- 1The First Clinical Medical College, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
Introduction: Macrophage polarization plays a crucial role in the development of various diseases. Simultaneously, macrophage polarization is intimately related to lipid metabolism. To assess the emerging trend of lipid metabolism during macrophage polarization, the present study was carried out.
Methods: First, 472 publications that explored lipid metabolism during macrophage polarization were gathered using the Web of Science Core Collection database (WoSCC). The emerging trends were then described using CiteSpace.
Results: Between 2013 and 2023, 46 countries/regions involving 268 institutions carried out studies in this field. The largest number of publications was found in China. Additionally, the most recent burst keywords included “immunometabolism”, “foam cell formation”, and “pathway”, which represented the current frontiers of research.
Discussion: The detailed analysis of publications pertaining to lipid metabolism during macrophage polarization reveals the current research status and identifies its hotspots.
Introduction
The process known as “macrophage polarization” refers to the ability of macrophages to modify their gene expression profile, metabolism, and function in response to microenvironmental stimulus (1). Numerous diseases, such as atherosclerosis (2), inflammatory bowel disease (3), and cancers (4), have been demonstrated to be significantly influenced by macrophage polarization throughout their development and progression. As known to all, macrophage lineage is characterized by heterogeneity and plasticity and undergoes phenotypic transformation under microenvironmental stimulation (5). It is well recognized that activated macrophages could be roughly categorized into two groups: M1-like macrophages, which demonstrate a pro-inflammatory phenotype, and M2-like macrophages, which demonstrate an anti-inflammatory phenotype. In detail, there are more refined subpopulation of macrophages including M1, M2a, M2b, and M2c (6, 7). Released cytokines are a major distinguishing feature between difference subpopulations of polarized macrophages. M1-like macrophages, which are classically activated, are typically interleukin (IL)-12high and IL-10low. According to the previous research, M1-like macrophages could release pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-6, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor−alpha (TNF-α) (1, 8). By contrast, M2-like macrophages, which are alternatively activated, are typically IL-10high and IL-12low. The anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory features of M2-like macrophages are well understood. In particular, M2a macrophages have been identified as wound-healing macrophages, have been reported to triggered in response to IL-4 and IL-13, and have the ability to release cytokines like transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) (9, 10). Furthermore, M2b macrophages are described as a “middle-of-the-road” and seem to be an exception due to their capacity to generate a number of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 (11). Additionally, M2c and M2b macrophages are referred to as regulatory macrophages. It has been verified that M2c macrophages could produce cytokines such as IL-10 (12).
Lipids were understood to be structural elements of nuclear, organelle, and cellular membranes. To note, the importance of lipids and their metabolites in modulating macrophage polarization in multiple ways, such as regulating inflammation, phagocytosis, and response to pathogens, has come to notice in recent years. And most importantly, there is an intricate relationship between the lipid metabolism and macrophage polarization (13). Bibliometrics is one of the most effective approaches for describing the trend of a particular field of research. Additionally, it could be employed to forecast research hotspots and identify emerging research interests. Thus, we conducted a bibliometric analysis of publications that focused on the lipid metabolism during macrophage polarization issued between 2013 and 2023. This work would provide a concise summary of the research’s accomplishments.
Methods
Data collection
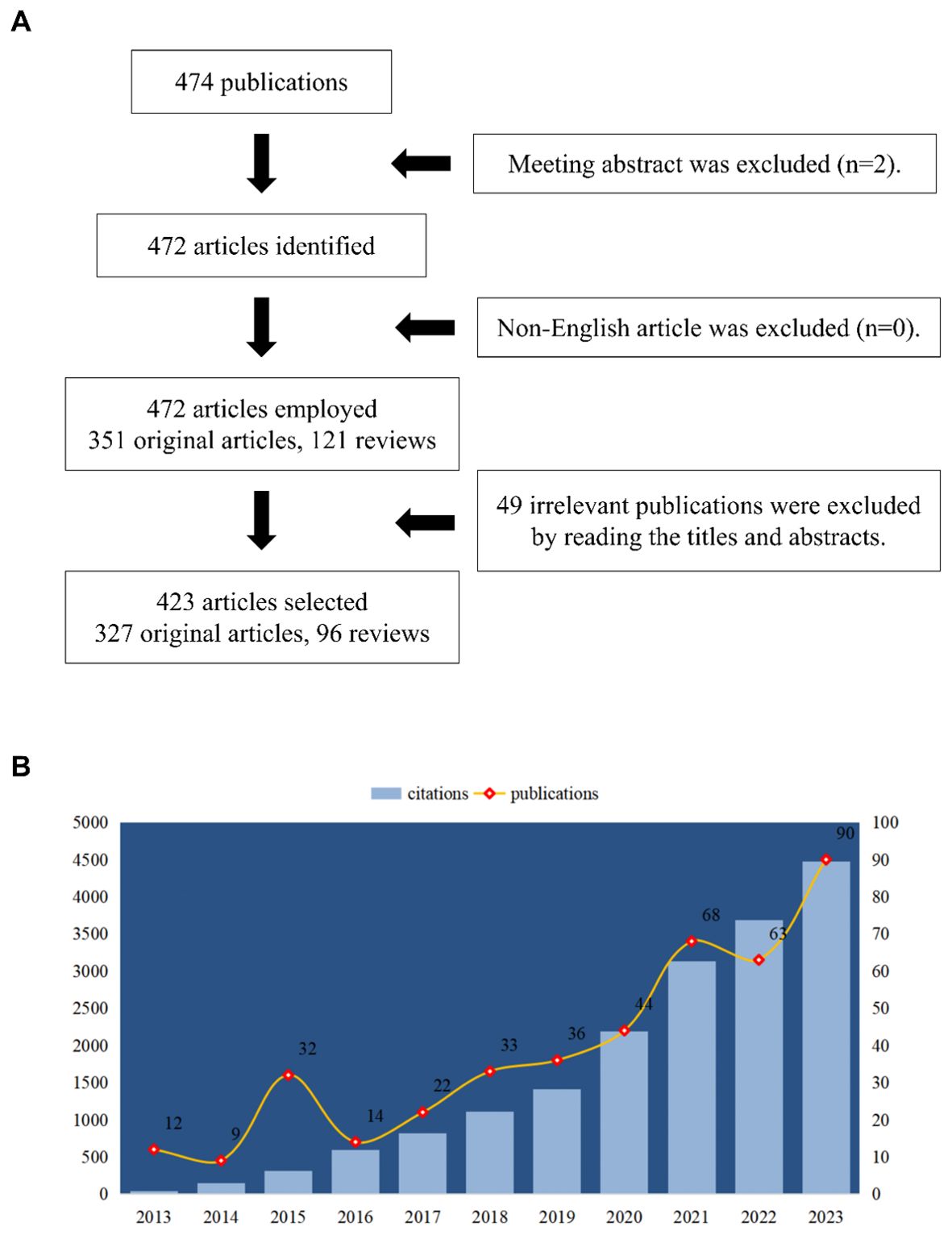
The research was conducted using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC). In order to prevent fluctuations in citations brought on by quick publication updates, the literature retrieval was completed in a single day (August 21, 2024). The search formula was set to TS= (macrophage polarization) and TS= (lipid metabolism). The first phase resulted in the acquisition of 474 publications (including early access) issued between 2013 and 2023. Then, 472 publications were included, comprising 351 articles and 121 review articles. Additionally, only English-language articles (n=472) were retained. In order to filter articles that were relevant to our study (lipid metabolism in macrophage polarization), we lastly reviewed the titles, abstracts, or even the whole texts of these publications. A total of 49 publications were excluded via this step. Finally, only 423 studies were enrolled for bibliometrics analysis. The detailed process was shown in Figure 1A. The number of publications and citations, titles, year of publication, countries/regions, affiliations, authors, journals, references, and keywords were all included.
Statistical analysis and visualization
Before analysis, the publications are briefly described as shown in Figure 1B. WOSCC was employed to export all data in the model of “full record and cited references.” Chen (14) developed the bibliometric analysis tool CiteSpace. To get rid of duplicate publications, we imported the “download.txt” file into CiteSpace 6.4.R1 at first. Numerous functions, including illustrating the authors, countries/regions, institutions collaboration, co-cited references, citation burst, keywords co-occurrence, and others, can be realized by it. At the same time, we can rapidly comprehend the growth of knowledge structures, milestone articles, emerging topics, and research hotspots and frontiers thanks to its unique betweenness centrality and bursts analysis. The time slice for our analysis is set to 1 year, the g-index to k = 25. In addition, the parameter settings also include selecting pathfinder, pruning sliced networks, and pruning the merged network. Finally, in the country analysis, we merged the “Peoples R China” and “Taiwan.” Meanwhile, in the keyword analysis, we merged the “macrophage polarization” and “polarization.”
