- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shaoxing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zhejiang, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Quzhou Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Quzhou, China
Nosocomial outbreaks caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) strains are rapidly emerging worldwide and are a cause for concern. In this study, a phylogenetic tree of 18 A. baumannii strains collected from a teaching hospital in China was constructed to explore the genetic relationship in the context of genomic insights. The study also aimed to explore the relationship among the strains and to assess the potential spread within the teaching hospital. All CRAB strains were collected from 17 patients, with the majority obtained from sputum samples (55.56%, 10/18). Moreover, 61.11% (11/18) of the CRAB strains were collected from the intensive care unit (ICU). Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) was performed using the Illumina and Oxford Nanopore platforms, and the bioinformatic analysis was subsequently performed. Based on the Pasteur multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme, 16 A. baumannii strains were classified as sequence type 2 (ST2). The remaining two A. baumannii strains belonged to two rare sequence types (STs), namely ST34 and ST23, respectively. KL and OCL analysis showed that the majority of the strains (61.11%, 11/18) contained KL7. Whole-genome sequencing revealed that 16 CRAB strains were OXA-23 producers, while the remaining two strains carried blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-72. Genetic structure analysis showed the context of blaNDM-1 was ISAba14-aph(3′)-VI-ISAba125-blaNDM-1-ble-MBL. Comparative genomics analysis revealed that 16 CRAB strains (ST2_Pas) had a close genetic relationship, and 8 CRAB strains possessed the same resistance gene profile, with only 1–6 SNPs observed among them. Therefore, there is an urgent need for increased surveillance of both patients and the hospital environment to prevent and control the spread of CRAB.
1 Introduction
Acinetobacter species, including Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Acinetobacter nosocomialis, Acinetobacter pittii, Acinetobacter dijkshoorniae, Acinetobacter lactucae, and Acinetobacter seifertii, are ubiquitous in diverse clinical settings and environments (Wong et al., 2017; Miller and Arias, 2024; Richards et al., 2024). Among these species, A. baumannii is an important opportunistic pathogen that primarily causes healthcare-associated infections, including bloodstream infections (BSIs), pneumonia, and urinary tract infections, especially in immunocompromised patients hospitalized in intensive care units (ICUs) (Harding et al., 2018; Wibberg et al., 2018; Wang S. H. et al., 2024). Carbapenems are usually the first-choice antibiotics recommended for treating serious infections caused by A. baumannii (Mathlouthi et al., 2016). However, outbreaks caused by carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii (CRAB) strains in hospitals are emerging rapidly worldwide and are a growing concern (Ruan et al., 2013).
The primary mechanism by which A. baumannii develops resistance to carbapenems is through the acquisition of genes encoding carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D (blaOXA-23, blaOXA-24, and blaOXA-58) (Doughty et al., 2023) and metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) enzymes, including blaNDM-1, blaIMP, blaVIM, and blaGIM (Bakour et al., 2015). The most commonly acquired class D carbapenemase gene worldwide is blaOXA-23 (Capodimonte et al., 2024; Wang W. et al., 2024). Based on previous studies, the blaOXA-23 gene is usually located in ISAba1-based transposons, namely Tn2006, Tn2008, Tn2009, and the AbaR4-type resistance island (Liu H. et al., 2023). Compared to blaOXA-23, blaNDM-1 is relatively rare. However, some studies from Algeria and Nepal have reported the coexistence of blaOXA-23 and blaNDM-1 genes (Ramoul et al., 2016; Joshi et al., 2017). Moreover, an increasing proportion of the coexistence of blaOXA-23 and blaNDM-1 in CRAB clinical isolates was found in an ICU in Hangzhou, China (Liu et al., 2024). The coexistence of blaOXA-23 and blaNDM-1 increases the resistance levels to carbapenems, resulting in limited treatment options (Liu et al., 2024).
In this study, a phylogenetic tree of A. baumannii strains collected from a teaching hospital in China was constructed to explore the genetic relationship in the context of genomic insights. This study also aimed to explore the relationship between the strains and assess the potential spread within this hospital. More importantly, the plasmid structure of the blaNDM-1 gene in a rare clinical CRAB isolate (belonging to ST34_Pas) was further explored. This study provides a basis for better understanding the characteristics of CRAB strains and supports better treatment strategies for OXA-23 or NDM-1-producing isolates.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial isolation and identification
A total of 18 A. baumannii strains were collected from a teaching hospital in Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, during routine diagnostic analysis from 2020 to 2024. All CRAB isolates were collected without applying specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. Isolate identification to the species level was conducted using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS; Bruker Daltonik GmbH, Bremen, Germany) and confirmed through 16S rRNA sequencing. The sequences of the primers were (27F-5’-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′ and 1492R-5’-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′).
2.2 Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST)
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of the 18 A. baumannii strains were determined using the VITEK 2 compact system with the AST-N335 card. The results were interpreted according to the recommendations outlined in the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) 2021 guidelines. The following antimicrobial agents were investigated in this study: imipenem (IPM), meropenem (MEM), ceftazidime (CAZ), ciprofloxacin (CIP), levofloxacin (LEV), tobramycin (TOB), and polymyxin (PB). In addition, the MIC of cefiderocol (CFDC) was determined using the broth microdilution method in iron-depleted cation-adjusted Mueller–Hinton broth (ID-CAMHB) according to the CLSI guidelines (Liu X. et al., 2023).
2.3 Mating experiments
To determine whether the plasmid carrying blaNDM-1 was transferable, conjugation experiments using E. coli J53 (Sodium azide resistant) as the recipient strain were carried out using the film mating method (Yang et al., 2021). Transconjugants were screened on Mueller–Hinton (MH) agar plates containing sodium azide (100 mg/L) and meropenem (4 mg/L), and the putative transconjugants were confirmed via PCR and MALDI-TOF MS. The putative transconjugants were first identified as E. coli using MALDI-TOF MS and then confirmed to carry the blaNDM-1 gene through PCR (Tian et al., 2023).
2.4 Whole-genome sequencing (WGS)
2.4.1 Illumina sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted using the Qiagen Mini Kit (Qiagen; Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. In brief, one colony from each purified culture was cultured in 2 mL MH broth for 24 h at 37°C. Cell pellets were harvested and added to 180 μL of Buffer ATL containing 20 μL of Proteinase K (Qiagen, Germany), followed by incubation for 2 h. Then, 200 μL of Buffer AL was added, and the mixture was incubated at 70°C for 10 min. The mixture was transferred to a QIAamp Mini spin column and centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 30 s. Then, the column was washed with Buffer AW1 and AW2. DNA was eluted with distilled water by centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 30 s. The quality and quantity of the DNA were assessed using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, United States) and a Qubit 4.0 fluorometer (Invitrogen, United States). Illumina sequencing libraries were prepared using the TruePrepTM DNA Library Prep Kit V2 (Vazyme) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Individual libraries were assessed using the QIAxcel Advanced automatic nucleic acid analyzer with a high-resolution gel cartridge (Qiagen, Germany) and were quantified by qPCR using the KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR Kit (Kapa KK4610, KAPA Biosystem, Wilmington, MA, United States). Paired-end sequencing (2 × 150-bp reads) was performed on the Illumina HiSeq X Ten platform (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, United States).
