Abstract
Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC), and post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome (PI-IBS), are characterized by immune-mediated intestinal inflammation and epithelial barrier dysfunction. Research indicates that the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)/interleukin-22 (IL-22) pathway is critical for intestinal homeostasis. This pathway can be activated by ligands from dietary and microbial sources (such as tryptophan metabolites), and AhR signaling in immune cells (particularly type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) and T cells) is the primary driver of IL-22 production. IL-22 protects the intestinal barrier and regulates inflammatory responses by promoting epithelial repair, enhancing mucus and antimicrobial defenses, and strengthening tight junctions. Dysregulation of this pathway plays a key role in the pathogenesis of chronic intestinal inflammation, leading to exacerbated inflammatory processes and mucosal damage. Given its central role in barrier defense and repair, targeting the AhR/IL-22 pathway has emerged as a novel therapeutic direction for restoring intestinal homeostasis. This review summarizes the mechanisms of action of this pathway in chronic intestinal inflammation and explores its potential as a novel therapeutic target.
1 Introduction
Chronic intestinal inflammatory disorders, encompassing UC, CD and PI-IBS, represent a group of persistent and recurrent conditions that profoundly impact patients’ quality of life. These disorders are pathologically defined by sustained inflammatory responses within the intestinal mucosa, with primary clinical manifestations including the recurrent onset and remission of symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue (1–3). Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) affects approximately 7 million people worldwide (4). Since the beginning of the 21st century, the morbidity of IBD has remained high in Western countries, while its incidence has surged in newly industrialized countries in Asia, Africa, and South America, becoming a major global public health challenge (5). High-income countries such as North America and Western Europe have the highest prevalence of IBD, while the incidence is rapidly increasing in low- and middle-income countries (6, 7). This indicates that the burden of IBD varies significantly across different regions and countries as socioeconomic development levels increase (7). Although the incidence of IBD in high-income countries tends to stabilize or decrease, its high prevalence and social burden remain a significant public health issue (8). Although current therapeutic approaches, including immunosuppressants, biologics, and agents targeting intestinal flora modulation, demonstrate efficacy in certain patients, a substantial proportion exhibit poor responsiveness to these treatments, and prolonged therapy may be associated with adverse effects (9, 10). Consequently, the identification of novel therapeutic targets and strategies is imperative to enhance the prognosis for individuals afflicted with chronic intestinal inflammation.
In recent years, significant attention has been directed towards elucidating the roles of tne AhR/IL-22 pathway in modulating intestinal immune responses and maintaining epithelial barrier integrity (11–13). The AhR functions as a ligand-activated transcription factor that is responsive to environmental cues, immune signaling, and cellular metabolic processes (14, 15). IL-22, a cytokine produced by specific immune cells, is instrumental in protecting the host from inflammatory damage in the gut by promoting the production of antimicrobial peptides and enhancing epithelial barrier function (16, 17). A growing body of evidence indicates that the AhR/IL-22 pathway is crucial for sustaining intestinal homeostasis and defense mechanisms. Upon activation, this pathway promotes the proliferation and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells, enhances the integrity of the mucosal barrier, and regulates inflammatory responses, thereby offering new therapeutic opportunities for the management of chronic intestinal inflammation (14, 18, 19). Consequently, pharmacotherapeutic strategies targeting the AhR/IL-22 pathway have emerged as a central focus in the research of chronic intestinal inflammation, offering promising potential for therapeutic intervention.
2 Biological basis of the AhR/IL-22 pathway
AhR is an essential ligand-activated transcription factor that is part of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) family, and it is widely expressed in both immune and non-immune cells (20). The primary intracellular role of AhR is to detect small environmental molecules, facilitated by its ligand-binding domain (LBD), which possesses a unique conformation capable of binding a diverse range of ligands (21, 22). These ligands include both exogenous and endogenous substances, such as environmental pollutants, dietary compounds, and tryptophan metabolites (23). In the absence of ligands, AhR is typically localized in the cytoplasm, where it forms complexes with molecular chaperones like heat shock protein 90 (HSP90), X-associated protein 2 (XAP2), and p23 (24). Upon ligand binding, AhR translocates to the nucleus and forms a heterodimer with the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator (ARNT), subsequently binding to specific DNA sequences (25, 26).
Activation of AhR can affect IL-22 production (Figure 1). In the canonical pathway, AhR: ligand: ARNT trimer binds to the dioxin response element (DRE) upstream of the AhR target gene regulatory region in the cell nucleus, thereby regulating gene transcription, including IL-22 (27). ILC3 is the main IL-22-producing cell, and activation of the AhR in ILC3 promotes IL-22 secretion (28). The AhR can control ILC3s proliferation and turnover by up-regulating the Kit and Notch pathways to manage the proliferation, differentiation, and turnover of ILCs, thereby maintaining the stability of the ILC cell pool to regulate IL-22 production (29). The activation of AhR facilitates the production of IL-22 by influencing monocytes and naïve CD4+ T cells, which subsequently differentiate into Th17/22 cells (30–32). Furthermore, AhR modulates IL-22 production by regulating the function of various immune cells that indirectly impact T cell activity and IL-22 synthesis (33). In non-canonical pathways, after AhR ligands bind to AhR, AhR can form complexes with transcription factors such as nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt). These complexes act together on the promoter region of the IL-22 gene to promote IL-22 production. Research also indicates that AhR not only independently regulates IL-22 production but also interacts with other signaling pathways. For instance, the Notch signaling pathway has been shown to augment IL-22 production in CD4+ T cells, contingent upon AhR activation (34). Additionally, interleukin-21 (IL-21) enhances IL-22 production by activating signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), which influences the epigenetic configuration of the IL-22 promoter and its interaction with AhR (35). Moreover, AhR activation elevates the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-22 and IL-10, while concurrently reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-6, and TNF-α (20).
Figure 1

Cellular mechanisms by which AhR affects IL-22 production. In the absence of ligands, AhR is typically localized in the cytoplasm, where it forms complexes with molecular chaperones such as HSP90, XAP2, and p23. In the canonical pathway, after AhR ligands bind to AhR, AhR enters the nucleus and forms heterodimers with ARNT. These heterodimers bind to the DRE element in the promoter region of the IL-22 gene, initiating transcription of the IL-22 gene, ultimately producing IL-22 protein. In the non-canonical pathway, after AhR ligands bind to AhR, AhR can form complexes with transcription factors such as NF-κB and RORγt. These complexes collectively act on the promoter region of the IL-22 gene, promoting the production of IL-22. AhR, Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor; DRE, Dioxin Response Element; IL-22R1, Interleukin-22 Receptor 1; IL-10R2, Interleukin-10 Receptor 2; ARNT, Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator; XAP2, Xenobiotic-Associated Protein 2; P23, Protein 23; HSP90, Heat Shock Protein 90.
IL-22 acts by binding to its receptor, which is a heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of the subunits interleukin-22 receptor 1 (IL-22R1) and IL-10R2 (36). The expression of IL-22R1 is mainly localized to non-immune tissues like the skin, lungs, small intestine, liver, colon, kidneys, and pancreas, whereas IL-10R2 is widely found in immune cells (37). When IL-22 binds to its receptor, it activates STAT3 through the JAK (Janus Kinase)-STAT pathway pathway and also triggers STAT1 (38). Additionally, the MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) pathway and the PI3K (Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase)-AKT (Protein Kinase B)-mTOR pathway are stimulated by IL-22 (39, 40). Through these signaling pathways, IL-22 plays a critical role in mucosal barrier immunity, tissue regeneration, and epithelial cell survival/proliferation. It further promotes the remodeling and repair of various tissues and organs, thereby sustaining the intrinsic host defense mechanisms that control pathogen invasion (40–42).
3 The role of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in intestinal homeostasis
3.1 The pathway of AhR/IL-22 signaling in the intestine
Signaling through the AhR/IL-22 pathway in intestinal epithelial cells involves a very complex process (Figure 2). In the gut, AhR regulates IL-22 production through interactions with various signaling pathways. The classical AhR/IL-22 signaling pathway in the intestine mainly regulates the expression of target genes such as IL-22 by ligand activation of AhR, nuclear translocation, and heterodimerization with ARNT, thereby maintaining intestinal barrier function and immunization homeostasis (43, 44). Gut microbes synthesize tryptophan derivatives, which act as ligands for AhR and can activate the AhR signaling pathway, promoting IL-22 secretion (45). AhR plays an important role in regulating immune cell homeostasis in the intestinal tract, particularly in the maintenance of ILC3s and IL-22-producing ILC22 cells (46, 47). In addition, AhR aids in the production of IL-22 by CD4+ T cells and monocytes in the intestinal lamina propria (48). AhR signaling is also required for the maintenance of IL-22 production by intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) (49). Non-classical signaling pathways involve the synergistic interaction between the AhR and NF-κB signaling pathways, as well as interactions with other transcription factors, which play an important role in regulating intestinal immune response and inflammation.The AhR signaling pathway can synergize with the Toll-like receptor (TLR)/NF-κB signaling pathway to jointly promote IL-22 production (50). Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyric acid, also promote the expression of AhR and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1α) through the inhibition of inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDAC) enzymes and activation of G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41), which in turn enhances IL-22 production (51, 52). The TGF-β signaling pathway is thought to play a role in regulating IL-22 production, especially in the context of intestinal tumorigenesis (53). Additionally, in the gut, AhR activity is regulated by cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1). CYP1 enzymes play an important role in regulating IL-22 production by metabolically removing AhR ligands, which, in turn, provides feedback regulation of the AhR signaling pathway (54). IL-22 shapes the composition and function of the intestinal microbiome, which can also lead to increased AhR signaling (55). These feedback mechanisms are crucial for preserving the balance of the intestinal immune system. IL-22, once produced, attaches to intestinal epithelial cells through its receptor, IL-22R1, and triggers downstream signaling pathways. For example, activation of the downstream STAT3 signaling pathway promotes epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation, and production of antimicrobial proteins (56). Thus, it plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal barrier function and regulating intestinal immunity.