Results
The trend of publications and citations
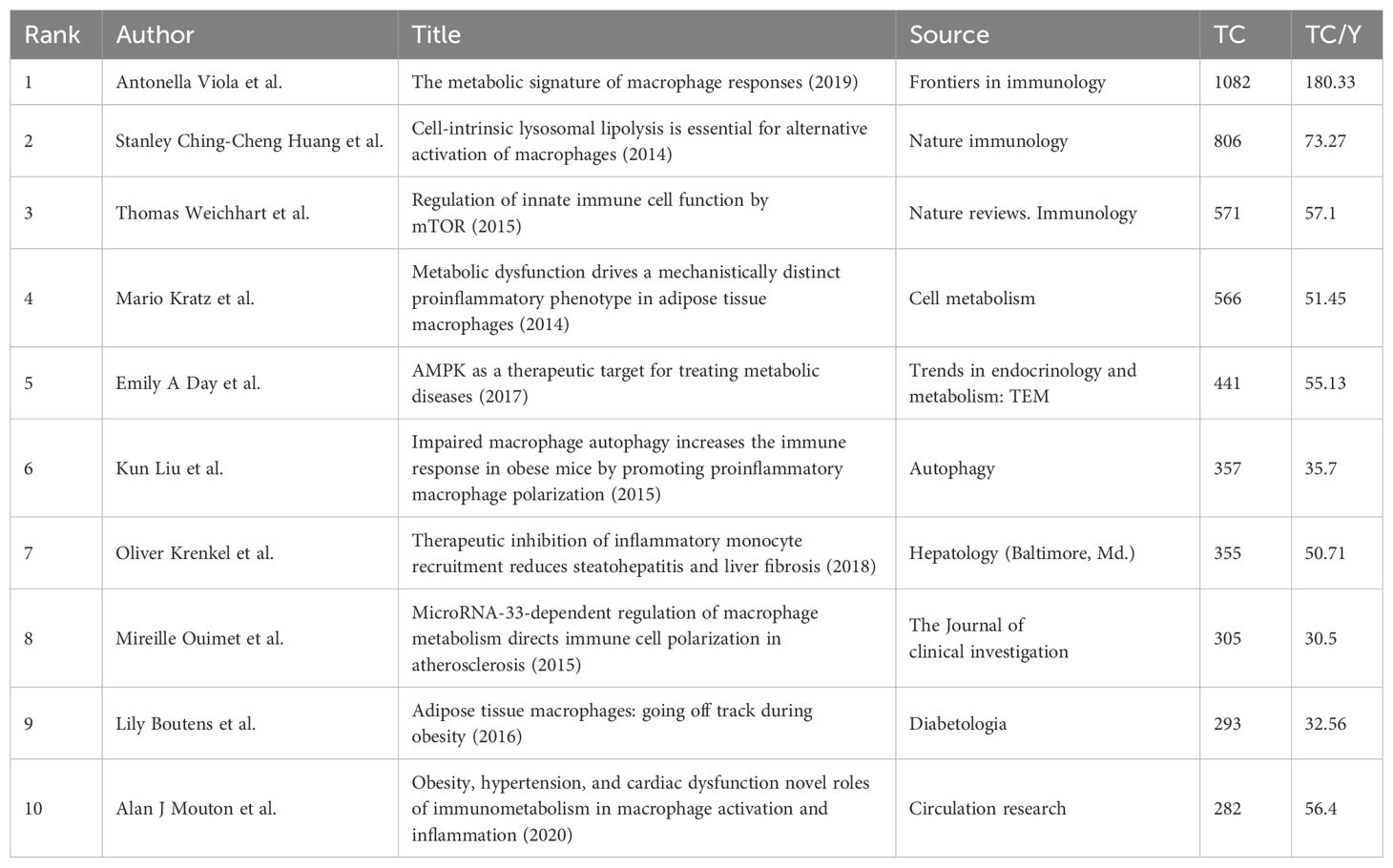
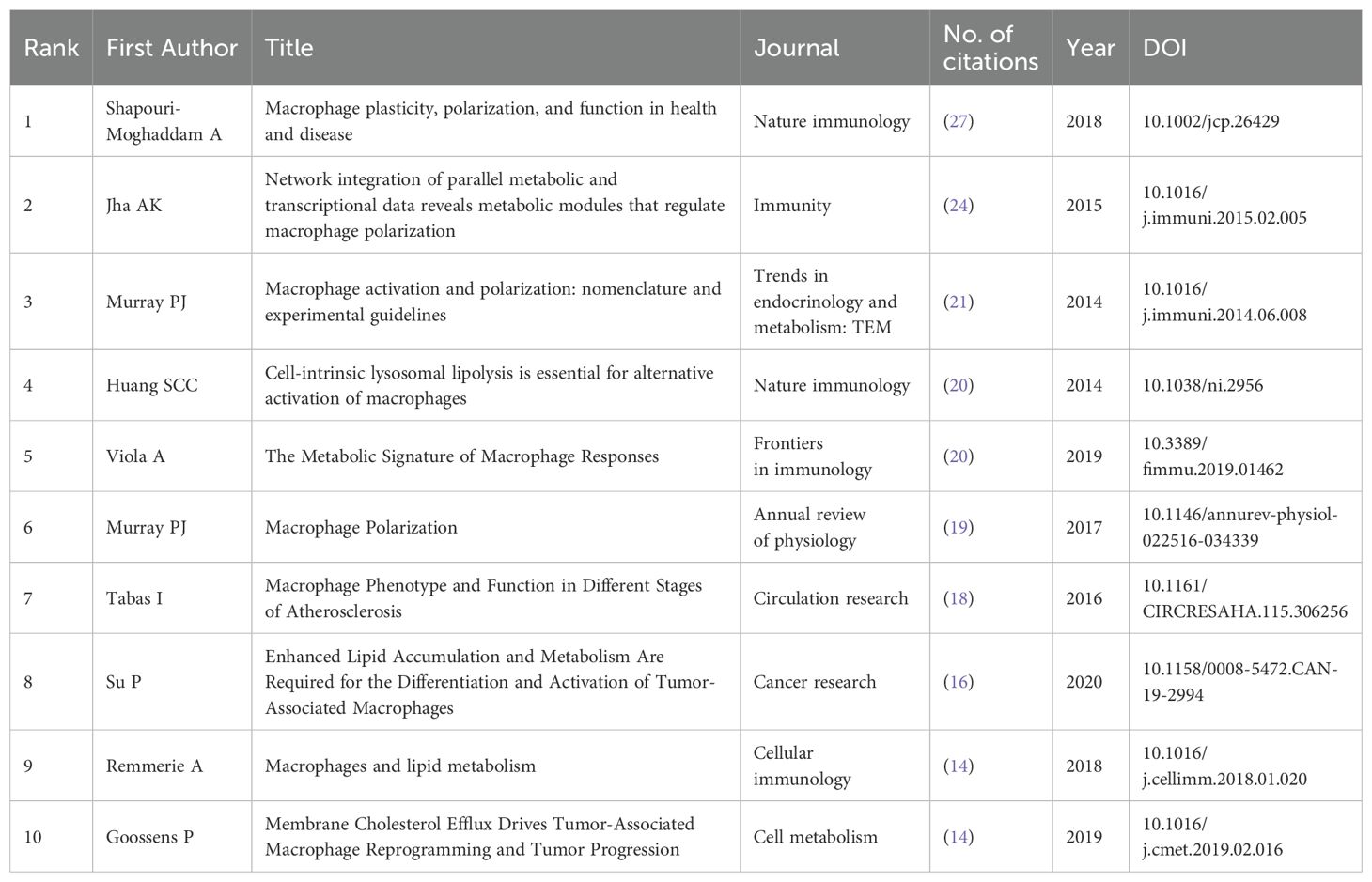
A total of 423 articles and review articles pertaining to macrophage polarization and lipid metabolism were filtered out between 2013 and 2023. Research trends were shown in Figure 1B, which illustrated the yearly increase of publications and citations. In addition, as shown in Figure 1B, the annual publications in this area were relatively low in 2013, 2015, and 2016. And as growing interest focused on lipid metabolism and macrophage polarization, the annual outputs in this field increased steadily and sharply from 2016 to 2023. In 2023, the number of issued articles reached 90, while the citations also reached a peak of 4477. Furthermore, as revealed in Table 1, the highly cited article issued in 2019 entitled “The metabolic signature of macrophage responses.” The total citations (TC) and total citations per year (TC/Y) were 1082 and 180.33, respectively.