2.4.2 Oxford Nanopore sequencing
Long-read sequencing was performed for two rare clinical CRAB isolates (belonging to ST34_Pas and ST23_Pas), which harbor blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-72 genes. For this process, DNA was extracted using the Gentra® Puregene® Yeast/Bact Kit (Qiagen, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol, with minor modifications. Oxford Nanopore sequencing libraries were prepared using the SQU-LSK109 Ligation Sequencing Kit (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, UK) in conjunction with the PCR-Free ONT EXP-NBD104 Native Barcode Expansion Kit (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, UK), following the native barcoding genomic DNA protocol. The DNA was processed without the optional shearing steps to select for long reads. After quantification of the individual libraries using the Qubit fluorometer and normalization of library concentrations, the library was sequenced on the GridION X5 platform (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, UK).
2.5 Bioinformatic analyses of the genomes
Genome assemblies of the short reads of Illumina were performed using the Shovill (version 1.0.9) pipeline. Assemblies of the short and long reads of Illumina and MinION were generated using Unicycler v0.4.8 (Wick et al., 2017). The quality of the 18 genome sequences was assessed using QUAST v5.0.2 (Gurevich et al., 2013). The quality results of the 18 assembly sequences are shown in Supplementary Table S1 (all N50 > 100 kb). Genome sequence prediction and annotation were performed using Prokka 1.11 (Seemann, 2014) and the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline (PGAP)1 (Tatusova et al., 2016). Antimicrobial resistance genes were identified using the ABRicate program2 according to the ResFinder database. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) using both the Oxford and Pasteur schemes was performed via the Center for Genomic Epidemiology (CGE) website3. Bacterial virulence factors were identified using the Virulence Factor Database (VFDB)4 (Liu et al., 2022). Capsular polysaccharide (K locus) and lipoolygosaccharide (OC locus) were further identified using Bautype and Kaptive v2.0.0 (Lam et al., 2022). Sequence comparisons were performed using BLASTn v2.4.0 (Zhang et al., 2000). Plasmid structure was visualized using DNAplotter.5 The origin-of-transfer (oriT) region and horizontal transfer of bacterial mobile genetic elements (MGEs) for plasmids were predicted using oriTDB6 (Liu et al., 2025). Similar plasmids were tracked using BacWGSTdb7 (Ruan and Feng, 2016). Default parameters were used for all software.
2.6 Comparative genomics analysis
Comparative genomics analysis of the 18 A. baumannii strains was performed. In detail, Snippy v4.4.58 was utilized to align the Illumina reads against the reference strain (A. baumannii ATCC 19606, accession number: GCF_900011295.1) and to generate a core genome alignment (approximately 4,000,000 bp), with repetitive regions removed using Gubbins v2.4.1 (Croucher et al., 2015). Final phylogenies were constructed using IQ-TREE v2.0.3 (Croucher et al., 2015; Nguyen et al., 2015). The resulting tree file was further visualized with the Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL v5) tool. The alignments were used to calculate SNP distances with SNP-dists V0.6.39 and visualized by RStudio version 3.5.3. Default parameters were used for all software.
3 Results
3.1 Collection of CRAB isolates and patients’ information
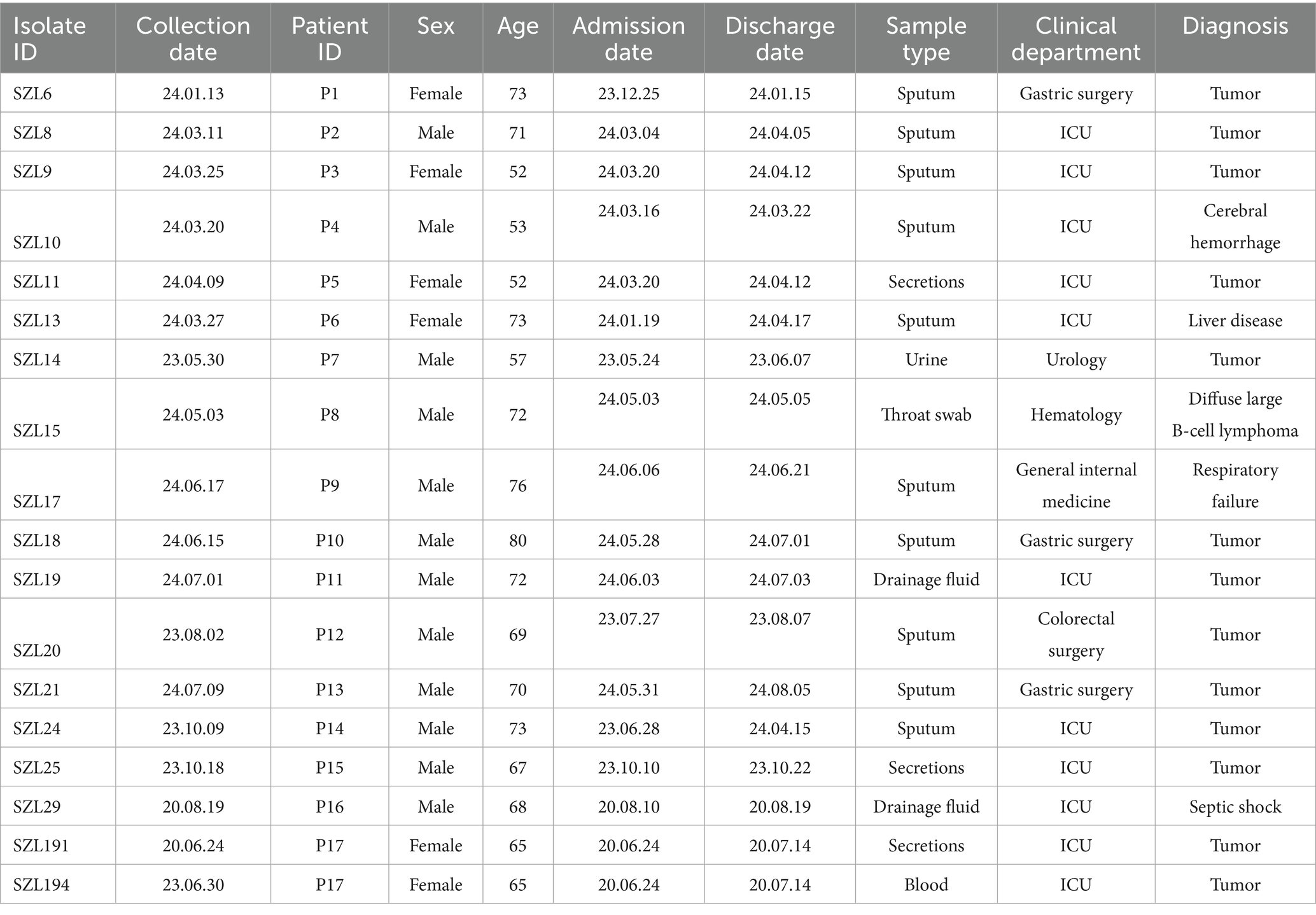
In this study, a total of 18 CRAB strains were collected from 17 patients (11 male and six female individuals; age range: 52–80 years) at a teaching hospital from 2020 to 2024. These strains were primarily collected from sputum samples (55.56%, 10/18), followed by secretions (16.67%, 3/18). Moreover, 61.11% (11/18) of the CRAB strains were collected from the ICU, while 16.67% (3/11) were collected from the gastric surgery department (Table 1). The remaining four strains were isolated from the urology, hematology, general internal medicine, and colorectal surgery departments, respectively (Table 1). The primary diagnosis among the 17 patients was tumor (72.22%, 13/18). Detailed information is provided in Table 1.
