- 1Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Embryo Development and Reproductive Regulation, College of Biological and Food Engineering, Fuyang Normal University, Fuyang, China
- 2Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Animal Nutritional Regulation and Health, College of Animal Science, Anhui Science and Technology University, Fengyang, China
Introduction: The positive rates and genetic identity of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis (G. duodenalis), and Enterocytozoon bieneusi (E. bieneusi) were unclear in crab-eating macaques in Suzhou and Beijing, China.
Methods: A total of 504 fecal samples were collected from crab-eating macaques on commercial farms in Beijing and Suzhou, China. The extracted DNA was analyzed for Cryptosporidium spp. and E. bieneusi by nested PCR and sequence analysis of the small subunit rRNA (SSU rRNA) gene and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) gene, respectively. The G. duodenalis was detected by nested PCR targeting β-giardin (bg) gene, glutamate dehydrogenase (gdh) gene, and triosephosphate isomerase (tpi) gene. The C. hominis identified were further subtyped by nested PCR and sequence analysis of the 60 kDa glycoprotein (gp60) gene.
Results: All 504 fecal samples collected from crab-eating macaques, the detection rates of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi were 11.9% (60/504), 5.6% (28/504), and 4.6% (23/504), respectively. The 15.1% (44/292) detection rate of Cryptosporidium spp. from crab-eating macaques in Suzhou was significantly higher than that in Beijing (2.8%; 6/212; χ2 = 20.6, df = 1, p < 0.0001). The detection rates of Cryptosporidium spp. and G. duodenalis were significant different between <2 months old animals and >24 months old animals (χ2 = 104.7, df = 1, p < 0.0001; χ2 = 6.6, df = 1, p = 0.0104). In contrast, there was no significant different in the detection rate of E. bieneusi in two age groups (χ2 = 2.2, df = 1, p = 0.1360). A total of one Cryptosporidium species, one G. duodenalis assemblage B, and 4 E. bieneusi genotypes have been identified, including C. hominis (n = 60), assemblage B (n = 28), CM1 (n = 14), Peru8 (n = 5), D (n = 3), and Type IV (n = 1). Among 60 C. hominis samples, five subtypes of five subtype families were successfully identified at the gp60 gene: IbA13G4 (n = 27), InA26 (n = 3), IfA17G2R3 (n = 3), IiA17 (n = 3), and IeA11G3T3 (n = 2).
Discussion: The results indicate that known zoonotic Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi are prevalent in crab-eating macaques. The crab-eating macaques could play a potential role in the zoonotic transmission of pathogens to humans.
1 Introduction
Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis (G. duodenalis), and Enterocytozoon bieneusi (E. bieneusi) are common zoonotic protozoan pathogens in humans, non-human primates, and ruminants, causing moderate-to-severe diarrhea in animals (Li W. et al., 2019; Cai et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2021b). These three gastrointestinal pathogens are mainly transmitted through food-borne transmission and water-borne transmission (Xiao, 2010). In non-human primates, crab-eating macaques are very similar to humans in physiology and genetics and are used in human disease research and drug experiments (Zhang et al., 2014). In the laboratory, crab-eating macaques have close contact with humans. Therefore, these animals could become potential hosts for zoonotic Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi.
So far 47 Cryptosporidium species and more than 120 Cryptosporidium genotypes have been recognized in humans and animals, and most of them are host-adapted (Ryan et al., 2021). Among them, C. hominis has a narrower host range and mainly detect in humans and non-human primates (Huang et al., 2025). Although, C. parvum has a broad host range and is rarely found in non-human primates (Feng et al., 2018). More than 10 subtype families of C. hominis have been recognized based on sequence analysis of the 60 kDa glycoprotein (gp60) gene (Xiao and Feng, 2017). Among these subtype families, Ia, Ib, Ie, and Ii were only found in humans and non-human primates (Feng and Xiao, 2017). By contrast, In subtype family was only found in crab-eating macaques in Hainan (Chen et al., 2019). These subtype families of C. hominis differ in virulence, with subtype IbA10G2 widely distributed in both industrialized and developing countries (Bouzid et al., 2013). Subtype IbA10G2 always causes C. hominis-associated outbreaks in industrialized countries (Feng et al., 2018). Therefore, there is a zoonotic potential for Cryptosporidium spp. in crab-eating macaques.
To date, 8 G. duodenalis assemblages (A-H) have been recognized in humans and animals, based on sequence analysis of triosephosphate isomerase (tpi) gene, β-giardin (bg) gene, and glutamate dehydrogenase (gdh) gene (Cai et al., 2021). Among 8 assemblages, assemblages A and B were most commonly found in humans and non-human primates. In contrast, assemblage E was mainly found in ruminants and occasionally found in humans (50 cases) and non-human primates (5 cases) (Brynildsrud et al., 2018; Cai et al., 2021). Previous studies have found that non-human primates were potential hosts for G. duodenalis (Feng and Xiao, 2011). Therefore, there has high zoonotic potential for assemblages A, B, and E of G. duodenalis in crab-eating macaques.
More than 500 genotypes and 15 genetic groups of E. bieneusi have been recognized in humans and animals, based on sequence analysis of internal transcribed spacer (ITS) gene (Li and Xiao, 2021; Li et al., 2022; Jiang et al., 2024). Among 15 groups, Group 1 was mainly found in humans and was considered zoonotic group (Li W. et al., 2019). At least 50 genotypes of E. bieneusi had been found in non-human primates, and these genotypes was clustered together with Group 1 (Chen et al., 2019). Genotypes A, D, Type IV, EbpC, Peru 7, Peru 8, Peru 11, BEB6, and I of E. bieneusi were associated with human microsporidiosis in many countries (Santín and Fayer, 2011; Wang et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2018). Among them, genotypes Type IV, Peru 8, and macaque 3 were a common genotype in humans and most animals, however, macaque3 was only detected in non-human primates in China (Karim et al., 2014b; Karim et al., 2014c; Chen et al., 2020). Therefore, there is a zoonotic potential for E. bieneusi in crab-eating macaques.
