- Department of Oncology, Tengzhou Central People’s Hospital, Tengzhou, Shandong, China
Purpose: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of CT-guided lung biopsy combined with microwave ablation (MWA) for solitary suspected malignant pulmonary nodules in post-radical surgery breast cancer patients.
Materials and methods: This retrospective study included 37 post-radical surgery breast cancer patients with solitary suspected malignant pulmonary nodules, treated with CT-guided lung biopsy and MWA between January 2014 and December 2018. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Clinical outcomes and complications were analyzed.
Results: Pathological results identified primary lung cancer in 5 patients (13.5%, 5/37) and metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma (breast origin) in 30 patients (81.1%, 30/37). Major complications included pneumothorax (n=8, 21.6%), chest pain (n=6, 16.2%), and hemoptysis (n=4, 10.8%). For metastatic cases, 2-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 86.2%, 58.3%, and 35.3%, respectively. The median progression-free survival after MWA was 35 months (range: 4–72; 95% CI: 24.53–46.48), and median overall survival was 44 months (95% CI: 32.55–55.45).
Conclusion: CT-guided lung biopsy combined with MWA is a safe and effective approach for managing solitary suspected malignant pulmonary nodules in post-radical surgery breast cancer patients.
Introduction
Breast cancer is one of the most common prevalent tumors among women, with a mortality-to-incidence ratio of 15% (1). Lung metastases are frequently witnessed in breast cancer patients (2). As a result, when intrapulmonary nodules are detected in breast cancer patients, they are frequently misdiagnosed as lung metastases. Nevertheless, studies have indicated that the incidence of primary lung cancer in breast cancer patients is approximately 1% (3–5), while the incidence of concurrent double primary cancer (with a time difference between diagnoses of no more than 6 months) is about 0.6% in breast cancer patients (4). Identifying a solitary pulmonary nodule in patients with breast cancer poses a diagnostic challenge. For such nodules, surgical resection is a feasible option. However, many patients are either unable or unwilling to undergo surgery due to factors such as advanced age, poor cardiopulmonary function, or other reasons. Recent studies (6–10) have demonstrated that lung biopsy combined with microwave ablation (MWA) for the solitary pulmonary nodule can yield outcomes similar to surgical resection.
However, there is scarce research exploring the application of this technology in breast cancer patients who have undergone radical surgery and subsequently developed a solitary pulmonary nodule. To fill this gap, we conducted a retrospective study to assess the efficacy of a concurrent diagnostic and therapeutic approach. This approach entailed conducting a CT-guided biopsy, immediately followed by MWA of the solitary pulmonary nodule suspected of malignancy in patients with a history of radical breast cancer surgery.
Materials and methods
Subjects
This retrospective study included 37 patients who underwent CT-guided lung biopsy combined with microwave ablation for suspected malignant solitary pulmonary nodules after radical mastectomy from January 2014 to December 2018. All patients had histopathologically confirmed invasive ductal carcinoma and underwent radical mastectomy. Chest computed tomography (CT) imaging demonstrated the existence of a newly identified solitary pulmonary nodule. The baseline imaging comprised chest and abdominal computed tomography (CT), enhanced cranial MRI, whole-body bone scan ECT, and, if accessible, positron-emission tomography (PET) CT. All patients were regarded as ineligible for reoperation or declined to undergo surgical resection.
Exclusion criteria encompassed the following: (1) Uncontrolled infectious inflammation around the lesion; (2) Skin infection or ulceration at the puncture site; (3) Severe pulmonary fibrosis, especially drug-induced fibrosis (11, 12); (4) Patients with a marked bleeding propensity and coagulation disorders; (5) Cachexia; (6) Severe cardiopulmonary insufficiency.
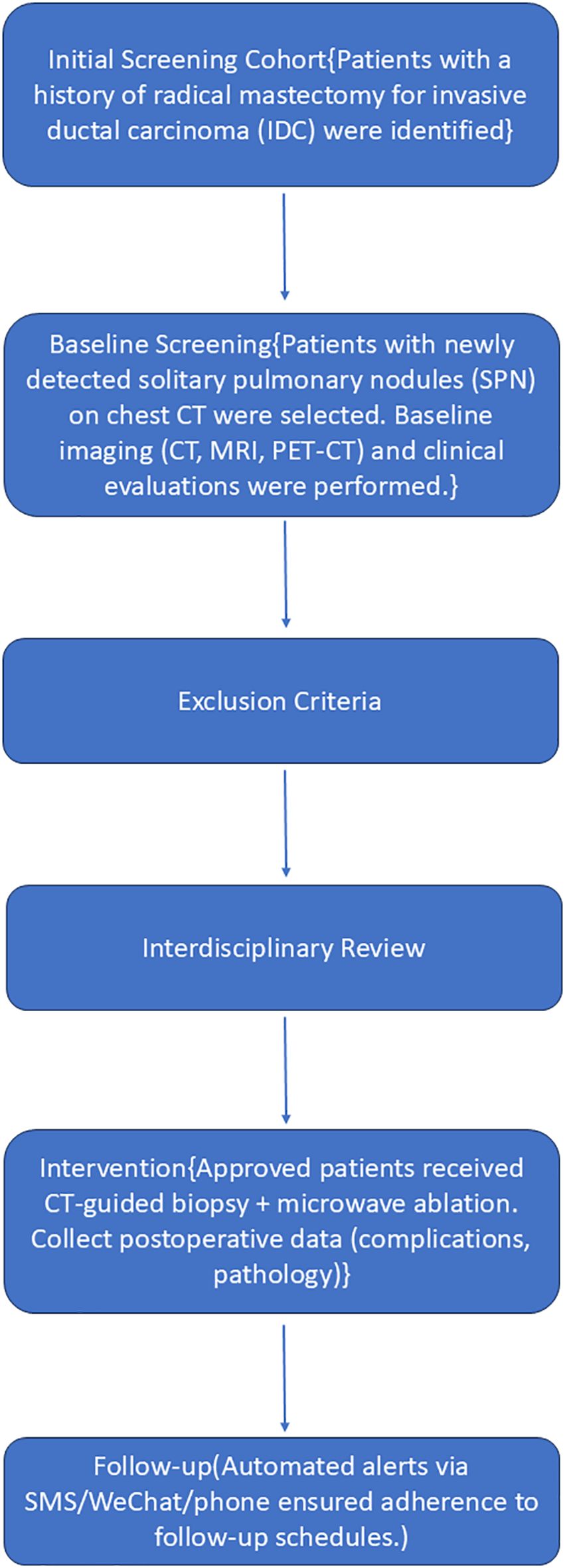
All cases were reviewed by an interdisciplinary oncology committee consisting of thoracic surgeons, respiratory physicians, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, diagnostic and interventional radiologists, pathologists, and anesthesiologists. The flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
Instrumentation
A Siemens Light Speed 64V spiral CT scanner (Germany) guided biopsy and MWA. Under CT guidance, transthoracic core biopsies used an 18G Argon coaxial system (MCXS1820LX semi-automatic). MWA employed an ECO-100A1 system (SFDA 20172011470; Nanjing ECO) with 2,450 ± 20 MHz frequency and 0-150W adjustable power. The 16G-20G microwave antenna (150-200mm length) featured a 15-mm active tip and water-cooled system to reduce surface temperature.
