- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
- 2Product Development Department, MedMind Technology Co, Ltd., Beijing, China
- 3Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China
Background: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in automatic image segmentation systems offers a novel approach to evaluating the clinical target volume (CTV) in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients. Utilizing imaging recurrence data, this study applies a recursive feature elimination algorithm to model and predict patient prognoses, aiming to enhance clinical guidance and prediction accuracy.
Materials and Methods: This research analyzed data from SCLC patients who received curative radiotherapy from January 1, 2010, to December 30, 2021, and had comprehensive follow-up records including pre- and post-treatment imaging. An AI-driven image segmentation system segmented the initial CTV, evaluating 110 clinical parameters. The recursive feature elimination method selected pertinent features, and a random forest-based recursive prediction model was developed to establish a clinically viable recurrence prediction model.
Results: 1. Local Control Analysis: A study of 180 patients, with a median follow-up duration of 36 months, revealed that 94 experienced recurrences, while 86 did not. Factors influencing local control rates included gender (male), age (>60 years), T stage, smoking index, and tumor size. Notably, tumor size (≥ 5cm) emerged as an independent factor significantly impacting local control rates, with a Hazard Ratio (HR) of 1.635 (95% CI: 1.055-2.536, p=0.028). 2. Recurrence Analysis: Tumor size (≥ 5cm) was also closely linked to patient local control rates, with a 3-year Local Control Rate Failure (LCRF) contrasting sharply between larger tumors (61.1%) and smaller tumors (86.7%, p=0.004). Upon analyzing recurrence patterns among 94 patients, a total of 170 instances were examined. Recurrence was most prevalent in regions 10R, 10L, 4R, and 7, accounting for 67.65% (115/170) of cases, while regions 2L and 3P showed no recurrences. The initial region of the primary tumor or metastatic lymph nodes was identified as a critical recurrence area, with a 100% recurrence rate in patients whose initial tumor region included 10 specific regions. The recurrence rates for initial tumor regions involving 4R, 7, 11R, and 11L ranged between 41.6% and 45.5%. 3. Development of a recurrence prediction model: utilizing an AI-powered automatic image segmentation system, multidimensional partition parameters, including 110 clinical variables, were analyzed. The recursive feature elimination method facilitated efficient feature selection. From this, a recurrence prediction model for small cell lung cancer was developed using a random forest algorithm, achieving a clinically significant accuracy rate of 77%. This model provides a reliable basis for enhancing the clinical application and decision-making process for medical practitioners.
Conclusion: The utilization of AI-based automatic image segmentation system for delineating the initial CTV has proven pivotal. Analysis and modeling of recurrent images reveal that the initial GTV and GTVnd are critical regions for recurrence. Leveraging partition parameter and variable information, we constructed a clinically viable recurrence prediction model. This model significantly aids in guiding the precise clinical targeting of treatment areas, demonstrating the potential of AI to enhance patient management and treatment outcomes in small cell lung cancer.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer is the second most common tumor worldwide and accounts for approximately 18.0% of cancer-related mortality (1). Treatment of lung cancer includes a combination of surgery, radiotherapy, and systemic therapy (chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted agents). Among these therapeutic modalities, radiotherapy is the only one that is indicated at all stages of the disease, in all pathologic types and physical states (2, 3).
The local recurrence rate of small-cell lung cancer is still high and seriously affects the survival of patients, especially recurrence within the radiotherapy field. Related studies on the prediction of recurrence models are mostly in clinical and imaging indexes, etc., and the models for evaluation and prediction are less reproducible and less accurate.
In recent years, with the great development of computer application in radiotherapy (RT), we can collect medical image data, clinical information, treatment records, etc. of patients with small cell lung cancer. Image segmentation is performed using deep learning techniques, such as convolutional neural network (CNN) (4–7). Train a network to automatically mark tumor tissue and normal tissue in the image. Features related to recurrence are extracted from image data. This may include the size, shape, location and other information of the tumor. These characteristics will help to analyze patterns associated with recurrence. Recursive feature elimination (RFE) algorithm is used to select features that are important for predicting recurrence, so as to improve the generalization ability of the model and help reduce over fitting. Through cross validation and other methods to evaluate the performance of the model, optimize the model parameters, and predict the possibility of its recurrence. This can provide doctors with auxiliary information to help them make more accurate clinical decisions.
Our previous research has confirmed that it can be applied to the delineation of clinical target volume (CTV) and organ at risk (OAR) of lung cancer, as well as to the application of artificial intelligence in automatic image segmentation system (8). Based on this, our research aims to evaluate, analyze, and model clinical targets in different lymphatic drainage areas based on artificial intelligence, It can also predict the prognosis and play a role in clinical guidance and prediction.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patients’ data and information
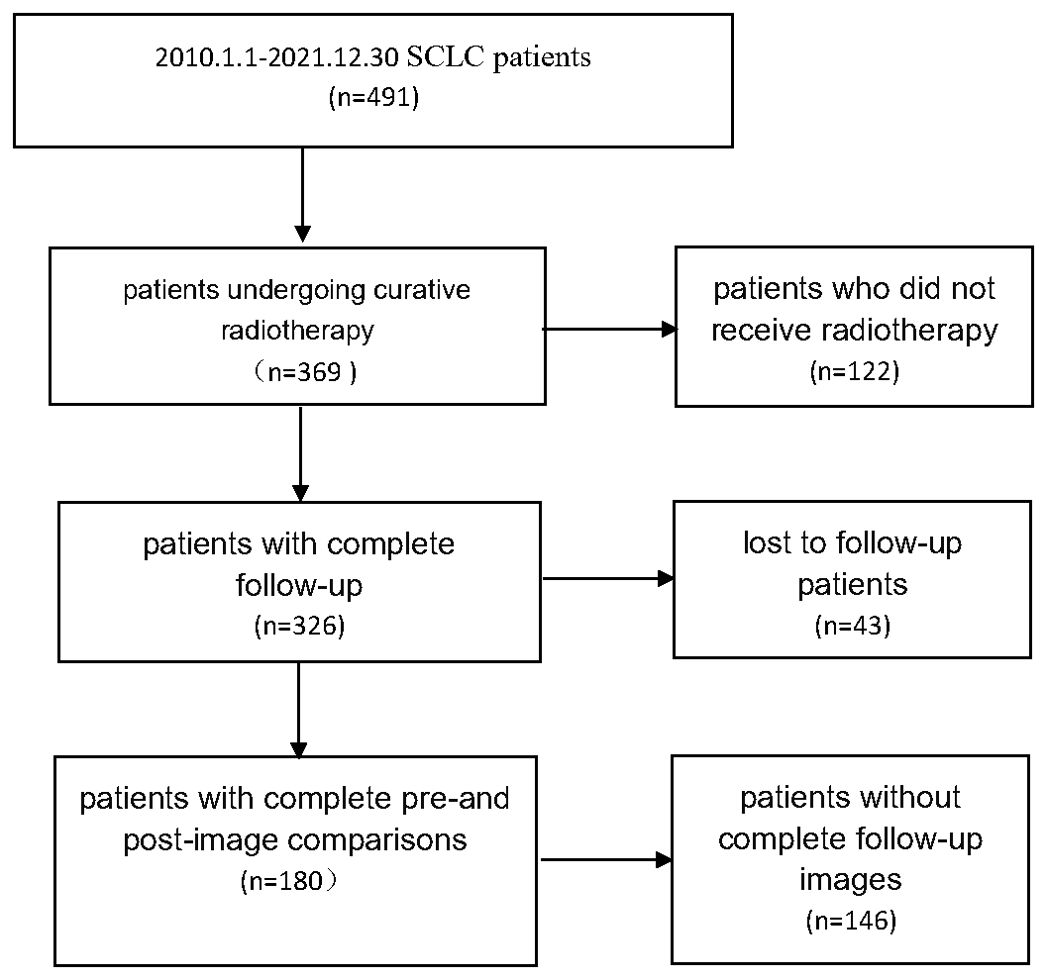
Small cell lung cancer patients from 2010.1.1 to 2021.12.30 were collected, and 180 patients who underwent radical radiotherapy with complete follow-up records and complete before and after image comparisons were collected. The details are shown in Figure 1.
