- School of Mechatronics and Automotive Engineering, Puyang Vocational and Technical College, Puyang, China
Introduction: Parallel hybrid vehicles face challenges in real-time torque distribution, including slow feedback speeds and suboptimal energy allocation, which constrain overall energy efficiency. This study aims to develop a high-precision, robust torque distribution model to enhance energy utilization while addressing interference from environmental noise and extreme temperatures.
Methods: A real-time torque distribution model integrates three core components: a Markov Decision Process framework transforms torque allocation into a mathematical optimization problem; the Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm enhanced with Prioritized Experience Replay dynamically generates control strategies; and Fiber Bragg Grating sensors achieve millisecond-level torque measurement by correlating shaft strain forces with wavelength shifts. Validation employed the Gamma Technologies Suite simulation platform and the Next Generation Simulation dataset, with benchmark comparisons against Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy, Fuzzy Logic Control, and Thermostat Strategy models.
Results: The optimized Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm achieved 93.2% accuracy and 1.0% loss rate upon convergence, with an average feedback time of 32 milliseconds. In simulated vehicle operations, torque distribution was completed within 70 milliseconds, while energy utilization rates reached 75.5% during startup, 42.3% in normal driving, 41.5% under acceleration, 22.5% during deceleration braking, and 50.0% in high-speed driving. Robustness testing demonstrated 82.3% accuracy under 300-decibel noise interference and 83.1% accuracy at 180-degree Celsius temperatures.
Discussion: The model establishes a closed-loop system that synergizes rapid Fiber Bragg Grating sensing with Markov Decision Process-driven decision-making, enabling efficient torque distribution under extreme operating conditions. While energy utilization during deceleration braking remains suboptimal, future work will optimize regenerative braking strategies through road condition prediction and advanced power devices. This approach provides a viable pathway to improve energy sustainability in hybrid transportation systems.
1 Introduction
With the advancement of society, people have gradually realized the irreversible environmental harm caused by the unrestricted use of fossil fuels, which further leads to an energy crisis (Li and Yue, 2024). In the automotive field, parallel hybrid vehicles have emerged as a new technology to address this issue. They maximize overall energy efficiency by dynamically allocating torque between different power sources. Although torque distribution technology can enhance engine energy utilization and stability, as shown by Morera-Torres et al., who improved the cornering speed and stability of formula-style race cars using torque distribution, existing technologies struggle to formulate reasonable strategies in a short time, resulting in reduced overall energy efficiency (Morera-Torres et al., 2022). Therefore, there is an urgent need for a real-time torque distribution method with fast feedback and reasonable allocation strategies. Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is a reinforcement learning algorithm known for its high stability and fast convergence speed (Sadhukhan and Selmic, 2022). The MDP enables the creation of a virtual environment based on environmental information, transforming complex decision-making problems into mathematical problems (Goyal and Grand-Clement, 2023). This mathematical framework has demonstrated significant value across diverse domains—from IoT resource allocation to medical decision support—by providing a universal methodology for optimizing sequential decisions under uncertainty. Its core capability to model state transitions and reward mechanisms aligns precisely with the dynamic requirements of real-time torque distribution, where millisecond-level responses to rapidly changing vehicle states are critical. Using MDP, the torque distribution problem can be transformed into a mathematical approximation process for finding the optimal solution, which is iteratively solved using PPO. Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) is a sensitive and convenient optical fiber passive device that can quickly and accurately measure engine torque (Mohapatra et al., 2022). Thus, this study proposes a real-time torque distribution algorithm that combines MDP and PPO. Based on this algorithm and FBG, a real-time torque distribution model is constructed, and the model’s performance is verified in subsequent simulation experiments. The innovation point of the research lies in transforming the torque distribution strategy problem of parallel hybrid vehicles into a computable mathematical optimization problem and achieving real-time dynamic optimal decision-making based on vehicle status through the MDP framework integrating the PPO algorithm. Meanwhile, it innovatively introduces fiber Bragg grating sensing technology to achieve rapid and high-precision real-time measurement of engine torque. The combination of the two builds a closed-loop system that integrates rapid perception and real-time decision-making, aiming to maximize the energy utilization efficiency of the system. It is expected that this model will effectively address the challenges faced by existing parallel hybrid vehicles and provide new ideas for the development of real-time allocation technologies in hybrid systems in other fields.
2 Related works
The MDP has gained widespread attention from scholars worldwide due to its strong adaptability and has been widely used in various research fields. For example, Heidari’s team applied MDP to analyze the offloading strategy in the Internet of Things. They built a reinforcement learning algorithm based on MDP and convolutional neural networks for acceleration. In the validation tests, the algorithm reduced offloading delay by 3.3% and improved energy efficiency by 4.2% (Heidari et al., 2023). To detect deteriorating components in devices in a timely manner, Kechagias’ team constructed a deterioration prediction model based on MDP, which transformed equipment maintenance into a linear programming problem. The results showed that this method could identify deteriorating components accurately and on time (Kechagias et al., 2024). Rosenstrom’s team proposed a digital model based on MDP for predicting the onset time of sepsis using electronic health records, aiming to determine the golden time for sepsis treatment. The model, by analyzing the hospitalization history of sepsis patients, reduced the mortality rate by 2.2% (Rosenstrom et al., 2022). Due to its high sample efficiency and fast convergence speed, PPO has also been applied by scholars worldwide in various research areas. For example, Kuai’s team proposed a PPO-based deep learning method to reduce hardware costs in virtual network mapping. This method adjusts mapping strategies based on the state of the service chain. The test results indicated that the algorithm outperformed greedy algorithms and random forests in optimizing virtual network mapping (Kuai et al., 2022). To address the limitations of traditional ground access networks in remote intelligent transportation systems, Hassan et al. proposed a PPO-based deep learning algorithm with an attention mechanism. This method, by decomposing offloading tasks between different servers into independent resource allocation problems, improved the performance of intelligent transportation systems (Hassan et al., 2023).
