- 1Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 2Department of General Practice, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 3Department of Neonatology, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare, multisystemic fibro-inflammatory condition affecting various organs, including kidneys, lungs, nasal cavity, pancreas, salivary glands, and orbit. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAVs) is a multi-systemic inflammatory vascular disease encompassing eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), and granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA). It often overlaps with the organs or tissues affected by IgG4-RD. Clinically, some individuals with IgG4-RD are ANCA-positive, while some with AAV exhibit elevated IgG4 levels or IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration, making these conditions difficult to distinguish. Reports have documented cases of overlap syndromes involving IgG4-RD and AAV, highlighting shared pathogenic mechanisms that may include macrophages, B cells, CD4+T cells, and inflammatory cytokines. However, the pathophysiological mechanism underlying these overlap syndromes remains unclear. This review examines potential pathophysiological links between IgG4-RD and AAVs (GPA/MPA) overlap syndromes.
1 Introduction
IgG4-RD is a rare fibroinflammatory condition characterized by the infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells, tumor-like mass formation, and elevated serum IgG4 levels (1). It affects a diverse range of organs, including the salivary glands, periorbital tissues, kidneys, lungs, pancreas, nasal cavity, pericardium, and skin (2). Approximately 15% of individuals with IgG4-RD exhibit renal involvement, predominantly tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN), while a smaller proportion may develop secondary membranous nephropathy (3, 4). The characteristic histological features of IgG4-RD include dense lymphocytic inflammation (IgG4-positive plasma cells > 10 per high-power field or IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%), storiform fibrosis, and obliterative phlebitis (5). ANCA positivity is observed in some IgG4-RD cases (6), raising questions about the potential overlap between IgG4-RD and AAVs (7).
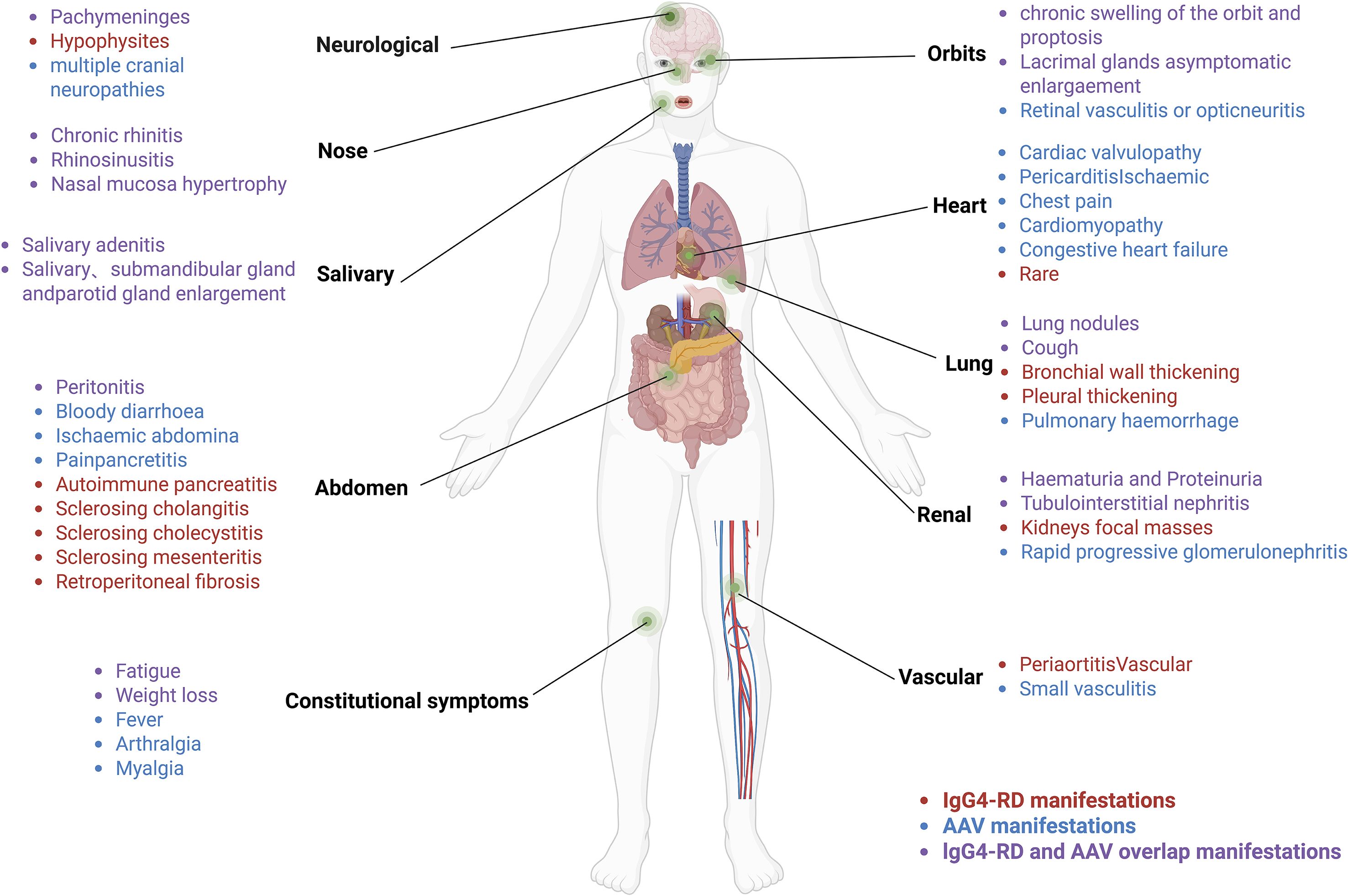
AAVs are autoimmune conditions characterized by vascular inflammation, endothelial damage, and tissue injury, often involving kidneys, lungs, sinuses, periorbital tissues, and salivary glands (8), sites that frequently overlap with those affected in IgG4-RD (9) (Figure 1). AAVs are clinically classified into three subtypes: GPA, MPA, and EGPA (10). Over 75% of individuals with AAVs experience renal involvement, often manifesting as rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, including hematuria, proteinuria, and reduced glomerular filtration rate (11). ANCAs are common biomarkers for AAVs, typically IgG, with IgG4-ANCA being the predominant subtype when MPA overlaps with IgG4-RD (12). Proteinase 3 (PR3) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) are the main target antigens of ANCAs (13). Approximately 60% of individuals with MPA are MPO-ANCA positive, exhibiting features such as necrotizing glomerulonephritis and pulmonary vasculitis (14), typically without granulomatous inflammation (15). Some individuals with MPA present with atypical symptoms, including pachymeningitis, orbital swelling, or chronic periaortic inflammation (9, 16), which may indicate overlap with IgG4-RD. GPA is predominantly PR3-ANCA positive in approximately 75% of cases and is commonly characterized by upper respiratory tract inflammation, pulmonary hemorrhage, granulomatous inflammation, and glomerulonephritis (17). Notably, some GPA cases exhibit IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration, infiltration on biopsies of the head and neck, such as sinuses and periorbital region, mimicking IgG4-RD (18). EGPA, while less prevalent than GPA and MPA, is frequently MPO-ANCA positive and primarily manifests as asthma, eosinophilia, and vasculitis (19). It demonstrates unique genetic, pathogenetic, and clinical features, distinguishing it as a separate entity (20, 21). Thus, this discussion focuses primarily on the pathogenesis of MPA/GPA.
Both IgG4-RD and AAVs are autoimmune diseases with notable similarities in organ involvement, clinical presentation, serology, imaging, and histopathology (18, 22, 23). Reports of IgG4-RD overlapping with MPA/GPA are increasing (13, 16, 24–27) (See Supplementary Table 1), suggesting the emergence of a novel overlap syndrome (9). This overlap implies potential pathophysiological connections between these conditions. Despite shared features such as B-cell maturation, CD4+T-cell differentiation, macrophage activation, and cytokine secretion, the pathophysiological mechanisms linking IgG4-RD and AAV overlap syndrome remain unclear. This review explores these potential connections to provide a foundation for improved diagnosis and early intervention in these diseases.
2 Immuno-pathophysiological mechanisms in IgG4-RD
In IgG4-RD, antigens activate the innate (e.g., macrophages) and adaptive (e.g., T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes) immune systems (28, 29). Extensive infiltration of these immune cells leads to organ swelling, storiform fibrosis, and obliterative phlebitis, as observed in tissue biopsies (30) (Figure 2).
