- 1African Membrane Society (AMSIC), a Ecole Nationale d’Ingénieurs du Mali Abderhamane Baba Touré, Mali, Bamako, Mali
- 2i2i Innovation MegaHub (i2iMegaHub), Accra, Ghana
The circular economy (CE) is gaining attention globally, given its potential to contribute significantly toward sustainable development. The demands for cleaner and safer water amid rising waterborne diseases and stringent environmental regulations are driving the need for reverse osmosis (RO) membrane desalination processes. RO membrane desalination processes are associated with extensive material and energy use, with resulting waste generation, and have ever-growing ecological footprints. Extensive theoretical knowledge on CE and sustainability exists, although it lacks the practical bridge to implementation. In this article, a structured and practical framework is developed and applied to an RO membrane desalination system. Features of this framework allowed breaking the RO membrane desalination system into phases of design (DP), manufacturing (MP), use (UP), and end-of-life (EoLP) and assessing it against both the 3R and 9R ladder strategic frameworks. The resulting CE and sustainability importance trend in the order of DP > MP > UP > EoLP allows for setting the initial implementation starting point, phase(s), or stage(s) for prioritization and maximization to overcome some of the initial implementation challenges. This opens the door for continuous improvements and incremental progress to take on an entire circular or sustainability project in the long term. CE broken into implementation clusters of circular business models (CBM), resource efficiency strategies (RES), and regenerative sustainability practices (RSP), assessed against each of DP, MP, UP, and EoLP phases, offered valuable insights into myriads of opportunities associated with RO membrane desalination system CE implementation. The framework provides step-by-step guidance to bridge the gap between CE and sustainability theoretical knowledge and practical implementations for industrial adoption to reap the countless opportunities.
1 Introduction
Membrane science and technology is a multidisciplinary field that deals with the design, development, and various applications of membranes. Applications of membranes involve separation, selective transport, controlled delivery, and discrimination. Above all, separation is gaining ground because of its wide applications and competitiveness with some existing conventional industrial processes (Anim-Mensah, 2025).
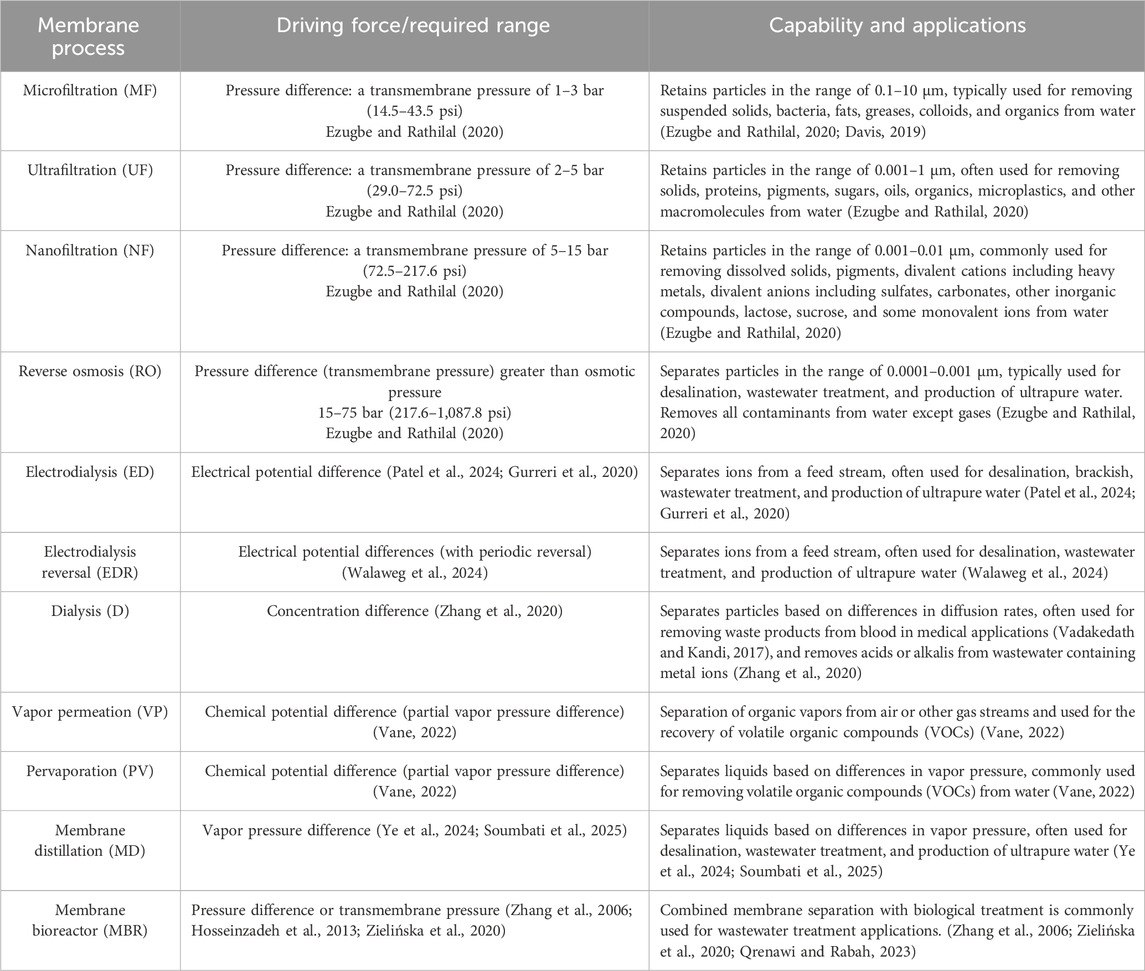
Membrane processes include microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF), reverse osmosis (RO), pervaporation (PV), vapor permeation (VP), dialysis (D), membrane distillation (MD), electrodialysis (ED), and reverse electrodialysis (RED-) (Koros et al., 1996).
Membrane separation processes involve driving pressure, temperature, concentration, and/or electrical forces (Lopez et al., 2023). Synthetic membranes of interest are made from materials including synthetic organic polymers, metallics, ceramics, zeolites, and their hybrids (Ezugbe and Rathilal, 2020). Polymeric pressure-driven membranes are gaining ground, given their flexibilities, including high surface area per volume (i.e., space efficiency), lower cost, ease of manufacturing, and use (Anim-Mensah, 2025).
The membrane filtration market, driven mostly by polymeric pressure-driven membranes, especially MF, UF, NF, and RO, is estimated to grow from 7.51 billion USD in 2024 to 13.03 billion USD in 2032 with a CAGR rate of 7.12% (Gotadki, 2025). RO membranes contributed to about 45% of the total market annual revenue in 2023 and are projected to grow at an 8.4% CAGR rate from 2024 to 2032 (Gotadki, 2025). The growth associated with RO membranes is driven by the need for cleaner and safer water due to the rising awareness of waterborne diseases, stringent environmental regulations, and growth in wastewater treatment (Precedence Research, 2025; Data Bridge Market Research, 2025). Other growing industries for RO membranes include chemical, petrochemical, biotechnology, food, beverage, dairy, and medical (Credence Research, 2024). Clean energy production from fuel cells (Tariq et al., 2024) and cleaner hydrogen from electrolyzers are also on the growth horizon (Anim-Mensah et al., 2024).
The human population globally is expected to grow from 7.8 billion (2020) to 9.7 billion (2050) (Gu et al., 2021), representing a 24.4% rise. EIA estimates approximately a 50% rise in global energy use from 2020 to 2050 (Courtney, 2021), while UNEP projects an 81% rise in municipal solid waste generation from 2.1 billion tons in 2023 to 3.8 billion tons in 2050 (UNEP, 2024). Plastic production and associated pollution, known to negatively impact the environment, are expected to double to 121 million MT by 2050, with a corresponding increase in greenhouse gas emissions of 37% to 3.35 billion tons CO2 equivalent in the absence of interventions (Pottinger et al., 2024).
The increasing human population presents challenges, including rising demands for resources with corresponding waste and pollution, in light of dwindling resources. If nothing is done about the conventional linear economic lifestyle, that is, take-make-use-dispose (Rajput and Singh, 2019; Korhonen et al., 2018), which is unsustainable, this will impact our own existence and that of future generations. This necessitates the need for interventions, of which a circular economy (CE) is an excellent choice.
CE is a sustainable economic model with regenerative systems aimed at reducing waste and excessive resource utilization by promoting reuse, recycling, and upcycling of products and regenerating materials at the end of their service life. This involves combinations of maximization and optimization. In basic terms, CE seeks to conserve natural resources and decrease waste and pollution while promoting sustainable economic growth. CE leads to protecting the environment, while the conventional linear economic model negatively impacts the environment (Rajput and Singh, 2019; Valencia et al., 2023). Lieder and Rashid consider CE as a “collaborative economy” where its implementation is based on resource scarcity (i.e., energy and material consumption), environmental impacts (i.e., solid waste, landfills, emissions or pollution) and economic benefits (i.e., cost reduction, increased revenue, or gross domestic product) (Lieder and Rashid, 2016; Arruda et al., 2021).
The European Commission projects that the adoption of CE principles by the European Union (EU) manufacturing sector could result in an annual economic gain of 600 billion euros, while the adoption by the global economy could create a 1,000 billion USD per annum market (Korhonen et al., 2018). Industries aligning their operations to comply with CE principles can reduce their ecological footprints, improve sustainability, and contribute to a more regenerative and restorative economy, collectively lowering humanity’s impacts on the earth (Kümmerer et al., 2020).
In general, the life cycle of pressure-driven membranes involved in separations is associated with material selection, membrane design, membrane fabrication, testing, membrane system design (Anim-Mensah, 2025), system construction and manufacturing, system installation, system commissioning, system operation, and decommissioning (Khanzada et al., 2024; Glover et al., 2022). This membrane life cycle in phases can be grouped into four groups: (1) design of the membrane and system; (2) production of the membrane and systems; (3) using the membrane and system; (4) end-of-life of the membrane and systems (König et al., 2024). In each phase, regulations and policies exist to assist in complying with CE principles to derive the necessary benefits.
CE pursuit is driven by a treasure of theoretical knowledge and the shared desire for sustainability. Nevertheless, the pathway to practical implementation is plagued with complex technical, social, and economic challenges (Chrispim et al., 2023; Ferriz-Papi et al., 2024). It is worth pointing out that neither the challenges nor the solutions are the same for every industry or application (Ferriz-Papi et al., 2024). Moreover, there is a need for strategic infrastructure development, robust business guidance and methodologies, innovative market solutions, and integrated methods to span entire value chains to overcome these challenges (Iacovidou et al., 2021; Ferriz-Papi et al., 2024).
The barriers to CE implementation are multilayered, ranging from internal company limitations to external regulatory and market factors. The bridge between theory and practice requires cross-disciplinary research and practical solutions to navigate these complexities. This calls for the development and implementation of effective strategies and plans to unlock the full potential of CE to drive sustainable growth (Chrispim et al., 2023; Iacovidou et al., 2021; Ferriz-Papi et al., 2024).
In this article, a structured CE implementation framework is developed and applied to reverse osmosis (RO) membrane desalination systems, which are pressure-driven, given their extensive use and growth. RO membrane desalination footprints are growing, given the increasing demands for cleaner and safer water (Zapata-Sierra et al., 2021). RO membrane desalination is associated with intensive material and energy use and waste generation (Miller et al., 2015), and adopting CE principles is necessary for sustainability compliance.
2 Literature review
2.1 Introduction to circular economy (CE)
2.1.1 Definition and overview of circular economy (CE)
In 2019, the Ellen McArthur Foundation stated, “A circular economy is a systemic approach to economic development designed to benefit businesses, society, and the environment. In contrast to the ‘take-make-waste’ linear model, a circular economy is regenerative by design and aims to gradually decouple growth from the consumption of finite resources” (Ellen McArthur Foundation, 2019).
After analyzing 114 CE definitions, Kirchherr et al. (2017) wrote that “A circular economy describes an economic system that is based on business models which replace the ‘end-of-life’ concept with reducing, alternatively reusing, recycling and recovering materials in production/distribution and consumption processes, thus operating at the micro level (products, companies, consumers), meso level (eco-industrial parks) and macro level (city, region, nation and beyond), with the aim to accomplish sustainable development, which implies creating environmental quality, economic prosperity, and social equity, to the benefit of current and future generations” (Kirchherr et al., 2017). Figge et al. considered this definition too broad and thought it failed to meet a good criterion for a CE definition (Figge et al., 2023). Kirchherr et al. conceptualized CE to have three (3) pillars of sustainability: environmental, social, and economic, and found 95 different definitions of CE among the 114 definitions reviewed (Kirchherr et al., 2017).
Moreover, Kirchherr et al. (2023), after analyzing 221 CE definitions, shared that the CE concept over the past 5 years has both been consolidated and differentiated, and sustainable development has been the main driver. Additionally, Kirchherr et al. pointed out the need for in-depth analysis to determine the necessity for conceptual consolidation and develop targeted strategies to facilitate its practical implementation. A pivotal inquiry persists concerning the capability of CE strategies to concurrently support both environmental sustainability and drive long-term economic development (Kirchherr et al., 2023).
Figge et al. defined CE after considering these four necessary criteria: (1) closed loop for resources opposing the necessity for virgin resource; (2) optimization of resource flows and their directions where input and output are the same in a fully circular system; (3) multilevel concept operating across two synergistic levels—a high level resource circularity-like cluster or industry-wide enabled by a low level activities including refuse, rethink, reduce, recycling, remanufacture, and many more to be executed by the implementor firms; (4) due to thermodynamic constraints and imperfect systems, circularity cannot be reached fully; hence, a steady state cannot be achieved, necessitating a diversified approach to reduce resource use sustainably (Figge et al., 2023).
Based on the foregoing four criteria, Figge et al. defined CE by writing, “a circular economy is a multi-level resource use system that stipulates the complete closure of all resource loops. Recycling and other means that optimize the scale and direction of resource flows contribute to the circular economy as supporting practices and activities. In its conceptual perfect form, all resource loops will be fully closed. In its realistic imperfect form, some use of virgin resources is inevitable” (Figge et al., 2023).
The above suggests the need for standardization of CE definitions and terminologies. Today, there is much evidence to confirm that many businesses have successfully implemented and are benefiting from CE, with the adoption rate gradually increasing (Ellen McArthur Foundation, 2015; Dey et al., 2022; Kansheba et al., 2025; Kirchherr et al., 2023).
