- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Wound Reconstructive Surgery, Tongji Hospital of Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, Huai’an 82 Hospital, Huaian, Jiangsu, China
Introduction: Sebaceous nevus (SN) is a rare, benign, congenital tumor. There is limited information on its clinical features, familial influences, quality of life (QoL) impact, and treatment outcomes in Chinese patients. This study aimed to comprehensively examine these aspects.
Methods: A questionnaire-based survey was conducted among patients with SN who visited the Department of Plastic Surgery at Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital between January 2018 and December 2023. Healthy control children were recruited using the ‘best friends’ principle to assess familial influences. QoL impact was measured using the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI).
Results: Our analysis revealed that the severity of skin-related symptoms correlated with the extent of hyperplasia and lesion size. Maternal factors during pregnancy—including medication use, secondhand smoke exposure, toxic chemical contact, and illness (notably COVID-19 infection)—were significantly associated with a higher incidence of SN. Most patients reported a mild to moderate QoL impact. Surgical treatment demonstrated higher satisfaction rates compared to laser therapy.
Discussion: These findings suggest that hyperplasia and lesion size may predict symptom severity. The observed association between maternal COVID-19 infection and the occurrence of SN warrants further investigation. Surgical intervention appears to be an effective treatment, particularly for easily removable lesions.
1 Introduction
Sebaceous nevus (SN), a rare kind of birthmark, occurs in approximately 1 in 1000 individuals, predominantly found on the head and neck regions (1, 2). SN lesions on the scalp often result in alopecia (3). A subset of SN, termed “large SN”, covers more than 1% of the body area, posing challenges in removal (4).
In our outpatient clinic, while some SN patients complain about disturbing symptoms like pruritus and bleeding, others remain asymptomatic. There is a pressing need to investigate the predictive phenotypic factors for symptoms.
Previous research has suggested that maternal factors during pregnancy may influence the risk of congenital skin diseases (5). However, their potential impact on SN development remains unexplored.
SN is driven by somatic mutations in genes like HRAS and KRAS (6). Nevertheless, six familial SN cases have been documented (7–12), yet studies investigating familial SN in Asian cohorts are lacking.
It is well-established that various skin diseases, such as acne and atopic dermatitis, significantly impact patients’ quality of life (QoL) (13, 14). Given the cosmetic concerns, treatment challenges due to recurrent lesions, associated symptoms, and the QoL of SN patients warrant attention.
Optimal SN management remains unclear, with no consensus on surgical interventions (15). Laser therapy, though commonly used, carries a nonnegligible recurrence rate (16). Patient satisfaction with different treatments (surgery versus laser therapy) has not been adequately studied.
To address these gaps, we initiated a retrospective study investigating SN epidemiology, clinical features, familial factors, QoL impact, and treatment outcomes. This research aims to provide insights into the etiology and pathogenesis of SN.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Questionnaire design
Our case questionnaire comprised four sections:
2.1.1 Clinal characteristics
This section recorded age of onset, SN hyperplasia status, complications, and skin-related symptoms (numbness, dryness, pruritus, pain, burning sensation, bleeding, and swelling). Symptoms were rated on a 4-point scale (0 = none; 1 = mild; 2 = moderate; 3 = severe).
2.1.2 Family factors
This part assessed maternal pregnancy factors and family history of patients. Additionally, for patients born after 2020, we included a question regarding any COVID-19 infection during their mother’s pregnancy.
2.1.3 Quality of life assessment
We utilized the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index© (CDLQI) to evaluate the impact of the skin disease on QoL of children patients (17). Ten items addressed QoL effects over the preceding week, scored on a 4-point Likert scale from ‘not at all’ (0) to ‘very much’ (3). Total scores were categorized: 0–1 (no effect), 2–6 (small effect), 7–12 (moderate effect), 13–18 (very large effect), and 19–30 (extremely large effect) (18).
2.1.4 Treatment satisfaction
This section documented post-treatment recurrence and satisfaction scores (0 = Dissatisfied; 1 = Somewhat dissatisfied; 2 = Acceptable; 3 = Satisfied).
The control questionnaire exclusively addressed maternal pregnancy factors.