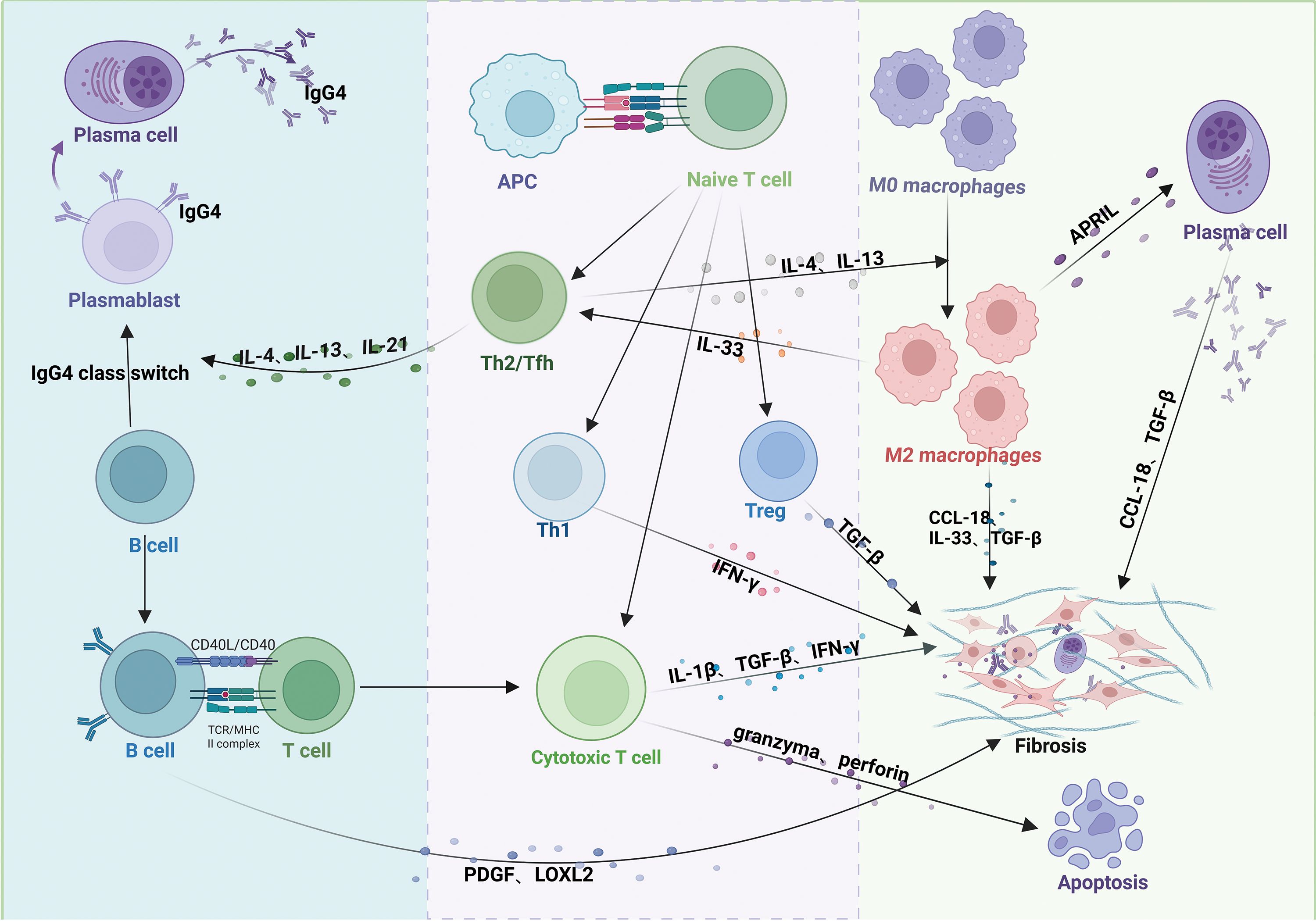
Figure 2. Pathogenic mechanisms of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) activate T cells, promoting differentiation into distinct subsets. Th2 and Tfh cells secrete IL-4, IL-13, and IL-21, driving B-cell maturation into plasma cells or plasmablasts and IgG4 class-switching. Th1 cells secrete IFN-γ; Treg cells secrete TGF-β; and CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) secrete IFN-γ, IL-1β, and TGF-β. These T-cell subsets collectively promote fibrosis in affected tissues. CD4+ CTLs additionally induce apoptosis via granzyme/perforin release. Activated B cells produce PDGF and LOXL2, activating fibroblasts and exacerbating fibrosis. IL-4/IL-13 from Th2 cells polarizes macrophages to an M2 phenotype. M2 macrophages enhance Th2 activation via IL-33 (positive feedback) and, alongside Th1 cells, Tregs, and CD4+ CTLs, contribute to fibrosis through profibrotic mediators (e.g., TGF-β, CCL-18).
B-lymphocytes play a central role in IgG4-RD pathogenesis, primarily differentiating into IgG4-positive plasma cells and infiltrating affected tissues (31). The clinical symptoms of patients with IgG4-RD significantly improve after depletion of the B cell lineage with rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal therapy), demonstrating the important pathogenic role of B cells in IgG4-RD (32, 33). T-cells contribute to B cell proliferation and differentiation in IgG4-RD (34). For example, T helper type 2 (Th2) and T follicular helper (Tfh) cells produce cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-4, IL-21, and IL-13, promoting B-cell maturation into plasma cells or plasmablasts and facilitating IgG4 isotype switching (35), highlighting the T cell-dependent nature of B-cell activation. In contrast, T helper type 1 (Th1) cells secrete interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which induces tissue fibrosis (36). Activated B cells present antigens to T cells via major histocompatibility complex class II, stimulating CD4+ T cells to differentiate into cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD4+CTLs) and secrete chemokines such as C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL)-5, which attract CD4+CTLs to affected tissues in IgG4-RD (37). CD4+CTLs aggregate around fibroblasts and release cytokines, including IL-1β, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), and IFN-γ, which promote tissue fibrosis (30, 38). They also induce apoptosis by releasing granzymes and perforin (39). Additionally, activated B cells produce platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF) and Lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2), activating fibroblasts or collagen fibers and exacerbating fibrosis in affected tissues (40).
Macrophages, particularly M2 macrophages, also contribute to the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD (41, 42). IL-4 and IL-13, produced by Th2 cells, drive macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype (43). In turn, M2 macrophages promote Th2 cell activation through the secretion of cytokines like IL-33 (44). M2 macrophages also produce IL-33, CCL-18, and TGF-β, which cause collagen deposition and extracellular matrix protein accumulation, thereby contributing to tissue fibrosis (42, 45, 46). Furthermore, macrophages express a plasma cell survival factor known as a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), which supports plasma cell infiltration and enhances IgG4 production in IgG4-RD (47).
3 Immuno-pathophysiological mechanisms in AAV
MPA and GPA are characterized by loss of immune tolerance to PR3 and MPO antigens on neutrophils, leading to necrotizing small vessel vasculitis, endothelial damage, and tissue fibrosis (48). B-lymphocytes are important in AAV pathogenesis, maturing and differentiating into plasma cells that produce ANCAs under the influence of cytokines such as IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, and IL-21 (49) (Figure 3).
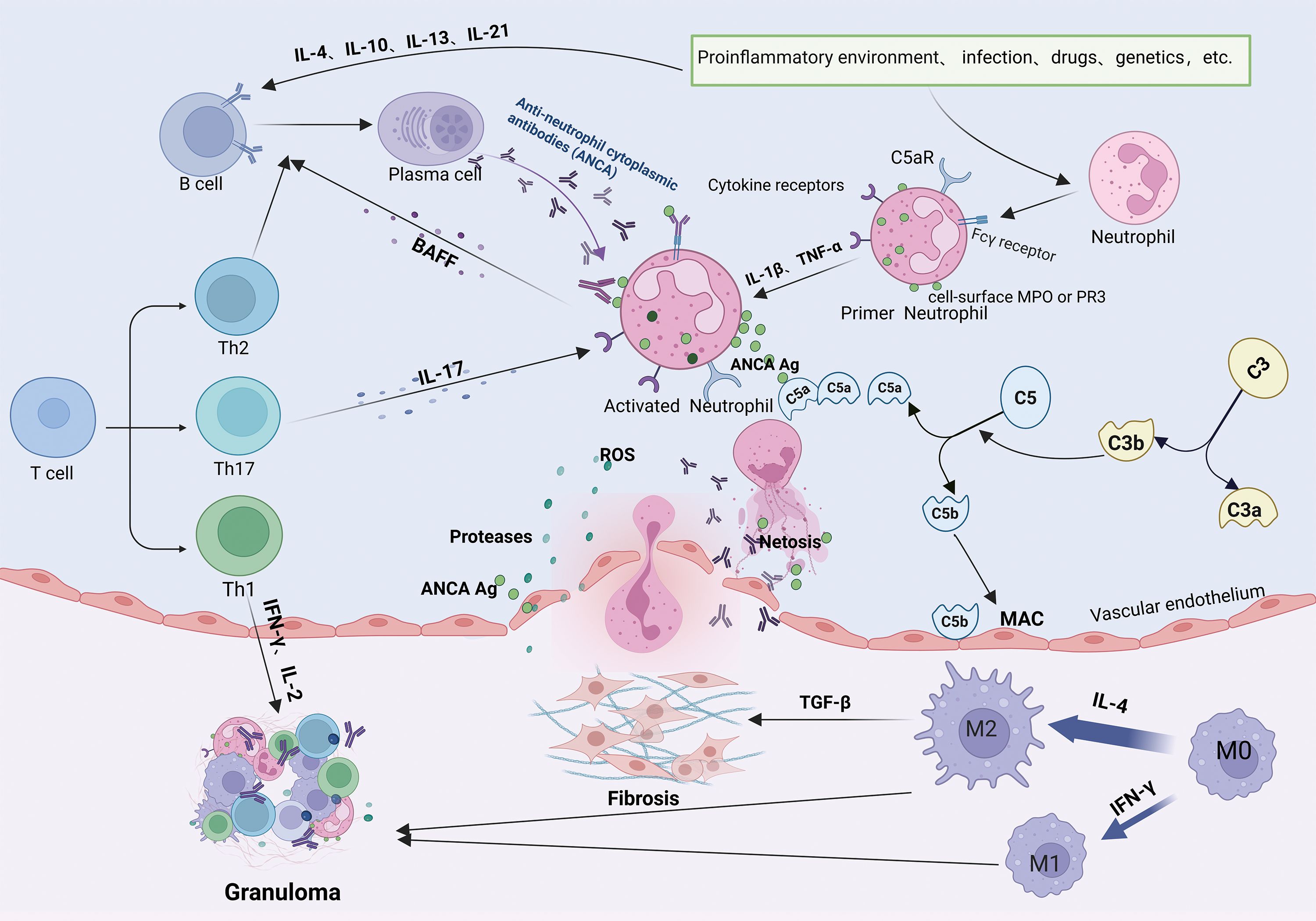
Figure 3. Pathogenic mechanisms of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Loss of B- and T-cell tolerance to ANCA antigens-triggered by inflammation, infections, drugs, or genetic factors-enables B-cell differentiation into antibody-producing plasma cells generating PR3-ANCA or MPO-ANCA antibodies. Antibodies bind to PR3/MPO antigens on neutrophils and synergize with complement (C5a) and cytokines (IL-17) to activate neutrophils. IL-17 further recruits neutrophils to inflammatory sites, where they release ROS, NETs, and proteolytic enzymes, inducing endothelial apoptosis, vascular destruction, and tissue injury. Activated neutrophils secrete BAFF, and Th2/Tfh cells produce IL-4/IL-21, collectively perpetuating pathogenic B-cell responses and autoantibody production. Concurrently, macrophage polarization (M2) and immune cell infiltration drive granuloma formation.