In the field of hybrid vehicle energy optimization, a number of relatively mature optimization theories and practical technologies have been developed, and many scholars have conducted in-depth research. For example, to address dynamic performance and energy efficiency issues, Nguyen et al. proposed a fuzzy reasoning management framework based on adaptive neural networks. This framework used dynamic programming to achieve global optimal torque distribution, which ultimately improved the overall efficiency of hybrid vehicles by 73.3% (Nguyen et al., 2023). To improve vehicle path tracking accuracy and energy efficiency, Tan et al. proposed a hierarchical control framework that simultaneously considers total demand torque and inter-axle torque. Experimental results showed that this framework optimized overall efficiency while ensuring path tracking accuracy (Tan et al., 2024). To optimize the overall performance of hybrid vehicles, Sun et al. proposed an optimization method using nested design, which solved the coupling problem between physical system parameters and control algorithms to formulate the best torque distribution strategy, thereby maximizing energy efficiency (Sun et al., 2023). Ricci’s team, in order to overcome the limitations of physical sensors in torque measurement, integrated Long Short-Term Memory with 1D Convolutional Neural Networks to propose a new method for replacing physical torque measurement devices. The test results indicated that the average error percentage of the method did not exceed 2% (Ricci et al., 2023). Kneissl et al. developed a simulation method based on co-simulation for developing new transmission systems and related operational strategies. By virtualizing the structural components of the car, they realized conceptual control of hybrid powertrains, significantly improving vehicle energy utilization (Kneissl et al., 2022). Wang J et al., aiming to optimize energy management strategies for hybrid power systems, took fuel cell hybrid commercial vehicles as the object and designed an energy management strategy based on the double-delay deep deterministic policy gradient. During the process, a fuel cell/battery/supercapacitor topology was constructed, and the supercapacitor was utilized to coordinate the power output. The results show that the proposed method significantly improves the economy and service life of the power system (Wang et al., 2022). Yang C et al. systematically reviewed the relevant strategies for hybrid vehicles and hybrid aircraft in view of the current research status and development needs of energy management strategies for hybrid power systems. During the process, they first sorted out the three major challenges faced by the hybrid vehicle strategy: real-time performance, adaptability to working conditions, and multi-objective optimization, as well as the solutions. Secondly, the hybrid aircraft strategy was summarized according to the architecture. This review provides guidance for research on energy management strategies for hybrid power systems in flying cars and promotes knowledge transfer (Yang et al., 2023). Scholars such as Chen W proposed an integrated ecological driving framework for fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles in multi-lane scenarios in response to the lack of continuous lateral dynamic coordination in energy-saving optimization of hybrid power systems. During the process, deep reinforcement learning was utilized to synchronously optimize trajectory planning and energy management strategies, taking spatial traffic information and vehicle power status as inputs. The results show that the proposed method effectively improves the health status of the power system (Chen et al., 2025).
Although the existing energy system optimization and torque distribution technologies for hybrid electric vehicles have made certain progress both in theory and application, they generally have core bottlenecks such as insufficient real-time performance and low efficiency in strategy generation. Traditional optimization methods often have heavy computational burden and slow response speed under complex dynamic working conditions, and are difficult to meet the demand for real-time torque distribution at the millisecond level during vehicle operation. Meanwhile, the traditional sensors relied on in the torque measurement process are prone to reduced accuracy and reliability in harsh environments such as high temperatures and high noise, further restricting the timeliness and accuracy of the overall distribution strategy. These limitations make it difficult for the existing system to maximize energy utilization efficiency in rapidly changing driving conditions. In summary, existing automotive energy system optimization and torque distribution technologies have made certain advancements in both theory and practical applications. However, they generally suffer from poor performance and long strategy formulation times. The PPO algorithm under the MDP framework can find an approximate optimal solution for torque distribution based on the vehicle’s status, while FBG can quickly measure real-time torque during operation. Therefore, this study innovatively proposes to integrate the MDP and PPO algorithms to construct a real-time torque distribution model based on FBG torque measurement, with the aim of meeting the real-time and accuracy requirements of torque distribution.
3 Construction of real-time torque distribution model based on MDP and PPO algorithms
3.1 Design of torque distribution algorithm based on MDP and PPO
The hybrid electric vehicle achieves a balance among power, economy, and energy efficiency through the coupling and complementarity of the engine and electric motor. In this process, only by accurately judging the vehicle’s operational state and formulating a reasonable torque distribution strategy can the maximum energy efficiency be achieved. The MDP can convert various environmental information into data types recognizable by the algorithm and iteratively train the reinforcement learning algorithm by constructing a virtual environment. Therefore, this study uses the MDP framework as the interactive hub between the engine and control system, enabling information exchange with the external environment through MDP, as shown in Figure 1.