Procedure of the operation
Prior to treatment, patients underwent thorough clinical evaluation, including laboratory tests, imaging, and pulmonary function assessments. Blood work included coagulation studies. Anticoagulants were held 1 week pre-procedure to minimize bleeding risk.
Patients were positioned supine or prone based on nodule location, secured with a vacuum-negative pressure pad, and the puncture site was marked on the skin.
An 18-gauge biopsy core needle was inserted into the center of the tumor through a coaxial cannula before initiating MWA. A biopsy was performed first to obtain two or three specimens from a single core needle. The tissue samples were preserved in 10% formalin and later evaluated pathologically after H&E staining. All biopsy specimens underwent immunohistochemical testing (including ER, PR, and HER-2). A CT scan was done to monitor for biopsy-related complications.
Under CT guidance, the MWA probe was accurately positioned in the pulmonary tumor. Limited pneumothorax without progression during MWA was acceptable. However, chest tube insertion was required for progressive pneumothorax interfering with probe placement or causing clinical symptoms. Ablation power was typically 30-50W for 3-10 minutes. CT scans monitored probe targeting, adjusted depth/angle, and ensured the intended ablation zone. Continuous monitoring of vital signs (BP, HR, ECG, SpO2) was performed throughout the procedure.
An immediate post-MWA CT scan frequently displayed ground-glass opacity (GGO) 0.5 to 1.0 cm in width at the periphery of the pulmonary nodule, indicating complete ablation (13, 14). The CT scan was also employed to assess for complications such as pneumothorax, hemothorax, or pleural effusion. If a progressive pneumothorax was detected, chest tube insertion would be indicated to manage the situation.
This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tengzhou Central People’s Hospital (Ethics Review No. 2018-Ethics Review-08). All participants provided written informed consent after detailed explanation of the procedures.
Assessment of therapeutic efficacy and follow-up
Patients underwent enhanced CT scans at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after MWA in the first year, and then every 6 months thereafter. Enhancement at the lesion site was considered indicative of incomplete treatment. Regions that remained unenhanced and were larger than the treated metastases were regarded as representing complete ablative necrosis and thus considered fully effective for the treatment.
The primary response rate was defined as the percentage of target tumors successfully eliminated during the initial ablation session. The assessment of the local efficacy of MWA was conducted by a single oncologist and two radiologists.
Survival outcomes included progression-free survival (the time from MWA until the recurrence of other metastases or death, PFS) and overall survival (the time from MWA until death, OS).
Statistical analysis
IBM SPSS 26.0 was used for statistical analysis. Data are presented as the total count (percentage) and mean values. The Chi-square test was utilized for categorical variables. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to determine the survival rate and local progression-free survival rate. In all statistical assessments, results were regarded as significant if p < 0.05.
Results
General information
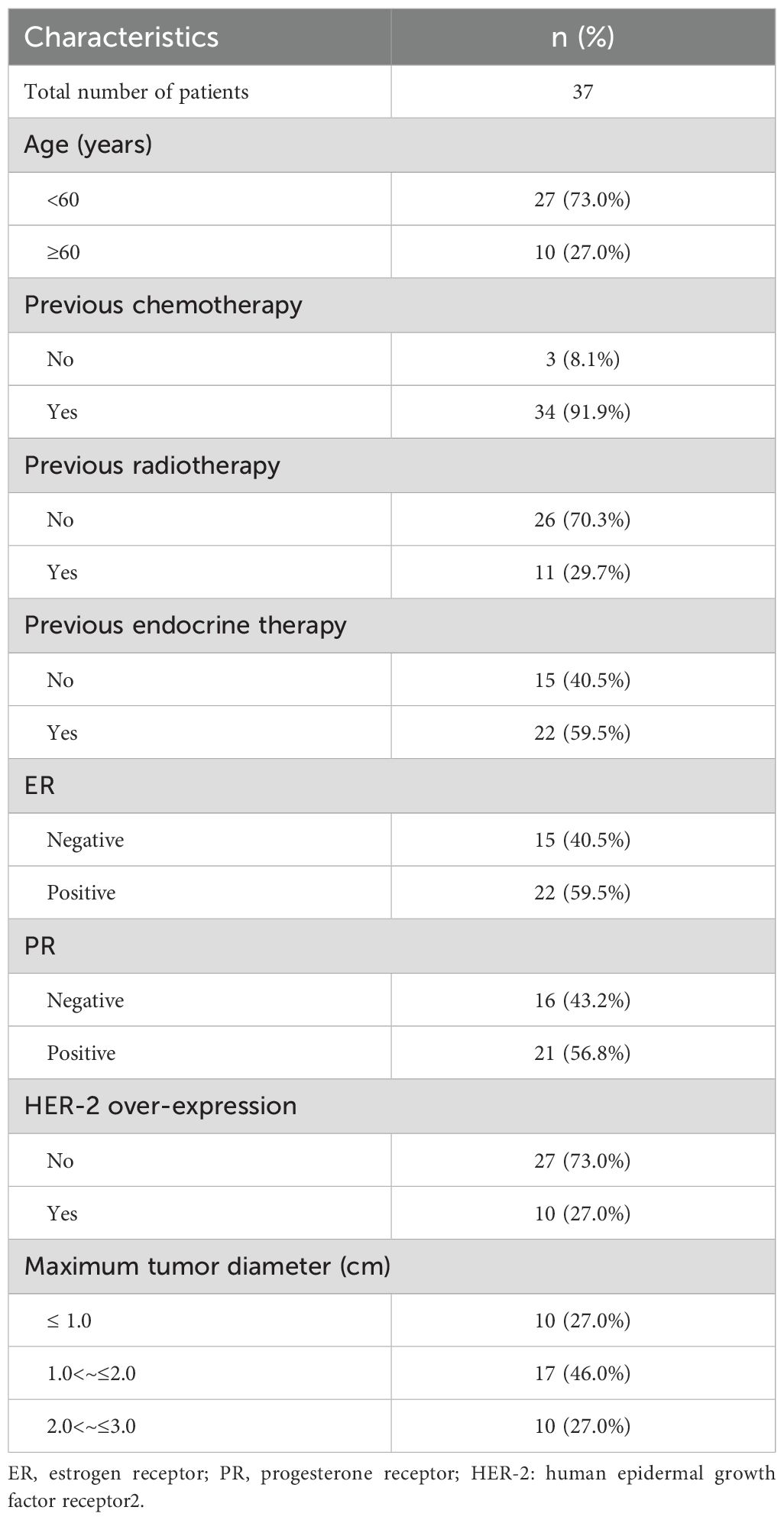
From January 2014 to December 2018, 37 female patients with a solitary suspected malignant pulmonary nodule after radical breast cancer surgery were treated with CT-guided lung biopsy combined with MWA in our hospital. All patients were female and had undergone modified radical mastectomy with pathologically confirmed invasive ductal carcinoma. The median age was 53 years (range: 27 to 73 years). HER-2 was detected by immunohistochemistry in all patients, and 10 were strongly positive (verified by FISH). 34 patients received adjuvant chemotherapy, 11 received adjuvant radiotherapy, 10 received adjuvant targeted therapy, and 22 received adjuvant endocrine therapy. The pulmonary nodules ranged in size from 6 to 28 mm (15.65 ± 6.13) (Table 1).
