- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, Sichuan, China
- 2North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, Sichuan, China
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) represents a major global health burden, characterized by dysregulated macrophage function and persistent inflammation. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs, have emerged as critical orchestrators of macrophage polarization and inflammatory responses in COPD pathogenesis. This comprehensive review synthesizes current evidence demonstrating how ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes drive disease progression. Pro-inflammatory miRNAs promote pathological M1 polarization through NF-κB and STAT3 pathways, while protective miRNAs facilitate inflammation resolution. LncRNAs exhibit sophisticated regulatory mechanisms through transcriptional scaffolding and competitive endogenous RNA networks. Clinical studies have successfully translated these mechanistic insights, establishing diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in human COPD patients. Despite significant progress, challenges remain including methodological heterogeneity, limited understanding of integrated regulatory networks, and clinical translation barriers. Future directions emphasize precision medicine approaches through ncRNA-based diagnostics and combination therapeutics. The evidence strongly supports the therapeutic potential of targeting ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes, offering transformative opportunities for personalized COPD management and improved patient outcomes.
1 Introduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) represents one of the major global health burden diseases, with statistics indicating that more than 174 million people worldwide were affected and represents the fourth leading cause of death in the United States (1). Despite significant advances in understanding COPD pathogenesis, the disease remains characterized by persistent inflammation and progressive airflow limitation. This results in substantial morbidity and mortality (2). The complex pathophysiology of COPD involves multiple cellular and molecular mechanisms, including abnormal inflammatory responses, impaired tissue repair, and dysregulated immune cell function (1, 2). Recent insights have moved beyond the traditional understanding of COPD as simply accelerated lung function decline. Current research now recognizes distinct disease trajectories and early pathobiological changes that precede clinically apparent disease (3). Understanding these complex pathophysiological mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic interventions.
Central to these pathophysiological processes, macrophages play a pivotal role in COPD pathogenesis, serving as key orchestrators of both innate and adaptive immune responses in the lung (4). Importantly, the pulmonary macrophage compartment comprises functionally and anatomically distinct populations: alveolar macrophages (AMs) residing in airspaces serve as sentinel cells for pathogen recognition and particle clearance, while interstitial macrophages (IMs) within the lung parenchyma primarily mediate tissue remodeling and stromal interactions (4, 5). Furthermore, these populations differ in developmental origin, with tissue-resident macrophages (embryonic-derived, self-renewing) displaying distinct transcriptional programs compared to recruited monocyte-derived macrophages that infiltrate during inflammation (5). In healthy individuals, these macrophage subsets maintain pulmonary homeostasis through coordinated phagocytosis, pathogen clearance, and tissue repair functions (5). However, in COPD pathogenesis, macrophage function becomes severely dysregulated across these distinct populations. This dysregulation is characterized by altered activation states, enhanced pro-inflammatory cytokine production, impaired phagocytic capacity, and defective efferocytosis (6). Critically, COPD significantly alters the balance between tissue-resident and recruited macrophages, with increased monocyte infiltration potentially creating distinct molecular signatures and functional properties (5, 6). The polarization of macrophages toward pro-inflammatory M1 phenotypes, coupled with impaired M2-mediated tissue repair mechanisms, contributes to persistent inflammation and progressive tissue destruction observed in COPD (7, 8).
The regulation of these complex macrophage functions involves multiple molecular mechanisms, among which non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), have emerged as critical regulators of gene expression and cellular function across various biological processes (9). These molecular regulators exert their effects through diverse mechanisms, including post-transcriptional gene silencing, chromatin modification, and competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks (9, 10). In the context of immune regulation, ncRNAs have been shown to control macrophage activation, polarization, and functional responses, thereby influencing inflammatory processes and disease outcomes (11, 12). Dysregulation of ncRNA expression patterns has been implicated in various respiratory diseases, suggesting their potential as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets (13).
The intersection of ncRNA biology and macrophage function has revealed complex regulatory networks that govern immune responses in health and disease (11, 12). Emerging evidence demonstrates that specific ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes play crucial roles in COPD pathogenesis, influencing inflammation resolution, tissue remodeling, and disease progression (14, 15). Studies in asthma and other inflammatory conditions have shown that ncRNAs can either promote or suppress macrophage-mediated inflammation, depending on the specific molecular context and disease stage (16, 17). Despite these advances, the precise mechanisms by which ncRNAs regulate macrophage function in COPD, and the therapeutic potential of targeting these pathways, remain incompletely characterized.
This comprehensive review aims to synthesize current knowledge on ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes in COPD, providing a systematic analysis of molecular mechanisms, clinical implications, and therapeutic prospects. We will examine the latest advances in understanding how different classes of ncRNAs modulate macrophage behavior in COPD pathogenesis, evaluate the translational potential of these findings, and identify key research gaps that warrant further investigation. By elucidating these complex regulatory networks, this review seeks to inform the development of novel precision medicine approaches for COPD management and highlight promising avenues for future therapeutic intervention.
2 Molecular mechanisms of ncRNA regulation of macrophage function
2.1 MiRNA-mediated macrophage regulation
MiRNAs represent the most extensively characterized class of ncRNAs in macrophage biology, functioning primarily through post-transcriptional gene silencing mechanisms (18). The canonical miRNA pathway involves binding to complementary sequences in the 3’ untranslated regions of target messenger RNAs (mRNAs), leading to mRNA degradation or translational repression (19). In macrophages, specific miRNAs have been identified as critical regulators of activation and polarization states, with distinct expression patterns associated with M1 and M2 phenotypes (20).
Several miRNAs have emerged as key modulators of macrophage polarization through targeting of transcription factors and signaling molecules. For instance, exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells can modulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization through regulation of the miR-451a/macrophage migration inhibitory factor axis, thereby promoting bone healing (20).
Similarly, in hepatic fibrosis, various miRNAs (miR-206, miR-26a, miR-155, and miR-148a) exert anti-fibrotic effects by regulating oxidative stress, modulating cytokine secretion, and promoting CD8+ T cell recruitment (21). These regulatory networks exemplify the fine-tuned control that miRNAs exert over macrophage functional states.
The therapeutic targeting of miRNAs in macrophages has shown promise in preclinical studies. MiRNA mimics and antagomirs have been successfully employed to modulate macrophage polarization in various disease models (22, 23). However, challenges remain in achieving cell-type-specific delivery and avoiding off-target effects, particularly given the widespread expression of many miRNAs across different cell types (24).
2.2 LncRNA regulatory networks
While miRNAs primarily regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level, lncRNAs exhibit more diverse regulatory mechanisms in macrophage regulation, including transcriptional modulation through DNA interaction, ceRNA/miRNA sponge activity, protein binding, and micropeptide encoding (25). Unlike miRNAs, lncRNAs can interact directly with chromatin-modifying complexes, transcription factors, and other regulatory proteins to influence gene expression at multiple levels (25, 26). This versatility allows lncRNAs to orchestrate complex gene expression programs associated with macrophage differentiation and activation.
Several lncRNAs have been identified as important regulators of macrophage polarization. For instance, lncRNA MIAT downregulates interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) to suppress macrophage inflammation (27). However, this anti-inflammatory effect is inhibited by ATP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation, highlighting the context-dependent nature of lncRNA MIAT function (27). Similarly, research has shown that human lncRNA SUGCT-AS1 can directly bind to heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (hnRNPU) and regulate its nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation. This translocation of hnRNPU modulates macrophage inflammation by altering the ratio of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT1) isoforms through regulation of MALT1 alternative splicing (28). Interestingly, macrophages themselves can secrete corresponding lncRNAs. Studies have revealed that M2 macrophage exosome-derived lncRNA AK083884 protects mice against coxsackievirus B3-induced viral myocarditis through regulating pyruvate kinase M2/hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha axis-mediated macrophage metabolic reprogramming (29). These findings unveil the intricate interplay between lncRNAs and macrophages.
2.3 CircRNA-mediated regulation
Building upon the diverse regulatory mechanisms of lncRNAs, circRNAs have emerged as important regulators of macrophage function, primarily through their role as miRNA sponges in ceRNA networks (30). Recent studies have identified several circRNAs that modulate macrophage polarization. For example, studies have demonstrated that exosome-based mitochondrial delivery of circRNA mSCAR can promote macrophage polarization toward the M2 subtype, attenuate systemic inflammation, and reduce mortality, thereby alleviating sepsis (31). Interestingly, additional research has shown that macrophage uptake of circRNAs is rapid, energy-dependent, and saturable. CircRNA uptake can lead to translation of coding sequences and antigen presentation, and the internalization pathway can influence immune activation following circRNA uptake. Further investigation revealed that macrophage scavenger receptor 1, toll-like receptors (TLRs), and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling are key regulators of receptor-mediated circRNA phagocytosis (32). These findings demonstrate the emerging importance of circRNAs in macrophage biology and their potential as therapeutic targets.
Moreover, the regulatory networks involving circRNAs are often complex, with individual circRNAs capable of binding multiple miRNAs and influencing numerous downstream targets (30, 33). This network complexity provides both opportunities and challenges for therapeutic intervention, as modulation of a single circRNA may have widespread effects on cellular function.
2.4 Integrated regulatory networks and cross-talk
The regulation of macrophage function involves complex interactions between different classes of ncRNAs, creating multilayered regulatory networks (17, 21). These networks exhibit significant cross-talk, with miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs often competing for binding sites and regulatory proteins (30, 33). Understanding these integrated networks is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies targeting ncRNA-macrophage axes.
Computational approaches have revealed extensive ceRNA networks in macrophages, with hundreds of lncRNAs and circRNAs predicted to interact with key regulatory miRNAs (34). Experimental validation of these networks has confirmed the functional importance of many predicted interactions, highlighting the coordinated nature of ncRNA-mediated regulation (35). The dynamic nature of these networks allows for context-dependent regulation, with different stimuli activating distinct regulatory modules.
The molecular mechanisms underlying ncRNA-mediated macrophage regulation demonstrate remarkable complexity and sophistication. MiRNAs primarily function through post-transcriptional gene silencing, targeting key transcription factors and signaling molecules that determine macrophage activation states. LncRNAs exhibit more diverse regulatory mechanisms, including chromatin modification, transcriptional scaffolding, and ceRNA network formation, providing multilayered control over macrophage phenotypes. CircRNAs, with their stable covalent structure, function predominantly as miRNA sponges, adding another dimension to regulatory networks. The extensive cross-talk between these ncRNA classes creates integrated regulatory circuits that enable context-dependent, fine-tuned control of macrophage responses. Understanding these interconnected mechanisms is essential for developing targeted therapeutic strategies that can modulate specific pathogenic pathways while preserving beneficial macrophage functions in respiratory diseases.