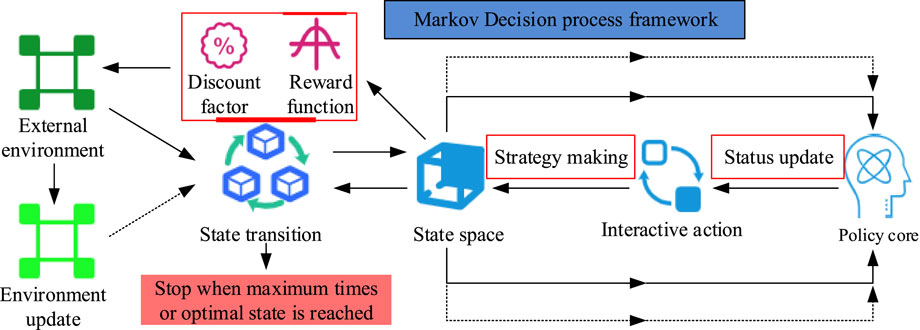
Figure 1. MDP framework for environmental interaction (Source from: https://icon.sucai999.com/and author self-drawn).
In Figure 1, the MDP framework consists of state space, policy core, interaction actions, state transitions, reward function, and discount factor. During environmental interaction, the MDP framework generates the initial state space based on the current environmental conditions. This state space is updated dynamically at regular intervals as the environment evolves. The policy core continuously monitors changes in the state space and responds by generating interaction actions. After executing an action, the environment undergoes changes that directly influence the formulation of the state transition strategy. Specifically, the state space integrates these environmental updates with the reward function and discount factor to formulate an optimized state transition strategy. This strategy is then output to the environment, driving its next update cycle. Crucially, the updated environmental state is fed back into the state space, creating a closed-loop system where environmental dynamics directly shape subsequent state transitions and policy decisions. The probability of each strategy occurring is shown in Equation 1.
In Equation 1,
In Equation 2,
In Equation 3,
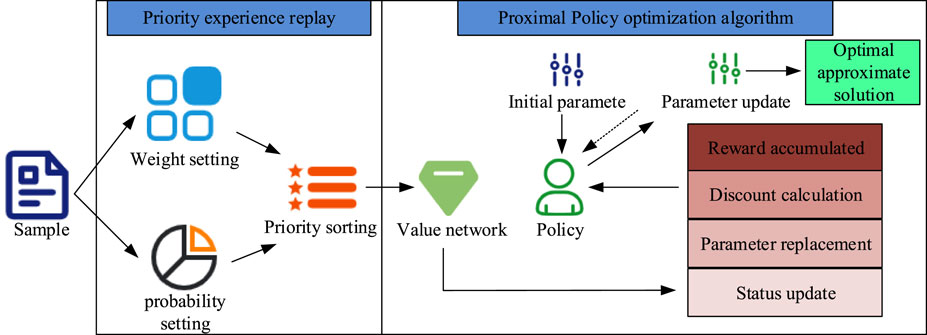
Figure 2. PER-optimized PPO algorithm flowchart (Source from: https://icon.sucai999.com/and author self-drawn).
In Figure 2, when samples are input, the PER algorithm first assigns sampling probabilities to all samples based on their importance. The importance of the samples is shown in Equation 4.
In Equation 4,
In Equation 5,
In Equation 6,
In Equation 7,
In Equation 8,
In Equation 9,
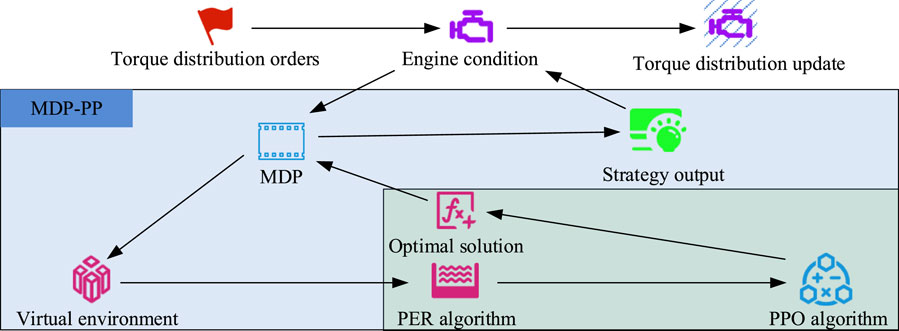
Figure 3. Optimized PPO algorithm flowchart under the MDP framework (Source from: https://icon.sucai999.com/and author self-drawn).
In Figure 3, the MDP-PP algorithm consists of two parts: the MDP framework and the optimized PPO. During real-time torque distribution, the MDP algorithm constructs a virtual internal environment based on engine speed, energy consumption, and other information. The virtual environment, as the data source for reinforcement learning algorithm training, converts external information changes into numerical changes. The function of the optimized PPO is to use the numerical information from the virtual environment in the MDP framework as samples for iterative training to find the optimal solution or an approximate optimal solution. The MDP framework treats this optimal solution as an interaction action, performs state updates, and updates the discount factor and reward function, outputting the updated strategy to the environment. The process of real-time torque distribution involves continuous updates to the engine state, virtual environment construction, PPO iteration to find the optimal value, and strategy output.
3.2 Construction of real-time torque distribution model based on FBG and MDP-PP
The real-time torque distribution of the parallel hybrid vehicle engine is a complex autonomous decision-making process in the vehicle control system. It typically requires cooperation between the vehicle control platform, driver’s intent inputs, algorithmic dynamic planning, and other factors. The MDP-PP proposed in this study only achieves the dynamic decision-making process of the algorithm. Therefore, in order to realize the complete real-time torque distribution of the parallel hybrid vehicle engine, this study proposes a real-time torque distribution process, which includes data collection, torque distribution strategy formulation, implementation of the distribution strategy, and feedback on the strategy’s effects. The specific steps of this process are shown in Figure 4.
