increasing GABA synthesis. Furthermore, PMVK directly binds to and stabilizes ACAT1 protein, facilitating the acetylation of GABA to generate 4-Ac-GABA. 4-Ac-GABA binds to the α3 subunit of the GABAAR on the surface of CD8+ T cells, inhibiting AKT1 phosphorylation, which subsequently reduces the expression of CD8+ T cell activation markers such as IFN-γ and granzyme B, and decreases their infiltration into the tumor microenvironment (Figure 2). Immunofluorescence conducted by Sparrow et al. (48) confirmed the presence of GABAAR subunits on the surface of both mouse and human T cells. Mouse T cells predominantly express the α2, α3, α5, β2, β3, γ1, and δ subunits, whereas human T cells highly express the α1, α5, β1, π, ρ1, and ρ2 subunits, with the ρ2 subunit being enriched on the surface of human T cells. Activation of GABAAR by benzodiazepines or neurosteroids significantly inhibited the proliferation of both mouse and human T cells, and this effect was reversed by GABAA receptor antagonists. These findings indicate that GABAA receptors play a crucial role in regulating T cell function; their activation can suppress T cell proliferation and immune activity, thereby potentially contributing to the regulation of immune responses and tumor immune evasion.
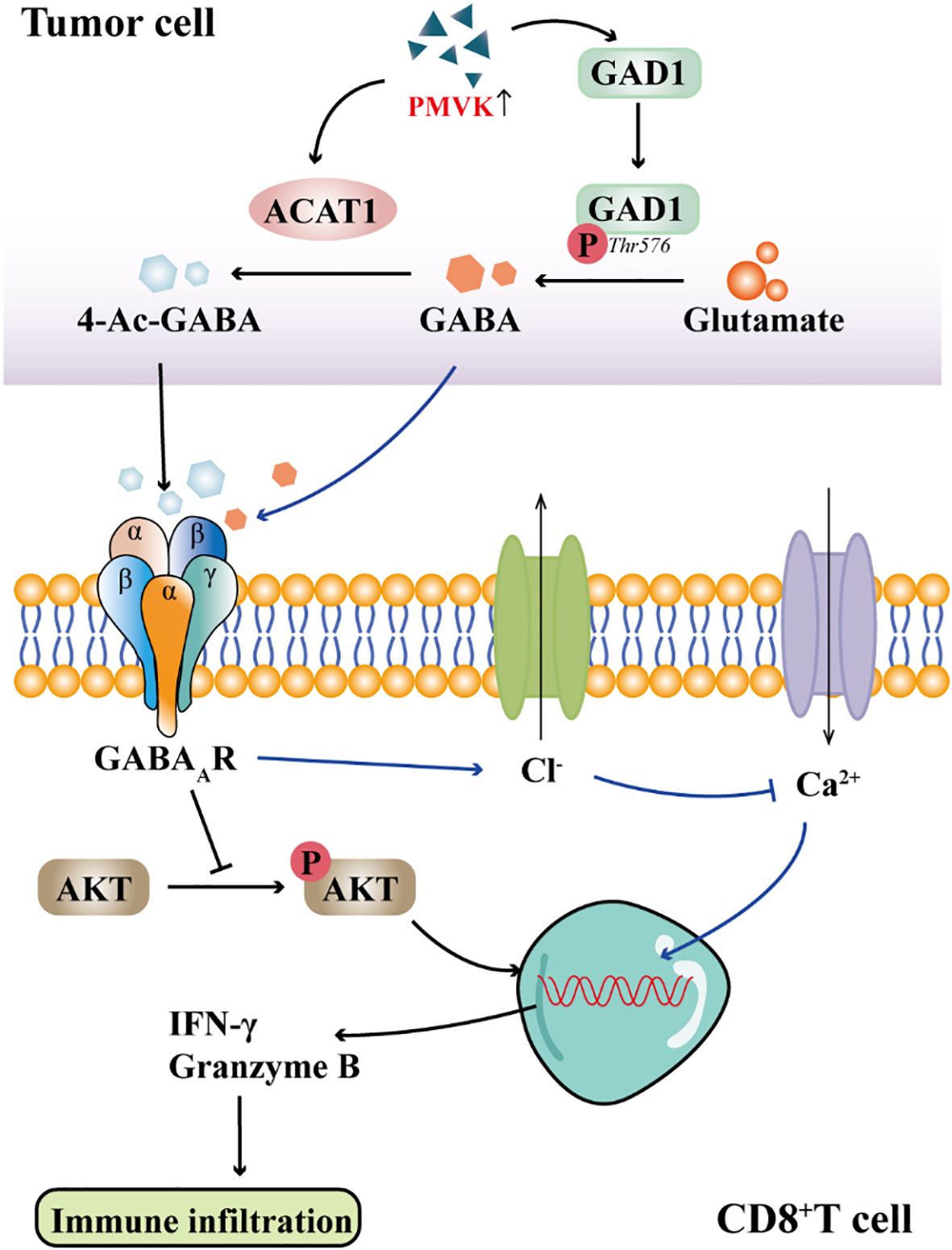
Figure 2. GABA signaling inhibits CD8+T cell immune infiltration. GABAAR on the membrane of CD8+T cells binds to 4-Ac-GABA from tumor cells, inhibits the phosphorylation of AKT and prevents the production of IFN-γ and Granzyme B, thereby affecting T cell activation and immune infiltration. Activation of GABAAR results in Cl− efflux, inhibition of Ca2+ influx, and ultimately inhibition of T cell activation.
