- 1Department of Dermatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 2Department of Dermatology, The Affiliated Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 3School of Pharmacy, Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by damage to dopaminergic neurons within the substantia nigra region of the midbrain. Melanoma, on the other hand, is a malignant skin tumor formed by the abnormal proliferation of melanocytes, often linked to genetic predisposition and ultraviolet exposure. Emerging evidence confirms a significant association between PD and melanoma, with individuals afflicted with PD displaying a higher susceptibility to melanoma development. The PARK family genes, known for their involvement in PD etiology, emerge as key players in elucidating this intricate relationship. Through a comprehensive review, it becomes evident that different PARK gene mutations exert varied impacts on both PD and melanoma pathogenesis. For instance, mutations in PARK1/4 influence α-synuclein aggregation in both PD and melanoma, while PARK8 mutations modulate autophagy pathways in both PD and melanoma. The roles of PARK2 and PARK13 in melanoma warrant further investigation. Additionally, PARK6 mutations influence mitophagy mechanisms in PD and melanoma, with implications regarding melanoma proliferation through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Therefore, delineating the precise contributions of PARK genes to PD and melanoma pathophysiology holds paramount importance in devising therapeutic strategies for both PD and melanoma.
1 Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is currently the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disease, and is usually accompanied by metabolic abnormalities (1, 2). Central to its pathology is the aberrant aggregation of α-synuclein (α-syn), which is implicated to a variety of neurodegenerative conditions (3). Alongside its hallmark, PD manifests numerous non-motor symptoms in addition to motor symptoms such as autonomic dysfunction, olfactory impairment (4), sleep disturbances (5), and cognitive decline (6). Skin manifestations in PD, often overlooked due to their non-specific nature and the lack of objective clinical measures, encompass symptoms such as dryness, pruritus, erythema, and desquamation, especially affecting the scalp and face (7).
There is increasing evidence suggesting a link between PD and various dermatological conditions such as melanoma (8), seborrheic dermatitis (9), dysregulated sweating (10), and bullous pemphigoid (11). Despite fundamental differences - PD entails cell degeneration while melanoma leads to cell proliferation - epidemiological data reveals a higher risk of melanoma among PD patients (12), with reciprocal risks noted in melanoma patients developing PD. A previous study reported that over a 5-year period, the risk of developing melanoma in patients with PD was 2.4-fold higher than in the healthy population (13). Melanoma, a highly malignant melanocyte-derived tumor, underscores the neuroprotective role of neuromelanin through dopaquinone scavenging (8), whereas, patients with PD exhibit significantly lower neuromelanin levels (14). Previous studies suggest that levodopa, a cornerstone PD therapy, may contribute to the development of melanoma, due to shared dopamine and melanin biosynthetic pathways (15), although contradictory findings exist (16).
The discovery of the PARK gene has played a crucial role in the history of PD research. PARK1 or PARK4 was the first PARK gene discovered to cause PD in 1996 (17). This discovery sets the stage for subsequent research. Then, PARK1-PARK18 genes were identified as being associated with PD (18). Inzelberg et al. reported that 48% of melanoma tissue samples have mutations in at least one PARK gene and 25% have mutations in multiple PARK genes (19). The high proportion of mutations in PARK genes in melanoma suggests a possible correlation between melanoma and PD.
Mutations within the PARK gene family are strongly associated with PD (20), yet their implications in melanoma remain unmapped. For instance, PARK1/4 encoded α-syn (PARK1/4) influences melanin and neuromelanin biosynthesis by regulation of tyrosinase (Tyr), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), and peroxidase (21). Elucidating shared pathogenic mechanisms in PD and melanoma holds significant therapeutic options for patients with PD and melanoma. However, the precise mechanisms underlying their association remains enigmatic. This review aims to dissect the roles of PARK genes - PARK1/4, PARK2, PARK5, PARK6, PARK7, PARK8, PARK13, PARK14, and PARK18 in both PD and melanoma, thereby fostering novel therapeutic strategies for these debilitating conditions.
2 Role of PARK family in PD and melanoma
2.1 α-syn/PARK1 a high risk for melanomas
PD exhibits significant clinical and genetic diversity. While its intricate causes and pathological mechanisms have hindered breakthroughs in disease-modifying therapies, recent genetic technologies have advanced research approaches. In this context, mitochondrial dysfunction has been recognized as a central pathogenic factor in both familial and sporadic PD cases. PARK genes play a pivotal role in maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis, overseeing processes including biogenesis and mitophagy, as well as functions such as energy production and oxidative stress regulation. These genes can interact with the autophagy pathway, initiate proinflammatory immune responses, and exacerbate oxidative stress, all of which contribute to the aggregation of α-synuclein. Thus, rectifying mitochondrial dysfunction emerges as a promising therapeutic approach for neuroprotection in PD, targeting the underlying mechanisms that lead to neuronal damage. Additionally, the SNCA gene, which encodes α-synuclein and is alternatively known as PARK1 or PARK4, is a significant causative factor in PD. Under normal physiological circumstances, α-synuclein may participate in functions like the preservation of synaptic structures and the facilitation of neural plasticity (22). Accumulation of misfolded α-syn in the brain induces the death of dopaminergic neurons in patients with PD (23). Notably, phosphorylated α-syn was detected in peripheral tissues of patients with PD especially at serine-129, which is the key event responsible for the formation of Lewy bodies in PD (24, 25). Tyr, an oxidase, serves as the rate-limiting enzyme in melanogenesis, while TH governs dopamine synthesis. α-syn interacts with Tyr, inhibits TH activity, and impedes dopamine and melanin synthesis (26, 27). Pan et al. demonstrated that α-syn overexpression in A375 melanoma cells reduces UV irradiation-induced melanin synthesis (26). This suggests that α-syn disrupts melanin production, which may enhance UV-induced DNA damage and, consequently, promote melanoma development (Figure 1). Furthermore, the PMEL gene encodes, a scaffold protein for melanin polymerization within melanosomes, and interacts with α-syn (28, 29), disrupting enzymes involved in melanin biosynthesis.