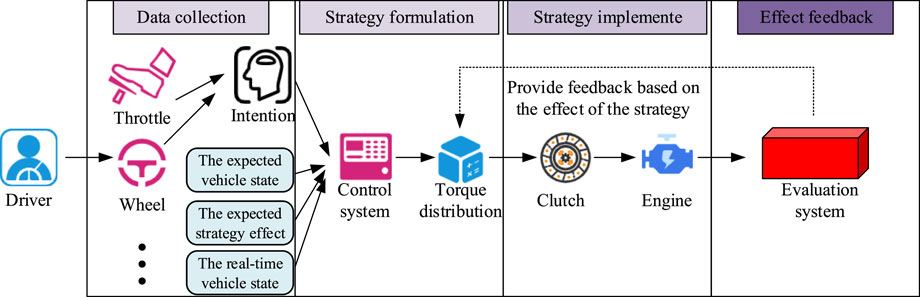
Figure 4. Real-time torque distribution workflow for parallel hybrid vehicle engine (Source from: https://icon.sucai999.com/and author self-drawn).
In Figure 4, during real-time torque distribution, the driver first conveys their intent to the vehicle through the accelerator, brake, etc. The control system then determines the engine operating state through sensors and predicts the upcoming operating state. The torque distribution process needs to formulate the best distribution plan based on the upcoming operating state and engine performance, which is then implemented by components such as the clutch to achieve real-time torque distribution. The strategy effect feedback system evaluates the torque distribution effect based on the driver’s intent, the expected vehicle state, the expected strategy effect, and the real-time vehicle state, and feeds this back to the torque distribution module. This feedback serves as reference data for formulating more effective torque distribution strategies. Existing real-time torque monitoring technologies often suffer from slow feedback speeds, which ultimately leads to untimely strategy implementation. FBG, on the other hand, is a high-precision fiber optic sensor that can quickly measure torque in complex environments (Miguel et al., 2022). In order to further improve the real-time torque distribution effect, this study proposes a real-time torque monitoring technology based on FBG. The workflow of the FBG in torque measurement is shown in Figure 5.
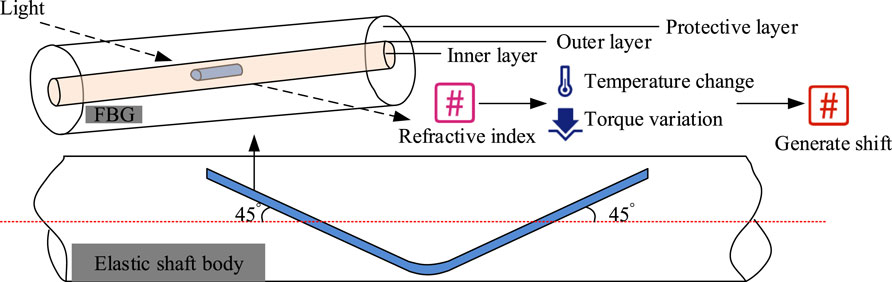
Figure 5. FBG structure and workflow diagram (Source from: https://icon.sucai999.com/and author self-drawn).
In Figure 5, when measuring torque with FBG, two optical fibers are attached at a 45° angle to the surface of the shaft. The FBG structure consists of an inner layer, an outer layer, and a protective layer. The inner layer is high-purity silica doped with a small amount of germanium, the outer layer is pure silica, and the protective layer is composed of large polymer molecules. The principle of torque measurement is that the heat energy and stress generated during the vehicle’s operation change the refractive index of the FBG, resulting in a shift in the central wavelength of the fiber. The mathematical relationship for this process is shown in Equation 10.
In Equation 10,
In Equation 11, the relationship between the shift and stress is ideal when temperature is constant. This study uses two identical optical fibers to eliminate the impact of temperature variations. In this case, the refractive index of the fiber and the central wavelength shift only depend on the stress applied. The elastic shaft can visualize the physical concept of torque. The calculation process for measuring torque with the elastic shaft is shown in Equation 12.
In Equation 12,
In Equation 13,
In Equation 14,
As shown in Equation 15, the shift of the two optical fibers is exactly opposite. The torque can be determined by the relationship between
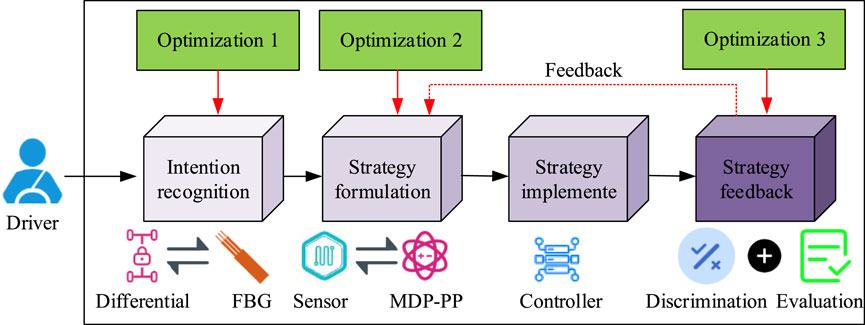
Figure 6. Real-time torque distribution model workflow integrating FBG and MDP-PP (Source from: https://icon.sucai999.com/and author self-drawn).
In Figure 6, compared to general engine torque distribution models, the model proposed in this study is optimized in three areas. First, the study replaces traditional strain force or magnetic force torque measurement technologies with FBG torque measurement technology, which is expected to offer higher measurement accuracy and feedback speed. Second, the study innovatively replaces the differential devices used in torque distribution with the constructed MDP-PP algorithm, expecting the reinforcement learning-based torque distribution module to provide higher energy utilization efficiency for the overall vehicle. Finally, the study adds feedback value to the torque distribution results, expecting the MDP-PP algorithm to incorporate historical torque distribution strategies to improve the distribution time and accuracy.
