- 1Department of General Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Breast Disease Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Ultrasound, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Background: For breast cancer, developing non-invasive methods to accurately predict axillary lymph node (ALN) status before surgery has become a general trend. This study aimed to develop and evaluate a nomogram to predict the probability of ALN metastasis (ALNM) preoperatively based on clinicopathological and ultrasonography (US) features.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with breast cancer by preoperative histopathologic biopsy in West China Hospital from 1 August, 2022 to 31 January, 2024 and undergoing surgical treatment with preoperative US in West China Hospital were prospectively included. Preoperative clinicopathological and US features, along with postoperative pathological ALN status, were collected. Patients included were randomly divided into a training set and a test set (7:3). In the training cohort, the independent predictors of ALNM were obtained by univariate and multivariate binary logistic regression analyses and were used to develop a binary logistic regression model presented as a nomogram. Model performance was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: A total of 610 patients were included for analysis: 427 in the training set and 183 in the test set. Molecular subtypes, tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer, tumor infiltration of the retromammary space, lymph node (LN) short axis, LN long/short (L/S) axis ratio, LN corticomedullary demarcation, and LN cortical thickness evenness were independent predictors of ALNM. The nomogram showed good discrimination with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.854 for the training set and 0.822 for the test set, presented good agreement between predicted and observed probabilities, and acquired net benefit across a wide threshold range.
Conclusions: The nomogram demonstrated strong discrimination, calibration, and clinical net benefit to assist clinical decisions.
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women (1). In, 2022, over 2 million new cases and 660,000 deaths occurred globally, with age-standardized incidence and mortality rates of 46.8 and 12.7 per 100,000, respectively (1). Metastasis is a major factor in cancer mortality (2), and lymph node (LN) status is crucial for breast cancer prognosis (3–5). For breast cancer, axillary lymph node (ALN) status is essential for staging, treatment, and prognosis (6–8), with ALN metastasis (ALNM) considered an indicator of recurrence and survival rates (9).
ALN dissection (ALND) was once the gold standard for ALNM assessment but was replaced by sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) (10) due to serious complications, such as pain, restricted shoulder movement, lymphedema, paresthesia, and numbness (11–14), marking a milestone in surgical de-escalation (15). Although SLNB is less invasive, it still poses the abovementioned moderate risks (16). Notably, 75% of patients with negative preoperative ALN ultrasonography (US) (17) and approximately 40% with positive US (18) had negative ALN upon pathological examination. The Sentinel Node vs Observation After Axillary Ultrasound (SOUND) randomized clinical trial showed that omitting axillary surgery was non-inferior to SLNB in patients with tumors ≤2 cm and negative ALN US (15), forecasting another shift in surgical de-escalation. Accurately identifying ALN status preoperatively is essential to avoid unnecessary axillary surgery in patients without ALNM.
US-guided core needle biopsy (CNB) and fine-needle aspiration (FNA) offer certain sensitivity, excellent specificity, and good positive predictive value (PPV) to preoperative ALN status assessment (19–24). To protect important vessels and nerves close to ALN, FNA is more commonly used but still carries potential risks (25) and has an unsatisfactory false-negative rate (FNR) of up to nearly 30% (24, 26). To avoid unnecessary invasive biopsies, developing non-invasive methods to accurately predict ALN status before surgery has become a general trend (27).
Currently, non-invasive imaging examinations such as US, mammography (MG), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET–CT) are used to predict ALN status preoperatively (27). US is preferred due to its convenience, low cost, no ionizing radiation, and abundant morphological information (28–30). Studies have indicated that LNs with asymmetry, thickened or irregular cortex, round shape and roundness index of approximately 1, enlarged size, ill-defined margins, or disappeared fatty hilum were more prone to metastatic LNs (10, 31, 32). However, there are no official consensus criteria to classify benign versus metastatic LNs based on US (10).
Previous studies created models to predict ALNM based on US features, but insufficiencies still existed (27, 29, 32–34). First, the features incorporated were inadequate, only involving LNs (29, 32, 34) or tumors (27), without important features like tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer or retromammary space (27, 29, 32–34). Second, these models relied on clinicopathological features from surgical specimens, unsuitable for preoperative assessment (33). Third, some models lacked comprehensive evaluation (27, 29, 32, 33). Until now, few studies have developed a comprehensive model based on preoperative clinicopathological and US features to predict ALNM, with adequate evaluation.
More comprehensively combining preoperative clinicopathological and US features by constructing a quantifiable model to more accurately predict preoperative ALN status needs urgent exploration. This study aimed to explore the risk factors of ALNM prospectively from preoperative clinicopathological features, as well as US features of tumor and LNs, and develop a nomogram to predict ALNM probability preoperatively for breast cancer, with a more comprehensive evaluation.
Materials and methods
Patient selection
Patients diagnosed with breast cancer by preoperative histopathologic biopsy in West China Hospital, Sichuan University, from 1 August, 2022 to 31 January, 2024 were prospectively included. The pathological diagnosis was based on the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Breast Tumors (35). Patients meeting the following criteria were excluded: 1) cancer primary focus and/or LN metastasis focus has been resected via breast surgery (including breast-conserving surgery, mastectomy, and even Mammotome) and/or axillary surgery (including ALND and SLNB), 2) inflammatory breast cancer, 3) a history of malignancy, and 4) necessary clinicopathological data were absent.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Clinicopathological feature collection
Patients’ clinical information was mainly collected by face-to-face inquiry, and histopathologic information of tumors was obtained from the electronic medical records. Clinical features included age at diagnosis, body mass index (BMI), age at menarche, the number of pregnancies and deliveries, menopause status at diagnosis, and neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) or not. BMI was calculated by formula weight/height2 (kg/m2), and the height and weight were measured in an outpatient setting. The histopathologic reports of preoperative US-guided CNB for breast primary tumors, including estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), Ki-67, and histologic types, were recorded. The features of the largest tumor were recorded for patients with multiple tumors. The status of ER, PR, HER2, and Ki-67 was evaluated by immunohistochemical (IHC) staining, and HER2 needed extra detection by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) when IHC showed 2+. ER or PR was identified as a positive result if the positivity rate was ≥1%, and HER2 was identified as a positive result if IHC staining presented 3+, or IHC showed 2+ but FISH showed positive. According to the St Gallen International Expert Consensus, 2013 (36), based on the status of ER, PR, HER2, and Ki-67, breast cancer was categorized into four molecular subtypes, as follows: luminal A subtype (ER+, PR ≥ 20%, HER2−, Ki-67 < 14%), luminal B subtype (ER+/PR+ but did not meet the condition of luminal A), HER2-enriched subtype (ER−, PR−, HER2+), and triple-negative subtype (ER−, PR−, HER2−).
US data collection
The US scans were evaluated 3–5 days before surgery by two ultrasound experts (with 5–10 years of experience in breast US) blinded to the axillary surgery plan, and the images and features for breasts and ALN were collected. They reached a consensus through discussion when any disagreements in the independent analysis were encountered. US features of the tumor included tumor size (maximum diameter of breast lesion), location, distance to the nipple, blood flow signals, infiltration status of the subcutaneous layer, and retromammary space. In this study, the blood flow signals of tumors were divided into two categories based on Adler grades: poor (Adler grades 0–1) and abundant (Adler grades 2–3) blood flow signals (37). The characteristics of the largest tumor were recorded for patients with multiple tumors. In addition, US features of LNs contained long and short axes, blood flow signal types and grades, margin, corticomedullary demarcation, and cortical thickness and evenness. The cortical thickness was measured based on the thickest location. Then, the LN long/short (L/S) axis ratio by long and short axes was calculated. The characteristics of the most suspicious LN (the largest one usually) were recorded.
Pathological ALN status
The surgery was performed by six specialists in breast surgery with more than 10 years of experience in breast cancer surgery. The ALN status reported by the postoperative histopathologic examination results of ALND or SLNB was recorded. Then, patients were divided into ALNM and non-ALNM groups by the ALN status. Macro-metastases (>2 mm) and micro-metastases (0.2–2 mm) were identified as ALNM, while isolated tumor cells (ITCs) (<0.2 mm) and negative SLN were considered non-ALNM (38).