A total of 180 patients were enrolled in the group, all of whom had complete imaging evaluation before treatment, compared images of the location of the recurrent focus, collected 16676 CT slices for localization, delineated the mediastinum, hilar lymph nodes and GTVnd layer by layer, and corrected the delineated CTV. All patients were scanned with Philips Brilliance Big Bore CT scanner before receiving radiotherapy, and the protocol of digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM) was followed. The matrix size of CT image is 512 × 512, the pixel spacing is 1.1543mm × 1.1543mm, and the layer thickness is 5mm. Keep patient information confidential during data collection and processing.
2.2 Perform regional segmentation of the mediastinal lymphatic drainage area
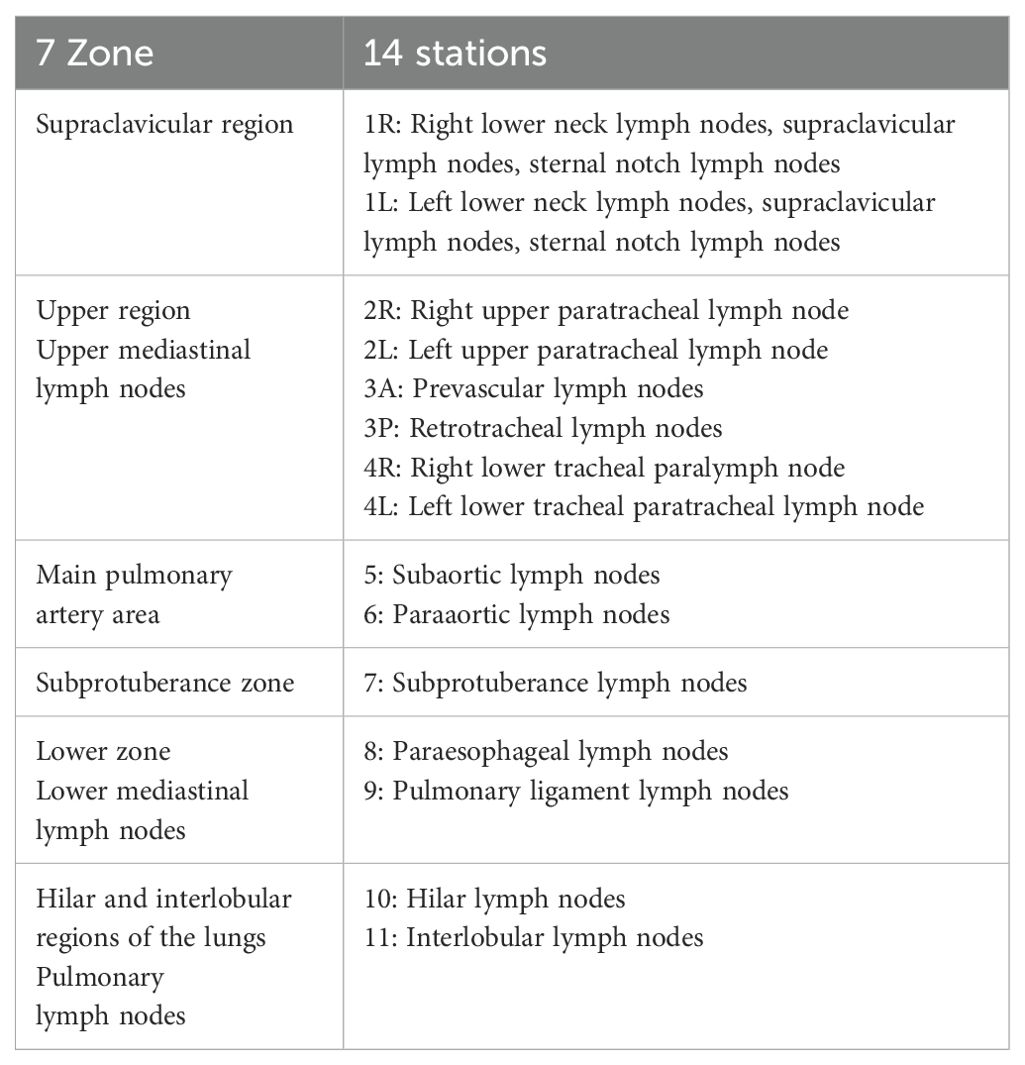
This study divides hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes into 14 stations according to the definition of boundary of mediastinal lymph node division by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) and the definition of lymph node division by the UICC and AJCC. The specific partitions are shown in Appendix 1. The clinical positioning CT images of 180 patients are divided into regions.
2.3 Follow-up recurrence information, search for predictive models
For the recurrence pattern and specific recurrence location of follow-up patients, the initial CTV of patients is divided into regions, and a recurrence prediction model based on partition information is established.
2.3.1 Automatic partition of CTV based on artificial intelligence
The previously published DiUnet (see Figure 2) is used for automatic CTV partitioning. This model uses the region of GTV as prior knowledge to fuse into the U-net model, uses GTV and CT images as dual channels for coding, extracts the image features of the two channels, and then carries out feature fusion to improve the accuracy of boundary recognition near GTV.