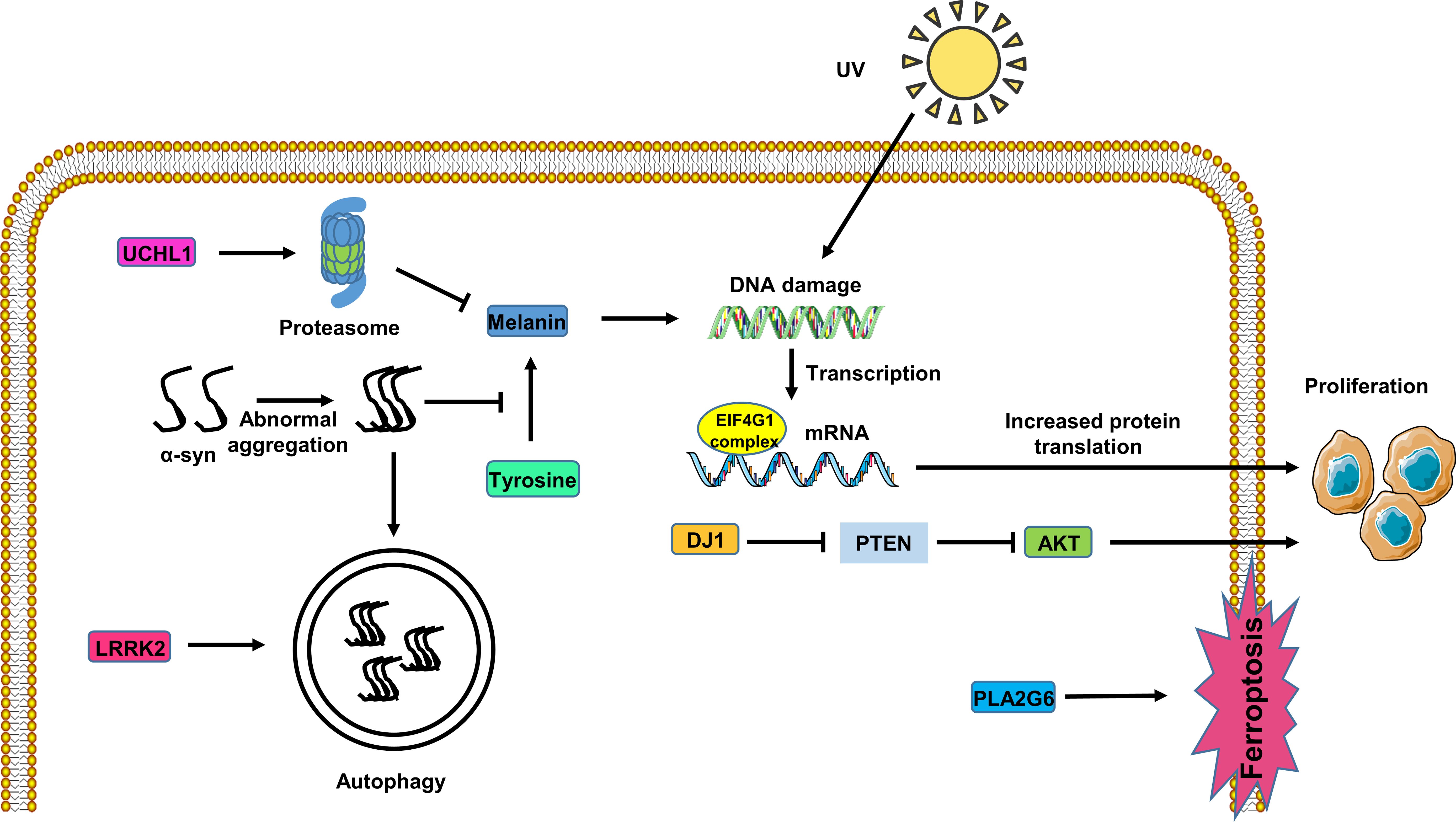
Figure 1. Potential role of the PARK genes in melanoma cells. UHCL1 expression activates the proteasome pathway, inhibiting melanin synthesis. Abnormal accumulation of α-syn inhibits melanin synthesis, rendering DNA susceptible to damage from UV radiation in melanoma cells. LRRK2 affects α-syn degradation through the autophagy pathway in melanoma cells. PLA2G6 expression inhibits melanoma cell ferroptosis. The EIF4F complex alters the initiation of mRNA translation, promoting melanoma cell proliferation. DJ1 expression fosters melanoma cell proliferation through the PTEN/AKT pathway.
A previous study revealed aggregation of α-syn in dermal nerve fibers and melanomas from patients with PD (30, 31). Conversely, healthy melanocytes do not exhibit detectable levels of α-syn (32), implying its specific aggregation in individuals with PD having afflicted skin. Interestingly, trace amounts of α-syn have been identified in the skin of patients with melanoma (33), indicating that α-syn is a nexus linking PD and melanoma. Moreover, the knockdown of α-syn expression inhibits invasion and migration by SK-MEL-28 and SK-MEL-29 melanoma cell lines. Gajendran N, Rajasekaran S, et al., used two human melanoma cell lines (SK-MEL-28 and SK-MEL-29), SNCA gene knockout (KO) clones, and two human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lines. In the melanoma cell lines, the absence of α-synuclein expression led to a significant decrease in the expression of L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) and N-cadherin, and also significantly weakened cell motility. Compared with the control group, the motility of the four tested SNCA-KO cells was reduced by an average of 75% (34). Turriani E, Lázaro DF, et al., found that particularly in advanced melanoma stages, the accumulation of α-syn ensures that autophagy is maintained at a homeostatic level, thereby promoting melanoma cell survival. In this experiment, treating melanoma cells with high α-synuclein expression with oligomer modulators that affect α-synuclein led to obvious changes in the morphology of melanoma cells and inhibited their proliferation (35). Knockdown of α-syn in SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells induces intracellular iron ions accumulation, triggering ferroptosis (36). These findings collectively suggest that aggregation of α-syn in PD may act as a catalyst for melanoma development by modulating melanocyte autophagy, ferroptosis, and melanin synthesis.
2.2 Parkin/PARK2 deficiency promotes melanoma
Parkin (Park2), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, is critical for maintaining mitochondrial function by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and degradation. However, recent evidence, as demonstrated by Dimasuay, Kris Genelyn, et al., suggests that Parkin is involved in promoting inflammation (37). Parkin plays a crucial role in degrading abnormally folded proteins, particularly in mitophagy (38). Mutations in the Parkin gene (PRKN) disrupt autophagy and proteasome pathways, widely considered as key pathogenic mechanisms in patients with PD (39, 40).
