- 1Department of Breast Surgery, Baoding No.1 Central Hospital, Baoding, Hebei, China
- 2Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding, Hebei, China
- 3Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding, China
This review summarizes the relationship between HER2 protein expression and the efficacy of three anti-HER2 targeted therapies in breast cancer patients: monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). The effectiveness of monoclonal antibody therapies positively correlates with HER2 protein expression levels, with HER2 IHC 3+ patients exhibiting better outcomes than IHC 2+/FISH+ patients. In contrast, those with low HER2 protein expression (IHC 1+ or 2+/FISH–) were not beneficial. In patients with HER2-positive breast cancer, the efficacy of T-DM1 is independent of HER2 protein expression levels. Patients with different HER2 expression levels can benefit from T-DXd treatment, with a potential positive correlation with HER2 expression levels. For TKIs, efficacy appeared to be positively correlated with HER2 expression, with HER2 IHC 3+ patients outperforming those with HER2 IHC 1+ or 2+/ISH+. However, high-level evidence to evaluate the relationship between HER2 expression levels and the efficacy of different targeted therapies is lacking. Determining whether HER2 protein expression levels influence treatment outcomes and whether tailored strategies based on HER2 protein expression levels should be implemented holds significant implications for advancing precision medicine in breast cancer.
Introduction
In 2022, approximately 2.309 million new cases of breast cancer were diagnosed globally, with 667,000 deaths, making it the second most common cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide (1). In China, 357,000 new female breast cancer cases and 75,000 deaths have been reported, ranking second in incidence and fifth in mortality among female cancers (2). HER2-positive breast cancer accounts for approximately 15–20% of all breast cancers, although this proportion varies across studies (3–7). HER2-positive breast cancer is characterized by aggressive biological behavior and poor prognosis. The advent of anti-HER2 targeted therapies has significantly improved patient outcomes. Currently, three anti-HER2 drugs are clinically available: 1. Monoclonal antibodies, such as trastuzumab, pertuzumab, and inetetamab; 2. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), such as T-DM1 and T-DXd; 3. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) include lapatinib, neratinib, tucatinib, and pyrotinib.
HER2, a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 185 kDa, comprises extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domains and serves as the target for anti-HER2 therapies. The first two drug classes target the extracellular ligand-binding domain, whereas the third targets the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. HER2 protein expression is commonly assessed using immunohistochemistry (IHC), categorized as overexpression (IHC 3+), moderate expression (IHC 2+), or low or ultra-low expression (IHC 1+ or 0) based on the number of stained tumor cells, staining intensity, and completeness of membrane staining.
Despite these advances, some patients fail to benefit from targeted therapy. Predictive biomarkers for therapeutic efficacy, including hormone receptor status, HER2 protein expression levels, HER2 gene copy number, HER2 heterogeneity, histological grade, Ki-67 index, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, have been explored, but no universally recognized predictive factor has been established.
Studies have suggested a correlation between HER2 protein expression and the efficacy of anti-HER2 therapies. However, high-level evidence for this is scarce. This review examines the relationship between HER2 protein expression and the efficacy of various anti-HER2 therapies, providing a foundation for future research.