3.2 Drug resistance profiles
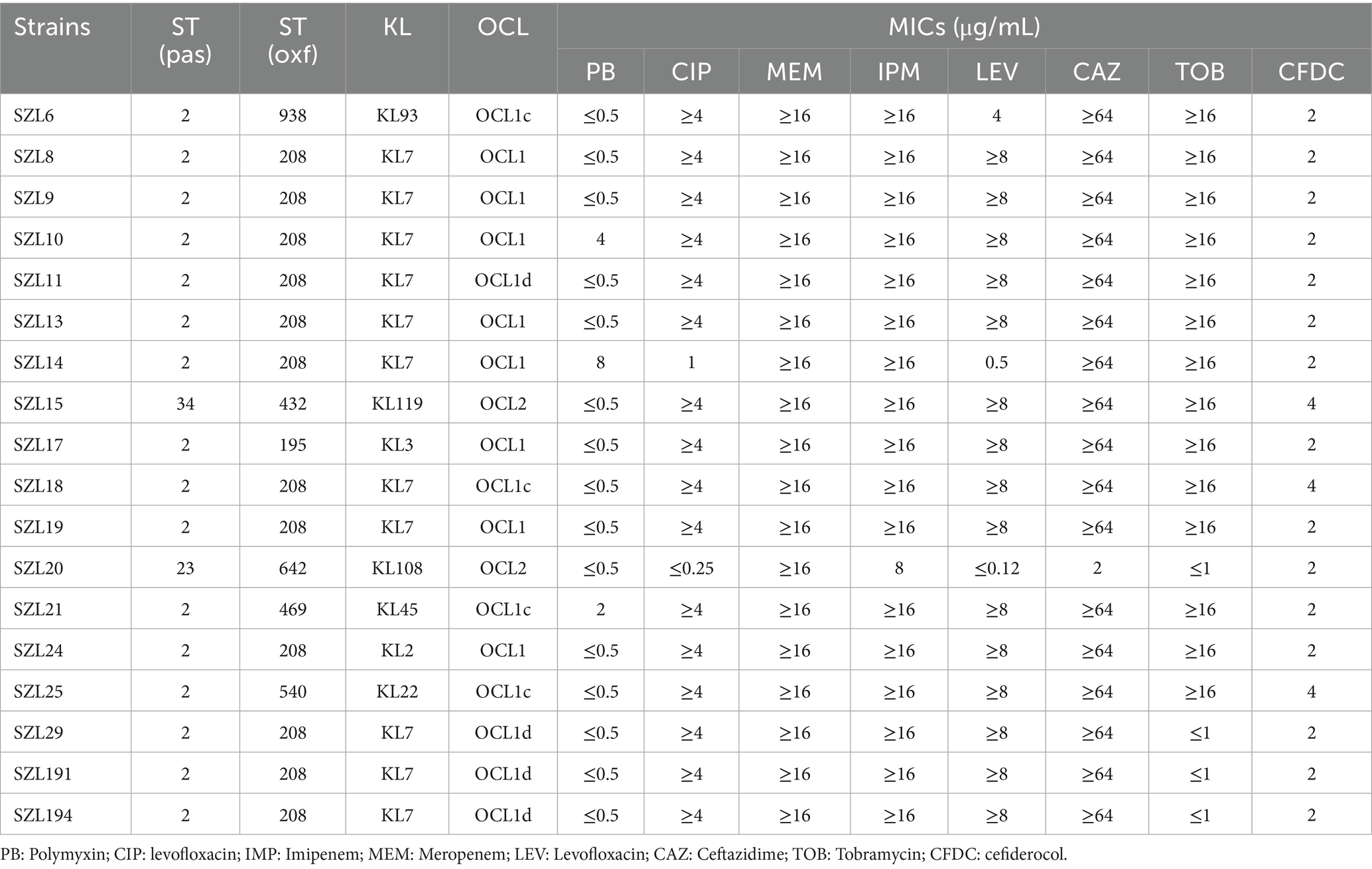
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) revealed that the 18 A. baumannii strains exhibited resistance to IMP and MEM (Table 2). Apart from SZL20, all other strains were resistant to CAZ, and 88.89% (16/18) of the strains were found to be resistant to CIP. Moreover, 83.33% (15/18) and 72.22% (13/18) of the strains were resistant to LEV and TOB, respectively (Table 2). In addition, two strains were observed to be resistant to PB, with MIC values of 4 and 8, respectively. Importantly, all A. baumannii strains were susceptible to CFDC, with MICs of 2 μg/mL or 4 μg/mL.
3.3 Virulence genes
Many virulence factors were identified in our CRAB strains, including the pga operon (pgaABCD), which encodes poly-β-1,6-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (PNAG), and the outer membrane protein gene ompA. In addition, the csu operon encoding Csu pili, the two-component regulatory system bfmRS, and other genes (bauABCDEF, basABCDEFGHIJ, and barAB) encoding acinetobactin for iron uptake were also identified in these strains.
3.4 Multilocus sequence typing (MLST), KL, and OCL
Based on the Pasteur MLST scheme, 16 A. baumannii strains were classified as sequence type 2 (ST2). The remaining two A. baumannii strains belonged to two rare sequence types (STs), namely ST34 and ST23, respectively (Table 2). Based on the Oxford MLST scheme, 12 A. baumannii strains belonged to ST208, while the remaining strains were assigned to ST938, ST432, ST195, ST642, ST469, and ST540, respectively (Table 2).
KL and OCL analysis showed that the majority of the strains (61.11%, 11/18) contained KL7. Concerning OCL types, OCL1, OCL1c, and OCL1d were identified, collectively accounting for 88.89% (16/18). The remaining two A. baumannii strains were classified as OCL2 (Table 2).
3.5 Resistance gene distribution and comparative genomics analysis of the A. baumannii strains
The analysis of the 18 CRAB genomes in this study revealed that, in addition to co-harboring chromosomal ant(3″)-IIa, many resistance genes conferring resistance to different types of antimicrobial agents were identified. Moreover, 16 CRAB strains were OXA-23 producers, and two strains were found to carry blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-72. In addition, 72.22% (13/18) of the strains were found to harbor the ribosome-methylase encoding gene armA. A total of 13 CRAB isolates were all resistant to TOB.
To explore the genetic relationship among the A. baumannii strains, comparative genomics analysis was performed on the 18 CRAB strains. The result showed that 16 CRAB strains (ST2_Pas) had a relatively close genetic relationship, which was consistent with the results of MLST (Figure 1A). We further constructed a tree of the 16 CRAB strains. The results revealed that SZL8, SZL9, SZL10, SZL10, SZL11, SZL13, SZL14, SZL18, and SZL19 had a near genetic relationship within our hospital (Figure 1B). Clinical data revealed that six of the eight strains were isolated from the ICU, suggesting possible transmission within the ICU of the teaching hospital. The eight CRAB clinical isolates shared the same resistance gene profile. Apart from SZL14, all other CRAB isolates were collected in 2024. The heatmap of the resistance genes is shown in Figure 1B. SNP analysis showed that only 1–6 SNPs were observed among these strains (Figure 2). In addition, SZL191 and SZL194 also had a quite close genetic relationship, and they were collected from the same patient (P17).