4 Performance verification of hybrid vehicle engine real-time torque distribution model
4.1 Performance verification of MDP-PP algorithm for strategy formulation
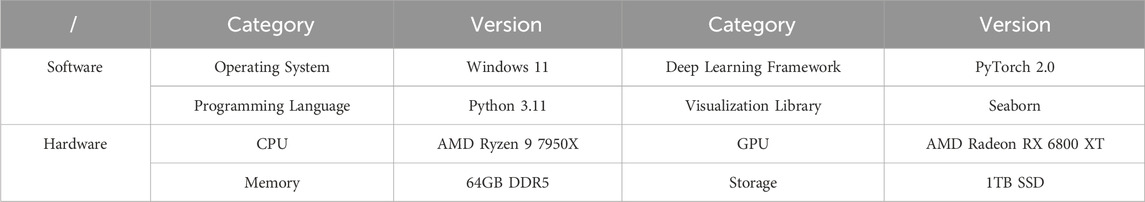
In order to validate the performance of the MPF model, the study first used the Next-Generation Simulation (NGSIM) dataset to test the performance of the MDP-PP algorithm. The NGSIM dataset consists of vehicle driving data collected from four typical traffic scenarios in the United States and contains 11.8 million vehicle data entries. Since its release, the dataset has been widely used in traffic flow analysis and algorithm training. During the test, the Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO) algorithm, Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm, and Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algorithm were used as comparisons. All algorithms were tested under the same conditions, and the laboratory equipment and configuration are listed in Table 1.
The GPU acceleration function is not used during the testing process. Accuracy and loss rate are among the most important metrics in deep learning algorithms. The experiment first compared the accuracy, loss rate, and Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve of each algorithm, and the results are shown in Figure 7.
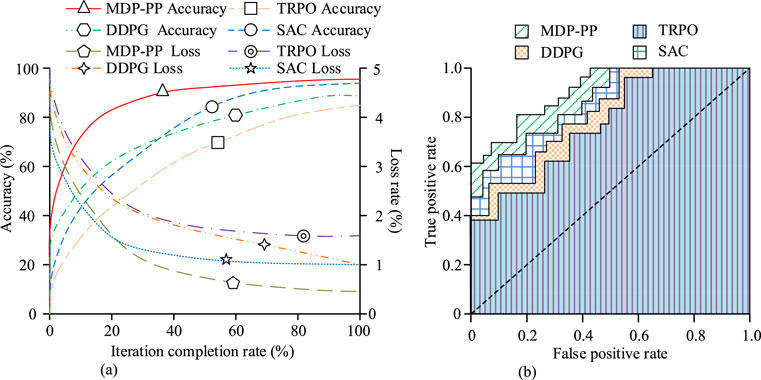
Figure 7. Comparison of loss rate, accuracy, and ROC curves (Source from: author self-drawn). (a) Loss rate and accuracy change. (b) Area under the ROC curve.
As shown in Figure 7a, when the iterations were completed, the accuracy of the MDP-PP algorithm reached 95.5%, and the loss rate was 0.5%. The SAC algorithm had an accuracy of 93.2% and a loss rate of 1.0%. The DDPG algorithm had an accuracy of 86.4% and a loss rate of 1.0%. The TRPO algorithm had an accuracy of 83.6% and a loss rate of 1.7%. The MDP-PP algorithm converged at an iteration rate of 40%, while only the SAC algorithm showed a trend toward convergence among the compared algorithms. As shown in Figure 7b, the ROC curve of the MDP-PP algorithm completely enveloped the ROC curves of the comparison algorithms, with the area under the ROC curve for the MDP-PP algorithm being 0.965, for SAC it was 0.927, for DDPG it was 0.871, and for TRPO it was 0.811. This clearly indicates that the overall performance of the MDP-PP algorithm is significantly superior to the comparison algorithms. Next, to verify the working efficiency of the MDP-PP algorithm, the study used 100 sets of driving data from the dataset to test the algorithm’s efficiency. The results are shown in Figure 8.
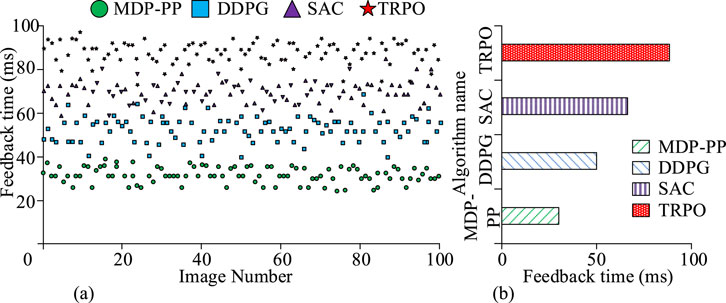
Figure 8. Comparison of torque distribution feedback time (Source from: author self-drawn).(a) Algorithm processing time distribution. (b) Average processing time.
As shown in Figures 8a,b, the maximum feedback time for the MDP-PP algorithm was 40 ms, the minimum was 25 ms, and the average was only 32 ms. The feedback time for the DDPG algorithm ranged from a maximum of 66 ms to a minimum of 39 ms, with an average of 50 ms. The SAC algorithm had a maximum feedback time of 83 ms, a minimum of 58 ms, and an average of 70 ms. The TRPO algorithm had a maximum feedback time of 97 ms, a minimum of 76 ms, and an average of 90 ms. Therefore, it can be concluded that the MDP-PP algorithm demonstrated higher working efficiency when formulating torque distribution strategies. Subsequently, to verify the applicability of the torque distribution strategy formulated by the MDP-PP algorithm, the energy efficiency and recovery rates of the torque distribution strategies from 100 tests of each algorithm were compared. The results are shown in Figure 9.
