- 1Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Bio-Resources, Key Laboratory for Microbial Resources of the Ministry of Education, Yunnan University, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 2School of Life Sciences, Yunnan University, Kunming, Yunnan, China
Trichoderma spp. are widely distributed across diverse environments and play a significant role in both ecosystem stability and economic applications. In this study, 57 Trichoderma strains were isolated from karst desert soil, of which 47 strains were identified as nine known species, while 10 strains were characterized as belonging to four novel species. Phylogenetic analyses, based on the combined sequences of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS), translation elongation factor 1-alpha (tef1-α), and RNA polymerase II second largest subunit (rpb2) genes, confirmed their distinct taxonomic positions. The results indicate that these four species are distributed across three known clades. Detailed morphological descriptions, cultural characteristics, and illustrations are provided for each new species, and comparisons are made with closely related taxa. The four new species are named Trichoderma calcicola, Trichoderma exigua, Trichoderma karsti, and Trichoderma xerophilum. This study documents the diversity of Trichoderma in rocky desertification ecosystems that remain agriculturally productive, suggesting their potential ecological adaptation to nutrient-poor, drought-prone, and calcium-rich soils, with implications for future biotechnological and biocontrol applications.
Introduction
The genus Trichoderma (Sordariomycetes, Hypocreales, and Hypocreaceae) exhibits global distribution, is widely found in diverse ecological niches such as soil, plant roots, and decaying wood, and demonstrates remarkable adaptability to various environmental conditions (Cai and Druzhinina, 2021; Cao et al., 2022; Migheli et al., 2009). Moreover, it is recognized for its significant ecological and economic importance. Trichoderma harzianum is widely used as a biocontrol agent in the field of agriculture because of its high level of antagonism against diverse phytopathogenic microorganisms (Erazo et al., 2021; Geng et al., 2022; Yan and Khan, 2021; Mitrović et al., 2025). Some Trichoderma species have also shown potential in suppressing pathogenic nematodes (Yao et al., 2023). Besides serving biocontrol agents against pathogen, Trichoderma species have been shown to promote plant growth (Subramaniam et al., 2022), enhance plant stress tolerance by producing valuable secondary metabolites (Cheng et al., 2012; Mukherjee et al., 2013; Fazeli-Nasab et al., 2022), and facilitate the remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals (Bandurska et al., 2021; Kidwai et al., 2022). Trichoderma reesei and its engineered strains represent significant cellulase producers that are commonly exploited for their carbohydrate-active enzyme content (Sperandio and Filho, 2021). Besides T. reesei, several other Trichoderma species also produce cellulase, xylanase, and pectinase (Gooruee et al., 2024). However, several Trichoderma species pose threats to the cultivation of edible fungi, the production of Gastrodia elata BI., and human health (Park et al., 2006; Kim et al., 2012; Sandoval-Denis et al., 2014; Ye et al., 2024).
Rocky desertification (RD), a severe form of karst ecosystem degradation, occurs when progressive soil erosion exposes the underlying bedrock, resulting in substantial agricultural and ecological deterioration. This process advances through multiple soil degradation pathways, including structural collapse, altered soil texture and porosity, reduced water-holding capacity, and nutrient depletion (Huang et al., 2009; Peng et al., 2013; Tang et al., 2013). These processes collectively disrupt ecosystem functioning and generate positive feedback loops that further accelerate RD. The Shilin Karst World Heritage Site in Yunnan Province, renowned for its towering limestone pinnacles, faces increasing threats from RD. Recent studies have demonstrated that the severity of RD drives significant shifts in fungi community composition; as RD intensifies, the abundance of Penicillium, Mortierella, and Metarhizium increases, whereas Myrothecium, Humicola, Paramyrothecium, and Chaetomium markedly decline (Yang, 2022). These patterns suggest that microbial indicators may serve as sensitive biomarkers for monitoring RD progression.
The diversity of Trichoderma species has been surveyed for different purposes (Mulatu et al., 2022; Cao et al., 2024; Tang et al., 2022). However, the diversity of Trichoderma in rocky desertification areas remains unreported. In this study, 57 strains of Trichoderma were isolated from the karst rocky desertification soils of Shilin, Yunnan Province. Among these strains, 47 were identified as known species, and 10 were designated as putative new species based on the BLASTn search results of the ITS sequence. To clarify their taxonomic positions, we used an integrative approach based on morphological characteristics and multilocus phylogenetic analyses (ITS, rpb2, and tef1-α). Furthermore, the analysis revealed significant genetic and morphological differences between the new species and their known counterparts, thereby confirming their status as a novel species. This study not only expands the current understanding of Trichoderma diversity in karst desertification ecosystems but also provides a baseline for future research on their ecological functions and potential agricultural applications.
Materials and methods
Sample collection and isolation
Soil samples were collected from the rocky desertification region in Shilin County, Kunming City, Yunnan Province (24.6° N, 103.4° E; altitude 1940 m a.s.l.). This area is characterized by exposed bedrock interspersed with gravel, sand, and soil. Despite the degradation, crops such as maize and soybeans are still cultivated, indicating that the region has not reached a fully desertified state. A total of 90 soil samples were collected from three sampling sites, with each located approximately 20 km apart. At each site, 30 samples were collected using a random sampling method, maintaining a minimum spacing of 5 m between sampling points. Samples were taken from a depth of 5–10 cm after the removal of surface plant debris and gravel. All samples were labeled with unique identifiers and detailed collection information. Subsequently, the samples were transferred to the laboratory and stored at 4°C until further analysis.
The soil fungal isolation steps were as follows: 10 g of soil were mixed with 90 mL of sterile water with an appropriate amount of sterile glass beads and then shaken thoroughly at 220 r/min−1 for 1 h. After allowing the suspension to stand for 2 min, the supernatant was collected and subjected to serial dilutions (10−1 to 10−4). Aliquots of 100 μL from the 10−2 to 10−4 dilutions were plated in triplicate onto Rose Bengal Agar (RBA; Guangdong Huankai Microbial Science and Technology Co., Ltd., China) supplemented with antibiotics (streptomycin, 40 mg/L; ampicillin, 30 mg/L) to suppress bacterial growth. The inoculated plates were incubated in a temperature-controlled chamber at 25°C for 5–7 days and monitored daily for colony growth.
After mycelia growth, well-developed colonies were subcultured onto potato dextrose agar plates (PDA: 200 g potato, 20 g dextrose, 18 g agar, and 1,000 mL distilled water) for further purification and identification. The resulting pure cultures were deposited in the Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Bio-Resources, Yunnan University (YMF), Kunming, China.
Morphology observation
Growth rates were measured on 9-cm-diameter Petri dishes containing three different media: PDA, cornmeal agar (CMA: 20 g cornmeal, 18 g agar, and 1,000 mL distilled water), and synthetic nutrient-poor agar (SNA: 1 g KH2PO4, 1 g KNO3, 0.5 g MgSO4, 0.5 g KCl, 0.2 g glucose, 0.2 g sucrose, 18 g agar, and 1,000 mL distilled water), at 25, 30, and 35°C under alternating 12-h light and 12-h dark cycles. After 3 days of incubation, the colony diameter was recorded, and the time required for complete colony coverage was documented. Furthermore, the morphological characters of colonies, such as colony appearance, color, and conidia production, were recorded at the same time. For microscopic morphology, including hyphae, conidiophores, phialides, conidia, and other structures, images were taken using an Olympus BX51 microscope (Tokyo, Japan) connected to a DP controller digital camera. At least 30 datasets were measured for each structure. Colonies were photographed after 7 days, and conidia were photographed after 14 days of production.
DNA extraction, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, and sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted following the method described by Ye et al. (2024). Briefly, 0.5 g of mycelia was transferred into a 2.0-mL microcentrifuge tube, to which steel beads and 700–800 μL of urea extraction buffer [7 mol/L of urea, 50 mmol/L of Tris–HCl, 62.5 mmol/L of NaCl, 10 g/L of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)] were also added, followed by 5 min of disruption at 50 Hz oscillation. The mixture was centrifuged at 12,000 r/min for 5 min, after which the supernatant was transferred to a 1.5-mL centrifuge tube and an equal volume of DNA extraction (phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol, 25:24:1) was added. The mixture was centrifuged at 12,000 r/min for 5 min, and the supernatant was transferred to a new 1.5-mL centrifuge tube, to which an equal volume of isopropanol and 1/10 volume of 3 mol/L of NaAc were added, followed by incubation at −20°C for 20 min. The mixture was then centrifuged at 12,000 r/min for 5 min, and the upper aqueous phase was discarded. The DNA pellets were washed twice with 70% ethanol, dried at 40°C, and then resuspended in 50 μL of sterile water for PCR analysis (Liu et al., 2005).