The concept of a circular economy (CE) creates a powerful tool to drive sustainability that businesses, policymakers, and individuals can understand and adopt (Corona et al., 2019; Korhonen et al., 2018). As a sustainable economic model, CE aims to reduce waste and resource consumption by promoting the reuse, recycling, and upcycling of products and materials while preserving the environment (Kümmerer et al., 2020). As a closed-loop system, CE ensures materials stay in use to derive maximum benefit, maximizing value while minimizing or eliminating waste, which is achievable through recycling, reuse, refurbishment, and repairs (Rajput and Singh, 2019).
Key aspects of CE include design for circularity where products and services are designed to be recycled, reused, biodegradable, or upcycled; sharing and collaboration where companies and individuals share resources, expertise, and assets to reduce waste and improve efficiency; and regeneration and restoration where natural resources are regenerated and restored, rather than depleted (Kümmerer et al., 2020; Arruda et al., 2021; Ellen McArthur Foundation, 2019).
2.1.2 The benefits of CE
CE benefits include resource maximization, resource efficiency, environmental sustainability, sustainable economy (Valencia et al., 2023), and social, environmental, and economic benefits (Arruda et al., 2021).
2.1.3 Drawbacks and challenges of CE
Despite the many benefits of CE, the drawbacks include limited circular material availability, implementation complexity, technology dependencies, scalability challenges, regulatory frameworks, lack of standardization, awareness, and education (Takacs et al., 2022), social impacts (Knäble et al., 2022), and higher initial costs (Itanola et al., 2024; Kochanski et al., 2024).
Challenges are technical, economic, policy, regulatory, and organizational in nature (Rosário et al., 2024; Galvão et al., 2018), which in basic terms include designing for circularity, closing the loop, materials biodegradability, sharing economy, and systemic change (Kirchherr et al., 2023). Another key challenge is the lack of consensus on the definition and terminology of a CE (Arruda et al., 2021). These drawbacks and challenges highlight the complexities and difficulties associated with transitioning to a CE. Transitioning will require clear objective statements, careful planning, collaboration, and innovation to successfully implement a CE.
2.2 Circular economy (CE) principles and compliance
2.2.1 Key principles of circular economy
CE principles refer to the concept of designing systems, products, and services to be restorative and regenerative by design, keeping existing resources in use for as long as possible, and deriving maximum value while minimizing or eliminating waste (Liang and Knauer, 2023). The strategic goal of CE includes addressing the challenges of resource scarcity, as waste disposal is a win-win manner from the perspectives of economic and value (Galvão et al., 2018).
2.2.2 Compliance with circular economy principles
CE compliance means adhering to regulations, standards, or guidelines that promote CE principles, such as reducing waste, increasing recycling, and using renewable resources. Governments, businesses, and individuals adopting these principles can contribute to a more circular and regenerative economy, reducing waste, promoting sustainable growth, and enhancing the wellbeing of life on earth (Korhonen et al., 2018).
2.3 Circulareconomyandsustainability relationship
2.3.1 Overview of the connection between circular economy and sustainability
Sustainability and a CE are closely interconnected concepts that aim to reduce humanity’s environmental footprint and promote a more regenerative and restorative economy. A CE is a key strategy for achieving sustainability, while sustainability provides a foundation for a CE (Walker et al., 2022). CE means of achieving sustainability includes closed-loop systems, regenerative practices, sharing, and collaboration, while sustainability as a foundation for circularity considers environmental awareness, social responsibility, and economic viability (Liang and Knauer, 2023).
2.3.2 Key differences between circular economy and sustainability
Key differences between sustainability and the CE revolve around the objective, scope, focus, and approach. Sustainability, being much broader, involves environmental, social, and economic aspects, while CE primarily focuses on resource management in terms of materials flow and waste reduction (Sustainability Directory, 2025).
In addition, sustainability aims at meeting today’s and future needs across various categories, while CE promotes regenerative systems that promote optimizing resources and reducing wastes in a closed loop. Moreover, sustainability relies on incremental improvements while addressing a host of issues, whereas CE requires a more radical transformation of systems and business models targeting resource management, with emphasis on minimization, reusing, recycling, upcycling, and regeneration (The Debrand Team, 2024).
Additionally, sustainability science’s fundamental concerns are from overexploitation of resources and environmental degradation, while pursuing continued growth. Circular economy, rooted similarly in sustainability, uniquely integrates a wide array of concepts. This convergence results in circular economy having a multifaceted definition, with its sole unifying objective being optimization of resource utilization (Velenturf and Purnell, 2021).
2.3.3 R-ladder strategy framework for sustainability and circularity
The R-Ladder is a framework comprising strategic “R” sustainability and circularity keywords arranged in hierarchical steps to close material loops toward greater alignment with sustainability and circularity (Alivojvodic and Kokalj, 2024).
The R-ladder objective is to reduce waste or maximize resource use, optimize resources, extract value, and promote regenerative growth. This leads to reduced environmental impacts while driving the realization of economic and new growth opportunities (Evolveable Consulting, 2024).
Many authors use a similar R0 to R9 (or 9R) strategic framework version and keywords with the “Rs” order of importance in order from refuse (R0), rethink (R1), reduce (R2), reuse (R3), repair (R4), refurbish (R5), remanufacture (R6), repurpose (R7), recycle (R8), to recover (R9) (Muñoz et al., 2024; Alivojvodic and Kokalj, 2024; Evolveable Consulting, 2024; Smol et al., 2024; Potting et al., 2017). This is shown hierarchically in Figure 1 with some explanations.
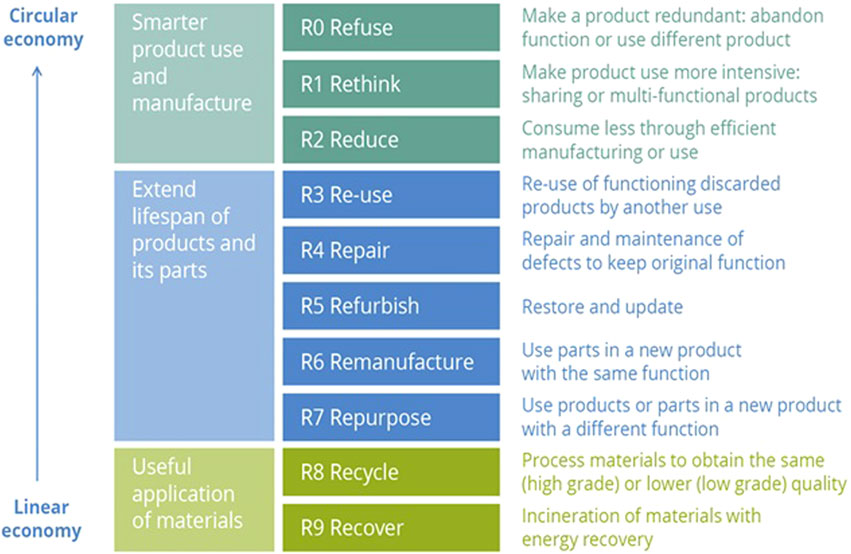
Figure 1. The 9R strategic framework toward circularity and sustainability in priority order (Potting et al., 2017).
Refuse (R0), rethink (R1), and reduce (R2), or R0–R2, on the top portion of the hierarchy, are referred to as “upper” R-strategies (3R). This is because they prevent waste before it occurs and are considered the most circular actions. They reduce the need for raw material use and energy inputs, hence closing the material loop (Evolveable Consulting, 2024).
Other versions of 9R (i.e., R0–R9), defined differently, include refuse/rethink (R0), reduce (R1), resell/reuse (R2), repair (R3), refurbish (R4), remanufacture (R5), repurpose (R6), recycle (R7), recover (R8), and re-mine (R9). In this situation, 3R, R0–R2, is defined differently as refuse/rethink (R0), reduce (R1), and resell/reuse (R2) (Superti et al., 2021). In other situations, 3R is defined to include reduce, reuse, and recycle as a strategy to maintain the highest use and value of products, components, and materials (Scarpellini et al., 2019; Khanna et al., 2022; Kirchherr et al., 2023). This suggests that depending on the objective, the “Rs” can be tailored to suit the need.
Evolvable Consulting defines the R0 to R9 (9R) strategic keywords as follows:
R0. Refuse: Avoiding or reducing wasteful habits
R1: Rethink: Revolutionize designs, processes, and operations.
R2: Reduce: Improve efficiency but not at the expense of quality, or reduce new resource use.
R3: Reuse: Increase product longevity or extend life.
R4: Repair: Preserve and restore functionality.
R5: Refurbish: Update to maintain usability.
R6: Remanufacture: Restore value.
R7: Repurpose: Rethink material application or find uses for old materials or equipment.
R8: Recycle: Cycle material back into production or waste into new materials.
R9: Recover: Harness energy or materials from non-recyclable waste.
Prioritizing the upper R-strategy keywords (R0–R2) lessens the environmental impacts by (1) lowering carbon footprints; (2) promoting designs that encourage durability, multifunctionality, modularity, and minimizing waste generation; (3) avoiding unnecessary consumption and pollution. Moreover, its economic benefits lead to (1) cost savings from the use of minimized raw materials and energy; (2) adopting CE business models, such as product-as-a-service (PaaS), to create recurring revenue streams; (3) brand reputation by offering sustainable products to consumers (Evolveable Consulting, 2024).
2.4 Circular economy, sustainability, and applications of optimization and maximization
2.4.1 Overview of optimization and maximization
Optimization and maximization are related concepts used in mathematics, engineering, economics, and for decision-making (McKelvey and Neves, 2021). They are also used extensively in circularity and sustainability to make informed decisions and have distinct similarities and differences. Similarities include goal orientation and concepts used for mathematical modeling, analysis, and supporting decision-making. However, they differ by their objectives, constraints, solution space, methodology, and real-world applicability (Chiandussi et al., 2012).
Optimization seeks out the best balance or most effective solution among competing goals and constraints (Dagdia and Mirchev, 2020), whereas maximization aims for the highest possible outcome regardless of the consequences (Farley, 2012). Moreover, optimization finds a feasible solution to real-life problems that have multiple factors and constraints (McKelvey and Neves, 2021; El-Halwagi, 2006), whereas maximization prioritizes a single, often short-term gain and frequently without fully considering potential trade-offs with other goals (Haessler, 2020).
Implementing an optimization or maximization framework involving (1) a clear problem statement defining the optimization or maximization problem, objective, constraints, and decision variables (Vasudeva et al., 2022); (2) formulating a model; (3) selecting appropriate solution algorithms to solve the formulated model; (4) testing and validating the model (Zeng et al., 2023).
2.4.2 Optimization and maximization techniques in circular economy and sustainability
On the one hand, optimization is applied to a CE to assist in balancing competing objectives, designing for circularity, and closed loops in material flows (Bal and Badurdeen, 2022). On the other hand, maximization seeks to ensure keeping materials in use for their high value to minimize scarcity, new material use, waste, and environmental degradation (Farley, 2012; Negrete-Cardoso et al., 2022). Both optimization and maximization techniques are used to achieve efficient use of resources, minimize waste, and promote environmentally friendly practices.
Optimization techniques application include (1) linear programing for allocating resources optimally and minimizing waste in especially supply chains (Eldein and Sobhi, 2019); (2) life cycle analysis (LCA) to assist optimizing product designs and end-of-life strategies to minimize environmental impacts (Sakib et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2024); (3) material flow optimization analysis to reduce waste and promote recycling (Islam and Huda, 2019; Čamaj et al., 2025); (4) energy system optimization to design and operate energy system with minimized greenhouse gas emissions while maximizing renewable energy (Wang et al., 2024; Hussain et al., 2025; Scarpellini et al., 2019).
Maximization techniques include applications such as (1) profit maximization from economic benefits while minimizing environmental cost in circular business models (CBMs) (Van Erkelens et al., 2025); (2) resource efficiency maximization by using renewable resources to minimize depleting and polluting non-renewable resources (Khan et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2025; Scarpellini et al., 2019); (3) value maximization where products and materials values are maximized by recycling, upcycling, and repurposing, to name a few (Smol et al., 2024).
These techniques are expected to assist CE implementers and adopters, such as policymakers and businesses, in designing and implementing effective CE systems.
2.4.3 Maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste in circular economy
Maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste, as core objectives of a circular economy, are examples of maximization (Hariyani et al., 2024). This results in net positive gains at reduced environmental impacts while businesses and societies extract maximum value.
Maximizing resource efficiency strategies include (1) design for circularity ensuring materials are easily reused, recycled or biodegradable (Kruczek et al., 2025); (2) resource optimization to ensure optimizing resource use, reduce consumption and waste generation (Hariyani et al., 2024); (3) closed-loop systems where materials are constantly cycled back into production to minimize waste and the need for the primary resource impacts (Kruczek et al., 2025); (4) sharing and collaboration promoting sharing, leasing and collaboration to promote resource utilization (Abdelmeguid et al., 2024).
Waste minimization strategies include (1) waste prevention, where generation is minimized from design standpoint and optimizing processes; (2) waste recycling and upcycling, where waste is converted to valuable resources (Abdelmeguid et al., 2024); (3) producer accountability for product lifecycle, ensuring producers are responsible from creation to disposal of their products (Liu et al., 2022); (4) the use of biodegradable materials, ensuring an easy return to nature with minimized environmental impacts (Kruczek et al., 2025).
2.5 Circular economy business models (CBMs)
2.5.1 Overview of CBMs
Circular economy business models (CBMs) come in various forms based on the value chains or life cycle phases in which they operate. A CBM conveys the mechanics of how value is generated and delivered to various stakeholders while minimizing ecological and social impacts (BOI, 2025).
Existing linear business models (LBMs) operate by acquiring natural resources, creating products, and disposing of waste with minimal recycling. CBMs design out waste and pollution and prolong the use of materials and products while regenerating natural systems. This ensures sourcing products and materials from the existing economy and not from ecological sources. CBMs create value for consumers by adding value to existing products and materials while creating valuable inputs for immediate consumers and beyond (BOI, 2025).
2.5.2 Types of circular economy business models
Depending on the value chain, types of CBMs include (1) circular inputs—using renewable, recycled and highly recyclable inputs in manufacturing to reduce and eliminate waste and pollution; (2) sharing economy concepts—maximizing idle assets across a community by providing customers access to products and services at affordable prices; (3) product-as-a-service (PaaS)—rather than owning an item outright, customers purchase services for a limited time where the owners are responsible for maintenance, upgrade, durability, and treatment at end of use and life; (4) product use extension—design products that are repairable, upgradable, reusable, ease to disassemble, recondition and recyclable components (Abdelmeguid et al., 2024; BOI, 2025); (5) resource recovery—recover materials, energy, and resources from end-of-life products and returning non-functional products to manufacturers for incentives on a contractual basis (Jensen, 2022). Other CBMs include (6) coordinating a circular value chain—recycle products for reuse; (7) circular product design—recycle products for reuse; (8) use-reuse-share-repair—recycled and reused parts to make durable products as input for other uses; (9) collection and reverse logistics—closing the loop by upcycling, repurposed, and reselling created products, and extending the useful lifetime of materials; (10) sorting and reprocessing—finding alternative value in parts that makes a product whole (BOI, 2025).
