- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 2Biological Resource Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 3Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
- 4Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Preventive Medicine, School of Public Health, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
Purpose: Ginger rhizomes have shown potential for promoting human health, including the prevention and treatment of cancer. Here, we investigated the anticancer activities of 6-gingerol and explored its mechanisms of action in ovarian cancer cells.
Methods: SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells were treated with different concentrations of 6-gingerol. Clonogenic assays, Flow cytometry, and Western blotting were used to evaluate cell survival and apoptosis. RT-qPCR and transfection experiments were performed to assess the role of miR-506, and bioinformatics tools were used to identify Gli3 as a target gene.
Results: In vitro, ovarian cancer cells underwent apoptosis following 6-gingerol treatment. 6-Gingerol suppressed Gli3 expression without affecting Bax, Bcl-2, or Bcl-xL levels. Low miR-506 expression was observed in ovarian cancer tissues, whereas 6-gingerol significantly promoted its expression. miR-506 directly suppressed Gli3 expression and induced apoptosis in SKOV3 cells.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that gingerol promoted the upregulation of miR-506, leading to the induction of apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. This study supports the potential of 6-gingerol-based therapy for ovarian malignancies.
Introduction
Ovarian cancer is the seventh most prevalent cancer in women and has the highest mortality rate among gynecological cancers (1). The five-year survival rate in patients with ovarian cancer is approximately 47% (2, 3). Due to the lack of specific and sensitive early detection methods, ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when metastasis has already occurred, limiting the effectiveness of surgical treatments and chemotherapy (4–7). Although poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors show promise, further clinical and laboratory studies are required to confirm their therapeutic efficacy (8, 9). Therefore, identifying new therapeutic targets for ovarian cancer is crucial.
Natural compounds with anticancer properties have shown effectiveness against various cancer types, often with minimal side effects (10, 11). Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) is a rich source of bioactive phytochemicals, with 6-gingerol being the primary phenolic compound. 6-Gingerol exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, and antioxidant effects (12–14). It stimulates antitumor activity in breast and cervical cancer, among other cancer types (15). However, the effects and mechanisms of 6-gingerol on ovarian cancer cell growth remain largely unknown.
This study aimed to determine whether 6-gingerol exerts anticancer effects on human ovarian cancer cells. We focused on the molecular mechanisms via which 6-gingerol suppresses cell growth and progression through the induction of apoptosis. Our findings revealed a strong correlation between Gli3 downregulation and 6-gingerol-induced apoptosis. Additionally, we confirmed that miR-506 is expressed at low levels in ovarian cancer tissues. By inhibiting Gli3 expression, miR-506 promotes apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. Furthermore, treatment with an miR-506-specific inhibitor reversed the cytotoxic effects of 6-gingerol. In conclusion, we investigated the effects of 6-gingerol on ovarian cancer cell proliferation and explored the underlying molecular mechanisms. Our study identified the miR-506/Gli3 signaling axis as a key pathway through which 6-gingerol induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells.
Methods and materials
Cell culture
The SKOV3 human ovarian carcinoma cell line was obtained and authenticated by the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (Invitrogen, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen), 1% streptomycin, and 1% ampicillin. Cells were maintained at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. 6-Gingerol was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (G1046).
Cell transfection
Transfection was performed using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Specifically, 2 µg of plasmids were transfected into cells that had been seeded on a six-well plate in the log phase 24 h prior. The transfection was performed using Lipofectamine 2000, and GFP transfection was used in parallel to estimate transfection efficiency. The pcDNA3.1-miR-506 plasmid and its scrambled negative control were obtained from GenePharma (Shanghai, China).
Clonogenic survival assay
Cells (1000 per dish) were seeded in triplicate in 100 mm Petri dishes and cultured in RPMI-1640 medium for 9 consecutive days. The medium was completely replaced on the day of seeding. Cells were fixed in 100% cold methanol for 15 min and stained with 0.25% crystal violet for another 15 min at room temperature. Colonies were washed with PBS and counted in three random fields.
PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted using a HiPure Universal miRNA kit (Magen, Guangzhou, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA quality and quantity were verified using a BioAnalyzer 2100 (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). cDNA was synthesized using a miScript Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). Real-time PCR was performed using a CFX Connect™ Real-Time System (Bio-Rad, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) and a miScript PCR Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturers’ instructions. Relative miR-506 expression was normalized to that of U6 rRNA and calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method. Moreover, 5s rRNA was used for normalization to determine relative expression. Primers were synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China). The following qPCR primers were used: miR-506 forward: 5′-GATCCTCTACTCAGAAGGGTGCCTTATTTTTG-3′; miR-506 reverse: 5′-AATTCAAAAATAAGGCACCCTTCTGAGTAGAG-3′; U6 forward: 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′; and U6 reverse: 5′-CGAATTTGCGTGTCATCCT-3′.
Western blotting
Total protein was extracted using a radioimmunoprecipitation assay, and concentrations were determined using a Pierce BCA Protein Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Proteins (30 µg/lane) were separated using 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). Membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat milk in PBS with 0.05% Tween-20 (PBST) and incubated overnight with primary antibodies at 4°C. Detection was performed using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL, Millipore) after incubation with the secondary antibodies and a wash with Tris-buffered saline. The antibodies used were anti-rabbit (ab6721, 1:2500) and anti-mouse (ab6789, 1:2500) (both from Abcam).
Cell apoptosis analysis
Apoptosis was analyzed using annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cytometry (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Cells in a single-cell suspension were incubated in the dark for 15 min in HEPES buffer and analyzed using ModFit software (BD Biosciences).