Monoclonal antibodies
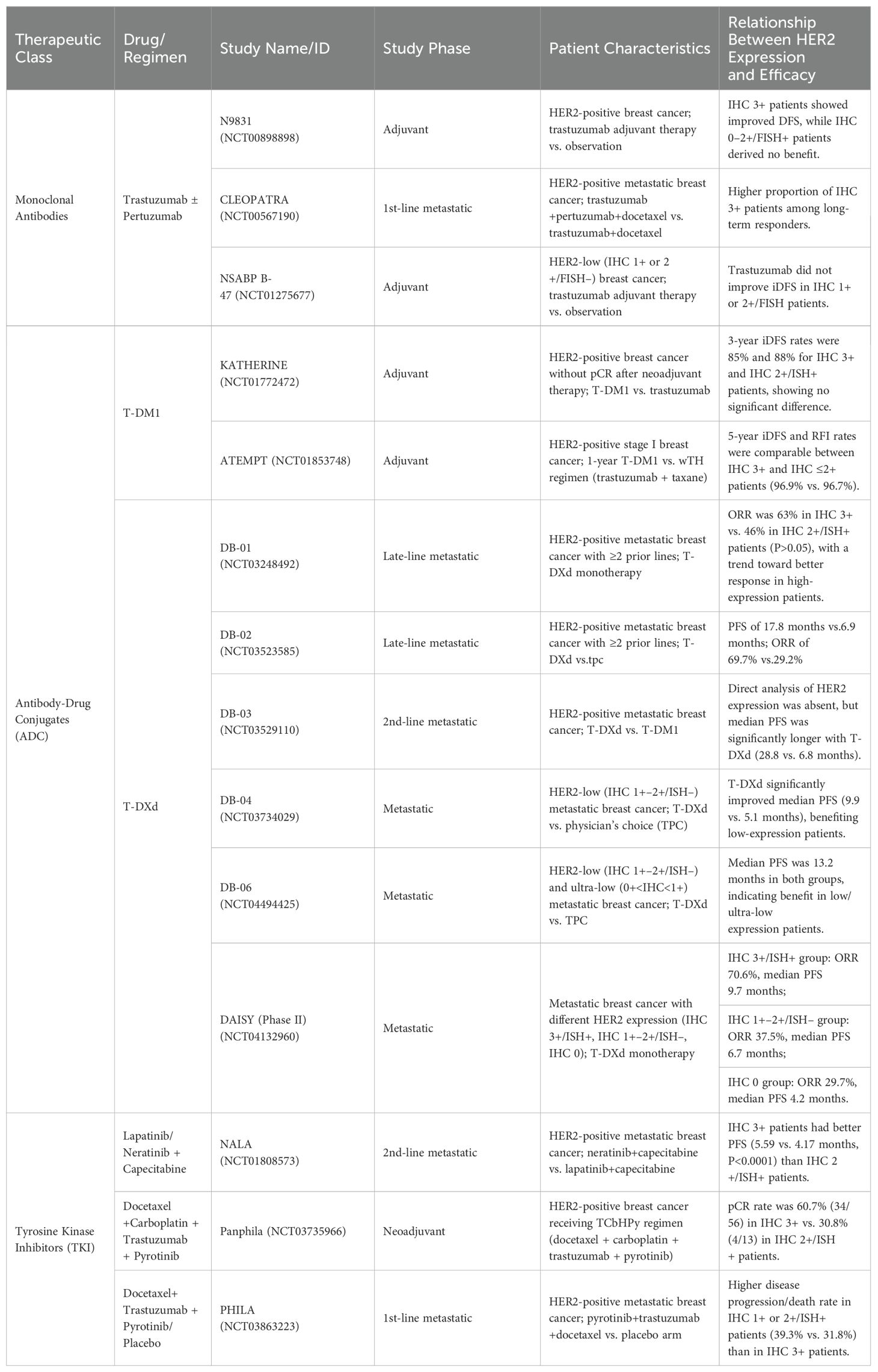
Trastuzumab was the first drug approved for HER2-positive breast cancer. It binds to the extracellular domain (ECD) IV of HER2, suppressing intracellular HER2 signaling pathways. Pertuzumab binds to ECD II, preventing HER2 heterodimerization with HER1, HER3, and HER4, blocking downstream tumor signaling. Guidelines recommend trastuzumab with or without pertuzumab as the first-line therapy for HER2-positive disease. Studies have indicated that HER2 protein expression levels correlate with the efficacy of trastuzumab with or without pertuzumab. Patients with HER2 IHC 3+ tumors showed better outcomes than those with HER2 IHC 2+/FISH+ tumors, whereas patients with low HER2 expression (IHC 1+ or 2+/FISH–) had no benefit.