2.5.3 Benefits and challenges of implementing CBMs
Benefits include (1) cost savings from minimizing waste, optimizing resources use and competitive advantage (Pilipenets et al., 2025; Rizos et al., 2016); (2) creating new markets, revenue streams and opportunities (Ntsondé and Aggeri, 2021); (3) brand reputation and commitment to sustainability (Rehman et al., 2023); (4) reducing the risk of resource scarcity, regulatory compliance, and environmental liabilities (Pilipenets et al., 2025); (5) driving innovation and competitiveness (Rehman et al., 2023).
Challenges include (1) high upfront or initial investment (Ting et al., 2023; Rizos et al., 2016); (2) changing behavioral norms and subsystems for integration (Sousa-Zomer et al., 2018; Ting et al., 2023); (3) advocacy and policy change to overcome regulatory barriers; (4) complexities, needed technologies and technical know-how (Ting et al., 2023; Rizos et al., 2016); (5) effective metrics and frameworks to assess impacts (Pilipenets et al., 2025).
2.6 Circular economy enabling technologies
Technology must be leveraged to drive CE implementation efficiencies and progress. Key technologies include digital technology such as IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics for optimizing resources and tracking material flows (Raut et al., 2025; Hariyani et al., 2024). Biodegradable materials can be created from biotechnology (Rosenboom et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023) and additive manufacturing (Agrawal and Bhat, 2025). Advanced materials can be designed and used for circularity and recyclability (Zeng, 2024). AI is used to (1) improve sorting for high recycling rates (Olawade et al., 2024); (2) predictive maintenance to extend product life (Dereci and Tuzkaya, 2024); (3) reduce waste and pollution from optimizing logistics (Zejjari and Benhayoun, 2024; Hussain et al., 2025), predicting demand fluctuation (Olawade et al., 2024; Zejjari and Benhayoun, 2024), and material traceability (Hung, 2025). Finally, the use of AI tools enables designers to make environmentally friendly choices (Zejjari and Benhayoun, 2024) based on data analysis (Raut et al., 2025) as well as real-time energy consumption analysis, and recommend changes to minimize wastage (Hung, 2025).
3 The membrane science and technology field
3.1 Overview
Membrane science and technology is a multidisciplinary field that deals with the design, development, and application of membranes for various applications. Membrane basic functions include separation, discrimination, selective transport, and controlled delivery (Anim-Mensah, 2025). Membrane processes have been used for different applications in industries, including water and wastewater treatment, wastewater management, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, medical, health, semiconductor, oil and gas, chemical, and energy production (Gotadki, 2025). Membrane key advantages include high energy efficiency, selectivity, precision, compactness, modular design, and lower environmental impact (Osman et al., 2024). Recent advances include nanotechnology, where nanostructured membranes have been developed for improved performance (Aydin et al., 2023). Biomimetic membranes are designed inspired by nature for enhanced selectivity and advanced and new materials discovery with improved membrane properties (Rahmah et al., 2024).
The outlook for the field of membrane science and technology includes playing critical roles in addressing global challenges, such as water scarcity, energy sustainability, and environmental pollution. Artificial intelligence (AI) is being employed in various ways to optimize membrane life cycles (Osman et al., 2024). Ongoing research and improvement will continue to push limits, enabling the development of new applications and technologies.
3.2 Membrane processes, driving forces, and applications
Membrane processes are separation technologies that use membranes to separate components of mixtures that are particles, molecules, or ions from feed streams based on size, charge, shape, affinity, and other properties using various driving forces (Vermaak et al., 2021).
Membrane separation systems offer versatile and efficient solutions to various industrial applications, providing high-quality separations with minimal energy requirements (Osman et al., 2024). This requires careful considerations, including the selection of membrane materials, membrane processes, operating conditions, and pre- and post-treatments to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the membrane systems (Poirier et al., 2023).
The choice of a membrane process depends on the specific separation requirements, feed stream characteristics, and driving force. Table 1 shows some membrane processes with their driving forces, capabilities, and applications. Pressure-driven membrane processes are of interest in this article.
3.3 Pressure-driven membrane separation system
A membrane separation system is a separation technology that uses membranes to separate components in a mixture that are particles, ions, or molecules from feed streams based on size, shape, charge, affinity, or other properties under a driving force (Anim-Mensah, 2007). The membrane acts as a barrier, allowing certain components to selectively pass through to achieve the desired separation and/or purification of interest (Sebiru, 2025).
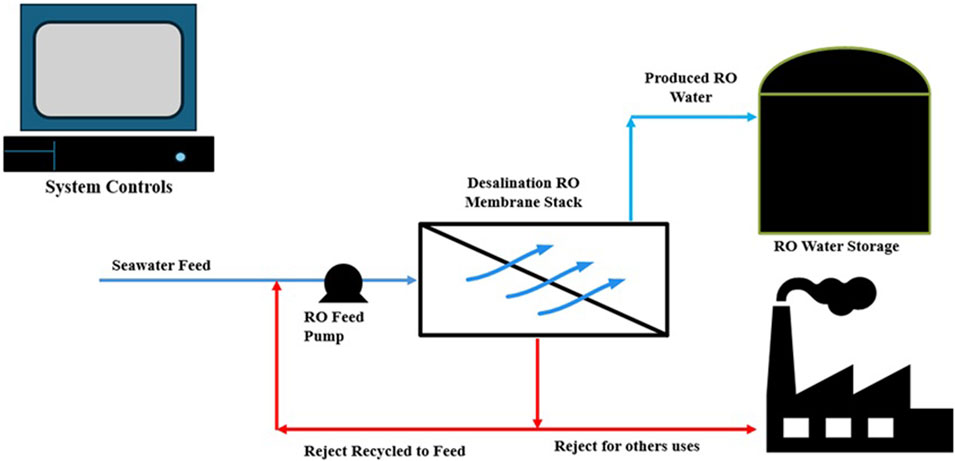
A pressure-driven membrane separation system comprises membrane modules that house membranes of flat, tubular, or spiral-wound configurations (Koros et al., 1996). Force is required to drive the feedstream through the membrane and result in the required separation or purification. Piping is required with the required components to control the various stream flow rates while transporting materials into dedicated tanks for each of the feed, permeate, and reject streams. Ancillaries include electricals, controls, sensors for measurements, and monitoring of process parameters, including flow, level, temperatures, pressures, and concentrations, to ensure the system operates within range while meeting product quality (Awerbuch et al., 2006). Some membrane systems are equipped with operational nuisance detection systems to detect membrane fouling and/or scaling and initiate necessary actions to maintain operational performance and longevity (Fortunato, 2020). Figure 2 shows a typical representation of a reverse osmosis (RO) membrane separation system.
In membrane separation involving liquids, there are three possible streams: feed, permeate, and retentate (or reject). The reject is the unpermeated products (Judd, 2003). There are situations where both the permeate and reject are of value or the reject is transformed into valuable products (upcycling). Generally, to achieve high-quality separations with minimal energy requirements, careful consideration is required to select and operate membranes optimally.
4 Membrane science and technology, and circular economy
4.1 Desalination RO membranes and circular economy
The field of membrane science and technology has witnessed significant growth in recent years and is expected to see more growth in the coming years. This is driven by increasing demand for sustainable solutions in water treatment, energy production, and industrial processes (Gotadki, 2025). To meet the growing demands for membranes, more resources will be needed, leading to associated generated wastes with their impacts if the conventional linear economic model, that is, “take-make-dispose,” is still practiced. More sustainable and reliable means are needed to ensure a sustainable future (Senán-Salinas et al., 2021), in which CE presents many opportunities.
In the membrane science and technology field, CE concepts translate into: (1) reducing membrane waste by developing sustainable membrane materials, designing modular, membrane systems, and implementing take-back programs for spent membranes; (2) increasing resource efficiency by optimizing membrane performance, reducing energy consumption, and promoting water conservation; (3) promoting membrane reuse and recycling by developing technologies for membrane cleaning, refurbishment, and recycling (Khanzada et al., 2024).
By adopting the principles of CE, membrane science and technology will ensure a sustainable future where waste is reduced, resource efficiency is increased, membrane reuse and recycling are promoted, environmental impacts are minimized, economic viability is improved, and innovation and sustainability are fostered (Vinayagam et al., 2024).
4.2 Membrane science and technology key groupings for CE implementation
Membrane life cycle phases (MLCPs) include material selection, membrane design, membrane testing, membrane manufacturing, system design (Anim-Mensah, 2025), system construction and testing, system installation and commissioning, and system operation and decommissioning (Khanzada et al., 2024; Glover et al., 2022). MLCPs can be grouped into four phases: (1) design of the membrane and system; (2) manufacturing of the membrane and systems; (3) use of membrane and systems; (4) end-of-life of membrane and system (König et al., 2024). Each of the phases has policies and regulations to assist the application of CE principles to drive activities sustainably. In each of the phases, opportunities exist to apply circular economy principles to derive the necessary benefits.
The membrane design phase (DP) includes membrane material specification and selection, membrane design, module design, and system design, while the membrane manufacturing phase (MP) includes material sourcing, membrane and module manufacturing, system construction, and integrations. The membrane use phase (UP) includes membrane system installation and testing, system commissioning and operation, and system parts performance, and the membrane end-of-life phase (EoLP) is mainly membrane and membrane system end-of-life and decommissioning (König et al., 2024). Policies and regulations (PRP) for each phase ensure alignment with CE principles to encourage sustainable practices. These groupings provide focus for CE implementation. Figure 3 shows the various MLCPs and policy and regulation considerations under consideration for CE implementation.
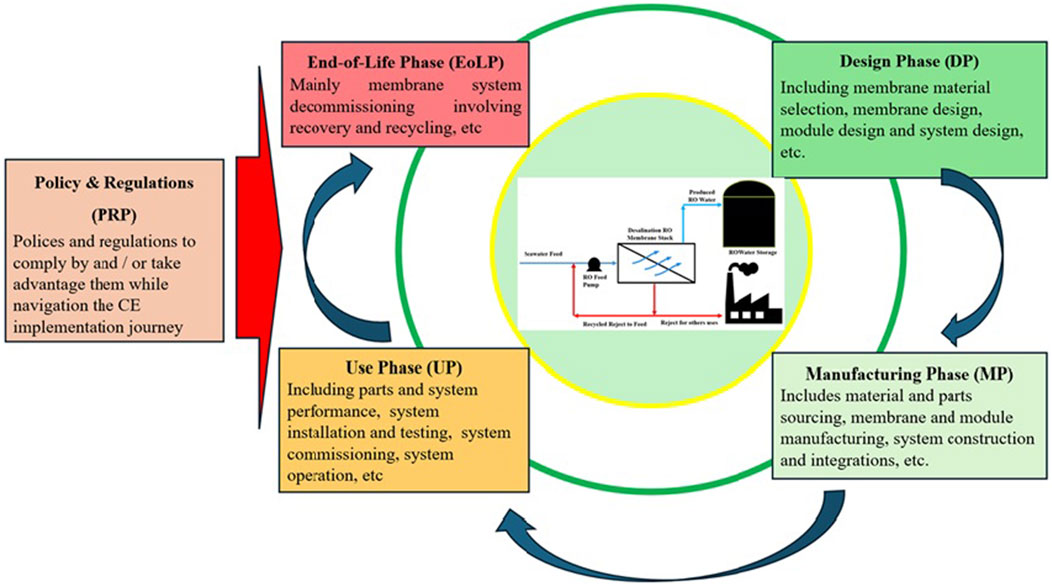
Figure 3. Membrane life cycle phases (MLCPs) with policies and regulations under consideration for CE implementation.
5 Circular and linear economies, membrane life cycle, and R-ladder strategies
The R-ladder is a strategic framework comprised of sustainability and circularity “R” keywords arranged in a hierarchical fashion. Figure 4 shows the relationship between circular and conventional linear economies, membrane life cycle phases (DP, MP, UP, and EoLP), and the various “R” keywords with importance towards sustainability and circularity (Malooly and Daphne, 2023).
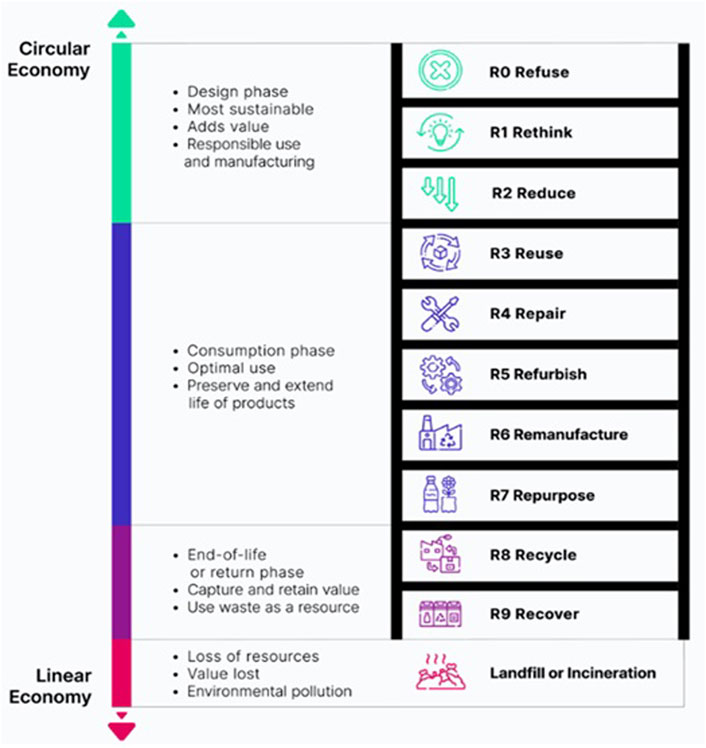
Figure 4. The different phases of R-ladder strategies that can be implemented (Malooly and Daphne, 2023).
In Figure 4, both the design and manufacturing phases are associated with the upper R-strategy keywords, that is, R0–R2 or 3R, which are considered as the most circular actions because they prevent waste before occurrence. The use and end-of-life phases are associated mostly with the next seven keywords, with the use phase (R3 to R7), linked to value retention and the end-of-life phase (R8 to R9) ensuring that materials cycle back into the system, closing the loop (Malooly and Daphne, 2023).