Additionally, B cells present antigens and provide co-stimulatory signals to activate T cells. Activated T cells exacerbate vascular inflammation responses by recognizing neutrophil surface antigens (50). Different subtypes of T cells have distinct roles in MPA/GPA pathogenesis. Th1 cells produce cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-2, promoting localized inflammatory responses and granuloma formation in GPA (51). Th2 cells secrete IL-4 and IL-13, facilitating plasma cell differentiation and ANCAs production (52). Under inflammatory conditions involving cytokines like IL-6, IL-23, and TGF-β, Th cells can differentiate into T helper type 17 (Th17) cells, which recruit neutrophils to affected tissues through IL-17 production (53). Neutrophils activated by ANCAs, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) play a central role in MPA/GPA pathogenesis. These neutrophils translocate MPO and PR3 antigens to their surface (54, 55). Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) further amplify inflammation by activating complement component C5a, which binds to the C5a receptors on the neutrophil’s surface (56), perpetuating a cycle of activation (57). Activated neutrophils release reactive oxygen species (ROS), proteases, and inflammatory cytokines, damaging vascular endothelial cells and promoting tissue injury (58). ANCAs also stimulate neutrophils to secrete B-cell activating factor (BAFF), enhancing B-cell differentiation and contributing to AAV relapse (59).
In MPA and GPA, biopsies of kidney and lung tissues reveal a significant increase in M2 macrophage infiltration (60, 61), suggesting their involvement in disease progression. MPO-ANCA induces the activation of M2 macrophages and the secretion of TGF-β, thereby exacerbating fibrosis (62). While M2 macrophages can exhibit anti-inflammatory effects through phagocytose apoptotic cells, a process called efferocytosis, PR3 inhibits this process (63), leading to incomplete neutrophil clearance and pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage involvement (64), which participate in GPA granuloma formation together with M2 macrophages (65).
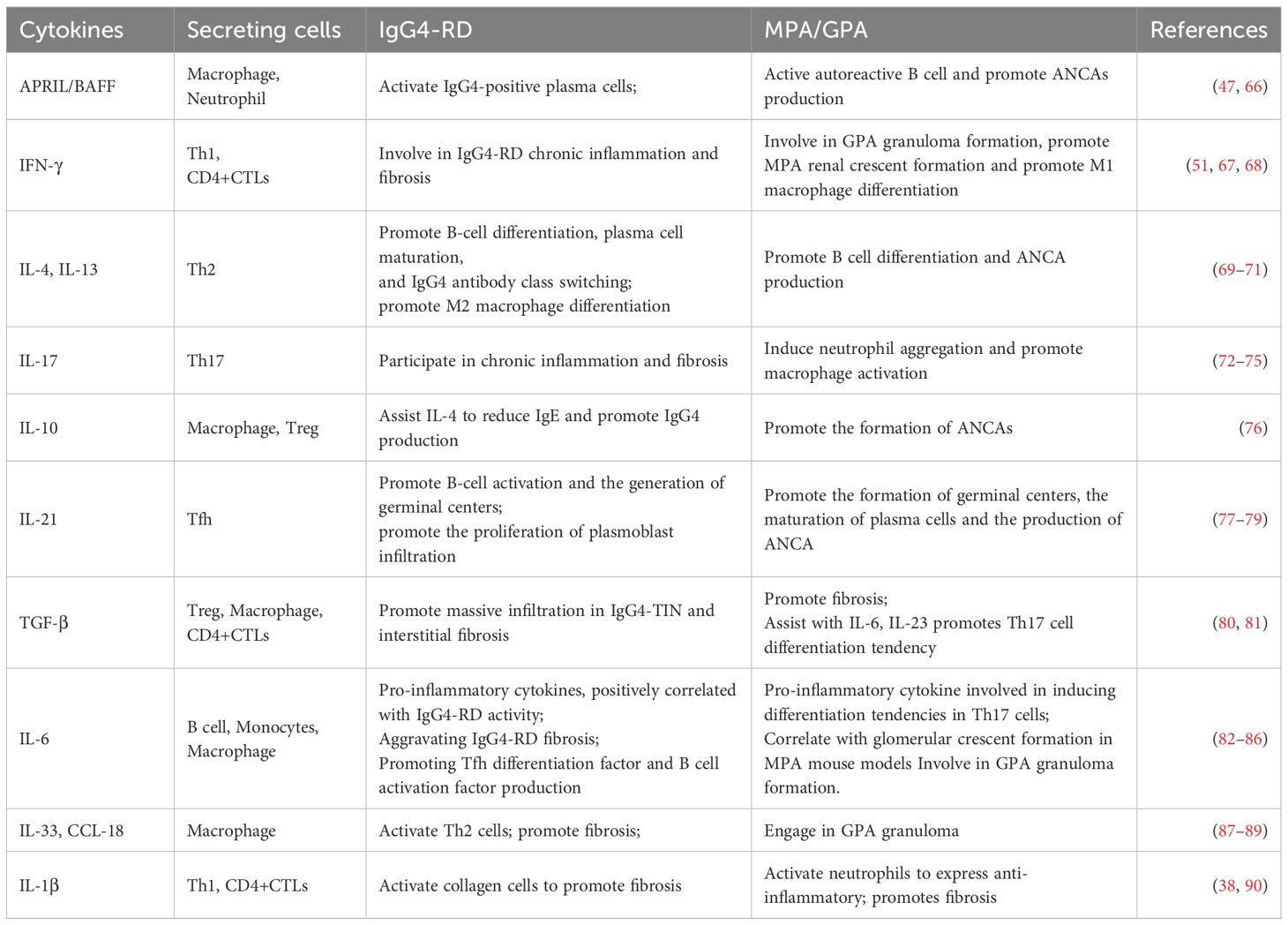
In summary, the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA are complex and multifaceted, involving B cells, T cells, macrophages, and numerous cytokines (e.g., IL-4, IL-13, IL-21, IL-17, TGF-β) (Table 1). These shared mechanisms suggest that IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA in overlap syndromes may be pathophysiological linked, potentially creating a feedback loop that worsens both conditions (Figure 4).
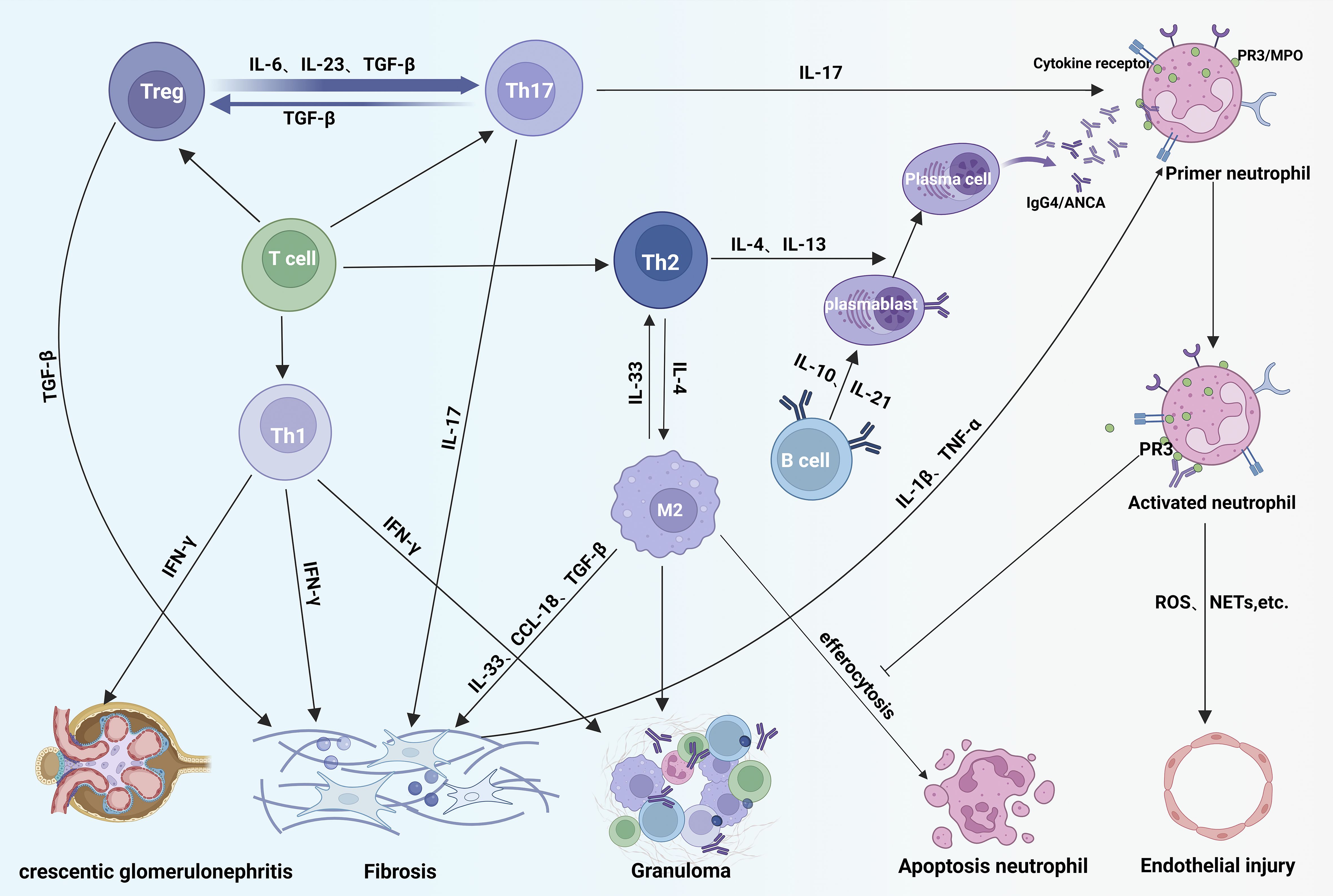
Figure 4. Immunopathogenic overlap in IgG4-RD and ANCA-associated vasculitis. In disease overlap syndromes, Th2-derived IL-4/IL-13 drive B-cell maturation and production of IgG4-class ANCA autoantibodies that bind neutrophil surface receptors, exacerbating vascular inflammation. Concurrently, Th1 cells promote tissue fibrosis and acute crescent formation via IFN-γ. Treg cells differentiate into Th17 cells under IL-23/IL-6/TGF-β stimulation; Th17-secreted IL-17 activates neutrophils, amplifying inflammation. IL-4 from Th2 cells polarizes macrophages toward an M2 phenotype. While M2 macrophages clear apoptotic neutrophils via efferocytosis, membrane PR3 on neutrophils inhibits this process, leading to neutrophil accumulation and sustained M2 activation that intensifies tissue damage. Fibrosis is aggravated by profibrotic mediators: IFN-γ (Th1), TGF-β (Treg), IL-17 (Th17), and IL-10/IL-13/CCL-18 (activated M2 macrophages) acting on fibroblasts.