2.2 Patients group
We conducted a nationwide questionnaire-based epidemiological survey of SN patients presenting to the Department of Plastic Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, between 1 January 2018 and 31 December 2023. Diagnoses were confirmed by two plastic surgeons. The cohort comprised 204 patients with isolated SN and 5 with concomitant SN and verrucous epidermal nevus (VEN). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants, their parents, or their legal guardians who completed the questionnaires. This study was approved by the IRB of Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital (approval No. 201743). The details of 5 patients were shown independently. For patients with isolated SN, we recorded demographic data, lesion localization, size, and pathological diagnosis. Among this cohort, 74 participants provided only demographic data and basic SN characteristics (size, onset site, location). Of the remaining patients, 130 completed both Part 1 (clinical characteristics) and family history questionnaires, with 104 able to recall maternal pregnancy events. Additional questions regarding maternal COVID-19 infection were answered by families of 53 patients born after 2020. Furthermore, 43 children aged 4–18 years with partially treated or untreated SN completed quality of life assessments. For treatment outcome analysis, we selected 31 patients with comparable lesion size and location who underwent either surgical excision (n=16) or laser therapy (n=15) to evaluate treatment satisfaction.
2.3 Controls group
Using demographic data from the 104 patients reporting maternal events, we recruited controls via the ‘best friends’ principle (individuals without SN or SN family history). We collected 136 control questionnaires, including 72 from individuals born after 2020.
2.4 Statistical analysis
The questionnaire data were managed in Excel and analyzed using R software (version 4.3.0). Continuous variables are reported as mean ± SD; categorical variables as frequencies (percentages). Regional distribution mapping used the ‘hchinamap’ package (v0.1.0). Case-control comparisons employed ‘epiDisplay’ (v3.5.0.2), calculating odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for categorical variables.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic data
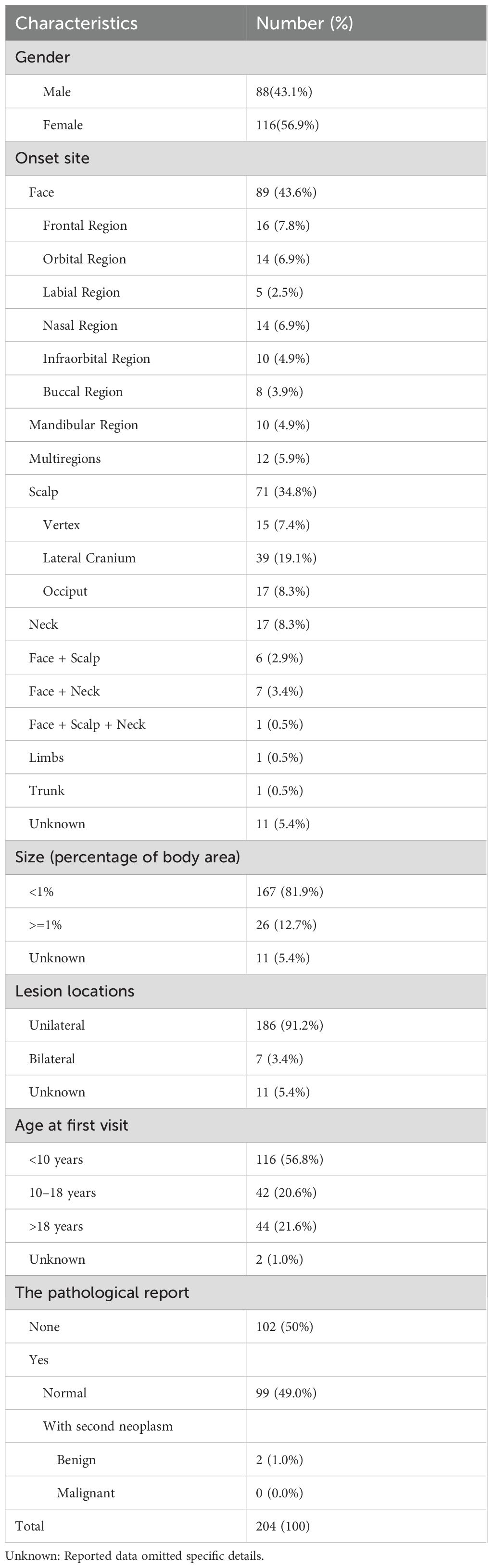
Table 1 presents the demographic and baseline clinical characteristics of 204 sebaceous nevus (SN) patients. The cohort showed female predominance (116 females vs. 88 males; ratio 1:1.32). Notably, secondary neoplasms developed in two patients: syringocystadenoma papilliferum in a 34-year-old male and sebaceoma in a 65-year-old female.