6 Circular economy implementation clusters for membrane life cycle assessment
CE implementation is driven by the challenges of resource scarcity, waste generation, environmental pollution, sustaining economic benefits (Lieder and Rashid, 2016), regulatory pressure, changing consumer behaviors, and increasing demands for more sustainable products and services (Mady et al., 2024).
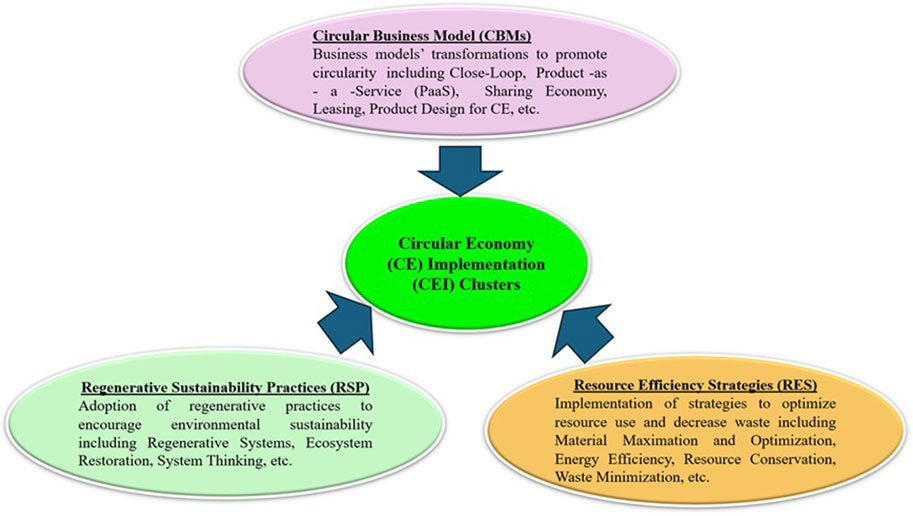
The principles for CE implementation can be grouped into clusters of (1) the circular business model (CBM); (2) resource efficiency strategies (RES); (3) regenerative sustainability practices (RSP). These clusters have associated economic benefits and promote the use of advanced technologies (Barros et al., 2021).
A CBM reflects on business model transformation to promote circularity, such as product-as-a-service (PaaS), where products are offered as services, promoting sharing, leasing, product take back, closing the loop, and designing products for a CE (Van Erkelens et al., 2025).
RES leads to the implementation of strategies to optimize resource use and decrease waste. This involves material maximization and optimization, energy efficiency, resource conservation, and waste minimization (König et al., 2024; Rao et al., 2024). RES also creates new revenue streams and jobs.
RSP drives the adoption of regenerative practices to encourage environmental sustainability. This includes regenerative systems, ecosystem restoration, biodegradable materials, and systems thinking (Kumar et al., 2025). RSP creates new revenue streams and jobs. Figure 5 shows a diagrammatic presentation of CE implementation clusters applicable to RO membrane desalination systems.
7 Methodology
7.1 Framework/methodology for prioritizing MLCPs for CE implementation using R-ladder strategies
This is a structured approach involving the assignment of relative scores to each of the phases based on their relative influence or impact on a specific R-strategy to rank the phases by importance. A higher score indicates a greater influence or impact on a specific R-strategy. The ranking helps determine the initial phase(s) for prioritization and maximization.
To ensure consistency and accuracy, prior to the relative scoring, it is essential to establish clear definitions, especially for each of the R-strategies, the phases involved, and the scoring ranges and steps. This enables applying the relative scoring and supporting reason methodology consistently to achieve reliable results. A team scoring approach is recommended; however, an individual with know-how, experience, and expertise could go through the scoring and reasoning process alone.
The relative scoring process is iterative and collaborative, involving key stakeholders who refine their assessments by reasoning until a consensus is reached. The process is presented in Figure 6. This approach guarantees that the evaluation is comprehensive and reflects the collective expertise and views of the team.
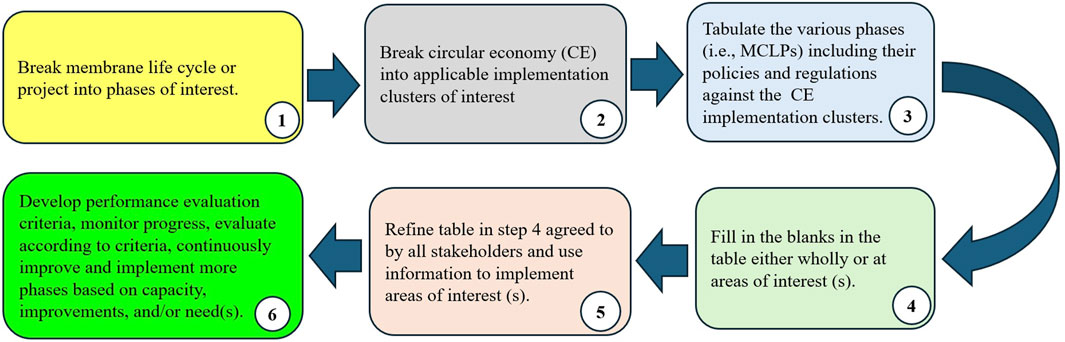
Figure 6. Visual representation of the framework/methodology for prioritizing MLCPs for CE implementation using R-ladder strategies.
The process is broken into easy-to-digest steps:
1. Break the membrane life cycle (MLC) or project into phases of interest.
2. Tabulate each of the phases against the R-strategies that align with circularity and sustainability of interest.
3. Develop a scoring scheme for relative scoring of each of the phases against the R-strategies of interest. High relative scores mean high circularity and sustainability importance, and vice versa.
4. Assign relative scores to each of the phases based on the specific R-strategy backed by reasons, iteratively until consensus is reached.
5. Sum all the assigned relative scores to a “total relative score” for each of the phases. High total relative score(s) are associated with high circularity and sustainability importance, and vice versa.
6. Arrange the total relative scores from high to low. The highest is an initial point or phase to allow for prioritization and maximization.
A step-by-step visual representation of the framework/methodology for prioritizing MLCPs for a CE implementation using R-ladder strategies is shown in Figure 6.
It is important to point out that the scoring for each of the phases against the R-strategies could either be a numeric scale (0–10) or a descriptive scale, such as low (L), medium (M), and high (H). Moreover, for the numeric scoring increment or steps, the smaller the step, the better the scoring could capture the nuanced differences of each of the phase’s influence or impacts on an R-strategy.
Alternatively, further granularity is achievable with a descriptive scale by including intermediate scores so that L, M, and H become low–low (LL), low–medium (LM) or medium-low (M), medium–medium (MM), medium–high (MH) or high–medium (HM), and high–high (HH). However, descriptive scoring will use numeric banding to assist scoring, for example, L (0–3.5), M (3.6–7.5), and H (>7.5) or for increased granularity, LL (0–2), ML (2.1–4), MM (4.4–6), MH (6.1–8), and HH (>8).
The use of relative scoring allows for flexibility in setting the scoring range and steps, enabling different teams or individuals to adapt the methodology to their specific needs.
7.1.1 Ranking membrane life cycle phase (MLCPs) with 3R and 9R ladder strategies
In a tabular form, each of the RO membrane desalination system life cycle phases is evaluated against 3R (R0–R2, refuse (R0), rethink (R1), and reduce (R2)) and 9R (R0–R9, refuse (R0), rethink (R1), reduce (R2), reuse (R3), repair (R4), refurbish (R5), remanufacture (R6), repurpose (R7), recycle (R8), and recover (R9)) strategies and keywords, with reasons for each ranking (Muñoz et al., 2024; Alivojvodic and Kokalj, 2024; Evolveable Consulting, 2024; Potting et al., 2017). The various R-strategies definitions are in Section 2.3.3 of this article, “R-ladder strategy framework for sustainability and circularity,” while what the DP, MP, UP, and EoLP phases are described in Section 4.2 of this article, “Membrane science and technology key groupings for CE implementation.”
Each of the phases is ranked from 0 to 10 in steps of 0.5 for the various phases based on the potential of CE influence or impacts. Increments of 0.5 are used to capture the nuance differences in influence or impacts of each of the phases. Higher scores imply greater importance. Prioritizing R-strategies provides opportunities for implementing more sustainable solutions while reducing waste, optimizing resources, and promoting regenerative growth through the membrane life cycle.
7.2 Framework/methodology for assessing MLCPs against CE implementation clusters
The step-by-step process for the assessment of the various phases with their associated policies and regulations (PRP) against CE implementation clusters is as follows.
1. Break the membrane life cycle (MLC) or project into phases of interest.
2. Break the circular economy (CE) into applicable implementation clusters of interest.
3. Tabulate the phases, including their policies and regulations against the CE implementation clusters.
4. Fill in the blanks in the table either wholly or areas of interest (s), which could be prioritizing area(s).
5. Refine the table in step 4, agreed to by all stakeholders, and use information to implement areas of interest.
6. Develop performance evaluation criteria, monitor progress, evaluate according to criteria, continuously improve, and implement more phases or stages in steps based on capacity, improvements, and/or need(s).
A step-by-step visual representation of the framework/methodology for assessing MLCPs against CE implementation clusters is shown in Figure 7.
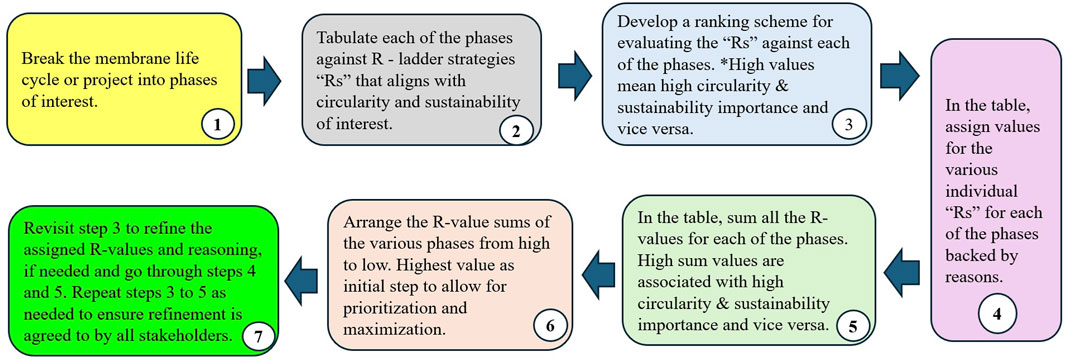
Figure 7. Visual representation of the framework/methodology for assessing MLCPs against CE implementation clusters.
A team approach is recommended; however, an individual with the know-how, experience, and expertise could go through the process alone.
7.2.1 Assessing membrane life cycle phase (MLCPs) against circular economy (CE) implementation clusters for execution
In a tabular form, each of the RO membrane desalination system life cycle phases (LCPs) with their associated policies and regulations (PRP) is assessed against CE implementation clusters. This presents the opportunity to focus on specific CE areas of interest for implementation.
The various definitions of CBM, RES, and RSP are available in Section 6.0 of this article, “Circular economy implementation clusters for membrane life cycle assessment.”
8 Results
Table 2 shows the RO membrane desalination system life cycle—DP, MP, UP, and EoLP—assessed with 3R and 9R ladder strategies for alignments and gaps with circularity and sustainability. For each of the 3R and 9R ladders, the higher the individual score or total score, the higher its importance on the path to higher circularity and sustainability. This ranking allows for accessing the initial step for prioritization for whole, stagewise, or phasewise CE implementation.
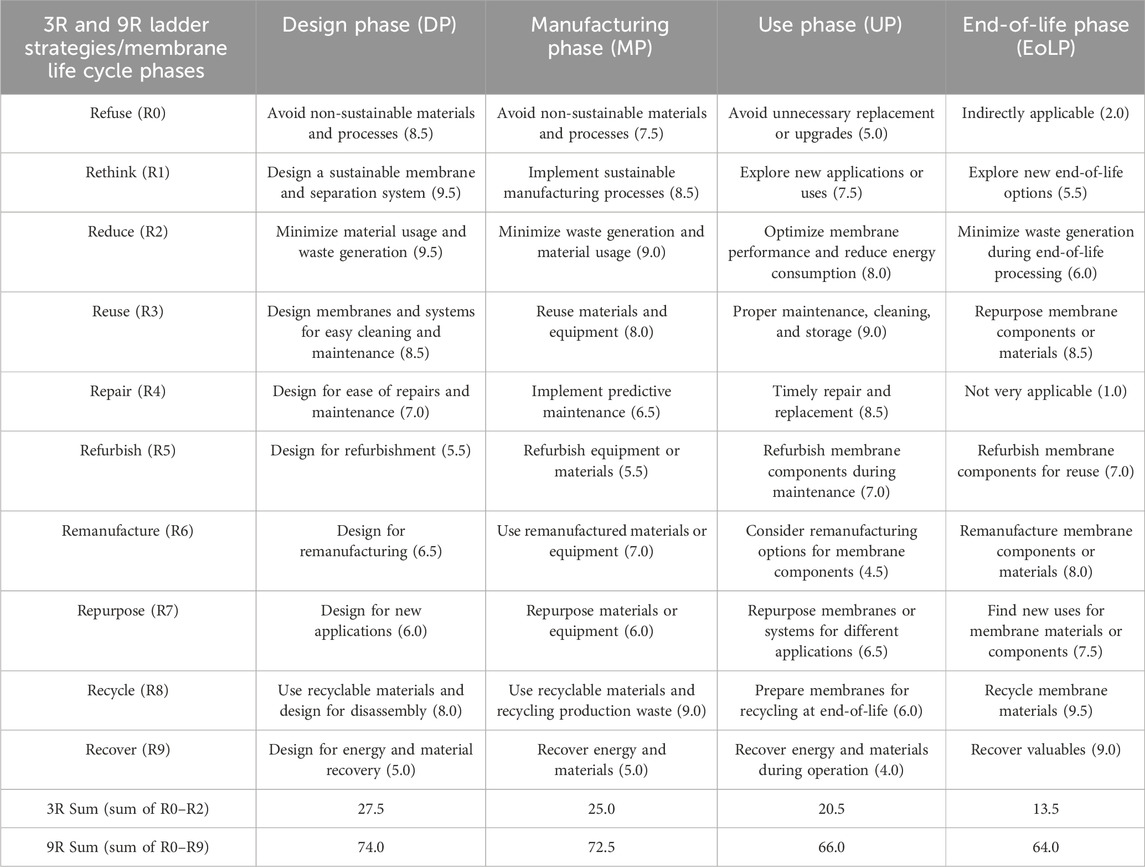
Table 2. Assessment of desalination RO membrane life cycle (i.e. DP, MP, UP and EoLP) with 3R and 9R ladder strategies for circularity and sustainability importance
Table 3 shows the results after RO membrane desalination system life cycle phases are evaluated against the CE implementation clusters in tabular form. Each unit in the table allows for focusing on a specific area requiring detailed analysis to derive optimum and maximum benefits.
