- 1Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering, Guru Nanak Dev Engineering College, Ludhiana, Punjab, India
- 2Jadara Research Center, Jadara University, Irbid, Jordan
- 3Department of Mechanical Engineering, Graphic Era (Deemed to be University), Dehradun, India
- 4University Centre for Research and Development, Chandigarh University, Gharuan, Mohali, India
- 5Centre for Research Impact AND Outcome, Chitkara University Institute of Engineering and Technology, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Punjab, India
- 6The Islamic University, Najaf, Iraq
- 7FH Campus Wien - University of Applied Sciences, Department of Engineering, Vienna, Austria
Monel-400, a nickel-copper-based alloy, is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and toughness across diverse operating environments. However, these desirable properties also make Monel-400 a challenging material to machine using conventional techniques, leading to excessive tool wear, poor surface finish, and high thermal stresses. There is currently no comprehensive review that systematically consolidates and compares non-conventional machining approaches applied to Monel-400 alloy. This review critically examines the non-conventional machining methods employed to address these challenges, including Electric Discharge Machining (EDM), Wire EDM (WEDM), Electrochemical Machining (ECM), Plasma Arc Cutting (PAC), Abrasive Water Jet Machining (AWJM), Photochemical Machining (PCM), and Hot Machining. A systematic comparison of process performance, surface integrity, material removal rate (MRR), Tool Wear Rate (TWR), Surface Roughness (Ra), and optimization strategies is presented. Key advancements such as hybrid dielectrics, cryogenic treatments, near-dry machining, and AI-based optimization techniques are discussed. Challenges related to surface defects, environmental sustainability, tool degradation, and process scalability are highlighted, along with identified research gaps. Future research directions emphasize the development of eco-friendly machining solutions, hybrid machining systems, real-time adaptive control, and life cycle assessments to enable sustainable industrial applications. This review consolidates fragmented knowledge, provides a roadmap for future innovation, and supports the advancement of efficient, precise, and environmentally responsible machining practices for Monel-400.
1 Introduction
Monel-400 and similar Ni-Cu alloys account for around 12% of specialty alloys utilized in the global marine, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries. Their adoption is projected to increase steadily at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by the growing demand for corrosion-resistant materials (Jaiswal, 2025). Nonetheless, machining high-strength nickel alloys such as Monel-400 is both costly and challenging, resulting in tool wear rate (TWR) that are 20%–30% higher and production times that are 15% longer than conventional materials like stainless steel. This situation has considerable economic repercussions in the manufacturing sectors (Demirbaş et al., 2025). The global nickel market, vital for producing Ni-based alloys like Monel-400, is expected to expand from $36 billion in 2024 to over $46 billion by 2030, driven by energy, aerospace, and marine industry applications (Bothare, 2024). This growth emphasizes the necessity for more efficient machining practices to enhance industrial advancement.
Monel was the first ever commercially developed Nickel-based alloy that served as the basis of Ni-Cu-based alloys. Its history dates back to the early 1900s when D.H. Browne working with Robert Stanley at International Nickel Company (Inco) found a way to refine Ni/Cu alloy from matte ore of Sudbury Mines that resulted in a silvery white alloy which later came to be known as ‘Monel’, named after company president ‘Ambrose Monell’. Two years after its discovery in 1906, Monel was extensively employed in architectural buildings and roofs in New York because it resisted atmospheric corrosion well. It was also heavily used by the U.S. Navy during World War I (Hodge, 2006; Shoemaker and Smith, 2006). The alloy was first patented on 30 January, 1906, by Ambrose Monell (U.S. patent 811,239) (Monell, 1906) and is now a Trademark of the Special Metals Corporation.
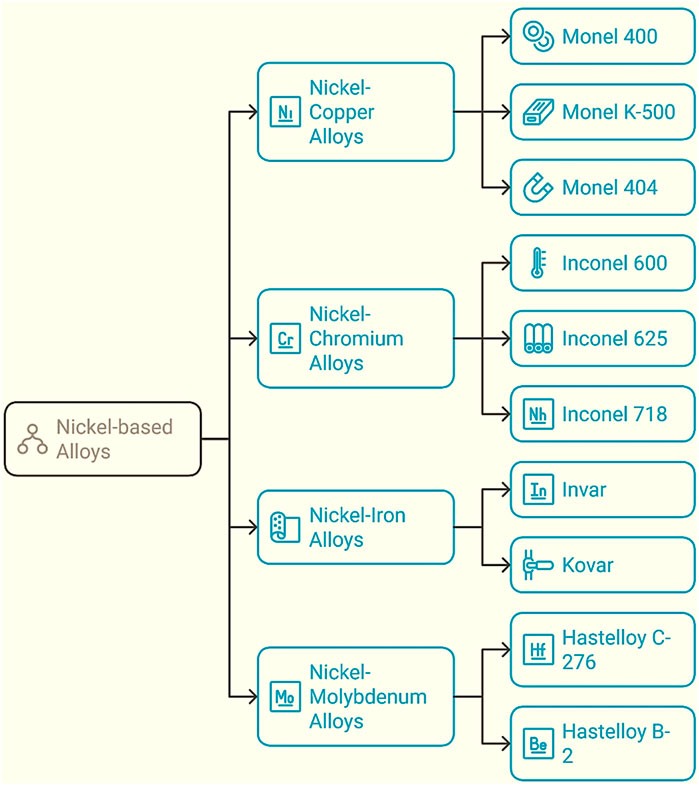
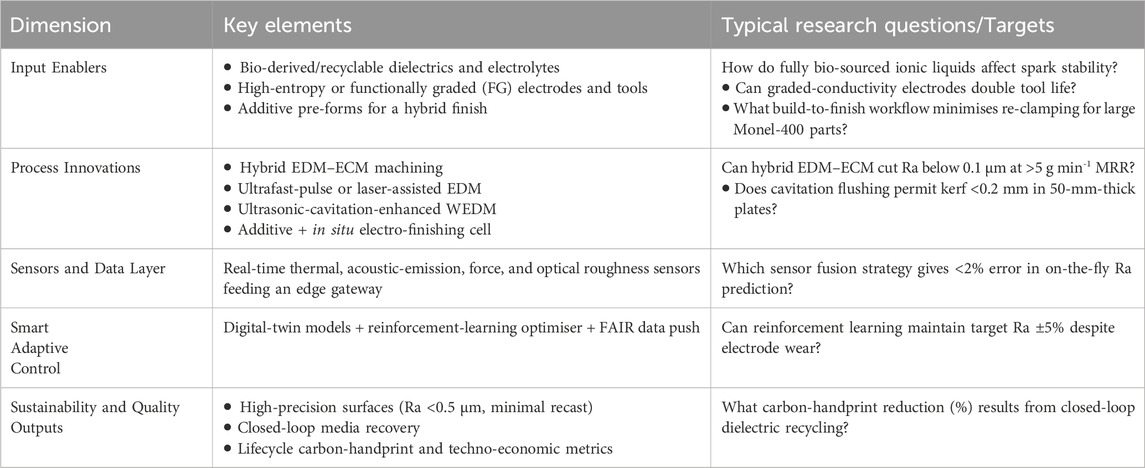
The main constituent element in Monel-400’s composition is Nickel (Ni), a versatile transition metal. Around 61% of the global production of nickel is utilized in making stainless steel. In comparison, 12% of the world production of Ni is used for processing Ni-based alloys (the rest is used to fabricate batteries, alloy steels, etc.) (Rebak, 2014). Ni can readily alloy with various elements and enhance corrosion resistance and strength at elevated temperatures (Ulutan and Ozel, 2011). This characteristic is a key factor contributing to the exceptional stability of Monel Alloy 400. Commercially fabricated Ni-based alloys can be mainly classified into two categories: High temperature alloys (HTAs), which are primarily employed for their capacity to withstand high temperatures, and corrosion-resistant alloys (CRAs), which are mainly targeted for use in aggressive corrosive environments such as marine equipment. At the same time, little focus is given to their mechanical strength (Sequeira et al., 2016; Klapper et al., 2017). Among the corrosion-resistant Alloys, Ni-Cu alloys are known for their resistance to acidic and alkaline corrosive media, weldability, and toughness across a wide temperature range (Rathi et al., 2023). Ni-Cu alloys are alloys with generally over 50% Nickel by weight percentage. Nickel and Copper are both transition metals sharing a lot of similarities, such as the same lattice structure (FCC), similar electronegativity, and valence state, resulting in complete solubility of Copper in Nickel and formation of a single-phase homogeneous Ni-Cu solid solution over the entire composition range (Marenych and Kostryzhev, 2020). Monel-400 is a nickel-copper solid solution demonstrating excellent resistance to acidic and alkaline corrosive environments. The Monel Family mainly consists of five commercially available alloys: Monel-400, Monel-401, Monel-404, Monel R-405 and Monel K-500, with Monel-400 being the most popular and oldest. A classification of Monel family as Ni-based Alloys is presented below, along with the chemical composition of Monel Alloy 400, Figure 1.
The chemical composition of Monel Alloy 400, as shown in Table 1, reveals the dominance of Nickel and Copper, which are primarily responsible for its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
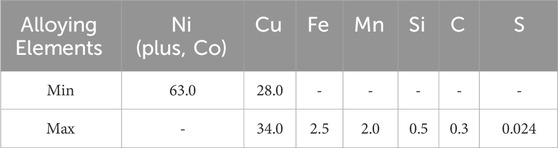
Table 1. Chemical Composition of Monel Alloy 400 (by wt%) (Special Metals, 2005).
Monel Alloy 400 is assigned UNS (Unified Number System) N0440. Monel Alloy 400 is exceptionally resistant to corrosion in sea water, as ascertained in several test experiments conducted by (Laque, 2009). Moreover, Wrought Monel is one of the best alloys used for handling mild reducing solutions such as Hydrofluoric acids (Rebak and Crook, 2000). It can also be sustained well in Dead Sea Water, de-aerated Sodium Sulphate solution (Al-Abdallah, 1996), and in aerated and de-aerated sodium chloride solutions (Ali and Ambrose, 1992; Sherif, 2012). It has even been found resistant to chloride-induced SCC (Stress Corrosion Cracking), unlike Austenitic SS (Stainless Steel) (Dutta, 2009). These unique corrosion-resistant properties of Monel, together with its higher strength and toughness derived from Nickel, enable its applications in heat pipes (Anderson et al., 2007; Rosenfeld and Gernert, 2008), Bipolar plates of proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) (Matboo Ghorbani et al., 2019; Sanjid et al., 2019), heat exchanger tubing (Rahoi et al.; Al-Hashem and Carew, 1995), steam generator tubing materials (De and Ghosal, 1981; Padma et al., 2001; Naraine and Riznic, 2017), Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER) Cells (Nady and Negem, 2016; Wang et al., 2019), oil and petrochemical industry (Katsamas et al., 2004; Knyazeva et al., 2020) and many more.
Recently, dissimilar Monel weldments have also become a subject of widespread research interest (Sabeeh et al., 2023; Yelamasetti et al., 2023). These applications demand the fabrication of Monel into intricate and complex shapes via machining with overall sound quality and Surface Finish, which is a rather challenging matter.
Monel-400, along with other nickel-based and Ni–Cu alloys, exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures in both acidic and alkaline environments. It also possesses high mechanical strength and excellent ductility at sub-zero temperatures. While a range of other alloys, such as Inconel (Ni-Cr-based) and Hastelloy (Ni-Mo-based), are widely employed in extreme operating conditions, the superior resistance of Monel-400 to hydrofluoric acid, seawater, and stress-corrosion cracking renders it particularly suitable for marine, chemical processing, and oil and gas applications. Its continued relevance is further highlighted by its historical significance as the first commercial nickel alloy and its sustained use in critical industrial applications.
In contrast, Monel K-500 offers enhanced strength but reduced ductility relative to Monel-400. Consequently, Monel-400 is preferable in applications where a balance of high corrosion resistance and superior formability is required, particularly in mildly alkaline environments (pH 6–9). This review, therefore, aims to systematically examine unconventional machining processes as they pertain specifically to the unique material behavior of Monel-400.
1.1 Rationale for non-conventional machining of Monel-400
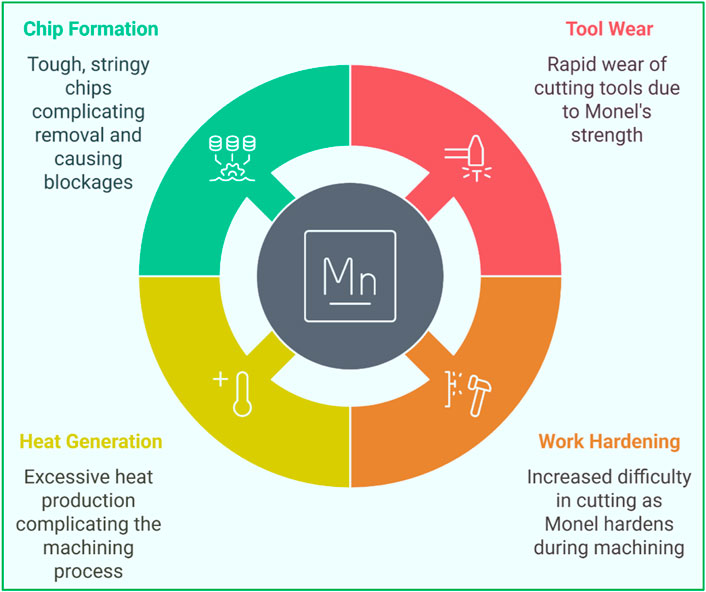
Monel-400 (UNS N04400) is a nickel–copper-based alloy renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and toughness across a broad temperature range. These attributes have led to its widespread application in highly critical and demanding industries, including marine engineering, petrochemical and chemical processing, aerospace, and nuclear energy systems. However, the very characteristics that render Monel-400 so valuable, such as high work hardenability, low thermal conductivity, and considerable ductility, also contribute to the tremendous difficulties encountered during conventional machining. Traditional machining processes often result in severe tool wear, thermal damage, compromised surface quality, and elevated manufacturing costs.
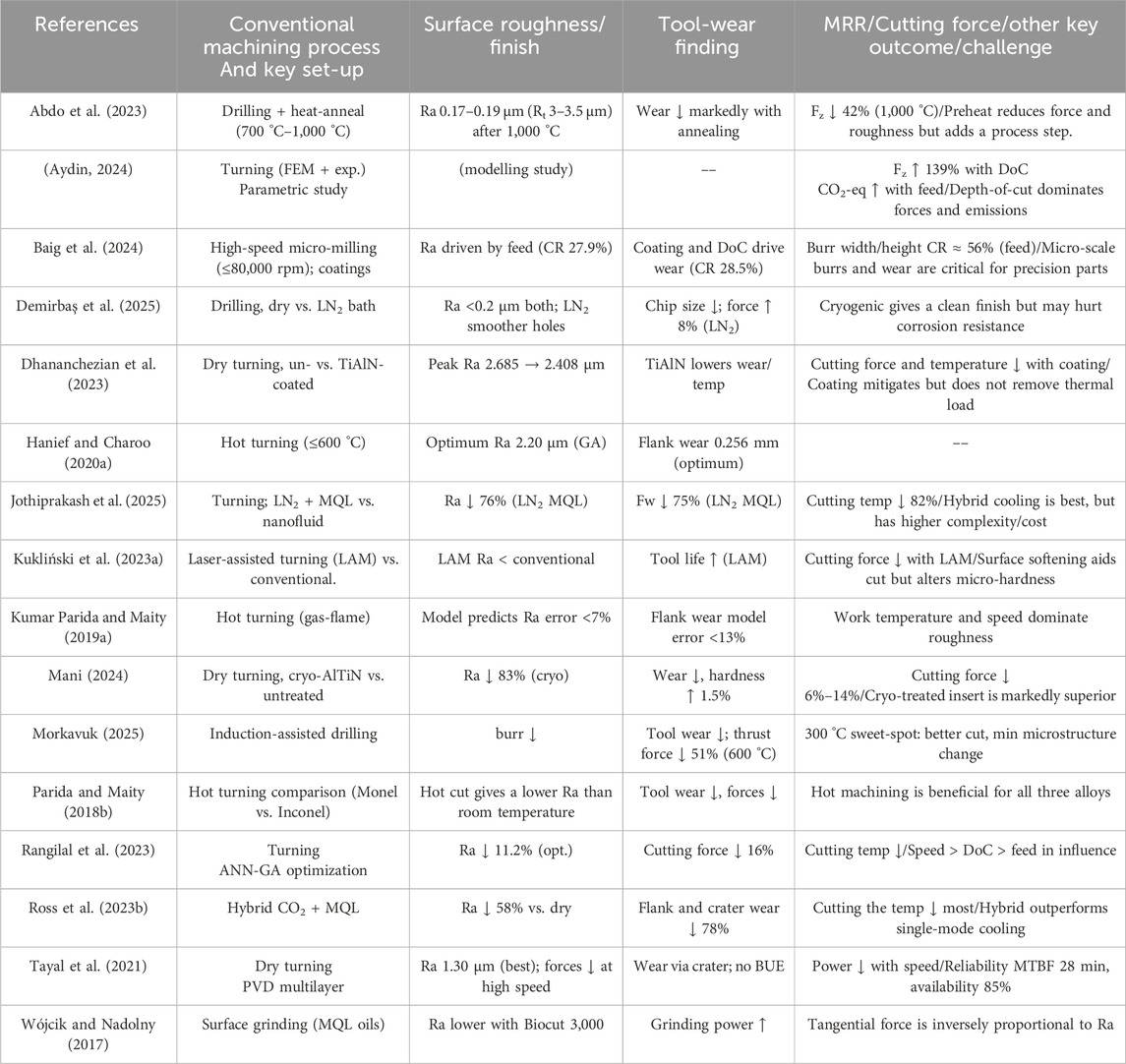
Despite notable advancements in cutting tool coatings and cooling/lubrication strategies, conventional machining methods still fall short in achieving the requisite surface integrity and dimensional tolerances for Monel-400. As evidenced in Table 2, even the use of coated tools and cryogenic or hybrid cooling techniques has proven insufficient in consistently delivering the desired surface finish. Conventional machining further suffers from excessive material wastage, prolonged cycle times, and frequent tool replacements, thereby rendering it economically unfeasible for precision and high-volume applications.
To address these challenges, non-conventional machining methods such as Electric Discharge Machining (EDM), Wire EDM (WEDM), Electrochemical Machining (ECM), Plasma Arc Cutting (PAC), Abrasive Water Jet Machining (AWJM), Photochemical Machining (PCM), and Hot Machining have been proposed as viable alternatives. These techniques provide specific advantages in processing difficult-to-machine materials by mitigating mechanical stresses and thermal deformations, minimizing tool wear, and enhancing both surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Unlike conventional methods that rely on direct mechanical interaction, non-conventional techniques operate based on thermal, chemical, or abrasive principles, thereby enabling low-contact or tool-wear-free machining. This facilitates the fabrication of intricate geometries, micro-scale features, and otherwise inaccessible regions with minimal damage and high precision. Furthermore, many of these processes can be integrated into hybrid or intelligent systems, offering scalable, repeatable, and sustainable manufacturing solutions. Thus, a comprehensive review of these non-conventional techniques is warranted to assess their applicability, optimization potential, and industrial readiness for machining Monel-400.
1.2 Challenges in conventional machining of Monel-400
Monel-400 alloy is widely recognized as a difficult-to-machine material when employing conventional machining methods, despite its favorable attributes such as mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and extended service life. Hard turning of this alloy poses significant challenges due to its pronounced work hardenability, low thermal conductivity, and strong affinity for cutting tools. These material properties often lead to adverse phenomena, including rapid tool wear, substandard surface finish, burr formation, poor dimensional accuracy, and elevated cutting forces. Such machining difficulties are further exacerbated in applications requiring precision machining and environmentally sustainable manufacturing, particularly within critical sectors such as aerospace, marine engineering, and nuclear power.
In response, various researchers have explored strategies to enhance the traditional machining performance of Monel-400, including pre-processing techniques (e.g., heat treatment), the application of advanced tool coatings, implementation of cryogenic cooling, and the optimization of machining parameters. Nevertheless, these approaches have not fully overcome the inherent limitations. Table 2 provides a summary of the machining challenges reported in the literature, focusing on key metrics such as surface roughness, material removal rate (MRR), tool wear, and aspects of process sustainability.
Despite the rising number of studies on non-conventional machining of Monel-400, there is no comprehensive review that critically compiles these findings, assesses optimization methods, identifies research gaps, and outlines future research paths. Existing research tends to be patchy and mainly concentrates on specific machining techniques. It does not offer a comprehensive or comparative overview and is, as a result, unable to guide researchers and industry professionals in selecting, enhancing, and integrating processes.
The present review seeks to fill this significant knowledge void by accumulating the current research on non-conventional machining of Monel-400. It methodically evaluates machining results, challenges, and optimization strategies and can provide side-by-side comparisons of various techniques. The review emphasizes the advantages and disadvantages of each method. It also frames a direction for future research and industrial progress in the practical and sustainable machining of Monel-400.400.
1.3 Research questions
To systematically guide this critical review on the non-conventional machining of Monel-400, the following research questions (RQs) were formulated.
• RQ1: What non-conventional machining processes have been explored for the efficient machining of Monel-400 alloy?
• RQ2: How do different non-conventional machining techniques influence key performance metrics such as MRR, Ra, TWR, and dimensional accuracy in Monel-400?
• RQ3: What optimization strategies (parametric adjustments, hybrid techniques, coolant selection) have been employed to enhance machining efficiency and surface integrity?
• RQ4: What are the primary challenges, limitations, and environmental concerns associated with non-conventional machining of Monel-400?
• RQ5: What are the critical research gaps and future directions to further advance the non-conventional machining processes for Monel-400 towards industrial scalability and sustainability?
These research questions set the analytical scope, guarantee a complete exploration of current research, and aid in determining areas of need for future research and innovation.
Machining Monel-400, an essential process in many industries, is highly challenging because of its strength, work-hardening, and low thermal conductivity. Though various experimental studies have researched non-traditional machining processes to overcome these challenges, the research is unorganized and incomplete. This paper attempts to fill this gap by organizing systematically, analyzing, and critically reviewing the non-traditional machining processes like EDM, WEDM, ECM, PAC, AWJM, PCM, and Hot Machining for Monel-400 specifically.