4 The role of B cells in IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA overlap syndrome
B cells play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA (37, 91), primarily by differentiating into plasma cells and secreting antibodies such as IgG4 or ANCAs. ANCA positivity has also been observed in some individuals with IgG4-RD (92), possibly due to non-pathogenic autoreactive B- cell secretion. Consequently, ANCA positivity does not exclude IgG4-RD. It has been shown that serum inflammatory markers, including IgG, IgG1, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein, are significantly elevated in ANCA-positive individuals with IgG4-RD. ANCA-positive individuals are more likely to exhibit kidney and lymph node involvement compared to ANCA-negative individuals (6). Thus, ANCAs exacerbate the inflammatory response in IgG4-RD, and the presence of MPA/GPA may further worsen IgG4-RD. ANCAs are pathogenic (19), and ANCA positivity often precedes clinical manifestations of AAV (93). Abbas et al. reported a case of PR3-ANCA-positive IgG4-RD confined to the lungs, which progressed to GPA after 16 months of follow-up (94), suggesting that ANCA-positive IgG4-RD may induce or exacerbate MPA/GPA. ANCAs are predominately of the IgG subtype (21). Holland et al. demonstrated that IgG4 subtypes isolated from ANCA antibodies in patients can activate neutrophils (95). Della-Torre et al. suggested that elevated IgG4 production in IgG4-RD promotes ANCA formation (96). High levels of IgG4 in IgG4-RD may activate neutrophils, increasing the risk of overlap with MPA/GPA and exacerbating the progression of MPA/GPA (96). There are significant increases in IgG4 ANCAs that have been observed in MPA/GPA with IgG4-RD overlap syndrome (97), activating neutrophils and stimulating the release of ROS (98, 99), further aggravating renal damage in MPA/GPA. In IgG4-RD, B cells also produce PDGF, which directly activates fibroblasts, promoting tissue fibrosis (100). This mechanism can exacerbate fibrosis in MPA/GPA-affected tissues in overlap syndromes.
While MPA does not feature granulomatous lesions (15), some individuals with MPA exhibit clinical features resembling IgG4-RD, including lymphadenopathy, elevated serum IgG4 levels, and TIN (9). For example, a patient with high serum IgG4, MPO-ANCA positivity, chest nodules, and elevated creatinine was diagnosed with IgG4 related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) and MPA overlap syndrome based on renal biopsy findings (101).In some GPA cases, elevated serum IgG4 levels, fibrosis, vascular occlusion, and IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration mimic IgG4-RD’s clinical histopathological features (102–104). Serum IgG4 concentrations correlate positively with organ involvement and predict disease recurrence (105, 106), so elevated IgG4 levels in MPA/GPA are associated with increased disease activity (107). The pathogenic role of IgG4 in IgG4-RD has not yet been clarified. Some studies suggest anti-inflammatory properties due to Fab arm exchange, poor C1q binding, and limited Fc receptor activation (108). However, elevated serum IgG4 may represent a failure of counter-regulation (1). Shiokawa et al. proved the pathogenic potential of IgG1/IgG4 antibodies from IgG4-RD causing pancreatic and salivary gland damage in a mouse model (109). Whether elevated IgG4 levels in MPA/GPA induce IgG4-RD progression requires further investigation. Notably, the number of plasmablasts is positively related to the levels of serum IgG4, inflammatory indicators, and the number of organs involved in IgG4-RD (110). Sometimes, IgG4-positive plasma cells were significantly increased in GPA biopsies of the sinuses, orbital/periorbital regions, kidneys, and dura mater (111). This suggests that IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration in GPA may aggravate tumor-like proliferation and worsening IgG4-RD.
4.1 BAFF/APRIL
BAFF of the TNF family and APRIL, produced by innate immune cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages, promote the survival and activation of B-cells (112). Increased production of BAFF and APRIL have been identified in several autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), AAV, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and IgG4-RD (112, 113). They bind to B cell or memory B cell receptors, promoting activation, antibody production, and IgG class switching (114). In IgG4-RD, APRIL facilitates IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration in affected tissues (47). Telitacicept, a BAFF/APRIL inhibitor, induces remission in refractory IgG4-RD, highlighting its critical role in disease pathogenesis (115). In AAV, BAFF/APRIL consistently elevated over normal patient’s matter at the active or remission stage (112). ANCAs stimulate neutrophils to produce BAFF, promoting autoreactive B cell activation and ANCA production (66). BAFF/APRIL levels correlate with MPA/GPA activity, and BAFF-driven autoreactive B-cell activation after B-cell depletion contributes to AAV relapse (116). Overall, BAFF and APRIL promote IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration and IgG4/ANCA production, exacerbating IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA overlap syndromes.
5 The role of T cells in IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA overlap syndrome
T cells, key components of the adaptive immune system, contribute significantly to the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines and stimulating B cells to produce IgG4/ANCA antibodies (30, 117). Activated CD4+ T cells differentiate into various subsets, including Th1, Th2, Th17, regulatory T (Treg) cells, and follicular helper T (Tfh) cells, each playing distinct roles in these diseases.
5.1 Th1/Th2 cells
Th1 and Th2 cells are closely associated with the immune responses in IgG4-RD and AAV. Th1 cells, driven by IL-12, mediate cellular immunity, while Th2 cells, stimulated by IL-4, regulate humoral immunity (118, 119).Th1 cells are elevated individuals within IgG4-RD compared to controls, contributing to chronic inflammation and fibrosis through IFN-γ secretion (67). Increased Th1 cells correlate with IgG4-RD activity and IgG4 antibody levels (120), while IFN-γ induced Tfh proliferation further enhances IgG4 production (121). In GPA granulomas, Th1 cells are abundant, and IFN-γ secretion promotes granuloma formation (51), exacerbating GPA when IgG4-RD is present. IFN-γ levels also correlate with renal crescent formation and hyperplasia in MPA (68, 118), suggesting that IFN-γ-driven Th1 cells aggravate renal injury in IgG4-TIN and MPA/GPA overlap syndrome (122).
A previous peripheral CD4+ T cells in IgG4-associated dacryoadenitis and salivary gland inflammation revealed that the lacrimal and salivary glands are predominantly infiltrated by Th2 cells (123). Similarly, Th2-mediated immune-inflammatory response is predominant in IgG4-associated autoimmune pancreatitis and cholangitis (124), underscoring the significant role of Th2 cells in IgG4-RD pathogenesis (69).Th2 cells are also dominant in the nasal mucosa in Wegener’s granulomatosis (125).During the progression of GPA from localized granulomatosis to generalized vasculitis, a polarization shift from Th1 to Th2 responses occurs (126). This Th1 to Th2 conversion is a hallmark of GPA disease progression (126, 127). In case reports of IgG4-RD overlapping with MPA/GPA, the condition frequently manifests with systemic involvement (96), and ANCA-positive individuals with IgG4-RD are more likely to present with systemic symptoms (97). Therefore, Th2 cell polarization may dominate in overlap syndromes. Th2 cells secrete cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13, which promote B-cell differentiation and IgG4-ANCA production (70). In vitro studies demonstrate that IL-4 stimulation alone induces the conversion of IgG to IgG4, significantly increasing plasma IgG4 concentrations (69), and IgG4 ANCA subtypes in individuals with overlap syndrome (97). Therapeutically, the anti-IL-4 receptor monoclonal antibody dupilumab has been shown to reduce tissue swelling in IgG4-RD and lower glucocorticoids requirements in affected individuals (71). These findings suggest that targeting IL-4 may serve as a common therapeutic strategy for both IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA overlap syndromes.
5.2 Th17/Treg cells
Th17 and Treg cells, which differentiate from CD4+ T cells, are central to autoimmune diseases, including IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA (128). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-23, and TGF-β, drive Th17 differentiations, while TGF-β alone favors Treg development (129). Both can be converted into each other.
Th17 cells, which produce IL-17, aggregate in IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA, promoting inflammation and fibrosis in affected tissues (72–74). They are also involved in a variety of autoimmune diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, AAV, SLE, and RA (128, 130, 131). IL-17 produced by Th17 cells contributes to fibrosis in IgG4-RD-affected tissues (132). Similarly, high levels of IL-17 in MPA/GPA may exacerbate IgG4-RD fibrosis. In MPA/GPA, Th17 cells play a central role by activating neutrophils and macrophages through IL-17 production (133). IL-17 enhances neutrophil expression of PR3 and MPO antigens, induces CXC chemokine release, and promotes adhesion molecule expression, facilitating neutrophil recruitment to inflammatory sites (75). Furthermore, IL-17 induces macrophages to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α, amplifying the inflammatory response (134). MPO-ANCA has been shown to stimulate IL-17 production, driving autoimmune anti-myeloperoxidase glomerulonephritis (74). Therefore, an increased Th17 and IL-17 in individuals with IgG4-RD may exacerbate ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis by activating neutrophils.
Treg cells are essential immunosuppressive cells that regulate inflammation by secreting TGF-β and IL-10 to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines production by macrophages and T cells (135).In IgG4-RKD, Tregs are significantly elevated, promoting IgG4 production by reducing IL-4 to IgE conversion, primarily via IL-10 secretion (76). Miyoshi et al. demonstrated that Treg levels positively correlate with serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-associated autoimmune pancreatitis (136). In IgG4-RKD, Tregs infiltrate renal tissue, promoting interstitial fibrosis by producing TGF-β (80). In MPA/GPA, Treg numbers increase during remission periods, suggesting a potential role in disease modulation (137). One study proposed that Tregs in MPA/GPA may differentiate from Th17 cells (138). However, in the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6, IL-23, and TGF-β, Tregs can convert into Th17 cells (81), perpetuating chronic autoimmune inflammation in MPA/GPA (139). This conversion may exacerbate the vascular inflammatory response in overlap syndromes involving IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA.