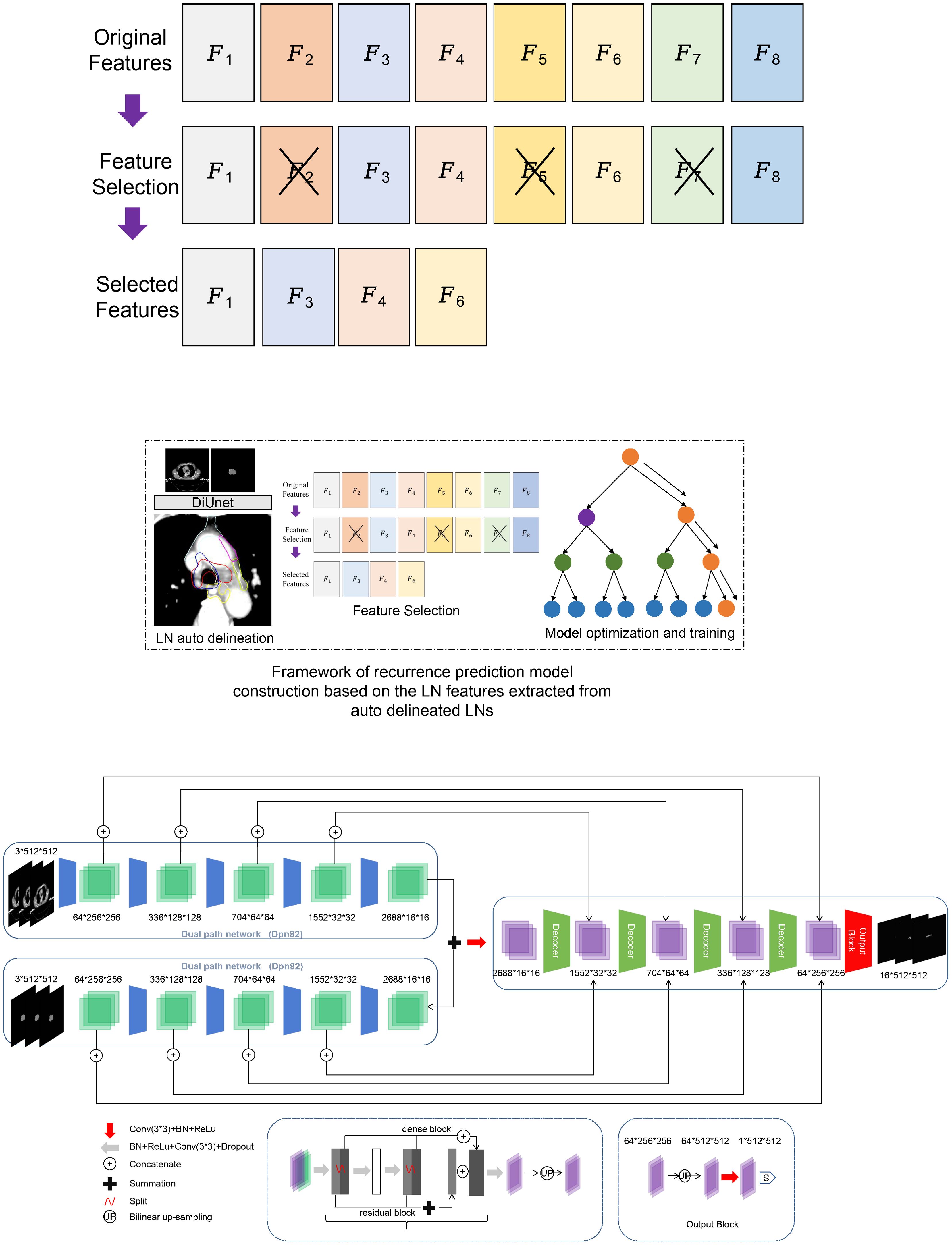
Figure 2. Framework of recurrence prediction model construction based on the LN features extracted from auto delineated LNs. (A) recurrence prediction model construction, (B) Framework of DiUnet.
2.3.2 Clinical parameter/variable information
After the 14 station area is automatically divided (See Table 1), the partition parameters can be calculated, and the ideaCTV is defined as the union area of all partitions violated by the CTV,
The formula for each partition parameter is:
Volume ratio of CTV in LN
CTV volume ratio in ideaCTV
Volume ratio of GTV in LN
Volume proportion of GTV in ideaCTV
Volume ratio of CTV-GTV in LN
Volume ratio of CTV GTV in ideaCTV
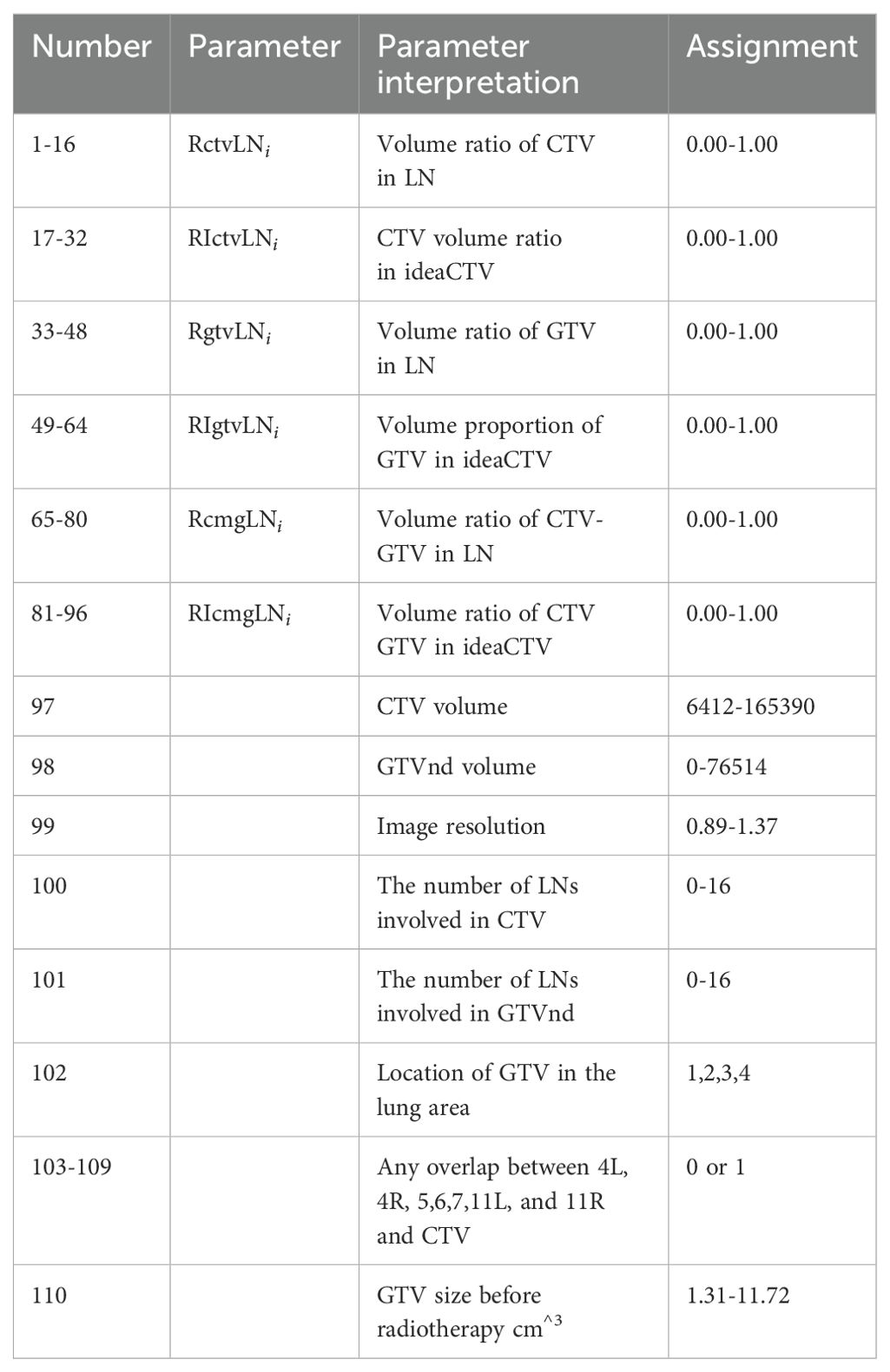
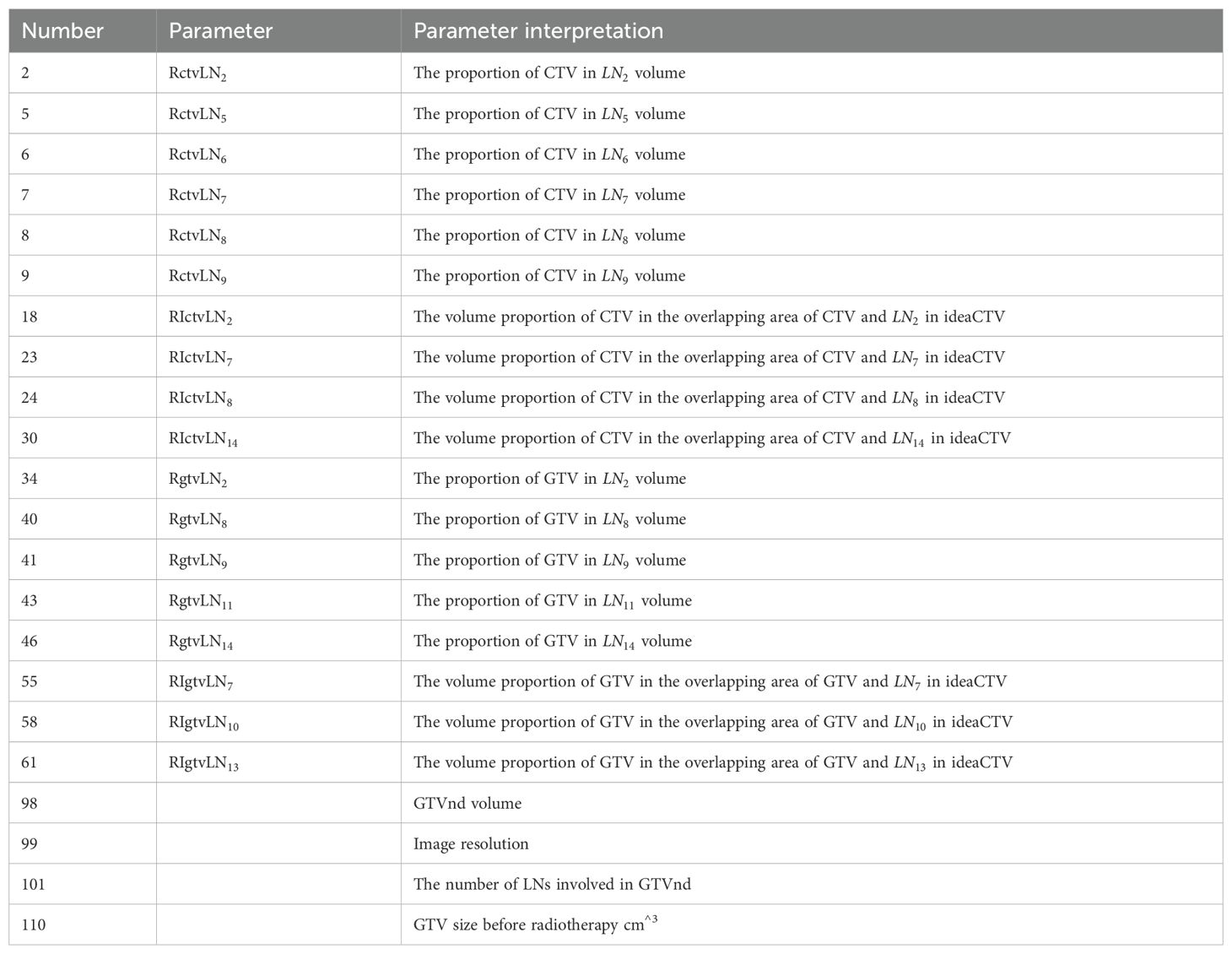
There are 110 partition parameter/variable information (See Table 2), including voxel resolution, CTV image volume, CTV volume proportion in LN, GTV size before radiotherapy, GTV image volume, GTV volume proportion in LN, lung area location and lymph drainage area coverage.
2.3.3 Model building: standardize the extracted feature parameters and reduce the dimension of features
Firstly, the correlation coefficient between each feature and other features is calculated, and redundant features are removed according to the correlation coefficient; To mitigate overfitting, the dataset was divided into training (80%) and validation (20%) subsets. The recursive feature elimination (RFE) process incorporated 5-fold cross-validation during feature selection to prioritize generalizable features. The random forest algorithm’s inherent bagging mechanism further reduces overfitting by aggregating predictions from multiple decision trees. Hyperparameters, including tree depth and the number of estimators, were optimized using grid search to balance model complexity and performance. Then, a new feature set is constructed with the remaining features, and the next round of training is carried out until all features are traversed. After feature screening, we reserved 27 feature dimensions.
The random forest method was used to build a prediction model for lung cancer recurrence (9). Random Forest Classifier (RF) is an algorithm that integrates multiple trees using integrated learning theory. Its basic unit is the decision tree. After random sampling of the original training data, use each decision tree in the forest to judge the unlabeled samples, and then apply the majority voting results of all decision trees to predict the unlabeled sample categories. This method has a relatively low trend of over fitting, and the model is as follows:
Among them, denotes the random forest pair sample . The predicted value of the Indicates that there are a total of Tree. Indicates that the first the training set used for the tree, the Indicates that the first tree learner.