By identifying critical process parameters, optimization techniques, material reactions, and technical constraints, the review provides an integrated framework for understanding the present status of Monel-400 machining. By giving researchers straightforward insights into performance trends in various machining processes, the review also highlights open technical problems. For practitioners, the research is a reference guide for selecting appropriate machining processes, optimizing operating conditions, and adopting improved and sustainable approaches. By suggesting future research directions, the review inspires innovation in hybrid machining technologies, green processing, intelligent manufacturing integration, and scalability in industrial processes. The research makes theoretical contributions and practical applications to the precision machining of advanced nickel-based alloys such as Monel-400.
2 Review methodology
This review uses a structured approach to analyze the non-conventional machining techniques used in Monel-400. A systematic literature search and selection process ensured relevance, quality, and comprehensiveness.
2.1 Literature search strategy
A thorough literature search was conducted across major scientific databases (Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect). The keywords and Boolean operators were employed to retrieve relevant studies as follows:
“Machining Monel-400”, “Monel non-conventional machining”, “EDM for Monel-400”, “Wire EDM for Monel-400”, “ECM for Monel-400”, “PAC for Monel-400”, “AWJM for Monel-400”, “PCM for Monel-400”, “Hot machining of Monel-400”, “Cryogenic machining for Monel”, “Surface integrity in Monel-400”
Most documents published between 2000 and 2025 were considered to capture foundational studies and the latest advancements.
2.1.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The selection of articles was based on the following criteria.
• Material:
Inclusion: Studies focusing on the machining of Monel-400.
Exclusion: Studies primarily related to other Ni-Cu alloys without a specific focus on Monel-400.
• Process:
Inclusion: Studies centered on non-conventional machining techniques such as EDM, WEDM, ECM, PAC, AWJM, PCM, and Hot Machining.
Exclusion: Studies based solely on conventional machining processes.
• Output Parameters:
Inclusion: Studies reporting at least one of the key performance metrics, MRR, Ra, TWR, Overcut (OC), Kerf Width, or Surface Integrity.
Exclusion: Articles that lack experimental validation or measurable outcomes.
• Language:
Inclusion: Articles published in English.
Exclusion: Non-English publications.
• Document Type:
Inclusion: Peer-reviewed journal articles and conference papers.
Exclusion: Review articles, patents, theses, and book chapters.
After screening based on titles and abstracts, the relevant documents were selected for full review. They mainly addressed non-conventional machining processes for Monel-400.
2.1.2 Data extraction and analysis
The selected documents were analysed critically, and the key information was extracted as follows.
• Type of machining process
• Input process parameters
• Output performance metrics (MRR, Ra, TWR, OC, etc.)
• Tool materials and electrode characteristics
• Coolant or dielectric types
• Optimization strategies and techniques
• Reported challenges, limitations, and surface characteristics
The extracted data were systematically compared and critically analyzed to identify trends, performance improvements, research gaps, and future opportunities in the non-conventional machining of Monel-400.
3 Critical review of research studies
3.1 Effect of tool coatings on machinability and surface quality of Monel-400
When Monel-400 is machined under dry machining conditions with uncoated carbide inserts, cutting zone temperatures as high as 230 °C are reached due to the low heat carrying capacity of Monel and limited conductivity of the uncoated tool, as shown in Figure 2. The peak of ≈230 °C corresponds to the highest cutting velocity investigated 114 m min-1; temperatures of 400 °C–600 °C are commonly reported when speeds exceed 150–200 m min-1 in dry turning of Monel-400 with uncoated or standard-coated inserts (Hanief and Charoo, 2020a). This leads to flaking and high-notch wear on the tool’s face and edge. Due to high heat generation at the cutting point, material particles from the workpiece deposit on the tool surface, initiating the diffusion wear mechanism (Dhananchezian et al., 2023). Also, when this Ni-Cu alloy was machined via single-point carbide PVD-coated (TiAlN-TiN) inserts, burnt chips tended to stay on the tool’s rake face, causing an adhesion wear mechanism. When removed, these sticky particles peel off a portion of a tool insert, leading to crater wear (Tayal et al., 2021). Mani (Mani, 2024) investigated dry turning performance with untreated and cryo-treated PVD-AlTiN inserts on Monel-400. Serrated (jaw-like) chips were obtained when machined with both inserts, but the chip size was comparatively smaller for cryo-treated inserts. Also, Untreated AlTiN inserts showed micro-cracks on cutting edges, increased flaking, and extensive coating delamination compared to cryo-treated inserts.
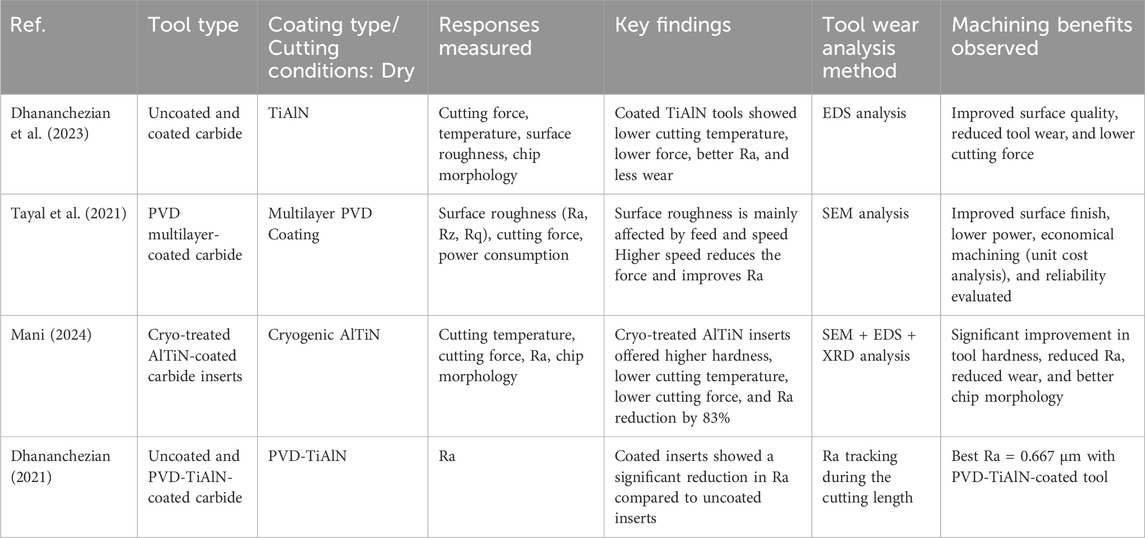
The studies reviewed in Table 3 indicate significant benefits of using coated carbide tools compared to uncoated tools during the machining of Monel 400 alloy in dry conditions. Coated TiAlN tools consistently displayed lower cutting forces, decreased cutting temperatures, and improved surface finish than their uncoated alternatives, as noted in (Dhananchezian et al., 2023; Dhananchezian, 2021). The use of multi-layer PVD coatings, examined by (Tayal et al., 2021) enhanced Ra and reduced power consumption, increasing the reliability and cost-effectiveness of machining processes. Additionally, the implementation of cryogenic treatment on AlTiN coatings, demonstrated by (Mani, 2024) Notably improved tool hardness and wear resistance, resulting in an 83% decrease in Ra and significant changes in chip morphology. Across all investigations, coated tools showcased less wear progression, better surface integrity, and higher machining efficiency, emphasizing the importance of surface engineering and tool treatment advancements for optimizing the machinability of difficult materials, Monel 400.
3.2 Effect of cooling and lubrication strategies on machining performance of Monel-400
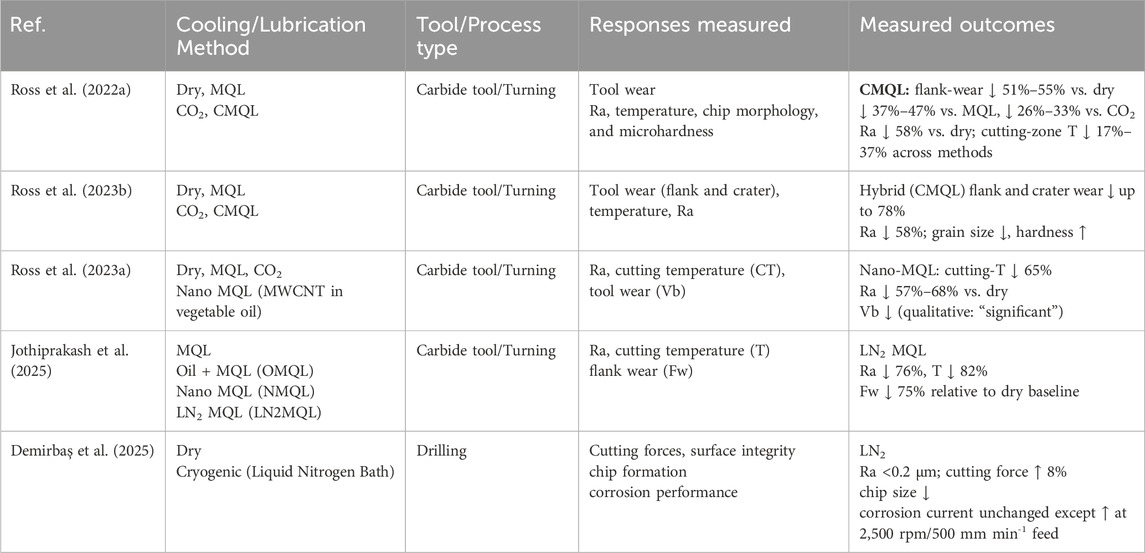
(Ross et al., 2023b) explored three different cooling strategies: MQL, Cryogenic CO2, and hybrid (CO2 + MQL), along with dry turning of Monel Alloy 400. Results showed that adhesion, abrasion, and chipping were standard wear mechanisms in dry, Cryogenic, and MQL environments. Cutting temperature directly affects Ra and tool wear in machining. Compared to dry environmental conditions, a reduction in cutting temperatures was observed to be 17.1% for MQL, 28.9% for CO2, and 37.1% for hybrid conditions. Similarly, another research also explored four different cooling environments: Dry, MQL, CO2, and CMQL (Combo of CO2 and MQL) in the machining of turning of Monel-400 by PVD-TiAlN inserts. It was observed that wear mechanisms such as BUE were predominantly observed in dry and MQL environments due to the inability of coolant to reach the high temperature cutting zone (caused by evaporation in case of MQL), while coating delamination and Abrasion wear effects were observed in the CO2 environment due to the absence of lube. Deteriorated surface (grooves, smearing, adherence of chip flakes) was observed in dry machining, followed by CO2 and MQL. Meanwhile, no primary wear mechanisms or surface defects were indicated in the CMQL machining conditions. Also, CMQL achieved the minimum Ra, which made it more efficient than other conditions (Ross et al., 2022a).
It can be observed from the literature that coated (and treated) inserts and hybrid cooling environments have shown some promise to limit the challenges in conventional machining of Monel Alloy 400. However, they further add to the machining cost, disturbing the process’s financial aspects. This led researchers worldwide to explore the Potentiality, feasibility, and reliability of advanced/non-conventional machining processes on Monel-400 alloy, viz., EDM, ECM, PAC, AWJM.
The reviewed studies in Table 4 constantly show the significant effect of advanced cooling and lubrication strategies on improving the machinability of Monel 400 alloy. The simultaneous application of cryogenic carbon dioxide and minimum quantity lubrication (CMQL), as realized by (Ross et al., 2022a; Ross et al., 2023b), led to the maximum flank and crater wear reductions, Ra, and cutting temperatures in comparison to dry, MQL, or CO2 alone, with maximum flank wear decrease by 78%. Nano-cutting fluid application, especially multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) based Nano MQL, also increased cooling efficiency by decreasing cutting temperature by 65% and improving surface finish and tool life remarkably (Ross et al., 2023a). Moreover (Jothiprakash et al., 2025), revealed that LN2MQL produced the maximum improvement in surface quality, temperature regulation, and tool wear reduction among all methods compared. In drilling processes (Demirbaş et al., 2025), demonstrated that surface finish and chip control were enhanced by cryogenic cooling, but at a minor compromise in corrosion resistance. Hybrid and cryogenic-based lubrication methods generally significantly improve machining performance, each method having unique advantages based on operation type and performance priority.
4 Non-conventional machining of Monel-400 alloy
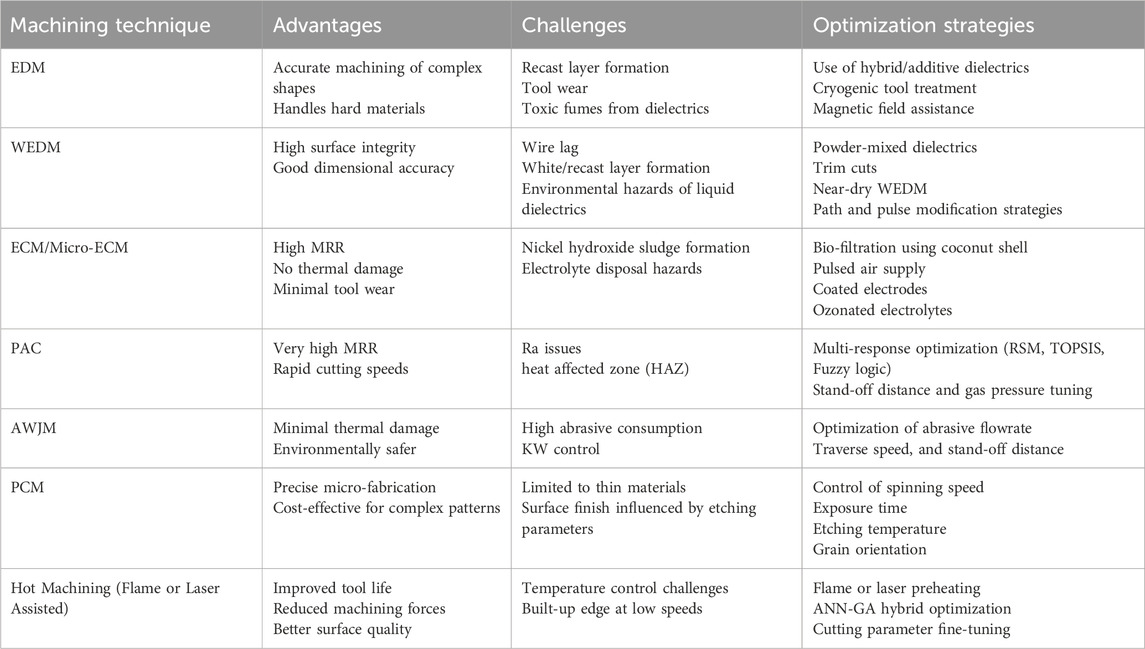
Despite being the ‘first’ ever commercial Ni-based alloy and its vast pool of applications, there has been no literature review reported on this alloy’s (Monel-400) non-conventional machining processes. Figure 3 illustrates the major unconventional machining processes for processing the Monel-400 alloy: EDM, WEDM, ECM/ECMM, PAC, AWJM, and Hot Machining. Each method is outlined with its major advantages, common difficulties, and significant breakthroughs based on knowledge from recent literature.
For example, EDM is highlighted for its maximum MRR and composite electrode usage, whereas WEDM is recognized for its accurate cutting with improved path modification. ECM/ECMM processes are known for tool wear-free machining and enhanced surface finish through electrolyte optimization. Techniques such as PAC and AWJM are classified as thermal and non-thermal, respectively, while hot machining is noted for minimizing tool wear through preheating techniques. The diagram above serves as a pictorial outline for Section 4, facilitating comparative assessments of each process’s suitability and performance for machining Monel-400.
4.1 Die-sinking Electric Discharge Machining: Tool and dielectric optimization
The origin of EDM can be traced back to the study of electricity and magnetism in the 18th and 19th centuries. Still, it was in 1943 when the destructive properties of electric discharges were first exploited (Uhlmann et al., 2005).
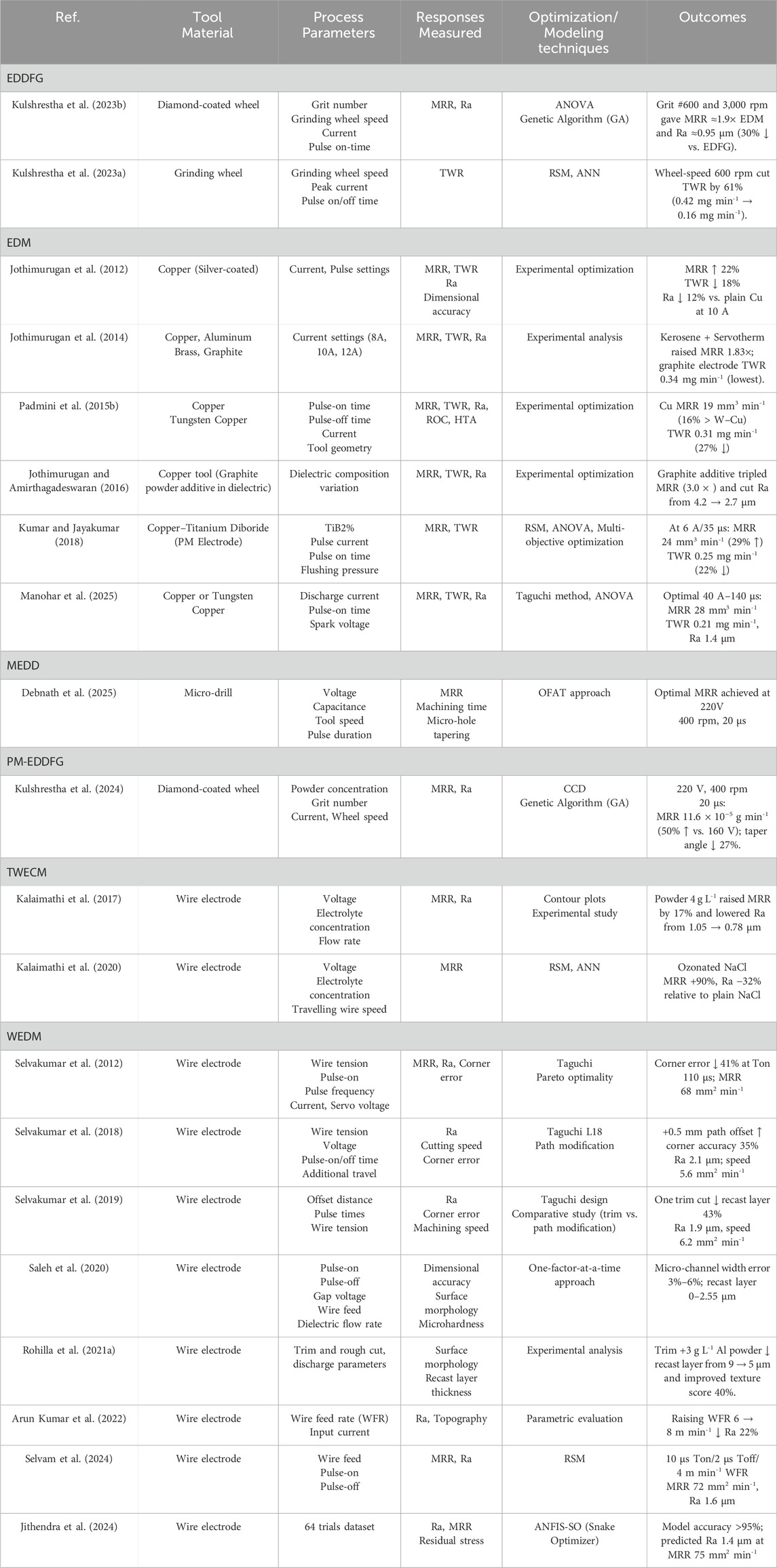
The combined research work in Table 5 from 2012 to 2025 offers remarkable progress in the non-conventional machining of Monel 400 and Monel K500 alloys through EDM, WEDM, ECM, TWECM, EDDFG, and PM-EDDFG processes. EDM research showed that tool material optimization (e.g., silver-coated copper, titanium diboride composites) and dielectric fluids (e.g., kerosene-servotherm with graphite additives) significantly improved MRR, minimized TWR, and enhanced surface quality. Adjusting pulse parameters, using path modification techniques, and employing multi-pass cutting methods constantly enhanced surface integrity, corner accuracy, and dimensional precision in WEDM. TWECM and ECM research proved that employing ozonated and optimized electrolytes significantly increased MRR and surface smoothness.
Sophisticated hybrid grinding processes such as EDDFG and PM-EDDFG demonstrated better machining performance than traditional EDM and grinding, significantly minimizing Ra and maximizing tool life, particularly through using diamond-coated wheels and MWCNT powders. Predictive modeling strategies such as RSM, ANN, Genetic Algorithms, and the new ANFIS-SO framework performed high-accuracy Ra, MRR, and residual stress forecasting, making the optimization process easier. Integrating intelligent optimization and hybrid processing approaches significantly increased machining efficiency, surface integrity, and predictive reliability, developing successful methodologies for hard-to-machine Monel alloy processing.
The variations of this process are categorized as follows.
4.1.1 Die-sinking EDM
EDM is one of the most widely adopted non-conventional machining processes for machining complex shapes and difficult-to-cut electrically conductive materials, such as Ni-based superalloys, Ti-based alloys, Co-based alloys, etc., by continuous spark generation and erosion (Benedict, 1987).
4.1.1.1 Studies on electrode material
Copper, Graphite, and Brass are the least commonly used tool electrodes in EDM, but the high TWR of Copper, Brass, and low mechanical strength of Graphite pose a challenge (Czelusniak et al., 2018). In this regard, M. Mahalingam et al. investigated process parameter optimization to minimize the TWR of Brass electrode for EDM of Monel-400. A study revealed that the Wear Rate of Brass increases with an increase in discharge current (due to the presence of low-melting zinc in Brass) and decreases with an increase in pulse-on time. Not only that, but an increase in gap voltage also drastically reduced the TWR, as shown below (Mahalingam and Varahamoorthi, 2020). An experimental investigation of P. Anand Kumar in EDM of Monel 400 using different electrode materials revealed that graphite has the highest MRR and is suitable for rough machining. At the same time, Brass, on the other hand, exhibits the best surface finish but has a higher TWR (Anandakumar and Shanthi, 2013). It can be noted that these conventional electrodes can only be optimized to a limited extent. Hence, various researchers are extensively employing cutting-edge materials such as composites and alloys as tool electrodes for machining superalloys. The study was conducted to obtain optimal setting parameters for composite copper titanium diboride powder metallurgy electrodes by desirability multi-response optimization in the EDM of Monel-400. This investigation revealed a considerable reduction in TWR, mainly due to the addition of titanium diboride, and this electrode was found most efficient at a low current setting. Optimality was achieved at 16% of titanium diboride, pulse current of 6 A, flushing pressure of 1 MPa, and pulse on time of 35 µs (Kumar and Jayakumar, 2018). Mustafa et al. explored the utilization of copper, graphite, and copper graphite electrodes in the EDM drilling of Monel-400 with MRR and Ra as output responses. Data from experiments concluded that Ra was lowest when drilling was done with the Composite Copper-Graphite electrode. Parameters corresponding to the maximum MRR were also calculated (Hadi and Ibrahim, 2022). A novel high-pressure flushing scheme lowered the WEDM spark gap to 0.109 mm and surface roughness to 2.2 µm on complex Inconel-718 profiles (Farooq et al., 2024).