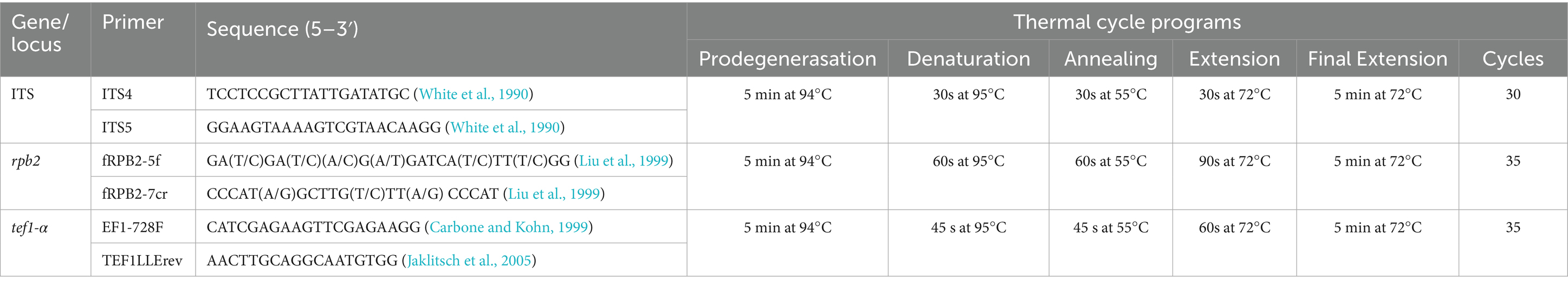
The ITS, rpb2, and tef1-α fragments were amplified using three pairs of primers: ITS4 and ITS5 for ITS (White et al., 1990), frpb2-5f and frpb2-7cr for rpb2 (Liu et al., 1999), and EF1-728F (Carbone and Kohn, 1999) and TEF1LLErev (Jaklitsch et al., 2005) for tef1-α. PCR amplifications were conducted in a 25-μL reaction system containing 12.5 μL of 2 × Master Mix (Accurate Biology), 9.5 μL of double-distilled water, and 1 μL each of forward primer, reverse primer, and DNA template. The PCR reactions were carried out using an Eppendorf Mastercycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) following the thermal cycling program described in Table 1. The PCR products were purified using a PCR product purification kit (Biocolor Bioscience and Technology Co., Shanghai, China) and subsequently sequenced in both directions using amplification primers on an ABI 3730 XL DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California). The obtained sequences were deposited in the GenBank database at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), and the corresponding accession numbers are provided in Table 2.
Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analyses
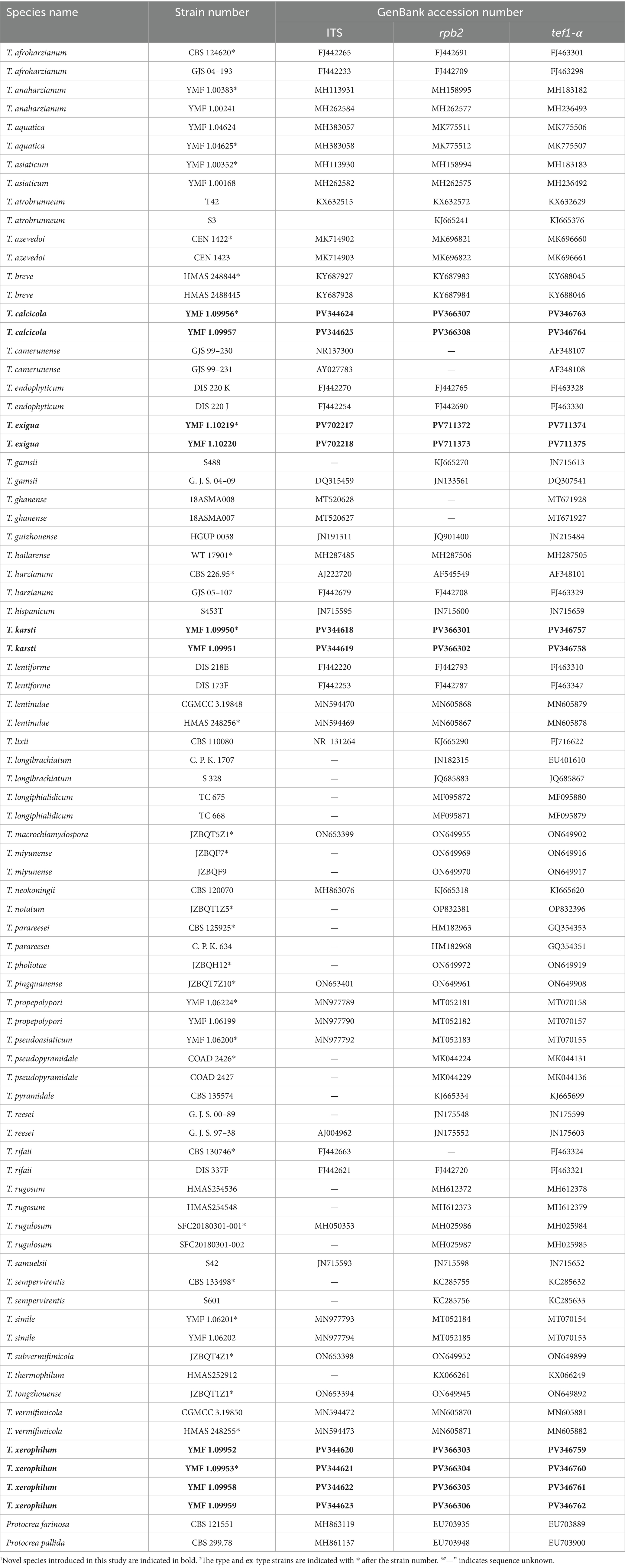
Preliminary BLASTn searches were conducted using the ITS, rpb2, and tef1-α sequences of the newly isolated strains against the NCBI database to identify closely related species. Both the reference sequences and the newly generated sequences in this study are listed in Table 2. Phylogenetic reconstruction was performed based on the concatenated sequences of the ITS, rpb2, and tef1-α loci. Sequence alignment was conducted using Clustal X 1.83 (Thompson et al., 1997) with default parameters, followed by trimming to appropriate lengths using MEGA11 (Tamura et al., 2021). Sequence assembly and alignment were carried out in BioEdit version 7.0 (Hall, 1999), with manual concatenation of the aligned sequences from the three loci. Missing nucleotide positions were filled with question marks “?” to facilitate subsequent analyses and to optimize the quality of sequence assembly. A sequence matrix (FASTA file) containing three gene loci was generated using BioEdit version 7.0, with a total of 3,024 characters (669 from ITS, 1,041 from rpb2, and 1,314 from tef1-α). The alignment data used in the phylogenetic analyses were deposited in TreeBASE.
Phylogenetic reconstruction of the newly identified species was conducted through both maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) approaches. For the ML analysis, the concatenated sequence matrix in FASTA format, assembled using BioEdit version 7.0 (Hall, 1999), was analyzed in IQ-TREE software (Nguyen et al., 2015). The optimal nucleotide substitution model was selected through ModelFinder, executed with the command iqtree -s example.fas -m MF -nt AUTO, which identified the TNe + I + G4 model as the best-fit evolutionary model based on the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC). Bootstrap support values were estimated from 1,000 replicates following the outgroup designation. Bayesian trees were constructed using MrBayes v3.1.2 (Huelsenbeck and Ronquist, 2001), with the best model chosen through MrModeltest 2.3. The Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) analysis was initiated with four parallel chains (one cold and three heated) per run, which proceeded for five million generations with sampling intervals of 500 generations until the average standard deviation of split frequencies fell below 0.01. The initial 25% of sampled generations were discarded as burn-in, with the remaining samples utilized to compute posterior probabilities for Bayesian phylogenetic reconstruction. Phylogenetic trees were visualized using FigTree version 1.4, with the nodal support values indicated by both maximum likelihood bootstrap proportions (MLBPs≥75%) and Bayesian posterior probabilities (BIPPs≥0.85).
Results
Diversity analysis
A total of 57 strains of Trichoderma were isolated and purified from rocky desertification soils based on the initial colony morphology. Among these strains, 47 were identified as known species, and 10 were designated as putative new species based on the BLASTn search results of the ITS sequence.
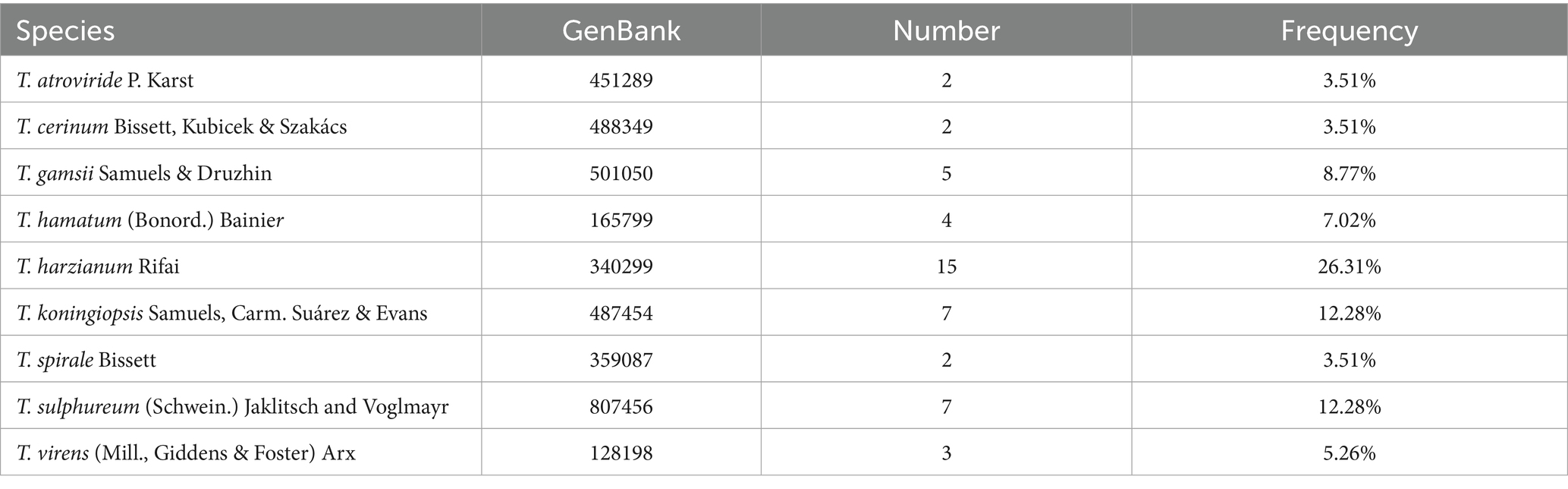
Phylogenetic analyses inferred from the ITS sequence were conducted to identify known species. The detailed species and their isolation frequencies are provided in Table 3. The highest isolation frequency was observed in T. harzianum, reaching 26.31%. The isolation frequencies of the remaining species were as follows: 12.28% each for Trichoderma koningiopsis and Trichoderma sulphureum, 8.77% for Trichoderma gamsii, 7.02% for T. hamatum, 5.26% for T. virens, and 3.51% each for T. atroviride, T. cerinum, and T. spirale.