3 Results
3.1 Basic patient information
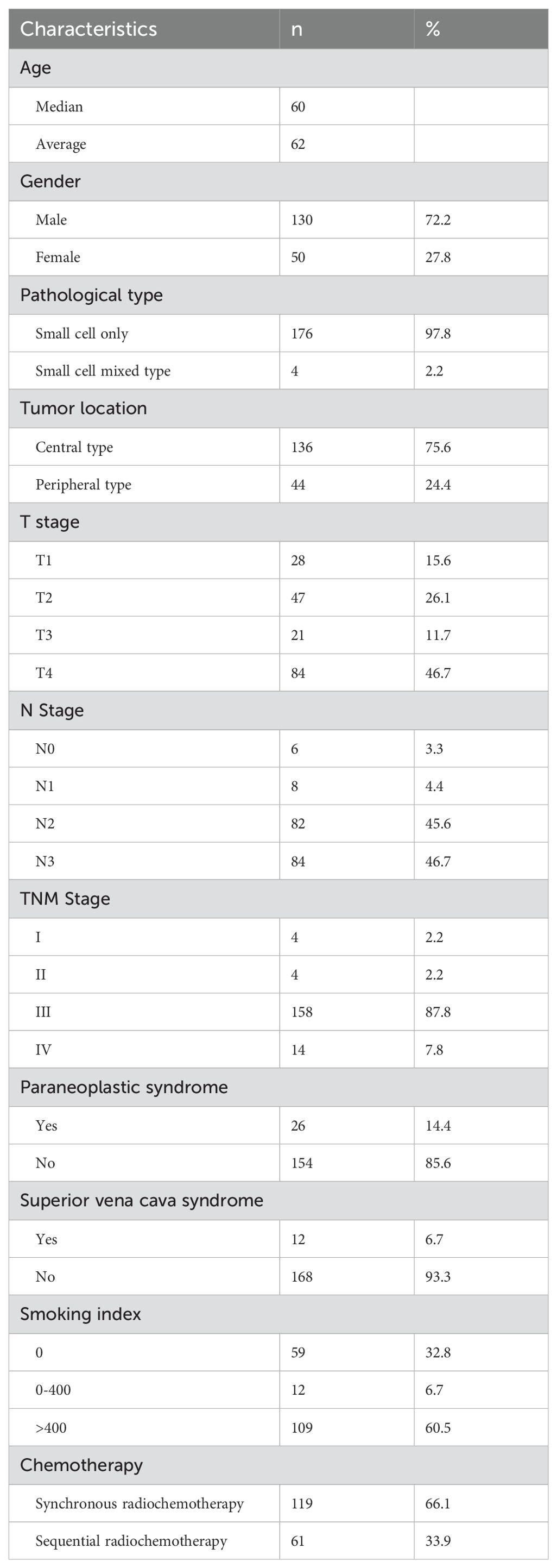
180 patients, the median age is 60 years old, 133 male patients (73.8%), 47 female patients (26.1%), 3 patients (1.7%) with complex pathological type, respectively, large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, atypical carcinoid, adenocarcinoma, 142 central type tumors (78.9%), 38 peripheral type tumors (21.1%), 155 patients (86.1%), 28 patients with paraneoplastic syndrome, Including 12 cases of SIADH, 3 cases of LAMBERT, 5 cases of ectopic ACTH, 8 cases of anti GABA2 receptor encephalitis, 119 cases (66.1%) of patients received synchronous radiotherapy and chemotherapy, 6MV X-ray radiotherapy, intensity modulated radiotherapy, 60Gy/30f, 2Gy/f, conventional segmentation mode, see Table 3 for details.
3.2 Summary of recurrence
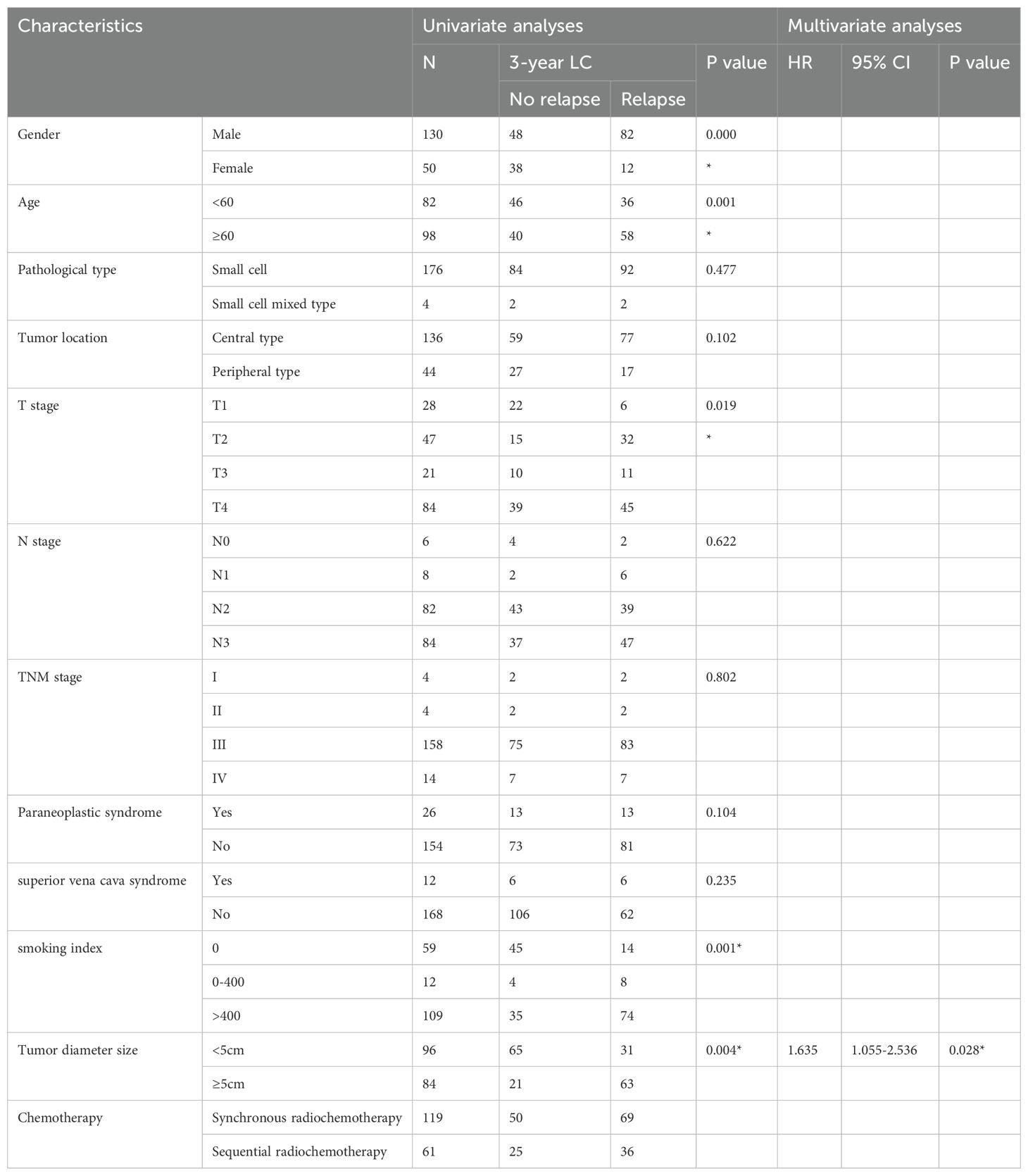
180 patients, median follow-up time 36 months, 94 patients with recurrence, 86 patients without recurrence, statistical clinical indicators include: whether the age is over 60, gender, whether other pathological types are mixed, tumor location (central type, peripheral type), T stage, N stage, clinical stage, whether there is paraneoplastic syndrome, smoking index The results showed that gender, age over 60, T stage, smoking index, and tumor size were related to the local control rate of patients. The tumor size was an independent factor related to the local control rate, HR 1.635 (95% CI 1.055-2.536), p=0.028. See Table 4 for details.
