- 1Oncology Unit, Casa di Cura Villa Salus, Messina, Italy
- 2Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Enna “Kore”, Enna, Italy
- 3Clinical Department of Oncology and Hematology, University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy
- 4Istituto Nazionale Tumori Di Napoli, IRCCS “G. Pascale”, Naples, Italy
- 5Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, University of Foggia, Foggia, Italy
- 6Division of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and Neuroendocrine Tumors, European Institute of Oncology (IEO), IRCCS, Milan, Italy
- 7Department Unit of Oncology, Medical Oncology Department, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Università Vita-Salute, Milano, Italy
- 8SCDU Oncologia, Ospedale Maggiore della Carità, Novara, Italy
- 9Medical Oncology Unit, AORN “San Pio”, Benevento, Italy
- 10Oncology Operative Unit, “Santa Maria delle Grazie” Hospital, ASL Napoli 2 NORD, Pozzuoli, Italy
- 11Oncology Division, Ospedale “San Giovanni di Dio”, Frattamaggiore, Italy
- 12Medical Oncology, Mauriziano Hospital, Turin, Italy
- 13Precision Medicine Department, Medical Oncology, University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”, Naples, Italy
Introduction: Literature has shown that there is a correlation between increased circulatory inflammatory factors and negative prognosis, which can be evaluated through the using the neutrophil and lymphocyte ratio (NLR). The aim of this research is to investigate the predictive and prognostic role of the NLR in recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (R/M HNSCC) patients, treated with immunotherapy, and its correlation to the overall survival (OS), progression free survival (PFS) and objective response rate (ORR).
Methods: This multicentric study coordinated by the Oncology Unit of University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”, retrospectively analyzed data from 135 patients diagnosed with R/M HNSCC from 13 Italian oncological centers.
Results: Two groups were made using the median NLR value of 4.2. 71 patients (52.6%) had NLR>4 and 64 patients (47.4%) had NLR<=4. Mean OS of patients with NLR>4 was significantly shorter than that of patients with NLR<=4 (23.1 vs 37.4 months, p= 0.002). Univariable analysis showed a statistically significant correlation between OS and NLR value (p=0.002), and between OS and ECOG (p=0.022). Median PFS stratified by NLR value, was statistically significant: 6.5 vs 20 months in patients with NLR>4 and NLR<=4, respectively (p= 0.013O). ORR in the general population was 32.6%. NLR-stratified ORR confirmed the unfavorable prognostic role of high NLR: 20% if NLR<=4, and 12.5% if NLR>4.
Discussion: Basal NLR value lower than the cut-off of 4 is independently associated with better OS, PFS and ORR in patients with R/M HNSCC treated with immunotherapy, in first- or second- line.
1 Introduction
Squamous cell carcinoma of the head/neck cancer (HNSCC) represents a malignant tumor of epithelial origin characterized by a marked chemo-radiosensitivity, which makes it treatable when diagnosed. However, even in cases where it is possible to treat the disease with curative intent (surgery associated adjuvant radiotherapy – RT– with chemotherapy -CT-, or chemoradiotherapy treatment with definitive intent) the risk of locoregional recurrence and/or distant metastasis remains high.
The advent of immunotherapy in clinical practice has revolutionized the therapeutic possibilities of oncology, offering a new therapeutic chance in the treatment of several neoplasms, including those of the head and neck district (1–3). Until the approval in Italy in 2020 of pembrolizumab use, the first-line therapy used in recurrent/metastatic (R/M) HNSCC cases, was the EXTREME protocol (anti-EGFR cetuximab, platinum and 5-fluorouracil). Now in these cases, specifically, pembrolizumab may be used in the forefront, alone or in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy and 5-fluorouracil, in those patients whose tumors express programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) with a combined positive score (CPS) equal to or more than 1, and nivolumab in patients relapsed within six months of treatment with platinum salts or in second line, regardless of the CPS (1, 4). Among the prognostic and predictive factors of head and neck cancer we can include: age, race, performance status (PS) at diagnosis, smoking habit, the stage of neoplasm, a previous RT in the adjuvant/definitive setting, positivity for HPV infection (1).
With the advent of precision medicine, it represents an extremely tempting challenge to search for new prognostic and predictive markers to personalize treatments more and more, thus identifying responders from non-responders, to save patients from the toxicity of unnecessary treatments (5, 6). It is now known that there is a correlation between tumor development/progression and the state of systemic inflammatory response (7). Several studies have shown that there is a correlation between increased circulatory inflammatory factors, which can be evaluated through the ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin, (so-called Glasgow prognostic score) and a negative prognosis (8). Similar results were also observed using the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (9–12). In fact, while neutrophil appears to be a snapshot of a pro-inflammatory systemic immune response, lymphopenia appears to adversely affect response to immunotherapy treatments. The functioning of programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor (PD1), in fact, is strictly dependent on the activity of T cells (13). The presence of a predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate pattern, consisting of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, CD4+ T helper 1 (Th1) cells, Natural Killer (NK) cells, and mature dendritic cells, can induce greater benefits from immunotherapy treatment compared to tumors lacking such infiltrating lymphocytes. Inflamed tumors, therefore, host a large number of T lymphocytes at the periphery and within the tumor, with increased expression of T cell activation markers, type 1 interferon, and high levels of Th1 cytokines and chemokines, which in turn can promote T cell recruitment and activate effector functions. Conversely, the non-inflamed tumor microenvironment has few effector T cells and a prevalence of cells expressing chronic inflammation markers such as macrophages, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), Th2 cytokines, and tumor-associated chemokines, resulting in the creation of an immunosuppressed microenvironment that allows tumor progression. Therefore, understanding whether a tumor is immunologically hot or cold has important therapeutic implications. In immunologically hot tumors, the problem is that cancer acts by activating molecular brakes (e.g., the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory signaling axis) that act on immune cells. The use of checkpoint antibodies that deactivate this brake, acting on the function of PD-1/PD-L1, allows T cells to regain their activity as tumor-recognizing cells (in practice, the “block” on immune activation is “unblocked”) (14–16).
With our study we wanted to investigate the predictive and prognostic role of the neutrophil/lymphocyte relationship in patients with R/M HNSCC, treated with immunotherapy (in first- or second-line) assessing the correlation between the value of NLR and the overall survival (OS), the progression free survival (PFS) and the objective response rate (ORR) of the patient population.