3 COPD pathogenesis and the role of macrophages
3.1 Overview of COPD pathogenesis
COPD pathogenesis involves complex interplay among genetic susceptibility, environmental exposures, and abnormal inflammatory responses. These factors lead to progressive airway and parenchymal destruction (1, 2). The disease is characterized by two major pathological features: emphysema, involving destruction of alveolar walls and loss of elastic recoil, and chronic bronchitis, characterized by airway inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, and airway wall thickening (2, 3). These pathological changes result from an imbalance between tissue destruction and repair processes, with inflammatory cells playing central roles in disease initiation and progression (4).
Cigarette smoke exposure represents the primary risk factor for COPD development, triggering a cascade of cellular and molecular events that ultimately lead to tissue damage (1, 2). The initial response to smoke exposure involves activation of epithelial cells and resident macrophages, leading to recruitment of inflammatory cells and production of pro-inflammatory mediators. Over time, this acute inflammatory response becomes dysregulated, resulting in chronic inflammation that persists even after smoking cessation (4–6).
Recent advances in understanding COPD pathogenesis have revealed the importance of early disease processes, including epigenetic modifications, altered lung development, and dysregulated immune responses (1–3). These insights have shifted the focus toward identifying early biomarkers and therapeutic targets that could prevent or slow disease progression before significant structural damage occurs (36).
3.2 Macrophage dysfunction in COPD
The pulmonary macrophage compartment encompasses distinct subsets with specialized functions that become differentially dysregulated in COPD (5). AMs, which reside in the airway lumen and alveolar spaces, constitute the predominant lung macrophage population and serve as the first line of defense against inhaled pathogens and particles. In contrast, IMs populate the lung parenchyma and primarily regulate tissue homeostasis and remodeling. These populations also differ by developmental origin: tissue-resident macrophages are embryonically derived and self-renewing, whereas monocyte-derived macrophages are recruited from circulating blood during inflammation. In healthy lungs, this heterogeneous macrophage network maintains homeostasis through coordinated clearance of inhaled particles, pathogens, and apoptotic cells (4–6). A key feature of macrophage dysfunction in COPD is impaired phagocytosis, particularly affecting clearance of bacteria and apoptotic cells (6). This defective function contributes to increased susceptibility to respiratory infections and persistent inflammation (37). Studies have demonstrated that alveolar macrophages from COPD patients exhibit reduced phagocytic capacity compared to healthy controls, with this impairment correlating with disease severity (38).
The polarization state of macrophages is also significantly altered in COPD, with evidence suggesting a predominance of M1-like inflammatory phenotypes and impaired M2-mediated repair responses (6). This imbalanced polarization contributes to sustained inflammation and defective tissue repair, perpetuating the cycle of tissue destruction characteristic of COPD (3). The molecular mechanisms underlying this polarization imbalance involve dysregulation of key transcription factors, including nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)-protein kinase B (AKT), and NF-E2-related factor 2 (4, 14, 39). A brief summary of the influence of macrophages on the disease progression of COPD is presented in Figure 1.
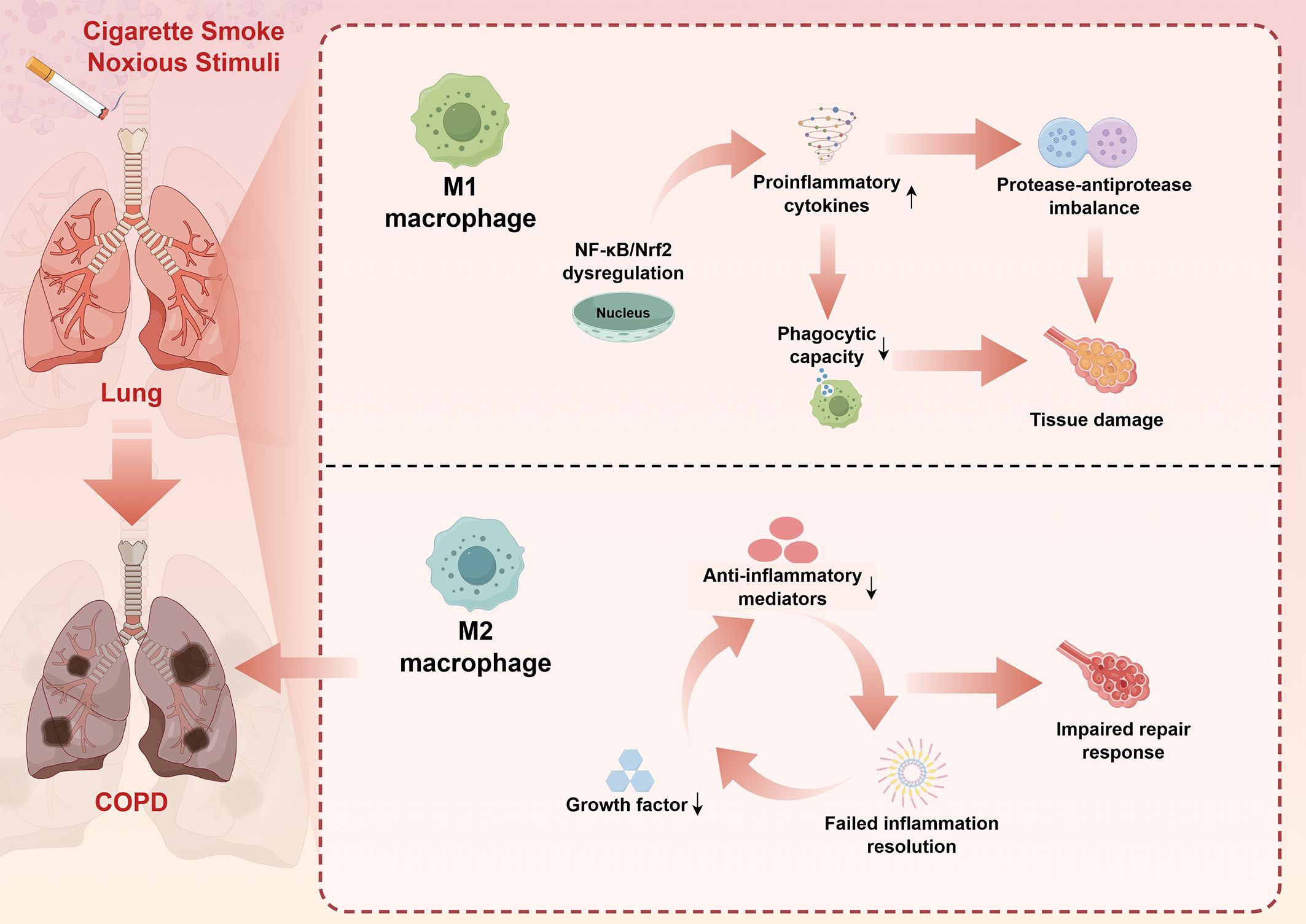
Figure 1. Macrophage dysfunction in COPD pathogenesis: A simplified mechanistic overview. This schematic diagram synthesizes key pathophysiological mechanisms derived from comprehensive literature review (Sections 3.1-3.5). Cigarette smoke and other noxious stimuli trigger dysregulated macrophage responses in the lung, leading to COPD development. The upper pathway illustrates M1 macrophage activation characterized by NF-κB/Nrf2 dysregulation, resulting in enhanced proinflammatory cytokine production, protease-antiprotease imbalance, impaired phagocytic capacity, and subsequent tissue damage. The lower pathway demonstrates M2 macrophage dysfunction, featuring reduced anti-inflammatory mediator production, decreased growth factor secretion, and failed inflammation resolution, ultimately contributing to impaired repair responses. Bidirectional arrows indicate the cyclical nature of inflammatory processes. This imbalanced M1/M2 polarization perpetuates chronic inflammation and progressive tissue destruction characteristic of COPD pathogenesis. The figure was created using Figdraw (www.figdraw.com). COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2.
3.3 Protease-antiprotease imbalance
Macrophages contribute significantly to the protease-antiprotease imbalance that is central to emphysema development (40). Activated macrophages release various proteases, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), neutrophil elastase, and cathepsins, which degrade extracellular matrix components (41). In COPD, this proteolytic activity is enhanced while antiprotease defenses are overwhelmed, leading to progressive tissue destruction (42).
Multiple MMPs have been demonstrated to participate in regulating COPD development and progression, and may serve as potential diagnostic markers for COPD patients. For instance, studies have found elevated serum MMP-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) levels, as well as increased MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratios in COPD patients. The imbalance between MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in COPD patients favors a pro-proteolytic environment, collectively highlighting the importance of the MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio as a potential biomarker for COPD diagnosis and severity assessment (43).
Additionally, other research has demonstrated that deflamin, a protein component extracted from lupin, can attenuate lung tissue damage in ozone-induced COPD mouse models by regulating MMP-9 catalytic activity (44). Notably, ncRNAs have also been proven to participate in regulating MMP expression. For example, the lncRNA TP73-AS1/miR-539/MMP-8 axis regulates M2 macrophage polarization in hepatocellular carcinoma through transforming growth factor-beta1 signaling (45). These findings provide further evidence for the interplay between ncRNAs and macrophages in COPD pathogenesis, while also highlighting the crucial role of protease dysregulation, represented by MMPs, in COPD pathogenesis.
3.4 Oxidative stress and macrophage function
Chronic exposure to cigarette smoke leads to sustained oxidative stress in the lung, significantly affecting macrophage function (6). Reactive oxygen species generated by activated macrophages contribute to tissue damage while also serving as signaling molecules that modulate inflammatory responses. The antioxidant capacity of macrophages becomes overwhelmed in COPD, leading to a pro-oxidant environment that perpetuates inflammation and tissue damage (46).
Oxidative stress affects multiple aspects of macrophage function, including phagocytosis, cytokine production, and cell survival. The dysregulation of antioxidant enzymes and reduced glutathione levels in COPD macrophages contribute to this oxidative burden (5, 6). Understanding the molecular mechanisms linking oxidative stress to macrophage dysfunction provides insights into potential therapeutic approaches targeting this pathway (1).
3.5 Macrophage-mediated tissue remodeling
Beyond their role in inflammation, macrophages are crucial mediators of tissue remodeling processes in COPD. The balance between tissue destruction and repair is significantly disrupted in COPD, with macrophages contributing to both processes (2, 3). M2 macrophages typically promote tissue repair through production of growth factors and anti-inflammatory mediators, but this repair response is often inadequate or misdirected in COPD (47).