Follow-up and research management
All the patients were followed up. The end-point of follow-up was the acquirement of ALN status by postoperative histopathologic examination. During the follow-up, NAT status was checked via electronic medical records when the patients were admitted to the hospital for surgery. The patients who were not undergoing a surgical treatment or refused preoperative US in West China Hospital were lost to follow-up.
The patients’ data were registered in an Excel spreadsheet and were managed by a dedicated researcher. Clinicopathological feature collection was performed by two researchers in charge of acquisition and recording. The US features were recorded by one of the two ultrasound experts after a consensus was reached. Another two researchers were responsible for follow-up until postoperative pathological ALN status was recorded.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 23.0 and the R software ver.4.3.2. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), while categorical variables were presented as numbers and percentages of the group they belong to and analyzed by χ2 test (Yates’ correction if necessary) or Fisher’s exact test, which was used to compare the data distribution of the training and test cohorts.
The patients included were randomly divided into a training set and a test set according to the proportion of 7:3. In the training cohort, the variables associated with ALN status were preliminarily screened by univariate binary logistic regression analysis. Those significant variables in univariate analysis were included in multivariate binary logistic regression analysis, using the forward stepwise (likelihood ratio), to acquire the independent predictors of ALNM. The p-values, odds ratios (ORs), and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were reported to present the analysis. The statistical analyses were two-sided, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The collinearity diagnosis of independent predictors was performed, and then the tolerance and variance inflation factor (VIF) were calculated.
The binary logistic regression model to predict ALNM was constructed using independent predictors and presented as a nomogram. The Hosmer–Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test was used to evaluate the fit level of the model. For the training and test cohorts, the discrimination of the model was evaluated by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve to calculate the area under the ROC curve (AUC). Next, for both cohorts, the calibration of the model was evaluated by bootstrapping with 500 resamples and presented by the calibration curve. Last, to evaluate the clinical value of the nomogram, the net benefits of the model for both cohorts were measured using decision curve analysis (DCA) and shown by the DCA curve. Moreover, sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, PPV, negative predictive value (NPV), detection rate, and FNR of the model at different threshold values in the training and test sets were calculated to provide references for threshold value selection in situations with different requirements.
Results
Patients’ characteristics
Overall, 854 patients were registered. A total of 176 patients were excluded because their cancer primary focus and/or LN metastasis focus had been resected, 40 patients were excluded due to inflammatory breast cancer, and 12 patients were excluded because their necessary clinicopathological information was absent. Ultimately, 228 patients were excluded, and 626 patients were included. Moreover, 14 patients were lost to follow-up because they did not undergo surgical treatment in West China Hospital, and two patients were lost to follow-up due to refusal to undergo preoperative US in West China Hospital. Finally, 16 patients were lost to follow-up, and the remaining 610 patients were included for analysis, which is illustrated in Figure 1.
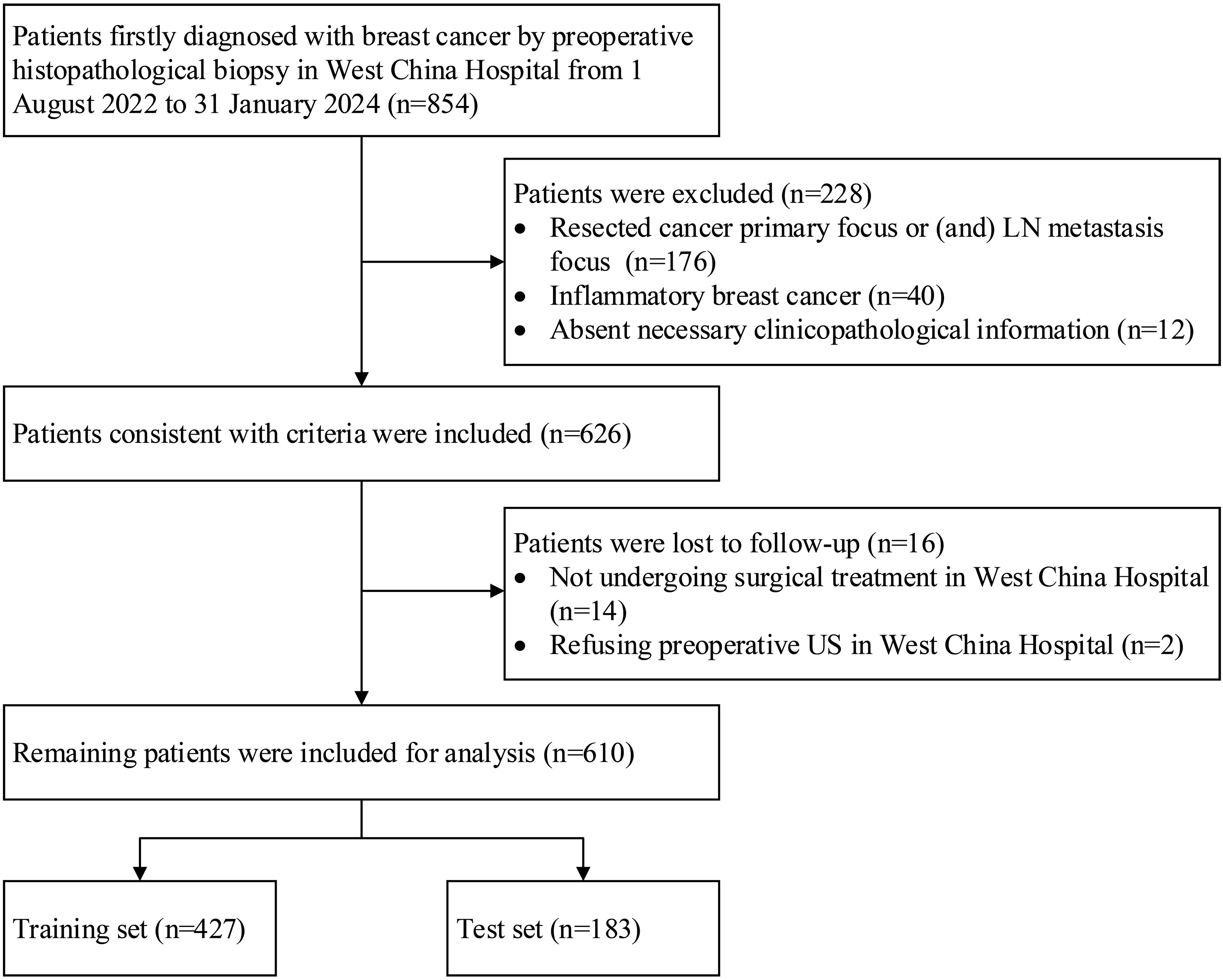
Figure 1. Flowchart of patients who were included, excluded, and lost to follow-up in the study. LN, lymph node; US, ultrasonography.
Of these 610 patients, 11 (1.8%) patients had unknown HER2 status, and one patient had unknown Ki-67 status. These missing data were not indispensable for model construction, so these patients were retained without handling their missing data. The mean age at diagnosis of the 610 patients was 50.9 ± 10.7 years (range, 25–86 years). As confirmed by postoperative histopathologic examination, 294 (48.2%) patients had ALNM, while the other 316 (51.8%) patients had negative ALN. In addition, 72 (11.8%) patients underwent NAT. More than half of the patients (55.6%) had tumors of the luminal B subtype, and most patients (94.8%) had ductal carcinoma. In addition, 84.4% of patients had LNs with a short axis <10 mm. The comparison of the clinicopathological and US features of patients between the training set (427 patients) and the test set (183 patients) is shown in Table 1. The distribution of variables between the two sets was basically consistent, with a slight difference in the tumor location (Table 1).