3.2 Clinical features
Detailed clinical data for 130 patients are presented in Supplementary Table S1, with most residing in Chinese coastal regions (Supplementary Figure S1). Supplementary Table S2 outlines the onset time and hyperplasia of lesions after birth in these patients, specifically. Notably, 3.1% (4/130) exhibited bilateral facial lesions, and 11.5% (15/130) developed SN after age 1 year. Hyperplasia occurred in 17.7% (23/130) of patients, manifesting as noticeable color deepening, accelerated growth relative to the body, and protrusion above the skin surface. And patient-reported triggers included puberty, mechanical irritation (scratching/rubbing), spicy foods, seasonal changes, and sun exposure.
Supplementary Table S3 delineates the frequencies of skin-related symptoms attributed to SN, with the top three incidences observed for itchiness, dryness, and bleeding. Statistical analysis revealed males demonstrated significantly higher pruritus risk compared to females (OR 0.46, 95% CI 0.22–0.93; p=0.03). The total skin symptom scores correlated positively with lesion size (p=0.029) and hyperplasia presence (p=0.033), but not with age, location, or onset time. Larger lesions increased risks of dryness (p=0.024), numbness (p=0.042), and bleeding (p=0.047). Hyperplasia showed significant associations with older age (OR: 5.18, 95%CI: 1.65~16.22, p<0.001), swelling symptoms (OR: 3.42, 95%CI: 1.1~10.66, p=0.038), larger lesion size (OR: 4.76, 95%CI: 1.55~14.6, p=0.009), and bilateral involvement (p<0.001). Refer to Supplementary Tables S4–S7 for detailed data.
Concurrent birthmarks occurred in 6.2% (8/130) of patients, including hyperpigmentation, congenital melanocytic nevi, and hemangiomas. Allergic disease history was present in 9.2% (12/130), consistent with general population rates (19–21). No systemic abnormalities were documented.
3.3 Family factors
This section encompasses maternal pregnancy factors and familial history.
3.3.1 Maternal pregnant factors
We compared maternal pregnancy exposures between 104 SN patients and 136 controls (Supplementary Table S8). Mothers of SN patients reported significantly higher rates of medical complications during pregnancy compared to controls (55.8% vs. 41.9%; p=0.033), primarily threatened miscarriage, cold and hyperemesis gravidarum. Notably, among 125 children born after 2020 (53 cases, 72 controls), maternal COVID-19 infection was more frequent in the SN cohort (OR 4.78, 95% CI 1.82–12.53; p<0.001). Furthermore, the infection rate was found to be independent of other pregnancy-related diseases but correlated with a history of drug use and chemical exposure during pregnancy. Even after adjusting for these factors, the infection rate remained statistically significant (refer to Supplementary Tables S9, S10); however, this finding need validation with a larger cohort.
Medication use during pregnancy was significantly more frequent among mothers of SN patients compared to controls (28.8% vs. 9.6%; OR 3.84, 95% CI 1.88-7.82; p<0.001), with diverse agents employed for pregnancy-related conditions. The heterogeneity of medications precluded drug-specific analysis. Secondhand smoke exposure affected 23.1% of SN mothers versus 11.0% of controls (OR 2.43, 95% CI 1.20-4.92; p=0.02). Chemical exposures during pregnancy were reported by 11 SN mothers (primarily formaldehyde: 9/11) compared to one control mother (non-formaldehyde exposure; OR 15.97, 95% CI 2.03–125.8; p<0.001). In one notable case, a third-trimester ultrasound detected fetal facial spots, with corresponding bilateral facial SN lesions manifesting postnatally.
3.3.2 Sebaceous nevus family history positive family
Three families demonstrated familial occurrence of SN or verrucous epidermal nevus (VEN). The family trees of these individuals are provided in the Supplementary Figure S2. Supplementary Figure S3 illustrates epidermal nevus lesions observed in one of the families.