3.2.1 Relationship between tumor size and recurrence
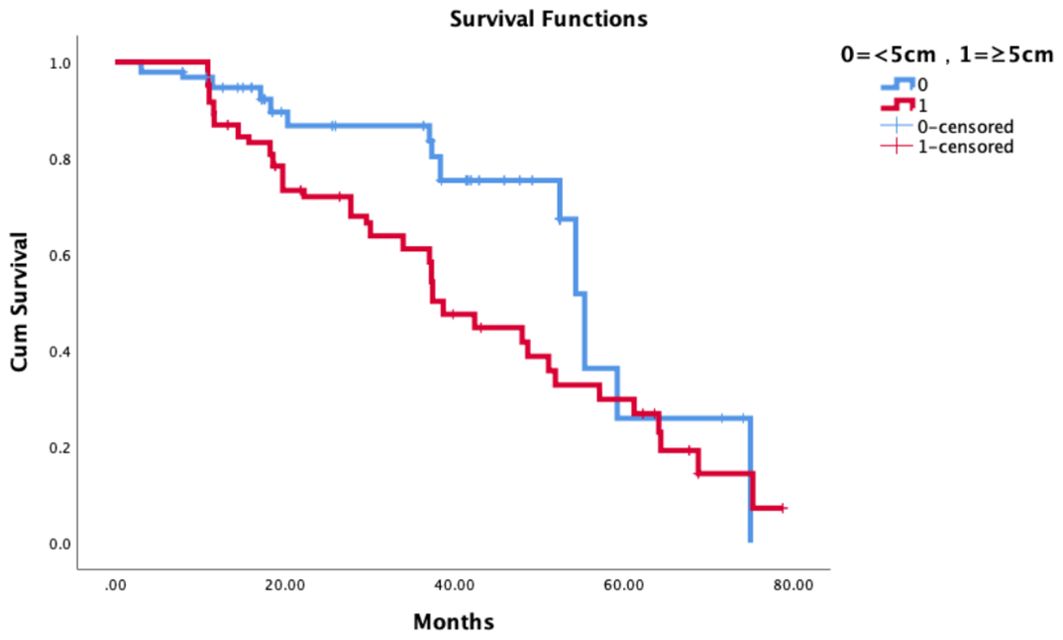
The median follow-up was 36 months. The tumor size was related to the local control rate of patients and was an independent correlation factor of the local control rate. The 3-year LCRF was 86.7% vs 61.1%, p=0.004. See Figure 3 for details.
3.2.2 Tumor location in relation to recurrence
Further, 94 patients with recurrence were divided according to regions, and a total of 170 cases were counted. The recurrence in 10R, 10L, 4R and 7 areas is the main, accounting for 67.65% (115/170), including 2 cases in 1L area, 3 cases in 1R area, 8 cases in 2R area, 3 cases in 3A area, 3 cases in 4L area, 24 cases in 4R area, 3 cases in 5 areas, 10 cases in 6 areas, 18 cases in 7 areas, 2 cases in 8 areas, 23 cases in 10L area, 50 cases in 10R area, 10 cases in 11L area, 11 cases in 11R area, and no recurrence in 2L area and 3P area. See Table 5 for details.
The initial area of the primary focus or metastatic lymph node is the key area of recurrence, mainly 10R and 10L. Patients with the initial tumor area involving 10 areas all experienced recurrence (100%). Patients with the initial tumor area involving 4R, 7, 11R and 11L also had a certain recurrence rate, 41.6% - 45.5%. See Appendix 2 for details.
The automatic image segmentation system of human intelligence is applied to carry out partition statistics on the initial clinical CTV of patients, and calculate the proportion range of the actual sketched/standard area of the recurrence area. The results show that,
3.3 Recurrence pattern searching
According to the multidimensional parameters in the machine learning prediction model, including 110 clinical parameters/variables information, the recurrence prediction model of small cell carcinoma of the lung was constructed based on the random forest machine learning method, and the exploration of the establishment of a clinically usable recurrence prediction model is detailed in Table 6.
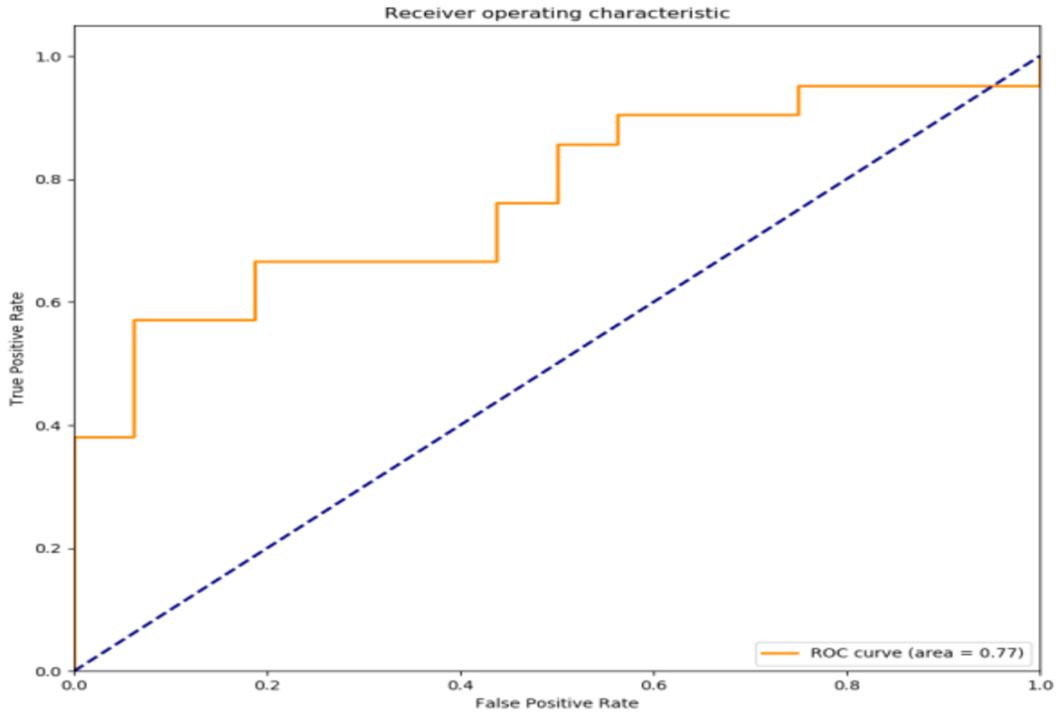
The filtered characteristics are shown in the following table. The ROC curve of the model built based on the filtered features is shown in Figure 4. The AUC value of this model is 0.77 in Table 7. The DiUnet segmentation achieved high accuracy across all lymph node regions, with DSC >0.85 for stations 4R, 7, and 10R, which are critical for recurrence prediction. Lower DSC (0.78) was observed in smaller regions (e.g., 3P), likely due to limited anatomical visibility on CT.