5.3 Tfh cells
Tfh cells are specialized CD4+ T cells involved in antibody class switching, plasma cell differentiation, and germinal center formation (140). These cells play pivotal roles in autoimmune diseases such as SLE, RA, IgG4-RD, AAV, and Sjögren’s disease (141). In IgG4-RD, Tfh cells proliferated, with a predominance of Tfh2 cells. Elevated Tfh2 levels correlate with IgG4-RD activity and serum IgG4 concentrations (142, 143), secreting IL-4 and IL-21 to promote IgG4 antibody production and B-cell proliferation (77, 144, 144). Tfh1 cells were also increased and positively correlated with IgG4-RD activity, independent of IgG4 levels (144).In MPA/GPA, Tfh2 cells increased significantly, promoting B cell proliferation, differentiation, and germinal center formation by secreting IL-4 and IL-21 (78, 79). Therefore, Tfh aggravates B cell proliferation and promotes the production of more IgG4-ANCA in IgG4-RD and AAV overlap syndromes. IL-21 produced by Tfh2 correlates with AAV activity and is identified as a risk factor for AAV activity (145), so high levels of IL-21 in IgG4-RD worsen AAV. Additionally, IL-21 assists IL-23 and TGF-β in Th17 differentiation (81), suggesting that elevated IL-21 in IgG4-RD contributes to Th17 polarization and overlap syndrome progression.
6 The role of macrophages in IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA overlap syndrome
Monocytes, as part of innate immunity, play critical roles in defending against pathogens, phagocytosing apoptotic cells, producing ROS, and presenting antigens (146).In IgG4-RD, monocytes secrete TGF-β and IL-1β, promoting fibrosis in affected tissues (147). In AAV, ANCAs activate monocytes to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6, which, in turn, activate neutrophils (148) and contribute to tubulointerstitial injury (149). In IgG4-RD, IL-1β also produced by CD4+ CTLs, high IL-1β may exacerbate MPA/GPA by activating neutrophils. When peripheral blood mononuclear cells are stimulated with PR3 or MPO, it results in an elevated production of IL-6 (150), This heightened IL-6 level subsequently promotes fibroblast proliferation as well as the synthesis of collagen and fibronectin, thereby worsening fibrosis in the tissues affected by IgG4-RD (82). Additionally, IL-6 can stimulate the production of Tfh differentiation factors and B cell activating factors in IgG4-RD, thereby promoting Tfh cell differentiation and B cell antibody production (82). In overlap syndromes involving IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA, monocyte proliferation releases various inflammatory cytokines, promoting vasculitis and fibrosis in affected tissues.
Monocytes differentiate into macrophages in inflamed tissues, which can be polarized into two subtypes: M1 macrophages (classically activated) and M2 macrophages (alternatively activated) (151). M1/M2 polarization mirrors Th1/Th2 differentiation (152). Th1 cytokines, such as IFN-γ, drive M1 polarization, and M1 macrophages secrete IL-6, IL-12, and IL-23, which promote Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation. In contrast, Th2 cytokines, such as IL-4 and IL-13, induce M2 polarization, and macrophages secrete IL-33 to enhance Th2 differentiation (44, 152).
In IgG4-RD, M2 macrophages promote fibrosis by producing IL-33, TGF-β, and CCL-18, which upregulate collagen production by fibroblasts (35, 153). Serum levels of these cytokines correlate with fibrosis severity in IgG4-RD (154). IL-33 interacts with ST2 on Treg cells, inducing TGF-β production and promoting fibrosis in IgG4-RD tissues (155, 156), which promotes fibrosis of the tissues involved in IgG4-RD (87). In MPA/GPA, elevated IL-33 enhances Th2 cell activity, stimulating plasma cell differentiation and ANCA production (88, 157). In conclusion, IL-33 promotes plasma cell differentiation and IgG4 subtype ANCAs production in IgG4-RD with MPA/GPA overlap syndromes. MPO-ANCA contributes to M2 polarization, secreting more TGF-β and exacerbating fibrosis (62, 158). So, MPO-ANCA may worsen the fibrosis of the affected tissues in patients with IgG4-RD.
Both M1 and M2 macrophages are present in GPA granuloma, and their differentiation depends on specific cytokine settings (65). However, a study of nasal mucosal biopsies in GPA indicated predominant M2 polarization (60). In MPA/GPA, M2 macrophages infiltrate renal tissues, activating endothelial cells and myofibroblasts to secrete pro-fibrotic factors such as IL-33, CCL-18, and TGF-β (64). Notably, excessive infiltration of M2 macrophages correlates positively with elevated serum creatinine levels and an increased risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with AAV (159). Therefore, M2 macrophage accumulation worsens fibrosis in MPA/GPA-affected tissues when it overlaps with IgG4-RD. While M2 macrophages play an anti-inflammatory role by destroying apoptotic cells called efferocytosis (160). PR3 antigen expressed on activated neutrophils interacts directly with the “eat-me” signaling calpain on neutrophils, thereby impairing efferocytosis (161), resulting in incomplete clearance of neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, driving continued ANCA production and promoting granuloma formation. Thus, PR3 exacerbates tissue damage in IgG4-RD by impairing M2 macrophage efferocytosis (18).
7 Conclusion
IgG4-RD is a fibroinflammatory disease of unknown etiology with multi-system involvement that frequently overlaps with ANCA-associated vasculitis, posing significant diagnostic challenges. The pathogenesis of IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA involves complex interactions between B cells, T cells, and monocyte-derived macrophages, which proliferate, differentiate, and secrete cytokines that drive inflammation and fibrosis. These immune mechanisms not only contribute to disease progression but also highlight potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Understanding the interplay between these cells and cytokines provides valuable insights into the management of IgG4-RD and MPA/GPA overlap syndromes.
Author contributions
CW: Data curation, Visualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. RH: Visualization, Resources, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XB: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Resources. YZ: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Resources. JZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Resources. WG: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. QG: Supervision, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Jilin Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Contract Number: YDZJ202201ZYTS010). All figures were created with BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1660956/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Perugino CA and Stone JH. IgG4-related disease: an update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2020) 16:702–14. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0500-7
2. Stone JH, Zen Y, and Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. New Engl J Med. (2012) 366:539–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1104650
3. Cortazar FB and Stone JH. IgG4-related disease and the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2015) 11:599–609. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.95
4. Saeki T and Kawano M. IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2014) 85:251–7. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.393
5. Deshpande V. The pathology of IgG4-related disease: critical issues and challenges. Semin Diagn Pathol. (2012) 29:191–6. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2012.08.001
6. Martín-Nares E and Hernandez-Molina G. What is the meaning of ANCA positivity in IgG4-related disease? Rheumatol (Oxford). (2021) 60:3845–50. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab124
7. Bravais J, Pogliaghi M, Polivka M, Sène D, and Roriz M. IgG4-related disease and ANCA positivity: an overlap syndrome? Qjm. (2017) 110:749–50. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcx134
8. Almaani S, Fussner LA, Brodsky S, Meara AS, and Jayne D. ANCA-associated vasculitis: an update. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:1446. doi: 10.3390/jcm10071446
9. Danlos FX, Rossi GM, Blockmans D, Emmi G, Kronbichler A, Durupt S, et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides and IgG4-related disease: A new overlap syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. (2017) 16:1036–43. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.07.020
10. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. (2013) 65:1–11. doi: 10.1002/art.37715
11. Koening CL and von Hennigs I. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) vasculitis: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and the evolving treatment landscape. Am J Manag Care. (2021) 27:S267–s76. doi: 10.37765/ajmc.2021.88746
12. Ma Y, Chen L, Xu Y, Han Q, Yu B, Yuan Y, et al. Clinical and pathological features of patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides concomitant with IgG4-related disease. Int J Rheum Dis. (2019) 22:2143–50. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.13726
13. Li ZY, Wang X, Xia X, Yu XJ, Wang SX, Chen W, et al. An overlap of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated glomerulonephritis and IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Chim Acta. (2020) 501:12–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.11.030
14. Greco A, De Virgilio A, Rizzo MI, Gallo A, Magliulo G, Fusconi M, et al. Microscopic polyangiitis: Advances in diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Autoimmun Rev. (2015) 14:837–44. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.05.005
15. Karras A. Microscopic polyangiitis: new insights into pathogenesis, clinical features and therapy. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. (2018) 39:459–64. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1673387
16. Gautier F, Neumann L, Adle-Biassete H, Rubenstein E, Bernat AL, Chimon A, et al. Pachymeningitis associated with IgG4-related disease and ANCA positivity: Case report and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev. (2023) 22:103285. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103285
17. Comarmond C and Cacoub P. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener): clinical aspects and treatment. Autoimmun Rev. (2014) 13:1121–5. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.017
18. Faz-Muñoz D, Hinojosa-Azaola A, Mejía-Vilet JM, Uribe-Uribe NO, Rull-Gabayet M, Muñoz-Castañeda WR, et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis and IgG4-related disease overlap syndrome: a case report and literature review. Immunol Res. (2022) 70:550–59. doi: 10.1007/s12026-022-09279-8
19. White J and Dubey S. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A review. Autoimmun Rev. (2023) 22:103219. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2022.103219
20. Vaglio A, Buzio C, and Zwerina J. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): state of the art. Allergy. (2013) 68:261–73. doi: 10.1111/all.12088
21. Kitching AR, Anders HJ, Basu N, Brouwer E, Gordon J, Jayne DR, et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2020) 6:71. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-0204-y
22. Soma Y, Kato M, Shimura G, Kamio M, and Iida M. Renal biopsy diagnosis of IgG4-related kidney disease with minor hematuria and mild renal dysfunction: lessons for the clinical nephrologist. J Nephrol. (2023) 36:639–42. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01506-7
23. Wu HHL, Wang CCY, Woywodt A, and Ponnusamy A. Concurrent presentation of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis and ANCA MPO crescentic glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol Case Stud. (2022) 10:47–53. doi: 10.5414/cncs110852
24. Jiang B, Sahenk Z, Satoskar A, Freimer M, and Ayoub I. Vasculitic neuropathy associated with IgG4-related kidney disease: A case report and literature review. Clin Nephrol. (2021) 96:175–79. doi: 10.5414/cn110547
25. Ohno K, Matsuda Y, Arai T, Sugihara T, Iga S, and Kimura Y. Myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive otitis media and rhinosinusitis with pathological features of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: A case report. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. (2016) 125:516–21. doi: 10.1177/0003489415625072
26. Torres Tienza S, Rueda Correa F, Campos Téllez S, and Jareño Esteban JJ. ANCA-associated vasculitis presenting with alveolar hemorrhage and renal involvement and igG4-related disease: A new overlap syndrome. Arch Bronconeumol. (2022) 58:431–32. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2022.02.017