Phylogenetic analyses
A concatenated dataset comprising ITS, rpb2 and tef1-α sequences (total length: 3,024 characters) was analyzed to determine the phylogenetic placement of the novel species. Phylogenetic trees were reconstructed through both ML and BI methods and exhibited consistent topological structures (Figure 1). Based on combined morphological characteristics and phylogenetic evidence, 10 isolates were identified as 4 new Trichoderma species, which are distributed across three different clades. The four new species were proposed as T. calcicola, T. exigua, T. karsti, and T. xerophilum, and each was supported by robust phylogenetic evidence and distinct morphological characteristics.
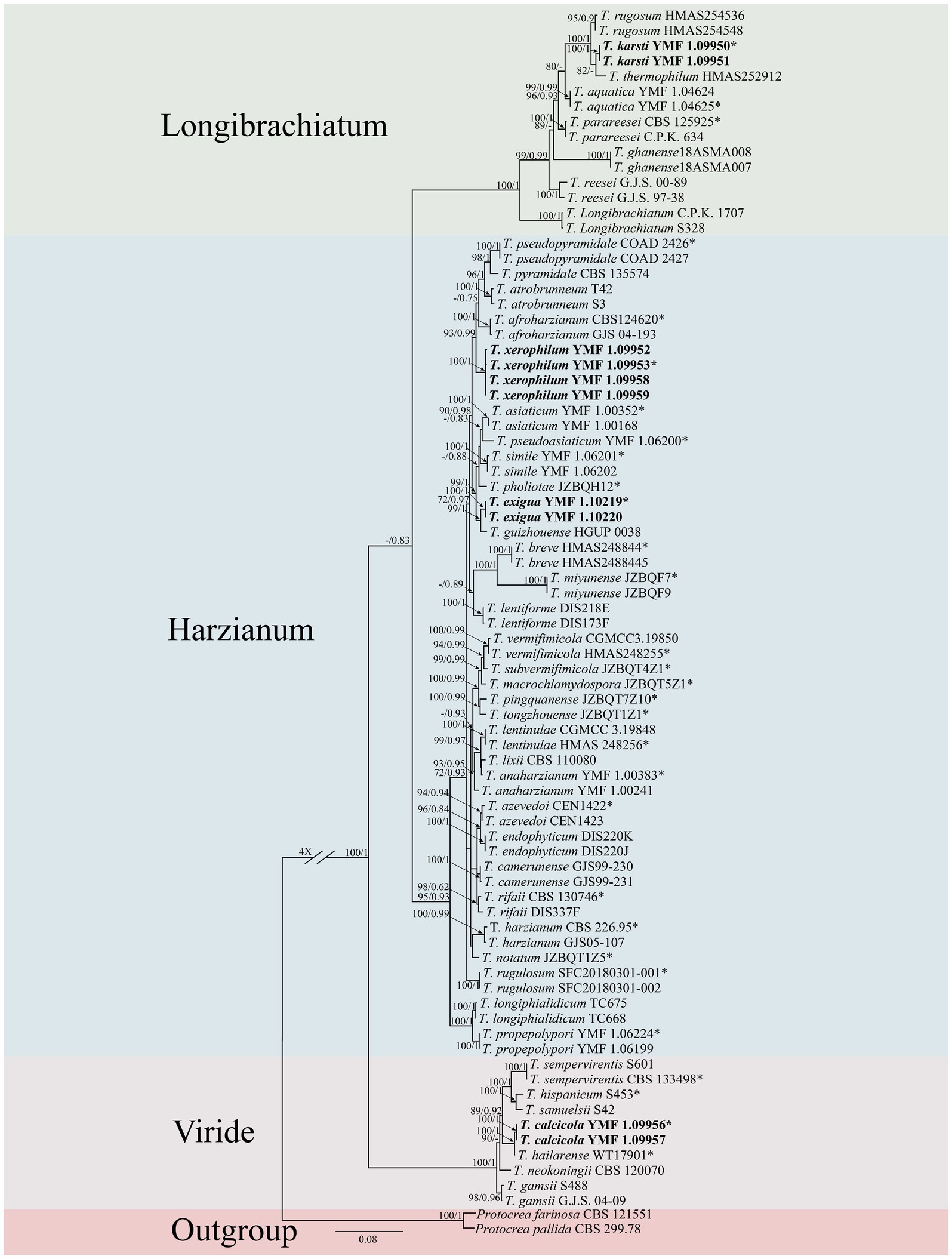
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of Trichoderma species based on the combined ITS, rpb2, and tef1-α gene sequences constructed using the maximum likelihood (ML) analysis and Bayesian inference (BI) analysis. The numbers above branches represent maximum-likelihood bootstrap percentages (left) and Bayesian posterior probabilities (right). ML bootstrap support (70) and Bayesian posterior probabilities (0.75) are shown on the respective branches. Protocrea farinose CBS 121551 and P. pallida CBS 299.78 were used as outgroups. Bold font indicates newly described species.
Two isolates were assigned to the Longibrachiatum clade, forming a new subclade corresponding to a novel species, designated as T. karsti (MLBP/BIPP = 100/1.00). In the Viride clade, two isolates formed a new subclade, defined as a novel species, designated as T. calcicola (MLBP/BIPP = 100/1.00). In the Harzianum clade, six isolates formed two new subclades, which were identified as novel species and named T. xerophilum (MLBP/BIPP = 100/1.00) and T. exigua (MLBP/BIPP = 100/1.00).
Taxonomy
Trichoderma karsti Z. F. Yu & X. W. Dai, sp. nov. Figure 2.
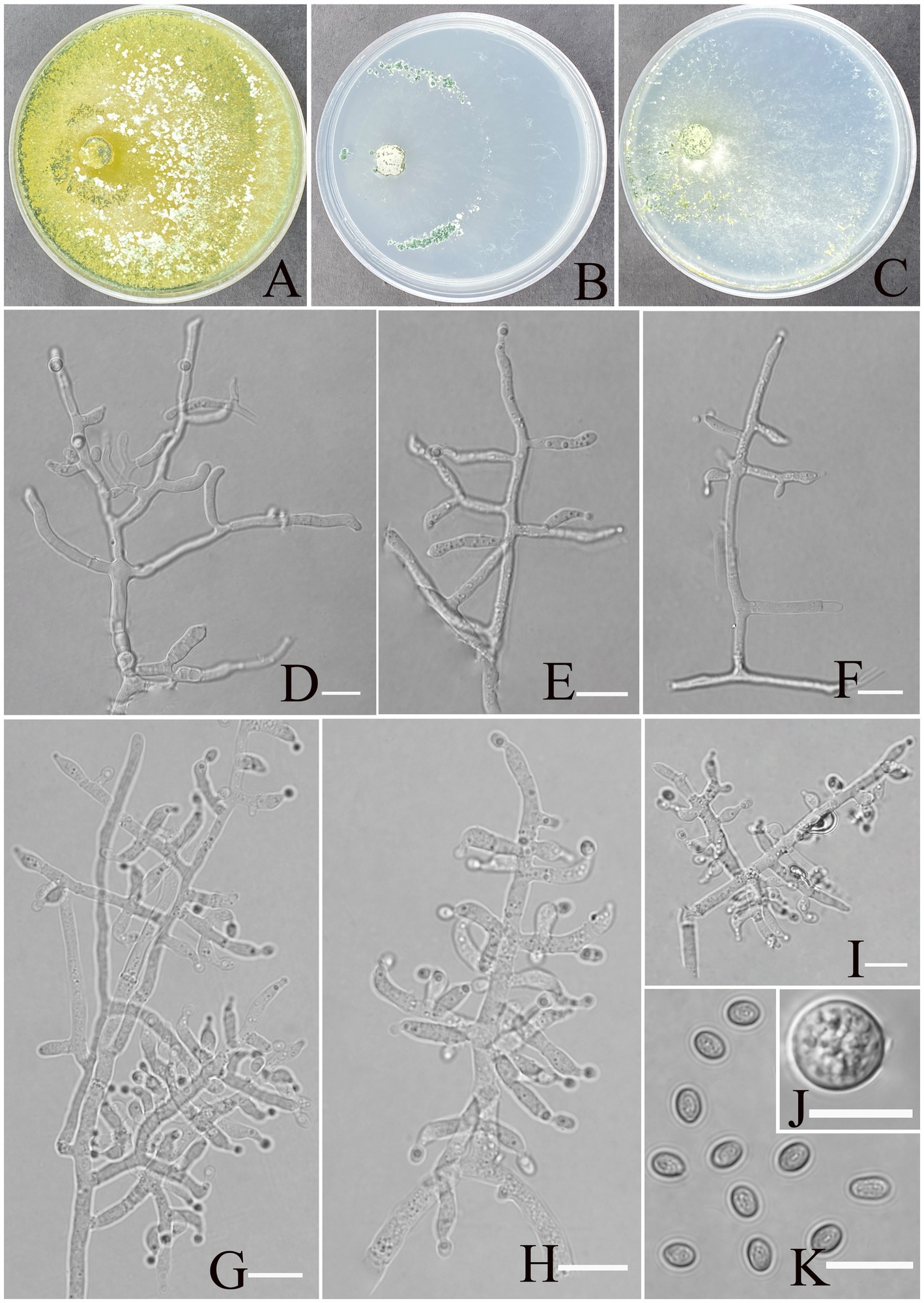
Figure 2. Morphology of Trichoderma karsti (YMF1.09950). (A–C) Cultures on PDA plates, 7d; CMA plates, 7d; SNA plates, 7d; 25°C; (D–I) conidiophores and phialides; (J) chlamydospores; and (K) conidia. Scale bars: 10 μm (D–K).
MycoBank No: 860053.