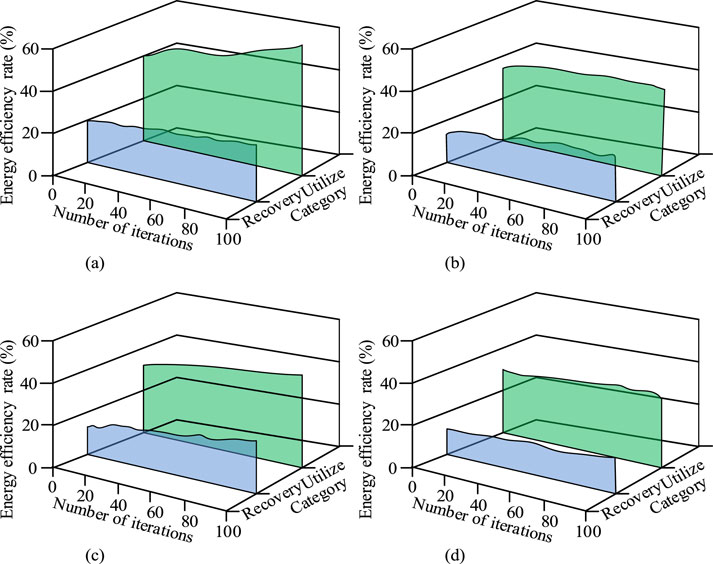
Figure 9. Comparison of energy efficiency and recovery rate of strategies formulated (Source from: author self-drawn). (a) Energy utilize rate and recovery rate of MDP-PP algorithm. (b) Energy utilize rate and recovery rate of DDPG algorithm. (c) Energy utilize rate and recovery rate of SAC algorithm. (d) Energy utilize rate and recovery rate of TRPO algorithm.
As shown in Figure 9a, the energy efficiency of the torque distribution strategy formulated by the MDP-PP algorithm increased from 40.1% to 57.4%, and the energy recovery efficiency increased from 20% to 27.4%. As shown in Figure 9b, the energy efficiency of the torque distribution strategy formulated by the DDPG algorithm increased from 36.1% to 42.1%, and the energy recovery rate increased from 17.3% to 20.1%. As shown in Figure 9c, the energy efficiency of the torque distribution strategy formulated by the SAC algorithm increased from 34.2% to 48.3%, and the energy recovery rate increased from 16.2% to 25.6%. As shown in Figure 9d, the energy efficiency of the torque distribution strategy formulated by the TRPO algorithm increased from 34.2% to 37.1%, and the energy recovery rate increased from 16.0% to 20.1%. These results show that the MDP-PP algorithm clearly outperforms the comparison algorithms, as it can formulate torque distribution strategies with higher energy efficiency and recovery rates.
4.2 Simulation performance verification of MPF model
After verifying the performance of the MDP-PP algorithm, the study used the Gamma Technologies Suite (GTS) coupled simulation platform to test the simulation performance of the MPF model. The GTS platform, developed by Gamma Technologies using Modelica language, is an intelligent tool focused on vehicle energy system modeling and optimization. It offers high openness and adaptability to various environments. During the simulation experiment, the Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy (ECMS), Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC), and Thermostat Strategy (TS) were used as comparison models for real-time torque distribution. To verify whether the MPF model had an advantage in processing speed, a simulation experiment was conducted to compare the processing efficiency. The results are shown in Figure 10.
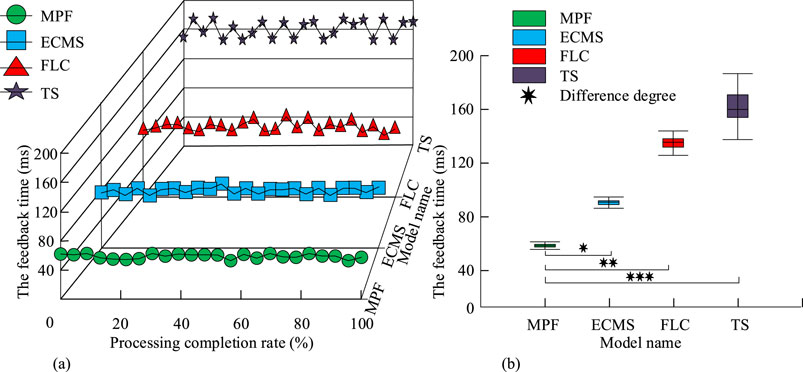
Figure 10. Feedback comparison of real-time torque distribution (Source from: author self-drawn). (a) The feedback time of the model in the process. (b) Box diagram of the average feedback time.
As shown in Figures 10a,b, the feedback time distribution for the MPF model was more concentrated, with a minimum value of 53 ms and a maximum value of 70.0 ms. The feedback time distribution for the ECMS model was also concentrated, with a minimum value of 92.1 ms and a maximum value of 101.2 ms. The feedback time distribution for the FLC model was more dispersed, with a minimum value of 125.9 ms and a maximum value of 142.7 ms. The feedback time distribution for the TS model was also more dispersed, with a minimum value of 137.5 ms and a maximum value of 182.3 ms. Therefore, it can be concluded that the MPF model demonstrated higher processing efficiency. Next, to verify the energy utilization efficiency of the MPF model, the energy efficiency and recovery rate during five driving phases—startup, normal driving, acceleration, deceleration braking, and high-speed driving—were compared. The results are shown in Figure 11.
