- 1College of Forestry, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China
- 2College of Desert Control Science and Engineering, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) communities are influenced by soil nutrients and plant and litter traits during forest ecosystem development. However, the extent to which these factors influence AMF communities in Xanthoceras sorbifolium plantations is unclear. In this study, rhizosphere soil samples were collected from 5-, 13-, 24-, 35-, 47-, and 56-year-old X. sorbifolium plantations. The AMF community was analyzed using Illumina MiSeq sequencing, and AMF spores were isolated and identified by wet sieving. The results showed that X. sorbifolium can establish a symbiotic relationship with AMF at different forest ages. In total, 5,876 AMF amplicon sequence variant (ASVs) were obtained from the soil samples and classified into 1 phylum, 4 classes, 6 orders, 12 families, and 15 genera. Glomus was the dominant genus. In addition, the diversity of AMF communities increased and then decreased with the age of X. sorbifolium, with no significant changes observed between 35-, 47-, and 56-year-old plantations. AMF community variance was primarily determined by soil-specific factors, with soil pH and root C content being the most influential. The results revealed the factors that drive AMF communities during the development of X. sorbifolium and provide valuable information for future conservation and planting management.
1 Introduction
Mycorrhizal symbiosis is a common form of mutually beneficial relationship between fungi and plants in nature. Arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) is a type of mycorrhiza, which is formed by the symbiosis between arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi (AMF) and host plants (Fei et al., 2022). AMF are non-specific beneficial microorganisms that can establish a symbiotic relationship with most higher terrestrial plants; thus, they are important components of natural ecosystems. AMF have an important role in the formation of stable soil aggregates, soil carbon and nitrogen cycling processes, and plant community succession ecological processes, with potentially valuable implications for sustainable ecosystems (Gui et al., 2017; Mohammadi et al., 2019). Changes in the structure and diversity of AMF communities affect plant performance and ecosystem stability (Wagg et al., 2011) and improve plant growth by increasing nutrient intake (Shao et al., 2021). Numerous studies have demonstrated that AMF communities are closely related to external environmental conditions such as soil physicochemical properties, vegetation type and altitude (Liu et al., 2023). However, for a single target plant, the age of the stand may be an important determinant affecting the AMF community (Zhang et al., 2022; Pereira et al., 2014).
During plant growth, tissues and organs such as leaves and root systems interact with each other and jointly regulate the functional traits of plants. Leaves, as an important organ for plant photosynthesis, have elemental contents that not only indicate the nutrient supply capacity of the soil but also characterize the response and adaptation to environmental changes (Wright et al., 2001). The plant root system is an important organ connecting the plant and the soil, and fine roots, as the most sensitive and active part of the root system, are an important source of soil nutrient pools, with the total global fine root C pool being more than 5% of the atmospheric C pool. Moreover, the fine roots are the main organ by which plants expand the soil space, thereby shaping the physical environment of the soil and allowing the transport of nutrients and C elements to the surrounding microorganisms (Nadelhoffer, 2000). The morphology and nutrient content of plant leaves and root systems change as the stand develops (Vergutz et al., 2012), and plants can adjust their resource acquisition strategies by adjusting the changes in leaves and root systems to adapt to the eco-physiological processes of the tree during development. AMF are closely related to plant leaf and root traits (Chen et al., 2022; Kong et al., 2016), and plants can influence soil AMF communities at a regional scale by providing different quantities and qualities of litter and root inputs to AMF communities (Korenblum et al., 2020). As the stand age increases, changes in stand structure and tree biomass directly affect litter quality and decomposition rates; moreover, changes in litter traits can alter nutrient availability, fundamentally affecting AMF communities (Li et al., 2019). Soil physicochemical conditions can indirectly influence forest development through plant function and changes in litter traits. Soil nutrients, physical structure, and pH have been shown in a large body of literature to have important effects on AMF communities (Bai et al., 2022; Bonfim et al., 2016). Thus, AMF communities may be determined by interactions among soil, plant, and litter traits, and these interactions may be related to stand development. Although the effects of stand development on AMF community composition and diversity have been noted (Bennett and Groten, 2022; Zhu et al., 2024), the effects of relevant factors on AMF community composition and diversity during stand development require further investigation.
Xanthoceras sorbifolium is a rare woody oil tree species endemic to northern China that can be used as biodiesel feedstock. It has strong ecological adaptability and resistance to adversity and is an excellent tree species for wind and sand control, soil and water conservation, and desertification control (Wang et al., 2021). As the national energy strategy changes, the X. sorbifolium industry has received increasing attention and the area of artificial planting has been expanding. Thus, large areas of X. sorbifolium-producing areas have been established in Ningxia and Inner Mongolia in China, and the mode of operation is mainly pure forest (Xie et al., 2010). However, pure forests are prone to soil degradation, community decline, and reduced productivity (Wang, 2023), which ultimately limit the sustainable management of plantation forests and the ecological benefits of vegetation restoration. The X. sorbifolium industry is in its infancy, and current research is mainly focused on medicinal value, nutrient composition, and breeding for rapid propagation (Lang et al., 2020; Ji et al., 2020). Moreover, studies on X. sorbifolium mycorrhizal material are extremely limited. Zhu et al. (2015) found that the diversity of the rhizosphere fungal community of X. sorbifolium in different forest ages (5–10 a) was significantly correlated with soil environmental factors. Scholars have also identified Vesicular-Arbuscular (VA) mycorrhizal fungal structures in 10–12 a X. sorbifolium root systems (Zheng, 2017). Compared to the singularity of X. sorbifolium mycorrhizal studies by previous scholars, the present study was conducted in Wengniute Banner, Chifeng City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, where X. sorbifolium plantation forests of different forest ages (5, 13, 24, 35, 47, and 56 years old) were selected, and AMF leaf blades, roots, litter, and rhizosphere soils were collected from AMFs of different forest ages. The objectives of this study were (1) to elucidate the patterns of changes in AMF community diversity, soil physicochemical properties, plant and litter characteristics with stand age in X. sorbifolium plantation forests. (2) Quantified the relative contributions of soil, plant, and litter properties and explored key drivers affecting AMF community change during X. sorbifolium development. A good understanding of the differences in soil microbial community composition and diversity in different stand stages of X. sorbifolium plantation forests, and in particular the magnitude of structuring effects, driven by changes in plant, root, or soil properties, which can provided reference for us to devise management strategies that regulate below-ground organisms in order to improve the nutrient sustainability of low-productivity X. sorbifolium plantation forests.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area
This study was conducted at a forest farm in Wudan Town (119°45′48″-120°43′58″E, 42°27′26″-42°38′33″N) (Figure 1), Wengnute Banner, Chifeng City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. The area has a typical temperate continental climate, with an average annual temperature of 5.9°C, average annual precipitation of 300–330 mm, and a soil type of mainly sandy chestnut-calcium soil.