The interaction between macrophages and other lung cells, including fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, is critical for proper tissue remodeling (48). Dysregulated communication between these cell types contributes to airway wall thickening, mucus gland hyperplasia, and abnormal repair responses observed in COPD (4–6). Understanding these cellular interactions provides insights into the complex pathophysiology of COPD and potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
In summary, COPD pathogenesis fundamentally involves dysregulated macrophage function at multiple levels. Chronic exposure to cigarette smoke and other noxious stimuli transforms protective alveolar macrophages into drivers of disease progression through impaired phagocytosis, aberrant M1/M2 polarization, excessive protease release, and defective tissue repair responses. The resulting protease-antiprotease imbalance, coupled with oxidative stress and abnormal tissue remodeling, creates a self-perpetuating cycle of inflammation and tissue destruction. The complex interactions between macrophages and other lung cells, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells, further amplify pathological processes. These multifaceted macrophage dysfunctions provide numerous potential intervention points for therapeutic targeting, emphasizing the central role of macrophage biology in COPD pathogenesis and the critical need to understand how ncRNAs regulate these processes. In the following sections, we examine how ncRNAs specifically modulate macrophage function in COPD, progressing from preclinical mechanistic studies to clinical translation.
4 NcRNA-macrophage regulatory axis in COPD: research progress
4.1 Preclinical studies
Preclinical investigations have identified distinct functional categories of ncRNAs that regulate macrophage polarization and inflammatory responses in COPD models. These studies reveal three major regulatory patterns: (1) pro-inflammatory ncRNAs that activate NF-κB and STAT3 pathways to drive M1 polarization; (2) protective ncRNAs that inhibit inflammation and prevent emphysema formation; and (3) metabolic ncRNAs that modulate lipid metabolism and cellular stress responses. The following sections synthesize key mechanistic insights, with comprehensive details provided in Tables 1, 2.
4.1.1 MiRNA-mediated macrophage regulation in COPD
MiRNAs have emerged as pivotal regulators of macrophage function in COPD pathogenesis, with distinct miRNAs exhibiting either pro-inflammatory or protective effects. These regulatory molecules orchestrate complex signaling networks that ultimately determine macrophage polarization states and functional outcomes in the diseased lung. The preclinical research results related to miRNAs involved in macrophage regulation in COPD are summarized in Table 1.
Pro-inflammatory miRNAs predominantly activate NF-κB and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathways to drive M1 polarization. miR-21 exemplifies this pattern, promoting COPD pathogenesis through a SATB1/S100A9/NF-κB signaling axis, with expression levels inversely correlating with lung function (14). Importantly, therapeutic miR-21 inhibition effectively suppresses inflammatory cell infiltration and improves lung function in experimental models (14). Intercellular communication amplifies these effects: epithelial cell-derived exosomal miRNAs (miR-125a-5p, miR-221-3p) promote M1 polarization in recipient macrophages via IL1RN/MyD88/NF-κB and SOCS3/STAT3 pathways, respectively (15, 49). Additional pro-inflammatory miRNAs including miR-27-3p, miR-155, miR-486-5p, and miR-1260 similarly activate macrophages through TLR signaling, mTORC2/RhoA, and NF-κB pathways (50–52, 60, 62).
In contrast, protective miRNAs inhibit inflammation and prevent emphysema formation. miR-195-5p suppresses COPD development by targeting siglec1 and inactivating NF-κB signaling (53), while miR-146a deficiency results in increased emphysema severity and enhanced pro-inflammatory mediator production in murine models (55). Paradoxically, miR-let-7c inhibits M2 macrophage polarization through the IL-6/STAT3 pathway, suggesting that excessive M2 polarization may contribute to emphysema rather than repair in COPD (54). Additional protective miRNAs (miR-513a-5p, miR-344b-1-3p, miR-150) negatively regulate TLR signaling and inflammatory responses (56, 57, 61).
Metabolic dysregulation represents a third regulatory layer. miR-103a downregulation in smokers and COPD patients impairs lipid metabolism through targeting low-density lipoprotein receptors, leading to lipid-laden macrophage formation (58). miR-451b protects against cigarette smoke-induced cellular stress by targeting the RhoA/ROCK2 pathway, decreasing inflammatory cytokine release and suppressing macrophage migration (59). These metabolic miRNAs collectively modulate lipid metabolism, cellular stress responses, and TLR signaling pathways.
Notably, fundamental alterations in miRNA processing machinery contribute to COPD pathogenesis. Cigarette smoke exposure causes global miRNA downregulation in alveolar macrophages through DICER SUMOylation, impairing the entire miRNA regulatory network (67). This processing defect, combined with specific miRNA-mRNA interaction networks identified through transcriptomic analyses (68), highlights the coordinated dysregulation of macrophage responses in COPD. Additional regulatory miRNAs and their mechanisms are detailed in Table 1.
4.1.2 LncRNA regulatory networks
LncRNAs exhibit diverse mechanisms of action in macrophage regulation, functioning as molecular scaffolds, transcriptional regulators, and ceRNAs. These versatile molecules orchestrate complex gene expression programs that significantly influence macrophage differentiation, activation, and functional responses in COPD. The preclinical research results related to lncRNAs involved in macrophage regulation in COPD are summarized in Table 2.
Pro-inflammatory lncRNAs drive M1 polarization through sophisticated molecular mechanisms. Cigarette smoke-exposed epithelial cell-derived exosomal lncRNA MEG3 promotes M1 macrophage polarization and pyroptosis by recruiting SPI1 to activate METTL3, which increases N6-methyladenosine methylation of TREM-1 mRNA (69). LncRNA MIR155HG demonstrates bidirectional regulatory capacity: overexpression promotes granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced M1 polarization and pro-inflammatory cytokine release, while knockdown enhances M2 development (70, 71). Serum-derived exosomal lncRNA TBX2-AS1 further exacerbates COPD by altering M1/M2 ratios through the miR-423-5p/miR-23b-3p axis (72), illustrating systemic lncRNA-mediated regulation.
Regulatory lncRNAs provide protective or modulatory functions through distinct mechanisms. LncRNA Cox2 serves as a negative regulator of smoke-induced inflammation, downregulating inflammatory gene expression in cigarette smoke-exposed macrophages (73). LncRNA IL7R, reduced in COPD patients with exacerbator phenotypes, mediates repressive chromatin states at pro-inflammatory gene promoters through H3K9ac reduction and H3K9me3/H3K27me3 increases (74). Post-translational regulation is exemplified by lncRNA PPP2R5C, which controls IL-1β ubiquitination through protein phosphatase 2A activity modulation (75).
The ceRNA mechanism represents a particularly important regulatory paradigm. LncRNA Clic5 functions as a molecular sponge for miR-212-5p, inhibiting particulate matter-induced apoptosis in alveolar macrophages (76). This network-level regulation allows coordinated control of multiple genes involved in macrophage function, providing fine-tuned inflammatory responses. Additional regulatory lncRNAs and their mechanisms are detailed in Table 2.
4.1.3 Multi-component regulatory systems and therapeutic implications
Systems-level analyses reveal complex ncRNA networks integrating multiple regulatory layers. Clinical correlations demonstrate that decreased miR-301a-5p in acute exacerbation patients regulates lung fibroblast and monocyte-derived macrophage migration through the MBD2/CXCL12/CXCR4/p-MEK/p-AKT pathway (63). The miR-380/CFTR axis illustrates bidirectional macrophage-epithelial communication: elevated miR-380 in COPD macrophage-derived exosomes promotes epithelial cell proliferation, mucin expression, and inflammatory cytokine secretion (64). Non-pharmacological interventions also operate through ncRNA mechanisms, as demonstrated by exercise training-induced miR-124-3p upregulation, which inhibits M1 macrophage activation by targeting ERN1 (65).
Comprehensive miRNAomics analyses of cigarette smoke-exposed epithelial cell-derived exosomes identified 27 differentially expressed miRNAs, with miR-21-3p and miR-27b-3p promoting both M1 and M2 polarization through PI3K-AKT and MAPK pathways (66). Transcriptomic profiling revealed four genes (NT5E, SDK1, TNS1, PCDH7) with significant miRNA-mRNA interactions in COPD airway epithelium, particularly the miR6511a-5p-NT5E interaction relevant across multiple cell types including alveolar macrophages (68).
Emerging evidence links metabolic reprogramming to immune dysfunction. Bioinformatics analyses identified five ferroptosis-related hub genes (HIF1A, IL6, PTGS2, CDKN1A, ATM) that influence COPD pathogenesis, with immune profiling revealing upregulated monocytes and M0 macrophages alongside downregulated M2 macrophages (78). Similarly, anoikis resistance mechanisms involving TNMD and lncRNA 656 correlate with altered infiltration of activated CD4 memory T cells, M1 macrophages, and NK cells (77).
Therapeutic translation has advanced through targeted delivery systems. Aspherical, nanostructured microparticles designed for siRNA delivery to macrophages achieved >30% TNF-α reduction in human macrophages, representing promising platforms for RNA therapy (79). These preclinical findings provide a robust mechanistic foundation for clinical investigation (Figure 2). The next section examines how these discoveries have been validated and extended in human COPD studies.