Etymology: Latin, karsti, refers to the holotype being isolated from karst soil.
Description: Sexual morph: Unknown. Asexual morph: Conidiophores consisting of a recognizable main axis with branches arranged either in pairs or singly, arising at an angle slightly less than 90° with respect to the main axis. The distance between two neighboring branches ranges from 3.5 to 13.2 μm. Phialides are commonly singly, opposite, ampulliform or narrowly vase-shaped, and the tip is long and curved, oriented an indefinite direction. They measure (6.2–)7.5–9.5(−11.3) × 2.3–4.1 μm, with a length-to-width (l/w) ratio of 1.9–4.6(−5.1), and, at base, they are 1.6–2.4(−3.5) μm wide and widest around the middle. Conidia are oval, elliptic, pale yellow-green, and smooth-walled, measuring 3.8–5.2 × 2.8–3.2 μm, with an l/w ratio of 1.1–1.4. Chlamydospores were observed growing at the tip of hyphae, round, measuring 8.2–10.8 × 7.1–9.7 μm, with a l/w ratio of 1.0–1.1.
Culture characteristics: optimum temperature for growth 30°C.
After 72 h, the colony radius on PDA was 64 mm at 25°C, 72 mm at 30°C, and 59 mm at 35°C, covering the plate after 3 days at 30°C. The colony is white, circular, and turns green after 3 days. Aerial hyphae are abundant, forming a dense mat. Pure yellow pigments are noted. A slight odor was noted.
Colony radius on CMA after 72 h: 12 mm at 25°C, 29 mm at 30°C, and 15 mm at 35°C. The colony lucency is circular, darkening to deep green as the incubation time extended. There was no diffusing pigment noted, and the odor was indistinct.
Colony radius on SNA after 72 h: 13 mm at 25°C, 34 mm at 30°C, and 30 mm at 35°C. The colony is white and turns green after 5 days. Sulphur yellow pigment was noted, and a slight odor was noted. Chlamydospores noted in all media.
Materials examined: China, Yunnan Province, Shilin Country, from soil of rocky desertification, August 2024, Z. F. Yu, (holotype YMF 1.09950). lbid. (cultures: YMF 1.09951).
Notes: From a systematic perspective, T. karsti is closely related to T. thermophilum and associated with T. rugosum. T. thermophilum and T. rugosum, which exhibit a sexual morph, T. karsti has only been observed in its asexual state (Qin and Zhuang, 2016; Zhang and Zhuang, 2018). The phialides of T. thermophilum and T. rugosum are relatively regular in morphology, while those of T. karsti are more curved and asymmetrical. In addition, the conidia of T. karsti are larger than those of T. thermophilum (3.8–5.2 × 2.8–3.2 vs. 2.7–6 × 2.3–3) and T. rugosum (3.8–5.2 × 2.8–3.2 vs. 3–4 × 2.2–3). The colonies of all three species are yellow on PDA and CMA, while they appear transparent or translucent on SNA. T. karsti has a mild odor, whereas no distinct odor was detected in the other two species.
Trichoderma xerophilum Z. F. Yu & X. W. Dai, sp. nov. Figure 3.
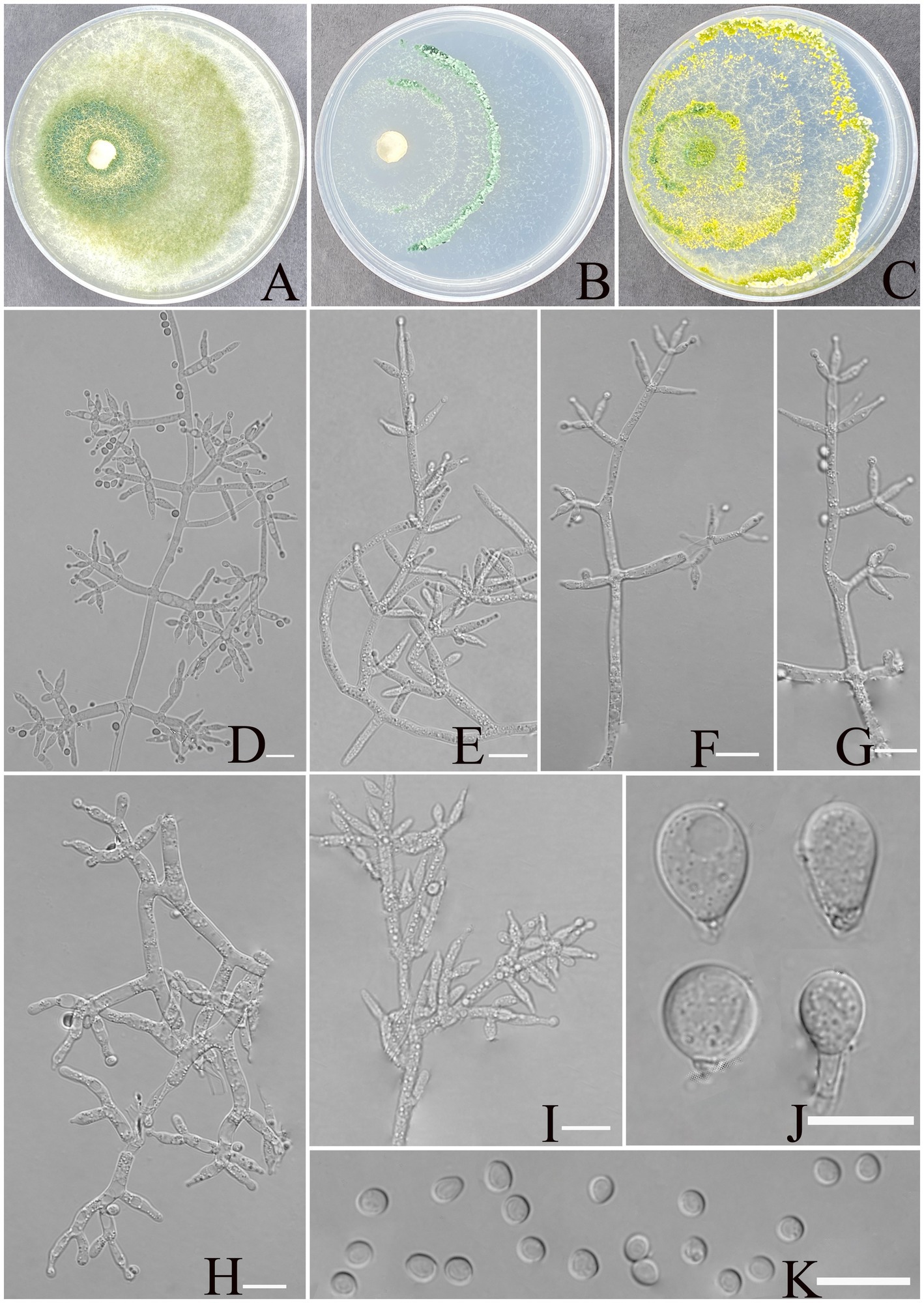
Figure 3. Morphology of Trichoderma xerophilum (YMF1.09953). (A–C) Cultures on PDA plates, 7d; CMA plates, 7d; SNA plates, 7d; 25°C; (D–I) conidiophores and phialides; (J) chlamydospores; and (K) conidia. Scale bars: 10 μm (D–K).
MycoBank NO: 860054.
Etymology: Latin, xerophilum, refers to the arid karst soil.
Description: sexual morph: unknown. Asexual morph: conidiophores comprising a recognizable main axis, primary branches that are mostly paired, occasionally 3 verticillate or solitary, and arise at an angle of approximately 90° from the main axis. Each branch terminates in a paired and a whorl of 3 together with a terminal phialide. Phialides ampulliform to narrowly vase-shaped, straight or slightly curved, mostly paired or whorls of 3 on terminal branches of the conidiophore, occasionally solitary, (5.5–)6.0–8.7(−11.5) × 2.1–3.2 μm, l/w ratio 2.3–4.9, 1.4–3.2 μm wide at base, widest around the middle. Conidia are oval, elliptic to subspheroidal, green, smooth, (3.1–)3.3–3.9(−4.2) × (2.5–)2.7–3.4 (−3.6) μm, with a l/w ratio of 1.0–1.2. The chlamydospores observed at the tips of hyphae exhibited two distinct morphological types: elliptical, measuring 10.0–12.9 × 7.8–9.2 μm with a length-to-width ratio of 1.2–1.6, and subglobose, measuring 8.5–11.2 × 6.6–9.4 μm with a length-to-width ratio of 1.0–1.2.
Culture characteristics: Optimum temperature for growth is 30°C.
Colony radius on PDA after 72 h: 55 mm at 25°C, 63 mm at 30°C, and 40 mm at 35°C, covering the plate after 3 days at 30°C. The colony is translucent, circular, and radial, with a white to pale grayish green. Aerial hyphae are abundant, forming a dense mat. Pure yellow pigments noted, slight odor noted.
Colony radius on CMA after 72 h: 25 mm at 25°C, 32 mm at 30°C, and 29 mm at 35°C. The colony lucency is circular, 1–2 zonate, darkening to green as incubation time extended. No diffusing pigment was noted, and odor was indistinct.
Colony radius on SNA after 72 h: 44 mm at 25°C, 50 mm at 30°C, and 30 mm at 35°C. The colony lucency is circular, three or more zonate, and the color changes to yellowish green after 3 days. Pure yellow pigments were noted, and a slight odor was noted. Chlamydospores were noted in all media.
Materials examined: China, Yunnan Province, Shilin Country, from soil of rocky desertification, August 2024, Z. F. Yu, (holotype YMF 1.09953). lbid. (cultures: YMF 1.09952, YMF 1.09958, YMF 1.09959).