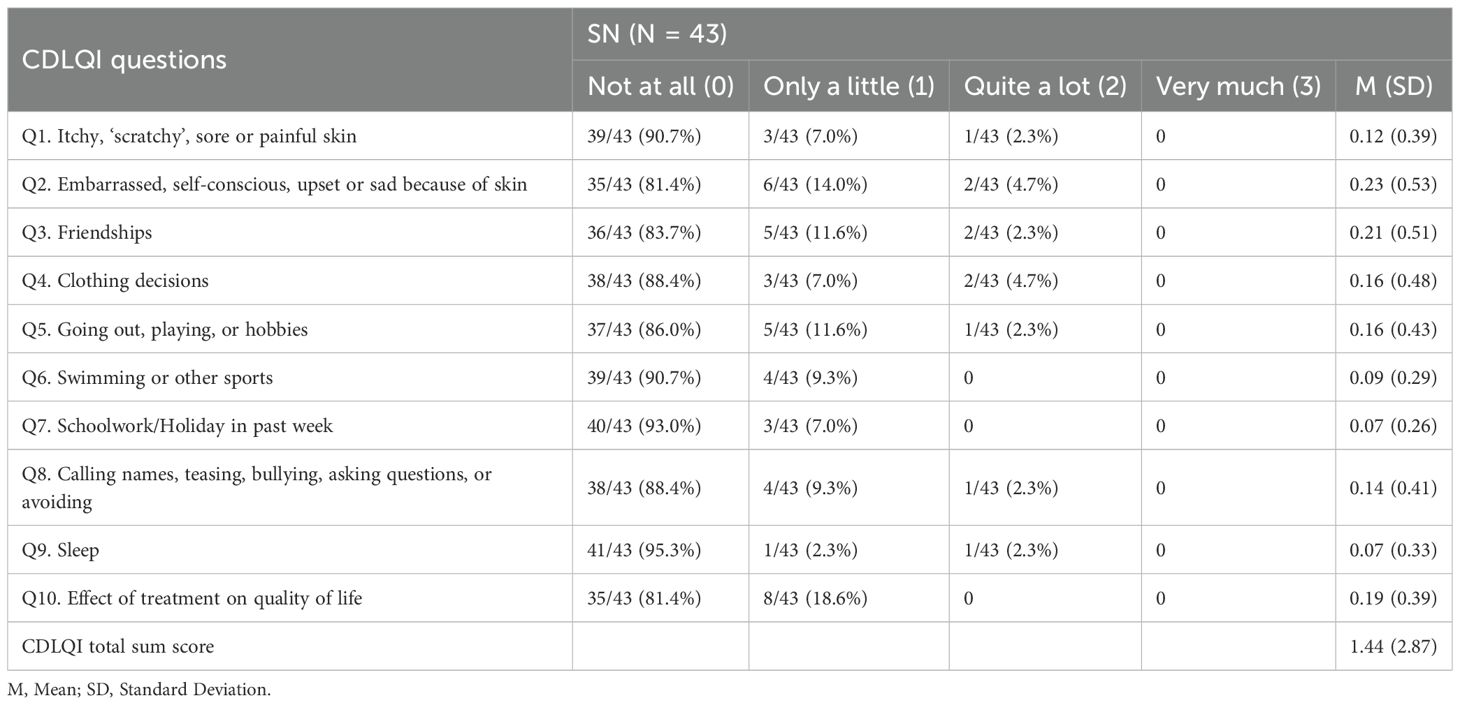
3.5 Quality of life
CDLQI assessment revealed variable quality of life impacts among SN patients (Table 2). Among the patients, 9.3% (4/43) reported a small effect (score 2-6), while an equal proportion reported a moderate effect (score 7-12). Significantly higher total scores correlated with male sex, lesions involving >1% body surface area (BSA), and head involvement. Specifically, males expressed more complaints than females in regards to ‘Q3’, ‘Q5’, and ‘Q6’. Patients with larger lesions were more susceptible to feelings of ridicule (‘Q8’) (p=0.005). Moreover, individuals with head involvement experienced greater impacts across all aspects compared to those with lesions on the neck. Refer to Supplementary Tables S11, S12 for detailed data.