Most studies have focused on neoadjuvant therapy. Several investigations have shown that pathologic complete response (pCR) rates are significantly higher in HER2 IHC 3+ patients than in HER2 IHC 2+/FISH+ patients (8–17). Limited data exist on adjuvant and salvage therapies, but the N9831 trial (NCT00898898) suggests that adjuvant trastuzumab improves disease-free survival (DFS) in HER2 IHC 3+ patients, with no benefit for HER2 IHC 0–2+/FISH+ patients (18). Similarly, the CLEOPATRA study (NCT00567190) found a higher proportion of HER2 IHC 3+ patients among long-term responders (19). However, the NSABP B-47 trial (NCT01275677) confirmed that trastuzumab provides no invasive DFS (iDFS) benefit for patients with low HER2 expression(IHC 1+ or 2+/FISH–) (20). Atallah suggests that adjuvant anti-HER2 therapy after surgery can improve breast cancer-specific survival in patients with HER-2 IHC3+ tumors and ER-/HER-2 IHC2+ tumors, but it has no significant impact on patients with ER+/HER-2 IHC2+ tumors (4).
The differential efficacy of monoclonal antibodies may result from: (1) Higher dependence of HER2 IHC 3+ tumors on HER2 signaling, providing more binding sites for antibodies to block signaling and inhibit proliferation (20); (2) Co-expression of estrogen receptor (ER) and HER2 in HER2 IHC 2+/FISH+ tumors, leading to signaling crosstalk and diminished inhibitory effects on proliferation (9).
Antibody-drug conjugates
T-DM1
Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) is the first ADC approved for HER2-positive breast cancer. It comprises trastuzumab connected via a stable linker to DM1, a maytansine derivative with a drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) of ~3.5:1. The KATHERINE trial (NCT01772472) demonstrated that adjuvant T-DM1 therapy significantly improves outcomes compared with trastuzumab in HER2-positive patients with non-pCR following neoadjuvant therapy. Subgroup analysis revealed that both HER2 IHC3+ and HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ patients benefit similarly from T-DM1, with 3-year invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) rates of 85% and 88%, respectively (21). The ATEMPT trial (NCT01853748) showed that in patients with HER2-positive stage I breast cancer, one year of adjuvant T-DM1 significantly improved 3-year iDFS compared to the wTH regimen. The 5-year iDFS rate was 97%, the recurrence-free interval (RFI) rate was 98.3%, the overall survival (OS) rate was 97.8%, and the breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) rate was 99.4%. Subgroup analysis demonstrated consistent efficacy across all subgroups, regardless of tumor size, hormone receptor status, or HER2 immunohistochemistry (IHC). The 5-year iDFS (96.9% vs. 96.7%) and RFI (98.4% vs. 97.8%) rates were comparable between IHC3+ and IHC ≤2+ patients (22).
These findings suggest that the efficacy of T-DM1 was observed with almost comparable outcomes in patients with HER2 IHC3+ and HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ patients. However, the efficacy of T-DM1 was limited in HER2-low patients.
T-DXd
Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) is a HER2 ADC comprising a humanized HER2 antibody with the same sequence as trastuzumab conjugated to deruxtecan (DXd). Based on the outstanding results from the DESTINY-Breast series (DB studies), T-DXd is considered a groundbreaking ADC drug with significant clinical potential. Key optimizations in its mechanism of action, such as the high cytotoxicity of topoisomerase inhibitors, the use of a tetrapeptide linker technology, a drug-to-antibody ratio of up to 8:1, and enhanced membrane permeability contributing to a powerful bystander effect, are the main reasons behind the impressive efficacy of T-DXd.