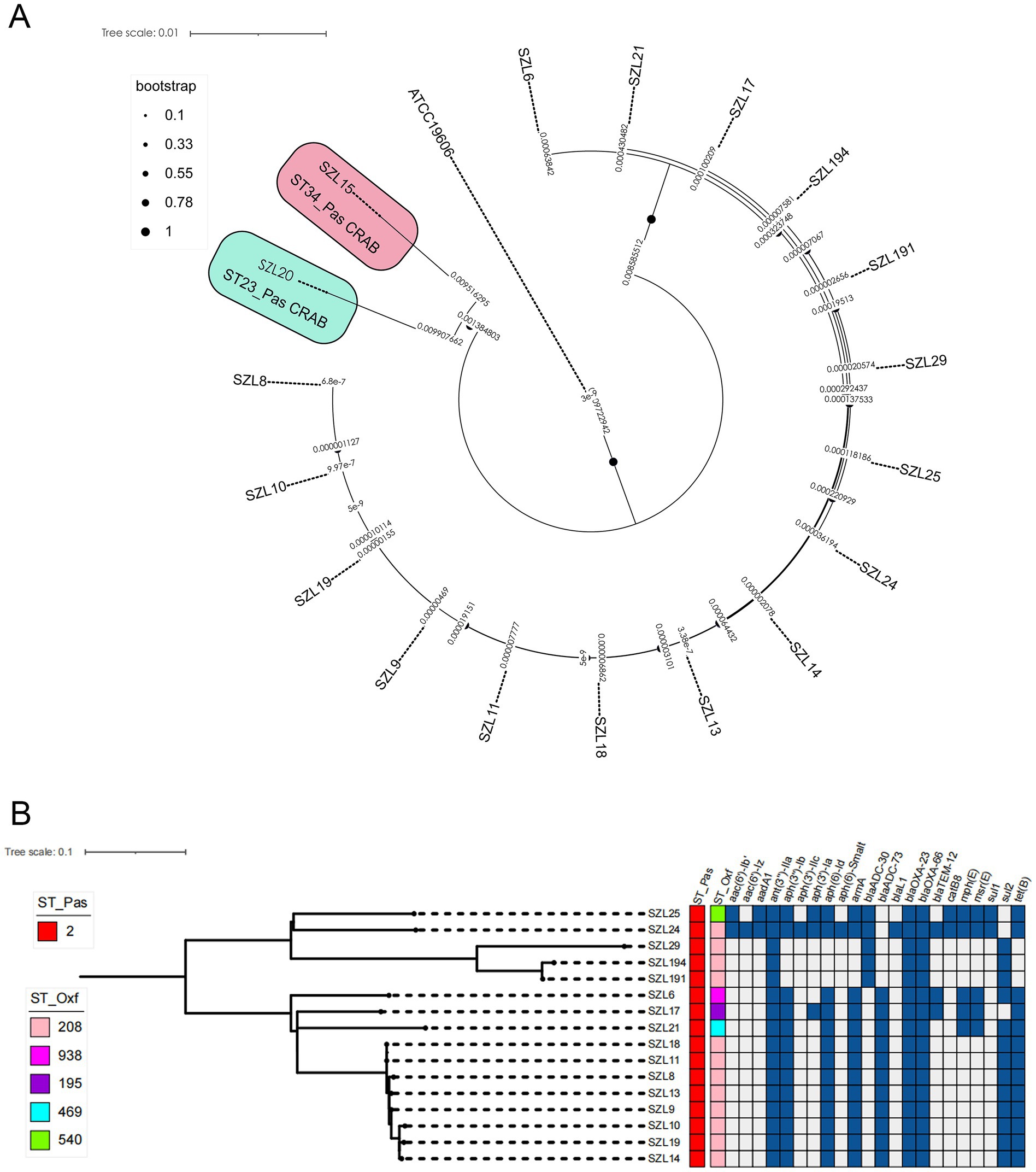
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of the 18 A. baumannii isolates. (A) Phylogenetic analysis was performed using the reference strain (A. baumannii ATCC 19606, accession number: GCF_900011295.1). Snippy v4.4.5 was utilized to align the Illumina reads against the reference strain and to generate a core genome alignment, with repetitive regions removed using Gubbins v2.4.1. Final phylogenies were constructed using IQ-TREE (version 2.0.3). Special STs (ST23 and ST34) are labelled, while the remaining strains are all ST2 CRAB strains. (B) Phylogenetic analysis was performed using IQ-TREE (version 2.0.3). The tree was visualized using iTOL v5. Isolate names, ST_Pasteur, ST_Oxford, and resistance genes are shown for each isolate.
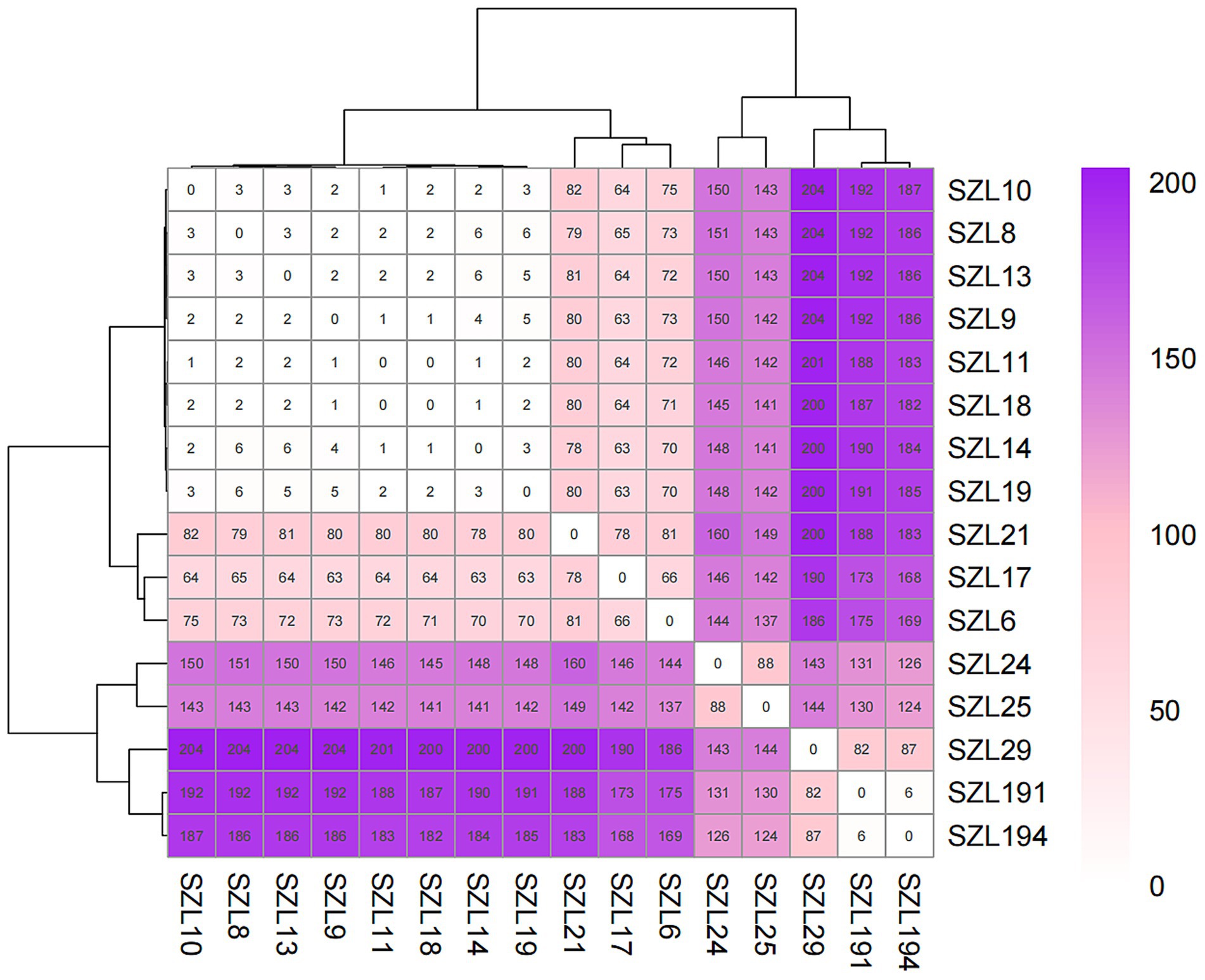
Figure 2. SNP matrix values for the ST2_Pasteur A. baumannii strains. SNP differences are indicated as numbers within the boxes.