All patients underwent technically successful lung biopsy combined with MWA. One month after the operation, a CT scan showed that 37 lesions were completely covered by the tumor coagulation area after ablation, and the primary effective rate was 100% (37/37).
Pathological results of puncture biopsy
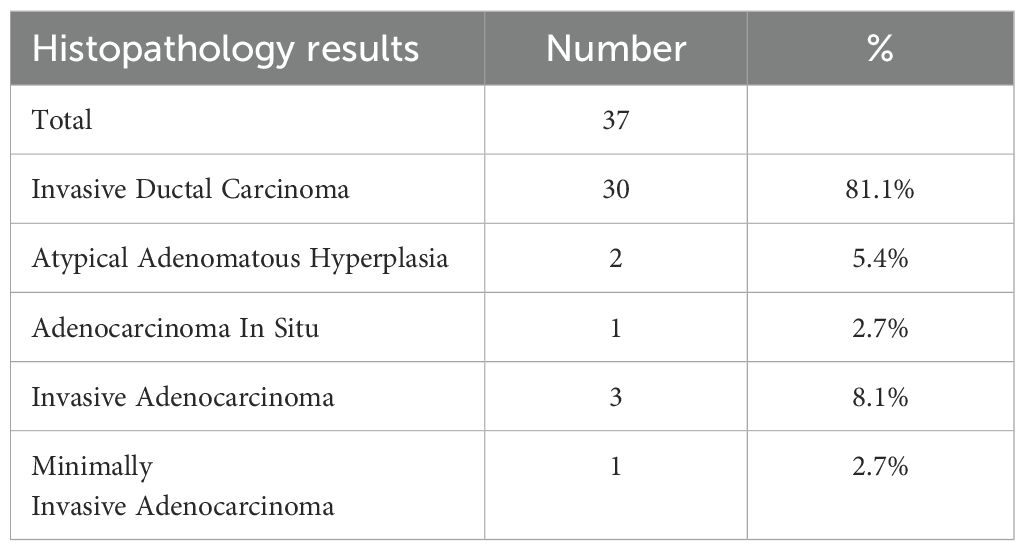
Among the 37 patients, 35 cases (35/37, 94.6%) were pathologically diagnosed as malignant tumors, among which 5 cases (5/37, 13.5%) were diagnosed as primary lung cancer (Figure 2). The biopsy pathology of 30 cases (30/37, 81.1%) was invasive ductal carcinoma (Table 2, Figure 3). The remaining 2 cases (2/37, 5.4%) were diagnosed as atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) (Table 2). A separate subgroup analysis was conducted for the clinical treatment of the 30 cases with lung metastases from breast cancer.
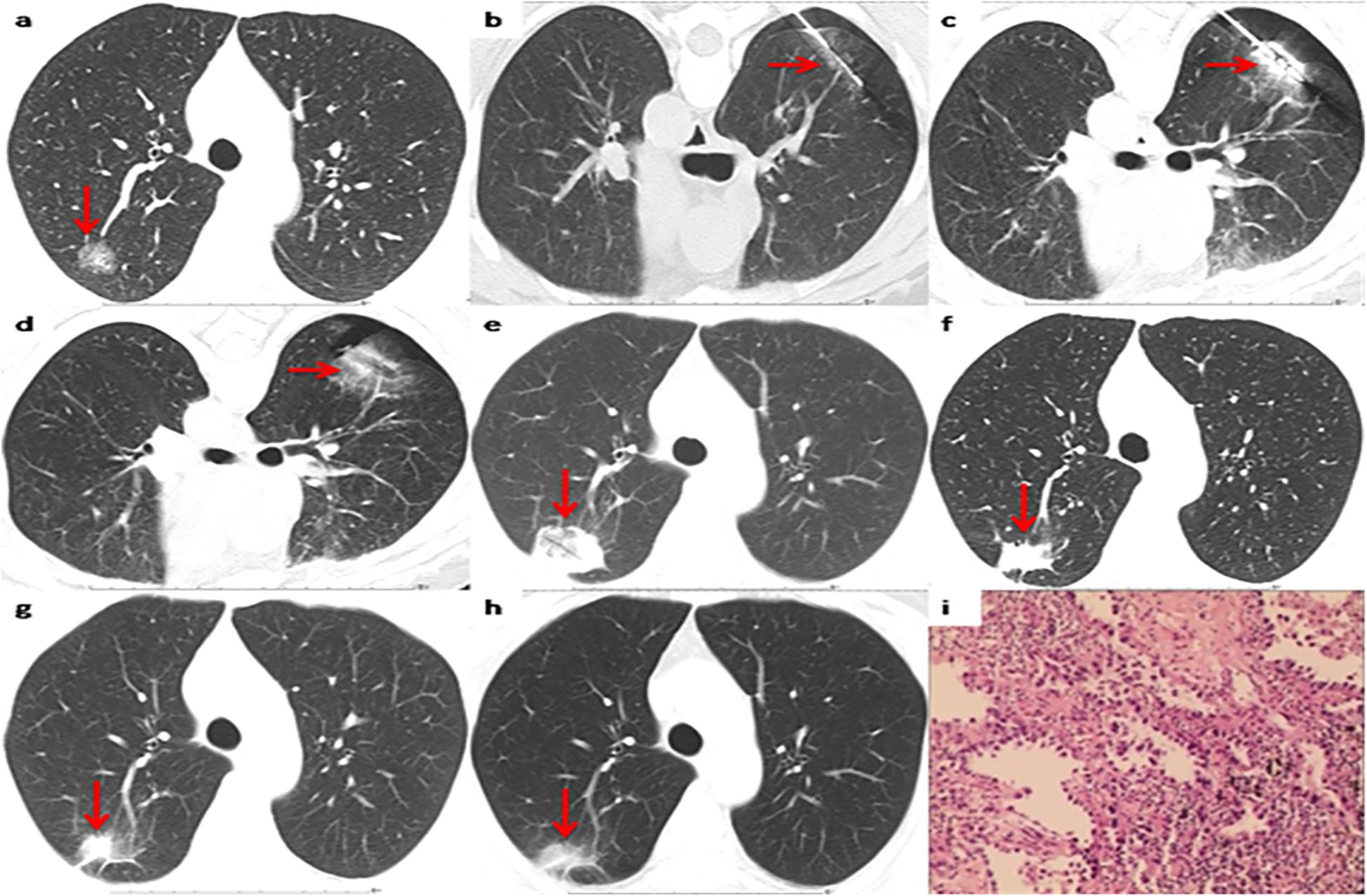
Figure 2. Representative CT scans of a patient with primary lung invasive adenocarcinoma after breast cancer surgery. (a) Preoperative image. (b) The biopsy needle has been inserted into the nodule center to complete the biopsy sectioning. (c) The MWA antenna has been inserted into the nodule center. (d) Postoperative image immediately after MWA. (e) 1 month after MWA. (f) 12months after MWA. (g) 36 months after MWA. (h) 60 months after MWA. (i) Pathological results of primary lung invasive adenocarcinoma biopsy.