Caspase inhibition assay
To determine whether apoptosis induced by 6-gingerol is caspase-dependent, SKOV3 cells were pre-treated with 20 µM Z-VAD-FMK (Selleck Chemicals) for 2 hours, followed by treatment with 20 µM 6-gingerol. Apoptosis was then assessed using Annexin V-FITC/PI staining.
Statistical analysis
Unless otherwise stated, all experiments were performed at least three times independently. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 11.5 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). One-way ANOVA and multiple t-tests were used to assess significance, with P < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
Results
6-gingerol induced apoptosis in SKOV3 cells
We conducted an in vitro evaluation to determine the potential cytotoxic effects of 6-gingerol on human ovarian carcinoma SKOV3 cells. SKOV3 cells were treated with 5 µM,10 µM,15 µM and 20 µM concentrations of 6-gingerol for 6 days, and their survival rates were assessed using a clonogenic assay. Figure 1a shows a significant decrease in clonogenic survivors at both concentrations. In the 5 µM group, the survival rates were91%, 3.2%, 0.9% and0.07% on the 2nd, 4th,6th and8th days of culture, respectively. In the 10 µM group, the survival rates were 61%, 9.1%, and 0.07% on the 2nd, 4th, and 6th days of culture, respectively. In the 15 µM group, the survival rates were 52%, 0.39%, and 0.023% on the 2nd, 4th, and 6th days of culture, respectively. In the 20 µM group, all cells died by the 6th day of culture. To further confirm apoptosis, we analyzed the levels of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in response to 6-gingerol treatment, using endogenous tubulin as a loading control. As shown in Figure 1b, caspase-3 and cleaved PARP levels increased with higher 6-gingerol concentrations. To assess the dose-dependent effects of 6-gingerol on ovarian cancer cell apoptosis, we treated SKOV3 cells with 0, 10, and 20 µM of 6-gingerol for 2 days and analyzed the results using flow cytometry. The data (Figures 1c, d) show that the extent of apoptosis in SKOV3 cells increased proportionally with the 6-gingerol concentration. To further confirm the caspase dependence of 6-gingerol-induced apoptosis,SKOV3 cells were pre-treated with 20 µM Z-VAD-FMK (Selleck Chemicals) for 2 hours, followed by treatment with 20 µM 6-gingerol and treated with 20 µM 6-gingerol directly for 2 days. The data (Figures 1e, f) show that the extent of apoptosis in SKOV3 cells decreased proportionally with the Z-VAD-FMK treatment. These findings provide valuable insight into the caspase dependence of 6-gingerol to induce significant apoptotic responses in ovarian cancer cells, suggesting its effectiveness as a therapeutic agent.