In addition, Parkin additionally functions as a cell cycle inhibitor and driver of apoptosis in melanoma cells. Mutations involving Parkin inhibit its ubiquitination function, thereby promoting survival of melanoma cell. Levin L, Srour S, et al.’s in vitro analysis indicated that wild-type Parkin exerts a tumor-suppressive effect in melanoma development, leading to cell cycle arrest, reduced metabolic activity, and apoptosis. Potential Parkin substrates in melanoma were identified using mass spectrometry-based analysis, and a functional protein association network was generated. The activity of mutant Parkin was evaluated through protein structure modeling and examination of Parkin E3 ligase activity. The Parkin-E28K mutation impairs Parkin’s ubiquitination activity and abolishes its tumor-suppressive effect. In summary, analysis of genomic sequences and in vitro data suggests that Parkin is a potential link between melanoma and Parkinson’s disease (41). Re-expression of Parkin in melanoma cell lines inhibits cell proliferation, whereas inhibition of Parkin in melanocytes stimulates cell proliferation (42). Parkin deficiency heightens cellular sensitivity to UV radiation and accelerates DNA damage (43). And overexpression of Parkin reduces melanoma cell growth and induces apoptosis (44). Nonetheless, Parkin plays a very important role in regulating melanoma cell proliferation, migration and resistance to UV radiation.
2.3 UCHL1/PARK5 reduces melanin production in melanoma
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) plays a crucial role in numerous cellular processes, with UPS dysfunction correlating with pathological changes in PD. In the past ten years, scientists have uncovered that a cluster of seemingly unrelated neurodegenerative disorders—including Parkinson’s disease—share striking similarities in cellular and molecular biology. All these neurodegenerative conditions involve protein misfolding and aggregation, triggering the formation of inclusion body aggregates within cells. These aggregates often contain chaperone proteins and ubiquitin (the proteolytic signal for the 26S proteasome), which assist in refolding misfolded proteins. The identification of disease-causing gene mutations encoding multiple ubiquitin-proteasome pathway proteins in Parkinson’s disease has further solidified the link between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and neurodegeneration (45). Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) belongs to the deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) family and serves as a crucial regulator of free ubiquitin levels in neurons (46). A deficiency of UCHL1 results in inadequate ubiquitination and subsequent protein accumulation in neurons (47). Dysregulation of UPS function is closely associated with abnormal α-syn aggregation. Previous studies have indicated decreased UCHL1 expression in the substantia nigra region of patients with PD (48).
UCHL1 overexpression in melanoma cells activates UPS-mediated degradation, consequently inhibiting microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) expression and reducing melanin production (49). This suggests a dual role for UCHL1 in both PD and melanoma, emphasizing its significance as a potential therapeutic target in these conditions (Figure 1).
2.4 Role of PINK1/PARK6 in melanoma
The PINK1/PARK6 gene encodes a serine/threonine protein kinase localized in mitochondria, which is crucial for protecting cells against stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by promoting mitophagy (50). PINK1 facilitates Parkin recruitment to mitochondria, promoting its ubiquitination and subsequent induction of mitophagy. Mutations in the PINK1 gene are associated with early-onset PD (51). Mutations in PARK6 also have been found in PD patients (52).
In melanoma cells, the knockdown of PINK1 inhibits BAY 87-2243, a potent inhibitor of the first oxidative phosphorylation complex)-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, mitophagy, and cell death (53). In tumor tissues, the tumor suppressor PTEN induces expression of PINK1, while PINK1, in turn, regulates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (54). Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a tumor suppressor that regulates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and its mutation has been reported to frequently occur in many human cancer cells (55). The experimental results of Yoon Jin Lee et al. show that the expression of PTEN in melanoma is lower than that in normal skin. Therefore, the regulatory effect of PTEN on the PI3K/AKT pathway may inhibit the development of melanoma. This suggesting that PINK1 may also influence melanoma progression through this pathway (56). However, the precise mechanisms underlying the PINK1’s involvement in melanoma development necessitate further investigation.
2.5 DJ1/PARK7 overexpression promotes melanoma
The protein DJ1, encoded by the PARK7 gene, is strongly associated with early-onset PD. DJ1 regulates intracellular redox balance, thereby inhibiting the accumulation of ROS and protecting dopaminergic neurons from α-syn aggregation-induced neurotoxicity (57). Mutations in PARK7 are associated with an early-onset familial form of PD (58). DJ1 is overexpressed in melanoma cells compared to healthy skin, which was found to reduce PTEN levels, thereby inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway and apoptosis in melanoma cells (56).
Additionally, the research results of Nerea Lago-Baameiro et al. show that PARK7-silenced uveal melanoma cells exhibit abnormalities in the PI3K/Akt pathway. In both primary and metastatic UM cell lines, a significant reduction in Akt phosphorylation is consistent with DJ-1 inhibition. The PI3K pathway is responsible for regulating cell survival, while the tumor suppressor gene PTEN antagonizes this pathway and is also inhibited by DJ-1. Therefore, DJ-1 overexpression not only promotes Akt phosphorylation but also enhances cell viability, indicating that DJ1 expression can promote the proliferation and invasion of uveal melanoma cells through the PTEN/AKT pathway (59) (Figure 1).
Moreover, a physical interaction between DJ1 and α-syn has been identified through molecular docking and protein–protein interaction network analyses. Modifying such interaction through drug administration may be a novel target for the treatment of melanoma. Quesnel A, Martin LD, et al. analyzed the expression profiles of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) extracted from the UCSC Xena database to determine the expression of α-synuclein and DJ-1 in primary and metastatic cutaneous melanoma (SKCM). Immunohistochemical techniques detected upregulated expression of aggregated α-synuclein in metastatic melanoma lymph nodes. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) studies showed that overexpression of α-synuclein in SK-MEL-28 cells promoted DJ-1 expression. Molecular docking analysis revealed that α-synuclein formed stable complexes with chemotherapeutic drugs such as temozolomide, dacarbazine, and doxorubicin, with differing binding modes. In temozolomide-treated SK-MEL-28 spheroids, the levels of both proteins decreased simultaneously, indicating that drug binding may affect protein-protein interactions and stability (60). These findings reveal the multifaceted role of DJ1 in both PD and melanoma, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target in both conditions.
2.6 Role of LRRK2/PARK8 in melanoma
Mutations in the Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene represents one of the most prevalent genetic risk factors for PD (61). Mutations in LRRK2 result in increased LRRK2 kinase activity, which induces lysosomal dysfunction, accumulation of α-syn, and neuronal damage (62). Patients with PD may have hyperactivation of the LRRK2 regardless of LRRK2 gene mutations (63). Therefore, inhibition of LRRK2 kinase and improvement of membrane transport and lysosomal function is a promising potential treatment for PD (64).