3.6 Genetic analysis of the chromosome and plasmids in the rare ST34 CRAB
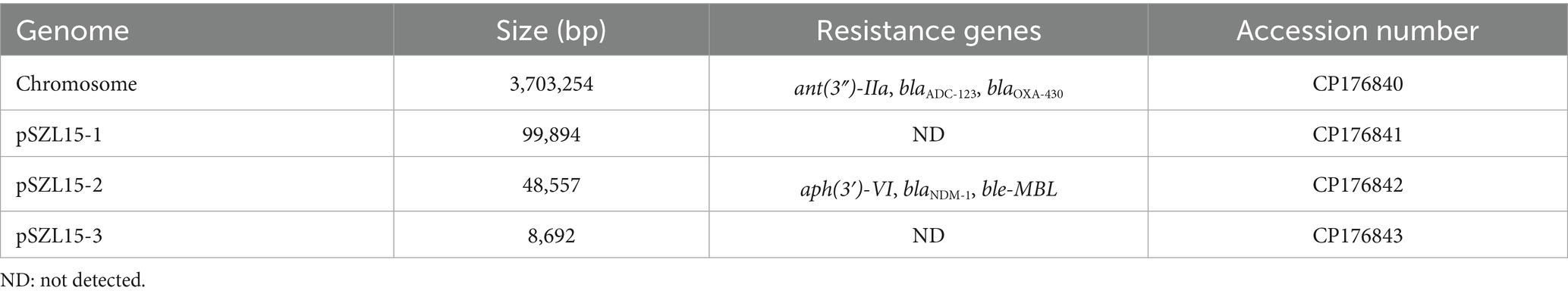
The hybrid assembly of the Illumina and MinION reads showed that the A. baumannii SZL15 strain possessed a circular chromosome of 3,703,254 bp (Table 3). A total of three plasmids were identified in this strain, namely pSZL15-1 to pSZL15-3, with sizes ranging between 8,692 bp and 99,894 bp. pSZL15-2 carried different kinds of resistance genes, and blaNDM-1 was identified in this plasmid. However, no resistance genes were found in pSZL15-1 and pSZL15-3 (Table 3).
3.7 Genetic features of the NDM-1-positive plasmid pSZL15-2 and identification of similar plasmids in the public database
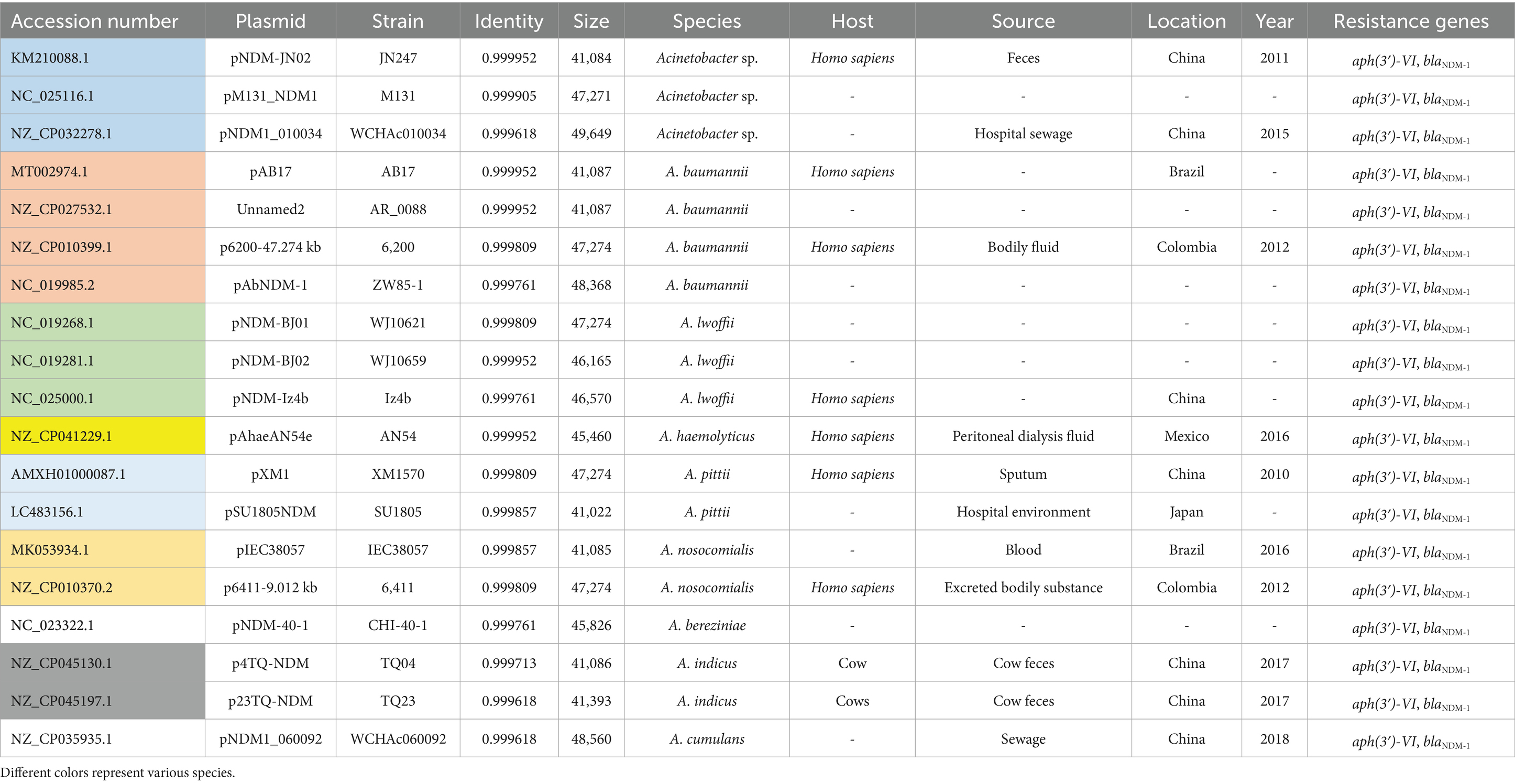
Genetic analysis revealed that the blaNDM-1 gene cluster was arranged sequentially as ISAba125, blaNDM-1, and ble-MBL elements (Figure 3). However, the upstream of ISAba125 was the genetic context of ISAba14-aph(3′)-VI (Figure 3). The blaNDM-1 gene was embedded within a Tn6924-like composite transposon. Mating assays were performed to explore the transfer ability of the blaNDM-1 gene, and the results showed that the blaNDM-1-harboring plasmid could not be transferred to the recipient strain. The result of oriTDB2 showed that no oriT was found in the blaNDM-1-harboring plasmid. Comparison with similar plasmids in public databases showed that blaNDM-1-positive plasmids share high sequence identity with plasmids identified in other Acinetobacter sp. and A. baumannii strains collected from different countries (Table 4). These plasmids were isolated from both patient and animal sources, suggesting potential horizontal transfer of blaNDM-1-positive plasmids across hosts.