Figure 2
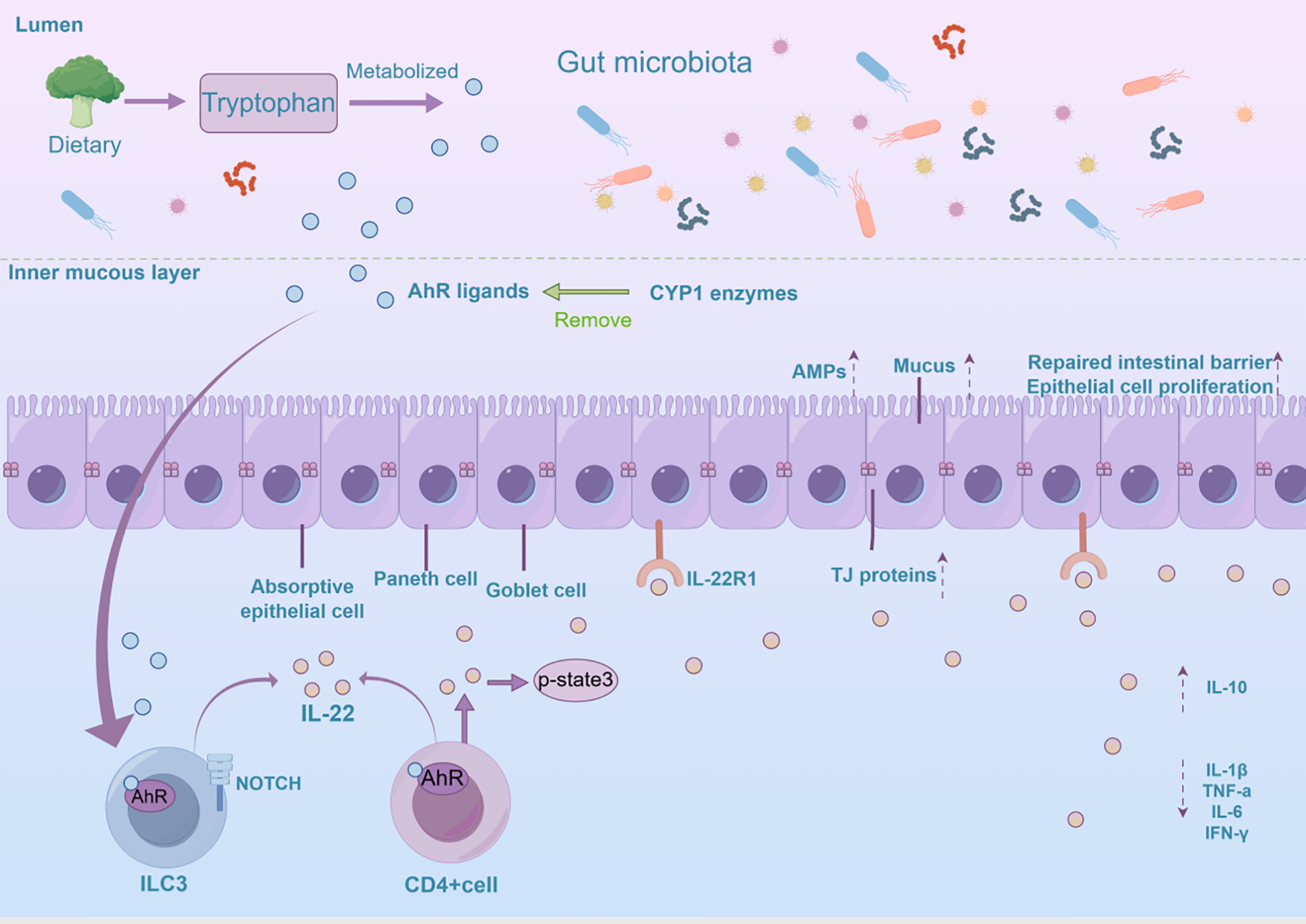
The mechanistic function of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in sustaining intestinal homeostasis is explored. AhR is activated in the intestine by various ligands, including tryptophan metabolites, microbiota-derived metabolites, and dietary compounds. This activation influences IL-22 expression in CD4+ T cells and ILC3s. IL-22 then promotes intestinal epithelial cell proliferation, tissue repair, and antimicrobial peptide secretion, maintaining the mucosal barrier, reducing inflammation, and supporting intestinal balance and homeostasis. ILC3, Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells; TJ protein, Tight Junction Protein; CYP1 enzymes, Cytochrome P450 enzymes; Amps, Antimicrobial Peptides.
3.2 The function of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in the intestine
The intestinal epithelial barrier’s integrity is crucial for the gut’s physiological function. Any impairment of this barrier may result in increased intestinal permeability, which can contribute to a range of disorders, including inflammatory bowel disease, allergic reactions, and metabolic diseases (57, 58). The intestinal epithelial barrier serves a critical function in inhibiting the translocation of deleterious substances, including bacteria and toxins, across the intestinal mucosa into adjacent tissues, organs, and the systemic circulation (59). It also inhibits the growth of harmful microorganisms, recognizes and removes invading pathogens while ensuring intestinal immune tolerance (60, 61).
The AhR/IL-22 signaling pathway is crucial for maintaining intestinal homeostasis by preserving mechanistic barriers, modulating immune responses, and fostering microbial symbiosis within the gut (62). In the context of IBD, dysregulation of the AhR/IL-22 pathway can result in aberrant immune responses, thereby exacerbating disease progression (20). This pathway contributes to the amelioration of intestinal barrier dysfunction by enhancing tight junction integrity and reducing epithelial permeability. Activation of the AhR/IL-22 pathway regulates the expression of tight junction proteins, such as claudin and occludin, which are vital for maintaining the structural integrity and selective permeability of the intestinal epithelium (63). IL-22 plays a pivotal role in promoting the repair and maintenance of intestinal structure and function. During instances of intestinal injury or inflammation, IL-22 stimulates the activation, proliferation, and differentiation of intestinal stem cells, thereby expediting the restoration of the intestinal epithelium (64, 65). Moreover, IL-22 stimulates mucin synthesis and glycosylation in intestinal epithelial cells, thereby strengthening the mucosal barrier function (66).
The activation of AhR can modulate host immune responses by regulating gut microbial communities and promoting intestinal health (67, 68). Additionally, IL-22 has been shown to further impact the immune status of the gut by altering the composition of the gut microbiota (69). It influences the gut microbiota by affecting epithelial cell growth and differentiation, as well as facilitating mucus secretion and the production of antimicrobial proteins (55). Furthermore, microbial metabolites can enhance IL-22 production by activating AhR, establishing a positive feedback loop that bolsters the immune defense mechanisms of the gut (32). Research indicates that IL-22 expression is intricately linked to the diversity of intestinal microbiota, with IL-22 deficiency potentially resulting in dysregulation of the intestinal microbiota and contributing to conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (20).
However, IL-22 does not invariably exert a protective effect. The role of IL-22 in IBD is complex. As mentioned earlier, under conditions such as impaired intestinal barrier function, infection, and inflammation, IL-22 can exert beneficial repair and defensive effects; however, in certain chronic inflammatory conditions and tumorigenesis, IL-22 may exacerbate the disease or promote tumor growth (66, 70, 71). In IBD, IL-22 promotes the chemotaxis of inflammatory cells and the expression of inflammatory factors, exacerbating the inflammatory reaction (66, 70). IL-22 can increase the expression of the tight junction protein Claudin-2, thereby increasing the permeability of the intestinal epithelium and reducing transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER), which may disrupt the integrity of the intestinal barrier and lead to excessive permeation of intestinal microorganisms (72, 73). Excessive IL-22 may also reduce the number of intestinal stem cells (ISCs), affecting the regenerative capacity of the intestinal epithelium, which may exacerbate intestinal mucosal injury in IBD (74, 75). IL-22 is involved in ER stress response (76, 77). IL-22 may enhance the growth and development of the intestine, as well as other tissues and neoplasms, by promoting angiogenesis (71, 78, 79). Consequently, the function of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in maintaining intestinal health and contributing to disease is multifaceted and complex.
4 The involvement of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in chronic inflammatory diseases of the intestinal tract
4.1 Ulcerative colitis
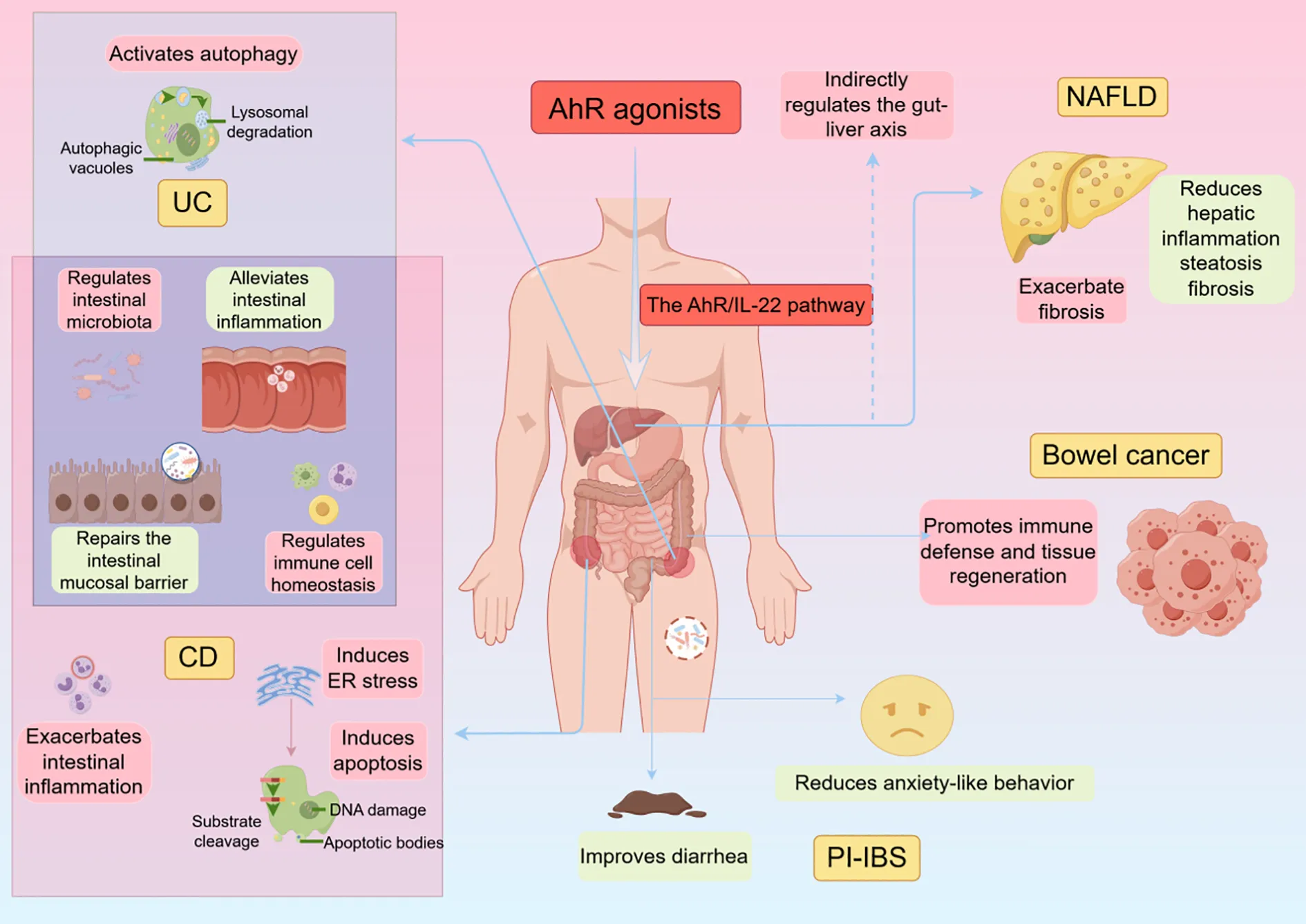
UC is a long-term inflammatory condition characterized by symptoms such as frequent diarrhea, mucus, abdominal pain, bloody stools, and pus in stools (80). The aetiology of UC is incompletely understood but has been linked to the interactions of genetic, environmental, and immune factors (80). Currently, clinically used medications for UC include 5-aminosalicylic acid analogs, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics (81). In the intestinal tissues of UC patients, AhR expression is significantly reduced, which correlates with increased inflammation and impaired intestinal barrier function. AhR activation leads to an increase in IL-22 production, which inhibits inflammation and maintains intestinal homeostasis. And AhR agonists are able to attenuate symptoms of the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in model mice by upregulating the expression of IL-22, and this model is highly similar to human UC (82).