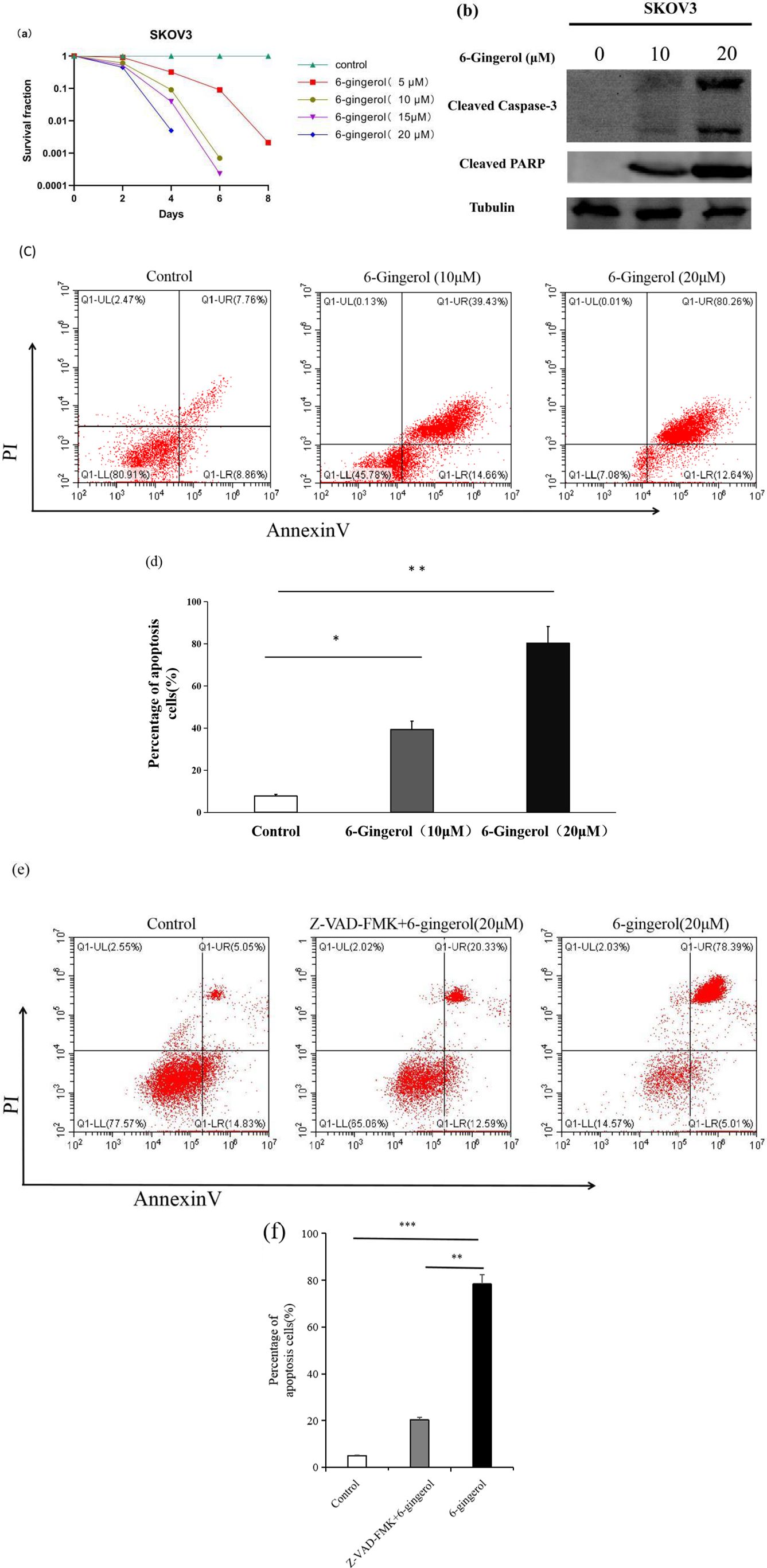
Figure 1. 6-gingerol induces apoptosis in SKOV3 cells. (a) Clonogenic survival assay showing the survival rates of SKOV3 cells treated with 5 µM,10 µM,15 µM and 20 µM 6-gingerol for different durations (1st, 2nd, 4th, and 6th days). Results are based on independent experiments (n = 3). (b) Western blot analysis of cleaved caspase-3 or and cleaved PARP levels in SKOV3 cells treated with 6-gingerol. Tubulin was used as the loading control. (c) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in SKOV3 cells treated with different 6-gingerol concentrations, using an Annexin V-FITC & propidium iodide (PI) apoptosis kit. Results are from three independent experiments (n = 3). (d) Quantification of apoptotic cells (double-positive for PI and Annexin V) from panel (c). Results are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001. (e) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in SKOV3 cells treated with 20 µM Z-VAD-FMK (Selleck Chemicals) for 2 hours, followed by treatment with 20 µM 6-gingerol and treated with 20 µM 6-gingerol directly for 2 days, using an Annexin V-FITC & propidium iodide (PI) apoptosis kit. Results are from three independent experiments (n = 3). (f) Quantification of apoptotic cells (double-positive for PI and Annexin V) from panel **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (e). Results are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001.
6-gingerol reduces Gli3 expression
Given that GL13 knockdown inhibits the growth and migration of ovarian cancer cells (16), we investigated Gli3 expression in 6-gingerol-induced apoptosis. As shown in Figures 2a, b, treatment with 6-gingerol significantly reduced Gli3 expression in SKOV3 cells. However, no notable changes in the levels of other apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bcl-2, Bcl-w, and Bik, were observed. These results suggest that Gli3 downregulation plays a critical role in 6-gingerol-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells.

Figure 2. 6-gingerol inhibits SKOV3 cells by reducing Gli3 expression. (a) Western blot analysis showing Gli3 protein levels in SKOV3 cells treated with 6-gingerol. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (b) Western blot analysis of apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl-xL, anti-Bcl-2, and Bax) in SKOV3 cells treated with 6-gingerol. Tubulin was used as a loading control.
6-gingerol upregulates miR-506