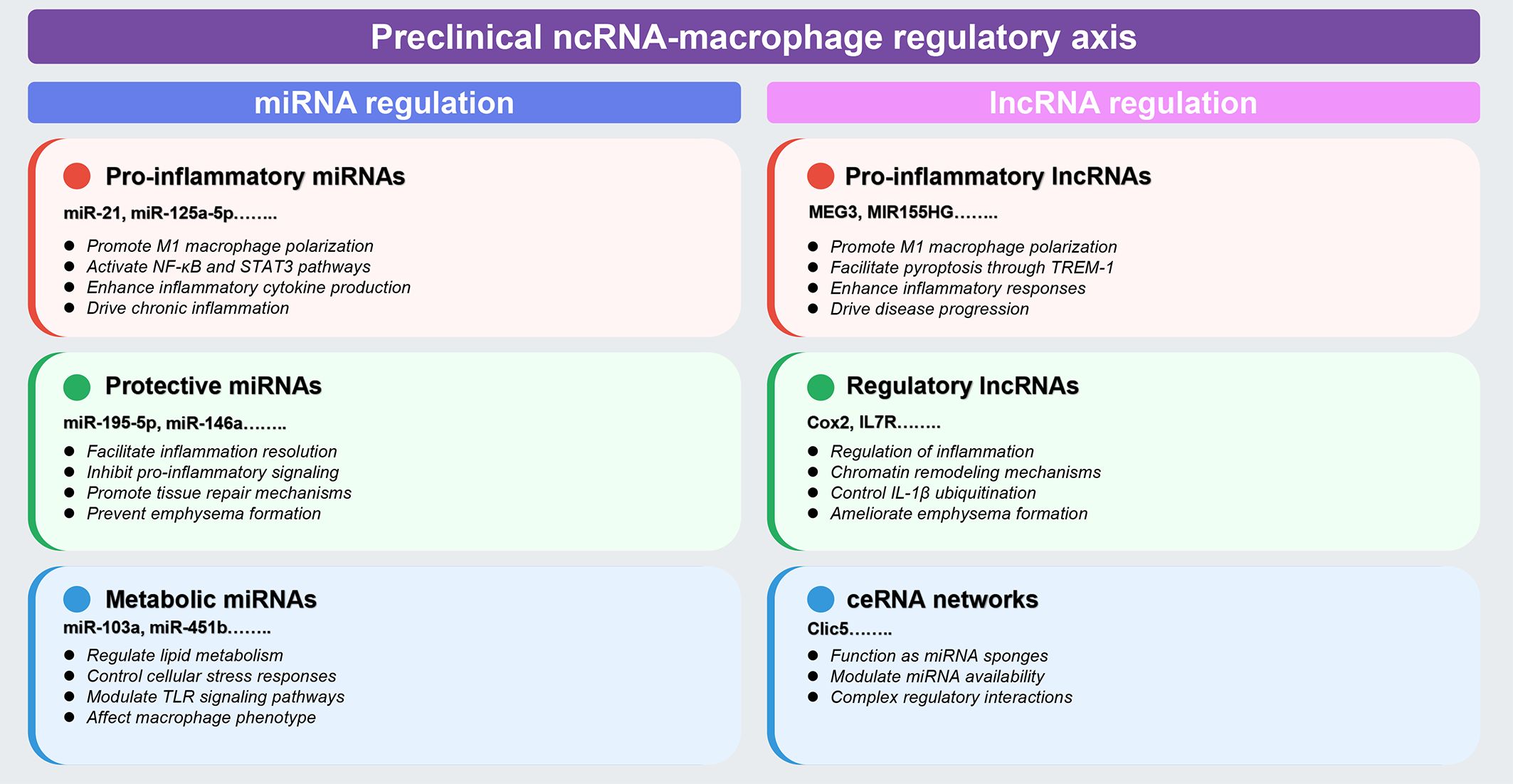
Figure 2. Preclinical landscape of ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes in COPD. This comprehensive schematic synthesizes preclinical evidence from animal models and in vitro studies (detailed in Tables 1, 2, Section 4.1). Color coding indicates functional categories: red boxes denote pro-inflammatory regulators, green boxes indicate protective/regulatory molecules, and blue boxes represent metabolic or ceRNA network components. Left panel (miRNA regulation): encompasses three major categories based on functional outcomes: (1) pro-inflammatory miRNAs (miR-21, miR-125a-5p, and others) that promote M1 macrophage polarization through NF-κB and STAT3 pathway activation; (2) protective miRNAs (miR-195-5p, miR-146a, and others) that facilitate inflammation resolution and prevent emphysema formation; and (3) metabolic miRNAs (miR-103a, miR-451b, and others) that regulate lipid metabolism and cellular stress responses. Right panel (lncRNA regulation): includes (1) pro-inflammatory lncRNAs (MEG3, MIR155HG, and others) that enhance inflammatory responses and drive disease progression through mechanisms including m6A methylation; (2) regulatory lncRNAs (Cox2, IL7R, and others) that control inflammation through chromatin remodeling and IL-1β ubiquitination; and (3) ceRNA networks (Clic5 and others) that function as miRNA sponges to modulate regulatory interactions. Classification criteria are based on demonstrated effects on macrophage polarization, inflammatory cytokine production, and disease outcomes in experimental models. The figure was created using Figdraw (www.figdraw.com). ceRNA, competitive endogenous RNA; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; miRNA, microRNA; ncRNA, non-coding RNA; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TREM-1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1.
4.2 Clinical studies
Clinical investigations have successfully translated preclinical findings into human COPD contexts, establishing ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes as clinically relevant mechanisms. These studies demonstrate three major translational achievements: (1) validation of global ncRNA dysregulation patterns in human alveolar macrophages; (2) identification of diagnostic biomarkers through ceRNA network analyses; and (3) discovery of novel RNA species that activate macrophage inflammatory responses. The following sections synthesize key clinical findings, with comprehensive details provided in Table 3.
4.2.1 Global ncRNA expression patterns and ceRNA networks
Comprehensive clinical evidence confirms global miRNA downregulation in alveolar macrophages from smokers and COPD patients. Microarray analyses reveal an “inverse” M1 mRNA expression program, with decreased M1-induced transcripts and increased M1-repressed transcripts (80). Notably, the magnitude of global miRNA decrease correlates with smoking history, and downregulated miRNAs are predicted to target upregulated mRNAs, confirming miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in human disease (80).
Clinical validation of ceRNA networks has identified diagnostic biomarkers with translational potential. The lncRNA 482-miR-6088-PRRC2B ceRNA network demonstrates positive correlation between lncRNA 482 and PRRC2B expression in COPD patient peripheral blood mononuclear cells, with receiver operating characteristic analysis confirming diagnostic value (81). Systematic analyses of RNA transcripts identified 18 hub genes, revealing dysregulated TGF-β and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways, with increased M2 macrophages and activated NK cells in COPD lung tissues (40).
4.2.2 Clinical biomarker development
Multiple biomarker discovery approaches have advanced clinical translation. SOCS3 regulation studies demonstrate significantly higher SOCS3+ alveolar macrophage percentages in smokers with and without COPD compared to non-smokers, correlating with TNF-α+ macrophages and CD8+ T cell infiltration (82). Importantly, CD14+SOCS3+ extracellular vesicles are increased in COPD patients, while SOCS3-suppressing miRNAs (miR-19a-3p, miR-221-3p) are elevated in smokers without COPD, suggesting protective mechanisms (82).
Large-scale expression analyses identified smoking-associated miRNA signatures. High miR-203a-3p and miR-375 expression in smokers’ airways demonstrate negative associations with pro-inflammatory pathway genes and positive associations with xenobiotic pathway genes (83). Cellular deconvolution analyses reveal that these miRNAs correlate with altered cellular proportions, including immune cells, fibroblasts, and smooth muscle cells (83).
Epigenetic mechanisms provide additional regulatory insights. miR-29b downregulation due to increased DNA methylation in COPD patient lung tissues reveals a negative feedback loop with DNMT3A that modulates cigarette smoke-induced M1 polarization (84). Regional expression analyses demonstrate divergent miRNA patterns between upper and lower lung lobes, with altered miR-93, miR-4454, miR-451a, and miR-663a expression in alveolar macrophages and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, potentially explaining upper lobe predominance (85).
4.2.3 Novel RNA species and predictive models
Clinical discoveries have expanded beyond conventional ncRNAs. Immunoactive signatures of circulating tRNA- and rRNA-derived RNAs reveal remarkable accumulation of 5’-tRNAValCAC half in COPD patient plasma, which activates human macrophages via TLR7 and induces cytokine production (86). Circulating rRNA-derived fragments similarly induce macrophage cytokine production, suggesting novel inflammatory mediators (86).
Machine learning approaches have enhanced translational potential. Algorithms predicted core miRNAs (hsa-miR-543, hsa-miR-181c, hsa-miR-200a), key immune cells (plasma cells, activated memory CD4 T cells, M2 macrophages), and characteristic genes (EGF, PLG, PTPN22, NR4A1) associated with COPD (87). Mendelian randomization analysis revealed causal relationships between 36 immune cell types and COPD, highlighting central immune dysfunction (87). Temporal progression studies demonstrate that specific miRNA signatures (hsa-miR-34a-5p, miR-17-5p, miR-106a-5p, miR-20a-5p) shift toward COPD patterns following cigarette smoke exposure, identifying early risk factors (88).
These clinical investigations successfully validate preclinical mechanisms while establishing ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes as clinically actionable targets. Human studies confirm global miRNA dysregulation, validate ceRNA networks with diagnostic potential, identify novel RNA species activating macrophages, and develop predictive models for disease progression. The integration of omics technologies, machine learning, and longitudinal analyses provides crucial validation for therapeutic development. Additional clinical findings and their translational implications are detailed in Table 3. The comprehensive clinical evidence, illustrated in Figure 3, supports advancing ncRNA-based precision medicine approaches for COPD management.
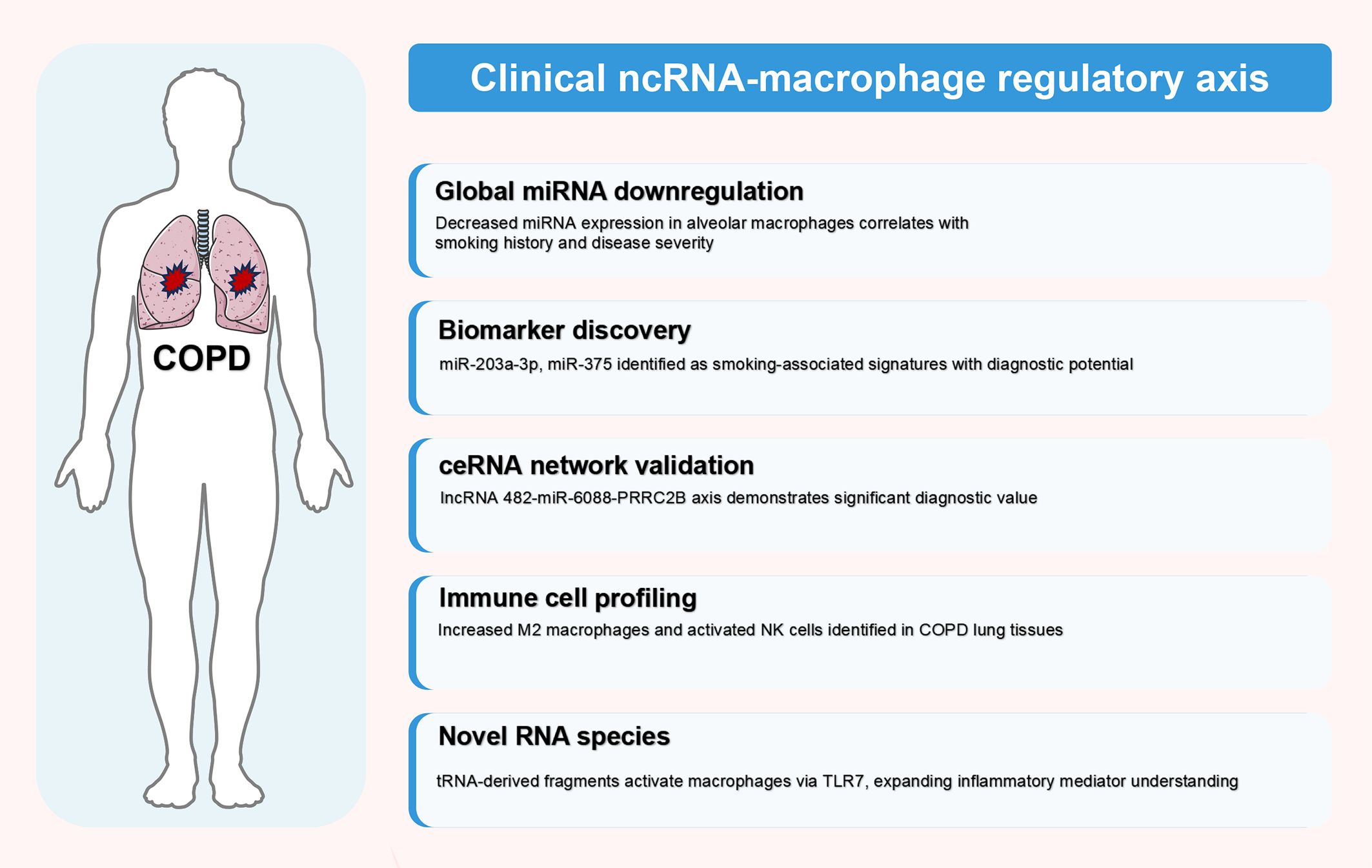
Figure 3. Clinical validation of ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes in human COPD. This figure illustrates clinical translation of ncRNA-macrophage regulatory mechanisms in human COPD patients, synthesizing findings from clinical studies detailed in Table 3 (Section 4.2). Evidence is categorized into five hierarchical domains based on translational relevance: global miRNA downregulation, biomarker discovery, ceRNA network validation, immune cell profiling, and novel RNA species identification. These clinical discoveries provide crucial validation of preclinical findings and establish the therapeutic potential of targeting ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes in COPD management. The figure was created using Figdraw (www.figdraw.com). ceRNA, competitive endogenous RNA; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; miRNA, microRNA; ncRNA, non-coding RNA.