3.6 Treatment outcome
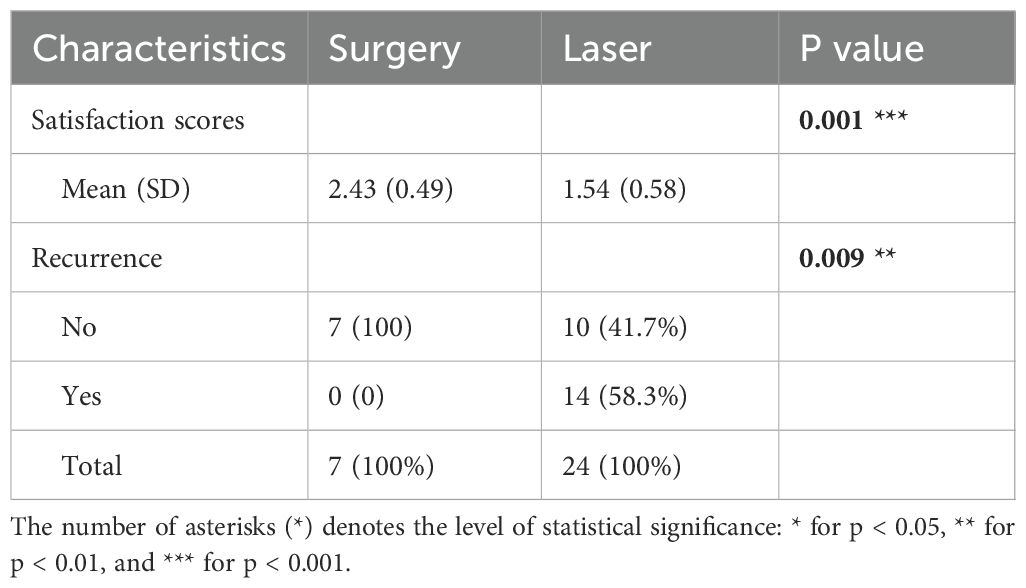
Out of the 31 patients, 7 underwent surgical treatment while 24 received laser therapy for their SN. The follow-up period ranged from 5 to 42 months, with a mean duration of 16 months. SN lesions in these patients comprised less than 1% of the body area and were deemed suitable for surgical removal. Analysis of satisfaction scores and recurrence rates is presented in Table 3. Notably, patients who underwent surgical resection reported higher satisfaction levels compared to those who received laser treatment.
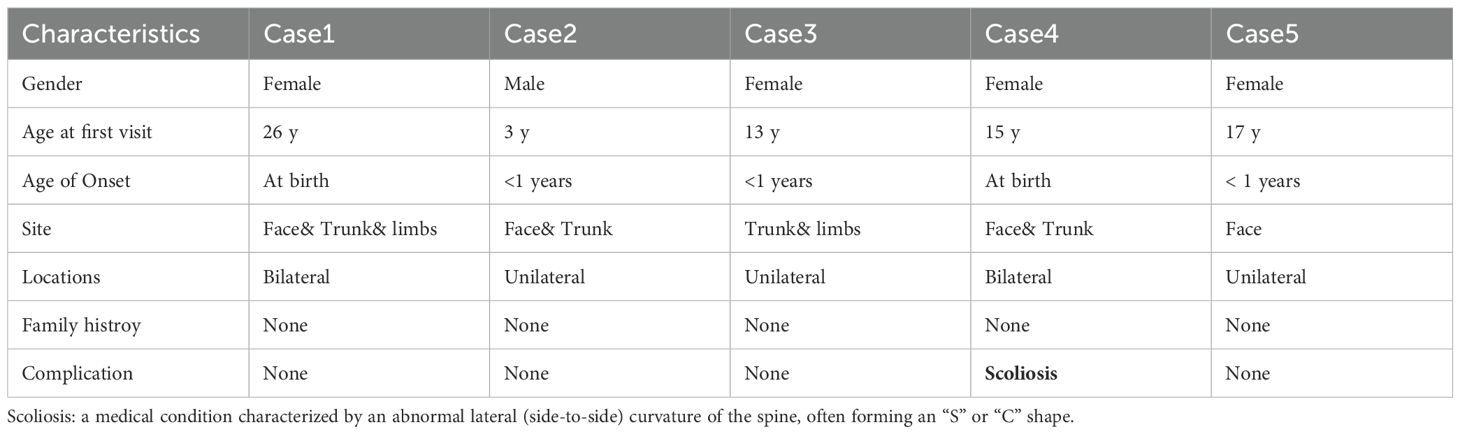
3.7 Five patients with concomitant SN and VEN
The details of the five patients are presented in Table 4 and Supplementary Figure S4. Among them, Case 4 showed abnormal ocular pigmentation and scoliosis. Multi-point biopsies were conducted for the lesion of Case5, with results illustrated in Supplementary Figure S5. The central region exhibited characteristics consistent with SN, while the peripheral area displayed features indicative of VEN.
4 Discussion
This comprehensive investigation delineates epidemiological patterns, clinical manifestations, familial factors, quality of life impacts, and treatment outcomes in sebaceous nevus (SN) patients. We observed significant female predominance (male:female = 1:1.32), contrasting with near-equal gender distributions in prior reports (22–24) but similar to the verrucous epidermal nevus (VEN) epidemiology research (25).