Evidence suggests that miRNAs are key regulators involved in cancer cell proliferation, differentiation, metastasis, and apoptosis. Therefore, we hypothesized that miRNAs might mediate the regulation of Gli3 expression by 6-gingerol. Using bioinformatics algorithms, including TargetScan, miRWalk, and miRDB, we identified seven candidate miRNAs that could potentially regulate Gli3 expression in response to 6-gingerol treatment. The relative expression of these miRNAs was determined using PCR and normalized to that of endogenous 5s rRNA. As shown in Figure 3, 6-gingerol treatment significantly upregulated miR-506 expression compared to other candidate miRNAs [(3.5 ± 0.6)-fold].
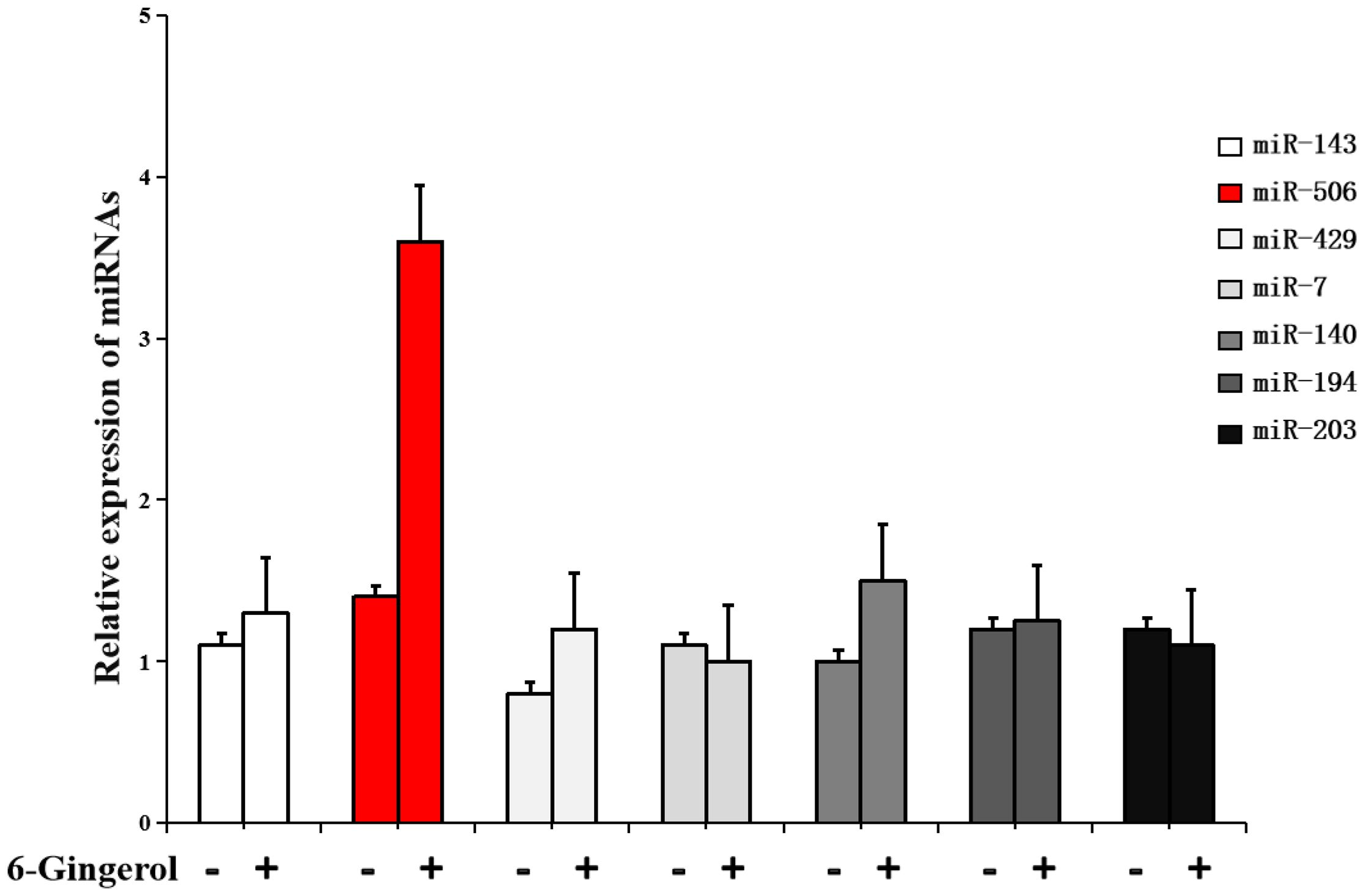
Figure 3. 6-gingerol increases microRNA (miR)-506 expression in SKOV3 cells. RT-PCR analysis showing the expression levels of candidate microRNAs predicted to target Gli3 in SKOV3 cells treated with 6-gingerol. Data are normalized to the levels of 5s rRNA.
miR-506 directly inhibits Gli3 and induces apoptosis in SKOV3 cells
To verify the effect of miR-506 on Gli3 expression and apoptosis, we transfected SKOV3 cells with miR-506. As shown in Figure 4a, upregulation of miR-506 significantly increased apoptosis in SKOV3 cells (45.2% ± 5.1%) compared to that in the scramble control (3.7% ± 0.3%, Figure 4b). Western blot analysis further showed that excessive miR-506 levels suppressed Gli3 protein expression (Figure 4c).
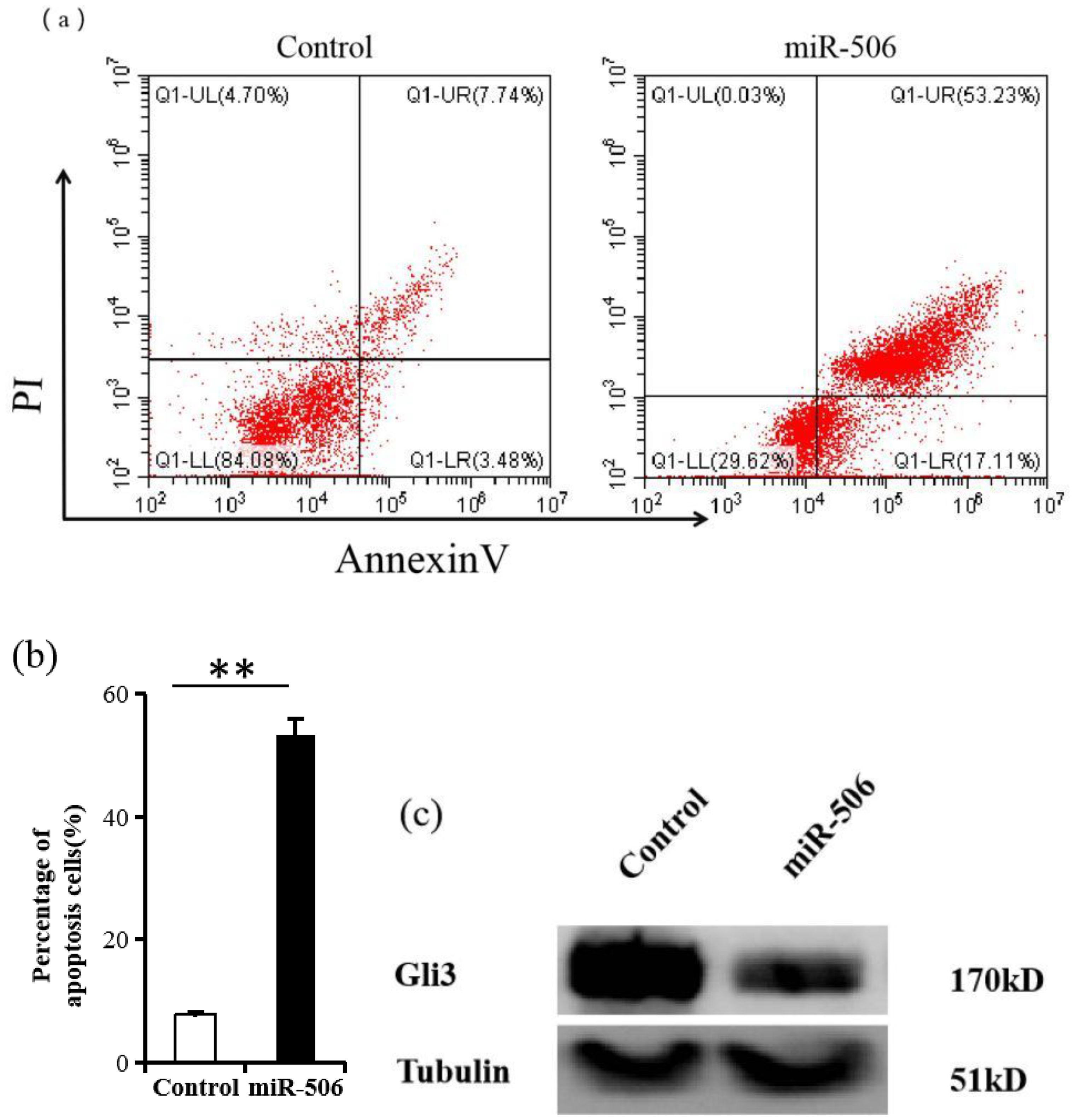
Figure 4. miR-506 suppresses Gli3 and induces apoptosis in SKOV3 cells. (a) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in SKOV3 cells after transfection with miR-506, using Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) staining. Results are based on three independent experiments (n = 3). (b) Quantification of apoptotic cells from panel (a). The data show the percentage of double-positive Annexin V and PI cells. Results are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01. (c) Western blot analysis showing Gli3 protein levels. Tubulin was used as a loading control.
6-gingerol induces apoptosis in SKOV3 cells via miR-506
We found that both 6-gingerol and miR-506 induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. To investigate whether miR-506 mediates the apoptosis effects of 6-gingerol, we used an miR-506-specific antagonist (antago-miR-506). As shown in Figure 5a, treatment with 20 μM 6-gingerol significantly reduced the survival rate of SKOV3 cells. This effect was reversed by co-treatment with antago-miR-506. Similarly, flow cytometry analysis showed that the apoptosis