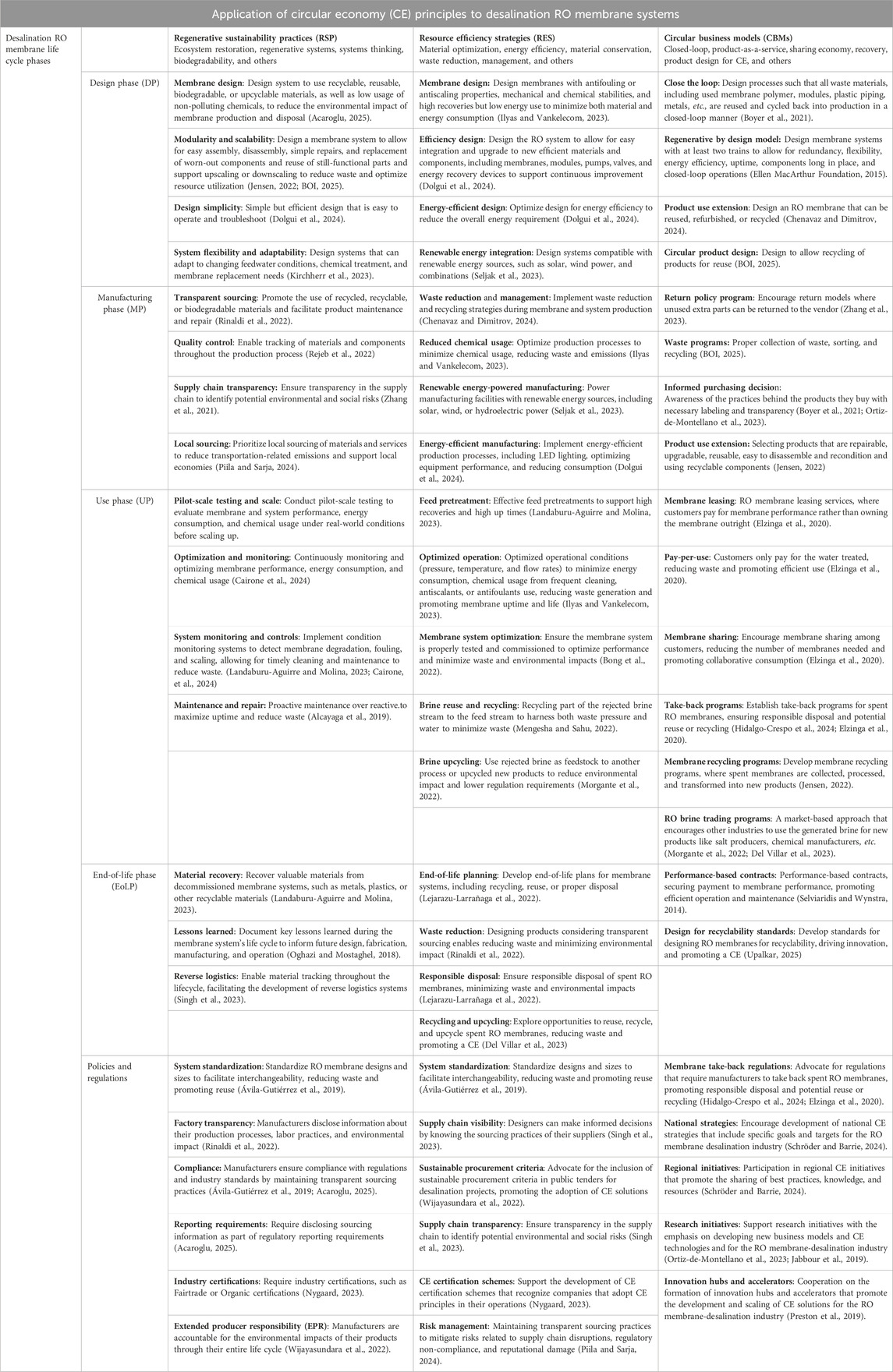
Table 3. Circular economy (CE) implementation clusters assessed against RO membrane desalination system phases.
9 Discussion
9.1 Assessment of RO membrane desalination system life cycle phases with 3R and 9R ladder strategies
Table 2 shows both the individual R-relative scores and the R-total relative scores associated with DP, MP, UP, and EoLP based on 3R and 9R strategic frameworks for circularity and sustainability. 3R, comprising refuse (R0), rethink (R1), and reduce (R2), is considered more circular because these steps prevent waste before its occurrence. However, 9R considers the entire life cycle because waste cannot be eliminated totally, and every effort toward sustainability improvements counts.
For both 3R and 9R, the possible R-total relative scores for the various phases (i.e., DP, MP, UP, and EoLP) are ranked in Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
The higher the numeric total relative score, the higher the alignment towards more circularity and sustainability. The individual R-relative scores associated with the phases are important for circularity and sustainability. However, the total relative scores suggest both DP and MP are comparatively better at driving circularity and sustainability than UP and EoLP, given their high individual relative scores and total relative scores associated with 3R in terms of preventing waste before occurrence.
However, no matter how well 3R is implemented, 9R is still relevant given that its regime covers all RO membrane desalination system phases. The trends suggest initially prioritizing either only DP or both DP and MP, given their high R-relative score or total relative scores, could lead to maximization based on available resources and know-how, while continuously improving to gradually take on the entire CE implementation project.
The relative scores and supporting rationale for the phases in Table 2 were based on the author’s knowledge, expertise, experience, and R-strategy definitions. For instance, in Table 2, the relative score for the design phase (DP) influence or impact on “Refuse or avoid (R0)” is 9.5, which is a high impact or influence on the circular economy of sustainability. The design phase (DP) merited the score given that (1) design decisions made during design phase have significant impact on an entire lifecycle, inclusive of MP, UP, and EoLP; (2) the design phase offers opportunities to design for circularity, such as designing for recyclability, reusability, and biodegradability; (3) design decisions can minimize waste and emissions throughout a lifecycle; (4) design decisions can impact production costs, material usage and cost, and end-of-life costs.
Prevention is key, and it is the design phase that offers the best opportunities to address prevention or minimization of waste and pollution most effectively. Design decisions have long-term impact on environmental and social footprints while offering prospects for innovation and creativity for designing sustainable products and services.
The manufacturing phase (MP) is critical for efficient production of the membranes, modules, membrane systems, and others; it is the design phase decisions that specify them and the system’s environmental impacts. The use phase (UP) is important for membrane system operation and maintenance, but design decisions can influence system efficiency, maintenance, and longevity. End-of-life (EoLP), crucial for waste management, nevertheless has a design phase determination for recyclability, reusability, or biodegradability. The above reasoning is what was used for the relative scoring of the various phases against the R-strategies. The ranking of DP, MP, UP, and EoLP is about the relative power of each phase to contribute to an effective sustainability or CE impacts, and the above explains why DP ranks higher than MP, UP, and EoLP.
All of the RO membrane desalination system life cycle phases rely on each other, although the criticality or importance of the phases is different. The design phase (DP) specifies or determines the manufacturing phase requirements and constraints, including the materials to use and how the system needs to be manufactured and operated (i.e., part of use). A well-designed system for circularity can minimize costs, reduce waste, and promote sustainability. Moreover, the design determines what material to select, use, how the various parts of a system need to be assembled and disassembled, how they work together, what energy sources to use, and much more.
The manufacturing phase (MP) ensures the RO membrane desalination system is built or constructed to the design specifications and quality, bringing the design into reality. A well-executed manufacturing RO membrane desalination system guarantees operating efficiently and safely, leading to minimizing costs, reducing waste, and promoting circularity and sustainability.
The use phase (UP) involves actual operation of the RO membrane desalination system to produce the required water for consumption or use. An effectively manufactured system guarantees that the operation will run efficiently and safely, ensuring high uptime, and in the long term, minimizing costs, reducing waste, and promoting sustainability. UP provides useful insights into the operational performance, maintenance needs, and hazards that feed into the end-of-life phase. The end-of-life phase (EoLP) ensures recovery, recycling, safe disposal, and repurposing of the various components or the whole of the RO membrane desalination system. This is crucial for environmental and safety compliance.
The right design will ensure that the system achieves the overarching goal for CE implementation, so long as manufacturing sticks with the design while the system is operated as stipulated by the design and manufacturing requirements. EoLP ensures that materials are cycled back to the system to close the loop. Policies and regulations (PRP) ensure DP, MP, UP, and EoLP are mindful of the various policies and regulations to stay compliant and not infringe while navigating the CE implementing journey.
This suggest an entire CE project broken into phases or stages allows for initial prioritization on the effective ones for maximization while limiting resources, managing complexities, mitigating risk, incremental learning, allocating resources effectively, building confidence, building capacity, effectively engaging stakeholders, building the know-how base, shifting mindset, and in the end, continuously improving along the journey to execute the entire project in phases or stages.
CE systems could be considered a continuum given the interconnectedness, continuous flows in different directions, and regenerative intent. The goal is to keep resources in a continuous cycle of reuse, recycling, and regeneration, mirroring the natural ecosystem where nothing goes to waste. The interconnected loops and flows are such that a disruption or break in one system could have ripple effects throughout an entire continuum or entire system. Regenerative intent requires maintaining the continuum to ensure lasting environmental and economic benefits.
A CE system considered as a continuum is an ideal system and opens the door for continuous improvement and progress. Continuous improvement suggests starting from somewhere, however imperfect, and continuously improving conscientiously. It is the desire not to break CE systems into discrete sections; however, given real-life constraints such as unavailable investment or high initial investment requirements, gaining expertise and improving incrementally comes with some initial transient imperfections. In essence, CE implementation is a journey where continuous innovation, adaptation, and collaboration are required to build a more sustainable and robust future. In the foregoing thoughts, CE implementation, decomposed into discrete clusters of CBM, RES, and RSP, provided the opportunity for implementation in phases or stages to allow taking a step-by-step approach to entirely implement a CE project that this article presents.
Implementing CE in phases or stages allows for reducing initial cost, provides the opportunity to gain experience, manage risk, and continually improve towards a perfect system. Moreover, each of the CE implementation clusters, that is, CBM, RES, and RSP, is aligned with R9. For CBM, the design strategy starts with refusing (R0) the unneeded and rethinking (R1) to make things more circular. Reduce (R2) is linked to resource efficiency by minimizing resource consumption. Core to CBM are value retention strategies such as reuse (R3), repair (R4), refurbish (R5), remanufacture (R6), and repurpose (R7), while recycling (R8) and recovering (R9) ensure cycling back to close the loops.
The 9R contribution to RES includes refusing (R0), where eliminating unnecessary resource use upfront, rethinking (R1) to optimizing product design for efficiency, and reduce (R2) to minimizing resource consumption. Extending product life and lowering the need for new resources is accomplished by reuse (R3), repair (R4), refurbish (R5), remanufacture (R6), and repurpose (R7). Recycle (R8) converts waste into new resources and lessens the need for virgin resources, while recovery (R9) allows reclaiming material or energy from waste, optimizing the use of resources. In conclusion, implementation of 9R leads to CE resource efficiency strategies (RES), minimizing resource extraction and consumption, maximizing resource value retention, while reuse closes the material loop to reduce waste and pollution.
9R contributes to RSP by promoting healthier systems while refusing (R0) harmful materials, rethinking (R1) to align designs to natural ecosystem and regenerative principles, while reduce (R2) lessens resource consumption to minimize environmental impacts. Extending lifespan and retaining value is accomplished by reuse (R3), repair (R4), refurbish (R5), remanufacture (R6), and repurpose (R7). Recycling (R8) and recovering (R9) materials close the loop and regenerate natural systems. In conclusion, implementation of 9R leads to CE regenerative sustainability practice by restoring and regenerating natural systems, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health, and creating positive environmental impacts, going beyond sustainability to regeneration.
Implementing any new concept, such as a CE framework, is a continuous journey of improvement and progress, rather than a fixed destination. While the potential benefits of the frameworks are listed, it is critical to acknowledge that some imperfections and challenges exist. Challenges could be technical issues that call for careful implementation, so as not to run into economic viability issues. This requires workaround strategies and plans to assist implementation.
R-ladder strategies involved in the framework have their own practical challenges, despite presenting avenues to assess and implement the circular economy and sustainability. A workaround strategy and planning may be necessary in situations lacking an R-strategy solution, or those with a solution that is too costly or ineffective. Given the evolving and improvement nature of the CE, implementation could be considered as work in progress, where it is prudent to start with the “low-hanging fruit,” that is, technically feasible and economically viable solutions that exist, while continually researching, learning, and improving. Moreover, a phased, staged, or stepwise approach, coupled with careful planning and a focus on economic viability, can help navigate these challenges.
Ultimately, any implementation strategy must weigh technical capabilities and economic viability and their trade-offs. A strategic approach, driven by a team with team members of stakeholders with diverse backgrounds, can help find a middle ground that leverages strengths to navigate challenges.
In the case of rethinking (R1) a design, several innovative designs could result, with different pros and cons. The goal is to select the best design that balances technical feasibility, economic viability, circular economy, and sustainability. While the best designs may initially be associated with higher costs, long-term benefits such as durability, energy efficiency, quality products, new revenue streams, and brand equity can outweigh these costs to drive favorable economics. In the case of refusing (R0), the challenge includes the nonexistence of circular materials or parts. Even if such parts exist, durability and quality concerns or high cost may not satisfy circular requirements such as “extended life in place.” While some “refusing” could be done, it may not be done totally in some cases due to issues. In this event, interim durable non-circular parts, components, or materials that allow satisfying “extended life in place” could be used. This, coupled with improved operational strategies, could lead to “extended life in place” that outweighs cost and is technically feasible, contributing to favorable economic feasibility in the long run. A CE, as pointed out, could be pursued with better workaround strategies to achieve the same end goal. The above rethinking (R1) and refusing (R0) cases buttress the suggestion to begin imperfectly and improve while solutions to challenges become available and at a reasonable cost to drive economic feasibility.