The enhancement of Ca2+ signaling can accelerate the activation process of T cells, thereby improving their responsiveness to tumor cells. Zhang et al. (40) implanted sustained-release GABA particles into muMt-/- mice and found that tumor growth in the mice was significantly increased. Further investigation revealed that GABA might regulate CD8+ T cell function by binding to the GABAAR on the surface of T cells, inhibiting Ca2+ influx.Consistent with these findings, Tian et al. (49) also discovered that GABA activates GABAAR on the surface of T cells, leading to the opening of Cl- channels, Cl- efflux, and membrane depolarization, which in turn inhibits Ca2+ influx (Figure 2). Ca2+ influx is a critical step for the activation of naïve T cells and the function of effector T cells. Activation of GABA receptors primarily causes T cells to arrest in the G0/G1 phase, preventing their entry into the proliferative cycle and thereby inhibiting clonal expansion. Although the expression of GABAAR subunits has been identified in T cells, the specific role of these subunits in regulating T cell function is not well defined. The effects of different subunits on T cell activity, polarization and immune escape may be different, and further studies are needed to clarify.
4.3 The effect of GABA on DCs
Dendritic cells (DCs) are key antigen-presenting cells that bridge innate and adaptive immunity. They capture and internalize foreign antigens, process them into peptide fragments, and present these peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules to T cell receptors (50). This process activates and directs T cells to mount a targeted immune response against specific pathogens or abnormal cells. Dendritic cells promote the recognition and elimination of tumor cells by activating CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and CD4+ helper T cells (51). In addition, Dcs regulate the immune microenvironment, influencing the development of immune tolerance and immune evasion. Tumor cells and their surrounding stroma secrete various immunosuppressive factors, such as TGF-β、IL-10 and VEGF, which inhibit the maturation and activation of dendritic cells, reducing their antigen-presenting capacity (52). In addition, metabolic products in the tumor microenvironment, such as lactate, can also suppress DCs function (53). Studies have shown that GABA receptors are not only present on T cells, B cells, and macrophages, but their expression profile also includes DCs (54). GABA is synthesized from glutamate catalyzed by GAD, which is expressed in DCs, indicating that DCs have the ability to produce GABA. At the same time, DCs express GATs on their surface, such as GAT1 and GAT3, enabling them to uptake extracellular GABA (55). Bekić et al. (56) found that in DCs, activation of the GABABR induces a conformational change that couples with intracellular Gαi proteins, thereby activating G protein-coupled signaling pathways and inhibiting adenylate cyclase activity. This leads to a reduction in intracellular cAMP levels. The lowered cAMP levels promote the transition of DCs from an “immature” to a “mature” phenotype, increasing the expression of MHC II, CD86, and CD40, as well as the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, which in turn induces T cell differentiation toward the Th1 phenotype. This study reveals that monocyte-derived DCs may promote T cell proliferation and Th1 polarization through the GABABR/cAMP signaling pathway. Similarly, Huang et al. (57) also demonstrated that inhibiting the expression of GABABR in DCs can suppress IL-6 production and hinder the differentiation of DCs into Th17 cells. Recent studies have further confirmed the regulatory role of GABA on dendritic cells (DCs) within the tumor microenvironment (TME). For example, one study demonstrated that tumor cells synthesize GABA through the expression of GAD1 and activate the β-catenin signaling pathway via GABA_B receptors, thereby inhibiting the recruitment of CD103+ DCs and the infiltration of T cells into the tumor, ultimately promoting immune evasion and tumor progression (6). These findings indicate that GABA not only exerts effects in in vitro monocyte-derived DC cultures but also modulates anti-tumor immune responses by affecting DC function within the tumor microenvironment. In summary, while the role of GABA in regulating T cells and macrophages has been relatively well studied, its effects on dendritic cells—especially within the tumor microenvironment—remain underexplored. Current evidence suggests that GABAergic signaling influences DC maturation and cytokine production, thereby shaping downstream T cell polarization. However, the specific consequences of this modulation in cancer settings, including its contribution to immune evasion or resistance to immunotherapy, warrant further investigation. In addition, Current research on the regulation of dendritic cells (DCs) by GABA is limited and yields somewhat contradictory results. On one hand, some studies suggest that GABA can promote DC maturation and antigen-presenting functions, thereby enhancing immune activation. On the other hand, other studies indicate that GABA may inhibit DC activity, reducing their capacity to stimulate T cells. These conflicting findings may be due to influences from different tumor types and microenvironmental factors, such as local cytokine levels, metabolic states, and interactions with other immune cells. Additionally, variations in experimental models and methodologies may also contribute to inconsistent observations. In summary, a deeper investigation into the specific effects of GABA on DCs within diverse tumor microenvironments is crucial for understanding its immunoregulatory roles and for developing related immunotherapeutic strategies.
