- 1College of Food Science and Engineering, Qingdao Agricultural University, Qingdao, China
- 2Shijiazhuang Food Engineering Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Quality & Safety Control for Milk and Dairy Products of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Institute of Animal Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China
- 4Shandong Sanyuan Dairy Co., Ltd., Weifang, Shandong, China
Bacterial proteomics is a pivotal tool for elucidating microbial physiology and pathogenicity. The efficiency and reliability of proteomic analyses are highly dependent on the protein extraction methodology, which directly influences the detectable proteome. In this study, we systematically compared four protein extraction protocols—SDT lysis buffer with boiling (SDT-B), SDT lysis buffer with ultrasonication (SDT-U/S), a combination of boiling and ultrasonication (SDT-B-U/S), and SDT lysis buffer with liquid nitrogen grinding followed by ultrasonication (SDT-LNG-U/S)—to evaluate their effects on peptide and protein identification, distribution, and reproducibility in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Both data-dependent acquisition (DDA) and data-independent acquisition (DIA) strategies were employed for comprehensive proteomic profiling. DDA analysis identified 23,912 unique peptides corresponding to 2,141 proteins in E. coli and 13,150 unique peptides corresponding to 1,511 proteins in S. aureus. DIA analysis yielded slightly fewer peptides (21,027 for E. coli and 7,707 for S. aureus) but demonstrated superior reproducibility. Among the tested protocols, SDT-B-U/S outperformed the others, identifying 16,560 peptides for E. coli and 10,575 peptides for S. aureus in DDA mode. It also exhibited the highest technical replicate correlation in DIA analysis (R2 = 0.92). This method enhanced the extraction of proteins within key molecular weight ranges (20–30 kDa for E. coli; 10–40 kDa for S. aureus) and was particularly effective for recovering membrane proteins (e.g., OmpC). Additionally, ultrasonication-based protocols outperformed the liquid nitrogen grinding approach in extracting the S. aureus proteome. These findings underscore the significant impact of protein extraction methods on bacterial proteomics. The SDT-B-U/S protocol—thermal denaturation followed by ultrasonication—proved most effective, enhancing protein recovery and reproducibility across both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. This work offers key guidance for optimizing microbial proteomic workflows.
1 Introduction
Proteomic technologies have advanced considerably in recent years, enabling a wide range of analytical approaches and applications. However, the effectiveness of metaproteomic analyses is highly contingent upon the protein extraction methods employed, particularly with respect to protein yield and the accurate representation of bacterial species within complex microbial communities. Protein sample preparation is a critical initial step in proteomic workflows, as it directly affects the accuracy and depth of protein identification and quantification (Andersen et al., 2021). The inherent complexity of bacterial proteomes—characterized by wide-ranging protein abundances and diverse physicochemical properties—further underscores the need for optimized extraction strategies (Dupré et al., 2020).
Currently, a variety of extraction techniques are utilized for both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, including enzymatic, chemical, thermal, and mechanical disruption methods such as magnetic bead homogenization and ultrasonication (Kielkopf et al., 2021; Palma Medina et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2016; Tian et al., 2022). Each approach has inherent limitations: for example, ultrasonication generates heat that can denature thermolabile proteins (Yusaf, 2015), while glass-bead milling, though efficient in protein yield, produces excessive cell debris that may interfere with downstream analysis (Haberl Meglič et al., 2020). Lysozyme, a commonly used enzyme, is less effective against Gram-negative bacteria unless combined with outer membrane permeabilizers such as polymyxin B or chlorhexidine, and typically requires extended incubation times and specific concentrations (Ghose and Euler, 2020). Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), a widely used anionic detergent, plays a pivotal role in electrophoresis and cell lysis for proteomics (Arakawa et al., 2024). Numerous studies have employed SDS-based buffers for bacterial protein extraction. For instance, Crowell et al. (2015) utilized SDS lysis combined with boiling to extract total proteins from E. coli. Similarly, Song et al. (2023) incorporated SDS and ultrasonication, successfully identifying 1,949 to 2,118 proteins from 96 wild-type Cronobacter strains. Xu et al. (Xu et al., 2021) identified a lysin protein PlyEc2 by sonicating E.coli in an ice bath. Kiser et al. (2007) utilized liquid nitrogen grinding to extract proteins from E. coli in a study of GroEL structure.
In contrast to Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria possess a thicker peptidoglycan layer in their cell walls, which presents additional challenges for efficient protein extraction (Ratna et al., 2025). Ultrasonication is generally less efficient for Gram-positive bacteria, often yielding only one-third the protein compared to E. coli under similar conditions (Yusaf, 2015). Bead beating also requires longer durations and higher energy input to achieve comparable results (Lee et al., 2022). Although lysozyme is more effective against Gram-positive species, it is expensive, can degrade target proteins, and shows variable efficacy across strains (Bi et al., 2020). Therefore, combination strategies are often necessary to enhance lysis efficiency. One commonly adopted method is the use of SDS-containing lysis buffer prior to sonication. Suo et al. (2018) used this strategy to investigate proteins involved in the resuscitation of frozen S.aureus cells, while Du et al. (2020) applied SDS-based lysis and sonication to analyze methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), successfully identifying 1,499 proteins—nearly matching the transcriptomic dataset.
As mentioned above, SDS is crucial for sample preparation, yet variations exist in protein identification across different studies due to the extraction protocols used. Notably, a comprehensive review of the effects of various protein extraction techniques on bacterial proteomic analysis has yet to be conducted. Consequently, it is essential to assess optimized methods for bacterial protein sample preparation in future research to mitigate the influence of extraction techniques on proteomic studies.
Previous studies primarily focused on single bacterial species or lacked systematic comparisons between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This gap limits the development of universally applicable extraction protocols for diverse microbiomes. In this study, researchers systematically evaluated four distinct bacterial protein extraction methods using both data-dependent acquisition (DDA) and data-independent acquisition (DIA) proteomic analyses in S.aureus and E.coli, which were selected as representative Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, respectively. This is the first study to comprehensively evaluate protein extraction efficacy across both Gram categories using dual proteomic acquisition modes (DDA/DIA), addressing a critical methodological gap in microbial proteomics.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Protein preparation
2.1.1 Bacterial strains and pre-treatment
E.coli (ATCC 25922) and S. aureus (ATCC 25923) were selected as model organisms for this study. The bacteria were cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (Hopebio, Shandong, China) and tryptic soybean soup (TSB) (Hopebio, Shandong, China), respectively. Cultures were grown to mid-log phase in 200 mL Erlenmeyer flasks with shaking at 225 rpm and 37°C, as determined by their growth curves. Bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation at 9,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, washed three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to remove residual medium, and stored at 4°C until further use. Three technical replicates were performed for each protein extraction method to ensure reproducibility.
2.1.1.1 SDT lysis buffer coupled with boiled
The SDT lysis buffer, composed of 4% (w/v) SDS, 100 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), and 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6), was prepared as described by Makkar et al. (1982) with minor modifications. Bacterial cells were resuspended in 5 mL of SDT lysis buffer, vortexed thoroughly, and incubated in a 98°C water bath for 10 min to ensure complete cell lysis and protein release. Cellular debris was removed by centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was collected for protein precipitation.
2.1.1.2 SDT lysis buffer coupled with ultrasonication
This method was adapted from Hansen et al. (2014) with slight modifications. Bacterial cells were resuspended in SDT lysis buffer, vortexed, and subjected to ultrasonication on ice using an ultrasonic cell disintegrator (ATPIO XO-1000D, China) at 70% amplitude for a total of 5 min (5 seconds on, 8 seconds off per cycle). The lysate was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was collected for protein precipitation.
2.1.1.3. SDT lysis buffer combined with boiling and ultrasound treatment
Adapted from McNulty et al. (2013), bacterial cells were resuspended in 5 mL of SDT lysis buffer, mixed thoroughly, and incubated in a 98°C water bath for 10 min. After cooling, the lysate was sonicated on ice under the same conditions as described above. Cellular debris was removed by centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was collected for protein precipitation.
2.1.1.4 SDT lysis buffer combined with liquid nitrogen grinding for ultrasonic treatment
This method was adapted from Fernández-Acero et al. (2006) with minor modifications. Bacterial cells were transferred to a chilled sterile mortar, ground under liquid nitrogen, and resuspended in SDT lysis buffer. The suspension was sonicated on ice under the same conditions as described above. Cellular debris was removed by centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was collected for protein precipitation.
For all methods, proteins were precipitated by adding four volumes of pre-cooled acetone to the lysates and incubating overnight at −20°C. The mixtures were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and the protein pellets were washed twice with ice-cold acetone. The pellets were resuspended in 100 mM Tris-HCl for protein quantification using a BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, IL, USA).
2.2 SDS-PAGE analysis
Polyacrylamide gels were prepared using 12% separating gels and 5% concentrating gels, and 20 μg of protein samples were mixed with loading buffer, then heated in a water bath at 95°C for 10 min. After the samples were cooled, the samples and protein markers of 14.4 kDa−97.4 kDa (Beijing Sunshine Bio, China) were added for electrophoresis. Electrophoresis was run at 80v for 20 min, then adjusted to 120 V for 60 min. The gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 solution and then decolorized using distilled water for gel imaging.