The connection between LRRK2 mutations and melanoma development remains inconclusive (65). A previous study has reported an increased melanoma risk among patients with PD having LRRK2 mutations (66). LRRK2 is emerging as a critical therapeutic target for autosomal dominant Parkinson’s disease (PD). The primary genetic cause of familial PD, which constitutes roughly 5-6% of familial instances and 2% of sporadic cases, lies in mutations within the LRRK2 gene. The most common mutation, G2019S, enhances kinase function, leading to phosphorylation of key serine sites that regulate LRRK2 activity, such as Ser910 and Ser935, which contributes to PD development. Development of LRRK2 inhibitors has become a focal area in PD therapy research. Preclinical studies have shown these inhibitors hold potential to alleviate PD-associated pathology by modifying the cellular distribution of LRRK2 and decreasing phosphorylation. Beyond its kinase activity, LRRK2 is implicated in autophagic processes and mitochondrial function. This involvement suggests that PD hallmarks like mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired autophagy could be tackled by LRRK2-targeted therapies. Additionally, selective LRRK2 inhibitors demonstrate promise in PD treatment, and further exploration of LRRK2’s molecular role in PD is crucial for developing effective therapies that can enhance patient outcomes and mitigate disease progression (67).
Given LRRK2’s involvement in the autophagy pathway, it is proposed that LRRK2 mutations in patients with PD impact α-syn clearance and aggregation, thereby influencing PD progression. Further exploration of this relationship is warranted to better comprehend the interplay between LRRK2, α-syn pathology, and melanoma development (Figure 1).
2.7 HTRA2/PARK13 expression suppresses melanoma
HTRA2, a member of the serine protease family, plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes, including maintenance of mitochondrial homeostasis and regulation of apoptosis (68). Gialluisi et al. proposed PARK13 as a candidate gene for late-onset PD (69). Its significance in preserving mitochondrial function and its dysregulation in PD pathogenesis have been documented (70, 71). PARK13 deficiency results in PD-like symptoms (72). Previous studies have reported that indirect phosphorylation of HTRA2 by PINK1 enhances cellular resistance to mitochondrial stress (70, 72).
Elevated expression of HTRA2 promotes apoptosis and augments the sensitivity of uveal melanomas to radiation therapy. Livin, also called melanoma inhibitor of apoptosis protein, suppresses apoptosis by binding and inhibiting caspases 3, 7 and 9 (73). Overexpression of livin renders malignant melanoma cells resistant to apoptotic stimuli. Notably, cleaved livin, upon interaction with HTRA2, relinquishes its anti-apoptotic function and assumes pro-apoptotic effects in melanoma cells (74). Although Yan et al. demonstrated HTRA2’s capability to cleave livin in vitro, its necessity for livin cleavage in melanoma cells remains uncertain (75). These findings suggest a potential role for HTRA2 in melanoma; however, the underlying mechanisms warrants further elucidation.
2.8 Knock down of PLA2G6/PARK14 inhibits melanoma
PLA2G6 encodes the iPLA2β protein, which participates in various physiological processes including lipid metabolism, maintenance of mitochondrial integrity, phospholipid remodeling, signal transduction and cell death (76, 77). Mutations in PLA2G6 have been identified as significant contributors to PD (78, 79). Deficiency of PLA2G6 promotes aggregation of α-syn, thus accelerating PD progression (80).
Moreover, PLA2G6 plays an important role in melanoma. Genome-wide association studies have strongly linked the PLA2G gene with melanoma (81). In human melanoma tissues, PLA2G6 expression is upregulated compared to adjacent tissues. Through the use of Oncomine and CCLE online databases, immunohistochemistry, RT-qPCR, and Western blot analysis, Yifei Wang et al. found that PLA2G6 knockdown significantly inhibits melanoma cell proliferation and metastasis while promoting cell apoptosis (82). Interestingly, PLA2G6 also mitigates ferroptosis in melanoma cells by regulating the transport of iron ions (82). Consequently, further exploration into the role of PLA2G6 in melanoma deserves to be conducted to unveil its potential as a therapeutic target (Figure 1).
2.9 Role of eIF4G/PARK18 in PD and melanoma
The PARK18 gene functions as a crucial component of the translation initiation complex eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF4F), which exhibits a significant association with the risk of developing PD (83, 84). However, eIF4G’s role as a PD gene remains somewhat contentious, given conflicting findings regarding the effects of eIF4G gene mutations on PD (85–87).
Conversely, studies have reported a higher prevalence of eIF4G mutations among melanoma patients (88). Mutations in eIF4G that perturb mRNA translation initiation may contribute to the proliferation of tumor cells (89), leading to drug resistance in melanoma (90). Targeting eIF4G and disrupting the EIF4F complex with the small molecule SBI-756 has shown promise in attenuating drug resistance in BRAF-mutant melanoma (91). Therefore, eIF4G emerges as a promising new potential target for therapeutic intervention in melanoma (Figure 1).
3 Discussion
This article provides an overview of the potential roles of PD-related genes (PARK gene family) in melanoma, including PARK1, PARK2, PARK5, PARK6, PARK7, PARK8, PARK13, PARK14, and PARK18 (Table 1). Mutations in the PARK1 gene have been implicated in promoting the development of both PD and melanoma. α-syn encoded by the PARK1 gene acts as a catalyst, promoting melanoma progression, which explains the increased risk of melanoma among individuals with PD. Consequently, drugs targeting α-syn accumulation may offer therapeutic potential in the treatment of melanoma. For example, in patients with more rapidly progressing PD, prasinezumab may reduce motor symptom progression to a greater extent (92). Syn-RIBOTAC was able to selectively degrade SNCA mRNA, which significantly reduces the level of α-syn (93). PD01A is in Phase II clinical trials and has a favorable safety profile (94). These drugs can promote the degradation of α-syn, or reduce the aggregation of α-syn, or inhibit the synthesis of α-syn, and are potentially valuable in the treatment of melanoma. Also, some drugs used to treat neurodegenerative diseases have potential therapeutic effects on melanoma (95).
The PARK2 gene exhibits divergent roles in PD and melanoma. In PD, PARK2 protects neurons by promoting mitophagy through ubiquitination, whereas in melanoma, it acts as a cell cycle inhibitor and apoptosis driver. However, the role of PARK2 in melanoma remains somewhat controversial, with evidence suggesting that its deficiency inhibits melanoma growth and metastasis (96).