27. Kuske L, Khalifa A, Wibisono A, Bräsen JH, and Witte T. MPO-ANCA-positive granulomatosis with polyangiitis and concurrent IgG4-related disease with periaortitis and tubulointerstitial nephritis: A case report of a new overlap syndrome? Int J Rheum Dis. (2023) 26:1821–1825. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.14680
28. Michailidou D, Schwartz DM, Mustelin T, and Hughes GC. Allergic aspects of igG4-related disease: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:693192. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.693192
29. Akiyama M and Takeuchi T. IgG4-related disease: beyond glucocorticoids. Drugs Aging. (2018) 35:275–87. doi: 10.1007/s40266-018-0534-6
30. Peyronel F, Fenaroli P, Maritati F, Schleinitz N, and Vaglio A. IgG4-related disease: advances in pathophysiology and treatment. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2023) 19:1–11. doi: 10.1080/1744666x.2023.2195627
31. Maritati F, Peyronel F, and Vaglio A. IgG4-related disease: a clinical perspective. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2020) 59:iii123–iii31. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez667
32. Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A, Witzig TE, Wallace ZS, Hart PA, et al. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:1171–7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206605
33. Tieu J, Smith R, Basu N, Brogan P, D’Cruz D, Dhaun N, et al. Rituximab for maintenance of remission in ANCA-associated vasculitis: expert consensus guidelines. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2020) 59:e24–32. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez640
34. Yamada K, Mizushima I, and Kawano M. New insights into the pathophysiology of IgG4-related disease and markers of disease activity. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2019) 15:231–39. doi: 10.1080/1744666x.2019.1560268
35. Liu C, Zhang P, and Zhang W. Immunological mechanism of IgG4-related disease. J Transl Autoimmun. (2020) 3:100047. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2020.100047
36. Touzani F and Pozdzik A. New insights into immune cells cross-talk during IgG4-related disease. Clin Immunol. (2019) 198:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2018.11.004
37. Hao Q, Sun M, and Liu Y. The spectrum of B cells in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic applications of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Clin Transl Immunol. (2023) 12:e1477. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1477
38. Maehara T, Mattoo H, Ohta M, Mahajan VS, Moriyama M, Yamauchi M, et al. Lesional CD4+ IFN-γ+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Ann Rheumatic Dis. (2017) 76:377–85. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209139
39. Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Maehara T, Deshpande V, Della-Torre E, Wallace ZS, et al. Clonal expansion of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2016) 138:825–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.12.1330
40. Pillai S, Perugino C, and Kaneko N. Immune mechanisms of fibrosis and inflammation in IgG4-related disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2020) 32:146–51. doi: 10.1097/bor.0000000000000686
41. Cai S, Hu Z, Chen Y, Zhong J, and Dong L. Potential roles of non-lymphocytic cells in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:940581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.940581
42. Ishiguro N, Moriyama M, Furusho K, Furukawa S, Shibata T, Murakami Y, et al. Activated M2 macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of igG4-related disease via toll-like receptor 7/interleukin-33 signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2020) 72:166–78. doi: 10.1002/art.41052
43. Van Dyken SJ and Locksley RM. Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-mediated alternatively activated macrophages: roles in homeostasis and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. (2013) 31:317–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095906
44. Furukawa S, Moriyama M, Miyake K, Nakashima H, Tanaka A, Maehara T, et al. Interleukin-33 produced by M2 macrophages and other immune cells contributes to Th2 immune reaction of IgG4-related disease. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:42413. doi: 10.1038/srep42413
45. Kasashima S, Kawashima A, Zen Y, Ozaki S, Kasashima F, Endo M, et al. Upregulated interleukins (IL-6, IL-10, and IL-13) in immunoglobulin G4-related aortic aneurysm patients. J Vasc Surg. (2018) 67:1248–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.12.140
46. Furukawa S, Moriyama M, Tanaka A, Maehara T, Tsuboi H, Iizuka M, et al. Preferential M2 macrophages contribute to fibrosis in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz’s disease. Clin Immunol. (2015) 156:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.10.008
47. Kawakami T, Mizushima I, Yamada K, Fujii H, Ito K, Yasuno T, et al. Abundant a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL)-producing macrophages contribute to plasma cell accumulation in immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2019) 34:960–69. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy296
48. Geetha D and Jefferson JA. ANCA-associated vasculitis: core curriculum 2020. Am J Kidney Dis. (2020) 75:124–37. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.04.031
49. Merino-Vico A, van Hamburg JP, and Tas SW. B lineage cells in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 23:387. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010387
50. Li SS, Wang SL, Zhang HJ, He SH, Liang X, and Li TF. The pathogenesis and treatment in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated vasculitis. Am J Transl Res. (2020) 12:4094–107.
51. Singh H, Kumar U, and Senapati S. Translational implications of humoral and cellular immune dysfunction in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Cytokine. (2023) 164:156154. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156154
52. Martinez Valenzuela L, Bordignon Draibe J, Fulladosa Oliveras X, Bestard Matamoros O, Cruzado Garrit JM, and Torras Ambros J. T-lymphocyte in ANCA-associated vasculitis: what do we know? A pathophysiological and therapeutic approach. Clin Kidney J. (2019) 12:503–11. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfz029
53. Nakazawa D, Masuda S, Tomaru U, and Ishizu A. Pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2019) 15:91–101. doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0145-y
54. Ge S, Zhu X, Xu Q, Wang J, An C, Hu Y, et al. Neutrophils in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Mechanisms and implications for management. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:957660. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.957660
55. Massicotte-Azarniouch D, Herrera CA, Jennette JC, Falk RJ, and Free ME. Mechanisms of vascular damage in ANCA vasculitis. Semin Immunopathol. (2022) 44:325–45. doi: 10.1007/s00281-022-00920-0
56. Noone D, Hebert D, and Licht C. Pathogenesis and treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis-a role for complement. Pediatr Nephrol. (2018) 33:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s00467-016-3475-5
57. Schreiber A and Kettritz R. The neutrophil in antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis. J Leukoc Biol. (2013) 94:623–31. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1012525
58. Kronbichler A, Lee KH, Denicolo S, Choi D, Lee H, Ahn D, et al. Immunopathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:7319. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197319
59. Holden NJ, Williams JM, Morgan MD, Challa A, Gordon J, Pepper RJ, et al. ANCA-stimulated neutrophils release BLyS and promote B cell survival: a clinically relevant cellular process. Ann Rheum Dis. (2011) 70:2229–33. doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.153890
60. de Souza AWS, van Timmeren M, Sanders J-S, Stegeman C, Heeringa P, Kallenberg CGM, et al. M2 macrophage is the predominant phenotype in airways inflammatory lesions in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2017) 19:100. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1310-4
61. Li J, Yu Y-F, Liu C-H, and Wang C-M. Significance of M2 macrophages in glomerulonephritis with crescents. Pathol - Res Pract. (2017) 213:1215–20. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.04.011
62. Popat RJ, Hakki S, Thakker A, Coughlan AM, Watson J, Little MA, et al. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies attenuate the monocyte response to LPS and shape macrophage development. JCI Insight. (2017) 2:e87379. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.87379
63. Gabillet J, Millet A, Pederzoli-Ribeil M, Tacnet-Delorme P, Guillevin L, Mouthon L, et al. Proteinase 3, the autoantigen in granulomatosis with polyangiitis, associates with calreticulin on apoptotic neutrophils, impairs macrophage phagocytosis, and promotes inflammation. J Immunol (Baltimore Md: 1950). (2012) 189:2574–83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200600
64. Vegting Y, Vogt L, Anders HJ, de Winther MPJ, Bemelman FJ, and Hilhorst ML. Monocytes and macrophages in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Autoimmun Rev. (2021) 20:102911. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102911
65. Hilhorst M, Shirai T, Berry G, Goronzy J, and Weyand CM. T cell—Macrophage interactions and granuloma formation in vasculitis. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:432. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00432
66. Scurt FG, Bose K, Hammoud B, Brandt S, Bernhardt A, Gross C, et al. Old known and possible new biomarkers of ANCA-associated vasculitis. J Autoimmun. (2022) 133:102953. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102953
67. Yang Y, Wang C, Shi L, Yang S, Liu Y, Luo J, et al. Clinical characteristics and CD4(+) T cell subsets in igG4-related disease. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:825386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.825386
68. Holdsworth SR, Kitching AR, and Tipping PG. Th1 and Th2 T helper cell subsets affect patterns of injury and outcomes in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. (1999) 55:1198–216. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00369.x
69. Akiyama M, Yasuoka H, Yoshimoto K, and Takeuchi T. Interleukin-4 contributes to the shift of balance of IgG subclasses toward IgG4 in IgG4-related disease. Cytokine. (2018) 110:416–19. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.05.009
70. Koneczny I, Tzartos J, Mané-Damas M, Yilmaz V, Huijbers MG, Lazaridis K, et al. IgG4 autoantibodies in organ-specific autoimmunopathies: reviewing class switching, antibody-producing cells, and specific immunotherapies. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:834342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.834342
71. Kanda M, Kamekura R, Sugawara M, Nagahata K, Suzuki C, Takano K, et al. IgG4-related disease administered dupilumab: case series and review of the literature. RMD Open. (2023) 9:e003026. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003026
72. Miossec P and Kolls JK. Targeting IL-17 and TH17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2012) 11:763–76. doi: 10.1038/nrd3794
73. Grados A, Ebbo M, Piperoglou C, Groh M, Regent A, Samson M, et al. T cell polarization toward TH2/TFH2 and TH17/TFH17 in patients with igG4-related disease. Front In Immunol. (2017) 8:235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00235
74. Gan PY, Steinmetz OM, Tan DS, O’Sullivan KM, Ooi JD, Iwakura Y, et al. Th17 cells promote autoimmune anti-myeloperoxidase glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2010) 21:925–31. doi: 10.1681/asn.2009070763
75. Fan X, Shu P, Wang Y, Ji N, and Zhang D. Interactions between neutrophils and T-helper 17 cells. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1279837. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279837
76. Moriyama M and Nakamura S. Th1/th2 immune balance and other T helper subsets in igG4-related disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. (2017) 401:75–83. doi: 10.1007/82_2016_40
77. Zotos D, Coquet JM, Zhang Y, Light A, D’Costa K, Kallies A, et al. IL-21 regulates germinal center B cell differentiation and proliferation through a B cell-intrinsic mechanism. J Exp Med. (2010) 207:365–78. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091777