Figures 4a,b demonstrate that the Cu-graphite composite electrode simultaneously yields the highest material-removal rate and the lowest surface roughness compared with pure Cu and pure graphite under the specified pulse settings.
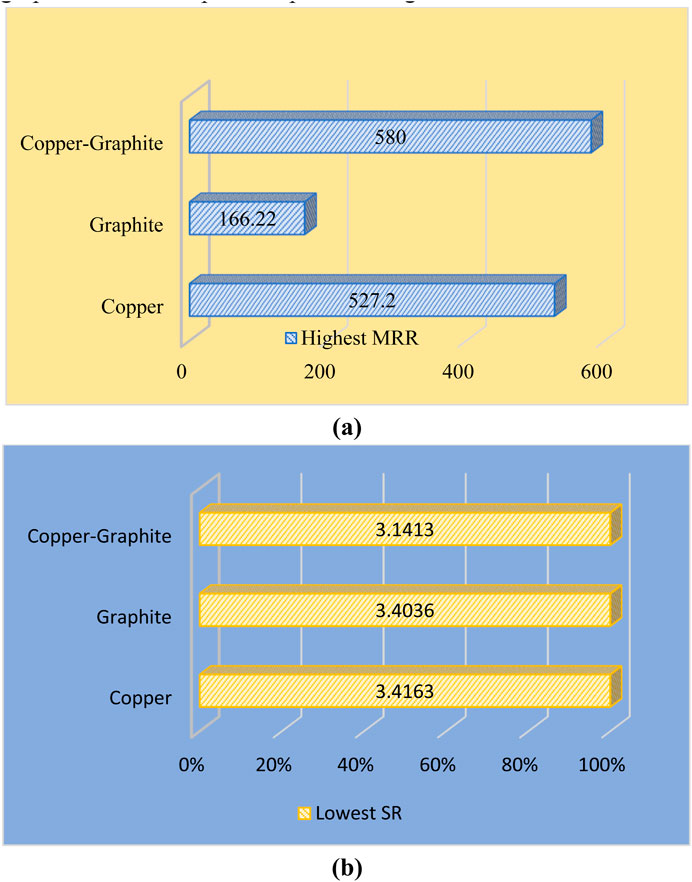
Figure 4. (a) Peak MRR values for Copper, Graphite, and Copper-Graphite composite electrode at Ip = 42 A, Toff = 25 µs, and Ton = 200 µs, (b) Lowest SR values for Copper, Graphite and Copper-Graphite composite electrode at Ip = 10 A, Toff = 12 µs and Ton = 50 µs.
4.1.1.2 Studies on the impact of dielectric fluids
The type of dielectric used dramatically influences the machining efficiency and output in EDM. Synthetic and hydrocarbon oil-based dielectric fluids emit fumes and vapors containing PAHs, Aliphatic hydrocarbons, Benzene, and various other toxic byproducts, causing health and environmental issues (Gupta and Gupta, 2018; Biswas and Rahul, 2021). Also, use of conventional dielectric fluids (such as Kerosene) results in deposition of carbon layer (Recast layer) over work surface causing low MRR and poor surface finish (Ekmekci, 2007). To overcome the drawbacks of conventional dielectrics, R. Jothimurugan et al. investigated 16 different proportions of Paraffin–Servotherm mixture as an electrolyte by machining holes in Monel–400 plate via EDM. They concluded the optimal ratio for paraffin–servotherm mixture to be 70:30, which not only enhanced MRR by 1.9-fold but also reduced TWR by 14% than that of Paraffin alone (mainly due to the deposition of nickel from workpiece to tool surface, thereby providing electric resistance) (Jothimurugan et al., 2019). (Jothimurugan and K S, 2014) screened 16 kerosene–servotherm formulations (additives: Si, Gr, Al, Cr, Ni) and identified a 75 : 25 vol% base mixture that increased MRR by 1.83 × and lowered TWR to 0.56 × relative to plain kerosene. Subsequently, dispersing 6 g L-1 of graphite in this optimised mixture boosted MRR even further from 10.4 mm3 min-1 with plain kerosene to 31.2 mm3 min-1 (≈3 ×) while cutting surface roughness from 4.2 µm to 2.7 µm.
4.1.1.3 Studies to augment machining efficiency
Another aspect is developing control over dimensional parameters to enhance efficiency in EDM, which can be challenging due to the underlying difficulties of overcutting (OC). The research efforts conducted to analyze the effect of the circle, rectangle, triangle, and square tool geometries and the process parameters in minimizing Radial Overcut (ROC). P et al., for EDM of Monel-400. Circular geometry of the tool was found to be the most optimal in reducing ROC, henceforth, honing machining efficiency and dimensional accuracy. Taguchi optimization and the corresponding parametric combination were also calculated (Padmini et al., 2015a). Moreover, an investigation found that cryogenic treatment improves tool life, reduces OC and improves surface quality (Grewal and Dhiman, 2019). In this context, the study on MRR and TWR for cryo-treated Monel-400 in the presence of an external magnetic field compared to untreated Monel-400. They found that cryogenic treatment enhanced electrical conductivity, thereby reducing power losses and TWR, while the magnetic field, on the other hand, effectively removed debris, thereby enhancing machining efficiency (Jadhav et al., 2015).
Upon reviewing the results presented in Table 6, it is clear that several strategies have been investigated to improve the machining efficiency of Monel-400 with EDM. The research primarily emphasizes optimizing tool materials, modifying dielectrics, controlling tool geometry, and applying cryogenic treatment alongside external magnetic fields. Each strategy aims to enhance critical output parameters, including MRR, TWR, Ra, and dimensional accuracy.
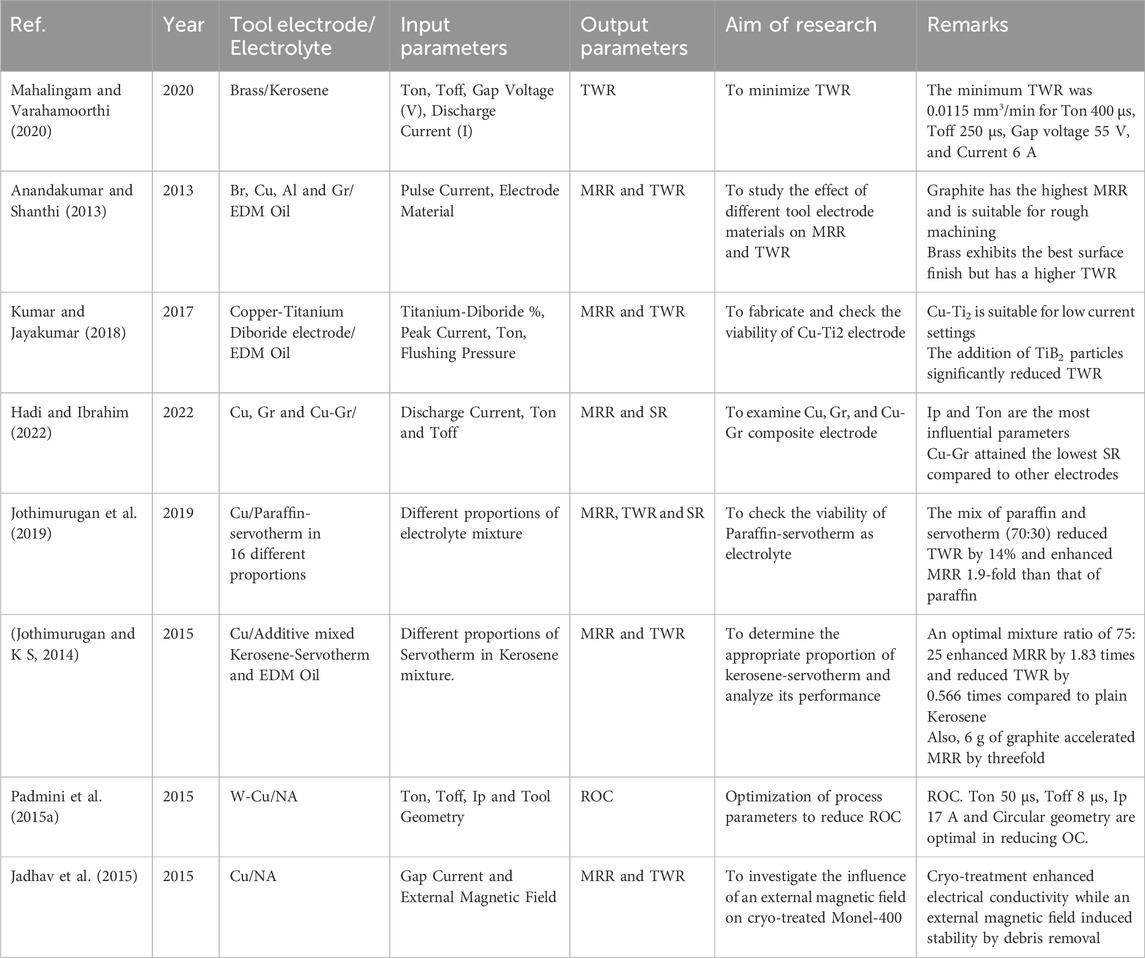
Table 6. Summary of strategies for enhancing the machining efficiency of Monel-400 in EDM operations.
In terms of electrode materials, studies (Anandakumar and Shanthi, 2013; Kumar and Jayakumar, 2018; Hadi and Ibrahim, 2022) reveal that graphite electrodes achieve the highest MRR and are well-suited for rough machining operations. However, they suffer from high wear, making them less favorable for finishing applications where surface quality is critical. Brass electrodes, in contrast, produce a superior surface finish but exhibit higher TWR. Researchers have introduced composite electrodes like Copper-Graphite and Copper-Titanium Diboride (Cu-Ti2) to overcome these trade-offs, significantly enhancing performance by reducing TWR and achieving a better balance between MRR and surface finish. Cu-Ti2 electrodes were highly efficient at low current settings, offering promising results for precision EDM.
Dielectric modifications also play a critical role in improving EDM outcomes. Studies (Jothimurugan et al., 2019) and (Jothimurugan and K S, 2014) demonstrate that mixing paraffin and servotherm in optimal proportions, or adding graphite particles to the kerosene-servotherm mixture, leads to remarkable enhancements in MRR (up to 1.9–3 times higher) while simultaneously reducing TWR. These modified dielectrics promote better spark stability and heat dissipation, minimizing electrode wear and improving material removal efficiency. Nevertheless, they introduce additional challenges related to fluid management and environmental considerations.
Optimization of tool geometry has also shown a direct impact on dimensional accuracy. Study (Padmini et al., 2015a) reported that circular tool geometries, coupled with appropriate pulse parameters (Ton, Toff, and Ip), are most effective in minimizing ROC. By reducing ROC, machining precision improves, and material wastage decreases, making the process more efficient. Although effective, adopting circular geometries may add to tool fabrication complexity in practical applications. Cryogenic treatment and magnetic field assistance represent another emerging area for machining improvement. Studies (Grewal and Dhiman, 2019; Jadhav et al., 2015) show that cryogenic treatment enhances the electrical conductivity of Monel-400 and extends tool life by reducing thermal-induced defects. Simultaneously, applying an external magnetic field during EDM operations improves debris evacuation from the spark gap, increasing machining stability and better surface quality. Although these techniques provide significant benefits, they also introduce additional costs and setup complexity, which must be considered during industrial application.
Optimizing tool materials and modifying dielectrics enhance MRR and surface quality, while optimizing tool geometry primarily concentrates on dimensional control. Techniques like cryogenic treatment and magnetic fields enhance the machining environment by reducing wear and increasing process stability. Each method tackles unique machining challenges, and their combined use can lead to synergistic benefits.
These advancements in tool material and dielectric selection demonstrate EDM’s effectiveness in machining Monel-400. Nevertheless, issues such as recast layers and tool wear underscore the need for ongoing optimization and alternative techniques like WEDM and ECM.
The machining efficiency of Monel-400 using EDM can be significantly enhanced through a comprehensive approach that includes optimizing electrode materials, employing hybrid or additive-based dielectric fluids, selecting appropriate tool geometries, and utilizing advanced techniques like cryogenic processing and magnetic field assistance. Although considerable advancements have been achieved, it is crucial to carefully evaluate process costs, operational complexity, and environmental sustainability for practical industrial application. Thoughtful integration of these strategies can result in highly efficient, precise, and sustainable EDM machining of Monel-400.
4.1.2 Wire EDM of Monel-400: Surface integrity and process optimization
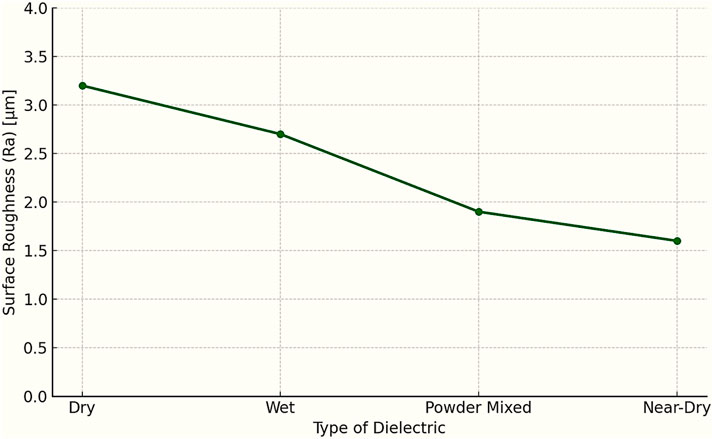
WEDM is a spin–off EDM process that was first introduced in the late 1960s, but it was in the 1970s that CNC-assisted WEDM gained popularity (Mandal, 2014). Wire EDM or WEDM is one of the most effective and widely used non-conventional processes in the manufacturing sector for machining various steels, carbides, alloys, and superalloys (Ho et al., 2004). But problems associated with the WEDM process, such as the White layer (or recast layer), emission of hazardous fumes in wet dielectric, and poor surface integrity, are significant shortcomings.
4.1.2.1 Studies on recast layer (or white layer)
Recast layer refers to the layer of unexpelled metal solidified on a work surface that melted as a result of very high temperatures produced by electric discharges, and this recast layer serves as a source of Tensile and Compressive residual stresses, porosity, and poor surface finish (Newton et al., 2009). In this study, Vinod Kumar et al. highlighted the importance of trim cut and powder mixed dielectric in reducing recast layer and improving surface finish for WEDM of Monel-400. They found that a trim cut successfully reduced the recast layer to 43% after the rough cut. On top of that, the addition of 3 g/L of Aluminum powder in the dielectric significantly improved the surface integrity and also reduced the recast layer from 9 μm to 5 µm (Rohilla et al., 2021a).
4.1.2.2 Studies on parametric optimization
Optimization is crucial to obtain the best MRR and surface integrity of the workpiece, which is time-consuming and tedious. Consequently, Vinod et al.'s desirability approach obtained optimal parametric conditions for a rough cut and trim cut (after one rough cut) for Monel-400 when machined via WEDM. Conclusions drawn from this experiment stated that increasing Ip and Ton increases MRR, but it adversely affects the SR. Also, increasing Toff decreases the MRR but improves the surface finish (Kumar et al., 2015). It can also be observed that research, as mentioned above, has only been carried out with a fixed thickness of the workpiece, which may or may not be suitable for the industry. For this Rationale, a research investigation to find optimal settings of WEDM of Monel-400 alloy in a range of thickness was carried out by G. Selvakumar et al., and a table for optimal machining of workpiece thickness was presented for individual optimal thickness settings (Gurusamy et al., 2012a). N.E. Arun Kumar et al. employed a different approach of cryogenic treatment to improve MRR and Ra values for WEDM of Monel 400 alloy. They conducted a comparative study of untreated and cryo-treated Brass Wire electrode by varying WEDM parametrics (Wire Tension, Ton, Toff, Peak Current, Servo Feed). It was observed that Wire Tension, Servo Feed, and Ton were the most predominant factors. As for electrodes, cryo-treated brass electrodes attained low MRR values but a superior surface finish compared to untreated electrodes. Cryogenic treatment reduces atomic vibrations and makes a structured atomic arrangement (Kumar N. E. A. et al., 2023).
4.1.2.3 Studies on the effect of liquid dielectric
Another major challenge hampering WEDM is the impact of liquid dielectric on the environment and Personnel health. Studies revealed that wet EDM with liquid dielectric produces hazardous fumes and gaseous byproducts. Hydrocarbon-based dielectrics (such as kerosene) have the worst effect in this case (Valaki et al., 2014). Kumar et al. adopted the Near-dry WEDM approach to minimize environmental and health hazards. An analysis was conducted to trace how parameters affected MRR and Ra of machined Monel-400 in Near-dry and wet WEDM. Although MRR was highest in wet WEDM, the Ra for near–dry EDM was always better than that of wet EDM. The surface plots shown below shed light on the same (Kumar et al., 2020). Yet another research study aimed to explore the influence of near-dry WEDM operational metrics on the kerf-width of the Monel-400 superalloy. They concluded that pulse-off is requisite in controlling kerf-width (Arun Kumar et al., 2021).
4.1.2.4 Studies on corner accuracy
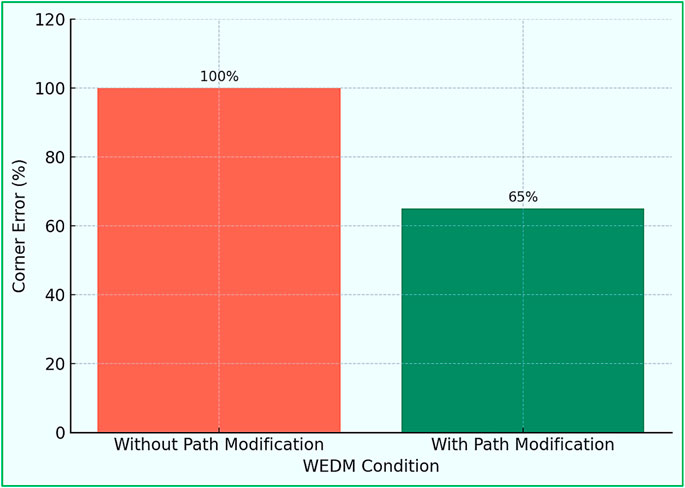
Wire electrodes in WEDM deform owing to their flexibility and gap force lagging behind the wire guide, which gives birth to corner errors (CE) and imperfect machined parts (Sarkar et al., 2011). Wire lag can be reduced either by path modification or pulse modification strategy as reported in literature (Haron et al., 2001; Puri and Bhattacharyya, 2003; Schumacher, 2004; Ji et al., 2012; Bergaley and Sharma, 2013). G Selvakumar et al. implemented a path modification strategy to minimize CE in WEDM of Monel–400. They found that an additional travel of 0.5 mm increased corner accuracy by 35% (Selvakumar et al., 2016). Another research study was conducted to study the impact of pulse modification strategy for Monel–400 with WEDM controllable and uncontrollable factors. This research study elucidates the effectiveness of the pulse modification strategy for improving MRR, but it is a waste of time for improving corner accuracy (Gurusamy et al., 2012b).
Table 7 summarizes various studies to enhance the performance of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (WEDM) for Monel-400 alloy by optimizing factors such as pulse timing, wire properties, dielectric environment, and cutting conditions. The research examines the impact of adjusting input parameters like pulse-on time (Ton), pulse-off time (Toff), peak current (Ip), servo voltage (SV), wire tension, and auxiliary methods like near-dry machining or cryogenic wire treatment on output metrics like MRR, Ra, kerf width (KW), and corner accuracy (CE).
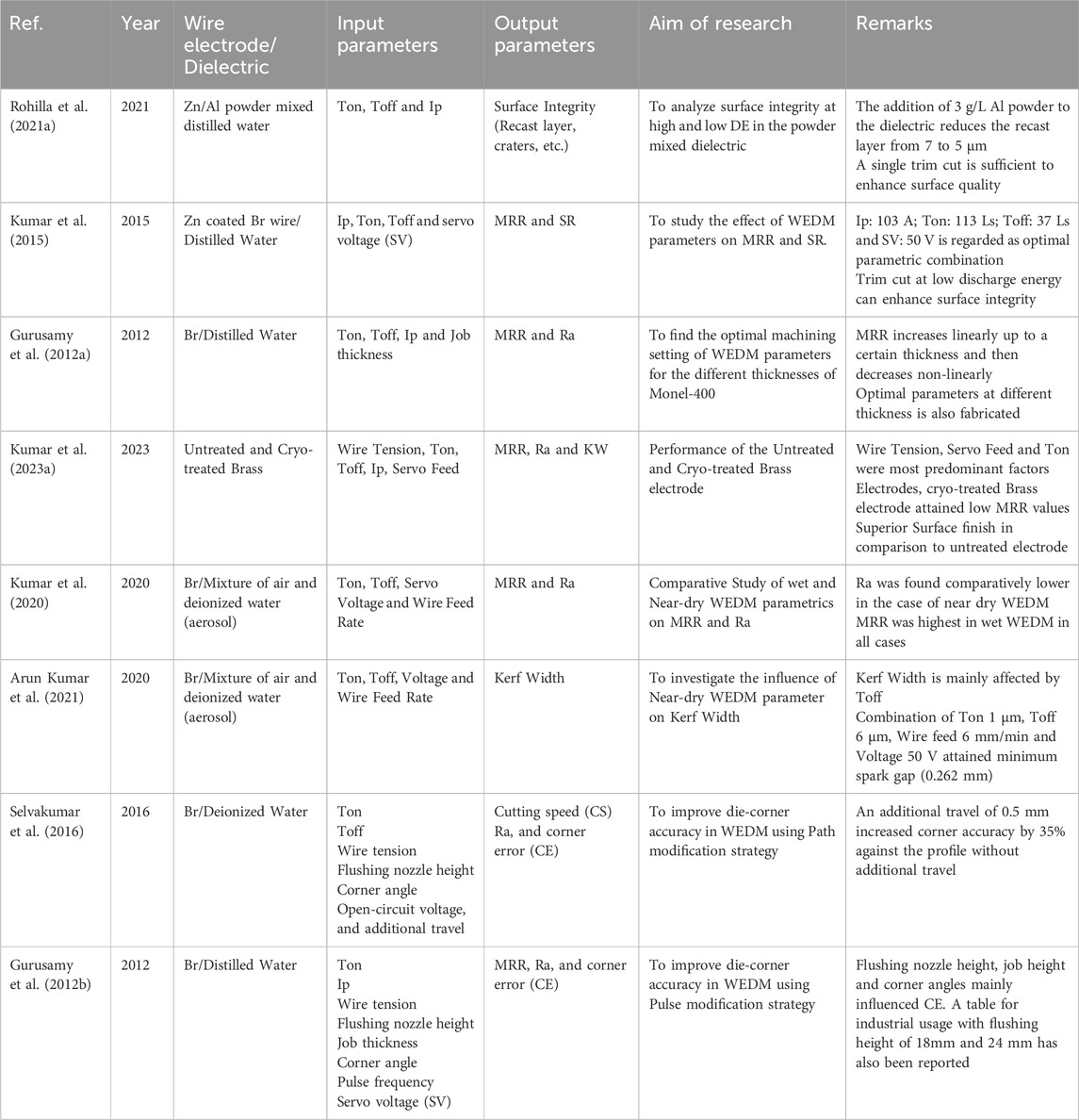
Table 7. Summary of parametric optimization and surface integrity improvements in WEDM of Monel-400 alloy.