5 GABA signaling pathway plays a key role in the mechanism of tumor immunosuppression and drug resistance
Studies have shown that GABA can upregulate the expression of PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells by activating the STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby suppressing anti-tumor immune responses (58). PD-L1 is an immune checkpoint protein expressed on tumor cells that binds to the PD-1 receptor on T cells, inhibiting their activity and promoting tumor immune evasion. As a key immune checkpoint molecule, PD-L1 interaction with PD-1 on T cells suppresses T cell function, allowing tumor cells to escape immune surveillance (59, 60). STAT3 is a well-established oncogenic signaling pathway in various types of cancers, and its sustained activation is closely associated with tumor proliferation, metastasis, and immune evasion. One study demonstrated that GABA and its derivative baclofen can downregulate the mRNA and protein levels of the E3 ubiquitin ligase STUB1, thereby enhancing the stability of PD-L1 and ultimately increasing its expression (61). This mechanism indicates that GABA not only functions within the nervous system but may also influence tumor immune evasion in the tumor microenvironment by regulating the expression of immune checkpoint proteins. Moreover, the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAAR, QH-II-066, enhances GABA receptor function and can synergize with PD-L1 inhibitors to improve anti-tumor efficacy. In a mouse tumor model where PD-1 blockade therapy was ineffective, Huang et al. (6) found that the use of a GAD1 inhibitor alone, or in combination with an anti-PD-1 antibody, significantly reduced tumor volume. Switchenko et al. (62) found that benzodiazepines bind to the αγ subunit interface of the GABAAR, enhancing the binding efficiency of GABA to its receptor and significantly increasing the chloride ion permeability of the melanoma cell membrane, thereby promoting chloride influx into the cells. Following benzodiazepine treatment, melanoma cells exhibited mitochondrial membrane depolarization, leading to apoptosis, a process associated with the p53 signaling pathway and cytokine expression. Regarding cancer stem cells, the π subtype of the GABA receptor (GABRP) is highly expressed on the membrane surface of triple-negative breast cancer stem cells. Li et al. (63) found that GABRP maintains the membrane abundance of EGFR by inhibiting its lysosomal degradation. The sustained activation of EGFR promotes the phosphorylation of ERK (p-ERK), thereby enhancing the self-renewal and proliferation of cancer stem cells. More importantly, although conventional chemotherapeutic agents such as paclitaxel and doxorubicin can induce the enrichment of cancer stem cells, knockdown of GABRP reverses this effect, suggesting that GABRP is one of the key mediators of chemotherapy resistance. This study indicates that targeting GABRP may be a promising strategy to overcome immune resistance. In addition, GABA signaling is also closely associated with the recruitment of tumor-associated macrophages. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, Jiang et al. (64) found that although GABRP does not exert its oncogenic effects through the conventional GABA/Cl- signaling pathway, it promotes the infiltration of immunosuppressive macrophages by interacting with KCNN4 and activating the Ca²+/NF-κB/CXCL5-CCL20 axis. This macrophage infiltration not only contributes to the formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment but also impairs T cell function and cooperates with other mechanisms to induce resistance to immunotherapy. Tumor immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance are closely related but not entirely equivalent concepts. Tumor immune evasion primarily refers to the processes by which cancer cells avoid recognition and elimination by the immune system through mechanisms such as downregulating antigen expression, secreting immunosuppressive factors, and recruiting suppressive immune cells. In contrast, immunotherapy resistance specifically describes the phenomenon where tumors show no response or reduced efficacy following treatments like immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies). Recent studies have revealed that GABA signaling is involved not only in classical immune evasion but also in mediating immunotherapy resistance by regulating immune checkpoint molecule expression, promoting the accumulation of immunosuppressive cells (such as regulatory T cells and tumor-associated macrophages), and suppressing the activity of effector CD8+ T cells (11, 40, 65). For example, GABA, through activation of GABAB receptors and downstream pathways, enhances the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, reduces infiltration and activity of anti-tumor T cells, thereby diminishing the efficacy of immunotherapy (66). Furthermore, currently, no GAD1-specific small-molecule inhibitors have entered cancer clinical trials. However, a preclinical study has shown that 3-mercaptopropionic acid (3−MPA), as a GAD1 inhibitor, can exert antitumor effects in osteosarcoma models by modulating the Wnt/β−catenin signaling pathway, suggesting that targeting GABA synthesis or metabolic pathways may hold therapeutic potential (67). Overall, these insights highlight the potential of targeting GABA signaling pathways as a novel strategy to overcome immunotherapy resistance.