2 Materials and methods
The department of Oncology of the University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” coordinated the retrospective collection of data of patients diagnosed with HNSCC, from 13 Italian oncological centers (A.O.U. “Luigi Vanvitelli”, Napoli; A.O.U. “Federico II”, Napoli; IRCSS Pascale, Napoli; A.O.U. Ospedali Riuniti, Foggia; A.O.R.N. Sant’Anna e San Sebastiano, Caserta; Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza, San Giovanni Rotondo; IRCCS San Raffaele, Milano; Ospedale Maggiore della Carità, Novara; A.O.R.N. “San Pio”, Benevento; Ospedale Santa Maria delle Grazie, Pozzuoli; Ospedale “San Giovanni di Dio”, Frattamaggiore; Ospedale Mauriziano, Torino; Casa di Cura Villa Salus, Messina).
We included patients older than 18, with histological diagnosis of HNSCC, performance status (PS) according to Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) between 0-2, who had received immunotherapy in the first- or second- line of treatment, and whose pre-treatment NLR values were known. Data were censored on 31/01/2024. The study was approved by the local ethics committee (prot. N°280, 06/10/2020).
2.1 Patient population
Data from 142 HNSCC patients were collected retrospectively from 2016 to 2024. Of these 142 patients 5 were excluded because they did not undergo immunotherapy treatment either in first- or second- line, 2 were excluded due to lack of data. 135 patients were included in the final analysis.
2.2 Data
We collected retrospectively patient data, including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), ECOG PS, smoking and/or alcohol habit, primary tumor localization, histology, stage, co-morbidity, previous treatments (including surgery, RT and/or adjuvant systemic medical therapy), treatments used in first- and second- line, site of re-appearance of disease and/or metastasization, NLR value, response and duration of treatment response.
The BMI was calculated by dividing the weight in kilograms by the square height in square meters, and a value of 18 was threshold for underweight. The NLR was calculated by dividing the neutrophil count by the lymphocyte count (obtained by researching in the blood registers of the different hospitals involved) before therapy. Stage was defined using the American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC) 8th edition classification. Response to treatment was measured by each center involved independently using Response assessment Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1.
To analyze the difference in outcomes, both OS and PFS stratified according to the pre-treatment value of NLR, we divided the patients, using the median NLR value of 4.2, into two groups: patients with NLR <= 4 and NLR > 4.
2.3 Objectives
Primary endpoint is the stratified OS based on the value of NLR<=4 or > 4; secondary endpoints are the PFS similarly stratified according to the cut off value of the NLR, and the objective response rate (ORR), stratified on the basis of the values of the neutrophil lymphocyte ratio.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with the software “Statistical Package for Social Sciences” (SPSS). The statistical significance of all hypothesis tests (α) was set to 0.05, so that a p < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