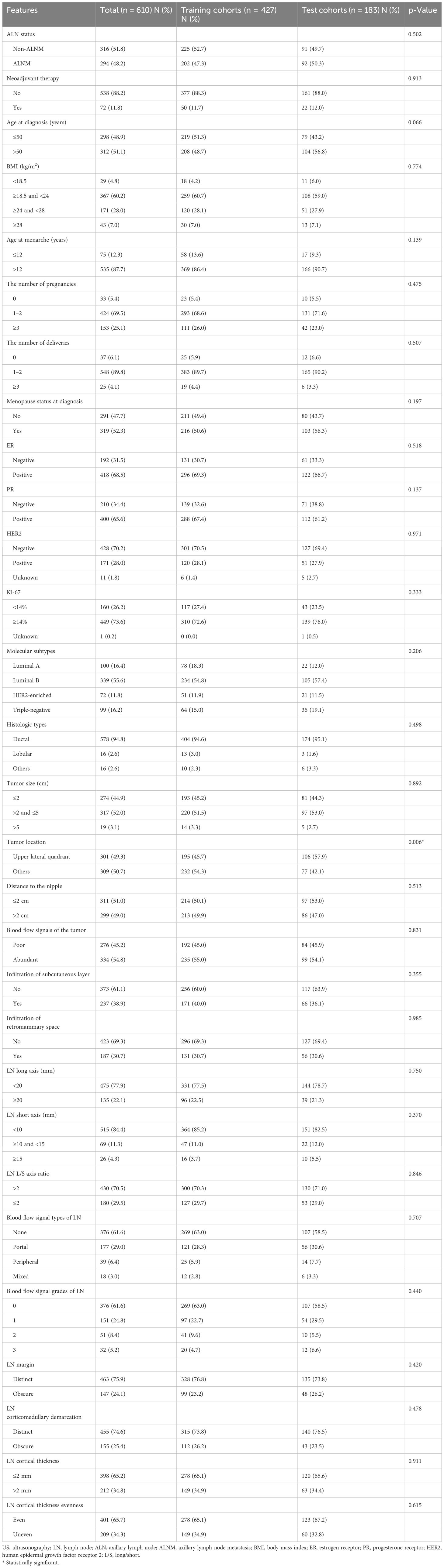
Table 1. Clinicopathological and US features of breast cancer patients in the training and test cohorts.
The clinicopathological and US features of patients with or without ALNM in the training and test cohorts are summarized in Table 2. In the training cohort, 202 (47.3%) patients had ALNM, and the remaining 225 (52.7%) patients had negative ALN. In the test cohort, 92 (50.3%) patients had ALNM, and the remaining 91 (49.7%) patients had negative ALN.
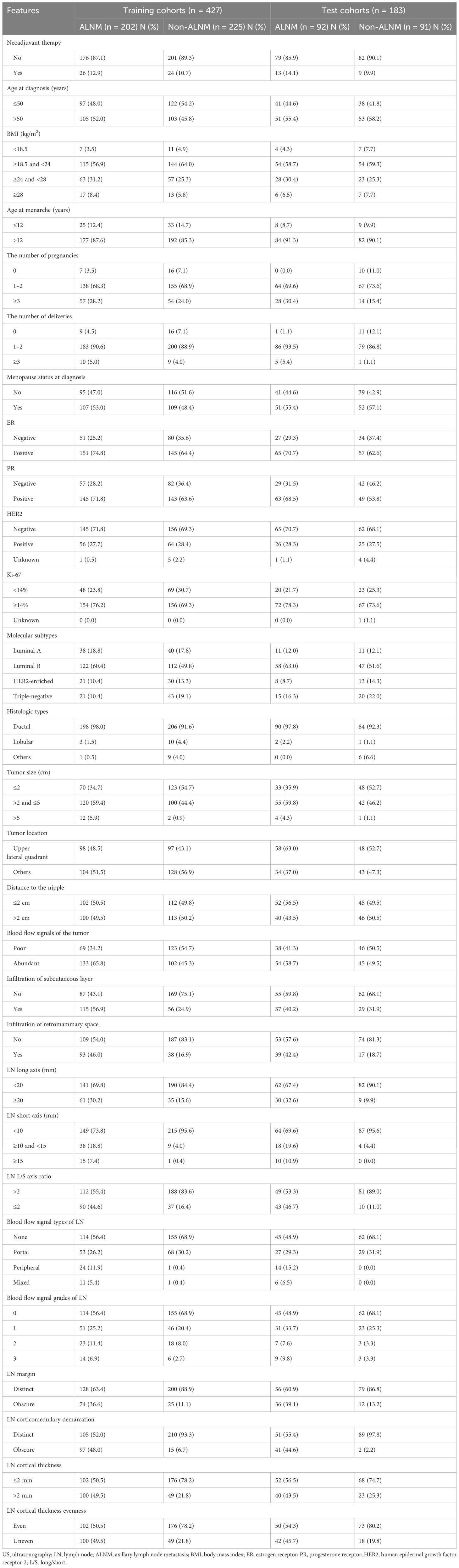
Table 2. Clinicopathological and US features of breast cancer patients with or without ALNM in the training and test cohorts.
Univariate analysis of ALNM
Univariate binary logistic regression analysis was conducted in the training set (Table 3). According to preoperative histopathologic biopsy, ER-positive, luminal A/B subtype, or ductal carcinoma was associated with ALNM. In addition, larger tumor size, abundant blood flow signals of the tumor, and tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer or retromammary space reported in preoperative US of breasts were also associated with ALNM. Moreover, according to preoperative US for ALN, longer LN long axis or short axis, smaller LN L/S axis ratio, peripheral or mixed blood flow signal type of LN, grade 3 blood flow signal of LN, obscure LN margin or corticomedullary demarcation, and thicker or more uneven LN cortex were also associated with ALNM.
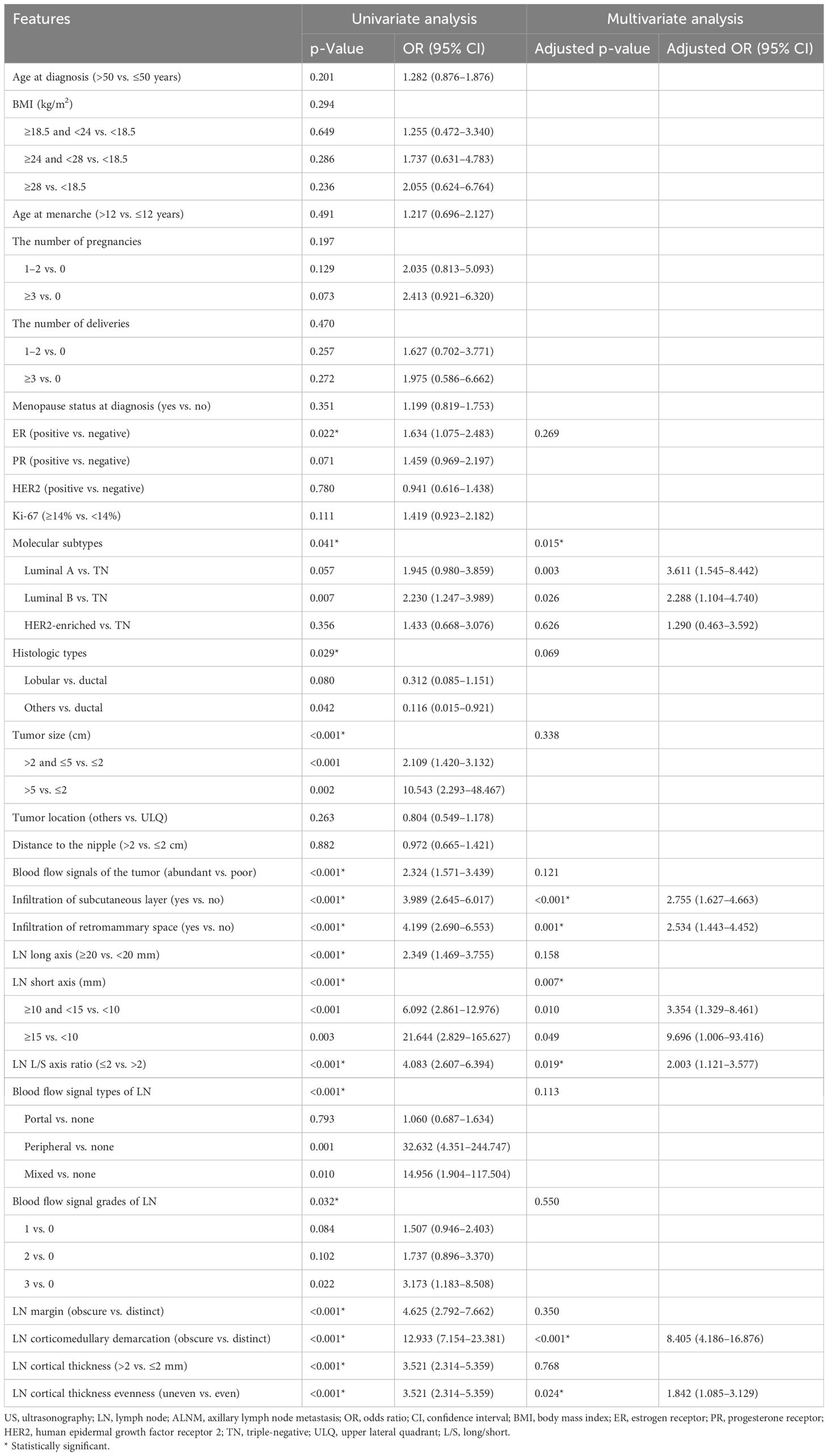
Table 3. Univariate and multivariate binary logistic regression analyses of clinicopathological and US features associated with ALNM.