PARK7, associated with early-onset PD, is significantly upregulated in melanoma, inhibiting apoptosis. Unlike its antioxidant function in PD, PARK7 downregulates the PTEN-regulated PI3K/AKT pathway, thereby regulating melanoma cell proliferation. Furthermore, the interaction between PARK7 and α-syn, although not well understood, may synergistically promote melanoma cell proliferation, given their elevated expression in melanoma.
PARK6 facilitates mitophagy by recruiting PARK2 to mitochondria. In melanoma, PARK6 regulates proliferation through the PI3K/AKT pathways independent of the PINK1/Parkin pathway. Reduced PARK14 expression promotes apoptosis in melanoma cells, and is implicated in ferroptosis due to its affect iron ion metabolism (82), suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target in melanoma.
Targeting PARK18 plays an important role in combating drug resistance in melanoma. The precise function of PARK13 in melanoma remains unclear, but it likely influences apoptosis and contributes to melanoma pathogenesis.
The correlation between PARK gene expression in melanoma and PD has not been fully elucidated. Previously, it was reported that approximately 48% of individuals carry at least one PARK gene mutation, while 25% had multiple PARK gene mutations in the melanoma tissue (41). PARK1, PARK2, PARK5, and PARK7 are usually overexpressed in melanoma. PARK1 expression in melanoma and PD contributes to disease progression. PARK2, PARK5, and PARK7 expression promotes melanoma proliferation and migration, which are negatively correlated with PD.
In summary, elucidating the roles of PARK genes in melanoma is essential for understanding the disease pathogenesis and facilitating early diagnosis and treatment (Figure 1). Given the close relationship between PD caused by mutations in PARK genes and melanoma, special attention should be paid to melanoma development in individuals with early-onset PD. Clinically, early detection of melanoma in patients with PD is paramount, and regular dermatological surveillance, including skin biopsies, is recommended. Clinicians should also educate patients with PD regarding the risk of developing melanoma and encourage sun protection practices to prevent melanoma development in the early stages of PD.
4 Conclusion
Melanoma may manifest in individuals with early-stage PD, potentially impacting their quality of life and increasing the risk of mortality. Understanding the involvement of PARK family-associated genes in melanoma is essential for effectively managing both PD and melanoma. Close monitoring of patient’s skin condition during anti-PD medication treatment is imperative to optimize therapeutic approaches.
Author contributions
JHW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. HJX: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JHC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. DRY: Writing – review & editing. YJL: Writing – review & editing. JLW: Writing – review & editing. JYC: Writing – review & editing. RXZ: Writing – review & editing. RQZ: Writing – review & editing. XWL: Writing – review & editing. FL: Writing – review & editing. RNZ: Writing – review & editing. ZY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82371567).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Yang W, Hamilton JL, Kopil C, Beck JC, Tanner CM, Albin RL, et al. Current and projected future economic burden of Parkinson's disease in the U.S. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. (2020) 6:15. doi: 10.1038/s41531-020-0117-1
2. Li H, Zeng F, Huang C, Pu Q, Thomas ER, Chen Y, et al. The potential role of glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2024) 30:e14411. doi: 10.1111/cns.14411
3. Surguchov A and Surguchev A. Synucleins: new data on misfolding, aggregation and role in diseases. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:3241. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123241
4. Oppo V, Melis M, Melis M, Tomassini Barbarossa I, and Cossu G. Smelling and tasting" Parkinson's disease: using senses to improve the knowledge of the disease. Front Aging Neurosci. (2020) 12:43. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00043
5. Loddo G, Calandra-Buonaura G, Sambati L, Giannini G, Cecere A, Cortelli P, et al. The treatment of sleep disorders in parkinson's disease: from research to clinical practice. Front Neurol. (2017) 8:42. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00042
6. Fang C, Lv L, Mao S, Dong H, and Liu B. Cognition deficits in parkinson's disease: mechanisms and treatment. Parkinsons Dis. (2020) 2020:2076942. doi: 10.1155/2020/2076942
7. Sondrup MA, Bjergen C, Gaarskjær AN, Joseph A, Lassen RS, Mamedov S, et al. Investigation of itch in Parkinson disease. Itch. (2021) 6:e49. doi: 10.1097/itx.0000000000000049
8. Bose A, Petsko GA, and Eliezer D. Parkinson's disease and melanoma: co-occurrence and mechanisms. J Parkinsons Dis. (2018) 8:385–98. doi: 10.3233/JPD-171263
9. Tanner C, Albers K, Goldman S, Fross R, Leimpeter A, Klingman J, et al. Seborrheic dermatitis and risk of future parkinson's disease (PD) (S42.001). Neurology. (2012) 78:S42.001–s42. doi: 10.1212/WNL.78.1_MeetingAbstracts.S42.001
10. Swinn L, Schrag A, Viswanathan R, Bloem BR, Lees A, and Quinn N. Sweating dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. (2003) 18:1459–63. doi: 10.1002/mds.v18:12
11. Furue M and Kadono T. Bullous pemphigoid: What's ahead? J Dermatol. (2016) 43:237–40. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.13207
12. Cui X, Liew Z, Hansen J, Lee PC, Arah OA, and Ritz B. Cancers preceding parkinson's disease after adjustment for bias in a danish population-based case-control study. Neuroepidemiology. (2019) 52:136–43. doi: 10.1159/000494292
13. Bertoni JM, Arlette JP, Fernandez HH, Fitzer-Attas C, Frei K, Hassan MN, et al. Increased melanoma risk in Parkinson disease: a prospective clinicopathological study. Arch Neurol. (2010) 67:347–52. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.1
14. Nagatsu T, Nakashima A, Watanabe H, Ito S, and Wakamatsu K. Neuromelanin in parkinson's disease: tyrosine hydroxylase and tyrosinase. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:4176. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084176
15. Fiala KH, Whetteckey J, and Manyam BV. Malignant melanoma and levodopa in Parkinson's disease: causality or coincidence? Parkinsonism Relat Disord. (2003) 9:321–7. doi: 10.1016/s1353-8020(03)00040-3
16. Zanetti R, Loria D, and Rosso S. Melanoma, Parkinson's disease and levodopa: causal or spurious link? A review of the literature. Melanoma Res. (2006) 16:201–6. doi: 10.1097/01.cmr.0000215043.61306.d7
17. Polymeropoulos MH, Higgins JJ, Golbe LI, Johnson WG, Ide SE, Di Iorio G, et al. Mapping of a gene for Parkinson's disease to chromosome 4q21-q23. Science. (1996) 274:1197–9. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5290.1197