OS was calculated from the start date of immunotherapy (first- or second- line) and death for any cause; PFS was evaluated from the date of onset of immunotherapy (first- or second- line) and the date of disease progression (distant metastases, locoregional recurrence or death for any cause). The median follow-up period was evaluated using the reverse Kaplan Meier. ORR of the general population and the two subgroups of patients were compared. The probability of survival (OS and PFS) was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method, with a 95% confidence interval (C.I.). The survival curves thus obtained were compared with the Log-Rank Test, in order to evaluate the differences in survival, based on the NLR value. Finally, a univariable and multivariate survival analysis was performed with the Cox proportional hazards regression model. In this case, after having established with univariable analysis the unfavorable prognostic role correlated with a high NLR value, all known prognostic variables (immunotherapy administration setting, BMI, smoking habit and previous RT) were included in the multivariate analysis to confirm the independent prognostic value of the NLR.
3 Results
3.1 Patient population
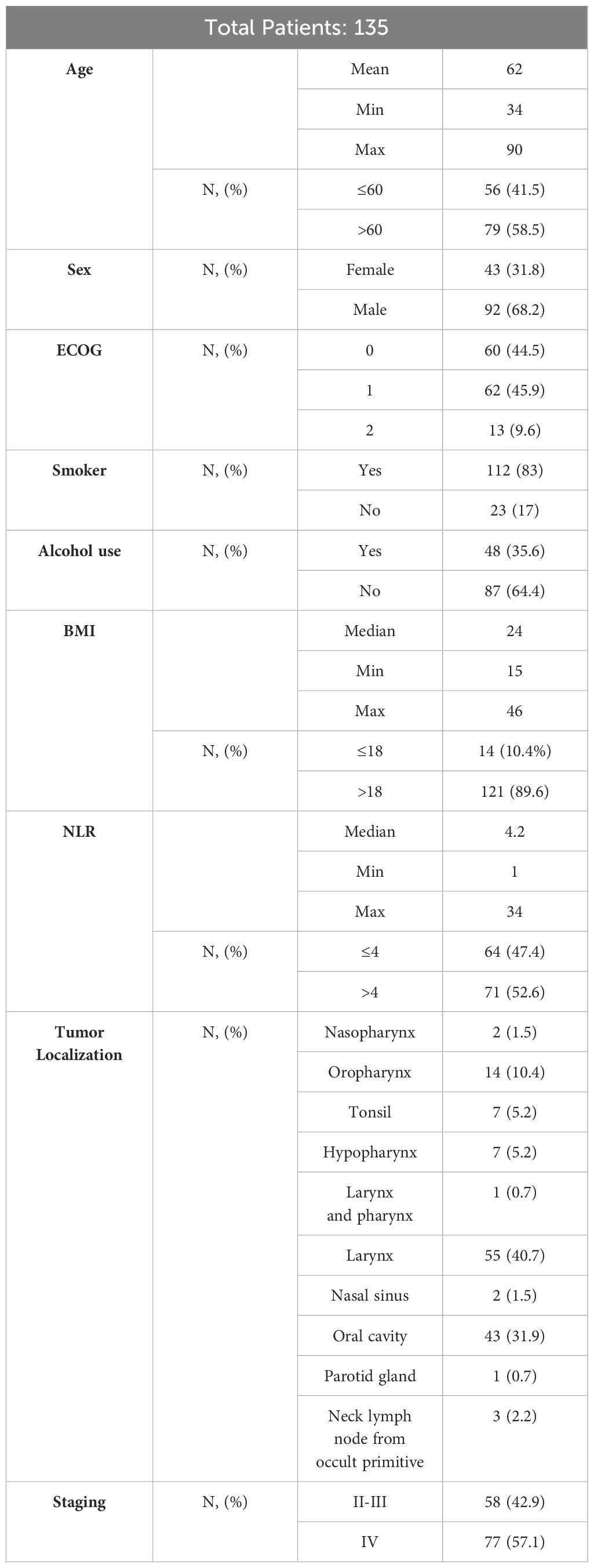
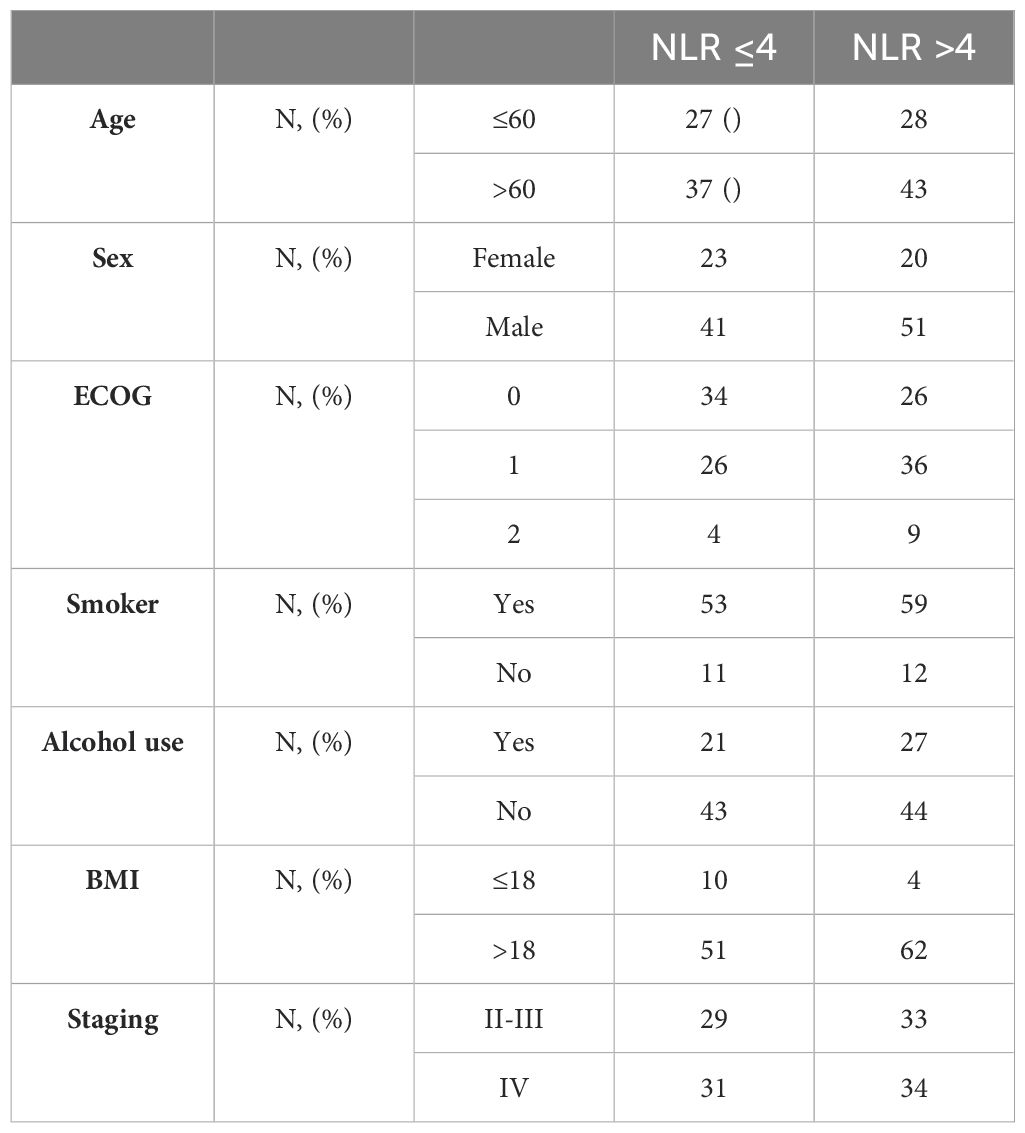
135 patients were included in the study, stratified on the basis of NLR in two groups. All patients had squamous cell carcinoma. The median of NLR was 4.2 (range 1 - 34), with 64 patients (47.4%) in the group with NLR<=4 and 71 patients (52.6%) with NLR >4. Basal characteristics of the population are reported in Tables 1, 2.
75 patients (55.6%) had undergone surgery, and 94 patients (69.6%) had received RT. 84 patients (62.2%) had received systemic medical treatment concurrently with RT (58 (69%) with cisplatin, 5 (6%) with carboplatin and 8 (9.5%) with cetuximab; in 13 patients (15.5%) the data was not found. At the time of progression 62 patients (45.9%) had resumption of non-visceral disease (locoregional, lymph node, bone) and 53 (39.3%) of visceral metastases patients. Specifically, 59 patients had lung involvement, 6 hepatic and 1 cerebral. In 20 patients, disease progression localization was not specified. 85 patients (63%) had received first-line immunotherapy (alone or in association with chemotherapy) and 50 (37%) in second-line. In first-line, 4.4% of patients were treated with CT alone, 23.7% with CT + anti EGFR, 34.1% with combination of platinum-based CT and immunotherapy, 1.5% with single agent anti EGFR, 34.1% with only immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI); 4 patients were treated in II line with nivolumab.
3.2 Response to treatments and prognostic factors
The average follow-up was 33.8 months for OS and 22.2 months for PFS. At data censoring, 48.1% of patients died, with a median OS of 17.6 months (IC 95%, 11.3-24.1) (Figure 1A). Mean OS of patients with NLR >4 was significantly shorter than that of patients with NLR <=4 (23.1 months vs 37.4 months, Hazard Ratio (HR) of 0.45 [IC 95%, 0.27-0.74] p= 0.002) (Figure 1B). Median OS in the NLR>4 group was 13.3 months; in the NLR<=4 group the value was not reached.