Patient-report hyperplasia triggers included puberty, mechanical friction, UV exposure, seasonal variation, and spicy foods. Statistical analyses confirmed symptom severity correlates with lesion size and hyperplasia presence, while hyperplasia itself associates with advanced age, larger lesions, and bilateral distribution—unstable lesions demonstrating heightened swelling symptoms. Although pubertal androgen surges may drive SN proliferation (26) and UV exposure has been implicated in secondary tumors (27), we found no direct hyperplasia-neoplasm association.
Regarding scratching friction, climate, and diet, further investigation is warranted to determine their impact on SN progression. S Pradhan demonstrated the existence of Malassezia globosa on a 3-month-old SN case infiltrated heavily by immune cells (28). This suggests a potential role for microbes in causing itching and promoting SN hyperplasia. Based on these findings, clinical practice may involve instructing patients to refrain from scratching SN lesions and consuming spicy foods, initiating interventions before puberty (29), and implementing sun protection measures.
Compared to controls, mothers of SN patients exhibited a higher incidence of pregnancy-related diseases, second-hand smoking exposure, medication use, and exposure to chemical substances (notably formaldehyde). Prenatal ultrasonography was found to have some efficacy in detecting large SN, although its role in early detection remains limited (30, 31). Interestingly, while there was no statistical difference in the incidence of common influenza, mothers of SN infants born during the COVID-19 pandemic showed a higher likelihood of COVID-19 infection during pregnancy compared to controls (OR 4.78, p<0.001). Whether this observation is incidental requires validation in a larger cohort. HPV has been detected in SN samples, implicating its potential role in SN development through the integration of HPV DNA into the host (32–34). HIV-infected patients have also been noted to develop SN-like lesions (35). However, the effect of COVID-19 on SN remains unknown. One hypothesis suggests that placental infection may lead to dysplasia (36) and fetal distress, thereby promoting somatic mutations (37). Another possibility is that intrauterine COVID-19 infection disrupts skin development, although no SN lesions have been reported post-COVID-19 infection (38). Unfortunately, patients whose mothers were infected with COVID-19 during pregnancy were not tested COVID-19 at birth, complicating making it challenging to determine whether the adverse uterine environment caused by COVID-19 infection or fetal infection itself impacts SN occurrence. While studies on the impact of COVID-19 infection on fetuses typically focus on severe adverse outcomes such as death and deformities (39, 40), its association with the incidence of body surface tumors has not been extensively explored. Therefore, our study represents the first to report a potential link between maternal COVID-19 and the development of fetal body surface tumors.
There were 3 cases with a positive family history of SN or VEN, whose inheritance did not conform to Mendelian inheritance patterns. Previous studies have demonstrated that SN is driven by somatic mutations in genes such as HRAS and FGFR3. However, homozygous mutations of those genes are typically lethal (41) and cannot be inherited by offspring or exhibit familial aggregation. Conducting genome-wide association studies (GWAS) (42) on large cohorts of the SN population may help identify SNP sites associated with SN and provide a foundation for prenatal screening and targeted drug treatments for large SN lesions.
For patients with SN presenting similar lesions, those undergoing surgical treatment reported higher satisfaction compared to those undergoing laser treatment. Given the progressive nature of SN in adolescents, we advocate early surgical removal for amenable lesions before puberty. Among patients treated with laser therapy, the recurrence rate was 14/24, which was lower than the 5/6 recurrence rate reported in previous study (16), though three patients experienced larger lesions post-treatment recurrence.
Regarding patients with both SN and VEN, we support the hypothesis suggesting that they are variants of each other (19 While Case 5 biopsies demonstrated distinct zonal histology (central SN vs. peripheral VEN), we observed no transitional morphology as described by Hafner (43). This phenomenon may be attributed to the stimulation of SN by the dilator, with epidermal hyperplasia preceding sebaceous hyperplasia. It has been suggested that mutant cells at the edge reach the end of differentiation and are unable to differentiate into sebaceous glands (44). Moving forward, dual-phenotype lesions will undergo DNA sequencing to confirm clonal origins and homology.