The analysis of countries/regions and institutions
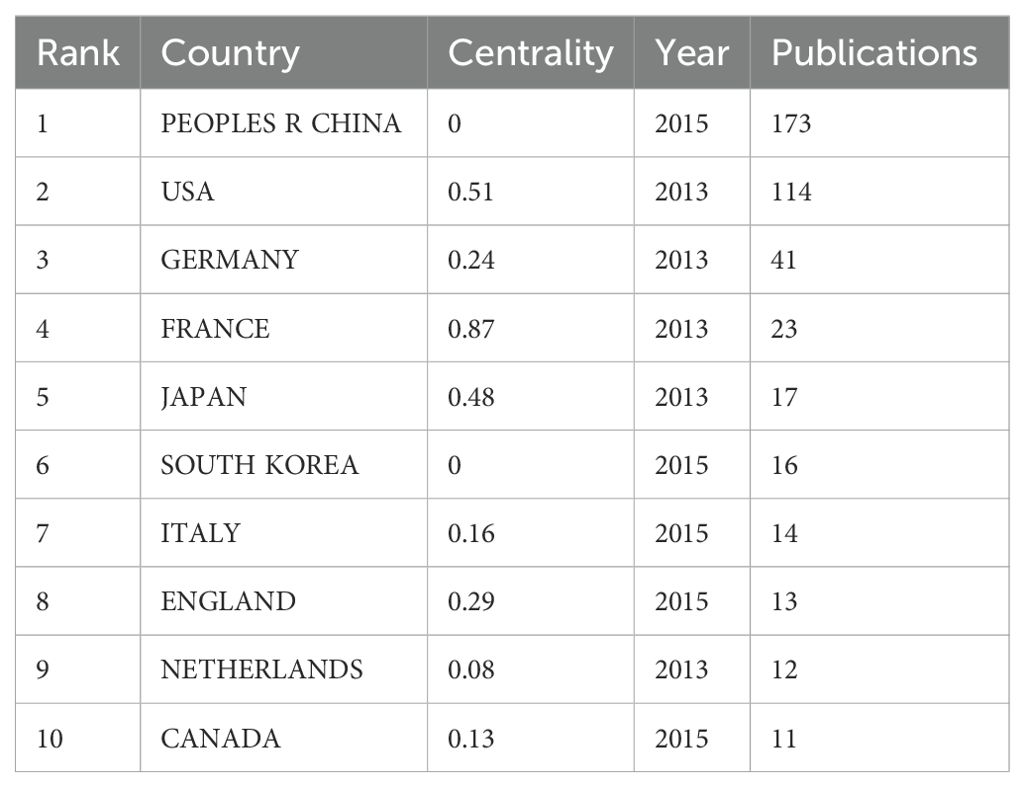
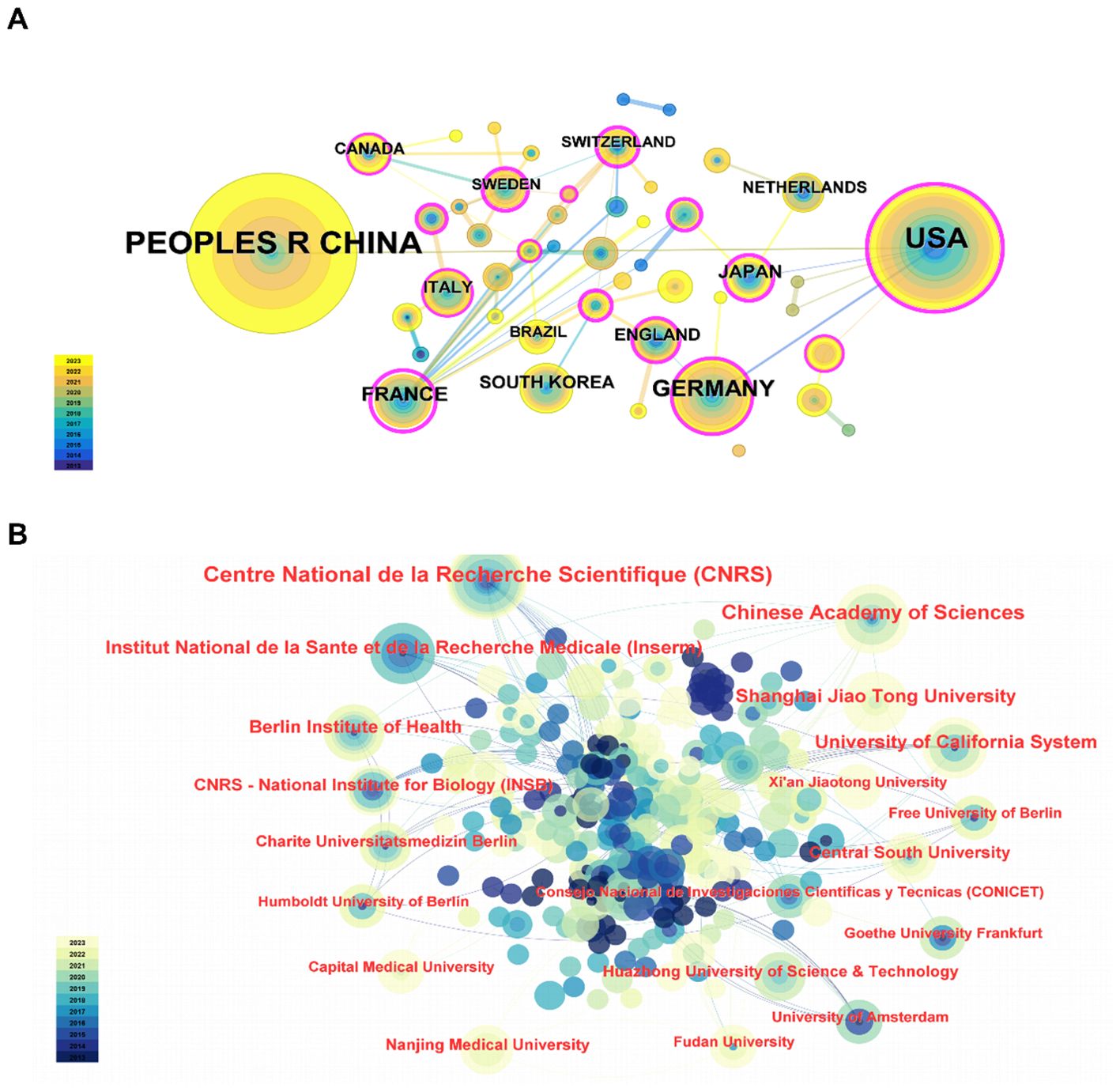
Studies in this area were conducted by 46 countries/regions involving 268 institutions between 2013 and 2023. The top 10 productive countries/regions were displayed in Table 2. Obviously, China exhibited the most significant number of publications related to lipid metabolism and macrophage polarization (n=173), which was followed by the USA (n=114) and Germany (n=41) in second and third place, respectively. In addition, a further co-authorship network to display the cooperation among countries/regions was mapped, as shown in Figure 2A. Among them, China cooperates most closely with the USA, while France cooperates very frequently with other countries.
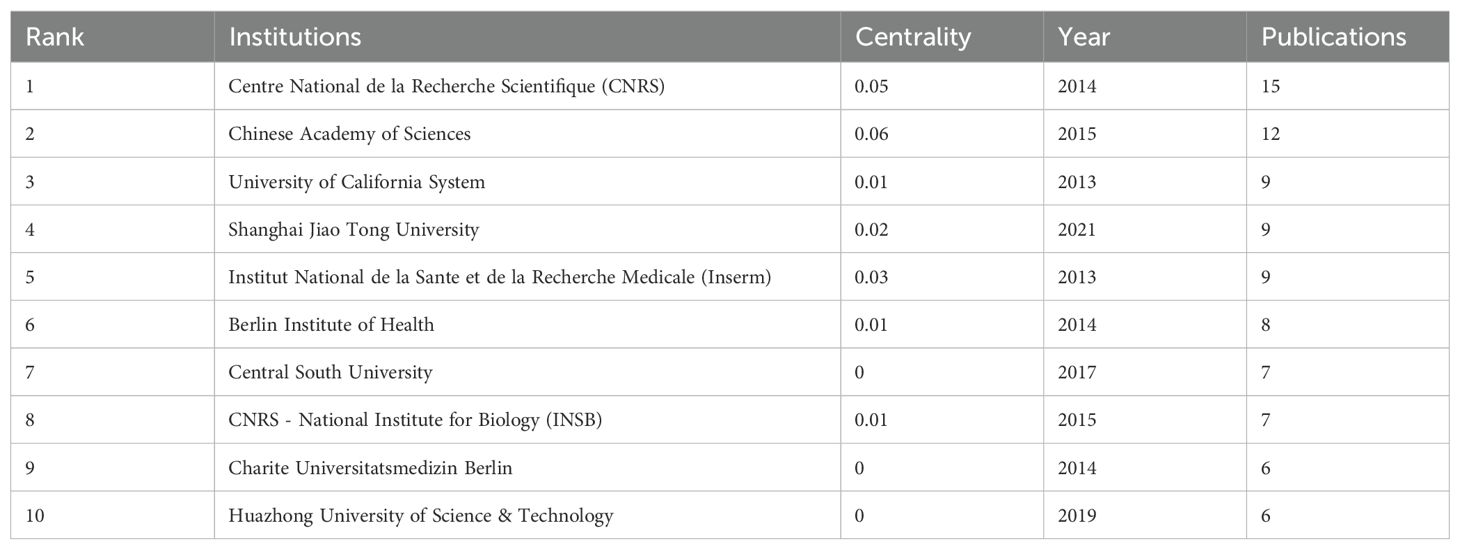
And then, Table 3 listed the top 10 productive institutions. Among them, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique and the Chinese Academy of Sciences led the outputs, followed by the University of California System. In detail, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique has published 15 articles since 2014. And the Chinese Academy of Sciences has published 12 articles since 2015. In addition, there are 9 publications published by the University of California System from 2013. Furthermore, the co-authorship network of institutions demonstrated relatively weak collaboration among them, suggesting that cooperation among institutions needs to be further strengthened (Figure 2B).