The reviewed studies highlight that surface integrity is essential for WEDM of Monel- 400. Incorporating aluminum powder into the dielectric, explored in (Rohilla et al., 2021a), notably enhanced surface quality by reducing the recast layer thickness from 7 to 5 μm, with a single trim cut adequate for improving surface finish. Concurrently, another study (Kumar et al., 2015) investigated the optimization of WEDM parameters without powder-mixed dielectrics, revealing that high peak current (103 A), Ton (113 µs), and well-optimized Toff (37 µs) achieved a favorable balance between MRR and Ra, although surface quality improved with additional trim cutting at lower discharge energy.
Additionally, the effect of workpiece thickness on WEDM performance was critically examined. A study (Gurusamy et al., 2012a) found that MRR initially increased linearly with thickness but exhibited a nonlinear decrease beyond a specific threshold. Optimal parameters were established for various thickness ranges to maintain consistent machining quality. Furthermore, research in (Kumar N. E. A. et al., 2023) revealed that cryogenic treatment of brass wires enhanced surface finish, albeit with a slight reduction in MRR, attributed to improved atomic ordering in the cryo-treated wires, allowing for better discharge process control.
The cooling environment also significantly impacts WEDM performance. Studies (Kumar et al., 2020; Arun Kumar et al., 2021) contrasted conventional wet WEDM with near-dry conditions, utilizing a blend of air and deionized water. Near-dry WEDM consistently yielded lower Ra values, although MRR was marginally elevated in traditional wet settings. Specifically, Toff proved to be the most sensitive parameter influencing KW, with the optimal settings of Ton at 1 µs, Toff at 6 µs, a wire feed of 6 mm/min, and a voltage of 50 V achieving the minimum spark gap of 0.262 mm.
Corner accuracy is a crucial factor in dimensional control and has been thoroughly examined in sources (Selvakumar et al., 2016; Gurusamy et al., 2012b). A strategy that modifies the path by adding an extra 0.5 mm resulted in a 35% enhancement in corner accuracy compared to an unaltered path. Additionally, pulse modification techniques, which adjust Ton, Ip, and the height of the flushing nozzle, were investigated to reduce corner errors; among these, the flushing nozzle height and job thickness showed the most significant impact. These methods are especially beneficial for sectors that require complex die-corner profiles with minimal distortion.
When evaluating various strategies, powder-mixed dielectrics and trim cuts present the clearest enhancements to surface integrity, whereas cryogenic treatment improves surface finish, albeit slightly diminishing the MRR. Near-dry WEDM is recognized as an environmentally friendly option that delivers excellent surface quality, though it may not completely match the MRR achieved in wet conditions. Parametric optimization across different thicknesses guarantees adaptability to various component geometries. For applications demanding high precision, modifications to both the path and pulses are essential for improving corner fidelity.
The efficient machining of Monel-400 using WEDM involves various strategies customized for specific application outcomes. Employing powder-mixed dielectrics and applying cryogenic treatments to wires can effectively produce high-quality surfaces, while nearly dry WEDM techniques support sustainability efforts. Precise management of pulse settings, wire feed rates, and supplementary methods like path modifications greatly enhances both dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Future research should focus on hybrid methodologies that combine powder mixing, cryogenic treatments, and sophisticated control techniques to achieve high MRR and outstanding surface finishes in an environmentally friendly way.
4.1.3 Micro-WEDM for high-precision machining of Monel-400
The demand for smaller and thinner products in recent years necessitates the development of diverse micro-machining processes for their manufacturing. Micro-WEDM is one such process that can machine 3-D complex and intricate shapes with high aspect ratios (Taylor et al., 2019). Lack of literature in this field instigated to attempt milling Microchannels on Monel-400 with a one-factor-at-a-time approach on Ra, surface morphology, and dimensional accuracy. Ton, Toff, and VGAP were the most effective parameters. They concluded that using lower to middle levels of TON, moderate levels of TOFF, and moderate VGAP can produce microchannels with satisfactory channel width (CHW) and depth (CHD), smooth surface morphology, and low recast layer thickness (Saleh et al., 2020).
4.2 Electrochemical Machining (ECM) of Monel-400
4.2.1 Die-sinking ECM: Electrolyte effects and surface finish analysis
4.2.1.1 Studies on the type of electrolyte
Experimental investigations have optimized process parameters to obtain the best MRR and Ra values in die-sinking ECM. Experimental investigations were conducted on the surface machining of Monel-400 alloy with a flat face tool electrode in flooded electrolyte conditions, employing two different electrolytes: aqueous NaCl solution and aqueous NaNO3 solution. Experimental results for optimal process parameters in both cases pointed out higher values of MRR with aqueous NaCl as an electrolyte, but comparatively lower Ra in the case of NaNO3 (Kalaimathi and Venkatachalam, 2014; Kalaimathi et al., 2014).
4.2.1.2 Studies on nickel presence
Further research has found that when this Ni-Cr superalloy is machined while immersed in an electrolyte, a toxic substance, Nickel-Hydroxide [Ni (OH2)], is formed in the sludge. To counter this problem, Metaheuristics: GWO (grey wolf optimizer), MFO (moth-flame optimization), and Nagarajan et al. employed PSO (particle swarm optimization) in devising optimal process parameters for minimizing nickel presence in the sludge with NaCl (+1% HCl) as electrolyte. They concluded that MFO and GWO were more efficient and resulted in the same parametric combination, i.e., EC of 132.014 g/L, Voltage of 13.2406V, and Flow Rate of 2.8455L/min for MRR = 0.242 g/min and NP = 57.7202 PPM (Nagarajan et al., 2022). Another approach to this problem was presented by Vengatajalapathi et al., who employed natural bio-adsorbents to adsorb Ni-ions from electrolytes after the ECM of the Monel-400 workpiece. Bio-adsorbents from natural environmental wastes such as coconut shell powder, wood dust powder, and bagasse were used as filtration material. It was observed that the lignin and holo-cellulose present in coconut powder adsorbed a significant amount of nickel content. Moreover, the voltage of 12.535V, electrolyte concentration (EC) of 130 g/L, and a flow rate of 1.768 L/min were found to discharge the minimum possible nickel contents of 49.8776 mg/L into the electrolyte (Sekar, 2022).
4.2.1.3 Environmental implications of electrolyte use in ECM
ECM is renowned for being tool-wear-free and machining hard materials with a perfect surface finish. ECM also generates serious environmental problems mainly because it employs electrolytes like NaCl, NaNO3, and hybrid chemical solutions. ECM produces toxic sludge with heavy metal ions like nickel hydroxide, which can pollute water sources if not appropriately treated. Spent electrolyte disposal is a cause for environmental concern in soil and aquatic environments. Some studies have tried to counter this by incorporating bio-adsorbents like coconut shell powder and bagasse or streamlining electrolyte concentration and flow to reduce nickel ion leaching. There is, however, a significant lack of closed-loop or recyclable electrolyte systems that are in accord with sustainable manufacturing practices. Future ECM developments must incorporate environmental protection mechanisms, like in situ filtration, electrolyte recovery units, and green electrolytes to fulfill the industry’s increasing demand for sustainable machining processes.
4.2.2 Electrochemical micro-machining: Tool design and overcut control
ECMM has shown promise in machining intricate and complex shapes on materials of any hardness with some electrical conductivity. It led researchers to explore the viability of this process for machining micro features in superalloys.
4.2.2.1 Studies on MRR and OC
Gokulanathan et al. drilled micro-holes in a 0.8 mm-thick plate of Monel-400 by utilizing a pulsed air supply and three different conditions regarding the use of three different electrolytes during machining: MGAE (Magnet Associated Electrolytes), MPME (Metal Particle Mixed Electrolytes), and CPME (Carbon Pellets Mixed Electrolytes). Conclusions pointed out that MPME corresponds to the highest MRR and OC value, while MGAE produces the least OC. Graphical analysis extends understanding of the effect of different electrolytes and process parameters on responses (Gokulanathan and Jegan, 2023). Furthermore, advances in micro–machining performance using aqueous NaNO3 as an electrolyte were studied with pulsed air supply through the tool holder. Three optimal techniques were applied: VIKOR, TOPSIS, and COPRAS, to grasp the best optimal combination for MRR and OC. They found that utilizing a pulsed air supply produced an increment of 42% in MRR compared to using only NaNO3 (Gokulanathan and Jegan, 2022). Additional exploration from research literature has pointed out that controlling OC in ECMM has been a challenging task and is essential for the growth of this process. S Ayyapan et al., employed ACT (Abrasive coated tool) and ECT (Epoxy coated tool) side insulation on copper tool electrode to check their usefulness in minimizing OC in ECMM of Monel-400. It was observed that ACT provided High MRR since it removed the passive metal oxide layer produced on the surface, while both ACT and ECT reduced OC because of the absence of electrochemical reaction from the tool side surface and workpiece (Ayyappan and Vengatajalapathi, 2020).
4.2.3 Travelling wire ECM (TWECM): Electrolyte enhancement and machinability
TWECM is a cutting-edge technology, similar to WEDM. Still, it has the edge over susceptibility to lower thermal damage to the workpiece and is an area worth delving into. Kalaimathi et al. have implemented an experimental investigation to assess the feasibility of ozonated aqueous NaCl solution on Monel-400 in TWECM. Results indicated a maximum increase of 90% in MRR and a 32% reduction in Ra of machined Monel-400. This was due to ozone decomposition into hydroxyl and peroxide radicals that undergo fast reactions with metal oxides and hydroxides, causing slug removal, thereby enhancing machining efficiency. SEM images of surface machined in ozonated electrolyte confirm better quality than with plain NaCl (Kalaimathi et al., 2017).
Table 8 summarizes important research initiatives that enhance the machining performance of Monel-400 through various ECM and Micro-ECM techniques. These studies examine several factors, including electrolyte selection, tool electrode types, pulse control strategies, and external enhancement techniques like pulsed air supply and electrolyte ozonation. The primary response parameters analyzed are MRR, Ra, Over-cut (OC), and Nickel Presence (NP) in sludge, aimed at achieving improved efficiency, superior surface quality, and environmental safety.
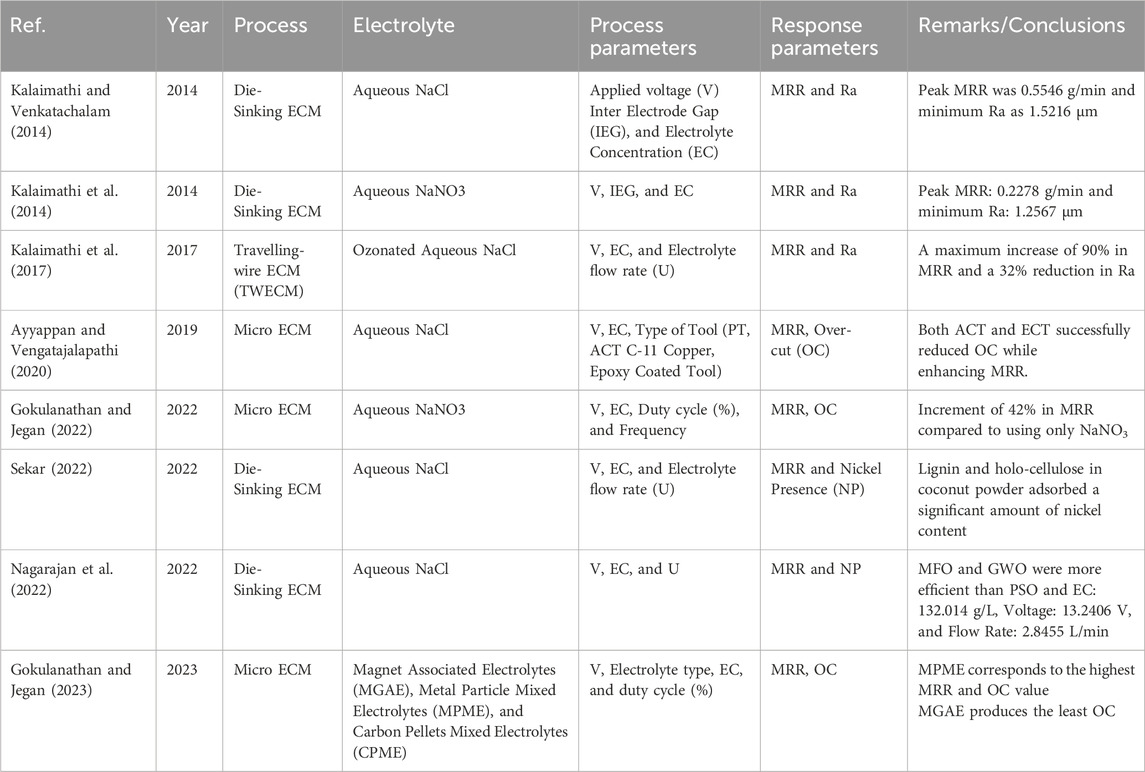
Table 8. Comparative analysis of process parameters and performance outcomes in ECM and Micro-ECM of Monel-400.
From the comparative evaluation, it is clear that electrolyte type significantly influences the machining characteristics. Studies (Kalaimathi and Venkatachalam, 2014; Kalaimathi et al., 2014) compared NaCl and NaNO3 electrolytes in die-sinking ECM, revealing that NaCl provides a higher MRR (0.5546 g/min) but at the expense of slightly rougher surfaces, whereas NaNO3, despite a lower MRR (0.2278 g/min), produced better surface finishes with Ra values as low as 1.2567 µm. This indicates that NaCl is preferable for bulk material removal applications, whereas NaNO3 is better suited for precision finishing operations.
Advanced techniques such as TWECM using ozonated NaCl electrolyte, explored in (Kalaimathi et al., 2017), demonstrated significant improvements in MRR (up to 90% increase) and Ra (32% reduction) compared to conventional NaCl solutions. The presence of ozone helped decompose metal oxides faster, thereby facilitating smoother machining and cleaner surfaces. Similarly, micro-ECM approaches with different electrolytic enhancements, such as magnet-associated, metal-particle mixed, and carbon-pellet mixed electrolytes (Gokulanathan and Jegan, 2023), highlighted that Metal Particle Mixed Electrolytes (MPME) yielded the highest MRR but at the cost of a larger OC. In contrast, Magnet Associated Electrolytes (MGAE) minimized OC, offering better dimensional control.
Electrode design modifications also played a key role. In the study (Ayyappan and Vengatajalapathi, 2020), abrasive-coated (ACT) and epoxy-coated (ECT) tools were used to reduce OC significantly while enhancing MRR in micro-ECM processes. This is attributed to suppressing stray currents and localized removal of oxide layers, thus improving machining precision. Furthermore, the application of pulsed air supply during micro-ECM with NaNO3 electrolyte, as studied in (Gokulanathan and Jegan, 2022), improved MRR by 42%, demonstrating that external interventions to promote electrolyte flow can dramatically influence process efficiency.
Another critical concern addressed was the environmental aspect, Nickel contamination in the electrolyte. Studies (Nagarajan et al., 2022; Sekar, 2022) applied optimization techniques (Metaheuristics like MFO and GWO) and bio-adsorbents like coconut shell powder to minimize nickel presence in sludge. These approaches not only maintained reasonable machining efficiency but also achieved significant reductions in heavy metal contamination, promoting eco-friendly machining practices.
A comparison of the studies shows that the efficiency of ECM for Monel-400 can be adjusted according to specific priorities. If achieving a high MRR is the primary aim, selecting NaCl and electrolyte modifications such as ozonation or MPME is the most effective approach. For critical needs of surface precision and minimal dimensional fluctuations, it is advisable to utilize NaNO3 electrolyte in conjunction with MGAE and coated tools. When prioritizing environmental sustainability, employing optimized electrolytes and bio-filtration methods proves to be an effective strategy for mitigation.
ECM and Micro-ECM processes for Monel-400 have become highly customizable and have been influenced by electrolyte selection, tool surface engineering, and additional techniques like ozonation and air pulsing, significantly affecting machining results. To further advance ECM technology for industrial applications of Monel-400, it is essential to integrate material removal efficiency with surface quality control and environmental considerations. Future research should emphasize hybrid electrolyte systems, enhancing eco-friendly dielectric alternatives, and the development of real-time control systems that balance productivity with sustainability.
4.3 Plasma Arc Cutting: High-temperature machining characteristics
4.3.1 Studies on optimization
PAC, an innovative thermal-based machining technology, was initially patented in 1955 and has come a long way since then (Nemchinsky and Severance, 2006). Although PAC has potential benefits like rapid cutting and processing a wide range of materials, diverse PAC process parameters make it hard to optimize quality control and process. Hence, various optimization techniques have been adopted by researchers over time, such as regression, TOPSIS, GA, Hybrid, MCDM, etc., to study the influence of predominant PAC process variables. D. Rajamani et al. adopted the ANOVA and RSM desirability approach to observe the impact of chief PAC parameters on optimizing Ra, Kerf-Width, and MH. They confided that stand-off distance and arc current greatly influence Ra, meanwhile, Kerf-Width and MH can be primarily controlled by cutting speed (Rajamani et al., 2018). Yet, another research was conducted for multi-response optimization of processed Monel-400 alloy by adopting a soft computing hybrid approach of ANFIS-ABC and GA-ANFIS with the same input and output variables as in the case of D. Rajamani et al. It can be pointed out that the values of optimal parameters in both cases were mostly alike. However, error prediction in Optimal values was a little higher in the latter (Kumar et al., 2021).
K. Ananthakumar led an investigation to enhance PAC performance characteristics: MRR, KT and HAZ, and their optimization via RSM methodology and TOPSIS technique. ANOVA analysis of this study revealed that stand-off distance and gas pressure were most influential for controlling MRR and improving HAZ, whereas KT was primarily affected by a change in cutting speed (K et al., 2019).
Another study examined the impact and optimization of PAC input parameters on machined Monel-400. However, a fuzzy logic expert system was employed this time, which is relatively superior and less time-consuming than most optimization techniques. The experimental results of this investigation revealed that the prediction error with this system was considerably lower than that found in the studies mentioned earlier. Moreover, results from the sensitivity analysis suggested the stand-off distance was the most sensitive parameter to MRR and HAZ, whereas both the stand-off distance and gas pressure were highly sensitive to KT (Rajamani et al., 2020).
The research presented in Table 9 collectively investigates different optimization methods used on the PAC of Monel-400 alloy. D. Rajamani et al. employed ANOVA and RSM desirability approaches to evaluate the influence of parameters like stand-off distance, arc current, and cutting speed on outputs such as Ra, KW, and microhardness (MH). Their results indicated that stand-off distance and arc current had the largest impact on Ra, whereas KW and MH were under the primary influence of cutting speed (Rajamani et al., 2018). Kumar et al. applied hybrid soft computing methods—ANFIS-ABC and GA-ANFIS—with identical parameters and results, and obtained mainly similar optimal values, albeit with slightly greater prediction error (Kumar et al., 2021).
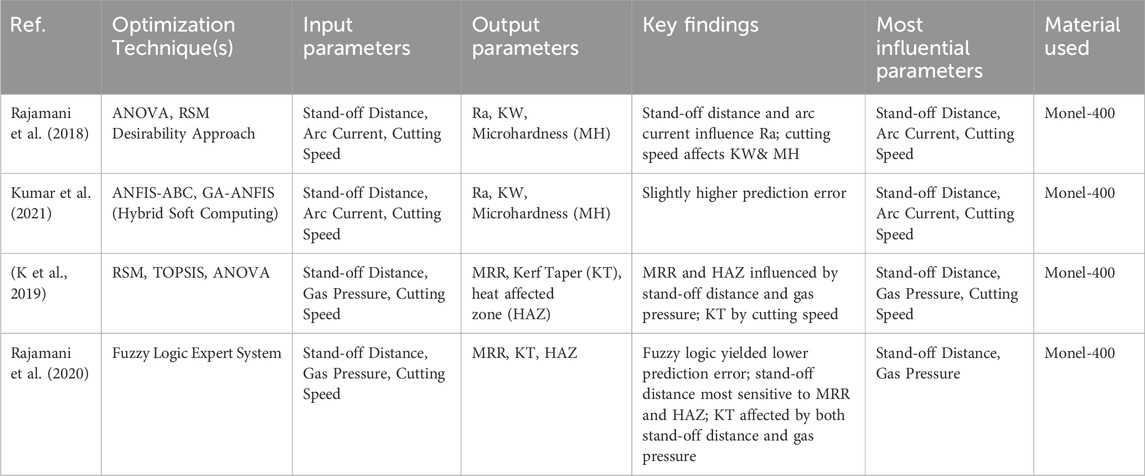
Table 9. Summary of optimization techniques and key findings for plasma arc cutting (PAC) of Monel-400 alloy.