A limitation of this study is that, the gender dimensions of patients was simply divided into male and female based solely on the visible external anatomy.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by review board of Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
JJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. TD: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. LA: Methodology, Writing – original draft. BL: Visualization, Writing – original draft. JG: Investigation, Writing – original draft. BW: Methodology, Writing – original draft. SW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. FX: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all of patients, control children and their parents.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1529249/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Waldman AR, Garzon MC, and Morel KD. Epidermal nevi: what is new. Dermatol Clin. (2022) 40:61–71. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2021.09.006
2. Rogers M. Epidermal nevi and the epidermal nevus syndromes: a review of 233 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. (1992) 9:342–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1992.tb00623.x
3. Elmas Ö and Akdeniz FaN. Dermoscopic aspect of verrucous epidermal nevi: new findings. Turk J Med Sci. (2019) 49:710–4. doi: 10.3906/sag-1811-27
4. Chepla KJ and Gosain AK. Giant nevus sebaceus: definition, surgical techniques, and rationale for treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2012) 130:296e–304e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182589df2
5. Kinsler VA, Birley J, and Atherton DJ. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children Registry for congenital melanocytic naevi: prospective study 1988-2007. Part 1-epidemiology, phenotype and outcomes. Br J Dermatol. (2009) 160:143–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08849.x
6. Groesser L, Herschberger E, and Ruetten A. Postzygotic HRAS and KRAS mutations cause nevus sebaceous and Schimmelpenning syndrome. Nat Genet. (2012) 44:783–7. doi: 10.1038/ng.2316
7. Monk BE and Vollum DI. Familial naevus sebaceus. J R Soc Med. (1982) 75:660–1. doi: 10.1177/014107688207500816
8. Benedetto L, Sood U, and Blumenthal N. Familial nevus sebaceus. J Am Acad Dermatol. (1990) 23:130–2. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81210-8
9. Sahl WJ Jr. Familial nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: occurrence in three generations. J Am Acad Dermatol. (1990) 22:853–4. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81183-8
10. Laino L, Steensel MA, and Innocenzi D. Familial occurrence of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: another case of paradominant inheritance? Eur J Dermatol. (2001) 11:97–8.
11. Hughes SM, Wilkerson AE, and Winfield HL. Familial nevus sebaceus in dizygotic male twins. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2006) 54:S47–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.040
12. Fearfield LA and Bunker CB. Familial naevus sebaceous of Jadassohn. Br J Dermatol. (1998) 139:1119–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.2576h.x
13. Olsen JR, Gallacher J, and Finlay AY. Quality of life impact of childhood skin conditions measured using the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI): a meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. (2016) 174:853–61. doi: 10.1111/bjd.14361
14. Salek MS, Jung S, and Brincat-Ruffini LA. Clinical experience and psychometric properties of the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI), 1995-2012. Br J Dermatol. (2013) 169:734–59. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12437
15. Wali GN, Felton SJ, and McPherson T. Management of naevus sebaceous: a national survey of UK dermatologists and plastic surgeons. Clin Exp Dermatol. (2018) 43:589–91. doi: 10.1111/ced.13422
16. Alkhalifah A, Fransen F, and Le Duff F. Laser treatment of epidermal nevi: A multicenter retrospective study with long-term follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2020) 83:1606–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.06.013
17. Lewis-Jones MS and Finlay AY. The Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI): initial validation and practical use. Br J Dermatol. (1995) 132:942–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1995.tb16953.x
18. Neuhaus K, Landolt MA, and Theiler M. Skin-related quality of life in children and adolescents with congenital melanocytic naevi - an analysis of self- and parent reports. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2020) 34:1105–11. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16131
19. Benjamin LT. Birthmarks of medical significance in the neonate. Semin Perinatol. (2013) 37:16–9. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2012.11.007
20. Dohil MA, Baugh WP, and Eichenfield LF. Vascular and pigmented birthmarks. Pediatr Clin North Am. (2000) 47:783–812. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(05)70240-6
21. Kim JT, Kim HS, and Chun YH. Effect of multi-ethnicity and ancestry on prevalence of allergic disease. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. (2020) 53:640–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2018.10.004
22. Idriss MH and Elston DM. Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 707 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2014) 70:332–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.004
23. Cribier B, Scrivener Y, and Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: A study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2000) 42:263–8. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(00)90136-1