The DB-01 study (NCT03248492) demonstrated the efficacy of T-DXd in HER2-positive patients who received multiple lines of prior treatment. In patients who had received a median of six prior lines of therapy, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 16.4 months, with an overall response rate (ORR) of 60.9%. Notably, HER2 protein expression level did not significantly impact treatment benefit, with no significant difference in ORR between IHC 3+ and IHC 2+/ISH+ patients (63% vs. 46%, P>0.05) (23).
The DB-02 study (NCT03523585) further confirmed that T-DXd significantly outperformed physician’s choice treatment (TPC regimens) in HER2-positive patients after multiple lines of treatment, with a median PFS of 17.8 months vs. 6.9 months and ORR of 69.7% vs. 29.2% (24).
The DB-03 study (NCT03529110) established T-DXd as the standard second-line treatment in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer, showing superior efficacy to T-DM1. The median PFS was 28.8 months vs. 6.8 months, with a 12-month PFS rate of 75.8% vs. 34.1% (P<0.001), and an ORR of 79.7% vs. 34.2% (25).
The DB-04 study (NCT03734029) demonstrated that, after 1–2 lines of chemotherapy, T-DXd significantly outperformed the TPC regimen in patients with HER2-low (IHC 1-2+/ISH-) advanced breast cancer, with a median PFS of 9.9 months vs. 5.1 months (P<0.001). T-DXd showed excellent efficacy in patients with low HER2 expression (IHC 1+-2+) (26).
At the 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting, the DB-06 study (NCT04494425) results were presented, showing that T-DXd significantly improved median PFS in patients with HER2-low (IHC 1+-2+/ISH-) and HER2-ultralow (0+<IHC<1+) advanced breast cancer compared to TPC, with a median PFS of 13.2 months for both groups. However, no direct comparison has been made between the two groups (27).
The phase 2 DAISY trial demonstrated HER2 expression is a determinant of T-DXd efficacy. The ORR and mPFS are 70.6%(95% CI 58.3–81) and 9.7 months (95% CI 6.8–13) in HER2 IHC 3+ or ISH+ cohort; 37.5%(95% CI 26.4–49.7) and 6.7 months (95% CI 4.4–8.3) in IHC 1+-2+/ISH- cohort; 29.7%(95% CI 15.9–47) and 4.2 months (95% CI 2.0–5.7) in HER2 IHC 0 cohort (28).
These DB series studies and the DAISY trial suggest that patients with varying HER2 protein expression levels can benefit from T-DXd treatment, with the degree of benefit potentially correlated with HER2 expression levels. The median PFS from DB-01, DB-02, and DB-03 studies enrolling patients with HER2-positive breast cancer were 16.4 months, 17.8 months, and 28.8 months, respectively. While the median PFS from DB-04 and DB-06 studies enrolling patients with HER2-low or ultralow breast cancer were 9.9 months and 13.2 months, respectively. IHC 3+ and IHC 2+/ISH+ patients appear to experience greater benefit compared to HER2-low (IHC 1+ or 2+/ISH-) and HER2-ultralow (0+<IHC<1+) patients. This was further confirmed by the DAISY trial. In HER2-positive patients, subgroup analysis of the DB-01 study indicated that HER2 protein expression level (IHC 3+ vs. IHC 2+/ISH+) did not affect the treatment benefit. More prospective studies are needed to compare the efficacy of T-DXd in patients with different HER2 expression levels.
The focality of HER2 expression might attenuate T-DM1 activity, which was unable to induce a bystander effect for surrounding HER2-negative cells due to a non-cleavable linker. This issue was resolved through T-Dxd. A unique feature of T-DXd is its ability to target HER2-low/ultralow patients. This remarkable efficacy appears multifactorial based on enhanced features of T-DXd compared with T-DM1, the ability to deliver a higher dose, and the bystander effect, tackling intratumor HER2 heterogeneity. However, a high percentage of HER2 IHC 0 cells in the tumor and their spatial distribution relative to HER2-overexpressing cells were associated with a decreased response to T-DXd. This may explain the potential correlation between the magnitude of benefit with T-DXd and HER2 expression.