K. Ananthakumar et al. maximized MRR, kerf taper (KT), and heat affected zone (HAZ) by applying RSM and TOPSIS. In their ANOVA test, stand-off distance and gas pressure were key parameters for maximizing MRR and HAZ, while KT was largely dependent on cutting speed (K et al., 2019). Another research work by Rajamani et al., using a fuzzy logic expert system, registered the least prediction error compared to all research works. This model classified stand-off distance as the most sensitive parameter to MRR and HAZ, and stand-off distance and gas pressure were highly sensitive regarding KT. Stand-off distance proved to be the most universally affecting parameter across optimization approaches and output responses (Rajamani et al.).
4.4 Abrasive Water Jet Machining of Monel-400: Process advantages and limitations
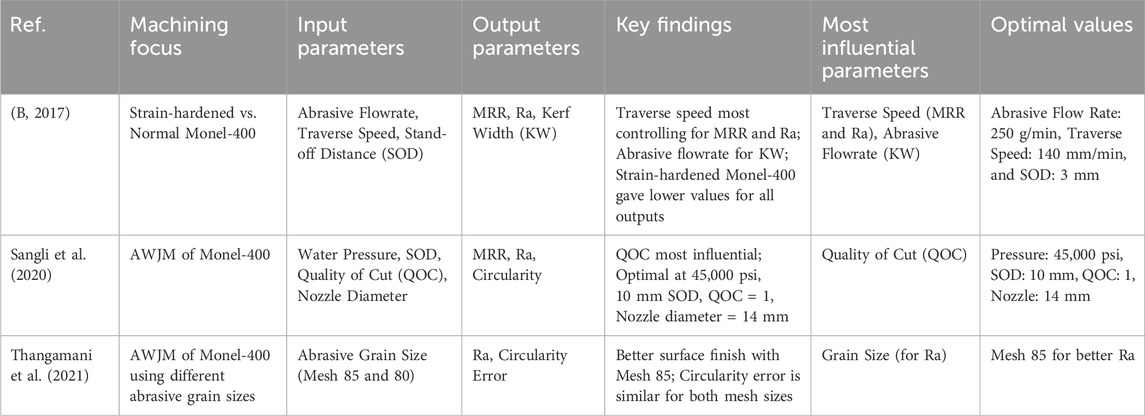
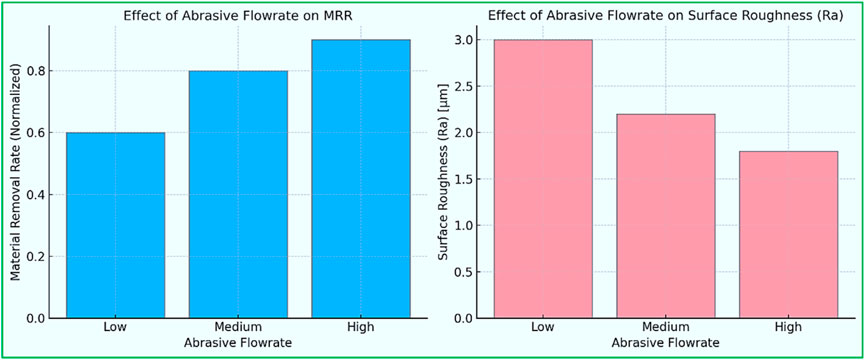
(Jonathan et al., 2017), instigated a comparative study for AWJM of strain hardened versus normal Monel-400. This study was conducted by varying the abrasive flow rate, Traverse speed, and SOD to enhance MRR, Ra, and KW. They observed that Traverse speed was the most controlling factor for MRR and Ra, while Abrasive flow rate was the most influential for KW. Secondly, results deduced that all three responses attained lower values in the case of strain-hardened Monel-400 compared to normal Monel-400.
(Sangli et al., 2020) analyzed the influence of AWJM parameters, namely, Water pressure, SOD, QOC (quality of cut), and Nozzle diameter, on MRR, Ra, and Circularity of machined Monel-400. The Grey analysis optimization technique was employed to find optimal input parameter values for the most efficient output. Peak performance was reached for pressure at 45,000 psi, standoff distance at 10 mm, quality of cut at 1, and nozzle diameter of 14 mm. Additionally, QOC was the most influential of all process parameters. A.C. Arun Raj et al. directed their study on minimizing Ra and circularity error for AWJM of Monel-400. For this purpose, they employed two different grain sizes (mesh 85 and mesh 80). They found that the surface finish of the workpiece was better when machined using 85 mesh grain, while the circularity value was almost similar in both cases (Thangamani et al., 2021).
Table 10 summarizes comparative studies on Abrasive Water Jet Machining (AWJM) of Monel-400. Arunkumar et al. made a comparative study of strain-hardened and regular Monel-400 by changing abrasive flow rate, traverse speed, and stand-off distance. They observed that traverse speed had a significant effect on MRR and Ra, whereas abrasive flow rate affected kerf width (KW). All values of output were lower for the strain-hardened type (B, 2017).
Grey analysis was used to optimize parameters like water pressure, stand-off distance, quality of cut (QOC), and nozzle diameter for outputs like MRR, Ra, and circularity. Their findings determined that QOC was the most significant parameter, and the best performance was at 45,000 psi pressure, 10 mm SOD, QOC level 1, and a 14 mm nozzle (Sangli et al., 2020). In another research, Arun Raj et al. examined the effect of abrasive grain size (mesh 85 vs. 80) on Ra and circularity error. Their results indicated that finer mesh (85) enhanced surface finish, whereas circularity was not significantly affected by grain size (Thangamani et al., 2021) The research highlights the central role of traverse speed, QOC, and abrasive characteristics in Monel-400’s AWJM performance.
4.5 Photochemical Machining: Precision etching for Monel-400
PCM is unmatched when fabricating highly intricate and complex cavities cost-effectively with low production rates. Mudigonda et al. (Mudigonda and Patil, 2015) explored the impact of Photolithography and parameters in creating micro-texture on Monel-400 sheets by PCM. This investigation concluded that spinning speed is most influential in deciding photoresist film thickness, while high exposure time results in more precise patterns. On top of that, Ra and depth of, etch of the machined workpiece were primarily dominated by etching temperature and etching time respectively.
(Patil and Mudigonda, 2016) accentuated the importance of rolling direction on the surface texture of machined microchannels. They focused on etching time, Temperature, and rolling direction effects on Undercut, Depth of, etch, Photoresist film thickness, and strength. Findings from this experiment indicated that the, etch depth along the rolling direction is greater than that across it, mainly due to residual stresses that cause a higher, etch rate along the rolling direction than across it. Also, an increase in the etching temperature increased the microchannel width. The same authors examined the effect of grain orientation on the Surface finish of Photochemically machined Monel-400. Results of this study corroborate prior research, showcasing that surface finish is higher when machined along the rolling direction. Subsequently, higher etching depth was observed along the rolling direction than across it (Patil and Mudigonda, 2017). PCM of Monel-400 was explored, employing the use of two contrasting etching agents: ferric chloride (FeCl3) and cupric chloride (CuCl2) at different temperatures and concentrations to obtain the best possible etching rate, etching depth, and undercut values. It was revealed that FeCl3 exhibits the best overall performance in all aspects as compared to CuCl2. Also, the effect of various geometric shapes was observed in terms of depth of, etch and weight loss. Triangular Geometry showed the highest depth of, etch and loss of weight, while the circle was the lowest (Patil et al., 2018; Patil et al., 2024).
Table 11 consolidates major studies on Photochemical Machining (PCM) of Monel 400. It emphasizes the impact of process parameters like spinning speed, etching time, temperature, and rolling direction on results such as photoresist film thickness, etch depth, and surface finish. Results always indicate that etching behavior is sensitive to material properties as well as processing conditions. Ferric chloride (FeCl3) is the most effective etchant, and triangular geometries lead to more aggressive etching compared to circular geometries.
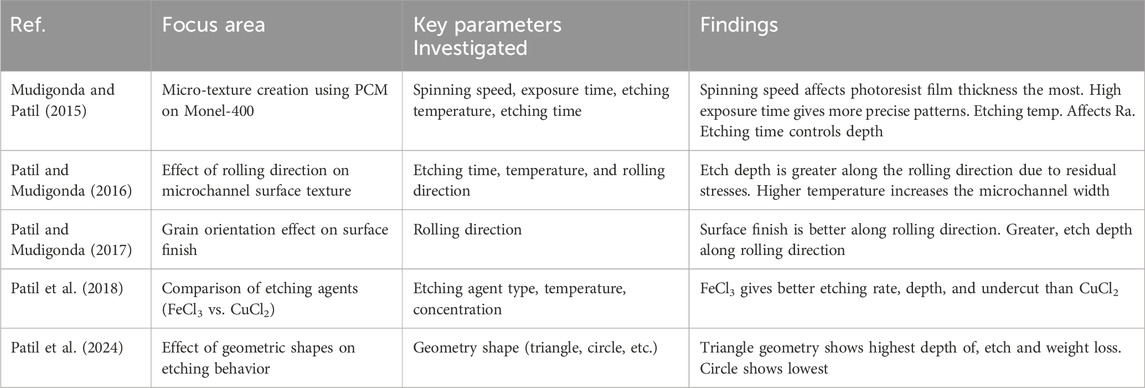
Table 11. Summary of key findings in photochemical machining (PCM) of monel 400 based on various studies.
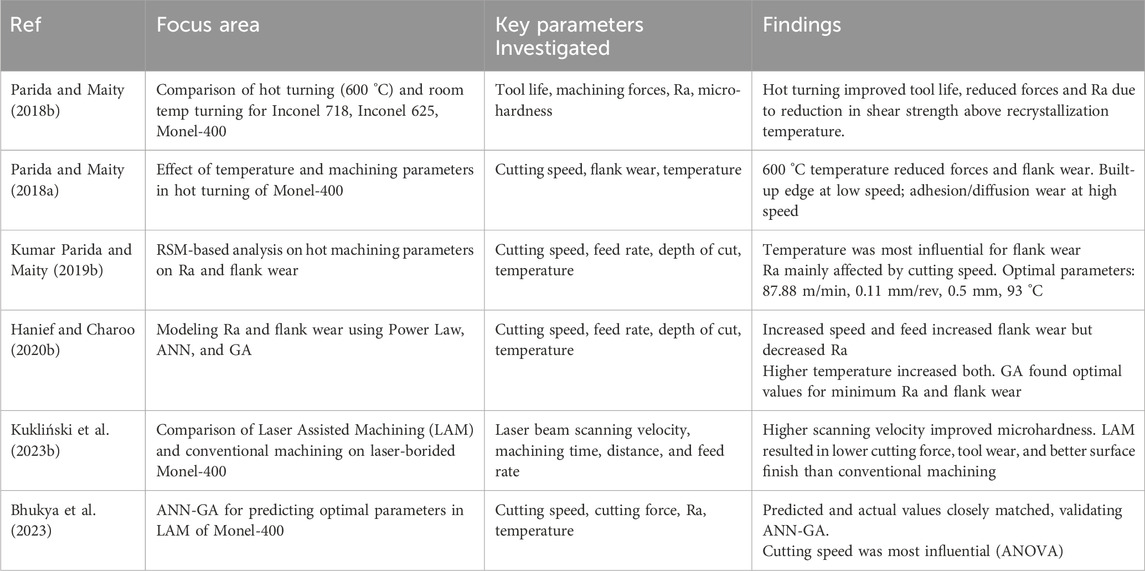
4.6 Hot machining: Preheating effects and tool life enhancement
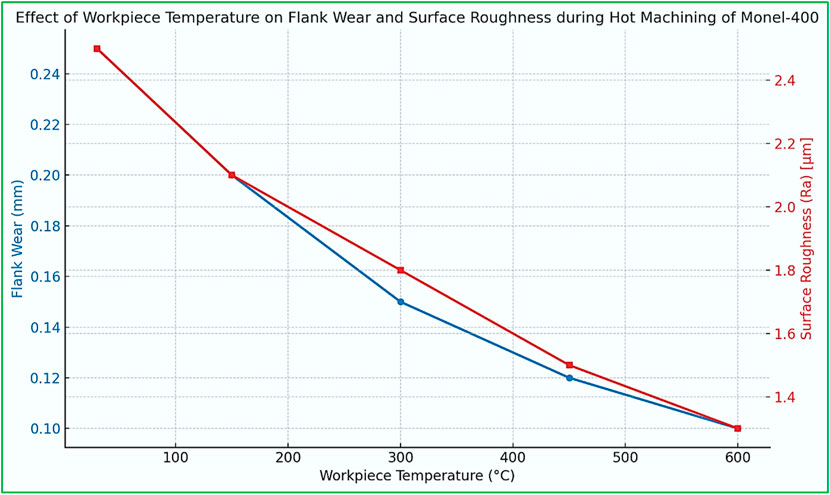
(Parida and Maity, 2018b) conducted a comparative study of hot turning (via flame heating) and turning at room temperature on Tool life, machining forces, Ra, and Microhardness of three Nickel-based alloys: Inconel 718, Inconel 625, and Monel-400. It was observed that hot turning (600 °C) improves tool life, machining forces, and Ra for all alloys compared to machining at ambient temperature (30 °C). This study entailed the importance of hot turning in significantly reducing machining forces (cutting, feed, and radial), all the while improving tool life, chiefly due to the reduction in shear strength of material when heated above recrystallisation temperature. The same authors studied the influence of machining parameters and heating temperatures in the hot turning operation of Monel-400. They found that as the temperature hit 600 °C, forces and flank wear reduced drastically. In addition, built-up-edge formation was primarily observed at low cutting speeds, whereas adhesion and diffusion wear were predominant under high-speed conditions (Parida A. and Maity K., 2018).
Another experimental study conducted an RSM-based analysis on the influence of hot machining (via flame heating) parameters on Ra and flank wear for Monel-400. They found out that temperature was the most influential factor affecting flank wear, whereas Ra was mainly affected by cutting speed, as evident from the plots below. Additionally, cutting speed of 87.88 m/min, feed rate 0.11 mm/rev, depth of cut 0.5 mm, and workpiece temperature of 93 °C were found to achieve minimum Ra and flank wear and were hence designated as optimal parametric combination (Kumar Parida and Maity, 2019b). Power law and ANN models were deployed to depict the influence of hot machining process parameters on Ra and Flank wear. They found that an increase in cutting speed and feed rate increased flank wear but decreased Ra. Secondly, a rise in temperature leads to an increase in both flank wear and Ra. What’s more, employed GA (Genetic Algorithm) found cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut, and temperature at 99.2758 mm/min, 0.1014 mm/rev, 0.5003 mm, and 92.9177 °C respectively as optimal parametric combination corresponding to minimum Ra and Flank wear (Hanief and Charoo, 2020b).
A comparative study was carried out by Damian et al., on Laser Assisted Machining (LAM) and Conventional machining of laser-borided Monel-400. Laser Beam Scanning Velocity, Distance from surface, Time of machining, and feed rate were varied, and their influence on Microhardness, Cutting Force, Ra, and tool wear was studied. Results of this experiment surmised that high values of laser beam scanning velocities resulted in high microhardness. More importantly, the values of cutting force and Tool Wear were relatively lower in the case of LAM than conventional machining. Also, the surface topography of LAM was better than conventional (Kukliński et al., 2023b; Bhukya et al., 2023) employed the ANN-GA hybrid technique to predict/forecast optimal process parameter values in Laser Assisted Machining of Monel-400. Experimentally found optimal values from this experiment were closely related to expected values of Ra, cutting force, and cutting temperature, reflecting the efficiency of the ANN-GA technique. Furthermore, cutting speed was found to be the most influential factor as indicated by ANOVA methodology.
Table 12 consolidates studies on hot machining of Monel 400, considering hot machining effects at high temperatures and aided machining techniques such as Laser Assisted Machining (LAM). Research indicates that hot machining enhances tool life, lowers machining forces and Ra, particularly at 600 °C. The best parameters for minimum Ra and flank wear were determined using RSM, ANN, and GA methods. LAM was superior to traditional machining in having a better surface finish and less wear of tools, and ANN-GA methods accurately predicted optimal machining conditions.
5 Integrated outcomes and comparative discussion
While extensive research exists on various non-conventional machining techniques for Monel-400, a comprehensive comparison of these processes is essential for informing industrial decision-making. The following synthesis is derived from the analyzed studies.
• EDM provides accurate machining of intricate shapes while maintaining a reasonable MRR. Nevertheless, challenges like recast layers, tool wear, and environmental issues from hydrocarbon-based dielectrics hinder its wider use unless optimization strategies like hybrid dielectrics and cryogenic treatments are implemented.
• WEDM offers superior surface integrity and dimensional accuracy, especially when utilizing powder-mixed dielectrics and trim cuts. Wire lag and white layer formation continue, requiring modifications in path/pulse strategies and near-dry methods to lessen environmental impacts.
• ECM and ECMM provide high MRR, minimal tool wear, and absent thermal damage. However, challenges such as sludge management (formation of nickel hydroxide) and environmental hazards linked to electrolyte disposal can be managed through eco-friendly filtration and improved flow dynamics.
• PAC achieves exceptionally high MRR, making it ideal for quick, large-scale operations. However, Ra and heat affected zone (HAZ) necessitate precise control of factors like stand-off distance and gas pressure, with hybrid soft-computing optimizations showing potential benefits.
• AWJM delivers good surface quality and slight thermal damage, offering a more environmentally safe alternative to EDM/PAC, yet attention to abrasive consumption costs and kerf control is critical.
• PCM and Hot Machining specialize in microfabrication and strength reduction before cutting. PCM is excellent for creating thin, intricate components with high precision, while hot machining improves tool lifespan and significantly lowers cutting forces in heavy-duty tasks.
Table 13 offers a comparative analysis of key non-conventional machining methods investigated for Monel-400, highlighting their main benefits, intrinsic challenges, and optimization techniques to enhance machining efficiency and surface quality. It is synthesized from various sources analyzing EDM (Ekmekci, 2007; Anandakumar and Shanthi, 2013; Jothimurugan and K S, 2014; Jadhav et al., 2015; Padmini et al., 2015a; Gupta and Gupta, 2018; Kumar and Jayakumar, 2018; Grewal and Dhiman, 2019; Jothimurugan et al., 2019; Mahalingam and Varahamoorthi, 2020; Biswas and Rahul, 2021; Hadi and Ibrahim, 2022), WEDM (Haron et al., 2001; Puri and Bhattacharyya, 2003; Schumacher, 2004; Sarkar et al., 2011; Gurusamy et al., 2012a; b; Ji et al., 2012; Bergaley and Sharma, 2013; Valaki et al., 2014; Kumar et al., 2015; Selvakumar et al., 2016; Kumar et al., 2020; Arun Kumar et al., 2021; Rohilla et al., 2021b; Kumar N. E. A. et al., 2023), ECM (Kalaimathi and Venkatachalam, 2014; Kalaimathi et al., 2014; Kalaimathi et al., 2017; Ayyappan and Vengatajalapathi, 2020; Gokulanathan and Jegan, 2022; Nagarajan et al., 2022; Gokulanathan and Jegan, 2023), PAC (Rajamani et al., 2018; K et al., 2019; Rajamani et al., 2020; Kumar et al., 2021), AWJM (B, 2017; Sangli et al., 2020; Thangamani et al., 2021), PCM (Mudigonda and Patil, 2015; Patil and Mudigonda, 2016; Patil and Mudigonda, 2017; Patil et al., 2018; Patil et al.), and Hot Machining (Parida A. and Maity K., 2018; Parida A. K. and Maity K., 2018; Kumar Parida and Maity, 2019b; Hanief and Charoo, 2020b; Bhukya et al., 2023; Kukliński et al., 2023b). Choosing the right machining approach depends on application specifics, including requirements for high MRR, excellent surface finish, precision, or eco-friendliness.
Thus, the hybridization of techniques and environmentally friendly adaptations is increasingly crucial for the efficient and sustainable machining of Monel-400.
Figure 5 illustrates the reduction in cutting temperature achieved under various cooling strategies implemented during the conventional machining of Monel-400. It is observed that dry machining results in minimal temperature reduction (∼5%), followed by a moderate improvement with Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) (∼10%). Cryogenic cooling with CO2 further enhances cooling performance (∼20% reduction), while the Hybrid strategy (CO2 + MQL) shows the highest temperature reduction (∼35%). These trends emphasize that Hybrid cooling strategies significantly outperform dry or single-cooling methods by improving heat dissipation at the tool–workpiece interface, thus enhancing machining performance and surface quality (Ross et al., 2022b; Ross et al., 2023c). This finding is consistent with experimental investigations conducted by Ross et al. (Ross et al., 2023c; Ross et al., 2022b), which demonstrated the superiority of hybrid cooling in lowering cutting temperatures, reducing tool wear, and minimizing Ra during Monel-400 machining.
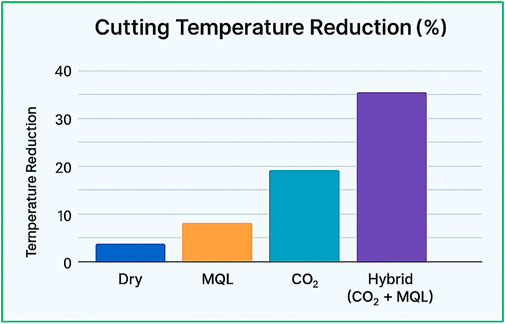
Figure 5. Cutting temperature reduction (%) under different cooling strategies during conventional machining of Monel-400.
Figure 6 presents a comparative evaluation of TWR and Ra for different types of cutting inserts used in the conventional machining of Monel-400. The inserts considered include Uncoated Carbide, PVD-TiAlN, Cryo-Treated Carbide, and Cryo-Treated PVD-TiAlN. It is observed that both TWR and Ra progressively decrease from the Uncoated Carbide to Cryo-Treated TiAlN inserts. The Uncoated Carbide insert exhibits the highest tool wear (16.5 mm3/min) and Ra (11.2 µm), while the Cryo-Treated TiAlN insert demonstrates the lowest values, with a TWR of 7.0 mm3/min and an Ra of 3.5 µm. This trend highlights the significant benefits of cryogenic treatment and advanced coatings in enhancing tool performance and achieving superior surface finishes during machining operations.
Figure 6. Comparison of tool wear rate (mm3/min) and surface roughness (Ra) (µm) for different cutting inserts during conventional machining of Monel-400.
The results shown in Figure 6 validate findings from (Mani, 2024), who reported that cryogenically treated and coated inserts exhibit markedly better performance when machining nickel-based alloys like Monel-400. The improvement can be attributed to enhanced microstructural stability and reduced thermal degradation of the cutting edge due to cryogenic processing. Furthermore, the TiAlN coatings provide superior oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, minimizing wear mechanisms such as flaking and diffusion wear. These enhancements improve machining efficiency, extend tool life, and improve surface quality, making them particularly advantageous for industrial applications involving difficult-to-machine materials like Monel-400.