In addition to Beijing and Suzhou, some studies on the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis and E. bieneusi in Nonhuman primates (NHPs) have also been conducted in China (Karim et al., 2014c; Karim et al., 2014d; Ye et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2021a; Shu et al., 2022). The crab-eating macaque farms in Beijing and Suzhou have the same history, however the scale of animals is different. The occurrence and genetic identity of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi were unclear in Suzhou and Beijing. Therefore, we examined the occurrence of three pathogens in crab-eating macaques in two cities in this study. The results of the study suggest that these three intestinal pathogens were prevalent and had high zoonotic potential in these animals.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Samples collection
A total of 504 fecal samples were collected from crab-eating macaques on commercial farms in Beijing and Suzhou, China. These farms from lab animal companies were certified by Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care and International Association for Assessment. The crab-eating macaques farms in Beijing and Suzhou were established in 2002. The farms in Beijing and Suzhou had 8,000 and 3,000 crab-eating macaques, respectively. These two farms mainly raised young animals (< 2 months old) and adult animals (> 24 months old) in Beijing and Suzhou, and crab-eating macaques of other ages were sent off farms and some animals were dispersed to laboratories around the world. Of these fecal samples, 292 were collected from 2 convenient age groups in Suzhou, including under 2 months animals (n = 72) and more than 24 months animals (n = 227). The 212 samples from crab-eating macaques were collected from 2 convenient age groups in Beijing, including under 2 months animals (n = 60) and more than 24 months animals (n = 152). These animals investigated were divided into 2 convenient age groups: < 2 months old (n = 132) and > 24 months old (n = 379) according to the true age information of animals at the time of sampling. Crab-eating macaques <2 months represent the juvenile stage of animals, whose immune systems are not fully developed and could be more susceptible to pathogens. Crab-eating macaques >24 months reach sexual maturity, and their immune function is basically established, which could effectively deal with common pathogens. The room in which the animals are kept is cleaned every day. All crab-eating macaques had no obvious clinical signs during the sample collection period. These collected samples were stored in 2.5% potassium dichromate until DNA extraction.
2.2 DNA extraction
The genomic DNA of approximately 200 mg samples in crab-eating macaques were extracted using the Fast DNA Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedical, Santa Ana, CA, USA) as previous described (Jiang et al., 2005). The genomic DNA that had been extracted was stored at −20°C before being used in Cryptosporidium species, C. hominis subtypes, G. duodenalis genotypes, and E. bieneusi genotypes analyses.
2.3 Detection of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi
The extracted DNA was analyzed for Cryptosporidium spp. by nested PCR and sequence analysis of the small subunit rRNA (SSU rRNA) gene (Xiao et al., 1999). The C. hominis identified were further subtyped by nested PCR and sequence analysis of the 60 kDa glycoprotein (gp60) gene (Alves et al., 2003). The E. bieneusi was detected by nested PCR targeting a 392-bp fragment of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of the rRNA gene (Sulaiman et al., 2003b). The G. duodenalis was detected by nested PCR targeting a 599-bp fragment of the glutamate dehydrogenase (gdh) gene, a 511-bp fragment of the β-giardin (bg) gene, and a 530-bp fragment of the triosephosphate isomerase (tpi) gene (Sulaiman et al., 2003a; Caccio and Ryan, 2008; Ye et al., 2014). Two replicates were used for PCR analysis of each sample with positive and negative samples. All primer sequences, cycling parameters, and expected products used are listed in Supplementary Table S1.
2.4 Sequence analysis
All positive secondary PCR products were sequenced sequenced bi-directionally in Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China) to identify Cryptosporidium species, C. hominis subtypes, G. duodenalis genotypes, and E. bieneusi genotypes. The nucleotide sequences were assembled using ChromasPro 2.1.5.0,1 edited using BioEdit 7.1.3.0,2 and aligned using ClustalX 2.0.11.3 The phylogenetic relationships of the C. hominis subtypes and E. bieneusi genotypes were analysed using maximum likelihood analysis implemented in Mega 7.04 based on substitution rates calculated with the general time reversible model as described (Yan et al., 2017).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Detection rates of Cryptosporidium species, G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi were compared between different age groups and cities using the Chi-square test implemented in SPSS v.20.0 (IBM Corp., New York, NY, USA). Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in crab-eating macaques
Of the 504 fecal samples collected from crab-eating macaques, the detection rate of Cryptosporidium spp. was 11.9% (60/504) in Suzhou and Beijing in present study. The 15.1% (44/292) detection rate of Cryptosporidium spp. from crab-eating macaques in Suzhou was significantly higher than that in Beijing (2.8%; 6/212; χ2 = 20.6, df = 1, p < 0.0001; Table 1). By age, the Cryptosporidium detection rates in crab-eating macaque of < 2 months and > 24 months were 32.6% (43/132) and 1.8% (7/379), respectively. The detection rate of Cryptosporidium spp. was significant different in two age groups (χ2 = 104.7, df = 1, p < 0.0001; Table 2).