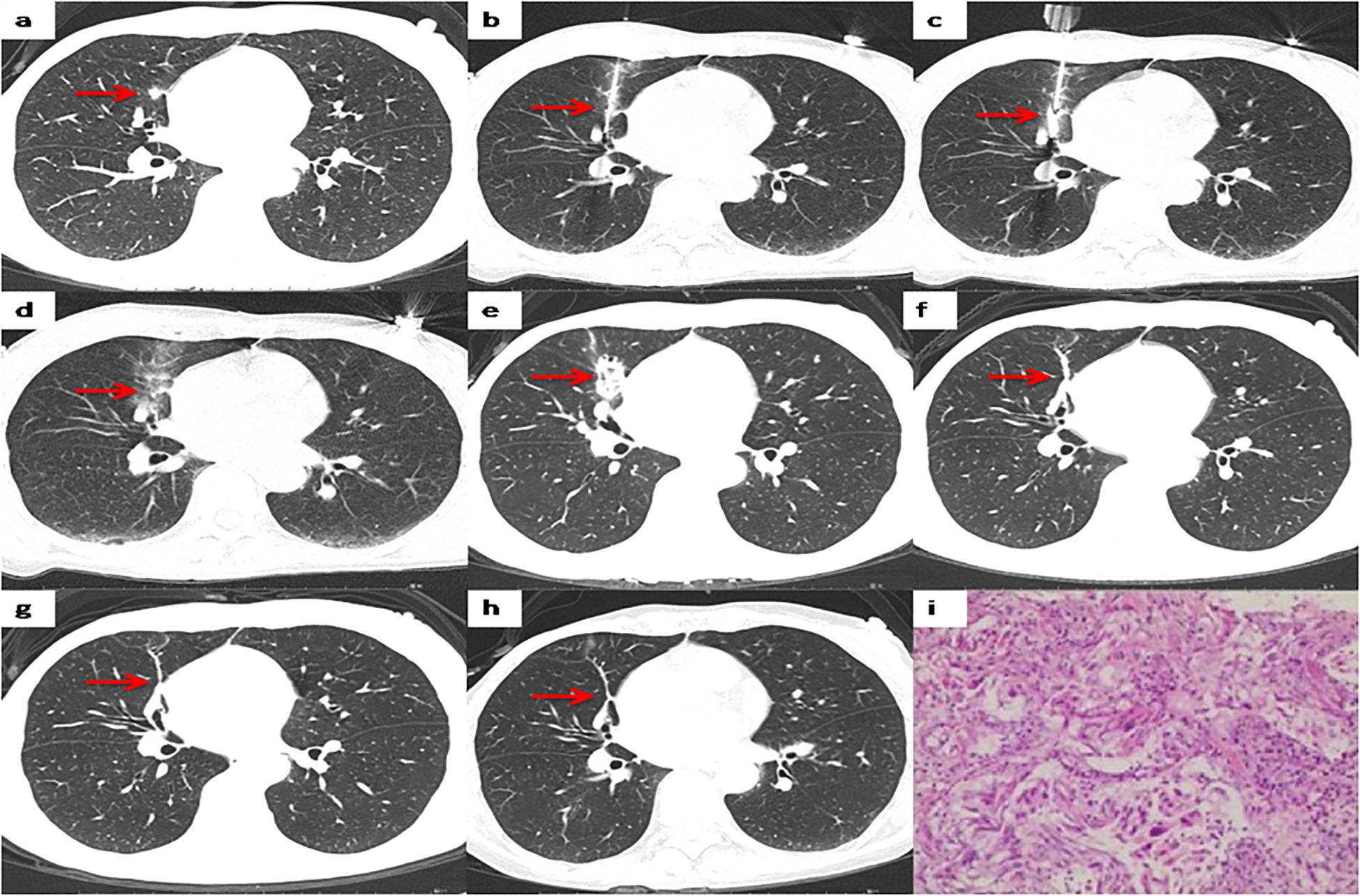
Figure 3. Representative CT scans of a patient with right lung metastases after breast cancer surgery. (a) Preoperative image. (b) The biopsy needle has been inserted into the nodule center to complete the biopsy sectioning. (c) The MWA antenna has been inserted into the nodule center. (d) Postoperative image immediately after MWA. (e) 1 month after MWA. (f) 12months after MWA. (g) 36 months after MWA. (h) 60 months after MWA. (i) Pathological results of lung metastases biopsy.