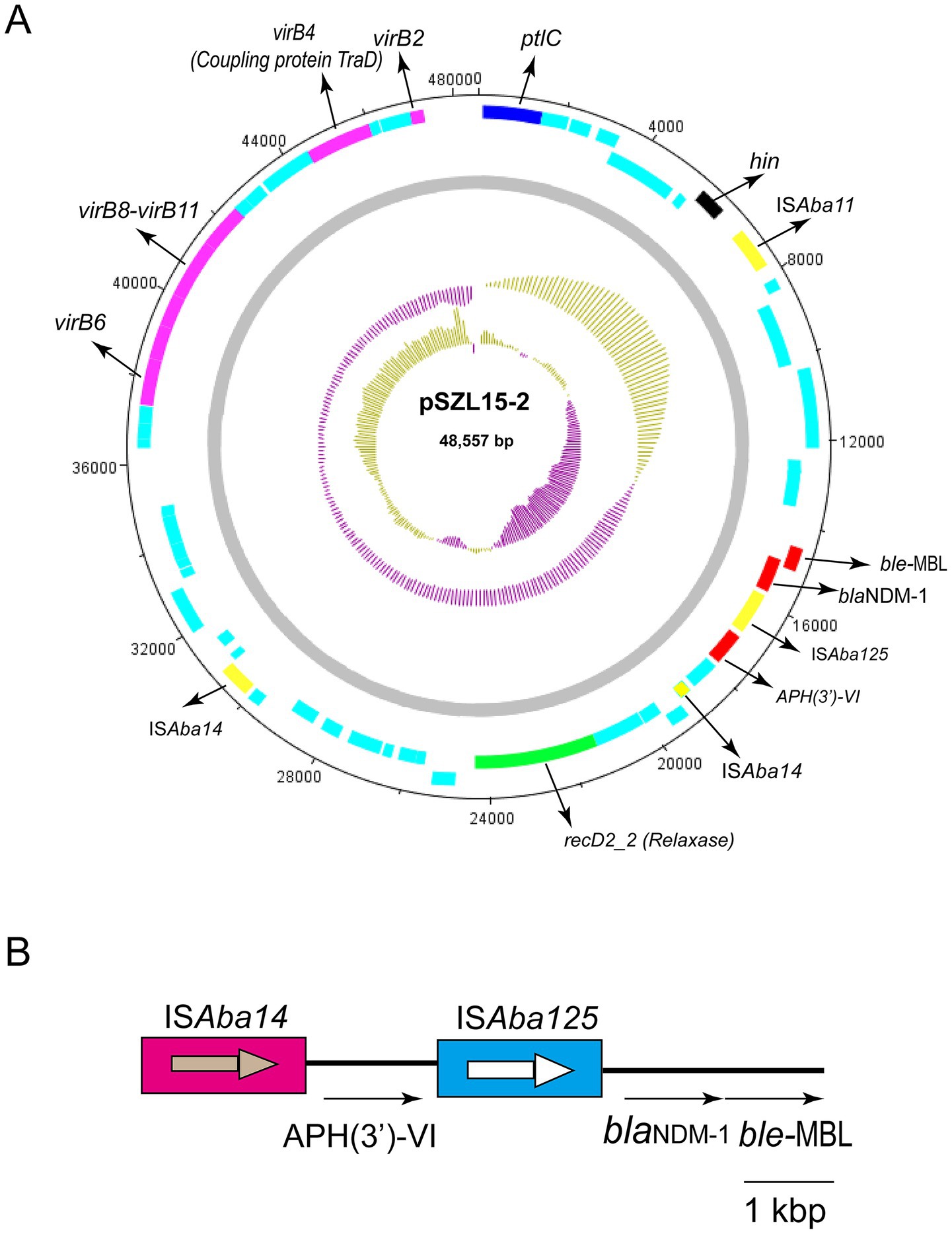
Figure 3. Circular map of pSZL15-2 and the genetic structure of blaNDM-1. (A) Circular map of the pSZL15-2 plasmid. IS copies are shown as yellow-filled boxes. Resistance genes are shown as red-filled boxes. T4SS-related genes, including virB, coupling protein, and relaxase encoding genes, are shown. Light blue-filled boxes represent other ORFs. (B) Structure of the blaNDM-1 gene.
4 Discussion
A. baumannii is a nosocomial pathogen that causes ventilator-associated infections and bloodstream infections (BSIs) in critically ill patients, and the spread of CRAB strains is of great concern (Harding et al., 2018). More importantly, CRAB can disseminate resistance rapidly via horizontal gene transfer (HGT) among various strains from environmental and patient sources, especially in the ICU (Zhao et al., 2022). Previous reports have shown that resistance to carbapenems is usually mediated by OXA-23, OXA-24, and OXA-58-type carbapenemases in A. baumanni (Mentasti et al., 2020). Consistent with previous studies, the production of the OXA-23 carbapenemase was the main resistance mechanism in this study (Liu et al., 2024). Further studies concerning the genetic environment of blaOXA-23 (Tn2006 or Tn2009 transposon) could be performed. Moreover, we found that the ICU is a crucial location for the development and spread of CRAB strains. In a recent report, Liu et al. found that 71.4% (55/77) of the ICUs were contaminated by CRAB strains, which is consistent with our findings (Doughty et al., 2023).
Apart from OXA-23-mediated carbapenem resistance, MBL-mediated resistance, such as NDM-1-mediated carbapenem resistance, was also observed in one rare CRAB strain. A. baumannii strains carrying blaNDM-1 have been reported in clinical and environmental isolates across several countries (Bontron et al., 2016; Jaidane et al., 2018). Notably, the most common A. baumannii strains harboring blaNDM-1 usually belonged to ST85 and ST25 in previous studies, which is distinct from our strain (Bakour et al., 2014; Rafei et al., 2015; Ramoul et al., 2016). Here, the blaNDM-1 gene was identified in a rare ST34 CRAB strain based on the Pasteur scheme. Previous studies have shown that plasmids containing conjugative elements, including the origin-of-transfer (oriT) region, relaxase enzyme, type IV coupling protein (T4CP) gene, and a gene cluster encoding the type IV secretion system (T4SS), are capable of transfer (Liu et al., 2025). The oriT region is essential for the transfer process, as it is recognized by the relaxase enzyme and undergoes nicking at a conserved site (nic), resulting in the formation of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) (Liu et al., 2025). However, no oriT region was found in our plasmid, which likely explains its lack of transferability.
Based on genetic structure analysis, we found that the blaNDM-1 gene was located within a 76-kb Tn6924-like composite transposon. Tn6924 and Tn6924-like transposons are novel members of the Tn7 family with ISAba14 and some resistance genes such as blaNDM and aph(3′)-VI (aphA6) (Mann et al., 2022). The Tn125 composite transposon contains two copies of ISAba125 with 3-bp target site duplications (TSDs). However, no ISAba14 was identified in the Tn125 composite transposon. Poirel et al. found that blaNDM-1 was located within the 10,099-bp composite transposon Tn125, bracketed by two copies of ISAba125 (Poirel et al., 2012). Tn125 seems to be the primary vehicle for the spread of blaNDM-1 in A. baumannii. Another study from China also identified the structure of Tn125 in A. baumannii strains (Liu et al., 2021), which differs from our research.