Increased intestinal permeability is one of the essential features of UC. Quercetin has been found to alleviate UC by activating AhR-mediated enhancement of tight junctions (TJs), thereby repairing intestinal barrier dysfunction (83). Indole-3-carbinol (I3C), a ligand of AhR derived from plants, exhibits promising therapeutic potential in the context of DSS-induced chronic colitis. I3C is posited to facilitate the restoration of epithelial integrity by enhancing the expression of tight junction proteins and reestablishing homeostasis within both the innate and adaptive components of the intestinal immune system. This effect is mediated through the downregulation of neutrophil and macrophage activity, alongside the modulation of Th17/Treg cell ratios (84). In a recent study using baicalein to treat UC in DSS-induced mice, it was found that baicalein improved symptoms and intestinal barrier function in mice with colitis by activating AhR, upregulating the expression of cytochrome P4501A1 (CYP1A1), promoting the production of IL-22 in ILC3,and enhancing the levels of tight junction proteins ZO-1 and occludin (85). Tryptophan supplementation-activated AhR-mediated induction of IL-22/Stat3 plays a crucial role in mucosal epithelial homeostasis and integrity (86).
Regulation of intestinal flora in UC involves the important AhR/IL-22 pathway. Amaranthus L.-derived exosome-like nanoparticle (PELN) treatment resulted in an increased abundance of Lactobacillus reuteri and indole derivatives, which activated AhR in conventional CD4+ T cells, leading to the down-regulation of Zbtb7b expression, differentiation of conventional CD4+ T cells into double-positive (DP) CD4+CD8+ T cells, and ultimately the attenuation of DSS-induced colitis in C57 mice (87). In DSS-induced UC in mice, atorvastatin can alleviate UC by regulating intestinal flora disorders, promoting microbial tryptophan metabolism, increasing the expression levels of AhR and IL-22, and further enhancing the expression levels of intestinal tight junction proteins such as ZO-1 and occludin (88). The combination of Rhizoma coptidis polysaccharides and berberine demonstrated more significant therapeutic effects by increasing the relative abundance of short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacteria, which, in turn, elevated the level of SCFAs and activated the AhR/IL-22 pathway (89). A novel anti-colitis mechanism of oligofructose (FOS) promotes the production of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and indole propionic acid (IPA) to trigger AhR/IL-22 axis activation by alleviating intestinal dysbiosis and modulating microbial tryptophan metabolism (45). Fucoidan was able to ameliorate chronic colitis by promoting intestinal IL-22 expression, upregulating colonic IL-22 and fucosyltransferase 2 (FUT2) expression, and inducing IL-22 release from CD4+ T cells through the AhR pathway as well as IL-22 secretion by ILCs, thereby ameliorating luminal and mucosal flora disorders in the small intestine and colon (90). Akkermansia muciniphila (Akk) is a probiotic that reduces colonic inflammation by modulating tryptophan (Trp) metabolism to activate AhR signaling and up-regulate AhR target genes, including CYP1A1, IL-10, and IL-22 (91). Chen et al. used an in vitro lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced intestinal crypt epithelial cell (IEC-6) model and an in vivo DSS-induced UC mouse model to demonstrate that Lactobacillus paracasei L21 and its heat-inactivated postbiotic mitigated DSS colitis similarly attenuated DSS-colitis by modulating the NF-κB and HIF1α/AhR-IL-22-mucin 2 (MUC2) axes (92). High indole-3-lactic acid (ILA) production is a key tryptophan metabolic characteristic of L. plantarum which activated AHR downstream signaling (such as CYP1A1, IL-22, and STAT3) to alleviate colitis (93).
Furthermore, the AhR/IL-22 pathway is vital in regulating antimicrobial peptide secretion by intestinal epithelial cells. A specific degree of polymerization of chitosan (COS) can regulate tryptophan metabolism through the AhR/IL-22 pathway, attenuate colon injury and inflammation, down-regulate the levels of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1)—an enzyme that plays a key role in the tryptophan metabolism pathway—and restore the levels of tryptophan metabolites. Additionally, it promotes MUC2 expression and repairs the intestinal mucosal barrier (94). In the DSS-induced UC in mice, enhancing tryptophan metabolism associated with intestinal flora by reorganizing the structure of the intestinal flora can activate the AhR/IL-22 pathway, stimulate the phosphorylation of STAT3, increase the expression of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) Reg3β and Reg3γ, limit bacterial colonization on mucosal surfaces, reduce bacterial translocation to protect the mucosa, and accelerate the proliferation of epithelial cells, thereby further restoring the structure and function of intestinal barriers (95). In addition, ISC (intestinal stem cell) regeneration was enhanced, and intestinal IL-22 secretion, along with its related transcription factor AHR, was increased in DSS-induced UC after L-fucose treatment. This treatment accelerated ISC proliferation and helped to heal the epithelial barrier through the activation of nuclear AHR, stimulating the secretion of IL-22 from CD4+ T cells in the splenocytes of mice and from ILC3 cells in the LPMCs (48). In a DSS-induced mouse organoid inflammation model, Hymenolepis nana antigens promote intestinal stem cell proliferation and differentiation through the AhR/IL-22 signaling pathway, thereby alleviating ulcerative colitis (96). In UC, the AhR/IL-22 pathway may also function through the activation of autophagy. The activation of autophagy not only helps to maintain the homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium but also attenuates the inflammatory response and reduces intestinal damage (97, 98). Therapeutic interventions targeting the AhR/IL-22 axis may offer novel avenues for the management of ulcerative colitis, potentially enhancing autophagic processes and improving intestinal health outcomes (99, 100).
The complexity of UC has historically hindered a comprehensive understanding of its etiology and the identification of drug targets. In the field of UC treatment, the AhR/IL-22 signaling pathway plays a multifaceted role: it promotes intestinal barrier repair, regulates immune responses, activates autophagy processes, modulates intestinal microbiota balance, and accelerates intestinal epithelial cell regeneration. These findings highlight the potential value of this pathway in UC treatment and provide important clues for developing novel therapeutic strategies and targets.
However, given the current research progress and limitations, existing studies primarily rely on cell experiments and animal models, lacking validation in clinical patients. It is recommended to conduct multicenter clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of AhR agonists in UC patients; or encourage researchers to explore the interactions between the AhR/IL-22 pathway and other signaling pathways to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the role of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in the pathogenesis of UC.
4.2 Crohn’s disease
CD is a multifaceted chronic inflammatory bowel disorder characterized by significant clinical symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, abdominal masses, and hematochezia (101). The precise etiology of Crohn’s disease remains incompletely elucidated; however, an increasing body of research indicates that interactions among genetic predispositions, dysbiosis of the gut microbiota, immune system dysregulation, and environmental influences are pivotal in the pathogenesis of the disease (102–106). Current therapeutic strategies for CD encompass aminosalicylic acid compounds (commonly known as 5-ASA agents), glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, and biologic therapies (107). Although these treatments have been effective in enhancing patients’ quality of life and managing disease activity, concerns persist regarding their potential adverse effects and the safety associated with prolonged use (108, 109).
In CD, changes in the AhR/IL-22 pathway have attracted widespread attention. Studies have shown that AhR activation is closely associated with the pathological processes of CD (20, 110). The 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzolsulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced mouse model can mimic multiple pathological traits of Crohn disease, and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), an environmental pollutant that mainly affects the human body through diet, can alleviate colon inflammation in the TNBS colitis mouse model by partially producing regulatory immune cells after activating AhR (111). In TNBS-induced colitis in humanized mice, the nontoxic AHR agonist methyl 2-(1’H-indole-3’-carbonyl)-thiazole-4-carboxylate (ITE) induced functional human Tregs, which inhibited effector T-cell proliferation in vitro in a CD39- and granzyme B-dependent manner, leading to the up-regulation of IL-22. This demonstrated that ITE promotes mucosal immune homeostasis and protects against the development of colitis (112). In patients with CD, Th17 cell activity is usually increased, leading to the overproduction of IL-22 (32). By activating AhR, certain endogenous ligands can promote IL-22 production and enhance Th17 cell activity (33). Infliximab (IFX) therapy markedly increased IL-22 mRNA expression in the intestinal mucosa of patients with CD. Furthermore, the inhibition of AhR significantly suppressed the differentiation of IL-22+CD4+T (Th22) cells induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) treatment in these patients (113). In patients with CD, the expression levels of IL-22 are frequently modified, potentially influencing the integrity of the intestinal barrier and the modulation of the immune response (77). In a mouse model of TNBS-induced colitis, Higher levels of IL-22 were observed in dendritic cells (DCs) with AhR activation mediated by 6-formylindole [3,2-b] carbazole (FICZ) (114).