Postoperative complications
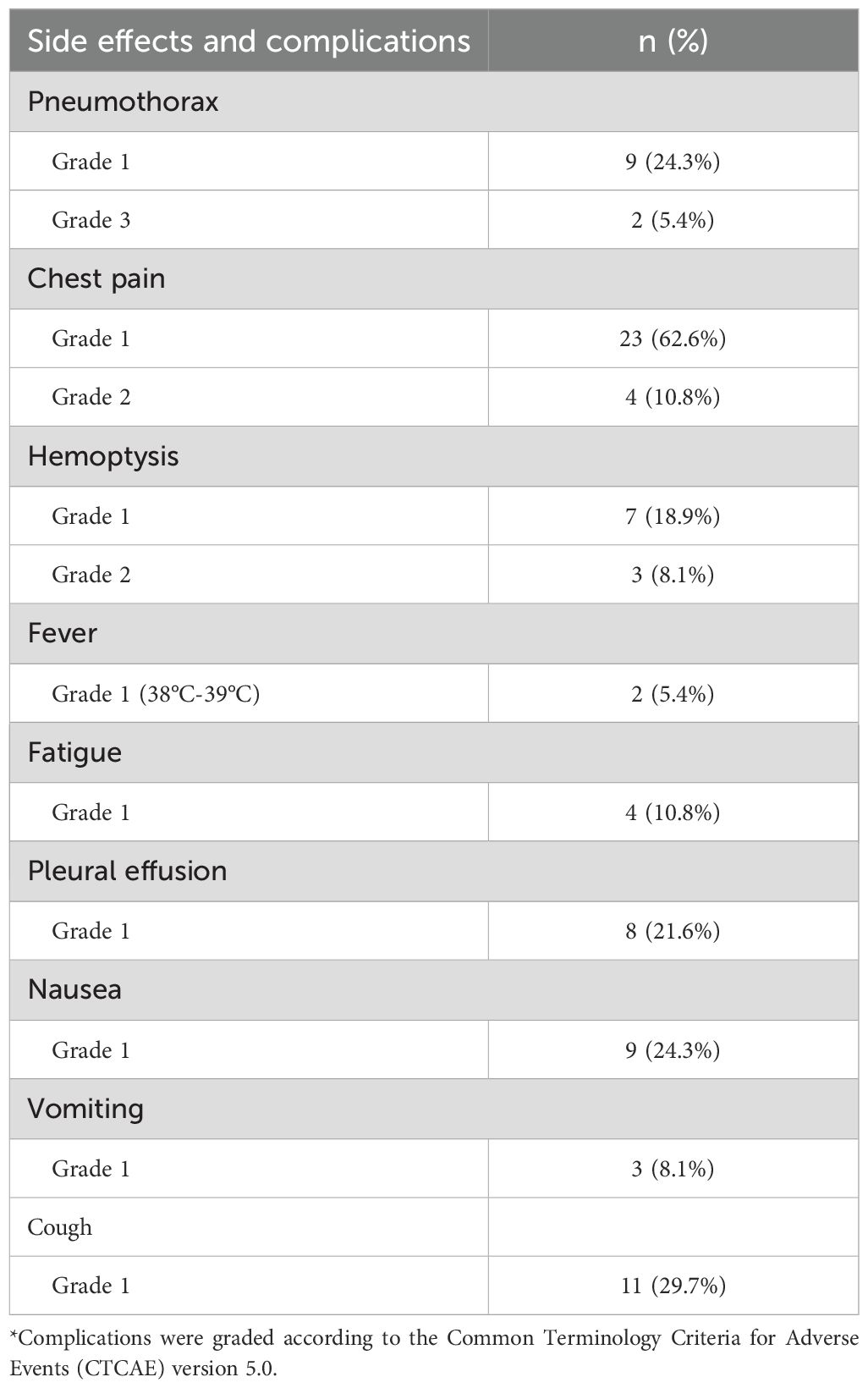
The major complications were pneumothorax, chest pain, and hemoptysis. Pneumothorax occurred in 11 of 37 cases (29.7%). Severe (lung compression >50%) and moderate (lung compression 20%-50%) pneumothorax occurred in two cases, and these patients underwent catheter drainage. The other nine patients’ pneumothorax was gradually absorbed without special treatment. The incidence of chest pain was 73.0% (27/37), and that of hemoptysis was 27.0% (10/37). Among the 10 hemoptysis cases, three were moderate (hemoptysis volume 10-100 mL), seven were mild (hemoptysis volume <10 mL), and there was no severe hemoptysis (hemoptysis volume >100 mL). No other complications such as needle implantation metastases, pulmonary embolism, or bronchopleural fistula were observed (Table 3).
Postoperative PFS of lung metastases subgroup
During follow-up, local progression at the ablation site (Local Tumor Progression, LTP) occurred in 16.7% (5/30) of cases during a median follow-up of 44 months. These five lesions were from five different patients, two of whom underwent a second ablation treatment and the other three who opted for medical therapy. The 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year cumulative LTP rates were 3.3%, 10.0%, and 16.7%, respectively.