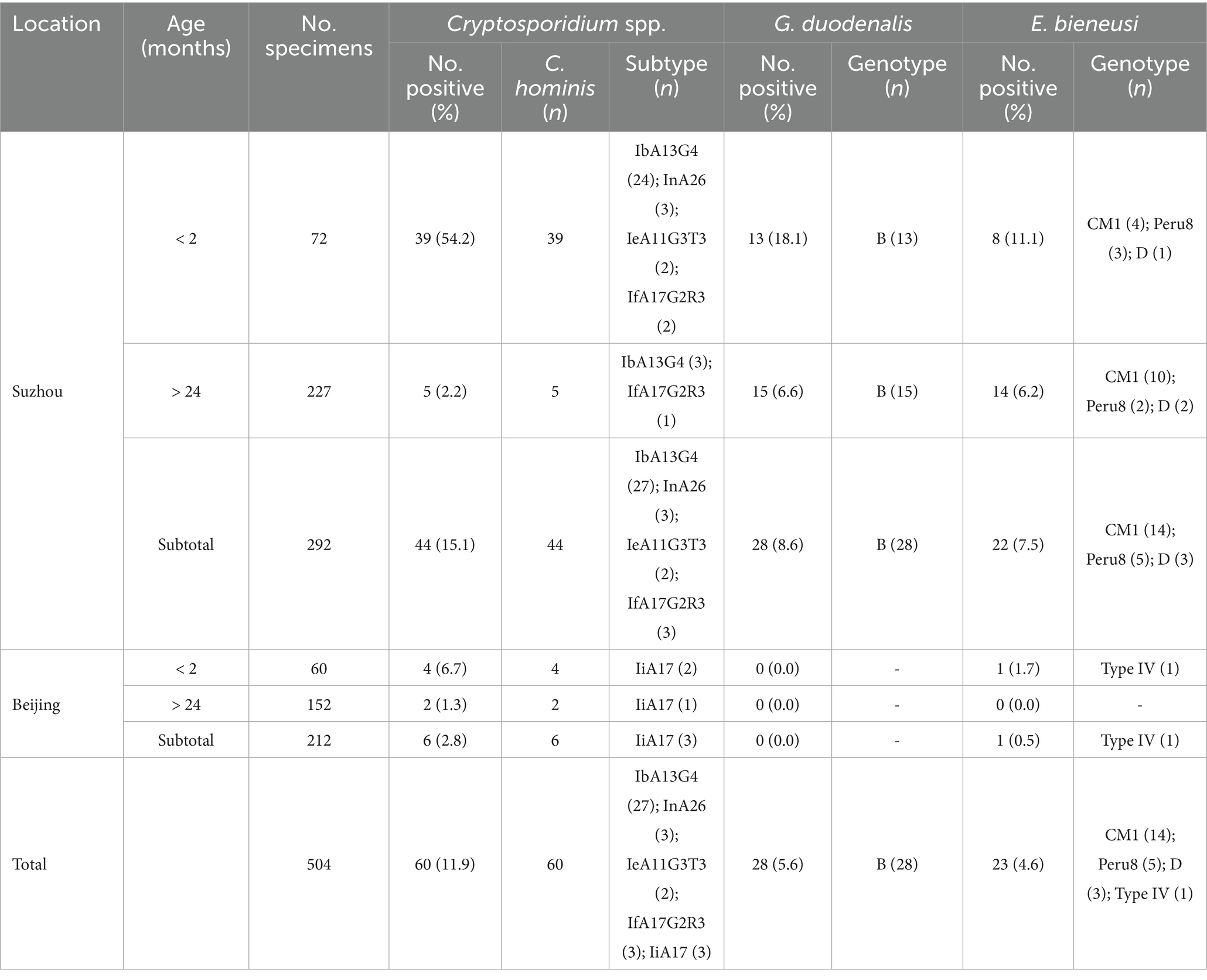
Table 1. Distribution of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi in crab-eating macaques, China.
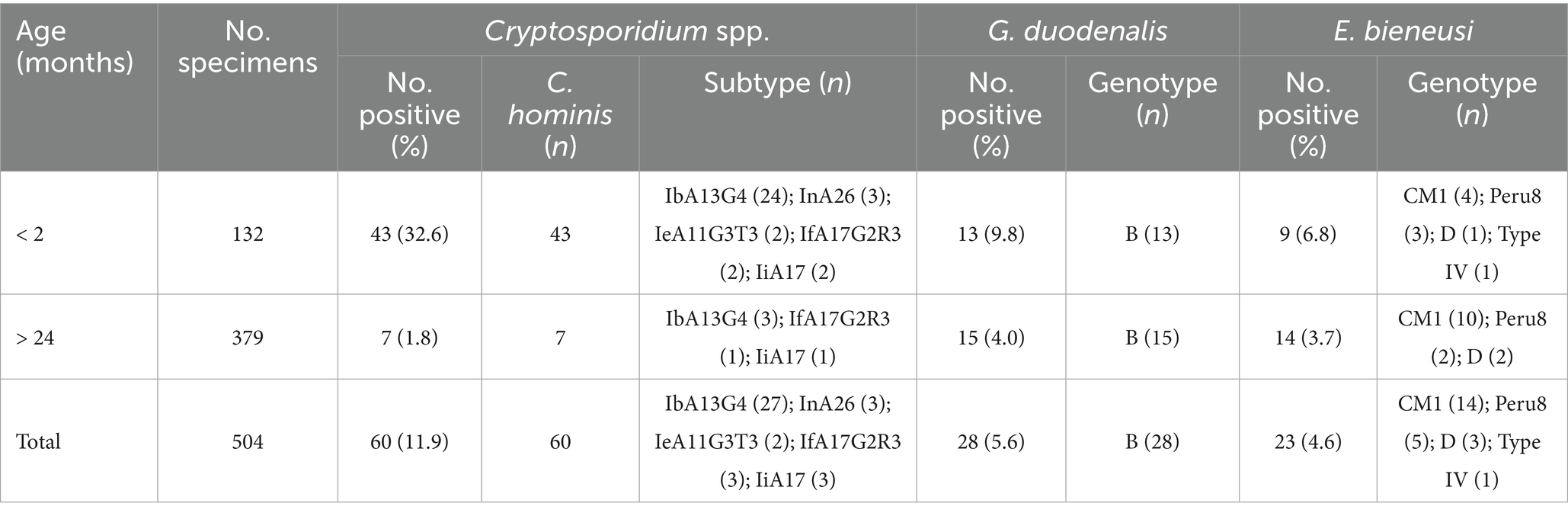
Table 2. Occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi in crab-eating macaques in China by age.
A total of 60 Cryptosporidium-positive samples were successfully sequenced based on the SSU rRNA gene. Only one Cryptosporidium species was identified, namely C. hominis (n = 60). The SSU rRNA gene sequences of C. hominis generated in this study had a single nucleotide variation from the reference sequences reported from Macaca mulatta (GenBank: ON023862). Of the 60 C. hominis samples, five subtypes of five subtype families were successfully identified at the gp60 gene: IbA13G4 (n = 27), InA26 (n = 3), IfA17G2R3 (n = 3), IiA17 (n = 3), and IeA11G3T3 (n = 2). The sequences from subtypes IfA17G2R3, IeA11G3T3, and IiA17 were identical to the reference sequence ON036042 from Macaca mulatta, AY738184 from children, and MK952706 from Macaca fascicularis, respectively. The sequences from subtypes IbA13G4 had TCA and TCG difference in compared to the reference sequence MK982515 from rhesus macaque. In contrast, the gp60 sequence of the InA26 had 9 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) compared to the reference sequence MG952711 obtained from Macaca fascicularis. In phylogenetic analysis of the C. hominis subtypes obtained from the study, emerging subtype IbA13G4 clustered with other If subtypes (Figure 1).