Authors and co-cited authors
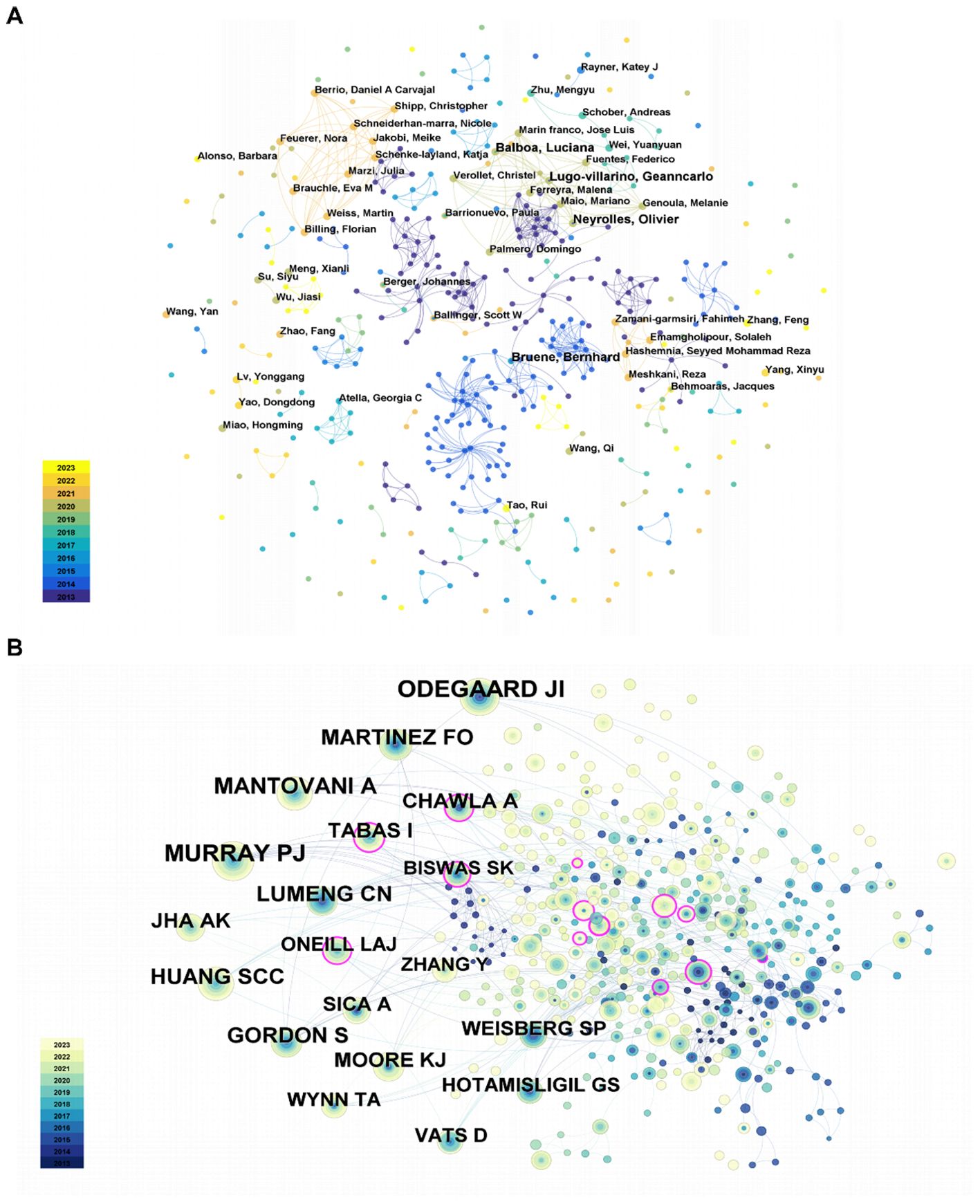
From 2013 to 2023, a total of 425 authors carried out the studies on lipid metabolism and macrophage polarization. The authors’ cooperation network is shown in Figure 3A.
It is evident that individual author collaboration networks are relatively clustered into clusters, possibly due to a preference for publishing in specific research areas. At the same time, the collaborations among the author clusters also needed to be further strengthened. In addition, the top 20 highly productive authors were summarized in Supplementary Table 1. The writers with the most publications, as indicated in Supplementary Table 1, published 3 papers in related topics. These authors include Neyrolles Olivier, Lugo-villarino Geanncarlo, Balboa Luciana, and Bruene Bernhard.
Neyrolles Olivier and Lugo-villarino Geanncarlo have been producing since 2014, while Balboa Luciana and Bruene Bernhard have been publishing since 2018 and 2013, respectively.
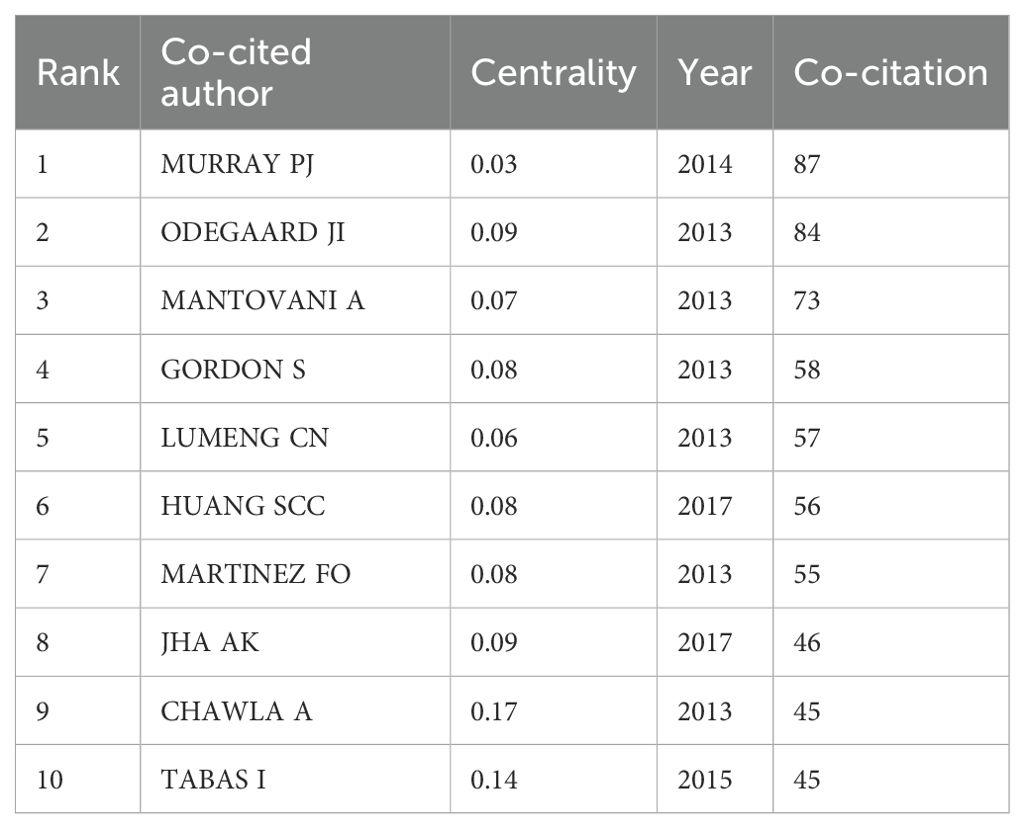
Co-cited authors are authors who are cited in articles at the same time. To illustrate the relationships between co-cited authors, a brief network was created (Figure 3B). Additionally, Table 4 included a detailed breakdown of the top 10 co-cited authors. Evidently, just 2 authors received more 80 citations, while 7 authors in total were co-cited more than 50 time. Lastly, the top three co-cited authors were MURRAY PJ, ODEGAARD JI, and MANTOVANI A. In detail, MURRAY PJ received 87 citations from 2014, ODEGAARD JI received 84 citations from 2013, and MANTOVANI A received 73 citations from 2013.