For membranes, especially polymeric membranes, the challenge remanufacturing (R6) faces includes the different membrane types (reverse osmosis (RO), nanofiltration (NF), ultrafiltration (UF), and microfiltration (MF)) with varying levels of complexities and flexibilities, (2) material of construction, and (3) different contaminants or foulants associated with the different membrane applications. These could impact effective cleaning and restoring membrane surfaces and structures, assessment, and addressing material degradation and ensure remanufactured membranes meet performance and quality standards. This could lead to high costs affecting favorable economics. This shows that currently not all the proposed R-strategies are technologically viable at scale, but research is ongoing and aspects of CE implementations are works in progress (WIPs).
9.2 Assessment of RO membrane desalination system life cycle with CE implementation cluster
Table 3 presents the various specific opportunities, what to do, and directions associated with assessing a desalination RO membrane life cycle with CE implementation clusters. Tables 2 and 3 work together. Table 2 provides information on where in an entire CE system could initially prioritize or focus on for maximization in the course of executing an entire circular and sustainability project, if needed.
It is worth noting that regulatory assistance and hindrances exist in the adoption of CE clusters, and the subsequent paragraphs discuss some of the hindrances, assistance, and regulatory evolution opportunities.
CBM-assisting regulations include (1) extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies that hold manufacturers responsible for the waste generated by their products, encouraging them to design more sustainable products and take back used products; (2) waste reduction and recycling target regulations set waste reduction and recycling targets can generate a favorable environment for CBMs, such as PaaS, which support waste reduction and material reuse; (3) green public procurement, where governments can use their purchasing power to boost sustainable products and services, creating the need for CBMs; (4) tax incentives, including green tax incentives, for sustainable businesses or products to encourage companies to adopt CBMs.
CBM-hindering regulations include (1) the existing linear economy-focused regulations, which often prioritize the conventional linear economy business models, making it challenging for CBMs to operate within the current regulatory framework; (2) a lack of clarity on product ownership where regulations may not visibly define product ownership in PaaS models, creating uncertainty and potential liability issues; (3) warranty and liability concerns where regulations may not consider addressing warranty and liability concerns specific to PaaS models, where products are used by multiple customers; (4) taxation and accounting rules that may not adapt to CBMs, making it difficult for companies to correctly account for their financial performance.
CBM-associated hindrances and assistances open the door for regulatory evolution opportunities, such as governments creating adaptive regulatory frameworks that encourage innovation and experimentation with CBMs, governments developing regulations specifically designed to support the development of CBMs, such as PaaS, and stakeholder engagement, where regulators engage with stakeholders such as businesses, NGOs, and consumers, to better understand the needs and challenges of CBMs.
RES-assisting regulations include (1) environmental regulations where standards set for environmental protection, such as air and water quality, can boost companies adopting resource efficiency strategies; (2) waste management regulations, where recycling targets and waste reduction goals can encourage resource efficiency; (3) energy efficiency standards for buildings, appliances, and industrial processes can drive the adoption of energy-efficient technologies; (4) green tax incentives for investments in resource-efficient technologies or practices can encourage companies to adopt resource efficiency strategies.
RES-hindering regulations include (1) existing linear economy-focused regulations that often prioritize conventional linear economy practices, making it challenging for companies to adopt resource efficiency strategies; (2) a lack of clear definitions and standards, making it difficult for companies to understand and comply with requirements; (3) inadequate enforcement of existing regulations, creating an uneven playing field, where companies that invest in resource efficiency are at a competitive disadvantage; (4) regulatory barriers to innovation where regulations are not designed to accommodate or make room for new technologies or innovative practices, impeding the adoption of resource efficiency strategies.
RES-associated hinderances and assistances open the door for regulatory evolution opportunities such as (1) governments creating integrated regulatory frameworks that promote resource efficiency across multiple sectors and industries; (2) regulations focusing on performance-based outcomes, such as energy efficiency or waste reduction, rather than prescriptive requirements; (3) governments providing incentives for companies to develop and adopt innovative resource-efficient technologies and practices, and (4) regulators engaging with stakeholders, including businesses, NGOs, and communities, to better understand the needs and challenges of resource efficiency and develop effective regulations.
RSP-assisting regulations include (1) environmental protection laws protecting ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources can boost regenerative practices; (2) conservation policies endorsing conservation and restoration of ecosystems can support regenerative sustainability; (3) green infrastructure incentives such as green roofs and urban forests, can reassure regenerative practices; (4) sustainable procurement policies promoting sustainable procurement can drive the need for regenerative products and services.
RSP-hindering regulations include (1) existing regulations often prioritize linear economy practices, making it challenging for regenerative practices to compete; (2) a lack of regenerative-specific regulations to address regenerative practices specifically, leading to uncertainty and barriers to adoption; (3) inadequate enforcement of environmental regulations can destabilize efforts to implement regenerative practices; (4) existing regulations may not accommodate or make room for new technologies or innovative regenerative practices, impeding their adoption.
RSP-associated hindrances and assistances open the door for regulatory evolution opportunities, such as (1) governments advancing policies specifically supportive of regenerative practices, such as ecosystem restoration and biodegradable materials, (2) regulations integrating systems thinking, considering the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic systems, (3) governments offering incentives for companies to develop and adopt regenerative technologies and practices, and (4) regulators bodies involving stakeholders, including businesses, NGOs, and communities, to better understand the needs and challenges of regenerative sustainability.
10 Conclusion
A wealth of knowledge on CE and sustainability exists; however, the challenge is implementation. This article seeks to provide frameworks with step-by-step practical guidance for implementation. A CE and sustainability implementation is not a destination but a journey with continuous improvements and progress, given that it is prone to imperfections, technical barriers, and economic viability challenges, where workaround plans and strategies, trade-offs, and steadfast commitment to succeed are necessary to reap the benefits.
These frameworks assist in bridging the gap between theory and practice and make it easier for practitioners and organizations to take that crucial first step towards CE implementation while gradually improving to execute an entire CE and sustainability project. One part of the framework involves ranking life cycle phases with the R-ladder strategy or R-strategy to determine the initial point or phase to prioritize and maximize CE implementation to reduce some initiation challenges, while the other part requires assessing the phases with the CE implementation clusters, laying out the various opportunities.
While the framework works as expected, it is important to point out that inherent issues with some of the R-ladder strategies or R-strategies exist, such as scalability, nonexistent technology, and economic viability issues, which implementation requires being circumspect of economic viability. Moreover, CBM, RES, and RSP could be assisted or hindered by existing laws, policies, practices, and regulations. At the same time, the hindrance opens the door for advocating, engagement with regulators, and training to drive CE and sustainability smooth implementations.
The frameworks applied to the RO membrane desalination system life cycle phases trend, according to CE and sustainability priority, in the order of DP > MP > UP > EoLP. Moreover, DP, MP, UP, and EoLP assessed with CBM, RES, and RSP laid out a bird’s-eye plan to visualize the various opportunities, areas to focus or improve, and associated policies and regulations to comply with and/or take advantage of for maximization and optimization.
This article shows the numerous opportunities that exist for the RO membrane desalination industry as well as the membrane industry as a whole to implement a circular economy, given the associated economic, social, and environmental benefits.
The concept presented here shows how industries could adopt the frameworks to assess and implement CE and sustainability projects for the benefits, while saving the earth and its inhabitants from environmental impacts.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ARA-M: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Software, Conceptualization, Validation, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdelmeguid, A., Afy-Shararah, M., and Salonitis, K. (2024). Towards circular fashion: management strategies promoting circular behaviour along the value chain. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 48, 143–156. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2024.05.010
Acaroglu, L. (2025). Design for circularity: principles for success. Disruptive Design. Available online at: https://medium.com/disruptive-design/design-for-circularity-3-principles-for-success-6866192a7f40#:∼:text=The%20significant%20difference%20is%20that,ve%20detailed%20in%20this%20article (Accessed March 20, 2025).
Agrawal, K., and Bhat, A. R. (2025). Advances in 3D printing with eco-friendly materials: a sustainable approach to manufacturing. RSC Sustain. 3, 2582–2604. doi:10.1039/D4SU00718B
Alcayaga, A., Wiener, M., and Hansen, E. G. (2019). Towards a framework of smart-circular systems: an integrative literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 221, 622–634. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.085
Alivojvodic, V., and Kokalj, F. (2024). “Redefining waste: R-strategies and metrics as a framework for driving progress of circular economy performance,” in New trends in engineering research 2024. CNNTech 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Editors N. Mitrovic, G. Mladenovic, and A. Mitrovic (Cham: Springer), 1216, 75–91. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-78635-8_9
Anim-Mensah, A. R. (2007). Evaluation of solvent resistant nano-filtration (SRNF) membranes for small-molecule purification and recovery of polar aprotic solvents for Re-use. Dissertation/doctorate Theis. Cincinnati (OH): University of Cincinnati. Available online at: http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=ucin1195148766.
Anim-Mensah, A. R. (2025). Pressure-driven polymeric membrane performance prediction, new membrane dimensionless number, and considerations for effective membrane design, selection, testing, and operation. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 3, 1454589. doi:10.3389/frmst.2024.1454589
Anim-Mensah, A., Drouiche, N., and Boulaiche, W. (2024). Assessment of the economic viability, environmental, and social impacts of green hydrogen production: an Algerian case study. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 3, 1382651. doi:10.3389/frmst.2024.1382651
Arruda, E. H., Melatto, R. A. P. B., Levy, W., and Conti, D. de M. (2021). Circular economy: a brief literature review (2015–2020). Sust. Ops Comp. 2, 79–86. doi:10.1016/j.susoc.2021.05.001
Ávila-Gutiérrez, M. J., Martín-Gómez, A., Aguayo-González, F., and Córdoba-Roldán, A. (2019). Standardization framework for sustainability from circular economy 4.0. Sustainability 11 (22), 6490. doi:10.3390/su11226490
Awerbuch, L., Pearce, G., Bartels, C., Mickley, M., and Voutchkov, N. (2006). “The guidebook to membrane desalination technology,”. Editor M. Wilf Balaban Desalination Publications. Available online at: https://www.desline.com/WilfBookIcomplete.pdf (Accessed March 30, 2025).
Aydin, D., Gübbük, İ. H., and Ersöz, M. (2023). Recent advances and applications of nanostructured membranes in water purification. Turk J. Chem. 48 (1), 1–20. doi:10.55730/1300-0527.3635
Bal, A., and Badurdeen, F. (2022). A simulation-based optimization approach for network design: the circular economy perspective. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 30, 761–775. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.033
Barros, M. V., Salvador, R., do Prado, G. F., de Francisco, A. C., and Piekarskli, C. M. (2021). Circular economy as a driver to sustainable businesses. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2, 100006. doi:10.1016/j.cesys.2020.100006
BOI (2025). 10 circular business model examples. Board of Innovation BOI. Available online at: https://www.boardofinnovation.com/blog/circular-business-model-examples/ (Accessed March 23, 2025).
Bong, C. P. C., Fan, Y. V., Lee, C. T., and Klemeš, J. J. (2022). Process analysis and optimisation for a sustainable circular economy. Clean. Eng. Tech. 11, 100578. doi:10.1016/j.clet.2022.100578
Boyer, R. H. W., Hunka, A. D., Linder, M., Whalen, K. A., and Habibi, S. (2021). Product labels for the circular economy: are customers willing to pay for circular? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 27, 61–71. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2020.10.010
Cairone, S., Hasan, S. W., Choo, K.-H., Lekkas, D. F., Fortunato, L., Zorpas, A. A., et al. (2024). Revolutionizing wastewater treatment toward circular economy and carbon neutrality goals: pioneering sustainable and efficient solutions for automation and advanced process control with smart and cutting-edge technologies. J. Water Proc. Eng. 63, 105486. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.105486
Čamaj, J., Bulková, Z., and Gašparík, J. (2025). Material flow optimization as a tool for improving logistics processes in the company. Appl. Sci. 15 (6), 3116. doi:10.3390/app15063116
Chenavaz, R. Y., and Dimitrov, S. (2024). From waste to wealth: policies to promote the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 443, 141086. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141086
Chiandussi, G., Codegone, M., Ferrero, S., and Varesio, F. E. (2012). Comparison of multi-objective optimization methodologies for engineering applications. Comput. Math. Appl. 63 (5), 912–942. doi:10.1016/j.camwa.2011.11.057
Chrispim, M. C., Mattsson, M., and Ulvenblad, P. (2023). The underrepresented key elements of circular economy: a critical review of assessment tools and a guide for action. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 3, 539–558. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2022.11.019
Corona, B., Shen, L., Reike, D., Carreón, J. R., and Worrell, E. (2019). Towards sustainable development through the circular economy—A review and critical assessment on current circularity metrics. Res., Conserv. Recycl. 151, 104498. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104498
Courtney, S. (2021). EIA projects nearly 50% increase in world energy use by 2050, led by growth in renewables. Today In Energy. Available online at: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=49876 (Accessed March 2, 2025).
Credence Research (2024). Reserve osmosis membrane market. Available online at: https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/reverse-osmosis-membrane-market (Accessed July 8, 2025).
Dagdia, Z. C., and Mirchev, M. (2020). “When evolutionary computing meets Astro- and geoinformatics,” in Knowledge discovery in big data from astronomy and Earth observation. Editors P. Škoda, and F. Adam (Elsevier), 283–306. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-819154-5.00026-6
Data Bridge Market Research (2025). Global reverse osmosis RO membrane market size, share, and trends analysis report – industry overview and forecast to 2032. Available online at: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-ro-membrane-filtration-market (Accessed July 1, 2025).
Davis, R. H. (2019). “Microfiltration in pharmaceutics and biotechnology,” in Current trends and future developments on (Bio-) membranes. Editors A. Basile, and C. Charcosset (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 29–67. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-813606-5.00002-6
Del Villar, A., Melgarejo, J., García-López, M., Fernández-Aracil, P., and Montano, B. (2023). The economic value of the extracted elements from brine concentrates of Spanish desalination plants. Desal 560, 116678. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2023.116678
Dereci, U., and Tuzkaya, G. (2024). An explainable artificial intelligence model for predictive maintenance and spare parts optimization. Supply Chain Anal. 8, 100078. doi:10.1016/j.sca.2024.100078
Dey, P. K., Malesios, C., Chowdhury, S., Saha, K., Pawan Budhwar, P., and De, D. (2022). Adoption of circular economy practices in small and medium-sized enterprises: evidence from Europe. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 248, 108496. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2022.108496
Dolgui, A., Ivanov, D., Brintrup, A., Chen, W., Shen (Jerry), B., and Paul, S. K. (2024). Design and management of energy-efficient and energy-resilient supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Res. 62 (24), 8921–8923. doi:10.1080/00207543.2024.2408904
El-Halwagi, M. M. (2006). Overview of optimization. Process Syst. Eng. 7, 285–314. doi:10.1016/S1874-5970(06)80012-3
Eldein, S. A. S., and Sobhi, N. (2019). Waste reduction by linear programing optimizing. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 610, 01207. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/610/1/012079
Ellen MacArthur Foundation (2015). Towards a circular economy: business rationale for an accelerated transition. Available online at: https://kidv.nl/media/rapportages/towards_a_circular_economy.pdf?1.2.1 (Accessed March 14, 2025).