induced by 6-gingerol in SKOV3 cells (68.2% ± 3.1%) was significantly reduced (9.4% ± 0.9%) when antago-miR-506 was introduced (P<0.05, Figures 5b, c). To elucidate the molecular mechanism, we performed western blot analysis to assess Gli3 expression in three groups: control, 6-gingerol, and 6-gingerol + antago-miR-506. As shown in Figure 5d, 6-gingerol treatment suppressed Gli3 expression; however, this suppression was reversed by antago-miR-506. These findings suggest that 6-gingerol induces apoptosis in SKOV3 cells by upregulating miR-506, which downregulates Gli3.
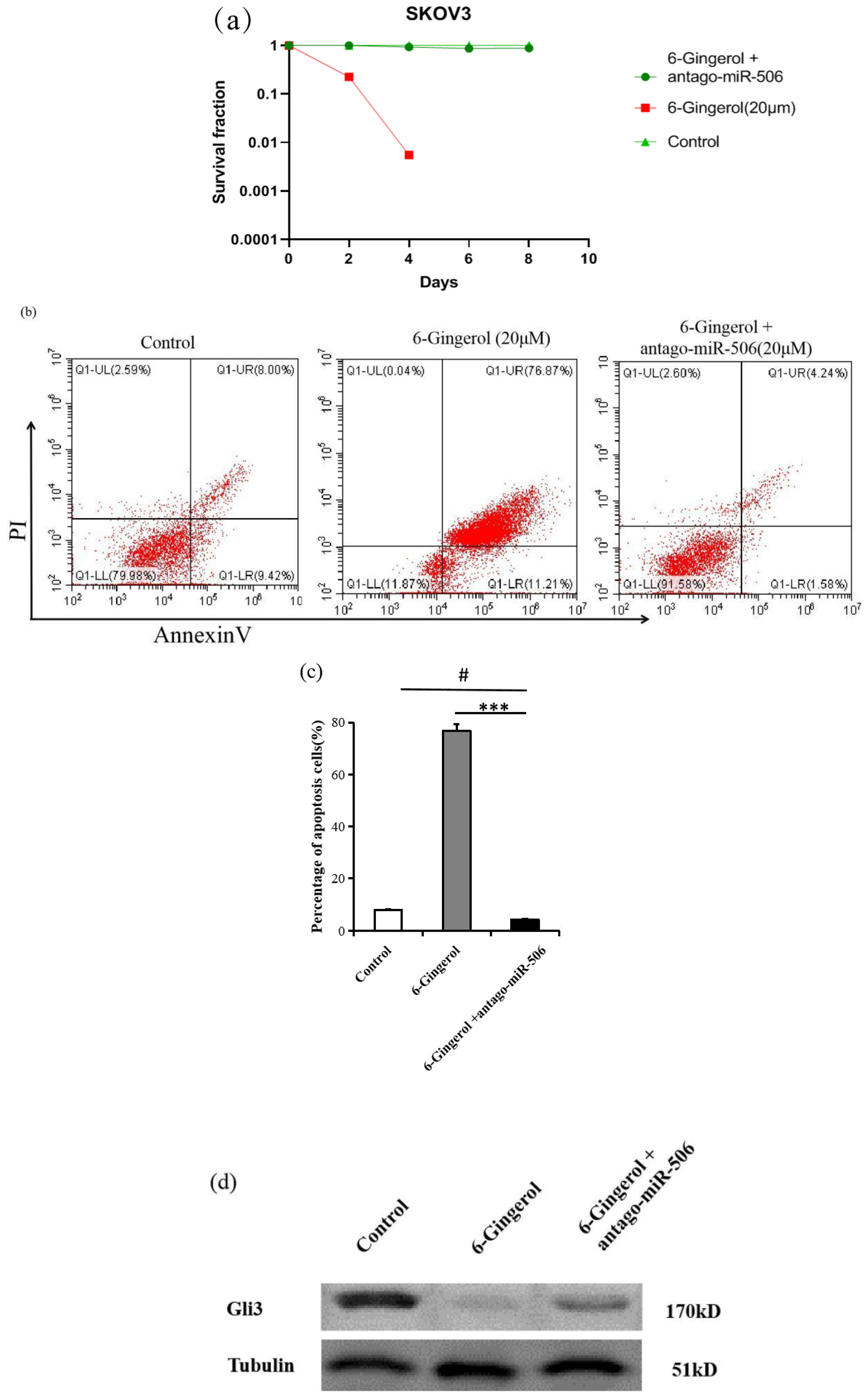
Figure 5. 6-gingerol induces apoptosis in SKOV3 cells via miR-506. (a) Clonogenic survival assay showing the percentage of SKOV3 cells surviving after treatment with 20 μM 6-gingerol or 20 μM 6-gingerol + antago-miR-506 over different time points (days 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8). Results are based on three independent experiments (n = 3). (b) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in SKOV3 cells treated with 6-gingerol or 6-gingerol + antago-miR-506 using Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) staining (n = 3) # P > 0.05, *** P < 0.001. (c) Quantification of apoptotic cells (double-positive for PI and Annexin V) from panel (b). Results are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). ***P < 0.001, #P > 0.05. (d) Western blot was performed with anti-Gli3 antibody. Tubulin was used as a loading control.
Discussion
Conventional anticancer therapies often lack specificity, targeting not only cancer cells but also healthy cells, leading to severe side effects. For example, platinum-based chemotherapy for ovarian cancer frequently causes gastrointestinal distress, bone marrow suppression, and liver and kidney damage (17, 18). Targeted therapies, while more specific, can still produce adverse effects, such as hypertension, proteinuria, and reduced blood cell counts. Natural compounds have emerged as promising alternatives to traditional treatments, offering increased efficiency with fewer side effects. These compounds can specifically target oncogenes and may also synergize with other chemotherapeutic agents (19, 20).
Throughout history, plant-based remedies have been widely used to treat various diseases, a practice that remains relevant today. Currently, herbal drugs account for over 50% of therapies in clinical trials (21). 