Co-citation analysis of references
One of the CiteSpace’s most distinctive features is the co-citation network, which enables us to comprehend the patterns and development contexts in a certain subject (15). In Figure 4A, the colors go from darker to lighter, indicating that the cited reference is more recent. It is evident that a sizable portion of the referenced sources are recent publications, which is helpful and potent to access the cutting-edge research directions through further literature analysis. In addition, Table 5 displayed the top 10 most cited references in detail. The most cited reference was published by Shapouri-Moghaddam A et al. (16). entitled “Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease.” In this review, the fundamental biology of macrophages, including their origin, differentiation and activation, tissue distribution, migration, and more, is covered in detail in this review. Secondly, it goes over the protective and pathogenic roles of the macrophages in both healthy and unhealthy pregnancies, atherosclerosis, fibrosis, wound healing, autoimmunity, metabolic disease and obesity, anti-microbial defense, anti-tumor immunity, and asthma and allergy. Furthermore, the reference ranked second in citations was written by Jha AK et al., which entitled “Network integration of parallel metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that regulate macrophage polarization.” The systemic alterations during murine M1-like and M2-like macrophage polarization were compiled in this article, with the former highly associated with TCA cycle fragmentation and the latter with activation of glutamine catabolism (17). In the meantime, Tabas I reviewed the latest developments on macrophage polarization and function in various atherosclerosis phases (18), showing that macrophage polarization might be crucial in every stage of this disease. Su P discovered a close connection between the fatty acid oxidation-dependent signaling pathway and human breast, colon, and prostate cancer. He suggested this pathway as a special mechanism that regulates the development and activity of protumor macrophages (19).
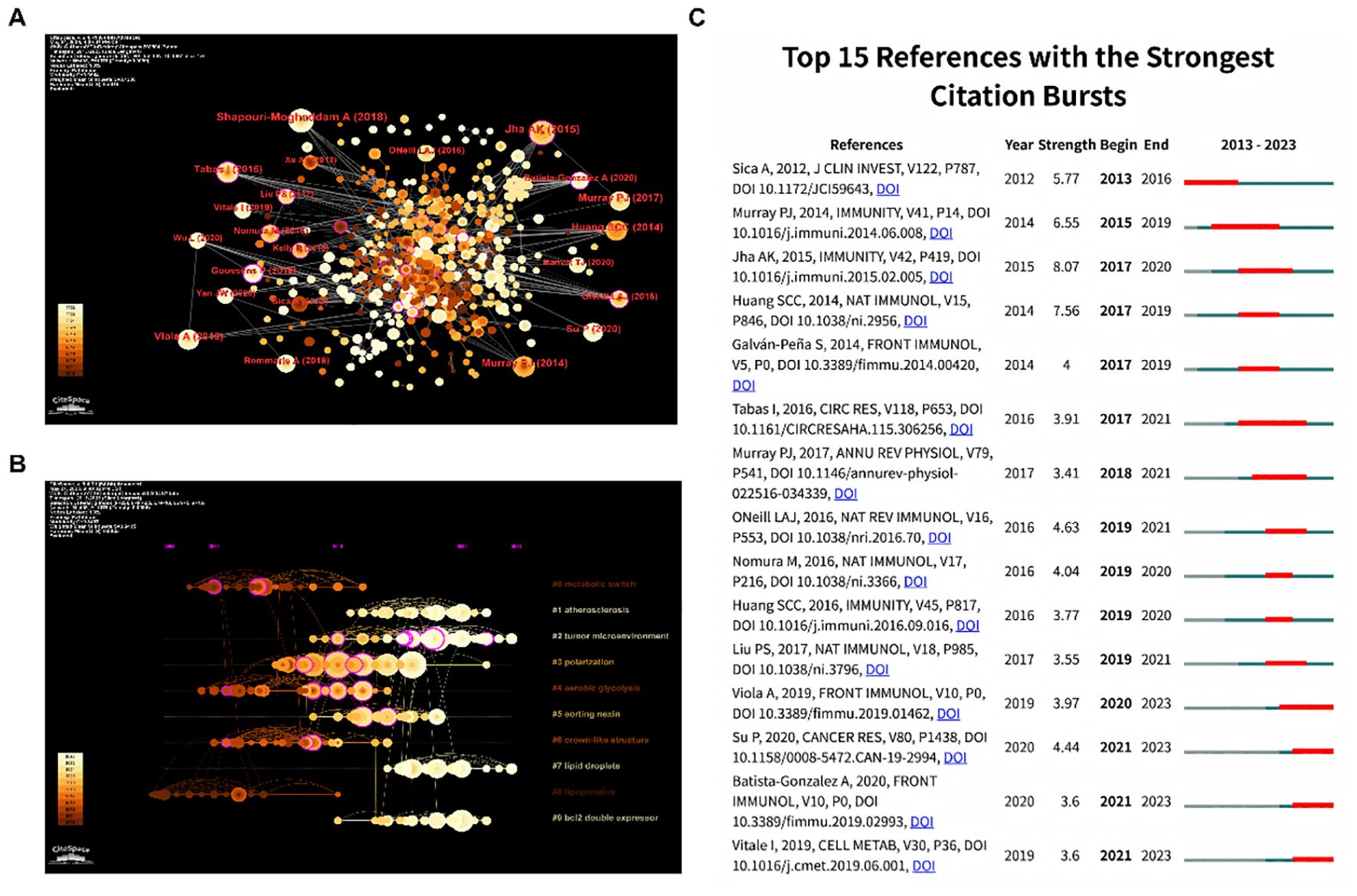
Figure 4. (A) References co-occurrence map. (B) References timeline view. (C) Burst analysis of references.
Furthermore, the timeline map (Figure 4B) was drawn after clustering and named with keywords. Additionally, each cluster’s progress might be more clearly presented. The upcoming trends were shown by clusters 1, 2, 7, and 9. And to note, investigations on the tumor microenvironment in particular are probably going to be an increasingly prevalent topic. Besides, the dense lines between Cluster 1 and Cluster 4 highlight the potential role of aerobic glycolysis in the development of atherosclerosis. Meanwhile, the lines between Cluster 6 and Cluster 8 were also relatively dense, which suggests a close relationship between crown-like structure and lipoprotein. To note, researchers focusing on tumor microenvironment and atherosclerosis are encouraged to enhance interdisciplinary collaboration.
Moreover, a visual map was further constructed to better illustrate the reference burst trend (Figure 4C). According to burst analysis, some authors have had a comparatively high number of citations in recent years. For example, the Metabolic Signature of Macrophage Responses was detailed in Viola A’s article, “The Metabolic Signature of Macrophage Responses,” which summarized that M1-like and M2-like macrophages are distinguished by particular pathways that control the metabolism of lipids and amino acids and influence their responses. All of these metabolic adaptations are useful to maintain their polarization in particular situations and to support macrophage activities (20). Besides, the study by Jha AK et al. (2015) got the greatest burst strength (8.07).