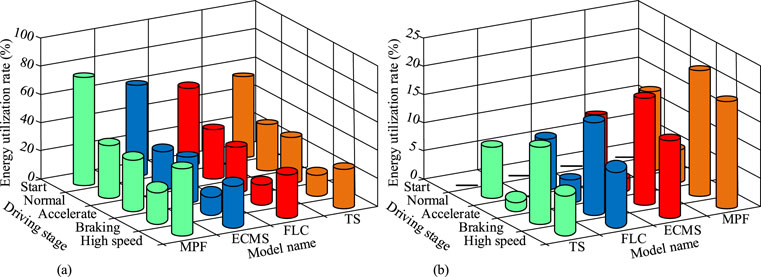
Figure 11. Energy efficiency comparison of each model in different driving phases (Source from: author self-drawn). (a) Comparison of energy utilization in different stages of each model. (b) Comparison of energy recovery rates in different stages of each model.
As shown in Figure 11a, the MPF model had higher energy efficiency than the comparison models in all five driving phases, with efficiencies of 75.5%, 42.3%, 41.5%, 22.5%, and 50.0%, respectively. As shown in Figure 11b, the energy recovery rate during startup for all models was 0%. However, in the other four driving phases—normal driving, acceleration, deceleration braking, and high-speed driving—the MPF model had higher energy recovery efficiency than the comparison models, with recovery rates of 14.1%, 4.7%, 23.4%, and 15.4%, respectively. This indicates that the MPF model achieved better overall energy utilization compared to the comparison models. Subsequently, to verify the robustness of the MPF model, each model was subjected to torque distribution accuracy tests under different intensities of environmental noise and temperature conditions. The results are shown in Figure 12.
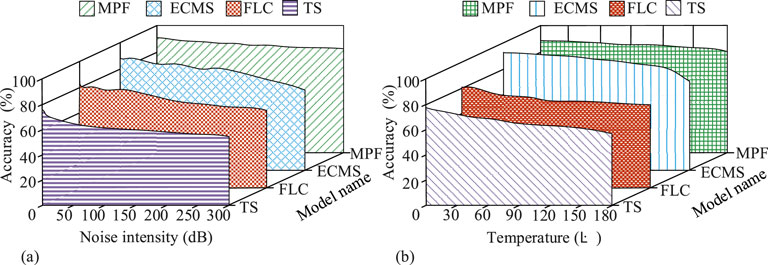
Figure 12. Robustness comparison under different noise and temperature environments (Source from: author self-drawn). (a) Allocation accuracy of each model under different noise intensities. (b) Allocation accuracy of each model under different noise intensities temperature.
As shown in Figure 12a, when the environmental noise intensity increased from 0 dB to 300 dB, the accuracy of the MPF model decreased from 92.1% to 82.3%, while the accuracy of the ECMS algorithm decreased from 90.1% to 73.5%, the accuracy of the FLC model decreased from 80.2% to 69.2%, and the accuracy of the TS model decreased from 75.5% to 60.3%. As shown in Figure 12b, as the environmental temperature increased from 0 °C to 180 °C, the accuracy of the MPF model decreased from 92.1% to 83.1%, while the accuracy of the ECMS algorithm decreased from 90.1% to 76.9%, the accuracy of the FLC model decreased from 80.2% to 70.2%, and the accuracy of the TS model decreased from 75.5% to 59.4%. In summary, the MPF model proposed in this study consistently outperformed the comparison models in terms of accuracy under various levels of environmental noise and temperature. This demonstrated that the MPF model had superior robustness.
5 Conclusion
To address the issue of insufficient real-time performance and accuracy in the engine torque distribution of existing parallel hybrid vehicles, this study innovatively proposed a torque distribution strategy formulation algorithm based on the MDP framework with an optimized PPO algorithm. Additionally, an FBG torque measurement method was integrated to construct a real-time engine torque distribution model for parallel hybrid vehicles. The simulation results showed that the model exhibited high energy utilization efficiency in the start-up, normal driving, acceleration, and high-speed driving stages (75.5%, 42.3%, 41.5%, and 50.0%, respectively). However, the energy utilization rate (22.5%) during the deceleration braking stage is relatively low. The potential reasons for this may involve the fact that the torque distribution strategies for regenerative braking and mechanical braking have not been fully optimized, the limitation of the recovered power due to the high battery state of charge, and the delay in control response under emergency braking conditions. Future work will explore the dynamic adjustment of the braking torque distribution ratio, introduce control strategies based on road condition prediction, and consider the use of higher-performance power devices such as silicon carbide to enhance the energy capture efficiency at this stage. In terms of robustness, the model maintained an accuracy of 82.3% and 83.1%, respectively, under 300 dB strong noise and 180 °C high-temperature environments, verifying the instantaneous reliability of the sensor and control algorithm under extreme conditions. In conclusion, the model successfully integrated the advantages of the MDP framework, the PPO algorithm, and the FBG torque measurement method, creating a real-time torque distribution model that meets the requirements for both efficiency and accuracy in high-noise and high-temperature environments during vehicle operation. However, the economic benefits of the model were not evaluated in this study. Future research will include a comprehensive evaluation of the model’s economic, power, and energy utilization efficiency, and will focus on its continuous optimization. At the same time, when conducting tests and analyses, the variables brought about by the degradation of mechanical performance during long-term operation were not considered for the time being. Subsequently, more abundant experimental Settings will be combined to further verify and enhance the overall durability of the system under high-temperature working conditions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing - original draft, Writing - review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Chen, W., Peng, J., Ma, Y., He, H., Ren, T., and Wang, C. (2025). Eco-driving framework for hybrid electric vehicles in multi-lane scenarios by using deep reinforcement learning methods. Green Energy Intelligent Transp., 100309. doi:10.1016/j.geits.2025.100309