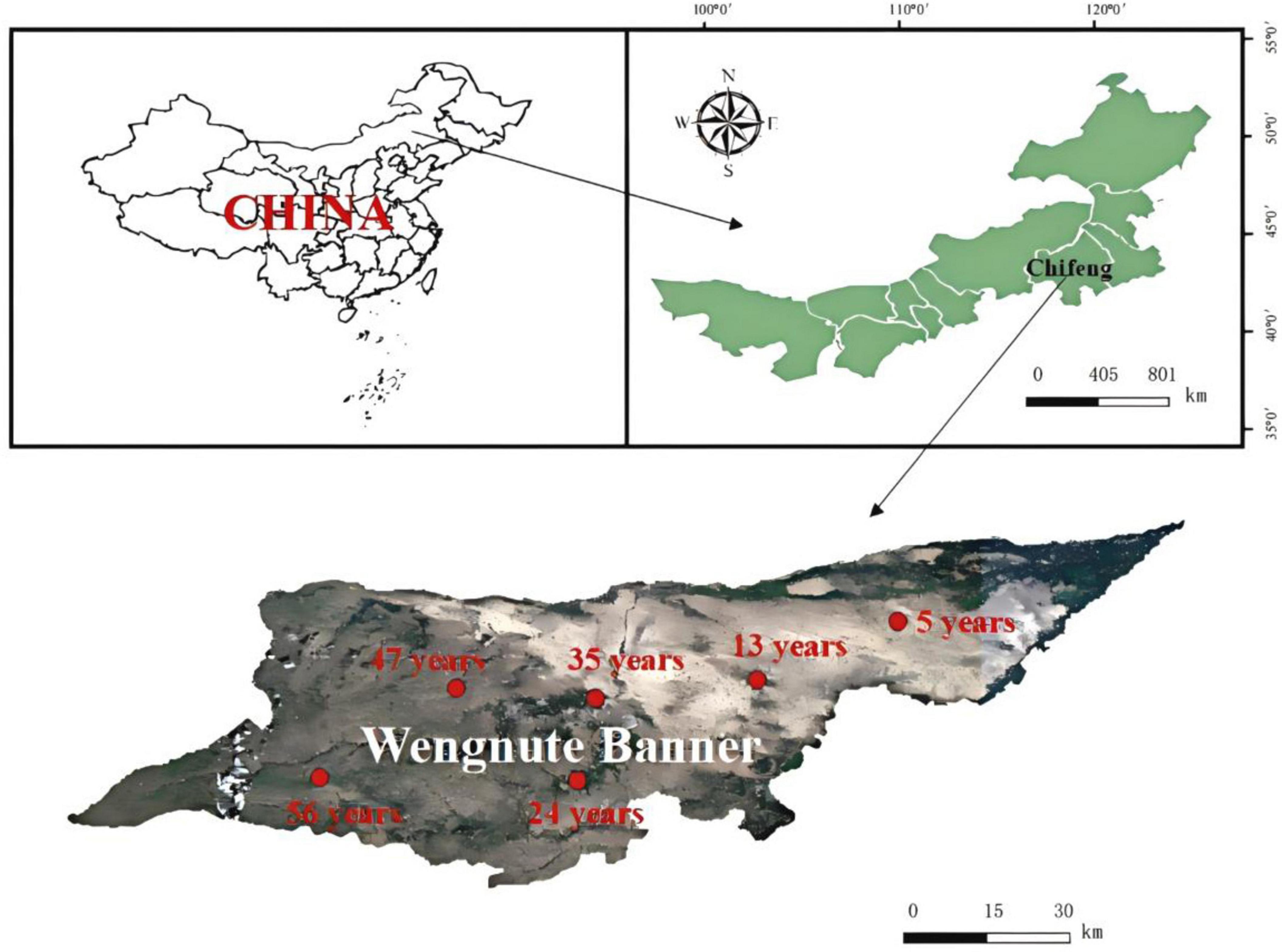
Figure 1. Location and sampling sites of forest farms in Udan Township, Wengniute Banner, Chifeng City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China.
2.2 Experimental design and plant and soil sampling
X. sorbifolium began to develop in the early 1960s and was planted on a large scale in the 1970s (Feng et al., 2022). The largest area of X. sorbifolium plantation forests in China was created in the study region, and the ideal chronological order of X. sorbifolium plantation forests with different developmental years was established, with the oldest being 56a. In August 2023, 5, 13, 24, 35, 47, and 56 years X. sorbifolium plantations (abbreviated as YF, MAF, NMF, MFI, MFII, and OMF, respectively) with similar stand conditions were selected. Three sample plots of 20 × 20 m were established in each stand, and the information of the sample plots is shown in Supplementary Table 1. In each sample plot, three X. sorbifolium with similar diameter at breast height (DBH) were randomly selected, and leaves, litter, rhizosphere soil, and fine roots (≤ 2 mm in diameter) were collected from each tree (see the Supplementary file for details on the sampling and measurement methods). Statistical results of plant and litter traits and soil properties are presented in Supplementary Tables 3–5, and specific variables and abbreviations are presented in Supplementary Table 2. All samples were taken back to the laboratory in a 4°C sampling box. The soil was divided into three portions, with one portion stored in a refrigerator at −80°C for soil DNA analysis, another portion of fresh soil was stored at 4°C for nitrate nitrogen (N-NO3–) and ammonium nitrogen (N-NH4+) analysis, and the remaining soil air-dried and passed through a 2 mm sieve for chemical analysis.
2.3 AMF colonization rate
The roots were cut into 1 cm pieces, decolorized in a KOH solution at 90°C for 60 min, and then rinsed. These root samples were softened with alkaline H2O2 (the softening time was adjusted according to the hardness of the roots), placed in 1% HCI solution for acidification, stained with Trypan blue dye solution containing 0.12% (w/v) at 80°C for 30 min, decolorized in lactic acid glycerol solution, washed with distilled water, sampled for microscopic examination, and photographed using an optical microscope (XSP-17C, ZSISS, Shanghai, China). Finally, the samples were observed and counted using the grid crossover method (McGonigle et al., 1990), and the AMF colonization rate was calculated. The AMF colonization rate (%) was calculated as the number of colonized root segments divided by the total number of tested root segments.
2.4 AMF spore identification
AMF spores were isolated using the wet sieve decantation-sucrose centrifugation method (Ianson and Allen, 1986). The morphology, color, and other characteristics of the AMF spores were observed using a microscope (XSP-17C, ZSISS, Shanghai, China), and descriptions and photographs for each species were obtained from the “Manual of Identification of Mycorrhizal Fungi of VA” (Wilson et al., 1983) and the International Center for the Preservation of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (INVAM).1 The spore density (SD), separation frequency (F), and relative abundance (RA) of AMF spores were also determined at each sampling site. The formulas for these indicators are as follows:
2.5 DNA extraction and Illumina MiSeq
DNA was extracted using a Soil DNA Kit (M5635-02; Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, United States). The quantity and quality of DNA were measured using a NanoDrop NC2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). The following PCR amplification primers were used to amplify the DNA samples: forward AMV4.5NF (5′-AAGCTCGTAGTTGAATTTCG-3′) and reverse AMDGR (5′-CCCAACTATCCCTATTAATCAT-3′). The PCR mixture consisted of 5 μl buffer (5 × ), 0.25 μl Fast pfu DNA polymerase (5 U/μl), 2 μl (2.5 mM) dNTPs, 1 μl (10 μM) forward and reverse primers, 1 μl DNA template, and 14.75 μl ddH2O. Thermal cycling began with an initial denaturation at 98°C for 5 min; followed by 25 cycles of 98°C for 30 s, 53°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 45 s; and a final cycle of 72°C for 5 min. The amplification products were subjected to 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, the target fragments were recovered using an Axygen Gel Recovery Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States), and paired-end sequencing was performed using an Illumina Miseq PE300 platform (Meiji Biomedical Technology Co., Shanghai, China).
Data de-duplication and quality filtering of the raw sequences were performed using FLASH (version 1.2.11) (Mago and Salzberg, 2011) and Fastp (version 0.20.0) (Chen et al., 2018). The sequences were then subjected to noise reduction and chimera removal using DADA2 in QIIME2 software (version 2019.4) to obtain Amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) (Callahan et al., 2016). The RDA Classifier Bayesian algorithm (version 2.11) was used to annotate the ASV taxonomy compared to the Maarj AM database, with a confidence threshold of 70%, and the community composition of each sample was counted at different species classification levels. The α-diversity index was calculated using the software QIIME2 (version 2019.4) (Bolyen et al., 2019).
2.6 Data analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to assess the AMF spore density, mycorrhizal colonization rate, soil physical and chemical properties, and plant and litter characteristics of X. sorbifolium. The significance of differences was tested via multiple comparisons using the least significant difference (LSD) method. The similarity of AMF communities in X. sorbifolium plantations of different ages was evaluated using non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analyses based on Bray-Curtis distance calculations. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to analyze the relationships between the relative abundance of AMF genera and soil nutrients, plant characteristics, and apomictic traits. Variance partitioning analyses (VPA) were conducted using the vegan package in R to quantify the independent contributions of soil, plant, and litter traits to AMF community structure and their interactions. To avoid multicollinearity, only variables with a variance inflation factor (VIF) less than 10 were included. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was performed on the selected variables in the VPA (Supplementary Table 7) using R 4.22 software to assess the relationship between soil, plant, and litter traits and AMF communities. Detrended correspondence analysis (DCA) of AMF species data prior to RDA indicated that RDA was more appropriate for inferring relationships between AMF communities and environmental factors. Monte Carlo permutation tests were used to identify significant environmental factors affecting AMF communities.
3 Results
3.1 AMF colonization and spores
The AMF mycelium, vesicle and arbuscular structures were clearly visible in the root system of X. sorbifolium of different forest ages under the microscope, indicating that X. sorbifolium of different forest ages had formed a stable symbiotic relationship with AMF and formed an Arum-type arbuscular mycorrhizal (Figure 2A). The main manifestation was that the mycelium entered the plant root system and mostly grew longitudinally along the root cells (Figure 2Aa), and the lateral bifurcated arbuscular directly penetrated the cell wall of the cortex to form a typical arbuscular structure (Figure 2Ab). And during the extension of the mycelium, the end expanded and developed into the vesicles of varying sizes and diverse morphologies (Figure 2Ac). Mycorrhizal colonization rates ranged from 63 to 95%, with NMF stands having the highest colonization rates, which were significantly higher than MFI, MFII, OMF, and YF stands (P<0.05), but were not significantly correlated with MAF stands (P > 0.05) (Figure 3A).