18. Klein C and Westenberger A. Genetics of parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2012) 2:a008888. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008888
19. Inzelberg R, Samuels Y, Azizi E, Qutob N, Inzelberg L, Domany E, et al. Parkinson disease (PARK) genes are somatically mutated in cutaneous melanoma. Neurol Genet. (2016) 2:e70. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000070
20. Li W, Fu Y, Halliday GM, and Sue CM. PARK genes link mitochondrial dysfunction and alpha-synuclein pathology in sporadic parkinson's disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:612476. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.612476
21. Xu S and Chan P. Interaction between neuromelanin and alpha-synuclein in parkinson's disease. Biomolecules. (2015) 5:1122–42. doi: 10.3390/biom5021122
22. Calabresi P, Mechelli A, Natale G, Volpicelli-Daley L, Di Lazzaro G, and Ghiglieri V. Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies: from overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:176. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05672-9
23. Li X, Wang W, Yan J, and Zeng F. Glutamic acid transporters: targets for neuroprotective therapies in parkinson's disease. Front Neurosci. (2021) 15:678154. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.678154
24. Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, de Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, et al. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem. (2006) 281:29739–52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600933200
25. Parra-Rivas LA, Madhivanan K, Aulston BD, Wang L, Prakashchand DD, Boyer NP, et al. Serine-129 phosphorylation of α-synuclein is an activity-dependent trigger for physiologic protein-protein interactions and synaptic function. Neuron. (2023) 111:4006–23.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.11.020
26. Pan T, Zhu J, Hwu WJ, and Jankovic J. The role of alpha-synuclein in melanin synthesis in melanoma and dopaminergic neuronal cells. PloS One. (2012) 7:e45183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045183
27. Tessari I, Bisaglia M, Valle F, Samorì B, Bergantino E, Mammi S, et al. The reaction of alpha-synuclein with tyrosinase: possible implications for Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:16808–17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709014200
28. Dean DN and Lee JC. Linking parkinson's disease and melanoma: interplay between α-synuclein and pmel17 amyloid formation. Mov Disord. (2021) 36:1489–98. doi: 10.1002/mds.28655
29. Dean DN and Lee JC. Defining an amyloid link Between Parkinson's disease and melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2020) 117:22671–3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009702117
30. Kuzkina A, Schulmeyer L, Monoranu CM, Volkmann J, Sommer C, and Doppler K. The aggregation state of α-synuclein deposits in dermal nerve fibers of patients with Parkinson's disease resembles that in the brain. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. (2019) 64:66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.03.003
31. Matsuo Y and Kamitani T. Parkinson's disease-related protein, alpha-synuclein, in Malignant melanoma. PloS One. (2010) 5:e10481. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010481
32. Inzelberg R, Flash S, Friedman E, and Azizi E. Cutaneous Malignant melanoma and Parkinson disease: Common pathways? Ann Neurol. (2016) 80:811–20. doi: 10.1002/ana.24802
33. Rodriguez-Leyva I, Chi-Ahumada E, Mejía M, Castanedo-Cazares JP, Eng W, Saikaly SK, et al. The presence of alpha-synuclein in skin from melanoma and patients with parkinson's disease. Mov Disord Clin Pract. (2017) 4:724–32. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.12494
34. Gajendran N, Rajasekaran S, and Witt SN. Knocking out alpha-synuclein in melanoma cells downregulates L1CAM and decreases motility. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:9243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36451-3
35. Turriani E, Lázaro DF, Ryazanov S, Leonov A, Giese A, Schön M, et al. Treatment with diphenyl-pyrazole compound anle138b/c reveals that α-synuclein protects melanoma cells from autophagic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2017) 114:E4971–e7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700200114
36. Shekoohi S, Rajasekaran S, Patel D, Yang S, Liu W, Huang S, et al. Knocking out alpha-synuclein in melanoma cells dysregulates cellular iron metabolism and suppresses tumor growth. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:5267. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84443-y
37. Dimasuay KG, Schaunaman N, Martin RJ, Pavelka N, Kolakowski C, Gottlieb RA, et al. Parkin, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, enhances airway mitochondrial DNA release and inflammation. Thorax. (2020) 75:717–24. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-214158
38. He Y, Wang W, Yang T, Thomas ER, Dai R, and Li X. The potential role of voltage-dependent anion channel in the treatment of parkinson's disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:4665530. doi: 10.1155/2022/4665530
39. Liang Y, Zhong G, Ren M, Sun T, Li Y, Ye M, et al. The role of ubiquitin-proteasome system and mitophagy in the pathogenesis of parkinson's disease. Neuromolecular Med. (2023) 25:471–88. doi: 10.1007/s12017-023-08755-0
40. Yi W, MacDougall EJ, Tang MY, Krahn AI, Gan-Or Z, Trempe JF, et al. The landscape of Parkin variants reveals pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic targets in Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet. (2019) 28:2811–25. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz080
41. Levin L, Srour S, Gartner J, Kapitansky O, Qutob N, Dror S, et al. Parkin somatic mutations link melanoma and parkinson's disease. J Genet Genomics. (2016) 43:369–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2016.05.005
42. Hu HH, Kannengiesser C, Lesage S, André J, Mourah S, Michel L, et al. PARKIN inactivation links parkinson's disease to melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2016) 108. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv340
43. Zhu X, Ma X, Tu Y, Huang M, Liu H, Wang F, et al. Parkin regulates translesion DNA synthesis in response to UV radiation. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:36423–37. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16855
44. Montagnani V, Maresca L, Apollo A, Pepe S, Carr RM, Fernandez-Zapico ME, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase PARK2, an inhibitor of melanoma cell growth, is repressed by the oncogenic ERK1/2-ELK1 transcriptional axis. J Biol Chem. (2020) 295:16058–71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014615