6-Gingerol, the most abundant and biologically active phenolic compound present in the roots of ginger (Zingiber officinale), which has been more studied and more bioavailable than other phenolic compounds in ginger, exemplifies the medicinal potential of such natural products. Ginger has been used for centuries in China as a culinary spice and medicinal remedy. Ginger has been a staple in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, valued for its anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anticancer properties. Notably, 6-gingerol induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells by activating Bax transcription and caspase-7 (22).
The ability of 6-gingerol to arrest the cell cycle and induce apoptosis has been shown in human cervical and oral cancer cells (23, 24). Furthermore, 6-gingerol exhibits cytoprotective effects by reducing apoptosis and oxidative stress, potentially via the activation of Nrf2 pathways and inhibition of p38/NF-κB signaling (25). However, the mechanisms underlying the cytotoxic effects of 6-gingerol in ovarian cancer cells were previously unclear. Our study demonstrates that a concentration of 10 μM 6-gingerol effectively suppresses the clonogenic capacity of SKOV3 cells, leading to apoptosis.
We identified Gli3, a zinc-finger transcription factor, as a key player in this process. Gli3 has been implicated in the growth and metastasis of several cancer types. Knockdown of Gli3 suppresses the proliferation and migration of androgen receptor-positive breast and ovarian cancer cells, which does not occur for androgen receptor-negative cells (16). Additionally, loss of Gli3 in fibroblasts reduces suppressor cells derived from myeloid lineages and enhances natural killer cell activity, thereby inhibiting tumor growth (26). In colorectal cancer, Gli3 knockdown reduces cell migration and invasion by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the ERK signaling pathway. Elevated Gli3 expression correlated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer (27, 28). These results complicate the role of Gli3 expression in tumor tissues. In our study, 6-gingerol treatment significantly reduced Gli3 protein levels in SKOV3 cells. Interestingly, the expression of other apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bcl-2, Bax, and Bcl-xL, remained unchanged. To further explore the regulation of Gli3, we examined the role of miR-506, a microRNA known to regulate cell growth, differentiation, and metastasis, in SKOV3 cells treated with 6-gingerol. Bioinformatics analysis predicted miR-506 as a potential regulator of Gli3 expression, and our results confirmed that 6-gingerol upregulates miR-506, which in turn suppresses Gli3 expression and induces ovarian cancer cell apoptosis.