Figure 7 presents a heatmap illustrating the influence of key input parameters, Pulse On-Time (Ton), Pulse Off-Time (Toff), Voltage, and Discharge Current, on the primary output responses during EDM of Monel-400. The output responses considered include MRR, TWR, and Ra. The darker shades in the heatmap indicate a more substantial influence. Discharge Current shows the highest influence on MRR and TWR, emphasizing its critical role in controlling productivity and tool wear. Voltage significantly impacts Ra, while Ton primarily influences MRR and Ra moderately. Meanwhile, Toff exhibits a moderate but relatively lesser influence across all outputs.
These observations align well with previous experimental studies by (Mahalingam and Varahamoorthi, 2020; Anandakumar and Shanthi, 2013), where discharge current and voltage were reported as the most sensitive parameters affecting machining efficiency and surface quality in EDM operations on Monel-400.
Figure 8 shows how Ra varies with different types of dielectrics used in the WEDM of Monel-400. Dry dielectric conditions lead to the greatest Ra (∼3.2 µm), suggesting a poorer surface finish due to unstable spark generation and insufficient debris removal. Switching to a wet dielectric (deionized water) slightly improves surface quality to ∼2.7 µm, while adding a powder-mixed dielectric greatly enhances the finish to ∼1.9 µm by facilitating uniform spark discharges and minimizing arcing. Near-dry dielectric conditions yield the best results, achieving the lowest Ra at ∼1.6 µm. This enhancement is due to better flushing characteristics and more stable plasma channel formation in near-dry conditions. These observations underscore the importance of optimizing dielectric conditions to improve surface integrity in WEDM processes for challenging materials like Monel-400 (Gurusamy et al., 2012a).
Figure 9 depicts the comparative analysis of corner error percentages observed during WEDM of Monel-400 under two conditions: without path modification and with path modification strategies. Without any path correction, the corner error is 100%, reflecting significant dimensional inaccuracies, especially at sharp corner transitions. However, implementing optimized path modification strategies reduces the corner error substantially to approximately 65%, marking an improvement of nearly 35%. The reduction is attributed to pre-compensated toolpath programming, which accounts for wire lag, spark expansion, and discharge delays at geometrical transitions (Selvakumar et al., 2016). This practice ensures enhanced precision and dimensional integrity in machining intricate profiles using Monel-400.
Figure 10 presents a comparative analysis of MRR and OC values for different electrolytes NaCl, NaNO3, Ozonated NaCl, and MPME employed in ECM and micro-ECM of Monel-400. Among these electrolytes, Ozonated NaCl exhibited the highest MRR (∼0.90 g/min) coupled with the lowest OC (∼0.08 mm), indicating excellent machining efficiency and dimensional accuracy. Traditional NaCl also showed a high MRR (∼0.55 g/min) but had a larger OC (∼0.15 mm), reducing dimensional control. Sodium Nitrate presented a moderate MRR (∼0.23 g/min) while maintaining a smaller OC (∼0.10 mm), reflecting a balanced performance. On the other hand, MPME offered a relatively high MRR (∼0.80 g/min) but featured a larger OC (∼0.18 mm), demonstrating a trade-off between speed and precision (Kalaimathi and Venkatachalam, 2014; Kalaimathi et al., 2014; Kalaimathi et al., 2017; Gokulanathan and Jegan, 2023). These results emphasize the significance of choosing the right electrolyte to achieve an optimal balance between MRR and machining accuracy when working with Monel-400.
Figure 10. Comparison of MRR and overcut for different electrolytes in ECM and Micro-ECM of Monel-400.
Figure 11 displays a grouped bar chart illustrating the optimization results from multiple responses for various parameter settings in the PAC of Monel-400. The evaluated responses are MRR, KW (inversely normalized to indicate better performance when lower), and HAZ (also inversely normalized). It is evident that optimal performance is achieved with high cutting speed and low stand-off distance settings, leading to higher MRR values while minimizing KW and HAZ (K et al., 2019; Rajamani et al., 2020). Additionally, high gas pressure settings further enhance MRR and thermal management. In contrast, low speeds and high stand-off distances result in suboptimal performance, marked by decreased cutting efficiency and increased thermal damage. These findings highlight the necessity of balancing stand-off distance, cutting speed, and gas pressure to optimize PAC results. This will enhance productivity and maintain dimensional accuracy and metallurgical integrity when machining Monel-400.
Figure 11. Multi-response optimization of plasma arc cutting (PAC) parameters for machining Monel-400.
Figure 12 illustrates how abrasive flow rate affects two key performance indicators: MRR and Ra in AWJM of Monel-400. The first subplot shows that MRR steadily increases with higher abrasive flow rates, signifying enhanced cutting efficiency attributed to improved energy transfer to the workpiece. Normalized MRR rises from about 0.6 at lower flow rates to 0.9 at higher flow rates. In contrast, the second subplot reveals a decrease in Ra as abrasive flow rate increases, indicating a better surface finish. Ra values decline from approximately 3.0 μm at low flow rates to 1.8 μm at high flow rates, demonstrating the dual advantage of increased material removal and improved surface quality at elevated abrasive concentrations (Sangli et al., 2020). These results underscore the importance of optimizing abrasive flow rate to maximize machining efficiency and enhance surface integrity during AWJM of challenging materials like Monel-400.
Figure 13 showcases how workpiece temperature affects two key machining results, flank wear and Ra, during the hot machining of Monel-400. As the temperature rises from 30 °C (room temperature) to 600 °C, flank wear and Ra steadily decline. Flank wear drops from about 0.25 mm at 30 °C to roughly 0.10 mm at 600 °C, indicating a notable enhancement in tool life due to the softening of the workpiece material at higher temperatures. In parallel, Ra also improves, decreasing from 2.5 µm to 1.3 µm in the same temperature span, which implies a smoother surface finish achieved through diminished cutting forces and improved plastic deformation (Kumar Parida and Maity, 2019b). These findings highlight that implementing controlled preheating or hot machining techniques can significantly boost machinability, extend tool lifespan, and yield high-quality surface finishes when working with challenging alloys like Monel-400.
To present a comprehensive picture of the strengths and weaknesses of each unconventional machining method, Table 14 presents a comparative overview in terms of critical performance parameters, economic considerations, and sustainability criteria. EDM has the highest MRR and flexibility for intricate geometry, but is characterized by high TWR and relatively lower sustainability. WEDM, although less productive in MRR terms, is excellent at accuracy and geometric flexibility and hence ideal for detailed die and mold work. ECM is the most environmentally friendly method because of the lack of tool wear and the presence of green electrolyte possibilities. However, it is challenging to machine parts that are geometrically involved. PAC provides high MRR and low tool costs but is restricted due to poor surface finish and thermal damage. AWJM gives moderate MRR and lower TWR but at increased abrasive cost. Although less studied, hot machining provides medium sustainability and less cutting resistance due to preheating, but with limited applicability. The table also identifies the increasing availability of green alternatives, particularly in WEDM and ECM. These findings assist strategic decision-making in choosing and optimizing machining techniques following precision, cost, and environmental considerations.
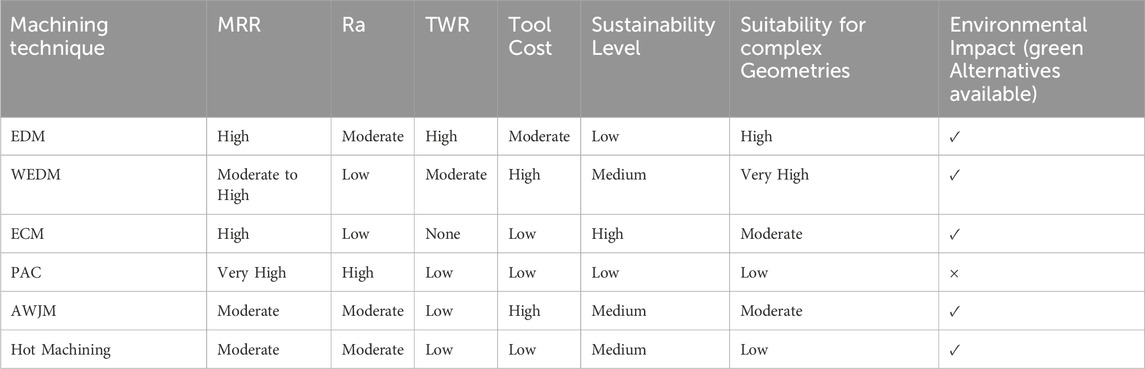
Table 14. Comparative summary of non-conventional machining techniques for Monel-400 alloy based on process performance, cost, sustainability, and environmental aspects.
Figure 14 is a radar chart comparing the performance of different non-traditional machining processes of Monel-400 along six key parameters: Ra, MRR, energy used, tool life, environmental sustainability, and scalability. ECM stands above others in resisting tool wear, environmental sustainability, and surface finish because of its contactless, electrochemical nature. EDM and WEDM are superior in high MRR and intricate geometries but are inferior in sustainability and energy efficiency. AWJM and Hot Machining have balanced performance with moderate MRR, tool wear, and environmental compatibility, whereas PAC provides the highest MRR and has poor surface quality and sustainability. Figure 14 facilitates visualization of productivity versus ecological responsibility trade-offs, aiding in choosing appropriate machining processes according to application priorities. This comparative platform supports the requirement for optimized or hybrid process integrations that deliver improved technical performance and environmental results.
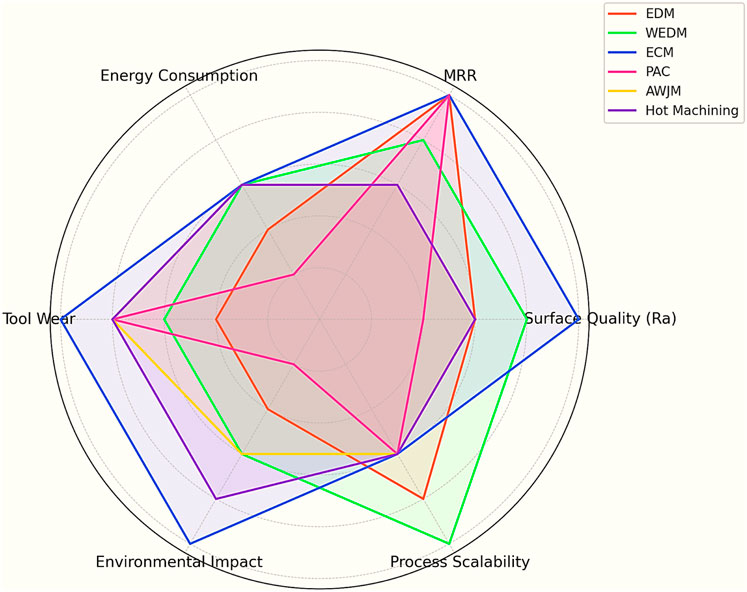
Figure 14. Comparative radar chart of non-conventional machining techniques for Monel-400 based on key performance and sustainability metrics.
Figure 15 juxtaposes MRR against Ra for representative data sets drawn from the literature: conventional dry turning, drilling with and without pre-annealing (Abdo et al., 2023), wire-EDM micro-channel cutting (Saleh et al., 2020), travelling-wire ECM with ozonated electrolyte (Kalaimathi et al., 2017), abrasive-water-jet trials reported by (Kukliński et al., 2023b), and electrical-discharge diamond-face grinding (EDDFG) (Kulshrestha et al., 2023b). Data points lying closest to the plotted Pareto frontier (lower Ra/higher MRR region) correspond to the non-conventional processes, particularly TW-ECM and EDDFG. At the same time, the conventional turning and drilling results fall well inside the dominated zone, confirming the marked trade-off advantage that non-conventional routes offer for Monel-400 machining.
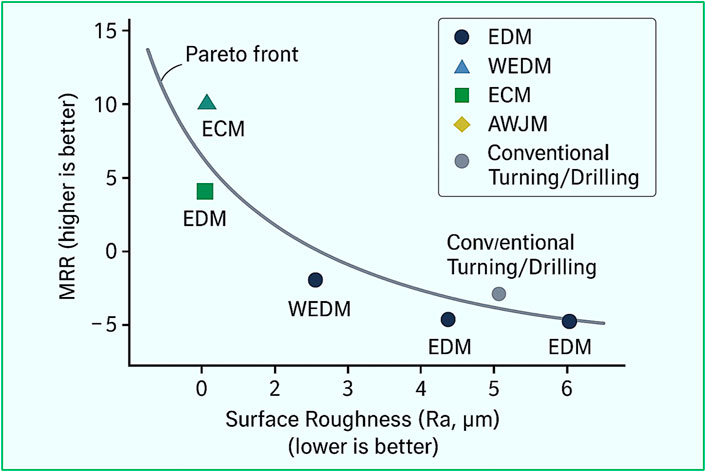
Figure 15. Pareto plot of surface roughness (Ra) versus MRR for conventional and non-conventional machining of Monel-400.
5.1 Identified best practices for Machining Monel-400
• Using hybrid or modified fluids (paraffin-servotherm mixtures, powder-mixed dielectrics) significantly enhances machining efficiency in EDM/WEDM.
• Cryogenic treatment of tools and electrodes improves wear resistance and surface quality.
• Near-dry machining or eco-friendly electrolyte strategies are essential for environmental sustainability in WEDM/ECM.
• Multi-response optimization methods (TOPSIS, RSM, ANN-GA) enable the fine-tuning of parameters for better trade-offs between MRR, Ra, and tool wear.
• Hot Machining and Laser Assisted Machining (LAM) effectively address the toughness-induced challenges of Monel-400 during cutting operations.
Future research should concentrate on hybrid process integrations, the environmental remediation of sludge and fumes, and techno-economic assessments for the industrial upscaling of these non-conventional techniques.
5.2 Environmental aspects and sustainability
As industries increasingly focus on sustainable practices, the environmental effects of nontraditional machining methods deserve significant scrutiny. Recent analyses of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) indicate that, while machine-learning–driven automation boosts process efficiency, it can also raise net energy demand and e-waste, underscoring the need to embed sustainability metrics into any new machining-data platform (Bhattacharjee and Kumar, 2023; Kumar and Jindal, 2023). While these advanced techniques offer enhanced productivity and precision, they also present ecological challenges that need resolution to meet green manufacturing objectives.
In EDM and WEDM, conventional hydrocarbon-based dielectrics like kerosene release harmful by-products, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and fine particulates, impacting environmental and occupational health. Future initiatives should concentrate on creating and implementing biodegradable, vegetable oil-based dielectrics and dry or near-dry EDM methods to cut emissions and foster safer work conditions.
ECM and micro-ECM, although free from thermal distortion, produce toxic sludge primarily consisting of nickel hydroxide. Eco-friendly machining of Monel-400 via ECM requires approaches such as green electrolyte formulations, optimized flow systems, efficient sludge management, and bio-adsorbents sourced from natural waste materials to reduce heavy metal contamination.
A PAC capable of high MRR is linked to fume generation and surface thermal degradation. Optimized gas pressures, advanced extraction systems, and stable arcs can lessen emissions and enhance environmental performance.
AWJM is somewhat more eco-friendly due to the lack of thermal damage; however, using abrasives still presents issues. Future research should investigate abrasive recycling, sustainable abrasive materials, and closed-loop water systems to diminish operational waste and resource consumption.
PCM utilizes chemical etching agents like ferric chloride and cupric chloride, which can result in soil and water pollution if improperly disposed of. Sustainable advancements involve greener etchants, chemical recovery methods, and controlled etching parameters to lessen environmental impacts.
Hot machining, such as flame and laser-assisted methods, promotes reduced tool wear and machining forces, indirectly saving energy. Nonetheless, flame heating can result in increased CO2 emissions. Adopting renewable energy sources for heating and refining hybrid heating strategies can enhance sustainability.
Integrating real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and life cycle assessment techniques across all nontraditional machining methods is crucial for promoting resource efficiency. Future directions will likely focus on smart manufacturing, AI-driven optimization, and Industry 4 4.0 technologies to ensure that machining Monel—400 remains efficient and environmentally responsible.
6 Challenges, research gaps, and future directions
6.1 Challenges and research gaps
Despite significant advancements in the non-conventional machining of Monel-400, various critical challenges and research gaps persist, restricting the comprehensive industrial adoption of these methods. The literature review highlights the following key issues.
• Surface Integrity Degradation: Despite advancements, non-conventional machining methods like EDM and WEDM frequently result in unwanted surface defects such as recast layers, microcracks, tensile residual stresses, and heat affected zone. The exploration of advanced techniques to eliminate or reduce these defects remains lacking.
• Environmental and Health Hazards: Employing hydrocarbon-based dielectrics in EDM/WEDM and chemical electrolytes in ECM poses significant environmental and health risks due to toxic fumes, sludge production, and challenges in waste disposal. There is a pressing need for further investigation into sustainable alternatives such as biodegradable dielectrics and eco-friendly electrolytes.
• Tool Wear and Electrode Degradation: In EDM and WEDM processes, tool and electrode wear hinder productivity and dimensional accuracy. Although cryogenic treatments and composite electrodes show potential, consistent solutions to reduce tool degradation under high energy densities are still required.
• Parametric Sensitivity and Process Stability: Non-conventional processes are highly sensitive to input parameters (like pulse timing, flushing rates, electrolyte flow, and gas pressure), often leading to unstable machining outcomes if these are not precisely controlled. Research remains limited on real-time adaptive control and intelligent monitoring systems for these processes.
• Limited Studies on Hybrid or Assisted Machining Techniques: While individual processes (such as EDM, ECM, AWJM) have been thoroughly studied, hybrid methods (like EDM-ECM or Laser-Assisted WEDM) are relatively unexamined for Monel-400. Synergistic combinations of processes could tackle existing limitations of single-process techniques, but comprehensive experimental validation is necessary.
• Scalability and Industrial Readiness: Most research has concentrated on small-scale laboratory experiments involving constant workpiece thickness, minimal part complexity, and controlled environments. There is a significant gap in research addressing the scaling of non-conventional machining for industrial components with large dimensions, intricate geometries, and varying operating conditions.
• Techno-Economic Analysis and Cost Optimization: Few studies have assessed the economic viability, energy consumption, and maintenance costs tied to the non-conventional machining of Monel-400. In-depth techno-economic evaluations are necessary to substantiate industrial implementation and optimize the cost-performance trade-offs.
• Data-Driven Modeling and Predictive Optimization: Although machine learning, ANN, and genetic algorithms have been applied in limited contexts for optimization, more robust data-driven models that incorporate process physics and experimental datasets are needed to predict optimal machining conditions reliably.
Table 15 highlights essential research gaps in existing literature on non-conventional machining of Monel-400 and suggests practical future directions. Despite the proven potential of EDM to attain high MRR and TWR, poor Ra persists due to extreme thermal stresses. The use of composite electrodes and AI-based control systems might alleviate these problems. Likewise, though ECM and TWECM are known to be sustainable, the ecological footprint of traditional electrolytes necessitates closed-loop fluid recuperation systems and bio-compatible substitutes. In WEDM, most studies are on fixed-thickness specimens with limited industrial applications; adaptive control models for changing workpiece sizes are suggested. PAC’s low surface finish and thermal effect necessitate fuzzy logic or MCDM-based optimization models. In addition, hybrid cooling technologies like CMQL and LN2-MQL are drastically under-explored in the context of non-conventional processes. Lastly, lifecycle assessment and circular economy design are not applied within process planning and material consumption. Closing these deficiencies will enhance machining performance and future developments towards sustainability and Industry 4.0 paradigms.
6.2 Future research directions
Monel-400 has been extensively investigated over the years; however, several technically significant and environmentally relevant challenges remain insufficiently explored. These represent specific, emergent research gaps that could meaningfully inform the next phase of scientific inquiry.
6.2.1 Ultrafast-pulse energy delivery
Gap: Recast layers and micro-cracks continue to persist even when utilizing EDM/WEDM at their most advanced operational levels.
Research Direction: Investigate the feasibility of sub-microsecond and femtosecond pulse generators, with and without laser assistance, to determine whether ultra-short thermal cycles can enable the machining of Monel-400 with near-zero resolidified layer thickness and minimal residual stress.
6.2.2 Bio-derived, recyclable media
Gap: The majority of proposed “green” dielectrics and electrolytes remain largely confined to laboratory settings, with limited evidence of practical recyclability.
Research Direction: Develop and validate the performance of fully bio-sourced ionic liquids and deep-eutectic solvents capable of supporting closed-loop metal-ion recovery systems—such as those based on electrodialysis or membrane-assisted solvent extraction—and quantify their lifecycle benefits relative to conventional hydrocarbon-based oils.
6.2.3 Additive-subtractive convergence
Gap: Large Monel-400 components are still predominantly manufactured through subtractive processes involving extensive removal of material from wrought stock.
Research Task: Integrate Directed Energy Deposition (DED) or wire-arc additive manufacturing with in situ electrochemical finishing (ECF) or low-power EDM trimming to enable single-cell workflows. This approach aims to achieve near-net-shape production with acceptable surface finishes on critical surfaces, without the need for re-clamping.
6.2.4 High-entropy or functionally-graded electrodes/tools
Gap: Process stability during extended production runs is frequently undermined by electrode or tool degradation.
Research Task: Develop nanocomposite or high-entropy alloy electrodes with graded electrical and thermal properties using advanced fabrication techniques such as laser powder bed fusion or cold-spray. Establish correlations between gradient compositions and wear behavior through detailed wear mapping, particularly in EDM, WEDM, and AWJM nozzles.
6.2.5 Cavitation-enhanced flushing
Gap: Material evacuation and wire deflection remain key challenges in deep-slot WEDM operations.
Research Orientation: Optimize cavitation control within the spark gap through the combination of high-frequency ultrasonic transducers and pressurized micro-bubble streams. Characterize the effects on wire stability, kerf width, and achievable aspect ratios when cutting thick Monel-400 plates.
6.2.6 Digital-twin and reinforcement-learning control
Gap: Existing adaptive control systems are limited primarily to basic lookup tables or PID controllers.
Research Direction: Develop real-time digital twins of EDM/ECM processes using physics-informed neural networks interfaced with reinforcement-learning agents. Demonstrate adaptive optimization of parameters such as discharge energy or electrolyte flow rates to maintain surface roughness targets despite variations in workpiece geometry or hardness.
6.2.7 Micro-scale residual-stress mapping
Gap: Surface integrity data for non-conventional machining is typically limited to surface roughness and microhardness measurements.