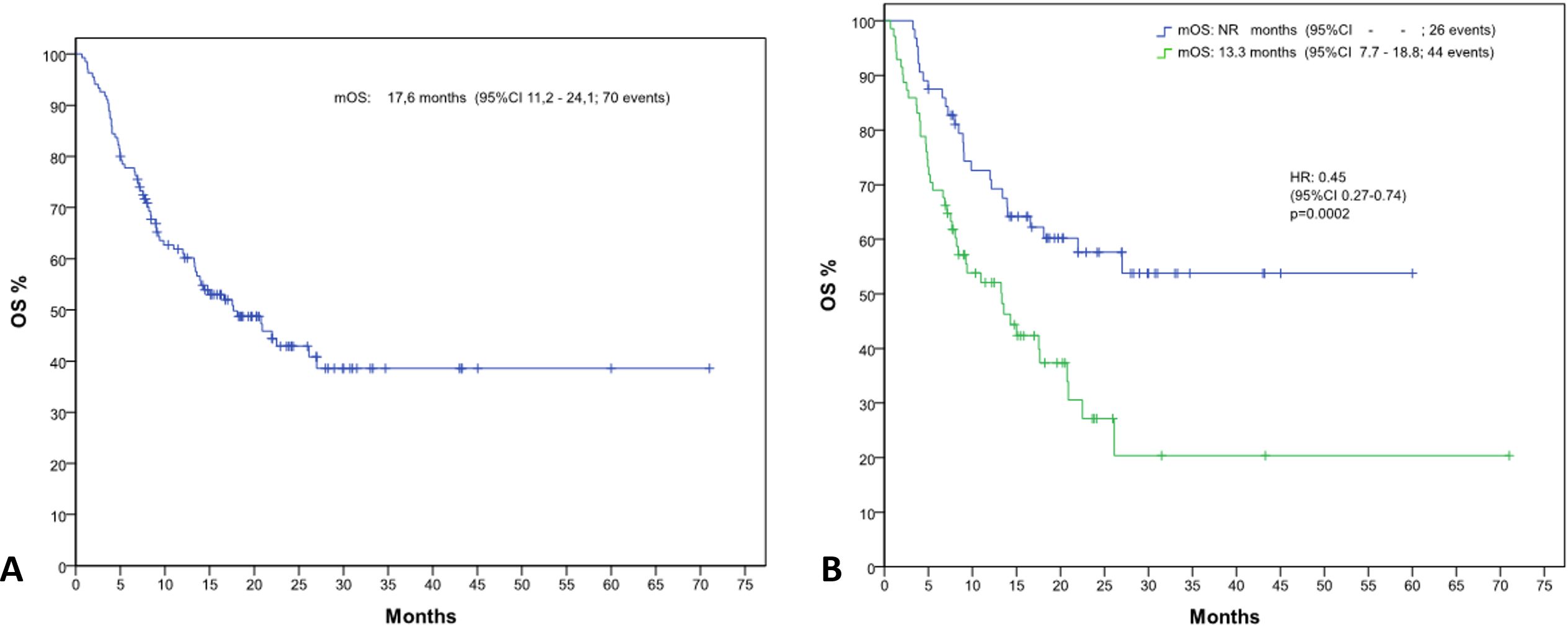
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curves depicting overall survival (OS) (A) for the entire patient population and (B) stratified by neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) groups (NLR ≤4 and NLR >4).
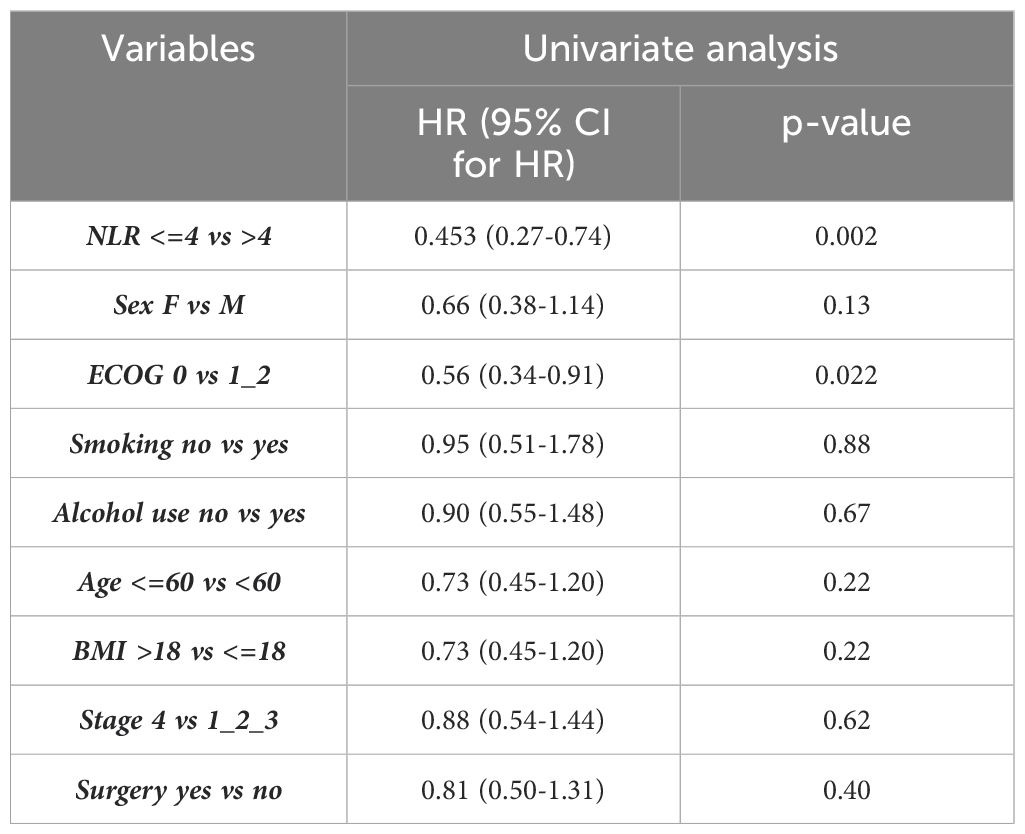
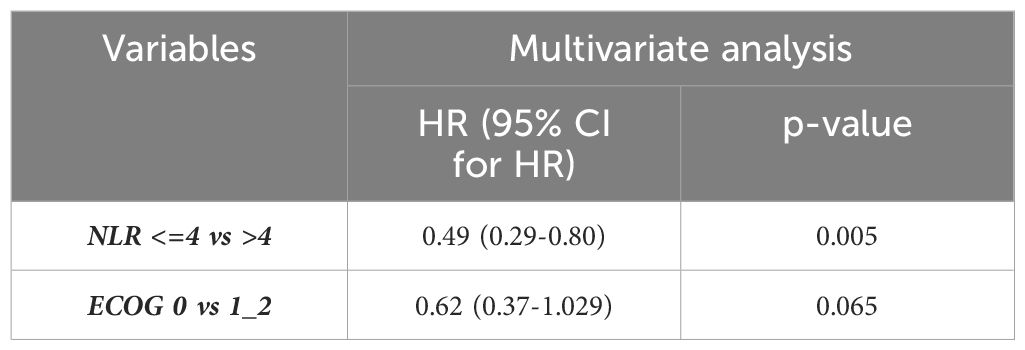
Univariable analysis showed a statistically significant correlation between the NLR value and OS, p=0.002, and between NLR and ECOG, p=0.022 (Table 3). The independent prognostic value of the NLR was confirmed by the multivariate analysis (p=0.005) (Table 4).