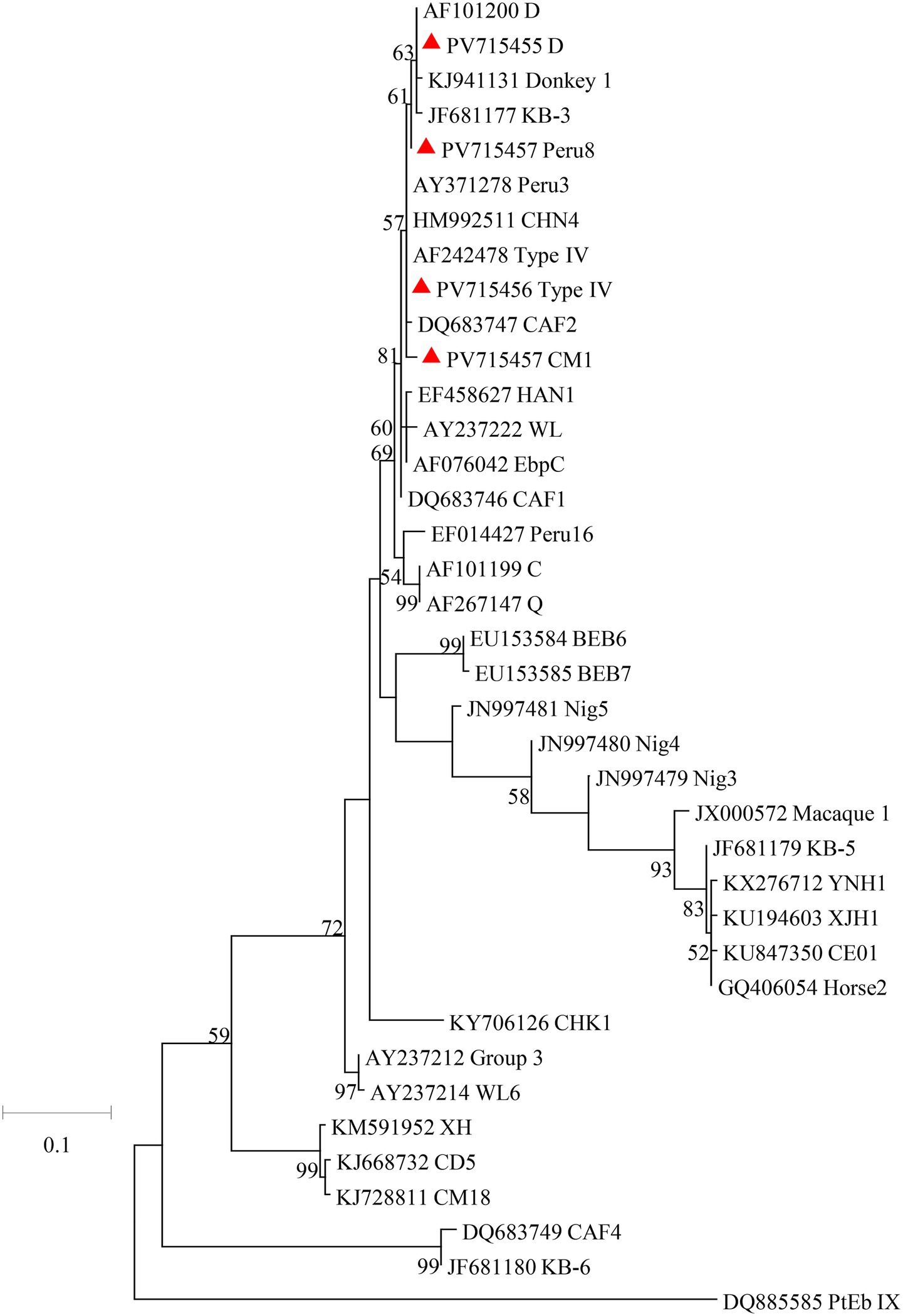
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationships of C. hominis subtypes based on maximum likelihood analysis. The subtypes of C. hominis that have been identified in this study are indicated by red triangles. Bootstrap values below 50% are not shown. Bar = 0.5 substitutions per site.
3.2 Occurrence of G. duodenalis in crab-eating macaques
In present study, the detection rate of G. duodenalis was 5.6% (28/504) in Suzhou and Beijing. The 8.6% (28/292) detection rate of G. duodenalis from crab-eating macaques in Suzhou was significantly higher than that in Beijing (0.0%; 0/212; χ2 = 21.5, df = 1, p < 0.0001; Table 1). By age, the G. duodenalis detection rates in crab-eating macaque of < 2 months and > 24 months were 9.8% (13/132) and 4.0% (15/379), respectively. The detection rate of G. duodenalis were significant different in two age groups (χ2 = 6.6, df = 1, p = 0.0104; Table 2).
The secondary PCR products from 28 G. duodenalis positive samples had been successfully sequenced. Only assemblage B was identified in these positive samples in Suzhou. The obtained sequences from assemblage B samples were identical to the GenBank reference sequence MK262843 from crab-eating macaque.
3.3 Occurrence of E. bieneusi in crab-eating macaques
In present study, the detection rate of E. bieneusi was 4.6% (23/504) in Suzhou and Beijing. The 7.5% (22/292) detection rate of E. bieneusi from crab-eating macaques in Suzhou was significantly higher than that in Beijing (0.5%; 1/212; χ2 = 14.0, df = 1, p = 0.0001; Table 1). By age, the E. bieneusi detection rates in crab-eating macaque of < 2 months and > 24 months were 6.8% (9/132) and 3.7% (14/379), respectively. There were no significant different in the detection rate of E. bieneusi in two age groups (χ2 = 2.2, df = 1, p = 0.1360; Table 2).
The ITS products from 23 E. bieneusi-positive specimens from crab-eating macaques were sequenced successfully. A total of 4 known genotypes were detected, including CM1 (n = 14), Peru8 (n = 5), D (n = 3), and Type IV (n = 1). Among them, CM1 was the dominant genotype in Suzhou, while only one genotype was found in Beijing. The sequences from genotypes CM1, Peru8, D, and Type IV were identical to the reference sequence KF305581 from Rhesus macaque, JF927959 from chicken, MT895457 from amur tiger, and AF242478 from human, respectively. In the maximum likelihood analysis of the E. bieneusi genotypes, genotypes CM1, Peru8, D, and Type IV were clustered with Group 1 (Figure 2).