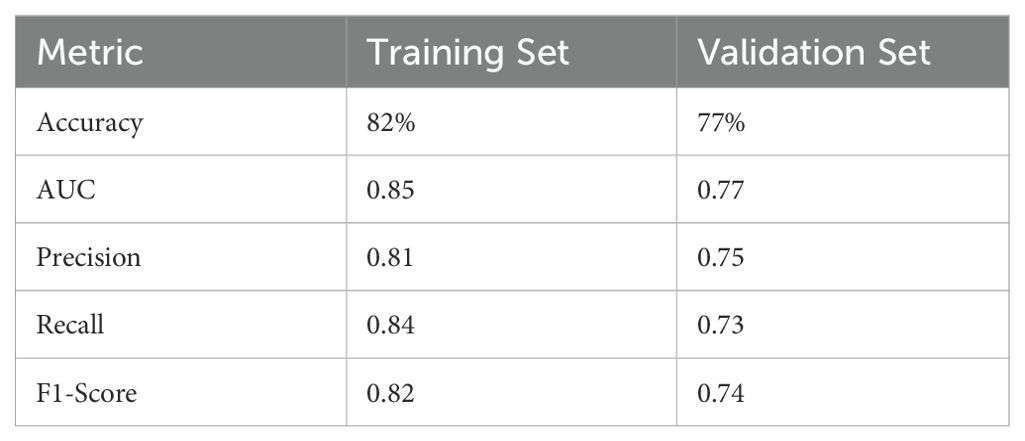
Table 7. Performance metrics of the random forest model on training and validation sets for SCLC recurrence prediction.
4 Discussion
Lung cancer usually involves multiple treatments, and 77% of lung cancer patients have evidence-based indications for radiotherapy (10–13). The use of radiotherapy can improve the local control rate and overall survival rate of lung cancer (14–16). The success of radiotherapy depends on the accurate irradiation of tumor targets. How to accurately delineate the clinical target volume (CTV) is a crucial step for the best effect of radiotherapy (17, 18). In clinical work, the quality of manual delineation of clinical target areas depends on the prior knowledge and clinical experience of radiation oncologists. However, images drawn by different doctors or the same doctor at different times will be different. However, clinical target delineation based on automatic segmentation technology of artificial intelligence can provide efficient and accurate delineation results, which have been confirmed in our previous research (8, 19). Based on our previous research, we can explore the integrity and accuracy of the involved lymph node region, and its impact on survival prognosis, local recurrence rate and lymph node failure rate. Based on this, our research uses the automatic image segmentation system of artificial intelligence to segment the clinical initial CTV region, analyze the recurrence image, and establish a clinically available recurrence prediction model using a random forest classifier, which plays a certain role in guiding the clinical application of actual CTV delineation.
At present, the research on clinical targets based on artificial intelligence and the method based on convolutional neural network (CNN) have been successfully applied to the delineation of dangerous organs and clinical targets of lung cancer. The published data related to deep learning mainly focus on the segmentation of postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) (19), dangerous organs (OAR) (20–23), and primary lung tumors (24), but there is no relevant research to delineate and evaluate the mediastinal lymph node region. Based on this, this study uses an automatic image segmentation system of human intelligence to perform the partition statistics of patients’ initial clinical CTV, The application includes clinical parameter/variable information, and recursive feature elimination method is used to select other features. A recursive prediction model with random forest is constructed by using the selected features.
In this study, 94 patients with recurrence among 180 patients were followed up for a median of 36 months. AI-driven automatic image segmentation system was used to partition the initial clinical CTV of patients. The results showed that patients in the area where the initial tumor was located involved in 10 areas had recurrence, and patients in the area where the initial tumor was located involved in 4R, 7, 11R, 11L also had a recurrence rate of 41.6% - 45.5%, The area where the primary focus or metastatic lymph node is initially located is the key area of recurrence. Therefore, the application includes 110 clinical parameter/variable information, and the recursive feature elimination method is used to select other features. The selected features are used to build a lung cancer recurrence prediction model based on the random forest classifier. The model demonstrates robust clinical feasibility for recurrence prediction.
This study is the first one to apply a human-intelligent automatic image segmentation system to accurately define and automatically segment the boundaries of mediastinal and hilar lymph node regions for clinical recurrence prediction modeling in radiation therapy for lung cancer. This study can provide valuable guidance for clinicians. This includes the possibility of integrating predictive modeling with actual clinical decision making. This may require more validation and practice, but it is expected to provide a more personalized treatment approach in the future.
This study not only demonstrates the clinical value of artificial intelligence (AI) in contouring the clinical target volume (CTV) and analyzing recurrence patterns in small cell lung cancer, but also provides an innovative teaching tool for medical education. The automatic segmentation model and recurrence prediction model based on DiUNet can serve as a teaching platform that combines theory and practice. This helps young doctors quickly master image segmentation techniques and recurrence pattern analysis, shortening the learning curve. By using the AI system, students can adjust and optimize segmentation results in practical operations. They can also perform case analyses using recurrence case data to develop clinical thinking skills. Moreover, the multi-disciplinary team cooperation model offers opportunities for collaborative learning in education. In the future, this model is expected to be extended to a broader field of medical education. It will provide support for training medical professionals with innovative and practical skills. There are some limitations in this study, firstly, this study is a single-center data with a small data sample size. This possible bias in the process of data collection and analysis can be followed by further expansion of the validation of larger samples, integration with data from other medical centers, and improvement of prediction models. In addition, observer bias from oncologist evaluation was unavoidable in this study. We believe that this method should be extended to other thoracic cancers involving the mediastinal lymphatic drainage region, such as esophageal cancer.
The possible aspects of patient privacy, data use and safety in this study were reviewed by the Ethics Committee of Peking Union Medical College Hospital.
The model’s AUC of 0.77 on the validation set underscores its generalizability, though future multi-center studies are needed to confirm robustness. The inclusion of segmentation metrics (DSC, HD) ensures the reliability of feature extraction, a cornerstone for predictive accuracy in AI-driven oncology models.