In summary, the extensive body of preclinical and clinical research has established ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes as fundamental components of COPD pathogenesis. Preclinical studies have identified specific miRNAs, lncRNAs, and their downstream targets that control macrophage polarization, inflammatory responses, and tissue repair mechanisms, with clear dichotomous patterns of pro-inflammatory versus protective regulatory networks. Clinical investigations have successfully validated these mechanistic findings in human disease, demonstrating altered ncRNA expression patterns in patient samples that correlate with disease severity, exacerbation frequency, and therapeutic responses. The identification of novel RNA species, including tRNA-derived fragments, and the application of machine learning approaches have expanded our understanding beyond traditional ncRNA categories. The convergence of preclinical mechanistic insights with clinical validation provides a robust foundation for developing ncRNA-based diagnostics and therapeutics, though significant challenges remain in achieving cell-type specificity and overcoming delivery barriers. These findings collectively underscore the translational potential of targeting ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes for precision medicine approaches in COPD management.
5 Systematic evaluation of current research: challenges and limitations
While both preclinical and clinical studies have significantly advanced our understanding of ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes in COPD, critical evaluation of the current evidence reveals important methodological limitations and knowledge gaps that must be addressed.
5.1 Research progress and methodological advances
Current research on ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes in COPD has demonstrated substantial methodological sophistication, particularly through the integration of multi-omics approaches with functional validation studies. Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies have enhanced understanding of macrophage heterogeneity within the COPD lung microenvironment (80), while sophisticated bioinformatics pipelines for ceRNA network construction have enabled accurate prediction and validation of complex regulatory interactions (40, 81).
Clinical translation efforts have yielded encouraging results in biomarker development and therapeutic target identification. The validation of specific miRNA signatures in large patient cohorts has demonstrated robust diagnostic and prognostic potential (83, 87), while the successful development of targeted delivery systems represents significant progress toward clinical implementation (79).
5.2 Critical limitations and knowledge gaps
5.2.1 Experimental design constraints and methodological heterogeneity
Despite significant progress, several fundamental limitations persist. The predominant reliance on cigarette smoke exposure models may not fully capture COPD complexity, particularly in patients with biomass exposure or genetic susceptibility factors. Additionally, the heterogeneity in macrophage isolation and characterization protocols across studies has introduced substantial variability in findings (40, 80–82).
Current isolation methods vary significantly: bronchoalveolar lavage yields primarily alveolar macrophages but may induce mechanical activation, while enzymatic digestion protocols use diverse conditions (collagenase: 0.5–2 mg/mL, elastase: 200–400 U/mL, Liberase™: 100-400 μg/mL, 30–90 minutes). Liberase™ provides superior interstitial macrophage yield, particularly for IM3 subsets, though elastase causes selective marker loss including CD64 and MerTK (89–91). Flow cytometry panels range from simple two-color staining to 12-parameter analyses, affecting M1/M2 classification reliability (53, 70).
The lack of standardized criteria for defining M1 and M2 polarization states, particularly in chronic inflammatory diseases, has complicated result interpretation and cross-study comparisons. Furthermore, conventional in vitro polarization protocols may inadequately reflect the complex, mixed activation states observed in human COPD lung tissue (70, 72).
5.2.2 Technical and clinical translation barriers
Current analytical approaches face technical limitations including variable sensitivity and specificity of ncRNA detection methods between platforms, leading to inconsistent results. Computational prediction algorithms for ncRNA target identification suffer from high false-positive rates requiring extensive experimental validation (66–68). Species-specific differences in ncRNA sequences and expression patterns between rodent models and humans pose substantial challenges for direct translation (50, 51, 67). Moreover, the complex pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of ncRNA-based therapeutics remain poorly understood, particularly regarding stability and delivery to specific lung cell populations.
The therapeutic delivery of ncRNA-based interventions represents a paramount barrier to clinical translation in COPD. Current delivery platforms each present distinct advantages and critical limitations. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), while clinically validated for systemic delivery, face challenges in pulmonary applications including rapid alveolar macrophage clearance, limited mucus penetration, and lack of cell-type specificity (92). Polymeric nanoparticles offer improved stability but suffer from size-dependent mucus barrier limitations and potential immunogenicity (93). Exosome-based systems provide natural biocompatibility but are hampered by low cargo loading efficiency, manufacturing standardization challenges, and heterogeneous populations (94). The study by Fischer et al. (79) achieved only 30% TNF-α knockdown using microparticulate siRNA delivery, highlighting the gap between current capabilities and the >70% suppression typically required for therapeutic efficacy. Inhaled formulations, while enabling local delivery with reduced systemic exposure, face stability challenges during aerosolization and impaired distribution due to COPD-associated mucociliary dysfunction (95).
Specific barriers further complicate clinical translation. RNA stability requires chemical modifications (2’-O-methyl, phosphorothioate) that may compromise specificity and increase toxicity (96). Targeting specificity remains suboptimal despite ligand-based approaches (mannose, antibodies), with the heterogeneity of lung macrophage populations requiring subset-specific strategies (97). Off-target effects persist even with local delivery, as partial complementarity and TLRs activation can trigger unintended responses (98). Among current technologies, LNPs are closest to clinical implementation with several candidates in respiratory disease trials, yet no inhaled ncRNA therapeutic has achieved regulatory approval for COPD (99). Future advances require integration of smart nanoparticles with stimuli-responsive release, biomimetic coatings for enhanced biocompatibility, and combination delivery strategies targeting multiple regulatory nodes simultaneously (100).
5.2.3 Clinical heterogeneity and mechanistic understanding
Current research has largely treated COPD as a homogeneous condition, despite growing recognition of distinct disease endotypes with different molecular characteristics. The extent to which ncRNA-macrophage regulatory patterns vary between different COPD phenotypes remains unclear (77, 78, 101).
Furthermore, the understanding of how individual ncRNA-macrophage pathways integrate into comprehensive regulatory networks remains limited. The temporal dynamics of network activation and the hierarchical organization of regulatory controls require further investigation (69, 75). Additionally, a fundamental limitation that has received insufficient attention is the heterogeneous nature of lung macrophage populations and their distinct roles in COPD pathogenesis.
5.2.4 Macrophage heterogeneity: a critical gap in current ncRNA research
Current ncRNA-macrophage research in COPD inadequately addresses the fundamental heterogeneity of pulmonary macrophage populations, representing a critical limitation affecting research interpretation and therapeutic development. Lung macrophages comprise anatomically and functionally distinct subsets: AMs residing in airspaces and IMs within lung parenchyma (102). AMs serve as sentinel cells for pathogen recognition and particle clearance, while IMs primarily mediate tissue remodeling and stromal interactions (5). In COPD, these populations exhibit distinct dysfunction patterns and molecular signatures that may respond differently to ncRNA regulatory networks (5, 90).
Additionally, developmental origin creates further complexity, with tissue-resident macrophages (embryonic-derived, self-renewing) displaying different transcriptional programs compared to recruited monocyte-derived macrophages that infiltrate during inflammation (103). COPD significantly alters this balance, increasing monocyte recruitment and potentially creating distinct ncRNA expression profiles between these populations (5, 6).
The failure to distinguish between macrophage subsets in current studies may mask cell type-specific regulatory networks, explain apparent contradictions in research findings, and limit therapeutic efficacy (104). Future research should employ single-cell RNA sequencing and subset-specific approaches to characterize ncRNA regulatory networks within defined macrophage populations, enabling development of precision therapeutic strategies targeting specific pathogenic mechanisms while preserving beneficial macrophage functions.
5.2.5 Experimental validation strategies for ceRNA networks
The computational prediction of ceRNA networks, while powerful, requires rigorous experimental validation to establish functional relevance in COPD pathogenesis. Multiple complementary approaches have been developed to validate these regulatory interactions, each providing distinct insights into network functionality.
Knockdown and overexpression experiments represent the foundational approach for ceRNA network validation. In COPD research, loss-of-function studies using siRNAs or short hairpin RNAs targeting specific lncRNAs or circRNAs can demonstrate their regulatory effects on miRNA availability and downstream target gene expression (66, 67, 70, 71). For instance, lncRNA-Clic5 plays a ceRNA regulatory role by sponging miR-212-5p to attenuate the regulation of RASSF1. Moreover, lncRNA-Clic5 overexpression inhibited rat alveolar macrophages apoptosis by targeting the miR-212-5p/RASSF1 pathway. Co-treatment with miR-212-5p and lncRNA-Clic5 in the presence of cow barn PM2.5 revealed that lncRNA-Clic5 reversed rat alveolar macrophages cell apoptosis induced by PM2.5 when miR-212-5p was overexpressed (76).
Dual-luciferase reporter assays provide direct evidence for miRNA-target binding within ceRNA networks. This approach involves cloning predicted miRNA binding sites from lncRNAs, circRNAs, or target mRNAs into luciferase reporter vectors (105). Co-transfection with miRNA mimics should result in decreased luciferase activity, while mutation of binding sites should abolish this effect. In COPD ceRNA research, this method has been crucial for validating interactions such as the lncRNA MIR155HG-miRNA-target networks that regulate macrophage polarization (70, 71).
RNA immunoprecipitation assays enable detection of RNA-protein and RNA-RNA interactions within endogenous cellular contexts. Using antibodies against Argonaute proteins, researchers can precipitate miRNA-containing RNA-induced silencing complexes and identify co-precipitated lncRNAs, circRNAs, and mRNAs (106). This technique has proven particularly valuable for validating ceRNA networks in primary alveolar macrophages from COPD patients, where artificial overexpression systems may not accurately reflect physiological conditions (107).