A protective function is played by IL-22 in CD to some extent by promoting the production of antimicrobial peptides and mucus that enhance intestinal barrier defense (66). IL-22 administration stimulates intestinal epithelial cells to upregulate the expression of tight junction proteins, such as claudin-1 and ZO-1, and enhances trans-epithelial resistance. This indicates that IL-22 plays a protective role in the intestinal mucosa of patients with CD by preserving the integrity of the epithelial barrier and mitigating inflammation (113). The activation of AhR enhances IL-22 production and affects the composition and function of the intestinal microbiota, which in turn influences the progression of CD (55). Ganoderic Acid A (GAA) can potentially ameliorate inflammatory bowel disease by modulating the intestinal flora and enhancing AhR activity, which in turn promotes IL-22 production and improves intestinal barrier function (115).
Despite the protective effects of IL-22, in the pathological state of CD, excess IL-22 may induce hyperproliferation of epithelial cells and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, further aggravating inflammation. Research has indicated that IL-22 might have a dual function in both acute and chronic inflammation in CD, aiding in the repair of epithelial cells while potentially worsening inflammation in certain situations (116). In patients with active Crohn’s disease CD, IL-22 induces an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-responsive transcriptional program in colonic epithelial cells, leading to a disease response characterized by the induction of apoptosis. In contrast, the genetic ablation or antibody blockade of IL-22 mitigates the ER stress response and alleviates the disease, indicating a pro-inflammatory role for IL-22 in CD (77). Furthermore, excessive activation of the IL-22 pathway may exacerbate intestinal inflammation and potentially increase the risk of colon cancer (117).
In summary, the AhR/IL-22 pathway plays a multifaceted role in CD, encompassing various mechanisms such as modulation of the immune response, enhancement of intestinal barrier function, and influence on the microbiota balance. Although IL-22 may have a protective role, its overexpression can intensify inflammation in the pathological context of CD. Consequently, a comprehensive investigation into the roles of AhR and IL-22 in CD not only enhances the understanding of its pathomechanisms but also identifies potential targets for the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
4.3 Post-infection irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a prevalent functional gastrointestinal disorder, the pathogenesis of which may be associated with a range of factors, including visceral hypersensitivity, dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota, dysfunction of the intestinal barrier, and low-grade inflammation. Its main symptoms include recurrent abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits, often accompanied by non-painful abdominal discomfort, anxiety, depression, and other psychiatric symptoms (118–120). After acute infectious diarrhea caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites, 10%-30% of patients develop symptoms of IBS with a predominantly diarrheal condition known as PI-IBS (121). Low-grade inflammation in the gut and increased intestinal permeability have been associated with dysfunction of the AhR/IL-22 pathway, which may lead to increased intestinal sensitization and worsening of symptoms in patients with IBS. For example, mice with AhR-specific deficiency in macrophages are more susceptible to TNBS-induced IBS (122, 123). Lactobacillus plantarum D266 (Lp D266) can shape the gut microbiota and enhance tryptophan (Trp) metabolism, thereby activating AhR and subsequently enhancing IL-22 production to maintain gut homeostasis. In addition, the combined use of Lp D266 and Trp can synergistically improve IBS symptoms (124). Although the detailed pathological mechanisms of PI-IBS are unknown, recent studies have shown changes in the AhR/IL-22 pathway within preclinical models of PI-IBS.Research has found that Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) can effectively prevent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) infection in piglets. The metabolites of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) interact with ILC3s in the jejunum of piglets through AhR. This interaction promotes the activation of ILC3s and the production of IL-22. Subsequently, IL-22 promotes the proliferation of porcine intestinal epithelial cell line J2 (IPEC-J2) cells and activates the STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby preventing PEDV infection (13). In a mouse model of PI-IBS, the AhR/IL-22 signaling pathway shows reduced expression, but administering IL-22 helps restore intestinal permeability and colonic sensitivity, enhances cognitive function, and lessens anxiety-like behavior (125). In PI-IBS, this pathway is closely related to the regulation of gut microbiota, immune response, and intestinal barrier function. The AhR/IL-22 pathway is anticipated to be a new target for addressing symptoms linked to post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome.
4.4 Other related diseases
4.4.1 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
The progression of NAFLD is a result of a multifactorial interaction in which chronic inflammation, abnormal lipid metabolism, and dysregulation of the intestinal-hepatic axis combine to assist in the commencement and evolution of the disease (126–128). AhR is expressed at high levels in resting hepatic stellate cells (HSC) but decreases with HSC activation. In studies of human and mouse hematopoietic stem cells, we found that AhR can block the activation of hematopoietic stem cells and the expression of genes required for liver fibrosis. Developing non-toxic AhR agonists or strategies to activate AhR signaling in HSCs could be used to prevent or treat liver fibrosis (129). Short-chain fatty acids and other metabolites produced by gut microbes can regulate hepatic metabolic and inflammatory pathways through interactions with host cell receptors (130). AhR activation promotes β-oxidation of hepatic fatty acids and reduces hepatic fat accumulation, thereby counteracting the development of NAFLD. Activation of AhR promotes the production of short-chain fatty acids, which, in turn, enhances gut barrier function and reduces hepatic fat deposition and inflammatory response (82, 131). Supplementation with quercetin alleviates obesity by restoring the gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by HFD in obese mice, thereby increasing IPA levels to activate the AhR/IL-22 pathway, which enhances intestinal barrier integrity and suppresses chronic inflammation (132). Additionally, activation of AhR is capable of influencing the activity of macrophages and other immune cells, thereby modulating the inflammatory environment of the liver (133). The “gut-liver axis” is one of the key factors in the pathogenesis of NAFLD, transporting intestinal microbial metabolites and inflammatory mediators to the liver via the portal vein, and the AhR may be indirectly involved in the regulation of NAFLD by influencing the composition of the gut microbiota (134). By regulating the metabolism of the gut microbiota, AhR may also influence the immune environment of the gut, which, in turn, improves liver health (135).
IL-22 promotes intestinal health by regulating the function of intestinal epithelial cells and inhibiting lipid absorption, thus alleviating metabolic disorders associated with obesity to a certain extent (136). IL-22 signaling is inhibited by a high-fructose and high-fat diet, which may affect the health status of the liver endogenously. High-fat diets not only lead to low-grade chronic inflammation but also alter the gut microbiota, which in turn affects IL-22 production (137). Obesity and high-calorie diets rapidly inhibit IL-22 production, leading to impaired gut barrier function, which exacerbates the risk of metabolic diseases (138). IL-22 plays a protective role in the liver, promoting hepatocyte survival and proliferation through the activation of signaling pathways (e.g., the STAT3 pathway) in hepatocytes, thereby reducing hepatocyte injury caused by NAFLD. Studies have shown that IL-22 is significantly upregulated in patients with chronic liver disease and correlates with hepatocyte proliferation and the degree of inflammation (139, 140). IL-22 inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, a role that is critical for reducing hepatic inflammation and promoting liver repair (141–143). By regulating metabolism-related signaling pathways such as AMPK, AKT, and mTOR, IL-22 not only improves the metabolic status of hepatocytes but also enhances the anti-apoptotic capacity of hepatocytes (143, 144). However, the role of IL-22 in liver fibrosis is dual: it promotes hepatocyte repair while potentially exacerbating fibrosis when overexpressed. This phenomenon may be related to the pro-inflammatory effects of IL-22, which can stimulate inflammatory responses and abnormal cell proliferation (145).
Nonetheless, there are fewer studies investigating the direct role of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in NAFLD, and its exact mechanism still needs further exploration. An in-depth study of this pathway’s mechanism may provide new insights for the treatment of NAFLD.
4.4.2 Bowel cancer
The AhR/IL-22 pathway is also important in bowel cancer. This pathway plays a crucial role in immune defense and tissue regeneration in the intestine, with multiple effects such as pro-survival signaling, cell migration, developmental abnormalities, and angiogenesis (146). AhR can influence the makeup of the gut microbiota by regulating other cytokines and signaling pathways, which can further affect the immune status of the intestinal tract and tumor progression (147, 148). IL-22 enhances intestinal barrier function and promotes the production of antimicrobial proteins, which may be protective against the development of intestinal cancers in some cases (66). In cases of chronic inflammation, the activation of the AhR/IL-22 pathway might result in the unusual growth of intestinal epithelial cells and the development of tumor (149). Even though IL-22 is known for its protective effects on intestinal health, its contribution to the progression of intestinal tumors may be exploited by tumor cells, thereby promoting tumor growth and metastasis (146). In some cases, overexpression of IL-22 is associated with the progression of intestinal tumors, while in other cases, it may inhibit tumorigenesis by promoting epithelial cell repair and regeneration (116, 146). IL-22 expression is significantly higher in human colon cancer tissue than in healthy tissue and promotes tumor cell proliferation. In addition, IL-22 may also support tumor growth by promoting angiogenesis (71, 78).
5 Conclusions and perspectives
This review consolidates current knowledge on the mechanistic role and therapeutic applications of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases. (Table 1, Table 2). The AhR/IL-22 signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the regulation of intestinal immunity, the maintenance of the mucosal barrier, and the modulation of inflammatory responses. Within the context of chronic intestinal inflammatory disorders, such as CD and UC, the activation of this pathway is intricately linked to the mitigation of inflammation and the stabilization of intestinal barrier function. Extensive research has demonstrated that this pathway’s activation can effectively promote the proliferation and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells, enhance mucosal barrier integrity, and modulate the inflammatory response appropriately. Additionally, its active involvement in maintaining microbial balance within the intestines and influencing the host immune response underscores its potential as a foundation for developing innovative therapeutic interventions.