The median PFS in the general population was 10.1 months (IC 95%, 4.4-15.8) (Figure 2A). Median PFS stratified by the NLR value, was statistically significant: 6.5 vs 20 months in patients with NLR>4 and NLR<=4, respectively (HR 0.57, [IC 95%, 0.36-0.87] p=0.013) (Figure 2B).
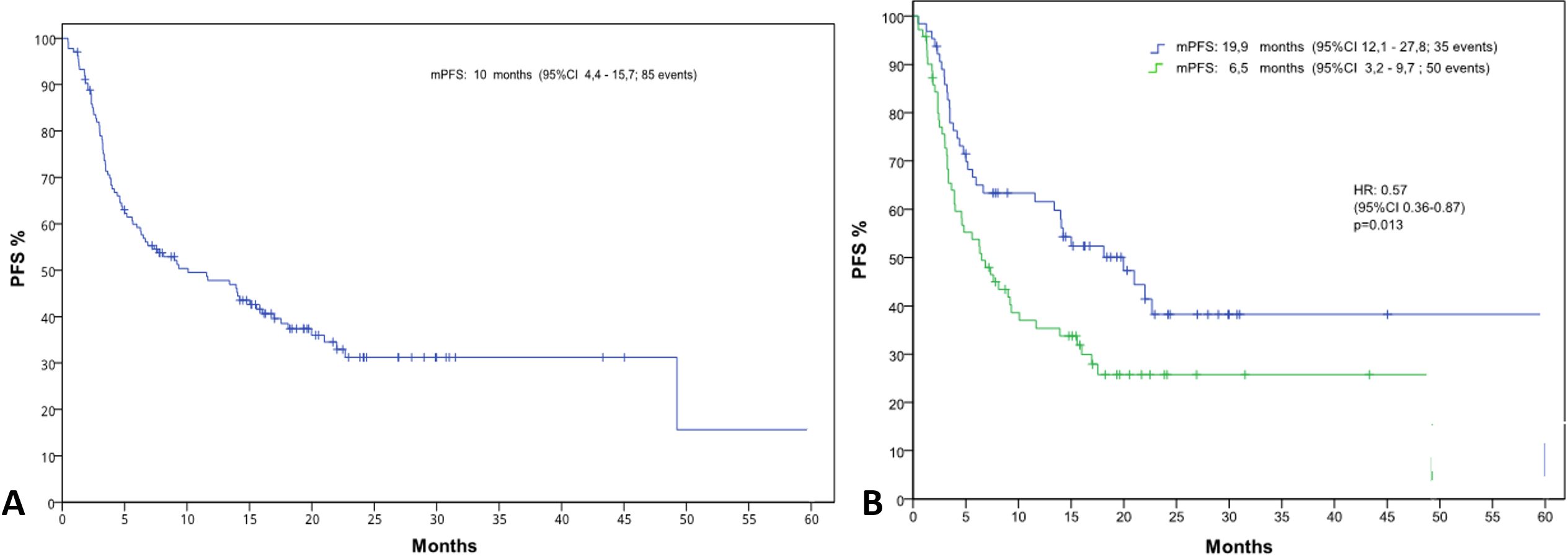
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier curves illustrating progression-free survival (PFS) (A) for the entire patient population and (B) stratified by neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) groups (NLR ≤4 and NLR >4).
Finally, we compared the ORR of the general population and the two subgroups of patients. ORR in the general population was 32.6% (out of a total of 135 patients, at the time of censure data were recorded: 42 partial response (PR), 44 stable disease (SD) and 47 progression disease (PD), 2 complete response (CR)). NLR-stratified ORR confirmed the unfavorable prognostic role of high NLR, with better ORR in the subgroup of patients with lower NLR. Specifically, in the subgroup of patients with NLR<=4, ORR was 20% (out of a total of 64 patients: 25 PR, 23 SD, 14 PD and 2 RC); while in the subgroup of patients with NLR>4, ORR was 12.5% (out of a total of 71 patients, 17 PR, 21 SD and 33 PD were registered). PD in the former group was 21.9%, in the latter 46.5%.
4 Discussion
Several parameters are routinely evaluated to try to establish the prognosis of a patient with HNSCC, from molecular biomarkers, quality of life assessments, gene expression and serological biomarkers (17–21). Tumor, Node, Metastasis (TNM) stage is considered a standard among prognostic factors of patients with HNSCC. In addition to stage, a low BMI at diagnosis, cigarette smoking habit are associated with a worse prognosis in these patients, while previous RT seems to boost the therapeutic effect of immunotherapy showing better ORR (22, 23). Prognostic factors for assessing the response to immunotherapy in HNSCC have not yet been clearly defined, which is why we have focused our attention on patients suffering from R/M HNSCC who received, in first- or second- line, treatment with anti PD-1 (pembrolizumab alone or in association with chemotherapy based on platinum + 5-fluorouracil and nivolumab) and we analyzed the association between outcomes and basal value of NLR.
The mechanisms behind the complex interaction between high NLR and poor prognosis of cancer patients are still poorly understood. One reason for the prognostic impact of NLR can be found in the association between high levels of NLR and the patient’s inflammatory state. Neutrophils, in fact, release several cytokines that block the host’s immune system against the tumor, thus allowing the neoplasm to grow uncontrollably, suppressing the activity of activated T cells and NK cells (24). Although several points of etiopathogenesis of this interaction have yet to be investigated and understood, the prognostic correlation between a high NLR and a worse prognosis in tumors of different anatomical districts is validated, including the head and neck (25–50). A high NLR is an established negative, independent, prognostic factor, for OS and appears to be related to both stage and PS at diagnosis (51).