Notes: Based on phylogenetic analyses, the four strains of T. xerophilum formed a single clade, sistering to the clade formed by T. afroharzianum, T. atrobrunneum, T. pyramidale, and T. pseudopyramidale. The phialides of T. afroharzianum (5.2–10.2 × 2.0–3.5 μm) and T. atrobrunneum (5.5–8.0 × 2.2–3.7 μm) are lageniform to ampulliform, whereas T. xerophilum exhibits longer phialides (6.0–8.7 × 2.4–3.2 μm) with a more pronounced length-to-width ratio, making it distinctive within the group. T. atrobrunneum does not mention the formation of chlamydospores, while T. afroharzianum rarely produces them (Chaverri et al., 2015). In contrast, T. xerophilum forms chlamydospores at the tips of hyphae, exhibiting two distinct morphological types. Furthermore, the phialides of T. pyramidale exhibit greater morphological diversity, ranging from lageniform to ampulliform and occasionally inequilateral or sigmoid, compared to the more uniform phialides of T. xerophilum (5.5–11.5(−17.5) × 2.8–3.7(−4.5) vs. 6.0–8.7(−11.5) × 2.1–3.2), thereby reflecting the morphological differences between the two species (Chaverri et al., 2015). Similarly, the phialides of T. pseudopyramidale (5.3–8.6(−9.1) × 2.2–2.9(−3.2) μm) are predominantly ampulliform to lageniform and usually formed in whorls, showing a somewhat narrower width than those of T. xerophilum (6.0–8.7(−11.5) × 2.1–3.2 μm) (del Carmen et al., 2021). These morphological characteristics distinctly set T. xerophilum apart from other closely related species.
Trichoderma calcicola Z. F. Yu & X. W. Dai, sp. nov. Figure 4.
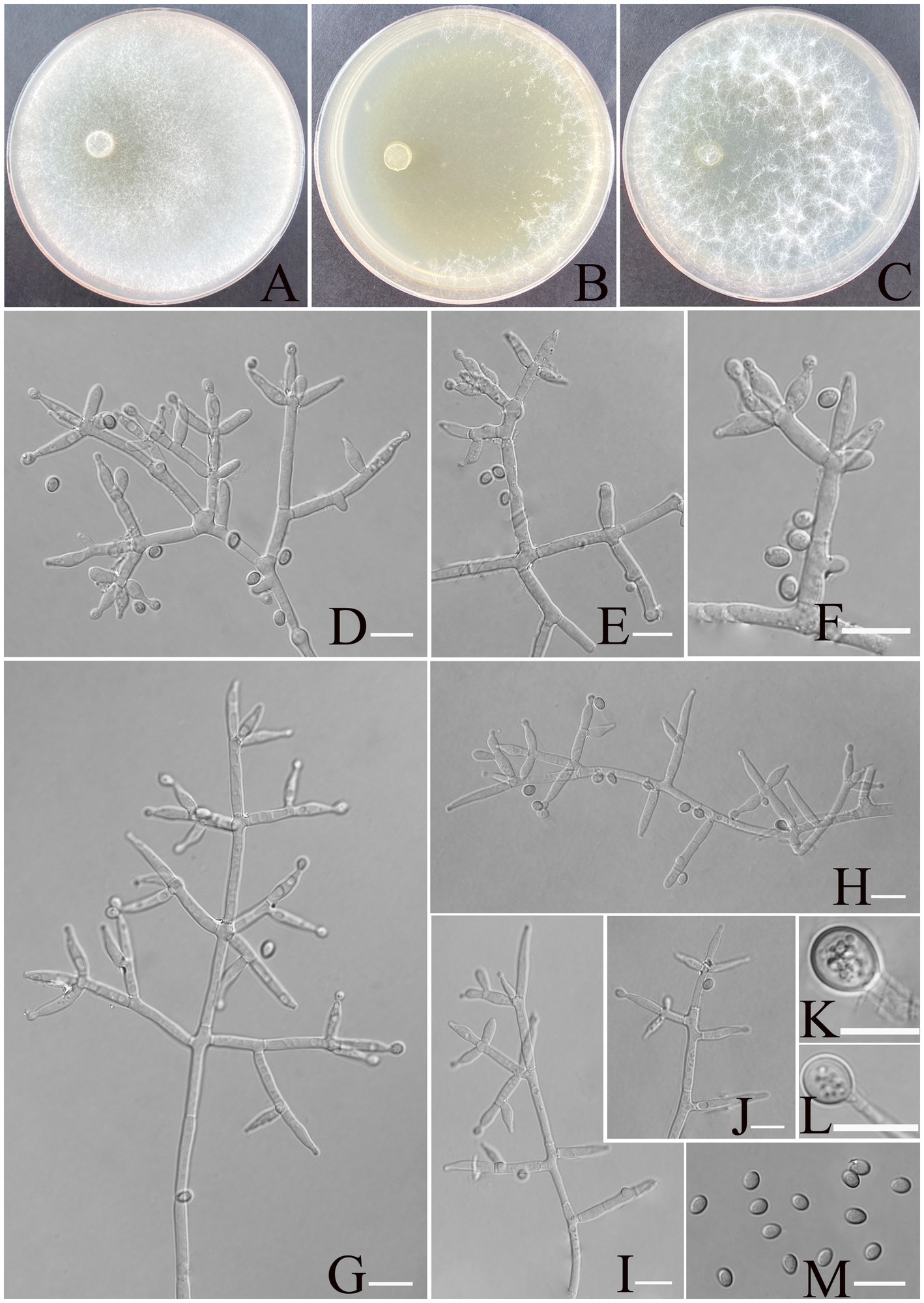
Figure 4. Morphology of Trichoderma calcicola (YMF1.09956). (A–C) Cultures on PDA plates, 7d; CMA plates, 7d; SNA plates, 7d; 25°C; (D–J) conidiophores and phialides; (K,L) chlamydospores; and (M) conidia. Scale bars: 10 μm (D–K).
MycoBank NO: 860055.
Etymology: Latin, calcicola, referring to the limestone-rich karst soil from which the strain was isolated.
Description: Sexual morph: Unknown. Asexual morph: Conidiophores and branches form a pyramidal structure, the distance between two neighboring branches (6.7–)8.0–25.0(−30.0) μm. Branches paired asymmetrically or solitary, occasionally in a whorl of 3 at an angle less than or near 90° concerning the main axis, branches terminating in a single, paired, or a whorl of three phialides. Phialides are spindle-shaped and lageniform, (6.4–)7.5–11.4(−12.0) × (2.6–)2.9–3.8(−4.0) μm, l/w ratio 1.4–3.5. Conidia thin-walled, ellipsoidal, rarely globose, green, smooth, (3.5–)3.8–4.5(−4.8) × (2.6–)2.8–3.2(−3.5) μm, l/w ratio 1.2–1.4. Chlamydospores were noted at the tip of hyphae, round, and measure 7.1–10.23 × 6.2–8.4 μm, with a l/w ratio of 1.1–1.2.
Culture characteristics: Optimum temperature for growth is 25°C.
Colony radius on PDA after 72 h: 55 mm at 25°C, 50 mm at 30°C, and 24 mm at 35°C, covering the plate after 3 days at 25°C. The colonies are white, circular, and fuzzy; aerial hyphae are abundant. No diffusing pigment noted, slight odor noted.
Colony radius on CMA after 72 h: 35 mm at 25°C, 32 mm at 30°C, and 24 mm at 35°C. The colony lucency is circular, the central air mycelia of the colony exiguity, and the margin dense. No diffusing pigment noted, slight odor noted.
Colony radius on SNA after 72 h: 40 mm at 25°C, 33 mm at 30°C, and 30 mm at 35°C. The colonies are white, circular, and fuzzy, aerial hyphae hairy to floccose, dense. Slight odor noted. Chlamydospores were observed in all media.
Materials examined: China, Yunnan Province, Shilin Country, from soil of rocky desertification, August 2024, Z. F. Yu, (holotype YMF 1.09956). lbid. (cultures: YMF 1.09957).
Notes: T. calcicola and T. hailarense are phylogenetically related but exhibit distinct differences in morphological and culture characteristics (Zhang et al., 2022). Regarding phialides, T. hailarense features longer lageniform phialides (8.0–15.5 μm × 2.5–3.6 μm), while T. calcicola possesses spindle- to lageniform-shaped phialides (6.4–12.0 μm × 2.6–4.0 μm). For conidia, T. hailarense yields delicately roughened, obovoid conidia (4.2–4.9 μm × 3.4–4.1 μm), whereas T. calcicola produces smooth, ellipsoidal conidia (3.5–4.8 μm × 2.6–3.5 μm). T. hailarense exhibits faster growth at 30°C, whereas T. calcicola shows better adaptation to growth conditions at 25°C.
Trichoderma exigua Z. F. Yu & X. W. Dai, sp. nov. Figure 5.