In recent years, several new ADC agents, such as SYD985, RC48-ADC, ZW49and ARX-788, have emerged. However, it remains unclear whether these drugs exhibit differential efficacies in patients with varying HER2 expression levels.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Currently available tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clinical use include lapatinib, neratinib, tucatinib, and pyrotinib. TKIs are small molecules that target the intracellular catalytic kinase domain of HER2, competing with ATP, blocking phosphorylation and activating downstream signaling cascades. Lapatinib and Tucatinib are reversible, while Neratinib and Pyrotinib are irreversible pan-HER TKIs that target EGFR, HER2, and HER4.
The NALA study (NCT01808573) aimed to compare the efficacy of lapatinib or neratinib in combination with capecitabine in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients, enrolling 621 patients who had received second-line treatment. The study found that the median progression-free survival (PFS) for the neratinib group was 5.6 months, compared to 5.5 months for the lapatinib group (P=0.059) (29). Subgroup analysis revealed that when both groups were combined, the PFS for HER2 IHC3+ patients was superior to that of HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ patients (5.59 months vs 4.17 months, P<0.0001), suggesting that HER2 IHC3+ patients are more sensitive to both lapatinib and neratinib than HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ patients. However, there is no separate analysis of the differences in efficacy between lapatinib and neratinib in HER2 IHC3+ and HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ patients (30).
The Panphila study (NCT03735966) was a single-arm phase II trial that enrolled 69 HER2-positive patients to evaluate the neoadjuvant efficacy of the TCbHPy regimen (docetaxel, carboplatin, trastuzumab, and pyrotinib). Subgroup analysis showed a trend towards higher pathologic complete response (pCR) rates in HER2 IHC3+ patients compared to HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ patients (34/56, 60.7% vs 4/13, 30.8%). However, the sample size of this study was relatively small (31).
The PHILA study (NCT03863223) aimed to compare the efficacy of first-line treatment with docetaxel and trastuzumab in combination with either pyrotinib or placebo in metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, enrolling 590 patients, including 297 in the pyrotinib group. In the pyrotinib group, the rate of disease progression or death was higher in HER2 IHC1+ or 2+/ISH+ patients (24/61, 39.3%) than in HER2 IHC3+ patients (75/236, 31.8%), although statistical analysis was not performed (32).
Currently, no studies have assessed the relationship between tucatinib efficacy and HER2 protein expression.
Existing studies suggest that the efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be related to HER2 protein expression levels, with HER2 IHC3+ patients showing better efficacy compared to HER2 IHC1+ or 2+/ISH+ patients. The differential efficacy may result from: HER2 protein overexpressing tumors showing significantly higher expression of several receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), including FGFR4, EGFR, and HER2 itself (33), providing more binding sites for antibodies to block signaling and inhibit proliferation. However, high-level evidence supporting this relationship is still lacking.
Conclusion and future directions
Currently, there is no universally accepted predictive factor to accurately forecast the efficacy of anti-HER2 targeted therapies. In clinical practice, the relationship between HER2 protein expression and the efficacy of anti-HER2 targeted therapies has gradually gained attention. Existing studies suggest that HER2 protein expression levels are associated with the efficacy of trastuzumab-based therapies with or without pertuzumab-targeted therapies. Patients with HER2 protein overexpression (IHC 3+) exhibit better therapeutic outcomes than those with moderate HER2 protein expression (HER2 IHC2+/FISH+). Conversely, patients with low HER2 protein expression (IHC 1+ or 2+/FISH-) did not benefit from these treatments. The efficacy of T-DM1 was observed with almost comparable outcomes in patients with HER2 IHC3+ and HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ patients. However, the efficacy of T-DM1 was limited in HER2-low patients. All patients, regardless of HER2 protein expression levels, benefited from T-DXd therapy, and the extent of the benefit appeared to be positively correlated with HER2 expression levels. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as lapatinib, pyrotinib, and tucatinib may show superior efficacy in HER2 IHC3+ patients compared to those with HER2 IHC2+/ISH+ expression.