Our study found a correlation between NLR<=4 and a better OS of patients treated with immunotherapy, in first- or second- line. The phase III KEYNOTE-048 (KN-048) trial, which compared in the first-line the standard treatment (EXTREME) with the use of pembrolizumab, alone or in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy, showed a median OS in the general population of 14.4 vs 6.5 months in the treated arm with only pembrolizumab and a 16 vs 5.2 months OS in the treated arm with pembrolizumab + CT (52). The OS data in our study cannot be compared with KN-048 since our OS was evaluated in all patients treated with immunotherapy, regardless of the treatment line. The KN-048 study reported the OS stratifying patients on the basis of the treatment received and the CPS value (> 20 and 1). Unfortunately, it was not possible in our case to stratify the OS obtained also on the basis of the value of the PD-L1, measured by CPS, since we did not have this data available in all patients. As for the study of the correlation between high NLR and reduced PFS, our analysis showed a statistically significant difference, with a delta of about 13.4 months in the two groups (19.9 vs 6.5).
Finally, our study showed better response rates in patients treated with immunotherapy and an NLR<=4 (ORR of 20% vs 12.5% respectively in the two groups). Notably, only two complete responses were observed in this group. The phase III CheckMate 141 (CM-141) trial reported an ORR of 13.3% with nivolumab, not comparable with the ORR of our study as it was evaluated in the sample of patients treated with immunotherapy, both at first- than in second- line, and not just in second- line as in the CM-141 study (53).
For our analysis we used a cut off value for NLR of 4 (considered the median of 4.2 in our sample). Several studies have investigated the connection between NLR and prognosis, using NLR cut-off values between 2 and 7 (30, 51, 54–58). Templeton et al. reported that the method used for selecting the NLR cut-off is often unclear, and several authors also demonstrated an association between the NLR cut-off used and the HR values reported for OS (59). Nonetheless, the effect of this association is very little relevant, and it is not clear how it influences the interpretation of the results on the data obtained from the analyses on NLR and OS. Moreover, to establish an absolute cut-off value, a control group of healthy subjects should be employed in such studies. Finally, it cannot be excluded that the optimal cut-off of NLR must be individualized based on the tumor site and the cohort of patients examined, but to determine this we need further investigation.
A limitation of our study is the small number of patients included, with a sample of 135 patients. However, we must correlate the number with the rather rare frequency of the pathology being studied. Further attention should be paid to the short observation time between the start of the first- or second- treatment line and the closure of the observation. Probably subsequent data analysis as well as reconfirming the statistically significant correlation between high NLR and negative prognostic impact in terms of OS could show a statistically significant correlation also between high NLR and shorter NLR PFS. Moreover, the limits related to the type of retrospective analysis, which by its nature can be associated with selection and survival bias.
In addition to the previously highlighted limits, we must consider that in our study neutrophils have not been isolated for further phenotypic characterization. It has recently been discovered that the role played by neutrophils on the microenvironment and on tumor biology varies depending on the predominant phenotype, distinct in pro-tumorigenic and anti-tumor, due to cytokines released into the bloodstream. To further complicate the close correlation between host immune system and tumor development there is also the percentages of the two phenotypes of neutrophils that are not constant over time but, on the contrary, tend to change, a phenomenon known as “Dynamic change of NLR” (56). Since phenotype characterization has not been carried out in our sample, the heterogeneity of pro-tumorigenic and anti-tumorigenic phenotypes cannot be assessed.
Although several studies have demonstrated a prognostic role of dynamic changes in NLR in various cancers, due to data limitations, including missing post-immunotherapy NLR values, incomplete PD-L1/CPS data, and the lack of HPV infection information, we were unable to explore several potentially important associations (50–58, 60–64). Specifically, we could not assess the prognostic role of dynamic NLR changes or stratify OS by PD-L1/CPS since data were often recorded as ranges (e.g., ‘>20’, ‘<1’), and we could not investigate the relationship between NLR and HPV status. Moreover, the small sample size, consisting only of white individuals, underscores the need for research that includes diverse populations to ensure generalizability.
5 Conclusions
Our study shows that a basal NLR value lower than the cut-off of 4 is independently associated with better OS, PFS and ORR in patients with R/M HNSCC treated with immunotherapy, in first- or second- line.
Our study presents limitations to be addressed: the small sample considered and the type of retrospective analysis that is, by nature, associated with potential biases, which could limit the validity of the results obtained. Despite the sample size, according to our analysis, NLR is also a useful biomarker in clinical practice, especially considering that it is easy to perform, repeatable, reliable, widely available and inexpensive. Furthermore, we cannot ignore the fact that NLR appears to be directly related to the immune status, inflammation and nutritional status of the host and it is therefore likely that its baseline value reflects the general condition of the patient, and that the better condition of the patient is, in turn, responsible for an impact on the effectiveness of immunotherapy, and therefore, ultimately, also prolonged improvements to the OS. In fact, what is not yet clear is whether the systemic inflammatory response is the reflection of a tumor that does not respond to treatments or a non-specific biomarker of the presence of a systemic proinflammatory state, associated ab initio with reduced survival. If this were the case, then NLR should be assessed in the same way as the correlation between prognosis and PS at diagnosis.
In light of these considerations, further studies are therefore necessary to confirm not only this result, but also to determine the weight of NLR in the context of other biomarkers commonly used for the evaluation of a potential benefit to the use of immunotherapy and above all to evaluate the mutual interaction of different prognostic factors. Only in this way will it be possible to establish in advance which patients will be able to benefit from immunotherapy, so as to be able to improve the prognosis as much as possible of a disease, which is extremely aggressive by its nature.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Comitato etico Università degli studi della Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
MC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GLG: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. VD: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. FP: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. GG: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. DC: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. AM: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. MP: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. AS: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. VR: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. LM: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. RA: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. FV: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. VF: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SF: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SL: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. FC: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MF: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Linee Guida Associazione Italiana di Oncologia Medica (AIOM). Available online at: https://www.aiom.it/linee-guida-aiom/ (Accessed July 8, 2024).