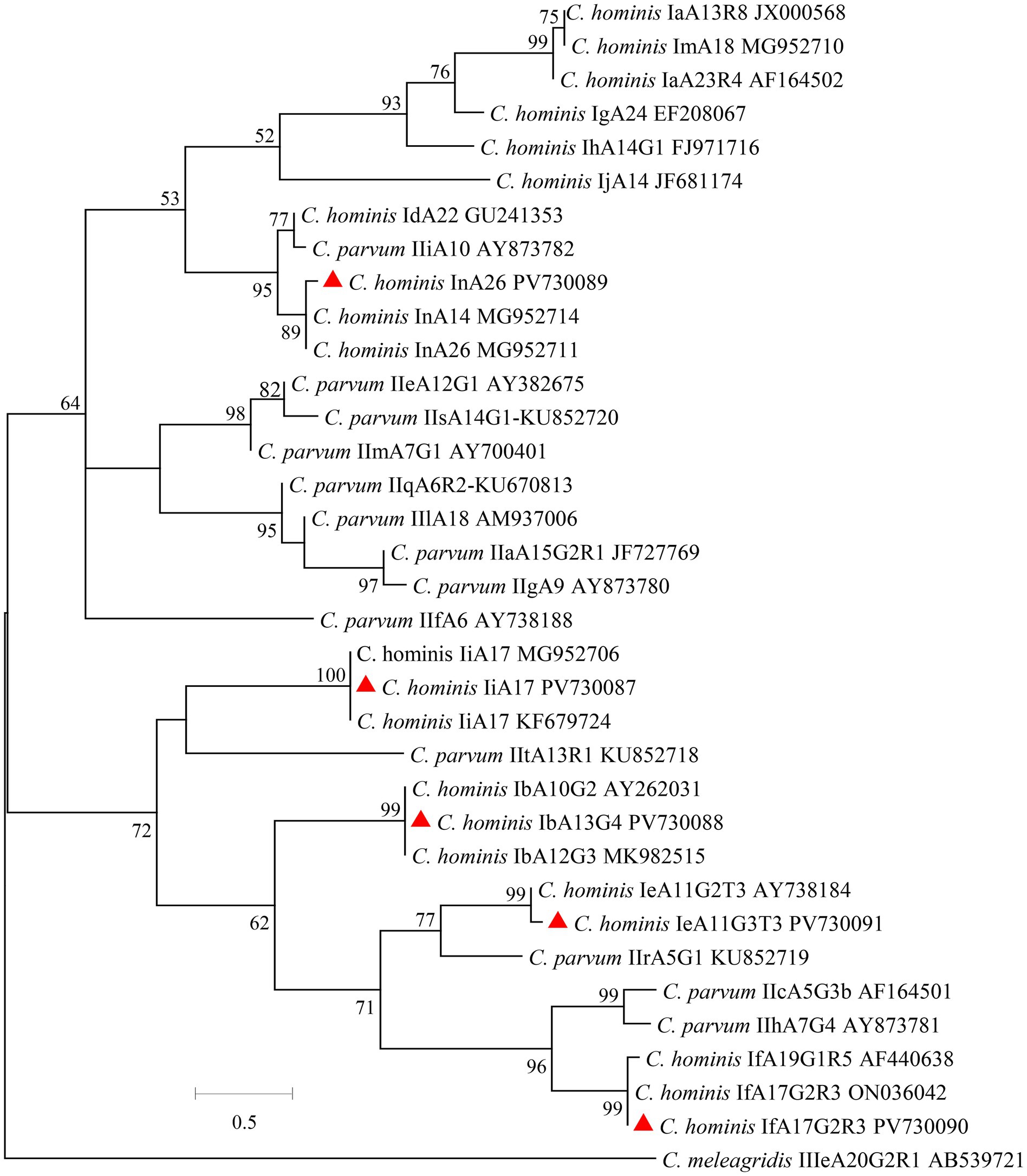
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships of E. bieneusi genotypes based on maximum likelihood analysis. The genotypes of E. bieneusi that have been identified in this study are indicated by red triangles. Bootstrap values below 50% are not shown. Bar = 0.1 substitutions per site.
4 Discussion
The results of this study indicate that Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi are prevalent in crab-eating macaques in Suzhou and Beijing of Chinese cities. Altogether, the detection rates for Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi were 11.9, 5.6, and 4.6%, respectively. The detection rate (11.9%) in this study for Cryptosporidium spp. was higher than that observed in free-range monkeys conducted in Shanxi (3.0%), Yunan (0 and 0.6%), Guangxi (1.0%), and Guizhou (0.7%) of China (Karim et al., 2014d; Du et al., 2015; Gu et al., 2016; Jia et al., 2022; Shu et al., 2022). However, it is similar to the prevalence in farmed crab-eating macaques in Hainan (9.1%) (Chen et al., 2019). The high detection rate of Cryptosporidium spp. in this study may be due to the highly intensive farming model in crab-eating macaque farms. Further comparison with other countries, the detection rate of farmed crab-eating macaques was also higher than that free-range NHPs in Thailand (1.0%), Kenya (2.6%), Madagascar (4.0%), and Rwanda (4.0%) (Li et al., 2011; Sak et al., 2014; Bodager et al., 2015; Sricharern et al., 2016). Therefore, the intensive farming of animals was conducive to the transmission of Cryptosporidium spp. The detection rates of G. duodenalis (5.6%) and E. bieneusi (4.6%) in this study are lower than those found in NHPs in other studies, which reported detection rates ranging from 8.5 to 32.3% for G. duodenalis and from 11.4 to 46.2% for E. bieneusi (Johnston et al., 2010; Beck et al., 2011; Ye et al., 2012; Du et al., 2015; Karim et al., 2015; Zhong et al., 2017). The low detection rate of these two pathogens may be due to the high prevalence of Cryptosporidium limit the transmission of them. Among the two cities, the detection rates of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi were higher in Suzhou, probably because of the higher stocking density on this farm. By age, the detection rates for Cryptosporidium spp. (32.6%), G. duodenalis (9.8%), and E. bieneusi (6.8%) in monkeys of under 2 months of age were higher than those over 2 years (1.8, 4.0%; 3.7%). Similar results have been found in other animals, including bamboo rats and horses (Li F. et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020). This may be related to the relatively low immunity of young crab-eating macaques.