Table 1
| Disease Mechanism |
UC | CD | IBS | NAFLD | Bowel cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maintaining intestinal epithelial cell integrity and function | + (85, 88, 94) |
+ (113) |
+ (123, 125) |
– | + (66) |
| Enhances intestinal cell repair and regeneration | + (48, 84, 99) |
+ (66, 116) |
– | – | + (116, 146) |
| Promotes hepatocyte proliferation | – | – | – | + (139, 140) |
– |
| Secretion of antimicrobial peptides | + (91, 94, 95) |
+ (66) |
– | – | + (66) |
| Regulation of immune cell function | + (85, 88, 91) |
+ (32, 33, 112) |
+ (122, 123) |
– | – |
| Suppression of the inflammatory response | + (85, 88, 94, 95) |
+ (111, 114) |
+ (122, 123) |
+ (141–143) |
– |
| Promotes inflammatory response | – | + (77, 116, 117) |
– | + (145) |
– |
| Modulation of the intestinal microbiota | + (45, 87, 88, 90, 95) |
+ (55, 115) |
+ (125) |
+ (134, 135) |
– |
| Regulation of lipid metabolism | – | – | – | + (129, 136) |
– |
| Activation of cell death | – | + (77) |
– | – | – |
| Inhibition of cell death | – | – | – | + (143, 144) |
– |
| Modulation of central nervous system sensitivity | – | – | + (125) |
– | – |
| Abnormal proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells | – | – | – | – | + (149) |
| Promotion of tumor invasion and metastasis | – | – | – | – | + (146) |
The role of the AhR/IL-22 pathway in chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases and other related conditions.
In Table 1, “+”indicates that published literature supports the effect; “-” indicates a lack of published literature to support the effect.
Table 2
| Name | Mechanism | Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitooligosaccharides | Restores the AHR-IL-22 pathway to normal, and promotes MUC2 expression | Alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice | (94) |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | Regulates Trp metabolism, activates AhR signaling and upregulates AhR target genes, such as IL-22 | Reduces colon inflammation | (91) |
| Atorvastatin | Regulates intestinal flora imbalance, enhances microbial tryptophan metabolism, and increases AhR and IL-22 expression. | Alleviates UC | (88) |
| Dietary tryptophan supplementation | Activates the AhR-mediated IL-22/Stat3 pathway | Amelioration of DSS-induced colitis | (86) |
| Fructo-oligosaccharides | Regulates microbial tryptophan metabolism promotes the production of IAA and IPA, thereby triggering AhR/IL-22 axis activation | Reduces symptoms of DSS-induced colitis | (45) |
| Portulaca oleracea L-derived exosome-like nanoparticles | Increasing the abundance of Lactobacillus reuteri and raising the levels of indole derivatives leads to the activation of AhR in conventional CD4+ T cells and increases IL-22 levels. | Reduces UC in mice | (87) |
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum D266 | Shaping the gut microbiota and Trp metabolism leads to activation of AhR and subsequent enhancement of IL-22 production | Improvement of IBS symptoms | (124) |
| Baicalein | Upregulates CYP1A1 expression and promotes IL-22 production in ILC3 through activation of AhR | Ameliorates symptoms and intestinal barrier function in UC mice | (85) |
| Coptis chinensis polysaccharides and Berberine |
Boosts SCFA-producing bacteria, raising SCFA levels and activating the AhR/IL-22 pathway | Improvement of symptoms in UC mice | (89) |
| L-Fucose | Stimulation of IL-22 secretion by CD4+ T cells in mouse splenocytes and ILC3 cells in LPMCs through activation of the nuclear AHR | Improvement of symptoms in UC mice | (48) |
| Fucoidan | Decreases UC-induced AhR and IL-22 expression | Treats with UC induced in rats | (90) |
| 6-formylindolo [3,2-b]carbazole | AHR physiological activator, FICZ/AHR/CYP1A1 feedback regulation, stimulates IL-22 expression by a variety of different immune cells (including ILC3) | Enhances the reinforcement of the intestinal epithelial barrier and aids in tissue repair, supporting intestinal balance. | (62) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | Promotes ILC3 activation and IL-22 production through AhR interaction with ILC3s | Prevention of virus enteric infections | (13) |
| Hymenolepis nana antigens | Enhances ISCs growth and development via the AhR/IL-22 pathway. | Alleviating symptoms in UC mice | (96) |
| Ganoderic acid A | Regulation of intestinal flora and enhancement of AhR activity to promote IL-22 production | Improvement of inflammatory bowel disease | (115) |
| Infliximab | Promotes IL-22+CD4+ T (Th22) cell differentiation in CD patients through AhR | improves CD symptoms | (113) |
| Dried ginger essential oil | Regulation of intestinal microbiota and tryptophan metabolite IAA-AHR/IL-22/STAT3 signaling axis | Alleviating 5-Fluorouracil-induced damage to the intestinal epithelial barrier in mice with mucositis | (12) |
| Lactobacillus paracaseiL21 | Activates the HIF1α/AhR pathway, increases IL-22 and mucins MUC2 to restore the goblet cell population | Alleviates DSS-induced colitis | (92) |
| Quercetin | Increases IPA levels to activate the AhR/IL-22 pathway | Reduces obesity and chronic intestinal inflammation | (132) |
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum producing high levels of indole-3-lactic acid | Activates AHR signaling in the intestine by metabolizing tryptophan, activating downstream AHR signaling (such as CYP1A1, IL-22, and STAT3) to alleviate colitis | Alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mouse models | (93) |
Outlines the mechanisms of action and effects of various compounds and pharmaceuticals on the AhR/IL-22 pathway.
Although the central role of the AhR-IL-22 axis in intestinal diseases is undeniable, further research is still needed to gain a deeper understanding of the pathological mechanisms underlying these diseases. While the role of AhR in immune regulation and maintaining intestinal homeostasis has become increasingly clear, the activation mechanisms of AhR in specific disease stages remain unclear. AhR has multiple ligands, whose sources and mechanisms of action are complex and diverse, making it extremely challenging to precisely elucidate the activation process of AhR (14, 150, 151). Additionally, the complex conversion mechanisms of IL-22 under pathological conditions require further exploration, as the molecular mechanisms and key influencing factors of its functional conversions remain poorly understood. This may be attributed to the high complexity of the intestinal microenvironment, where factors such as cell types, cytokine networks, and the intestinal microbiome may all influence IL-22’s function (70, 152, 153). Future research should investigate the precise activation mechanisms of AhR in the context of specific intestinal diseases, elucidating the key nodes and microenvironmental factors involved in IL-22 functional conversion.
Furthermore, although the AhR/IL-22 pathway has demonstrated significant therapeutic potential in basic research on chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases, its clinical application still faces numerous challenges. Current clinical trials are mostly in the preliminary exploratory phase, lacking clear definitions and strict application of treatment parameters, which limits the full realization of their clinical efficacy and may pose potential safety issues (14, 154, 155). To advance the clinical application of the AhR/IL-22 pathway, future research should prioritize high-quality clinical trials to accurately define treatment parameters, including optimal dosage, administration frequency, treatment duration, and patient selection criteria. Although the clinical application of the AhR/IL-22 pathway holds great promise, its advancement must be conducted with scientific rigor. Further research is necessary to develop more precise targeted interventions to drive progress in the treatment of intestinal diseases. In fact, the AhR/IL-22 pathway has emerged as a key regulatory pathway in intestinal diseases and represents a promising target for novel targeted therapeutic interventions in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases.
Statements
Author contributions
HK: Writing – original draft. ZC: Writing – review & editing. BW: Writing – review & editing. ZYC: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the 2021 Zhejiang Famous Veteran Traditional Chinese Medicine Expert Inheritance Studio Construction Project [No. GZS2021018]. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Yuan Y Wang X Huang S Wang H Shen G . Low-level inflammation, immunity, and brain-gut axis in IBS: unraveling the complex relationships. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2263209. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2263209
2
Nobrega VG Silva INDN Brito BS Silva J Silva MCMD Santana GO . The onset of clinical manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Arq Gastroenterol. (2018) 55:290–95. doi: 10.1590/S0004-2803.201800000-73
3
Wellens J Sabino J Vanuytsel T Tack J Vermeire S . Recent advances in clinical practice: mastering the challenge-managing IBS symptoms in IBD. Gut. (2025) 74:312–21. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-333565
4
The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:17–30. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30333-4
5
Wang S Dong Z Wan X . Global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease and its associated anemia, 1990 to 2019 and predictions to 2050: An analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019. Autoimmun Rev. (2024) 23:103498. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103498
6
Cao L Dayimu A Guan X Duan M Zeng S Wang H et al . Global evolving patterns and cross-country inequalities of inflammatory bowel disease burden from 1990 to 2019: a worldwide report. Inflammation Res. (2024) 73:277–87. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01836-7
7
Dou Z Zheng H Shi Y Li Y Jia J . Analysis of global prevalence, DALY and trends of inflammatory bowel disease and their correlations with sociodemographic index: Data from 1990 to 2019. Autoimmun Rev. (2024) 23:103655. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103655
8
Zhou J Bao J Liao X Chen Y Wang L Fan Y et al . Trends and projections of inflammatory bowel disease at the global, regional and national levels, 1990-2050: a bayesian age-period-cohort modeling study. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:2507. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-17431-8
9
Papamichael K Afif W Drobne D Dubinsky MC Ferrante M Irving PM et al . Therapeutic drug monitoring of biologics in inflammatory bowel disease: unmet needs and future perspectives. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 7:171–85. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00223-5
10
Altieri G Zilli A Parigi TL Allocca M Furfaro F Fiorino G et al . Dual therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Biomolecules. (2025) 15:1–2. doi: 10.3390/biom15020222
11
Su Y Wang M Wu Z Huang P Zeng J . Dihydrosanguinarine enhances tryptophan metabolism and intestinal immune function via AhR pathway activation in broilers. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2025) 16:94. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01220-x
12
Zhao X Xu L Li K Tang F Liu D Zhang J et al . Exploring dried ginger essential oil as a therapeutic strategy for 5-FU-induced mucositis: Gut microbiota and tryptophan metabolite IAA-AHR/IL-22/STAT3 signaling axis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 345:119616. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119616
13
Wang J Zhao Y Cui T Bao H Gao M Cheng M et al . AhR ligands from LGG metabolites promote piglet intestinal ILC3 activation and IL-22 secretion to inhibit PEDV infection. J Virol. (2024) 98:e103924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01039-24
14
Bahman F Choudhry K Al-Rashed F Al-Mulla F Sindhu S Ahmad R . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor: current perspectives on key signaling partners and immunoregulatory role in inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1421346. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421346
15
Hua X Chen Y Ding S Fang J . Tryptophan metabolism and the intestinal microbiota: Implications for inflammatory bowel disease. Microbiol Res. (2025) 300:128280. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2025.128280