2. Fasano M, D’Onofrio I, Belfiore MP, Angrisani A, Caliendo V, Della Corte CM, et al. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in elderly patients: role of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:472. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030472
3. Addeo R, Pompella L, Vitale P, Fattoruso SIS, Di Giovanni I, Perri F, et al. The art of counseling in the treatment of head and neck cancer: exploratory investigation among perceptions of health professionals in southern Italy. Curr Oncol. (2022) 29:6277–86. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090493
4. Belfiore MP, Nardone V, D’Onofrio I, Pirozzi M, Sandomenico F, Farese S, et al. Recurrent versus metastatic head and neck cancer: an evolving landscape and the role of immunotherapy. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:2080. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092080
5. Menditti D, Santagata M, Imola G, Stagliano S, Vitagliano R, Boschetti CE, et al. Personalized medicine in oral oncology: imaging methods and biological markers to support diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC): A narrative literature review. J Pers Med. (2023) 13:1397. doi: 10.3390/jpm13091397
6. Fasano M, Perri F, Della Corte CM, Di Liello R, Della Vittoria Scarpati G, Cascella M, et al. Translational insights and new therapeutic perspectives in head and neck tumors. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:1045. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081045
7. Wang D, DuBois RN. Immunosuppression associated with chronic inflammation in the tumor microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. (2015) 36:1085–93. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv123
8. McMillan DC. Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and survival in patients with cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2009) 12:223–6. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32832a7902
9. Kao SC, Pavlakis N, Harvie R, Vardy JL, Boyer MJ, van Zandwijk N, et al. High blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an indicator of poor prognosis in Malignant mesothelioma patients undergoing systemic therapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2010) 16:5805–13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2245
10. Porrata LF, Ristow K, Habermann T, Inwards DJ, Micallef IN, Markovic SN. Predicting survival for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients using baseline neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. Am J Hematol. (2010) 85:896–9. doi: 10.1002/ajh.21849
11. Lee YG, Chang H, Keam B, Chun SH, Park J, Park KU, et al. Outcomes and biomarkers of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with refractory head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: KCSG HN18-12. Cancer Res Treat. (2021) 53:671–7. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.824
12. Truong AA, Lee RH, Wu X, Algazi AP, Kang H, El-Sayed IH, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and pembrolizumab outcomes in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2025) 172:548–55. doi: 10.1002/ohn.1088
13. Ho WJ, Yarchoan M, Hopkins A, Mehra R, Grossman S, Kang H. Association between pretreatment lymphocyte count and response to PD1 inhibitors in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Immunother Cancer. (2018) 6:84. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0395-x
14. Zheng S, Wang W, Shen L, Yao Y, Xia W, Ni C. Tumor battlefield within inflamed, excluded or desert immune phenotypes: the mechanisms and strategies. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2024) 13:80. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00543-1
15. Shen A, Garrett A, Chao CC, Liu D, Cheng C, Wang Z, et al. A comprehensive meta-analysis of tissue resident memory T cells and their roles in shaping immune microenvironment and patient prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1416751. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1416751
16. Bronte G, Calabro L, Olivieri F, Procopio AD, Crino L. The prognostic effects of circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells in non-small cell lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23:1551–61. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00946-6
17. Hadler-Olsen E, Wirsing AM. Tissue-infiltrating immune cells as prognostic markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. (2019) 120:714–27. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0409-6
18. Lo Giudice G, Colella G, Boschetti CE, Colella C, Tartaro G, Cirillo N. Increased delay in diagnosis, but not treatment, among patients with oral cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2023) 149:91–2. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2022.3652
19. Kang D, Liu S, Yuan X, Liu S, Zhang Z, He Z, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic indicators in patients with head and neck Malignancy treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:18215–40. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05504-5
20. Belfiore MP, Gallo L, Reginelli A, Parrella PM, Russo GM, Caliendo V, et al. Quantitative evaluation of the lymph node metastases in the head and neck Malignancies using diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient mapping: A bicentric study. Magnetochemistry. (2023) 9:124. doi: 10.3390/magnetochemistry9050124
21. Pekarek L, Garrido-Gil MJ, Sanchez-Cendra A, Cassinello J, Pekarek T, Fraile-Martinez O, et al. Emerging histological and serological biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Applications in diagnosis, prognosis evaluation and personalized therapeutics (Review). Oncol Rep. (2023) 13:213. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8650
22. Saowapa S, Polpichai N, Siladech P, Wannaphut C, Tanariyakul M, Wattanachayakul P, et al. BMI association with treatment outcomes in head and neck cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). (2025) 8:e70147. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70147
23. Jokimaki A, Hietala H, Lemma J, Karhapaa H, Rintala A, Kaikkonen JP, et al. Previous radiotherapy improves treatment responses and causes a trend toward longer time to progression among patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor-related adverse events. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2023) 72:3337–47. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03494-4
24. Mascarella MA, Mannard E, Silva SD, Zeitouni A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in head and neck cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck. (2018) 40:1091–100. doi: 10.1002/hed.25075
25. Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. (2013) 63:11–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21166
26. MacDonald N. Cancer cachexia and targeting chronic inflammation: a unified approach to cancer treatment and palliative/supportive care. J Support Oncol. (2007) 5:157–62.
27. Zahorec R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts–rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl Lek Listy. (2001) 102:5–14.