The OCL and KL gene clusters, which are responsible for the biosynthesis of the OCL and capsule, respectively, serve as potentially useful epidemiological markers (Tian et al., 2022). They may play an important role in vaccine development (Tian et al., 2022). In the current study, we identified KL7 and OCL1 as the important types; vaccines targeting these types could be explored in the future. Previous studies have shown that ST208 (Oxford scheme) and KL7 isolates exhibit higher virulence and biofilm formation ability, with KL7 A. baumannii isolates also showing higher capsule production (Chen et al., 2024). Another finding was that the majority of the isolates belonged to ST2 based on the Pasteur MLST scheme. In a previous study, researchers found that OXA-23-producing global clone 2 (GC2) isolates dominated (99.3%) in an ICU in Zhejiang, China (Doughty et al., 2023). They confirmed that all OXA-23-producing isolates were resistant to imipenem, meropenem, and ciprofloxacin but remained sensitive to polymyxin B and tigecycline. Therefore, polymyxin B and tigecycline can be effective treatment options for OXA-23-positive CRAB isolates. Moreover, cefiderocol (FDC; S-649266), a novel siderophore cephalosporin, has been proven to possess a broad activity against CRAB in vitro and in vivo (Karruli et al., 2023). However, a study from Spain reported that cefiderocol-resistant strains were related to NDM-1 carbapenemase production and mutations in AmpC. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor NDM-1-producing CRAB isolates in clinical settings to avoid treatment failure due to inappropriate antimicrobial choices.
In addition, a multi-country cohort study showed that 49 (77%) of 64 strains from Fiji and all 32 (100%) strains from Samoa belonged to ST2 CRAB (Baleivanualala et al., 2023; Baleivanualala et al., 2024). These results highlight the global importance of ST2 CRAB and underscore the urgent need for more effective measures to prevent further clonal spread. Furthermore, based on SNP differences, we also obtained evidence of clonal strain transmission in this hospital via core-genome (cg) SNP-based phylogenetic tree and SNP analyses. The clonal spread may have been facilitated by contact between healthcare workers and contaminated environmental surfaces within the hospital. Effective infection control measures, such as implementing “water-free” cleaning methods for patients, ceasing the operation of sinks, increasing the frequency of cleaning hospital device surfaces, and enforcing hand hygiene practices among staffs (Liu et al., 2024), need to be implemented in hospitals to reduce the risk of further CRAB spread, especially in the ICU. Moreover, new drugs such as cefiderocol and sulbactam-durlobactam have demonstrated effective therapeutic capabilities and should be considered promising treatment options for infections caused by CRAB.
However, some limitations remain in this study. The virulence level was not assessed using an insect larvae model or murine infection model. In addition, this was a single-center, observational, retrospective study with a small sample size. We need to collect more CRAB isolates from multiple hospitals, as well as all global CRAB genomes, for a comprehensive comparative genomics analysis. In addition, further investigations are needed to determine whether blaNDM-1-harboring resistance plasmids could be transferred to other recipient bacteria via conjugation or transformation.
In conclusion, this genome-based study of clinical CRAB isolates collected from a teaching hospital in China between 2020 and 2024 revealed their epidemiological and genomic characteristics.
The OXA-type carbapenemase-encoding gene (blaOXA-23) was the major determinant of carbapenem resistance. Clone spread has occurred within this hospital. Therefore, it is urgent to implement a routine screening procedure to monitor the presence of CRAB among patients admitted to hospital units, such as ICUs, to prevent and control the spread of CRAB in high-risk patients.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, PRJNA1202876.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by local Ethics Committees of the Hospital with the approval number: IRB-2024-554 (IIT). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing. CM: Writing – review & editing. YF: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Shaoxing Health Science and Technology Project, China (2024SKY059).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1575257/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/annotation_prok/
2. ^https://github.com/tseemann/abricate
3. ^https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/MLST/
5. ^https://www.sanger.ac.uk/tool/dnaplotter/
6. ^https://bioinfo-mml.sjtu.edu.cn/oriTDB2/
7. ^http://bacdb.cn/BacWGSTdb/index.php
References
Bakour, S., Olaitan, A. O., Ammari, H., Touati, A., Saoudi, S., Saoudi, K., et al. (2015). Emergence of Colistin- and Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ST2 clinical isolate in Algeria: first case report. Microb. Drug Resist. 21, 279–285. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2014.0214
Bakour, S., Touati, A., Bachiri, T., Sahli, F., Tiouit, D., Naim, M., et al. (2014). First report of 16S rRNA methylase ArmA-producing Acinetobacter baumannii and rapid spread of metallo-beta-lactamase NDM-1 in Algerian hospitals. J. Infect. Chemother. 20, 696–701.
Baleivanualala, S. C., Isaia, L., Devi, S. V., Howden, B., Gorrie, C. L., Matanitobua, S., et al. (2023). Molecular and clinical epidemiology of carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ST2 in Oceania: a multicountry cohort study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac 40:100896. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100896
Baleivanualala, S. C., Matanitobua, S., Soqo, V., Smita, S., Limaono, J., Sharma, S. C., et al. (2024). Molecular and clinical epidemiology of carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacterales in Fiji: a multicentre prospective observational study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac 47:101095.
Bontron, S., Nordmann, P., and Poirel, L. (2016). Transposition of Tn125 encoding the NDM-1 Carbapenemase in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 7245–7251. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01755-16
Capodimonte, L., Meireles, F. T. P., Bahr, G., Bonomo, R. A., Dal Peraro, M., Lopez, C., et al. (2024). OXA beta-lactamases from Acinetobacter spp. are membrane bound and secreted into outer membrane vesicles. MBio :e0334324.
Chen, J., Li, G., Shao, Y., Cheng, Z., Wan, F., Wu, D., et al. (2024). Clinical, phenotypic characterization and genomic analysis of the mucoid Acinetobacter baumannii from a teaching hospital. Microb. Pathog. 196:106929. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106929
Croucher, N. J., Page, A. J., Connor, T. R., Delaney, A. J., Keane, J. A., Bentley, S. D., et al. (2015). Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:e15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1196
Doughty, E. L., Liu, H., Moran, R. A., Hua, X., Ba, X., Guo, F., et al. (2023). Endemicity and diversification of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit. Lancet Reg Health West Pac 37:100780. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100780
Gurevich, A., Saveliev, V., Vyahhi, N., and Tesler, G. (2013). QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29, 1072–1075. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Harding, C. M., Hennon, S. W., and Feldman, M. F. (2018). Uncovering the mechanisms of Acinetobacter baumannii virulence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16, 91–102. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.148
Jaidane, N., Naas, T., Oueslati, S., Bernabeu, S., Boujaafar, N., Bouallegue, O., et al. (2018). Whole-genome sequencing of NDM-1-producing ST85 Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Tunisia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 52, 916–921. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.05.017
Joshi, P. R., Acharya, M., Kakshapati, T., Leungtongkam, U., Thummeepak, R., and Sitthisak, S. (2017). Co-existence of Bla(OXA-23) and Bla(NDM-1) genes of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from Nepal: antimicrobial resistance and clinical significance. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 6:21. doi: 10.1186/s13756-017-0180-5
Karruli, A., Migliaccio, A., Pournaras, S., Durante-Mangoni, E., and Zarrilli, R. (2023). Cefiderocol and Sulbactam-Durlobactam against Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics (Basel) 12. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12121729
Lam, M. M. C., Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Holt, K. E., and Wyres, K. L. (2022). Kaptive 2.0: updated capsule and lipopolysaccharide locus typing for the Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex. Microb. Genom. 8. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000800
Liu, X., Chang, Y., Xu, Q., Zhang, W., Huang, Z., Zhang, L., et al. (2023). Mutation in the two-component regulator BaeSR mediates cefiderocol resistance and enhances virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii. mSystems 8:e0129122.