The C. hominis subtypes found in this study belongs to highly divergent subtypes. Five subtypes of C. hominis were identified in crab-eating macaques in this study, namely IbA13G4 (n = 27), InA26 (n = 3), IiA17 (n = 3), IfA17G2R3 (n = 3), and IeA11G3T3 (n = 2). The emerging subtype IbA13G4 was dominant subtypes in this study, and was detected in crab-eating macaques for the first time. In previous studies, many outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis were caused by Ib subtype family around the world (Yang et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2025). The subtype IbA10G2 is responsible for most outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis in humans in both industrialized and developing countries (Cacciò and Chalmers, 2016; Feng et al., 2018). Furthermore, previous studies have shown that IbA12G3 induced a significantly higher intensity of oocyst and had higher parasite loads in the mouse intestine (Huang et al., 2024). Similarly, the Ie, If, and Ii subtype families are common in humans worldwide (Xiao and Feng, 2017). Among them, subtypes IeA11G3T3 and IiA17 were occasionally found in cancer patients and HIV-infected patients, they are apparently zoonotic (Sannella et al., 2019; Makipour et al., 2025). In contrast, the subtype IfA17G2R3 and InA26 were only found in rhesus monkeys in Guizhou and in crab-eating macaques in Hainan, respectively (Chen et al., 2019; Jia et al., 2022). Therefore, these two subtypes have potential zoonotic risk. In the future, we will conduct more studies to evaluate the infectivity and pathogenicity of C. hominis subtypes in animals.
The crab-eating macaques could be reservoirs for zoonotic assemblage B. Similar to other studies in crab-eating macaques, only assemblage B was found in this study (Karim et al., 2014d; Cai et al., 2021). Previous studies have shown that assemblage B had the broadest host range, and assemblage B was responsible for most giardiasis cases in humans (Feng and Xiao, 2011). In contrast, the assemblage A and E were occasionally found in non-human primates. A few studies had shown that the assemblage A was found in some non-human primates in China (Karim et al., 2014d; Ye et al., 2014) and other countries (Sricharern et al., 2016; Brynildsrud et al., 2018). In addition, assemblage E were found in five non-human primates (Brynildsrud et al., 2018). In present study, assemblage B was the only assemblage in the crab-eating macaques. This could have been due to the confined nature of animals in the facility, which limits the introduction of other genotypes. The common occurrence of assemblage B suggested that G. duodenalis from crab-eating macaques has high zoonotic potential.
Crab-eating macaques may potentially contribute to the zoonotic transmission of E. bieneusi genotypes to humans. In this study, 4 E. bieneusi genotypes were found, namely CM1 (14 specimens), Peru8 (5 specimens), D (3 specimens), and Type IV (1 specimen) and these genotypes belong to the zoonotic Group 1. Among these genotypes of E. bieneusi, genotypes D, Peru 8, and Type IV are mainly identified in humans, and have been frequently documented in domestic and wild animals, including non-human primates (Li W. et al., 2019; Li and Xiao, 2021; Li et al., 2022). In previous studies, the genotype CM1 has been only found in non-human primates in Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunan, and Sichuan of China and it was not found in humans (Karim et al., 2014a; Karim et al., 2014b). This is probably because only a small number of studies have been performed on human E. bieneusi infection in China. The common occurrence of zoonotic genotypes suggested that E. bieneusi from crab-eating macaques has high zoonotic potential.
5 Conclusion
This study reported the prevalence of Cryptosporidium spp., G. duodenalis, and E. bieneusi in crab-eating macaques in Beijing and Suzhou cities, China. The results indicate that known zoonotic C. hominis, Assemblage B, and E. bieneusi genotypes are prevalent in crab-eating macaques. Crab-eating macaques are in close contact with humans. Therefore, crab-eating macaques may play a potential role in the zoonotic transmission of pathogens to humans. Further studies are needed to monitor the molecular epidemiology of these three pathogens in farmed crab-eating macaques.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, PV730087-PV730091 and PV715454-PV715457.