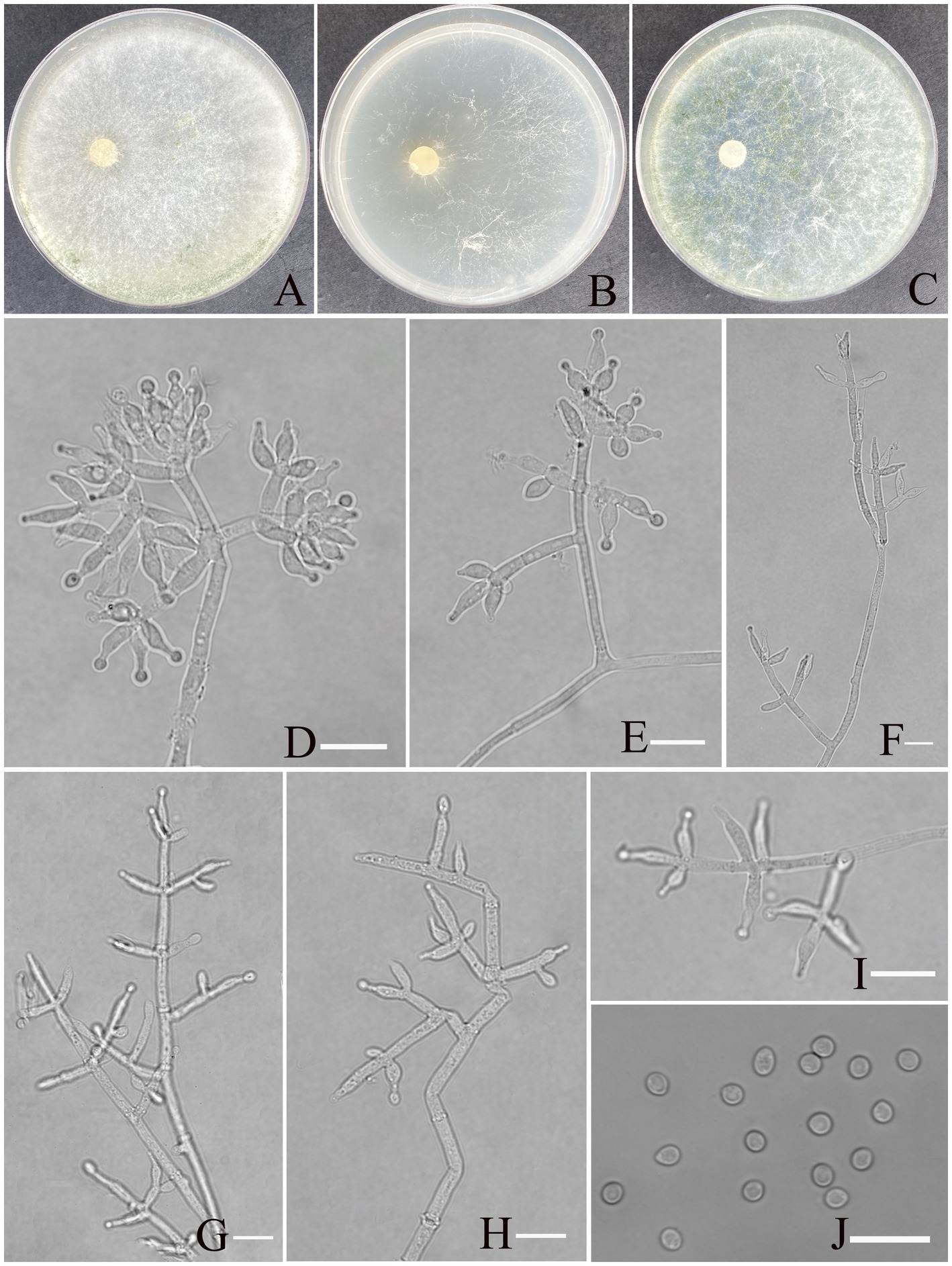
Figure 5. Morphology of Trichoderma exigua (YMF 1.10219). (A–C) Cultures on PDA plates, 7d; CMA plates, 7d; SNA plates, 7d; 25°C; (D–I) conidiophores and phialides; (J) conidia. Scale bars: 10 μm (D–J).
MycoBank NO: 860056.
Etymology: Latin, exigua, refer exiguous conidiation.
Description: Sexual morph: Unknown. Asexual morph: Conidiophores more or less symmetrical, main axis recognizable, branches arising at an angle of less than 90° concerning the main axis. Most branches are paired or form a whorl of 3, occasionally solitary. Phialides concentrated on the apex of conidiophores, arranged in 2–5 whorls, less solitary, ampulliform or narrowly vase-shaped, straight or curved, with an indefinite direction. (5.5–)6.5–9.7(−12.0) × (2.0–) 2.6–3.5(−4.2) μm, l/w ratio1.6–3.5. Conidia oval, elliptic, green, smooth, (2.7–)2.9–3.5(−4.1) × (2.4–)2.5–2.8(−3.0) μm, l/w ratio 1.1–1.3. Chlamydospores not found.
Culture characteristics: Optimum temperature for growth is 30°C.
Colony radius on PDA after 72 h: 51 mm at 25°C, 60 mm at 30°C, and 42 mm at 35°C, covering the plate after 3 days at 30°C. The colony is white, circular, and turns primrose after 3 days. Aerial hyphae are abundant, forming a dense mat. No diffusing pigment noted, slight odor noted.
Colony radius on CMA after 72 h: 30 mm at 25°C, 35 mm at 30°C, and 27 mm at 35°C. The colony is lucency, with the air mycelium having more edges and less center; no diffusing pigment was noted, and odor was indistinct.
Colony radius on SNA after 72 h: 40 mm at 25°C, 51 mm at 30°C, and 33 mm at 35°C. The colony is white, circular. Three days later, the center of the colony turns yellow-green. No diffusing pigment was noted, and odor was indistinct.
Materials examined: China, Yunnan Province, Shilin Country, from soil of rocky desertification, August 2024, Z. F. Yu, (holotype YMF 1.10219). lbid. (cultures: YMF 1.10220).
Notes: T. exigua and T. guizhouense are phylogenetically related but exhibit distinct differences in morphological and culture characteristics (Li et al., 2013). However, T. exigua possesses distinctly longer lageniform phialides than the ampulliform to lageniform phialides of T. guizhouense (6.5–9.7 × 2.6–3.5 vs. 4.5–10 × 2–3); the phialides of the former are organized in 2–5 whorls, while those of the latter are often in a whorl of 3. Moreover, conidia of T. exigua are smooth, oval to elliptic, and larger (2.4–3.0 vs. 2–3), while conidia of T. guizhouense are globose.
Finally, regarding culture characteristics, T. guizhouense exhibits rapid growth, with a colony radius of 57–58 mm on PDA at 25°C after 72 h, whereas T. exigua shows slower growth. Both species lack diffusing pigments, although T. guizhouense may produce a brown diffusing pigment in some strains, and both species emit a slight odor.
Discussion
Current taxonomic resolution within the Trichoderma genus has been achieved through integrative analyses incorporating phylogenetic, morphological, ecological, and biogeographical data. Notably, two genetic loci, rpb2 and tef1-α, have been established as the standard molecular markers for the identification of novel Trichoderma species (Cao et al., 2024). These molecular markers, along with comprehensive morphological examination, have significantly enhanced the precision of species delimitation within this genus. This study used a comprehensive analysis of multi-gene sequences (ITS, rpb2 and tef1-α) along with morphological characteristics to systematically elucidate the phylogenetic relationships among the species. Based on the multi-gene phylogenetic tree, the four new species were classified into three distinct clades: Longibrachiatum, Viride, and the Harzianum clades. Furthermore, all clades exhibited high maximum likelihood bootstrap proportions and Bayesian posterior probabilities, providing strong support for their phylogenetic classification.
The newly described species T. calcicola belong to the Viride clade, one of the most species-rich and widely distributed clades within the genus Trichoderma. The Viride clade, initially referred to as the “section Trichoderma,” is represented by the type species T. viride Pers (Bissett, 1991). Building upon the study of Samuels et al. (2006), Jaklitsch et al. (2013) further analyzed the complex group; subsequently, Jaklitsch and Voglmayr (2015) formally renamed the clade the Viride clade through the construction of an updated phylogenetic tree. Species in this clade primarily exhibit verticillate or pachybasium-like conidiophores, with phialides arranged in whorls or pairs and producing green conidia, yet they display significant diversity in colony morphology, growth rates, and conidial shape and size (Qin and Zhuang, 2016). Members of this clade demonstrate remarkable ecological versatility, having been isolated from diverse substrates such as decaying corticated branches, fungal stromata, phyllosphere habitats, and various soil ecosystems, attesting to their broad geographical distribution and adaptive capacity (Kredics et al., 2014; Jaklitsch and Voglmayr, 2015). T. calcicola aligns with the clade’s traits in its conidiophore branching, phialide arrangement, and green conidia. The newly described species, T. xerophilum and T. exigua, belong to the Harzianum clade, a cosmopolitan and widely distributed group. The clade displays a complex speciation history and diverse morphological characteristics (Atanasova et al., 2010; Druzhinina et al., 2010; Qin and Zhuang, 2017; Ye et al., 2023). Species within the Harzianum clade typically produce diverse pustules in culture, exhibiting variation in conidiophore morphology, phialide shapes, and conidial characteristics (Chaverri and Samuels, 2003; Jaklitsch, 2009; Zheng et al., 2021; Ye et al., 2023). Even in the present study, morphological characteristics of T. xerophilum and T. exigua also vary in the l/w ratio of phialides and arrangement. The taxonomy of the Harzianum clade was revised by Chaverri et al. (2015), who emphasized the need to use the secondary barcode tef1-α to accurately identify species within this complex. Subsequently, numerous species within this clade have been extensively reported, further enriching their diversity (Jaklitsch and Voglmayr, 2015; Qiao et al., 2018; Zhang and Zhuang, 2018; Phookamsak et al., 2019; Gu et al., 2020; Barrera et al., 2021; Cao et al., 2022, 2024; Ye et al., 2023).
Trichoderma karsti was robustly assigned to the Longibrachiatum clade, with high statistical support in phylogenetic analyses, and the species morphologically aligns with the diagnostic traits of the Longibrachiatum clade. In contrast to the other clades, the Longibrachiatum clade appears to be monophyletic (Samuels et al., 1998, 2012; Zhang and Zhuang, 2018). Samuels et al. conducted a comprehensive revision of this clade, describing eight new taxonomic units, including Trichoderma aethiopicum, and expanding the known species within the clade to 21, along with the development of a systematic identification key. Additionally, the re-description of species such as T. parareesei and the first identification of the sexual form of T. gilliesii significantly refined the taxonomic framework, laying a crucial foundation for future phylogenetic and functional studies. Following this methodological framework, an expanding array of species has been systematically identified and reported in this clade (Yabuki et al., 2013; Jaklitsch and Voglmayr, 2015; Qin and Zhuang, 2016; Zheng et al., 2021).