16
Ouyang W O’Garra A . IL-10 family cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: from basic science to clinical translation. Immunity. (2019) 50:871–91. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.020
17
Dean LS Threatt AN Jones K Oyewole EO Pauly M Wahl M et al . I don’t know about you, but I’m feeling IL-22. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2024) 80:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2024.11.001
18
Metidji A Omenetti S Crotta S Li Y Nye E Ross E et al . The environmental sensor AHR protects from inflammatory damage by maintaining intestinal stem cell homeostasis and barrier integrity. Immunity. (2019) 50:1542. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.05.024
19
Li J Shi M Wang Y Liu J Liu S Kang W et al . Probiotic-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate AFB1-induced intestinal injury by modulating the gut microbiota and AHR activation. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:697. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02979-3
20
Pernomian L Duarte-Silva M de Barros Cardoso CR . The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) as a potential target for the control of intestinal inflammation: insights from an immune and bacteria sensor receptor. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2020) 59:382–90. doi: 10.1007/s12016-020-08789-3
21
Gruszczyk J Grandvuillemin L Lai-Kee-Him J Paloni M Savva CG Germain P et al . Cryo-EM structure of the agonist-bound Hsp90-XAP2-AHR cytosolic complex. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:7010. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34773-w
22
Song Y Slominski RM Qayyum S Kim T Janjetovic Z Raman C et al . Molecular and structural basis of interactions of vitamin D3 hydroxyderivatives with aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR): An integrated experimental and computational study. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 209:1111–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.048
23
Opitz CA Litzenburger UM Sahm F Ott M Tritschler I Trump S et al . An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. (2011) 478:197–203. doi: 10.1038/nature10491
24
Stockinger B Shah K Wincent E . AHR in the intestinal microenvironment: safeguarding barrier function. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:559–70. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00430-8
25
Esser C Rannug A . The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology, and toxicology. Pharmacol Rev. (2015) 67:259–79. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009001
26
Seok S Lee W Jiang L Molugu K Zheng A Li Y et al . Structural hierarchy controlling dimerization and target DNA recognition in the AHR transcriptional complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2017) 114:5431–36. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1617035114
27
Roman AC Carvajal-Gonzalez JM Merino JM Mulero-Navarro S Fernandez-Salguero PM . The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the crossroad of signalling networks with therapeutic value. Pharmacol Ther. (2018) 185:50–63. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.12.003
28
Xing Z Li X He J Chen Y Zhu L Zhang X et al . OLFM4 modulates intestinal inflammation by promoting IL-22(+)ILC3 in the gut. Commun Biol. (2024) 7:914. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06601-y
29
Golub R . The Notch signaling pathway involvement in innate lymphoid cell biology. BioMed J. (2021) 44:133–43. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.12.004
30
Doulabi H Masoumi E Rastin M Foolady Azarnaminy A Esmaeili S Mahmoudi M . The role of Th22 cells, from tissue repair to cancer progression. Cytokine. (2022) 149:155749. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155749
31
Ma Z Akhtar M Pan H Liu Q Chen Y Zhou X et al . Fecal microbiota transplantation improves chicken growth performance by balancing jejunal Th17/Treg cells. Microbiome. (2023) 11:137. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01569-z
32
Yang W Yu T Huang X Bilotta AJ Xu L Lu Y et al . Intestinal microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulation of immune cell IL-22 production and gut immunity. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:4457. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18262-6
33
Schiering C Vonk A Das S Stockinger B Wincent E . Cytochrome P4501-inhibiting chemicals amplify aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation and IL-22 production in T helper 17 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. (2018) 151:47–58. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.02.031
34
Li Y Li L Gao Y . The role of notch signaling pathway in adult patients with Epstein-Barr virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. (2024) 32:920–26. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2024.03.041
35
Yeste A Mascanfroni ID Nadeau M Burns EJ Tukpah A Santiago A et al . IL-21 induces IL-22 production in CD4+ T cells. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3753. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4753
36
Yu Y Qiao M Liu J Guo Y Sun Y . The reciprocal regulation between autophagy and IL-22: implications for immunity and therapy. Clin Exp Med. (2025) 25:187. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01695-y
37
Seth P Dubey S . IL-22 as a target for therapeutic intervention: Current knowledge on its role in various diseases. Cytokine. (2023) 169:156293. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156293
38
Wang X Li L Yuan G Zhu L Pei C Hou L et al . Interleukin (IL)-22 in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.): Immune modulation, antibacterial defense, and activation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2022) 131:796–808. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.10.051
39
Ye J Wang Y Xu Y Wang Z Liu L Wang M et al . Interleukin-22 deficiency alleviates doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and cardiac injury via the p38 MAPK/macrophage/Fizz3 axis in mice. Redox Biol. (2020) 36:101636. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101636
40
Chen G Lv C Nie Q Li X Lv Y Liao G et al . Essential Oil of Matricaria chamomilla Alleviate Psoriatic-Like Skin Inflammation by Inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR and p38MAPK Signaling Pathway. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. (2024) 17:59–77. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S445008
41
Sajiir H Ramm GA Macdonald GA McGuckin MA Prins JB Hasnain SZ . Harnessing IL-22 for metabolic health: promise and pitfalls. Trends Mol Med. (2025) 31:574–84. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.10.016
42
Qin J Zhu W Zhou W . Navigating the paradox of IL-22: friend or foe in hepatic health? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2025) 40:1393–408. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16991
43
Diao X Shang Q Guo M Huang Y Zhang M Chen X et al . Structural basis for the ligand-dependent activation of heterodimeric AHR-ARNT complex. Nat Commun. (2025) 16:1282. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56574-7
44
Fu Y Lyu J Wang S . The role of intestinal microbes on intestinal barrier function and host immunity from a metabolite perspective. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1277102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1277102
45
Yang C Du Y Li Q Liu L Zhao L Gao C et al . Fructo-oligosaccharides alleviated ulcerative colitis via gut microbiota-dependent tryptophan metabolism in association with aromatic hydrocarbon receptor activation in mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:27912–22. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c07248
46
Lee JS Cella M McDonald KG Garlanda C Kennedy GD Nukaya M et al . AHR drives the development of gut ILC22 cells and postnatal lymphoid tissues via pathways dependent on and independent of Notch. Nat Immunol. (2011) 13:144–51. doi: 10.1038/ni.2187
47
Wang H Wang T He Z Wen C Huang L Wang M . Deciphering the role of innate lymphoid cells group 3 in the gut microenvironment: A narrative review of their novel contributions to autoimmune disease pathogenesis. J Inflammation Res. (2025) 18:5741–57. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S512652
48
Tan C Hong G Wang Z Duan C Hou L Wu J et al . Promoting effect of L-fucose on the regeneration of intestinal stem cells through AHR/IL-22 pathway of intestinal lamina propria monocytes. Nutrients. (2022) 14:15–16. doi: 10.3390/nu14224789
49
Chen X Zhu Y Wei Y Fan S Xia L Chen Q et al . Glutamine alleviates intestinal injury in a murine burn sepsis model by maintaining intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte homeostasis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 940:175480. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175480
50
Ishihara Y Kado SY Bein KJ He Y Pouraryan AA Urban A et al . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling synergizes with TLR/NF-kappaB-signaling for induction of IL-22 through canonical and non-canonical AhR pathways. Front Toxicol. (2021) 3:787360. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2021.787360
51
Iraporda C Errea A Romanin DE Cayet D Pereyra E Pignataro O et al . Lactate and short chain fatty acids produced by microbial fermentation downregulate proinflammatory responses in intestinal epithelial cells and myeloid cells. Immunobiology. (2015) 220:1161–69. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.06.004
52
Fujiwara H Docampo MD Riwes M Peltier D Toubai T Henig I et al . Microbial metabolite sensor GPR43 controls severity of experimental GVHD. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:3674. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06048-w
53
Xue J Nguyen DTC Habtezion A . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates pancreatic IL-22 production and protects mice from acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2012) 143:1670–80. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.08.051
54
Schiering C Wincent E Metidji A Iseppon A Li Y Potocnik AJ et al . Feedback control of AHR signalling regulates intestinal immunity. Nature. (2017) 542:242–45. doi: 10.1038/nature21080
55
Mar JS Ota N Pokorzynski ND Peng Y Jaochico A Sangaraju D et al . IL-22 alters gut microbiota composition and function to increase aryl hydrocarbon receptor activity in mice and humans. Microbiome. (2023) 11:47. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01486-1
56
Zhou L Chu C Teng F Bessman NJ Goc J Santosa EK et al . Innate lymphoid cells support regulatory T cells in the intestine through interleukin-2. Nature. (2019) 568:405–09. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1082-x
57
Neurath MF Artis D Becker C . The intestinal barrier: a pivotal role in health, inflammation, and cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2025) 10:573–92. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00390-X
58
Kumar A Jayawardena D Priyamvada S Anbazhagan AN Chatterjee I Saksena S et al . SLC26A3 (DRA, the congenital chloride diarrhea gene): A novel therapeutic target for diarrheal diseases. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2025) 19:101452. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.101452
59
Suzuki T . Regulation of the intestinal barrier by nutrients: The role of tight junctions. Anim Sci J. (2020) 91:e13357. doi: 10.1111/asj.13357
60
Chairatana P Nolan EM . Defensins, lectins, mucins, and secretory immunoglobulin A: microbe-binding biomolecules that contribute to mucosal immunity in the human gut. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. (2017) 52:45–56. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2016.1243654
61
Kayama H Okumura R Takeda K . Interaction between the microbiota, epithelia, and immune cells in the intestine. Annu Rev Immunol. (2020) 38:23–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-070119-115104
62
Rannug A . How the AHR became important in intestinal homeostasis-A diurnal FICZ/AHR/CYP1A1 feedback controls both immunity and immunopathology. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5–9. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165681
63