Fluorescence in situ hybridization and proximity ligation assays provide spatial validation of ceRNA interactions within specific cell types and subcellular compartments. In COPD research, these techniques have been particularly useful for confirming co-localization of interacting RNAs in alveolar macrophages and epithelial cells (60, 108).
These diverse methodologies provide robust frameworks for the systematic investigation and validation of ceRNA networks in COPD, thereby strengthening the methodological rigor and reliability of related research. As technological capabilities continue to advance, more comprehensive analyses of ceRNA networks are expected, enabling deeper mechanistic understanding and uncovering novel molecular insights into the pathogenesis and progression of COPD.
5.3 Quality assessment and reproducibility concerns
Systematic assessment reveals significant variations in study quality and reporting standards. While some investigations demonstrate rigorous experimental design, others suffer from inadequate sample sizes, lack of proper validation, and insufficient characterization of experimental conditions (86, 88).
The field may be subject to publication bias, with negative results underrepresented in the literature, potentially overestimating therapeutic potential while underestimating clinical translation challenges. Additionally, reproducibility concerns persist due to variations in experimental protocols, reagent sources, and analytical methods across different laboratories (66–68).
Current ncRNA-macrophage research in COPD suggests substantial mechanistic progress yet faces significant challenges in standardization, clinical translation, and comprehensive network understanding. Addressing these limitations through standardized protocols, physiologically relevant models, and systematic approaches to identified knowledge gaps will be crucial for realizing therapeutic potential.
While substantial progress has been made in elucidating ncRNA-macrophage regulatory networks in COPD, critical limitations persist that must be addressed to realize therapeutic potential. The field faces significant methodological challenges including heterogeneous experimental protocols, inadequate representation of macrophage subset diversity, and limited understanding of integrated regulatory networks. The predominant use of cigarette smoke models may not capture the full spectrum of COPD phenotypes, particularly those related to biomass exposure or genetic susceptibility. Technical barriers such as species-specific ncRNA differences, computational prediction accuracy, and delivery system optimization remain substantial obstacles to clinical translation. Perhaps most critically, the failure to adequately address macrophage heterogeneity—including distinct anatomical populations and developmental origins—represents a fundamental gap that may explain conflicting findings and limit therapeutic efficacy. Addressing these challenges through standardized protocols, advanced single-cell technologies, and comprehensive network analyses will be essential for advancing the field toward clinical implementation.
6 Future research directions and perspectives
Addressing the identified limitations requires strategic deployment of emerging technologies and innovative experimental approaches. The following priorities will accelerate translation of ncRNA-macrophage research into clinical applications.
6.1 Technological innovation
The integration of single-cell multi-omics technologies with spatial transcriptomics will provide unprecedented resolution of ncRNA-macrophage interactions within the COPD lung microenvironment. Machine learning approaches will accelerate ncRNA-target interaction prediction and enable development of predictive models for therapeutic responses (40, 68). Human lung organoids derived from patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells will provide physiologically relevant platforms that accounting for genetic diversity and disease heterogeneity (109).
6.2 Therapeutic development
Future strategies will embrace precision medicine through companion diagnostics based on ncRNA expression profiles, enabling patient stratification for optimal interventions (83, 87). Combination therapy approaches targeting multiple ncRNA pathways simultaneously will enable comprehensive macrophage function modulation, while advanced delivery systems will achieve cell-type-specific targeting with improved stability (35, 79). Particularly, miRNAs represent attractive therapeutic targets due to their small size, sequence-specific targeting, and critical roles in disease pathogenesis. Emerging platforms include miRNA-derived oligonucleotide therapeutics and lipid nanoparticle-based delivery systems for miRNA-derived chemically modified nucleoside drugs, demonstrating enhanced stability and cellular uptake (110, 111).
6.3 Clinical implementation
Multicenter validation studies with standardized protocols will establish diagnostic and prognostic value of ncRNA signatures (81, 86). Development of point-of-care diagnostic devices will facilitate precision medicine implementation in routine practice. Regulatory framework development and economic evaluations will be essential for successful clinical translation of ncRNA-based therapeutics.
The future of ncRNA-macrophage research in COPD lies at the intersection of technological innovation, precision medicine, and systems biology approaches. Integration of single-cell multi-omics with spatial transcriptomics and machine learning will enable unprecedented resolution of cellular heterogeneity and regulatory networks within the lung microenvironment. The development of advanced delivery systems, including cell-type-specific nanoparticles and engineered exosomes, coupled with combination therapeutic strategies targeting multiple regulatory nodes, holds promise for overcoming current translational barriers. The implementation of companion diagnostics based on ncRNA signatures will facilitate patient stratification and personalized treatment selection. Success will require coordinated efforts across disciplines, including standardization of research protocols, establishment of robust biomarker validation frameworks, and development of appropriate regulatory pathways for ncRNA-based therapeutics. These advances position the field for transformative breakthroughs that could fundamentally alter COPD management, moving from symptomatic treatment toward disease-modifying interventions that target the underlying molecular pathophysiology.
7 Conclusion
This comprehensive review has elucidated the pivotal role of ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes in COPD pathogenesis. Our analysis reveals a dichotomous regulatory pattern. Pro-inflammatory miRNAs (miR-21, miR-125a-5p, miR-221-3p) promote pathological M1 macrophage polarization through NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways, while protective miRNAs (miR-195-5p, let-7c, miR-146a) facilitate inflammation resolution and tissue repair (14, 15, 49, 52–54). LncRNAs demonstrate sophisticated regulatory mechanisms through transcriptional scaffolding and ceRNA networks, with molecules such as MEG3 and MIR155HG driving inflammatory responses (69, 70, 74, 75).
Clinical validation studies have successfully translated these mechanistic insights into human disease contexts, establishing ncRNA signatures as potential diagnostic biomarkers and identifying actionable therapeutic targets (40, 80–84). The discovery of dysregulated ncRNA expression patterns in COPD patients, coupled with their correlation with disease severity and progression, supports the development of precision medicine approaches. Notably, the therapeutic potential of targeting ncRNA-macrophage regulatory axes has been demonstrated through successful modulation of macrophage polarization and inflammatory responses in preclinical models, offering promising avenues for combination therapeutics.
Despite significant progress, several challenges must be addressed to realize the full therapeutic potential of ncRNA-based interventions. These include methodological standardization across studies, species-specific differences limiting clinical translation, and the need for advanced delivery systems to achieve cell-type-specific targeting (67, 79, 80). Future research should prioritize the integration of single-cell multi-omics technologies with spatial transcriptomics to better understand ncRNA-macrophage interactions within the lung microenvironment. The development of companion diagnostics based on ncRNA expression profiles will enable patient stratification for personalized therapeutic interventions. Ultimately, continued interdisciplinary collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and regulatory experts will be essential for translating these promising findings into clinical practice and improving outcomes for COPD patients worldwide.
Author contributions
XY: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. XL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis. XC: Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No.2024YFFK0140) and Bureau of Science and Technology Nanchong City (No. 22SXQT0216).
Acknowledgments
The illustrations for this manuscript were created using figdraw (www.figdraw.com).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. During the preparation of this work the authors used (ChatGPT 4.0, GPT-4, Open AI) in order to improve readability and language. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ferrera MC, Labaki WW, and Han MK. Advances in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Annu Rev Med. (2021) 72:119–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-080919-112707
2. Christenson SA, Smith BM, Bafadhel M, and Putcha N. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. (2022) 399:2227–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00470-6
3. Lange P, Celli B, Agustí A, Boje Jensen G, Divo M, Faner R, et al. Lung-function trajectories leading to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:111–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411532
4. Ryan EM, Sadiku P, Coelho P, Watts ER, Zhang A, Howden AJM, et al. NRF2 activation reprograms defects in oxidative metabolism to restore macrophage function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2023) 207:998–1011. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202203-0482OC
5. Little I, Bersie S, Redente EF, McCubbrey AL, and Tarling EJ. Alveolar macrophages: guardians of the alveolar lipid galaxy. Curr Opin Lipidol. (2025) 36:153–62. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000987
6. Zhang F, Cui Y, Zhang T, and Yin W. Epigenetic regulation of macrophage activation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1445372. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1445372
7. Xu HP, Niu H, Wang H, Lin J, and Yao JJ. Knockdown of RTEL1 alleviates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by modulating M1, M2 macrophage polarization and inflammation. COPD. (2024) 21:2316607. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2024.2316607
8. Li Y, Yang Y, Guo T, Weng C, Yang Y, Wang Z, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 determines the cell fate of ferroptotic death of alveolar macrophages in COPD. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1162087. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1162087
9. Loganathan T and Doss CGP. Non-coding RNAs in human health and disease: potential function as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Funct Integr Genomics. (2023) 23:33. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00947-4
10. Nemeth K, Bayraktar R, Ferracin M, and Calin GA. Non-coding RNAs in disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat Rev Genet. (2024) 25:211–32. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00662-1
11. Ciullo A, Li L, Li C, Tsi K, Farrell C, Pellegrini M, et al. Non-coding RNA yREX3 from human extracellular vesicles exerts macrophage-mediated cardioprotection via a novel gene-methylating mechanism. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45:2660–73. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae357
12. Ahmad I, Valverde A, Naqvi RA, and Naqvi AR. Long non-coding RNAs RN7SK and GAS5 regulate macrophage polarization and innate immune responses. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:604981. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.604981
13. Stachowiak Z, Narożna B, and Szczepankiewicz A. Non-coding RNAs in pulmonary diseases: comparison of different airway-derived biosamples. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:2006. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032006
14. Kim RY, Sunkara KP, Bracke KR, Jarnicki AG, Donovan C, Hsu AC, et al. A microRNA-21-mediated SATB1/S100A9/NF-κB axis promotes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 13:eaav7223. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav7223
15. Wang R, Zhu Z, Peng S, Xu J, Chen Y, Wei S, et al. Exosome microRNA-125a-5p derived from epithelium promotes M1 macrophage polarization by targeting IL1RN in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 137:112466. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112466