Goyal, V., and Grand-Clement, J. (2023). Robust markov decision processes: beyond rectangularity. Math. Operations Res. 48 (1), 203–226. doi:10.1287/moor.2022.1259
Hassan, S. S., Park, Y. M., Tun, Y. K., Saad, W., Han, Z., and Hong, C. S. (2023). Satellite-based ITS data offloading and computation in 6G networks: a cooperative multi-agent proximal policy optimization DRL with attention approach. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 23 (5), 4956–4974. doi:10.1109/TMC.2023.3300314
Heidari, A., Jamali, M. A. J., Navimipour, N. J., and Akbarpour, S. (2023). A QoS-aware technique for computation offloading in IoT-edge platforms using a convolutional neural network and markov decision process. IT Prof. 25 (1), 24–39. doi:10.1109/mitp.2022.3217886
Kechagias, G., Diamantidis, A., Dimitrakos, T., and Tsakalerou, M. (2024). Optimal maintenance of deteriorating equipment using semi-markov decision processes and linear programming. Int. J. Industrial Eng. Manag. 15 (1), 81–95. doi:10.24867/ijiem-2024-1-349
Kneissl, J., Lion, A., Breuer, F., Pfund, S., Wagner, P., Ille, T., et al. (2022). Development of a variable torque distribution for fully electric and hybrid heavy-duty trucks based on a modular simulation methodology. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 23 (1), 13–29. doi:10.1007/s12239-022-0002-5
Kuai, Z., Wang, T., and Wang, S. (2022). Fair virtual network function mapping and scheduling using proximal policy optimization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 70 (11), 7434–7445. doi:10.1109/tcomm.2022.3211071
Li, S., and Yue, Q. (2024). Analysis on the energy demand, CO2 and pollutant emissions, and health benefits from urban road transport sector: a case study of shenyang. Green Low-Carbon Econ. 2 (3), 143–150. doi:10.47852/bonviewglce3202682
Lou, Z., Wang, Y., Shan, S., Zhang, K., and Wei, H. (2024). Balanced prioritized experience replay in off-policy reinforcement learning. Neural Comput. Appl. 36 (25), 15721–15737. doi:10.1007/s00521-024-09913-6
Miguel, L. P., Teloli, R. O., da Silva, S., and Chevallier, G. (2022). Probabilistic machine learning for detection of tightening torque in bolted joints. Struct. Health Monit. 21 (5), 2136–2151. doi:10.1177/14759217211054150
Mohapatra, A. G., Talukdar, J., Mishra, T. C., Anand, S., Jaiswal, A., Khanna, A., et al. (2022). Fiber bragg grating sensors driven structural health monitoring by using multimedia-enabled iot and big data technology. Multimedia Tools Appl. 81 (24), 34573–34593. doi:10.1007/s11042-021-11565-w
Morera-Torres, E., Ocampo-Martinez, C., and Bianchi, F. D. (2022). Experimental modelling and optimal torque vectoring control for 4WD vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 71 (5), 4922–4932. doi:10.1109/tvt.2022.3158091
Nguyen, C. T. P., Nguyễn, B. H., Trovão, J. P. F., and Ta, M. C. (2023). Torque distribution optimization for a dual-motor electric vehicle using adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 38 (4), 2784–2795. doi:10.1109/tec.2023.3285225
Ricci, F., Petrucci, L., and Mariani, F. (2023). Hybrid LSTM+ 1DCNN approach to forecasting torque internal combustion engines. Vehicles 5 (3), 1104–1117. doi:10.3390/vehicles5030060
Rosenstrom, E., Meshkinfam, S., Ivy, J. S., Goodarzi, S. H., Capan, M., Huddleston, J., et al. (2022). Optimizing the first response to sepsis: an electronic health record-based markov decision process model. Decis. Anal. 19 (4), 265–296. doi:10.1287/deca.2022.0455
Sadhukhan, P., and Selmic, R. R. (2022). Proximal policy optimization for formation navigation and obstacle avoidance. Int. J. Intelligent Robotics Appl. 6 (4), 746–759. doi:10.1007/s41315-022-00245-z
Sun, X., Dong, Z., Jin, Z., Lei, G., and Tian, X. (2023). System-level energy management optimization of power-split hybrid electric vehicle based on nested design. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electron. 71 (9), 10987–10997. doi:10.1109/tie.2023.3340212
Tan, S., Wang, Y., Zheng, X., Zhang, N., Luo, T., Pan, B., et al. (2024). Energy-efficient torque allocation strategy for autonomous distributed drive electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 10 (4), 8275–8285. doi:10.1109/tte.2024.3362810
Wang, J., Zhou, J., and Zhao, W. (2022). Deep reinforcement learning based energy management strategy for fuel cell/battery/supercapacitor powered electric vehicle. Green Energy Intelligent Transp. 1 (2), 100028. doi:10.1016/j.geits.2022.100028
Keywords: hybrid vehicle, real-time torque distribution, MDP, PPO, fiber bragg grating sensor
Citation: Wang J (2025) Real-time torque distribution simulation of parallel hybrid vehicle engine. Front. Mech. Eng. 11:1647691. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2025.1647691
Received: 16 June 2025; Accepted: 06 August 2025;
Published: 21 August 2025.
Edited by:
Liguo Zang, Nanjing Institute of Technology (NJIT), ChinaReviewed by:
Lei Zhang, Beijing Institute of Technology, ChinaWang Hongliang, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Wang, d2oxMDYwQDE2My5jb20=
 Jing Wang
Jing Wang