Li M Oshima T Ito C Yamada M Tomita T Fukui H et al . Glutamine blocks interleukin-13-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. Digestion. (2021) 102:170–79. doi: 10.1159/000502953
64
Gronke K Hernandez PP Zimmermann J Klose CSN Kofoed-Branzk M Guendel F et al . Interleukin-22 protects intestinal stem cells against genotoxic stress. Nature. (2019) 566:249–53. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0899-7
65
Hou Q Ye L Liu H Huang L Yang Q Turner JR et al . Lactobacillus accelerates ISCs regeneration to protect the integrity of intestinal mucosa through activation of STAT3 signaling pathway induced by LPLs secretion of IL-22. Cell Death Differ. (2018) 25:1657–70. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0070-2
66
Keir M Yi T Lu T Ghilardi N . The role of IL-22 in intestinal health and disease. J Exp Med. (2020) 217:e20192195. doi: 10.1084/jem.20192195
67
Palrasu M Kakar K Marudamuthu A Hamida H Thada S Zhong Y et al . AhR activation transcriptionally induces anti-microbial peptide alpha-defensin 1 leading to reversal of gut microbiota dysbiosis and colitis. Gut Microbes. (2025) 17:2460538. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2460538
68
Barreira-Silva P Lian Y Kaufmann SHE Moura-Alves P . The role of the AHR in host-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Immunol. (2025) 25:178–94. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01088-4
69
He Y Feng D Hwang S Mackowiak B Wang X Xiang X et al . Interleukin-20 exacerbates acute hepatitis and bacterial infection by downregulating IkappaBzeta target genes in hepatocytes. J Hepatol. (2021) 75:163–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.02.004
70
Cineus R Luo Y Saliutina M Manna S Cancino CA Velasco Blazquez L et al . The IL-22-oncostatin M axis promotes intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis. Nat Immunol. (2025) 26:837–53. doi: 10.1038/s41590-025-02149-z
71
Klotskova H Kidess E Nadal AL Brugman S . The role of interleukin-22 in mammalian intestinal homeostasis: Friend and foe. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2024) 12:e1144. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1144
72
Patnaude L Mayo M Mario R Wu X Knight H Creamer K et al . Mechanisms and regulation of IL-22-mediated intestinal epithelial homeostasis and repair. Life Sci. (2021) 271:119195. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119195
73
Wang Y Mumm JB Herbst R Kolbeck R Wang Y . IL-22 increases permeability of intestinal epithelial tight junctions by enhancing claudin-2 expression. J Immunol. (2017) 199:3316–25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700152
74
Zha J Li H Lin Q Kuo W Jiang Z Tsai P et al . Interleukin 22 expands transit-amplifying cells while depleting Lgr5(+) stem cells via inhibition of Wnt and notch signaling. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 7:255–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.09.006
75
Sommer K Wiendl M Muller TM Heidbreder K Voskens C Neurath MF et al . Intestinal mucosal wound healing and barrier integrity in IBD-crosstalk and trafficking of cellular players. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:643973. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.643973
76
Pavlidis P Tsakmaki A Pantazi E Li K Cozzetto D Digby-Bell J et al . Interleukin-22 regulates neutrophil recruitment in ulcerative colitis and is associated with resistance to ustekinumab therapy. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:5820. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33331-8
77
Powell N Pantazi E Pavlidis P Tsakmaki A Li K Yang F et al . Interleukin-22 orchestrates a pathological endoplasmic reticulum stress response transcriptional programme in colonic epithelial cells. Gut. (2020) 69:578–90. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318483
78
Protopsaltis NJ Liang W Nudleman E Ferrara N . Interleukin-22 promotes tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. (2019) 22:311–23. doi: 10.1007/s10456-018-9658-x
79
Chiriac MT Buchen B Wandersee A Hundorfean G Gunther C Bourjau Y et al . Activation of epithelial signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 by interleukin 28 controls mucosal healing in mice with colitis and is increased in mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. (2017) 153:123–38. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.015
80
Fakhoury M Negrulj R Mooranian A Al-Salami H . Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments. J Inflammation Res. (2014) 7:113–20. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S65979
81
Di Sabatino A Biancheri P Rovedatti L Macdonald TT Corazza GR . Recent advances in understanding ulcerative colitis. Intern Emerg Med. (2012) 7:103–11. doi: 10.1007/s11739-011-0719-z
82
Monteleone I Rizzo A Sarra M Sica G Sileri P Biancone L et al . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-induced signals up-regulate IL-22 production and inhibit inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. (2011) 141:237–48. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.007
83
Wang X Xie X Li Y Xie X Huang S Pan S et al . Quercetin ameliorates ulcerative colitis by activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor to improve intestinal barrier integrity. Phytother Res. (2024) 38:253–64. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8027
84
Riemschneider S Hoffmann M Slanina U Weber K Hauschildt S Lehmann J . Indol-3-carbinol and quercetin ameliorate chronic DSS-induced colitis in C57BL/6 mice by AhR-mediated anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:11–14. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052262
85
Li Y Wang X Su Y Wang Q Huang S Pan Z et al . Baicalein ameliorates ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal epithelial barrier via AhR/IL-22 pathway in ILC3s. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2022) 43:1495–507. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00781-7
86
Islam J Sato S Watanabe K Watanabe T Ardiansyah Hirahara K et al . Dietary tryptophan alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis through aryl hydrocarbon receptor in mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2017) 42:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.12.019
87
Zhu M Xu H Liang Y Xu J Yue N Zhang Y et al . Edible exosome-like nanoparticles from portulaca oleracea L mitigate DSS-induced colitis via facilitating double-positive CD4(+)CD8(+)T cells expansion. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:309. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02065-0
88
Gou Y Cai S Chen Y Hou X Zhang J Bi C et al . Atorvastatin improved ulcerative colitis in association with gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism. Life Sci. (2024) 351:122790. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122790
89
Wang X Liang F Dai Z Feng X Qiu F . Combination of Coptis chinensis polysaccharides and berberine ameliorates ulcerative colitis by regulating gut microbiota and activating AhR/IL-22 pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 318:117050. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117050
90
Bagalagel A Diri R Noor A Almasri D Bakhsh HT Kutbi HI et al . Curative effects of fucoidan on acetic acid induced ulcerative colitis in rats via modulating aryl hydrocarbon receptor and phosphodiesterase-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2022) 22:196. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03680-4
91
Gu Z Pei W Shen Y Wang L Zhu J Zhang Y et al . Akkermansia muciniphila and its outer protein Amuc_1100 regulates tryptophan metabolism in colitis. Food Funct. (2021) 12:10184–95. doi: 10.1039/d1fo02172a
92
Chen J Zhang L Jiao Y Lu X Zhang N Li X et al . Lacticaseibacillus paracasei L21 and its postbiotics ameliorate ulcerative colitis through gut microbiota modulation, intestinal barrier restoration, and HIF1alpha/AhR-IL-22 axis activation: combined in vitro and in vivo evidence. Nutrients. (2025) 17:16–21. doi: 10.3390/nu17152537
93
Zuo X Zhang T Dong X Liu J Liu Y . Identification of the key tryptophan metabolic characteristics of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum for aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation and ulcerative colitis alleviation. Food Res Int. (2025) 203:115766. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.115766
94
Wang Y Ji X Zhao M Li J Yin H Jin J et al . Modulation of tryptophan metabolism via AHR-IL22 pathway mediates the alleviation of DSS-induced colitis by chitooligosaccharides with different degrees of polymerization. Carbohydr Polym. (2023) 319:121180. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121180
95
Zhang Y Han L Dong J Yuan Z Yao W Ji P et al . Shaoyao decoction improves damp-heat colitis by activating the AHR/IL-22/STAT3 pathway through tryptophan metabolism driven by gut microbiota. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 326:117874. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117874
96
Cui X Cheng Y Wang H Li X Li J Zhang K et al . Hymenolepis nana antigens alleviate ulcerative colitis by promoting intestinal stem cell proliferation and differentiation via AhR/IL-22 signaling pathway. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2024) 18:e12714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012714
97
Pott J Kabat AM Maloy KJ . Intestinal Epithelial Cell Autophagy Is Required to Protect against TNF-Induced Apoptosis during Chronic Colitis in Mice. Cell Host Microbe. (2018) 23:191–202. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.12.017
98
Pott J Maloy KJ . Epithelial autophagy controls chronic colitis by reducing TNF-induced apoptosis. Autophagy. (2018) 14:1460–61. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1450021
99
Aden K Tran F Ito G Sheibani-Tezerji R Lipinski S Kuiper JW et al . ATG16L1 orchestrates interleukin-22 signaling in the intestinal epithelium via cGAS-STING. J Exp Med. (2018) 215:2868–86. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171029
100
Huang F . Therapeutic potential of nutritional aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in gut-related inflammation and diseases. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:5–6. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122912
101
Feuerstein JD Cheifetz AS . Crohn disease: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Mayo Clin Proc. (2017) 92:1088–103. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2017.04.010
102
Khor B Gardet A Xavier RJ . Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. (2011) 474:307–17. doi: 10.1038/nature10209
103
Cleynen I Gonzalez JR Figueroa C Franke A McGovern D Bortlik M et al . Genetic factors conferring an increased susceptibility to develop Crohn’s disease also influence disease phenotype: results from the IBDchip European Project. Gut. (2013) 62:1556–65. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300777
104
Markelova M Senina A Khusnutdinova D Siniagina M Kupriyanova E Shakirova G et al . Association between taxonomic composition of gut microbiota and host single nucleotide polymorphisms in Crohn’s disease patients from Russia. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:1–2. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097998
105
Estevinho MM Midya V Cohen-Mekelburg S Allin KH Fumery M Pinho SS et al . Emerging role of environmental pollutants in inflammatory bowel disease risk, outcomes and underlying mechanisms. Gut. (2025) 74:477–86. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-332523
106
Jacob EM Borah A Pillai SC Kumar DS . Inflammatory bowel disease: the emergence of new trends in lifestyle and nanomedicine as the modern tool for pharmacotherapy. Nanomaterials (Basel). (2020) 10:1–3. doi: 10.3390/nano10122460
107
Magro F Cordeiro G Dias AM Estevinho MM . Inflammatory bowel disease - non-biological treatment. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 160:105075. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105075
108
Townsend CM Nguyen TM Cepek J Abbass M Parker CE MacDonald JK et al . Adalimumab for maintenance of remission in Crohn’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 5:CD12877. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012877.pub2
109
Adegbola SO Sahnan K Warusavitarne J Hart A Tozer P . Anti-TNF therapy in Crohn’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:12–14. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082244