The role of miR-506 in cancer is context-dependent. In some cancer types, miR-506 acts as a tumor suppressor, whereas in others, it may function as an oncogene (29). For instance, Tong et al. (30) reported a high miR-506 expression in HCPT-resistant SW1116/HCPT colon cancer cells, suggesting its role in tumor suppression. Similarly, Streicher et al. (31) showed that the miR-506–514 cluster is consistently overexpressed in most melanomas, independent of the presence of B-raf or N-ras mutations. This cluster, or one of its sub-clusters (Sub-cluster A) comprising six mature miRNAs, can inhibit cell growth, promote apoptosis, and reduce invasiveness and colony formation in melanoma cell lines by reducing the expression of its target genes. Conversely, Luo et al. (32) found that miR-506 expression is reduced in glioblastoma. Overexpression of miR-506 in these cells suppressed cell growth, blocked the G1/S cell cycle transition, and inhibited cell invasion into glioblastoma cells. Zhang et al. (33) reported that cancer tissues and cultured cells exhibited lower miR-506 levels. They found that miR-506 expression was negatively correlated with EZH2 expression, lymph node invasion, tumor growth, metastasis, and TNM stage. Higher miR-506 levels were associated with a more favorable prognosis in patients. Consistent with these findings, we observed that miR-506 expression was significantly downregulated in ovarian cancer tissues. Our results showed that upregulation of miR-506 reduces ovarian cancer cell proliferation by targeting the transcription factor Gli3.
This study has several limitations. First, although SKOV3 cells are representative of high-grade serous ovarian cancer, validation in additional cell lines (e.g., CAOV3, OVCAR3) would strengthen the findings. Second, the functional role of Gli3 in migration/invasion was not examined, which should be addressed in future studies given its known metastatic functions. These limitations do not affect the core mechanistic conclusions but highlight directions for further research.
In summary, Our findings demonstrate that 6-gingerol induces ovarian cancer cell apoptosis through miR-506-mediated Gli3 suppression, providing an alternative to conventional Bax/Bcl-2-targeting approaches. Interestingly, while 6-gingerol has shown promise in combination with cisplatin (34), our work reveals its equally potent single-agent activity through this newly identified pathway. The clinical relevance of miR-506 downregulation in patient tumors further supports the therapeutic potential of 6-gingerol, particularly for tumors with impaired miR-506/Gli3 regulation.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author contributions
JX: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. H-HW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. HJ: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. X-QT: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. X-JH: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. X-XC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Research Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangxi Province (2019B028), Jiangxi Province Science and Technology Infrastructure Platform Construction Project (20203CCD46007), the Science and Technology Plan Fund of Jiangxi Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission (No. 202210036), Science and technology plan project of Jiangxi Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2021B672), Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (190141), National Natural Science Foundation of China (#81760504), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Senior Project (No. 20242BAB25485), and General Project of Science and Technology Plan of Jiangxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2024B0268). We hereby declare that: All funders (including the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation and Jiangxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine) had no involvement in the study design, data collection/analysis, manuscript preparation, or publication decision.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Boyd J. Specific keynote: hereditary ovarian cancer: what we know. Gynecologic Oncol. (2003) 88:S8–S10. doi: 10.1006/gyno.2002.6674
2. Moufarrij S, Dandapani M, Arthofer E, Gomez S, Srivastava A, Lopez-Acevedo M, et al. Epigenetic therapy for ovarian cancer: promise and progress. Clin Epigenetics. (2019) 11:7. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0602-0
3. Lheureux S, Braunstein M, and Oza AM. Epithelial ovarian cancer: Evolution of management in the era of precision medicine. CA Cancer J Clin. (2019) 69:280–304. doi: 10.3322/caac.21559
4. Stewart C, Ralyea C, and Lockwood S. Ovarian cancer: an integrated review. Semin Oncol Nurs. (2019) 35:151–6. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2019.02.001
5. Bonifácio VDB. Ovarian cancer biomarkers: moving forward in early detection. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1219:355–63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34025-4_18
6. Sun Y, Meng C, and Liu G. MicroRNA-506-3p inhibits ovarian cancer metastasis by down-regulating the expression of EZH2. J Cancer. (2022) 13:943–50. doi: 10.7150/jca.66959
7. Kuroki L and Guntupalli SR. Treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer. BMJ. (2020) 371:m3773. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3773
8. Yang C, Xia BR, Zhang ZC, Zhang YJ, Lou G, and Jin WL. Immunotherapy for ovarian cancer: adjuvant, combination, and neoadjuvant. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:577869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.577869
9. O’Malley DM. New therapies for ovarian cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2019) 17:619–21. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.5018
10. Kang DY, Sp N, Kim DH, Joung YH, Lee HG, Park YM, et al. Salidroside inhibits migration, invasion and angiogenesis of MDA-MB 231 TNBC cells by regulating EGFR/Jak2/STAT3 signaling via MMP2. Int J Oncol. (2018) 53:877–85. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4430
11. Sp N, Kang DY, Jo ES, Rugamba A, Kim WS, Park YM, et al. Tannic acid promotes TRAIL-induced extrinsic apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial ROS in human embryonic carcinoma cells. Cells. (2020) 9:282. doi: 10.3390/cells9020282
12. Wen J, Wang J, Li P, Wang R, Wang J, Zhou X, et al. Protective effects of higenamine combined with [6]-gingerol against doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and toxicity in H9c2 cells and potential mechanisms. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 115:108881. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108881