6 Clinical translation and future perspectives
Despite the growing body of evidence implicating GABAergic signaling in tumor progression and immune modulation, the clinical translation of GABA-targeted therapies remains challenging. Most current findings are derived from in vitro studies or murine models, and several key barriers must be addressed before clinical application can be realized. First, off-target effects are a significant concern, especially given the widespread expression of GABA receptors and enzymes in both tumor and non-tumor tissues (68). Second, receptor-subtype selectivity remains poorly defined in the context of the tumor microenvironment (TME), where multiple GABA receptor subtypes may exhibit divergent roles across cell types. Third, the blood–tumor barrier (BTB) poses a major pharmacological obstacle, limiting the bioavailability of systemically administered agents to solid tumors. Finally, the dose-dependent neurotoxicity of GABAergic modulators, particularly in the central nervous system, necessitates careful safety evaluation. To move toward translational application, it is critical to integrate GABA-targeted strategies into the broader landscape of cancer immunotherapy. Recent studies have demonstrated how soluble PD-L1, cytokine profiles, and lymphocyte subsets can serve as circulating biomarkers to predict response to immune checkpoint inhibitors, particularly in melanoma (69). Moreover, next-generation CAR T-cell therapies are being engineered to resist hostile metabolic environments, such as hypoxia and high lactate, by enhancing mitochondrial resilience—thereby improving efficacy in solid tumors (70). In gastric cancer, evolving insights into the PD-1/PD-L1 axis have highlighted the need for combinatorial checkpoint blockade and personalized immunotherapy based on TME profiling (71). Additionally, interrupting extracellular vesicle-mediated communication between tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) offers a novel approach to reprogramming the immunosuppressive TME (72). Combination strategies involving GABA-targeted therapies are an exciting and evolving frontier in cancer immunotherapy. Beyond PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, future research may explore the integration of GABA modulators with other immunotherapeutic approaches such as CTLA-4 inhibitors, CAR-T cells, and oncolytic viruses. These combinations may synergistically reshape the tumor immune microenvironment while mitigating adverse effects. Additionally, co-administration with metabolic reprogramming agents, cytokine inhibitors, or neuroprotective compounds may further enhance therapeutic efficacy and safety. Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge the ongoing role of traditional medicine, particularly in regions where herbal and mineral-based therapies remain widely used. Several recent studies have investigated both the mechanisms and clinical impact of traditional formulations, including the potential involvement of ion channels and metabolic pathways in the anticancer activity of so-called “toxic medicines” used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) (73, 74). Clinical reports have also demonstrated meaningful effects of traditional medicine on cancer outcomes (75, 76). Notably, biomarker-guided integration of traditional and modern therapies is emerging as a translationally viable direction. For instance, a recent study demonstrated that traditional medicine could counteract Trichostatin A–induced esophageal cancer progression when combined with biomarker-based strategies (77). These findings highlight the potential of holistic and multi-modal treatment paradigms in the context of GABA-targeted cancer immunotherapy. Taken together, the future of GABA-targeted cancer immunotherapy will likely depend on synergizing metabolic modulation with immunologic precision, as well as overcoming structural and pharmacodynamic barriers through advanced drug delivery and rational combination strategies.
7 Conclusion
In this review, we summarized the mechanisms of GABA synthesis and metabolism, as well as its immunosuppressive effects within the tumor microenvironment. We focused on how GABA influences tumor immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance by modulating key immune cells, including T cells, TAMs, and DCs. Although numerous studies have preliminarily revealed the pivotal role of GABA signaling in reshaping the tumor immune microenvironment and promoting immune evasion, its immunoregulatory mechanisms remain largely unclear. GABA suppresses the anti-tumor activity of various immune cells, including T cells and macrophages, but the specific receptor subtypes, signaling pathways, and functional differentiation involved remain to be fully elucidated. Moreover, the GABA pathway exhibits significant heterogeneity across different tumor types and tissue contexts. In most peripheral solid tumors, elevated expression of GAD1 and downregulation of GABA-degrading enzyme ABAT in tumor cells lead to the accumulation of GABA in the tumor microenvironment, thereby promoting tumor growth and immune evasion (78). In contrast, in brain metastases, upregulation of ABAT is frequently observed, facilitating the catabolism of neuron-derived GABA for tumor energy metabolism, suggesting that the function of GABA signaling varies dramatically depending on the tumor context. These contrasting roles likely arise from context-specific factors such as differences in GABA receptor subtype expression, microenvironmental signals (e.g., cytokines, cell types, neuronal innervation), and regional metabolic constraints (78). Understanding these determinants will be crucial for developing tissue-selective GABA-targeted strategies.
Emerging technologies such as single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics hold great promise in this regard, enabling high-resolution dissection of GABA signaling networks across diverse cellular subsets and anatomical regions (79, 80). For example, single-cell studies have identified novel exhausted CD8+ T-cell markers in breast cancer, revealed drug-tolerant persister cell vulnerabilities in colorectal cancer (81), and mapped glioma cell motility modulated by voltage-gated sodium channel β3 subunits (82). These insights underscore the power of single-cell approaches to uncover cellular heterogeneity and rare functional states. Compared to traditional bulk RNA sequencing, which captures averaged gene expression across mixed populations, single-cell analyses offer finer granularity and can resolve intra-tumoral heterogeneity, although at the cost of higher technical complexity and resource demands. A combination of both strategies may provide a more comprehensive understanding of the GABAergic immunoregulatory landscape. Additionally, the cellular sources of GABA in the tumor microenvironment remain poorly characterized; B cells, tumor cells, and even neurons may all contribute to its synthesis and secretion, forming a complex immunoregulatory network. In terms of therapeutic strategies, targeting GABA-synthesizing enzymes or receptors to enhance anti-tumor immunity has shown promise in animal models. However, most related studies remain at the preclinical stage, lacking systematic safety evaluations and clinical evidenc. Future research should systematically compare the immunoregulatory effects of GABA signaling across multiple tumor models to identify suitable therapeutic targets and responsive patient populations. Integrating advanced techniques such as single-cell genomics and spatial transcriptomics will be essential for elucidating the cellular sources and functional pathways of intratumoral GABA signaling. Furthermore, exploring synergistic mechanisms with existing immunotherapies—such as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors—may provide both theoretical support and practical strategies for the clinical translation of GABA-targeted interventions. Given the critical role of GABA in the nervous system, therapies targeting GABA signaling may cause various neurological side effects such as sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor dysfunction. These adverse effects mainly result from systemic modulation of GABA receptors in the central nervous system. To overcome this challenge, recent studies have explored strategies for tumor microenvironment-specific modulation (83). These include utilizing nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for targeted transport, designing prodrugs that are locally activated within tumors to reduce systemic exposure, and developing highly selective agents targeting specific GABA receptor subtypes to minimize central nervous system involvement (84). Such approaches not only improve the safety and efficacy of treatment but also offer new avenues for precise immunotherapy targeting GABA signaling in tumors (85). Finally, future studies should also focus on how GABA-mediated intercellular communication dynamically regulates the immune landscape—balancing immune activation, suppression, and cell fate decisions—and how multi-target strategies combining GABA receptor modulators with other checkpoint inhibitors or metabolic regulators may help overcome tumor immune evasion. By leveraging the convergence of immunology, metabolism, and spatial genomics, the next phase of GABA-based immunotherapy research will provide new theoretical foundations and translational strategies for personalized cancer treatment.