5 Conclusion
The automatic image segmentation system of artificial intelligence is used to segment the initial CTV of small cell lung cancer patients. Based on the analysis and modeling of recurrent images, the results show that the initial tumor GTV and the initial metastatic lymph node GTVnd are the key areas of recurrence. According to clinical parameters/variable information, the use of random forest classifier can establish a clinically available recurrence prediction model, it plays a guiding role in the clinical application of CTV delineation, and has certain clinical practicability.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by PUMCH Institutional Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because Retrospective studies, from the design of the study to the retrospective analysis, are not designed to harm patients or affect treatment decisions.
Author contributions
JieS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft. JinS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HG: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QC: Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ML: Resources, Writing – review & editing. KH: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. FZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. CAMS innovation fund for medical sciences(CIFMS)2022-12M-C&T-B-018.National high level hospital clinical research funding 2022-PUMCH-A-102.
Conflict of interest
Authors SW and QC were employed by the company MedMind Technology Co, Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Shafiq J, Hanna TP, Vinod SK, Delaney GP, Barton MB. A population-based model of local control and survival benefit of radiotherapy for lung cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). (2016) 28:627–38. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2016.05.006
3. Delaney GP, Barton MB. Evidence-based estimates of the demand for radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). (2015) 27:70–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2014.10.005
4. Xiang L, Wang Q, Nie D, Zhang L, Jin X, Qiao Y, et al. Deep embedding convolutional neural network for synthesizing CT image from T1-Weighted MR image. Med Image Anal. (2018) 47:31–44. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2018.03.011
5. Feng M, Valdes G, Dixit N, Solberg TD. Machine learning in radiation oncology: opportunities, requirements, and needs. Front Oncol. (2018) 8:110. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00110
6. Huang X, Wang J, Tang F, Zhong T, Zhang Y. Metal artifact reduction on cervical CT images by deep residual learning. BioMed Eng Online. (2018) 17:175. doi: 10.1186/s12938-018-0609-y
7. Park S, Lee SJ, Weiss E, Motai Y. Intra- and inter-fractional variation prediction of lung tumors using fuzzy deep learning. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. (2016) 4:4300112. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2016.2516005
8. Shen J, Zhang F, Di M, Shen J, Wang S, Chen Q, et al. Clinical target volume automatic segmentation based on lymph node stations for lung cancer with bulky lump lymph nodes. Thorac Cancer. (2022) 13:2897–903. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14638
9. Rahman R, Dhruba SR, Ghosh S, Pal R. Functional random forest with applications in dose-response predictions. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:1628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38231-w
10. Brown S, Banfill K, Aznar MC, Whitehurst P, Faivre Finn C. The evolving role of radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Radiol. (2019) 92:20190524. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20190524
11. MacManus M, Everitt S, Hicks RJ. The evolving role of molecular imaging in non-small cell lung cancer radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. (2015) 25:133–42. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2014.12.001
12. Baker S, Dahele M, Lagerwaard FJ, Senan S. A critical review of recent developments in radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol. (2016) 11:115. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0693-8
13. Zhu M, Li S, Yuan L, Liu S, Li J, Zhang D, et al. Correction: The high-risk features and effect of postoperative radiotherapy on survival for patients with surgically treated stage IIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol. (2024) 22:6. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03263-8
14. Sanuki N, Takeda A, Eriguchi T, Tsurugai Y, Tateishi Y, Kibe Y, et al. Local control correlates with overall survival in radiotherapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review. Radiother Oncol. (2023) 183:109664. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2023.109664
15. Zhao J, Wu L, Hu C, Bi N, Wang L. Radiotherapy fraction in limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the modern era: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 8006 reconstructed individual patient data. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 15(1):277. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010277
16. Hamaji M. Surgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: prospective clinical trials of the past, the present, and the future. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2020) 68:692–6. doi: 10.1007/s11748-019-01239-8
17. Ganti AKP, Loo BW, Bassetti M, Blakely C, Chiang A, D'Amico TA, et al. Small cell lung cancer, version 2.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2021) 19:1441–64. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0058
18. De Ruysscher D, Faivre-Finn C, Moeller D, Nestle U, Hurkmans CW, Le Pechoux C, et al. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) recommendations for planning and delivery of high-dose, high precision radiotherapy for lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. (2017) 124:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.06.003
19. Bi N, Wang J, Zhang T, Chen X, Xia W, Miao J, et al. Deep learning improved clinical target volume contouring quality and efficiency for postoperative radiation therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:1192. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01192
20. Lustberg T, van Soest J, Gooding M, Peressutti D, Aljabar P, van der Stoep J, et al. Clinical evaluation of atlas and deep learning based automatic contouring for lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. (2018) 126:312–7. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.11.012
21. Giri MG, Cavedon C, Mazzarotto R, Ferdeghini M. A Dirichlet process mixture model for automatic (18)F-FDG PET image segmentation: Validation study on phantoms and on lung and esophageal lesions. Med Phys. (2016) 43:2491. doi: 10.1118/1.4947123
22. Feng X, Qing K, Tustison NJ, Meyer CH, Chen Q. Deep convolutional neural network for segmentation of thoracic organs-at-risk using cropped 3D images. Med Phys. (2019) 46:2169–80. doi: 10.1002/mp.2019.46.issue-5
23. Yang J, Veeraraghavan H, Armato SG 3rd, Farahani K, Kirby JS, Kalpathy-Kramer J, et al. Autosegmentation for thoracic radiation treatment planning: A grand challenge at AAPM 2017. Med Phys. (2018) 45:4568–81. doi: 10.1002/mp.2018.45.issue-10
24. Xie H, Chen Z, Deng J, Zhang J, Duan H, Li Q. Automatic segmentation of the gross target volume in radiotherapy for lung cancer using transresSEUnet 2.5D Network. J Transl Med. (2022) 20:524. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03732-w
Appendix 1 14-station mediastinal lymph node compartmentalization definitions.
Keywords: small cell lung cancer, clinical target volume (CTV), artificial intelligence, local recurrence, prediction model
Citation: Shen J, Wang S, Guan H, Di M, Liu Z, Chen Q, Li M, Shen J, Hu K and Zhang F (2025) Artificial intelligence in automatic image segmentation system for exploring recurrence patterns in small cell carcinoma of the lung. Front. Oncol. 15:1534740. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1534740
Received: 26 November 2024; Accepted: 04 April 2025;
Published: 01 May 2025.
Edited by:
Russell K. Hales, Johns Hopkins University, United StatesReviewed by:
Yujin Xu, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, ChinaAditya Apte, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Wang, Guan, Di, Liu, Chen, Li, Shen, Hu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Shen, c2hlbmppZXB1bWNoQDE2My5jb20=; Fuquan Zhang, emhhbmdmdXF1YW4zQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jing Shen
Jing Shen Shaobin Wang2†
Shaobin Wang2† Qi Chen
Qi Chen Jie Shen
Jie Shen Ke Hu
Ke Hu Fuquan Zhang
Fuquan Zhang