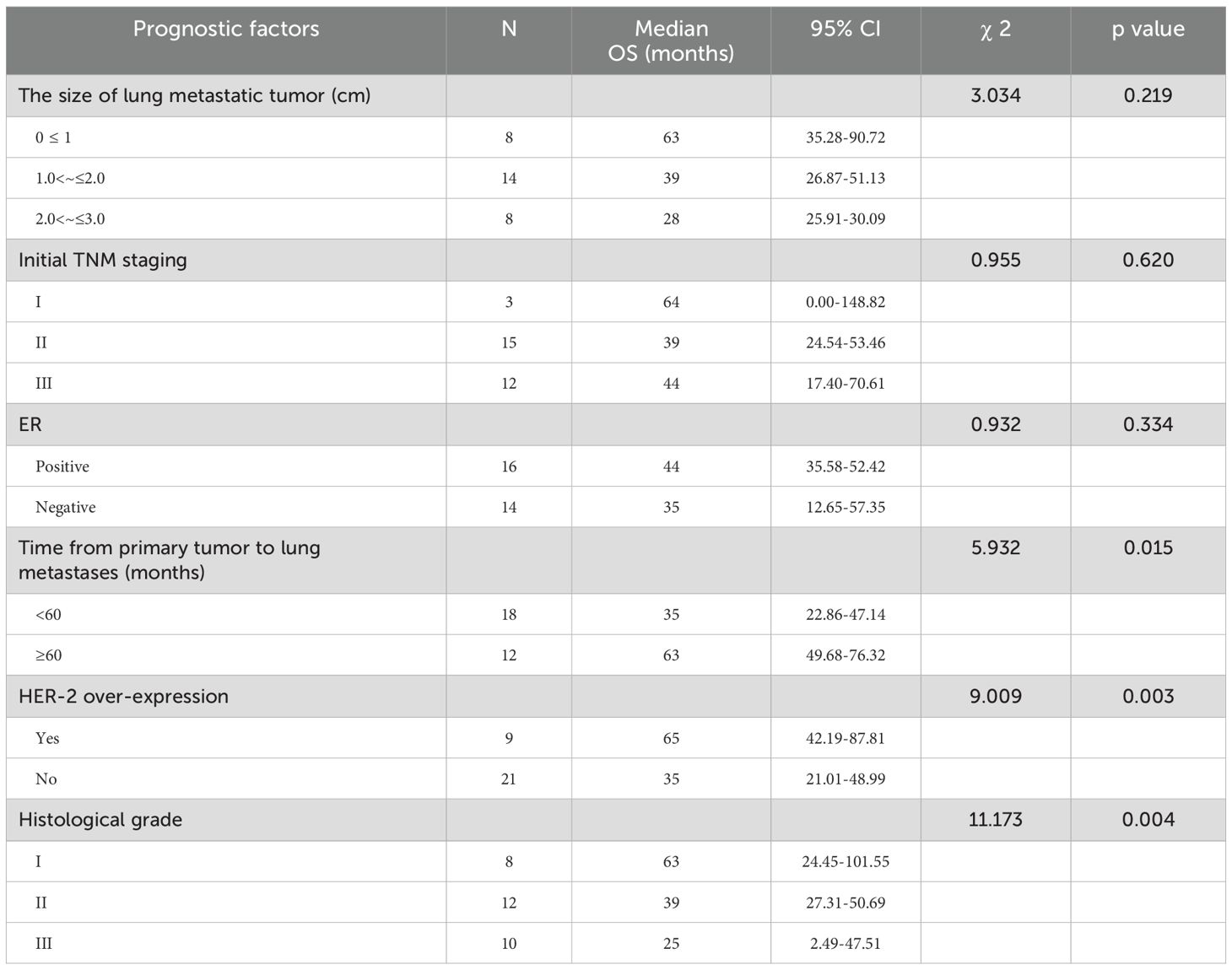
The median time from MWA of lung metastases to disease progression was 35 months (ranged 4-72 months, 95% confidence interval 24.53–46.48). Univariate analysis indicated that the PFS after MWA was related to time from primary tumor to lung metastases, HER-2 over-expression, and histological grade (P<0.05) (Table 4). Cox regression analysis demonstrated that time from the primary tumor to lung metastases and histological grade had a significant effect on PFS (P<0.05).
Postoperative OS of lung metastases subgroup
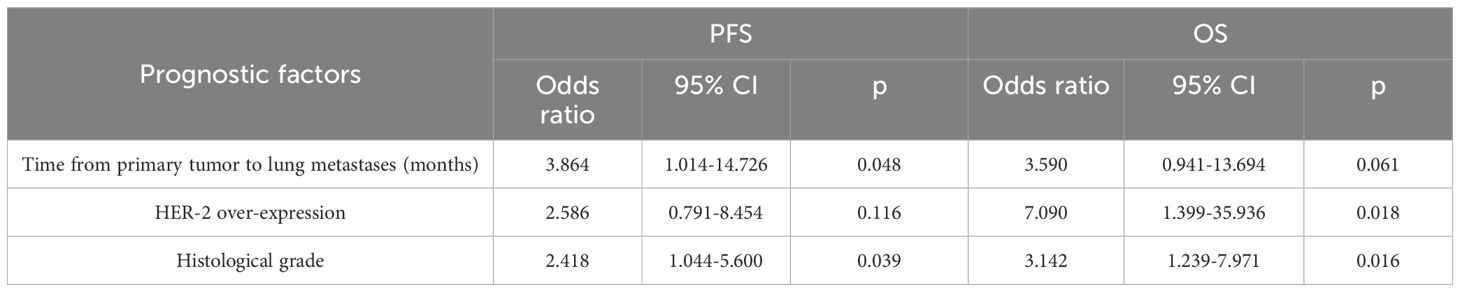
The 2-year, 3-year and 5-year survival rates were 86.2%, 58.3% and 35.3% respectively. The median OS time in the lung metastases subgroup was 44 months (95% confidence interval 32.55–55.45). Univariate analysis revealed that OS was related to the time from primary tumor to lung metastases, HER-2 over-expression and histological grade (P<0.05) (Table 5). Cox regression analysis demonstrated that HER-2 over-expression and histological grade had a significant effect on OS (P<0.05) (Table 6).
Discussion
In the context of a history of breast cancer, a solitary pulmonary nodule could potentially be lung metastases, primary lung cancer, or benign lung lesions (15). According to a review (16), the incidence of metastatic lesions ranged from 34% to 75%, that of primary lung cancer varied from 12% to 48%, and for benign lesions, it was from 14% to 18%. This study, focusing on CT-guided lung biopsy combined with MWA for suspected malignant nodules, found primary lung cancer in 13.5% (5/37) and breast cancer metastases in 81.1% (30/37), yielding a 94.6% malignancy rate (35/37)—higher than historical data. This phenomenon may be related to the following reasons: (1) The breast cancer TNM stage of the patient group included in this study at the initial treatment was relatively late; (2) tissue sampling via biopsy improving diagnostic accuracy; (3) Small sample size with selection bias; (4) The included patients had a longer follow-up time and regular periodic examinations, enabling earlier detection of malignant lesions and increasing the detection rate of malignant tumors.
In 2021, WHO histological classification of lung tumors defined atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) as glandular prodromal lesions (17). Asymptomatic slow-growing glandular prodromal lesions can be managed conservatively with careful observations and regular follow-up. Even after surgical treatment, the 5-year disease-free survival rate of patients after complete surgical resection of AIS is 100% or close to 100% (18). In this study, 3 cases of glandular prodromal lesions were not only pathologically diagnosed but also inactivated by thermal ablation after synchronous diagnosis and treatment. While conservative observation is typical for such lesions, the protocol’s synchronous biopsy-ablation approach prioritized timely intervention, aligning with the patients’ high-risk profile and the procedure’s demonstrated safety.