As a potential natural biocontrol resource or a contaminant of cultured mushrooms, Trichoderma has attracted considerable attention. Recent studies have documented Trichoderma diversity across multiple ecological niches, including: (1) plant-associated habitats (endophytic, epiphytic, and rhizosphere environments) (Xia et al., 2011; Mulatu et al., 2022); (2) fungal cultivation systems including edible mushroom substrates and medicinal fungi growth media (Wang et al., 2022; Cao et al., 2024); and (3) diverse ecosystems spanning alpine wetlands, forested areas, grasslands, wetlands, and agricultural landscapes (Tang et al., 2022; Dou et al., 2019). Sometimes, nationwide investigations of Trichoderma diversity were also conducted (Ahedo-Quero et al., 2024). Notably, Trichoderma asperellum appeared to be associated with the roots of the plant (Xia et al., 2011; Mulatu et al., 2022). Except for cultivation substrates of Lentinula edodes (Cao et al., 2024), T. harzianum was the predominant species in other natural ecosystems, either in agricultural or undisturbed soil. Its widespread distribution may be attributed not only to ecological plasticity but also to its competitive advantage in resource-poor environments, which may be a key factor in its success as a biocontrol agent. Previous studies have also demonstrated that both T. harzianum and T. asperellum can promote seed germination, highlighting their practical potential in agriculture (Muradov et al., 2025).
In our survey, the most abundant species was also T. harzianum with an isolation frequency of 26.31%, which is close to 23% in alpine wetlands with a similar arid and barren environment to karst desert soil. This consistency suggests that T. harzianum may exhibit habitat-specific adaptation to stressful environments. Future comparative studies across different ecosystems may further elucidate its ecological preferences and functional potential. Recent studies have shown that Trichoderma spp. significantly enhance organic matter decomposition by increasing CO₂ release and residue turnover (Organo et al., 2022), suggesting that they may play an important role in nutrient cycling and ecosystem recovery in karst desertification soils.
Nevertheless, this study has some limitations. The culture-dependent approach used here may underestimate total fungal diversity by missing unculturable or slow-growing taxa. In addition, all samples were collected from a soil depth of 5–10 cm, potentially overlooking fungi present in deeper horizons or at the rhizoplane. Future studies should incorporate high-throughput sequencing and functional assays to comprehensively characterize the ecological roles and adaptive mechanisms of Trichoderma in karst desert environments.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accession numbers PV344624, PV702217, PV344618, and PV344620.
Author contributions
X-WD: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. X-KZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. X-HL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. MQ: Resources, Writing – original draft. M-HM: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. YH: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing. Z-FY: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing. Q-QL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. FZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1400700), and this study was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation Program of PR China (32170017, 32370017).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahedo-Quero, H., Aquino-Bolanos, T., Ortiz-Hernandez, Y., and Garcia-Sanchez, E. (2024). Trichoderma diversity in Mexico: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diversity 16:68. doi: 10.3390/d16010068
Atanasova, L., Jaklitsch, W., Komoń-Zelazowska, M., Kubicek, C., and Druzhinina, I. (2010). Clonal species Trichoderma parareesei sp. nov. likely resembles the ancestor of the cellulase producer Hypocrea jecorina/T. Reesei. Appl. Environ. Microb. 76, 7259–7267. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01184-10
Bandurska, K., Krupa, P., Berdowska, A., Jatulewicz, I., and Zawierucha, I. (2021). Mycoremediation of soil contaminated with cadmium and lead by Trichoderma sp. Ecol. Chem. Engin. S 28, 277–286. doi: 10.2478/eces-2021-0020
Barrera, V., Iannone, L., Romero, A., and Chaverri, P. (2021). Expanding the Trichoderma harzianum species complex: three new species from argentine natural and cultivated ecosystems. Mycologia 113, 1136–1155. doi: 10.1080/00275514.2021.1947641
Bissett, J. (1991). A revision of the genus Trichoderma II. Infrageneric classification. Canad. J. Botany 69, 2357–2372. doi: 10.1139/b91-297
Cai, F., and Druzhinina, I. (2021). In honor of John Bissett: authoritative guidelines on molecular identification of Trichoderma. Fungal Divers. 107, 1–69. doi: 10.1007/s13225-020-00464-4
Cao, Z., Qin, W., Zhao, J., Liu, Y., Wang, S., and Zheng, S. (2022). Three new Trichoderma species in Harzianum clade associated with the contaminated substrates of edible fungi. J. Fungi 8:1154. doi: 10.3390/jof8111154
Cao, Z., Zhao, J., Liu, Y., Wang, S., Zheng, S., and Qin, W. (2024). Diversity of Trichoderma species associated with green mold contaminating substrates of Lentinula edodes and their interaction. Front. Microbiol. 14:1288585. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1288585
Carbone, I., and Kohn, L. (1999). A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 91, 553–556. doi: 10.1080/00275514.1999.12061051
Chaverri, P., Branco-Rocha, F., Jaklitsch, W., Gazis, R., Degenkolb, T., and Samuels, G. (2015). Systematics of the Trichoderma harzianum species complex and the re-identification of commercial biocontrol strains. Mycologia 107, 558–590. doi: 10.3852/14-147
Chaverri, P., and Samuels, G. (2003). Hypocrea/Trichoderma (Ascomycota, Hypocreales, Hypocreaceae): species with green ascospores. Stud. Mycol. 48, 1–116. doi: 10.1023/B:MYCO.0000003579.48647.16
Cheng, C., Yang, C., and Peng, K. (2012). Antagonism of Trichoderma harzianum ETS 323 on Botrytis cinerea mycelium in culture conditions. Phytopathology 102, 1054–1063. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-11-11-0315
del Carmen, H., Rodríguez, M., Evans, H., de Abreu, L., de Macedo, D., Ndacnou, M., et al. (2021). New species and records of Trichoderma isolated as mycoparasites and endophytes from cultivated and wild coffee in Africa. Sci. Rep. 11:5671. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84111-1
Dou, K., Gao, J., Zhang, C., Yang, H., Jiang, X., Li, J., et al. (2019). Trichoderma biodiversity in major ecological systems of China. J. Microbiol. 57, 668–675. doi: 10.1007/s12275-019-8357-7
Druzhinina, I., Kubicek, C., Komoń-Zelazowska, M., Mulaw, T., and Bissett, J. (2010). The Trichoderma harzianum demon: complex speciation history resulting in coexistence of hypothetical biological species, recent agamospecies and numerous relict lineages. BMC Evol. Biol. 10, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-94
Erazo, J., Palacios, S., Pastor, N., Giordano, F., Rovera, M., Reynoso, M., et al. (2021). Biocontrol mechanisms of Trichoderma harzianum ITEM 3636 against peanut brown root rot caused by Fusarium solani RC 386. Biol. Control 164:104774. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2021.104774
Fazeli-Nasab, B., Shahraki-Mojahed, L., Piri, R., and Sobhanizadeh, A. (2022). “Trichoderma: improving growth and tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses in plants” in Trends of applied microbiology for sustainable economy, Soni, R., Suyal, D. C., Yadav, A. N., and Goel, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 525–564. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-91595-3.00004-5
Geng, L., Fu, Y., Peng, X., Yang, Z., Zhang, M., Song, Z., et al. (2022). Biocontrol potential of Trichoderma harzianum against Botrytis cinerea in tomato plants. Biol. Control 174:105019. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2022.105019
Gooruee, R., Hojjati, M., Behbahani, B., Shahbazi, S., and Askari, H. (2024). Extracellular enzyme production by different species of Trichoderma fungus for lemon peel waste bioconversion. Biomass Convers. Bior 14, 2777–2786. doi: 10.1007/s13399-022-02626-7
Gu, X., Wang, R., Sun, Q., Wu, B., and Sun, J. (2020). Four new species of Trichoderma in the Harzianum clade from northern China. MycoKeys 73, 109–132. doi: 10.3897/mycokeys.73.51424
Hall, T. (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. 41, 95–98. doi: 10.1021/bk-1999-0734.ch008
Huang, Y., Zhao, P., Zhang, Z., Li, X., He, C., and Zhang, R. (2009). Transpiration of Cyclobalanopsis glauca (syn. Quercus glauca) stand measured by sap-flow method in a karst rocky terrain during dry season. Ecol. Res. 24, 791–801. doi: 10.1007/s11284-008-0553-6
Huelsenbeck, J., and Ronquist, F. (2001). MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17, 754–755. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754
Jaklitsch, W. (2009). European species of Hypocrea part I. The green-spored species. Stud. Mycol. 63, 1–91. doi: 10.3114/sim.2009.63.01
Jaklitsch, W., Komon, M., Kubicek, C., and Druzhinina, I. (2005). Hypocrea voglmayrii sp. nov. from the Austrian Alps represents a new phylogenetic clade in Hypocrea/Trichoderma. Mycologia 97, 1365–1378. doi: 10.1080/15572536.2006.11832743
Jaklitsch, W., Samuels, G., Ismaiel, A., and Voglmayr, H. (2013). Disentangling the Trichoderma viridescens complex. Persoonia 31, 112–146. doi: 10.3767/003158513X672234
Jaklitsch, W., and Voglmayr, H. (2015). Biodiversity of Trichoderma (Hypocreaceae) in southern Europe and Macaronesia. Stud. Mycol. 80, 1–87. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2014.11.001
Kidwai, M., Malik, A., Dhull, S., Rose, P., and Garg, V. (2022). Bioremediation potential of Trichoderma species for metal(loid)s. In: Malik, A., Kidwai, M. K., Garg, V. K. (Eds.), Bioremediation of toxic metal(loid)s. (CRC Press), 137–152.