24. Rosen H, Schmidt B, and Lam HP. Management of nevus sebaceous and the risk of Basal cell carcinoma: an 18-year review. Pediatr Dermatol. (2009) 26:676–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2009.00939.x
25. Rogers M, McCrossin I, and Commens C. Epidermal nevi and the epidermal nevus syndrome. A Rev 131 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. (1989) 20:476–88. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70061-x
26. Hamilton KS, Johnson S, and Smoller BR. The role of androgen receptors in the clinical course of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. Mod Pathol. (2001) 14:539–42. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880346
27. Kim YS, Park GS, and Chung YJ. Whole-exome sequencing of secondary tumors arising from nevus sebaceous revealed additional genomic alterations besides RAS mutations. J Dermatol. (2023) 50:1072–5. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16784
28. Pradhan S, Ran X, and Zhang C. Cover Image: Naevus sebaceus affected by overgrowth of Malassezia globosa. Br J Dermatol. (2018) 179:1432–3. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17155
29. Heister M, Häfner HM, and Breuninger H. Tumescent local anaesthesia for early dermatosurgery in infants. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2017) 31:2077–82. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14461
30. Kuentz P, Fraitag S, and Gonzales M. Mosaic-activating FGFR2 mutation in two fetuses with papillomatous pedunculated sebaceous naevus. Br J Dermatol. (2017) 176:204–8. doi: 10.1111/bjd.14681
31. Neis AE, Johansen KL, and Harms RW. Sonographic characteristics of linear nevus sebaceous sequence. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2006) 27:323–4. doi: 10.1002/uog.2639
32. Carlson JA, Cribier B, and Nuovo G. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis-associated and genital-mucosal high-risk human papillomavirus DNA are prevalent in nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2008) 59:279–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.03.020
33. Akagi K, Symer DE, and Mahmoud M. intratumoral heterogeneity and clonal evolution induced by HPV integration. Cancer Discov. (2023) 13:910–27. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-22-0900
34. Raghu P, Tran TA, and Rady P. Ileostomy-associated chronic papillomatous dermatitis showing nevus sebaceous-like hyperplasia, HPV 16 infection, and lymphedema: a case report and literature review of ostomy-associated reactive epidermal hyperplasias. Am J Dermatopathol. (2012) 34:e97–102. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0b013e3182562526
35. Itin PH and Gilli L. Molluscum contagiosum mimicking sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn, ecthyma and giant condylomata acuminata in HIV-infected patients. Dermatology. (1994) 189:396–8. doi: 10.1159/000246887
36. Alcover N, Regiroli G, and Benachi A. Systematic review and synthesis of stillbirths and late miscarriages following SARS-CoV-2 infections. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2023) 229:118–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.01.019
37. Li M, Brokaw A, and Furuta AM. Non-human primate models to investigate mechanisms of infection-associated fetal and pediatric injury, teratogenesis and stillbirth. Front Genet. (2021) 12:680342. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.680342
38. Polly S, Muser IM, and Fernandez AP. Update in cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: Special populations. Cleve Clin J Med. (2023) 90:43–52. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.90a.22013
39. Lindsay L, Calvert C, and Shi T. Neonatal and maternal outcomes following SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 vaccination: a population-based matched cohort study. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5275. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40965-9
40. Crovetto F, Crispi F, and Llurba E. Impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection on pregnancy outcomes: A population-based study. Clin Infect Dis. (2021) 73:1768–75. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab104
41. Kim YE, Kim YS, and Lee HE. Reversibility and developmental neuropathology of linear nevus sebaceous syndrome caused by dysregulation of the RAS pathway. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:112003. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112003
42. Mountjoy E, Schmidt EM, and Carmona M. An open approach to systematically prioritize causal variants and genes at all published human GWAS trait-associated loci. Nat Genet. (2021) 53:1527–33. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00945-5
43. Hafner C, Landthaler M, and Happle R. Nevus marginatus: a distinct type of epidermal nevus or merely a variant of nevus sebaceus? Dermatology. (2008) 216:236–8. doi: 10.1159/000112933
Keywords: sebaceous nevus, clinical features, familial factors, quality of life, treatment, COVID-19
Citation: Jin J, Dai T, An L, Lai B, Gu J, Wei B, Wang S and Xie F (2025) Unveiling new insights: a comprehensive questionnaire-based single-center study of sebaceous nevus. Front. Oncol. 15:1529249. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1529249
Received: 19 November 2024; Accepted: 08 September 2025;
Published: 25 September 2025.
Edited by:
Kamran Avanaki, University of Illinois Chicago, United StatesReviewed by:
Yanfei Zhang, Xi’an Jiaotong University, ChinaSoysal Baş, Independent Researcher, Istanbul, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Jin, Dai, An, Lai, Gu, Wei, Wang and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Xie, eGllZmVuZ2hlQDE2My5jb20=; Shen Wang, MzkxMjg1OTdAcXEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jiamin Jin
Jiamin Jin Tao Dai2†
Tao Dai2† Lu An
Lu An Jieyu Gu
Jieyu Gu Boxuan Wei
Boxuan Wei Feng Xie
Feng Xie