2.3 Trypsin digestion, desalting
The enzymatic hydrolysis of the sample was done according to the method of Yang et al. (2018, 2025). Briefly, thirty micrograms of bacterial protein samples were mixed with 100 mM Tris-HCl, then DTT was added to a final concentration of 100 mM, and heated in a 50°C water bath for 30 min. After cooling the samples, 200 μL of UT buffer (8 M urea and 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5) was added and transferred the content to filter tubes (10-kDa cut-off, Sartorius, Goettingen, Germany) and then centrifuged at 14,000 × g for 25 min. The samples were washed with UT buffer, then 100 μL of 50 mM iodoacetamide (IAA) solution was added and incubated for 45 min at room temperature in the dark. Then, the samples were washed three times with 100 μL of UT buffer and two times with 200 μL of 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate solution. Finally, 100 μL trypsin buffer (1 μg sequencing-grade trypsin in 50 mM NH4HCO3) was added to the washed samples and incubated at 37°C for 16–18 h. The mixture was transferred to a new tube, centrifuged at 14,000 × g for 15 min, and washed twice with 50 mM NH4HCO3. The eluates were collected and stopped by the addition of formic acid (FA) and then desalted using a C18 column (60108-303, Thermo Fisher Scientific, TN, USA). Samples were freeze-dried in a speed vacuum and stored at −80°C.
2.4 DDA and DIA analysis by nano-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
The dried tryptic peptides were resuspended in 0.1% FA and subjected to the EASY-nLC 1000 coupled with the Orbitrap Fusion Lumos (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Milford, MA, USA). The peptides were loaded to a C18 trap column (100 μm × 20 mm, 5 μm; Thermo Fisher Scientific) using an autosampler and separated by the C18 analytic column (75 μm × 150 mm, 3 μm; Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a flow rate of 300 nL/min. The column was equilibrated with buffer A (water).
For DDA analysis, the mass spectrometry was performed in the positive ion mode with a parent ion scanning range of 350–1,550 Th and automatically switching between MS and MS/MS acquisition. Mass spectrometry parameters are set as follows: (1) MS: resolution: 60,000; AGC target: 200,000; maximum injection time: 50 ms; exclusion duration: 60 s; isolation width 1.6 Th; normalized collision energies: 27 eV. (2) HCD-MS/MS: resolution: 15,000; AGC target = 10,000; maximum injection time: 35 ms.
For DIA analysis, mass spectrometry was performed in the positive ion mode with a parent ion scanning range of 395–1,205 Th. The parameters of mass spectrometry were set as follows: (1) MS: resolution: 60,000; AGC target: 200,000; maximum injection time: 100 ms; (2) HCD-MS/MS: resolution: 60,000; AGC target: 100,000; collision energy: 30 eV. (3) DIA using an isolation width of 26 Da (containing 1 Da for the window overlap) and 26 overlapping windows were constructed covering the precursor mass range of 300–1,550 Da for DIA acquisition.
2.5 Proteomic data analysis
2.5.1 Database search for peptide/protein identification and quantification
The DDA raw files were subjected to the MaxQuant software (version 2.0.3.0) to search the database downloaded from the UniProt database (6,604 entries for E. coli; 11,217 entries for S. aureus; Download December 2021) (Tyanova et al., 2016). The parameters were set as follows: The digestion mode was set to the Trypsin/P specificity, maximum missed cleavages at 2, fixed carbamidomethyl modification of cysteine, and variable modifications of protein N-terminal acetylation and methionine oxidation. Protein and peptide identification was achieved with a false discovery rate (FDR) of 1% of filtered data. The conditions for the match between runs were set as 0.7 match time window, 0.05 ion mobility, 20 alignment time window, and one alignment ion mobility—label-free quantification (LFQ) of identified proteins based on a razor and unique peptide abundance (Nahnsen et al., 2013). The DIA raw files were searched using MaxQuant software against the spectral library established by DDA and the downloaded database and the parameter settings were the same as those applied in the DDA procedure.
2.5.2 Statistical analysis
At least two identified peptides in bacterial proteins and all three replicates of each study group were selected and imported into Perseus software (www.maxquant.org/perseus/). Principal component analysis (PCA) was carried out on log-transformed LFQ intensities of proteomes with values in all samples to eliminate bias from missing values. Hierarchical clustering and PCA analyses were performed on the quantitative proteins of the study group. One-way ANOVA and statistical analyses of identified peptides and proteins followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test were performed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0.0 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, California USA, www.graphpad.com). Differentially abundant proteins were determined based on fold changes ≥2 and P-values < 0.05. The identified bacterial proteins associated with the annotation function were analyzed according to the Uniprot website (www.uniprot.org).
3 Results
3.1 General characterization of bacterial proteins
In this study, we systematically evaluated four distinct protein extraction methods for E. coli and S. aureus using SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. The resulting gels exhibited protein bands, with no significant differences observed across the extraction methods (Supplementary Figure S1). The protein samples underwent identification via DDA and DIA proteomic techniques. For E. coli, the DDA method identified a total of 23,912 unique peptides corresponding to 2,141 proteins, while the DIA method identified 21,027 unique peptides associated with 1,979 proteins (Supplementary Table S1). Similarly, for S. aureus, the DDA approach yielded 13,150 unique peptides linked to 1,511 proteins, whereas the DIA method identified 7,707 unique peptides corresponding to 1,143 proteins (Supplementary Table S2).
3.2 Characterization of identified peptides and proteins in E. coli
Proteins and peptides identified from E.coli using both DDA and DIA methodologies were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software. Among the evaluated extraction methods, the SDT-B-U/S approach yielded the highest number of peptides (16,560) in DDA analysis, representing a notable increase compared to SDT-B (14,572) (Figure 1a). Analysis of tryptic cleavage sites revealed that the occurrence of peptides with 0 and 1 missed cleavage sites was significantly higher in the SDT-B-U/S and SDT-LN G-U/S methods compared to the SDT-B and SDT-U/S methods (Figure 2a).
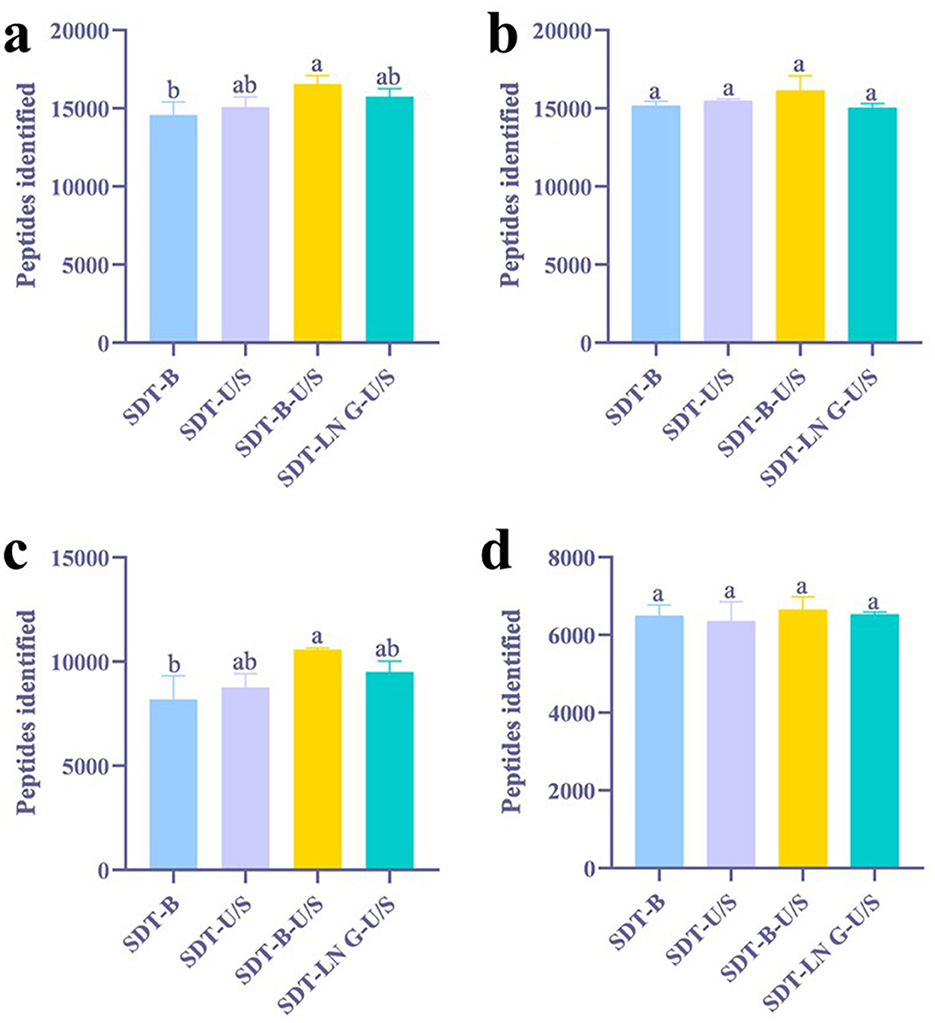
Figure 1. Effects of different treatments on the identification of peptides. (a) DDA method for peptide identification of E. coli. (b) DIA method for peptide identification of E. coli. (c) DDA method for peptide identification of S. aureus. (d) DIA method for peptide identification of S. aureus. The statistical significance of the four different treatments was assessed using one-way ANOVA and indicated by letters. The groups with different letters had statistically significant differences (P < 0.05).