45. Behl T, Kumar S, Althafar ZM, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, et al. Exploring the role of ubiquitin-proteasome system in parkinson's disease. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:4257–73. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02851-1
46. Jara JH, Frank DD, and Özdinler PH. Could dysregulation of UPS be a common underlying mechanism for cancer and neurodegeneration? Lessons from UCHL1. Cell Biochem Biophys. (2013) 67:45–53. doi: 10.1007/s12013-013-9631-7
47. Osaka H, Wang YL, Takada K, Takizawa S, Setsuie R, Li H, et al. Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 binds to and stabilizes monoubiquitin in neuron. Hum Mol Genet. (2003) 12:1945–58. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg211
48. BarraChina M, Castaño E, Dalfó E, Maes T, Buesa C, and Ferrer I. Reduced ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-1 expression levels in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurobiol Dis. (2006) 22:265–73. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.11.005
49. Seo EY, Jin SP, Sohn KC, Park CH, Lee DH, and Chung JH. UCHL1 regulates melanogenesis through controlling MITF stability in human melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol. (2017) 137:1757–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.03.024
50. Pickrell AM and Youle RJ. The roles of PINK1, parkin, and mitochondrial fidelity in Parkinson's disease. Neuron. (2015) 85:257–73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.007
51. Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, et al. Hereditary early-onset Parkinson's disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science. (2004) 304:1158–60. doi: 10.1126/science.1096284
52. Krohn L, Grenn FP, Makarious MB, Kim JJ, Bandres-Ciga S, Roosen DA, et al. Comprehensive assessment of PINK1 variants in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. (2020) 91:168.e1–.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.03.003
53. Basit F, van Oppen LM, Schöckel L, Bossenbroek HM, van Emst-de Vries SE, Hermeling JC, et al. Mitochondrial complex I inhibition triggers a mitophagy-dependent ROS increase leading to necroptosis and ferroptosis in melanoma cells. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:e2716. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.133
54. O'Flanagan CH, Morais VA, and O'Neill C. PINK1, cancer and neurodegeneration. Oncoscience. (2016) 3:1–2. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.v3i1
55. Cantley LC and Neel BG. New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1999) 96:4240–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4240
56. Lee YJ, Kim WI, Park TH, Bae JH, Nam HS, Cho SW, et al. Upregulation of DJ-1 expression in melanoma regulates PTEN/AKT pathway for cell survival and migration. Arch Dermatol Res. (2021) 313:583–91. doi: 10.1007/s00403-020-02139-1
57. Dolgacheva LP, Berezhnov AV, Fedotova EI, Zinchenko VP, and Abramov AY. Role of DJ-1 in the mechanism of pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. J Bioenerg Biomembr. (2019) 51:175–88. doi: 10.1007/s10863-019-09798-4
58. Liu LL, Han Y, Zhang ZJ, Wang YQ, Hu YW, Kaznacheyeva E, et al. Loss of DJ-1 function contributes to Parkinson's disease pathogenesis in mice via RACK1-mediated PKC activation and MAO-B upregulation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2023) 44:1948–61. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01104-8
59. Lago-Baameiro N, Santiago-Varela M, Camino T, Silva-Rodriguez P, Bande M, Blanco-Teijeiro MJ, et al. PARK7/DJ-1 inhibition decreases invasion and proliferation of uveal melanoma cells. Tumori. (2023) 109:47–53. doi: 10.1177/03008916211061766
60. Quesnel A, Martin LD, Tarzi C, Lenis VP, Coles N, Islam M, et al. Uncovering potential diagnostic and pathophysiological roles of α-synuclein and DJ-1 in melanoma. Cancer Med. (2024) 13:e6900. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v13.1
61. Tolosa E, Vila M, Klein C, and Rascol O. LRRK2 in Parkinson disease: challenges of clinical trials. Nat Rev Neurol. (2020) 16:97–107. doi: 10.1038/s41582-019-0301-2
62. Araki M, Ito G, and Tomita T. Physiological and pathological functions of LRRK2: implications from substrate proteins. Neuronal Signal. (2018) 2:Ns20180005. doi: 10.1042/NS20180005
63. Di Maio R, Hoffman EK, Rocha EM, Keeney MT, Sanders LH, De Miranda BR, et al. LRRK2 activation in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Sci Transl Med. (2018) 10:5429. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aar5429
64. Taymans JM, Fell M, Greenamyre T, Hirst WD, Mamais A, Padmanabhan S, et al. Perspective on the current state of the LRRK2 field. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. (2023) 9:104. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00544-7
65. Koros C, Simitsi AM, Bougea A, Papagiannakis N, Antonelou R, Pachi I, et al. Double trouble: association of Malignant melanoma with sporadic and genetic forms of parkinson's disease and asymptomatic carriers of related genes: A brief report. Medicina (Kaunas). (2023) 59:1360. doi: 10.3390/medicina59081360
66. Gao X, Simon KC, Han J, Schwarzschild MA, and Ascherio A. Family history of melanoma and Parkinson disease risk. Neurology. (2009) 73:1286–91. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bd13a1
67. Hyderi Z, Farhana MS, Singh TP, and Ravi AV. Therapeutic targeting of autosomal parkinson's disease by modulation of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein. Brain Res. (2025) 1860:149674. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149674
68. Zurawa-Janicka D, Skorko-Glonek J, and Lipinska B. HtrA proteins as targets in therapy of cancer and other diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2010) 14:665–79. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2010.487867
69. Gialluisi A, Reccia MG, Modugno N, Nutile T, Lombardi A, Di Giovannantonio LG, et al. Identification of sixteen novel candidate genes for late onset Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurodegener. (2021) 16:35. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00455-2
70. Dagda RK and Chu CT. Mitochondrial quality control: insights on how Parkinson's disease related genes PINK1, parkin, and Omi/HtrA2 interact to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis. J Bioenerg Biomembr. (2009) 41:473–9. doi: 10.1007/s10863-009-9255-1
71. Abou-Sleiman PM, Muqit MM, and Wood NW. Expanding insights of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2006) 7:207–19. doi: 10.1038/nrn1868
72. Plun-Favreau H, Klupsch K, Moisoi N, Gandhi S, Kjaer S, Frith D, et al. The mitochondrial protease HtrA2 is regulated by Parkinson's disease-associated kinase PINK1. Nat Cell Biol. (2007) 9:1243–52. doi: 10.1038/ncb1644
73. Shiloach T, Berens C, Danke C, Waiskopf O, Perlman R, and Ben-Yehuda D. tLivin displays flexibility by promoting alternative cell death mechanisms. PloS One. (2014) 9:e101075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101075