Ethics statement
The animal studies were approved by Research Ethics Committee of the Fuyang Normal University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
Author contributions
HZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. HC: Software, Writing – review & editing. CH: Software, Writing – review & editing. WL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. FL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Key Projects of Scientific Research Plan of Colleges and Universities of Anhui Province (2023AH050427), the Veterinary Science Peak Discipline Project of Anhui Science and Technology University (XK-XJGF002), the National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (202410371016), the Scientific research project of Fuyang Normal University (2023KYQD0003), and the Biological and Medical Sciences of Applied Summit Nurturing Disciplines in Anhui Province (Anhui Education Secretary Department [2023]13).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1641632/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
Alves, M., Xiao, L., Sulaiman, I., Lal, A. A., Matos, O., and Antunes, F. (2003). Subgenotype analysis of Cryptosporidium isolates from humans, cattle, and zoo ruminants in Portugal. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 2744–2747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.41.6.2744-2747.2003
Beck, R., Sprong, H., Bata, I., Lucinger, S., Pozio, E., and Cacciò, S. M. (2011). Prevalence and molecular typing of Giardia spp. in captive mammals at the zoo of Zagreb, Croatia. Vet. Parasitol. 175, 40–46. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.09.026
Bodager, J. R., Parsons, M. B., Wright, P. C., Rasambainarivo, F., Roellig, D., Xiao, L., et al. (2015). Complex epidemiology and zoonotic potential for Cryptosporidium suis in rural Madagascar. Vet. Parasitol. 207, 140–143. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.11.013
Bouzid, M., Hunter, P. R., Mcdonald, V., Elwin, K., Chalmers, R. M., and Tyler, K. M. (2013). A new heterogeneous family of telomerically encoded Cryptosporidium proteins. Evol. Appl. 6, 207–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-4571.2012.00277.x
Brynildsrud, O., Tysnes, K. R., Robertson, L. J., and Debenham, J. J. (2018). Giardia duodenalis in primates: classification and host specificity based on phylogenetic analysis of sequence data. Zoonoses Public Health 65, 637–647. doi: 10.1111/zph.12470
Cacciò, S. M., and Chalmers, R. M. (2016). Human cryptosporidiosis in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 22, 471–480. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.04.021
Caccio, S. M., and Ryan, U. (2008). Molecular epidemiology of giardiasis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 160, 75–80. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.04.006
Cai, W., Ryan, U., Xiao, L., and Feng, Y. (2021). Zoonotic giardiasis: an update. Parasitol. Res. 120, 4199–4218. doi: 10.1007/s00436-021-07325-2
Chen, L., Hu, S., Jiang, W., Zhao, J., Li, N., Guo, Y., et al. (2019). Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium hominis subtypes in crab-eating macaques. Parasit. Vectors 12:350. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3604-7
Chen, L., Li, N., Guo, Y., Zhao, J., Feng, Y., and Xiao, L. (2020). Multilocus sequence typing of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in crab-eating macaques (Macaca fascicularis) in Hainan, China. Parasit. Vectors 13:182. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04046-w
Du, S. Z., Zhao, G. H., Shao, J. F., Fang, Y. Q., Tian, G. R., Zhang, L. X., et al. (2015). Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in captive non-human primates in Qinling Mountains. Korean J. Parasitol. 53, 395–402. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2015.53.4.395
Feng, Y., Ryan, U. M., and Xiao, L. (2018). Genetic diversity and population structure of Cryptosporidium. Trends Parasitol. 34, 997–1011. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2018.07.009
Feng, Y., and Xiao, L. (2011). Zoonotic potential and molecular epidemiology of Giardia species and giardiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 24, 110–140. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00033-10
Feng, Y., and Xiao, L. (2017). Molecular epidemiology of cryptosporidiosis in China. Front. Microbiol. 8:1701. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01701
Gu, Y., Wang, X., Zhou, C., Li, P., Xu, Q., Zhao, C., et al. (2016). Investigation on Cryptosporidium infections in wild animals in a zoo in Anhui Provinece. J Zoo Wildl Med. 47, 846–854. doi: 10.1638/2015-0301.1
Guo, Y., Li, N., Feng, Y., and Xiao, L. (2021a). Zoonotic parasites in farmed exotic animals in China: implications to public health. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 14, 241–247. doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2021.02.016
Guo, Y., Ryan, U., Feng, Y., and Xiao, L. (2021b). Emergence of zoonotic Cryptosporidium parvum in China. Trends Parasitol. 38, 335–343. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.12.002
Huang, W., Feng, Y., and Xiao, L. (2025). Cryptosporidium hominis. Trends Parasitol. 29:s1471-4922(25)00095-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2025.04.001
Huang, W., He, W., Huang, Y., Tang, Y., Chen, M., Sun, L., et al. (2024). Multicopy subtelomeric genes underlie animal infectivity of divergent Cryptosporidium hominis subtypes. Nat. Commun. 15:10774. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54995-4
Jia, R., Wen, X., Guo, Y., Xiao, L., Feng, Y., and Li, N. (2022). Decline in Cryptosporidium infection in free-ranging rhesus monkeys in a park after public health interventions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:901766. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.901766
Jiang, J., Alderisio, K. A., Singh, A., and Xiao, L. (2005). Development of procedures for direct extraction of Cryptosporidium DNA from water concentrates and for relief of PCR inhibitors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 1135–1141. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.3.1135-1141.2005
Jiang, S., Yu, S., Feng, Y., Zhang, L., Santin, M., Xiao, L., et al. (2024). Widespread distribution of human-infective Enterocytozoon bieneusi genotypes in small rodents in Northeast China and phylogeny and zoonotic implications revisited. Acta Trop. 253:107160. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2024.107160
Johnston, A. R., Gillespie, T. R., Rwego, I. B., Mclachlan, T. L., Kent, A. D., and Goldberg, T. L. (2010). Molecular epidemiology of cross-species Giardia duodenalis transmission in western Uganda. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 4:e683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000683
Karim, M. R., Dong, H., Li, T., Yu, F., Li, D., Zhang, L., et al. (2015). Predomination and new genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in captive nonhuman primates in zoos in China: high genetic diversity and zoonotic significance. PLoS One 10:e0117991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117991
Karim, M. R., Dong, H., Yu, F., Jian, F., Zhang, L., Wang, R., et al. (2014a). Genetic diversity in Enterocytozoon bieneusi isolates from dogs and cats in China: host specificity and public health implications. J. Clin. Microbiol. 52, 3297–3302. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01352-14
Karim, M. R., Wang, R., Dong, H., Zhang, L., Li, J., Zhang, S., et al. (2014b). Genetic polymorphism and zoonotic potential of Enterocytozoon bieneusi from nonhuman primates in China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 1893–1898. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03845-13
Karim, M. R., Wang, R., He, X., Zhang, L., Li, J., Rume, F. I., et al. (2014c). Multilocus sequence typing of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in nonhuman primates in China. Vet. Parasitol. 200, 13–23. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.12.004