110
Zhao X Li J Ma J Jiao C Qiu X Cui X et al . MiR-124a mediates the impairment of intestinal epithelial integrity by targeting aryl hydrocarbon receptor in Crohn’s disease. Inflammation. (2020) 43:1862–75. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01259-0
111
Benson JM Shepherd DM . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by TCDD reduces inflammation associated with Crohn’s disease. Toxicol Sci. (2011) 120:68–78. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq360
112
Goettel JA Gandhi R Kenison JE Yeste A Murugaiyan G Sambanthamoorthy S et al . AHR activation is protective against colitis driven by T cells in humanized mice. Cell Rep. (2016) 17:1318–29. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.09.082
113
Fang L Pang Z Shu W Wu W Sun M Cong Y et al . Anti-TNF therapy induces CD4+ T-cell production of IL-22 and promotes epithelial repairs in patients with Crohn’s disease. Inflammation Bowel Dis. (2018) 24:1733–44. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy126
114
Cui X Ye Z Wang D Yang Y Jiao C Ma J et al . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation ameliorates experimental colitis by modulating the tolerogenic dendritic and regulatory T cell formation. Cell Biosci. (2022) 12:46. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00780-z
115
Kou R Li Z Wang J Jiang S Zhang R He Y et al . Ganoderic acid A mitigates inflammatory bowel disease through modulation of AhR activity by microbial tryptophan metabolism. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:17912–23. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01166
116
Ouyang W . Distinct roles of IL-22 in human psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2010) 21:435–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2010.10.007
117
Mizoguchi A Yano A Himuro H Ezaki Y Sadanaga T Mizoguchi E . Clinical importance of IL-22 cascade in IBD. J Gastroenterol. (2018) 53:465–74. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1401-7
118
Enck P Aziz Q Barbara G Farmer AD Fukudo S Mayer EA et al . Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2016) 2:16014. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.14
119
Aguilera-Lizarraga J Hussein H Boeckxstaens GE . Immune activation in irritable bowel syndrome: what is the evidence? Nat Rev Immunol. (2022) 22:674–86. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00700-9
120
JohnBritto JS Di Ciaula A Noto A Cassano V Sciacqua A Khalil M et al . Gender-specific insights into the irritable bowel syndrome pathophysiology. Focus on gut dysbiosis and permeability. Eur J Intern Med. (2024) 125:10–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2024.03.011
121
Ghoshal UC Gwee K . Post-infectious IBS, tropical sprue and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: the missing link. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 14:435–41. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.37
122
Matricon J Meleine M Gelot A Piche T Dapoigny M Muller E et al . Review article: Associations between immune activation, intestinal permeability and the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2012) 36:1009–31. doi: 10.1111/apt.12080
123
Xu X Dong Q Zhong Q Xiu W Chen Q Wang J et al . The flavonoid kurarinone regulates macrophage functions via aryl hydrocarbon receptor and alleviates intestinal inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome. J Inflammation Res. (2021) 14:4347–59. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S329091
124
Xia B Lin T Li Z Wang J Sun Y Wang D et al . Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Regulates Intestinal Physiology and Enteric Neurons in IBS through Microbial Tryptophan Metabolites. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:17989–8002. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c03087
125
Meynier M Baudu E Rolhion N Defaye M Straube M Daugey V et al . AhR/IL-22 pathway as new target for the treatment of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome symptoms. Gut Microbes. (2022) 14:2022997. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.2022997
126
Gehrke N Schattenberg JM . Metabolic inflammation-A role for hepatic inflammatory pathways as drivers of comorbidities in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:1929–47. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.020
127
Han H Jiang Y Wang M Melaku M Liu L Zhao Y et al . Intestinal dysbiosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): focusing on the gut-liver axis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 63:1689–706. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1966738
128
Jennison E Byrne CD . The role of the gut microbiome and diet in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2021) 27:22–43. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0129
129
Yan J Tung H Li S Niu Y Garbacz WG Lu P et al . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology. (2019) 157:793–806. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.05.066
130
Lee K Jayaraman A . Interactions between gut microbiota and non-alcoholic liver disease: The role of microbiota-derived metabolites. Pharmacol Res. (2019) 142:314. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.013
131
Kim MH Kang SG Park JH Yanagisawa M Kim CH . Short-chain fatty acids activate GPR41 and GPR43 on intestinal epithelial cells to promote inflammatory responses in mice. Gastroenterology. (2013) 145:396–406. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.056
132
Lu J Huang Y Zhang Y Xie J Guo Q Yang H et al . Quercetin ameliorates obesity and inflammation via microbial metabolite indole-3-propionic acid in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1574792. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1574792
133
Hooper LV . You AhR what you eat: linking diet and immunity. Cell. (2011) 147:489–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.004
134
Ding Y Yanagi K Cheng C Alaniz RC Lee K Jayaraman A . Interactions between gut microbiota and non-alcoholic liver disease: The role of microbiota-derived metabolites. Pharmacol Res. (2019) 141:521–29. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.01.029
135
Wrzosek L Ciocan D Hugot C Spatz M Dupeux M Houron C et al . Microbiota tryptophan metabolism induces aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation and improves alcohol-induced liver injury. Gut. (2021) 70:1299–308. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321565
136
Gaudino SJ Singh A Huang H Padiadpu J Jean-Pierre M Kempen C et al . Intestinal IL-22RA1 signaling regulates intrinsic and systemic lipid and glucose metabolism to alleviate obesity-associated disorders. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:1597. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45568-6
137
Zhang P Liu J Lee A Tsaur I Ohira M Duong V et al . IL-22 resolves MASLD via enterocyte STAT3 restoration of diet-perturbed intestinal homeostasis. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:2341–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.08.012
138
Zou J Chassaing B Singh V Pellizzon M Ricci M Fythe MD et al . Fiber-mediated nourishment of gut microbiota protects against diet-induced obesity by restoring IL-22-mediated colonic health. Cell Host Microbe. (2018) 23:41–53. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.11.003
139
Ouyang H Wei S Gao B Qian X Chen Y Lu J et al . Delivery of Synthetic Interleukin-22 mRNA to Hepatocytes via Lipid Nanoparticles Alleviates Liver Injury. Small. (2024) 20:e2401499. doi: 10.1002/smll.202401499
140
Park O Wang H Weng H Feigenbaum L Li H Yin S et al . In vivo consequences of liver-specific interleukin-22 expression in mice: Implications for human liver disease progression. Hepatology. (2011) 54:252–61. doi: 10.1002/hep.24339
141
Feng D Kong X Weng H Park O Wang H Dooley S et al . Interleukin-22 promotes proliferation of liver stem/progenitor cells in mice and patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. (2012) 143:188–98. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.03.044
142
Chen J Sun S Li H Cai X Wan C . IL-22 signaling promotes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via STAT3/CD155 signaling axis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1373321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1373321
143
Wu Y Min J Ge C Shu J Tian D Yuan Y et al . Interleukin 22 in liver injury, inflammation and cancer. Int J Biol Sci. (2020) 16:2405–13. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.38925
144
Chen W Zai W Fan J Zhang X Zeng X Luan J et al . Interleukin-22 drives a metabolic adaptive reprogramming to maintain mitochondrial fitness and treat liver injury. Theranostics. (2020) 10:5879–94. doi: 10.7150/thno.43894
145
Sertorio M Hou X Carmo RF Dessein H Cabantous S Abdelwahed M et al . IL-22 and IL-22 binding protein (IL-22BP) regulate fibrosis and cirrhosis in hepatitis C virus and schistosome infections. Hepatology. (2015) 61:1321–31. doi: 10.1002/hep.27629
146
Lim C Savan R . The role of the IL-22/IL-22R1 axis in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2014) 25:257–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.04.005
147
Shadboorestan A Koual M Dairou J Coumoul X . The role of the Kynurenine/AhR pathway in diseases related to metabolism and cancer. Int J Tryptophan Res. (2023) 16:934169806. doi: 10.1177/11786469231185102
148
Mladenova D Kohonen-Corish MRJ . Review: Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease–insights into the mechanisms of inflammation-associated colorectal cancer. In Vivo. (2012) 26:627–46.
149
Waldner MJ Neurath MF . Mechanisms of immune signaling in colitis-associated cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2015) 1:6–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2014.11.006
150
Pan Y Deng Y Yang H Yu M . The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: A promising target for intestinal fibrosis therapy. Pharmacol Res. (2025) 219:107909. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107909
151
Pei T Li W Zhou Z Zhang Q Yu G Yin S et al . The relationship between tryptophan metabolism and gut microbiota: Interaction mechanism and potential effects in infection treatment. Microbiol Res. (2025) 298:128211. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2025.128211
152
Xiong L Diwakarla S Chatzis R Artaiz O Macowan M Zhang S et al . Acute exposure to high-fat diet impairs ILC3 functions and gut homeostasis. Immunity. (2025) 58:1185–200. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2025.03.017
153
Zhang Y Jing Y He J Dong R Li T Li F et al . Bile acid receptor FXR promotes intestinal epithelial ferroptosis and subsequent ILC3 dysfunction in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Immunity. (2025) 58:683–700. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2025.02.003
154
Yan T Shi L Liu T Zhang X Yang M Peng W et al . Diet-rich in wheat bran modulates tryptophan metabolism and AhR/IL-22 signalling mediated metabolic health and gut dysbacteriosis: A novel prebiotic-like activity of wheat bran. Food Res Int. (2023) 163:112179. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112179
155
Danne C Lamas B Lavelle A Michel M Da Costa G Pham H et al . Dissecting the respective roles of microbiota and host genetics in the susceptibility of Card9(-/-) mice to colitis. Microbiome. (2024) 12:76. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01798-w
Summary
Keywords
the AhR/IL-22 pathway, chronic intestinal inflammation, immune response, AhR, IL-22
Citation
Kang H, Chen Z, Wang B and Chen Z (2025) The AhR/IL-22 axis in chronic gut inflammation: unraveling mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Front. Immunol. 16:1668173. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1668173
Received
17 July 2025
Accepted
29 August 2025
Published
12 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Yukihiro Yamaguchi, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, United States
Reviewed by
Rasheed Ahmad, Dasman Diabetes Institute, Kuwait
Akbar Farjadfar, Fasa University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Kang, Chen, Wang and Chen.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiyun Chen, jcyjzxchen@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.