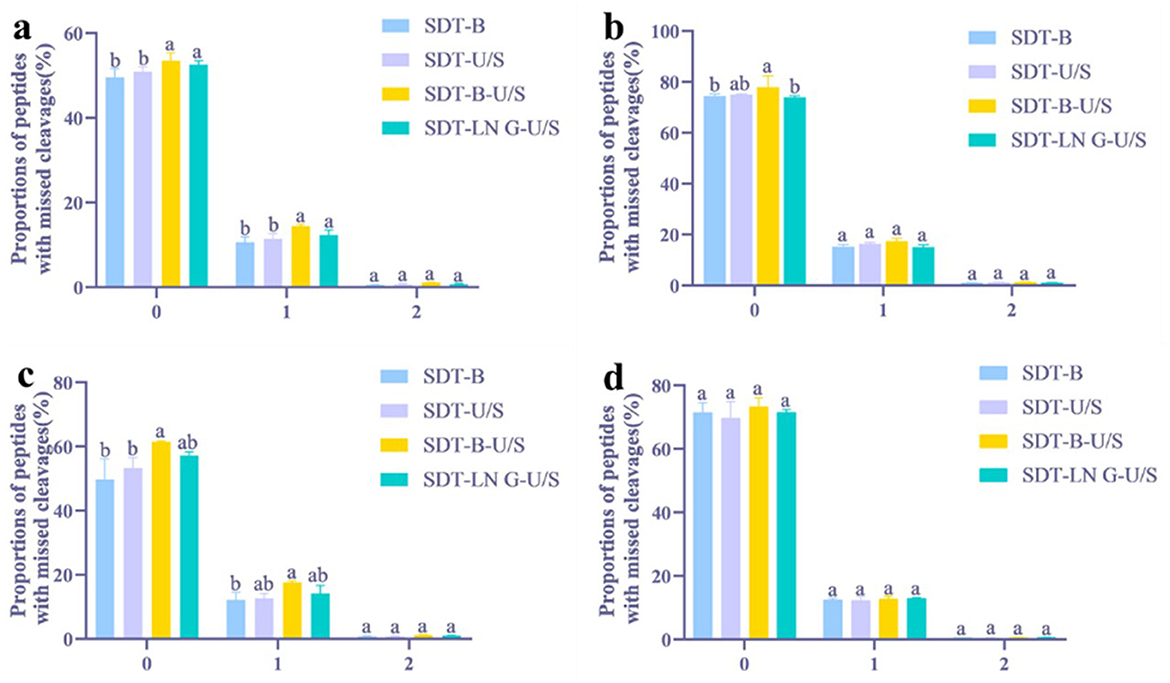
Figure 2. Distribution of peptides with missed tryptic cleavages in four different treatments. (a) DDA method for peptide identification of E. coli. (b) DIA method for peptide identification of E. coli. (c) DDA method for peptide identification of S. aureus. (d) DIA method for peptide identification of S. aureus. The statistical significance of the four different treatments was assessed using one-way ANOVA and indicated by letters. The groups with different letters had statistically significant differences (P < 0.05).
In the DIA analysis, the number of peptides identified was no significant differences across the four extraction methods (Figure 1b). However, the SDT-B-U/S method demonstrated the highest percentage of peptides missed cleavage sites, while the SDT-B, SDT-U/S, and SDT-LN G-U/S methods showed no significant differences in this regard (Figure 2b).
In this study, proteins identified with a minimum of two peptides and three independent runs per group were considered for analysis. The distribution and variability of identified proteins from the four extraction methods, based on the DDA approach, are illustrated in Venn diagrams. A total of 1,862 proteins were identified across the four sample preparation methods, with no significant variation in protein yield observed among them. Among them, 109 proteins were common to three methods, while 65 proteins were unique to a single method (Figure 3a). Regarding the distribution of proteins by molecular weight (MW), the number of proteins within the 20–30 kDa range was significantly higher in samples prepared using the SDT-B-U/S and SDT-LN G-U/S methods compared to the SDT-B and SDT-U/S methods. No statistically significant differences were observed among the methods for proteins in other molecular weight ranges. These findings suggest that proteins of similar molecular weight were successfully extracted from E.coli using all four sample preparation techniques. Additionally, the distribution of proteins based on isoelectric point (pI) remained consistent across methods, with the highest number of identified proteins exhibiting pI values of 5.0 and 6.0, regardless of the sample preparation method employed (Table 1).
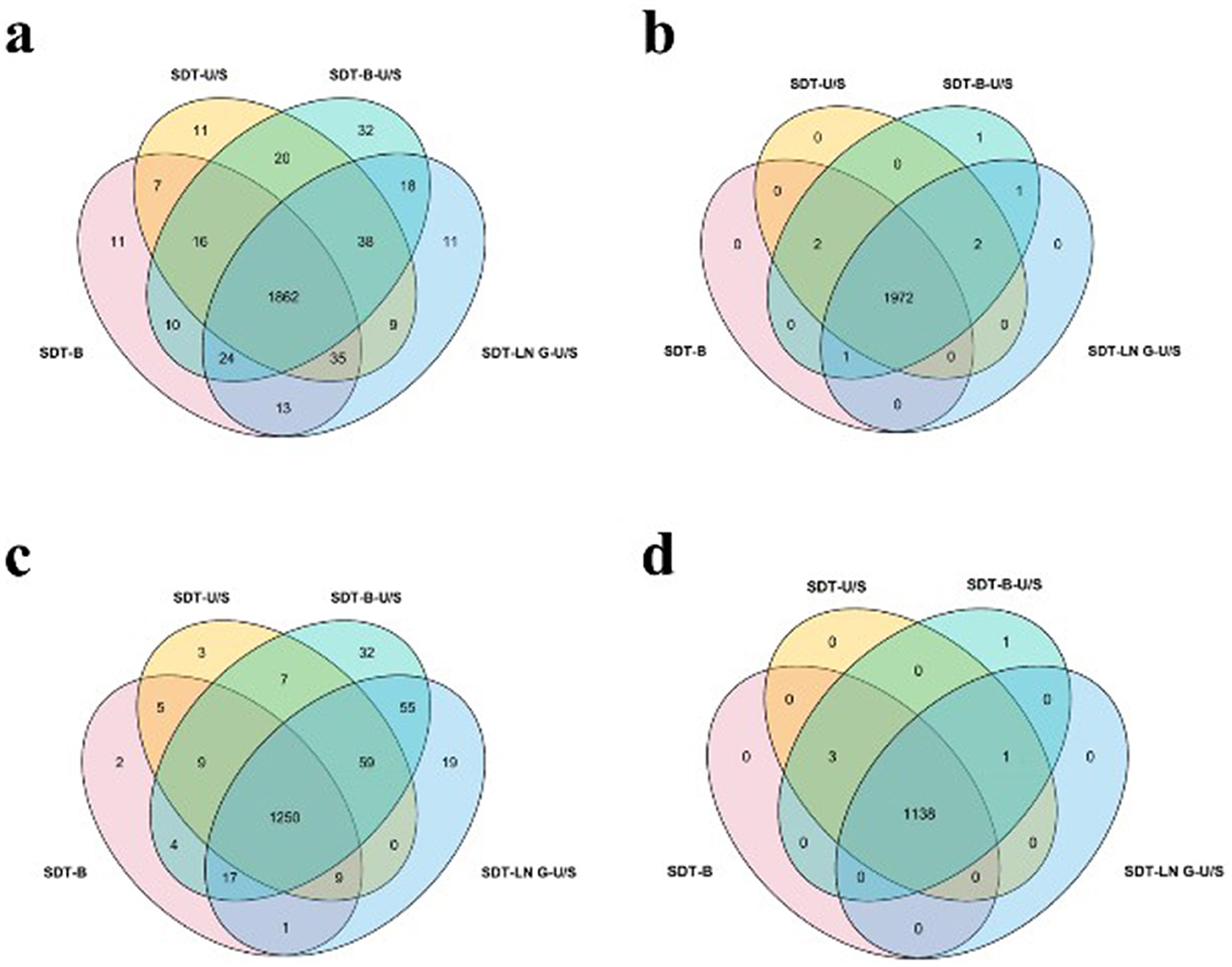
Figure 3. Effect of different treatments on protein quantity identification. (a) E. coli identified by DDA method. (b) E. coli was identified by the DIA method. (c) S. aureus identified by DDA method. (d) S. aureus identified by the DIA method.