Multivariate analysis of ALNM
As shown in Table 3, multivariate binary regression analysis revealed that molecular subtypes, tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer, tumor infiltration of the retromammary space, LN short axis, LN L/S axis ratio, LN corticomedullary demarcation, and LN cortical thickness evenness were independent predictors of ALNM. Compared with triple-negative (TN) subtypes, luminal A (adjusted OR [95% CI], 3.611 [1.545–8.442], p = 0.003) and B (adjusted OR [95% CI], 2.288 [1.104–4.740], p = 0.026) subtypes were both more prone to ALNM. In addition, tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer (adjusted OR [95% CI], 2.755 [1.627–4.663], p < 0.001) and the retromammary space (adjusted OR [95% CI], 2.534 [1.443–4.452], p = 0.001) were both risk factors of ALNM. Moreover, the risk of metastasis greatly increased when the LN short axis was too long. Compared with short axis <10 mm, ≥10 and <15 mm indicated that ALNM risk was more than three times (adjusted OR [95% CI], 3.354 [1.329–8.461], p = 0.010), while short axis ≥15 mm indicated that ALNM risk was nearly 10 times (adjusted OR [95% CI], 9.696 [1.006–93.416], p = 0.049). LNs with L/S axis ratio ≤2 had a higher risk of metastasis than LNs with L/S axis ratio >2 (adjusted OR [95% CI], 2.003 [1.121–3.577], p = 0.019). In addition, LNs with obscure corticomedullary demarcation (adjusted OR [95% CI], 8.405 [4.186–16.876)], p < 0.001) had a great risk of metastasis, and uneven cortex (adjusted OR [95% CI], 1.842 [1.085–3.129], p = 0.024) also increased the metastasis risk of LN. According to the multicollinearity test, there was no collinearity among these independent predictors (tolerance > 0.2 and VIF < 5).
Nomogram development and test
A binary logistic regression model to predict the probability of ALNM was developed based on the abovementioned independent predictors and presented as a nomogram (Figure 2). The Hosmer–Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test suggested that the model fit well (p = 0.770).
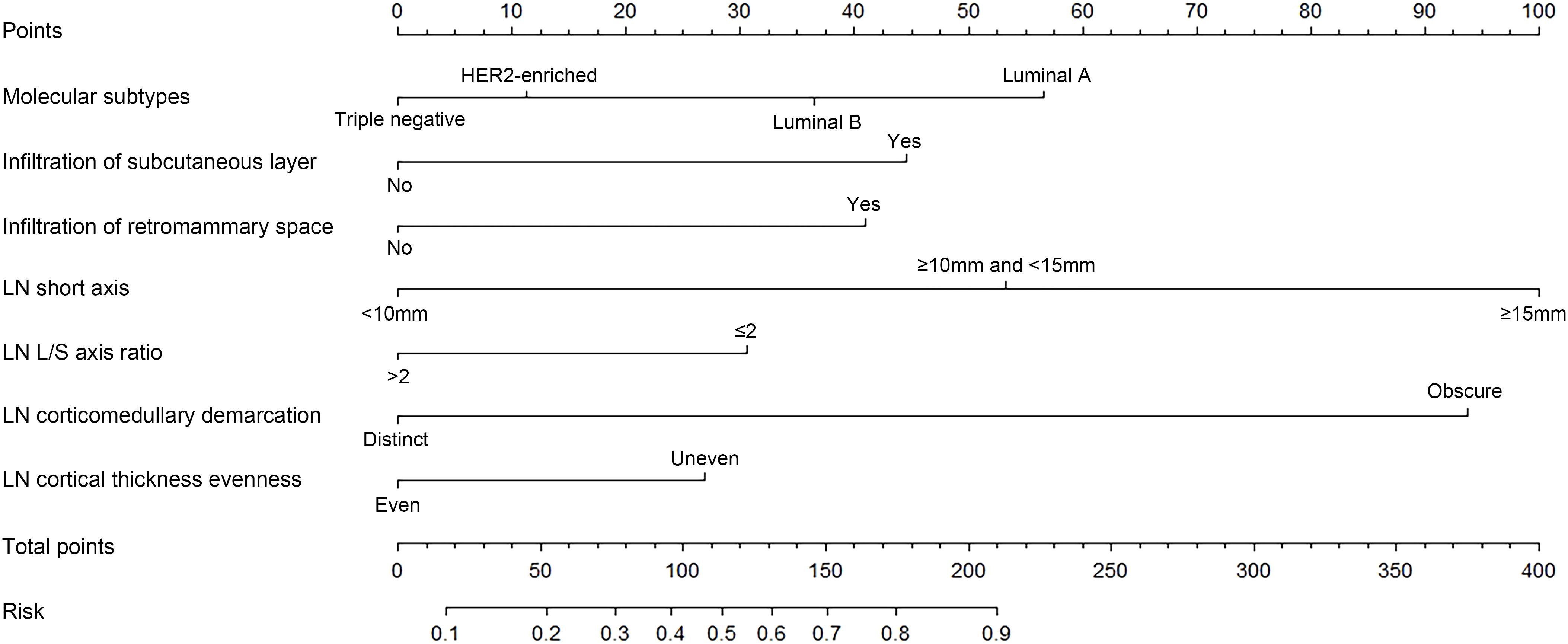
Figure 2. A nomogram to predict axillary lymph node (LN) metastasis (ALNM) preoperatively in patients with breast cancer. Molecular subtypes, tumor infiltration of subcutaneous layer, tumor infiltration of retromammary space, LN short axis, LN long/short (L/S) axis ratio, LN corticomedullary demarcation, and LN cortical thickness evenness were finally selected to develop the model.
According to further evaluation, the model had good discrimination ability with AUCs of 0.854 (95% CI, 0.818–0.890) and 0.822 (95% CI, 0.762–0.882) for the training set and the test set, respectively (Figures 3A, B). Moreover, the calibration curves indicated good agreement between predicted and observed probabilities, with the mean absolute error of 0.009 and 0.048 (500 repetitions) for the training set and the test set, respectively (Figures 3C, D). In the test set, when the observed probability was in the middle range (approximately 0.3–0.85), the model slightly overestimated the risk; however, when the observed probability was low or high (roughly <0.3 or >0.85), the model slightly underestimated the risk. DCA curves showed that the model could acquire net benefit with a threshold range of roughly 0.15–0.9 and 0.15–0.95 for the training group and the test group, respectively (Figures 3E, F). In particular, the model acquired greater net benefit (≥0.4) when the threshold range was approximately 0.15–0.65 and 0.15–0.8 for the training group and test group, respectively. Therefore, it was demonstrated that the model was of great benefit to guide clinical decisions for predicting ALNM.