78. Long Y, Feng J, Ma Y, Sun Y, Xu L, Song Y, et al. Altered follicular regulatory T (Tfr)- and helper T (Tfh)-cell subsets are associated with autoantibody levels in microscopic polyangiitis patients. Eur J Immunol. (2021) 51:1809–23. doi: 10.1002/eji.202049093
79. Yoon T, Ahn SS, Song JJ, Park YB, and Lee SW. Serum interleukin-21 positivity could indicate the current activity of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a monocentric prospective study. Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 38:1685–90. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04506-4
80. Uchida K and Okazaki K. Roles of regulatory T and B cells in igG4-related disease. IgG4-related disease. Curr Topics Microbiol Immunol. (2016) 401:93–114. doi: 10.1007/82_2016_41
81. Yang L, Anderson DE, Baecher-Allan C, Hastings WD, Bettelli E, Oukka M, et al. IL-21 and TGF-β are required for differentiation of human TH17 cells. Nature. (2008) 454:350–52. doi: 10.1038/nature07021
82. Zongfei J, Rongyi C, Xiaomeng C, Lili M, Lingying M, Xiufang K, et al. In vitro IL-6/IL-6R trans-signaling in fibroblasts releases cytokines that may be linked to the pathogenesis of igG4-related disease. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1272. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01272
83. Chiorini JA, Tsukuda S, Ikeura T, Ito T, Nakamaru K, Masuda M, et al. Clinical implications of elevated serum interleukin-6 in IgG4-related disease. PloS One. (2020) 15:e0027479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227479
84. Berti A, Warner R, Johnson K, Cornec D, Schroeder DR, Kabat BF, et al. The association of serum interleukin-6 levels with clinical outcomes in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. J Autoimmun. (2019) 105:102302. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.07.001
85. Henderson SR, Horsley H, Frankel P, Khosravi M, Goble T, Carter S, et al. Proteinase 3 promotes formation of multinucleated giant cells and granuloma-like structures in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:848–56. doi: 10.1136/ard-2021-221800
86. Yoon T, Ahn SS, Ko E, Song JJ, Park YB, and Lee SW. IL-6 receptor expression on the surface of T cells and serum soluble IL-6 receptor levels in patients with microscopic polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:7059. doi: 10.3390/jcm12227059
87. Kurimoto M, Watanabe T, Kamata K, Minaga K, and Kudo M. IL-33 as a critical cytokine for inflammation and fibrosis in inflammatory bowel diseases and pancreatitis. Front Physiol. (2021) 12:781012. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.781012
88. Hladinova Z, Hruskova Z, Svobodova B, Malickova K, Lanska V, Konopásek P, et al. Increased levels of soluble ST2 in patients with active newly diagnosed ANCA-associated vasculitis. Mediators Inflammation. (2015) 2015:603750. doi: 10.1155/2015/603750
89. Maehara T, Koga R, and Nakamura S. Immune dysregulation in immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. (2023) 59:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2022.12.002
90. O’Brien EC, Abdulahad WH, Rutgers A, Huitema MG, O’Reilly VP, Coughlan AM, et al. Intermediate monocytes in ANCA vasculitis: increased surface expression of ANCA autoantigens and IL-1β secretion in response to anti-MPO antibodies. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:11888. doi: 10.1038/srep11888
91. Sciascia S, Ponticelli C, and Roccatello D. Pathogenesis-based new perspectives of management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Autoimmun Rev. (2022) 21:103030. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.103030
92. Erden A, Bolek EC, Yardimci KG, Kilic L, Bilgen SA, and Karadag O. Do ANCA-associated vasculitides and IgG4-related disease really overlap or not? Int J Rheum Dis. (2019) 22:1926–32. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.13693
93. Oristrell J, Loureiro-Amigo J, Solans R, Valenzuela MP, Monsálvez V, Segarra A, et al. Relapse rate and renal prognosis in ANCA-associated vasculitis according to long-term ANCA patterns. Clin Exp Immunol. (2021) 203:209–18. doi: 10.1111/cei.13530
94. Abbass K and Krug H. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis in a patient with biopsy-proven IgG4-related pulmonary disease and coincident small cell lung cancer. BMJ Case Rep. (2019) 12:e226280. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-226280
95. Holland M, Hewins P, Goodall M, Adu D, Jefferis R, and Savage CO. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody IgG subclasses in Wegener’s granulomatosis: a possible pathogenic role for the IgG4 subclass. Clin Exp Immunol. (2004) 138:183–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02566.x
96. Della-Torre E, Lanzillotta M, Campochiaro C, Bozzalla E, Bozzolo E, Bandiera A, et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positivity in IgG4-related disease: A case report and review of the literature. Med (Baltimore). (2016) 95:e4633. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000004633
97. Bello F. The uncertain meaning of ANCA positivity in IgG4-related disease. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2021) 60:3492–93. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab368
98. Su T, Yang L, Cui Z, Wang SX, and Zhao MH. Concurrent IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis and IgG4 myeloperoxidase-anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positive crescentic glomerulonephritis: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e6707. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000006707
99. Pankhurst T, Nash G, Williams J, Colman R, Hussain A, and Savage C. Immunoglobulin subclass determines ability of immunoglobulin (Ig)G to capture and activate neutrophils presented as normal human IgG or disease-associated anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody (ANCA)-IgG. Clin Exp Immunol. (2011) 164:218–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04367.x
100. Della-Torre E, Rigamonti E, Perugino C, Baghai-Sain S, Sun N, Kaneko N, et al. B lymphocytes directly contribute to tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG(4)-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2020) 145:968–81.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.07.004
101. Liang P, Chen W, Yue S, Han Q, Zhu L, Li J, et al. An overlap of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and IgG4-related disease: distinct clinicopathologic clues for precise diagnosis. (2021). doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-161443/v1
102. Touge H, Tomita K, Yamasaki A, and Shimizu E. A case of proteinase 3 anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (PR3-ANCA) positive/IgG4-related lung disease. Respir Med Case Rep. (2017) 20:92–4. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2017.01.001
103. Chang SY, Keogh KA, Lewis JE, Ryu JH, Cornell LD, Garrity JA, et al. IgG4-positive plasma cells in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study on 43 granulomatosis with polyangiitis and 20 control cases. Hum Pathol. (2013) 44:2432–7. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.05.023
104. Kaushik P, Stone JH, Anderson JT, Dugar S, Mathew R, Nikolic B, et al. Medical mirroring: granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly Wegener’s) mimicking immunoglobulin-G4 related disease. Int J Rheum Dis. (2018) 21:885–89. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.12687
105. Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, Mahajan VS, Della Torre E, Lee H, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheumatic Dis. (2015) 74:190–95. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205233
106. Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Kulikova M, Lu L, Deshpande V, et al. Predictors of disease relapse in IgG4-related disease following rituximab. Rheumatology. (2016) 55:1000–08. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev438
107. Akiyama M. Serum IgG4 level and IgG4 subclass of ANCA as disease biomarker for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Int J Rheum Dis. (2020) 23:126–27. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.13768
108. Rispens T and Huijbers MG. The unique properties of IgG4 and its roles in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:763–78. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00871-z
109. Shiokawa M, Kodama Y, Kuriyama K, Yoshimura K, Tomono T, Morita T, et al. Pathogenicity of IgG in patients with IgG4-related disease. Gut. (2016) 65:1322–32. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310336
110. Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Della-Torre E, Sekigami Y, Carruthers M, Wallace ZS, et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2014) 134:679–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.034
111. Chang SY, Keogh K, Lewis JE, Ryu JH, and Yi ES. Increased igG4-positive plasma cells in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A diagnostic pitfall of igG4-related disease. Int J Rheumatol. (2012) 2012:121702. doi: 10.1155/2012/121702
112. Shimojima Y, Kishida D, Ichikawa T, Takamatsu R, Nomura S, and Sekijima Y. Features of BAFF and APRIL receptors on circulating B cells in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. (2023) 213:125–37. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad024
113. Kiyama K, Kawabata D, Hosono Y, Kitagori K, Yukawa N, Yoshifuji H, et al. Serum BAFF and APRIL levels in patients with IgG4-related disease and their clinical significance. Arthritis Res Ther. (2012) 14:R86. doi: 10.1186/ar3810
114. Moriyama M, Tanaka A, Maehara T, Furukawa S, Nakashima H, and Nakamura S. T helper subsets in Sjögren’s syndrome and IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis: a critical review. J Autoimmun. (2014) 51:81–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.07.007
115. Cai S, Hu Z, Chen Y, Chen Y, Ming B, Gao R, et al. BLyS/APRIL dual inhibition for IgG4-RD: a prospective single-arm clinical trial of telitacicept. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:881–83. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223529
116. Tsuboi K, Noguchi K, Kitano M, Furukawa T, Hashimoto T, Azuma N, et al. Serum B cell activating factor (BAFF) as a biomarker for induction of remission with rituximab in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Immunol Med. (2022) 45:238–43. doi: 10.1080/25785826.2022.2094592
117. Kronbichler A, Bajema IM, Bruchfeld A, Mastroianni Kirsztajn G, and Stone JH. Diagnosis and management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Lancet. (2024) 403:683–98. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01736-1
118. Tipping PG and Kitching AR. Glomerulonephritis, Th1 and Th2: what’s new? Clin Exp Immunol. (2005) 142:207–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02842.x
119. Sanders JS, Stegeman CA, and Kallenberg CG. The Th1 and Th2 paradigm in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Kidney Blood Press Res. (2003) 26:215–20. doi: 10.1159/000072987
120. Xia C, Liu C, Liu Y, Long Y, Xu L, and Liu C. Increased circulating th1 and tfh1 cell numbers are associated with disease activity in glucocorticoid-treated patients with igG4-related disease. J Immunol Res. (2020) 2020:3757015. doi: 10.1155/2020/3757015
121. Lee SK, Silva DG, Martin JL, Pratama A, Hu X, Chang PP, et al. Interferon-γ excess leads to pathogenic accumulation of follicular helper T cells and germinal centers. Immunity. (2012) 37:880–92. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.010
122. Lee LY, Yap H, Sampson S, Ford B, Hayman G, Marsh J, et al. IgG4- related disease as a rare cause of tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Clin Immunol. (2014) 34:548–50. doi: 10.1007/s10875-014-0049-9
123. Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, Miyake K, Hayashida J-N, Maehara T, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and the initiation of Mikulicz disease. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64:254–63. doi: 10.1002/art.33320
124. Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K, Kawano M, Yamada K, Takahira M, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology. (2007) 45:1538–46. doi: 10.1002/hep.21697
125. Balding CE, Howie AJ, Drake-Lee AB, and Savage CO. Th2 dominance in nasal mucosa in patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin Exp Immunol. (2001) 125:332–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.125002332.x
126. Mueller A, Holl-Ulrich K, Feller AC, Gross WL, and Lamprecht P. Immune phenomena in localized and generalized Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2003) 21:S49–54.