This review is more aligned with current clinical practice, and its conclusions hold practical significance for clinical work. The review focuses on analyzing, synthesizing, and summarizing data from multiple rigorous, high-evidence-level large-scale clinical studies, particularly the IHC 3+ and IHC 2+ subgroups (Table 1), ultimately concluding that HER2 protein expression level is a robust predictive biomarker for anti-HER2 therapy response. The authors propose that for HER2-dependent breast cancer patients with IHC 3+ status, de-escalation therapy may be considered. One of the most promising advantages of targeted therapy is its ability to minimize chemotherapy-related toxicity while maintaining efficacy, thereby reducing reliance on cytotoxic drugs, improving patients’ quality of life, and lowering healthcare costs. Currently, treatment guidelines do not differentiate between IHC 2+ and IHC 3+ HER2-positive breast cancer patients. However, a shift in therapeutic strategy may be warranted—for instance, combining large and small molecular-targeted agents to enhance efficacy and overcome resistance, or exploring ADCs alone or in combination with TKIs. The ultimate goal is to improve long-term survival and cure rates, which holds profound implications for precision medicine in breast cancer. Challenges in HER2 IHC Interpretation and Emerging Solutions Current HER2 immunohistochemical (IHC) assessment remains hampered by inaccuracy and limitations, including subjective quantification of positive cell percentage, membrane staining intensity evaluation, and exclusion of false positives (e.g., edge artifacts), all of which demand substantial time and expertise. Moreover, temporal and spatial heterogeneity in HER2-positive breast cancer is a key determinant of therapeutic response and resistance. To address these issues, researchers are actively developing novel HER2 detection technologies. For example, optimizing AI models by training them on extensive HER2-stained datasets enriched with metastatic samples could enhance both precision and efficiency, thereby addressing subjectivity and variability concerns. Beyond HER2 status, pathway crosstalk and interactions introduce substantial uncertainty during treatment. Identifying the dominant biological drivers of individual tumors (e.g., whether ER or HER2 signaling primarily governs tumor growth and progression) is critical. Thus, differential gene expression (DGE) analysis of relevant pathways represents a vital direction for future research.
However, there is currently a lack of high-level evidence evaluating the relationship between HER2 protein expression levels and the efficacy of different anti-HER2 targeted therapies. High-quality, prospective controlled studies are needed to further clarify the relationship between HER2 protein expression level and the efficacy of various targeted therapies and in the future, treatment strategies can be adjusted individually according to HER2 expression level to improve the precision of breast cancer treatment.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author, Chongzhu Hu, upon reasonable request.