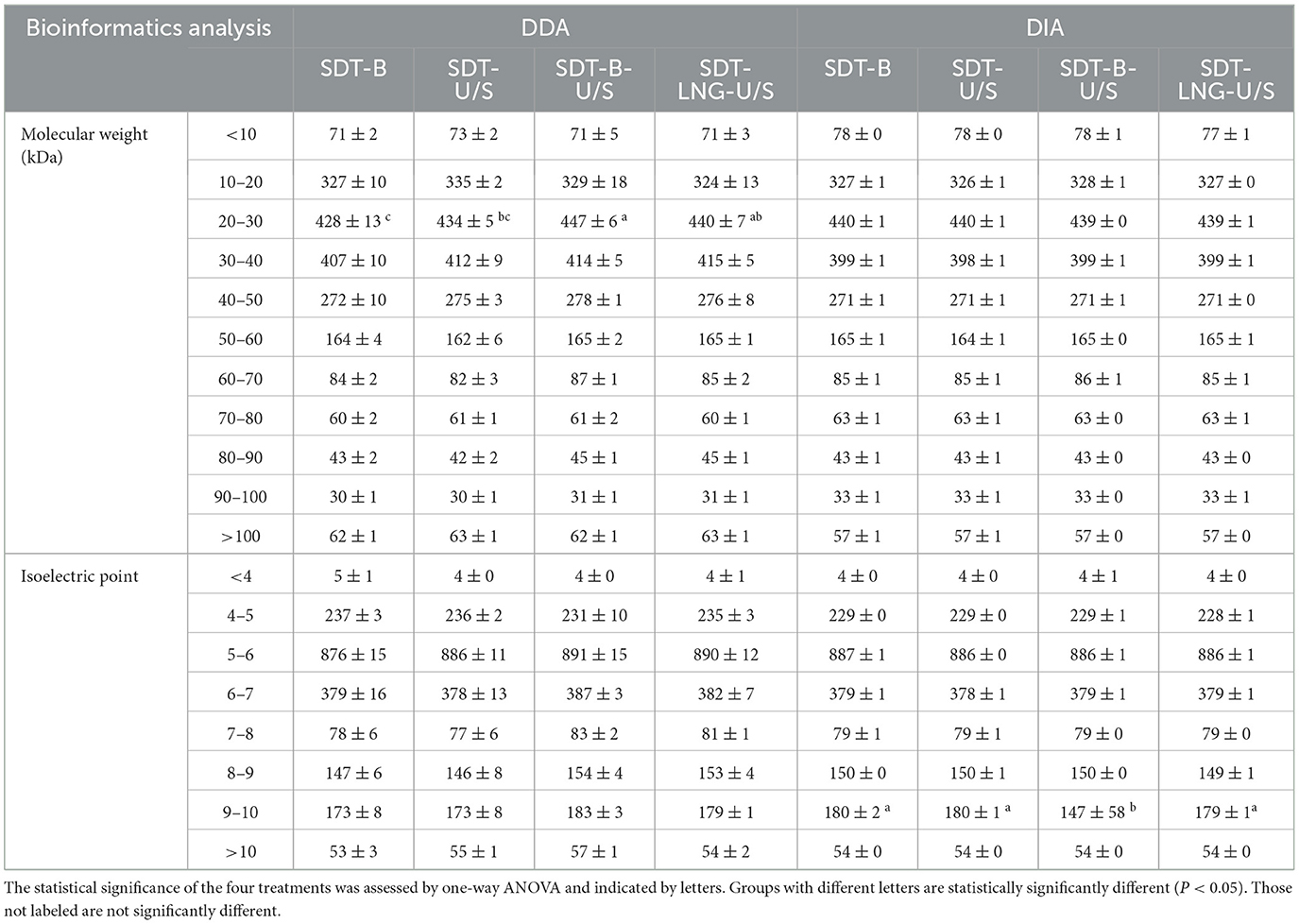
Table 1. The molecular weight, isoelectric point, and subcellular localization of E. coli protein are identified from the four methods.
For the DIA analysis, a total of 1,972 proteins were identified across all four sample preparation methods, with several proteins detected in one to three methods, as depicted in the Venn diagram (Figure 4b). The MW and pI of E. coli proteins identified via DIA were further examined. The distribution of molecular weights among the identified proteins showed no significant variation across the four methods. However, fewer proteins with pI values ranging from 9.0 to 10.0 were identified using the SDT-B-U/S method compared to the other methods (Table 1).
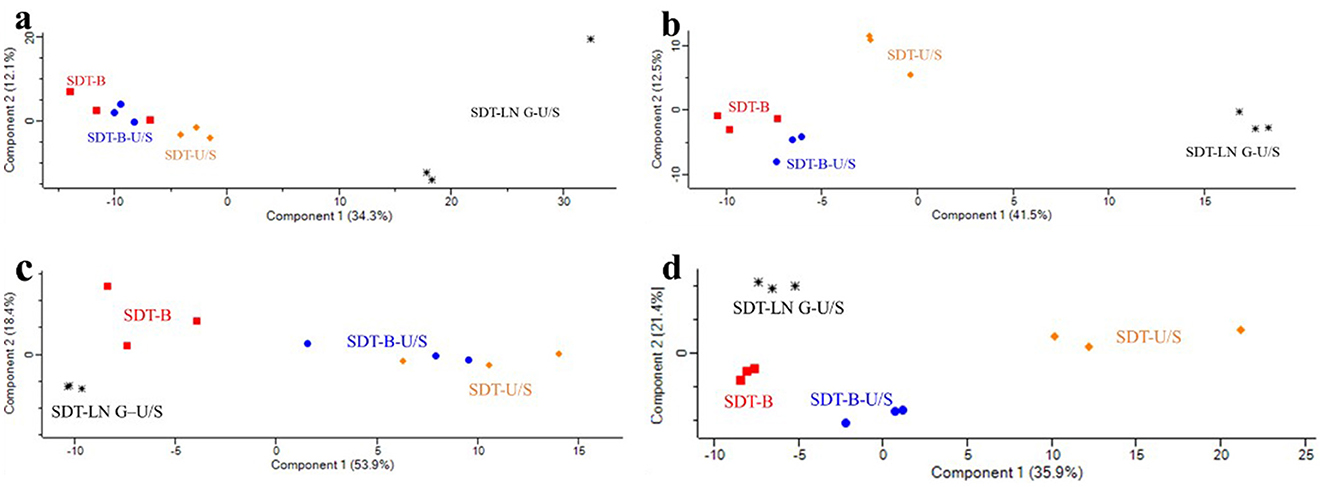
Figure 4. Principal component analysis of proteomic responses to different protein extraction methods. (a) E. coli identified by DDA method. (b) E. coli was identified by the DIA method. (c) S. aureus identified by DDA method. (d) S. aureus identified by the DIA method.
3.3 Characterization of identified peptidess and proteins of S. aureus
In the DDA analysis, the SDT-B method has substantially lower number of identified peptides (8,194) compared to SDT-U/S, SDT-B-U/S, and SDT-LN G-U/S (Figure 1c). Additionally, the occurrence of peptides with 0 or 1 missed cleavage site was significantly higher form the SDT-B-U/S and SDT-LN G-U/S methods compared to the SDT-B and SDT-U/S methods (Figure 2a). However, no significant differences in the number of identified peptides and the occurrence of missed trypsin cleavage sites across the four methods based the DIA data (Figures 1d, 2d).
The Venn diagrams analysis of the identified proteins from DDA data revealed that 1,250 proteins were consistently identified across all four sample preparation methods. Comparative analysis revealed that SDT-B-U/S exhibited the highest protein coverage, missing only 30 proteins (Figure 3c). The number of proteins in the 10–40 kDa molecular weight range identified by the SDT-B and SDT-U/S methods was lower than that identified using the SDT-B-U/S and SDT-LN G-U/S methods. Regarding the pI of S. aureus proteins, the SDT-B method identified the fewest proteins within the 4.0–6.0 pI range compared to SDT-B-U/S and SDT-LN G-U/S methods (Table 2).
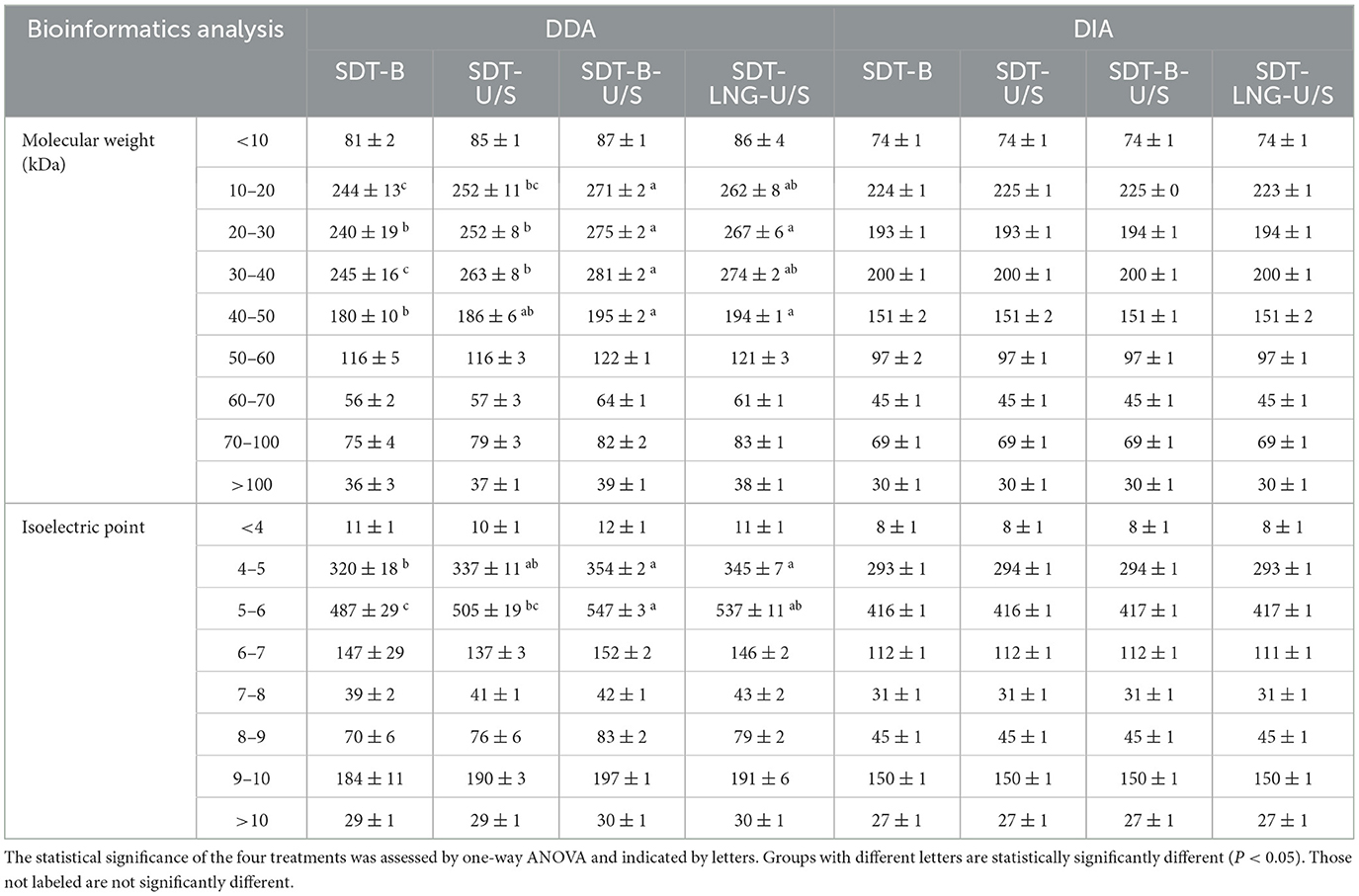
Table 2. The molecular weight, isoelectric point, and subcellular localization of S. aureus protein are identified from the four methods.