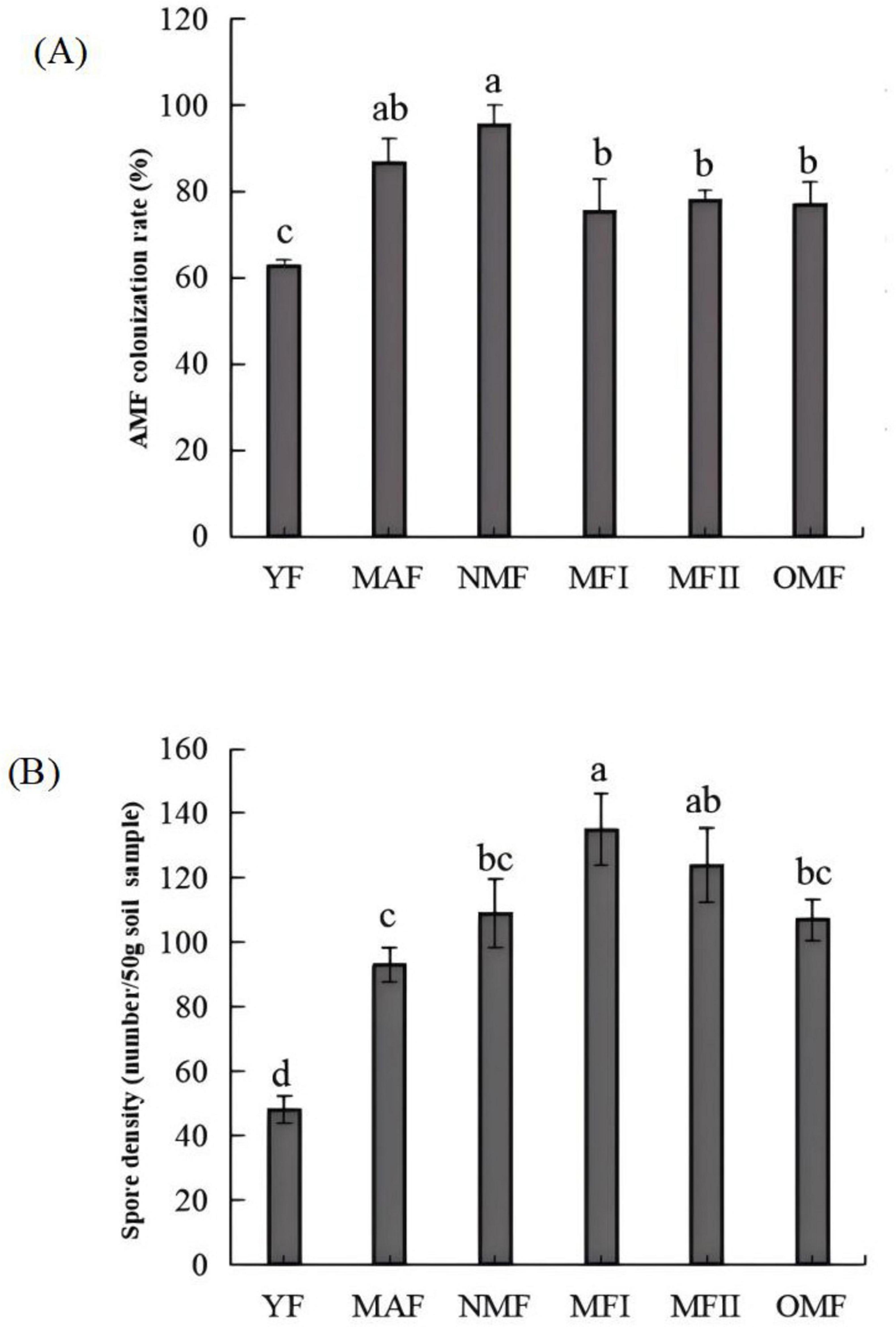
Figure 2. (A) Structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in the root systems of X. sorbifolium. V, vesicles; H, hypha; Ar, arbuscular; Eh, external hyphae; (B) AMF spore morphotypes. (a) Glomus multiforum; (b) Glomus melanosporum; (c) Glomus reticulatum; (d) Glomus constrictum; (e) Paraglomus occultum; (f) Glomus geosporum; (g) Claroideoglomus etunicatum; (h) Acaulospora lavis; and (i) Funneliformis mosseae.
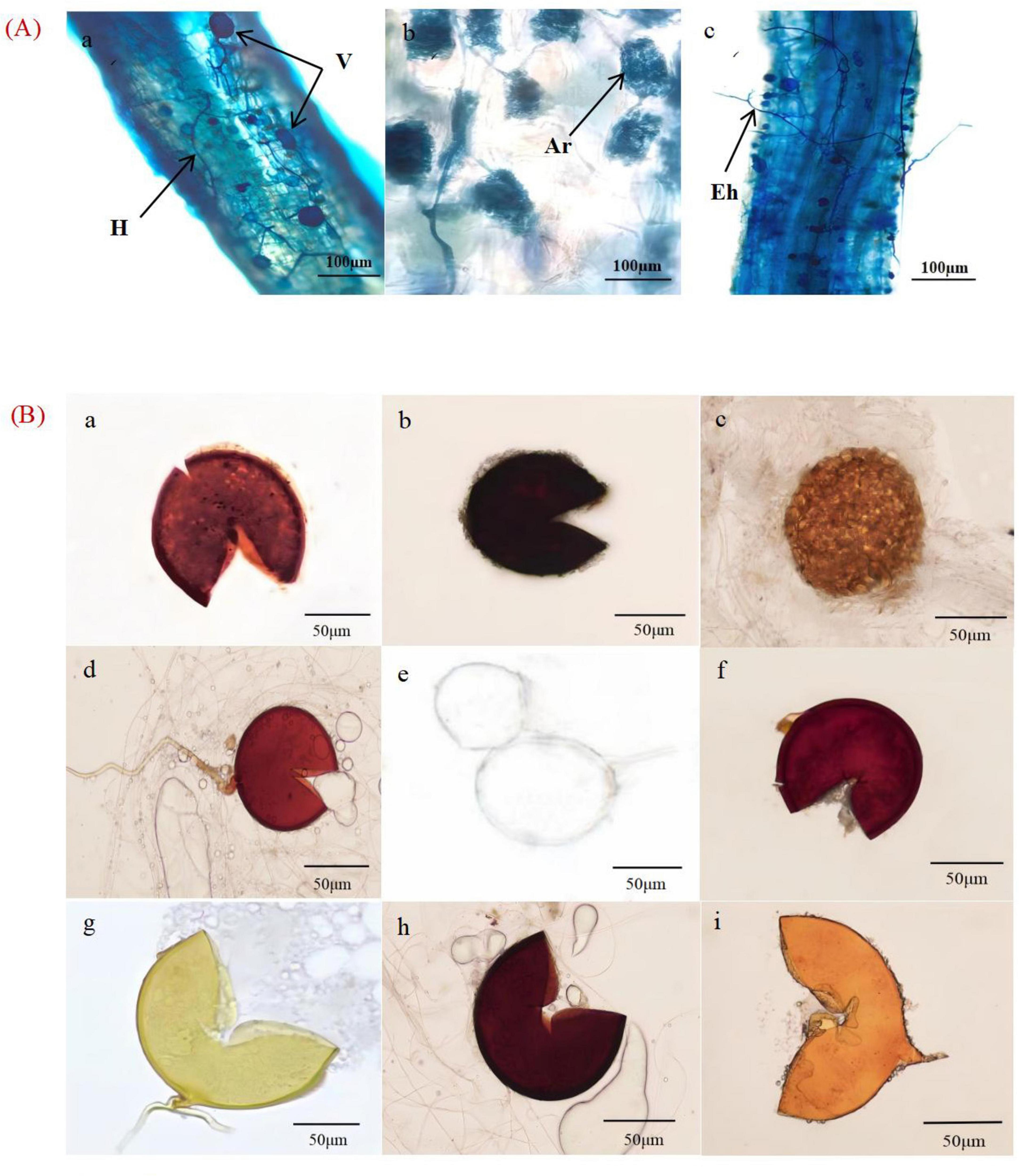
Figure 3. Mycorrhizal colonization rate (A) and spore density (B) of X. sorbifolium. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at p < 0.05. YF, 5 years; MAF, 13 years; NMF, 24 years; MFI, 35 years; MFII, 47 years; OMF, 56 years.