Analysis of keywords
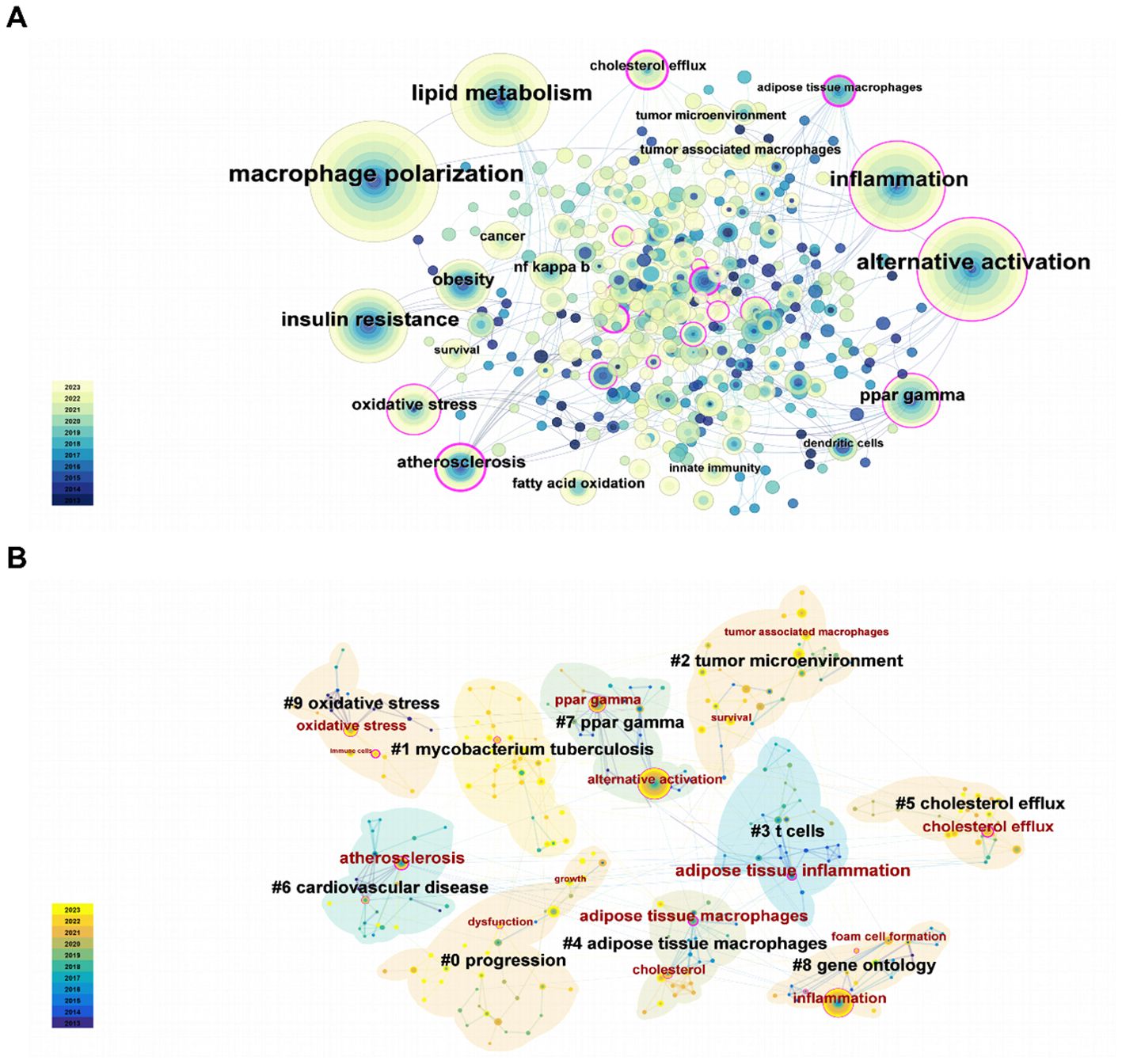
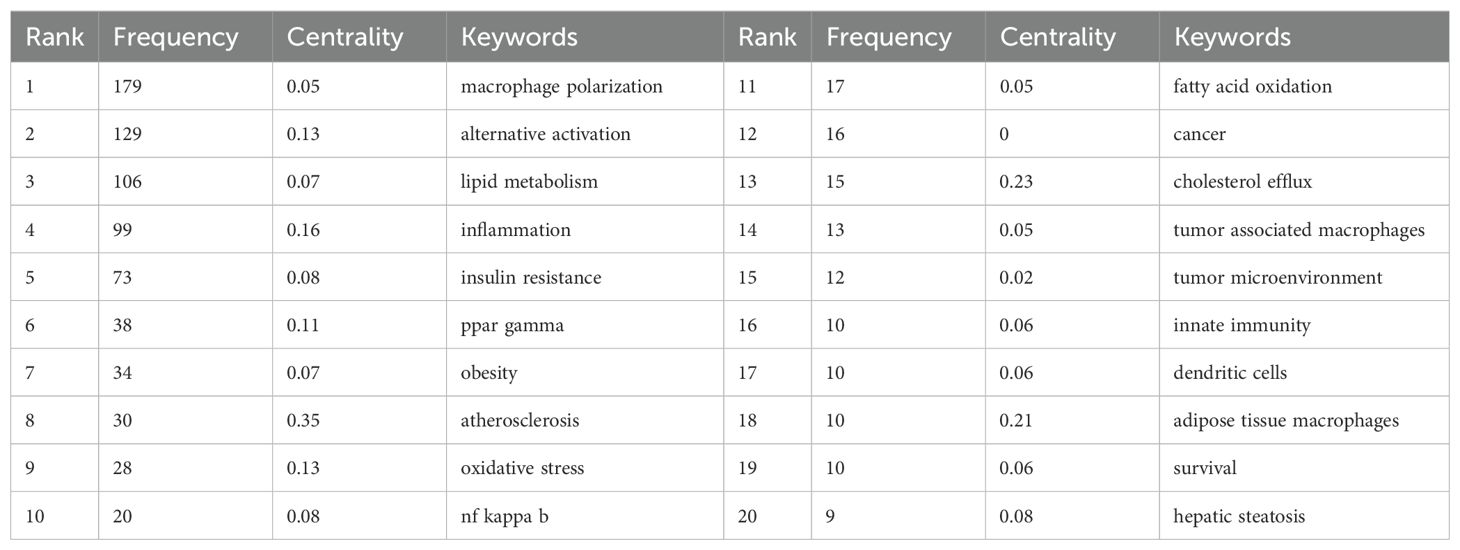
First of all, a total of 19 keywords were identified as occurring more than 10 times, which have been illustrated in Figure 5A. As illustrated in Table 6, “alternative activation,” “inflammation,” “insulin resistance,” and “ppar gamma” were the keywords that appeared most frequently for pathological processes in this field, except for the topic terms of “macrophage polarization” and “lipid metabolism.” And interestingly, we discovered the presence of some keywords (innate immunity and dendritic cells), which may indicate that lipid metabolism mediates close communication between immune cells.
Moreover, keywords after clustering help to characterize the distribution of research content on a specific topic (Figure 5B). This led to the creation of a visual representation of keyword co-occurrence clusters. First of all, the cluster’s mean silhouette value was 0.9062 and its modularity Q was 0.7696, respectively, ensuring the high standards of this analysis. Unquestionably, the largest cluster was undoubtedly cluster #0, which was named “progression,” followed by “mycobacterium tuberculosis,” “tumor microenvironment,” “t cell,” “adipose tissue macrophage,” “cholesterol efflux,” and so on. Furthermore, specific representative nodes of each cluster were labeled. Interestingly, tumor microenvironment was the designation given to cluster #2, which included nodes recognized as survival and tumor-associated macrophages. In addition, t cells was the label given to cluster #3, which included nodes recognized as adipose tissue inflammation.
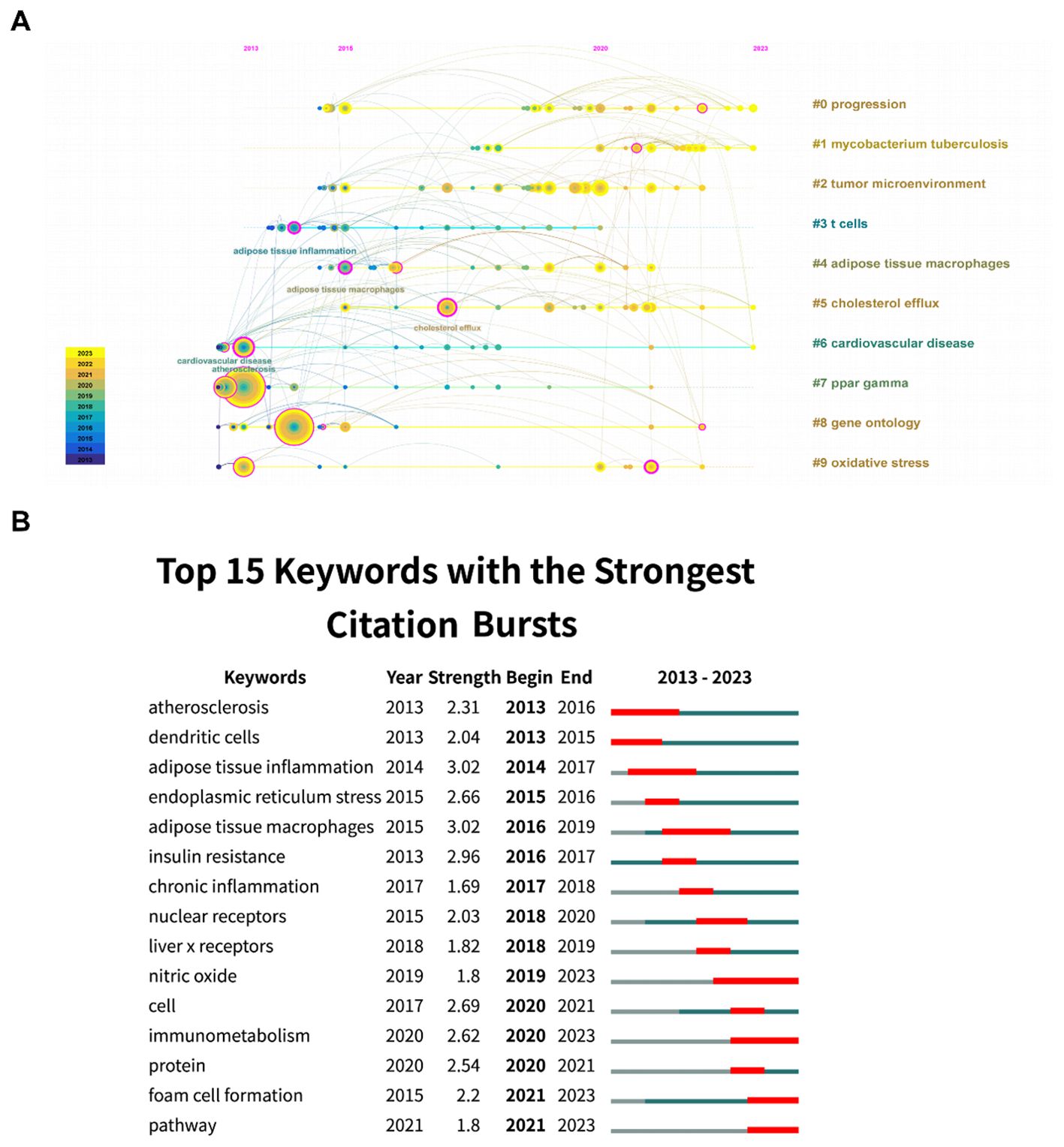
From a timeline perspective, keywords were shown in Figure 6A based on their year of appearance. We performed further analysis of the burst of keyword citations. As illustrated in Figure 6B, “atherosclerosis” got the highest strength. Besides, “nitric oxide” had experienced the most prolonged bursts lasting over four years (2019-2023). Additionally, the most recent burst keywords included “immunometabolism,” “foam cell formation,” and “pathway,” which might represent the current frontiers of research.