Author contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
TThe author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
2. Klein C, Brinkmann U, Reichert JM, and Kontermann RE. The present and future of bispecific antibodies for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2024) 23:301–19. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-00896-6
3. Sonkin D, Thomas A, and Teicher BA. Cancer treatments: Past, present, and future. Cancer Genet. (2024) 286-287:18–24. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2024.06.002
4. Liu H and Dilger JP. Different strategies for cancer treatment: Targeting cancer cells or their neighbors? Chin J Cancer Res = Chung-kuo yen cheng yen chiu. (2025) 37:289–92. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2025.02.12
5. Piot L, Heroven C, Bossi S, Zamith J, Malinauskas T, Johnson C, et al. GluD1 binds GABA and controls inhibitory plasticity. Science. (2023) 382:1389–94. doi: 10.1126/science.adf3406
6. Huang D, Wang Y, Thompson JW, Yin T, Alexander PB, Qin D, et al. Cancer-cell-derived GABA promotes β-catenin-mediated tumour growth and immunosuppression. Nat Cell Biol. (2022) 24:230–41. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00820-9
7. Joghataei MT, Bakhtiarzadeh F, Dehghan S, Ketabforoush A, and Golab F. Zarbakhsh S et al: The role of neurotransmitters in glioblastoma multiforme-associated seizures. Int J Dev Neurosci. (2023) 83:677–90. doi: 10.1002/jdn.10294
8. Huang Q, Lei Y, Li X, Guo F, and Liu M. A highlight of the mechanisms of immune checkpoint blocker resistance. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:580140. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.580140
9. Yu J, Ling S, Hong J, Zhang L, Zhou W, Yin L, et al. TP53/mTORC1-mediated bidirectional regulation of PD-L1 modulates immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11(11):e007479. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007479
10. Bao H, Peng Z, Cheng X, Jian C, Li X, Shi Y, et al. GABA induced by sleep deprivation promotes the proliferation and migration of colon tumors through miR-223-3p endogenous pathway and exosome pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer research: CR. (2023) 42:344. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02921-9
11. Zhou X, Chen Z, Yu Y, Li M, Cao Y, Prochownik EV, et al. Increases in 4-Acetaminobutyric acid generated by phosphomevalonate kinase suppress CD8(+) T cell activation and allow tumor immune escape. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2024) 11:e2403629. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403629
12. Pathak A, Palasalava S, Knott MV, Colon B, Ciervo E, Zhou Y, et al. γ-aminobutyric acid receptor B signaling drives glioblastoma in females in an immune-dependent manner. bioRxiv: preprint server Biol. (2024). doi: 10.1101/2024.07.18.603996
13. Li TJ, Jiang J, Tang YL, and Liang XH. Insights into the leveraging of GABAergic signaling in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:14498–510. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6102
14. Deng Z, Li D, Wang L, Lan J, Wang J, and Ma Y. Activation of GABA(B)R attenuates intestinal inflammation by reducing oxidative stress through modulating the TLR4/myD88/NLRP3 pathway and gut microbiota abundance. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 13(9):1141. doi: doi:10.3390/antiox13091141
15. Wang J, Owji AP, Kittredge A, Clark Z, Zhang Y, and Yang T. GAD65 tunes the functions of Best1 as a GABA receptor and a neurotransmitter conducting channel. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:8051. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52039-5
16. Bolneo E, Chau PYS, Noakes PG, and Bellingham MC. Investigating the role of GABA in neural development and disease using mice lacking GAD67 or VGAT genes. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(14):7965. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147965
17. Eprintsev AT, Anokhina GB, Shakhov ZN, Moskvina PP, and Igamberdiev AU. The role of glutamate metabolism and the GABA shunt in bypassing the tricarboxylic acid cycle in the light. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(23):12711. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312711
18. Perucca E, White HS, and Bialer M. New GABA-targeting therapies for the treatment of seizures and epilepsy: II. Treatments Clin Dev CNS Drugs. (2023) 37:781–95. doi: 10.1007/s40263-023-01025-4
19. Perucca E, Bialer M, and White HS. New GABA-targeting therapies for the treatment of seizures and epilepsy: I. Role of GABA as a modulator of seizure activity and recently approved medications acting on the GABA system. CNS Drugs. (2023) 37:755–79. doi: 10.1007/s40263-023-01027-2
20. Shaye H, Stauch B, Gati C, and Cherezov V. Molecular mechanisms of metabotropic GABA(B) receptor function. Sci Adv. (2021) 7(22):eabg3362. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg3362