Kim, C., Park, M., Kim, S., Maekawa, N., and Yu, S. (2012). Identification of Trichoderma, a competitor of shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes), and competition between Lentinula edodes and Trichoderma species in Korea. Plant Pathol. J. 28, 137–148. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2012.28.2.137
Kredics, L., Hatvani, L., Naeimi, S., Körmöczi, P., Manczinger, L., Vágvölgyi, C., et al. (2014). “Biodiversity of the genus Hypocrea/Trichoderma in different habitats” in Biotechnology and biology of Trichoderma (Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier), 3–24. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-59576-8.00001-1
Li, Q., Tan, P., Jiang, Y., Hyde, K., Mckenzie, E., Bahkali, A., et al. (2013). A novel Trichoderma species isolated from soil in Guizhou, T. Guizhouense. Mycol. Prog. 12, 167–172. doi: 10.1007/s11557-012-0821-2
Liu, S., Jin, P., and Dai, F. (2005). A rapid and simple extraction method for plant pathogenic fungi. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 35, 362–365.
Liu, Y., Whelen, S., and Hall, B. (1999). Phylogenetic relationships among Ascomycetes: evidence from an RNA polymerase II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16, 1799–1808. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026092
Migheli, Q., Balmas, V., Komoñ-Zelazowska, M., Scherm, B., Fiori, S., Kopchinskiy, A., et al. (2009). Soils of a Mediterranean hot spot of biodiversity and endemism (Sardinia, Tyrrhenian Islands) are inhabited by pan-European, invasive species of Hypocrea/Trichoderma. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 35–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01736.x
Mitrović, I., Čanak, P., Tančić Živanov, S., Farkaš, H., Vasiljević, M., Ćujić, S., et al. (2025). Trichoderma harzianum in biocontrol of maize fungal diseases and relevant mycotoxins: from the laboratory to the field. J. Fungi 11, 416. doi: 10.3390/jof11060416
Mukherjee, P., Horwitz, B., Herrera-Estrella, A., Schmoll, M., and Kenerley, C. (2013). Trichoderma research in the genome era. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 51, 105–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102353
Mulatu, A., Megersa, N., Abena, T., Kanagarajan, S., Liu, Q., Tenkegna, T., et al. (2022). Biodiversity of the genus Trichoderma in the rhizosphere of coffee (Coffea arabica) plants in Ethiopia and their potential use in biocontrol of coffee wilt disease. Crops 2, 120–141. doi: 10.3390/crops2020010
Muradov, P., Bakhshaliyeva, K., Mamedaliyeva, M., Maharramova, M., Aliyev, F., Isayeva, K., et al. (2025). General characteristics of the means obtained from species belonging to the genus Trichoderma karst distributed in Azerbaijan. Edelweiss Appl. Sci. Technol. 9, 1556–1562. doi: 10.55214/25768484.v9i2.4809
Nguyen, L., Schmidt, H., Von Haeseler, A., and Minh, B. (2015). IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32, 268–274. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu300
Organo, N., Granada, S., Pineda, H., Sandro, J., Nguyen, V., and Gummert, M. (2022). Assessing the potential of a Trichoderma-based compost activator to hasten the decomposition of incorporated rice straw. Sci. Rep. 12, 448.
Park, M., Bae, K., and Yu, S. (2006). Two new species of Trichoderma associated with green mold of oyster mushroom cultivation in Korea. Mycobiology 34, 111–113. doi: 10.4489/MYCO.2006.34.3.111
Peng, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, R., Xiong, K., and Lan, A. (2013). Soil erosion monitoring and its implication in a limestone land suffering from rocky desertification in the Huajiang canyon, Guizhou, Southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 69, 831–841. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1968-5
Phookamsak, R., Hyde, K., Jeewon, R., Bhat, D., Jones, E., Maharachchikumbura, S., et al. (2019). Fungal diversity notes 929-1035: taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions on genera and species of fungi. Fungal Divers. 95, 1–273. doi: 10.1007/s13225-019-00421-w
Qiao, M., Du, X., Zhang, Z., Xu, J., and Yu, Z. (2018). Three new species of soil-inhabiting Trichoderma from Southwest China. MycoKeys 44, 63–80. doi: 10.3897/mycokeys.44.30295
Qin, W., and Zhuang, W. (2016). Four new species of Trichoderma with hyaline ascospores in the Brevicompactum and Longibrachiatum clades. Mycosystema 35, 1317–1336. doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.160158
Qin, W., and Zhuang, W. (2017). Seven new species of Trichoderma (Hypocreales) in the harzianum and strictipile clades. Phytotaxa 305, 121–139. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.305.3.1
Samuels, G., Dodd, S., Lu, B., Petrini, O., Schroers, H., and Druzhinina, I. (2006). The Trichoderma koningii aggregate species. Stud. Mycol. 56, 67–133. doi: 10.3114/sim.2006.56.03
Samuels, G., Ismaiel, A., Mulaw, T., Szakacs, G., Druzhinina, I., Kubicek, C., et al. (2012). The Longibrachiatum clade of Trichoderma: a revision with new species. Fungal Divers. 55, 77–108. doi: 10.1007/s13225-012-0152-2
Samuels, G., Petrini, O., Kuhls, K., Lieckfeldt, E., and Kubicek, C. (1998). The Hypocrea schweinitzii complex and Trichoderma sect. Longibrachiatum. Stud. Mycol. 41, 1–54.
Sandoval-Denis, M., Sutton, D., Cano-Lira, J., Gené, J., Fothergill, A., Wiederhold, N., et al. (2014). Phylogeny of the clinically relevant species of the emerging fungus Trichoderma and their antifungal susceptibilities. J. Clin. Microbiol. 52, 2112–2125. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00429-14
Sperandio, G., and Filho, E. (2021). An overview of Trichoderma reesei co-cultures for the production of lignocellulolytic enzymes. Appl. Microbiol Biot. 105, 3019–3025. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11261-7
Subramaniam, S., Zainudin, N., Aris, A., and Hasan, Z. (2022). Role of Trichoderma in plant growth promotion. Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 257–280. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-91650-3_9 Advances in Trichoderma Biology for Agricultural Applications Springer:
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., and Kumar, S. (2021). MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 3022–3027. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
Tang, Y., Li, J., Zhang, X., Yang, P., Wang, J., and Zhou, N. (2013). Fractal characteristics and stability of soil aggregates in karst rocky desertification areas. Nat. Hazards 65, 563–579. doi: 10.1007/s11069-012-0383-2
Tang, G., Li, Y., Zhou, Y., Zhu, Y., Zheng, X., Chang, X., et al. (2022). Diversity of Trichoderma species associated with soil in the Zoige alpine wetland of Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 12:21709. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25223-0
Thompson, J., Gibson, T., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D. (1997). The CLUST AL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Wang, Y., Zeng, L., Wu, J., Jiang, H., and Mei, L. (2022). Diversity and effects of competitive Trichoderma species in Ganoderma lucidum-cultivated soils. Front. Microbiol. 13:1067822. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1067822
White, T., Bruns, T., Lee, S., Taylor, W., Lee, S., and Shawe-Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications, vol. 1 Innis, M. A., Gelfand, D. H., Sninsky, J. J., White, T. J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 315–322. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-372180-8.50042-1
Xia, X., Lie, T., Qian, X., Zheng, Z., Huang, Y., and Shen, Y. (2011). Species diversity, distribution, and genetic structure of endophytic and epiphytic Trichoderma associated with banana roots. Microb. Ecol. 61, 619–625. doi: 10.1007/s00248-010-9770-y
Yabuki, T., Miyazaki, K., and Okuda, T. (2013). Japanese species of the Longibrachiatum clade of Trichoderma. Mycoscience 55, 196–212. doi: 10.1016/j.myc.2013.08.006
Yan, L., and Khan, R. (2021). Biological control of bacterial wilt in tomato through the metabolites produced by the biocontrol fungus, Trichoderma harzianum. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 31, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/s41938-020-00351-9
Yang, X. (2022). Soil fungal diversity in typical rocky desertification regions of Yunnan Province (master’s thesis, Yunnan university)
Yao, S., Zhou, B., Duan, M., Cao, T., Wen, Z., Chen, X., et al. (2023). Combination of biochar and Trichoderma harzianum can improve the phytoremediation efficiency of Brassica juncea and the rhizosphere micro-ecology in cadmium and arsenic contaminated soil. Plants 12:2939. doi: 10.3390/plants12162939
Ye, C., Jing, T., Sha, Y., Mo, M., and Yu, Z. (2023). Two new Trichoderma species (Hypocreales, Hypocreaceae) isolated from decaying tubers of Gastrodia elate. MycoKeys 99, 187–207. doi: 10.3897/mycokeys.99.109404
Ye, C., You, Y., Li, W., Jing, T., Mo, M., and Yu, Z. (2024). Diversity of Trichoderma species associated with the black rot disease of Gastrodia elata, including four new species. Front. Microbiol. 15:1420156. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1420156
Zhang, G., Yang, H., Zhang, X., Zhou, F., and Zhao, H. (2022). Five new species of Trichoderma from moist soils in China. MycoKeys 87, 133–157. doi: 10.3897/mycokeys.87.76085
Zhang, Y., and Zhuang, W. (2018). New species of Trichoderma in the Harzianum, Longibrachiatum and Viride clades. Phytotaxa 379, 131–142. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.379.2.1
Keywords: diversity, karst soils, multi-locus phylogeny, new species, Trichoderma
Citation: Dai X-W, Zhang X-K, Li X-H, Li Q-Q, Zhang F, Qiao M, Mo M-H, Huang Y and Yu Z-F (2025) Trichoderma diversity from karst area in Yunnan, Shilin, and four new species. Front. Microbiol. 16:1645607. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1645607
Edited by:
Sumit Singh Dagar, Agharkar Research Institute, IndiaReviewed by:
Soner Soylu, Mustafa Kemal University, TürkiyeKlaudyna Spychała, University of Wrocław, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Dai, Zhang, Li, Li, Zhang, Qiao, Mo, Huang and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Huang, eWRodWFuZ3lpbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ze-Fen Yu, emZ5dTIwMjFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Xing-Wen Dai1,2
Xing-Wen Dai1,2 Ze-Fen Yu
Ze-Fen Yu