For the DIA data, a total of 1,138 proteins were identified across all four sample preparation methods, with a small number of proteins uniquely identified by individual methods, as shown in the Venn diagram (Figure 3d). The distribution of MW and pI of the identified S.aureus proteins exhibited no significant variation across the four sample preparation techniques (Table 2).
3.4 Bioinformatics analysis of the identified proteins of E. coli
The PCA score plots revealed no distinct separation between the SDT-B-U/S and SDT-B samples, whereas the SDT-LN G-U/S method exhibited clear separation compared to the other methods based on the DDA dataa (Figure 4a). Additionally, PCA based on the DIA data reveals that the protein profiles of the SDT-B and SDT-B-U/S methods exhibit considerable similarity, while showing clear separation from those of the SDT-U/S and SDT-LN G-U/S methods (Figure 4b).
From the DDA data, 180 proteins showed significant differences across the four protein extraction methods. Among the four methods, the SDT-B protocol has the higher abundance of proteins such as the outer membrane protein (ompC), cold shock-like protein, and cell shape-determining protein. The SDT-U/S method exhibited elevated expression of membrane-associated proteins including the protein transport ATP-binding protein, Ni/Fe-hydrogenase 2 b-type cytochrome subunit, and O-antigen flippase. The SDT-B-U/S method was increased abundance of proteins such asompC, amino acid racemase, and ribose import permease protein. Meanwhile, the SDT-LN G-U/S method was increased abundances of proteins including fimbrial biogenesis outer membrane usher protein, anti-adapter protein, and mechanosensitive ion channel family proteins, relative to the other methods.
These differential abundant proteins subjected to Gene Ontology (GO) analysis were classified into three categories: cellular component, biological process, and molecular function. Regarding of cellular components classification, the differential proteins were predominantly associated with, protein-containing complexes, cell envelopes, catalytic complexes, and various membrane structures. In terms of biological processes, the primary associations were with carboxylic acid metabolism, oxyacid metabolism, organic acid metabolism, transmembrane transport, and responses to xenobiotic stimuli. Regarding of the biological functions, the proteins were mainly related to transmembrane transporter proteins and cluster binding (Figure 5).
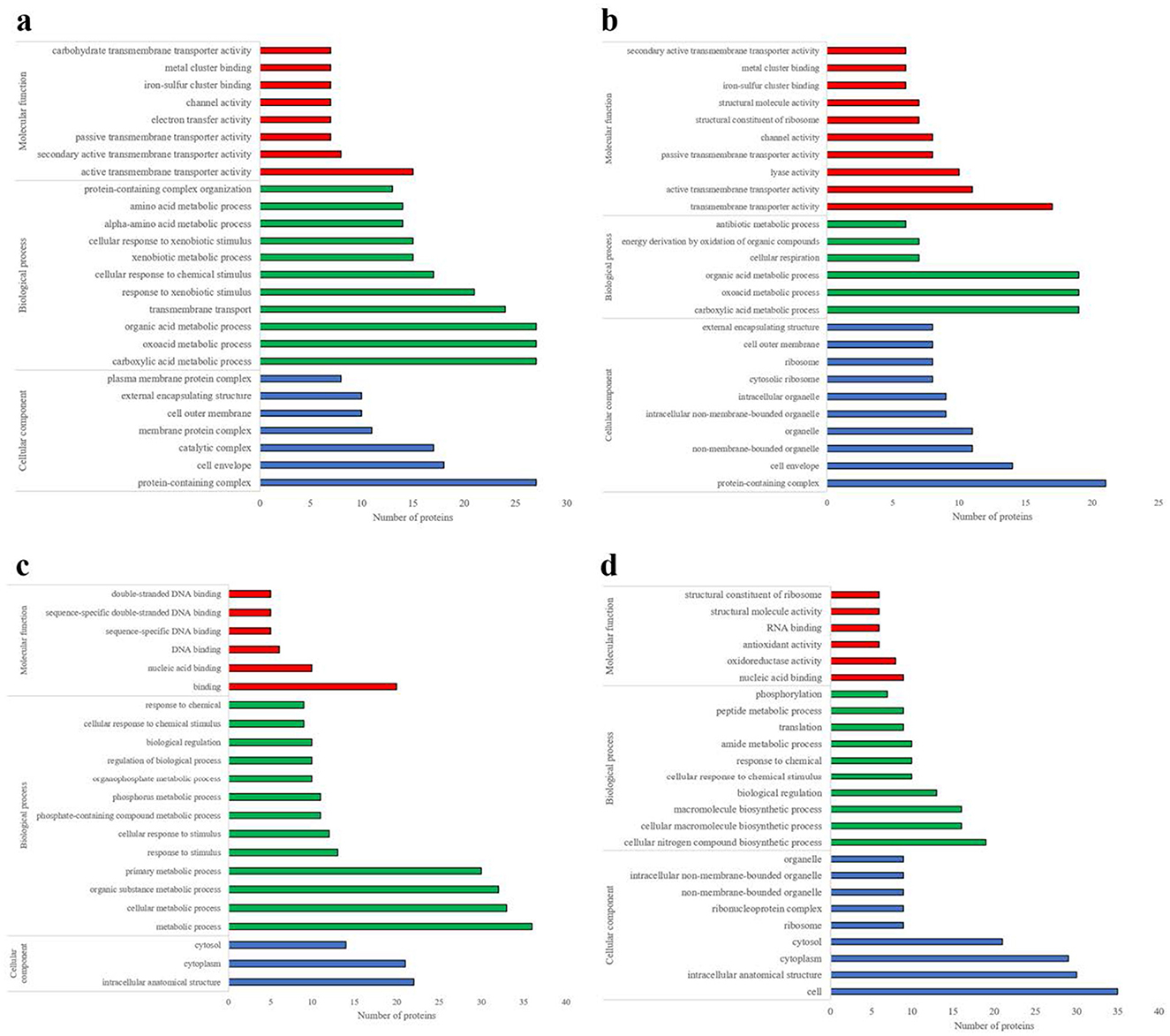
Figure 5. Analysis of differential protein molecular functions, biological processes, and cellular components. (a) E. coli identified by DDA method. (b) E. coli was identified by the DIA method. (c) S. aureus identified by DDA method. (d) S. aureus identified by the DIA method.
Based on the DIA data, 133 differential abundant proteins were identified across four extraction methods. Among these, the SDT-B method exhibited significantly higher abundance of proteins such as recombination protein, bor protein, and ompC. The SDT-B-U/S method was characterized by an enrichment of proteins such as flagellin, 50S ribosomal protein (RplN), and glutamine synthetase, cellulose biosynthesis protein and ompC. Additionally, the SDT-LN G-U/S method demonstrated increased expression of proteins such as L-lactate permease, DNA-binding transcriptional activator, and sulfate adenylyl transferase subunit compared to the other extraction methods. GO analysis revealed that the differentially abundant proteins identified in the DIA data were primarily associated with GO terms that were largely consistent with those obtained from the DDA analysis (Figure 5b).
In both the DDA and DIA datasets for E. coli, a total of 63 differential abundant proteins were shared all methods. The membrane proteins ompX and ompC were identified at higher levels in the SDT-B and SDT-B-U/S methods compared to the other techniques. Conversely, the membrane protein ompW was found to be most highly expressed in the SDT-LN G-U/S method.