Research Guidance: Employ advanced characterization techniques—such as synchrotron X-ray diffraction or high-resolution electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD)—to investigate subsurface residual stress fields and grain substructure evolution following hybrid EDM-ECM processes, with subsequent evaluation of corrosion-fatigue performance under marine conditions.
6.2.8 Open data and FAIR workflows
Gap: Parameter–response datasets in Monel-400 machining are fragmented and rarely machine-readable.
Research Guideline: Establish a community-curated repository for Monel-400 machining data adhering to FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable). Include raw sensor data, annotated microstructural images, and executable computational notebooks to support surrogate modeling and broader reproducibility.
6.2.9 Techno-economic and carbon-handprint benchmarking
Gap: Existing life-cycle assessments seldom provide comparative analyses of competing non-conventional machining approaches on standardized geometries.
Research Scope: Conduct cradle-to-gate techno-economic and carbon-handprint assessments of scaled EDM–ECM hybrid processes and cryogenic drilling for critical aerospace components. Include considerations for tooling fabrication, media recovery/reuse, and end-of-life recycling.
Focusing on these nine strategic gaps will not only enhance the fundamental understanding of Monel-400 machining but also accelerate the transition of non-conventional processes from laboratory-scale research to robust, sustainable industrial implementation.
Table 16 presents the proposed research framework aimed at advancing sustainable, high-precision machining of Monel-400 using non-conventional processes. The framework is structured across five key dimensions: input enablers, process innovations, sensor and data infrastructure, smart adaptive control, and sustainability outputs, each accompanied by illustrative research questions. This tabular representation concretizes how future research can integrate advances in materials, processing, and control systems to achieve defined precision and environmental objectives. It enables a comprehensive mapping from eco-friendly working fluids, hybrid EDM–ECM or cavitation-enhanced WEDM strategies, and digital-twin reinforcement-learning control loops, to lifecycle carbon-handprint metrics, thereby offering a unified landscape for guiding future developments in sustainable machining of Monel-400. Machine learning prediction error <4% for MRR, TWR, and Ra in EDM of squeeze-cast TiB2/AA6061 composites, enabling data-driven multi-objective optimization (Kumar R. et al., 2023). A systematic review shows AI-driven machining can cut shop-floor energy use by up to 20% but faces data-quality and scalability gaps (Kaur et al., 2025).
6.3 Implications of the study
The critical review of non-conventional machining processes for Monel-400 alloy offers several significant implications for academic research, industrial practice, and future technological innovation.
• Comprehensive Knowledge Consolidation: This study systematically analyzes and compares diverse non-conventional machining techniques, including EDM, WEDM, ECM, PAC, AWJM, PCM, and Hot Machining. It provides an integrated knowledge base that researchers and engineers can directly utilize to understand the behavior of Monel-400 under various machining environments.
• Process Selection Guidance: The comparative evaluation of machining processes, their advantages, limitations, and optimization strategies is a practical decision-making guide for manufacturing industries. It helps them select the most suitable machining method based on operational needs, surface quality requirements, and economic considerations.
• Identification of Research Gaps: The study highlighted tenacious challenges such as tool wear, surface integrity degradation, environmental concerns, and scaling limitations, highlighting specific research gaps that need immediate attention. This offers a roadmap for future investigations to improve the machining performance and sustainability of Monel-400 processing.
• Foundation for Sustainable Manufacturing: The emphasis on eco-friendly dielectrics, green electrolytes, hybrid machining strategies, and real-time monitoring aligns with the global push towards sustainable manufacturing practices. Adopting the recommendations outlined can significantly reduce environmental impact while maintaining high productivity.
• Enabling Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 Integration: The study underscores the importance of AI-driven optimization, real-time adaptive controls, and data-driven modeling. Implementing these innovations can elevate Monel-400 machining into smart manufacturing, enabling integration with Industry 4.0 frameworks for enhanced efficiency, quality assurance, and predictive maintenance.
• Stimulating Hybrid and Multiscale Machining Research: The review nurtures a move towards more advanced, adaptive, and customized machining approaches. It encourages exploration into hybrid machining techniques and multi-objective optimization. This will enable the production of complex, high-precision Monel-400 components for critical applications in the aerospace, marine, chemical, and nuclear sectors.
7 Conclusion
This critical review systematically evaluated non-conventional machining methods for Monel-400. Monel-400 is a high-performing nickel-copper alloy with outstanding corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Monel-400 still has problems while machining. The critical review indicated that conventional machining techniques face significant limitations due to excessive tool wear, high cutting temperatures, and surface damage. The non-conventional machining methods present feasible alternatives for achieving high-precision machining of Monel-400.
EDM was identified as the most extensively investigated non-conventional technique. Despite ongoing issues like recast layer formation and tool wear, EDM provides exceptional flexibility for complex shapes. Improvements through hybrid dielectrics, cryogenic treatments, and magnetic field assistance have significantly enhanced MRR and Ra. WEDM showed enhanced surface integrity, exclusively with powder-mixed dielectrics and trim cuts. At the same time, near-dry WEDM options proved more environmentally sustainable without significantly compromising machining quality.
ECM and ECMM have shown significant benefits with minimal thermal damage and excellent surface finishes. Approaches like ozonated electrolytes, bio-adsorbents, and pulsed air supply substantially increased MRR, reduced OC, and improved eco-sustainability. PAC achieved very high MRRs suitable for rapid processing, but careful optimization of the stand-off distance and gas pressure is vital to managing KW and heat affected zone. AWJM effectively minimized thermal impact, optimizing abrasive flow rate and traverse speed, and improving surface quality.
PCM focused on producing intricate microstructures, with critical parameters like spinning speed, temperature, and exposure time. Hot Machining (including Laser-Assisted Machining) greatly enhanced tool life, lowered cutting forces, and improved surface finishes, particularly when maintaining optimal preheating temperatures around 600 °C.
The comparative analysis of non-conventional machining methods highlighted that each technique has unique advantages and drawbacks. At the same time, strategically optimizing process parameters, tool materials, cooling methods, and hybrid integrations can significantly boost machining efficiency and surface integrity. EDM and ECM are the most extensively studied processes for Monel-400, with emerging methods like near-dry WEDM, Hot Machining, and ECM utilizing eco-friendly electrolytes showing substantial promise for future advancements.
However, notable gaps persist concerning environmental sustainability, large-scale industrial adoption, and the implementation of smart monitoring and AI-driven predictive control systems. Intensive research on hybrid machining, sustainable fluids, scalable models, and life cycle assessments could address these challenges and facilitate the sustainable, high-performance machining of Monel-400. The review provided a consolidated knowledge base, actionable insights, and a strategic plan for researchers and industries focused on enhancing non-conventional machining technologies for Monel-400. It contributes to more efficient, precise, and environmentally responsible manufacturing practices.
To achieve the full potential of unconventional machining methods for Monel-400, standard benchmarking protocols must be defined to facilitate uniform measurement of performance parameters like MRR, Ra, TWR, energy efficiency, and environmental effects across various processes and configurations. Variability in experimental design, tool materials, and electrolyte formulations currently precludes direct comparison and affects technology take-up. The combination of AI-based real-time control systems presents revolutionary potential for machining precision improvement, process stability enhancement, and sustainability. The next-generation of machining platforms can self-tune the process parameters to tool wear patterns, thermal behaviors, and material responses through machine learning models, adaptive feedback control methods, and prediction analytics. The smart systems can decrease resource usage, minimize fault rates, and enhance repeatability in a manufacturing setup. Therefore, moving towards a standardized, AI-enabled, and green machining environment is technically possible and inevitable for the sustainable production of next-generation alloys such as Monel-400.
7.1 Limitations of the review and future work
This review presents an in-depth critical assessment of non-conventional machining processes for Monel-400, yet it has certain limitations that need to be considered. The analysis primarily concentrates on key processes, including EDM, WEDM, ECM, PAC, AWJM, PCM, and Hot Machining. At the same time, less attention has been given to advancing techniques such as Ultrasonic-Assisted Machining and Laser Beam Machining due to a lack of extensive studies. The review mainly integrated qualitative trends and experimental findings without conducting formal statistical meta-analyses across different works. The evaluation predominantly relied on laboratory-scale experiments since large-scale industrial uses of non-conventional machining for Monel-400 are still inadequately reported. Additionally, the choice to include documents from peer-reviewed English journals may present a publication bias, and the technology readiness levels (TRLs) concerning these methods for industrial use were not quantitatively evaluated.
Future research should broaden its focus to incorporate new hybrid and assisted machining techniques applicable to Monel-400 and similar high-strength metals to fill these gaps. Conducting a data-driven meta-analysis aggregating findings from various studies could enhance comparative insights. In addition, documenting real-world case studies and pilot production experiments would help validate these machining approaches’ scalability and commercial feasibility. Upcoming investigations should include life cycle assessments (LCA), carbon footprint analysis, and other sustainability metrics to assess environmental effects thoroughly. Implementing machine learning-based real-time optimization and dynamic process control could significantly transform non-conventional machining techniques, fostering smarter and more adaptable manufacturing methods for complex nickel-copper alloys like Monel-400.
This comprehensive review amalgamates and evaluates recent studies on the unconventional machining of Monel-400, examining techniques like EDM, WEDM, ECM, PAC, AWJM, PCM, and Hot Machining. The main conclusions indicate that EDM and WEDM achieve remarkable precision but encounter issues with recast layers and surface integrity. On the other hand, ECM methods offer high MRR with reduced thermal damage, though they raise environmental concerns. PAC and AWJM provide fast processing capabilities, and optimization strategies greatly enhance their performance. Meanwhile, PCM and Hot Machining offer unique advantages for detailed microfabrication and better machinability due to thermal softening. Future research should aim at creating hybrid machining solutions that leverage the strengths of various techniques, develop environmentally friendly dielectric and electrolyte alternatives, integrate real-time adaptive control systems, and advocate for sustainability through life cycle assessments. Prioritizing eco-efficient, AI-driven, and digitally adjusted machining technologies will be essential for advancing the industrial processing of Monel-400.
Author contributions
KS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – original draft. RmK: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SS: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. RjK: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. FS: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JL: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdo, B. M. A., Almuzaiqer, R., Noman, M. A., and Chintakindi, S. (2023). Investigation of heat annealing and parametric optimization for drilling of Monel-400 alloy. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 7 (5), 170. doi:10.3390/jmmp7050170
Al-Abdallah, M. M. (1996). Impedance measurements on inconel and Monel alloys in Dead Sea water and sulphate solution. Br. Corros. J. 31 (3), 213–217. doi:10.1179/bcj.1996.31.3.213
Al-Hashem, A., and Carew, J. (1995). Effectiveness of cathodic protection of UNS N04400 heat exchanger tubes for sea water service. Br. Corros. J. 30 (4), 312–316. doi:10.1179/bcj.1995.30.4.312
Ali, J. A., and Ambrose, J. R. (1992). The relationship between copper component dissolution kinetics and the corrosion behaviour of monel-400 alloy in de-aerated NaCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 33 (7), 1147–1159. doi:10.1016/0010-938X(92)90169-4
Anandakumar, P., and Shanthi, P. (2013). Experimental investigations into the electrical discharge machining of Monel 400 using different electrodes and dielectric mediums. Int. J. Mech. Engg. Rob. Res. 2 (3). Available online at: https://www.ijmerr.com/show-122-457-1.html.
Anderson, W., Bonner Iii, R., Dussinger, P., Hartenstine, J., Sarraf, D., and Locci, I. (2007). Intermediate temperature fluids life tests - experiments, 17. doi:10.2514/6.2007-4808
Arun Kumar, N. E., Sathishkumar, N., Raviraj, E., Pathri Narayanan, M., and Eugene, R. (2021). Influence of near dry wirecut electrical discharge machining parameters on kerf width in Monel 400. Mater. Today Proc. 39, 1519–1526. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.471
Arun Kumar, N. E., Suresh Babu, A., Subramanian, M., and Pradeep Kumar, C. (2022). INFLUENCE of WIRE-EDM PARAMETERS on SURFACE CHARACTERISTICS of SUPERALLOY MONEL 400. Surf. Rev. Lett. 29 (3), 2250031. doi:10.1142/S0218625X22500317
Aydin, K. (2024). Investigation of optimal machining Monel 400 superalloy considering carbon emissions using FEM, regression and ANN methods. J. Clean. Prod. 447, 141616. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141616
Ayyappan, S., and Vengatajalapathi, N. (2020). Experimental Study on material removal rate and over-cut in electrochemical machining of monel 400 alloys with coated Tools.”, 255–268.
Baig, A., Khan, M. A., Jaffery, S. H. I., Khan, M., Naseer, R., Shah, I., et al. (2024). Experimental evaluation of machinability of monel 400 alloy during high speed micro milling using various tool coatings. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 18 (5), 298–317. doi:10.12913/22998624/190624
Benedict, G. F. (1987). “Electrical discharge machining (EDM),” in Non-Traditional manufacturing processes (New York and Basel: Marcel Dekker, Inc.), 207.
Bergaley, A., and Sharma, N. (2013). Optimization of Electrical and Non Electrical Factors in EDM for Machining Die Steel Using Copper Electrode by Adopting Taguchi Technique.
Bhattacharjee, A., and Kumar, R. (2023). “Environmental impact of operations and supply chain from Fourth Industrial Revolution and machine learning approaches,” in Machine learning for sustainable manufacturing in industry 4.0 (Boca Raton: CRC Press), 76–104.
Bhukya, R., Bharat, N., Bose, P. S. C., and Rao, C. (2023). Optimization of machining behaviour of monel 400 super alloy using ANN and GA technique.
Biswas, S., and Rahul, (2021). The outcome of dielectric fluids in electrical discharge machining performance: a review. Mater. Today Proc. 56. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.12.138
Bothare, V. (2024). Nickel Market Size, Growth and Forecast Report by 2033. Maharashtra, India: Annual Reports, Investor Presentations and Straits Research. Available online at: https://straitsresearch.com/report/nickel-market.
Czelusniak, T., Higa, C. F., Torres, R. D., Laurindo, C. A. H., de Paiva Júnior, J. M. F., Lohrengel, A., et al. (2018). Materials used for sinking EDM electrodes: a review. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41 (1), 14. doi:10.1007/s40430-018-1520-y
De, P. K., and Ghosal, S. K. (1981). A comparative Study of stress corrosion cracking of steam generator tube materials in water at 315 C. Corrosion 37 (6), 341–349. doi:10.5006/1.3577283
Debnath, K., Dutta, H., Chaurasia, S., Rout, M., and Veeman, D. (2025). Micro-machining of Monel K500 using electrical discharge drilling: insights into hole tapering mechanism and surface morphology. Phys. Scr. 100 (2), 025014. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/ada4f5
Demirbaş, A., Köklü, U., Morkavuk, S., Giasin, K., Kocaman, E., and Sarıkaya, M. (2025). Machining-Induced damage and corrosion behavior of Monel-400 alloy under cryogenic cooling conditions: a sustainable initiative. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. - Green Technol. 12 (2), 493–508. doi:10.1007/s40684-024-00664-2
Dhananchezian, M. (2021). “Experimental investigation on dry turned Monel 400 alloy surface parameters with uncoated and coated tool,” in Materials today: proceedings, 8303–8306.
Dhananchezian, M., Rajkumar, K., and Prithivirajan, S. (2023). Cutting velocity influenced machinability of Monel 400 by coated tool. Mater. Manuf. Process. 38 (1), 116–125. doi:10.1080/10426914.2022.2105883
Dutta, R. S. (2009). Corrosion aspects of ni–cr–fe based and Ni–Cu based steam generator tube materials. J. Nucl. Mater. 393 (2), 343–349. doi:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2009.06.020
Ekmekci, B. (2007). Residual stresses and white layer in electric discharge machining (EDM). Appl. Surf. Sci. - APPL SURF SCI 253, 9234–9240. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.05.078
Farooq, M. U., Kumar, R., Khan, A., Singh, J., Anwar, S., Verma, A., et al. (2024). Sustainable machining of Inconel 718 using minimum quantity lubrication: artificial intelligence-based process modelling. Heliyon 10 (15), e34836. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34836
Gokulanathan, L., and Jegan, A. (2022). Optimization of pulsed Current electrochemical micro machining of MONEL 400 alloy in NaNO3 electrolyte. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 17 (8), 220846. doi:10.20964/2022.08.55
Gokulanathan, L., and Jegan, A. (2023). Experimental investigation of micro-ECM on MONEL 400 alloy using particles mixed electrolyte. Chem. Industry Chem. Eng. Q. 30, 13. doi:10.2298/CICEQ221115013G
Grewal, G., and Dhiman, D. (2019). Effect of deep cryogenic treatment on copper electrode for non-traditional electric discharge machining (EDM). Mech. Sci. 10, 413–427. doi:10.5194/ms-10-413-2019
Gupta, K., and Gupta, M. K. (2018). Developments in nonconventional machining for sustainable production: a state-of-the-art review. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part C 233 (12), 4213–4232. doi:10.1177/0954406218811982
Gurusamy, S., Sarkar, S., and Mitra, S. (2012a). Experimental analysis ON WEDM OF MONEL 400 alloys IN a range OF thicknesses, IV.
Gurusamy, S., Sarkar, S., and Mitra, S. (2012b). Experimental investigation on die corner accuracy for wire electrical discharge machining of Monel 400 alloy. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 226, 1694–1704. doi:10.1177/095440541245660
Hadi, M., and Ibrahim, A. (2022). Effect of copper-graphite composite electrode on material removal rate and surface roughness in MONEL 400 during electrical discharge machining. Metallurgical Mater. Eng. 28, 245–255. doi:10.30544/817
Hanief, M., and Charoo, M. S. (2020a). Modeling and optimization of flank wear and surface roughness of monel-400 during hot turning using artificial intelligence techniques. Metallurgical Mater. Eng. 26 (1), 57–69. doi:10.30544/473
Hanief, M., and Charoo, M. S. (2020b). Modeling and optimization of flank wear and surface roughness of Monel-400 during hot turning using artificial intelligence techniques. Metallurgical Mater. Eng. 26, 57–69.
Haron, C., Ginting, A., and Fauziah, M. (2001). Investigation on the influence of machining parameters when machining tool steel using EDM. J. Mater. Process. Technol. - J MATER PROCESS TECHNOL 116, 84–87. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(01)00846-9
Ho, K. H., Newman, S. T., Rahimifard, S., and Allen, R. D. (2004). State of the art in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 44 (12), 1247–1259. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.04.017
Hodge, F. G. (2006). The history of solid-solution-strengthened Ni alloys for aqueous corrosion service. JOM 58 (9), 28–31. doi:10.1007/s11837-006-0078-9
Jadhav, R., Jatti, V., and Singh, T. (2015). Magnetic field assisted electric discharge machining of cryo-treated monel 400 alloy. Appl. Mech. Mater. 787, 371–375. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.787.371
Jaiswal, C. (2025). Corrosion resistant alloy market research report 2025-2034, 111. NY, United States: Market Research Future MRFR/CnM/8344-HCR. Available online at: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/corrosion-resistant-alloy-market-9822.
Jameson, E. C. (2001). “Description and development of electrical discharge machining (EDM),” in Electrical discharge machining (Society of Manufacturing Engineers), 8.
Ji, R., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Cai, B., Ma, J., and Li, X. (2012). Influence of dielectric and machining parameters on the process performance for electric discharge milling of SiC ceramic. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 59 (1), 127–136. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3493-1
Jithendra, T., Sharief Basha, S., Das, R., and Gajjela, R. (2024). Modeling and optimization of WEDM of monel 400 alloy using ANFIS and snake optimizer: a comparative study. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 238 (5), 1573–1589. doi:10.1177/09544062231187207
Jonathan, B., Libnish, S., and Arunkumar, N. (2017). An experimental investigation on strain-hardened monel 400 using abrasive water jet machining. Int. J. Eng. Res. V6. doi:10.17577/IJERTV6IS050047
Jothimurugan, R., and Amirthagadeswaran, K. S. (2016). Performance of additive mixed kerosene-servotherm in electrical discharge machining of monel 400™. Mater. Manuf. Process. 31(4), 432–438. doi:10.1080/10426914.2014.98402
Jothimurugan, R., and K S, D. A. (2014). Performance of additive Mixed Kerosene–Servotherm in electrical discharge machining of monel 400™. Mater. Manuf. Process. 31, 1–7. doi:10.1080/10426914.2014.984202
Jothimurugan, R., Amirthagadeswaran, K. S., and Daniel, J. (2012). Performance of silver coated copper tool with Kerosene-servotherm dielectric in EDM of Monel 400TM. J. Appl. Sci. 12 (10), 999–1005. doi:10.3923/jas.2012.999.1005
Jothimurugan, R., Amirthagadeswaran, K. S., and Suresh Kannan, N. (2014). Performance of tool electrode materials and dielectric media in electric discharge machining of monel 400™. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 9(23), 20899–20909.
Jothimurugan, R., Sai, S. R., and Suresh, G. (2019). Enhancing performance measures in electrical discharge machining of monel 400TM using paraffin-servotherm. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 6 (12), 2647–2651. Available online at: https://www.irjet.net/archives/V6/i12/IRJET-V6I12386.pdf.
Jothiprakash, V. M., Naresh Babu, M., Anandan, V., and Dinesh Babu, M. (2025). Turning of monel 400 using nanoparticles and cryogenic conditions. Mater. Manuf. Process. 40 (5), 679–688. doi:10.1080/10426914.2025.2462841
Kalaimathi, M., and Venkatachalam, G. (2014). Experimental investigations on the electrochemical machining characteristics of monel 400 alloys and optimization of process parameters. Jordan J. Mech. Industrial Eng. 8, 143–151. Available online at: https://jjmie.hu.edu.jo/vol%208-3/JJMIE-141-13-01.pdf.