For patients with advanced lung metastases of breast cancer, systemic treatment such as chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and anti-HER2 are main methods of therapy. There is currently no consensus on whether solitary lung metastases need surgery. Friedel et al. (19) reported 467 patients with lung metastases from breast cancer, of which 84% patients underwent complete resection, and the 5 -, 10 -, and 15-year survival rates were 38%, 22%, and 20%, respectively. According to the International Lung Metastases Registry (20), the median OS and 5-year OS rates in patients undergoing surgical resection of lung metastases from breast cancer were 37 months and 38% in the R0 group. As a minimally invasive technique, local thermal ablation has been applied to the treatment of early lung cancer, and the number of lung cancer patients treated each year is rapidly increasing (21–24). It has been proved that percutaneous thermal ablation can also effectively treat lung metastases (25–28). In this study, the 5-year survival rate of patients with lung metastases who underwent needle biopsy combined with MWA was 35.3%, which was similar to that reported in previous studies. These findings may be explained by three key factors. First, all breast cancer patients with lung metastases received personalized multimodal therapy post-MWA, integrating chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, targeted agents, and immunotherapy as indicated. Second, MWA effectively debulked local tumors, reducing the risk of systemic spread. Third, comprehensive pre-treatment staging excluded extrapulmonary disease in all enrolled patients.
In this study, the median time from MWA of lung metastases to disease progression was 35 months (range 4–72 months, 95% CI 24.53–46.48). Univariate analysis revealed that post-MWA PFS correlated significantly with time from primary tumor to lung metastases, HER-2 overexpression, and histological grade (P<0.05, Table 4). Cox regression showed time from primary to lung metastases and histological grade significantly affected PFS (P<0.05, Table 6), confirming them as independent prognostic factors for local control in breast cancer patients with lung metastases. The median overall survival (OS) time in the lung metastases subgroup was 44 months (95% confidence interval 32.55–55.45). Univariate analysis showed that OS was related to the time from primary tumor to lung metastases, HER-2 over-expression, and histological grade (P<0.05, Table 5). Cox regression showed HER-2 overexpression and histological grade significantly impacted OS (P<0.05, Table 6), confirming them as independent prognostic factors for breast cancer patients with lung metastases. This study identified time from primary to lung metastases, histological grade, and HER-2 status as key prognostic factors in breast cancer lung metastases. These findings warrant validation in larger studies.
Needle biopsy and MWA have similar procedures and complications (pneumothorax, bleeding, etc.) (29–31). Complications are closely related to the physiological conditions of lung tissue and the times of pleural puncture (32). Chi et al. (33) reported that the incidence of pneumothorax was 25%in coaxial biopsy combined with MWA for ground-glass nodes. In this study, the incidence of pneumothorax was 29.7%, which was higher than previously reported in the literature. Wang et al. (34) reported that the incidence of hemoptysis following pulmonary nodule ablation was 22%. In this study, the incidence of hemoptysis was 27%, which was higher than previously reported in the literature. These differences may be because most patients in this study had pulmonary nodules with a maximum diameter less than 2cm (73.0%). Due to small nodule size, multiple adjustments of the biopsy needle are needed for accuracy, and all patients require 2-3 biopsies. These multiple operations increase the risk of damage to lung tissues and blood vessels, raising the incidence of hemoptysis.
This study has inherent limitations. As a retrospective analysis, it relies on pre-existing records, susceptible to incomplete data, inaccuracies, and selection bias. The small sample size compromises statistical power, limiting generalizability. Notably, no comparative analysis was performed with alternative modalities (surgical resection, SBRT, RFA). The lack of head-to-head comparisons hinders definition of MWA’s clinical role. Prospective, multicenter randomized controlled trials with larger cohorts are needed to rigorously assess MWA’s efficacy and safety profile.
In conclusion, this study shows that concurrent lung biopsy with MWA demonstrates significant clinical value for suspected malignant pulmonary nodules, enabling simultaneous diagnosis and therapeutic intervention. However, patient selection and optimal treatment timing remain key challenges in clinical implementation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The Ethics Committee of Tengzhou Central People’s Hospital granted approval for this retrospective study (Ethics Review Number 2018-Ethics Review-08). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
CX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. PL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis. SY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Visualization. QM: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. QY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MH: Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YB: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. KZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the local institutional review board for approving this study. We also appreciate the efforts of the interdisciplinary oncology committee, including thoracic surgeons, respiratory physicians, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, diagnostic and interventional radiologists, pathologists, and anesthesiologists, for their comprehensive review of all cases.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. (2020) 70:7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590
2. Winer EP, Morrow M, Osbourne CK, and Harris JR. Malignant tumors of the breast. In: De Vita VT Jr., Hellman S, and Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer. Principles & practice of oncology, 6th. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia (2001). p. 1651–716.
3. Schonfeld SJ, Curtis RE, Anderson WF, and de González AB. The risk of a second primary lung cancer after a first invasive breast cancer according to estrogen receptor status. Cancer Causes Control. (2012) 23:1721–8. doi: 10.1007/s10552-012-0054-3
4. Shoji F, Yamashita N, Inoue Y, Kozuma Y, Toyokawa G, Hirai F, et al. Surgical resection and outcome of synchronous and metachronous primary lung cancer in breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res. (2017) 37:5871–6. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12032
5. Wang R, Yin Z, Liu L, Gao W, Li W, Shu Y, et al. Second primary lung cancer after breast cancer: A population-based study of 6,269 women. Front Oncol. (2018) 8:427–37. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00427
6. Gao F, Han X, Dou W, and Li Z. CT-guided microwave ablation and biopsy of highly suspected Malignant ground-glass nodule of lung with co-axle technique. Chin J Interv Imaging Ther. (2020) 17:464–7. doi: 10.13929/j.issn.1672-8475.2020.08.004
7. Chi J, Ding M, Wang Z, Hu H, Shi Y, Cui D, et al. Pathologic diagnosis and genetic analysis of sequential biopsy following coaxial low-power microwave thermal coagulation for pulmonary ground-glass opacity nodules. Cardiovasc InterventRadiol. (2021) 44:1204–13. doi: 10.1007/s00270-021-02782-9
8. Yao W, Lu M, Fan W, Huang J, Gu Y, Gao F, et al. Comparison between microwave ablation and lobectomy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: A propensity score analysis. Int J Hyperthermia. (2018) 34:1329–36. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1434901
9. Wei Z, Wang Q, Ye X, Yang X, Huang G, Li W, et al. Microwave ablation followed by immediate biopsy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Hyperthermia. (2018) 35:262–8. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1494856
10. Zhong L, Sun S, Shi J, Cao F, Han X, Bao X, et al. Clinical analysis on 113 patients with lung cancer treated by percutaneous CT-guided microwave ablation. J Thorac Dis. (2017) 9:590–7. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.03.14
11. Alexander ES and Dupuy DE. Lung cancer ablation: technologies and techniques. Semin InterventRadiol. (2013) 30:141–50. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1342955
12. Bhatia S, Pereira K, Mohan P, Narayanan G, Wangpaichitr M, Savaraj N, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in primary non-small cell lung cancer: what a radiologist needs to know. Indian J Radiol Imaging. (2016) 26:81–91. doi: 10.4103/0971-3026.178347
13. Kuroki M, Nakada H, Yamashita A, Sawaguchi A, Uchino N, Sato S, et al. Loss of cellular viability in areas of ground-glass opacity on computed tomography images immediately after pulmonary radiofrequency ablation in rabbits. Jpn J Radiol. (2012) 30:323–30. doi: 10.1007/s11604-012-0054-y
14. Bojarski JD, Dupuy DE, and Mayo-Smith WW. CT imaging findings of pulmonary neoplasms after treatment with radiofrequency ablation: results in 32 tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2005) 185:466–71. doi: 10.2214/ajr.185.2.01850466
15. Yoshimoto M, Tada K, Nishimura S, Makita M, Iwase T, Kasumi F, et al. Favourable long-term results after surgical removal of lung metastases of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2008) 110:485–91. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9747-9
16. Rashid OM and Takabe K. The evolution of the role of surgery in the management of breast cancer lung metastases. J Thorac Dis. (2012) 4:420–4. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.07.16
17. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumours. In: Thoracic tumours, 5th. IARC Press, Lyon (2021).