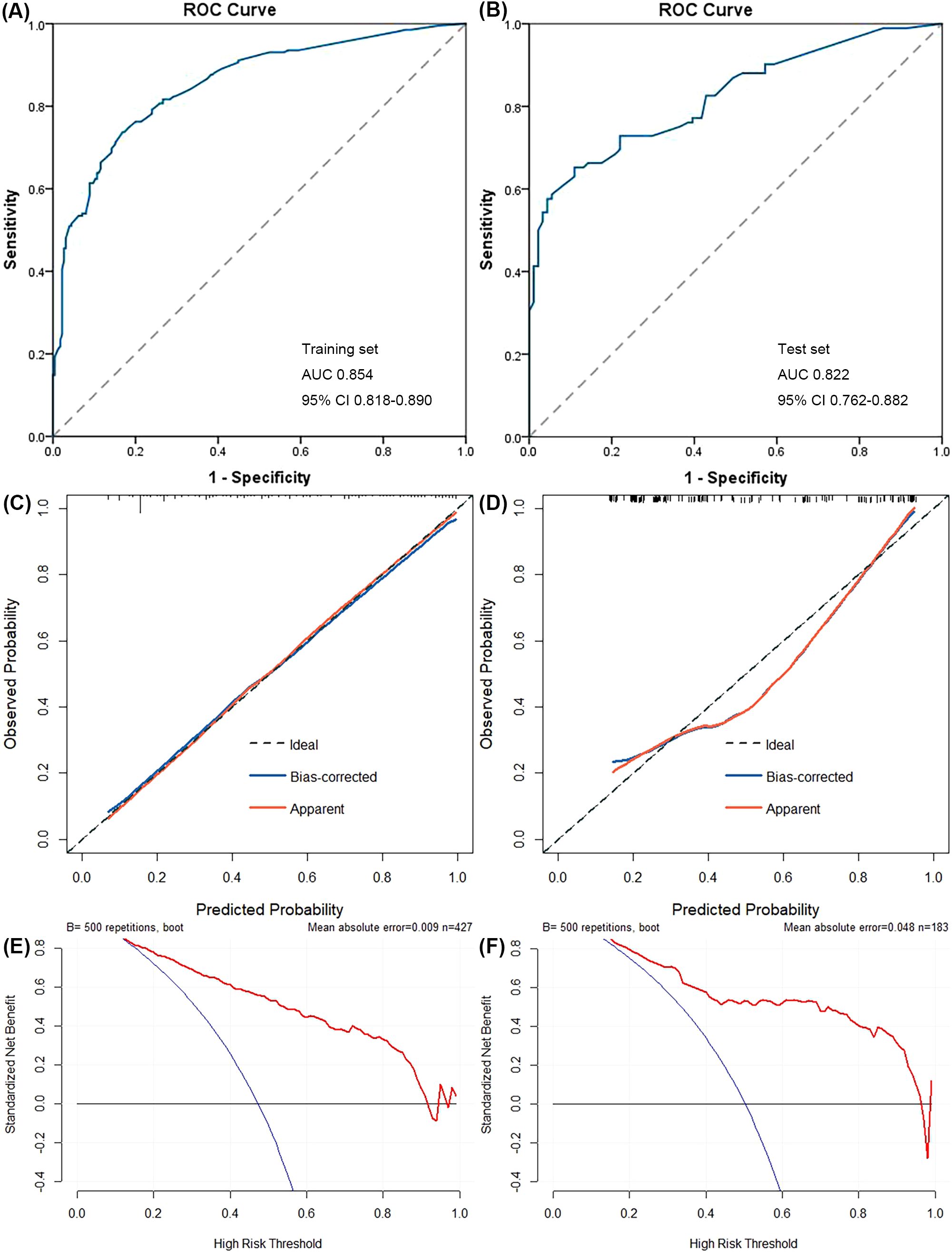
Figure 3. Performance of the nomogram was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (A, B), the calibration curves (C, D), and the decision curve analysis (DCA) (E, F). The area under ROC curve (AUC) of the model was 0.854 (95% CI, 0.818–0.890) and 0.822 (95% CI, 0.762–0.882) for the training set (A) and the test set (B), respectively. After 500 resampling, the mean absolute error of the model was 0.009 and 0.048 for the training set (C) and the test set (D), respectively. The model could acquire net benefit when the risk threshold was located at 0.15–0.9 and 0.15–0.95 for the training set (E) and the test set (F), respectively.
As shown in Table 4, with a risk threshold value of 0.5, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the model were 71.3%, 84.9%, and 78.5%, respectively, for the training set and 65.2%, 87.9%, and 76.5%, respectively, for the test set. Meanwhile, the detection rates were 41.7% and 38.8% in the training set and the test set, respectively, and these patients were identified to have ALNM and were likely to undergo further invasive examinations. In addition, the performance at different threshold values was presented to provide references for threshold value selection in situations with different requirements. For example, with a threshold value of 0.231, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 90.6%, 55,1%, and 71.9%, respectively, for the training set and 82.6%, 57.1%, and 69.9%, respectively, for the test set; the detection rates were 66.5% and 62.8% in the training set and the test set, respectively.
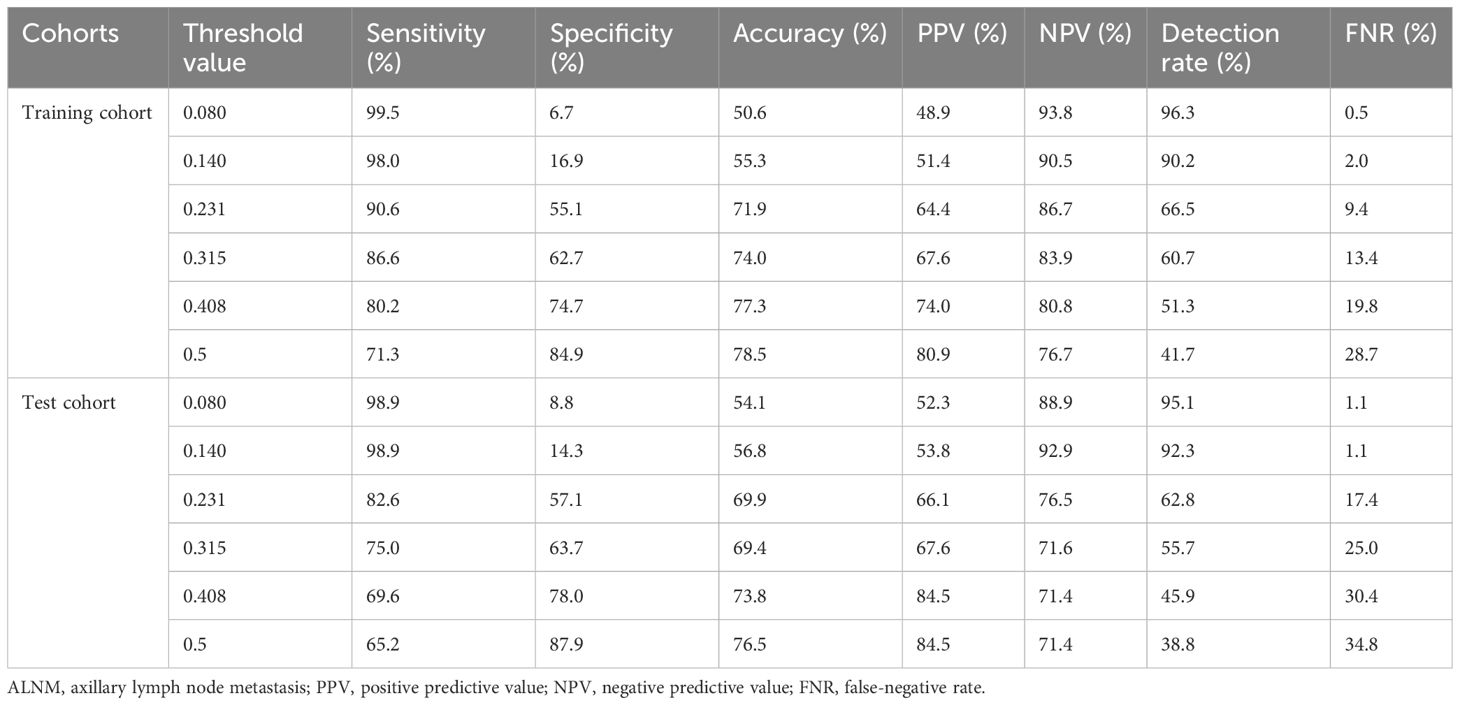
Table 4. Performance of the logistic regression model for ALNM prediction in the training and test cohorts when the threshold value varied.