21. Evenseth LSM, Gabrielsen M, and Sylte I. The GABA(B) receptor-structure, ligand binding and drug development. Molecules. (2020) 25(13):3093. doi: 10.3390/molecules25133093
22. Qian X, Zhao X, Yu L, Yin Y, Zhang XD, Wang L, et al. Current status of GABA receptor subtypes in analgesia. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115800. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115800
23. Sente A, Desai R, Naydenova K, Malinauskas T, Jounaidi Y, Miehling J, et al. Differential assembly diversifies GABA(A) receptor structures and signalling. Nature. (2022) 604:190–4. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04517-3
24. Thompson SM. Modulators of GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders: past, present, and future. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2024) 49:83–95. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01728-8
25. Mendes FRS, da Silva AW, Ferreira MKA, Rebouças EL, Moura Barbosa I, da Rocha MN, et al. GABA(A) and serotonergic receptors participation in anxiolytic effect of chalcones in adult zebrafish. J Biomol Struct Dyn. (2023) 41:12426–44. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2167116
26. Osse AML, Pandey RS, Wirt RA, Ortiz AA, Salazar A, Kimmich M, et al. Reduction in GABAB on glia induce Alzheimer’s disease related changes. Brain Behav Immun. (2023) 110:260–75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.03.002
27. Cheng YT, Luna-Figueroa E, Woo J, Chen HC, Lee ZF, Harmanci AS, et al. Inhibitory input directs astrocyte morphogenesis through glial GABA(B)R. Nature. (2023) 617:369–76. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06010-x
28. Dai M and Liang PJ. GABA receptors mediate adaptation and sensitization processes in mouse retinal ganglion cells. Cognit Neurodyn. (2024) 18:1021–32. doi: 10.1007/s11571-023-09950-2
29. Xie J, Liu W, Deng X, Wang H, Ou X, An X, et al. Paracrine orchestration of tumor microenvironment remodeling induced by GLO1 potentiates lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Advanced Sci. (2025) 2025:e00722. doi: 10.1002/advs.202500722
30. Xie J, Xie Y, Tan W, Ye Y, Ou X, Zou X, et al. Deciphering the role of ELAVL1: Insights from pan-cancer multiomics analyses with emphasis on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Trans Internal Med. (2025) 13:138–55. doi: 10.1515/jtim-2025-0009
31. Xie J, Lin X, Deng X, Tang H, Zou Y, Chen W, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles: regulators and therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Drug resistance (Alhambra Calif). (2025) 8:2. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.152
32. Zhou Y, Khawkhiaw K, Thithuan K, and Saengboonmee C. Activation of the γ-aminobutyric acid receptor type B suppresses the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. (2025) 45:1513–23. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17533
33. Yeo M, Chen Y, Jiang C, Chen G, Wang K, Chandra S, et al. Repurposing cancer drugs identifies kenpaullone which ameliorates pathologic pain in preclinical models via normalization of inhibitory neurotransmission. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:6208. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26270-3
34. Tagore M, Hergenreder E, Perlee SC, Cruz NM, Menocal L, Suresh S, et al. GABA regulates electrical activity and tumor initiation in melanoma. Cancer Discov. (2023) 13:2270–91. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0389
35. Yang Y, Ren L, Li W, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Ge B, et al. GABAergic signaling as a potential therapeutic target in cancers. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 161:114410. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114410
36. Xie J, Liu M, Deng X, Tang Y, Zheng S, Ou X, et al. Gut microbiota reshapes cancer immunotherapy efficacy: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. iMeta. (2024) 3:e156. doi: 10.1002/imt2.156
37. Cheng K, Cai N, Zhu J, Yang X, Liang H, and Zhang W. Tumor-associated macrophages in liver cancer: From mechanisms to therapy. Cancer Commun (London England). (2022) 42:1112–40. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12345
38. Li M, Yang Y, Xiong L, Jiang P, Wang J, and Li C. Metabolism, metabolites, and macrophages in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:80. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01478-6
39. Dong Y, Wang G, Nie D, Xu Y, Bai X, Lu C, et al. Tumor-derived GABA promotes lung cancer progression by influencing TAMs polarization and neovascularization. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 126:111217. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111217
40. Zhang B, Vogelzang A, Miyajima M, Sugiura Y, Wu Y, Chamoto K, et al. B cell-derived GABA elicits IL-10(+) macrophages to limit anti-tumour immunity. Nature. (2021) 599:471–6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04082-1