Ellen MacArthur Foundation (2019). Circular economy in detail. Available online at: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/the-circular-economy-in-detail-deep-dive (Accessed July 26, 2025).
Elzinga, R., Reike, D., Negro, S. O., and Boon, W. P. C. (2020). Consumer acceptance of circular business models. J. Clean. Prod. 254, 119988. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.119988
Evolveable Consulting (2024). The R-Ladder: a stepping stone to circular economy. Available online at: https://evolveable.com/the-r-ladder-a-stepping-stone-to-circular-economy/ (Accessed July 15, 2025).
Ezugbe, E. O., and Rathilal, S. (2020). Membrane technologies in wastewater treatment: a review. Membr. (Basel) 10 (5), 89. doi:10.3390/membranes10050089
Farley, J. (2012). Ecosystem services: the economics debate. Ecosyst. Serv. 1 (1), 40–49. doi:10.1016/j.ecoser.2012.07.002
Ferriz-Papi, J. A., Lee, A., and Alhawamdeh, M. (2024). Examining the challenges for circular economy implementation in construction and demolition waste management: a comprehensive review using systematic methods. Buildings 14 (5), 1237. doi:10.3390/buildings14051237
Figge, F., Thorpe, A., and Gutberlet, M. (2023). Definitions of the circular economy: circularity matters. Ecol. Econ. 208, 107823. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2023.107823
Fortunato, L. (2020). Fouling monitoring in membrane filtration systems. IntechOpen. doi:10.5772/intechopen.88464
Galvão, A. G., De Nadae, J., Clemente, D., Chinen, G., and De Carvalho, M. (2018). Circular economy: overview of barriers. Procedia CIRP 73, 79–85. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2018.04.011
Glover, C. J., Phillips, J. A., Marchand, E. A., and Hiibel, S. R. (2022). Modeling and life cycle assessment of a membrane bioreactor–membrane distillation wastewater treatment system for potable reuse. Separations 9 (6), 151. doi:10.3390/separations9060151
Gotadki, R. (2025). Membrane filtration market overview. Available online at: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/membrane-filtration-market-24478 (Accessed March 12, 2025).
Gu, D., Andreev, K., and Dupre, M. E. (2021). Major trends in population growth around the world. China CDC Wkly. 3 (28), 604–613. doi:10.46234/ccdcw2021.160
Gurreri, L., Tamburini, A., Cipollina, A., and Micale, G. (2020). Electrodialysis applications in wastewater treatment for environmental protection and resources recovery: a systematic review on progress and perspectives. Membr. (Basel) 9, 146. doi:10.3390/membranes10070146
Haessler, P. (2020). Strategic decisions between short-term profit and sustainability. Admin. Sci. 10 (3), 63. doi:10.3390/admsci10030063
Hariyani, D., Hariyani, P., Sanjeev Mishra, S., and Sharma, M. K. (2024). Leveraging digital technologies for advancing circular economy practices and enhancing life cycle analysis: a systematic literature review. Waste Manag. Bull. 2 (3), 69–83. doi:10.1016/j.wmb.2024.06.007
Hidalgo-Crespo, J., Riel, A., Duberg, J. V., Bunodiere, A., and Golinska-Dawson, P. (2024). An exploratory study for product-as-a-service (PaaS) offers development for electrical and electronic equipment. Procedia CIRP 122, 521–526. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2024.01.076
Hosseinzadeh, M., Mehrnia, M. R., and Mostoufi, N. (2013). Experimental study and modeling of fouling in immersed membrane bioreactor operating in constant pressure filtration. Math. Problems Eng 2013, 1–7. doi:10.1155/2013/456143
Hung, M. (2025). AI has redefined supply chain efficiency and traceability. It’s only starting. RFID Journal. Available online at: https://www.rfidjournal.com/expert-views/ai-has-redefined-supply-chain-efficiency-and-traceability-its-only-starting/223795/(Accessed July 14, 2025).
Hussain, J., Lee, C.-C., and Lev, B. (2025). Optimizing AI-based emission reduction efficiency and subsidies in supply chain management: a sensitivity-based approach with duopoly game dynamics. J. Clean. Prod. 494, 144991. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.144991
Iacovidou, E., Hahladakis, J. N., and Purnell, P. (2021). A systems thinking approach to understanding the challenges of achieving the circular economy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 24785–24806. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-11725-9
Ilyas, A., and Vankelecom, I. F. J. (2023). Designing sustainable membrane-based water treatment via fouling control through membrane interface engineering and process developments. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 312, 102834. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2023.102834
Islam, M. T., and Huda, N. (2019). Material flow analysis (MFA) as a strategic tool in E-waste management: applications, trends and future directions. J. Environ. Manag. 244, 344–361. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.062
Itanola, M., Griffiths, P., and Motawa, I. (2024). Closing the loop in building services: a systematic review of circular economy applications. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 0 (0), 293–315. doi:10.1177/01436244241296762
Jabbour, C. J. C., Jabbour, A. B. L., Sarkis, J., and Filho, M. G. (2019). Unlocking the circular economy through new business models based on large-scale data: an integrative framework and research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 144, 546–552. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2017.09.010
Jensen, H. H. (2022). 5 circular economy business model that offer competitive advantage. Geneva, Switzerland: World Economic Forum. Available online at: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2022/01/5-circular-economy-business-models-competitive-advantage/.
Judd, S. (2003). “Membrane technology,” in Membranes for industrial wastewater recovery and Re-use. Editors S. Judd, and B. Jefferson (London United Kingdom: Elsevier Science), 13–74. doi:10.1016/B978-185617389-6/50003-5
Kansheba, J. M., Fubah, C. N., and Acikdilli, G. (2025). Circular economy practices in international business: what do we know and where are we heading? Bus. Strategy Environ. 34 (1), 296–315. doi:10.1002/bse.3978
Khan, S. A. R., Zia-Ul-Haq, H. M., Ponce, P., and Janjua, L. (2023). Re-investigating the impact of non-renewable and renewable energy on environmental quality: a roadmap towards sustainable development. Res. Policy 81, 103411. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103411
Khanna, M., Gusmerotti, N. M., and Frey, M. (2022). The relevance of the circular economy for climate change: an exploration through the theory of change approach. Sustainability 14 (7), 3991. doi:10.3390/su14073991
Khanzada, N. K., Al-Juboori, R. A., Khatri, M., Ahmed, F. E., Ibrahim, Y., and Hilal, N. (2024). Sustainability in membrane technology: membrane recycling and fabrication using recycled waste. Membr. (Basel). 14 (2), 52. doi:10.3390/membranes14020052
Kirchherr, J., Reike, D., and Hekkert, M. (2017). Conceptualizing the circular economy: an analysis of 114 definitions. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 127, 221–232. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.005
Kirchherr, J., Yang, N.-H. N., Schulze-Spüntrup, F., Heerink, M. J., and Hartley, K. (2023). Conceptualizing the circular economy (revisited): an analysis of 221 definitions. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 194, 107001. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.107001
Knäble, D., Puente, E. Q., Pérez-Cornejo, C., and Baumgärtler, T. (2022). The impact of the circular economy on sustainable development: a European panel data approach. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 34, 233–243. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2022.09.016
Kochanski, M., Lotz, M. T., and Korczak, K. (2024). Benchmarking circular economy measures in buildings along the 11R framework: a systematic review of quantified impacts on material use, energy consumption, GHG emissions, and costs. J. Clean. Prod. 485 (144337), 144337–146526. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144337
König, K., Mathieu, J., and Vielhaber, M. (2024). Resource conservation by means of lightweight design and design for circularity - a concept for decision making in the early phase of product development. Res., Conserv. Recycl. 201, 107331. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.107331
Korhonen, J., Honkasalo, A., and Seppälä, J. (2018). Circular economy: the concept and its limitations. Ecol. Econs. 143, 37–46. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.06.041
Koros, W. J., Ma, Y. H., and Shimidzu, T. (1996). Terminology for membranes and membrane processes (IUPAC Recommendations 1996). Pure Appl. Chem. 68 (7), 1479–1489. doi:10.1351/pac199668071479
Kruczek, M., Jąderko-Skubis, K., Markowska, M., Zgórska, A., and Białowąs, M. (2025). Circularity potential identification for new bio-materials using material flow analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 982, 179649. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2025.179649
Kumar, S., Sakagami, K., and Lee, H. P. (2025). Beyond sustainability: the role of regenerative design in optimizing indoor environmental quality. Sustainability 17 (6), 2342. doi:10.3390/su17062342
Kümmerer, K., Clark, J. H., and Zuin, V. G. (2020). Rethinking chemistry for a circular economy. Science 367 (6476), 369–370. doi:10.1126/science.aba4979
Landaburu-Aguirre, J., and Molina, S. (2023). Circular economy in membrane technology. Membr. (Basel) 8, 784. doi:10.3390/membranes13090784
Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A., Landaburu-Aguirre, J., Senán-Salinas, J., Ortiz, J. M., and Molina, S. (2022). Thin film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membrane technology towards a circular economy. Membr 12 (9), 864. doi:10.3390/membranes12090864
Liang, Y., and Knauer, K. M. (2023). Trends and future outlooks in circularity of desalination membrane materials. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2, 1169158. doi:10.3389/frmst.2023.1169158
Lieder, M., and Rashid, A. (2016). Towards circular economy implementation: a comprehensive review in context of manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 115, 36–51. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.042
Liu, Z., Wan, M.-D., Zheng, X.-X., and Koh, S. C. L. (2022). Fairness concerns and extended producer responsibility transmission in a circular supply chain. Ind. Mark. Manag. 102, 216–228. doi:10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.01.014
Liu, M., Zhu, G., and Tian, Y. (2024). The historical evolution and research trends of life cycle assessment. Green Carbon 2 (4), 425–437. doi:10.1016/j.greenca.2024.08.003
Lopez, K. P., Wang, R., Hjelvik, E. A., Lin, S., and Straub, A. P. (2023). Toward a universal framework for evaluating transport resistances and driving forces in membrane-based desalination processes. Sci. Adv. 4 (1), 9. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade0413
Mady, K., Anwar, I., and Abdelkareem, R. S. (2024). Nexus between regulatory pressure, eco-friendly product demand and sustainable competitive advantage of manufacturing small and medium-sized enterprises: the mediating role of eco-innovation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-05096-1
Malooly, L., and Daphne, T. (2023). R-Strategy for a circular economy, circularise. Available online at: https://www.circularise.com/blogs/r-strategies-for-a-circular-economy (Accessed July 19, 2025).
McKelvey, F., and Neves, J. (2021). Introduction: optimization and its discontents. Rev. Comm. 21 (2), 95–112. doi:10.1080/15358593.2021.1936143
Mengesha, A., and Sahu, O. (2022). Sustainability of membrane separation technology on groundwater reverse osmosis process. Clean. Eng. Tech 7, 100457. doi:10.1016/j.clet.2022.100457
Miller, S., Shemer, H., and Semiat, R. (2015). Energy and environmental issues in desalination. Desalination 366, 2–8. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2014.11.034
Morgante, C., Vassallo, F., Xevgenos, D., Cipollina, A., Micari, M., Tamburini, A., et al. (2022). Valorisation of SWRO brines in a remote island through a circular approach: techno-economic analysis and perspectives. Desal 542, 116005. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2022.116005
Muñoz, S., Hosseini, M. R., and Crawford, R. H. (2024). Towards a holistic assessment of circular economy strategies: the 9R circularity index. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 47, 400–412. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2024.04.015
Negrete-Cardoso, M., Rosano-Ortega, G., Álvarez-Aros, E. L., Tavera-Cortés, M. E., Vega-Lebrún, C. A., and Sánchez-Ruíz, F. J. (2022). Circular economy strategy and waste management: a bibliometric analysis in its contribution to sustainable development, toward a post-COVID-19 era. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 29 (41), 61729–61746. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-18703-3
Ntsondé, J., and Aggeri, F. (2021). Stimulating innovation and creating new markets – the potential of circular public procurement. J. Clean. Prod. 308, 127303. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127303
Nygaard, A. (2023). Is sustainable certification’s ability to combat greenwashing trustworthy? Front. Sustain 4, 1188069. doi:10.3389/frsus.2023.1188069
Oghazi, P., and Mostaghel, R. (2018). Circular business model challenges and lessons learned - an industrial perspective. Sustainability 10 (3), 739. doi:10.3390/su10030739
Olawade, D. B., Fapohunda, O., Wada, O. Z., Usman, S. O., Ige, A. O., Ajisafe, O., et al. (2024). Smart waste management: a paradigm shift enabled by artificial intelligence. Waste Manag. Bull. 2 (2), 244–263. doi:10.1016/j.wmb.2024.05.001
Osman, A. I., Chen, Z., Elgarahy, A. M., Farghali, M., Mohamed, I. M. A., Priya, A., et al. (2024). Membrane technology for energy saving: principles, techniques, applications, challenges, and prospects. Adv. Energy Sust. Res. 5, 2400011. doi:10.1002/aesr.202400011
Ortiz-de-Montellano, C. G- S., Samani, P., and Van der Meer, Y. (2023). How can the circular economy support the advancement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)? A comprehensive analysis. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 40, 352–362. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2023.07.003
Patel, S. K., Lee, B., Westerhoff, P., and Elimelech, M. (2024). The potential of electrodialysis as a cost-effective alternative to reverse osmosis for brackish water desalination. Water Res. 250, 121009. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2023.121009
Piila, N., and Sarja, M. (2024). Extraordinary supply chain disruptions and the circular economy transition in the construction industry – an opportunity within crisis? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 47, 71–86. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2024.03.032
Pilipenets, O., Gunawardena, T., Hui, F. K. P., Mendis, P., and Aye, L. (2025). A novel circular economy framework: assessing process circularity through resource flow and emissions analysis. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 215, 108083. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.108083
Poirier, K., Lotfi, M., Garg, K., Patchigolla, K., Anthony, E. J., Faisal, N. H., et al. (2023). A comprehensive review of pre- and post-treatment approaches to achieve sustainable desalination for different water streams. Desal 566, 116944. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2023.116944
Potting, J., Hekkert, M. P., Worrell, E., and Hanemaaijer, A. (2017). Circular economy: measuring innovation in the product chain. Available online at: https://circulareconomy.pt/en/about-circular-economy/(Accessed July 29, 2025).