The effect of certain metabolites on macrophage polarization
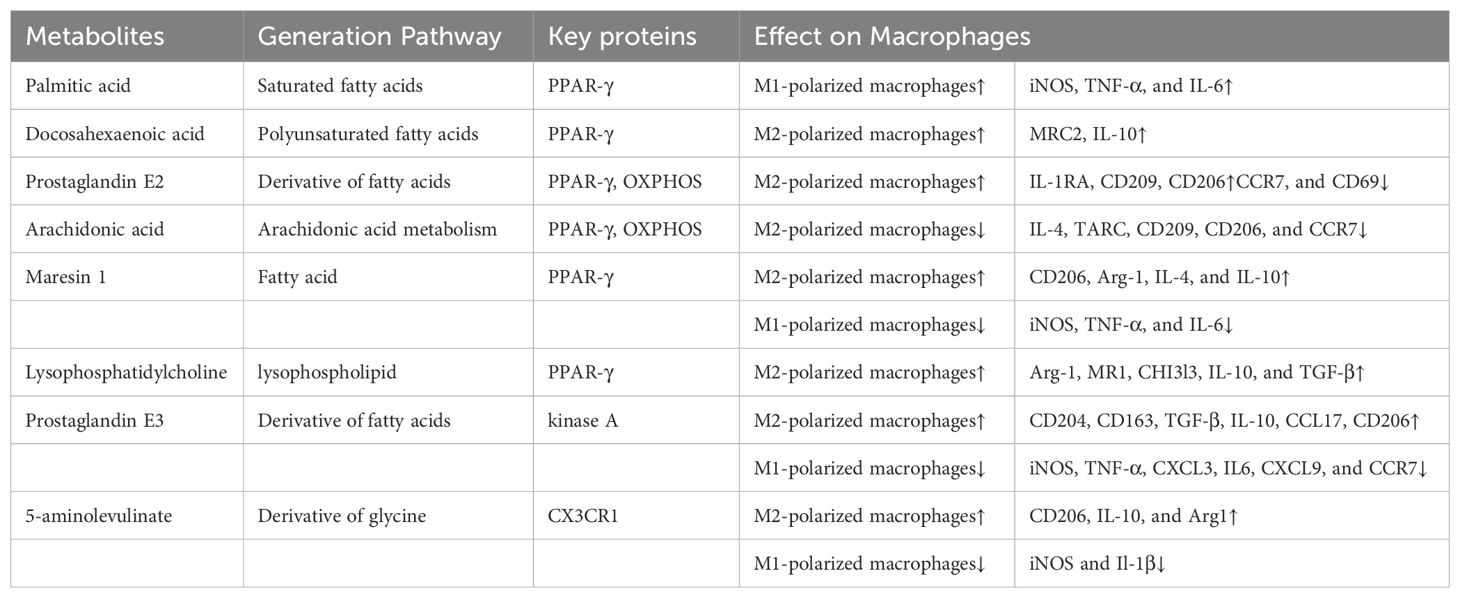
Based on the selected literature, we further analyzed the different effects of several metabolites on macrophage polarization and the important enzymes involved in this process (Table 7), in order to thoroughly elucidate the role of lipid metabolism in macrophage polarization. As illustrated in Table 7, some lipid metabolites, such as palmitic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, prostaglandin E2, arachidonic acid, maresin 1, lysophosphatidylcholine, prostaglandin E3, and 5-aminolevulinate, have a significant impact on macrophage polarization and alter the expression levels of certain proteins. Additionally, it is suggested that PPAR-γ, OXPHOS, kinase A, and CX3CR1 are important enzymes in this process. To note, PPAR-γ seems to be a key enzyme of particular interest.
Discussion
By analyzing the main areas of knowledge and emerging trends of lipid metabolism during macrophage polarization, we have gained some meaningful information. First of all, this study covered 423 publications in all. What’ more, annually increasing publications and citations of them were observed with time. In addition, not only is China the most productive country, one of the most productive organizations (Chinese Academy of Sciences) is also located in China. To note, according to the timelines of references, macrophage polarization in tumor microenvironment and atherosclerosis has lately attracted researchers’ close attention. Meanwhile, according to the timelines of keywords, macrophage polarization in mycobacterium tuberculosis and tumor microenvironment has lately attracted researchers’ close attention. Taken together, tumor microenvironment is an attractive and potential study subject in related academic fields.
However, according to the timelines of references and keywords, the lines between tumor microenvironment and other clusters are relatively lacking. Therefore, researchers focusing on tumor microenvironment are encouraged to enhance interdisciplinary collaboration. Citation burst analysis is a tool visualizing the emerging and potential research trends in a field. To investigate possible research directions for research in areas pertaining to the tumor microenvironment, citation burst analysis were employed. Citation burst analysis of keywords revealed that keywords of nuclear receptors, liver x receptors, nitric oxide, cell, immunometabolism, protein, foam cell formation, and pathway burst from 2018 to 2023. Taken together, the emerging and potential research trends are focused on study of mechanisms at the cellular level. Furthermore, in reference citation burst analysis, the most substantial citation burst publication was issued by Antonio Sica et al. in 2012, which reviewed the molecules and mechanisms underlying macrophage polarization and plasticity (21). The second citation burst review article was published by Peter J Murray et al. in Immunity in 2014 (22). Their team clarified the origin of macrophages and proposed a common definition of macrophage activation in that review. And the third citation burst publication is produced by Abhishek K Jha et al. in 2015. In this study, an integrated high-throughput transcriptional-metabolic profiling and analysis workflow was used to describe systemic alterations that occurred throughout the polarization of M1-like and M2-like murine macrophages. More detailed, glutamine catabolism and UDP-GlcNAc-associated modules are closely related with the occurrence of M2-like macrophages. Accordingly, M2-like macrophages and the chemokine CCL22 production were reduced by glutamine deprivation or N-glycosylation inhibition. Remarkably, metabolites could play a significant role in macrophage polarization. Therefore, metabolite-based unfolding of macrophage polarization at the cellular level is a potentially valuable research direction. Therefore, we summarized the metabolites generated in lipid metabolism, and illustrated its effect on macrophage polarization as below.
According to the issued publications, metabolites generated in lipid metabolism could impact on the fate of macrophage polarization (Table 7). According to investigation by Hui-Min Wu et al., certain lipids may cause macrophage polarization, which then affects hepatocyte lipid metabolism directly. In detail, their team confirmed that palmitic acid (PA), as one of the saturated fatty acids, induced M1-like macrophage polarization with upregulation of iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-6. While docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), as one of the polyunsaturated acids, induced M2-like macrophage polarization with upregulation of MRC2 and IL-10 (23). Miao Xu et al. have reported that arachidonic acid could prevent M2-like macrophage polarization. But interestingly, by elevating the relative expression of IL-1RA, CD209, and CD206 and decreasing the relative expression of CCR7, and CD69, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), a metabolite of arachidonic acid, inversely promotes M2-like macrophage polarization (24). To note, PPARγ links these two processes by regulating oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). In 2022, Dongdong Yao et al. published an article in Biomaterials advances (25). They summarized that MaR1 is strongly capable of triggering peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) activation and M2-like macrophage polarization with upregulation of CD206, Arg-1, IL-4, and IL-10. Besides, MaR1 had a strong capability and performance in depressing M1-like macrophage polarization with downregulation of iNOS, IL-6, and TNF-α. Leonardo Santos Assunção et al. have demonstrated the immunomodulatory property of lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) (26). In detail, their team summarized that lysophosphatidylcholine generated from schistosomal is strongly linked to M2-like macrophage polarization accompanied by increases in Arg-1, MR1, CHI3l3, IL-10, and TGF-β. Furthermore, the effects of the above metabolites on macrophage polarization are largely dependent on PPARγ activity.