The spore density was calculated using Equation 1. The spore density first increased and then decreased with the increase in plantation age. The spore density was calculated according to Equation 1. A total of 48–135 spores were collected from the rhizosphere soil of X. sorbifolium at different stand ages (Figure 1B). Spore density increased and then decreased with forest age, and MFI stands had the highest spore density, which was significantly higher than that of YF, MAF, NMF, and OMF (P < 0.05), but was not significantly correlated with the age of MFII stands (P > 0.05). 18 species of spores, belonging to 7 genera of AMF were identified by spore morphological methods. The relative abundance, separation frequency and importance value of spores were calculated by Equations 2–4. The results showed that Glomus was the most abundant and was the dominant genus. Glomus multiforum and Glomus melanosporum were detected in different forest stands and were the dominant species in the site (Supplementary Table 6). Figure 2B shows pictures of spores with high importance values in the X. sorbifolium AMF.
3.2 Abundance and diversity of AMF in Xanthoceras sorbifolium
Bioinformatic analysis identified 483,488 sequences from the 24 soil samples, with 82,837 for YF, 76,987 for NMF, 71,565 for MAF, 75,711 for MFI, 88,856 for MFII, and 87,532 for OMF. Similarity clustering based on the 97% queue value yielded 4,523 AMF ASVs, and the number of total ASVs was 47 (Supplementary Figure 1).
AMF community diversity varied substantially among different stand ages, with similar trends in the Chao1 and observed_species indexes. The highest index values were observed in the MAF, while significant differences were not observed among the MFI, MFII, and OMF stands. The Shannon and Simpson diversity indexes reached their highest values in the NMF and lowest values in the YF (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Alpha diversity of X. sorbifolium. YF, 5 years; MAF, 13 years; NMF, 24 years; MFI, 35 years; MFII, 47 years; OMF, 56 years.
3.3 AMF compositions and structures
The obtained ASVs belonged to 1 phylum, 4 classes, 6 orders, 12 families, and 15 genera, and the AMF community was dominated by Paraglomus and Glomus, which presented relative abundances ranging from 15.13 to 47.3% and 12.03 to 58.74%, respectively (Figure 5A). Bray-Curtis based NMDS analyses found significant differences in soil microbial communities between stand ages (R = 0.37, p = 0.04) (Figure 5A). Soil AMF communities were closer in MAF and NMF stands, and MFI, MFII, and OMF stands, indicating higher community similarity (Figure 5B).
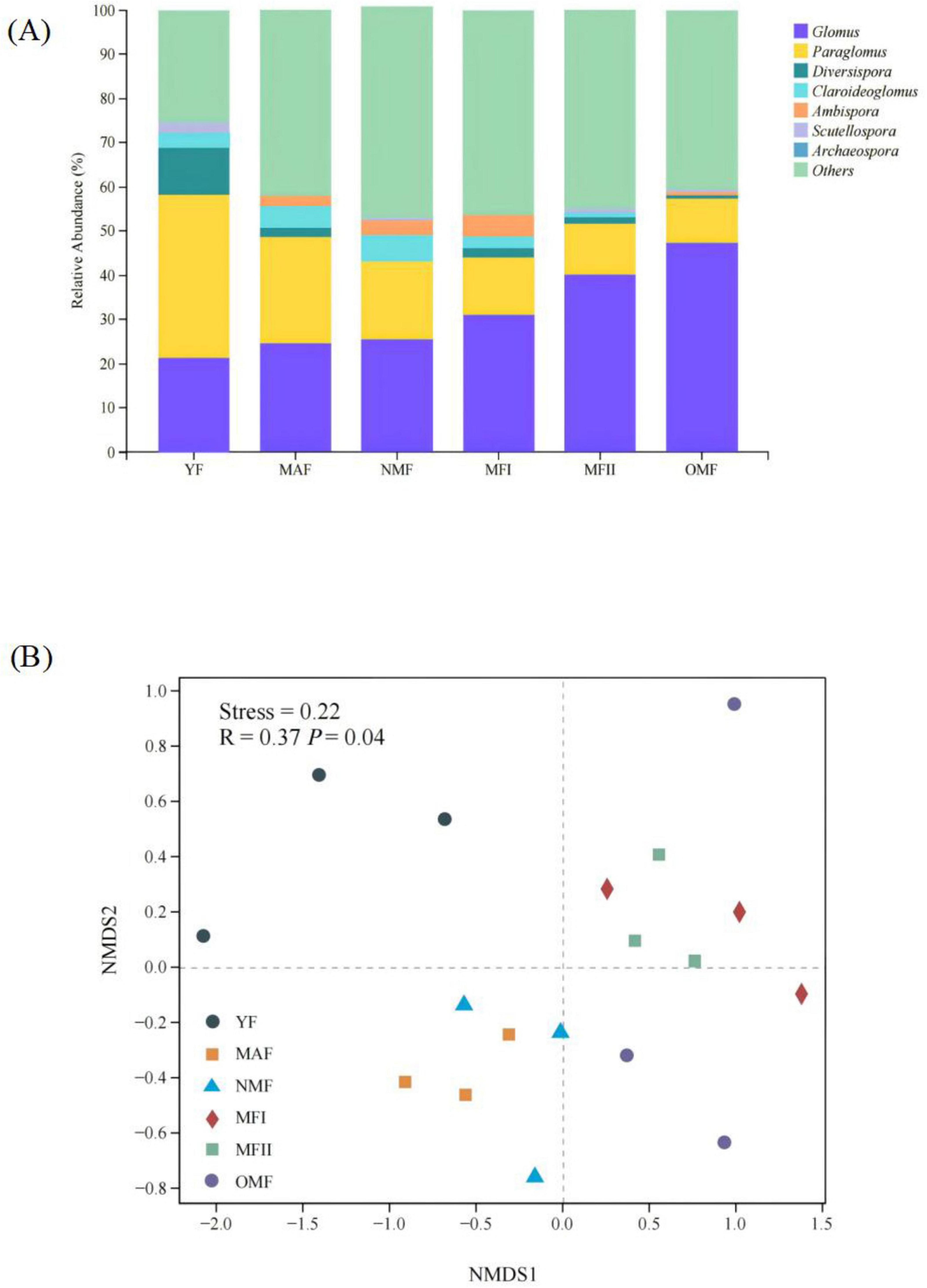
Figure 5. (A) Relative abundance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) genera in X. sorbifolium. (B) Non-metric multi-dimensional scaling (NMDS) of the AMF communities associated with X. sorbifolium. YF, 5 years; MAF, 13 years; NMF, 24 years; MFI, 35 years; MFII, 47 years; OMF, 56 years.
3.4 Environmental variables driving AMF composition and community structure
Correlation analysis showed that the soil characteristic variables were strongly correlated with the AMF genus. Ten of the indicators were correlated with soil AMF genus (Table 1). Among them, Glomus was significantly and positively correlated with soil SOC, TN, AP, pH (P < 0.05) and highly significantly and positively correlated with soil N:P (P < 0.01). However, Paraglomus showed highly significant negative correlation with SOC, TN and TP (P < 0.01), and significant negative correlation with AP and pH (P < 0.05). Diversispora showed highly significant negative correlation with TN and TP (P < 0.01);significant positive correlation with NH4+, BD, and soil C: N (P < 0.05), and highly significant positive correlation with soil C: P showed highly significant positive correlation (P < 0.01). A total of 10 variables in plant traits were correlated with AMF genus. Among them, root-related variables were more strongly correlated with AMF genus than leaf variables. Only 6 of the litter traits (ULB, SLB, ULC, ULP, SL C:N, and SL C:P) were correlated with AMF genus. Among them, all four variables, ULB, SLB, ULC, and SL C:N, were significantly and positively correlated with Glomus (P < 0.05). Diversispora was significantly negatively correlated with ULB (P < 0.05) and highly significantly negatively correlated with SLB (P < 0.01); Scytellospora was significantly negatively correlated with ULB, ULC, and ULP (P < 0.05), highly significantly positively correlated with SL C:N (P < 0.01), and significantly positively correlated with SL C:P (P < 0.05).