Discussion
In this study, we prospectively included patients with breast cancer and collected preoperative clinicopathological features and US features of tumors and LNs to explore the risk factors of ALNM. The results suggested that molecular subtypes, tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer, tumor infiltration of the retromammary space, LN short axis, LN L/S axis ratio, LN corticomedullary demarcation, and LN cortical thickness evenness were independent predictors of ALNM. Then, we developed a logistic regression model based on these predictors and presented it as a nomogram to predict ALNM, displaying a good performance in discrimination ability, calibration ability, and net benefit for both the training set and test set.
In our predictive model, LN corticomedullary demarcation was one of the most important predictors, showing the highest predictive value, and LN cortical thickness evenness also exhibited a slight predictive value. LNs with obscure corticomedullary demarcation had more than eight times the risk of metastasis than LNs with distinct corticomedullary demarcation, while LNs with uneven cortex had nearly two times the risk than LNs with even cortex. Previous studies also suggested that corticomedullary demarcation (34) and asymmetrical cortex (33) were independent predictors of ALNM. In addition, LN short axis was one of the most important predictors, and the L/S axis ratio also presented some predictive value. Compared with short axis <10 mm, ≥10 and <15 mm indicated that ALNM risk was more than three times, while short axis ≥15 mm indicated that ALNM risk was nearly 10 times. Rounder LNs (L/S axis ratio ≤2) had roughly two times the risk of metastasis than oval LNs (L/S axis ratio >2). Studies have also reported that LN short diameter (29) and LN L/S axis ratio (33) were independent predictors of ALNM. Overall, studies have indicated that both LN size and morphological features were equally important for LN metastasis prediction (39, 40), which was consistent with our results.
Molecular subtypes were also an important independent predictor of ALNM, but the specific relationship is quite controversial. Although some studies have failed to discover the association between the molecular subtypes and the ALN status (41), many studies have revealed that molecular subtypes were associated with ALNM (27, 42–52). Some studies have shown that non-luminal subtypes (TN or HER2-enriched) were associated with a higher risk of ALNM (45, 52) and that the luminal A subtype had a lower risk of ALNM than the other subtypes (27, 45, 52). Other studies have suggested that luminal subtypes (A or B) were more prone to ALNM (43, 44, 47, 51), which was consistent with our study. In our study, adjusted by multivariate analysis, tumors of the luminal A subtype had more than three times the risk of ALNM than tumors of TN, while the luminal B subtype had more than two times the risk, and although the luminal B subtype seemed to have a higher risk before adjustment, there was no significant difference between the luminal A and B subtypes. As is known to us, TN is always associated with a worse prognosis, but many studies (including ours) have shown that TN has a lower risk of ALNM (43, 44, 51). Therefore, the poor prognosis of TN may be due to distant spread, rather than regional spread (45, 51). In addition, the luminal A subtype is always considered to have the best prognosis (27), but many studies (including ours) have suggested that it was more prone to ALNM than TN and HER2-enriched (44, 47). The reason may be that the luminal A subtype has positive ER and high expression of PR, and positive ER (29, 53) or PR (34, 54, 55) may mean a higher risk of ALNM according to previous studies. The specific mechanism of the phenomenon has been unknown, but we deduced that tumors of luminal subtypes may prefer lymphatic metastasis, and thus, patients are more likely to benefit from local therapy; also, tumors of non-luminal subtypes may prefer hematogenous metastasis, and thus, distant metastasis may occur earlier (29).
In our study, two variables of the primary tumor were incorporated into the model innovatively: tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer and tumor infiltration of the retromammary space. The results indicated that both of them were independent predictors of ALNM, and patients with one of the infiltration patterns above had more than two times the risk of ALNM than patients with neither pattern. A previous study suggested that infiltration of subcutaneous adipose tissue (ISAT) was an independent predictor of ALNM, and tumors with ISAT were 2.72 times more likely to develop ALNM than those without ISAT (56), which was consistent with our study. Lymphatic capillaries are densely distributed at subcutaneous adipose tissue (57, 58), which may make tumors with infiltration of the subcutaneous layer more prone to ALNM. In addition, another study also showed that infiltration of the retromammary space was associated with ALNM, but the specific mechanism has been unknown (59). The deep lymphatics of breasts drain through the retromammary space (60), which may be an underlying mechanism.
In recent years, increasing prediction models based on imaging examinations, particularly US, have been developed to evaluate the ALN status of breast cancer preoperatively. However, the features incorporated in these studies were inadequate. Some studies incorporated US features of LNs only (29, 32, 34), and another study incorporated US features of primary tumors only (27). For a study incorporating the US features of both tumors and LNs, the clinicopathological characteristics were from surgical specimens, which also limited the preoperative application of the model (33). We prospectively comprehensively incorporated preoperative US features of tumors and LNs, as well as acquired clinicopathological characteristics from preoperative biopsy, and developed a nomogram to predict ALN status preoperatively, successfully resolving the questions raised above.
The American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 (ACOSOGZ0011) randomized clinical trial suggested no benefit from ALND for patients with ≤2 SLN metastasis and receiving standard therapy (61). For more than 20 years, SLNB has been the standard for ALN staging in early breast cancer to identify patients benefiting from ALND, which represented a milestone in surgical de-escalation (15). The SOUND trial showed that omitting axillary surgery was non-inferior to SLNB in patients with tumors ≤2 cm and negative ALN US (15), which may become another milestone in surgical de-escalation. Therefore, preoperative ALN evaluation is critical for identifying patients who can safely omit axillary surgery (29). To be exact, our study provided an important reference for the accurate prediction of preoperative ALN status based on non-invasive techniques and preliminary evidence for the precise selection of patients who can omit SLNB safely.
Our study has some advantages. First, the patients were prospectively included, and the features were prospectively collected. Second, the US features of the primary tumors and LNs were incorporated relatively comprehensively, and clinicopathological characteristics were all acquired from biopsy preoperatively, which was beneficial for the preoperative sufficient evaluation of ALN status and corresponded more with determination scenarios of SLNB omission. Third, patients who underwent NAT were included, which broadened the application of the nomogram. At last, the model was evaluated relatively comprehensively from the three dimensions: discrimination, calibration, and net benefits. Nevertheless, our study also has some limitations. First, our study was a single-center study, and it needs to be further tested in external test cohorts from other institutions to evaluate its predictive ability and generalizability. Second, there were still slight differences between the training and test sets, even if the division was random. Third, US features depend on ultrasound specialists’ judgments, which are subjective and inevitably biased. At last, manual feature extraction to construct logistic regression models is simpler but less abundant, compared with radiomics feature extraction by artificial intelligence to develop machine learning or deep learning models.
Conclusion
In conclusion, molecular subtypes, tumor infiltration of the subcutaneous layer, tumor infiltration of the retromammary space, LN short axis, LN L/S axis ratio, LN corticomedullary demarcation, and LN cortical thickness evenness were independent predictors of ALNM in breast cancer. Based on these independent predictors, we developed a logistic regression model and presented it as a nomogram to predict ALNM, which displayed a good performance in discrimination ability, calibration ability, and net benefits for both the training set and test set, and it could assist clinical decisions.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YP: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QT: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YX: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the clinical research incubation program, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (21HXFH011).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Zifeng Sun from Northwestern University, Xi’an, China, for the guidance on the R software and Rui Gao from West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, for the suggestions that helped improve the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
LN, lymph node; ALN, axillary lymph node; ALNM, axillary lymph node metastasis; ALND, axillary lymph node dissection; SLNB, sentinel lymph node biopsy; US, ultrasonography; SOUND, Sentinel Node vs Observation After Axillary Ultrasound; CNB, core needle biopsy; FNA, fine-needle aspiration; PPV, positive predictive value; FNR, false-negative rate; MG, mammography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET–CT, positron emission tomography–computed tomography; WHO, World Health Organization; BMI, body mass index; NAT, neoadjuvant therapy; ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IHC, immunohistochemical; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; TN, triple-negative; L/S, long/short; ITC, isolated tumor cell; SLN, sentinel lymph node; SD, standard deviation; OR, odds ratios; CI, confidence intervals VIF, variance inflation factor; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; AUC, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; DCA, decision curve analysis; NPV, negative predictive value; ISAT, infiltration of subcutaneous adipose tissue; MSKCC, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center; LVI, lymphovascular invasion; ACOSOGZ0011, American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011.