18. Liu Q, Zeng Y, Liu B, Wang Y, Li XF, Zhou DQ, et al. Clinical and CT radiomic features for predicting pulmonary nodules in adenocarcinoma. Chin Comput Med Imag. (2022) 28:245–50. doi: 10.19627/j.cnki.cn31-1700/th.2022.03.020
19. Friedel G, Pastorino U, Ginsberg RJ, Goldstraw P, Johnston M, Pass H, et al. Results of lung metastasectomy from breast cancer: prognostic criteria on the basis of 467 cases of the International Registry of lung metastases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. (2002) 22:335–44. doi: 10.1016/S1010-7940(02)00331-7
20. Pagani O, Senkus E, Wood W, Colleoni M, Cufer T, Kyriakides S, et al. International guidelines for management of metastatic breast cancer: can metastatic breast cancer be cured? J Natl Cancer Inst. (2010) 102:456–63. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2016.08.016
21. De Baere T, Tselikas L, Catena V, Buy X, Deschamps F, Palussière J, et al. Percutaneous thermal ablation of primary lung cancer. DiagnInterv Imaging. (2016) 97:1019–24. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2016.08.016
22. Healey TT, March BT, Baird G, and Dupuy DE. Microwave ablation for lung neoplasms: a retrospective analysis of long-term results. J VascIntervRadiol. (2017) 28:206–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.10.030
23. Yang X, Ye X, Zheng A, Huang G, Ni X, Wang J, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation of stage I medically inoperable non-small cell lung cancer: clinical evaluation of 47cases. J Surg Oncol. (2014) 110:758–63. doi: 10.1002/jso.23701
24. Han X, Yang X, Ye X, Liu Q, Huang G, Wang J, et al. Computed tomography-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of patients 75 years of age and older with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Indian J Cancer. (2015) 52:e56–60. doi: 10.4103/0019-509X.172514
25. Ferguson J, Izahrani N, Zhao J, Glenn D, Power M, Liauw W, et al. Long term results of RFA to lung metastases from colorectal cancer in 157 patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2015) 41:690–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2015.01.024
26. Mat Sui Y, Hiraki T, and Gobara H. Long-term survival following percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of colorectal lung metastases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. (2015) 26:303. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.11.013
27. de Baère T, Aupérin A, and Deschamps F. Radiofrequency ablation is a valid treatment option for lung metastases: experience in 566 patients with 1,037 metastases. Ann Oncol. (2015) 26:987–91. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv037
28. Vogl TJ, Eckert R, and Naguib NN. Thermal ablation of colorectal lung metastases: retrospective comparison among laser-induced thermotherapy, radiofrequency ablation, and microwave ablation. AJRAm J Roentgenol. (2016) 207:1340–9. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14401
29. Gould MK, Donington J, Lynch WR, Mazzone PJ, Midthun DE, Naidich DP, et al. Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: When is it lung cancer? Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed; American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. (2013) 143:e93S–e120S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2351
30. Maxwell AW, Healey TT, and Dupuy DE. Percutaneous thermal ablation for small-cell lung cancer: Initial experience with ten tumors in nine patients. J VascInterv Radiol. (2016) 27:1815–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.09.009
31. Chassagnon G, Gregory J, Al Ahmar M, Magdeleinat P, Legmann P, Coste J, et al. Risk factors for hemoptysis complicating 17–18-gauge CT-guided transthoracic needle core biopsy: Multivariate analysis of 249 procedures. DiagnIntervRadiol. (2017) 23:347–53. doi: 10.5152/dir.2017.160338
32. Wei Y, Xiao Y, Zhang X, He X, Zhang X, Zhang X, et al. Clinical application of CT-guided percutaneous RFA combined with halfway biopsy for pulmonary nodule and management for prevention of intraoperative bleeding. Chin J Interv Imaging Ther. (2021) 18:8–12. doi: 10.13929/j.issn.1672-8475.2021.01.003
33. Chi J, Wang Z, Ding M, Hu H, and Zhai B. Technical safety and efficacy of a blunt-tip microwave ablation electrode for CT-guided ablation of pulmonary ground-glass opacity nodules. EurRadiol. (2021) 31:7484–90. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07774-4
Keywords: lung biopsy, microwave ablation (MWA), pulmonary nodule, breast cancer, lung metastases
Citation: Xing C, Li P, Yang S, Man Q, Zhang X, Yuan Q, Hu M, Bai Y and Zhang K (2025) Investigation of the efficacy and safety of lung biopsy plus microwave ablation for a solitary suspected malignant pulmonary nodule after radical mastectomy. Front. Oncol. 15:1525114. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1525114
Received: 08 November 2024; Accepted: 17 July 2025;
Published: 13 August 2025.
Edited by:
Sharon R. Pine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesReviewed by:
Zhengyu Lin, First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, ChinaHong-Tao Hu, Henan Provincial Cancer Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Xing, Li, Yang, Man, Zhang, Yuan, Hu, Bai and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kaixian Zhang, a2FpeGlhbnpoYW5ndHpAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Chao Xing
Chao Xing Peishun Li
Peishun Li Sen Yang
Sen Yang Xusheng Zhang
Xusheng Zhang Qianqian Yuan
Qianqian Yuan Kaixian Zhang
Kaixian Zhang