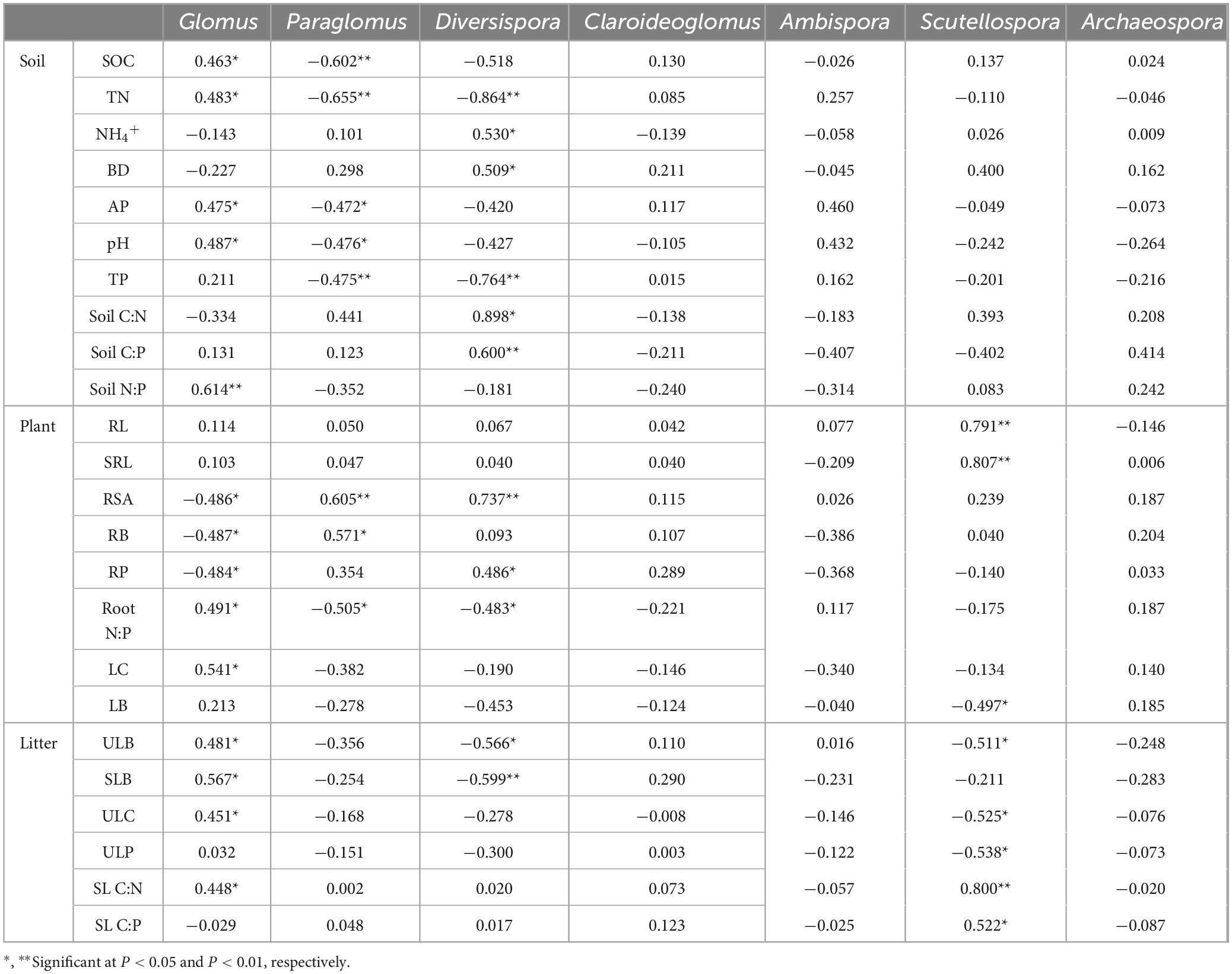
Table 1. Spearman’s correlation analysis between the relative abundance of AMF genera and soil, plant, and litter variables.
The VPA results showed that soil, plant, and litter variables together explained 60% of the variation in AMF communities, and the selected variables are listed in Supplementary Table 7 (Figure 6A). The pure effects of soil, litter, and plant traits were 24, 6, and 13%, respectively. Soil properties and plant traits together explained 12% of the variation in AMF communities, and soil and litter traits together accounted for 3% of the variation in AMF. Soil, plant, and litter traits all explained highly significant of the variance in AMF communities (P < 0.001) (Table 2).

Figure 6. (A) VPA describes the proportion of AMF community variation explained by three sets of predictors: soil nutrients, plant and litter traits. Each shaded section indicates the individual contributions of the identified factors to the changes in soil properties, and the overlapping circles indicate common effects. Explained variance scores are corrected R2-values. (B) RDA of the relationship between Bray-Curtis dissimilarity of AMF communities and variables selected for VPA results. *, **Significant at P< 0.05 and P< 0.01, respectively. RC, Root carbon; SRL, Specific root length; RSA, Root surface area; AP, available phosphorus; SLB, semi-decomposed litter biomass; SOC, soil organic carbon; WC, water content; LC, leaf carbon; LN, leaf nitrogen; ULC, Undecomposed litter C; BD, bulk density; NH4+: NH4+-N; LP, Leaf phosphorus; TP, total phosphorus. YF, 5 years; MAF, 13 years; NMF, 24 years; MFI, 35 years; MFII, 47 years; OMF, 56 years.

Table 2. Variance analysis of the AMF community characteristics explained by soil, plant, and litter characteristics.
RDA showed that the first axis explained 43.73% and the second axis explained 27.39%, with the two axes together explaining 71.12% of the total variance (Figure 6B). Monte Carlo tests further indicated that soil pH, NH4+, and SOC, plant RC and SRL, and litter ULC were significant indicators and major contributors affecting the AMF communities (Table 3).
4 Discussion
This study presents the first comprehensive analysis of the AMF in X. sorbifolium plantations in Inner Mongolia, China. The results indicate that X. sorbifolium root systems form Arum-type structures (Figure 2A), with all showing high colonization rates (Figure 3A), indicating a robust symbiotic relationship with the AMF. In this experiment, a total of 7 genera and 18 species of AMF were identified from the rhizosphere soil of X. sorbifolium by morphological identification (Supplementary Table 6). Morphological identification of AMF has obvious limitations due to the complexity of their morphological characteristics, the fact that some physiological indicators and morphological features are susceptible to change with the developmental stages and habitat conditions, and the fact that some AMF do not produce spores at all at certain times of the year (Redecker et al., 2003). In order to improve the scientific validity of the morphological identification results, the diversity of X. sorbifolium AMF was further analyzed using Illumina MiSeq sequencing techniques, which yielded a total of 51 species in 7 genera after annotation. However, studies using a combination of traditional and molecular methods will further elucidate our uncertain understanding of plant-associated mycorrhizal genera. The results of the present study were the same for both identifications, with Glomus being the dominant genus, a result that is also consistent with the majority of studies, where Glomus has shown a high level of adaptability in different habitat environments in symbiosis with different host plants (Bonfim et al., 2016; Coutinho et al., 2015).
With the development of the stand, Glomus and Paraglomus maintained a high abundance (Figure 5A). This is partly related to the fact that they have high spore production and a unique reproductive strategy that allows them to reproduce directly through mycelium and mycorrhizae and partly due to their high resistance to adverse environments and ability to adapt to highly cyclical and disturbed environments (Gu et al., 2022; Fall et al., 2022). This finding is in line with Marinho et al. (2004), who suggested that dominant taxa are more capable of adapting to new and constantly changing environments. In the present study, Glomus abundance was found to increase gradually with the number of years of cultivation, which may be related to the growth and reproduction characteristics of this genus of AMF. Glomus easily survives and spreads by mycelium, mycospores or fragments, and they are more resistant and resilient to ecological disturbances. Consequently, Glomus colonization became more stable and its abundance gradually increased with years of cultivation. However, Paraglomus abundance and Glomus abundance presented opposite change trends and gradually decreased as the forest age increased, which was due to the competitive relationship between Paraglomus abundance and Glomus (Michael et al., 2010).
The results of this experiment showed that AMF α-diversity in X. sorbifolium did not change regularly with increasing stand age but showed an overall increasing and then decreasing trend (Figure 4). This is consistent with the results of previous studies on Pinus massoniana plantations (Pan et al., 2021). However, Dong et al. (2021) pointed out that the AMF diversity index decreased and then increased with the development of Pinus massoniana, while Gao et al. (2023) showed that the diversity index of Chinese fir plantations gradually increased with the age of the forest. Consistent conclusions have not been reached about the change rule of AMF community diversity in forest soil with stand age, indicating that the successional pattern of AMF communities is very complex and difficult to predict based on the long-term development of the forest stand (Robin et al., 2019). Changes in AMF community diversity due to different stand ages are not only influenced by metabolic activities and reproduction, but also by soil physicochemical properties, plant, and litter characteristics. In addition, changes in soil enzyme activities can affect AMF growth and diversity. Studies have shown that soil enzyme activity may decrease with increasing stand age, which may indirectly affect AMF diversity (Li et al., 2024).