13. Kubra IR and Rao LJ. An impression on current developments in the technology, chemistry, and biological activities of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2012) 52:651–88. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2010.505689
14. Hong MK, Hu LL, Zhang YX, Xu YL, Liu XY, He PK, et al. 6-Gingerol ameliorates sepsis-induced liver injury through the Nrf2 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 80:106196. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106196
15. de Lima RMT, Dos Reis AC, de Menezes APM, Santos JVO, Filho JWGO, Ferreira JRO, et al. Protective and therapeutic potential of ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract and [6]-gingerol in cancer: A comprehensive review. Phytother Res. (2018) 32:1885–907. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6134
16. Lin M, Zhu H, Shen Q, Sun LZ, and Zhu X. Gli3 and androgen receptor are mutually dependent for their Malignancy-promoting activity in ovarian and breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. (2022) 92:110278. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110278
17. Yang L, Xie H-J, Li Y-Y, Wang X, Liu X-X, and Mai J. Molecular mechanisms of platinum-based chemotherapy resistance in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. (2022) 47:82. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8293
18. Garrido MP, Fredes AN, Lobos-González L, Valenzuela-Valderrama M, Vera DB, and Romero C. Current treatments and new possible complementary therapies for epithelial ovarian cancer. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:77. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010077
19. Naus PJ, Henson R, Bleeker G, Wehbe H, Meng F, and Patel T. Tannic acid synergizes the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs in human cholangiocarcinoma by modulating drug efflux pathways. J Hepatol. (2007) 46:222–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2006.08.012
20. Joung YH, Na YM, Yoo YB, Darvin P, Sp N, Kang DY, et al. Combination of AG490, a Jak2 inhibitor, and methylsulfonylmethane synergistically suppresses bladder tumor growth via the Jak2/STAT3 pathway. Int J Oncol. (2014) 44:883–95. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2250
21. Sekiwa Y, Kubota K, and Kobayashi A. Isolation of novel glucosides related to gingerdiol from ginger and their antioxidative activities. J Agric Food Chem. (2000) 48:373–7. doi: 10.1021/jf990674x
22. Wala K, Szlasa W, Sauer N, Kasperkiewicz-Wasilewska P, Szewczyk A, Saczko J, et al. Anticancer efficacy of 6-gingerol with paclitaxel against wild type of human breast adenocarcinoma. Molecules. (2022) 27:2693. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092693
23. Kapoor V, Aggarwal S, and Das SN. 6-Gingerol Mediates its Anti Tumor Activities in Human Oral and Cervical Cancer Cell Lines through Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest. Phytother. Res. (2016) 30:588–95. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5561
24. Rastogi N, Duggal S, Singh SK, Porwal K, Srivastava VK, Maurya R, et al. Proteasome inhibition mediates p53 reactivation and anti-cancer activity of 6-Gingerol in cervical cancer cells. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:43310. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6383
25. Han X, Liu P, Zheng B, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Xue Y, et al. 6-Gingerol exerts a protective effect against hypoxic injury through the p38/Nrf2/HO-1 and p38/NF-κB pathway in H9c2 cells. J Nutr Biochem. (2022) 104:108975. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.108975
26. Scales MK, Velez-Delgado A, Steele NG, Schrader HE, Stabnick AM, Yan W, et al. Combinatorial Gli activity directs immune infiltration and tumor growth in pancreatic cancer. PloS Genet. (2022) 18:e1010315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010315
27. Shen M, Zhang Z, and Wang P. Gli3 promotes invasion and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. BioMed Res Int. (2021) 2021:8889986. doi: 10.1155/2021/8889986
28. Iwasaki H, Nakano K, Shinkai K, Kunisawa Y, Hirahashi M, Oda Y, et al. Hedgehog Gli3 activator signal augments tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer via upregulation of adherence-related genes. Cancer Sci. (2013) 104:328–36. doi: 10.1111/cas.12073
29. Li J, Ju J, Ni B, and Wang H. The emerging role of miR-506 in cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:62778–88. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11294
30. Tong JL, Zhang CP, Nie F, Xu XT, Zhu MM, Xiao SD, et al. MicroRNA 506 regulates expression of PPAR alpha in hydroxycamptothecin-resistant human colon cancer cells. FEBS Lett. (2011) 585:3560–8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.10.021
31. Streicher KL, Zhu W, Lehmann KP, Georgantas RW, Morehouse CA, Brohawn P, et al. A novel oncogenic role for the miRNA-506–514 cluster in initiating melanocyte transformation and promoting melanoma growth. Oncogene. (2012) 31:1558–70. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.345
32. Luo Y, Sun R, Zhang J, Sun T, Liu X, and Yang B. miR-506 inhibits the proliferation and invasion by targeting IGF2BP1 in glioblastoma. Am J Transl Res. (2015) 7:2007–14.
33. Zhang Y, Lin C, Liao G, Liu S, Ding J, Tang F, et al. MicroRNA-506 suppresses tumor proliferation and metastasis in colon cancer by directly targeting the oncogene EZH2. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:32586–601. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5309
Keywords: ovarian cancer, 6-gingerol, apoptosis, miR-506, Gli3
Citation: Xiong J, Wu H-H, Jiang H, Li H, Tan X-Q, He X-J and Cheng X-X (2025) 6-gingerol promotes apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through miR-506/Gli3 signaling pathway activation. Front. Oncol. 15:1547771. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1547771
Received: 18 December 2024; Accepted: 25 August 2025;
Published: 12 September 2025.
Edited by:
Paolo Andreini, University of Siena, ItalyReviewed by:
Subramanyam Dasari, Indiana University Bloomington, United StatesHariprasath Lakshmanan, JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, India
Copyright © 2025 Xiong, Wu, Jiang, Li, Tan, He and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong-Hu Wu, d2hodmlyZ2lsQDEyNi5jb20=; Xiao-Ju He, ODAyNDgzODVAcXEuY29t; Xue-Xin Cheng, Y3h4bmN1QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jun Xiong1†
Jun Xiong1† Hong-Hu Wu
Hong-Hu Wu Xiao-Qing Tan
Xiao-Qing Tan Xiao-Ju He
Xiao-Ju He Xue-Xin Cheng
Xue-Xin Cheng