28. Li MX, Liu XM, Zhang XF, Zhang JF, Wang WL, Zhu Y, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. (2014) 134:2403–13. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28536
29. Benson AB 3rd, Schrag D, Somerfield MR, Cohen AM, Figueredo AT, Flynn PJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology recommendations on adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2004) 22:3408–19. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.05.063
30. Schulz WA, Sorensen KD. Epigenetics of urological cancers. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:4775. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194775
31. Wei Y, Jiang YZ, Qian WH. Prognostic role of NLR in urinary cancers: a meta-analysis. PloS One. (2014) 9:e92079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092079
32. Lu Y, Huang HH, Lau WKO. Evaluation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator in a Singapore cohort of patients with clinically localized prostate cancer treated with prostatectomy. World J Urol. (2020) 38:103–9. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02752-4
33. Mjaess G, Chebel R, Karam A, Moussa I, Pretot D, Abi Tayeh G, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in urological tumors: an umbrella review of evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Acta Oncol. (2021) 60:704–13. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2021.1886323
34. Masood S. Prognostic/predictive factors in breast cancer. Clin Lab Med. (2005) 25:809–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2005.08.012
35. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. (2011) 144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
36. Ethier JL, Desautels D, Templeton A, Shah PS, Amir E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. (2017) 19:2. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0794-1
37. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. (2015) 65:5–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21254
38. Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. (2001) 357:539–45. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04046-0
39. Grange JM, Krone B, Mastrangelo G. Infection, inflammation and cancer. Int J Cancer. (2011) 128:2240–1. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25533
40. Moore MM, Chua W, Charles KA, Clarke SJ. Inflammation and cancer: causes and consequences. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2010) 87:504–8. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2009.254
41. Zhao QT, Yang Y, Xu S, Zhang XP, Wang HE, Zhang H, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in lung cancers: a meta-analysis including 7,054 patients. Onco Targets Ther. (2015) 8:2731–8. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S90875
42. Proctor MJ, Morrison DS, Talwar D, Balmer SM, Fletcher CD, O’Reilly DS, et al. A comparison of inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with cancer. A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Eur J Cancer. (2011) 47:2633–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.03.028
43. Davey RJ, van der Westhuizen A, Bowden NA. Metastatic melanoma treatment: Combining old and new therapies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2016) 98:242–53. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.11.011
44. Caterino M, Pirozzi M, Facchini S, Zotta A, Sica A, Lo Giudice G, et al. Sorafenib in metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma with BRAF K601E mutation on liquid biopsy: A case report and literature review. Medicina (Kaunas). (2022) 58:666. doi: 10.3390/medicina58050666
45. Eggermont AM, Spatz A, Robert C. Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet. (2014) 383:816–27. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60802-8
46. Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong SJ, Thompson JF, Ding S, Byrd DR, et al. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors among 2,313 patients with stage III melanoma: comparison of nodal micrometastases versus macrometastases. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:2452–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.1627
47. Thompson JF, Soong SJ, Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Ding S, Coit DG, et al. Prognostic significance of mitotic rate in localized primary cutaneous melanoma: an analysis of patients in the multi-institutional American Joint Committee on Cancer melanoma staging database. J Clin Oncol. (2011) 29:2199–205. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.5812
48. Balch CM, Soong SJ, Gershenwald JE, Thompson JF, Coit DG, Atkins MB, et al. Age as a prognostic factor in patients with localized melanoma and regional metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. (2013) 20:3961–8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-013-3100-9
49. Garbe C, Eigentler TK, Keilholz U, Hauschild A, Kirkwood JM. Systematic review of medical treatment in melanoma: current status and future prospects. Oncologist. (2011) 16:5–24. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0190
50. Ding Y, Zhang S, Qiao J. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in melanoma: Evidence from a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Med (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e11446. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011446
51. Ma SJ, Yu H, Khan M, Gill J, Santhosh S, Chatterjee U, et al. Evaluation of optimal threshold of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and its association with survival outcomes among patients with head and neck cancer. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e227567. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7567
52. Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, Soulieres D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr., et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. (2019) 394:1915–28. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7
53. Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr., Fayette J, Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, et al. Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:1856–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602252
54. Song Y, Yang Y, Gao P, Chen X, Yu D, Xu Y, et al. The preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is a superior indicator of prognosis compared with other inflammatory biomarkers in resectable colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:744. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3752-0
55. Bagley SJ, Kothari S, Aggarwal C, Bauml JM, Alley EW, Evans TL, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2017) 106:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.01.013
56. Ferrucci PF, Gandini S, Battaglia A, Alfieri S, Di Giacomo AM, Giannarelli D, et al. Baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with outcome of ipilimumab-treated metastatic melanoma patients. Br J Cancer. (2015) 112:1904–10. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.180
57. Wu MY, He XY, Hu CS. Tumor regression and patterns of distant metastasis of T1-T2 nasopharyngeal carcinoma with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0154501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154501
58. Gu X, Gao X, Li X, Qi X, Ma M, Qin S, et al. Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in prostate cancer: evidence from 16,266 patients. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:22089. doi: 10.1038/srep22089
59. Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Seruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocana A, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2014) 106:dju124. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju124
60. Piccard H, Muschel RJ, Opdenakker G. On the dual roles and polarized phenotypes of neutrophils in tumor development and progression. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2012) 82:296–309. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2011.06.004
61. Dan J, Tan J, Huang J, Zhang X, Guo Y, Huang Y, et al. The dynamic change of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is predictive of pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer. (2020) 27:982–8. doi: 10.1007/s12282-020-01096-x
62. Kim JY, Jung EJ, Kim JM, Lee HS, Kwag SJ, Park JH, et al. Dynamic changes of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts breast cancer prognosis. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:1206. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07700-9
63. Li Z, Zhao R, Cui Y, Zhou Y, Wu X. The dynamic change of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio can predict clinical outcome in stage I-III colon cancer. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:9453. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27896-y
Keywords: HNSCC, NLR, immunotherapy, immunotherapy biomarkers, ICI
Citation: Caterino M, Lo Giudice G, Damiano V, Perri F, Giordano G, Ciardiello D, Mirabile A, Pirozzi M, Sponghini AP, Ricci V, Montella L, Addeo R, Vignani F, Famiglietti V, Farese S, Di Lorenzo S, Ciardiello F and Fasano M (2025) Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio: a potential biomarker in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 15:1557652. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1557652
Received: 08 January 2025; Accepted: 14 April 2025;
Published: 06 May 2025.
Edited by:
Ming Xu, Shimonoseki City University, JapanReviewed by:
Lindsey Sloan, University of Minnesota, United StatesKatherine Wai, University of California, San Francisco, United States
Copyright © 2025 Caterino, Lo Giudice, Damiano, Perri, Giordano, Ciardiello, Mirabile, Pirozzi, Sponghini, Ricci, Montella, Addeo, Vignani, Famiglietti, Farese, Di Lorenzo, Ciardiello and Fasano. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Francesco Perri, Zi5wZXJyaUBpc3RpdHV0b3R1bW9yaS5uYS5pdA==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Marianna Caterino
Marianna Caterino Giorgio Lo Giudice
Giorgio Lo Giudice Vincenzo Damiano
Vincenzo Damiano Francesco Perri
Francesco Perri Guido Giordano
Guido Giordano Davide Ciardiello
Davide Ciardiello Aurora Mirabile
Aurora Mirabile Mario Pirozzi
Mario Pirozzi Andrea Pietro Sponghini8
Andrea Pietro Sponghini8 Liliana Montella
Liliana Montella Francesca Vignani
Francesca Vignani Fortunato Ciardiello
Fortunato Ciardiello Morena Fasano
Morena Fasano