The VPA results were consistent with our second hypothesis that AMF community variation with stand development was due to the combined effects of soil, plant, and litter characteristics. Of these, the soil variable independently accounted for the largest proportion of the total variance in AMF community composition, suggesting that soil properties had a significant effect on soil AMF composition (Table 1) and represented the most important driver of AMF communities (Figure 6A). Substantial evidence has shown that soil properties are the main drivers of AMF community structure and diversity (Cusack et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2020). Of the soil variables, pH, NH4+, and SOC were identified as important parameters affecting AMF communities (Figure 6B and Table 3). Soil pH, as a key soil property, is extremely important in the shaping of AMF communities in natural and plantation forest ecosystems, and soil pH ultimately affects AMF colonization in host plants and AMF communities by influencing AMF extraradical mycelial growth, spore density, and abundance (Adenan et al., 2021; Ma et al., 2021). The results of this study showed that pH is significantly positively correlated with Glomus and significantly negatively correlated with Paraglomus (Supplementary Table 8). The results also suggested that Glomus is more effective at colonizing neutral and alkaline soils, whereas the production of Paraglomus is associated with acidic soils. These results are consistent with those of Jiang et al. (2020), who showed that different AMF taxa have different preferences for soil pH. However, Yang (2022) reported that pH was positively correlated with AMF abundance, which is inconsistent with the results of our study showing that soil pH was significantly negatively correlated with α-diversity (Supplementary Table 8). These contrasting results are likely related to the differences in soil acidity, as the soil samples analyzed by Yang (2022) were alkaline, whereas the soil samples analyzed in this study were neutral or weakly acidic. Plants can directly utilize NO3– and NH4+, which are mainly produced by decomposition of soil microorganisms decomposition, and AMF plays a very important role in the nitrogen cycle because they can directly take up and transfer NH4+ and NO3– in the soil, which is the basis for maintaining the nitrogen balance of the ecosystem (Hodge and Storer, 2015). In this study, NH4+ had a significant effect on the AMF community while NO3– had no significant effect. The reason may be that compared AMF absorbed NH4+ faster than NO3– and the cost of NH4+ uptake and assimilation by AMF extraradical mycelia was less than that of NO3– (Wei et al., 2016). Because NH4+ is more readily emitted by NH3 and N2O, this may affect the survival and activities of AMF, which in turn affects its symbiotic relationship with plants (Li S. J. et al., 2020). SOC was significantly and positively correlated with AMF diversity in the present study, which is consistent with the results of the study on the effects of geographic distance on AMF fungal communities in fruit trees (Jiang et al., 2018). Most scholars believe that an increase in soil SOC will promote AMF to decompose more organic compounds, which can improve the water retention capacity and increase nutrient supply of the soil, and further have a direct positive effect on the AMF community (Jiang et al., 2020). In this study, soil SOC was also found to be significantly positively correlated with the dominant genus of X. sorbifolium, Glomus, which taxonomically belongs to Glomerales. In addition, soil AMF under this order establish symbiotic relationships with host plants through vesicles and tend to use the vesicles to store lipids and SOC as energy (Brands et al., 2018). The study by Souza and Freitas (2017) similarly demonstrated the strong association of Glomerales with SOC.
In this study, plant traits were also identified as important drivers of AMF communities (Figure 6A), with root C and SRL identified as important influencing factors (Figure 6B and Table 3). Soil substrate is the basic condition for plant growth, and the necessary elements and nutrients required to support plant growth originate from root uptake in the soil, and plant root traits and root nutrients may also drive AMF communities. C input from fine roots is a major input to soil organic carbon stocks (McCormack et al., 2015), and C constitutes the basic structure of plants, accounting for approximately 50% of plant biomass. When soil nutrients are limiting factors, host plants usually trade large amounts of their own carbon to mycorrhizal symbionts, allowing more mycorrhizal fungal partners to compete for carbohydrates thereby increasing nutrient uptake benefits. Root C had a significant effect on AMF community structure in X. sorbifolium, which may be functionally related to the density of the root tissues (Wang et al., 2016), with the lower the density of root tissues the lower their activity and nutrient The lower the root tissue density the higher the activity and nutrient uptake capacity and the higher the nitrogen content and lower the carbon content. The growth of AMF requires a carbon source and other nutrients, so it significantly affects the AMF community structure. SRL, a functional strategy representing resource acquisition strategy, is an important indicator of the efficiency of nutrient uptake by fine roots. A significant relationship between root morphological traits (SRL and RSA) and AMF composition and diversity was found in this study (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 8), which is consistent with a previous study (Prada-Salcedo et al., 2021). Higher SRL and RSA provides more space for AMF survival. The fine root is where AMF exchanges material with the host plant, and AMF is more sensitive to changes in fine root traits. On the other hand, it may be because SRL and RSA can directly reflect the survival strategy of the species and the soil environmental conditions. In addition, the morphological characteristics of the root system are directly related to the nutrient uptake and carbon allocation strategy of the plant, which determines the quantity and quality of root litter and secretion and influences the changes of the AMF community. Plant characteristics are not the main driver of differences in AMF diversity. Plant investment in AMF may be lower due to changes in soil fertility and tree nutrient status along the stand age gradient. In addition, among plant leaf traits, only the leaf biomass and leaf C content were significantly correlated with AMF composition (Table 1), and AMF diversity was correlated with leaf biomass (Supplementary Table 8). Our findings are similar to the results of Li M. Y. et al. (2020), who showed that the low correlation between leaf traits and AMF composition and diversity was due to the indirect effect of leaf traits on AMF communities and revealed that material exchange between the two was subordinate to a large and complex interaction system.
Litter is the material basis of natural ecosystems, and its decomposition is a key process of nutrient cycling, which plays an important role in productivity improvement in natural ecosystems (Fang et al., 2020). In forest ecosystems, the majority of available nutrients are concentrated in the litter layer, which is not directly accessible to plant roots. Mycorrhizal fungi are crucial for releasing nutrients from the litter, improving nutrient uptake by plants, and promoting changes in loamy nutrient content. Although AMF has no known saprophytic capacity and relies on plants for carbohydrates (Smith et al., 2011), Kong et al. (2018) found that AMF mycelia proliferate in decomposing organic matter. In addition, Hodge et al. (2001) found that AMF favor the colonization of soils with added plant litter rather than host plants alone, suggesting that litter may represent a potential source of carbon. Mei et al. (2021) concluded that AMF can alleviate nutrient limitation in soil microorganisms and positively influence litter decomposition. The results of this study showed that AMF communities were correlated with undecomposed litter C content and certain litter traits were significantly correlated with the relative abundance of Glomus (Table 1). Glomus colonizes and proliferates in leaf litter and is commonly found in a variety of ecosystems. The mycelium of AMF in litter acquires litter-bound nutrients and releases the nutrients to the associated host plants as well as nearby soil microbes (Bunn et al., 2019). We found that litter N:P was strongly correlated with AMF diversity (Supplementary Table 8), which is because litter inputs can differentially regulate N and P use efficiency across the stand age gradient, thereby affecting AMF communities.
5 Conclusion
Our results showed that X. sorbifolium formed a good symbiotic relationship with AMF in different stand ages and formed Arum-type arbuscular mycorrhizal. Both Glomus and Paraglomus were dominant genera in different stand ages, Glomus gradually increased with stand age, and Paraglomus gradually decreased with stand age. Chao1, Shannon, Simpson, and Observed_species indices showed a tendency to first increase and then decrease with stand age. AMF community changes were jointly influenced by soil, plant and litter traits, and soil traits had a greater influence on AMF communities than plant and litter traits. Among them, soil (SOC, pH, NH4 +), root (SRL, C), and litter ULC variables were important factors affecting AMF communities. These results suggest that future management practices for X. sorbifolium plantation forests should consider the unique responses of AMF communities to soil properties, litter and plant traits. In the future, we should further investigate the driving mechanisms behind rhizosphere soil nutrient, litter, and plant-AMF community interactions in X. sorbifolium, which is crucial for developing more targeted and sustainable management strategies for X. sorbifolium plantations.
Data availability statement
Raw data have been deposited to National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under the BioProject number PRJNA1253386. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.