Author contributions
JL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. XP: Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. YY: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. RY: Validation, Writing – review & editing. XH: Formal Analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YD: Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CH: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Medical Science Research Project of Hebei (project number: 20251432). The funding organizations had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Zheng R, Chen R, Han BF, Wang SM, Li L, Chen K, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. Chin J Oncol. (2024) 46:221–31. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20240119-00035
3. Arias VEA, Gobbi H, Ioshii SO, Scapulatempo C, Paz ARD, Silva VDD, et al. Assessment of HER-2 status in invasive breast cancer in Brazil. Rev da Associacao Med Bras (1992). (2017) 63:566–74. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.63.07.566
4. Atallah NM, Alsaleem M, Toss MS, Mongan NP, and Rakha E. Differential response of Her2-positive breast cancer to anti-Her2 therapy based on Her2 protein expression level. Br J Cancer. (2023) 129:1692–705. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02426-4
5. Waks AG and Winer EP. Breast cancer treatment: A review. JAMA. (2019) 321:288–300. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19323
6. Loibl S and Gianni L. HER2-positive breast cancer. Lancet (London England). (2017) 389:2415–29. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)32417-5
7. Xin L, Zhou SC, Jiang ZF, and Liu YH. Survey of neoadjuvant therapy for early Her-2 positive breast cancer in 118 tertiary hospitals in China. Chin J Pract Surg. (2024) 44:98–102. doi: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2024.01.16
8. Krystel-Whittemore M, Xu J, Brogi E, Ventura K, Patil S, Ross DS, et al. Pathologic complete response rate according to Her2 detection methods in Her2-positive breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant systemic therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2019) 177:61–6. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05295-9
9. Zhu P, Lv H, Bai Q, Shui R, Xu X, and Yang W. Efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy on HER2-positive breast cancer: A clinicopathological analysis. Chin J Pathol. (2023) 52:907–11. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20230213-00123
10. Chen W, Li FX, Lu DL, Jiang J, and Li J. Differences between the efficacy of Her2(2+)/fish-positive and Her2(3+) in breast cancer during dual-target neoadjuvant therapy. Breast (Edinburgh Scotland). (2023) 71:69–73. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2023.07.008
11. Yue R, Kong L, Hao X, Yang J, Han M, Cui G, et al. Her2 protein expression levels predict efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: A real-world study. Chin J Clin Med. (2023) 17:765–70. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2023.07.002
12. Xu B, Shen J, Zhang L, Zhao W, and Wang L. Her2 protein expression level is positively associated with the efficacy of neoadjuvant systemic therapy in Her2-positive breast cancer. Pathology Res Pract. (2022) 234:153900. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153900
13. Katayama A, Miligy IM, Shiino S, Toss MS, Eldib K, Kurozumi S, et al. Predictors of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant treatment and changes to post-neoadjuvant Her2 status in Her2-positive invasive breast cancer. Modern Pathol. (2021) 34:1271–81. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00738-5
14. Orrù S, Pascariello E, Pes B, Rallo V, Barbara R, Muntoni M, et al. Biomarker dynamics affecting neoadjuvant therapy response and outcome of HER2-positive breast cancer subtype. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:12869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40071-2
15. Yan H, Xiao H, Zhu J, Zhang J, and Liu Z. Association between the HER2 protein Expression Level and the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast Cancer. Cancer Manage Res. (2020) 12:12715–22. doi: 10.2147/cmar.s278694
16. Wang Y, Singh K, Dizon D, Graves T, Amin A, and Yakirevich E. Immunohistochemical Her2 score correlates with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in Her2-positive primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2021) 186:667–76. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06124-8
17. Chen HL, Chen Q, and Deng YC. Pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant anti-Her2 therapy is associated with Her2 immunohistochemistry score in HER2-positive early breast cancer. Medicine. (2021) 100:e27632. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000027632
18. Perez EA, Reinholz MM, Hillman DW, Tenner KS, Schroeder MJ, Davidson NE, et al. HER2 and chromosome 17 effect on patient outcome in the N9831 adjuvant trastuzumab trial. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:4307–15. doi: 10.1200/jco.2009.26.2154
19. Swain SM, Miles D, Kim SB, Im YH, Im SA, Semiglazov V, et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (CLEOPATRA): end-of-study results from a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:519–30. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30863-0