127. Masutani K, Tokumoto M, Nakashima H, Tsuruya K, Kashiwagi M, Kudoh Y, et al. Strong polarization toward Th1 immune response in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. (2003) 59:395–405. doi: 10.5414/cnp59395
128. Dolff S, Witzke O, and Wilde B. Th17 cells in renal inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. (2019) 18:129–36. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.08.006
129. Lee G. The balance of th17 versus treg cells in autoimmunity. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:730. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030730
130. Nogueira E, Hamour S, Sawant D, Henderson S, Mansfield N, Chavele KM, et al. Serum IL-17 and IL-23 levels and autoantigen-specific Th17 cells are elevated in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2010) 25:2209–17. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp783
131. Yasuda K, Takeuchi Y, and Hirota K. The pathogenicity of Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Semin Immunopathol. (2019) 41:283–97. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00733-8
132. Ohta N, Makihara S, Okano M, Kurakami K, Ishida A, Furukawa T, et al. Roles of IL-17, Th1, and Tc1 cells in patients with IgG4-related sclerosing sialadenitis. Laryngoscope. (2012) 122:2169–74. doi: 10.1002/lary.23429
133. Wilde B, Thewissen M, Damoiseaux J, Hilhorst M, van Paassen P, Witzke O, et al. Th17 expansion in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): the role of disease activity, immune regulation and therapy. Arthritis Res Ther. (2012) 14:R227. doi: 10.1186/ar4066
134. Jovanovic DV, Di Battista JA, Martel-Pelletier J, Jolicoeur F, He Y, Zhang M, et al. IL-17 stimulates the production and expression of proinflammatory cytokines, IL-β and TNF-α, by human macrophages. J Immunol. (1998) 160:3513–21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.160.7.3513
135. Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF, and Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. (2012) 30:531–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141623
136. Miyoshi H, Uchida K, Taniguchi T, Yazumi S, Matsushita M, Takaoka M, et al. Circulating naïve and CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. (2008) 36:133–40. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181577553
137. Mirouse A, Cacoub P, and Saadoun D. Regulatory T cells and systemic vasculitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2023) 35:25–30. doi: 10.1097/bor.0000000000000915
138. Abdulahad WH, Lamprecht P, and Kallenberg CGM. T-helper cells as new players in ANCA-associated vasculitides. Arthritis Res Ther. (2011) 13:236. doi: 10.1186/ar3362
139. Kimura A and Kishimoto T. IL-6: regulator of treg/th17 balance. Eur J Immunol. (2010) 40:1830–35. doi: 10.1002/eji.201040391
140. Akiyama M, Suzuki K, Yasuoka H, Kaneko Y, Yamaoka K, and Takeuchi T. Follicular helper T cells in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Rheumatology. (2018) 57:236–45. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex171
141. Wei XD and Niu XY. T follicular helper cells in autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. (2023) 134:102976. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102976
142. Kubo S, Nakayamada S, Zhao J, Yoshikawa M, Miyazaki Y, Nawata A, et al. Correlation of T follicular helper cells and plasmablasts with the development of organ involvement in patients with IgG4-related disease. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2018) 57:514–24. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex455
143. Chen Y, Lin W, Yang H, Wang M, Zhang P, Feng R, et al. Aberrant expansion and function of follicular helper T cell subsets in igG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2018) 70:1853–65. doi: 10.1002/art.40556
144. Akiyama M, Yasuoka H, Yamaoka K, Suzuki K, Kaneko Y, Kondo H, et al. Enhanced IgG4 production by follicular helper 2 T cells and the involvement of follicular helper 1 T cells in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther. (2016) 18:167. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1064-4
145. Xu J, Zhao H, Wang S, Zheng M, and Shuai Z. Elevated level of serum interleukin-21 and its influence on disease activity in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies against myeloperoxidase-associated vasculitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. (2022) 42:290–300. doi: 10.1089/jir.2022.0014
146. Hume DA, Irvine KM, and Pridans C. The mononuclear phagocyte system: the relationship between monocytes and macrophages. Trends Immunol. (2019) 40:98–112. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2018.11.007
147. Sohn K-H, Ham J, Chung SJ, Kang H-R, and Kim HY. Analysis of innate and adaptive immunological characteristics in patients with igG4-related disease. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2020) 181:807–12. doi: 10.1159/000508699
148. Brunini F, Page TH, Gallieni M, and Pusey CD. The role of monocytes in ANCA-associated vasculitides. Autoimmun Rev. (2016) 15:1046–53. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.07.031
149. Tashiro M, Sasatomi Y, Watanabe R, Watanabe M, Miyake K, Abe Y, et al. IL-1β promotes tubulointerstitial injury in MPO-ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. (2016) 86:190–99. doi: 10.5414/CN108902
150. Popa ER, Franssen CF, Limburg PC, Huitema MG, Kallenberg CG, and Tervaert JW. In vitro cytokine production and proliferation of T cells from patients with anti-proteinase 3- and antimyeloperoxidase-associated vasculitis, in response to proteinase 3 and myeloperoxidase. Arthritis Rheum. (2002) 46:1894–904. doi: 10.1002/art.10384
151. Funes SC, Rios M, Escobar-Vera J, and Kalergis AM. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology. (2018) 154:186–95. doi: 10.1111/imm.12910
152. Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ, and Hill AM. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol. (2000) 164:6166–73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.12.6166
153. Chinju A, Moriyama M, Kakizoe-Ishiguro N, Chen H, Miyahara Y, Haque A, et al. CD163+ M2 macrophages promote fibrosis in igG4-related disease via toll-like receptor 7/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4/NF-κB signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2022) 74:892–901. doi: 10.1002/art.42043
154. Akiyama M, Yasuoka H, Yoshimoto K, and Takeuchi T. CC-chemokine ligand 18 is a useful biomarker associated with disease activity in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. (2018) 77:1386–87. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212110
155. Liew FY, Girard JP, and Turnquist HR. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:676–89. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.95
156. Wu Y, Liu J, Yu T, Zhang J, Jin X, Ye Y, et al. The function of IL-33/ST2 signaling axis in treg cells activating fibrosis in IgG4-related disease. Hum Immunol. (2022) 83:295–305. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2022.01.009
157. Hoffmann JC, Patschan D, Dihazi H, Müller C, Schwarze K, Henze E, et al. Cytokine profiling in anti neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a cross-sectional cohort study. Rheumatol Int. (2019) 39:1907–17. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04364-y
158. Hauer HA, Bajema IM, van Houwelingen HC, Ferrario F, Noël LH, Waldherr R, et al. Renal histology in ANCA-associated vasculitis: differences between diagnostic and serologic subgroups. Kidney Int. (2002) 61:80–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00089.x
159. Bitton L, Vandenbussche C, Wayolle N, Gibier JB, Cordonnier C, Verine J, et al. Tubulointerstitial damage and interstitial immune cell phenotypes are useful predictors for renal survival and relapse in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. J Nephrol. (2020) 33:771–81. doi: 10.1007/s40620-019-00695-y
160. Ohlsson SM, Pettersson Å, Ohlsson S, Selga D, Bengtsson AA, Segelmark M, et al. Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated systemic vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. (2012) 170:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04633.x
Keywords: IgG4-RD, AAVs, GPA/MPA, pathophysiology, overlap syndrome
Citation: Wang C, He R, Bai X, Zhang Y, Li J, Zhao J, Gao W and Guo Q (2025) Immune cell crosstalk between ANCA-associated vasculitis and IgG4-related disease: an unresolved pathogenic link. Front. Immunol. 16:1660956. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1660956
Received: 07 July 2025; Accepted: 29 September 2025;
Published: 16 October 2025.
Edited by:
Yasuhiro Shimojima, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, JapanCopyright © 2025 Wang, He, Bai, Zhang, Li, Zhao, Gao and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiaoyan Guo, c25hbmFAamx1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡ORCID: Ronghua He, orcid.org/0000-0001-5748-8885
Qiaoyan Guo, orcid.org/0000-0003-3725-8067
 Cui Wang
Cui Wang Ronghua He
Ronghua He Xue Bai
Xue Bai Yarui Zhang1
Yarui Zhang1 Qiaoyan Guo
Qiaoyan Guo