Author contributions
YZ: Writing – original draft. YM: Writing – review & editing. XM: Writing – original draft. CL: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the High-level/excellent Doctor Introduction Project of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (NDYB2021-9), the Natural Science Foundation Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2023QN03049) and the Third Xinjiang Scientifc Expedition Program (2022xjkk0403).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1579868/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
Adenan, S., Oja, J., Alatalo, J. M., Shraim, A. M., Alsafran, M., Tedersoo, L., et al. (2021). Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and its chemical drivers across dryland habitats. Mycorrhiza 31, 685–697. doi: 10.1007/s00572-021-01052-3
Bai, B., Liu, W., and Qiu, X. (2022). The root microbiome: Community assembly and its contributions to plant fitness. J. Integ. Plant Biol. 64, 230–232. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13226
Bennett, A. E., and Groten, K. (2022). The costs and benefits of plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal interactions. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 73, 649–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-102820-124504
Bolyen, E., Rideout, J. R., Dillon, M. R., Bokulich, N. A., Abnet, C. C., Al-Ghalith, G. A., et al. (2019). Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 852–857. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Bonfim, J. A., Vasconcellos, R. L. F., Gumiere, T., de Lourdes Colombo Mescolotti, D., Oehl, F., and Nogueira Cardoso, E. J. B. (2016). Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a Brazilian Atlantic Forest toposequence. Microb. Ecol. 71, 164–177. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0661-0
Brands, M., Wewer, V., Keymer, A., Gutjahr, C., and Dörmann, P. (2018). The Lotus japonicus acyl-acyl carrier protein thioesterase FatM is required for mycorrhiza formation and lipid accumulation of Rhizophagus irregularis. Plant J. 95, 219–232. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13943
Bunn, R. A., Simpson, D. T., Bullington, L. S., Lekberg, Y., and Janos, D. P. (2019). Revisiting the ‘direct mineral cycling’ hypothesis: Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonize leaf litter, but why? ISME J. 13, 1891–1898. doi: 10.1038/s41396-019-0403-2
Callahan, B. J., Mcmurdie, P. J., Rosen, M. J., Han, A. W., Johnson, A. J. A., and Holmes, S. P. (2016). DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 13, 581–583. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., and Gu, J. (2018). Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Chen, Y. F., Wen, Z. M., Qu, F., Liu, Q. Q., Xing, X. S., Luo, H., et al. (2022). Diversity of soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation planted in successive rotations. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univer. 51, 510–516. doi: 10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).2022.04.009
Coutinho, E. S., Fernandes, G. W., Berbara, R. L. L., Valério, H. M., and Goto, B. T. (2015). Variation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities along an altitudinal gradient in rupestrian grasslands in Brazil. Mycorrhiza 25, 627–638. doi: 10.1007/s00572-015-0636-5
Cusack, D. F., Silver, W. L., Torn, M. S., Burton, S. D., and Firestone, M. K. (2011). Changes in microbial community characteristics and soil organic matter with nitrogen additions in two tropical forests. Ecology 92, 621–632. doi: 10.1890/10-0459.1
Dong, H. Y., Ge, J. F., Sun, K., Wang, B. Z., Xue, J. M., and Steve, A. (2021). Change in root-associated fungal communities affects soil enzymatic activities during Pinus massoniana forest development in subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 482:118817. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118817
Fall, F., Sanguin, H., Fall, D., Tournier, E., Bakhoum, N., Ndiaye, C., et al. (2022). Changes in intraspecific diversity of the arbuscular mycorrhizal community involved in plant-plant interactions between Sporobolus robustus Kunth and Prosopis juliflora (Swartz) DC along an environmental gradient. Microb. Ecol. 83, 886–898. doi: 10.1007/s00248-021-01779-8
Fang, M., Liang, M. X., and Liu, X. B. (2020). Abundance of saprotrophic fungi determines decomposition rates of leafs litter from arbuscular mycorrhizal and ectomycorrhizal trees in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 149:107966. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107966
Fei, S. L., Kivlin, S. N., Domke, G. M., Jo, I., LaRue, E. A., and Phillips, R. P. (2022). Coupling of plant and mycorrhizal fungal diversity: Its occurrence, relevance, and possible implications under global change. New Phytol. 234, 1960–1966. doi: 10.1111/nph.17954
Feng, X. J., Wang, X. Y., Pei, R. H., and Xing, Y. C. (2022). Preliminary study on seedling technology of medicinal plant Xanthoceras sorbifolium. Agric. Technol. 42, 56–59. doi: 10.19754/j.nyyjs.20220430016
Gao, L. W., Zhang, Q. X., Peng, Z. W., Wu, X. S., Yan, Q., Wang, Y. Z., et al. (2023). Characteristics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community in Cunninghamia lanceolata at different ages in mid-subtropical areas. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univer. 52, 185–194. doi: 10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).2023.02.006
Gu, T. Y., Mao, Y. Y., Chen, C., Wang, Y., Lu, Q., Wang, H. Q., et al. (2022). Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi in rhizosphere soil and roots in Vetiveria zizanioides plantation chronosequence in coal gangue heaps. Symbiosis 86, 111–122. doi: 10.1007/s13199-022-00829-0
Gui, H., Hyde, K., Xu, J., and Mortimer, P. (2017). Arbuscular mycorrhiza enhance the rate of litter decomposition while inhibiting soil microbial community development. Sci. Rep. 7:42184. doi: 10.1038/srep42184
Hodge, A., and Storer, K. (2015). Arbuscular mycorrhiza and nitrogen: Implications for individual plant through to ecosystems. Plant Soil 386, 1–19. doi: 10.1007/s11104-014-2162-1
Hodge, A., Campbell, C. D., and Fitter, A. H. (2001). An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus accelerates decomposition and acquires nitrogen directly from organic material. Nature 413, 297–299. doi: 10.1038/35095041
Ianson, D. C., and Allen, M. F. (1986). The effects of soil texture on extraction of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spores from arid soils. Mycologia 78, 164–168. doi: 10.1080/00275514.1986.12025227
Ji, N. N., Chao, L. J., Wang, M. M., and Wang, H. F. (2020). Establishment of in vitro cultures in Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. Mol. Plant Breed. 18, 2671–2677. doi: 10.13271/j.mpb.018.002671
Jiang, S. J., Liu, Y. J., Luo, J. J., Qin, M. S., Johnson, N. C., Öpik, M., et al. (2018). Dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community structure and functioning along a nitrogen enrichment gradient in an alpine meadow ecosystem. New Phytol. 220, 1222–1235. doi: 10.1111/nph.15112
Jiang, S. T., Hu, X. X., Kang, Y. L., Xie, C. Y., An, X. R., Dong, C. X., et al. (2020). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in the rhizospheric soil of litchi and mango orchards as affected by geographic distance, soil properties and manure input. Appl. Soil Ecol. 152:103593. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103593
Kong, D., Wang, J. J., Kardol, P., Wu, H. F., Zeng, H., Deng, X. B., et al. (2016). Economic strategies of plant absorptive roots vary with root diameter. Biogeosciences 13, 415–424. doi: 10.5194/bg-13-415-2016
Kong, X., Jia, Y., Song, F., Tian, K., Lin, H., Bei, Z., et al. (2018). Insight into litter decomposition driven by nutrient demands of symbiosis system through the hypha bridge of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 25, 5369–5378. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0877-2
Korenblum, E., Dong, Y., and Szymanski, J. (2020). Rhizosphere microbiome mediates systemic root metabolite exudation by root-to-root signaling. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 117, 3874–3883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1912130117
Lang, Y., Sun, Y., Feng, Y., Qi, Z., Yu, M., and Song, K. (2020). Recent progress in the molecular investigations of yellow horn (Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge). Bot. Rev. 86, 136–148. doi: 10.1007/s12229-020-09224-0
Li, M. Y., Jiang, X. Y., and Jin, H. R. (2020). Modes of uptake and translocation of NO3- affecting growth of host plants in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Soil J. 57, 1483–1491. doi: 10.11766/trxb201909090476s
Li, S. J., Wang, H., Gou, W., Wu, G. Q., and Su, P. X. (2020). Relationship between leaf functional traits of mixed desert plants and microbial diversity in rhizosphere. J. Appl. Ecol. 29, 1713–1722. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.09.001
Li, T. H., You, M., Xu, J. Y., Li, R. C., Qian, Y., Zhang, X. Y., et al. (2024). Effects of stand age on soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities in long period management Cunninghamia lanceolata forests. J. Central South For. Univer. 44, 23–50. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2024.12.002
Li, X., Guo, J. P., and Zhang, Y. X. (2019). Effects of cutting pretreatment andmatrix formulation on hardwood cutting rooting of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Shanxi. Agricul.Sci. 47, 628–630.