Karim, M. R., Zhang, S., Jian, F., Li, J., Zhou, C., Zhang, L., et al. (2014d). Multilocus typing of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis from non-human primates in China. Int. J. Parasitol. 44, 1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.07.006
Li, W., Feng, Y., and Santin, M. (2019). Host specificity of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and public health implications. Trends Parasitol. 35, 436–451. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.04.004
Li, W., Feng, Y., and Xiao, L. (2022). Enterocytozoon bieneusi. Trends Parasitol. 38, 95–96. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.08.003
Li, W., Kiulia, N. M., Mwenda, J. M., Nyachieo, A., Taylor, M. B., Zhang, X., et al. (2011). Cyclospora papionis, Cryptosporidium hominis, and human-pathogenic Enterocytozoon bieneusi in captive baboons in Kenya. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49, 4326–4329. doi: 10.1128/JCM.05051-11
Li, F., Su, J., Chahan, B., Guo, Q., Wang, T., Yu, Z., et al. (2019). Different distribution of Cryptosporidium species between horses and donkeys. Infect. Genet. Evol. 75:103954. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.103954
Li, W., and Xiao, L. (2021). Ecological and public health significance of Enterocytozoon bieneusi. One Health 12:100209. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2020.100209
Li, F., Zhang, Z., Hu, S., Zhao, W., Zhao, J., Kváč, M., et al. (2020). Common occurrence of divergent Cryptosporidium species and Cryptosporidium parvum subtypes in farmed bamboo rats (Rhizomys sinensis). Parasit. Vectors 13:149. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04021-5
Makipour, H., Haghighi, A., Halakou, A., Dayer, D., Bitaraf, S., Farhadi Kia, A., et al. (2025). Identifying zoonotic risks: molecular insights into Cryptosporidium and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in pediatric cancer patients in Ahvaz, 2024. Parasitol. Res. 124:55. doi: 10.1007/s00436-025-08500-5
Ryan, U. M., Feng, Y., Fayer, R., and Xiao, L. (2021). Taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium and Giardia – a 50 year perspective (1971-2021). Int. J. Parasitol. 51, 1099–1119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2021.08.007
Sak, B., Petrželková, K. J., Květoňová, D., Mynářová, A., Pomajbíková, K., Modrý, D., et al. (2014). Diversity of microsporidia, Cryptosporidium and Giardia in mountain gorillas (Gorilla beringei beringei) in volcanoes National Park, Rwanda. PLoS One 9:e109751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109751
Sannella, A. R., Suputtamongkol, Y., Wongsawat, E., and Cacciò, S. M. (2019). A retrospective molecular study of Cryptosporidium species and genotypes in HIV-infected patients from Thailand. Parasit. Vectors 12:91. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3348-4
Santín, M., and Fayer, R. (2011). Microsporidiosis: Enterocytozoon bieneusi in domesticated and wild animals. Res. Vet. Sci. 90, 363–371. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2010.07.014
Shu, F., Song, S., Wei, Y., Li, F., Guo, Y., Feng, Y., et al. (2022). High zoonotic potential of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in wild nonhuman primates from Yunnan Province, China. Parasit. Vectors 15:85. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05217-7
Sricharern, W., Inpankaew, T., Keawmongkol, S., Supanam, J., Stich, R. W., and Jittapalapong, S. (2016). Molecular detection and prevalence of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. among long-tailed macaques (Macaca fascicularis) in Thailand. Infect. Genet. Evol. 40, 310–314. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.02.004
Sulaiman, I. M., Fayer, R., Bern, C., Gilman, R. H., Trout, J. M., Schantz, P. M., et al. (2003a). Triosephosphate isomerase gene characterization and potential zoonotic transmission of Giardia duodenalis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 9, 1444–1452. doi: 10.3201/eid0911.030084
Sulaiman, I. M., Fayer, R., Lal, A. A., Trout, J. M., Schaefer, F. W.3rd, and Xiao, L. (2003b). Molecular characterization of microsporidia indicates that wild mammals harbor host-adapted Enterocytozoon spp. as well as human-pathogenic Enterocytozoon bieneusi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 4495–4501. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.8.4495-4501.2003
Wang, S. S., Li, J. Q., Li, Y. H., Wang, X. W., Fan, X. C., Liu, X., et al. (2018). Novel genotypes and multilocus genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in pigs in northwestern China: a public health concern. Infect. Genet. Evol. 63, 89–94. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.05.015
Wang, L., Xiao, L., Duan, L., Ye, J., Guo, Y., Guo, M., et al. (2013). Concurrent infections of Giardia duodenalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Clostridium difficile in children during a cryptosporidiosis outbreak in a pediatric hospital in China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 7:e2437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002437
Xiao, L. (2010). Molecular epidemiology of cryptosporidiosis: an update. Exp. Parasitol. 124, 80–89. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2009.03.018
Xiao, L., Escalante, L., Yang, C., Sulaiman, I., Escalante, A. A., Montali, R. J., et al. (1999). Phylogenetic analysis of Cryptosporidium parasites based on the small-subunit rRNA gene locus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 1578–1583. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.4.1578-1583.1999
Xiao, L., and Feng, Y. (2017). Molecular epidemiologic tools for waterborne pathogens Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 8-9, 14–32. doi: 10.1016/j.fawpar.2017.09.002
Yan, W., Alderisio, K., Roellig, D. M., Elwin, K., Chalmers, R. M., Yang, F., et al. (2017). Subtype analysis of zoonotic pathogen Cryptosporidium skunk genotype. Infect. Genet. Evol. 55, 20–25. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.08.023
Yang, X., Guo, Y., Xiao, L., and Feng, Y. (2021). Molecular epidemiology of human cryptosporidiosis in low- and middle-income countries. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 34:00087-19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00087-19
Ye, J., Xiao, L., Li, J., Huang, W., Amer, S. E., Guo, Y., et al. (2014). Occurrence of human-pathogenic Enterocytozoon bieneusi, Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium genotypes in laboratory macaques in Guangxi, China. Parasitol. Int. 63, 132–137. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2013.10.007
Ye, J., Xiao, L., Ma, J., Guo, M., Liu, L., and Feng, Y. (2012). Anthroponotic enteric parasites in monkeys in public park, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 18, 1640–1643. doi: 10.3201/eid1810.120653
Zhang, X. L., Pang, W., Hu, X. T., Li, J. L., Yao, Y. G., and Zheng, Y. T. (2014). Experimental primates and non-human primate (NHP) models of human diseases in China: current status and progress. Dongwuxue Yanjiu 35, 447–464. doi: 10.13918/j.issn.2095-8137.2014.6.447
Keywords: Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, crab-eating macaque, zoonosis, China
Citation: Zhang H, Chen H, He C, Li W and Li F (2025) Distribution of human-pathogenic Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in crab-eating macaques in China. Front. Microbiol. 16:1641632. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1641632
Edited by:
Hong Yin, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Na Li, South China Agricultural University, ChinaXinan Meng, South China Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen, He, Li and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenchao Li, bGl3ZW4zMDNAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Falei Li, ZmxpQGZ5bnUuZWR1LmNu
 Huilin Zhang
Huilin Zhang Huiyang Chen1
Huiyang Chen1 Wenchao Li
Wenchao Li Falei Li
Falei Li