41. Ruiz-Rodríguez VM, Torres-González CA, Salas-Canedo KM, Pecina-Maza NQ, Martínez-Leija ME, Portales-Pérez DP, et al. Dynamical changes in the expression of GABAergic and purinergic components occur during the polarization of THP-1 monocytes to proinflammatory macrophages. Biochem Biophys Rep. (2023) 36:101558. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101558
42. Xia Y, He F, Wu X, Tan B, Chen S, Liao Y, et al. GABA transporter sustains IL-1β production in macrophages. Sci Adv. (2021) 7(15):eabe9274. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe9274
43. Liu Q, Li Y, Shi Y, Tan J, Yan W, Zhang J, et al. The protective effect of gamma aminobutyric acid B receptor activation on sympathetic nerve remodeling via the regulation of M2 macrophage polarization after myocardial infarction. Rev Port Cardiol. (2023) 42:125–35. doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2021.10.011
44. Sun S, Chen X, Ding N, Zhang M, Li X, Chen L, et al. : Gamma-aminobutyric acid-mediated neuro-immune interactions in glioblastoma: Implications for prognosis and immunotherapy response. Life Sci. (2024) 357:123067. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123067
45. Dou Z, Li M, Shen Z, Jiang H, Pang X, Li T, et al. GAD1-mediated GABA elicits aggressive characteristics of human oral cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 681:80–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.09.041
46. Tharp KM, Kersten K, Maller O, Timblin GA, Stashko C, Canale FP, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages restrict CD8(+) T cell function through collagen deposition and metabolic reprogramming of the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat Cancer. (2024) 5:1045–62. doi: 10.1038/s43018-024-00775-4
47. Park SS, Kwon MR, Ju EJ, Shin SH, Park J, Ko EJ, et al. Targeting phosphomevalonate kinase enhances radiosensitivity via ubiquitination of the replication protein A1 in lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:3583–94. doi: 10.1111/cas.15896
48. Sparrow EL, James S, Hussain K, Beers SA, Cragg MS, and Bogdanov YD. Activation of GABA(A) receptors inhibits T cell proliferation. PloS One. (2021) 16:e0251632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251632
49. Tian J, Dang H, O’Laco KA, Song M, Tiu BC, Gilles S, et al. Homotaurine treatment enhances CD4(+) and CD8(+) regulatory T cell responses and synergizes with low-Dose anti-CD3 to enhance diabetes remission in type 1 diabetic mice. Immunohorizons. (2019) 3:498–510. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.1900019
50. Maier B, Leader AM, Chen ST, Tung N, Chang C, LeBerichel J, et al. Author Correction: A conserved dendritic-cell regulatory program limits antitumour immunity. Nature. (2020) 582:E17. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2326-5
51. Magen A, Hamon P, Fiaschi N, Soong BY, Park MD, Mattiuz R, et al. Intratumoral dendritic cell-CD4(+) T helper cell niches enable CD8(+) T cell differentiation following PD-1 blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Med. (2023) 29:1389–99. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02345-0
52. Sharma P, Zhang X, Ly K, Kim JH, Wan Q, Kim J, et al. Hyperglycosylation of prosaposin in tumor dendritic cells drives immune escape. Science. (2024) 383:190–200. doi: 10.1126/science.adg1955
53. Luo Y, Li L, Chen X, Gou H, Yan K, and Xu Y. Effects of lactate in immunosuppression and inflammation: Progress and prospects. Int Rev Immunol. (2022) 41:19–29. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1974856
54. Fuks JM, Arrighi RB, Weidner JM, Kumar Mendu S, Jin Z, Wallin RP, et al. GABAergic signaling is linked to a hypermigratory phenotype in dendritic cells infected by Toxoplasma gondii. PloS Pathog. (2012) 8:e1003051. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003051
55. Barragan A, Weidner JM, Jin Z, Korpi ER, and Birnir B. GABAergic signalling in the immune system. Acta Physiol (Oxf). (2015) 213:819–27. doi: 10.1111/apha.12467
56. Bekić M, Vasiljević M, Stojanović D, Kokol V, Mihajlović D, Vučević D, et al. Phosphonate-Modified cellulose nanocrystals potentiate the th1 polarising capacity of monocyte-Derived dendritic cells via GABA-B receptor. Int J Nanomedicine. (2022) 17:3191–216. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S362038
57. Huang S, Mao J, Wei B, and Pei G. The anti-spasticity drug baclofen alleviates collagen-induced arthritis and regulates dendritic cells. J Cell Physiol. (2015) 230:1438–47. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24884
58. Ankit K, Umesh KS, and Anurag C. Honokiol analogs: a novel class of anticancer agents targeting cell signaling pathways and other bioactivities. Future Med Chem. (2013) 5(7):809–829. doi: 10.4155/fmc.13.32
59. Wang Q, Zheng C, Hou H, Bao X, Tai H, Huang X, et al. Interplay of sphingolipid metabolism in predicting prognosis of GBM patients: towards precision immunotherapy. J Cancer. (2024) 15:275–92. doi: 10.7150/jca.89338