Liu, G., Li, X., Guan, J., Tai, C., Weng, Y., Chen, X., et al. (2025). oriTDB: a database of the origin-of-transfer regions of bacterial mobile genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 53, D163–D168. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae869
Liu, H., Liu, X., He, J., Zhang, L., Zhao, F., Zhou, Z., et al. (2023). Emergence and evolution of OXA-23-producing ST46(pas)-ST462(Oxf)-KL28-OCL1 carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii mediated by a novel ISAba1-based Tn7534 transposon. Antibiotics 12. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020396
Liu, H., Moran, R. A., Chen, Y., Doughty, E. L., Hua, X., Jiang, Y., et al. (2021). Transferable Acinetobacter baumannii plasmid pDETAB2 encodes OXA-58 and NDM-1 and represents a new class of antibiotic resistance plasmids. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 76, 1130–1134. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab005
Liu, H., Moran, R. A., Doughty, E. L., Hua, X., Snaith, A. E., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Longitudinal genomics reveals carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii population changes with emergence of highly resistant ST164 clone. Nat. Commun. 15:9483. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53817-x
Liu, B., Zheng, D., Zhou, S., Chen, L., and Yang, J. (2022). VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, D912–D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1107
Mann, R., Rafei, R., Gunawan, C., Harmer, C. J., and Hamidian, M. (2022). Variants of Tn6924, a novel Tn7 family transposon carrying the Bla(NDM) metallo-beta-lactamase and 14 copies of the aphA6 amikacin resistance genes found in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol. Spectr. 10:e0174521.
Mathlouthi, N., El Salabi, A. A., Ben Jomaa-Jemili, M., Bakour, S., Al-Bayssari, C., Zorgani, A. A., et al. (2016). Early detection of metallo-beta-lactamase NDM-1- and OXA-23 carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii in Libyan hospitals. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 48, 46–50.
Mentasti, M., Prime, K., Sands, K., Khan, S., and Wootton, M. (2020). Rapid detection of OXA-23-like, OXA-24-like, and OXA-58-like carbapenemases from Acinetobacter species by real-time PCR. J. Hosp. Infect. 105, 741–746. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2020.06.015
Miller, W. R., and Arias, C. A. (2024). ESKAPE pathogens: antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 22, 598–616. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01054-w
Nguyen, L. T., Schmidt, H. A., Von Haeseler, A., and Minh, B. Q. (2015). IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32, 268–274. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu300
Poirel, L., Bonnin, R. A., Boulanger, A., Schrenzel, J., Kaase, M., and Nordmann, P. (2012). Tn125-related acquisition of blaNDM-like genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56, 1087–1089. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05620-11
Rafei, R., Pailhories, H., Hamze, M., Eveillard, M., Mallat, H., Dabboussi, F., et al. (2015). Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii in different hospitals in Tripoli, Lebanon using Bla(OXA-51-like) sequence based typing. BMC Microbiol. 15:103. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0441-5
Ramoul, A., Loucif, L., Bakour, S., Amiri, S., Dekhil, M., and Rolain, J. M. (2016). Co-occurrence of blaNDM-1 with blaOXA-23 or blaOXA-58 in clinical multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in Algeria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 6, 136–141. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.05.003
Richards, G. A., Perovic, O., and Brink, A. J. (2024). The challenges of difficult-to-treat Acinetobacter infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 37:e0009324.
Ruan, Z., Chen, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhou, H., Zhou, Z., Fu, Y., et al. (2013). Wide distribution of CC92 carbapenem-resistant and OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii in multiple provinces of China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 42, 322–328. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.06.019
Ruan, Z., and Feng, Y. (2016). BacWGSTdb, a database for genotyping and source tracking bacterial pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D682–D687. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1004
Seemann, T. (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30, 2068–2069. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Tatusova, T., Dicuccio, M., Badretdin, A., Chetvernin, V., Nawrocki, E. P., Zaslavsky, L., et al. (2016). NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 6614–6624. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw569
Tian, C., Shi, Y., Ren, L., Huang, D., Wang, S., Zhao, Y., et al. (2023). Emergence of IS26-mediated pLVPK-like virulence and NDM-1 conjugative fusion plasmid in hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Genet. Evol. 113:105471. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2023.105471
Tian, C., Xing, M., Fu, L., Zhao, Y., Fan, X., and Wang, S. (2022). Emergence of uncommon KL38-OCL6-ST220 carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter pittii strain, co-producing chromosomal NDM-1 and OXA-820 carbapenemases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:943735. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.943735
Wang, W., Weng, J., Wei, J., Zhang, Q., Zhou, Y., He, Y., et al. (2024). Whole genome sequencing insight into carbapenem-resistant and multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii harboring chromosome-borne Bla(OXA-23). Microbiol Spectr 12:e0050124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00501-24
Wang, S. H., Yang, K. Y., Sheu, C. C., Lin, Y. C., Chan, M. C., Feng, J. Y., et al. (2024). Efficacy of combination therapy with standard-dose carbapenem for treating nosocomial pneumonia caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in intensive care units: a multicentre retrospective propensity score-matched study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 63:107044. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.107044
Wibberg, D., Salto, I. P., Eikmeyer, F. G., Maus, I., Winkler, A., Nordmann, P., et al. (2018). Complete genome sequencing of Acinetobacter baumannii strain K50 discloses the large conjugative plasmid pK50a encoding carbapenemase OXA-23 and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase GES-11. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62.
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L., and Holt, K. E. (2017). Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13:e1005595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595
Wong, D., Nielsen, T. B., Bonomo, R. A., Pantapalangkoor, P., Luna, B., and Spellberg, B. (2017). Clinical and pathophysiological overview of Acinetobacter infections: a century of challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 30, 409–447. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00058-16
Yang, X., Dong, N., Liu, X., Yang, C., Ye, L., Chan, E. W., et al. (2021). Co-conjugation of virulence plasmid and KPC plasmid in a clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae strain. Front. Microbiol. 12:739461. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.739461
Zhang, Z., Schwartz, S., Wagner, L., and Miller, W. (2000). A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 7, 203–214. doi: 10.1089/10665270050081478
Keywords: CRAB, WGS, comparative genomics analysis, SNP, plasmid structure
Citation: Dong S, Lou J, Mao C, Fang Y and Zhang H (2025) Phylogenomic analysis of OXA-23-positive and genetic context of rare NDM-1-producing carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in a teaching hospital in China. Front. Microbiol. 16:1575257. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1575257
Edited by:
Moataz Abd El Ghany, The University of Sydney, AustraliaReviewed by:
Atef M. Shibl, Alfaisal University, Saudi ArabiaHifzur Ansari, King Abdullah International Medical Research Center (KAIMRC), Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Lou, Mao, Fang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuejuan Fang, MTUxNjgzMjY3MTRAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Huan Zhang, dHNoYWJAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Su Dong
Su Dong Jianjiang Lou1
Jianjiang Lou1