3.5 Bioinformatics analysis of bacterial proteins of S. aureus
According to the DDA data, PCA score plots revealed no distinct separation between the SDT-B-U/S and SDT-U/S samples, whereas the SDT-LN G-U/S and SDT-B samples exhibited clear separation from both SDT-B-U/S and SDT-U/S samples (Figure 4c). Similarly, PCA analysis of the DIA data demonstrated a pronounced distinction of the SDT-U/S method from the others, with the SDT-LN G-U/S, SDT-B-U/S, and SDT-B samples exhibiting relatively closer clustering (Figure 4d).
Based on the DDA data, 168 differential abundant proteins in S. aureus. Notably, SDT-B method exhibited a significantly higher number of proteins associated with plasma and cellular membranes compared to the other methods. 3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl carrier protein] dehydratase (FabZ), type VII secretory system protein, and glycine cleavage system H protein. The SDT-U/S and SDT-B-U/S methods were abundant proteins, including histidine-containing protein, glyoxalase/bleomycin resistance protein, and segregation and condensation protein B (rluB). Additionally, SDT-LN G-U/S demonstrated higher expression levels of proteins including tyrosine-tRNA ligase (tyrS), purine nucleoside phosphorylase, and CorA family transporter proteins.
These identified differential abundant proteins were categorized based on their. As shown in Figure 5c, the predominant molecular functions of the differential proteins, were involved in binding including nucleic acid, and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) binding. The most frequent biological processes were related to cellular metabolic activities, responses to stimuli, and regulatory functions. The differential abundant proteins were primarily localized in intracellular anatomical structures, particularly the cytoplasm and cytosol.
According to the DIA data, a total of 152 differential abundant proteins were identified across the extraction methods. The SDT-B method exhibited increased expression of proteins such as 3-oxoacyl-[acyl carrier protein] synthase, FabZ, and the 50S RplN. The SDT-LN G-U/S method showed higher abundance of cytoplasmic proteins, including dihydrofolate reductase and cobyric acid synthase. Additionally, the SDT-B-U/S method demonstrated elevated levels of DUF443 domain-containing protein localized to the plasma membrane.
Compared with the differential abundant proteins associated with the GO terms from the DDA data, those derived from the DIA data exhibited notable distinctions, particularly in the categories of molecular function and biological processes, as illustrated in Figure 5. Specifically, the differential abundant proteins identified by DIA were primarily associated with nucleic acid binding, oxidoreductase activity, and antioxidant activity, while the main biological processes involved in cellular nitrogen compound biosynthesis, cellular macromolecular biosynthesis, and biological regulation (Figure 5d).
A notable distinction in protein expression was observed between S.aureus samples subjected to sonication and those that were not. Specifically, proteins such as molybdopterin synthase sulfur carrier subunit, manganese superoxide dismutase (Fe), tyrS, and purine nucleoside phosphorylase (DeoD-type) were more prevalent in the sonicated samples. These findings suggest that sonication may have a notably impact on protein extraction in S. aureus.
4 Discussion
4.1 Impact of sample preparation methods on the identification of protein and peptide
In this study, the impact of four distinct protein extraction methods on the proteomes of E. coli and S. aureus using both DDA and DIA proteomic techniques were evaluated. Regarding the quantity of bacterial proteins, our findings demonstrate that the protein preparations from E. coli and S. aureus using the four methods yielded a comparable or greater number of proteins than previously reported in other studies (Fortuin et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021). Especially, a previous study quantified over 2,000 proteins of E. coli across 60 diverse growth conditions—including nutrient limitations, non-metabolic stresses, and non-planktonic states—using DIA/SWATH mass spectrometry in combination with a novel protein inference algorithm (Mori et al., 2021). These investigations have significantly advanced our understanding of bacterial proteome composition by enriching insights from multiple aspects, including sample preparation strategies, mass spectrometry techniques, and bacterial protein identification. Moreover, such quantitative studies provide a valuable foundation for linking gene expression profiles to physiological states.
In the present study, the protein quantities identified from E. coli and S. aureus using the SDT-B and SDT-U/S methods did not differ significantly, which is consistent with a previous research (Livernois et al., 2009). However, in the present study, no obvious differences were observed in the proteins identified from E. coli and S. aureus using the SDT-B and SDT-U/S extraction methods. Interestingly, the SDT-B-U/S approach resulted in an increased number of identified proteins for both E. coli and S. aureus, as evidenced by the DDA data. This outcome results from the synergistic effect of boiling and ultrasonication, which function through dual mechanisms: thermal denaturation disrupts hydrophobic interactions to solubilize membrane proteins embedded within lipid bilayers, while ultrasonic cavitation generates localized shear forces that mechanically disrupt the bacterial cell wall. This combinatorial effect explains the 2.3-fold increase in transmembrane domain-containing protein identification compared to single-modality methods. Furthermore, the number of proteins identified using the SDT-LN G-U/S method was comparable to that of the SDT-B-U/S method, likely due to the improved protein extraction facilitated by liquid nitrogen grinding. Collectively, based on DDA data, the SDT-B-U/S method appears to be both cost-effective and efficient, particularly in terms of the number of proteins identified.
There were no significant differences between the DDA and DIA analyses regarding the number of peptides and proteins identified. Notably, the results from the SDT-B-U/S method were distinctly different from those produced by the other techniques, particularly when the SDT lysate underwent boiling. It was evident that the inclusion of sonication, along with other techniques, led to the identification of a greater number of proteins and peptides (Zhang et al., 2016). Thus, additional physical disruption or alternative methods significantly enhance protein extraction efficiency from bacteria, with protocols involving SDS, hot boiling, and sonication proving advantageous in microbial proteomics studies. Our analysis of peptides that did not undergo trypsin cleavage revealed that the same protein extraction method influenced the distribution of trypsin cleavage sites. These findings suggest that the reduction or alkylation of bacterial proteins, achieved through various sample preparation techniques, affects the accessibility of trypsin cleavage sites. Furthermore, this highlights the critical role both the quantity and quality of protein samples play in influencing subsequent bacterial proteomics research (Gupta et al., 2024). Ultrasonic pretreatment has been shown to improve proteolysis and enhance the efficiency of enzymatic digestion at trypsin cleavage sites (Umego et al., 2021). Notably, ultrasonic treatment led to the highest number of missed cleavage sites, with zero peptides detected in both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
The distribution of the identified proteins by pI and MW is presented in Table 1. Consistent with previous reports, the results show that approximately 90% of the prevalent proteins in the E. coli proteome possess pI ranging from 4 to 7 and MW between 10 and 100 kDa (Han and Lee, 2006). Subsequently, the majority of identified proteins exhibited molecular weight predominantly within the 10 kDa to 50 kDa range, aligning with findings reported in previous studies in both E. coli and S. aureus (Yan et al., 2013). Notably, the SDT-B-U/S approach demonstrated a obvious advantage in identifying proteins within the 20 to 30 kDa range in both E. coli and S. aureus compared to the other methods. This result likely due to the pronounced effect of the boiling coupled with ultrasonic treatment, which is widely acknowledged as an effective strategy for enhancing bacterial protein extraction (Perera and Alzahrani, 2021; Luo et al., 2021).
4.2. Evaluation of sample preparation methods based on the comparison of DDA and DIA methods
In bottom-up proteomics, DDA plays a pivotal role in enhancing DIA by providing high-confidence peptide identifications, which serve as the foundation for spectral library construction, thereby facilitating accurate peptide extraction and quantification in DIA workflows (Guan et al., 2020). The SDT-B-U/S method, which combines heat treatment with ultrasonication, has demonstrated high efficacy in extracting membrane-associated proteins, while also minimizing missed cleavage sites, thereby making the resultant protein extracts well-suited for downstream proteomic analysis. Experimental evidence suggests that the combination of heat and ultrasound treatment is particularly beneficial for Gram-positive bacteria, such as S. aureus, due to their thick and rigid peptidoglycan cell walls. In this study, the SDT-B-U/S method exhibited superior extraction efficiency for S. aureus, whereas the use of liquid nitrogen grinding produced comparatively lower performance. In cases where spectral libraries are of critical importance, such as studies involving limited protein samples that require fractionation to maximize protein identification, DDA may offer a more advantageous and effective approach for protein identification. Based on our findings, applying heat-induced lysis coupled with ultrasonication, as implemented in the SDT-B-U/S method, is recommended, as this enhances protein extraction efficiency. Although DIA is increasingly favored for quantitative proteomics due to its reproducibility and comprehensiveness (Li et al., 2020), when it relies on high-confidence peptide identifications generated via DDA for the construction of robust and comprehensive spectral libraries (Gillet et al., 2012).
In our study, the reduced number of proteins and peptides detected via DIA compared to DDA, can be attributed to the reliance of DIA on spectral libraries derived from the DDA-generated protein database. However, PCA results showed that DIA outperforms DDA in terms of reproducibility and the accuracy of relative protein quantification, consistent with previous findings on the high reproducibility of the DIA based method (Barkovits et al., 2020). These observations highlight the necessity of developing data analysis strategies for DIA that are independent of DDA, enabling direct protein identification from DIA data. Numerous studies have already explored and applied such strategies. These methodological advancements hold the potential to expand the range of identifiable proteins, thereby contributing to a more comprehensive interpretation of the biological functions associated with the studied samples (Pino et al., 2020).