60. Han Y, Liu D, and Li L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. (2020) 10:727–42.
61. Sun X, Lin M, Tian Z, Ma Y, and Lv L. GABA/baclofen stabilizes PD-L1 and enhances immunotherapy of breast cancer. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e28600. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28600
62. Pomeranz Krummel DA, Nasti TH, Kaluzova M, Kallay L, Bhattacharya D, Melms JC, et al. Melanoma cell intrinsic GABA(A) receptor enhancement potentiates radiation and immune checkpoint inhibitor response by promoting direct and T cell-Mediated antitumor activity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2021) 109:1040–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.10.025
63. Gao M, Ling M, Tang X, Wang S, Xiao X, Qiao Y, et al. Comparison of high-throughput single-cell RNA sequencing data processing pipelines. Briefings Bioinf. (2021) 22(3):bbaa116. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa116
64. Jiang SH, Zhu LL, Zhang M, Li RK, Yang Q, Yan JY, et al. : GABRP regulates chemokine signalling, macrophage recruitment and tumour progression in pancreatic cancer through tuning KCNN4-mediated Ca(2+) signalling in a GABA-independent manner. Gut. (2019) 68:1994–2006. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317479
65. van Baalen A, Häusler M, Plecko-Startinig B, Strautmanis J, Vlaho S, Gebhardt B, et al. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome without detect able autoantibodies and response to immunotherapy: a case series and discussion of epileptogenesis in FIRES. Neuropediatrics. (2012) 43:209–16. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1323848
66. Rusche T, Yaldizli Ö, Galbusera R, Mutke M, Halter JP, Lieb J, et al. Anti-GABA(A) receptor encephalitis 14 months after allogeneic haematopoietic stem-cell transplant for acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet (London England). (2024) 403:469–70. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02831-3
67. Jian C, Wang B, Mou H, Zhang Y, Yang C, Huang Q, et al. A GAD1 inhibitor suppresses osteosarcoma growth through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e31444. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31444
68. Guo C, Ma X, Gao F, and Guo Y. Off-target effects in CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. Front bioengineering Biotechnol. (2023) 11:1143157. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1143157
69. Splendiani E, Besharat ZM, Covre A, Maio M, Di Giacomo AM, and Ferretti E. Immunotherapy in melanoma: Can we predict response to treatment with circulating biomarkers? Pharmacol Ther. (2024) 256:108613. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108613
70. Ramapriyan R, Vykunta VS, Vandecandelaere G, Richardson LGK, Sun J, Curry WT, et al. Altered cancer metabolism and implications for next-generation CAR T-cell therapies. Pharmacol Ther. (2024) 259:108667. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108667
71. Yu X, Zhai X, Wu J, Feng Q, Hu C, Zhu L, et al. Evolving perspectives regarding the role of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in gastric cancer immunotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2024) 1870:166881. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166881
72. Niu L, Wang Q, Feng F, Yang W, Xie Z, Zheng G, et al. Small extracellular vesicles-mediated cellular interactions between tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages: Implication for immunotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2024) 1870:166917. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166917
73. Hengrui L. An example of toxic medicine used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for cancer treatment. J traditional Chin Med = Chung i tsa chih ying wen pan. (2023) 43:209–10. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.02.001
74. Hengrui L. Toxic medicine used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for cancer treatment: are ion channels involved? J traditional Chin Med = Chung i tsa chih ying wen pan. (2022) 42:1019–22. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220815.005
75. Su XL, Wang JW, Che H, Wang CF, Jiang H, Lei X, et al. Clinical application and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of lung cancer. Chin Med J. (2020) 133:2987–97. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001141
76. Liu Y, Yang S, Wang K, Lu J, Bao X, Wang R, et al. Cellular senescence and cancer: Focusing on traditional Chinese medicine and natural products. Cell proliferation. (2020) 53:e12894. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12894
77. Liu HR. Harnessing traditional medicine and biomarker-driven approaches to counteract Trichostatin A-induced esophageal cancer progression. World J Gastroenterol. (2025) 31:106443. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.106443
78. Xie M, Qin H, Liu L, Wu J, Zhao Z, Zhao Y, et al. GABA regulates metabolic reprogramming to mediate the development of brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer research: CR. (2025) 44:61. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03315-9
79. Liu H, Hamaia SW, Dobson L, Weng J, Hernández FL, Beaudoin CA, et al. The voltage-gated sodium channel β3 subunit modulates C6 glioma cell motility independently of channel activity. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2025) 1871:167844. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167844
80. Nojima Y, Yao R, and Suzuki T. Single-cell RNA sequencing and machine learning provide candidate drugs against drug-tolerant persister cells in colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2025) 1871:167693. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167693
81. Liu H, Dong A, Rasteh AM, Wang P, and Weng J. Identification of the novel exhausted T cell CD8 + markers in breast cancer. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:19142. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70184-1
82. Liu H and Li Y. Potential roles of Cornichon Family AMPA Receptor Auxiliary Protein 4 (CNIH4) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer biomarkers: section A Dis Markers. (2022) 35:439–50. doi: 10.3233/CBM-220143
83. Sabit H, Pawlik TM, Radwan F, Abdel-Hakeem M, Abdel-Ghany S, Wadan AS, et al. Precision nanomedicine: navigating the tumor microenvironment for enhanced cancer immunotherapy and targeted drug delivery. Mol Cancer. (2025) 24:160. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02357-z
84. Kyu Shim M, Yang S, Sun IC, and Kim K. Tumor-activated carrier-free prodrug nanoparticles for targeted cancer Immunotherapy: Preclinical evidence for safe and effective drug delivery. Advanced Drug delivery Rev. (2022) 183:114177. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114177
Keywords: GABA signaling, tumor immunotherapy, tumor microenvironment, immune cell reg ulation, cancers
Citation: Zhao Y, Xu J, Yang K and Bao L (2025) Targeting GABA signaling in the tumor microenvironment: implications for immune cell regulation and immunotherapy resistance. Front. Immunol. 16:1645718. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1645718
Received: 12 June 2025; Accepted: 22 July 2025;
Published: 05 August 2025.
Edited by:
Hailin Tang, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (SYSUCC), ChinaReviewed by:
Can Xu, Hebei University, ChinaHengrui Liu, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom
Boxuan Zhou, Shenzhen Hyzen Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Xu, Yang and Bao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li Bao, YmFvbGkxMTA1QDE2My5jb20=
 Yuanqing Zhao
Yuanqing Zhao Jin Xu2,3
Jin Xu2,3 Li Bao
Li Bao