16. Tian C, Gao J, Yang L, and Yuan X. Non-coding RNA regulation of macrophage function in asthma. Cell Signal. (2023) 112:110926. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110926
17. Yang K, Zeng L, Ge A, Wang S, Zeng J, Yuan X, et al. A systematic review of the research progress of non-coding RNA in neuroinflammation and immune regulation in cerebral infarction/ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:930171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930171
18. Ramanujam D, Schön AP, Beck C, Vaccarello P, Felician G, Dueck A, et al. MicroRNA-21-dependent macrophage-to-fibroblast signaling determines the cardiac response to pressure overload. Circulation. (2021) 143:1513–25. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050682
19. Lehmann J, Yazbeck A, Hackermüller J, and Canzler S. An extended miRNA repertoire in Rattus norvegicus. Front Bioinform. (2025) 5:1545680. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2025.1545680
20. Li R, Li D, Wang H, Chen K, Wang S, Xu J, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via miR-451a/MIF. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:149. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02823-1
21. Yu W, Wang S, Wang Y, Chen H, Nie H, Liu L, et al. MicroRNA: role in macrophage polarization and the pathogenesis of the liver fibrosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1147710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1147710
22. Ying W, Gao H, Dos Reis FCG, Bandyopadhyay G, Ofrecio JM, Luo Z, et al. MiR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:781–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.12.019
23. Lin R, Yin J, Huang J, Zou L, Liu L, Tang W, et al. Macrophage-derived ectosomal miR-350-3p promotes osteoarthritis progression through downregulating chondrocyte H3K36 methyltransferase NSD1. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:223. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01986-5
24. Tan H, Song Y, Chen J, Zhang N, Wang Q, Li Q, et al. Platelet-like fusogenic liposome-mediated targeting delivery of miR-21 improves myocardial remodeling by reprogramming macrophages post myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2021) 8:e2100787. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100787
25. Cheng J, Meng J, Zhu L, and Peng Y. Exosomal noncoding RNAs in Glioma: biological functions and potential clinical applications. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:66. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01189-3
26. Nojima T and Proudfoot NJ. Mechanisms of lncRNA biogenesis as revealed by nascent transcriptomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2022) 23:389–406. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00447-6
27. Wang Z, Kun Y, Lei Z, Dawei W, Lin P, and Jibo W. LncRNA MIAT downregulates IL-1β, TNF-α to suppress macrophage inflammation but is suppressed by ATP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Cycle. (2021) 20:194–203. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1867788
28. Lim YH, Yoon G, Ryu Y, Jeong D, Song J, Kim YS, et al. Human lncRNA SUGCT-AS1 regulates the proinflammatory response of macrophage. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:13315. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713315
29. Zhang Y, Zhu L, Li X, Ge C, Pei W, Zhang M, et al. M2 macrophage exosome-derived lncRNA AK083884 protects mice from CVB3-induced viral myocarditis through regulating PKM2/HIF-1α axis mediated metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Redox Biol. (2024) 69:103016. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.103016
30. Firoozi Z, Shahi A, Mohammadisoleimani E, Afzali S, Mansoori B, Bahmanyar M, et al. CircRNA-associated ceRNA networks (circCeNETs) in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Life Sci. (2024) 349:122715. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122715
31. Fan L, Yao L, Li Z, Wan Z, Sun W, Qiu S, et al. Exosome-Based Mitochondrial Delivery of circRNA mSCAR Alleviates Sepsis by Orchestrating Macrophage Activation. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2205692. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205692
32. Amaya L, Abe B, Liu J, Zhao F, Zhang WL, Chen R, et al. Pathways for macrophage uptake of cell-free circular RNAs. Mol Cell. (2024) 84:2104–18. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.04.022
33. Tay Y, Rinn J, and Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. (2014) 505:344–52. doi: 10.1038/nature12986
34. Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, and Yang JH. starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. (2014) 42:D92–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1248
35. Ma B, Wang S, Wu W, Shan P, Chen Y, Meng J, et al. Mechanisms of circRNA/lncRNA-miRNA interactions and applications in disease and drug research. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 162:114672. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114672
36. Martinez FJ, Han MK, Allinson JP, Barr RG, Boucher RC, Calverley PMA, et al. At the root: defining and halting progression of early chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2018) 197:1540–51. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201710-2028PP
37. Asare PF, Hurtado PR, Tran HB, Perkins GB, Roscioli E, and Hodge S. Reduction in Rubicon by cigarette smoke is associated with impaired phagocytosis and occurs through lysosomal degradation pathway. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23:4041–55. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01105-1
38. Belchamber KBR, Singh R, Batista CM, Whyte MK, Dockrell DH, Kilty I, et al. Defective bacterial phagocytosis is associated with dysfunctional mitochondria in COPD macrophages. Eur Respir J. (2019) 54:1802244. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02244-2018
39. Dong Y, Dong Y, Zhu C, Yang L, Wang H, Li J, et al. Targeting CCL2-CCR2 signaling pathway alleviates macrophage dysfunction in COPD via PI3K-AKT axis. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:364. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01746-z
40. Li B, Zhang J, Dong H, Feng X, Yu L, Zhu J, et al. Systematic analysis of various RNA transcripts and construction of biological regulatory networks at the post-transcriptional level for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:790. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04674-7
41. Russell RE, Thorley A, Culpitt SV, Dodd S, Donnelly LE, Demattos C, et al. Alveolar macrophage-mediated elastolysis: roles of matrix metalloproteinases, cysteine, and serine proteases. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2002) 283:L867–73. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00020.2002
42. Di Stefano A, Nucera F, Rosani U, Brun P, Gnemmi I, Maniscalco M, et al. Impaired SERPIN-protease balance in the peripheral lungs of stable COPD patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:2832. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072832
43. Dimic-Janjic S, Hoda MA, Milenkovic B, Kotur-Stevuljevic J, Stjepanovic M, Gompelmann D, et al. The usefulness of MMP-9, TIMP-1 and MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio for diagnosis and assessment of COPD severity. Eur J Med Res. (2023) 28:127. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01094-7
44. Baltazar-García EA, Vargas-Guerrero B, Lima A, Boavida Ferreira R, Mendoza-Magaña ML, Ramírez-Herrera MA, et al. Deflamin attenuated lung tissue damage in an ozone-induced COPD murine model by regulating MMP-9 catalytic activity. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:5063. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105063
45. Chen J, Huang ZB, Liao CJ, Hu XW, Li SL, Qi M, et al. LncRNA TP73-AS1/miR-539/MMP-8 axis modulates M2 macrophage polarization in hepatocellular carcinoma via TGF-β1 signaling. Cell Signal. (2020) 75:109738. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109738
46. Wiegman CH, Li F, Ryffel B, Togbe D, and Chung KF. Oxidative stress in ozone-induced chronic lung inflammation and emphysema: A facet of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1957. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01957
47. She Y, Xu X, Yu Q, Yang X, He J, and Tang XX. Elevated expression of macrophage MERTK exhibits profibrotic effects and results in defective regulation of efferocytosis function in pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. (2023) 24:118. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02424-3
48. Tesfaigzi Y, Curtis JL, Petrache I, Polverino F, Kheradmand F, Adcock IM, et al. Does chronic obstructive pulmonary disease originate from different cell types? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2023) 69:500–7. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0175PS
49. Jia H, He W, Wu B, Zhong Z, Chang Y, Liu Y, et al. Cigarette smoke-induced exosomal miR-221-3p facilitates M1 macrophage polarization via the STAT3 pathway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Aging (Albany NY). (2024) 16:12379–91. doi: 10.18632/aging.206095
50. Wang D, He S, Liu B, and Liu C. MiR-27-3p regulates TLR2/4-dependent mouse alveolar macrophage activation by targetting PPARγ. Clin Sci (Lond). (2018) 132:943–58. doi: 10.1042/CS20180083
51. Yang X, Zeng X, Shu J, Bao H, and Liu X. MiR-155 enhances phagocytosis of alveolar macrophages through the mTORC2/RhoA pathway. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e34592. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034592
52. De Smet EG, Van Eeckhoutte HP, Avila Cobos F, Blomme E, Verhamme FM, Provoost S, et al. The role of miR-155 in cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammation and COPD. Mucosal Immunol. (2020) 13:423–36. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0241-6
53. Li S, Jiang L, Yang Y, Cao J, Zhang Q, Zhang J, et al. MiR-195-5p inhibits the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via targeting siglec1. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2020) 39:1333–44. doi: 10.1177/0960327120920923
54. Liu T, Zhang Z, Shen W, Wu Y, and Bian T. MicroRNA let-7 induces M2 macrophage polarization in COPD emphysema through the IL-6/STAT3 pathway. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2023) 18:575–91. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S404850
55. Yoshikawa H, Sato T, Horikoshi K, Komura M, Nitta NA, Mitsui A, et al. miR-146a regulates emphysema formation and abnormal inflammation in the lungs of two mouse models. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2024) 326:L98–110. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00080.2023
56. Zhou J, Du JY, Xu R, Wu XJ, and Zhang GY. Reduced miR-513a-5p expression in COPD may regulate airway mucous cell hyperplasia through TFR1-dependent signaling. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2024) 40:139–49. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12777
57. Xu H, Wu Y, Li L, Yuan W, Zhang D, Yan Q, et al. MiR-344b-1-3p targets TLR2 and negatively regulates TLR2 signaling pathway. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2017) 12:627–38. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S120415
58. Zhu Y, Han Y, Almuntashiri S, Dutta S, Wang X, Owen CA, et al. Dysregulation of miR-103a mediates cigarette smoking-induced lipid-laden macrophage formation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2022) 67:695–707. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2022-0202OC
59. Shen W, Wang S, Wang R, Zhang Y, Tian H, Wang X, et al. Transcription Factor p300 Regulated miR-451b Weakens the Cigarette Smoke Extract-Induced Cellular Stress by Targeting RhoA/ROCK2 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:7056283. doi: 10.1155/2022/7056283
60. Zhang J, Xu Z, Kong L, Gao H, Zhang Y, Zheng Y, et al. miRNA-486-5p promotes COPD progression by targeting HAT1 to regulate the TLR4-triggered inflammatory response of alveolar macrophages. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2020) 15:2991–3001. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S280614
61. Xue H and Li MX. MicroRNA-150 protects against cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and airway epithelial cell apoptosis through repressing p53: MicroRNA-150 in CS-induced lung inflammation. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2018) 37:920–8. doi: 10.1177/0960327117741749
62. Li S, Jiang L, Yang Y, Cao J, Zhang Q, Zhang J, et al. Siglec1 enhances inflammation through miR-1260-dependent degradation of IκBα in COPD. Exp Mol Pathol. (2020) 113:104398. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104398
63. Shen W, Weng Z, Fan M, Wang S, Wang R, Zhang Y, et al. Mechanisms by which the MBD2/miR-301a-5p/CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway regulates acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2020) 15:2561–72. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S261522
64. Fan Y, Feng X, Zhu G, Zhang J, Dong Y, and Bai C. Alveolar macrophages in rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) promotes proliferation, mucin and inflammatory factors secretion of airway epithelial cells and its mechanism. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2023) 39:1–8.