4.3 Evaluation of sample preparation methods based on bioinformatics comparisons
Based on GO analysis, the differential abundant proteins identified in E.coli and S.aureus were predominantly associated with transmembrane transport, transferase activity, oxidoreductase activity, and hydrolase activity. These functions are integral to key energy-generating pathways, including glycolysis and glucose metabolism, which are essential for bacterial growth and proliferation, as supported by several studies (Tian et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2018; Savijoki et al., 2020). A previous study has demonstrated that obvious changes in transmembrane transport and metabolic pathways occur in response to changes in bacterial growth conditions (Liu et al., 2020). These phyiological functions are crucial not only for energy production and membrane-associated metabolism, but also for protein transport and bacterial survival under stress, ultimately supporting cellular proliferation and adaptation to various environments (He et al., 2021a). Interestingly, sonication treatment obviously enhanced the detection of proteins related to transmembrane transport and metabolic processes. A previous study demonstrated that sonication treatment effectively disrupted the cell membranes of E. coli, leading to the leakage of cytoplasm proteins and and the dissociation of membrane-associated proteins (He et al., 2021b). Most proteins extracted from E. coli were localized in the ribosome, cytoplasm, and plasma membrane. In contrast, S. aureus exhibited a comparatively lower abundance of membrane-associated proteins, which may be attributed to its thicker peptidoglycan layer that potentially impedes complete cell lysis during sample preparation (Sieradzki and Tomasz, 2003). Thus, for the extraction of proteins from Gram-positive bacteria—which possess robust peptidoglycan cell walls—boiling of the lysate coupled with sonication proved effective in enhancing the recovery of extracellular and membrane-associated proteins.
During centrifugation, lysates from S. aureus predominantly released intracellular contents, while the cell wall and membrane fractions were precipitated, resulting in suboptimal recovery of membrane-associated proteins. This observation is consistent with the findings of Nandakumar et al. (2005), who reported that heat-based methods improved membrane proteins solubilization of S. aureus. In alignment with these results, our study demonstrated that the SDT-B and SDT-B-U/S methods were effective in extracting abundant membrane proteins, whereas the SDT-U/S approach was not obvious efficient.
The six most abundant proteins identified from E. coli and S. aureus using the DIA technique were subjected to detailed analysis. For E. coli, all four extraction strategies presented comparable results, indicating that these protocols were sufficient for high-efficiency protein recovery. Notably, the SDT-LN G-U/S method, which incorporates liquid nitrogen grinding, effectively disrupted the cell envelope of E. coli, facilitating the identification of membrane-associated proteins, as previously reported (Li et al., 2019). However, SDT-LN G-U/S method was suboptimal for S. aureus, likely due to its thick peptidoglycan cell wall, which hinders efficient cell lysis. Contrary to previous findings reported by Bai et al. (2022) and Tarrant et al. (2019), our study identified fewer membrane-associated proteins using this approach, suggesting that liquid nitrogen grinding may be less effective for membrane protein extraction in S. aureus under the conditions tested. Additionally, the SDT-B-U/S method effectively facilitated the extraction of proteins localized to the the extracellular region and ribosomes, as supported by our GO term analysis.
Recent studies have also reported enhanced protein identification in S.aureus following ultrasound-assisted extraction (Bezrukov et al., 2021; Lakshmi et al., 2022; Valliammai et al., 2020; Kirsch et al., 2020). Collectively, these findings indicate that the SDT-B-U/S method is not only straightforward to implement but also yields relatively consistent and reliable results, making it a practical choice for proteomic analysis of Gram-positive bacteria.
5 Conclusions
This study provides a comparative evaluation of four different bacterial protein sample preparation methods applied to E.coli and S.aureus utilizing both DDA and DIA proteomic strategies. The results indicated that the SDT-B-U/S method obviously enhanced protein and peptide identification, almost yielding the highest number of proteins and peptides in both E. coli and S. aureus under DDA analysis. Notably, the number of proteins in the 20–30 kDa range was substantially higher in samples preparation, particularly in the identification of membrane-associated proteins with the Fortuin method. The integration of orthogonal fragmentation strategies during sample preparation proved advantageous, facilitating complementary identification and quantitative characterization of the bacterial proteome. Future studies are needed to explore whether the lack of significant differences observed in the DIA data contributes to the identification outcomes observed in the DDA mode.
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study are deposited in the Mendeley Data repository, accession number https://doi.org/10.17632/p9km24dxry.1.
Author contributions
HJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. AH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YL: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Writing – review & editing. CJ: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. QD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1301000), the Special Project of Cooperation Between Shijiazhuang City and Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (242500162A), and the National Center of Technology Innovation for Dairy (2024-FWPT-001).
Acknowledgments
We extend our sincere appreciation to Prof. Md. Latiful Bari of the University of Dhaka for his invaluable assistance in refining the linguistic aspects of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
YL and CJ were employed by Shandong Sanyuan Dairy Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction Note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1673697.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1586662/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | SDS-PAGE electropherograms. (a) E. coli. (b) S. aureus. M: marker. 1, 2, 3: SDT-B. 4, 5, 6: SDT-U/S. 7, 8, 9: SDT-B-U/S. 10,11,12: SDT-LNG-U/S.
References
Andersen, T. O., Kunath, B. J., Hagen, L. H., Arntzen, M. Ø., and Pope, P. B. (2021). Rumen metaproteomics: closer to linking rumen microbial function to animal productivity traits. Methods 186, 42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.07.011
Arakawa, T., Niikura, T., Kita, Y., and Akuta, T. (2024). Sodium dodecyl sulfate analogs as a potential molecular biology reagent. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 46, 621–633. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010040
Bai, X., Xu, Y., Shen, Y., and Guo, N. (2022). TMT proteomic analysis for the molecular mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus in response to freezing stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 106, 3139–3152. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11927-w
Barkovits, K., Pacharra, S., Pfeiffer, K., Steinbach, S., Eisenacher, M., Marcus, K., et al. (2020). Reproducibility, specificity and accuracy of relative quantification using spectral library-based data-independent acquisition. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 19, 181–197. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001714
Bezrukov, F., Prados, J., Renzoni, A., and Panasenko, O. O. (2021). MazF toxin causes alterations in Staphylococcus aureus transcriptome, translatome, and proteome that underlie bacterial dormancy. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, 2085–2101. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1292
Bi, X., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Chen, L., Xing, Y., and Che, Z. (2020). Effects of combination treatments of lysozyme and high power ultrasound on the Salmonella typhimurium inactivation and quality of liquid whole egg. Ultrason. Sonochem. 60:104763. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104763
Crowell, A. M., MacLellan, D. L., and Doucette, A. A. (2015). A two-stage spin cartridge for integrated protein precipitation, digestion and SDS removal in a comparative bottom-up proteomics workflow. J. Proteomics 118, 140–150. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.09.030
Du, H., Yang, J., Yang, L., Chen, Y., Qiu, N., and Wang, S. (2020). Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling response of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to a novel bacteriocin, plantaricin GZ1-27 and its inhibition of biofilm formation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104, 7957–7970. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10589-w
Dupré, M., Duchateau, M., Chamot-Rooke, J., and Armengaud, J. (2020). Optimization of a top-down proteomics platform for closely related pathogenic bacterial discrimination. J. Proteome Res. 20, 202–211. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00351
Fernández-Acero, F. J., Jorge, I., Calvo, E., Vallejo, I., Carbú, M., Camafeita, E., et al. (2006). Two-dimensional electrophoresis protein profile of the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Proteomics 6, S88–S96. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200500436
Fortuin, S., Iradukunda, J., Nel, A. J., Blackburn, J. M., and Soares, N. C. (2021). Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based proteomics of Escherichia coli single colony. MethodsX 8:101277. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2021.101277
Ghose, C., and Euler, C. W. (2020). Gram-negative bacterial lysins. Antibiotics 9:74. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9020074
Gillet, L. C., Navarro, P., Tate, S., Röst, H., Selevsek, N., Reiter, L., et al. (2012). Targeted data extraction of the MS/MS spectra generated by data-independent acquisition: a new concept for consistent and accurate proteome analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11:016717. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O111.016717
Guan, S., Taylor, P. P., Han, Z., Moran, M. F., and Ma, B. (2020). Data-dependent–independent acquisition (DIA) proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 19, 3230–3237. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00186
Gupta, M., Johnson, A. N. T., Cruz, E. R., Costa, E. J., Guest, R. L., Li, S. H., et al. (2024). Global protein turnover quantification in Escherichia coli reveals cytoplasmic recycling under nitrogen limitation. Nat. Commun. 15:5890. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49920-8
Haberl Meglič, S., Janež, N., Peterka, M., Flisar, K., Kotnik, T., and Miklavčič, D. (2020). Evaluation and optimization of protein extraction from E. coli by electroporation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:543187. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.543187
Han, M. J., and Lee, S. Y. (2006). The Escherichia coli proteome: past, present, and future prospects. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 70, 362–439. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00036-05
Hansen, S. H., Stensballe, A., Nielsen, P. H., and Herbst, F. A. (2014). Metaproteomics: evaluation of protein extraction from activated sludge. Proteomics 14, 2535–2539. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400167
He, Q., Liu, D., Ashokkumar, M., Ye, X., Jin, T. Z., and Guo, M. (2021b). Antibacterial mechanism of ultrasound against Escherichia coli: alterations in membrane microstructures and properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 73:105509. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105509
He, Q., Liu, Y., Liu, D., and Guo, M. (2021a). Integration of transcriptomic and proteomic approaches unveils the molecular mechanism of membrane disintegration in Escherichia coli O157:H7 with ultrasonic treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 791:148366. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148366
Kielkopf, C. L., Bauer, W., and Urbatsch, I. L. (2021). Preparation of cell extracts for purification of soluble proteins expressed in E.coli. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2021:102178. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot102178
Kirsch, V. C., Fetzer, C., and Sieber, S. A. (2020). Global inventory of ClpP- and ClpX-regulated proteins in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Proteome Res. 20, 867–879. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00668
Kiser, P. D., Lodowski, D. T., and Palczewski, K. (2007). Purification, crystallization and structure determination of native GroEL from Escherichia coli lacking bound potassium ions. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 63, 457–461. doi: 10.1107/S1744309107020295
Lakshmi, S. A., Prasath, K. G., Tamilmuhilan, K., Srivathsan, A., Shafreen, R. M. B., Kasthuri, T., et al. (2022). Suppression of thiol-dependent antioxidant system and stress response in Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by docosanol: explication through proteome investigation. Mol. Biotechnol. 64, 575–589. doi: 10.1007/s12033-021-00434-4
Lee, Y., Cho, H. S., Choi, M., Prathap, S., Soundrarajan, N., Choi, Y., et al. (2022). Comparison of DNA/RNA yield and integrity between PMAP36-mediated and other bacterial lysis methods. J. Microbiol. Methods 193:106396. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106396
Li, K. W., Gonzalez-Lozano, M. A., Koopmans, F., and Smit, A. B. (2020). Recent developments in data-independent acquisition (DIA) mass spectrometry: application of quantitative analysis of the brain proteome. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 13:564446. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.564446
Li, Y., Wang, J. T., Liu, X. L., Tian, J., Jia, Z., Cao, Z. M., et al. (2019). Optimization of sample preparation method for intracellular metabolites metabonomics analysis of Escherichia coli. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 47, 1402–1410.