74. Nachmias B, Ashhab Y, Bucholtz V, Drize O, Kadouri L, Lotem M, et al. Caspase-mediated cleavage converts Livin from an antiapoptotic to a proapoptotic factor: implications for drug-resistant melanoma. Cancer Res. (2003) 63:6340–9. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14559822
75. Yan H, Brouha B, Liu T, Raj D, Biddle D, Lee R, et al. Proteolytic cleavage of Livin (ML-IAP) in apoptotic melanoma cells potentially mediated by a non-canonical caspase. J Dermatol Sci. (2006) 43:189–200. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2006.05.007
76. Murakami M, Taketomi Y, Miki Y, Sato H, Hirabayashi T, and Yamamoto K. Recent progress in phospholipase A2 research: from cells to animals to humans. Prog Lipid Res. (2011) 50:152–92. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2010.12.001
77. Ramanadham S, Ali T, Ashley JW, Bone RN, Hancock WD, and Lei X. Calcium-independent phospholipases A2 and their roles in biological processes and diseases. J Lipid Res. (2015) 56:1643–68. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R058701
78. Miki Y, Yoshizawa T, Morohashi S, Seino Y, Kijima H, Shoji M, et al. Neuropathology of PARK14 is identical to idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. (2017) 32:799–800. doi: 10.1002/mds.26952
79. Gregory A, Westaway SK, Holm IE, Kotzbauer PT, Hogarth P, Sonek S, et al. Neurodegeneration associated with genetic defects in phospholipase A(2). Neurology. (2008) 71:1402–9. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000327094.67726.28
80. Mori A, Hatano T, Inoshita T, Shiba-Fukushima K, Koinuma T, Meng H, et al. Parkinson's disease-associated iPLA2-VIA/PLA2G6 regulates neuronal functions and α-synuclein stability through membrane remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2019) 116:20689–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902958116
81. Roos L, Sandling JK, Bell CG, Glass D, Mangino M, Spector TD, et al. Higher nevus count exhibits a distinct DNA methylation signature in healthy human skin: implications for melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. (2017) 137:910–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.11.029
82. Wang Y, Song H, Miao Q, Wang Y, Qi J, Xu X, et al. PLA2G6 silencing suppresses melanoma progression and affects ferroptosis revealed by quantitative proteomics. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:819235. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.819235
83. Deng H, Gao K, and Jankovic J. The VPS35 gene and Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. (2013) 28:569–75. doi: 10.1002/mds.25430
84. Deng H, Wu Y, and Jankovic J. The EIF4G1 gene and Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand. (2015) 132:73–8. doi: 10.1111/ane.12397
85. Blanckenberg J, Ntsapi C, Carr JA, and Bardien S. EIF4G1 R1205H and VPS35 D620N mutations are rare in Parkinson's disease from South Africa. Neurobiol Aging. (2014) 35:445.e1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.08.023
86. Lesage S, Condroyer C, Klebe S, Lohmann E, Durif F, Damier P, et al. EIF4G1 in familial Parkinson's disease: pathogenic mutations or rare benign variants? Neurobiol Aging. (2012) 33:2233.e1–.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.05.006
87. Nishioka K, Funayama M, Vilariño-Güell C, Ogaki K, Li Y, Sasaki R, et al. EIF4G1 gene mutations are not a common cause of Parkinson's disease in the Japanese population. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. (2014) 20:659–61. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.03.004
88. Jaiswal PK, Koul S, Palanisamy N, and Koul HK. Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4 Gamma 1 (EIF4G1): a target for cancer therapeutic intervention? Cancer Cell Int. (2019) 19:224. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0947-2
89. Cai J, Li L, Ye L, Jiang X, Shen L, Gao Z, et al. Exome sequencing reveals mutant genes with low penetrance involved in MEN2A-associated tumorigenesis. Endocr Relat Cancer. (2015) 22:23–33. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0225
90. Boussemart L, Malka-Mahieu H, Girault I, Allard D, Hemmingsson O, Tomasic G, et al. eIF4F is a nexus of resistance to anti-BRAF and anti-MEK cancer therapies. Nature. (2014) 513:105–9. doi: 10.1038/nature13572
91. Feng Y, Pinkerton AB, Hulea L, Zhang T, Davies MA, Grotegut S, et al. SBI-0640756 attenuates the growth of clinically unresponsive melanomas by disrupting the eIF4F translation initiation complex. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:5211–8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0885
92. Pagano G, Taylor KI, Anzures Cabrera J, Simuni T, Marek K, Postuma RB, et al. Prasinezumab slows motor progression in rapidly progressing early-stage Parkinson's disease. Nat Med. (2024) 30:1096–103. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02886-y
93. Tong Y, Zhang P, Yang X, Liu X, Zhang J, Grudniewska M, et al. Decreasing the intrinsically disordered protein α-synuclein levels by targeting its structured mRNA with a ribonuclease-targeting chimera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2024) 121:e2306682120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2306682120
94. Volc D, Poewe W, Kutzelnigg A, Lührs P, Thun-Hohenstein C, Schneeberger A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the α-synuclein active immunotherapeutic PD01A in patients with Parkinson's disease: a randomised, single-blinded, phase 1 trial. Lancet Neurol. (2020) 19:591–600. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30136-8
95. Dhiman S, Singla S, Kumar I, Palia P, Kumar P, Goyal SJCCM, et al. Protection of Viola odorata L. against Neurodegenerative Diseases: Potential of the Extract and Major Phytoconstituents. Clin Complementary Med Pharmacol. (2023) 3:100105. doi: 10.1016/j.ccmp.2023.100105
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, PARK gene family, α-synuclein, pathogenesis, melanoma
Citation: Wu J, Xiong H, Chen J, Yang D, Li Y, Wang J, Chen J, Zhang R, Zhang R, Li X, Li F, Zhang R and Yang Z (2025) Link between Parkinson’s disease and melanoma: insights into the influence of the PARK gene family. Front. Oncol. 15:1506744. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1506744
Received: 06 October 2024; Accepted: 18 July 2025;
Published: 11 August 2025.
Edited by:
Yiqun Shellman, University of Colorado Hospital, United StatesReviewed by:
Nour S. Erekat, Jordan University of Science and Technology, JordanMartin Emiliano Cesarini, INEBA Institute of Neurosciences Buenos Aires, Argentina
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Xiong, Chen, Yang, Li, Wang, Chen, Zhang, Zhang, Li, Li, Zhang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhi Yang, dmlweXpAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jinghua Wu
Jinghua Wu Haojun Xiong1,2†
Haojun Xiong1,2† Zhi Yang
Zhi Yang