65. Zeng H, Liu X, Liu P, Jia S, Wei G, Chen G, et al. Exercise’s protective role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via modulation of M1 macrophage phenotype through the miR-124-3p/ERN1 axis. Sci Prog. (2025) 108:368504251360892. doi: 10.1177/00368504251360892
66. Chen Z, Wu H, Shi R, Fan W, Zhang J, Su W, et al. miRNAomics analysis reveals the promoting effects of cigarette smoke extract-treated Beas-2B-derived exosomes on macrophage polarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 572:157–63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.07.093
67. Gross TJ, Powers LS, Boudreau RL, Brink B, Reisetter A, Goel K, et al. A microRNA processing defect in smokers’ macrophages is linked to SUMOylation of the endonuclease DICER. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:12823–34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.565473
68. Chang WA, Tsai MJ, Jian SF, Sheu CC, and Kuo PL. Systematic analysis of transcriptomic profiles of COPD airway epithelium using next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2018) 13:2387–98. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S173206
69. Wang L, Yu Q, Xiao J, Chen Q, Fang M, and Zhao H. Cigarette Smoke Extract-Treated Mouse Airway Epithelial Cells-Derived Exosomal LncRNA MEG3 Promotes M1 Macrophage Polarization and Pyroptosis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Upregulating TREM-1 via m6A Methylation. Immune Netw. (2024) 24:e3. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e3
70. Li N, Liu Y, and Cai J. LncRNA MIR155HG regulates M1/M2 macrophage polarization in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 117:109015. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109015
71. Song J, Wang Q, and Zong L. LncRNA MIR155HG contributes to smoke-related chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by targeting miR-128-5p/BRD4 axis. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40:BSR20192567. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192567
72. Wang J, Luo Q, Gu T, An F, Zhou Y, Min Y, et al. Serum-Derived Exosomal TBX2-AS1 Exacerbates COPD by Altering the M1/M2 Ratio of Macrophages through Regulating the miR-423-5p/miR-23b-3p Axis. Immunol Invest. (2025) 54:271–95. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2024.2434692
73. Salih MM, Robinson EK, Malekos E, Perez E, Capili A, Kim K, et al. LincRNA-cox2 regulates smoke-induced inflammation in murine macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2023) 68:511–22. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2022-0413OC
74. Wu SM, Feng PH, Chuang HC, Ho SC, Fan Chung K, Chen KY, et al. Impaired lnc-IL7R modulatory mechanism of Toll-like receptors is associated with an exacerbator phenotype of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. FASEB J. (2020) 34:13317–32. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000632R
75. Wang M, Zhu M, Jia X, Wu J, Yuan Q, Xu T, et al. LincR-PPP2R5C regulates IL-1β ubiquitination in macrophages and promotes airway inflammation and emphysema in a murine model of COPD. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 139:112680. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112680
76. Sun K, Sun Y, Du X, Zhang X, Ma Z, Gao Y, et al. Lnc-Clic5 as a sponge for miR-212-5p to inhibit cow barn PM2.5-induced apoptosis in rat alveolar macrophages. Toxicology. (2024) 504:153797. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2024.153797
77. Chen D, Yi R, Hong W, Wang K, and Chen Y. Anoikis resistance of small airway epithelium is involved in the progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1155478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155478
78. Yang YC, Zhang MY, Liu JY, Jiang YY, Ji XL, and Qu YQ. Identification of ferroptosis-related hub genes and their association with immune infiltration in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by bioinformatics analysis. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2022) 17:1219–36. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S348569
79. Fischer T, Tschernig T, Drews F, Brix K, Meier C, Simon M, et al. siRNA delivery to macrophages using aspherical, nanostructured microparticles as delivery system for pulmonary administration. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. (2021) 158:284–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.11.024
80. Graff JW, Powers LS, Dickson AM, Kim J, Reisetter AC, Hassan IH, et al. Cigarette smoking decreases global microRNA expression in human alveolar macrophages. PloS One. (2012) 7:e44066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044066
81. Huang W, Luo T, Lan M, Zhou W, Zhang M, Wu L, et al. Identification and characterization of a ceRNA regulatory network involving LINC00482 and PRRC2B in peripheral blood mononuclear cells: implications for COPD pathogenesis and diagnosis. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2024) 19:419–30. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S437046
82. Tinè M, Balestro E, Carpi S, Neri T, Biondini D, Conti M, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 expression and its regulation in relation to inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1320077. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1320077
83. van Nijnatten J, Brandsma CA, Steiling K, Hiemstra PS, Timens W, van den Berge M, et al. High miR203a-3p and miR-375 expression in the airways of smokers with and without COPD. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:5610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09093-0
84. Qiu J, Liu X, Yang G, Gui Z, and Ding S. MiR-29b level-mediated regulation of Klotho methylation via DNMT3A targeting in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cells Dev. (2023) 174:203827. doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2023.203827
85. Armstrong DA, Nymon AB, Ringelberg CS, Lesseur C, Hazlett HF, Howard L, et al. Pulmonary microRNA profiling: implications in upper lobe predominant lung disease. Clin Epigenet. (2017) 9:56. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0355-1
86. Shigematsu M, Kawamura T, Deshpande DA, and Kirino Y. Immunoactive signatures of circulating tRNA- and rRNA-derived RNAs in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2024) 35:102285. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102285
87. Cao Z, Zhao S, Hu S, Wu T, Sun F, and Shi LI. Screening COPD-related biomarkers and traditional chinese medicine prediction based on bioinformatics and machine learning. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2024) 19:2073–95. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S476808
88. Mirra D, Esposito R, Spaziano G, Rafaniello C, Panico F, Squillante A, et al. miRNA signatures in alveolar macrophages related to cigarette smoke: assessment and bioinformatics analysis. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:1277. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031277
89. Busch CJ, Favret J, Geirsdóttir L, Molawi K, and Sieweke MH. Isolation and long-term cultivation of mouse alveolar macrophages. Bio Protoc. (2019) 9:e3302. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3302
90. Colella P, Sayana R, Suarez-Nieto MV, Sarno J, Nyame K, Xiong J, et al. CNS-wide repopulation by hematopoietic-derived microglia-like cells corrects progranulin deficiency in mice. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:5654. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49908-4
91. Busch CJ, Subramanian S, Linares J, Favret J, Yuda RAA, and Sieweke MH. Isolation, ex vivo expansion, and lentiviral transduction of alveolar macrophages. Methods Mol Biol. (2024) 2713:231–51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3437-0_16
92. Lokugamage MP, Vanover D, Beyersdorf J, Hatit MZC, Rotolo L, Echeverri ES, et al. Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of nebulized therapeutic mRNA to the lungs. Nat BioMed Eng. (2021) 5:1059–68. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00786-x
93. Leal J, Dong T, Taylor A, Siegrist E, Gao F, Smyth HDC, et al. Mucus-penetrating phage-displayed peptides for improved transport across a mucus-like model. Int J Pharm. (2018) 553:57–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.09.055
94. Mendt M, Kamerkar S, Sugimoto H, McAndrews KM, Wu CC, Gagea M, et al. Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight. (2018) 3:e99263. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.99263
95. Kumar R, Mehta P, Shankar KR, Rajora MAK, Mishra YK, Mostafavi E, et al. Nanotechnology-assisted metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) for high-performance pulmonary drug delivery applications. Pharm Res. (2022) 39:2831–55. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03286-y
96. Khvorova A and Watts JK. The chemical evolution of oligonucleotide therapies of clinical utility. Nat Biotechnol. (2017) 35:238–48. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3765
97. Glass Z, Lee M, Li Y, and Xu Q. Engineering the delivery system for CRISPR-based genome editing. Trends Biotechnol. (2018) 36:173–85. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.11.006
98. Judge AD, Sood V, Shaw JR, Fang D, McClintock K, and MacLachlan I. Sequence-dependent stimulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nat Biotechnol. (2005) 23:457–62. doi: 10.1038/nbt1081
99. Damase TR, Sukhovershin R, Boada C, Taraballi F, Pettigrew RI, and Cooke JP. The limitless future of RNA therapeutics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2021) 9:628137. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.628137
100. Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, and Langer R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:101–24. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
101. Liang Z, Zhong N, Chen R, Ma Q, Sun Y, Wen F, et al. Investigation of the Clinical, Radiological and Biological Factors Associated with Disease Progression, Phenotypes and Endotypes of COPD in China (COMPASS): study design, protocol and rationale. ERJ Open Res. (2021) 7:00201–2021. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00201-2021
102. Ge R. Targeting airway macrophages for inflammatory lung diseases-insights from traditional Chinese medicine. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:1086. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-4845
103. Yona S, Kim KW, Wolf Y, Mildner A, Varol D, Breker M, et al. Fate mapping reveals origins and dynamics of monocytes and tissue macrophages under homeostasis. Immunity. (2013) 38:79–91. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.12.001
104. Aran D, Looney AP, Liu L, Wu E, Fong V, Hsu A, et al. Reference-based analysis of lung single-cell sequencing reveals a transitional profibrotic macrophage. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:163–72. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0276-y
105. Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG. Analyzing miRNA-lncRNA interactions. Methods Mol Biol. (2016) 1402:271–86. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3378-5_21
106. Keene JD, Komisarow JM, and Friedersdorf MB. RIP-Chip: the isolation and identification of mRNAs, microRNAs and protein components of ribonucleoprotein complexes from cell extracts. Nat Protoc. (2006) 1:302–7. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.47
107. Gu P, Wang Z, Yu X, Wu N, Wu L, Li Y, et al. Mechanism of KLF9 in airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2023) 11:e1043. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1043
108. Deng H, Zhu S, Yu F, Song X, Jin X, and Ding X. Wenshen yiqi granule alleviates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via the long noncoding RNA-XIST/microRNA-200c-3p axis. Pulm Circ. (2025) 15:e70040. doi: 10.1002/pul2.70040
109. Leibel SL, McVicar RN, Winquist AM, Niles WD, and Snyder EY. Generation of complete multi-cell type lung organoids from human embryonic and patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells for infectious disease modeling and therapeutics validation. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. (2020) 54:e118. doi: 10.1002/cpsc.118
110. Momin MY, Gaddam RR, Kravitz M, Gupta A, and Vikram A. The challenges and opportunities in the development of microRNA therapeutics: A multidisciplinary viewpoint. Cells. (2021) 10:3097. doi: 10.3390/cells10113097
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, non-coding RNAs, macrophages, inflammation, biomarkers
Citation: Yong X, Luo X, Chen X and Yu C (2025) Orchestrating inflammation: non-coding RNAs as master regulators of macrophage function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-an update. Front. Immunol. 16:1679730. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1679730
Received: 05 August 2025; Accepted: 15 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Daniela Novick, Weizmann Institute of Science, IsraelReviewed by:
Dharmendra Kumar Soni, Amity University Haryana, IndiaFlavia Bazzoni, University of Verona, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Yong, Luo, Chen and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chengxiu Yu, eWN4MTgyMzMxOTMzQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xinyu Yong1,2†
Xinyu Yong1,2† Chengxiu Yu
Chengxiu Yu