Pottinger, S., Geyer, R., Biyani, N., Martinez, C. C., Nathan, N., Morse, M. R., et al. (2024). Pathways to reduce global plastic waste mismanagement and greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. Science 386 (6726), 1168–1173. doi:10.1126/science.adr3837
Precedence Research (2025). Water treatment systems market advancements in sustainable water purification technologies. Available online at: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/water-treatment-systems-market (Accessed July 1, 2025).
Preston, F., Lehne, J., and Wellesley, L. (2019). An inclusive circular economy: priorities for developing countries. Chatham House Royal institute of International Affairs; Energy, Environ. and Res. Dept. Available online at: https://www.chathamhouse.org/sites/default/files/publications/research/2019-05-22-Circular%20Economy.pdf (Accessed March 24, 2025).
Qrenawi, L. I., and Rabah, F. K. J. (2023). Membrane bioreactor (MBR) as a reliable technology for wastewater treatment: review. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 9 (1), 548826. doi:10.22079/jmsr.2022.548826.1532
Rahmah, W., Khoiruddin, K., Wenten, I. G., and Kawi, S. (2024). Advancing carbon capture with bio-inspired membrane materials: a review. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 13, 100318. doi:10.1016/j.ccst.2024.100318
Rajput, S., and Singh, S. P. (2019). Connecting circular economy and industry 4.0. Int. J. Info. Mgt 49, 98–113. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.03.002
Rao, Y. S., Jp, R., Thomas, S. A., Agrawal, D. A. K., Uvaneswaran, S. M., and Hajra, D. V. (2024). Circular economy strategies for resource efficiency and sustainable development in manufacturing industries. South East. Eur. J. Public Health, 14–29. doi:10.70135/seejph.vi.2576
Raut, S., Hossain, N. U. I., Kouhizadeh, M., and Fazio, S. A. (2025). Application of artificial intelligence in circular economy: a critical analysis of the current research. Sustain. Futur. 9, 100784. doi:10.1016/j.sftr.2025.100784
Rehman, U., Gyamfi, S., Rasool, S. F., Ahkar, F., Hussain, K., and Prokop, V. (2023). The nexus between circular economy innovation, market competitiveness, and triple bottom lines efficiencies among SMEs: evidence from emerging economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 122274–122292. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-30956-0
Rejeb, A., Suhaiza, Z., Rejeb, K., Seuring, S., and Treiblmaier, H. (2022). The internet of things and the circular economy: a systematic literature review and research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 350, 131439. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131439
Rinaldi, F. R., Di Bernardino, C., Cram-Martos, V., and Pisani, M. T. (2022). Traceability and transparency: enhancing sustainability and circularity in garment and footwear. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 18 (1), 132–141. doi:10.1080/15487733.2022.2028454
Rizos, V., Behrens, A., Van der Gaast, W., Hofman, E., Ioannou, A., Kafyeke, T., et al. (2016). Implementation of circular economy business models by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): barriers and enablers. Sustainability 8 (11), 1212. doi:10.3390/su8111212
Rosário, A. T., Lopes, P., and Rosário, F. S. (2024). Sustainability and the circular economy business development. Sustainability 16 (14), 6092. doi:10.3390/su16146092
Rosenboom, J. G., Langer, R., and Traverso, G. (2022). Bioplastics for a circular economy. Nat. Rev. Mater 7, 117–137. doi:10.1038/s41578-021-00407-8
Sakib, M. N., Kabir, G., and Ali, S. M. (2024). A life cycle analysis approach to evaluate sustainable strategies in the furniture manufacturing industry. Sci. Total Environ. 907, 167611. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167611
Scarpellini, S., Portillo-Tarragona, P., Aranda-Usón, A., and Llena-Macarulla, F. (2019). Definition and measurement of the circular economy’s regional impact. J. Environ. Plan. Mgt 62 (13), 2211–2237. doi:10.1080/09640568.2018.1537974
Schröder, P., and Barrie, J. (2024). How the circular economy can revive the sustainable development goals, priorities for immediate global action, and a policy blueprint for the transition to 2050, environment and society centre. Available online at: https://www.chathamhouse.org/sites/default/files/2024-09/2024-09-19-how-the-circular-economy-can-revive-the-sdgs-schröder-barrie.pdf (Accessed March 26, 2025).
Sebiru (2025). The cell membrane: a selective barrier for cells. Elsevier.blog. Available online at: https://elsevier.blog/cell-membrane-selective-barrier/(Accessed April 13, 2025).
Seljak, T., Baleta, J., and Mikulčić, H. (2023). Integration of energy systems, circular economy and efficiency measures. Clean. Chem. Eng. 5, 100088. doi:10.1016/j.clce.2022.100088
Selviaridis, K., and Wynstra, F. (2014). Performance-based contracting: a literature review and future research directions. Int. J. Prod. Res. 53 (12), 3505–3540. doi:10.1080/00207543.2014.978031
Senán-Salinas, J., Blanco, A., Garcia-Pacheco, R., Landaburu-Aguirre, J., and Garcia-Calvo, E. (2021). Prospective life cycle assessment and economic analysis of direct recycling of end-of-life reverse osmosis membranes based on geographic information systems. J. Clean. Prod. 282, 124400. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124400
Singh, A. K., Kumar, V. R. P., Irfan, M., Mohandes, S. R., and Awan, U. (2023). Revealing the barriers of blockchain technology for supply chain transparency and sustainability in the construction industry: an application of pythagorean FAHP methods. Sustainability 15 (13), 10681. doi:10.3390/su151310681
Smol, M., Marcinek, P., and Duda, J. (2024). Circular business models (CBMs) in environmental management -analysis of definitions, typologies and methods of creation in organizations. Sustainability 16 (3), 1209. doi:10.3390/su16031209
Soumbati, Y., Bouatou, I., Abushaban, A., Belmabkhout, Y., and Necibi, C. M. (2025). Review of membrane distillation for desalination applications: advanced modeling, specific energy consumption, and water production cost. J. Water Proc. Eng. 71, 107296. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2025.107296
Sousa-Zomer, T. T., Magalhães, L., Zancul, E., and Cauchick-Miguel, P. A. (2018). Exploring the challenges for circular business implementation in manufacturing companies: an empirical investigation of a pay-per-use service provider. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 135, 3–13. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.033
Superti, V., Houmani, C., and Binder, C. R. (2021). A systemic framework to categorize circular economy interventions: an application to the construction and demolition sector. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 173, 105711. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105711
Sustainability Directory (2025). What is the difference between sustainability and circularity? Available online at: https://sustainability-directory.com/question/what-is-the-difference-between-sustainability-and-circularity/(Accessed March 24, 2025).
Takacs, F., Brunner, D., and Frankenberger, K. (2022). Barriers to a circular economy in small- and medium-sized enterprises and their integration in a sustainable strategic management framework. J. Clean. Prod. 362, 132227. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132227
Tariq, A. H., Kazmi, S. A. A., Hassan, M., Ali, S. A. M., and Anwar, M. (2024). Analysis of fuel cell integration with hybrid microgrid systems for clean energy: a comparative review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 52 D, 1005–1034. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.07.238
The Debrand Team (2024). Sustainability vs circularity: what’s the difference. Available online at: https://debrand.ca/blog/sustainability-vs-circularity/(Accessed February 5, 2025).
Ting, L. S., Zailani, S., Sidek, N. Z. M., and Shaharudin, M. R. (2023). Motivators and barriers of circular economy business model adoption and its impact on sustainable production in Malaysia. Environ. Dev. Sustain 23, 17551–17578. doi:10.1007/s10668-023-03350-6
UNEP (2024). Global waste management outlook report. Available online at: https://www.unep.org/resources/global-waste-management-outlook-2024 (Accessed March 2, 2025).
Upalkar, S. (2025). Circular economy in engineering: designing for recyclability. Cureus Part of SpingerNature. Available online at: https://www.cureusjournals.com/blog/circular-economy-in-engineering-designing-for-recyclability (Accessed March 18, 2025).
Vadakedath, S., and Kandi, V. (2017). Dialysis: a review of the mechanisms underlying complications in the management of chronic renal failure. Cureus 9 (8), e1603. doi:10.7759/cureus.1603
Valencia, M., Bocken, N., Loaiza, C., and De Jaeger, S. (2023). The social contribution of the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 408, 137082. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137082
Van Erkelens, A. M., Van Bommel, K., Quintelier, K. J. P., Thompson, N. A., and Verver, M. (2025). Implementing circular business models in linear economic systems: the case of a new venture addressing the embeddedness paradox. J. Clean. Prod. 496, 145073. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.145073
Vane, L. M. (2022). Effect of membrane performance variability with temperature and feed composition on pervaporation and vapor permeation system design for solvent drying. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 97 (10), 2706–2719. doi:10.1002/jctb.7161
Vasudeva, J. S., Bhargava, S., and Sharma, D. K. (2022). “Optimization techniques and computational intelligence with emerging trends in cloud computing and internet of things, Chapter 4,” Advances in biomedical information, applications of computational intelligence in multi-disciplinary research. Editors A. A. Elngar, R. Chowdhury, M. Elhoseny, and V. E. Balas Cambridge, MA: Elsevier, Academic Press, 47–66. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-823978-0.00012-5
Velenturf, A. P. M., and Purnell, P. (2021). Principles for a sustainable circular economy. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 27, 1437–1457. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2021.02.018
Vermaak, L., Neomagus, H. W. J. P., and Bessarabov, D. G. (2021). Recent advances in membrane-based electrochemical hydrogen separation: a review. Membr 11 (2), 127. doi:10.3390/membranes11020127
Vinayagam, V., Sikarwar, D., Das, S., and Pugazhendhi, A. (2024). Envisioning the innovative approaches to achieve circular economy in the water and wastewater sector. Environ. Res. 241, 117663. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.117663
Walaweg, D. D., Wickramasingha, W. S. B., Sandaruwan, R. D. C., Udayanga, S., Perera, I. J. J. U. N., Nawalage, N. M. S. K., et al. (2024). Electrodialysis reversal (EDR) technology: a viable solution for addressing water quality challenges in the dry zone, Sri Lanka. Water Pract. Technol. 19 (10), 3972–3986. doi:10.2166/wpt.2024.243
Walker, A. M., Opferkuch, K., Lindgreen, E. R., Raggi, A., Simboli, A., Vermeulen, W. J., et al. (2022). What is the relation between circular economy and sustainability? Answers from frontrunner companies engaged with circular economy practices. Circ. Econ. Sust. 2, 731–758. doi:10.1007/s43615-021-00064-7
Wang, Y., Li, S., Sinnah, Z. A. B., Ghandour, R., Khan, M. N., and Ali, H. E. (2024). Optimizing energy efficiency and emission reduction: leveraging the power of machine learning in an integrated compressed air energy storage-solid oxide fuel cell system. Energy 313, 133962. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.133962
Wang, Y., He, Y., and Gao, X. (2025). Synergizing renewable energy and circular economy strategies: pioneering pathways to environmental sustainability. Sustainability 17 (5), 1801. doi:10.3390/su17051801
Wijayasundara, M., Polonsky, M., Noel, W., and Vocino, A. (2022). Green procurement for a circular economy: what influences purchasing of products with recycled material and recovered content by public sector organisations? J. Clean. Prod. 377, 133917. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133917
Ye, Y., Zhao, L., Liu, Z., Wang, Z., and Niu, Q. J. (2024). Recent advances in novel membranes for improved anti-wettability in membrane distillation: a mini review. Desal 571, 117066. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2023.117066
Zapata-Sierra, A., Cascajares, M., Alcayde, A., and Manzano-Agugliaro, F. (2021). Worldwide research trends on desalination. Desal 519, 115305. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2021.115305
Zejjari, I., and Benhayoun, I. (2024). The use of artificial intelligence to advance sustainable supply chain: retrospective and future avenues explored through bibliometric analysis. Discov. Sustain. 5, 174. doi:10.1007/s43621-024-00364-6
Zeng, X. (2024). A review on design of sustainable advanced materials by using artificial intelligence. Adv. Mater. Sustain. Manuf. 1, 10006. doi:10.35534/amsm.2024.10006
Zeng, Z., Lu, D., Hu, Y., Augenbroe, G., and Chen, J. (2023). A comprehensive optimization framework for the design of high-performance building systems. J. Build. Eng. 65, 105709. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2022.105709
Zhang, J., Chua, H. C., Zhou, J., and Fane, A. G. (2006). Factors affecting the membrane performance in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 284 (1–2), 54–66. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2006.06.022
Zhang, X., Fan, M., Li, W., Wu, C., Han, X., Zhong, S., et al. (2020). Application and modeling of pressure-concentration double-driven diffusion dialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 595, 117478. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117478
Zhang, D., Huang, X., Wen, Y., Trivedi, P., and Joghee, S. (2021). Sustainable circular business model for transparency and uncertainty reduction in supply chain management. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 16 (4), 959–975. doi:10.3390/jtaer16040054
Zhang, D., Frei, R., Wills, G., Gerding, E., Bayer, S., and Senyo, P. K. (2023). Strategies and practices to reduce the ecological impact of product returns: an environmental sustainability framework for multichannel retail. Bus. Strategy Environ 32 (7), 4636–4661. doi:10.1002/bse.3385
Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Chen, X., Yu, X., Li, W., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Sustainable bioplastics derived from renewable natural resources for food packaging. Matter 6 (1), 97–127. doi:10.1016/j.matt.2022.11.006
Keywords: circular economy implementation, circular economy implementation framework, circular economy implementation guidance, circular business model, resource efficiency strategies, regenerative sustainability practices, R-ladder strategies application, reverse osmosis membrane desalination
Citation: Anim-Mensah AR (2025) Circular economy (CE) implementation framework development and application to reverse osmosis (RO) membrane desalination systems. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 4:1604508. doi: 10.3389/frmst.2025.1604508
Received: 02 April 2025; Accepted: 30 September 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Kibrom Alebel Gebru, Adigrat University, EthiopiaReviewed by:
Bhaumik Sutariya, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), IndiaYunxia Hu, Tianjin Polytechnic University, China
Yawei Du, Hebei University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Anim-Mensah. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Alexander R. Anim-Mensah, aTJpbWVnYWh1YkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Alexander R. Anim-Mensah
Alexander R. Anim-Mensah