Liu, M., Yue, Y. J., Wang, Z. H., Li, L., Duan, G. Z., Bai, S. L., et al. (2020). Composition of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community and changes in diversity of the rhizosphere of Clematis fruticosa over three seasons across different elevations. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 71, 511–523. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12884
Liu, S., Lu, X., Yang, G., He, C., Shi, Y., Li, C., et al. (2023). Variation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi communities in the rhizosphere soil of Eucalyptus plantations based on different stand ages and its effect on phosphorus fractionation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 189:104908. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2023.104908
Ma, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, D., Gua, X., Yang, T., Xiang, X., et al. (2021). Differential responses of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities to long-term fertilization in the wheat rhizosphere and root endosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 87:e00349–21. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00349-21
Mago, T., and Salzberg, S. L. (2011). FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27, 2957–2963. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507
Marinho, F., Oehl, F., da Silva, I., Coyne, D., da Nóbrega Veras, J. S., and Maia, L. C. (2004). High diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in nature and anthropized sites of a Brazilian tropical dry forest (Caatinga). Mycorrhiza 14, 241–244. doi: 10.1016/j.funeco.2018.11.014
McCormack, M. L., Dickie, I. A., and Eissenstat, D. M. (2015). Redefining fine roots improves understanding of below-ground contributions to terrestrial biosphere processes. New Phytol. 207, 505–518. doi: 10.1111/nph.13363
McGonigle, T. P., Miller, M. H., Evans, D. G., Fairchild, G. L., and Swan, J. A. (1990). A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 115, 495–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1990.tb00476.x
Mei, L. L., Zhang, P., Cui, G. W., Yang, X., Zhang, T., and Guo, J. (2021). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi promote litter decomposition and alleviate nutrient limitations of soil microbes under warming and nitrogen application. Appl. Soil Ecol. 171: 104318. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104318
Michael, H. E., Clay, F., and Matthew, P. R. (2010). Bacterial competition: Surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8, 15–25. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2259
Mohammadi, M., Modarres-Sanavy, S. A. M., Pirdashti, H., Zand, B., and Tahmasebi-Sarvestani, Z. (2019). Arbuscular mycorrhizae alleviate water deficit stress and improve antioxidant response more than nitrogen fixing bacteria or chemical fertilizer in the evening primrose. Rhizosphere 18, 71–76. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2018.11.008
Nadelhoffer, K. J. (2000). The potential effects of nitrogen deposition on fine-root production in forest ecosystems. New Phytol. 147, 131–139. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00677.x
Pan, J., Guo, Q., Li, H., Luo, S., Zhang, Y., Yao, S., et al. (2021). Dynamics of soil nutrients, microbial community structure, enzymatic activity, and their relationships along a chronosequence of Pinus massoniana plantations. Forests 12:376. doi: 10.3390/f12030376
Pereira, C. M. R., da Silva, D. K. A., Ferreira, A. C. A., Goto, B., and Maia, L. C. (2014). Diversity of arbuscular my fungi in Atlantic forest areas under different land uses. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 185, 245–252. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2014.01.005
Prada-Salcedo, L. D., Goldmann, K., Heintz-Buschart, A., Reitz, T., Wambsganss, J., Bauhus, J., et al. (2021). Fungal guilds and soil functionality respond to tree community traits rather than to tree diversity in European forests. Mol. Ecol. 30, 572–591. doi: 10.1111/mec.15749
Redecker, D., Hijri, I., and Wiemken, A. (2003). Molecular identification of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in roots: Perspectives and problems. Folia Geobot. 38, 113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02803144
Robin, A., Pradier, C., Sanguin, H., Mahé, F., Lambais, G. R., de Araujo Pereira, A. P., et al. (2019). How deep can ectomycorrhizas go? A case study on Pisolithus down to 4 meters in a Brazilian eucalypt plantation. Mycorrhiza 29, 637–648. doi: 10.1007/s00572-019-00917-y
Shao, Y. D., Hu, X. C., Wu, Q. S., Yang, T. Y., Srivastava, A. K., Zhang, D. J., et al. (2021). Mycorrhizas promote P acquisition of tea plants through changes in root morphology and P transporter gene expression. S. Afr. J. Bot. 137, 455–462. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2020.11.028
Smith, S. E., Jakobsen, I., Grønlund, M., and Smith, F. A. (2011). Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant phosphorus nutrition: Interactions between pathways of phosphorus uptake in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots have important implications for understanding and manipulating plant phosphorus acquisition. Plant Physiol. 156, 1050–1057. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.174581
Souza, T., and Freitas, H. (2017). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community assembly in the Brazilian tropical seasonal dry forest. Ecol. Proc. 6:2. doi: 10.1186/s13717-017-0072-x
Vergutz, L., Manzoni, S., and Porporato, A. (2012). Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrient in eaves of terrestrial plants. Ecolog. Monogr. 82, 205–220. doi: 10.1890/11-0416.1
Wagg, C., Jansa, J., Stadler, M., Schmid, B., and van der Heijden, M. G. (2011). Mycorrhizal fungal identity and diversity relaxes plant-plant competition. Ecology 92, 1303–1313. doi: 10.1890/10-1915.1
Wang, C. (2023). Effects of different silvicultural patterns on the growth of Xanthoceras sorbifolia plants and the soil microenvironment. Special Econ. Flora Fauna. 26, 42–44.
Wang, N., Sun, Z. F., and Qi, C. Y. (2021). Effects of cutting pretreatment and matrix formulation on hardwood cutting rooting of Xanthoceras sorbifolia. Shanxi Agricul. Sci. 41, 74–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4713.2023.08.014
Wang, W. N., Wang, Y., Wang, S. Z., Wang, Z. Q., and Gu, J. C. (2016). Effects of elevated N availability on anatomy, morphology and mycorrhizal colonization of fine roots: A review. J. Appl. Eco. 27, 1294–1302. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201604.032
Wei, L. L., Lu, C. Y., Ding, J., and Yu, S. (2016). Functional relationships between arbuscular mycorrhizal symbionts and nutrient dynamics in plant-soil-microbe system. J. Ecol. 57, 1483–1491. doi: 10.5846/stxb201412042407
Wilson, J. M., Trinick, M. J., and Parker, C. A. (1983). The identification of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi using immunofluorescence. Soil Biol. Biochem. 15, 439–445. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(83)90009-3
Wright, I. J., Reich, P. B., and Westoby, M. (2001). Strategy shifts in leaf physiology, structure and nutrient content between species of high- and low-rainfall and high- and low-nutrient habitats. Funct. Ecol. 15, 423–434. doi: 10.1046/j.0269-8463.2001.00542.x
Xie, Z. Y., Zhang, W. H., and Liu, X. C. (2010). Growth and physiological characteristics of Xanthoceras sorbifolia seedlings under soil drought stress. Northwest J. Bot. 30, 948–954. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2010.06705
Yang, W. Y. (2022). Biodiversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in black soil region of northeast China and the response to soil organic carbon. Univer. Chinese Acad. Sci. 1–122. doi: 10.27536/d.cnki.gccdy.2022.000018
Zhang, L., Zhou, J., George, T. S., Limpens, E., and Feng, G. (2022). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi conducting the hyphosphere bacterial orchestra. Trends Plant Sci. 27, 402–411. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2021.10.008
Zheng, L. Y. (2017). Isolation and propagation of Xanthoceras sorbifolium VA mycorrhizal fungi and the effects of seedling mycorrhisation. Northern Gardening. 21, 122–129. doi: 10.13456/j.cnki.lykt.2013.12.001
Zhu, L., Huang, J., Chen, T. Y., and Zhou, Y. B. (2015). Root-associated and endophytic fungal community diversity in Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge plantation. J. Northeast For. Univ. 5, 105–111. doi: 10.13759/j.cnki.dlxb.20150522.007
Keywords: Xanthoceras sorbifolium, stand age, forest management, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi community
Citation: Zhang Y, Ma Y, Ma X and Li C (2025) Temporal changes in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi communities and their driving factors in Xanthoceras sorbifolium plantations. Front. Microbiol. 16:1579868. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1579868
Received: 19 February 2025; Accepted: 29 April 2025;
Published: 29 May 2025.
Edited by:
Xiancan Zhu, Anhui Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Jadson Belem De Moura, Evangelical School of Goianésia, BrazilBae Young Choi, Korea National University of Transportation, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Ma, Ma and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yunxia Ma, MTU3MjY2Njk3NUBxcS5jb20=
 Yuexin Zhang
Yuexin Zhang Yunxia Ma2*
Yunxia Ma2*