20. Fehrenbacher L, Cecchini RS, Geyer CE Jr., Rastogi P, Costantino JP, Atkins JN, et al. Nsabp B-47/Nrg oncology phase iii randomized trial comparing adjuvant chemotherapy with or without trastuzumab in high-risk invasive breast cancer negative for Her2 by fish and with Ihc 1+ or 2. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:444–53. doi: 10.1200/jco.19.01455
21. Mamounas EP, Untch M, Mano MS, Huang CS, Geyer CE Jr., von Minckwitz G, et al. Adjuvant T-Dm1 versus trastuzumab in patients with residual invasive disease after neoadjuvant therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer: subgroup analyses from Katherine. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:1005–14. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.04.011
22. Tarantino P, Tayob N, Villacampa G, Dang C, Yardley DA, Isakoff SJ, et al. Adjuvant trastuzumab emtansine versus paclitaxel plus trastuzumab for stage I human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: 5-year results and correlative analyses from attempt. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:3652–65. doi: 10.1200/jco.23.02170
23. Modi S, Saura C, Yamashita T, Park YH, Kim SB, Tamura K, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-positive breast cancer. New Engl J Med. (2020) 382:610–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1914510
24. André F, Hee Park Y, Kim SB, Takano T, Im SA, Borges G, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with Her2-positive metastatic breast cancer (Destiny-breast02): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England). (2023) 401:1773–85. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)00725-0
25. Cortés J, Kim SB, Chung WP, Im SA, Park YH, Hegg R, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine for breast cancer. New Engl J Med. (2022) 386:1143–54. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2115022
26. Modi S, Jacot W, Yamashita T, Sohn J, Vidal M, Tokunaga E, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated Her2-low advanced breast cancer. New Engl J Med. (2022) 387:9–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2203690
27. Bardia A, Hu X, Dent R, Yonemori K, Barrios CH, O’Shaughnessy JA, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan after endocrine therapy in metastatic breast cancer. New Engl J Med. (2024) 391(22):2110–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2407086
28. Mosele F, Deluche E, Lusque A, Le Bescond L, Filleron T, Pradat Y, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in metastatic breast cancer with variable Her2 expression: the phase 2 daisy trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:2110–20. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02478-2
29. Saura C, Oliveira M, Feng YH, Dai MS, Chen SW, Hurvitz SA, et al. Neratinib plus capecitabine versus lapatinib plus capecitabine in Her2-positive metastatic breast cancer previously treated with ≥ 2 Her2-directed regimens: phase iii nala trial. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:3138–49. doi: 10.1200/jco.20.00147
30. Saura C, Matito J, Oliveira M, Wildiers H, Brufksy AM, Waters SH, et al. Biomarker analysis of the phase III nala study of neratinib + Capecitabine versus lapatinib + Capecitabine in patients with previously treated metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:5818–27. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-21-1584
31. Liu Z, Wang C, Chen X, Zhu J, Sun X, Xia Q, et al. Pathological response and predictive role of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in HER2-positive early breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant pyrotinib plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy (Panphila): A multicentre phase 2 trial. Eur J Cancer (Oxford England: 1990). (2022) 165:157–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.01.022
32. Ma F, Yan M, Li W, Ouyang Q, Tong Z, Teng Y, et al. Pyrotinib versus placebo in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel as first-line treatment in patients with HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer (Phila): randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). (2023) 383:e076065. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076065
33. Dybdal N, Leiberman G, Anderson S, McCune B, Bajamonde A, Cohen RL, et al. Determination of HER2 gene amplification by fluorescence in situ hybridization and concordance with the clinical trials immunohistochemical assay in women with metastatic breast cancer evaluated for treatment with trastuzumab. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2005) 93:3–11. doi: 10.1007/s10549-004-6275-8
Keywords: HER2 protein expression, breast cancer, targeted therapy, efficacy prediction, treatment strategies
Citation: Liu J, Peng X, Yang Y, Yue R, Huang X, Du Y and Hu C (2025) Current research status on HER2 protein expression levels and the efficacy of targeted therapy in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1551415. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1551415
Received: 25 December 2024; Accepted: 18 June 2025;
Published: 30 June 2025.
Edited by:
Agnieszka Jagiełło-Gruszfeld, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, PolandReviewed by:
Tasaduq H. Wani, University of Oxford, United KingdomJianbo Zhou, Sichuan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Peng, Yang, Yue, Huang, Du and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chongzhu Hu, aGN6Njk5OEBzaW5hLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jiani Liu
Jiani Liu Xinyu Peng2†
Xinyu Peng2†