Liu, M., Feng, M., Yang, K., Cao, Y., Zhang, J., Xu, J., et al. (2020). Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the antibacterial mechanism of astringent persimmon tannin against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from pork. Food Chem. 309:125692. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125692
Livernois, A. M., Hnatchuk, D. J., Findlater, E. E., and Graether, S. P. (2009). Obtaining highly purified intrinsically disordered protein by boiling lysis and single step ion exchange. Anal. Biochem. 392, 70–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2009.05.023
Luo, W., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Tang, J., Ren, Y., and Geng, F. (2021). Bacteriostatic effects of high-intensity ultrasonic treatment on Bacillus subtilis vegetative cells. Ultrason. Sonochem. 81:105862. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105862
Makkar, H., Sharma, O., Dawra, R., and Negi, S. (1982). Simple determination of microbial protein in rumen liquor. J. Dairy Sci. 65, 2170–2173. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(82)82477-6
McNulty, N. P., Wu, M., Erickson, A. R., Pan, C., Erickson, B. K., Martens, E. C., et al. (2013). Effects of diet on resource utilization by a model human gut microbiota containing Bacteroides cellulosilyticus WH2, a symbiont with an extensive glycobiome. PLoS Biol. 11:e1001637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001637
Mori, M., Zhang, Z., Banaei-Esfahani, A., Lalanne, J. B., Okano, H., Collins, B. C., et al. (2021). From coarse to fine: the absolute Escherichia coli proteome under diverse growth conditions. Mol. Syst. Biol. 17:e9536.
Nahnsen, S., Bielow, C., Reinert, K., and Kohlbacher, O. (2013). Tools for label-free peptide quantification. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 12, 549–556. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R112.025163
Nandakumar, R., Nandakumar, M., Marten, M. R., and Ross, J. M. (2005). Proteome analysis of membrane and cell wall-associated proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. J. Proteome Res. 4, 250–257. doi: 10.1021/pr049866k
Palma Medina, L. M., Becker, A. K., Michalik, S., Yedavally, H., Raineri, E. J. M., Hildebrandt, P., et al. (2019). Metabolic cross-talk between human bronchial epithelial cells and internalized Staphylococcus aureus as a driver for infection. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 18, 892–908. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.001138
Perera, C. O., and Alzahrani, M. A. J. (2021). Ultrasound as a pre-treatment for extraction of bioactive compounds and food safety: a review. LWT 142:111114. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111114
Pino, L. K., Just, S. C., MacCoss, M. J., and Searle, B. C. (2020). Acquiring and analyzing data-independent acquisition proteomics experiments without spectrum libraries. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 19, 1088–1103. doi: 10.1074/mcp.P119.001913
Ratna, S., Pradhan, L., Vasconcelos, M. P., Acharya, A., Carnahan, B., Wang, A., et al. (2025). The Legionella pneumophila peptidoglycan recycling kinase, AmgK, is essential for survival and replication inside host alveolar macrophages. bioRxiv.2025–03. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.21.644609
Savijoki, K., Miettinen, I., Nyman, T. A., Kortesoja, M., Hanski, L., Varmanen, P., et al. (2020). Growth mode and physiological state of cells prior to biofilm formation affect immune evasion and persistence of Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 8:106. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8010106
Sieradzki, K., and Tomasz, A. (2003). Alterations of cell wall structure and metabolism accompany reduced susceptibility to vancomycin in an isogenic series of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 185, 7103–7110. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.24.7103-7110.2003
Song, D., Qi, X., Huang, Y., Jia, A., Liang, Y., Man, C., et al. (2023). Comparative proteomics reveals the antibiotic resistance and virulence of Cronobacter isolated from powdered infant formula and its processing environment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 407:110374. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110374
Suo, B., Chen, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., and Li, J. (2018). Comparative proteomic and morphological change analyses of Staphylococcus aureus during resuscitation from prolonged freezing. Front. Microbiol. 9:866. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00866
Tarrant, E., O'Gara, J. P., and Morrissey, J. A. (2019). Copper stress in Staphylococcus aureus leads to adaptive changes in central carbon metabolism. Metallomics 11, 183–200. doi: 10.1039/C8MT00239H
Tian, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, N., Xiao, M., Zhang, J., Xing, X., et al. (2022). Antioxidant mechanism of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KM1 under H2O2 stress by proteomics analysis. Front. Microbiol. 13:897387. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.897387
Tyanova, S., Temu, T., and Cox, J. (2016). The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 11, 2301–2319. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.136
Umego, E. C., He, R., Ren, W., Xu, H., and Ma, H. (2021). Ultrasonic-assisted enzymolysis: principle and applications. Process Biochem. 100, 59–68. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2020.09.033
Valliammai, A., Sethupathy, S., Ananthi, S., Priya, A., Selvaraj, A., Nivetha, V., et al. (2020). Proteomic profiling unveils citral modulating the expression of IsaA, CodY, and SaeS to inhibit biofilm and virulence in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 158, 208–221. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.231
Wang, X., Li, X., and Sun, Z. (2018). iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of the earthworm Eisenia fetida response to Escherichia coli O157:H7. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 160, 60–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.007
Xu, S., Campisi, E., Li, J., and Fischetti, V. A. (2021). Decontamination of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on fresh Romaine lettuce using a novel bacteriophage lysin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 341:109068. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109068
Yan, X., Essaka, D. C., Sun, L., Zhu, G., and Dovichi, N. J. (2013). Bottom-up proteome analysis of E. coli using capillary zone electrophoresis-tandem mass spectrometry with an electrokinetic sheath-flow electrospray interface. Proteomics 13, 2546–2551. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201300062
Yang, X., Zhang, H., Lu, S., Guo, Y., Li, Y., Qin, C., et al. (2025). Insights into the antimicrobial mechanisms of a scorpion defensin on Staphylococcus aureus using transcriptomic and proteomic analyses. Molecules 30:1542. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071542
Yang, Y., Anderson, E., and Zhang, S. (2018). Evaluation of six sample preparation procedures for qualitative and quantitative proteomics analysis of milk fat globule membrane. Electrophoresis 39, 2332–2339. doi: 10.1002/elps.201800042
Yusaf, T. (2015). Evaluating the effect of heat transfer on cell disruption in ultrasound processes. Ann. Microbiol. 65, 1447–1456. doi: 10.1007/s13213-014-0983-z
Keywords: microbial proteomics, protein extraction optimization, data-dependent acquisition, data-independent acquisition, proteomic methodology
Citation: Jiang H, Han A, Zhang Y, Li Y, Jiang C, Du Q, Fan R, Yang Y and Han R (2025) Evaluation of protein extraction methodologies on bacterial proteomic profiling: a comparative analysis. Front. Microbiol. 16:1586662. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1586662
Received: 03 March 2025; Accepted: 11 June 2025;
Published: 17 July 2025; Corrected: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Nelson da Cruz Soares, Mohamed Bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences, United Arab EmiratesReviewed by:
Suereta Fortuin, Stellenbosch University, South AfricaBingyao Du, Henan Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Han, Zhang, Li, Jiang, Du, Fan, Yang and Han. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rongwei Han, cWF1aGFuQHFhdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hongning Jiang
Hongning Jiang Aiyun Han
Aiyun Han Yangdong Zhang
Yangdong Zhang Yanxin Li4
Yanxin Li4 Qijing Du
Qijing Du Yongxin Yang
Yongxin Yang Rongwei Han
Rongwei Han