Kalaimathi, M., Venkatachalam, G., Makhijani, N., Agrawal, A., and Sivakumar, M. (2014). Investigations on machining of monel 400 alloys using electrochemical machining with sodium nitrate as electrolyte. Appl. Mech. Mater. 592-594, 467–472. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.592-594.467
Kalaimathi, M., Venkatachalam, G., Sivakumar, M., and Ayyappan, S. (2017). Experimental investigation on the suitability of ozonated electrolyte in travelling-wire electrochemical machining. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39 (11), 4589–4599. doi:10.1007/s40430-017-0748-2
Kalaimathi, M., Venkatachalam, G., and Sivakumar, M. (2020). An experimental investigation and modelling for travelling wire electrochemical machining of Monel 400 alloys. Int. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 34 (3), 259–281. doi:10.1504/IJMTM.2020.107307
K, A., Rajamani, D., Esakki, B., and Davim, J. P. (2019). Measurement and optimization of multi-response characteristics in plasma arc cutting of Monel 400™ using RSM and TOPSIS. Measurement 135, 725–737. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2018.12.010
Katsamas, A. I., Haidemenopoulos, G. N., Zervaki, A. D., and Melas, I. (2004). Stress-corrosion cracking of a monel 400 tube. J. Fail. Analysis Prev. 4 (6), 44–50. doi:10.1361/15477020421764
Kaur, R., Kumar, R., and Aggarwal, H. (2025). Systematic review of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in machining operations: advancements, challenges, and future directions. Archives Comput. Methods Eng. doi:10.1007/s11831-025-10290-z
Klapper, H. S., Zadorozne, N. S., and Rebak, R. B. (2017). Localized corrosion characteristics of nickel alloys: a review. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 30 (4), 296–305. doi:10.1007/s40195-017-0553-z
Knyazeva, Z. V., Yudin, P. E., Petrov, S. S., and Maksimuk, A. V. (2020). Using metal-sprayed coatings to protect submersible electric pump motors from the impact of complicating factors in oil Wells. Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Metals 61 (5), 592–599. doi:10.3103/S1067821220050065
Kukliński, M., Przestacki, D., Bartkowska, A., Kieruj, P., and Radek, N. (2023a). Conventional and laser-assisted machining of laser-borided Monel 400 alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 126 (11-12), 5677–5687. doi:10.1007/s00170-023-11477-z
Kukliński, M., Przestacki, D., Bartkowska, A., Kieruj, P., and Radek, N. (2023b). Conventional and laser-assisted machining of laser-borided Monel 400 alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 126 (11), 5677–5687.
Kulshrestha, A. S., Haldar, B., Unune, D. R., and Dargar, A. K. (2023a). Evaluating the performance of electrical discharge face grinding on super alloy monel 400. Mater. Res. Express 10 (9), 096516. doi:10.1088/2053-1591/acfb5e
Kulshrestha, A. S., Singh, M., Unune, D. R., and Dargar, A. K. (2023b). An investigation on tool wear rate in the electrical discharge face grinding process for the machining of Monel 400. Int. J. Abras. Technol. 11 (3), 196–211. doi:10.1504/IJAT.2023.130844
Kulshrestha, A. S., Kalos, P., Unune, D. R., and Dargar, A. K. (2024). Assessment of the performance of the electrical discharge face grinding process with powder mixed dielectric. Sadhana - Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 49 (4), 284. doi:10.1007/s12046-024-02634-5
Kumar, P. M. K. S., and Jayakumar, N. (2018). Multiobjective optimization and analysis of copper–titanium diboride electrode in EDM of monel 400™ alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33(13), 1429–1437. doi:10.1080/10426914.2017.1415439
Kumar, R., and Jindal, C. (2023). “Applications of machine learning in smart factory in fourth-generation industrial environment,” in Machine learning for sustainable manufacturing in industry 4.0 (Boca Raton: CRC Press), 122–138.
Kumar, V., Kumar, V., and Jangra, K. K. (2015). An experimental analysis and optimization of machining rate and surface characteristics in WEDM of Monel-400 using RSM and desirability approach. J. Industrial Eng. Int. 11 (3), 297–307. doi:10.1007/s40092-015-0103-0
Kumar, N. E. A., A, S. b., Natesan, S., and Kumar C, P. (2020). Influence of near-dry ambiance on WEDM of Monel superalloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 36, 827–835. doi:10.1080/10426914.2020.1866191
Kumar, M., Rajamani, D., Abouel Nasr, E., Esakki, B., Mohamed, H., and Astarita, A. (2021). A hybrid approach of ANFIS—Artificial bee colony Algorithm for intelligent modeling and optimization of Plasma Arc cutting on monel™ 400 alloy. Materials 14, 6373. doi:10.3390/ma14216373
Kumar, N. E. A., Subramanian, M., A, S. b., and Elakkiyadasan, R. (2023a). Performance evaluation of cryogenic treated and untreated brass electrode in wire-EDM. Mater. Manuf. Process. 38, 1–12. doi:10.1080/10426914.2023.2165664
Kumar, R., Channi, A. S., Kaur, R., Sharma, S., Grewal, J. S., Singh, S., et al. (2023b). Exploring the intricacies of machine learning-based optimization of electric discharge machining on squeeze cast TiB2/AA6061 composites: insights from morphological, and microstructural aspects in the surface structure analysis of recast layer formation and worn-out analysis. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 26, 8569–8603. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.09.127
Kumar Parida, A., and Maity, K. (2019a). Modeling of machining parameters affecting flank wear and surface roughness in hot turning of Monel-400 using response surface methodology (RSM). Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 137, 375–381. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2019.01.070
Kumar Parida, A., and Maity, K. (2019b). Modeling of machining parameters affecting flank wear and surface roughness in hot turning of Monel-400 using response surface methodology (RSM). Measurement 137, 375–381.
Laque, F. (2009). The Behavior Of Nickel Copper Alloys In Sea Water. J. Am. Soc. Nav. Eng. 53, 29–64. doi:10.1111/j.1559-3584.1941.tb01509.x
Mahalingam, M., and Varahamoorthi, R. (2020). Investigation on tool wear rate of brass tool during machining of Monel 400 alloy using electric discharge machine. Mater. Today Proc. 26, 1213–1220. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.244
Mandal, A., and Dixit, A. R. (2014). State of art in wire electrical discharge machining process and performance. Int. J. Mach. Mach. Mater. 16, 1–21. doi:10.1504/IJMMM.2014.063918
Mani, D. (2024). Investigate the comparative performance of dry turning Monel 400 alloy by untreated and cryo-treated AlTiN carbide tools. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 10 (3), 1–19. doi:10.1080/2374068X.2023.2204031
Manohar, G., Chandrasekar, G., Radhakrishnan, G., Raj, P. A. C., and Ram, S. (2025). Evaluation of optimal responses in Monel 400 alloy using computer based unconventional machining process. Interactions 246 (1), 51. doi:10.1007/s10751-025-02257-0
Marenych, O., and Kostryzhev, A. (2020). Strengthening mechanisms in nickel-copper alloys: a review. Met. Basel 10 (10), 1358. doi:10.3390/met10101358
Matboo Ghorbani, M., Taherian, R., and Bozorg, M. (2019). Investigation on physical and electrochemical properties of TiN-Coated monel alloy used for bipolar plates of Proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Mater. Chem. Phys. 238, 121916. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121916
Morkavuk, S. (2025). Improving machinability of Ni-based Monel 400 superalloy: a novel thermal-assisted drilling method based induction heating. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-025-15783-6
Mudigonda, S., and Patil, D. H. (2015). Some investigations on surface texturing on monel 400 using photochemical machining. doi:10.1115/msec2015-9294
Nady, H., and Negem, M. (2016). Ni–Cu nano-crystalline alloys for efficient electrochemical hydrogen production in acid water. RSC Adv. 6 (56), 51111–51119. doi:10.1039/C6RA08348J
Nagarajan, V., Ayyappan, S., Nagarajan, L., Salunkhe, S., Abouel Nasr, E., Shanmugam, R., et al. (2022). Meta-Heuristic technique-based parametric optimization for electrochemical machining of monel 400 alloys to investigate the material removal rate and the sludge. Appl. Sci. 12, 2793. doi:10.3390/app12062793
Naraine, M., and Riznic, J. (2017). The current status of CANDU steam generators, V009T15A001, doi:10.1115/icone25-66001
Nemchinsky, V., and Severance, S. (2006). What we know and what we do not know about plasma arc cutting. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, R423–R438. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/39/22/R01
Newton, T. R., Melkote, S. N., Watkins, T. R., Trejo, R. M., and Reister, L. (2009). Investigation of the effect of process parameters on the formation and characteristics of recast layer in wire-EDM of Inconel 718. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 513-514, 208–215. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2009.01.061
Padma, S., Subramanian, V. A. L. R., Vs, S., Velmurugan, S., and Narasimhan, S. (2001). Corrosion of carbon steel and Monel-400 in EDTA based steam generator cleaning formulations. Mater. Corros. 52, 771–777. doi:10.1002/1521-4176(200110)52:10<771::aid-maco771>3.0.co;2-7
Padmini, P., Senthamilperarasu, S., Shanmuganathan, B., Anbusagar, N. R. R., and Sengottuvel, P. (2015a). An investigation of the influences of EDM parameters and tool geometries on radial overcut for monel 400 material with tungsten copper electrode. Appl. Mech. Mater. 766-767, 908–913. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.766-767.908
Padmini, P., Shanmuganathan, B., Senthamilperarasu, S., and Sengottuvel, P. (2015b). An investigation of the influences of EDM parameters and tool geometries for MONEL 400 material with copper electrode. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 10 (13), 10961–10969. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.766-767.908
Parida, A., and Maity, K. (2018a). Experimental investigation on tool life and chip morphology in hot machining of Monel-400. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 21, 371–379. doi:10.1016/j.jestch.2018.04.003
Parida, A. K., and Maity, K. (2018b). Comparison the machinability of Inconel 718, Inconel 625 and Monel 400 in hot turning operation. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 21 (3), 364–370. doi:10.1016/j.jestch.2018.03.018
Patil, D., and Mudigonda, S. (2016). The effect of the rolling direction, temperature, and etching time on the photochemical machining of monel 400 microchannels. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2016/6751305
Patil, D. H., and Mudigonda, S. (2017). Investigation on effect of grain orientation in photochemical machining of Monel 400. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32, 1831–1837. doi:10.1080/10426914.2017.1291953
Patil, D. H., Thorat, S. B., Khake, R. A., and Mudigonda, S. (2018). Comparative Study of FeCl3 and CuCl2 on geometrical features using photochemical machining of monel 400. Procedia CIRP 68, 144–149. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.084
Patil, D., Shrikant, T., and Sadaiah, M. (2024). Study of the effect of PCM process parameters on geometry type, Ra, depth of etch, undercut comparing FeCl3 and CuCl2 etchants on Monel 400. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 10(3), 1956–1976. doi:10.1080/2374068X.2023.2205668
Puri, A. B., and Bhattacharyya, B. (2003). An analysis and optimisation of the geometrical inaccuracy due to wire lag phenomenon in WEDM. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 43 (2), 151–159. doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(02)00158-X
Rahoi, D. W., Scarberry, R. C., Crum, J. R., and Morris, P. E. (1973). Performance of MONEL alloy 400 in Feedwater Heaters. J. Eng. Power 95 (1), 27–35. doi:10.1115/1.3445691
Rajamani, D., K, A., Esakki, B., and Davim, J. P. (2018). Experimental investigation and optimization of PAC parameters on Monel 400 superalloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 1864–1873. doi:10.1080/10426914.2018.1532085
Rajamani, D., Nasr, E. A., Esakki, B., Kasi, A., and Mohamed, H. (2020). Prediction and analysis of multi-response characteristics on plasma Arc cutting of monel 400™ alloy using mamdani-fuzzy logic System and sensitivity analysis. Materials 13 (16), 3558. doi:10.3390/ma13163558
Rangilal, B., Bharat, N., Bose, P. S. C., and Rao, C. S. P. (2023). Optimization of machining behaviour of monel 400 super alloy using ANN and GA technique. NanoWorld J. 9 (Special Issue 1), S96–S100. doi:10.17756/nwj.2023-s1-020
Rathi, N., Kumar, P., Kumar khatkar, S., and Gupta, A. (2023). Non-conventional machining of nickel based superalloys: a review. Mater. Today Proc. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2023.02.176
Rebak, R. B. (2014). “Crystalline alloys: nickel,” in Environmental degradation of advanced and traditional engineering materials Editors L. H. Hihara, R. P. I. Adler, and R. M. Latanision (Boca Raton: CRC Press), 197–218.
Rebak, R., and Crook, P. (2000). Nickel alloys for corrosive environments. Adv. Mater. Process. 157, 37–42.
Rohilla, V. K., Goyal, R., Kumar, A., Singla, Y. K., and Sharma, N. (2021a). Surface integrity analysis of surfaces of nickel-based alloys machined with distilled water and aluminium powder-mixed dielectric fluid after WEDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 116 (7-8), 2467–2472. doi:10.1007/s00170-021-07610-5
Rohilla, V. K., Goyal, R., Kumar, A., Singla, Y. K., and Sharma, N. (2021b). Surface integrity analysis of surfaces of nickel-based alloys machined with distilled water and aluminium powder-mixed dielectric fluid after WEDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 116 (7), 2467–2472.
Rosenfeld, J., Gernert, N., and El-Genk, M. S. (2008). Life Test results for Water Heat Pipes operating at 200 °C to 300 °C. AIP Conf. Proc. 969, 123–130. doi:10.1063/1.2844957
Ross, N. S., Ganesh, M., Srinivasan, D., Gupta, M. K., Korkmaz, M. E., and Krolczyk, J. B. (2022a). Role of sustainable cooling/lubrication conditions in improving the tribological and machining characteristics of Monel-400 alloy. Tribol. Int. 176, 107880. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107880
Ross, N. S., Ganesh, M., Srinivasan, D., Gupta, M. K., Korkmaz, M. E., and Krolczyk, J. B. (2022b). Role of sustainable cooling/lubrication conditions in improving the tribological and machining characteristics of Monel-400 alloy. Tribol. Int. 176, 107880.
Ross, N. S., Ganesh, M., Ananth, M. B. J., Kumar, M., Rai, R., Gupta, M. K., et al. (2023a). Development and potential use of MWCNT suspended in vegetable oil as a cutting fluid in machining of Monel 400. J. Mol. Liq. 382, 121853. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2023.121853
Ross, N. S., Gopinath, C., Sivaraman, V., Ananth, M. B. J., Gupta, M. K., Erdi Korkmaz, M., et al. (2023b). A new approach of measurement and analysis of PVD - TiAlN coated carbide tools in machining of Monel 400 alloy under hybrid cooling conditions. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 221, 113428. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2023.113428
Ross, N. S., Gopinath, C., Sivaraman, V., Ananth, M. B. J., Gupta, M. K., Erdi Korkmaz, M., et al. (2023c). A new approach of measurement and analysis of PVD - TiAlN coated carbide tools in machining of Monel 400 alloy under hybrid cooling conditions. Measurement 221, 113428.
Sabeeh, M., Abtan, A., and Moosa, A. (2023). Microstructure and mechanical properties assessments of 304 austenitic stainless steel and monel 400 dissimilar GTAW weldment. Revue des Compos. des matériaux avancés 33, 135–144. doi:10.18280/rcma.330301
Saleh, M., Anwar, S., El-Tamimi, A., Mohammed, M. K., and Ahmad, S. (2020). Milling microchannels in monel 400 alloy by wire EDM: an experimental analysis. Micromachines 11 (5), 469. doi:10.3390/MI11050469
Sangli, S., Prakash, S., Sriram, S., A.C, A., and Thangamani, G. (2020). Process parameter optimization of abrasive water jet machining on monel k400 alloy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 912, 032004. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/912/3/032004
Sanjid, A., Rahman, M. A., and Raman, R. K. (2019). Durable degradation resistance of graphene coated nickel and Monel-400 as bi-polar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Carbon 151, 68–75. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2019.05.071
Sarkar, S., Sekh, M., Mitra, S., and Bhattacharyya, B. (2011). A novel method of determination of wire lag for enhanced profile accuracy in WEDM. Precis. Engineering-journal Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. - PRECIS ENG 35, 339–347. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2011.01.001
Schumacher, B. M. (2004). After 60 years of EDM the discharge process remains still disputed. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 149 (1), 376–381. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2003.11.060
Sekar, R. (2022). Eco-friendly filtration of Nickel from the sludge during electrochemical machining of Monel 400 alloys. 22, 203–211. doi:10.30955/gnj.004226
Selvakumar, G., Sarkar, S., and Mitra, S. (2012). Experimental investigation on die corner accuracy for wire electrical discharge machining of Monel 400 alloy. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 226 (10), 1694–1704. doi:10.1177/0954405412456660
Selvakumar, G., Bravilin Jiju, K., Sarkar, S., and Mitra, S. (2016). Enhancing die corner accuracy through trim cut in WEDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 83 (5), 791–803. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7606-0
Selvakumar, G., Thiruppathi Kuttalingam, K. G., Selvaraj, M., and Manohar, J. (2018). Enhancing die corner accuracy using path modification strategy in wire electrical discharge machining of Monel 400. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 232 (2), 207–216. doi:10.1177/0954406216679436
Selvakumar, G., Balasubramanian, V., Vijayan, S., and Lenin, N. (2019). Effects of multi-pass cutting during wire electrical discharging. Materialpruefung/Materials Test. 61 (9), 901–906. doi:10.3139/120.111400
Selvam, R., Vignesh, M., Pugazhenthi, R., Anbuchezhiyan, G., and Satyanarayana Gupta, M. (2024). Effect of process parameter on wire cut EDM using RSM method. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 18 (5), 2957–2968. doi:10.1007/s12008-023-01391-9
Sequeira, C. A. C., Cardoso, D. S. P., Amaral, L., Šljukić, B., and Santos, D. M. F. (2016). On the performance of commercially available corrosion-resistant nickel alloys: a review: a Rev. 34(4), 187–200. doi:10.1515/corrrev-2016-0014
Sherif, E.-S. M. (2012). Effects of exposure time on the anodic dissolution of Monel-400 in aerated stagnant sodium chloride solutions. J. Solid State Electrochem. 16 (3), 891–899. doi:10.1007/s10008-011-1438-0
Shoemaker, L. E., and Smith, G. D. (2006). A century of monel metal: 1906–2006. JOM 58 (9), 22–26. doi:10.1007/s11837-006-0077-x
Tayal, A., Kalsi, N. S., Gupta, M. K., Garcia-Collado, A., and Sarikaya, M. (2021). Reliability and economic analysis in sustainable machining of Monel 400 alloy. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 235 (21), 5450–5466. doi:10.1177/0954406220986818
Taylor, D., Liu, C., Mou, J., and Jahan, M. P. (2019). “Micro-Wire-EDM,” in Micro-electrical discharge machining processes: technologies and applications. Editors G. Kibria, M. P. Jahan, and B. Bhattacharyya (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.), 67–92.
Thangamani, G., Sangli, S., A.C, A., Nanditta, R. V., and Goyal, K. (2021). Performance characteristics of abrasive water-jet machining on monel 400 using two different abrasive grain size. AIP Conf. Proc. 2395, 040006. doi:10.1063/5.0068390
Uhlmann, E., Piltz, S., and Doll, U. (2005). Machining of micro/miniature dies and moulds by electrical discharge machining—Recent development. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 167, 488–493. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.06.013
Ulutan, D., and Ozel, T. (2011). Machining induced surface integrity in titanium and nickel alloys: a review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 51 (3), 250–280. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.11.003
Valaki, J. B., Rathod, P. P., and Khatri, B. C. (2014). Environmental impact, personnel health and operational safety aspects of electric discharge machining: a review. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part B 229 (9), 1481–1491. doi:10.1177/0954405414543314
Wang, G., wz, l., Huang, B., Li, X., Lu, J., and Zhuang, L. (2019). Exploring the composition-activity relation of Ni-Cu binary alloy electrocatalysts for hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline media. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 3160–3165. doi:10.1021/acsaem.8b02206
Wójcik, R., and Nadolny, K. (2017). Effects of a variety of cutting fluids administered using the minimum quantity lubrication method on the surface grinding process for nickel-based alloys. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 18 (9), 728–740. doi:10.1631/jzus.A1600416
Yelamasetti, B., N, S. S., Saxena, K. K., Gupta, N., P, N. K., and Shelare, S. D. (2023). “Metallurgical, mechanical and corrosion behavior of Interpulse and pulsed current TIG dissimilar welds of Monel 400 and AISI 316L,” in Proceedings of the institution of mechanical engineers, part E. doi:10.1177/09544089231216029
Glossary
ANN Artificial Neural Network
AWJM Abrasive Water Jet Machining
C Carbon
CMQL Cryogenic Minimum Quantity Lubrication
CO2 Carbon Dioxide Cooling
ECM Electrochemical Machining
ECMM Electrochemical Micro-Machining
EDM Electric Discharge Machining
Fe Iron
GA Genetic Algorithm
HAZ Heat Affected Zone
HER Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
KW Kerf Width
LAM Laser Assisted Machining
MCDM Multi-Criteria Decision Making
Mg Magnesium
Mn Manganese
Monel-400 Nickel-Copper Based Alloy (UNS N04400)
MQL Minimum Quantity Lubrication
MRR Material Removal Rate
NSGA-II Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II
OC Overcut
PAC Plasma Arc Cutting
PCM Photochemical Machining
PVD Physical Vapor Deposition
Ra Surface Roughness
ROC Radial Overcut
RSM Response Surface Methodology
S Sulphur
Si Silicon
TiAlN Titanium Aluminium Nitride Coating
TOPSIS Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution
TWR Tool Wear Rate
WEDM Wire Electric Discharge Machining
Keywords: Monel-400, non-conventional machining, electric discharge machining (EDM), electrochemical machining (ECM), surface integrity, process optimization
Citation: Singh K, Kumar R, Singh S, Kumar R, Sead FF and Lozanović J (2025) Non-conventional machining of Monel-400 alloy: a critical review of techniques, challenges, and sustainable prospects. Front. Mech. Eng. 11:1639320. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2025.1639320
Received: 01 June 2025; Accepted: 14 August 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Thangarasu S. K., Anna University, IndiaReviewed by:
Prosun Mandal, National Institute of Technology, IndiaDinesh Kumar Madheswaran, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, India
Copyright © 2025 Singh, Kumar, Singh, Kumar, Sead and Lozanović. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Raman Kumar, c2VoZ2FsOTFAeWFob28uY28uaW4=; Jasmina Lozanović, amFzbWluYS5sb3phbm92aWNAZmgtY2FtcHVzd2llbi5hYy5hdA==
†ORCID: Kamalpreet Singh, orcid.org/0009-0001-6307-1178; Raman Kumar, orcid.org/0000-0003-2934-7609; Sehijpal Singh, orcid.org/0000-0003-2562-0524; Rajender Kumar, orcid.org/0000-0002-3531-630X
 Kamalpreet Singh
Kamalpreet Singh Raman Kumar
Raman Kumar Sehijpal Singh1,3†
Sehijpal Singh1,3† Jasmina Lozanović
Jasmina Lozanović