References
1. Cancer Today. Lyon, France: World Health Organization (2022). Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (Accessed May 31, 2024).
2. Li YL and Hung WC. Reprogramming of sentinel lymph node microenvironment during tumor metastasis. J Biomed Sci. (2022) 29:022–00868. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00868-1
3. Alvarez S, Añorbe E, Alcorta P, López F, Alonso I, and Cortés J. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: A systematic review. AJR Am J roentgenology. (2006) 186:1342–8. doi: 10.2214/AJR.05.0936
4. García Fernández A, Fraile M, Giménez N, Reñe A, Torras M, Canales L, et al. Use of axillary ultrasound, ultrasound-fine needle aspiration biopsy and magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative triage of breast cancer patients considered for sentinel node biopsy. Ultrasound Med Biol. (2011) 37:16–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.10.011
5. Koelliker SL, Chung MA, Mainiero MB, Steinhoff MM, and Cady B. Axillary lymph nodes: us-guided fine-needle aspiration for initial staging of breast cancer–correlation with primary tumor size. Radiology. (2008) 246:81–9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2463061463
6. Gradishar WJ, Moran MS, Abraham J, Abramson V, Aft R, and Agnese DNccn Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, Breast Cancer. Pennsylvania, USA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2024). Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/genetics_bop.pdf (Accessed May 31, 2024).
7. Fisher B, Bauer M, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Fisher ER, Cruz AB, et al. Relation of number of positive axillary nodes to the prognosis of patients with primary breast cancer. Nsabp Update Cancer. (1983) 52:1551–7. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831101)52:9<1551::AID-CNCR2820520902>3.0.CO;2-3
8. Carter CL, Allen C, and Henson DE. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. (1989) 63:181–7. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890101)63:1<181::AID-CNCR2820630129>3.0.CO;2-H
9. Huston TL and Simmons RM. Locally recurrent breast cancer after conservation therapy. Am J Surg. (2005) 189:229–35. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.07.039
10. Tahmasebi A, Qu E, Sevrukov A, Liu JB, Wang S, Lyshchik A, et al. Assessment of axillary lymph nodes for metastasis on ultrasound using artificial intelligence. Ultrason Imaging. (2021) 43:329–36. doi: 10.1177/01617346211035315
11. Velanovich V and Szymanski W. Quality of life of breast cancer patients with lymphedema. Am J Surg. (1999) 177:184–7. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(99)00008-2
12. Maunsell E, Brisson J, and Deschênes L. Arm problems and psychological distress after surgery for breast cancer. Can J Surg J canadien chirurgie. (1993) 36:315–20.
13. Ashikaga T, Krag DN, Land SR, Julian TB, Anderson SJ, Brown AM, et al. Morbidity results from the nsabp B-32 trial comparing sentinel lymph node dissection versus axillary dissection. J Surg Oncol. (2010) 102:111–8. doi: 10.1002/jso.v102:2
14. McLaughlin SA, Wright MJ, Morris KT, Sampson MR, Brockway JP, Hurley KE, et al. Prevalence of lymphedema in women with breast cancer 5 years after sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary dissection: patient perceptions and precautionary behaviors. J Clin oncology: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2008) 26:5220–6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.3766
15. Gentilini OD, Botteri E, Sangalli C, Galimberti V, Porpiglia M, Agresti R, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy vs no axillary surgery in patients with small breast cancer and negative results on ultrasonography of axillary lymph nodes: the sound randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2023) 9:1557–64. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.3759
16. Langer I, Guller U, Berclaz G, Koechli OR, Schaer G, Fehr MK, et al. Morbidity of sentinel lymph node biopsy (Sln) alone versus sln and completion axillary lymph node dissection after breast cancer surgery: A prospective swiss multicenter study on 659 patients. Ann Surg. (2007) 245:452–61. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000245472.47748.ec
17. Diepstraten SC, Sever AR, Buckens CF, Veldhuis WB, van Dalen T, van den Bosch MA, et al. Value of preoperative ultrasound-guided axillary lymph node biopsy for preventing completion axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. (2014) 21:51–9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-013-3229-6
18. Nori J, Vanzi E, Bazzocchi M, Bufalini FN, Distante V, Branconi F, et al. Role of axillary ultrasound examination in the selection of breast cancer patients for sentinel node biopsy. Am J Surg. (2007) 193:16–20. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.02.021
19. Bonnema J, van Geel AN, van Ooijen B, Mali SP, Tjiam SL, Henzen-Logmans SC, et al. Ultrasound-guided aspiration biopsy for detection of nonpalpable axillary node metastases in breast cancer patients: new diagnostic method. World J Surg. (1997) 21:270–4. doi: 10.1007/s002689900227
20. Houssami N, Ciatto S, Turner RM, Cody HS 3rd, and Macaskill P. Preoperative ultrasound-guided needle biopsy of axillary nodes in invasive breast cancer: meta-analysis of its accuracy and utility in staging the axilla. Ann Surg. (2011) 254:243–51. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31821f1564
21. Krishnamurthy S, Sneige N, Bedi DG, Edieken BS, Fornage BD, Kuerer HM, et al. Role of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of indeterminate and suspicious axillary lymph nodes in the initial staging of breast carcinoma. Cancer. (2002) 95:982–8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10786
22. Mainiero MB, Cinelli CM, Koelliker SL, Graves TA, and Chung MA. Axillary ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration in the preoperative evaluation of the breast cancer patient: an algorithm based on tumor size and lymph node appearance. AJR Am J roentgenology. (2010) 195:1261–7. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.4414
23. Tahir M, Osman KA, Shabbir J, Rogers C, Suarez R, Reynolds T, et al. Preoperative axillary staging in breast cancer-saving time and resources. Breast J. (2008) 14:369–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2008.00600.x
24. Rautiainen S, Masarwah A, Sudah M, Sutela A, Pelkonen O, Joukainen S, et al. Axillary lymph node biopsy in newly diagnosed invasive breast cancer: comparative accuracy of fine-needle aspiration biopsy versus core-needle biopsy. Radiology. (2013) 269:54–60. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13122637
25. Abe H, Schmidt RA, Sennett CA, Shimauchi A, and Newstead GM. Us-guided core needle biopsy of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer: why and how to do it. Radiographics. (2007) 27:S91–9. doi: 10.1148/rg.27si075502
26. Nakano Y, Noguchi M, Yokoi-Noguchi M, Ohno Y, Morioka E, Kosaka T, et al. The roles of (18)F-fdg-pet/ct and us-guided fnac in assessment of axillary nodal metastases in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan). (2017) 24:121–7. doi: 10.1007/s12282-016-0684-5
27. Xiong J, Zuo W, Wu Y, Wang X, Li W, Wang Q, et al. Ultrasonography and clinicopathological features of breast cancer in predicting axillary lymph node metastases. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:022–10240. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10240-z
28. Marino MA, Avendano D, Zapata P, Riedl CC, and Pinker K. Lymph node imaging in patients with primary breast cancer: concurrent diagnostic tools. Oncologist. (2020) 25:e231–e42. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0427
29. Qiu SQ, Zeng HC, Zhang F, Chen C, Huang WH, Pleijhuis RG, et al. A nomogram to predict the probability of axillary lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer patients with positive axillary ultrasound. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:21196. doi: 10.1038/srep21196
30. Sun SX, Moseley TW, Kuerer HM, and Yang WT. Imaging-based approach to axillary lymph node staging and sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with breast cancer. AJR Am J roentgenology. (2020) 214:249–58. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.22022
31. Ojeda-Fournier H and Nguyen JQ. Ultrasound evaluation of regional breast lymph nodes. Semin Roentgenol. (2011) 46:51–9. doi: 10.1053/j.ro.2010.06.007
32. Akissue de Camargo Teixeira P, Chala LF, Shimizu C, Filassi JR, Maesaka JY, and de Barros N. Axillary lymph node sonographic features and breast tumor characteristics as predictors of Malignancy: A nomogram to predict risk. Ultrasound Med Biol. (2017) 43:1837–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.05.003
33. Zong Q, Deng J, Ge W, Chen J, and Xu D. Establishment of simple nomograms for predicting axillary lymph node involvement in early breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res. (2020) 12:2025–35. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S241641
34. Wang XF, Zhang GC, Zuo ZC, Zhu QL, Liu ZZ, Wu SF, et al. A novel nomogram for the preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:7039–50. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v12.6
35. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Who Classification of Tumours, Breast Tumours, 5th ed. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (2019).
36. Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the st gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann oncology: Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2013) 24:2206–23. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt303
37. Adler DD, Carson PL, Rubin JM, and Quinn-Reid D. Doppler ultrasound color flow imaging in the study of breast cancer: preliminary findings. Ultrasound Med Biol. (1990) 16:553–9. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(90)90020-D
38. Giuliano AE, Connolly JL, Edge SB, Mittendorf EA, Rugo HS, Solin LJ, et al. Breast cancer-major changes in the american joint committee on cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2017) 67:290–303. doi: 10.3322/caac.21393
39. Farrokh D, Ameri L, Oliaee F, Maftouh M, Sadeghi M, Forghani MN, et al. Can ultrasound be considered as a potential alternative for sentinel lymph node biopsy for axillary lymph node metastasis detection in breast cancer patients? Breast J. (2019) 25:1300–2. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13475
40. Fidan N, Ozturk E, Yucesoy C, and Hekimoglu B. Preoperative evaluation of axillary lymph nodes in Malignant breast lesions with ultrasonography and histopathologic correlation. J Belgian Soc Radiol. (2016) 100:58. doi: 10.5334/jbr-btr.899
41. Jones T, Neboori H, Wu H, Yang Q, Haffty BG, Evans S, et al. Are breast cancer subtypes prognostic for nodal involvement and associated with clinicopathologic features at presentation in early-stage breast cancer? Ann Surg Oncol. (2013) 20:2866–72. doi: 10.1245/s10434-013-2994-6
42. Van Calster B, Vanden Bempt I, Drijkoningen M, Pochet N, Cheng J, Van Huffel S, et al. Axillary lymph node status of operable breast cancers by combined steroid receptor and her-2 status: triple positive tumours are more likely lymph node positive. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2009) 113:181–7. doi: 10.1007/s10549-008-9914-7
43. Cheang MC, Voduc D, Bajdik C, Leung S, McKinney S, Chia SK, et al. Basal-like breast cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior prognostic value than triple-negative phenotype. Clin Cancer research: an Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2008) 14:1368–76. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-07-1658
44. Mattes MD, Bhatia JK, Metzger D, Ashamalla H, and Katsoulakis E. Breast cancer subtype as a predictor of lymph node metastasis according to the seer registry. J Breast Cancer. (2015) 18:143–8. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.2.143
45. Howland NK, Driver TD, Sedrak MP, Wen X, Dong W, Hatch S, et al. Lymph node involvement in immunohistochemistry-based molecular classifications of breast cancer. J Surg Res. (2013) 185:697–703. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.06.048
46. Wang NN, Yang ZJ, Wang X, Chen LX, Zhao HM, Cao WF, et al. A mathematical prediction model incorporating molecular subtype for risk of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in sentinel lymph node-positive breast cancer patients: A retrospective analysis and nomogram development. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan). (2018) 25:629–38. doi: 10.1007/s12282-018-0863-7
47. Zhou W, He Z, Xue J, Wang M, Zha X, Ling L, et al. Molecular subtype classification is a determinant of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with positive sentinel lymph nodes. PloS One. (2012) 7:e35881. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035881
48. Reyal F, Rouzier R, Depont-Hazelzet B, Bollet MA, Pierga JY, Alran S, et al. The molecular subtype classification is a determinant of sentinel node positivity in early breast carcinoma. PloS One. (2011) 6:e20297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020297
49. Zhang J, Li X, Huang R, Feng WL, Kong YN, Xu F, et al. A nomogram to predict the probability of axillary lymph node metastasis in female patients with breast cancer in China: A nationwide, multicenter, 10-year epidemiological study. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:35311–25. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13330
50. Dihge L, Bendahl PO, and Rydén L. Nomograms for preoperative prediction of axillary nodal status in breast cancer. Br J Surg. (2017) 104:1494–505. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10583
51. Holm-Rasmussen EV, Jensen MB, Balslev E, Kroman N, and Tvedskov TF. Reduced risk of axillary lymphatic spread in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2015) 149:229–36. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3225-y
52. Gülben K, Berberoğlu U, Aydoğan O, and Kınaş V. Subtype is a predictive factor of nonsentinel lymph node involvement in sentinel node-positive breast cancer patients. J Breast Cancer. (2014) 17:370–5. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2014.17.4.370
53. Qiu PF, Liu JJ, Wang YS, Yang GR, Liu YB, Sun X, et al. Risk factors for sentinel lymph node metastasis and validation study of the mskcc nomogram in breast cancer patients. Japanese J Clin Oncol. (2012) 42:1002–7. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys150
54. Silverstein MJ, Skinner KA, and Lomis TJ. Predicting axillary nodal positivity in 2282 patients with breast carcinoma. World J Surg. (2001) 25:767–72. doi: 10.1007/s00268-001-0003-x
55. Viale G, Zurrida S, Maiorano E, Mazzarol G, Pruneri G, Paganelli G, et al. Predicting the status of axillary sentinel lymph nodes in 4351 patients with invasive breast carcinoma treated in a single institution. Cancer. (2005) 103:492–500. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20809
56. Zhang Y, Li J, Fan Y, Li X, Qiu J, Zhu M, et al. Risk factors for axillary lymph node metastases in clinical stage T1-2n0m0 breast cancer patients. Medicine. (2019) 98:e17481. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000017481
57. Yu H, Zhang S, Zhang R, and Zhang L. The role of vegf-C/D and flt-4 in the lymphatic metastasis of early-stage invasive cervical carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer research: CR. (2009) 28:98. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-98
58. Shayan R, Inder R, Karnezis T, Caesar C, Paavonen K, Ashton MW, et al. Tumor location and nature of lymphatic vessels are key determinants of cancer metastasis. Clin Exp metastasis. (2013) 30:345–56. doi: 10.1007/s10585-012-9541-x
59. Nakano Y, Monden T, Tamaki Y, Kanoh T, Iwazawa T, Matsui S, et al. Importance of the retro-mammary space as a route of breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan). (2002) 9:203–7. doi: 10.1007/BF02967590
60. Tanis PJ, Nieweg OE, Valdés Olmos RA, and Kroon BB. Anatomy and physiology of lymphatic drainage of the breast from the perspective of sentinel node biopsy. J Am Coll Surg. (2001) 192:399–409. doi: 10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00776-6
61. Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, Beitsch PD, Brennan MB, Kelemen PR, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the acosog Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. Jama. (2017) 318:918–26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470
Keywords: breast cancer, axillary lymph nodes (ALN), ultrasonography (US), nomogram, preoperative
Citation: Guo X, Ling Y, Peng Y, Tan Q, Xie Y, Zhao H and Lv Q (2025) A preoperative prediction model for ipsilateral axillary lymph node metastasis of breast cancer based on clinicopathological and ultrasonography features: a prospective cohort study. Front. Oncol. 15:1536984. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1536984
Received: 29 November 2024; Accepted: 29 May 2025;
Published: 01 October 2025.
Edited by:
Haiyan Li, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Giovanni Tazzioli, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, ItalyXinmiao Yu, China Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Guo, Ling, Peng, Tan, Xie, Zhao and Lv. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qing Lv, bHZxaW5nQHdjaHNjdS5jbg==; Haina Zhao, MjMyMDg0NDEzN0BxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xinyi Guo
Xinyi Guo Yue Ling1,2†
Yue Ling1,2† Qiuwen Tan
Qiuwen Tan Haina Zhao
Haina Zhao Qing Lv
Qing Lv