In addition, Jing Cui et al. (27) summarized that Prostaglandin E3 (PGE3), a fatty acid derivative, may suppress M1-like macrophage polarization while promoting M2a macrophage polarization. More detailed, PGE3 could potently increase the relative expression of CD204, CD163, TGF-β, IL-10, CCL17, and CD206, while decrease the relative levels of iNOS, TNF-α, CXCL3, IL6, CXCL9, and CCR7. Guanghui Jin et al. reported that 5-aminolevulinate (5-ALA) triggered M2-like macrophage polarization and upregulated CD206, IL-10, and Arg1. Simultaneously, it suppressed M1-like macrophage polarization and downregulated iNOS and Il-1β (28). Notably, CX3CR1 is the key enzyme in this process.
Studies mentioned above suggested the potential value of lipid metabolism and macrophage polarization in cancer research, especially tumor microenvironment. To note, PPAR-γ seemed to be a potential target. Accordingly, a recent publication by Vikash Kansal et al. (29) focused on the effect of statin drugs on immune checkpoint blockade in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). In this study, stains were experimentally shown to enhance responses to immunotherapies for HNSCC, which encourages further investigation into the application of medications that target lipid metabolism in combination with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and other clinical treatment in modern cancer management.
What’ more, specific representative nodes of each cluster were labeled in the analysis of keywords. Surprisingly, tumor microenvironment was the label given to cluster #2, which included nodes recognized as survival and tumor-associated macrophages. To note, survival data is essential for studying tumors. Therefore, it is worthwhile to investigate not just lipid metabolism and macrophage polarization in the tumor microenvironment, but also survival in combination with these factors since it may lead to new discoveries. Additionally, there is a dearth of research in this area. According to Jake et al., the plasma metabolome was considerably changed by acute-on-chronic liver failure, specifically in the areas of energy metabolism, oxidative stress pathways, steroid hormones, and membrane lipid metabolism. Several metabolites were substantially linked to pre-ACLF in the non-ACLF group and/or 90-day mortality in the ACLF group. Furthermore, they developed assays for HBV-related ACLF with greater accuracy than current techniques, based on novel metabolite biomarkers (30). The esteemed journal Journal of Hepatology published this finding. Taken together, combining lipid and macrophage metabolism might be useful for tumor clinical research.
Based on bibliometrics analysis, we have provided a relative comprehensive summary of lipid metabolism in macrophage polarization, and we look forward to further trends in this field. However, there are still several limitations in our study due to the nature of bibliometrics. To begin, despite our effects to included publications from WoSCC, we have missed some articles that are not included in WoSCC. Second, bibliometrics analysis was carried out using natural language processing and machine learning, which may cause some degree of bias. Lastly, we focused on only one specific area in this study, which may have led to a lack of a macroscopic perspective on the overall trend of research on macrophage polarization.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
CY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The research was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Project for the key discipline of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2017-XK-A09), the Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2023ZR102, No. 2024ZL382), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang province (No. LQ22H290002, No. LY21H290001), and Medical and Health Platform Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2022RC109).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1532862/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | Top 20 productive authors.
References
1. Gao H, Huang FY, and Wang ZP. Research trends of macrophage polarization: A bibliometric analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). (2018) 131:2968–75. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.247215
2. Monaco C and Dib L. Breaking the macrophage code in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 119:1622–3. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad072
3. Hegarty LM, Jones GR, and Bain CC. Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 20:538–53. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00769-0
4. Zhang Q and Sioud M. Tumor-associated macrophage subsets: shaping polarization and targeting. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:7493. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087493
5. Gordon S and Martinez FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. (2010) 32:593–604. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.007
6. Colin S, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, and Staels B. Macrophage phenotypes in atherosclerosis. Immunol Rev. (2014) 262:153–66. doi: 10.1111/imr.2014.262.issue-1
7. Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, and Locati M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. (2004) 25:677–86. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2004.09.015
8. Verreck FA, de Boer T, Langenberg DM, Hoeve MA, Kramer M, Vaisberg E, et al. Human IL-23-producing type 1 macrophages promote but IL-10-producing type 2 macrophages subvert immunity to (myco)bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2004) 101:4560–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400983101
9. Jetten N, Verbruggen S, Gijbels MJ, Post MJ, De Winther MP, and Donners MM. Anti-inflammatory M2, but not pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo. Angiogenesis. (2014) 17:109–18. doi: 10.1007/s10456-013-9381-6
10. Lee CG, Homer RJ, Zhu Z, Lanone S, Wang X, Koteliansky V, et al. Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J Exp Med. (2001) 194:809–21. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.6.809
11. Mosser DM. The many faces of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol. (2003) 73:209–12. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0602325
12. Pannellini T, Iezzi M, Carlo ED, Eleuterio E, Coletti A, Modesti A, et al. The expression of LEC/CCL16, a powerful inflammatory chemokine, is upregulated in ulcerative colitis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. (2004) 17:171–80. doi: 10.1177/039463200401700209
13. Vassiliou E and Farias-Pereira R. Impact of lipid metabolism on macrophage polarization: implications for inflammation and tumor immunity. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:12032. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512032
14. Chen C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2004) 101 Suppl 1:5303–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307513100
15. Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S, and Tseng H. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2012) 12:593–608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
16. Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:6425–40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v233.9
17. Jha AK, Huang SC, Sergushichev A, Lampropoulou V, Ivanova Y, Loginicheva E, et al. Network integration of parallel metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity. (2015) 42:419–30. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.02.005
18. Tabas I and Bornfeldt KE. Macrophage phenotype and function in different stages of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118:653–67. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306256
19. Su P, Wang Q, Bi E, Ma X, Liu L, Yang M, et al. Enhanced lipid accumulation and metabolism are required for the differentiation and activation of tumor-associated macrophages. Cancer Res. (2020) 80:1438–50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2994
20. Viola A, Munari F, Sánchez-Rodríguez R, Scolaro T, and Castegna A. The metabolic signature of macrophage responses. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1462. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01462
21. Sica A and Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:787–95. doi: 10.1172/JCI59643
22. Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA, Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. (2014) 41:14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008
23. Wu HM, Ni XX, Xu QY, Wang Q, Li XY, and Hua J. Regulation of lipid-induced macrophage polarization through modulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activity affects hepatic lipid metabolism via a Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 35:1998–2008. doi: 10.1111/jgh.v35.11
24. Xu M, Wang X, Li Y, Geng X, Jia X, Zhang L, et al. Arachidonic acid metabolism controls macrophage alternative activation through regulating oxidative phosphorylation in PPARγ Dependent manner. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:618501. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.618501
25. Yao D, Zou Y, and Lv Y. Maresin 1 enhances osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells by modulating macrophage peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ-mediated inflammation resolution. Biomater Adv. (2022) 141:213116. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.213116
26. Assuncão LS, Magalhães KG, Carneiro AB, Molinaro R, Almeida PE, Atella GC, et al. Schistosomal-derived lysophosphatidylcholine triggers M2 polarization of macrophages through PPARγ dependent mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. (2017) 1862:246–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.11.006
27. Cui J, Shan K, Yang Q, Qi Y, Qu H, Li J, et al. Prostaglandin E(3) attenuates macrophage-associated inflammation and prostate tumour growth by modulating polarization. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:5586–601. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.v25.12
28. Liu J, Wei Y, Jia W, Can C, Wang R, Yang X, et al. Chenodeoxycholic acid suppresses AML progression through promoting lipid peroxidation via ROS/p38 MAPK/DGAT1 pathway and inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization. Redox Biol. (2022) 56:102452. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102452
29. Kansal V, Burnham AJ, Kinney BL, Saba NF, Paulos C, Lesinski GB, et al. Statin drugs enhance responses to immune checkpoint blockade in head and neck cancer models. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e005940. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005940
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, macrophage polarization, lipid metabolism, tumor microenvironment, atherosclerosis
Citation: Ye C, Ru X and Guo Y (2025) Scientometric analysis of lipid metabolism in macrophage polarization: 2013-2023. Front. Oncol. 15:1532862. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1532862
Received: 03 February 2025; Accepted: 30 May 2025;
Published: 19 June 2025.
Edited by:
Miguel Martin-Perez, University of Barcelona, SpainReviewed by:
Ning Yu, Shanghai Innovation Center of TCM Health Service, ChinaPeng Chen, Zhejiang University, China
Yifei Zhu, Fudan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Ye, Ru and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Guo, Z3VveW9uZzEwNDdAemNtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Chenxiao Ye
Chenxiao Ye Xiaosong Ru
Xiaosong Ru Yong Guo
Yong Guo